Page 1

Colour Television Chassis
TPN16.1E
LA
Contents Page Contents Page
1. Revision List 2
2. Technical Specs, Diversity, and Connections 2
3. Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List 5
4. Mechanical Instructions 9
Cable dressing (24" 5211 series) 9
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 14
6. Alignments 21
7. Circuit Descriptions 23
8. IC Data Sheets 30
9. Block Diagrams
Block Diagrams 37
10. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts Drawing PWB
A 715G7734 PSU
B 715G6947 SSB 42 57-58
J 715G8009 IR/LED Panel 59 60
11. Styling Sheets
J 715G8009 IR/LED Panel 61
38 40-41
Published by CQZ/SC 1610 Quality Printed in the Netherlands Subject to modification EN 3122 785 20100
2016-Mar-11
2016 ©
TP Vision Netherlands B.V.
All rights reserved. Specifications are subject to change without notice. Trademarks are the
property of Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. or their respective owners.
TP Vision Netherlands B.V. reserves the right to change products at any time without being obliged to adjust
earlier supplies accordingly.
PHILIPS and the PHILIPS’ Shield Emblem are used under license from Koninklijke Phili ps Electronics N.V.
Page 2
EN 2 TPN16.1E LA1.
Revision List
1. Revision List
Manual xxxx xxx xxxx.0
• First release.
2. Technical Specs, Diversity, and Connections
Index of this chapter:
• Specifications are indicative (subject to change).
2.1 Technical Specifications
2.2 Directions for Use
2.3 Connections
2.4 Chassis Overview
2.1 Technical Specifications
For on-line product support please use the links in Table 2-1.
Here is product information available, as well as getting started,
user manuals, frequently asked questions and software &
Notes:
drivers.
• Figures can deviate due to the different set executions.
Table 2-1 Described Model Numbers and Diversity
24 910 11
Mechanics
CTN
24PFK5211/12 2-1 4-1 4-2 4-3 4-4 4-5 4-6 9.1 10.1 10.2 10.3 11.1
24PFT5211/12 2-1 4-1 4-2 4-3 4-4 4-5 4-6 9.1 10.1 10.2 10.3 11.1
24PFT5211/60 2-1 4-1 4-2 4-3 4-4 4-5 4-6 9.1 10.1 10.2 10.3 11.1
Connection Overview
Wire Dressing
Stand Removal
Rear Cover Removal
Speaker Removal
SSB Removal
Block
Diagrams Schematics
IR/LED Board Removal
Block Diagram
Power Supply
2.2 Directions for Use
Directions for use can be downloaded from the following
websites:
http://www.philips.com/support
http://www.p4c.philips.com
SSB
J (IR/LED )
Styling
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 3
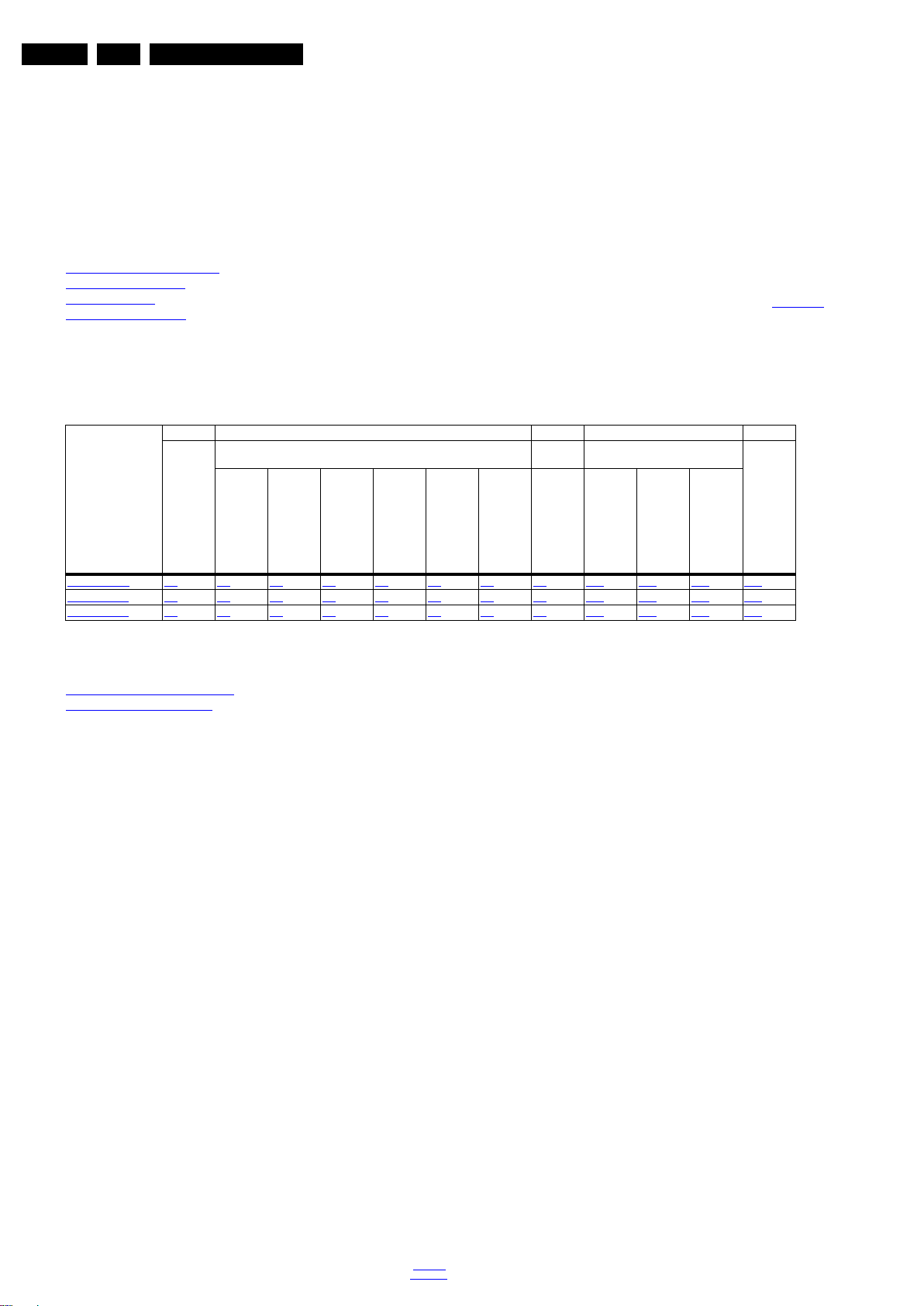
2.3 Connections
TV ANTENNA
VGA / DVI
AUDIO IN
DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
SCART
(RGB/CVBS)
SE
RV.U
HDMI 1
ARC
HDMI2
SAT
VGA
20060_001.eps
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Side ConnectorsRear Connectors
(Optional)
1 2 3 4
10000_022_090121.eps
090121
1
6
10
11
5
15
10000_002_090121.eps
090127
10000_017_090121.eps
090428
19
1
18 2
Technical Specs, Diversity, and Connections
EN 3TPN16.1E LA 2.
Figure 2-1 Connection overview
Note: The following connector colour abbreviations are used
5 - PC IN:VGA
(acc. to DIN/IEC 757): Bk= Black, Bu= Blue, Gn= Green,
Gy= Grey, Rd= Red, Wh= White, Ye= Yellow.
2.3.1 Side Connections
1 - Common Interface
68p- See figure 10-2-6
2 - USB 2.0
jk
1 -Video Red 0.7 V
2 -Video Green 0.7 V
3 -Video Blue 0.7 V
4-n.c.
Figure 2-3 VGA connector
/ 75 W j
PP
/ 75 W j
PP
/ 75 W j
PP
5 -Ground Gnd H
Figure 2-2 USB (type A)
1-+5V k
2 -Data (-) jk
3 -Data (+) jk
4 -Ground Gnd H
3 - Head phone (Output)
Bk -Head phone 80 - 600 / 10 mW
ot
2.3.2 Rear Connections
4 - Audio - In: Left / Right, VGA
Bu -Audio L/R in 0.5 V
/ 10 kW jq
RMS
6 -Ground Red Gnd H
7 -Ground Green Gnd H
8 -Ground Blue Gnd H
9-+5V
+5 V j
DC
10 - Ground Sync Gnd H
11 - Ground Red Gnd H
12 - DDC_SDA DDC data j
13 - H-sync 0 - 5 V j
14 - V-sync 0 - 5 V j
15 - DDC_SCL DDC clock j
6 - HDMI 2: Digital Video - In, Digital Audio with ARC In/Out
Figure 2-4 HDMI (type A) connector
back to
div. table
1 -D2+ Data channel j
2 -Shield Gnd H
3 -D2- Data channel j
2016-Mar-11
Page 4

EN 4 TPN16.1E LA2.
10000_017_090121.eps
090428
19
1
18 2
Technical Specs, Diversity, and Connections
4 -D1+ Data channel j
5-Shield Gnd H
6 -D1- Data channel j
7 -D0+ Data channel j
8-Shield Gnd H
9 -D0- Data channel j
10 - CLK+ Data channel j
11 - Shield Gnd H
12 - CLK- Data channel j
13 - Easylink/CEC Control channel jk
14 - ARC Audio Return Channel k
15 - DDC_SCL DDC clock j
16 - DDC_SDA DDC data jk
17 - Ground Gnd H
18 - +5V j
19 - HPD Hot Plug Detect j
20 - Ground Gnd H
7 - HDMI 1 ARC: Digital Video - In, Digital Audio with ARC In/Out
Figure 2-5 HDMI (type A) connector
1 -D2+ Data channel j
2-Shield Gnd H
3 -D2- Data channel j
4 -D1+ Data channel j
5-Shield Gnd H
6 -D1- Data channel j
7 -D0+ Data channel j
8-Shield Gnd H
9 -D0- Data channel j
10 - CLK+ Data channel j
11 - Shield Gnd H
12 - CLK- Data channel j
13 - Easylink/CEC Control channel jk
14 - ARC Audio Return Channel k
15 - DDC_SCL DDC clock j
16 - DDC_SDA DDC data jk
17 - Ground Gnd H
18 - +5V j
19 - HPD Hot Plug Detect j
20 - Ground Gnd H
8 - Cinch: Digital Audio - Out
BK - Coaxial 0.4 - 0.6V
/ 75 W kq
PP
9 - Service / UART
1 -Ground Gnd H
2 -UART_TX Transmit k
3 -UART_RX Receive j
10 - EXT1: Video RGB/YC - In, CVBS - In/Out, Audio - In/Out
20
21
10000_001_090121.eps
2
1
090121
Figure 2-6 SCART connector
1 -Audio R 0.5 V
2 -Audio R 0.5 V
3 -Audio L 0.5 V
/ 1 k k
RMS
/ 10 k j
RMS
/ 1 k k
RMS
4 -Ground Audio Gnd H
5 -Ground Blue Gnd H
6 -Audio L 0.5 V
7 -Video Blue/C-out 0.7 V
/ 10 k j
RMS
/ 75 jk
PP
8 -Function Select 0 - 2 V: INT
4.5 - 7 V: EXT 16:9
9.5 - 12 V: EXT 4:3 j
9 -Ground Green Gnd H
10 - n.c.
11 - Video Green 0.7 V
/ 75 j
PP
12 - n.c.
13 - Ground Red Gnd H
14 - Ground P50 Gnd H
15 - Video Red/C 0.7 V
16 - Status/FBL 0 - 0.4 V: INT
/ 75 j
PP
1 - 3 V: EXT / 75 j
17 - Ground Video Gnd H
18 - Ground FBL Gnd H
19 - Video CVBS 1 V
20 - Video CVBS/Y 1 V
21 - Shield Gnd H
/ 75 k
PP
/ 75 j
PP
11 - TV ANTENNA - In
Signal input from an antenna, cable or satellite.
12 - SAT- In
Signal input from an antenna, cable or satellite.
2.4 Chassis Overview
Refer to 9. Block Diagrams for PWB/CBA locations.
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 5

Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
3. Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
Index of this chapter:
3.1 Safety Instructions
3.2 Warnings
3.3 Notes
3.4 Abbreviation List
3.1 Safety Instructions
Safety regulations require the following during a repair:
• Connect the set to the Mains/AC Power via an isolation
transformer (> 800 VA).
• Replace safety components, indicated by the symbol h,
only by components identical to the original ones. Any
other component substitution (other than original type) may
increase risk of fire or electrical shock hazard.
Safety regulations require that after a repair, the set must be
returned in its original condition. Pay in particular attention to
the following points:
• Route the wire trees correctly and fix them with the
mounted cable clamps.
• Check the insulation of the Mains/AC Power lead for
external damage.
• Check the strain relief of the Mains/AC Power cord for
proper function.
• Check the electrical DC resistance between the Mains/AC
Power plug and the secondary side (only for sets that have
a Mains/AC Power isolated power supply):
1. Unplug the Mains/AC Power cord and connect a wire
between the two pins of the Mains/AC Power plug.
2. Set the Mains/AC Power switch to the “on” position
(keep the Mains/AC Power cord unplugged!).
3. Measure the resistance value between the pins of the
Mains/AC Power plug and the metal shielding of the
tuner or the aerial connection on the set. The reading
should be between 4.5 M and 12 M.
4. Switch “off” the set, and remove the wire between the
two pins of the Mains/AC Power plug.
• Check the cabinet for defects, to prevent touching of any
inner parts by the customer.
3.2 Warnings
• All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to
electrostatic discharges (ESD w). Careless handling
during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that,
during repair, you are connected with the same potential as
the mass of the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep
components and tools also at this same potential.
• Be careful during measurements in the high voltage
section.
• Never replace modules or other components while the unit
is switched “on”.
• When you align the set, use plastic rather than metal tools.
This will prevent any short circuits and the danger of a
circuit becoming unstable.
3.3 Notes
3.3.1 General
• Measure the voltages and waveforms with regard to the
chassis (= tuner) ground (H), or hot ground (I), depending
on the tested area of circuitry. The voltages and waveforms
shown in the diagrams are indicative. Measure them in the
Service Default Mode with a colour bar signal and stereo
sound (L: 3 kHz, R: 1 kHz unless stated otherwise) and
picture carrier at 475.25 MHz for PAL, or 61.25 MHz for
NTSC (channel 3).
• Where necessary, measure the waveforms and voltages
with (D) and without (E) aerial signal. Measure the
voltages in the power supply section both in normal
operation (G) and in stand-by (F). These values are
indicated by means of the appropriate symbols.
3.3.2 Schematic Notes
• All resistor values are in ohms, and the value multiplier is
often used to indicate the decimal point location (e.g. 2K2
indicates 2.2 k).
• Resistor values with no multiplier may be indicated with
either an “E” or an “R” (e.g. 220E or 220R indicates 220 ).
• All capacitor values are given in micro-farads (10
nano-farads (n 10
• Capacitor values may also use the value multiplier as the
decimal point indication (e.g. 2p2 indicates 2.2 pF).
• An “asterisk” (*) indicates component usage varies. Refer
to the diversity tables for the correct values.
• The correct component values are listed on the Philips
Spare Parts Web Portal.
3.3.3 Spare Parts
For the latest spare part overview, consult your Philips Spare
Part web portal.
3.3.4 BGA (Ball Grid Array) ICs
Introduction
For more information on how to handle BGA devices, visit this
URL: http://www.atyourservice-magazine.com
“Magazine”, then go to “Repair downloads”. Here you will find
Information on how to deal with BGA-ICs.
BGA Temperature Profiles
For BGA-ICs, you must use the correct temperature-profile.
Where applicable and available, this profile is added to the IC
Data Sheet information section in this manual.
3.3.5 Lead-free Soldering
Due to lead-free technology some rules have to be respected
by the workshop during a repair:
• Use only lead-free soldering tin. If lead-free solder paste is
required, please contact the manufacturer of your soldering
equipment. In general, use of solder paste within
workshops should be avoided because paste is not easy to
store and to handle.
• Use only adequate solder tools applicable for lead-free
soldering tin. The solder tool must be able:
– To reach a solder-tip temperature of at least 400°C.
– To stabilize the adjusted temperature at the solder-tip.
– To exchange solder-tips for different applications.
• Adjust your solder tool so that a temperature of around
360°C - 380°C is reached and stabilized at the solder joint.
Heating time of the solder-joint should not exceed ~ 4 sec.
Avoid temperatures above 400°C, otherwise wear-out of
tips will increase drastically and flux-fluid will be destroyed.
To avoid wear-out of tips, switch “off” unused equipment or
reduce heat.
• Mix of lead-free soldering tin/parts with leaded soldering
tin/parts is possible but PHILIPS recommends strongly to
avoid mixed regimes. If this cannot be avoided, carefully
clear the solder-joint from old tin and re-solder with new tin.
3.3.6 Alternative BOM identification
It should be noted that on the European Service website,
“Alternative BOM” is referred to as “Design variant”.
The third digit in the serial number (example:
AG2B0335000001) indicates the number of the alternative
B.O.M. (Bill Of Materials) that has been used for producing the
specific TV set. In general, it is possible that the same TV
model on the market is produced with e.g. two different types
of displays, coming from two different suppliers. This will then
back to
div. table
-9
), or pico-farads (p 10
. Select
EN 5TPN16.1E LA 3.
-6
),
-12
).
2016-Mar-11
Page 6

EN 6 TPN16.1E LA3.
10000_053_110228.eps
110228
Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
result in sets which have the same CTN (Commercial Type
Number; e.g. 28PW9515/12) but which have a different B.O.M.
number.
By looking at the third digit of the serial number, one can
identify which B.O.M. is used for the TV set he is working with.
If the third digit of the serial number contains the number “1”
(example: AG1B033500001), then the TV set has been
manufactured according to B.O.M. number 1. If the third digit is
a “2” (example: AG2B0335000001), then the set has been
produced according to B.O.M. no. 2. This is important for
ordering the correct spare parts!
For the third digit, the numbers 1...9 and the characters A...Z
can be used, so in total: 9 plus 26= 35 different B.O.M.s can be
indicated by the third digit of the serial number.
Identification: The bottom line of a type plate gives a 14-digit
serial number. Digits 1 and 2 refer to the production centre (e.g.
SN is Lysomice, RJ is Kobierzyce), digit 3 refers to the B.O.M.
code, digit 4 refers to the Service version change code, digits 5
and 6 refer to the production year, and digits 7 and 8 refer to
production week (in example below it is 2010 week 10 / 2010
week 17). The 6 last digits contain the serial number.
Figure 3-1 Serial number (example)
3.3.7 Board Level Repair (BLR) or Component Level Repair (CLR)
If a board is defective, consult your repair procedure to decide
if the board has to be exchanged or if it should be repaired on
component level.
If your repair procedure says the board should be exchanged
completely, do not solder on the defective board. Otherwise, it
cannot be returned to the O.E.M. supplier for back charging!
3.3.8 Practical Service Precautions
• It makes sense to avoid exposure to electrical shock.
While some sources are expected to have a possible
dangerous impact, others of quite high potential are of
limited current and are sometimes held in less regard.
• Always respect voltages. While some may not be
dangerous in themselves, they can cause unexpected
reactions that are best avoided. Before reaching into a
powered TV set, it is best to test the high voltage insulation.
It is easy to do, and is a good service precaution.
3.4 Abbreviation List
0/6/12 SCART switch control signal on A/V
board. 0 = loop through (AUX to TV),
6 = play 16 : 9 format, 12 = play 4 : 3
format
AARA Automatic Aspect Ratio Adaptation:
algorithm that adapts aspect ratio to
remove horizontal black bars; keeps
the original aspect ratio
ACI Automatic Channel Installation:
algorithm that installs TV channels
directly from a cable network by
means of a predefined TXT page
ADC Analogue to Digital Converter
AFC Automatic Frequency Control: control
signal used to tune to the correct
frequency
AGC Automatic Gain Control: algorithm that
controls the video input of the feature
box
AM Amplitude Modulation
AP Asia Pacific
AR Aspect Ratio: 4 by 3 or 16 by 9
ASF Auto Screen Fit: algorithm that adapts
aspect ratio to remove horizontal black
bars without discarding video
information
ATSC Advanced Television Systems
Committee, the digital TV standard in
the USA
ATV See Auto TV
Auto TV A hardware and software control
system that measures picture content,
and adapts image parameters in a
dynamic way
AV External Audio Video
AVC Audio Video Controller
AVIP Audio Video Input Processor
B/G Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 5.5 MHz
BDS Business Display Solutions (iTV)
BLR Board-Level Repair
BTSC Broadcast Television Standard
Committee. Multiplex FM stereo sound
system, originating from the USA and
used e.g. in LATAM and AP-NTSC
countries
B-TXT Blue TeleteXT
C Centre channel (audio)
CEC Consumer Electronics Control bus:
remote control bus on HDMI
connections
CL Constant Level: audio output to
connect with an external amplifier
CLR Component Level Repair
ComPair Computer aided rePair
CP Connected Planet / Copy Protection
CSM Customer Service Mode
CTI Color Transient Improvement:
manipulates steepness of chroma
transients
CVBS Composite Video Blanking and
Synchronization
DAC Digital to Analogue Converter
DBE Dynamic Bass Enhancement: extra
low frequency amplification
DCM Data Communication Module. Also
referred to as System Card or
Smartcard (for iTV).
DDC See “E-DDC”
D/K Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 6.5 MHz
DFI Dynamic Frame Insertion
DFU Directions For Use: owner's manual
DMR Digital Media Reader: card reader
DMSD Digital Multi Standard Decoding
DNM Digital Natural Motion
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 7

Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
EN 7TPN16.1E LA 3.
DNR Digital Noise Reduction: noise
reduction feature of the set
DRAM Dynamic RAM
DRM Digital Rights Management
DSP Digital Signal Processing
DST Dealer Service Tool: special remote
control designed for service
technicians
DTCP Digital Transmission Content
Protection; A protocol for protecting
digital audio/video content that is
traversing a high speed serial bus,
such as IEEE-1394
DVB-C Digital Video Broadcast - Cable
DVB-T Digital Video Broadcast - Terrestrial
DVD Digital Versatile Disc
DVI(-d) Digital Visual Interface (d= digital only)
E-DDC Enhanced Display Data Channel
(VESA standard for communication
channel and display). Using E-DDC,
the video source can read the EDID
information form the display.
EDID Extended Display Identification Data
(VESA standard)
EEPROM Electrically Erasable and
Programmable Read Only Memory
EMI Electro Magnetic Interference
EPG Electronic Program Guide
EPLD Erasable Programmable Logic Device
EU Europe
EXT EXTernal (source), entering the set by
SCART or by cinches (jacks)
FDS Full Dual Screen (same as FDW)
FDW Full Dual Window (same as FDS)
FLASH FLASH memory
FM Field Memory or Frequency
Modulation
FPGA Field-Programmable Gate Array
FTV Flat TeleVision
Gb/s Giga bits per second
G-TXT Green TeleteXT
H H_sync to the module
HD High Definition
HDD Hard Disk Drive
HDCP High-bandwidth Digital Content
Protection: A “key” encoded into the
HDMI/DVI signal that prevents video
data piracy. If a source is HDCP coded
and connected via HDMI/DVI without
the proper HDCP decoding, the
picture is put into a “snow vision” mode
or changed to a low resolution. For
normal content distribution the source
and the display device must be
enabled for HDCP “software key”
decoding.
HDMI High Definition Multimedia Interface
HP HeadPhone
I Monochrome TV system. Sound
2
C Inter IC bus
I
2
I
D Inter IC Data bus
2
S Inter IC Sound bus
I
carrier distance is 6.0 MHz
IF Intermediate F requency
IR Infra Red
IRQ Interrupt Request
ITU-656 The ITU Radio communication Sector
(ITU-R) is a standards body
subcommittee of the International
Telecommunication Union relating to
radio communication. ITU-656 (a.k.a.
SDI), is a digitized video format used
for broadcast grade video.
Uncompressed digital component or
digital composite signals can be used.
back to
div. table
The SDI signal is self-synchronizing,
uses 8 bit or 10 bit data words, and has
a maximum data rate of 270 Mbit/s,
with a minimum bandwidth of 135
MHz.
iTV Institutional TeleVision; TV sets for
hotels, hospitals etc.
LS Last Status; The settings last chosen
by the customer and read and stored
in RAM or in the NVM. They are called
at start-up of the set to configure it
according to the customer's
preferences
LATAM Latin America
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LED Light Emitting Diode
L/L' Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 6.5 MHz. L' is Band
I, L is all bands except for Band I
LPL LG.Philips LCD (supplier)
LS Loudspeaker
LVDS Low Voltage Differential Signalling
Mbps Mega bits per second
M/N Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 4.5 MHz
MHEG Part of a set of international standards
related to the presentation of
multimedia information, standardised
by the Multimedia and Hypermedia
Experts Group. It is commonly used as
a language to describe interactive
television services
MIPS Microprocessor without Interlocked
Pipeline-Stages; A RISC-based
microprocessor
MOP Matrix Output Processor
MOSFET Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect
Transistor, switching device
MPEG Motion Pictures Experts Group
MPIF Multi Platform InterFace
MUTE MUTE Line
MTV Mainstream TV: TV-mode with
Consumer TV features enabled (iTV)
NC Not Connected
NICAM Near Instantaneous Compounded
Audio Multiplexing. This is a digital
sound system, mainly used in Europe.
NTC Negative Temperature Coefficient,
non-linear resistor
NTSC National Television Standard
Committee. Color system mainly used
in North America and Japan. Color
carrier NTSC M/N= 3.579545 MHz,
NTSC 4.43= 4.433619 MHz (this is a
VCR norm, it is not transmitted off-air)
NVM Non-Volatile Memory: IC containing
TV related data such as alignments
O/C Open Circuit
OSD On Screen Display
OAD Over the Air Download. Method of
software upgrade via RF transmission.
Upgrade software is broadcasted in
TS with TV channels.
OTC On screen display Teletext and
Control; also called Artistic (SAA5800)
P50 Project 50: communication protocol
between TV and peripherals
PAL Phase Alternating Line. Color system
mainly used in West Europe (colour
carrier = 4.433619 MHz) and South
America (colour carrier
PAL M = 3.575612 MHz and
PAL N = 3.582056 MHz)
PCB Printed Circuit Board (same as “PWB”)
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
2016-Mar-11
Page 8

EN 8 TPN16.1E LA3.
Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
PDP Plasma Display Panel
PFC Power Factor Corrector (or
Pre-conditioner)
PIP Picture In Picture
PLL Phase Locked Loop. Used for e.g.
FST tuning systems. The customer
can give directly the desired frequency
POD Point Of Deployment: a removable
CAM module, implementing the CA
system for a host (e.g. a TV-set)
POR Power On Reset, signal to reset the uP
PSDL Power Supply for Direct view LED
backlight with 2D-dimming
PSL Power Supply with integrated LED
drivers
PSLS Power Supply with integrated LED
drivers with added Scanning
functionality
PTC Positive Temperature Coefficient,
non-linear resistor
PWB Printed Wiring Board (same as “PCB”)
PWM Pulse Width Modulation
QRC Quasi Resonant Converter
QTNR Quality Temporal Noise Reduction
QVCP Quality Video Composition Processor
RAM Random Access Memory
RGB Red, Green, and Blue. The primary
color signals for TV. By mixing levels
of R, G, and B, all colors (Y/C) are
reproduced.
RC Remote Control
RC5 / RC6 Signal protocol from the remote
control receiver
RESET RESET signal
ROM Read Only Memory
RSDS Reduced Swing Differential Signalling
data interface
R-TXT Red TeleteXT
SAM Service Alignment Mode
S/C Short Circuit
SCART Syndicat des Constructeurs
d'Appareils Radiorécepteurs et
SCL Serial Clock I
Téléviseurs
SCL-F CLock Signal on Fast I
SD Standard Definition
SDA Serial Data I
SDA-F DAta Signal on Fast I
2
C
2
C bus
2
C
2
C bus
SDI Serial Digital Interface, see “ITU-656”
SDRAM Synchronous DRAM
SECAM SEequence Couleur Avec Mémoire.
Colour system mainly used in France
and East Europe. Colour
carriers = 4.406250 MHz and
4.250000 MHz
SIF Sound Intermediate Frequency
SMPS Switched Mode Power Supply
SoC System on Chip
SOG Sync On Green
SOPS Self Oscillating Power Supply
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface bus; a
4-wire synchronous serial data link
standard
S/PDIF Sony Philips Digital InterFace
SRAM Static RAM
SRP Service Reference Protocol
SSB Small Signal Board
SSC Spread Spectrum Clocking, used to
reduce the effects of EMI
STB Set Top Box
STBY STand-BY
SVGA 800 × 600 (4:3)
SVHS Super Video Home System
SW Software
SWAN Spatial temporal Weighted Averaging
Noise reduction
SXGA 1280 × 1024
TFT Thin Film Transistor
THD Total Harmonic Distortion
TMDS Transmission Minimized Differential
Signalling
TS Transport Stream
TXT TeleteXT
TXT-DW Dual Window with TeleteXT
UI User Interface
uP Microprocessor
UXGA 1600 × 1200 (4:3)
V V-sync to the module
VESA Video Electronics Standards
Association
VGA 640 × 480 (4:3)
VL Variable Level out: processed audio
output toward external amplifier
VSB Vestigial Side Band; modulation
method
WYSIWYR What You See Is What You Record:
record selection that follows main
picture and sound
WXGA 1280 × 768 (15:9)
XTAL Quartz crystal
XGA 1024 × 768 (4:3)
Y Luminance signal
Y/C Luminance (Y) and Chrominance (C)
signal
YPbPr Component video. Luminance and
scaled color difference signals (B-Y
and R-Y)
YUV Component video
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 9
4. Mechanical Instructions
20100_100.eps
CN401
CN9101
CN8601
CN701
CN601
CN702
CN408
MAIN POWER SUPPLY
(1054)
A
IR/LED BOARD
(1056)
J
SSB
(1053)
B
ECN408
ECN701
ECN702
ECN401
ECN401
ECN601
ECN601
LOUDSPEAKER
(1184)
Index of this chapter:
4.1 Cable Dressing
4.2 Service Positions
4.3 Assembly/Panel Removal (for 24"Pxx5211)
4.4 Set Re-assembly
4.1 Cable Dressing
Mechanical Instructions
Notes:
• Figures below can deviate slightly from the actual situation,
due to the different set executions.
EN 9TPN16.1E LA 4.
Figure 4-1 Cable dressing (24" 5211 series)
back to
div. table
2016-Mar-11
Page 10
EN 10 TPN16.1E LA4.
20100_101.eps
2
1
4
3
Mechanical Instructions
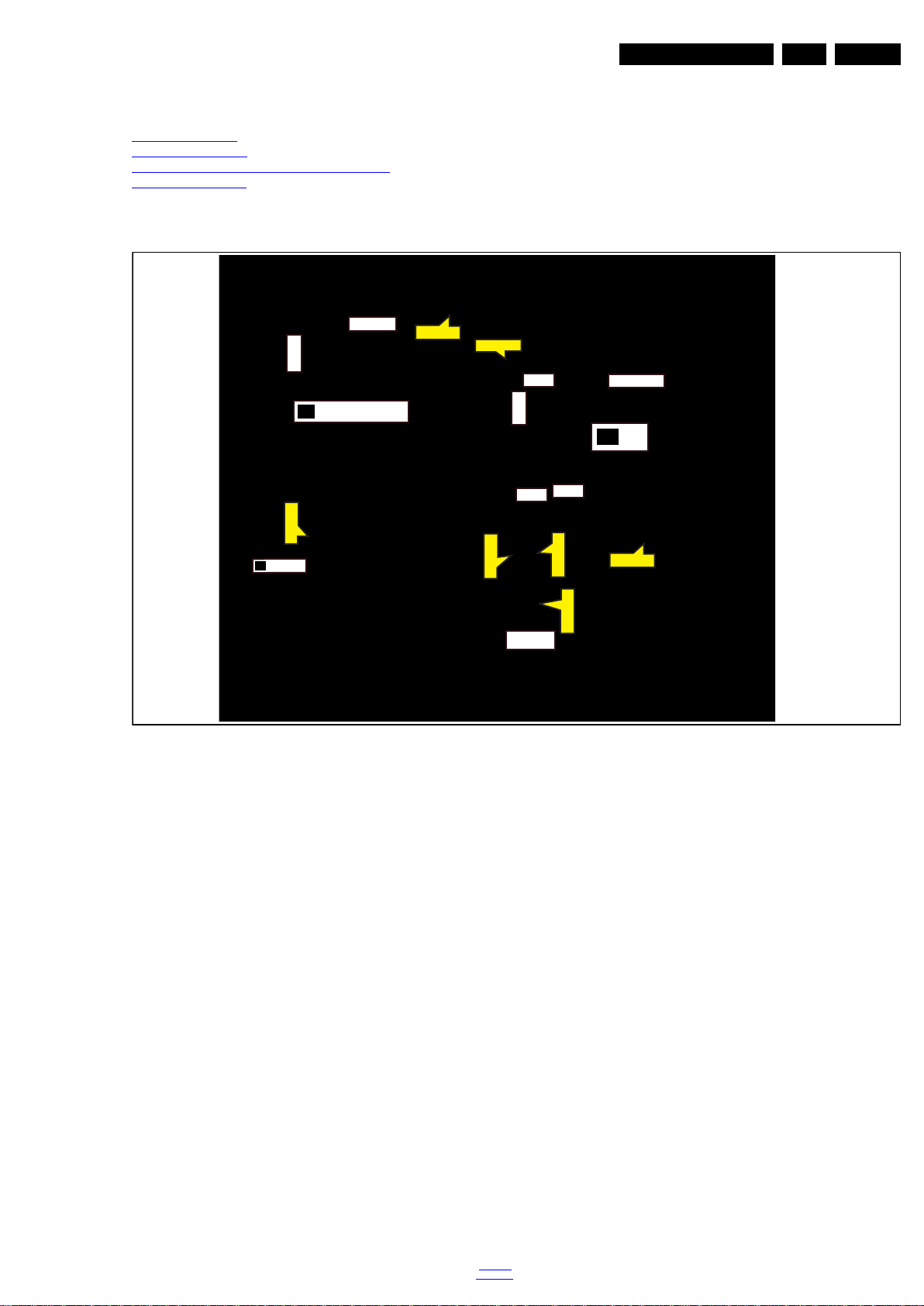
4.2 Se rvice Positions
For easy servicing of a TV set, the set should be put face down
on a soft flat surface, foam buffers or other specific workshop
tools. Ensure that a stable situation is created to perform
measurements and alignments. When using foam bars take
care that these always support the cabinet and never only the
display. Caution: Failure to follow these guidelines can
seriously damage the display!
Ensure that ESD safe measures are taken.
4.3 Assembly/Panel Removal (for 24"Pxx5211)
Instructions below apply to the 24PFK5211/12, but will be
similar for other 24"Pxx5211 series models.
4.3.1 Stand
Refer to Figure 4-2
1. Remove the fixation area [2] that locked from the clips [1]
and the fixation area [4] that locked from the clips [3]. Refer
to Figure 4-2
2. Take the stand bracket out from the set.
for details.
for details.
2016-Mar-11
Figure 4-2 Stand removal
back to
div. table
Page 11
Mechanical Instructions
20100_102.eps
5
5
EN 11TPN16.1E LA 4.
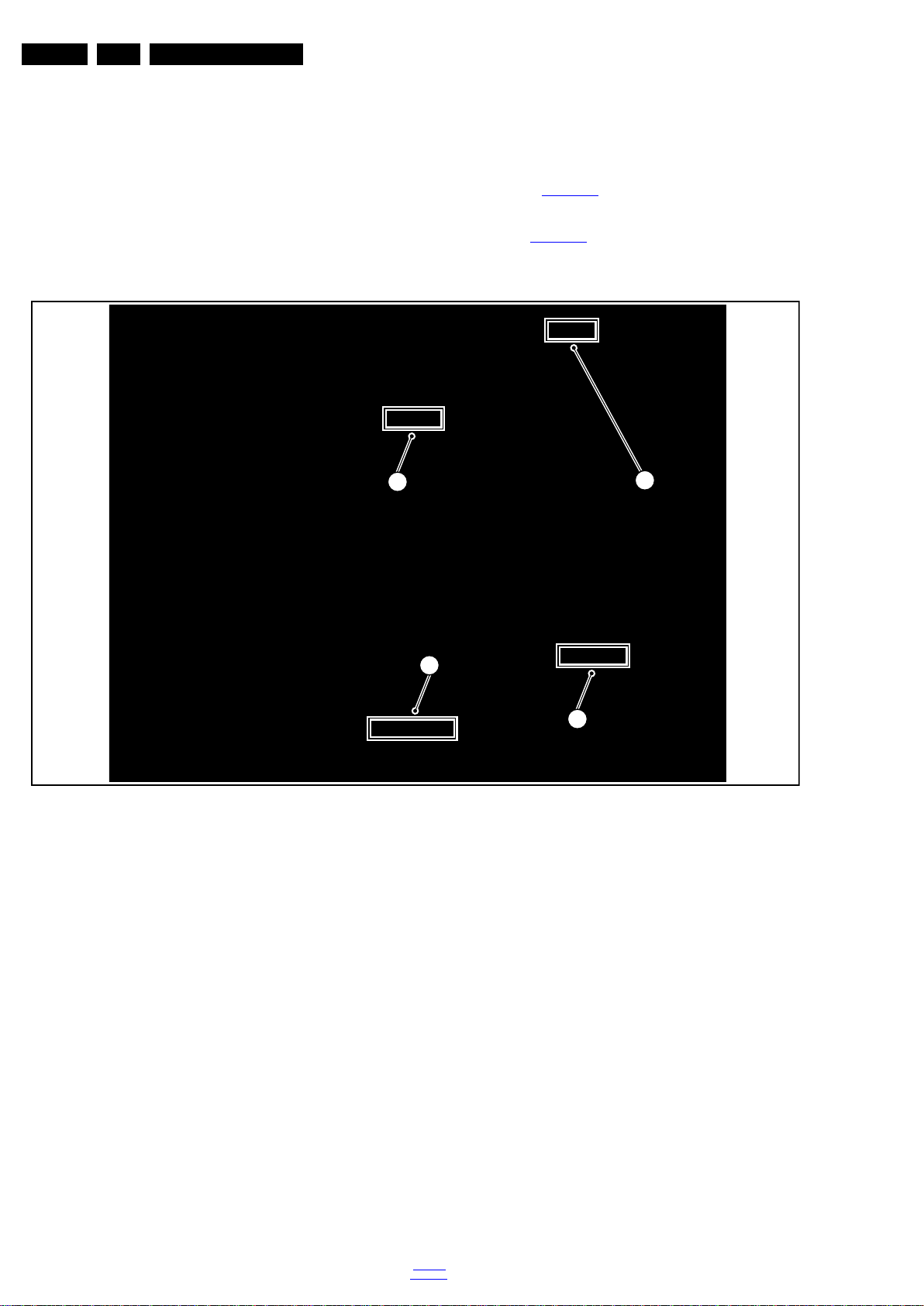
4.3.2 Rear Cover
Refer to Figure 4-3
Warning: Disconnect the mains power cord before removing
the rear cover.
for details.
1. At the indicated areas [5] the cover is securd by clips. Be
very careful with releasing those.
2. Gently lift the rear cover from the TV. Make sure that wires
and cables are not damaged while lifting the rear cover
from the set.
Figure 4-3 Rear cover removal
back to
div. table
2016-Mar-11
Page 12
EN 12 TPN16.1E LA4.
20100_103.eps
1
Q4 × 12
1
1
2
3
20100_104.eps
2
1
3
3
3
3
Mechanical Instructions
4.3.3 Speaker
Refer to Figure 4-4
Warning: Disconnect the mains power cord before removing
the rear cover.
1. Remove the fixation screws [1] that secure the rear cover.
Refer to Figure 4-4
for details.
for details.
2. Release the connectors [2] and [3] that connect speake
with the SSB. Refer to Figure 4-4
3. Gently lift the Speaker from the TV. Make sure that wires
and cables are not damaged while lifting the rear cover
from the set.
for details.
4.3.4 Small Signal Board (SSB)
Refer to Figure 4-5
Caution: it is mandatory to remount all different screws at their
original position during re-assembly. Failure to do so may result
in damaging the SSB.
1. Release the clips from the LVDS connector that connect
with the SSB[1].
Caution: be careful, as these are very fragile connectors!
2. Unplug all other connectors [2] .
3. Remove all the fixation screws from the SSB [3].
4. The SSB can now be shifted from side connector cover,
then lifted and taken out of the I/O bracket. Refer to
Figure 4-5
for details.
for details.
Figure 4-4 Speaker removal
Figure 4-5 SSB removal
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 13

4.3.5 IR/LED Board
20100_105.eps
2
Step 1
Step 2
1
1
Mechanical Instructions
EN 13TPN16.1E LA 4.
Refer to Figure 4-6
1. Remove the area clips [1] from the stand bracket, pull out
the assy from the set. Refer to Figure 4-6
2. Carefully Releas the cover secured by clips, then unplug
the connector [2] from the IR/LED board. The IR/LED
Board can now be lifted and taken out from the cover.
for details.
for details.
Figure 4-6 IR/LED Board removal
4.3.6 Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Caution: it is mandatory to remount all different screws at their
original position during re-assembly. Failure to do so may result
in damaging the PSU.
1. Gently unplug all connectors from the PSU.
2. Remove all fixation screws from the PSU.
3. The PSU can be taken out of the set now.
4.3.7 LCD Panel
1. Remove the SSB as described earlier.
2. Remove the PSU as described earlier.
3. Remove the stand bracket as described earlier.
4. Remove the IR/LED as described earlier.
5. Remove the fixations screws that fix the metal clamps to
the front bezel. Take out those clamps.
6. Remove all other metal parts not belonging to the panel.
7. Lift the LCD Panel from the bezel.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
4.4 Set Re-assembly
To re-assemble the whole set, execute all processes in reverse
order.
Notes:
• While re-assembling, make sure that all cables are placed
and connected in their original position. See Figure 4-1
• Pay special attention not to damage the EMC foams on the
SSB shields. Ensure that EMC foams are mounted
correctly.
.
back to
div. table
2016-Mar-11
Page 14

EN 14 TPN16.1E LA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Index of this chapter:
5.1 Service Modes
5.2 Stepwise Start-up
5.3 Service Tools
5.4 Software Upgrading
5.5 Error Codes
5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure
5.7 Fault Finding and Repair Tips
5.1 Service Modes
The Service Mode feature is split into follow parts:
• Service Alignment Mode (SAM).
• Factory Mode.
• Customer Service Mode (CSM).
SAM and the Factory mode offer features, which can be used
by the Service engineer to repair/align a TV set. Some features
are:
• Make alignments (e.g. White Tone), reset the error buffer
(SAM and Factory Mode).
• Display information (“SAM” indication in upper right corner
of screen, error buffer, software version, operating hours,
options and option codes, sub menus).
Display Option Code Selection
When after an SSB or display exchange, the display option
code is not set properly, it will result in a TV with “no display”.
Therefore, it is required to set this display option code after
such a repair.
To do so, press the following key sequence on a standard RC
transmitter: “062598” directly followed by MENU and “xxx”,
where “xxx” is a 3 digit decimal value of the panel type. When
the value is accepted and stored in NVM, the set will switch to
Stand-by, to indicate that the process has been completed.
During this algorithm, the NVM-content must be filtered,
because several items in the NVM are TV-related and not SSB
related (e.g. Model and Prod. S/N). Therefore, “Model”
and “Prod. S/N” data is changed into “See Type Plate”. In case
a call centre or consumer reads “See Type Plate” in CSM
mode.
5.1.2 Service Alignment Mode (SAM)
Purpose
• To modify the NVM.
• To display/clear the error code buffer.
• To perform alignments.
The CSM is a Service Mode that can be enabled by the
consumer. The CSM displays diagnosis information, which the
customer can forward to the dealer or call centre. In CSM
mode, “CSM”, is displayed in the top right corner of the screen.
The information provided in CSM and the purpose of CSM is to:
• Increase the home repair hit rate.
• Decrease the number of nuisance calls.
• Solved customers’ problem without home visit.
Note: For the new model range, a new remote control (RC) is
used with some renamed buttons. This has an impact on the
activation of the Service modes. For instance the old “MENU”
button is now called “HOME” (or is indicated by a “house” icon).
5.1.1 General
Next items are applicable to all Service Modes or are general.
Life Timer
During the life time cycle of the TV set, a timer is kept (called
“Op. Hour”). It counts the normal operation hours (not the
Stand-by hours). The actual value of the timer is displayed in
SAM in a decimal value. Every two soft-resets increase the
hour by + 1. Stand-by hours are not counted.
Software Identification, Version, and Cluster
The software ID, version, and cluster will be shown in the main
menu display of SAM and CSM.
The screen will show: “AAAAB-X.YYY”, where:
• AAAA is the chassis name: TPN161E x.yy.
• B is the region indication: E = Europe, A = AP/China, U =
NAFTA, L = LATAM.
• X is the main version number: this is updated with a major
change of specification (incompatible with the previous
software version). Numbering will go from 1 - 99 and
AA - ZZ.
- If the main version number changes, the new version
number is written in the NVM.
- If the main version number changes, the default settings
are loaded.
• YYY is the sub version number: this is updated with a minor
change (backwards compatible with the previous
versions). Numbering will go from 000 - 999.
- If the sub version number changes, the new version
number is written in the NVM.
- If the NVM is refreshed, the software identification,
version, and cluster will also be written to NVM.
Specifications
• Operation hours counter (maximum five digits displayed).
• Software version, error codes, and option settings display.
• Error buffer clearing.
• Option settings.
• Software alignments (White Tone).
• NVM Editor.
• Set screen mode to full screen (all content is visible).
How to Activate SAM
To activate SAM, use one of the following methods:
• Press the following key sequence on the remote control
transmitter: “062596”, directly followed by the “INFO/OK”
button. Do not allow the display to time out between entries
ying the sequence.
while ke
After entering SAM, the following items are displayed,
with “SAM” in the upper right corner of the screen to indicate
that the television is in Service Alignment Mode.
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 15
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 15TPN16.1E LA 5.
Table 5-1 SAM mode overview
Main Menu Sub-menu 1 Sub-menu 2 Description
System Information Op Hour e.g. 00082 This represents the life timer. The timer counts normal operation hou rs, but does no t
Clear Press [OK] to clean the Error Codes
RGB Align Warm R Gain To align the White Tone. See
Upload to USB Copy Channel List to USB To upload several settings from the TV to an USB stick
Download from USB Copy Channel List from USB To download several settings from the USB stick to the TV
immediately
G Gain
B Gain
Normal R Gain
G Gain
B Gain
Cool R Gain
G Gain
B Gain
Store Store the RGB value
count Stand-by hours.
Erases the contents of the error buffer. Select this menu item and press the MENU
RIGHT key on the remote control. The content of the error buffer is cleared.
paragraph 6.3 Software Alignments in the Alignments section for a detailed
description
How to Navigate
• In the SAM menu, select menu items with the UP/DOWN
keys on the remote control transmitter. The selected item
will be indicated. When not all menu items fit on the screen,
use the UP/DOWN keys to display the next/previous menu
items.
• With the “LEFT/RIGHT” keys, it is possible to:
– (De) activate the selected menu item.
– (De) activate the selected sub menu.
– Change the value of the selected menu item.
• When you press the MENU button once while in top level
SAM, the set will switch to the normal user menu (with the
SAM mode still active in the background).
• Press the following key sequence on the remote control
transmitter: “062596” directly followed by the “Home/Menu”
button to switch to (do not allow the display to time out
between entries while keying the sequence).
How to Store SAM Settings
To store the settings changed in SAM mode (except the
RGB Align settings), leave the top level SAM menu by using
the POWER button on the remote control transmitter or the
television set. The mentioned exceptions must be stored
separately via the STORE button.
How to Exit SAM
Use one of the following methods:
• Switch the set to STANDBY by pressing the mains button
on the remote control transmitter or the television set.
• Via a standard RC-transmitter, key in “00” sequence.
Note: When the TV is switched “off” by a power interrupt while
in SAM, the TV will show up in “normal operation mode” as
soon as the power is supplied again. The error buffer will not be
cleared.
5.1.3 Contents of the Factory mode:
Purpose
• To perform extended alignments.
Specifications
• Displaying and or changing Panel ID information.
• Displaying and or changing Tuner ID information.
• Error buffer clearing.
• Various software alignment settings.
• Testpattern displaying.
• Public Broadcasting Service password Reset.
•etc.
How to Activate the Factory mode
To activate the Factory mode, use the following method:
• Press the following key sequence on the remote control
transmitter: from the “menu/home” press “1999”, directly
followed by the “Back/Return” button. Do not allow the
display to time out between entries while keying the
sequence.
After entering the Factory mode, the following items are
displayed,
Table 5-2 Factory mode overview
Item Item value
0 F/W VERSION Press OK Displays the software versions of the supplier, Flash PQ, Smart Picture, BL Dimming,
1 Board ID 715G6079_3in1 Dispaly the Board ID; be careful changing this, it can result in not correct displaying the screen!
2 PANEL_ID 22 Displays and change s the Panel ID with the left an d right cursor; be car eful changing thi s, it can
3 DB COPY TV to USB Press OK DB COPY TV to USB
4 DB READ USB to TV Press OK DB READ USB to TV
5 CLR_TEMP_R 90 Red colour temperature setting
6 CLR_TEMP_G 98 Green colour temperature setting
7 CLR_TEMP_B 128 Blue colour temperature setting
8 AUTO_COLOR Press OK PC: any pattern that has black and white, YPbPr: SMPTE bar (colour bar), any timing.
9 ADC_GAIN_R 0 Red ADC gain
10 ADC_GAIN_G 0 Green ADC gain
11 ADC_GAIN_B 0 Blue ADC gain
12 ADC_OFFSET_R 0 Red ADC offset
13 ADC_OFFSET_G 0 Green ADC offs et
14 ADC_OFFSET_B 0 Blue ADC offset
15 VIRGING_MODE off Use this to return the set to virgin mode. Depends whether the set has been used already.
16 E_Fuse on E-fuse mode
Default value
Description24"
Source Meter, the Picture Quality checksum, the Dimming library, the Source meter library, the
Flash AQ, MCU and OAD software versions.
result in not correct displaying the screen!
back to
div. table
2016-Mar-11
Page 16
EN 16 TPN16.1E LA5.
Item Item value
17 ORT_MODE off ORT mode
18 AGEING MODE off Use this for aging a new LCD p an el
19 AUD_LIMITE_MODE 1 Three modes,0: off, 1: adaptive mode, 2: fixed mode
20 AUD_THRESHOLD_BYTE1 100 Limit threshold
21 AUD_THRESHOLD_BYTE2 200 Limit threshold
22 AUD_THRESHOLD_BYTE3 100 Limit threshold
23 AUD_GAIN_LINEIN 0 Line-in audio gain
24 AUD_GAIN_HDMI -10 HDMI audio gain
25 AUD_GAIN_ATV 0 Analogue TV audio gain
26 AUD_GAIN_DTV 0 Digital TV audio gain
27 AUD_GAIN_USB 0 U SB audio gain
28 AUD_GAIN_BT 0
29 TUNER_ID 0 Displays and changes the Tuner ID with the left and right cursor. Not to be changed when the
30 CIPLUS QUERY Press OK Shows the Validity of the CI+ key and the supplier information
31 CIPLUS UPDATE Press OK Used to enter a new CI+ code into the NVM. This can only be used when no CI+ code exists in
32 CI Key Type Selection ProductKey CI Key Type Selection
33 AQ_TABLE_INDEX 16 Audio Quality index
34 EDID UPDATE Press OK Used to enter a new EDID codes into the NVM
35 LVDS SSC Ratio 5% LVDS SSC ratio
36 LVDS SSC Freq 30KHz LVDS SSC frequency
37 DDR SSC Ratio 2% DDR SSC ratio
38 DDR SSC Freq 30KHz DDR SSC frequency
39 Panel H.Flip off Flip panel
40 Panel V.Flip off Flip panel
41 Panel ABSwap on ABSwap panel
42 Watchdog 5sec Watchdog
43 Backlight PWM freq.(Hz) 150 Backlight PWM frequency
44 Backlight PWM Limit 20 Backlight PWM Limit
45 VGA_TxRx_Mode off VGA_TxRx_Mode
46 LVDS Driving 2 LVDS Driving
47 LVDS Format VESA 8bit LVDS Format
48 Ziggo Aging Press OK Ziggo Aging
49 SPDIF On Enable/Disable SPDIF source
50 Standard PWM Gain 100 Standard PWM Gain
51 ECO PWM Gain 100 ECO PWM Gain
52 VGA port on Enable/Disable VGA port
53 Zero Detect Enable on Zero Detect Enable
54 Copy PQ table to TV Press OK Copy PQ table to TV
55 Copy AQ table to TV Press OK Copy AQ table to TV
56 Headphon e on Enable/Disable Headphone source
57 EnhancedH/88 on EnhancedH/88
58 Joysticker Enable Off Joysticker Enable
59 Ambilight Enable Off Ambilight Enable
60 Lounge Light Enable Off Lounge Light Enable
61 FRC F/W Upgrad e Press OK FRC F/W Upgrade
62 Satellite Tuner Slave Address 0xC6 TUNER Address
63 912_SSC_LVDS_PERCENT 0 Percent of 912_SSC_LVDS
64 912_SSC_LVDS_FREQ 0 912_SSC_LVDS_FREQ
65 912_LVDS_DRIVING 0 912_LVDS_DRIVING
66 912_LVDS_ FOR M AT JEDIA 8bit The format for 912_LVDS
67 EXIF_FACTORY Press OK Exits the Factory mode
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Default value
Description24"
tuner is replaced with the corre ct service part.
the NVM
How to Exit the Factory mode
Use one of the following methods:
• Select EXIT_FACTORY from the menu and press the “OK”
button.
Note: When the TV is switched “off” by a power interrupt, or
normal switch to “stand-by” while in the factory mode, the TV
will show up in “normal operation mode” as soon as the power
is supplied again. The error buffer will not be cleared.
5.1.4 Customer Service Mode (CSM)
Purpose
The Customer Service Mode shows error codes and
information on the TVs operation settings.The call centre can
instruct the customer (by telephone) to enter CSM in order to
identify the status of the set.This helps the call centre to
diagnose problems and failures in the TV set before making a
service call.
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
The CSM is a read-only mode; therefore, modifications are not
possible in this mode.
Specifications
• Ignore “Service unfriendly modes”.
• Line number for every
line (to make CSM language independent).
• Set the screen mode to full
screen (all contents on screen is visible).
• After leaving the Customer Service Mode, the original
settings are restored.
• Possibility to use “CH+” or “CH-” for channel surfing, or
enter the specific channel number on the RC.
How to Activate CSM
To activate CSM, press the following key sequence on a
standard remote control transmitter: “123654” (do not allow the
display to time out between entries while keying the sequence).
Page 17
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
19080_206_110323.eps
120224
Power Off
Standby
Soft Mode
Power On
Semi-
Standby
Standby
Switch
Off(Mains
Power Plug)
Standby Soft Mode
Command Received,
previously in Standby
Soft Mode (Power tact
switch)
TV Wakeup
commands
Received
(TV Wakeup
keys)
Digital
background
tasks started
Digital
background
tasks completed
Swith On,
previously in
Standby/Semi-
Standby (Mains
Power Plug)
Standby
Soft Mode
Command
Received
(Power tact
switch)
Switch Off (Mains
Power Plug)
Switch Off
(Mains Power
Plug)
Swith On,
previously in
Standby Soft Mode
(Mains Power Plug)
Standby
commands
Received (RC
Standby key)
Standby Soft Mode
Command Received,
previously in Standby
Soft Mode (Power
tact switch)
TV Wakeup
commands
Received
(TV Wakeup
keys)
Switch On, previously
in Power On Mode
(Power tact switch)
Standby Soft Mode
Command Received,
(Power tact switch)
Switch Off (Mains
Power Plug)
Switch On,previously in
TV Operation Mode
(Mains Power Plug)
EN 17TPN16.1E LA 5.
After entering the Customer Service Mode, the following items
are displayed.
Note: Activation of the CSM is only possible if there is no (user)
menu on the screen!
Contents of CSM
• 1.1 Set Type This information is very helpful for a
helpdesk/workshop as reference for further diagnosis. In
this way, it is not necessary for the customer to look at the
rear of the TV-set. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is
initialized after corruption, this set type has to be re-written
to NVM.
• 1.2 Production code Displays the production
code (the serial number) of the TV. Note that if an NVM is
replaced or is initialized after corruption, this production
code has to be re-written to NVM.
• 1.3 Installation date Indicates the date of the first
installation of the TV. This date is acquired via time
extraction.
• 1.4 SSB Gives an identification of the SSB as stored in
NVM. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is initialized after
corruption, this identification number has to be re-written to
NVM. This identification number is the 12NC number of the
SSB.
• 1.5 Display 12NC NVM read/write.
• 1.6 PSU 12NC NVM read/write.
• 2.1 Current Main SW Displays the built-in main software
version. In case of field problems related to software,
software can be upgraded. As this software is consumer
upgradeable, it will also be published on the internet.
• 2.2 Standby SW Displays the built-in stand-by processor
software version. Upgrading this software will be possible
via USB.
• 2.3 Panel Code Displays the Display Code number.
• 2.4 NVM Version The version of NVM.
• 3.1 Signal Quality Analog/digital signal strength.
• 3.2 Child lock Not active / active. This is a combined item
for locks. If any lock (channel lock, parental lock) is active,
it is indicated as “active”.
• 3.3 HDCP keys Indicates the validity of the HDMI keys (or
HDCP keys). In case these keys are not valid and the
customer wants to make use of the HDMI functionality, the
SSB has to be replaced.
How to Navigate
By means of the “CURSOR-DOWN/UP” knob (or the scroll
wheel) on the RC-transmitter, can be navigated through the
menus.
How to Exit CSM
To exit CSM, use one of the following methods.
• Press the MENU/HOME button on the remote control
transmitter.
• Press the POWER button on the remote control
transmitter.
• Press the POWER button on the television set.
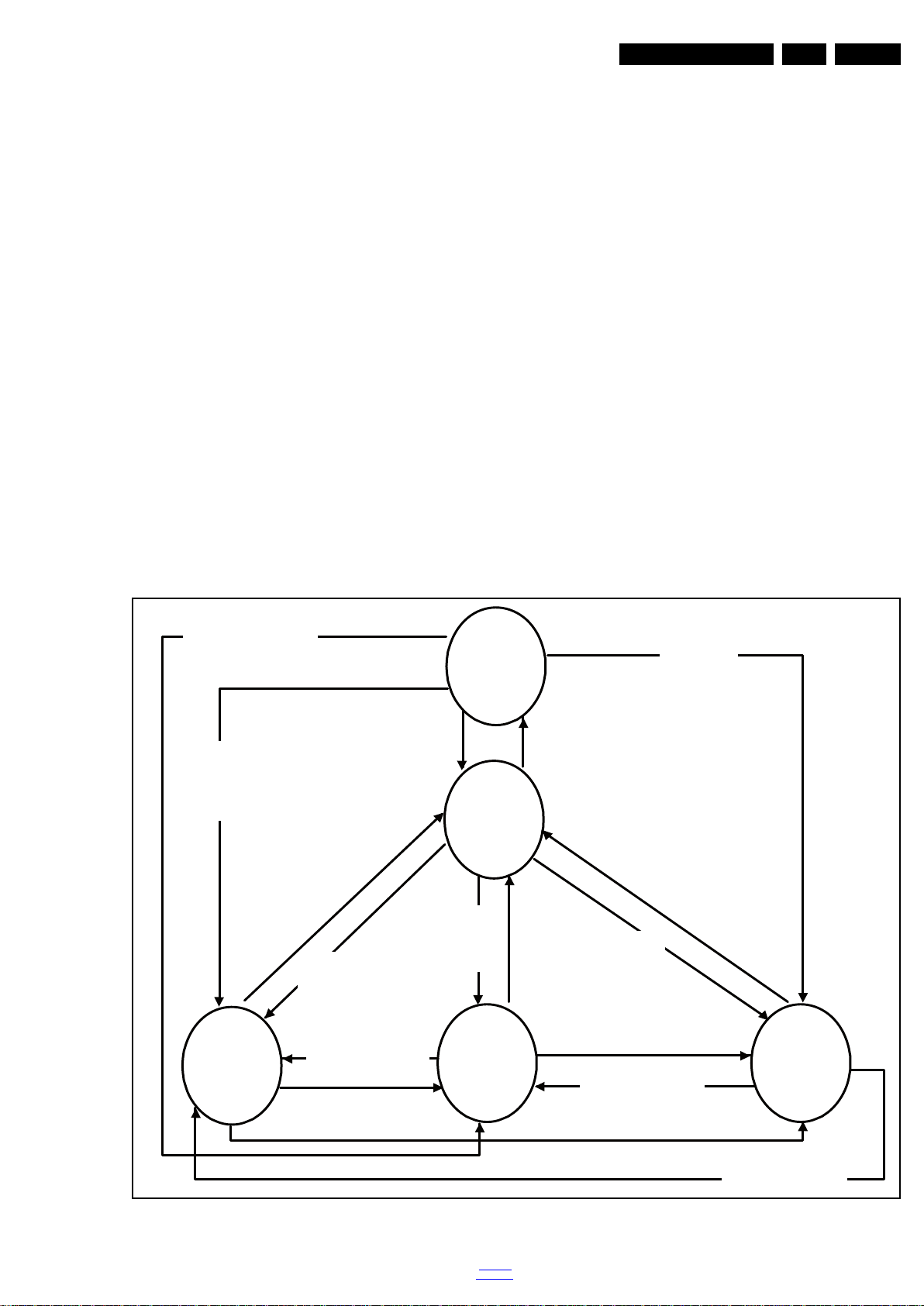
5.2 Stepwise Start-up
Figure 5-1 Stepwise Start-up
back to
div. table
2016-Mar-11
Page 18
EN 18 TPN16.1E LA5.
19080_207_110324.eps
110324
19080_208_110324.eps
110324
19080_209_110324.eps
110324
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5.3 Service Tools
5.3.1 ComPair
The ComPair Tool is no longer supported here. Still, the interface box can be used as level shifter between the TV chassis and PC.
5.4 Software Upgrading
5.4.1 Description
It is possible for the user to upgrade the main software via the
USB port. This allows replacement of a software image in a
stand alone set. A description on how to upgrade the main
software can be found in the DFU or on the Philips website.
5.4.2 Introduction
Philips continuously tries to improve its products, and it’s
recommend that the TV software is updated when updates are
available. Software update files can be obtained from the
dealer or can be downloaded from the following websites:
http://www.philips.com/support
Preparing a portable memory for software upgrade
The following requirements have to be met:
1. A personal computer connected to the internet.
2. An archive utility that supports the ZIP-format (e.g. WinZip
for Windows or Stufflt for Mac OS).
3. A FAT formatted USB memory stick (preferably empty).
6. Upgrading will now begins and the status of the updating
progress will be displayed.
7. When the TV software is updated. Remove your USB flash
drive, then select [Restart] and press OK to restart the
TV.See Figure 5-4
.
Figure 5-2 Update the TV software [1/3]
Note:
1. Only FAT/DOS-formatted memory sticks are supported.
2. Only use software update files that can be found on the
http://www.philips.com/support
web site.
5.4.3 Check the current TV software version
Before starting the software upgrade procedure, it is advised to
check that what the current TV software:
1. Press the “1 2 3 6 5 4” button on the remote control to enter
the CSM mode.
2. Use the up/down cursor keys to select “Current Main
Software”.
If the current software version of the TV is the same as the
latest update file found on http://www.philips.com/support
not necessary to update the TV software.
5.4.4 Download the latest software
1. Open the internet page http://www.philips.com/support
2. Find information and software related to the TV.
3. Select the latest software update file and download it to the
PC.
4. Insert the USB memory stick into one of the USB ports of
the PC.
5. Decompress the downloaded ZIP file and copy it to the root
directory of the USB flash drive.
5.4.5 Update the TV software
1. Turn the TV on and wait for it to boot completely.
2. Insert the USB memory stick that contains the software
update files in one of the TV’s USB ports.
3. The TV will detect the USB memory stick automatically.
Then a window jumps out as Figure 5-2
.
Note: If the USB flash drive is not detected after power up,
disconnect it and re-insert it.
4. Select [Update] and press OK. See Figure 5-2
5. To proceed, In next menu select [Start] and press OK to
.
2016-Mar-11
start software updates. See Figure 5-3
Figure 5-3 Update the TV software [2/3]
, it is
.
Figure 5-4 Update the TV software [3/3]
Note:
• Do not remove the USB flash drive during the software
update.
• If a power failure occurs during the update, do not remove
the USB flash drive from the TV. The TV will continue the
software update as soon as the power comes up again.
• If an error occurs during the update retry the procedure or
contact the dealer.
• We do not recommend downgrading to an older version.
• Once the upgrade is finished, use the PC to remove the TV
software from the USB portable memory.
.
back to
div. table
Page 19

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 19TPN16.1E LA 5.
5.4.6 Content and Usage of the One-Zip Software File
Below you find a content explanation of the One-Zip file, and
instructions on how and when to use it. Only files that are
relevant for Service are mentioned here.
• EDID_clustername.zip: Contains the EDID content of the
different EDID NVMs.
• FUS_clustername_version.zip: Contains the file
downloaded which is needed to upgrade the TV main
software and the software download application.
• NVM_clustername_version.zip: Default NVM content.
5.4.7 How to Copy NVM Data to/from USB
When copying data to and from a USB memory stick, the folder
“repair” is used. When inserting an empty USB memory stick,
and downloading data to the stick, the TV will create this folder.
When sending data from a USB memory stick to a TV, the
intended data must be available in the “repair” folder.
Note that when copying EDID data to the TV, all necessary
EDID files must be in this folder.
Service mode overview for your reference.
Table 5-3 Service mode overview
Service Modes Description
SAM Service alignment mode
Factory Mode Used for extended alignments
CSM 3-page compact CSM pages. There will be CSM dump to
USB SW upgradeable SW-upgrading of flash memories NT72453 can be done
NVM-Editor in SAM NVM-editor will function as in the pa st: Address and Value
Service Data New Service data in SAM for CTN, Prod. no., 12NC
USB copy/paste in
SAM
UART logging There will be printout available in UART. No specifications
Blind SAM RC sequence “062598” + “Menu” +
Clear Buffer RC sequence “062599” + “OK” or via SAM
USB-stick upon entering CSM-mode
via USB. The main SW can be upgraded via the ZIP file
downloaded.
field is a decimal value via digit entry
programming with virtual keyboard
Channel list, NVM data, Readable info, EDID
of the printout, per MTK provision/definition.
“Panel code”
Example:
– ERROR: 000 000 000 000 000: No errors detected
– ERROR: 013 000 000 000 000: Error code 13 is the
last and only detected error
– ERROR: 034 013 000 000 000: Error code 13 was
detected first and error code 34 is the last detected
(newest) error
• Via the blinking LED procedure (when you have no
picture). See paragraph 5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure
5.5.3 Error codes
In this chassis only “layer 2” error codes are available and point
to problems on the SSB. They are triggered by LED blinking
when CSM is activated. Only the following layer 2 errors are
defined:
Table 5-4 Error code table
Layer-2 error code Defective device
13 General I2C bus error on the SSB
16 +12 V missing or low, PSU defective
27 Channel decoder error on the SSB
34 Tuner I2C bus error on the SSB
35 EEPROM I2C error on SSB, M24C64
5.5.4 How to Clear the Error Buffer
The error code buffer is cleared in the following cases:
• By using the CLEAR command in the SAM menu
• By using the CLEAR command in the Factory mode:
• By using the following key sequence on the remote control
transmitter: “062599” directly followed by the OK button.
• If the contents of the error buffer have not changed for 50
hours, the error buffer resets automatically.
Note: If you exit SAM by disconnecting the mains from the
television set, the error buffer is not reset.
5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure
5.6.1 Introduction
.
5.5 Error Codes
5.5.1 Introduction
Error codes are required to indicate failures in the TV set. In
principle a unique error code is available for every:
• Activated (SW) protection.
• Failing I
• General I
The last five errors, stored in the NVM, are shown in the
Service menu’s. This is called the error buffer.
The error code buffer contains all errors detected since the last
time the buffer was erased. The buffer is written from left to
right. When an error occurs that is not yet in the error code
buffer, it is displayed at the left side and all other errors shift one
position to the right.
An error will be added to the buffer if this error differs from any
error in the buffer. The last found error is displayed on the left.
An error with a designated error code never leads to a
deadlock situation. It must always be diagnosable (e.g. error
buffer via OSD or blinking LED).
In case a failure identified by an error code automatically
results in other error codes (cause and effect), only the error
code of the MAIN failure is displayed.
5.5.2 How to Read the Error Buffer
You can read the error buffer in three ways:
• On screen via the SAM/CSM (if you have a picture).
2
C device.
2
C error.
The software is capable of identifying different kinds of errors.
Because it is possible that more than one error can occur over
time, an error buffer is available, which is capable of storing the
last five errors that occurred. This is useful if the OSD is not
working properly.
Errors can also be displayed by the blinking LED procedure.
The method is to repeatedly let the front LED pulse with as
many pulses as the error code number, followed by a period of
1.5 seconds in which the LED is “off”. Then this sequence is
repeated.
Example (1): error code 4 will result in four times the sequence
LED “on” for 0.25 seconds / LED “off” for 0.25 seconds. After
this sequence, the LED will be “off” for 1.5 seconds. Any RC
command terminates the sequence. Error code LED blinking is
in red color.
Example (2): the content of the error buffer is “12 9 6 0 0” After
entering SAM, the following occurs.
• 1 long blink of 5 seconds to start the sequence.
• 12 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds.
• 9 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds.
• 6 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds.
• 1 long blink of 1.5 seconds to finish the sequence.
• The sequence starts again with 12 short blinks.
5.6.2 How to Activate Blinking LED Procedurer
Use one of the following methods:
• Activate CSM.The blinking front LED will show the layer 1
error(s), this works in “normal operation” mode or
back to
div. table
2016-Mar-11
Page 20

EN 20 TPN16.1E LA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
automatically when the error/protection is monitored by the
standby processor.
In case no picture is shown and there is no LED blinking,
read the logging to detect whether “error devices” are
mentioned. (see section “5.7 Fault Finding and Repair
Tips, 5.7.4 Guidelines Uart logging”).
• Activate SAM. The blinking front LED will show the entire
content of the LAYER 2 error buffer, this works in “normal
operation” mode.
5.7 Fault Finding and Repair Tips
Note:
• It is assumed that the components are mounted correctly
with correct values and no bad solder joints.
• Before any fault finding actions, check if the correct options
are set.
5.7.1 NVM Editor
In some cases, it can be convenient if one directly can change
the NVM contents. This can be done with the “NVM Editor” in
SAM mode. With this option, single bytes can be changed.
Caution:
• Do not change these, without understanding the function of
each setting, because incorrect NVM settings may
seriously hamper the correct functioning of the TV set!
• Always write down the existing NVM settings, before
changing the settings. This will enable you to return to the
original settings, if the new settings turn out to be incorrect.
5.7.6 No Picture via HDMI input
Check if HDCP key is valid. This can be done in CSM.
5.7.7 TV Will Not Start-up from Stand-by
Possible Stand-by Controller failure. Re-flash the software.
5.7.8 Audio Amplifier
The Class D-IC U606 has a powerpad for cooling. When the IC
is replaced it must be ensured that the powerpad is very well
pushed to the PWB while the solder is still liquid. This is needed
to insure that the cooling is guaranteed, otherwise the Class
D-IC could break down in short time.
5.7.9 CSM
When CSM is activated and there is a USB memory stick
connected to the TV, the software will dump the complete CSM
content to the USB memory stick. The file (Csm.txt) will be
saved in the root of the USB memory stick.
5.7.10 Loudspeakers
Make sure that the volume is set to minimum during
disconnecting the speakers in the ON-state of the TV. The
audio amplifier can be damaged by disconnecting the speakers
during ON-state of the set!
5.7.2 CSM
When CSM is activated and there is an USB stick connected to
the TV set, then the software will collect the complete CSM
content in a file Csm.xml and dump the file in a folder “CSM” on
the USB stick.
When this mechanism works it can be concluded that a large
part of the operating system is already working (SOC, USB ...).
5.7.3 No Picture
When you have no picture, first make sure you have entered
the correct display code. See paragraph 6.4 Option Settings
the instructions. See also Table 6-3
.
5.7.4 Guidelines Uart logging
Possible cases:
Uart loggings are displayed:
• We can conclude that the TV-set is starting up and
thatcommunication with the flash RAM seems to be
supported. The processor is able to read and write in the
DRAMs.
• We can not yet conclude that flash RAM and DRAMs are
fully operational/reliable.There still can be errors in the data
transfers, DRAM errors, read/write speed and timing
control.
Uart loggings report fault conditions, error messages, error
codes and fatal errors:
• Some failures are indicated by error codes in the logging,
check referring to Table 5-4.
2C bus errors.
•I
• Not all failures or error messages should be interpreted as
fault. For instance the root cause can be wrong option
codes settings.
5.7.11 Display option code
Attention: In case the SSB is replaced, always check the Panel
Code in CSM, even when picture is available. Performance
with the incorrect display option code can lead to unwanted
side-effects for certain conditions.
for
5.7.5 Unstable Picture via HDMI input
Check if HDMI EDID data is properly programmed.
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 21

6. Alignments
Index of this chapter:
6.1 General Alignment Conditions
6.2 Hardware Alignments
6.3 Software Alignments
6.4 Option Settings
6.5 Reset of Repaired SSB
6.1 General Alignment Conditions
Perform all electrical adjustments under the following
conditions:
• Power supply voltage: 90 - 264 V
• Connect the set to the mains via an isolation transformer
with low internal resistance.
• Allow the set to warm up for approximately 15 minutes.
• Measure voltages and waveforms in relation to correct
ground (e.g. measure audio signals in relation to
AUDIO_GND).
Caution: It is not allowed to use heat sinks as ground.
• Test probe: R
> 10 MW, Ci < 20 pF.
i
• Use an isolated trimmer/screwdriver to perform
alignments.
, 50/ 60 ± 3 Hz.
AC
Alignments
In case you have a colour analyser:
• Measure with a calibrated (phosphor- independent) color
analyser (e.g. Minolta CA-210) in the centre of the screen.
Consequently, the measurement needs to be done in a
dark environment.
• Adjust the correct x, y coordinates (while holding one of the
White point registers R, G or B on max. value) by means of
decreasing the value of one or two other white points to the
correct x, y coordinates (see Table 6-1 White D alignment
values). Tolerance: dx: ± 0.003, dy: ± 0.003.
• Repeat this step for the other colour Temperatures that
need to be aligned.
• When finished return to the SAM root menu and press
STANDBY on the RC to store the aligned values to the
NVM.
Table 6-1 White D alignment values
Value Cool (11000 K) Normal (9000 K) Warm (6500 K)
x 0.276 0.287 0.313
y 0.282 0.296 0.329
EN 21TPN16.1E LA 6.
6.2 Hardware Alignments
Not applicable.
6.3 Software Alignments
Put the set in SAM mode (see Chapter 5. Service Modes, Error
Codes, and Fault Finding). The SAM menu will now appear on
the screen. Select RGB Align and go to one of the sub menus.
The alignments are explained below.
The following items can be aligned:
• White point.
To store the data:
• Press OK on the RC before the cursor is moved to the
left.
• Select “Store” and press OK on the RC.
• Switch the set to stand-by mode.
For the next alignments, supply the following test signals via a
video generator to the RF input:
• EU/AP-PAL models: a PAL B/G TV-signal with a signal
strength of at least 1 mV and a frequency of 475.25 MHz
• US/AP-NTSC models: an NTSC M/N TV-signal with a
signal strength of at least 1 mV and a frequency of
61.25 MHz (channel 3).
• LATAM models: an NTSC M TV-signal with a signal
strength of at least 1 mV and a frequency of
61.25 MHz (channel 3).
6.3.1 RGB Alignment
Before alignment, set the picture as follows:
Picture Setting
Dynamic backlight Off
Dynamic Contrast Off
Color Enhancement Off
Picture Format Unscaled
Light Sensor Off
Brightness 50
Color 0
Contrast 100
If you do not have a colour analyser, you can use the default
values. This is the next best solution. The default values are
average values coming from production (statistics).
6.3.2 Display Adjustment
You can use the default values. The default values are average
values coming from production.
• Enter SAM mode.
• Select a colour temperature (e.g. COOL, NORMAL, or
WARM).
• Set the RED, GREEN and BLUE default values according
to the values in Table 6-2
.
• When finished press OK on the RC, then press STORE to
store the aligned values to the NVM.
• Restore the initial picture settings after the alignments.
Table 6-2 White tone default settings
Picture mode Screen size
Normal (9000K) 24PFK5211/12 106 112 128
24PFT5211/12 107 113 126
24PFT5211/60 108 113 125
Cool (11000K) 24PFK5211/12 90 98 128
24PFT5211/12 92 99 127
24PFT5211/60 91 99 128
Warm (6500K) 24PFK5211/12 128 123 116
24PFT5211/12 127 122 115
24PFT5211/60 128 121 114
Colour temperature
Red Green Blue
This group setting of colour temperature will be applied
automatically to the TV / VGA / HDMI / AV sources.
Note: The information of the RGB value is only for reference,
the specific value is based on model adjustment.
6.4 Option Settings
6.4.1 Introduction
White Tone Alignment:
• Activate SAM.
• Select “RGB Align.” and choose a color temperature.
• Use a 100% white screen as input signal and set the
following values:
– “Red BL Offset” and “Green BL Offset” to “7” (if
present).
– All “White point” values initial to “128”.
back to
div. table
The microprocessor communicates with a large number of I
ICs in the set. To ensure good communication and to make
digital diagnosis possible, the microprocessor has to know
which ICs to address. The presence / absence of these
MT5561 ICs is made known by the option codes.
Notes:
2016-Mar-11
2
C
Page 22

EN 22 TPN16.1E LA6.
Alignments
• After changing the option(s), save them by pressing the OK
button on the RC before the cursor is moved to the left,
select STORE and press OK on the RC.
• The new option setting is only active after the TV is
switched “off” / “stand-by” and “on” again with the mains
switch (the NVM is then read again).
6.4.2 Option Code Overview
Enter SAM mode to check the option codes. they could be
edited in the NVM.
6.4.3 Display Code Overview
Press the following key sequence on a standard RC
transmitter: “062598” directly followed by MENU and “xxx”,
where “xxx” is a 3 digit decimal value of the panel type: see
column “Display Code” in Table 6-3
. After resetting the Display
Code, restart the set immediately.
Table 6-3 Display code overview
CTN_ALT BOM# Panel Type Display Code
24PFK5211/12 TPM236WF1-HJJP02.N SC4M WH 022
24PFT5211/12 TPM236WF1-HJJP02.N SC4M WH 022
24PFT5211/60 TPM236WF1-HJJP02.N SC4M WH 022
6.5.2 SSB Identification
SSB’s of this chassis are identified by a “715” code on the SSB.
715Axxxx-Nnn-MMM-OOOO
• 715 main category, Printed Wiring Board
• Axxxx sub category, sequential coding number
• Nnn Version code
• N Development number
• nn Production number
• MMM Mounting variation code
• OOOO Optional variation code
Make sure when replacing an SSB the SSB identification codes
match the replacement panel.
6.6 Cable position numbers
In this chassis, the cable position numbers can be defined via
the rule that the number is always starting with an “E” followed
by the connector number of the current sourcing board. The
order is always seen from where the power initiates from. So
from PSU to SSB, from SSB to IR/LED panel, from IR/LED
panel to keyboard control panel. For example, a cable from the
PSU connector CN902 to the SSB connector CN701, will have
the position number ECN902.
6.5 Reset of Repaired SSB
A very important issue towards a repaired SSB from a Service
repair shop (SSB repair on component level) implies the reset
of the NVM on the SSB.
A repaired SSB in Service should get the service Set type
“00PF0000000000” and Production code “00000000000000”.
Also the virgin bit is to be set. To set all this, you can use the
“NVM editor” and “Dealer options” items in SAM (do not forget
to “store”).
After a repaired SSB has been mounted in the set (set repair
on board level), the type number (CTN) and production code of
the TV has to be set according to the type plate of the set. For
this, you can use the NVM editor in SAM.
In case of a display replacement, reset the “Operation hours
display” to “0”, or to the operation hours of the replacement
display.
Remark:
- After the NVM has been replaced, go to SAM and scroll to the
<Reload MAC address> (see figure 1*).
- Select the item and press <OK> on the RC.
6.5.1 Reset of Repaired SSB
Instruction
After NVM replacement, reload MAC address via SAM
menu.This ensures the correct MAC address to be available in
CSM for future repair actions.
Way of working:
• After the NVM has been replaced, go to SAM and scroll to
the <Reload MAC address> .
• Select the item and press <OK> on the RC.
Notes:
• Only applicable to all related models that are “Smart TV
level 0”enabled (only YouTube access). For models
without internet connection feature, no action is needed.
• HDCP keys are located in the NVM.
New NVM EEPROMs are shipped with pre-loaded HDCP keys.
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 23

7. Circuit Descriptions
Index of this chapter:
7.1 Introduction
7.2 Power Supply
7.3 DC/DC Converters
7.4 Front-End Analogue and DVB-T, DVB-C; ISDB-T reception
7.5 Front-End DVB-S(2) reception
7.6 HDMI
7.7 Video and Audio Processing - NT72453MBG-BA
Notes:
•Only new circuits (circuits that are not published recently)
are described.
• Figures can deviate slightly from the actual situation, due
to different set executions.
• For a good understanding of the following circuit
descriptions, please use the wiring, block (see chapter
9. Block Diagrams
10. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
you will find a separate drawing for clarification.
) and circuit diagrams (see chapter
).Where necessary,
Circuit Descriptions
7.1 Introduction
The TPN16.1E LA is a new chassis launched in Europe in
2016. The whole range is covered by NT72453.
The major deltas versus its predecessor support DVB-TC;
DVB-TC/T2; DVB-TC/S2 with also multi-media, ARC, CEC
function.
The TPN16.1E LA chassis comes with the following stylings:
• series xxPxx5211
7.1.1 Implementation
Key components of this chassis are:
• NT72453MBG-BA/B TFBGA-466 TV Processor
• Tuner EU ST42CS-2-E for K/H/T models (DVB-C/T/T2&
Analogue)
• Tuner EU DNBU02112IH2 for K models ( DVB-S/S2)
• DEMODULATOR Si2166-B22-GMR QFN-48 for K models
• AUDIO AD87588-LG48NAY 20W E-LQFP-48 150
• AUDIO AD22650-QH14NAR - TSSOP-14
7.1.2 TPN16.1E LA Architecture Overview
For details about the chassis block diagrams refer
to 9. Block Diagrams
Figure 9.1
.
EN 23TPN16.1E LA 7.
. An overview architecture can be found in
back to
div. table
2016-Mar-11
Page 24

EN 24 TPN16.1E LA7.
7.1.3 SSB Cell Layout
Circuit Descriptions
DC/DC
COMMON INTERFACE
DDR
NT72453
HDMI
SERVICE
CONNECTOR
HDMI
SPDIF OUT
SCART
AUDIO IN
Analog Input
Figure 7-1 SSB layout cells (top view)
USB
SATTUNER
Headphone
Power Button
20100_200.eps
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 25

7.2 Power Supply
20100_201.eps
Display power
Platform
NT72453
Platform power
1 power- PCB
LVDS AMP
Low stby
power
Ac-input + Mains filter
BL-ON/OFF
PS-ON
AC IN
CN9901
CN8601(For 715G7734)
DIM
12V
12V_A
12V
CN701
AMP
12V
Refer to figure Figure 7-2 for the power architecture of this
platform.
Circuit Descriptions
EN 25TPN16.1E LA 7.
7.2.1 Power Supply Unit
All power supplies are a black box for Service. When defective,
a new board must be ordered and the defective one must be
returned, unless the main fuse of the board is broken. Always
replace a defective fuse with one with the correct
specifications! This part is available in the regular market.
Consult the Philips Service web portal for the order codes of the
boards.
Important delta’s with the TPN16.1E LA classis platform are:
• New power architecture for LED backlight
• “Boost”-signal is now a PWM-signal + continuous variable.
The control signals are:
• Lamp “on/off”
• DIM (PWM) (not for PSDL)
In this manual, no detailed information is available because of
design protection issues.
The output voltages to the chassis are:
• +5V output (stand-by mode)
• +12V (on-mode)
• +12V_audio (audio power)
• +25V (Boost for backlight for 715G7734)
• Output to the display; in case of
- IPB: High voltage to the LCD panel
- PSL and PSLS (LED-driver outputs)
- PSDL (high frequent) AC-current.
Figure 7-2 Power Architecture
7.2.2 Diversity
The diversity in power supply units is mainly determined by the
diversity in displays.
The following displays can be distinguished:
• CCFL/EEFL backlight: power panel is conventional IPB
• LED backlight:
- side-view LED without scanning: PSL power panel
- side-view LED with scanning: PSLS power panel
- direct-view LED without 2D-dimming: PSL power panel
- direct-view LED with 2D-dimming: PSDL power panel.
PSL stands for Power Supply with integrated LED-drivers.
PSLS stands for a Power Supply with integrated LED-drivers
with added Scanning functionality (added microcontroller).
PSDL stands for a Power Supply for Direct-view LED backlight
with 2D-dimming.
7.2.3 Connector overview
Table 7-1 Connector overview
back to
div. table
Connector
Number
Description to SSB to panel
Pin 16 5
1DIMVLED+
2On/offn.c.
3PS_ONLED4n.c.n.c.
5GNDn.c.
6GND7GND-
CN9101 CN8602
2016-Mar-11
Page 26

EN 26 TPN16.1E LA7.
20060_202.eps
NT72453
+5V_SW
500 mA
PWR_ON_2
370 mA
BUCK CONVERTER
TUNER
MAIN CHIP
MAIN CHIP
640 mA
MAIN CHIP
PANEL_T-CON
11mA
SI2166
U201
AO4449
Q701
DV15
NT78822
U201
+5V_SW
+5V_STB
455 mA
PWR_ON_2
TCL_Tuner
DVB-C/T/T2
BUCK CONVERTER
PWR_12V
S2_DEMOD
PWR_ON_2
CI CARD PWR
USB multi-media
POWER protect
AVDD1V2
DV11
Depend on panel
G5250M1T1U
U102
NT72567BG
PCMCIA CARD
+5V_STB
2866 mA(5V)
FB751
K9F1G08U0D
-SIB0
BUCK CONVERTER
1404 mA
PANEL_22"~55"
1mA
FB411
80 mA
FB750
+3V3_TUNER
AD87588
M5723B
U701
MAIN CHIP
10mA
+5V_SW
PANEL_VCC_ON/OFF
FB412
AUDIO AMP
AP3417C
U702
1050mA
POWER SWITCH
DV33
PANEL_VCC
USB
LDO
T2_DEMOD
80 mA
AON4421
Q750
LVDS_VDD
1367 mA
LDO
AZ1117CD
U705
110 mA
POWER SWITCH
+12V_SW
+5V_SW
AUDIO_12V
+5V_SW
1367 mA
VCC_CI
+5V_SW
230 mA
TUNER
PWR_ON_2
285mA
PWR_12V
500 mA
MHL
1367 mA
2581 mA(5V)
230 mA
NT72453
BUCK CONVERTER
LG_Tuner
DVB-S/S2
NAND FLASH
LNB POWER
1.3A
NT72453
TPS54428
U706
CI_PWR_EN
+5V or +12V
MP8126
U202
295 mA
AZ1117_1.35A
U203_SOT-223
1500 mA
AP3417C_1.2A
U703_SOT_23_5
Circuit Descriptions
Connector
Number
CN9101 CN8602
Description to SSB to panel
Pin 16 5
8GND9+12V-A10 +12V-A 11 +12V 12 +12V 13 +12V 14 +12V 15 5.2v 16 5.2v -
7.3 DC/DC Converters
The on-board DC/DC converters deliver the following voltages
(depending on set execution):
• +5V-STANDBY, permanent voltage for the Stand-by
controller, LED/IR receiver and controls.
• +12V, input from the power supply for the panel
common(active mode)
• +12V, input from the power supply for the AMP
• +1V5, from the power supply for the scaler IC NT72453
• +1V1, from the power supply for the scaler IC NT72453
• +1V5, supply voltage for DDR2 (diagram B03B)
• +3V3, genenal supply voltage
• +5V, supply voltage for USB and CAM
• +3V3-TUN, supply voltage for tuner
• +3V3 from the power supply for the scaler IC NT72453
• +5V_SW, input intermediate supply voltage for USB
• +3V3_T2, voltage for Tuner single decoder
• +1V2_T2, voltage for Tuner single decoder
Figures gives a graphical representation of the DC/DC
converters with its current consumptions :
2016-Mar-11
Figure 7-3 DC/DC converters
back to
div. table
Page 27

7.3.1 Power layout SSB
Circuit Descriptions
C626 PVDD(12V)
L704,DV33
L703, +5V_STB
EN 27TPN16.1E LA 7.
L701, DV11
U203, +3V3_Tuner
L702, DV15
U102, VCC_CI
U705, AVDD1V2
20100_202.eps
Figure 7-4 Power SSB Top View
back to
div. table
2016-Mar-11
Page 28

EN 28 TPN16.1E LA7.
20060_209.eps
C707,+5V_SW
IF_AGC
IF
NT725453
IF_AGC
ST42CS-2-E
I2C
I2C
20060_204.eps
Circuit Descriptions
Figure 7-5 Power SSB Bottom View
7.4 Front-End Analogue and DVB-T, DVB-C; ISDB-T reception
7.4.1 DVB-T/C DTV part
The Front-End for DVB-T/C DTV part consist of the following
key components:
• TUNER EUROPE system ST42CS-2-E
• SCALER NT72453MBG-BA/B TFBGA-466
Below find a block diagram of the front-end application for
DVB-T/C DTV part.
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Figure 7-6 Front-End DVB-T2 DTV block diagram
Page 29

Circuit Descriptions
IF
TS DATA
RF_AGC
NT72453
Demod
NT78822QG/A
IF_AGC
ST42CS-2-E
I2C
IF-AGC
I
2
C
I
2
C
20060_205.eps
TS DATA
IP/IN/OP/ON
Tuner I2C
Tuner I2C
System I2C
NT72453MBG-BA/B
LNB power
Si2166
S2 tuner
S2 function
20060_206.eps
20060_207.eps
NT72453MBG
HDMI1
HDMI 2
CN501
CN502
RX
RX
I2C
I
2
C
EN 29TPN16.1E LA 7.
7.4.2 DVB-T2 DTV part
The Front-End for DVB-T2 DTV part consist of the following
key components:
• TUNER EUROPE system ST42CS-2-E
• SCALER NT72453MBG-BA/B TFBGA-466
• DEMODULATOR NT78822QG/A QFN-48 for DVB-T2
DTV part
Below find a block diagram of the front-end application for
DVB-T2 DTV part.
Figure 7-7 Front-End DVB-T2 DTV block diagram
7.5 Front-End DVB-S(2) reception
The Front-End for the DVB-S(2) application consist of the
following key components:
• TUNER EUROPE DNBU02112IH2
• SCALER NT72453MBG-BA/B TFBGA-466
• DEMODULATOR Si2166-B22-GMR QFN-48 for T/T2
Below find a block diagram of the front-end application for
DVB-S(2) reception.
7.6 HDMI
Refer to figure 7-9 HDMI input configuration for the application.
Figure 7-9 HDMI input configuration
The following HDMI connector can be used:
• HDMI 1: HDMI input ( TV digital interface support HDCP)
with digital audio/PC DVI input/ARC
• HDMI 2: HDMI input ( TV digital interface support HDCP)
with digital audio/PC DVI input
• +5V detection mechanism
• Stable clock detection mechanism
• HPD control
• Sync detection
• TMDS output control
• CEC control
7.7 Video and Audio Processing NT72453MBG-BA
The NT72453MBG-BA is the main audio and video processor
(or System-on-Chip) for this platform. It has the following
features:
• Multi-standard digital video decoder (MPEG-1, MPEG-2,
H.264, MPEG-4)
• Integrated ISDB-T, DVB-T/DVB-C, ITU-T J.83B, ATSC
channel decoder
• Integrated video and audio ADC
• Integrated standby controller
• 2D-Graphic engine/OSD
• Integrated USB2.0 high speed host controlle
• Visual effect processor
• Built-in 16bit DDR3-SDRAM KGD
Figure 7-8 Front-End DVB-S2 DTV block diagram
The application supports the following protocols:
• Polarization selection via supply voltage ( 18V = horizontal,
13V = vertical)
• Band selection via “toneburst” (22kHz): tone “on” = “high”
• Satellite ( LNB) selection via DiSEqC 2.0 protocol
band, tone “off” = “low” band
• Reception of DVB-S ( supporting QPSK encoded signals)
and DVB-S2 ( supporting QPSK, 8PSK encoded signals)
back to
div. table
The NT72453MBG-BA/D is an integrated TV system-on-chip
which complaints with variety ATV as NTSC,PAL and
SECAM,and DTV standards as ISDB-T,DVB-T/C, integrates
DTV and multi-media AV decoder,SIF demodulator,and
support A/V post-processing. The integrated video ADC and
video decoder support PC VGA port, YPbPr, SCART, CVBS
and S-Video Input. Regarding the tuner input, The digital VIF
performs the universal analog TV demodulation (NTSC, PAL,
and SECAM), including IF processing, AGC, video
demodulation, and second sound IF generation (SSIF).The
video decoder supports universal TV video format. The
integrated audio ADC supports stereo audio input
corresponding to video input sources. The integrated TV sound
decoder supports universal TV sound format.The advanced
picture quality and color engine create more vivid image
impression than ever. The HDMI receiver v1.4a, supports deep
color, CEC features and 3D formats. The USB high speed host
supports updating firmware code, multi-media playback from
the external USB flash devices.The standby controller can
operate sololy from the main system, powered by the standby
power source from power module, consumes as low current as
possible. It meets the requirement of Green appliance.
For a functional diagram of the NT72453MBG-BA, refer
to Figure 8-1
.
2016-Mar-11
Page 30

EN 30 TPN16.1E LA8.
19790_302.eps
Block diagram
Pinning information
NT7245MBG
USB
Host/Device/
(Root Hub)
TV_ADC_123
DRAM Controller
DRAM Controller
Multi-Media
Decoder
TMDS RX
TV_ADC_0
Audio ADC
Audio
Processor
Audio DAC
System
CPU
STBC
Ethernet
MAC
Flash/
Card Ctrl.
TV DAC
De-
interlace
Visual
Effect
Processor
Display
Processor
LVDS TX
Graphic
OSD
VGA,
YPbPr
HDMI_A/MHL
HDMI_B
CVBS
Tuner
L/R
I2S Input
L/R
I2S Output,
S/PDIF
LVDS
Nand Flash
SPI Flash
CI/CI+
Ethernet
Phy
H/V SYNC,
CEC, IR, Buttons
USB Flash
CVBS
I2S, S/PDIF
Encoder
DDR3
IP
Noise
Reduction
Demod/SIF
ADC
Video
Decoder
SIF
SIF
Decoder
TS
Demod
TS Demux
D-VIF
Demod
Over
Driver
USB
Host/Device/
(Root Hub)
TV_ADC_123
DRAM Controller
DRAM Controller
Multi-Media
Decoder
TMDS RX
TV_ADC_0
Audio ADC
Audio
Processor
Audio DAC
System
CPU
STBC
Ethernet
MAC
Flash/
Card Ctrl.
TV DAC
De-
interlace
Visual
Effect
Processor
Display
Processor
LVDS TX
Graphic
OSD
VGA,
YPbPr
HDMI_A/MHL
HDMI_B
CVBS
Tuner
L/R
I2S Input
L/R
I2S Output,
S/PDIF
LVDS
Nand Flash
SPI Flash
CI/CI+
Ethernet
Phy
H/V SYNC,
CEC, IR, Buttons
USB Flash
CVBS
I2S, S/PDIF
Encoder
DDR3
IP
Noise
Reduction
Demod/SIF
ADC
Video
Decoder
SIF
SIF
Decoder
TS
Demod
TS Demux
D-VIF
Demod
Over
Driver
IC Data Sheets
8. IC Data Sheets
This chapter shows the internal block diagrams and pin
configurations of ICs that are drawn as “black boxes” in the
electrical diagrams (with the exception of “memory” and “logic”
ICs).
8.1 Diagram 10-2-4 NT72453_ADC/DAC/AUDIO/SIF, B04, NT72453MBG-BA (IC U401)
2016-Mar-11
Figure 8-1 Internal block diagram and pin configuration
back to
div. table
Page 31

8.2 Diagram 10-2-1 System Power, B01, M5723B (IC U701)
19760_300.eps
Block diagram
Pinning information
FB1
10
8
7
1
2
3
4
EN1
AGND
AGND
LX
PGND
IN1
OUT2
9
6
5
EN2
IN2
Thermal
Pad
FB1
10
8
7
1
2
3
4
EN1
AGND
AGND
LX
PGND
IN1
OUT2
9
6
5
EN2
IN2
Thermal
Pad
FB1
10
8
7
1
2
3
4
EN1
AGND
AGND
LX
PGND
IN1
OUT2
M5723B
9
6
5
EN2
IN2
Thermal
Pad
IN1
+
CONTROL
HDRV
A1
+
100mΩ
80mΩ
LDRV
R
S
Q
Thermal
Shutdown
UVLO
OSC
Compensation
+
EA
VREF
LX
Zero Current Detect
Current Sense
OC
0.6V
FB1
IN2
OUT2
SHUTDOWN
LOGIC
1.25V
Vref
炼
ERROR
AMP
為
OVER CURRENT
PROTECT & DYNAMIC
FEEDBACK
AGND
R1
R2
OVER TEMP.
PROTECT
EN1
PGND
EN2
IN1
+
CONTROL
HDRV
A1
+
100mΩ
80mΩ
LDRV
R
S
Q
Thermal
Shutdown
UVLO
OSC
Compensation
+
EA
VREF
LX
Zero Current Detect
Current Sense
OC
0.6V
FB1
IN2
OUT2
SHUTDOWN
LOGIC
1.25V
Vref
炼
ERROR
AMP
為
OVER CURRENT
PROTECT & DYNAMIC
FEEDBACK
AGND
R1
R2
OVER TEMP.
PROTECT
EN1
PGND
EN2
IC Data Sheets
EN 31TPN16.1E LA 8.
back to
div. table
Figure 8-2 Internal block diagram and pin configuration
2016-Mar-11
Page 32

EN 32 TPN16.1E LA8.
19790_300.eps
Block diagram
Pinning information
MX30LF1G08AA
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
R/B#
RE#
CE#
NC
NC
VCC
VSS
NC
NC
CLE
ALE
WE#
WP#
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
NC
NC
NC
NC
IO7
IO6
IO5
IO4
NC
NC
NC
VCC
VSS
DNU
NC
NC
IO3
IO2
IO1
IO0
NC
NC
NC
NC
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
troP OI
Control
Logic
High Voltage
Circuit
Address
Counter
Data
Buffer
Memory
Array
CED-X
Page Buffer
Y-DEC
CLE
ALE
CE#
WE#
RE#
R/B#
WP#
IO[7:0]
IC Data Sheets
8.3 Diagram 10-2-7 NT72453_STBC/FLASH, B07, MX30LF1G08AA (IC U405)
Figure 8-3 Internal block diagram and pin configuration
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 33

8.4 Diagram 10-2-8 NT72453_USB/GPIO, B10, Si2166-B22 (IC U201)
19790_303.eps
Block diagram
Pinning information
Si2166
Si2166B
(GND_PAD)
QFN-48
7x7mm
343536
21
22
23
24
3 4 5
33
20
6327
28293031 27
8 9 10 11 12
15
16
17
18
19
40
39
38
37
41
46
45
44
43
42
MP_A
S_ADC_IP
S_ADC_IN
S_ADC_QP
S_ADC_QN
SDA_MAST
SCL_MAST
NC
NC
NC
DISEQC_OUT
MP_B
SCL_HOST
DISEQC_CMD
GND
SDA_HOST
TS_VAL
DISEQC_IN
TS_DATA[1]
TS_DATA[5]
TS_DATA[4]
TS_DATA[3]
GND
VDD_VIO
TS_DATA[2]
TS_DATA[0]/TS_S
TS_CLK
TS_SYNC
47
14
TS_DATA[7]
RESETB
XTAL_I/CLK_I
XTAL_O
GND
VDD_VCORE
VDD_VANA
ADDR
GND
GPIO_0
48
13
21
26 25
TS_DATA[6]
TS_ERR/GPIO
CLK_IN_OUT
GND
VDD_VCORE
VDD_VCORE
VDD_VIO
VDD_VCORE
MP_D
MP_C
HDTV MPEG S.o.C.
Si2166B
HOST_SCL
HOST_SDA
FRONT
END
OSC
& PLL
QPSK
8PSK
DEMOD
S_ADC_IN
S_ADC_IP
S_ADC_QN
S_ADC_QP
ADC (I)
ADC (Q)
EQUAL-
IZER
I2C
SWITCH
TUN_SDA
TUN_SCL
GPIOCTRL
MPEG TS
INTERFACE
I2C
I/F
MP_x
GPIO_0
RESETB1.2, 3.3V
DSP &
SYNCHRO
DVB-S/S2
FEC MODULE
DiSEqC
TM
2.0
DISEQC_IN
DISEQC_OUT
AGCs
Ext. Clk or Xtal
QPSK / 8PSK
Satellite
ZIF Tuner
CLK_IN_OUT
LDPC BCH
VITERBI RS
TS_ERR/
GPIO_1
TS_SYNC
TS_VAL
8
TS_CLK
TS_DATA
IC Data Sheets
EN 33TPN16.1E LA 8.
Figure 8-4 Internal block diagram and pin configuration
back to
div. table
2016-Mar-11
Page 34

EN 34 TPN16.1E LA8.
19790_304.eps
Block diagram
Pinning information
MP8126DF
SGND
BYPASS
VDD
COMP
EN
EP
LINEDROP
POK
13V/18V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
PGND
SW
BST
VBOOST
VOUT
ILIMIT
TCAP
EXTM
TOP VIEW
Vref
Boost
Driver
22kHz
Shaper
13V / 18V
Switch
8~14V Vin
BYPASS
13V/18V
POK
VBOOST
COMP
BST
+1V Offset
Internal
Regulator
Charge
Pump
TCAP
EXTM
VDD
SGND
PGND
SW
POK
LINEDROP
13V/18V
VOUT
ILIMIT
EN
Current
Limit
IC Data Sheets
8.5 Diagram 10-2-10 Tuner/T2 demod, B10, MP8126DF (IC U202)
2016-Mar-11
Figure 8-5 Internal block diagram and pin configuration
div. table
back to
Page 35

8.6 Diagram 10-2-11 SPK AMP/HP OUT, B11, AD87588 (IC U601)
19790_301.eps
Block diagram
Pinning information
AD87588
IC Data Sheets
EN 35TPN16.1E LA 8.
Figure 8-6 Internal block diagram and pin configuration
back to
div. table
2016-Mar-11
Page 36

EN 36 TPN16.1E LA8.
Personal Notes:
10000_012_090121
110
IC Data Sheets
2016-Mar-11
back to
div. table
Page 37

9. Block Diagrams
19790_400.eps
9.1 Block diagram
Block Diagrams
EN 37TPN16.1E LA 9.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 38

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
20060_500.eps
POWER
A01 A01
2015-10-24
3
715G7734
POWER
U9901
NC/CAP004DG-TL
NC
1
D1
2
D1
3
NC4NC
5
D2
6
D2
7
NC
8
+12V_A
R9908
R9909
+12VS
CN9902
NC/CONN
L
1
N
2
C9901
470nF 275V
R9110
47R 1%
-
+
BD9902
GBL408-C
2
1
3
4
R9140
22 OHM 1/4W
!
PS_ON
C9307
NC/1uF
C9308
NC/1uF
R9141
680R 1/8W 1%
A
R9104
82K OHM 1%
R9125
620K 1/8W 1%
C9113
2.2NF
R9129
470OHM +-5% 1/8W
FB9302
BEAD
1 2
R9121
2K4 1/8W 5%
T9101
POWER X'FMR
1
2
3
5
6
7
8
9
10
4
!
DIM
R9111
10K OHM +-5% 1/8W
!
CN9901
AC 2P
12
L9903
4mH
1
2
4
3
PS_ON
R9131
1K 1/8W
R9144
NC/8.2K 1/8W
Q9102
2N3904
R9122
9.1K OHM
+18V
C9904
1NF 250V
PS_ON
R9901
620K +-1% 1/4W
R9124
10K OHM +-5% 1/8W
!
C9107
3.3NF 500V
+12V
FB9301
NC/BEAD
1 2
L9901
18MH
1
2
4
3
R9105
82K OHM 1%
C9140
NC/1N 50V
R9145
NC/ 100K 1/ 8W 1%
HS9101
HEAT SINK
1
2
3
4
Q9106
NC/2N7002K
+12VS
NC
R9115
22 OHM 1/4W
R9345
NC/20K 1%
U9102
EL817M(X)
1
23
4
+12VS
!
!
R9143
NC/ 100K 1/ 8W 1%
R9902
620K +-1% 1/4W
C9106
330PF 50V
D9109
SR34H
1 2
!
C9117
220nF50V
t
NR9901
2.5R
12
+5.2V
R9903
620K +-1% 1/4W
! !!
R9904
620K +-1% 1/4W
!!
!
R9106
82K OHM 1%
C9104
0.1uF 50V
F9901
NC/T4AL 250V
C9110
0.1uF 50V
D9105
PR1007G
+12V_A
+12V
R9127
3.3M 1/ 4W
L9101
3UH
R9109
10R 1/8W 5%
+18V
FB9901
127R
12
C9119
0.1uF 50V
R9107
82K OHM 1%
! !
C9908
NC
C9903
1000PF 250V
ON/OFF
C9902
1000PF 250V
-
+
BD9901
NC/KBJ608G-FUC
2
1
3
4
+
C9121
470uF 25V
R9116
22 OHM 1/4W
R9307
NC/ 270K +-1% 1/8W
C9124
1NF
RV9901 680V
R9126
9.31K +-1% 1/8W
+
C9109
470uF 25V
C9112
0.1uF 50V
For Q9101
R9146
0 OHM +-5% 1/8W
U9103
TL431G-AE2-R
NC
C9127
1nF 50V
C9128
1nF 50V
Q9306
NC/P1604ED
!!
+12V_A
+12V
+
C9116
330UF 35V
CN9101
CONN
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
+5.2V
D9103
FR107G-A0
FB9908
BEAD
1 2
D9104
IN4148W
FB9906
NC
1 2
D9106
IN4148W
R9907
D9110
SR510-22
1 2
D9111
SR510-22
1 2
D9112
SR510-22
1 2
D9101
SR510-22
1 2
C9129
NC
FB9902
127R
12
SG9902 SG9901
C9306
NC/ 100N 50V
C9323
NC/220N 50V
C9336
NC/220N 50V
R9130
1K OHM
D9102
SR515
D9107
SR515
D9108
SR515
+
C9801
100uF 450V
ZD9101
BZT52-B22
1 2
Q9101
TK6A65D(STA4,X,M)
R9112
510K 1/4W
T4AH/250V
C9108
470pF 1KV
R9142
3.3M 1/ 4W
R9102
510K 1/4W
R9103
510K 1/4W
+
C9105
10UF50V
+
C9102
2.2UF 50V
R9302
NC/100K 1/8W
C9125
1NF
R9117
NC
R9304
NC/ 100K 1/ 8W
R9113
1K 1/4W
L9301
R9358
NC/30R 1/4W
R9342
NC/200R
C9330
NC/1N 50V
R9361
NC/30R
R9344
NC/3K OHM 1%
U9301
NC/AOZ3015AI
PGND
1
VIN
2
AGND
3
VCC4FB
5
COMP
6
LX
7
EN
8
+
C9332
NC470U F 25V
R9347
NC/2K
C9333
NC/2N2 50V
COLD
HOT
C9335
NC/ 2N 2 50V
C9334
NC/100N 50V
+
C9122
330UF 35V
!
R9118
NC
R9348
NC/10.5K
F9902
1 2
3 4
U9101
PF6005AS
BNO
1
FB
2
CS
3
GND4OUT
5
VCC
6
NC
7
VCC
8
R9138
22 OHM 1/4W
R9906
620K +-1% 1/4W
R9905
620K +-1% 1/4W
R9139
NC
+
C9101
NC/470uF 25V
JUMPER
C9103
2.2NF
R9120
22 OHM 1/4W
R9119
NC
C9910
100PF 250V
C9126
NC/100PF
R9123
43K 1/8W 1%
C9907
100PF 250V
!
+
C9331
NC/ 470U F 25V
R9149
22 OHM 1/4W
Q9305
NC/2N7002K
R9148
22 OHM 1/4W
R9150
NC
ZD9104
BZT52-B16G
1 2
R9108
4R7 1/4W 5%
R9128
3.3M 1/ 4W
A
JUMPER
ZD9301
NC/BZT52-B5V1
12
R9101
0.27R 2W
R9114
110K
+
C9111
470UF 25V
NC
NC
!
C9906
NC/47pF
10. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
10.1 A 715G7734 PSU
10-1-1 Power
EN 38TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 39

10-1-2 LED Driver
20060_501.eps
LED DRIVER
A02 A02
2015-10-24
715G7734
LED DRIVER
C8617
100PF 500V
ZD8601
BZT52-B18
1 2
R8603
33K 1/8W 5%
ZD8602
BZT52-B18
1 2
Q8601
AOD2922
C8623
NC
R8606
330K 1/8W 5%
R8656
1.5R 1%
D8602
1N4148
+
C8601
330UF 35V
+18V
OUT
R8604
33R 1/8W 5%
R8608
4.7KOH M +-1% 1/8W
C8603
47nF 50V
C8607
220pF 50V
C8605
0.1uF 50V
C8611
0.47U F 50V
C8609
0.1uF 50V
+12V
Q8603
DTA144WN3/S
Q8602
2N7002K
C8604
0.47U F 50V
C8621
0.1uF 50V
Vcc2
Vcc2
CN8601
NC/CONN
1
2
3
45
ON/OFF
L8602
47uH
D8603
IN4148W RHG
D8604
IN4148W RHG
R8605
1K 1/8W
R8602
NC
R8616
0 OHM +-5% 1/8W
R8617
62K 1/8W 1%
D8601
SR506
1 2
R8652
1.2R 1%
R8653
1.2R 1%
R8654
1.2R 1%
R8655
1.2R 1%
DIM
C8606
1NF
Add ON/OFF Fu nction
R8611
NC
R8612
100K
U8601
PF7708BS
LED
1
VCC
2
CS/OVP
3
OUT4GND
5
DIM
6
GM
7
FB
8
R8601
0R05
FB8605
BEAD
1 2
+
C8616
NC/220uF 50V
C8610
22pF 50V
R8647
10K OHM +-5% 1/8W
CN8602
CONN
1
2
3
4
5
6
78
C8602
220nF50V
OUT
+
C8612
220uF 50V
R8609
10R 1/ 8W 5%
VLED+
VLED+LED-
LED-
R8615
22K 1/4W
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 39TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 40

10-1-3 Power layout top
20060_502.eps
2015-08-01
715G7734
LAYOUT TOP
U9102
R9101
R8601
SU1
J9112
SU4
D9102
D9107
D9108
L9903
D9110
D9112
J9102
D9111
D9103
SU2
C9102
D9101
J9118
J9110
J9109
J9111
J9116
J9119
J9117
J9101
J9113
SU3
F9901
J9115
D8601
J9107
J9108
J9104
J9120
J9106
J9103
T9101
BD9901
BD9902
DR8
DR10
DR1
MH28
DR3
DR2DR4
DR7
DR5
DR11
DR6
MH7
C8601
C9109
C9111
C9116
C9121
C9122
C9126
CN8602
CN9902
FB9906
HS9101
L8602
L9101
MH1
MH3
D9105
L9901
NR9901
FB8605
SG9901
SG9902
C9105
C8612
C8616
C9908
R9130
C9331
C9332
L9301
R9907
FB9908
C9101
FB9301
CN9101
C9801
FB9302
Q9101
C9906
FB9901
FB9902
R9908
C9907
C9910
C9902
C9903
RV9901
MH5
F9902
R9909
D8602
CN8601
CN9901
C9904
C9113
MH6
C9901
C9103
MH2
Q9102
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 40TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 41

10-1-4 Power layout bottom
20060_503.eps
2015-08-01
715G7574
LAYOUT BOTTOM
MH11
MH14
MH19
R9145
R8647
R9342
R9348
R9347
R9109
R9110
R9111
R9114
R9121
R9122
R9123
R9124
R9126
R9131
R9141
R9125
C9336
C8605
C8610
C9106
C9110
C9112
C9117
C9119
C9124
C9127
C9128
R8652
R8653
R8654
R8655
R9112
R9102
R9103
R9104
R9105
R9106 R9107
R9108
R9113
R9115
R9116
R9117
R9118
R9119
R9120
R9138
R9139
R8612
JR9104
JR9101
C9129
C8621
C8602
C8607
C9125
R8611
C8606
C8623
C9140
C9330
C9333C9334
C9335
R8616
R9344
R8615
R9127
R9128
R9142
R9358
R9361
C9108
C9107
C8617
R9903
R9904
C9306
C9307
C9308
R9302
R9304
R9307
Q9306
C9323
JR9105
R9345
JR9107
JR9102
JR9108
R8602
JR9103
R9146
C9104
R9148
R9149
R9150
R9140
R9129
R8604
R8608
R9143
R9144
JR9109
R8603
C8603
U9901
R8656
C8604
C8609
C8611
R8605
R8606
Q8603
R8617
R8609
U8601
U9101
U9301
R9901
R9902
R9905
R9906
MH4
ZD9301
Q8602
Q9305
Q9106
U9103
SG1
SG2
Q8601
D9109
D8604
D8603
D9104
ZD9104
D9106
ZD8601
ZD8602
ZD9101
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 41TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 42

10.2 B 715G6947 SSB
19790_500.eps
System Power
B01 B01
2014-09-22
3
715G6947
System Power
C728
NC
R734
470R 1%
PWR_12V 13,17
+5V_SW 9,11,13,16,17,18
DV33 5,7,10,11,12,13,14,17,18
DV33SB 6,10,11,12,18
DV15 12
DV11 12
GND 5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18
+5V_STB 6
DV33
DV11
PWR_12V
+5V_STB
GND
DV33SB
+5V_SW
DV15
U702
AP3417C
EN
1
GND
2
LX
3
VIN
4
FB
5
R733
18Kohm 1/16W +/-1%
BL_DIMMING_912 18
BL_DIMMING_912
C710
NC/100N 16V
+5V_STB
R724
100OHM
+5V_STB
L701
2.2uH
C719
1uF 10V
DV33SB
R710
18Kohm 1/16W +/-1%
DV11
C713
4.7UF 10% 10V
DV33
R738
NC/1K
R705
4K7 1/16W 5%
Backlight ON/OFF Control
BL_DIMMING 11
BL_ON/OFF 10
PWR_ON 10
PWR_ON
BL_ON/OFF
BL_DIMMING
C742
100NF 25V
C736
NC
BackLight_SW:
BackLight on: High
BackLight of f: Low
+5V_SW
+5V_STB
R702
BRIGHT_ADJ
R706
51K 1/16W 5%
Q702
LMBT3904LT1G
C706
220NF 16V
C709
NC/4.7UF 10% 10V
R704
47K
PWR_ON_2
R707
0R05 4A 1/4W
+5V_STB to +5V_SW
Q701
AO4449 -7A/-30V
S
1
S
2
S
3
G
4
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D702
NC/BAS316
+
C707
100UF 16V
DV33
Backlight Brightness Contr o l
BL_DIM(PWM for Bright_Adj):
Max: + 3V3
Min: 0V
R703
0R05 OHM
C735
NC
C718
2.2UF
AVDD1V2
AVDD1V2 13
AVDD1V2
L704
2.2uH
C717
10UF 6. 3V
PWR_ON_2
R742
NC/100OHM
R719
4K7
GPIO
PWR_ON_2
C712
10UF 6.3V
STB CONTORL
R711
47K 1/16W 5%
"PWR_ON"
Normal:Low
Standby:High
U705
VI3VO
2
GND
1
PWR_ON_2 18
DV33
R727
10K
C711
4.7UF 10% 10V
BL_DIMMING_912
R728 NC
C702
10UF 25V
C703
NC/ 100N F 16V
BRIGHT_ADJ
TP703
TP701
AUDIO_12V
TP704
PWR_12V PWR_12V
R701
100OHM
PWR_12V_AL
TP702
PWR_ON_2
C701
100NF 16V
PWR_12V_AL
AUDIO_12V
INVERTER_ON_OFF
TP710
C708
2.2nF 50V
CN701
CONN
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
R725
100OHM
BL_DIMMING
AUDIO_12V 14
AUDIO_12V
C723
NC
Q703
LMBT3904LT1G
1
3
2
DV33 to AVDD1V2
+5V_SW to DV33
+5V_SW DV33
INVERTER_ON_OFF
R723
47K 1/16W 5%
R736
20K 1%
C744
1UF 25V
R714
100K 1%
C721
100NF 16V
R720
124K 1%
C743 100N F 16V
+5V_STB
PWR_12V
R737
1K5 1%
C724
22pF 50V
C747
8.2NF 50V
C745
1UF 25V
U706
TPS54428DDAR
EN
1
VFB
2
VREG5
3
SS4GND
5
SW
6
VBST
7
VIN
8
E-PAD
9
L703
3.3uH
C746
22UF 10V
R722 0R05
C722
22UF 10V
R729
33K 1%
C715
NC/100N16V
R709
150K 1%
R721 0R051/8W
C729
NC/100N16V
BL_ON/OFF
12V TO 5VSB
R741
47K
C727
4.7UF 10% 10V
R726
10K
+5V_SW to DV15
R717
NC/ 47K 1/ 16W 5%
CORE POWER 1.2V
L702 2.2uH
C730
10UF 6. 3V
U703
AP3417C
EN
1
GND
2
LX
3
VIN
4
FB
5
R708
150K 1%
DV15
R718
100K 1%
C716
NC/100N16V
+5V_SW
PWR_ON_2
C740
10UF 16V
C720
NC/100N16V
R712
47K 1/16W 5%
C751 100NF 16V
+5V_SW
DC POWE R INPUT
INVERTER_ON_OFF
Normal:High
Standby:Low
BRIGHT_ADJ
Normal:PWM or DC 3V3 Max
Standby: 0 V
R739
NC/1K
U701
M5723B-33F61U
EN1
1
AGND
2
FB1
3
AGND
4
EN25IN2
6
OUT2
7
IN1
8
PGND
9
LX
10
E-PAD
11
R715
NC/10K 1/ 16W 5%
R716
4K7 1/16W 5%
DV33SB
DV33SB +5V_STB
PWR_ON
PWR_ON_2
10-2-1 System Power
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 42TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 43

10-2-2 SPDIF/UART INPUT
19790_501.eps
SPDIF/UART INPUT
B02 B02
2014-09-22
4
715G6947
SPDIF/UART INPUT
U-ART
R1015
NC / 75 OH M +-5% 1/16W
SPDIF_OUT
C1001
NC/100N16V
R1014
NC / 220 OH M
ZD109
NC/EGA10603V05A1-B
1 2
C1002
NC / 470pF 50V
SPDIF_OUT
DV33
C1004
100NF 16V
R1003
10K
R1004
100OHM
GND
+5V_STB
PWR_12V
DV33
PWR_12V 4,13,17
+5V_SW
DV33SB
DV15
DV33 4,7,10,11,12,13,14,17,18
DV33SB 4,6,10,11,12,18
+5V_SW 4,9,11,13,16,17,18
GND 4,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18
+5V_STB 4,6
DV15 4,12
MIPS/UART/I2C/ICE
AU DIO /IF
AU DIO /IF
MIPS_RXB 11,16,18
SPDIF_OUT
MIPS_TXB
MIPS_RXB
SPDIF_OUT 7
MIPS_TXB 11,16,18
VGA_RIN
VGA_RIN 7,16
VGA_LIN 7,16
VGA_LIN
CN118
3P
GND
1
VCC
2
VIN
3
GND
4
GND
5
R4604
100OHM
ZD461
MLVG0402
1 2
CN410
1
2
3
R1019
4K7 1/16W 5%
TP403
MIPS_TXB 11,16,18
MIPS_RXB 11,16,18
MIPS_TXB
MIPS_RXB
R1020
4K7 1/16W 5%
TP401
R4605
100OHM
ZD462
MLVG0402
1 2
TP402
DV33 DV33
2nd
CN117
NC/RCA JACK
1
2
088G 78F112VCL
388G0359010VAT
1st
SPDIF Out(Co-Layout)
088G 359 10 JT
388G078F118VQS
MIPS_RXB
MIPS_TXB
2nd
1st
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 43TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 44

10-2-3 HDMI
19790_502.eps
HDMI
B03 B03
2014-09-22
4
715G6947
HDMI
PWR5V_1
M_RX1_2B
M_RX1_2
M_RX1_1
M_RX1_C
M_RX1_CB
CEC_1
HDMI1_SCL
HDMI1_SDA
PWR5V_2
CN501
HDMI CONN
SHELL1
20
SHELL2
21
D2+
1
D2 Shield
2
D2-
3
D1+
4
D1 Shield
5
D1-
6
D0+
7
D0 Shield
8
D0-
9
CK+
10
CK Shield
11
CK-
12
CE Remote
13
NC
14
DDC CLK
15
DDC DATA
16
GND
17
+5V
18
HP DET
19
SHELL4
23
SHELL3
22
SHELL5
24
R501
22R 1/16W 5%
R511
47K 1/16W 5%
SCL_1
R510
4K7 1/16W 5%
SDA_1
+5V_STB
R513
5K1 1/16W 5%
Rear HDMI 1
R509
27K 1/16W 5%
D501
BAS316
A1K
2
DV33SB
CEC_1 HDMI_CEC
HDMI1_HPD
H: Standby,Normal
L: AC off
R514
47K 1/16W 5%
PWR_12V
DV33
+5V_SW
DV15
GND
DV33SB
+5V_STB
PWR_12V 4,13,17
DV33SB 4,10,11,12,18
PWR5V_1
+5V_STB 4
DV33 4,5,7,10,11,12,13,14,17,18
DV15 4,12
+5V_SW 4,9,11,13,16,17,18
PWR5V_1 8
GND 4,5,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18
PWR5V_2
PWR5V_2 8
M_RX1_0B
M_RX1_0
M_RX1_C
M_RX1_CB
M_RX1_1
M_RX1_1B
M_RX1_2
HDMI_ARC
HDMI1_SCL
HDMI1_SDA
M_RX1_2B
M_RX1_0B 8
M_RX1_C 8
M_RX1_2B 8
HDMI_CEC
R505
1K 1/16W 5%
Rear HDMI 2
M_RX1_1 8
M_RX1_0 8
M_RX1_CB 8
HDMI1_SCL 8
M_RX1_1B 8
M_RX1_2 8
HDMI2_HPD
H: Standby,Normal
L: AC off
HDMI_CEC 8
HDMI_ARC 8
HDMI1_SDA 8
MIPS/UART/I2C/ICE
M_RX2_C 8
M_RX2_2B 8
M_RX2_0B 8
M_RX2_0 8
M_RX2_CB 8
M_RX2_0
GPIO
M_RX2_1B 8
M_RX2_2 8
M_RX2_1 8
M_RX2_CB
M_RX2_1
M_RX2_1B
M_RX2_2
M_RX2_0B
HDMI2_SCL 8
HDMI2_SCL
HDMI2_SDA
M_RX2_2B
M_RX2_C
HDMI2_HPD 10
HDMI2_SDA 8
HDMI1_HPD
HDMI2_HPD
MIPS_TXB 5,11,16,18
HDMI1_HPD 10
MIPS_TXB
MIPS_RXB
HDMI
MIPS_RXB 5,11,16,18
R549
51R
HDMI_ARC
UART SEL
HDMI_ARC_OUT
from Scaler ARC
Grounding
Grounding
ZD501
MLVG0402
1 2
R523
5K1 1/16W 5%
R507
4K7 1/16W 5%
R504
22R 1/16W 5%
R520
22R 1/16W 5%
R521
22R 1/16W 5%
HDMI1_HPD
FB502 120R
1 2
HDMI_ARC_OUT
M_RX1_1B
CEC_2
ZD502
MLVG0402
1 2
CN502
HDMI CONN
SHELL1
20
SHELL2
21
D2+
1
D2 Shield
2
D2-
3
D1+
4
D1 Shield
5
D1-
6
D0+
7
D0 Shield
8
D0-
9
CK+
10
CK Shield
11
CK-
12
CE Remote
13
NC
14
DDC CLK
15
DDC DATA
16
GND
17
+5V
18
HP DET
19
SHELL4
23
SHELL3
22
SHELL5
24
R516
4K7 1/16W 5%
R518
4K7 1/16W 5%
+5V_STB
Q502
LMBT3904LT1G
1
3
2
R517
1K 1/16W 5%
M_RX2_2B
M_RX2_1
HDMI2_HPD
M_RX2_CB
M_RX2_C
M_RX2_2
M_RX2_0
M_RX2_0B
M_RX2_1B
HDMI2_SCL
CEC_2
SCL_2
SDA_2 HDMI2_SDA
M_RX1_0
M_RX1_0B
Q501
LMBT3904LT1G
1
3
2
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 44TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 45

10-2-4 NT72453_ADC/DAC/AUDIO/SIF
19790_503.eps
NT72453_ADC/DAC/AUDIO/SIF
B04 B04
2014-10-08
4
715G6947
NT72453_ADC/DAC/AUDIO/SIF
C180
2.2UF
C181 100N F 16V
R144 330R 1/16W 5%
R4029
100OHM
R4019
NC/ 1K 1/ 16W 5%
R4020
10K 1/16W
C4026
100NF 16V
C161
NC/12P 50V
DV33
R636
NC/ 0R 05 1/ 16W
DEMOD_D+
I2SOUTC_DATA
I2SOUTC_MCLK 14
TUN_DIF-
SPDIF_OUT
I2SOUTC_WS
R638 22R 1/16W 5%
I2SOUTC_WS 14
I2SOUTC_BCLK 14
I2SOUTC_DATA 14
IFAGC_SW
R4021
NC/ 10K 1/ 16W
DV33
IF_AGC_1
TUN_DIF+
R639 22R 1/16W 5%
DEMOD_D-
T2_DEMOD_RSTn 13
I2SOUTC_MCLK
C166
100NF 16V
R637 22R 1/16W 5%
IF_AGC
I2SOUTC_BCLK
C137
NC/ 47pF 50V
R177 10K 1/16W
C165
100NF 16V
AUOUT_L0 18
AUOUT_R0 18
R130
100OHM
CVBS_OUT
R131
100OHM
TP429
C130 47N16V
C128
47N16V
C133 47N16V
R132
100OHM
SCT1_R
C154
100NF 16V
VGA_VS#
SC_CVBS_Y
R134 330R 1/16W 5%
C127 470PF
VGA_HS#
C124 47N16V
C125 47N16V
C126 47N16V
C134 47N16V
SCT1_B
VGA_B#
SOY1
C151
100NF 16V
R129
100OHM
VGA_R#
VGA_G#
C182
100NF 16V
C183
100NF 16V
AUDIO /IF
SCART1_LIN 15
IF_AGC 13
SPDIF_OUT 5
TUN_DIF- 13
SCART1_RIN 15
TUN_DIF+ 13
I2SOUTC_WS 14
I2SOUTC_BCLK 14
I2SOUTC_DATA 14
I2SOUTC_MCLK 14
AUOUT_R1 14
AUOUT_L1 14
VGA_RIN
VGA_LIN 16
VGA_RIN 16
AUOUT_L1
VGA_LIN
VGA_LIN 16
VGA_G#
VGA_VS#
VGA_HS#
AUOUT_R1
VGA_SDA 10,16
VGA_SCL 10,16
VGA_RIN 16
VGA_SDA
VGA_HS#16
VGA_VS#16
VGA_SCL
VGA_B# 16
VGA_LIN
VGA_R#
VGA_RIN
VGA_B#
VGA_R# 16
VGA_G# 16
I2SOUTC_WS
SPDIF_OUT
TUN _DI F+
IF_AGC
I2SOUTC_MCLK
I2SOUTC_BCLK
I2SOUTC_DATA
IFAGC_SW13
IFAGC_SW
SCART1_RIN
SCART1_LIN
TUN _DI F-
FB104 300R
1 2
NT72453
AUDIO/IF
U401E NT72453MBG-BA/B
AUD_VRM
E22
DACOUT_R1
D21
DACOUT_L1
D22
DACOUT_R0
C21
DACOUT_L0
C22
AUD_VRP
E23
ADIN_R2
G21
ADIN_L2
G22
ADIN_R1
F21
ADIN_L1
F22
ADIN_R0
F23
ADIN_L0
E21
SPDIF_OUT/CI_IORD#/GPD_28
M2
I2S_OUT_A_DATA/PTSIN1_D5/GPD_9
K2
I2S_OUT_A_WS/PTSIN1_D6/GPD_10
K1
I2S_OUT_A_BCLK/PTSIN1_D7/GPD_11
L3
I2S_OUT_A_MCLK/PTSIN2_ERROR/GPD_12
J5
I2SIN_DATA/PTSIN1_D2/GPD_6
J3
I2SIN_WS/PTSIN1_D3/GPD_7
J2
I2SIN_MCLK/PTSIN1_D4/GPD_8
K3
DEMOD-
H22
DEMOD+
H23
VIF_IF_AGC/DEMOD_IF_AGC/PTSOUT_VALID/PTSIN2_VALID/DEMODOUT_VALID/GPD_14
J4
PTSOUT_CLK/PTSIN2_CLK/DEMODOUT_CLK/GPD_13
J6
SIF+
J22
SIF-
J23
I2SIN_BCLK/CI_HA1/CI_ALE8/GPE_3
R3
SPDIF_IN/CI_IREQ#/GPD_27
M3
DEMOD_Emerg/PTSOUT_START/PTSIN2_START/DEMODOUT_START/GPD_15
K6
AUD_VCM
G18
IF_2+
J18
IF_2-
J19
NC
V15
CLK_OUT
W15
ADC/DAC
+5V_SW4,9,11,13,16,17,18
PWR_12V 4,13,17
DV15 4,12
DV33SB 4,6,10,11,12,18
DV33 4,5,10,11,12,13,14,17,18
PWR5V_1 6,8
GND 4,5,6,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18
+5V_STB 4,6
SCT1_B 15
SOY1 15
SCT1_R 15
DV11 4,12
SCT1_G 15
SC_CVBS_Y 15
DV11
SCT1_G
SCT1_R
+5V_STB
PWR_12V
DV33
SOY1
SC_CVBS_Y
SCT1_B
+5V_SW
DV15
GND
DV33SB
PWR5V_1
C160 10UF 6.3V
C162 10UF 6.3V
PC in
SCART1_LIN
VGA_RIN
NT72453
ADC/DAC
U401C NT72453MBG-BA/B
VGA_B
N22
VGA_G
M22
VGA_R
M23
ADC3VMID
R20
ADC3M
R22
YPBPR0_PB
R21
ADC2M
P23
YPBPR0_Y
P21
ADC1VMID
P18
ADC1M
N21
YPBPR0_PR
P22
SCART1_B
P20
SCART1_G
N18
SCART1_R
N19
SCART0_FB
L20
SCART0_Y
L21
ADC0M
L22
CVBS0
L23
CVBS_OUT
K22
SOG_0
R23
SOG_1
M21
SOG_2
P19
VGA_HS
R19
VGA_VS
R18
TUNER_CVBSIN
K21
SCART in
VGA_LIN
SCART1_RIN
C159 10UF 6.3V
C149 10UF 6.3V
C139470pF
R151 1K
TP437TP
R183 470R 1/ 16W 5%
R182 470R 1/ 16W 5%
C176 3.3NF 50V
C177 3.3NF 50V
R180 470R 1/ 16W 5%
R181 470R 1/ 16W 5%
HP out
AUOUT_L1
AUOUT_R0
AUOUT_R1
C169 3.3NF 50V
C170 3.3NF 50V
AUOUT_L0
C155 100NF 16V
C156 100NF 16V
C178 100NF 16V
C1712.2UF
C179
100NF 16V
C172
100NF 16V
SCT1_G
R133 100OHM
AUOUT_L0
AUOUT_R0
R135 330R 1/16W 5%
R136100OHM
R149 100OHM
R150 100OHM
R143330R 1/16W 5%
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 45TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 46

10-2-5 NT72453_HDMI/LVDS OUT
19790_504.eps
NT72453_HDMI/LVDS OUT
B05 B05
2014-09-22
4
715G6947
NT72453_HDMI/LVDS OUT
M_RX2_2 6
M_RX1_2 6
HDMI_CEC 6
PWR5V_1 6
HDMI1_SDA 6
M_RX2_2B 6
M_RX2_0 6
M_RX2_C 6
+5V_STB 4,6
HDMI1_SCL 6
GND 4,5,6,7,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18
M_RX2_1B 6
M_RX2_0B 6
M_RX1_2B 6
HDMI_ARC 6
DV15 4,12
M_RX1_1 6
M_RX2_1 6
M_RX1_0 6
DV33SB 4,6,10,11,12,18
HDMI2_SCL 6
M_RX2_CB 6
DV33 4,5,7,10,11,12,13,14,17,18
PWR_12V 4,13,17
M_RX1_C 6
+5V_SW 4,9,11,13,16,17,18
M_RX1_CB 6
M_RX1_1B 6
HDMI2_SDA 6
PWR5V_2 6
M_RX1_0B 6
HDMI
PWR5V_2
HDMI2_SDA
M_RX1_0B
M_RX1_0
NT72453
HDMI/MHL
U401A NT72453MBG-BA/B
RXB_2+
AA14
RXB_2-
AB13
RXB_1+
AC13
RXB_1-
AA13
RXB_0+
AC12
RXB_0-
AB12
RXB_CLK+
AA12
RXB_CLK-
AB11
PWR5V_B/SBTC_GPF_7
AB17
RXA_2+
AA11
RXA_2-
AB10
RXA_1+
AC10
RXA_1-
AA10
RXA_0+
AC9
RXA_0-
AB9
RXA_CLK+
AA9
RXA_CLK-
AB8
PWR5V_A/STBC_GPF_4
AC16
HDMI_CEC/STBC_GPF_0
AA15
HDMIB_SDA/STBC_GPF6
AA17
HDMIB_SCL/STBC_GPF5
AB16
HDMIA_SDA/STBC_GPF3
AA16
HDMIA_SCL/STBC_GPF2
AC15
HDMI_ARC
AA8
MHL_CBUS/STBC_GPG_30
AB14
STBC_GPF_15/(BS_16)
W19
MHL_CDS/STBC_GPF_1
AB15
BS16
LVDS_A1-
LVDS_BCLK-
LVDS_B0+
LVDS_A1+
LVDS_B1-
LVDS_BCLK+
LVDS_B0-
LVDS_B3-
LVDS_B1+
LVDS_ACLKLVDS_A3-
LVDS_A2-
LVDS_B3+LVDS_A3+
LVDS_A2+
LVDS_ACLK+
LVDS_A4+
LVDS_A4-
LVDS_B2-
LVDS_B4+
LVDS_B2+
LVDS_A0-
LVDS_B4-
LVDS_A0+
HDMI1_SCL
HDMI1_SDA
HDMI2_SCL
NT72453
LVDS
U401B NT72453MBG-BA/B
LVO_4+
A9
LVO_4-
C8
LVO_3+
A8
LVO_3-
B8
LVO_CLK+
C7
LVO_CLK-
B7
LVO_2+
C6
LVO_2-
B6
LVO_1+
A6
LVO_1-
C5
LVO_0+
A5
LVO_0-
B5
LVE_0-
C10
LVE_0+
B11
LVE_1-
A11
LVE_1+
C11
LVE_2-
A12
LVE_2+
B12
LVE_CLK-
C12
LVE_CLK+
B13
LVE_3-
C13
LVE_3+
B14
LVE_4-
A14
LVE_4+
C14
NC
B9
NC
C9
REXT_LVDS
B10
R503
4.7K 1/ 16W
R506
10K
R508
10K
R502
4.7K 1/ 16W
M_RX1_1
M_RX1_C
M_RX1_2B
M_RX1_CB
M_RX1_1B
M_RX1_2
M_RX2_1
HDMI_ARC
M_RX2_0
M_RX2_2
M_RX2_1B
M_RX2_2B
M_RX2_0B
M_RX2_CB
M_RX2_C
HDMI_CEC
PWR5V_1
LVDS_B0+ 17
LVDS_B0- 17
LVDS_B0+
LVDS_B0-
LVDS_B1+ 17
LVDS_B1- 17
LVDS_B1+
LVDS_B1-
LVDS_B2+ 17
LVDS_B2- 17
LVDS_B2+
LVDS_B2-
LVDS_BCLK+ 17
LVDS_BCLK- 17
LVDS_BCLK+
LVDS_BCLK-
LVDS_B3+17
LVDS_B3-17
LVDS_B3+
LVDS_B3-
LVDS_B4+ 17
LVDS_B4- 17
LVDS_B4+
LVDS_B4-
LVDS_A0+ 17
LVDS_A0- 17
LVDS_A0+
LVDS_A0-
LVDS_A1+ 17
LVDS_A1- 17
LVDS_A1+
LVDS_A1-
LVDS_ACLK- 17
LVDS_A2- 17
LVDS_ACLK-
LVDS_A2-
LVDS_A3-17
LVDS_ACLK+ 17
LVDS_A3-
LVDS_ACLK+
LVDS_A3+17
LVDS_A4+
LVDS_A4-
LVDS_A3+
BS16 10
LVDS_A4- 17
LVDS_A4+ 17
LVDS_A2+ 17
LVDS_A2+
BS16
PWR_12V
M_RX1_CB
DV15
M_RX2_1B
DV33
M_RX1_1
PWR5V_2
M_RX1_0
M_RX1_2B
PWR5V_1
M_RX2_CB
M_RX1_C
+5V_SW
M_RX2_1
M_RX2_C
HDMI_CEC
DV33SB
HDMI1_SDA
HDMI2_SCL
M_RX1_0B
+5V_STB
HDMI2_SDA
M_RX1_1B
GND
HDMI1_SCL
M_RX2_0B
M_RX2_2B
M_RX1_2
M_RX2_0
HDMI_ARC
M_RX2_2
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 46TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 47

10-2-6 NT72453_CI
19790_505.eps
NT72453_CI
B06 B06
2014-09-22
4
715G6947
NT72453_CI
NT72453 GPIO
U401F NT72453MBG-BA/B
PTSOUT_CLK/PTSIN2_CLK/DEMODOUT_CLK/GPA_13
F20
PTSOUT_VALID/PTSIN2_VALID/DEMODOUT_VALID/VIF_IF_AGC/DEMOD_IF_AGC/GPA_14
D20
PTSOUT_D0/PTSIN2_D0/DEMODOUT_D0/RMII_RX_D0/GPA_16
D19
PTSOUT_D1/PTSIN2_D1/DEMODOUT_D1/RMII_RX_D1/GPA_17
E19
PTSOUT_D2/PTSIN2_D2/DEMODOUT_D2/RMII_REF_CLK/GPA_18
F18
PTSOUT_D3/PTSIN2_D3/DEMODOUT_D3/RMII_TX_D0/GPA_19
E18
PTSOUT_D4/PTSIN2_D4/DEMODOUT_D4/RMII_TX_D1/GPA_20
F17
PTSOUT_D5/PTSIN2_D5/DEMODOUT_D5/RMII_TX_EN/GPA_21
E17
PTSOUT_D6/PTSIN2_D6/DEMODOUT_D6/RMII_MDC/GPA_22
D17
PTSOUT_D7/PTSIN2_D7/DEMODOUT_D7/RMII_MDIO/GPA_23
F16
PTSOUT_START/PTSIN2_START/DEMODOUT_START/DEMOD_Emergency/GPA_15
F19
PTSIN1_START/STSIN1_START/I2C_MB_SCL/GPA_3
B20
PTSIN1_VALID/STSIN1_VALID/I2C_MB_SDA/GPA_2
A20
PTSIN1_CLK/STSIN1_CLK/I2C_MA_SCL/GPA_1
A21
CI_RST/RMII_CRS/GPA_24
C20
CI_REG#/MIPS_UART_C_RX/INT2/GPB_0
D11
CI_CD_0#/RMII_RXERR/GPA_25
C16
CI_IORD#/SPDIF_OUT/GPA_28
B15
CI_HWAIT#/MIPS_UART_D_TX/I2C_MF_SCL/GPB_1
F11
CI_CE#/BT_SHOP_VS_IN/BT_SHOP_LR_IN/GPA_26
B16
CI_IOWR#/MIPS_UART_A_TX/INT8/GPA_29
A15
CI_HAD0/I2S_OUT_B_MCLK/ LED_PW M_3/GPB_17
G15
CI_HAD1/I2S_OUT_B_BCLK/LED_PWM_4/GPB_18
F14
CI_HAD2/I2S_OUT_B_WS/LED_PWM_5/GPB_19
G14
CI_HAD3/I2S_OUT_B_DATA/LED_PWM_6/GPB_20
G13
CI_HAD4/I2S_OUT_C_MCLK/LED_PWM_7/GPB_21
D9
CI_HAD5/I2S_OUT_C_BCLK/3D_IR/3D_BT/3D_Active/GPB_22
G8
CI_HAD6/I2S_OUT_C_WS/LR0_DELAY/GPB23
D8
CI_HAD7/I2S_OUT_C_DATA/LR1_DELAY/GPB_24
F8
CI_HA0/CI_ALE0/MIPS_UART_D_RX/I2C_MF_SDA/GPB_2
G11
CI_HA1/CI_ALE8/I2S_IN_BCLK/GPB_3
F15
CI_HA2/GPB_4
G10
CI_HA3/GPB_5
D14
CI_HA4/FRC_Dimming1/DSU_BRE/GPB_6
D13
CI_HA5/FRC_Dimming2/DSU_ACT/GPB_7
G9
CI_HA6/DSU_TX/GPB_8
E6
CI_HA7/DSU_RX/GPB_9
E7
CI_HA8/DSU_EN/GPB_10
F10
CI_HA9/FR_PWM/LED_VS_OUT/GPB_11
F9
CI_HA10/Tensilica_TCK/USB0_PWEN/GPB_12
F7
CI_HA11/Tensilica_TMS/USB1_PWEN/GPB_13
F13
CI_HA12/Tensilica_TDO/LED_PWM_0/GPB_14
D6
CI_HA13/Tensilica_TDI/LED_PWM_1/GPB_15
F6
PTSIN1_ERROR/STSIN0_ERROR/I2C_MA_SDA/GPA_0
B21
PTSIN2_ERROR/DEMODOUT_ERROR/I2S_OUT_A_MCLK/CI_CD1#/GPA_12
E20
CI_HA14/Tensilica_TRST/LED_PWM_2/Y DIO/GPB_16
D5
PTSIN1_D0/STSIN1_DATA/I2C_MC_SDA/GPA_4
C19
PTSIN1_D1/I2C_MC_SCL/GPA_5
B19
PTSIN1_D2/I2S_IN_DATA/GPA_6
C18
PTSIN1_D3/I2S_IN_WS/GPA_7
B18
PTSIN1_D4/I2S_IN_MCLK/DEMOD_Debug_LED/GPA_8
A18
PTSIN1_D5/I2S_OUT_A_DATA/GPA_9
C17
PTSIN1_D6/I2S_OUT_A_WS/GPA_10
A17
PTSIN1_D7/I2S_OUT_A_BCLK/GPA_11
B17
STSIN0_CLK/CI_CD_1#/INT_1/GPC_0
B4
STSIN0_VALID/INT_2/GPC_1
C4
STSIN0_START/INT_3/GPC_2
B3
STSIN0_DATA/INT_4/GPC_3
A3
CI_WE#/MIPS_UART_C_TX/INT1/GPA_31
D16
CI_IREQ#/SPDIF_IN/MPLL_TEST/ GPA_27
C15
CI_OE#/MIPS_UART_A_RX/INT9/GPA_30
E16
CI_INDATA2
CI_OUTDATA0
CI_A8
CI_D7
CI_OUTDATA3
CI_IOWR#
CI_INDATA6
CI_INDATA7
CI_CE1#
CI_A13
CI_INDATA3
CI_OUTDATA6
CI_A14
CI_INDATA0
CI_OUTDATA2
CI_REG#
CI_INVALID
CI_OUTCLK
CI_OUTSYNC
CI_A10
CI_A6
CI_A12
CI_A7
CI_D0
CI_D1
CI_A2
CI_A1
CI_A3
CI_D2
CI_A0
CI_A5
CI_A4
CI_D3
CI_INCLK
CI_OUTDATA4
CI_INSYNC
CI_WE#
CI_OE#
CI_D4
CI_OUTDATA7
CI_OUTDATA1
CI_IORD#CI_A11
CI_D5
CI_IREQ#
CI_INDATA1
CI_OUTVALID
CI_OUTDATA5
CI_CD1#
CI_WAIT#
CI_A9
CI_D6
CI_CE2#
CI_RESET
CI_WP#
C1305
10UF 16V
CI_INDATA5
CI_INDATA4
DV11
+5V_STB
PWR_12V
DV33SB
+5V_SW
DV15
GND
CI_INDATA0
CI_INVALID
+5V_SW 4,11,13,16,17,18
PWR_12V 4,13,17
CI_INSYNC
CI_INCLK
DV33SB 4,6,10,11,12,18
DV15 4,12
CI_INDATA4
CI_INDATA3
+5V_STB 4,6
DV11 4,12
CI_INDATA2
CI_INDATA1
CI_INDATA5
CI_INDATA7
GND 4,5,6,7,8,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18
CI_INDATA6
CI_INCLK 13
CI_INSYNC 13
CI_INDATA7 13
CI_INVALID 13
CI_INDATA4 13
CI_INDATA6 13
CI_INDATA3 13
CI_INDATA5 13
CI_INDATA1 13
CI_INDATA2 13
CI_INDATA0 13
GPIO
R4170 47R 1/ 16W 5%
CI_PWR_EN
CI_INCLK
C4161 N C / 10PF 50V
R4169 47R 1/ 16W 5%
CI_INVALID
CI_INSYNC
CI_OUTVALID
CI_OUTSYNC
CI_OUTCLK
CI_INDATA_2
CI_INDATA_1
CI_INDATA_4
CI_INDATA_0
CI_INDATA_3
CI_INDATA_5
CI_INDATA_6
CI_INDATA_7
CI_OCP
CI_RESET
CI_CD1#
CI_OE#
CI_D_0
CI_D_6
CI_D_3
CI_D_7
CI_A_11
CI_D_5
CI_D_4
CI_D_1
CI_A_12
CI_D_2
CI_A_6
CI_A_3
CI_A_14
CI_A_13
CI_A_5
CI_A_2
CI_A_4
CI_A_7
CI_A_1
CI_A_8
CI_A_9
CI_A_0
CI_A_10
CI_IORD#
CI_IREQ#
CI_WAIT#
CI_IOWR#
CI_REG#
CI_WE#
CI_OUTDATA_1
CI_OUTDATA_6
CI_OUTDATA_5
CI_OUTDATA_7
CI_CE1#
CI_OUTDATA_2
CI_OUTDATA_3
CI_OUTDATA_0
CI_OUTDATA_4
CI_A_6CI_A6
CI_A_1CI_A1
CI_INDATA_4CI_INDATA4
CI_A_4CI_A4
CI_A_3CI_A3
CI_A_2CI_A2
CI_INDATA_7CI_INDATA7
CI_INDATA_5CI_INDATA5
CI_A_12CI_A12
CI_A_5CI_A5
CI_INDATA_6CI_INDATA6
CI_A_14CI_A14
CI_INDATA_1CI_INDATA1
CI_INDATA_3CI_INDATA3
CI_INDATA_2CI_INDATA2
CI_A_7CI_A7
CI_D_1CI_D1
CI_OUTDATA_2CI_OUTDATA2
CI_D_2CI_D2
CI_OUTDATA_0CI_OUTDATA0
CI_A_0CI_A0
CI_OUTDATA_1CI_OUTDATA1
CI_D_0CI_D0
CI_OUTDATA_6CI_OUTDATA6
CI_INDATA_0CI_INDATA0
CI_A_8CI_A8
CI_A_10CI_A10
CI_OUTDATA_7CI_OUTDATA7
CI_A_13CI_A13
CI_A_11CI_A11
CI_A_9CI_A9 CI_D_5CI_D5
CI_OUTDATA_5CI_OUTDATA5
CI_D_7CI_D7
CI_D_6CI_D6
CI_OUTDATA_3CI_OUTDATA3
CI_D_3CI_D3
CI_D_4CI_D4
CI_OUTDATA_4CI_OUTDATA4
C1301
NC/10PF 50V
PCMCIA
CN159
PCMCIA CARD
A15
20
A16
19
CE1#
7
OE#
9
WE#
15
READY#:IREQ#
16
GND
1
GND
34
D0
30
D1
31
D2
32
D3
2
D4
3
D5
4
D6
5
D7
6
A0
29
A1
28
A2
27
A3
26
A4
25
A5
24
A6
23
A7
22
A8
12
A9
11
A10
8
A11
10
A12
21
A13
13
A14
14
WP#
33
VPP1
18
VCC
17
GND
68
CD2#
67
D10
66
D9
65
D8
64
BVD1#:STSCHG
63
BVD2#:SPKR
62
GND
35
CD1#
36
D11
37
D12
38
D13
39
D14
40
D15
41
CE2#
42
VS1#
43
IORD#
44
IOWR#
45
A17
46
A18
47
A19
48
A20
49
A21
50
VCC
51
VPP2
52
A22
53
A23
54
A24
55
A25
56
VS2#
57
RESET
58
WAIT#
59
INPACK
60
REG#
61
69697070717172
72
R4166 10K
R4162 10K
R4165 10K
CI_WP#
R4163 10K
CI_RESET
CI_IREQ#
R4164 10K
CI_CD1#
R4161 10K
CI_WAIT#
VCC_CI
CI_CE2#
VCC_CI
VCC_CIVCC_CI
VCC_CI
U102
G5250M1T1U
OUT
1
GND
2
OC
3
EN
4
IN
5
R1302
4K7 1/16W 5%
+5V_SW
+5V_SW
CI_OCP
VCC_CI
CI_PWR_EN
PCMCIA Slot
CI Bus Power Contro l
C1303100NF 16V
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 47TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 48

10-2-7 NT72453_STBC/FLASH
19790_506.eps
NT72453_STBC/FLASH
B07 B07
2014-10-08
4
715G6947
NT72453_STBC/FLASH
PANEL_VCC_ON/OFF
Reset IC
STBC_RSTn
R168 100OHM
R161
10K
HP_EN
HP_EN 14
HP_EN
R167
NC/10K
PWM_LOGO 11
PWM_LOGO
ZD102
NC/MLVG0402
1 2
BL_ON/OFF
R109
1M 1/16W
C186
15PF50V
X10 3
12.000 MHZ
1
24
3
C187
68pF 50V
C704
2.2nF 50V
INT_IR
BATH_AMP_EN
IR / KEY BOARD CONN .
BATH_AMP_EN 18
PWR_ON
C184
1nF
LED_R
HDMI2_HPD 6
HDMI2_HPD
HDMI1_HPD
HDMI1_HPD 6
C4208 10UF 6.3V X5R +-20%
BS16
R4245 10KR4258 NC/ 1K 1/ 16W 5%
R4246 10K
BS17
R4259 NC/ 1K 1/ 16W 5%
R4252 10K
R4238 10K
R4256
1K 1/16W 5%
IR_SSB
R4253 NC/ 1K 1/ 16W 5%
R4225 NC/10K 1/ 16W 5%
R4212 NC/10K 1/ 16W 5%
R4251 NC/ 1K 1/ 16W 5%
R4220 10K
R4233 10K
BS18
R4247 NC/10KR4260 1K 1/16W 5%
R4214 NC/10K 1/ 16W 5%
R4241 10K
R4244 10K
R4240 10K
R4213 1K 1/16W 5%
R4250 1K 1/16W 5%
R4237 10K
R4206 NC/10K 1/ 16W 5%
R4207 10K
STB CONTORL
R4255 NC/ 1K 1/ 16W 5%
R4211
1K 1/16W 5%
R4249 1K 1/16W 5%
R4248 NC/ 1K 1/ 16W 5%
R4242 10K
R4239 10K
R4254 NC/ 1K 1/ 16W 5%
R4243 NC/10K 1/ 16W 5%
BS9
DV33
DV33SB
BS3
Burn_In_Line
BS8
BS5
BS4
BS2
BS10
GPIO
BS6
BS1
BS0
BS14
BS11
BS15
BS13
BS12
R4257 NC/ 1K 1/ 16W 5%
R110
0R
C4207
1UF 6. 3V
Boot strap
NT72453
STBC
Flash
U401D NT72453MBG-BA/B
STBC_GPF17/STBC_RSTout(BS10)
V18
PW_EN
W18
STBC_RSTn
Y18
SAR_ADC5/STBC_GPG18/SD_CMD
AB20
SAR_ADC4/STBC_GPG17/SD_CLK
AB19
SAR_ADC3/STBC_GPG16/SD_PWEN#
AA18
SAR_ADC0/STBC_GPG13
AB18
STBC_IR/STBC_GPF16
W21
STBC_GPF_12(BS7)
Y20
STBC_GPG_12(BS14)
V19
STBC_GPG_11(BS13)
V20
STBC_GPG_10(BS12)
W20
STBC_GPG_9(BS11)
W22
STBC_GPF_14/TEST_MODE_0(BS_9)
Y22
STBC_GPF_13(BS8)
Y21
STBC_GPF_11(BS6)
Y19
SPI_DO(DIO0)/STBC_GPF22(BS4)
AC22
SPI_DI(DIO1)/STBC_GPF21
AB23
SPI_CLK/STBC_GPF20
AC21
SPI_CS0/STBC_GPF18
AA23
SPI_HOLD(DIO3)/STBC_GPF24(BS5)
AB22
SPI_WP#(DIO2)/STBC_GPF23
Y23
XTAL_OUT
V22
XTAL_IN
V23
NAND_D0/SD_DAT0/STBC_GPF25
V8
NAND_RE#/STBC_GPG6
W12
NAND_ALE/STBC_GPG4(BS3)
V12
NAND_WE#/STBC_GPG3
Y11
NAND_CLE/STBC_GPG2(BS15)
W11
NAND_CE0#/STBC_GPG7
V13
NAND_CE1#/STBC_GPG8(BS17)
W13
NAND_WP#/STBC_GPG5
Y12
NAND_RB#/STBC_GPG1
V11
TEST_EN
U17
SAR_ADC6/STBC_GPG27
AA20
SAR_ADC7/STBC_GPG28
AB21
VGA_SDA/STBC_GPG25
T19
VGA_SCL/STBC_GPG26
T18
NAND_D1/SD_DAT1/STBC_GPF26
W8
NAND_D2/SD_DAT2/STBC_GPF27
Y8
NAND_D3/SD_DAT3/STBC_GPF28
V9
NAND_D4/STBC_GPF29
Y9
NAND_D5/STBC_GPF30
W9
NAND_D6/STBC_GPF31
V10
NAND_D7/STBC_GPG0
W10
SAR_ADC8/STBC_GPG29(BS18)
AA21
SAR_ADC1/STBC_GPG14/SD_CD#
AA19
SAR_ADC2/STBC_GPG15/SD_WP
AC18
SPI_CS1/STBC_GPF19
AA22
IR_RC
FB106 120R
1 2
LED_R
R4222
0R
HDMI2_HPD
HDMI1_HPD
R4218
0R05 1/16W
DV11
DV33
PWR_12V
+5V_STB
DV33SB
GND
DV15
+5V_SW
CN401
CONN
2
4
6
8
10
1
3
5
7
9
U410
AZ809ANSTR -E1
GND
1
RESET
2
Vcc
3
ONENAND_D3
ONENAND_D2
ONENAND_D1
ONENAND_D6
ONENAND_D5
ONENAND_D4
ONENAND_D0
ONENAND_D7
R4235
100K 1%
VGA_SDA16
VGA_SCL16
BS6
Key1 18
Key1
Burn_In_Line
BS8
BS12
BS13
BS14
BS11
ZD103
NC/MLVG0402
1 2
DV33SB
BS18
KEY_ADC0
INT_IR
BS16 8
BS16
ONENAND_D7
PANEL_VCC_ON/OFF
BL_ON/OFF
ONENAND_D6
ONENAND_D5
ONENAND_D4
BS0
BS1
ONENAND_D1
ONENAND_D0
ONENAND_D2
ONENAND_D3
SCT1_DET
BS011
BS111
NAND_R/B#
BS3
BS15
C4204
100NF 16V
PWR_12V 4,13,17
+5V_SW 4,9,11,13,16,17,18
NAND_CE0#
NAND_WP#
BS2
BS10
R4201
10K
DV33SB 4,6,11,12,18
NAND_RE#
C4201
100NF 16V
R4203
10K
DV33 4,5,7,11,12,13,14,17,18
DV15 4,12
R4202
10K
DV11 4,12
DV33SB_NAND
DV33SB_NAND
+5V_STB 4,6
GND 4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18
PWR_ON 4
SCT1_DET 15
U405
MX30LF1G08AA-T1 1Gb 48-TSOP
NC23
39
NC1
1
NC2
2
NC3
3
NC4
4
NC5
5
NC26
46
ALE
17
CLE
16
WE
18
NC17
26
NC8
11
WP
19
RY/BY1
7
NC9
14
NC10
15
NC18
27
NC19
28
NC11
20
NC12
21
NC13
22
I/O3
32
NC20
33
VSS2
36
VCC1
12
RE
8
VCC2
37
I/O2
31
I/O1
30
I/O0
29
VSS1
13
NC25
45
I/O7
44
I/O6
43
I/O5
42
I/O4
41
NC24
40
NC14
23
NC1524NC16
25
CE1
9
NC21
34
NC22
35
NC27
47
PRE
38
NC6
6
NC7
10
NC28
48
BL_ON/OFF 4
DV33SB
DV33SB_NAND
PANEL_VCC_ON/OFF 17
DV33SB_NAND
Ambi-Temp
NAND_WE#
BS211
PWR_ON
IR_RC 18
IR_RC
NAND_RE#
BS15
BS17
NAND_WE#
BS3
NAND_CE0#
NAND_R/B#
NAND_WP#
C152
1uF 10V
C153
100NF 16V
DV33SB
C148
100pF 50V
DV33SB
R164
30K
IR_SSB18
IR_SSB
BATH_AMP_EN
BS5
BS4
Ambi-Temp 18
Ambi-Temp
BS9
PWM_LOGO
C4206
NC/ 100P 50V
DV33
(KEY_MENU_L_R_SOURCE)
KEY_UP_DN_DCSW
R4521
3.9K 1%
KEY_ADC0 Key1
R4515
100OHM
C4501
100NF 25V
DV33SB
R732
0R05 1/16W
U401
STBC_RSTn
R730
0R05 1/16W
HS1
HEAT SINK
1
2
SW401
NC
123
4
Key1
SCT1_DET
R731
NC/ 0R 05 1/ 16W
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 48TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 49

10-2-8 NT72453_USB/GPIO
19790_507.eps
NT72453_USB/GPIO
B08 B08
2014-09-23
4
715G6947
NT72453_USB/GPIO
EJTAG_TMS
EJTAG_INT
TP430
TP432
TP433
TP431
EJTAG_TRST
TP434
EJTAG_TCK
EJTAG_TDO
EJTAG_TDI
MIPS_EJTAG
R4371
4K7 1/16W 5%
R4368
4K7 1/16W 5%
R4367
47K 1/16W 5%
R4369
4K7 1/16W 5%
R4370
4K7 1/16W 5%
DV33
S2_T2_SDA
USB_EN
SI2C_SCL
SI2C_SDA
Ambi-light
HP_DET 14
DV11
HP_DET
DV15
GND
DV33SB
+5V_STB
DV33
PWR_12V
S2_T2_SDA 13
S2_T2_SDA
S2_T2_SCL
+5V_SW
T2_DEMOD_RSTn 7,13
S2_T2_SCL 13
T2_D EMOD_R STn
BL_DIMMING
AMP_RESET 14
TUN ER_SCL
TUN ER_SDA
AMP_SDA
MIPS_RXB 5,16,18
BL_DIMMING 4
AMP_SCL
MIPS_RXB
MIPS_TXB
AMP_SDA 14
MIPS_TXB 5,16,18
AMP_SCL 14
TUN ER_SCL 13
TUN ER_SDA 13
LNB_EN
AMP_RESET
HP_DET
GPIO
MIPS/UART/I2C/ICE
LNB_EN 13
+5V_SW 4,9,13,16,17,18
PWR_12V 4,13,17
S2_T2_SCL
DV15 4,12
DV33 4,5,7,10,12,13,14,17,18
DV33SB 4,6,10,12,18
GND 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,17,18
+5V_STB 4,6
DV11 4,12
SI2C_SCL17
SI2C_SDA17
SI2C_SCL
SI2C_SDA
LR_SYNC_IN
PWM_IN18
2D_3D_SEL
LR_SYNC_IN
PWM_IN
LR_SYNC_IN18
LDC_EN
AGING_EN
SCN_EN
SEL_LVDS
Ambilight
2D_3D_SEL18
SEL_LVDS18
AGING_EN18
BS010
SCN_EN18
LDC_EN18
BS210
BS1
BS0
BS2
BootStrap Optoin
BS110
VCOM_SCL
VCOM_SDA
VCOM_SCL 17
VCOM_SDA 17
AGING_EN
LDC_EN
2D_3D_SEL
SCN_EN
R4372
NC/4K7 1/16W 5%
R4373
NC/4K7 1/16W 5%
R4363
NC/ 100R 1/ 16W 5%
USB_EN
R4366
43K 1/16W
R4376
43K 1/16W
U411
G5250M1T1U
OUT
1
GND
2
OC
3
EN
4
IN
5
R4365
NC/10K 1/16W 5%
C1711
100N 16V
R4375
NC/100R 1/16W 5%
MIPS UART/I2C/ICE
USBx2
Ethernet
MIPS GPIO
NT72453
USB/GPIO
EtherNET
UART/I2C
STBC UART/I2C
U401G
NT72453MBG-BA/B
MIPS-TRST/GPC_11
C3
MIPS-TCK/GPC_7
E5
MIPS-TMS/GPC_8
F4
MIPS-TDI/GPC_10
D4
MIPS-TDO/GPC_9
E4
I2CMA_SDA/PTSIN1_ERROR/STSIN0_ERROR/GPD_0
F2
I2CMA_SCL/PTSIN1_CLK/STSIN1_CLK/GPD_1
G3
I2CMB_SDA/PTSIN1_VALID/STSIN1_VALID/GPD_2
G1
I2CMB_SCL/PTSIN1_START/ STSIN1_START/GPD_3
H3
I2CME_SDA/GPC_18
D1
I2CME_SCL/GPC_17
D2
UARTA_RX/CI_OE#/GPD_30
N2
UARTB_TX/INT_5/GPC_4
F3
UARTB_RX/INT_6/GPC_5
E2
UARTC_TX/CI_WE#/GPD_31
N1
UARTC_RX/CI_REG#/GPE_0
P3
USB1_D-
C23
USB1_D+
B23
USB0_D-
B22
USB0_D+
A22
RMII_CLK/PTSOUT_D2/PTSIN2_D2/DEMODOUT_D2/GPD_18
L7
RMII_TX_EN/PTSOUT_D5/PTSIN2_D5/DEMODOUT_D5/GPD_21
M6
RMII_TX_D0/PTSOUT_D3/PTSIN2_D3/DEMODOUT_D3/GPD_19
L6
RMII_TX_D1/PTSOUT_D4/PTSIN2_D4/DEMODOUT_D4/GPD_20
M7
RMII_RXERR/CI_CD_0#/GPD_25
L1
RMII_CRS/CI_RST/GPD_24
G2
RMII_RX_D0/PTSOUT_D0/PTSIN2_D0/DEMODOUT_D0/GPD_16
K4
RMII_RX_D1/PTSOUT_D1/PTSIN2_D1/DEMODOUT_D1/GPD_17
K5
RMII_MDC/PTSOUT_D6/PTSIN2_D6/DEMODOUT_D6/GPD_22
M5
RMII_MDIO/PTSOUT_D7/PTSIN2_D7/DEMODOUT_D7/GPD_23
N7
GPE_4/CI_HA2
R2
GPC_12/INT_7(BS0)
A2
GPE_24/LR1_DELAY/CI_HAD7/I2S_OUT_C_DATA
V1
GPE_23/LR0_DELAY/CI_HAD6/I2S_OUT_C_WS
U2
LED_PWM7/CI_HAD4/I2S_OUT_C_MCLK/GPE_21
U3
GPE_22/3D_IR/3D_BT/3D_Activ e/CI_HAD5/I2S_OUT_C_BCLK
U1
LED_PWM6/CI_HAD3/I2S_OUT_B_DATA/GPE_20
V2
LED_PWM5/CI_HAD2/I2S_OUT_B_WS/GPE_19
V5
LED_PWM4/CI_HAD1/I2S_OUT_B_BCLK/GPE_18
U6
LED_PWM3/CI_HAD0/I2S_OUT_B_MCLK/GPE_17
U5
LED_PWM2/YDIO/CI_HA14/Tensilica_TRST/GPE_16
T5
LED_PWM1/CI_HA13/Tensilica_TDI/GPE_15
T6
MIPS-INT/INT_0/GPC_6
F5
I2CM1_SCL/STBC_GPG24
U22
I2CM1_SDA/STBC_GPG23
U23
UART1_RX/STBC_GPG22/UARTB_RX
T21
UART1_TX/STBC_GPG21/UARTB_TX
T22
GPE_5/CI_HA3
T3
GPE_7/FRC_Dimming2/DSU_ACT/CI_HA5
T1
GPE_8/DSU_TX/CI_HA6
N5
GPE_9/DSU_RX/CI_HA7
N6
GPE_10/DSU_EN/CI_HA8
P7
GPE_11/FR_PWM/LED_VS_OUT/CI_HA9
P6
LED_PWM0/CI_HA12/Tensilica_TDO/GPE_14
R5
UARTA_TX/CI_IOWR#/GPD_29
N3
GPE_6/FRC_Dimming1/DSU_BRE/CI_HA4
T2
USB0_PWEN/CI_HA10/Tensilica_TCK/GPE_12
R7
USB1_PWEN/CI_HA11/Tensilica_TMS/GPE_13
R6
GPC_13/INT_8(BS1)
B1
GPC_14/INT_9(BS2)
B2
GPD_26/BT_SHOP_VS_IN/BT_SHOP_LR_IN/CI_CE#
L2
I2CMC_SDA/PTSIN1_D0/GPD_4
H1
I2CMC_SCL/PTSIN1_D1/GPD_5
H2
I2CMD_SDA/GPC_16
D3
I2CMD_SCL/GPC_15
C2
UART0_TX/I2CM0_SDA/I2C_S_SDA/STBC_GPG19
U21
UART0_RX/I2CM0_SCL/I2C_S_SCL/STBC_GPG20
U20
UARTD_TX/I2C_MF_SCL/CI_HWAIT#/GPE_1
P1
UARTD_RX/I2C_MF_SDA/CI_HA0/CI_ALE0/GPE_2
P2
I2CM0_SDA/STBC_GPG31
U19
I2CM0_SCL/STBC_GPH0
U18
I2CMF_SDA/GPC_20
E1
I2CMF_SCL/GPC_19
E3
USB_REXT
A23
GPC_21
G5
GPC_22
G4
GPC_23
H6
GPC_24
H5
VCOM_SDA
C4209
1nF 50V
R4374
43K 1/16W
USB0_D-
USB0_D+
EJTAG_TRST
EJTAG_TDI
EJTAG_TCK
EJTAG_TDO
EJTAG_TMS
C4210
1nF 50V
VCOM_SCL
C4211
1nF 50V
C4212
1nF 50V
TP405
TUN ER_SDA
TUN ER_SCL
AMP_SDAFRC_RST
MIPS_TXB
DV33SB
SEL_LVDS
AMP_RESET
FRC_RST
PWM_LOGO
FRC_RST18
AMP_SCL
C726
3.9PF 50V
C725
3.9PF 50V
PWM_IN
388G352F6B3AXH2nd
1st088G352F6B3ACL
USB 2.0
BL_DIMMING
USB0_D+
R105
12K 1% 1/16W
LNB_EN
MIPS_RXb
PWM_LOGO 10
PWM_LOGO
USB0_D-
TP435
1234
CN103
USB CONN
1
2
3
4
65
C4362
10uF 16V
+5V_SW
TP436
R4361
0R05 1/16W
BS2
BS0
BS1
EJTAG_INT
C1403
22UF 10V
R4362 0R05 1/16W
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 49TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 50

10-2-9 NT72453_POWER
19790_508.eps
NT72453_POWER
B09 B09
2014-10-22
4
715G6947
NT72453_POWER
FB443
120R
1 2
C13064.7UF 6.3V
C4481
NC/10UF 6. 3V 20%
C4465
220NF 16V
DV11
CORE11V
FB442
120R
1 2
C4479
10UF 6. 3V 20%
FB445
120R
1 2
C4468
100NF 16V
C4467
100NF 16V
C4478
4.7UF
C4466
220NF 16V
C17410UF 6. 3V
FB447
120R
1 2
C146 100NF 16V
C16710UF 6. 3V
C175100N F 16V
C4480
10UF 6.3V 20%
DV15_CLKDV15_MMU
DV15
DV15_CLK
DV15_MMU
C168100NF 16V
C173100NF 16V
C164100N F 16V
C163100NF 16V
C1581UF 6. 3V
C4488
10UF 6. 3V 20%
453_3V3
DV11 4
DV33 4,5,7,10,11,13,14,17,18
+5V_SW 4,9,11,13,16,17,18
DV33SB 4,6,10,11,18
DV15 4
GND 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,13,14,15,16,17,18
+5V_STB 4,6
DV33SB
+5V_STB
DV11
DV33
DV15
GND
+5V_SW
C714 4. 7U F 10% 10V
C4486 100NF 16V
FB450
120R
1 2
ADC_3V3
FB444
120R
1 2
453_3V3
AU_3V3
DEMOD_3V3
C4471 220N F 10V
C4402 4.7UF 6.3V
C4469 100NF 16V
DV12
LVDS TVDAC
CORE-1.1V
TVADCDEMODHDMI AUDIO
USB
DDR
NT72453
POWER/GND
STBC & XTAL
GPIO
CLK_OUT
NT72453MBG-BA/BU401H
VDD33_AUADC
H18
VDD11_DDR
P12
GND_DEMOD
K19
VDD33_HDMI
W14
GND_TVADC0
L18
VDD33_TVADC1
M20
VDD33_TVDAC
R14
VDD33_HDMI
V14
VDD33_IO
H12
VDD33_DLL
T13
GND_CLK
AA1
GND_HDMI
T14
VDD33_AUDAC
H19
GND_HDMI
U14
VDD15_CLK
AB1
VDD33_IO
H11
VDD11_DEMOD
H21
VDD33_TVADC0
L19
GND_LVDS
J13
VDD_CORE
U12
VDD_CORE
U11
VDD_CORE
U10
VDD_COREU9VDD_CORE
T12
VDD_CORE
T11
VDD_CORE
T10
VDD15_MMU
AC5
VDD15_MMU
AA6
VDD15_MMU
AB6
VDD33_USB
G19
GND_LVDS
J14
GND_TVADC1
M18
GND
G6
GND
G7
GND
G16
GND
H7
GND
H8
GND
H9
GND
H10
GND
H15
GND
H16
GND
H17
GND
J7
GND
J8
GND
J9
GND
J10
GND
J11
GND
J15
GND
J16
GND
J17
GNDK7GNDK8GNDK9GND
K10
GND
K11
GND
K16
GND
K17
GND
K18
GND
L8
GND
L14
GND
L15
GND
L16
GND
L17
GNDM8GNDM9GND
M10
GND
M11
GND
M12
GND
M13
GND
M14
GND
M16
GNDN8GND
N10
GND
N11
GND
N16
GND
N17
GND
P10
GND
P11
VDD15_DRAM
AB3
VDD15_DRAM
AC3
VDD15_DRAM
AB4
VDD15_MMU
AB5
VDD15_MMU
AA5
GND
L11
GND
L12
GND
L13
GND
M15
GND
N12
GND
N14
GND
N15
GND
P16
GND
P17
GND
R10
GND
R15
GND
R16
GND
R17
GND
T7
VDD_CORE
U13
GND
G17
GND
R12
VDD33_LVDS
H14
VDD33_LVDS
H13
GND
K13
GND
K14
GND
K15
GNDL9GND
L10
GND
M17
GND
P13
GND
P14
GND
P15
GND
R11
VDD33_DEMOD
J21
GNDT8GNDT9GND
T16
GNDU7GNDU8GNDV3GNDV6GNDV7GND
W3
GND
N13
GND_XTAL
U16
VDD33_STBC
V17
VDD33_XTAL
V16
VDD33_STBC
W17
EFUSE_EN
T17
VDD10_STBC
AC19
GND_XTAL
V21
VDD11_HDMI
R13
VDD15_MMU
AC6
DDR_VREFCA
W2
DDR_ZQ
Y1
VDD25_CAP
M19
NC
A1
NC
AC1
NC
AC23
DDR_VREFDQ
W1
VDD33_CLK
W16
GND_CLK
U15
GNDP8GND
P9
GNDR8GND
R9
GND
T15
GNDW4GNDW5GNDW6GNDW7GNDY2GNDY3GNDY4GNDY5GNDY6GNDY7GND
AA2
GND
AA3
GND
AA4
GND
AA7
GND
AB7
GND
AC7
DDR_RESET
AB2
STBC_GPF_10
AC2
453_3V3_HDMI
DV12
453_3V3_HDMI
C157 100NF 16V
MVREF
DV15_MMU
R186 1K 1/ 16W 5%
C4487
10UF 6. 3V
R187 1K 1/ 16W 5%
C4403
4.7UF 6. 3V
R188 240 OH M +-1% 1/16W
453_3V3_IO
453_3V3
DV15_MMU
C4470 4. 7U F 10% 10V
C1307 1UF 6. 3V
453_3V3_IO
FB103 300R
1 2
DV33SB
CORE11V
DV15_CLK
C4482
10UF 6. 3V
C4474
100NF 16V
FB441
120R
1 2
C4462
100NF 16V
C4464
220NF 16V
DV33
C4483
4.7UF 10% 10V
453_3V3
FB446
120R
1 2
ADC_3V3
C4461
100NF 16V
C4463
220NF 16V
FB449
120R
12
DEMOD_3V3
AU_3V3
C4484
220NF 16V
FB448
120R
1 2
FB102 300R
1 2
C4485 100NF 16V
CORE11V
453_3V3_IO
453_3V3_IO
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 50TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 51

10-2-10 Tuner/T2 demod
19790_509.eps
Tuner/T2 demod
B10 B10
2014-10-22
4
715G6947
Tuner/T2 demod
TU10 2
ANT
1
3.3V
2
SDA
3
SCL
4
IF_N
5
IF_P
6
IF_AGC
7
TH1
8
TH2
9
TH3
10
TH4
11
TH5
12
TH6
13
C239
NC
TU10 3
TH1
12
TH2
13
TH3
14
TH4
15
LNB A
1
NC
2
TU3.3V
3
NC
4
QP Output
5
IP Output
6
NC
7
AGC
8
X-OUT
9
SDA
10
SCL
11
C215
NC
TS_T2_DQ7
TS_T2_DQ6
TS_T2_DQ5
T2_DEMOD_RSTn
X20 1
NC
1
2 4
3
S2T2_TUN_SCL
H/T model : TCL ST42CS-2-E
K model : Samsung DTOS40CIL034B
C221
NC
C217
NC
C234
NC
C132
NC/10PF 50V
R318
NC
R322 NC
R319
NC
S2T2_TUN_SDA
U201
NC
MP_A
1
MP_B
2
GPIO_0
3
NC
4
NC
5
NC
6
VDD_Vcore
7
GND
8
VDD_VIO
9
SCL_Host
10
SDA_Host
11
TS_VLD
12
XTAL _O
32
RESETB
31
MP_D
30
MP_C
29
VDD_Vcore
28
GND
27
TS_ERR/GPIO_1
26
TSD7
25
TS_SYNC13TS_CLK14TS_D0/SER15TS_D116TS_D217TS_D318TS_D419VDD_Vcore20GND21VDD_VIO22TSD523TSD6
24
XTAL_I/CLK_IN
33
ADDR
34
GND
35
VDD_Vana
36
NC37NC38NC39NC
40
ADC_P
41
ADC_N
42
NC
43
CLK_IN_OU T
44
SDA_T
45
SCL_T
46
GND
47
VDD_Vcore
48
EPad
49
TUN_DIF -_DEMOD
+1.2V_T2
TUN_DIF+_DEMOD
C220 NC
C213 NC
R315
NC
QP
+1.2V_T2
+3.3V_T2
+3.3V_T2
C216
NC
C214
NC
R316
NC
C223
NC
C211
NC
DV33
SI2166 S_ADC_QN
+1.2V_T2
+1.2V_T2
SI2166 S_ADC_QP
SI2166 S_ADC_IN
SI2166 S_ADC_IP
Pin-to-Pin compatible
with Si2166 ( DVB_S/S2)
R321 NC
C224
NC
C240
NC
C243
NC
T2 Demod : 356G0575048607
S2 Demod : 356G0575048606
DVB-T/T2 De mo dulator
SI2166 DISEQC_OUT
C135
NC/10PF 50V
C236
NC
13/18V_SW
C253
NC
QN
IN
R215 NC
D502
NC
1 2
R227 NC
D503
NC
1 2
D504
NC
1 2
L202 NCL201
NC
ZD202
NC
1 2
R213
NC
U202
NC
SGND
1
BYPASS
2
VDD
3
COMP
4
EN
5
LINEDROP
6
POK7TCAP
10
ILIMIT
11
VOUT
12
VBOOST
13
BST
14
SW
15
PGND
16
13V/18V8EXTM
9
EP
17
R210
NC
R221
NC
DISEQC_OUT
ZD201
NC
1 2
C233 NC
R212
NC
C245
NC
R225
NC
R224
NC
Q201
NC
1
3 2
C296
NC
R216
NC
TUN ER_LN B
R214
NC
R217
NC
LNB_EN
R226
NC
DV33
LNB_LINEDROP
T2_IF_AGC_TUNER
R339
NC
R223
NC
IFAGC SWITCH
PWR_12V
IF_AGC
R208 NC
Tuner
SoC
Demod IC
R344
NC
C248 NC
Q202NC
R345NC
C249 NC
IF_AGC_T
R209 NC
R346 22R 1/16W 5%
R337
0R05 1/16W
T2_IF_AGC_TUNER
R211
NC
C255
NC/100NF 16V
DV33
R341
0R05 1/16W
PWR_12V
DV33
PWR_12V
IFAGC_SW
R222 NC
C230NC
C227NC
LINEDROP:
Low: 13/18V
High:
14/19V
13/18V_ SW:
Low: 18V
High: 13V
LNB POWER SUPPLY
R218
NC
R220
NC
S2T2_TUN_SCL
S2T2_TUN_SDA
R207
NC
DV33
R219
NC
C241NCC242
NC
S2_TUNER_SCL
S2_TUNER_SDA
C246
NC
LNB_EN:
Low: disable
High: enable
ESD & Surge
Protect
+3V3_VCC_S2
C209
NC
+3V3_TUNER
TS_T2_SYNC
CI_INSYNC
CI_IN CLK
RP201
NC
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
FB203
NC
1 2
C208
NC
CI_IN VALID
CI_INDATA4
CI_INDATA3
CI_INDATA2
CI_INDATA1
CI_INDATA0
CI_INDATA7
CI_INDATA6
CI_INDATA5
TS_T2_SYNC
TS_T2_CLK
TS_T2_DQ0
TS_T2_DQ7
TS_T2_DQ6
TS_T2_DQ5
TS_T2_DQ4
TS_T2_VAL
R331NC
TS_T2_DQ1
TS_T2_DQ3
TS_T2_DQ2
C247
NC
R328 NC
R329 NC
RP202
NC
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
C237
NC
C131
NC/10PF 50V
R336
NC
NC NC
S2T2_DEMOD_SCL
YesYes
R343
R335
NC
Yes
R338R336
H
T2/K
R338 NC
NC
Yes
R335
NC
DV33
S2T2_DEMOD_SDA
TS_T2_CLK
S2_T2_SDA
S2_T2_SCL
R343 NC
C251
NC
TS_T2_DQ0
TS_T2_DQ1
C238
NC
C226NC
C225NC
C244
NC
FB105
120R 1A
1 2
+5V_SW
R201
1K5 1/16W 5%
TUNER_SDA
TUNER_SCL
C136
NC/150pF 50V
C202
100NF 16V
C256
68P 50V
R139
0R05 1/16W
R140
0R05 1/16W
TUN_DIF-#T2
TUN _SCL
R203 100R 1/16W 5%
TUN_DIF+#T2
R202
1K5 1/16W 5%
R142
0R05 1/16W
T2 TUNER
R141
0R05 1/16W
TUN_DIF-
S2T2_DEMOD_SCL
R137
0R05 1/16W
TUN_DIF+
R138
0R05 1/16W
C138
NC/10PF 50V
DV33
LGTuner wit h DVB-S/S2
TUN _SDA
S2 TUNER
C231
1NF 50V
R204 100R 1/16W 5%
+3V3_TUNER
U203
AZ1117CH-3. 3TRG1
ADJ(GND )
1
VOUT2VIN
3
4
4
C257
68P 50V
TDQS-A751F
R340 22R 1/16W 5%
TUN_DIF+#T2
IF_AGC_T
TUN_DIF-#T2
C203
100NF 16V
S2_TUNER_SCL
S2_TUNER_SDA
IF_AGC_S2_TUNER
C201
10UF 10V
TUNER_LNB
C210
NC
C207
NC
IP
co-layout
LGTuner with DVB-C/T/T2
from scaler
ST42CS-2-E
+3V3_TUNER
IP
S2T2_DEMOD_SDA
C204
22UF 10V
C250
NC
DISEQC_OUT
13/18V_SW
TUN_DIF-_DEMOD
TUN_SDA
LNB_LINED ROP
TUN_DIF+_DEMOD
TUN_SCL
R323 NC
C232
NC
TS_T2_VAL
FB211
NC
1 2
IF_AGC_S2_TUN ER
R342
NC
C218
NC
C222
NC
R326 NC
R325 NC
DV33
+1.2V_T2
+3.3VA_T2
C235
NC
+3.3V_T2
DV33
AVDD1V2
IN
C228NC
FB208
NC
1 2
FB210
NC
1 2
C298
NC
R320
NC
C212
NC
C229NC
QP
TS_T2_DQ4
TS_T2_DQ3
TS_T2_DQ2
C297
NC
C219
NC
QN
AVDD1V2 4
AVDD1V2
PWR_12V 4,17
PWR_12V
Tuner
GPIO
IFAGC_SW7
IFAGC_SW
DV33 4,5,7,10,11,12, 14,17,18
DV33SB 4,6,10,11,12,18
+5V_SW 4,9,11,16,17,18
GND 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12, 14,15,16,17,18
+5V_STB 4, 6
DV11 4,12
TUN_DIF- 7
TUN ER_SCL 11
TUN ER_SDA 11
IF_AGC 7
TUN_DIF+ 7
TUN ER_SCL
TUN ER_SDA
TUN_DIF-
+5V_SW
+5V_STB
DV33
DV11
IF_AGC
LNB_EN
TUN_DIF+
GND
DV33SB
Demod
LNB_EN 11
CI_IN CLK
CI_INDATA0
S2_T2_SDA
CI_INDATA2
CI_INDATA1
CI_INSYNC
CI_INVALID
CI_INDATA7
CI_INDATA6
CI_INDATA5
CI_INDATA4
CI_INDATA3
CI_INSYNC 9
CI_INVALID 9
CI_INCLK 9
S2_T2_SCL 11
CI_INDATA3 9
CI_INDATA6 9
CI_INDATA7 9
CI_INDATA2 9
CI_INDATA4 9
CI_INDATA5 9
S2_T2_SDA 11
CI_INDATA0 9
CI_INDATA1 9
T2_DEMOD_RSTn
T2_DEMOD_RSTn 7
S2_T2_SCL
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 51TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 52

10-2-11 SPK AMP/HP OUT
19790_510.eps
SPK AMP/HP OUT
B11 B11
2014-10-22
4
715G6947
SPK AMP/HP OUT
L602 15uH
L603 15uH
Option
Anti-pop
L604 15uH
C602
100NF 25V
Ground in bottom side need connector
it togother, heat sink is also.
Main filter Option
(10Wx2 ,6R)
Default :
C607
100N 50V
C608
100N 50V
R634
22R 1/16W 5%
Q602
LMBT3904LT1G
1
3
2
HP_EN
+
C626
470uF 25V
R611
47K
C621
10UF 16V
C610
100N 50V
HP_EN
C603
100NF 25V
C632 N C / 470pF 50V
Reserve for hotel
C618
0.1UF 16V
DV15 4,12
DV11 4,12
AUDIO_12V 4
AUDIO_12V
AMP_SCL 11
GND 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,15,16,17,18
+5V_STB 4,6
AMP_SDA 11
AMP_RESET 11
I2SOUTC_DATA 7
I2SOUTC_WS 7
I2SOUTC_BCLK 7
I2SOUTC_MCLK 7
+5V_SW 4,9,11,13,16,17,18
AUOUT_R1 7
AUOUT_L1 7
DV33 4,5,7,10,11,12,13,17,18
DV33SB 4,6,10,11,12,18
AMP_SDA
AMP_SCL
DV33SB
DV11
AMP_RESET
AUOUT_R1
DV33
AUOUT_L1
C604
100NF 25V
GND
DV15
+5V_SW
+5V_STB
I2SOUTC_MCLK
I2SOUTC_DATA
I2SOUTC_WS
I2SOUTC_BCLK
GPIO
AUDIO /IF
MIPS/UART/I2C/ICE
HP_DET 11
HP_EN 10
HP_DET
HP_EN
HPOUTR
CN601
CONN
1
2
3
4
5 6
Q603
NC/LMBT3904LT1G
1
3
2
HPOUTR
R658
NC\100R
C619
0.1UF 16V
(AD87588
P2P
AD82588B)
H
L: -( R611 / R608 )
Stereo
L
QFP48
HPOUTL
Separate
VCC trace
R: -( R609 / R607 )
HP Gain
CFG1CFG0
C606
33nF 50V
RSPK-
HP_DET
PWRDN-HP
CN602
PHONE J AC K
1
2
4
5
3
R628
180K
R631
NC
PWRDN
DV33
L601 15uH
R630 0R 05 1/ 16W
R633
10K
HS2
HEAT SINK
1
2
U602
ZD602
MLVG0402
12
R608
12K 1%
ZD601
MLVG0402
12
R610
1K
R607
12K1%
R613 10R 1/ 16W 1%
R621
470K
DV33
PWRDN-HP
Q601
LMBT3906LT1G
1
23
R614
DV33
R620
0R05 1/16W
R629
NC\10K
R657
NC\0R 05 1/ 16W
DV33
R626
1K 1/16W 5%
R622
1K
I2SOUTC_WS
I2SOUTC_DATA
C629
100NF 16V
DV33
AMP_RESET
C624 330PF 50V
R627
NC/ 4K7 1/ 16W 5%
LSPK+
AMP_SDA
PVDD
R609
47K
C625
NC/ 100N F 16V
C617 100N F 16V
R632
NC/10K
LSPK-
R601
0R05 1/16W
C622 330PF 50V
RSPK+
C612
100NF 16V
AMP_SA0
C614
68PF 50V
I2SOUTC_MCLK
LA
AMP_SCL
RA
R623
10K
RB
C627
100NF 16V
R602
0R05 1/16W
R603
NC\ 10R 1/ 16W 1%
AMP_SA1
R624
10K
AMP_DEF
RB
AMP_SCL
AMP_SDA
LA
R604
43K 1/16W
RA
LB
AUD_V33
LB
AMP_SA1AMP_SA0
PVDD
DV33
R617
NC/10K
R625
10K
C628
100NF 16V
C611
100NF 16V
C631 N C / 470pF 50V
R616
NC/10K
R615
NC/10K
I2SOUTC_BCLK
PVDD
DV33
DV33
DV33
C623
100NF 16V
AMP_DEF
R618
4K7 1/16W 5%
R612
10R 1/16W 1%
DV33
AUOUT_L1
PWRDN
C615
68PF 50V
AUD_V33HP
C620
10UF 16V
U601
AD87588-LG48NAY
SDATA1
1
MS
2
PLL
3
CFG0
4
CFG1
5
CLK_OUT
6
DGND
7
DVDD
8
SDATA0
9
LRCIN
10
BCLK
11
MCLK
12
RINN13OUTR14VSS15EN16PVSS17CN18CP19PVDD20PGND21UVP22OUTL23LINN
24
SDA
25
SCL
26
SA0
27
SA1
28
DEF
29
DGND
30
DVDD
31
PD#
32
ERROR#
33
RESET#
34
LREX
35
LINEIN
36
NC
37
VDDRA
38
RA
39
GNDR
40
RB
41
VDDRB
42
VDDLB
43
LB
44
GNDL
45
LA
46
VDDLA
47
NC
48
THERMALPAD
49
C601
100NF 25V
R619
4K7 1/16W 5%
DV33
R606
43K 1/16W
FB604
120R
1 2
AUD_V33
AUD_V33HP
FB603
120R
1 2
DV33
AUDIO_12V
PVDD
FB601
120R
1 2
FB602
120R
1 2
C616 100N F 16V
AMP_RESET
R605
1K
AUOUT_R1
C609
33nF 50V
HPOUTL
C605
100N 50V
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 52TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 53

10-2-12 SCART
19790_511.eps
B12 B12
2014-10-22
4
715G6947
SCART
SCART
SC_CVBS_Y
SCT1_G
SCT1_R
SOY1
SCT1_B
GND 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,17,18
GND
SCART1_LIN
SCART1_RIN
SC_CVBS_Y 7
SCT1_B 7
SOY1 7
SCT1_G 7
SCT1_R 7
SCART1_LIN 7
SCART1_RIN 7
ZD112
AZ5125-01H.R7G(5.5V)
1 2
ZD113
AZ5125-01H.R7G(5.5V)
1 2
ZD114
AZ5125-01H.R7G(5.5V)
1 2
ZD115
AZ5125-01H.R7G(5.5V)
1 2
ZD116
AZ5125-01H.R7G(5.5V)
1 2
ZD117
AZ5125-01H.R7G(5.5V)
1 2
ZD118
AZ5125-01H.R7G(5.5V)
1 2
ZD119
AZ5125-01H.R7G(5.5V)
1 2
L1100
1.8UH
C1108
220pF 50V
C1109
220pF 50V
---><---|>
SCART Audio Input
SCT1_AV_IN
R1103
75 OHM +-5% 1/16W
SCT1_AV_IN
R1102
75 OHM +-5% 1/16W
SCT1_FS_IN
-------><-------
SCT1_AUL_IN
R1105
10K
SCT1_FS_IN
388G355HLB1VYG
R1101
75 OHM +-5% 1/ 16W
-------><-------
SCT1_FB_IN
SCT1_G_IN
R1110
10K
C1105
NC/470PF
SCT1_G
Function Select
SCT1_AUR_IN
---><---|>
SCART 21P
CN151
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
---><---|>
R1107
75 OHM +-5% 1/16W
2nd
SC_CVBS_Y
C1107 470PF
SCT1_R_IN
R1106
75 OHM +-5% 1/ 16W
Helf SCART(RGB+CVBS+L/R IN)
SCT1_FB_IN
R1108
10K
SCT1_B
RGB IN
SCT1_R_IN
C1106 470PF
---><---|>
C1104
15PF50V
1st
FAST BLANKING/SOY
C1101
NC/47pF 50V
SCT1_AUR_IN
SCT1_B_IN
SCART1_RIN
388G355HLB1VVA
SCT1_B_IN
SCT1_R
R1104
39K 1/16W 5%
CVBS IN
-------><-------
SCART1_LIN
SCT1_G_IN
C1103
15PF50V
---><---|>
SCT1_AUL_IN
C1110
15PF50V
SOY1
R1109 10K
SCT1_DET
R1111 10K
SCT1_DET
SCT1_DET 10
AUDIO /IF
ADC/DAC
STB CONTORL
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 53TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 54

10-2-13 VGA
19790_512.eps
VGA
B13 B13
2014-10-08
4
715G6947
VGA
D101
NC
1
3
2
MIPS_RXB
VGA In
VGA_RIN
VGA_LIN
R102
10K 1%
R103 10K
R101
10K 1%
C101 470PF
C76 470PF
VGA_PLUGPWR
VGA_SDA
VGA_SCL
R155 NC
MIPS_TXB
VGA_B#
ZD123
12
ZD122
NC
12
ZD124
12
R145
NC
R148
NC
CN101
NC
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
11
12
13
14
15
10
1716
18 19
VGA_VS#
VGA_HS#
VGA_R#
VGA_G#
VGA_PLUGPWR
ZD101
NC
1 2
+5V_SW
R152 NC
FB108
1 2
CN605
PHON E J AC K
1
2
3
FB109
1 2
FB110
NC
1 2
ZD125
12
ZD121
NC
12
ZD120
12
ZD110
NC/MLVG0402
1 2
ZD111
NC/MLVG0402
1 2
R124
NC
R125
NC
ZD126
12
R126
NC
R127NCR128
NC
R104 10K
PC / DVI Audio in
R146 NC
MIPS_RXB 5,11,18
VGA_B#
VGA_G#
MIPS_RXB
VGA_G# 7
VGA_R# 7
VGA_HS#
VGA_R#
VGA_VS#7
VGA_HS#7
VGA_B# 7
VGA_VS#
VGA_SDA 10
VGA_RIN
VGA_SCL
VGA_SDA
VGA_RIN 7
VGA_SCL 10
+5V_SW
VGA_LIN
GND 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,17,18
VGA_LIN 7
MIPS_TXB 5,11,18
+5V_SW4,9,11,13,17,18
MIPS_TXB
R147 NC
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 54TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 55

10-2-14 LVDS
19790_513.eps
LVDS
B14 B14
2014-10-09
4
715G6947
LVDS
R740 NC/0R051/8W
C764
10UF 16V
PANEL_VCC_ON/OFF
PANEL_VCC_ON/OFF 10
DV33
DV33
R4108
NC/ 4K7 1/ 16W 5%
R4109
NC/ 4K7 1/ 16W 5%
HO PE 23.6 panel use
VCOM_SCL
VCOM_SDA
R4111
NC/ 100R 1/ 16W 5%
R4110
NC/ 100R 1/ 16W 5%
LVDS_BCLK-8
LVDS_B2+8
LVDS_A2-8
LVDS_ACLK-8
LVDS_A1-8
LVDS_B1+8
LVDS_B0-8
LVDS_A1+8
LVDS_B1-8
LVDS_A0+8
LVDS_B2-8
LVDS_B4+8
LVDS_B4-8
LVDS_B0+8
LVDS_A4+8
LVDS_B3+8
LVDS_A0-8
LVDS_A3+8
LVDS_A4-8
LVDS_B3-8
LVDS_A3-8
LVDS_BCLK+8
LVDS_ACLK+8
PWR5V_2 6,8
LVDS_A2+8
+5V_STB
+5V_SW
DV33SB 4,6,10,11,12,18
PWR_12V 4,13
DV33 4,5,7,10,11,12,13,14,18
+5V_SW4,9,11,13,16,18
PWR5V_1 6,8
DV15
GND 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,18
PWR5V_1
DV33SB
PWR_12V
PWR5V_2
+5V_STB 4,6
DV15 4,12
LVDS_A1+
DV33
GND
LVDS_B3-
LVDS_A2-
LVDS_BCLK+
LVDS_B4-
LVDS_B0+
LVDS_ACLK+
LVDS_B3+
LVDS_B0-
LVDS_ACLK-
LVDS_B1+
LVDS_A3+
LVDS_B4+
LVDS_B1-
LVDS_A3-
LVDS_B2+
LVDS_A0+
LVDS_B2-
LVDS_A4-
LVDS_A0-
LVDS_A2+
LVDS_BCLK-
LVDS_A1-
LVDS_A4+
LVDS_BCLK+LVDS_BCLK-LVDS_ACLK+LVDS_ACLK-
C4102
12P 50V
C4103
12P 50V
C4105
12P 50V
C4104
12P 50V
VCOM_SCL 11
VCOM_SDA 11
VCOM_SCL
VCOM_SDA
SCL_FRC
SDA_FRC
PANEL_VCC_ON/OFF
C757
100NF 25V
R768
NC/0R051/8W
Q750
AON4421
D
1
D
2
D
3
G4S
5
D
6
D
7
D
8
SI2C_SDA
PANEL_VCC_ON/OFF
H PANEL ON
L PANEL
OFF
PWR_12V+5V_SW
C758
470NF 10V
R735
0R051/8W
PANEL_VCC
Q751
MMBT3904
R771 4K7 1/16W 5%
R770
10K
PANEL_VCC
+
C772
100UF 16V
R154
0R05 OHM
R153
150K 1/16W 5%
R772
10K
R765
47K 1/16W 5%
SI2C_SCL SDA_FRC
R4221
0R
DV33
R4107
NC/ 0R 05 1/ 16W
PANEL_VCC
R4106
NC/ 100R 1/ 16W 5%
CN408
CONN
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
36
38
40
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
27
29
31
33
35
37
39
PANEL_VCC
LVDS_B3+
LVDS_B2+
LVDS_A0-
LVDS_A3-
LVDS_B3-
LVDS_B1-
LVDS_BCLK+
LVDS_B1+
LVDS_BCLK-
LVDS_B2-
LVDS_B0-
LVDS_A3+
LVDS_ACLK+
LVDS_A2+
LVDS_A0+
LVDS_ACLK-
LVDS_A2-
LVDS_A1+
LVDS_Format
LVDS_A1-
LVDS_B4+LVDS_B4-
LVDS_A4- LVDS_A4+
LVDS_B0+
R4219
0R
SCL_FRC
SI2C_SCL 11
SI2C_SDA 11
SI2C_SCL
SI2C_SDA
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 55TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 56

10-2-15 AmbiLight
19790_514.eps
Ambilight
B15 B15
2014-10-09
4
715G6947
Ambilight
FRC_RST
DV33
R641 0R
+5V_SW 4,9,11,13,16,17
DV33SB 4,6,10,11,12
+5V_SW
DV33SB
Ambi-Temp 10
Key1 10
Ambi-Temp
Key1
BL_DIMMING_912 4
BL_DIMMING_912
FRC_RST11
Bathroom SPK audio out for BUH
Key1
Ambi-Temp
AUOUT_R0
AUOUT_L0
R6350R
C613
NC/1N 50V
BATH_L_R
+12V_AL
+12V_AL
FB101
120R
1 2
PWR_12V_AL
Ambient Light Power
DV33SB
+5V_SW
IR_RC
MIPS_RXB
MIPS_TXB
IR_SSB
CN116
NC/CONN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1314
BATH_L_R
BATH_AMP_EN
PWR_ON_2
IR_SSB
IR_RC
IR_SSB10
IR_RC 10
SEL_LVDS
LR_SY NC_IN
PWM_IN
PWR_12V 4,13,17
PWM_IN 11
LDC_EN
LDC_EN 11
LR_SYNC_IN 11
AGING_EN
2D_3D_SEL
AGING_EN 11
2D_3D_SEL 11
PWR_12V
SCN_EN
SCN_EN 11
SEL_LVDS 11
DV33
GND
DV33 4,5,7,10,11,12,13,14,17
GND 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17
MIPS_RXB 5,11,16
MIPS_TXB
MIPS_RXB
AUOUT_R0 7
AUOUT_L0 7
MIPS_TXB 5,11,16
BATH_AMP_EN 10
BATH_AMP_EN
AUOUT_L0
AUOUT_R0
PWR_ON_2 4
PWR_ON_2
For BUH daughter board
C102
NC/100NF 16V
2D_3D_SEL
SEL_LVDS
AGING_EN
LR_SYNC_IN
PWM_IN
SCN_EN LDC_EN
Ambient Light C onnector
CN115
NC
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
BL_DIMMING_912 FRC_RST
C633
NC/1N 50V
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 56TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 57

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
19790_515.eps
2014-11-11
C
LAYOUT TOP
715G6947
C171
C727
C772
D501
FB108
FB109
FB110
FB203
FB208
FB210
FB211
FB441
FB442
FB445
FB446
FB447
FB601
FB602
FB603
FB604
R216
R217
X201
ZD201
ZD202
R768
R735
C718
C746
C713
C722
R721
C714
FB448
X103
C4478
C4483
C204
C1305
C243
C606
C609
C709
FB449
C730
R707
D702
FB101
C1403
C605
C607
C608
C610
C240
C1306
C149
C159
C160
C162
C239
C712
C4208
L703
L601L602L603 L604
R722
C232
C744
C745
C747
C201
C702
L1100
R703
R728
C711
C717
C4362
C723
C735
C167
C174
C4479C4480
C4481
FB443
C208
C740
C298
C764
R740
C4470
FB444
C620
C621
U401
C180
C4488
C4487
FB450
FB106
FB105
C4403
C244
C4402
C758
H5
H6
H9
CN103
CN117
CN118
CN151
CN401
CN408
CN410
CN501 CN502
CN601
D502
D503
D504
HS1
HS2
L702
Q201
Q202
Q502
Q702
Q703
R1003
R1004
R1014
R1015
R1019
R1020
R104
R105
R1101
R1102
R1103
R1104
R1105
R1106 R1107R1108
R1109
R1110
R1111
R124
R125
R126 R127R128
R129
R130
R1302
R131
R132
R135
R138
R141
R161
R164
R167
R168
R177
R180
R181
R186
R187
R188
R201
R202R203
R204
R207
R208
R209
R210
R211
R213
R214
R215
R218
R219
R220
R221
R222
R223
R224
R225
R226
R227
R315
R316
R318
R319
R320
R321
R322
R323
R325
R326
R328
R329
R331
R335
R336
R337
R338
R339
R340
R341
R342
R343
R344
R345
R346
R4019
R4029
R4106
R4107
R4161
R4162
R4163
R4164
R4165
R4166
R4169
R4170
R4201
R4202
R4203
R4206
R4207
R4211R4212
R4213R4214
R4218
R4220
R4225
R4233
R4235
R4237
R4238
R4239
R4240
R4241
R4242
R4243
R4244
R4245
R4246
R4247
R4248
R4249
R4250
R4251
R4252
R4253
R4254
R4255
R4256
R4257
R4258
R4259
R4260
R4367
R4368
R4369
R4370
R4371
R4515
R4521
R4604R4605
R503
R504
R505
R507
R509
R510
R511
R513
R514
R516
R517
R518
R520
R521
R549
R601
R602
R604
R605
R606
R607
R608
R609
R610
R611
R612
R613
R614
R615
R616
R617
R618
R619
R620
R621
R622
R623
R624
R625
R626
R627
R628
R629
R639
R631
R701
R706
R704
R705
R708
R737
R710
R712
R714
R715
R716
R717
R718
R719
R736
R724
R725
R726
R727
R730
R731
R732
R765
R770
R771
RP201 RP202
SW401
U102
U203
U405
U410
U703
ZD109
H2 H3
H4
C249
C1001
C1004
C1101
C1103 C1104 C1105C1106
C1107
C1108
C1109
C1110
C124
C125
C126
C127
C128
C130
C1301
C1303
C133
C151
C152
C153
C154
C148
C157
C165
C166
C169
C170
C172
C186 C187
C202
C203
C131
C207
C209
C210
C211
C212
C213
C214
C215
C216
C217
C218
C219
C220
C221
C222
C223
C224
C225
C226
C227
C228
C229
C230
C233
C234
C235
C236
C237
C238
C241
C242
C245
C246
C247
C248
C250
C251
C253
C255
C256C257
C297
C4026
C4161
C4201
C4204
C4206
C4207
C4461
C4462
C4463
C4464
C4465
C4466C4467
C4468
C4474
C4484
C4485
C4501
C601
C602
C603
C604
C611
C612
C632
C614
C615
C616
C617
C132
C622
C623
C624
C625
C627
C628
C629
C701
C708
C710
C716
C719
C720
C751
C715
CN101
C757
Q751
U411
R153
R4375R4365
C721
L701
C743
CN605
C146
C158
C163
C164
C175
C168
C173
C177
C613
C725 C726
C101
C76
ZD601
ZD602
ZD120
ZD121
ZD122
ZD123
ZD124
ZD125
ZD126
R4020
R501
R502
R641
R523
R635
R4363
R633
R711
R101
R103
CN159
R657
ZD461 ZD462
ZD501
ZD502
C1307
C102
C296
C4482
C703
R212
R702
R720
C4486
R634
R4376
C134
ZD101
ZD110
ZD111
R102
R109
C136
C138
R134
R137
R139
R140
R142
R143
R144
C137
H7
H8
Q701
C706
C707
CN701
C1711
L201
L202
C231
C4102
C4103
C4104
C4105
C618
C619
C736
R154
R4219
R4361
R4362
R4366
CN115
D101
C1002
C631
C724
C742
R146
R147
R630
R637
R638
U705
U702
C728
C729
L704
R709
R723
R729
Q750
R734
U3
U2
U5
U1
U4
R145
R148
H1
CN602
C176
CN116
C633
R182
R183
R4108
R4109
R4110
R4111
R4221
R632
R658
R738 R739
TU103
Q501
Q601
Q602
Q603
R4222
TU102
C4469
C155
C156
C178
C179
R133
R136
R149
R150
C135
C139
C181
C182
C183
C4471
FB102
FB103
FB104
R110
R151
R152
R155
R4372
R4373
R506
R508
C704
FB502
C184
C4209
C4210
C4211
C4212
R4374
R741
R772
R742
R733
ZD102
ZD103
U706
U202
U701
U601
U201
ZD115
ZD113
ZD114
ZD112
ZD116ZD117 ZD118
C626
ZD127ZD119
EN 57TPN16.1E LA 10.
10-2-16 SSB layout top
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 58

10-2-17 SSB layout bottom
19790_516.eps
2014-11-11
3
715G6947
Power layout bottom
TP401
TP402
TP403
TP429
TP430
TP431
TP432
TP433
TP434
TP701
TP702
TP703
TP704
TP710
TP405
TP435
TP436
TP437
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 58TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 59

10.3 J 715G8009 IR/LED Panel
20050_526.eps
IR & LED & Light Sensor
J J
2015-08-26
715G8009
IR & LED & Light Sensor
C201
1uF 10V
St andby LED
3V3SB
R204
100R 1/16W 5%
R203
NC/ 2K7 1/ 16W 5%
RC-IR
RC-IR
3V3SB
LS_SDA
LS_SCL
DVD3V3
LED201
GPSS008RC4
12
Red
DVD3V3
U221
NC/ JSA-1130
ADDR
1
VDD
2
GND3SCL
4
SDA
5
INT
6
R224
NC/ 0R 05 1/ 16W
Light Sensor
R222
NC/ 10K 1/ 16W 5%
C222 NC/ 1uF 10V
R221
NC/ 10K 1/ 16W 5%
LS_SCL
LS_SDA
R223
NC/ 0R 05 1/ 16W
JSA-1130
R223R224
JSA-1130NCNC 0R
0R
I2C addr
0x45
0x44
C221 NC/ 100N 16V
LS_SDA
LS_SCL
DVD3V3
C202
1uF 10V
IR Receiver
3V3SB
R202
1K 1/16W 5%
LED_R
Q201
BC847BW
LED_R
R201
100R 1/16W 5%
ZD201
MLVG0402
12
U201
TSOP75436TR
GND
1
VCC
2
Vout
3
GND
4
CN201
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1415
3V3SB
10-3-1 IR & LED & Light Sensor
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 59TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 60

10-3-2 IR/LED board layout
20050_527.eps
2015-08-27
715G8009
IR/LED panel
layout top/bottom
U201
CN201
R204
R202
R203
Q201
Q1
Q3
C201
C202
ZD201
U221
LED201
C221
C222
R201
R221
R222
R223
R224
Q2
Q4
Layout IR/LED panel (top side)
Layout IR/LED panel (bottom side)
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 60TPN16.1E LA 10.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
Page 61

11. Styling S heets
20100_800.eps
5211 series 24"
Pos No. Description Remarks
0030 Bezel
0040 Rear cover
0050 Stand Assy
1050 Display panel
1053 Panel SSB
1054 Power Supply Unit
1056 IR/LED panel
1077 BlueTooth Module
1176 Remote control Not displayed
1184 Speaker
FOR ELECTRICAL PARTS/ASSEMBLIES SEE WIRING DIAGRAM CHAPTER 9
1053
0030
1077
1184
0040
0050
1054
1056
1050
11.1 5211 series 24"
Styling Sheets
EN 61TPN16.1E LA 11.
2016-Mar-04
back to
div.table
 Loading...
Loading...