Page 1

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide
Upgrade Guide
Page 2

Page 3

Version Information
PGP Universal Server Upgrade Guide. PGP Universal Server Version 3.1.0. Released September 2010.
Copyright Information
Copyright © 1991-2010 by PGP Corporation. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document can be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written permission of PGP Corporation.
Trademark Information
PGP, Pretty Good Privacy, and the PGP logo are registered trademarks of PGP Corporation in the US and other countries. IDEA is a trademark of
Ascom Tech AG. Windows and ActiveX are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. AOL is a registered trademark, and AOL Instant
Messenger is a trademark, of America Online, Inc. Red Hat and Red Hat Linux are trademarks or registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc. Linux is a
registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. Solaris is a trademark or registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. AIX is a trademark or registered
trademark of International Business Machines Corporation. HP-UX is a trademark or registered trademark of Hewlett-Packard Company. SSH and
Secure Shell are trademarks of SSH Communications Security, Inc. Rendezvous and Mac OS X are trademarks or registered trademarks of Apple
Computer, Inc. All other registered and unregistered trademarks in this document are the sole property of their respective owners.
Licensing and Patent Information
The IDEA cryptographic cipher described in U.S. patent number 5,214,703 is licensed from Ascom Tech AG. The CAST-128 encryption algorithm,
implemented from RFC 2144, is available worldwide on a royalty-free basis for commercial and non-commercial uses. PGP Corporation has secured a
license to the patent rights contained in the patent application Serial Number 10/655,563 by The Regents of the University of California, entitled Block
Cipher Mode of Operation for Constructing a Wide-blocksize block Cipher from a Conventional Block Cipher. Some third-party software included in PGP
Universal Server is licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL). PGP Universal Server as a whole is not licensed under the GPL. If you would
like a copy of the source code for the GPL software included in PGP Universal Server, contact PGP Support (
may have patents and/or pending patent applications covering subject matter in this software or its documentation; the furnishing of this software or
documentation does not give you any license to these patents.
https://support.pgp.com). PGP Corporation
Acknowledgments
This product includes or may include:
-- The Zip and ZLib compression code, created by Mark Adler and Jean-Loup Gailly, is used with permission from the free Info-ZIP implementation,
developed by zlib (
under the MIT License found at
freely available high-quality data compressor, is copyrighted by Julian Seward, © 1996-2005. -- Application server (
http://www.apache.org/), Jakarta Commons (http://jakarta.apache.org/commons/license.html) and log4j, a Java-based library used to parse
server (
HTML, developed by the Apache Software Foundation. The license is at
binding framework for moving data from XML to Java programming language objects and from Java to databases, is released by the ExoLab Group
under an Apache 2.0-style license, available at
Foundation that implements the XSLT XML transformation language and the XPath XML query language, is released under the Apache Software
License, version 1.1, available at
Protocol") used for communications between various PGP products is provided under the Apache license found at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.txt. -- mx4j, an open-source implementation of the Java Management Extensions (JMX), is released
under an Apache-style license, available at
Independent JPEG Group. (
distributed under the MIT License
distributed by University of Cambridge. ©1997-2006. The license agreement is at
and Domain Name System (DNS) protocols developed and copyrighted by Internet Systems Consortium, Inc. (
implementation of daemon developed by The FreeBSD Project, © 1994-2006. -- Simple Network Management Protocol Library developed and
copyrighted by Carnegie Mellon University © 1989, 1991, 1992, Networks Associates Technology, Inc, © 2001- 2003, Cambridge Broadband Ltd. ©
2001- 2003, Sun Microsystems, Inc., © 2003, Sparta, Inc, © 2003-2006, Cisco, Inc and Information Network Center of Beijing University of Posts and
Telecommunications, © 2004. The license agreement for these is at
by Network Time Protocol and copyrighted to various contributors. -- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol developed and copyrighted by OpenLDAP
Foundation. OpenLDAP is an open-source implementation of the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). Copyright © 1999-2003, The
OpenLDAP Foundation. The license agreement is at
OpenBSD project is released by the OpenBSD Project under a BSD-style license, available at
bin/cvsweb/src/usr.bin/ssh/LICENCE?rev=HEAD. -- PC/SC Lite is a free implementation of PC/SC, a specification for SmartCard integration is released
under the BSD license. -- Postfix, an open source mail transfer agent (MTA), is released under the IBM Public License 1.0, available at
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/ibmpl.php. -- PostgreSQL, a free software object-relational database management system, is released under a
BSD-style license, available at
PostgreSQL database using standard, database independent Java code, (c) 1997-2005, PostgreSQL Global Development Group, is released under a
BSD-style license, available at
database management system, is released under a BSD-style license, available at
version of cron, a standard UNIX daemon that runs specified programs at scheduled times. Copyright © 1993, 1994 by Paul Vixie; used by permission. -
- JacORB, a Java object used to facilitate communication between processes written in Java and the data layer, is open source licensed under the
GNU Library General Public License (LGPL) available at
is an open-source implementation of a CORBA Object Request Broker (ORB), and is used for communication between processes written in C/C++ and
the data layer. Copyright (c) 1993-2006 by Douglas C. Schmidt and his research group at Washington University, University of California, Irvine, and
Vanderbilt University. The open source software license is available at
downloading files via common network services, is open source software provided under a MIT/X derivate license available at
http://curl.haxx.se/docs/copyright.html. Copyright (c) 1996 - 2007, Daniel Stenberg. -- libuuid, a library used to generate unique identifiers, is released
under a BSD-style license, available at
libpopt, a library that parses command line options, is released under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License available at
http://directory.fsf.org/libs/COPYING.DOC. Copyright © 2000-2003 Free Software Foundation, Inc. -- gSOAP, a development tool for Windows clients
to communicate with the Intel Corporation AMT chipset on a motherboard, is distributed under the gSOAP Public License version 1.3b, available at
http://www.zlib.net). -- Libxml2, the XML C parser and toolkit developed for the Gnome project and distributed and copyrighted
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html. Copyright © 2007 by the Open Source Initiative. -- bzip2 1.0, a
http://jakarta.apache.org/), web
www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.txt. -- Castor, an open-source, data-
http://www.castor.org/license.html. -- Xalan, an open-source software library from the Apache Software
http://xml.apache.org/xalan-j/#license1.1. -- Apache Axis is an implementation of the SOAP ("Simple Object Access
http://mx4j.sourceforge.net/docs/ch01s06.html. -- jpeglib version 6a is based in part on the work of the
http://www.ijg.org/) -- libxslt the XSLT C library developed for the GNOME project and used for XML transformations is
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html. -- PCRE Perl regular expression compiler, copyrighted and
http://www.pcre.org/license.txt. -- BIND Balanced Binary Tree Library
http://www.isc.org) -- Free BSD
http://net-snmp.sourceforge.net/about/license.html. -- NTP version 4.2 developed
http://www.openldap.org/software/release/license.html. Secure shell OpenSSH developed by
http://www.openbsd.org/cgi-
http://www.postgresql.org/about/licence. -- PostgreSQL JDBC driver, a free Java program used to connect to a
http://jdbc.postgresql.org/license.html. -- PostgreSQL Regular Expression Library, a free software object-relational
http://www.postgresql.org/about/licence. -- 21.vixie-cron is the Vixie
http://www.jacorb.org/lgpl.html. Copyright © 2006 The JacORB Project. -- TAO (The ACE ORB)
http://www.cs.wustl.edu/~schmidt/ACE-copying.html. -- libcURL, a library for
http://thunk.org/hg/e2fsprogs/?file/fe55db3e508c/lib/uuid/COPYING. Copyright (C) 1996, 1997 Theodore Ts'o. --
Page 4

http://www.cs.fsu.edu/~engelen/license.html. -- Windows Template Library (WTL) is used for developing user interface components and is distributed
under the Common Public License v1.0 found at
automate a variety of maintenance functions and is provided under the Perl Artistic License, found at
http://www.perl.com/pub/a/language/misc/Artistic.html. -- rEFIt - libeg, provides a graphical interface library for EFI, including image rendering, text
rendering, and alpha blending, and is distributed under the license found at
http://refit.svn.sourceforge.net/viewvc/*checkout*/refit/trunk/refit/LICENSE.txt?revision=288. Copyright (c) 2006 Christoph Pfisterer. All rights
reserved. -- Java Radius Client, used to authenticate PGP Universal Web Messenger users via Radius, is distributed under the Lesser General Public
License (LGPL) found at
Copyright (c) 2009, Yahoo! Inc. All rights reserved. Released under a BSD-style license, available at
JSON-lib version 2.2.1, a Java library used to convert Java objects to JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) objects for AJAX. Distributed under the
Apache 2.0 license, available at
available at
available at
available at
common configuration file format used on Windows, on other platforms. Distributed under the MIT License found at
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html. Copyright 2006-2008, Brodie Thiesfield. -- uSTL provides a small fast implementation of common
Standard Template Library functions and data structures and is distributed under the MIT License found at
license.html. Copyright (c) 2005-2009 by Mike Sharov <msharov@users.sourceforge.net>. -- Protocol Buffers (protobuf), Google's data interchange
format, are used to serialize structure data in the PGP SDK. Distributed under the BSD license found at
license.php. Copyright 2008 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
Additional acknowledgements and legal notices are included as part of the PGP Universal Server.
http://ezmorph.sourceforge.net/license.html. -- Apache Commons Lang, used by JSON-lib, is distributed under the Apache 2.0 license,
http://commons.apache.org/license.html. -- Apache Commons BeanUtils, used by JSON-lib, is distributed under the Apache 2.0 license,
http://commons.apache.org/license.html. -- SimpleIni is an .ini format file parser and provides the ability to read and write .ini files, a
http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html. -- Yahoo! User Interface (YUI) library version 2.5.2, a Web UI interface library for AJAX.
http://json-lib.sourceforge.net/license.html. -- EZMorph, used by JSON-lib, is distributed under the Apache 2.0 license,
http://opensource.org/licenses/cpl1.0.php. -- The Perl Kit provides several independent utilities used to
http://developer.yahoo.com/yui/license.html. --
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-
Export Information
Export of this software and documentation may be subject to compliance with the rules and regulations promulgated from time to time by the Bureau
of Export Administration, United States Department of Commerce, which restricts the export and re-export of certain products and technical data.
Limitations
The software provided with this documentation is licensed to you for your individual use under the terms of the End User License Agreement provided
with the software. The information in this document is subject to change without notice. PGP Corporation does not warrant that the information meets
your requirements or that the information is free of errors. The information may include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. Changes may be
made to the information and incorporated in new editions of this document, if and when made available by PGP Corporation.
Unsupported Third Party Products
By utilizing third party products, software, drivers, or other components ("Unsupported Third Party Product") to interact with the PGP software and/or by
utilizing any associated PGP command or code provided by to you by PGP at its sole discretion to interact with the Unsupported Third Party Product
("PGP Third Party Commands"), you acknowledge that the PGP software has not been designed for or formally tested with the Unsupported Third Party
Product, and therefore PGP provides no support or warranties with respect to the PGP Third Party Commands or the PGP software's compatibility with
Unsupported Third Party Products. THE PGP THIRD PARTY COMMANDS ARE PROVIDED "AS IS," WITH ALL FAULTS, AND THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO
SATISFACTORY QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, ACCURACY, AND EFFORT IS WITH YOU. TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE
LAW, PGP DISCLAIMS ALL REPRESENTATIONS, WARRANTIES, AND CONDITIONS, WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING ANY
WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, TITLE, NONINFRINGEMENT, QUIET
ENJOYMENT, AND ACCURACY WITH RESPECT TO THE PGP THIRD PARTY COMMANDS OR THE PGP SOFTWARE'S COMPATIBILITY WITH THE
UNSUPPORTED THIRD PARTY PRODUCT.
4
Page 5
Contents
Introduction
Who Should Read This Guide 1
Common Criteria Environments 1
Using the PGP Universal Server with the Command Line 1
Symbols 2
Getting Assistance 2
Getting product information 2
Contact Information 3
1
Upgrading the PGP Universal Server 5
Licensing the Upgrade 5
Backing Up the Data and Organization Key 6
Overview 7
Best Practices for Upgrade 10
Supported Client and PGP Universal Server Version Combinations 11
Configuring the PGP Universal Server 13
Restoring Configuration and Data 13
Migrating Groups from Version 2.x 14
Restoring Mail Policy Rules 15
Migrating a Cluster 21
Cluster Migration Overview 21
Identifying Cluster Synchronization Issues Prior to Migration 23
Accessing the PGP Universal Server using SSH 24
Migrating your Primary Cluster Server 25
Migrating a Secondary Cluster Member 27
Manually Reconfiguring Non-replicated Server Settings 28
Changing Your Web Messenger Message Replication Settings 29
Index 31
i
Page 6
Introduction
1
This Upgrade Guide describes how to upgrade PGP Universal™ Server software,
and how to migrate your data to new versions. It explains how to upgrade
previous versions of PGP Universal Server to version 3.1.0, and how to migrate
a cluster to version 3.1.0.
This section provides a high-level overview of PGP Universal Server.
Who Should Read This Guide
This Upgrade Guide is for the person or persons who will be upgrading the
software or migrating the data of your organization’s PGP Universal Server
environment. These are the PGP administrators.
Common Criteria Environments
To be Common Criteria compliant, please refer to the best practices shown in
PGP Universal Server 2.9 Common Criteria Supplemental. Note that these best
practices supersede recommendations made elsewhere in this and other
documentation.
Using the PGP Universal Server with the Command Line
Using the PGP Universal Server command line for read-only access (such as to
view settings, services, logs, processes, disk space, query the database, etc) is
supported. However, performing configuration modifications via the command
line voids your PGP Support agreement unless these procedures are followed.
Any changes made to the PGP Universal Server via the command line must be:
Authorized in writing by PGP Support.
Implemented by a PGP Partner, reseller or internal employee who is
certified in the PGP Advanced Administration and Deployment Training.
Summarized and documented in a text file in
/var/lib/ovid/customization on the PGP Universal Server itself.
1
Page 7

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Introduction
Changes made through the command line might not persist through reboots
and might be incompatible with future releases. PGP Support can require
reverting any custom configurations on the PGP Universal Server back to a
default state when troubleshooting new issues.
Symbols
Notes, Cautions, and Warnings are used in the following ways.
Note: Notes are extra, but important, information. A Note calls your attention
to important aspects of the product. You can use the product better if you
read the Notes.
Caution: Cautions indicate the possibility of loss of data or a minor security
breach. A Caution tells you about a situation where problems can occur
unless precautions are taken. Pay attention to Cautions.
Warning: Warnings indicate the possibility of significant data loss or a major
security breach. A Warning means serious problems will occur unless you
take the appropriate action. Please take Warnings very seriously.
Getting Assistance
For additional resources, see these sections.
Getting product information
The following documents and online help are companions to the PGP Universal
Server Administrator’s Guide. This guide occasionally refers to information that
can be found in one or more of these sources:
Online help is installed and is available within the PGP Universal Server
product.
PGP Universal Server Installation Guide—Describes how to install the
PGP Universal Server software.
PGP Universal Server Upgrade Guide—Describes the process of
upgrading your PGP Universal Server.
PGP Universal Mail Policy Diagram—Provides a graphical representation
of how email is processed through mail policy. You can access this
document via the PGP Universal Server online help.
Tutorials—Provides animated introductions on how to manage the mail
policy feature in PGP Universal Server 2.5 and later, and how upgraded
PGP Universal Server settings migrate into the new mail policy feature.
2
Page 8

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Introduction
You can also access all the documentation and tutorials by clicking the
online help icon in the upper-right corner of the PGP Universal Server
screen.
PGP Universal Satellite for Windows and Mac OS X include online help.
PGP Universal Server and PGP Satellite release notes are also provided,
which may have last-minute information not found in the product
documentation.
The documentation, provided as Adobe Acrobat PDF files, are available on the
Documentation (
Portal.
Once PGP Universal Server is released, additional information regarding the
product is added to the online Knowledge Base available on PGP Corporation’s
Support Portal (
https://pgp.custhelp.com/app/docs) section on the PGP Support
https://support.pgp.com).
Contact Information
Contacting Technical Support
To learn about PGP support options and how to contact PGP Technical
Support, please visit the PGP Corporation Support Home Page
https://support.pgp.com).
(
To access the PGP Support Knowledge Base or request PGP Technical
Support, please visit PGP Support Portal Web Site
https://support.pgp.com). Note that you may access portions of the
(
PGP Support Knowledge Base without a support agreement;
however, you must have a valid support agreement to request
Technical Support.
To access the PGP Support forums, please visit PGP Support
http://forum.pgp.com). These are user community support forums hosted
(
by PGP Corporation.
Contacting Customer Service
For help with orders, downloads, and licensing, please visit PGP
Corporation Customer Service (
https://pgp.custhelp.com/app/cshome).
Contacting Other Departments
For any other contacts at PGP Corporation, please visit the PGP Contacts
Page (
http://www.pgp.com/about_pgp_corporation/contact/index.html).
For general information about PGP Corporation, please visit the PGP Web
Site (
http://www.pgp.com).
3
Page 9

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Introduction
4
Page 10
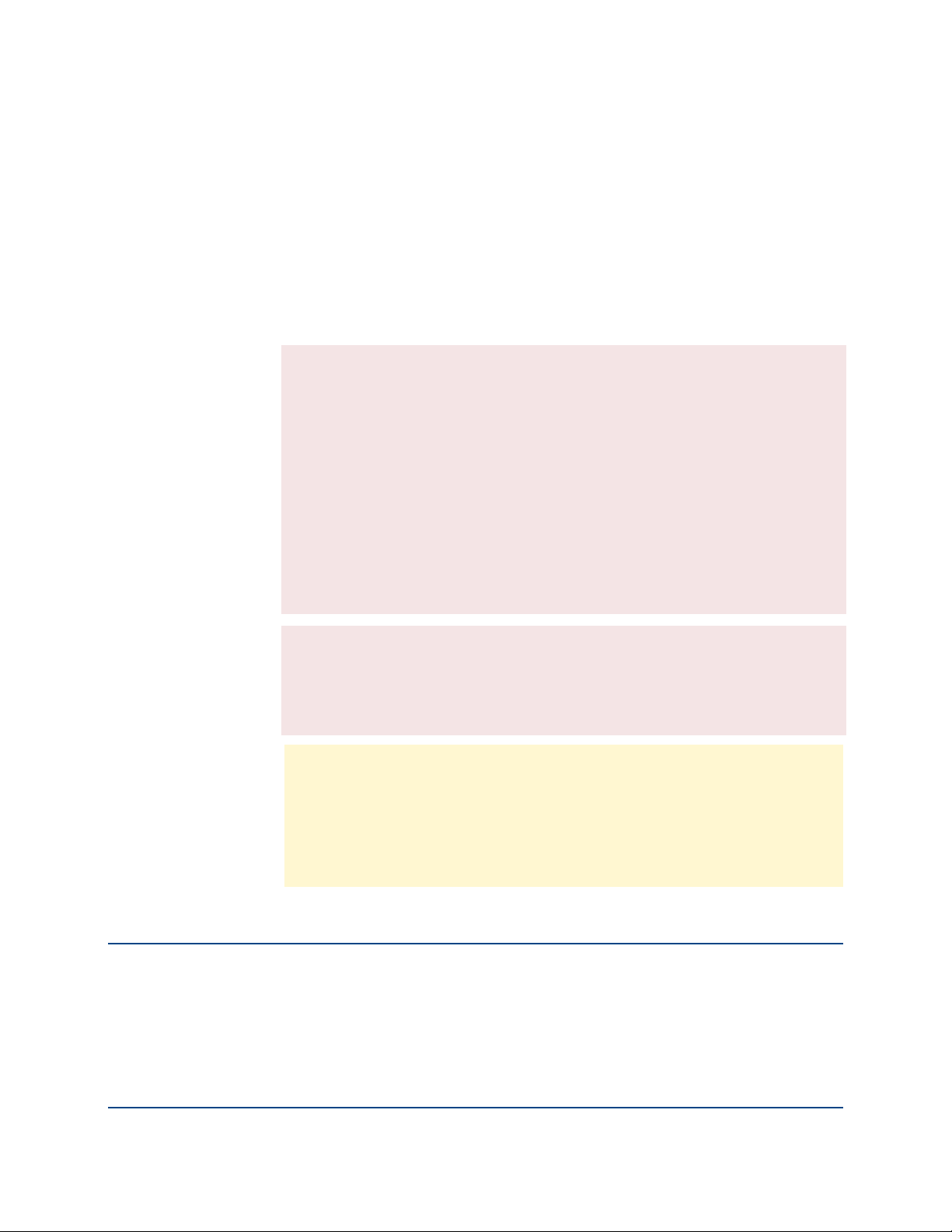
Upgrading the PGP
2
Universal Server
This chapter describes how to upgrade previous versions of PGP Universal
Server to version 3.1 for a single server.
Warning: If you have a hardware token Ignition Key or a Hardware Security
Module (HSM), you must contact PGP Technical Support before migrating to
PGP Universal Server 3.1.0. Migration to version 3.1.0 requires the creation
of a new setting on the upgraded (3.1.0) version of PGP Universal Server
before you restore the backup from your previous system. This setting can
only be added through SSH access, with the help of PGP Technical Support.
If you migrate to version 3.1.0 without adding this preference, you will be
locked out of the user interface after upgrade and you will not be able to use
your hardware token Ignition Key to unlock your PGP Universal Server.
This can also occur if you upgrade from 3.0.0 to 3.1.0 using a PUP update. If
you plan to do a PUP update from 3.0.0, you must edit the settings in your
3.0.0 installation BEFORE you do the update. You do not need to change any
settings if you are running PGP Universal Server version 3.0.1.
Warning: If you plan to migrate a cluster from PGP Universal Server version
2.x to PGP Universal Server version 3.1.0, you must run the most recent
pgpSyncUsers utility on your 2.x cluster to ensure the user data is consistent
prior to beginning the migration process. See Migrating a Cluster (on page 21)
for details.
Important: In order to successfully migrate your data from PGP Universal
Server 2.x to PGP Universal Server version 3.1.0, you should plan to have
disk space available equal to 10 times the size of the backup file (the backup
file will be significantly smaller that the size of the original 2.x database). For
example, if your version 2.x backup file is 1 GB in size, you should have 10
GB of disk space available to allow for the migration and re-expansion of your
data into the 3.1 database.
Licensing the Upgrade
The licensing mechanism for the PGP Universal Server and the managed PGP
Desktop has changed as of PGP Universal Server version 3.1. However, if you
have a valid subscription license or Perpetual 2.0 License, you will not need a
new license to use PGP Universal Server 3.1.0.
5
Page 11

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
If you had PGP Desktop licenses configured through Consumer (User) Policies,
these will continue to be valid and the appropriate features will be enabled after
you upgrade.
However, if you perform a new installation of PGP Universal Server version 3.1,
you will not be able to add your old PGP Desktop licenses through the Client
Licensing page of your Consumer Policies. You will need to restore a backup
that includes your previous licenses in order to continue to use your old PGP
Desktop licenses.
Backing Up the Data and Organization Key
Warning: Back up the Organization Key and all the data from your PGP
Universal Server before you upgrade. Make sure you back up your data to an
external location, because the software installation process will delete all data
stored on your PGP Universal Server. For more information, see the
documentation you received with your version of PGP Universal Server.
Caution: If you do not or cannot use FTP to back up your data to an external
location, contact PGP Support (PGP Corporation Support Home Page
(https://support.pgp.com)).
Export the entire keypair of the Organization Key.
1 From Organization > Organization Keys (for versions prior to 3.0) or Keys
> Organization Keys (for version 3.0 or later), select the Organization Key.
The Organization Key Info dialog appears.
2 Click Export.
The Export Key dialog appears.
3 Select Export Keypair and type the passphrase. Click Export to save the
Organization Keypair to your desktop.
4 Back up the server data and configuration to an external server location.
From System > Backups, click Backup Location.
The Backup Location dialog appears.
5 Specify the remote location where you want the data to be saved, and click
Save. It is important that you save the data somewhere other than the PGP
Universal Server itself, because all data on the PGP Universal Server will be
erased during the software installation.
The Backups page appears.
6 Click Backup Now to back up the data.
6
Page 12

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Overview
There are two methods available for upgrading a PGP Universal Server:
The migration process, where you back up data to an external location,
install the new software version from CD or DVD, and then restore your
data. Follow the instructions in the PGP Universal Server Installation Guide
to perform an installation from DVD.
The PUP update process, where you download and install a PGP Update
Package (PUP)format file from within the administrative interface of your
PGP Universal Server. This method automatically preserves your data and
system settings. For instructions on performing a PUP update, see the PGP
Universal Server Administrator's Guide.
Note: Not all upgrades are available as PUP update files. Some upgrades may
require a full migration where you to back up your system, perform a new
installation of the software, and restore your backup. The upgrade to version
3.1.0 from versions prior to 3.0 is an example.
Note: The licensing mechanism for the PGP Universal Server and the
managed PGP Desktop has changed as of PGP Universal Server version 3.1.
However, these changes have minimal effects on the upgrade process -- your
existing PGP Universal Server and PGP Desktop licenses will still be valid
after you upgrade.
If you perform a migration (where you back up your system, perform a new
installation, and then restore your backup) your previous licenses will be
restored, and all features that were previously enabled will continue to be
enabled. The same will be true if you upgrade from PGP Universal Server
3.0.0 or 3.0 1 using the PUP upgrade process.
Warning: There are special requirements for upgrading a cluster running
version 2.x software. For instructions on migrating a cluster, see Migrating a
Cluster (on page 21) in thePGP Universal Server Upgrade Guide.
The following applies to PGP Universal Servers that you will run as standalone systems.
The upgrade to PGP Universal Server version 3.1.0 from a version prior to
version 3.0.0 requires a migration: you must back up your current system, install
the upgrade from DVD, and then restore your data.
You can migrate to PGP Universal Server 3.1.0 from version 2.7.0 or later. If you
are running a version prior to 2.7.0, you must first upgrade to 2.7.0.
If you are running PGP Universal Server version 3.0.0 or later, you can use the
PUP update process to update to version 3.1.0.
7
Page 13

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Important: Before you upgrade to PGP Universal Server 3.1.0, you must
back up your data and your organization key to an external location. You will
need your organization key to restore your backed-up data.
You can migrate directly to PGP Universal Server version 3.1.0 from any of the
following previous versions:
2.7.0
2.7.1
2.7.2
2.8.0
2.8.1
2.8.2
2.8.3
2.9.0
2.9.1
2.10.0
2.12.0
2.12 R2
3.0.0
3.0.1
Note: On PGP Universal Server 3.1.0, you can only restore backed-up data from
version 2.7.0 and later. To upgrade from version 2.5.3 or 2.6.x you must first
migrate to version 2.7.0. To upgrade from a version prior to 2.5.3, you must first
upgrade to 2.5.3 and then upgrade to 2.7.0. The software installation process
deletes all data on the system. In order to migrate your existing user data and
configuration settings, you must create a backup to an external location before
upgrading, and then restore the backup to the new installation after the
upgrade. You will need both the backed-up data file and the Organization Key
used to encrypt and decrypt the backup file.
The detailed instructions for installing the software from DVD can be found in
the PGP Universal Server Installation Guide. Once the software has been
installed and the Setup Assistant has started, there are several paths you can
take through the setup, depending on how you want to restore your data.
Caution: It is not possible to upload backups of 2GB or larger through the
PGP Universal Server web interface. Contact PGP Support (PGP Corporation
Support Home Page (https://support.pgp.com)) for help restoring your data.
The following sections describe the steps required to perform an upgrade from
a previous version of PGP Universal Server for a single server that is not a
cluster member.
For instructions on migrating a cluster, see Migrating a Cluster (on page
8
21).
Page 14

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Note: As part of restoring a backup onto the 3.1.0 system, data from the
earlier version must be migrated to the new 3.1.0 database. Once the
migration completes, the system may remain busy for a time due to database
activity. This is a normal part of the upgrade process.
To migrate from a version of PGP Universal Server prior to 2.5.3:
1 Log in to your PGP Universal Server administrative interface.
2 Back up your version 2.0.x system data to an external location. (See the
PGP Universal Server Administrator's Guide for your software version for
installation, backup and restore instructions and best practices.)
3 Migrate to version 2.0.6 using the 2.0.6 CD. Restore your backed-up data.
4 Back up your version 2.0.6 data to an external location.
5 Migrate to version 2.5.0 using the 2.5.0 CD. Restore your backed-up data.
6 Go to
http://www.pgp.com/downloads/updates/index.html.
7 One at a time, download and install PUP updates for versions 2.5.1, 2.5.2,
and 2.5.3.
Note: You do not need to back up and restore data when upgrading using
a PUP file. However, it is always a good idea to have a current backup
when performing maintenance tasks on PGP Universal Server.
Note: When installing multiple PUP updates, download and install them
one at a time. If you download multiple PUP updates before you begin
installing them, only the first installation succeeds.
8 Back up your version 2.5.3 data and organization key to an external
location.
9 Migrate to version 2.7.0 and restore your backed up data.
10 Back up your version 2.7.0 data to an external location.
11 Upgrade to version 3.1.0 using the 3.1.0 DVD, following the instructions in
the PGP Universal Server Installation Guide.
12 Restore your backed-up data.
To migrate from PGP Universal Server 2.5.3 or 2.6.x:
1 Log in to your PGP Universal Server administrative interface.
2 Back up your data and organization key to an external location.
3 Migrate to version 2.7.0 and restore your backed up data.
4 Back up your version 2.7.0 data to an external location.
5 Upgrade to version 3.1.0 using the 3.1.0 DVD, following the instructions in
the PGP Universal Server Installation Guide.
6 Restore your backed-up data.
9
Page 15

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
To migrate from PGP Universal Server 2.7.0 or later
1 Log in to your PGP Universal Server administrative interface.
2 Back up your data and organization key to an external location.
3 Upgrade to version 3.1.0 using the 3.1.0 DVD, following the instructions in
the PGP Universal Server Installation Guide.
4 Restore your backed-up data.
To upgrade from PGP Universal Server 3.0 or later
1 Backup up your version 3.0 data and organization key to an external
location. (This is not required for the update, but is strongly recommended).
2 Go to
3 Download the PUP update for version 3.1.0 and copy it to the computer
4 Log in to the PGP Universal Server administrative interface.
5 Select the System tab, and then click Updates.
6 Click Upload Update Packages to upload the update package from your
7 Browse to find the file you want, then click Upload.
8 Click the icon in the Install column to install the update.
Note: You do not need to back up and restore data when upgrading using a
PUP file. However, it is always a good idea to have a current backup when
performing maintenance tasks on PGP Universal Server.
http://www.pgp.com/downloads/updates/index.html.
running PGP Universal Server version 3.0.
Note: You must have a valid maintenance agreement with PGP
Corporation to access PUP updates. For more information, see
http://www.pgp.com/products/upgrade.
hard drive.
The Upload Update dialog box appears.
The update package appears on the list.
The text in the Date of Last Action column says “Currently Installing” while
the install is in progress.
Best Practices for Upgrade
PGP Corporation recommends that you install and test the upgrade in a lab
or staging environment before integrating the upgrade into your network.
10
Page 16

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Back up the Organization Key and all the data from your PGP Universal
Server before you upgrade. Make sure you back up your data to an external
location, because the upgrade process will delete all data stored on your
PGP Universal Server. For more information, see the documentation you
received with your version of PGP Universal Server. If you do not or cannot
use FTP to back up your data to an external location, contact PGP Support
(PGP Corporation Support Home Page (
Remember to keep a copy of the installation media saved, in case you
need to revert back to the previous version.
During upgrade, the PGP Universal Server does not process email. Before
you upgrade your PGP Universal Server, make sure it has been temporarily
removed from the mailflow.
If your network includes an MTA, reconfigure the MTA to stop routing
email through the PGP Universal Server.
https://support.pgp.com)).
a If all your company’s email routes through your PGP Universal Server,
configure your MTA to halt outbound email processing.
Or
If email that matches criteria in your MTA content filter routes through
the PGP Universal Server, configure the MTA to queue email that
matches the criteria.
b Configure the MTA to queue incoming email that normally passes
through the PGP Universal Server; for example, signed and/or
encrypted email.
c Examine the PGP Universal Server log files to make sure that no email
is passing through the PGP Universal Server.
d Upgrade your PGP Universal Server and restore your user data.
e After your PGP Universal Server has been successfully upgraded,
reconfigure your MTA to resume routing email to the PGP Universal
Server.
Note: You can find more information online about moving to PGP Universal
Server 3.1.0 at the PGP Corporation website (http://www.pgp.com).
Supported Client and PGP Universal Server Version Combinations
PGP Corporation supports backward compatibility for clients only. For example,
PGP Universal Server 2.0 is not supported for use with PGP Desktop 9.9.
PGP Universal Server 3.1.0 supports managing policy of these versions (and
subsequent maintenance releases of each) of PGP Desktop:
9.5.3
9.6.3
9.7.1
11
Page 17

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
9.8.2
9.9.0
9.10
9.12
10.0.0
10.0.1
10.0.2
10.1.0
Note: For the most current information on which client versions are
supported, see the Knowledge Base.
Note: There are certain features of PGP Desktop version 10.1 that may
require the addition of preference settings in PGP Universal Server to change
the default behavior or to enable new features. For information on the
features that require additional preferences, and for instructions on how to
add these preferences, see Knowledge Base Article 2212
http://support.pgp.com/?faq=2212.
PGP Universal Server 3.1.0 supports managing policy of these versions (and
subsequent maintenance releases of each) of PGP Universal Satellite:
2.5.3
2.6.3
2.7.1
2.8.2
2.9.0
2.10
2.12
3.0
3.0.1
3.1.0
Note: Policy options for features that are non-existent in supported legacy
versions are ignored by those installations.
PGP Universal Server 3.1.0 provides limited management support (without
policy) back to PGP Desktop version 9.0 and PGP Universal Satellite version 2.0.
12
Page 18

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Configuring the PGP Universal Server
Now that you have the data from the previous version saved, it can be brought
into a PGP Universal Server during configuration using the Setup Assistant.
This procedure describes how to upgrade to the latest version of the software
and restore all the data and configuration information to the PGP Universal
Server.
To upgrade and restore your data and configuration information:
1 Install the upgrade software as described in the PGP Universal Server
Installation Guide.
2 Begin configuration of the PGP Universal Server using the Setup Assistant.
In the Setup Assistant, you can elect to perform a New Installation, or you
can restore your back-up configuration and data as part of the process. If
you elect to perform a new installation you can restore your backup later
through the PGP Universal Server administrative interface.
For more information on using the Setup Assistant to configure the PGP
Universal Server as a new installation, see the PGP Universal Server
Installation Guide.
For instructions on restoring your backed up configuration and data using
the Setup Assistant, follow the instructions in Restoring Configuration and
Data (on page
13).
Restoring Configuration and Data
To restore backed-up data during the installation of the server:
1 Access the Setup Assistant for the new server.
2 On the Welcome page, read the text and then click Forward.
The End User License Agreement page appears.
3 Read the text, click I Agree at the end, then click Forward.
The Setup Type page appears.
4 Select Restore, then click Forward.
The Import Organization Key page appears.
5 Upload a file containing your Organization Key, then click Forward.
The Upload Current Backup File page appears.
13
Page 19

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
6 Click Choose File, select the backup file from which you want to restore,
then click OK. When the Upload Current Backup File page appears again,
click Forward.
Caution: It is not possible to upload backups of 2GB or larger through the
PGP Universal Server web interface. Contact PGP Support (PGP
Corporation Support Home Page (https://support.pgp.com)) for help
restoring your data.
The backup will install.
When installation is complete, the Network Configuration Changed page
appears and the server restarts automatically. You can also check the
update or migration logs for the message "Database migration check
completed."
You will be redirected to the PGP Universal Server administrative interface.
The server is configured with the settings from the backup file you
selected.
Your PGP Desktop license(s) have been restored along with the appropriate
Consumer Policy setting. If your existing PGP Desktop licenses are valid
and provide the features you need, there is no need to change to the new
default PGP Desktop client license.
Your mail policy and proxy settings have been reproduced in the new mail
policy feature. For more information on mail policy and reproducing your
previous settings, see Migrating Groups from Version 2.x (on page
Restoring Mail Policy Rules (on page
Administrator’s Guide.
7 Continue setting up the PGP Universal Server. For more information on
configuring the PGP Universal Server after the Setup Assistant is complete,
see the PGP Universal Server Administrator's Guide.
Note: The new software version is running in Learn Mode.
Migrating Groups from Version 2.x
Caution: After migrating from a previous version of PGP Universal Server,
you must make sure that the groups are in the correct priority order. If groups
are prioritized in the wrong order, users will not receive the correct policy
settings.
In PGP Universal Server versions 2.12 and earlier, if a user could be matched to
more than one user policy, then the user received the policy with the name that
came first in alphabetical order. Administrators could not change this ordering.
In PGP Universal Server 3.1, because users can belong to more than one group,
you must make sure that the policies are ranked correctly.
14),
15), and the PGP Universal Server
14
Page 20

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Restoring Mail Policy Rules
In PGP Universal Server version 3.1, new actions are available for use in mail
policy chains. The Outbound policy chain has been enhanced to include three
new rules:
Sign + Encrypt Buttons: a rule that takes effect when the user selects
both the sign and encrypt plug-in buttons.
Sign Button: a rule that takes effect when the user selects the sign plug-in
button.
Encrypt Button: a rule that takes effect when the user selects the encrypt
plug-in button.
However, when you restore your data from a previous release, the Outbound
policy chain definition is overwritten with the backed-up Outbound policy chain,
and these three rules are missing from the policy chain. Therefore, you must
manually add these three rules back into the Outbound policy chain.
To add these rules back to the Outbound policy chain, perform the following
steps.
Add the Sign+Encrypt Buttons rule
1 From the PGP Universal Server administrative interface, go to the Mail >
Mail Policy page, and click on the Outbound policy chain.
The Outbound policy chain details page appears.
2 Click Add Rule... to go to the Add Rule page.
3 Type "Sign + Encrypt Buttons" in the Rule Name field.
4 Type "User selects both sign and encrypt plugiin buttons." in the
Description field.
5 Under the Conditions tab, set the following:
Condition statement: leave If all the following are true selected.
Fill in the first condition row so that it contains the following:
Message header X-PGP-Sign-Button contains selected
Click Add Condition and fill in the second condition row so that it
contains the following:
Message header X-PGP-Encrypt-Button contains selected
15
Page 21

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Your conditions dialog should look like the following example.
6 Under the Actions tab, set the following:
Action: select Send (encrypted/signed)
Under Encrypt to: check Recipient's key and Require verified key.
Check Sign.
Your action dialog should look like the following example.
7 Under the Key Search tab, set the following:
Check Search for keys in additional locations:
From the drop-down menu select Keyserver of sender or recipient
address, then add PGP Global Directory.
Make sure that the Keyserver of sender or recipient address is first in
the list, followed by the PGP Global Directory. (To change the order,
select the correct number from the drop-down list to the left of the row,
and the rows will automatically renumber.)
16
Page 22

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Your Key Search dialog should look like the following example.
8 Click Save to save the rule. You are returned to the Outbound policy details
page where your new rule has been added to the end of the policy chain.
9 Change the number of your new Sign + Encrypt Buttons rule to be
number 10 in the list, following the Always Encrypt Sensitive Messages
rule, but before the Application is Server rule. When you change the rule
number, the rules will re-order automatically.
Add the Sign Button rule
1 From the PGP Universal Server administrative interface, go to the Mail >
Mail Policy page, and click on the Outbound policy chain, and click Add
Rule... to go to the Add Rule page.
2 Type "Sign Button" in the Rule Name field.
3 Type "User selects sign plug-in button." in the Description field.
4 Under the Conditions tab, set the following:
Condition statement: leave If all the following are true selected.
Fill in the first condition row so that it contains the following:
Message header X-PGP-Sign-Button contains selected
Your conditions dialog should look like the following example.
5 Under the Actions tab, set the following:
Action: select Send (encrypted/signed).
Check Sign.
17
Page 23

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Your action dialog should look like the following example.
6 You do not need to make any changes to the Key Search tab.
7 Click Save to save the rule. You are returned to the Outbound policy details
page where your new rule has been added to the end of the policy chain.
8 Change the number of your new Sign Button rule to be number 11 in the
list, following the Sign + Encrypt Buttons rule, but before the Application
is Server rule.
Add the Encrypt Button rule
1 From the PGP Universal Server administrative interface, go to the Mail >
Mail Policy page, and click on the Outbound policy chain, and click Add
Rule... to go to the Add Rule page.
2 Type "Encrypt Button" in the Rule Name field.
3 Type "User selects encrypt plug-in button." in the Description field.
4 Under the Conditions tab, set the following:
Condition statement: leave If all the following are true selected.
Fill in the first condition row so that it contains the following:
Message header X-PGP-Encrypt-Button contains selected
Your conditions dialog should look like the following example.
5 Under the Actions tab, set the following:
18
Page 24

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Action: select Send (encrypted/signed)
Under Encrypt to: check Recipient's key and Require verified key.
Your action dialog should look like the following example.
6 Under the Key Search tab, set the following:
Check Search for keys in additional locations:
From the drop-down menu select Keyserver of sender or recipient
address, then add PGP Global Directory.
Make sure that the Keyserver of sender or recipient address is first in
the list, followed by the PGP Global Directory.
Your Key Search dialog should look like the following example.
7 Click Save to save the rule. You are returned to the Outbound policy details
page where your new rule has been added to the end of the policy chain.
8 Change the number of your new Encrypt Button rule to be number 12 in
the list, following the Sign Button rule, but before the Application is
Server rule.
19
Page 25

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Upgrading the PGP Universal Server
Your Outbound policy chain is now updated to restore the rules added for PGP
Universal Server version 3.1. It should look like the following example:
20
Page 26

Migrating a Cluster
3
This chapter describes how to upgrade a PGP Universal Server cluster to
version 3.1.0 from a cluster prior to version 3.0.
For an overview of clustering in PGP Universal Server version 3.1, see the
chapter "Clustering your PGP Universal Servers" in the PGP Universal Server
Administrator's Guide.
Important: Before you install any new software on any of your cluster
members, you must run the pgpSyncUsers utility on your version 2.x PGP
Universal Server Primary cluster member to ensure there are not data
inconsistencies between your primary and secondary servers.
Inconsistencies may cause user data to be migrated incorrectly.
Cluster Migration Overview
For the most part, all members of a cluster share the same database and
configuration information -- changes on one are replicated to all the other cluster
members. The cluster migration process preserves this relationship
Your Primary server must be migrated first. As part of the backup restoration
process, the Primary's 2.x data is migrated into the version 3.1 database. The
former primary then acts as the sponsoring server for the other cluster
members, and its data is replicated to each cluster member as it is joined to the
new 3.1.0 cluster. The join process also attempts a limited automatic
reconciliation of any data that already exists on the joining server. In the case of
Web Messenger running in Home Server mode, the Web Messenger data is
migrated individually on the each cluster member, and is not replicated to other
cluster members.
If there are inconsistencies or conflicts in the data between the 2.x Primary and
its secondary servers, the migration process may not be able to reconcile those
inconsistencies. Therefore PGP has provided a utility, pgpSyncUsers, that will
identify data inconsistencies between your Primary and Secondary cluster
members.
This pgpSyncUsers utility must be run on your 2.x cluster prior to
beginning the migration to PGP Universal Server 3.1.0. For instructions on
obtaining and using the pgpSyncUsers utility, see Knowledge Base Article 2089
http://support.pgp.com/?faq=2089) available on the PGP Support Home Page
(
(
https://support.pgp.com).
21
Page 27

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Migrating a Cluster
IMPORTANT: If you have made customizations to your PGP Universal Server
configuration (or had customization done by PGP's Professional Services
Organization) it may be necessary to perform those customizations again
after you have migrated your cluster. Please contact PGP Technical Support
for help before you begin your migration.
Cluster Migration Requirements
All members of a PGP Universal Server cluster must be running the same
software version. Member servers do not share the software upgrade; you
must migrate each server individually.
To upgrade a cluster successfully, you must be running PGP Universal Server
version 2.10.0 or later. If you are running an earlier version, you will need to
upgrade the PGP Universal Server software on each server.
The Primary server must be upgraded and restored first, and it must act as the
sponsor for the other servers joining the cluster. You should upgrade all the
members of the cluster at the same time. However, email will not move
through your network if you have all the servers down at the same time. See
the discussion about temporarily stopping the mailflow in Best Practices for
Upgrade (on page
10).
IMPORTANT: You must run the pgpSyncUsers utility on your version 2.10 or
2.12 cluster in order to indentify and correct data inconsistencies between
your Primary and Secondary servers prior to beginning the migration.
Summary of the Cluster Migration Process
The basic process for upgrading a cluster is summarized in the following steps,
and is described in more detail in the following sections.
1 Insure that your PGP Universal Server cluster members are running PGP
Universal Server version 2.10 or later. If not, upgrade to version 2.12.
2 Download, install, and run the pgpSyncUsers utility to identify any data that
may not be consistent between you primary and secondary cluster
members. Data that is out of sync may not migrate correctly to version
3.1.0. For detailed instructions, see Identifying Cluster Synchronization
Issues Prior to Migration (on page
3 Back up ALL cluster members to an external location (the upgrade process
deletes all data stored on the PGP Universal Server). For detailed
information on backing up your PGP Universal Servers, including their
Organization Keys, see Backing Up the Data and Organization Key (on page
6).
4 Install the 3.1.0 software on your Primary, following the instructions in
Upgrade Steps (on page
restore its backup. This server becomes the sponsoring server for
recreating the cluster.
8) for your PGP Universal Server version, and
23).
22
Page 28

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Migrating a Cluster
When the restore has completed, the former secondaries are listed as
"pending" cluster members in the System > Clustering page of the former
Primary's administrative interface.
5 Install the 3.1.0 software on each of the secondaries.
6 Restore each secondary's backup (the backups you took in Step 3) before
you join the secondaries to the new cluster.
DO NOT use the Cluster Member option in the Setup Assistant.
Note: If you were running PGP Universal Web Messenger in your cluster
in High Availability mode, and the pgpSyncUsers utility did not identify any
data inconsistencies, you may be able to skip the data restoration step.
See Manually Reconfiguring Non-replicated Server Settings (on page 28)
for more information.
7 On the former secondary (after the restore of the backup), go to the
System > Clustering page in PGP Universal Server's administrative
interface, and request a Join to the cluster, providing the IP address of the
former Primary as the sponsoring server.
8 From the sponsoring server's administrative interface, after the secondary
has requested a join and is in a waiting state, go to the System >
Clustering page and click the Contact button next to the secondary's
name in the list of pending cluster members. This initiates the join and the
data replication process.
Note: Detailed instructions on migrating your Primary and Secondary cluster
members are provided in Migrating your Primary Cluster Server (on page 25)
and Migrating a Secondary Cluster Member (on page 27).
When the cluster migration is complete, all cluster members will have the same
(replicated) database and many of the same configuration settings. In a cluster
from version 3.0 onwards, all cluster members act as peers, where every server
in a cluster can serve all types of requests, and any server can initiate persistent
changes.
Note: When you restore your data from a release earlier than version 3.0,
some of the rules in the Outbound mail policy are lost. You must re-enter
those rules manually, following the instructions in Restoring Mail Policy Rules
(on page 15). Since Mail Policies are global, you only need to do this on one
server in the cluster; you can do this on the sponsoring server before you join
the other cluster members, or you can do it on any cluster member after it
has been joined to the cluster.
Identifying Cluster Synchronization Issues Prior to Migration
Prior to migrating a PGP Universal Server cluster to version 3.1.0 you must run
the pgpSyncUsers utility on the Primary of your 2.x cluster to determine if there
are inconsistencies in the data between your Primary and Secondary servers.
23
Page 29

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Migrating a Cluster
If the utility identifies data consistency or other data problems, please contact
PGP Technical Support prior to beginning your cluster migration. The migration
process may not be able to reconcile data inconsistencies, and in some cases
inconsistent data from a Secondary may be lost.
For instructions on obtaining and using the pgpSyncUsers utility, see
Knowledge Base Article 2089 (
on the PGP Support Home Page (
Your PGP Universal Server 2.x cluster must be running PGP Universal
Server version 2.10 or 2.12. If you running a version earlier than 2.10, it is
recommended you upgrade to 2.12.
To install and run the pgpSyncUsers utility you must have command line
access via SSH to your PGP Universal Server cluster Primary server. See
Accessing the PGP Universal Server using SSH (UN) (see "
PGP Universal Server using SSH" on page
SSH access to your Primary server.
If the pgpSyncUsers utility identifies inconsistencies in user data, you can
use the utility to synchronize that user data across your cluster members. If
the utility detects other problems, contact PGP Technical Support for help.
http://support.pgp.com/?faq=2089) available
https://support.pgp.com).
Accessing the
24) for information on setting up
To access the PGP Support Knowledge Base or request PGP Technical
Support, please visit PGP Support Portal Web Site
(
https://support.pgp.com).
Accessing the PGP Universal Server using SSH
To gain command line access to a PGP Universal Server, you will need to create
an SSHv2 key, and add it to the superuser administrator account on the PGP
Universal Server. You can do this using a utility such as PuTTYgen to create an
SSHv2 key, and PuTTY to log in to the command line interface. You add the
SSHv2 key to your superuser administrator account through the PGP Universal
Server administrative interface.
Many SSH utilities can be used to gain command line access. PuTTY is a free
suite of SSH tools. The PuTTY suite includes PuTTYgen, PuTTY, PSFTP, and
Pageant the PuTTY authentication agent. The PuTTYgen and PuTTY.exe files are
also available to be downloaded separately from many Internet software
repositories.
For detailed instructions on setting up command line access to the PGP
Universal Server, see PGP KB article 1840
https://pgp.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/1840), available on the PGP
(
Support Knowledge Base (
To access the PGP Support Knowledge Base or request PGP Technical Support,
please visit PGP Support Portal Web Site (
you may access portions of the PGP Support Knowledge Base
(
http://support.pgp.com) without a support agreement; however, you must have
a valid support agreement to request Technical Support.
http://support.pgp.com).
https://support.pgp.com). Note that
24
Page 30

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Migrating a Cluster
Migrating your Primary Cluster Server
The steps to migrate your cluster Primary are:
1 Insure that your PGP Universal Server cluster members are running PGP
Universal Server version 2.10 or later. If not, upgrade to version 2.12.
2 Download, install, and run the pgpSyncUsers utility to identify any data that
may not be consistent between you primary and secondary cluster
members. Data that is out of sync may not migrate correctly to version
3.1.0. For detailed instructions, see Knowledge Base Article 2089
http://support.pgp.com/?faq=2089).
(
3 Back up your Primary PGP Universal Server, including the Organization Key,
to an external location. The upgrade process will delete all data on the PGP
Universal Server. For detailed information see Backing Up the Data and
Organization Key (on page
Warning: Make sure you perform the backup after you have identified
and corrected any data synchronization problems within your 2.x clusters
by running the pgpSyncUsers utility.
6).
4 Migrate your Primary to PGP Universal Server version 3.1.0, following the
instructions in Upgrade Steps (on page
Detailed instructions for installing the 3.1.0 software and running the Setup
Assistant are found in the PGP Universal Server Installation Guide.
When you get to the Setup Assistant, you can use either the New
Installation option or the Restore option.
Do not select the Cluster Member option for your Primary.
5 If you used the New Installation option in the Setup Assistant, restore the
backup onto the former Primary from the PGP Universal Server
administrative interface (under System > Backups).
After the restore has finished, the former secondaries appear as Pending
cluster members on the former Primary's System > Clustering page. A
Contact button appears next to each pending member in the list.
Your former secondaries will appear as Pending cluster members until they
have been rejoined to the cluster. The join action must be requested by
each former secondary. The Contact button will not have an effect until
the former secondary has been migrated and has requested a join to the
cluster.
8).
25
Page 31

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Migrating a Cluster
Note: In order for the sponsoring server to successfully contact the
joining server, the hostname and IP address of the joining server must be
resolvable via DNS. If not, the sponsoring server will not be able to
contact the joiner, and the join will not succeed. If your cluster members
do not have DNS resolvable hostnames, contact PGP Technical Support
for help.
6 Once a secondary has been migrated to version 3.1.0 and has requested a
join, go to the System > Clustering page in the sponsoring server's
administrative interface, and click the Contact button next to the
secondary that is joining the cluster.
The joining cluster member's status changes from "Pending" to
"Replicating" when the Contact button is clicked.
This initiates the actual join process, which involves replicating data from
the sponsor to the new cluster member. The configuration settings for the
PGP Universal Server you are installing as a cluster member (including
administrator login and password, primary domain, and ignition key (if any))
are replicated from the sponsoring server.
The join process also performs a reconciliation of data that may have
existed uniquely on the former secondary. In particular, if your cluster was
previously running PGP Universal Web Messenger in Home Server mode,
the join process migrates all Web Messenger data that was kept uniquely
on the secondary.
Note: If the database on the sponsoring server in a cluster has a very
large database, the join of a cluster member may take a very long time. To
avoid a join failure it may be necessary to increase the join timeout value
setting prior to initiating the join. This setting can only be modified
through SSH access, with the help of PGP Technical Support.
Note: PGP Universal Server 3.1 allows you to specify whether a cluster
member is located in your DMZ, and whether it should be allowed to host
private keys for internal users. When you migrate a secondary from an earlier
release, it is migrated with the default settings: not located in the DMZ, and
allowed to host private keys. You can change these settings through the Edit
Member page, accessed by clicking the cluster member name on the
System > Clustering page.
Note: Remember to restore your Outbound Mail Policy following the
instructions in Restoring Mail Policy Rules (on page 15) on one of the servers
in your cluster. You can do this on any cluster member after it has been
joined to the cluster, and the changes will be replicated to the other cluster
members.
26
Page 32

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Migrating a Cluster
Migrating a Secondary Cluster Member
1 Back up each of your secondary servers, including their Organization Keys,
to an external location. For detailed information see Backing Up the Data
and Organization Key (on page
Warning: Make sure you perform the backups after you have identified
and corrected any data synchronization problems within your 2.x clusters
by running the pgpSyncUsers utility.
2 Migrate your secondary server to PGP Universal Server version 3.1.0,
following the appropriate instructions in Upgrade Steps (on page
Detailed instructions on installing the 3.1.0 software and running the Setup
Assistant are found in the PGP Universal Server Installation Guide.
3 Restore the backup. You can use the Restore option in the Setup Assistant
to do this.
As an alternative, you can use the New Installation option in the Setup
Assistant, and restore the backup from the PGP Universal Server
administrative interface (under System > Backups).
6).
8).
There are several configuration settings that are not replicated from the
sponsor, including the network settings, server SSL/TLS certificates, mail
routes, and mail proxies. In addition, your log files are not preserved
through the migration process. Restoring the backup restores all of these.
Note: Restoring the backup to a secondary may not be necessary under
certain conditions:
- You are not running PGP Universal Web Messenger in Home Server
mode, or Web Messenger was not running on this server.
- The pgpSyncUsers utility did not identify any data inconsistencies
between your cluster members.
- You do not need to preserve server-specific settings for mail routes,
mail proxies, or external LDAP servers.
- You do not need to restore the SSL/TSL certificate for this secondary
server.
See the discussion in Manually Reconfiguring Non-replicated Server
Settings (on page 28) for more information.
4 After the restore operation has completed, log in to the administrative
interface on the former secondary, go to the System > Clustering page,
and click Join Cluster.... Enter the hostname or IP address of the
sponsoring server (the former Primary) and click Save.
After a warning, the joining server is put into a wait state until contact is
initiated from the sponsoring server. You can cancel the join process by
clicking the Cancel button.
27
Page 33

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Migrating a Cluster
5 After the joining server is in its Wait state, the sponsoring server can
initiate the actual join and data replication process.
From the sponsoring server's administrative interface, go to the System >
Clustering page and click the Contact button next to the secondary that is
waiting for the join to proceed.
6 On the joining (former secondary) server, when contact is received from
the sponsoring PGP Universal Server the Waiting message is replaced by
the Replicating Cluster Data page. A progress bar shows the progress of
the data replication process.
Repeat these steps to migrate and rejoin all your former secondaries to the
version 3.1.0 cluster. Use the former Primary as the sponsoring server in all
cases.
Manually Reconfiguring Non-replicated Server Settings
If you do not plan to restore the backup onto a secondary, but would like to
preserve certain non-replicated settings, you can individually restore those
settings after you have migrated to the 3.1.0 software.
Note: In all cases you should back up the data from every individual cluster
member to an external location. However, you may choose not to restore the
secondary backups, and rely on the data replicated from your Primary server
if you do not have individual settings for your secondary cluster members.
Saving selected non-replicated settings:
Export or note the following, as appropriate to your installation.
1 Export your server SSL/TLS certificates:
On each secondary, go to the System > Network page, and click
Certificates... at the bottom of the dialog.
Select the certificate you want to export; the Certificate Info page
appears.
Click Export to export the certificate as a PKCS#12 file.
If you have multiple certificates, you should export all of them.
2 Note the settings of your mail routes and proxies; you will need to re-
configure these on the secondary after you have installed the 3.1.0
software.
3 If you want to save your logs separately from the full backup, export them
to an external location:
In the administrative interface, go to the Reporting > Logs page and
click the Export Logs... button at the bottom of the page.
28
Page 34

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Migrating a Cluster
Restoring your selected non-replicated settings.
After you have installed and configured the PGP Universal Server 3.1.0 software
on your former secondary, BEFORE you join this server to the new 3.1.0
cluster, restore your certificates, mail route and mail proxy configurations.
It is not possible to restore your log files manually, you must restore the full
backup if you want to restore the log files to a secondary.
1 If your Secondary used a different SSL/TLS certificate from the former
Primary, import the certificate you exported in Step 1 above:
a When the replication has completed, log in to the cluster member's
administrative interface,
b Go to the System > Network page, and click Certificates... at the
bottom of the dialog.
c Click Add Certificates...; the New SSL/TLS Certificate dialog appears.
d Click Import... to go to the Import SSL/TLS Certificate page, where
you can import your saved PKCS#12 file.
2 From the cluster member's administrative interface, configure the
appropriate mail routes and mail proxies.
To configure a mail route, go to the Mail > Mail Routes page, and
click Add Mail Route.... For detailed instructions, see "Specifying Mail
Routes" in the PGP Universal Server Administrator's Guide.
To configure a mail proxy or proxies, go to the Mail > Mail Proxies
page, and click Add Proxy.... For detailed instructions, see
"Configuring Mail Proxies" in the PGP Universal Server Administrator's
Guide.
Changing Your Web Messenger Message Replication Settings
In PGP Universal Server version 3.1, if you are running PGP Universal Web
Messenger in a cluster, you can control how Web Messenger message
replication is handled. As in previous PGP Universal Server versions, you can
have Web Messenger messages replicated to all cluster members (as in the
former High Availability mode), or not replicated (as in the former Home Server
mode). In addition, you can now choose to have Web Messenger messages
replicated only to a subset of servers that are running Web Messenger. This
enables you to take advantage of the PGP Universal Server replication services
without incurring the costs of replicating to all Web Messenger servers in the
cluster. For example, if you have four servers running Web Messenger, you can
elect to have messages replicated only to two of the four servers.
29
Page 35

PGP Universal™ Server Upgrade Guide Migrating a Cluster
When the cluster migration from a version 2.x cluster is complete, Web
Messenger message replication will be Off if your 2.x cluster was running in
Home Server mode. If the cluster was running in High Availability mode,
message replication will be set to All.
To change the message replication settings, go to the Services > Web
Messenger page, select the Options tab and click Edit.... You can do this from
the administrative interface of any of the cluster members - the message
replication setting is global.
30
Page 36

Index
B
backups
upgrading software version • 6
best practices • 10
L
Learn Mode
software upgrades • 13
M
mail policy
migrating clusters • 21
reproducing proxy settings • 21
upgrading previous versions • 21
migration
mail policy • 21
proxy settings • 21
MTA • 10
O
Organization Key
upgrading software version • 6
U
upgrading
backing up and restoring data • 6
backing up Organization Key • 6
best practices • 10
clusters • 21
configuring the PGP Universal Server • 13
from version 2.0.6 • 7
from versions before 2.0.6 • 7
Learn Mode • 13
license requirement • 5, 13
MTA • 10
overview • 7
restoring configuration and data • 13
Setup Assistant • 13
V
version compatibility • 11
P
proxies
setting migration • 21
R
restoring
data and configuration during upgrade • 13
S
Setup Assistant
restoring from a server backup • 13
31
 Loading...
Loading...