Page 1

User Guide
PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1
02_104P 4.4 SR1 User Guide
Page 2

- 2 -
Page 3

Notices
Version Information
PGP Endpoint Application Control User Guide - PGP Endpoint Application Control Version 4.4 SR1 Released: August 2009
Document Number: 02_104P_4.4 SR1_092391106
Copyright Information
Copyright© 1991-2009 by PGP Corporation. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document can be
reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without
the express written permission of PGP Corporation.
Trademark Information
PGP, Pretty Good Privacy, and the PGP logo are registered trademarks of PGP Corporation in the
US and other countries. IDEA is a trademark of Ascom Tech AG. Windows and ActiveX are registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. AOL is a registered trademark, and AOL Instant Messenger is a
trademark, of America Online, Inc. Red Hat and Red Hat Linux are trademarks or registered trademarks
of Red Hat, Inc. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. Solaris is a trademark or registered
trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. AIX is a trademark or registered trademark of International Business
Machines Corporation. HP-UX is a trademark or registered trademark of Hewlett-Packard Company. SSH
and Secure Shell are trademarks of SSH Communications Security, Inc. Rendezvous and Mac OS X
are trademarks or registered trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc. All other registered and unregistered
trademarks in this document are the sole property of their respective owners.
Licensing and Patent Information
The IDEA cryptographic cipher described in U.S. patent number 5,214,703 is licensed from Ascom Tech
AG. The CAST-128 encryption algorithm, implemented from RFC 2144, is available worldwide on a royaltyfree basis for commercial and non-commercial uses. PGP Corporation has secured a license to the patent
rights contained in the patent application Serial Number 10/655,563 by The Regents of the University of
California, entitled Block Cipher Mode of Operation for Constructing a Wide-blocksize block Cipher from a
Conventional Block Cipher. Some third-party software included in PGP Universal Server is licensed under
the GNU General Public License (GPL). PGP Universal Server as a whole is not licensed under the GPL.
If you would like a copy of the source code for the GPL software included in PGP Universal Server, contact
PGP Support (http://www.pgp.com/support). PGP Corporation may have patents and/or pending patent
applications covering subject matter in this software or its documentation; the furnishing of this software or
documentation does not give you any license to these patents.
Acknowledgements
This product includes or may include:
• The Zip and ZLib compression code, created by Mark Adler and Jean-Loup Gailly, is used with
permission from the free Info-ZIP implementation, developed by zlib (http://www.zlib.net). • Libxml2,
the XML C parser and toolkit developed for the Gnome project and distributed and copyrighted under
the MIT License found at http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html. Copyright © 2007 by
the Open Source Initiative. • bzip2 1.0, a freely available high-quality data compressor, is copyrighted
- 3 -
Page 4

PGP Endpoint Application Control
by Julian Seward, © 1996-2005. • Application server (http://jakarta.apache.org/), web server (http://
www.apache.org/), Jakarta Commons (http://jakarta.apache.org/commons/license.html) and log4j, a
Java-based library used to parse HTML, developed by the Apache Software Foundation. The license
is at www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.txt. • Castor, an open-source, databinding framework for
moving data from XML to Java programming language objects and from Java to databases, is released
by the ExoLab Group under an Apache 2.0-style license, available at http://www.castor.org/license.html.
• Xalan, an open-source software library from the Apache Software Foundation that implements the
XSLT XML transformation language and the XPath XML query language, is released under the Apache
Software License, version 1.1, available at http://xml.apache.org/xalan-j/#license1.1. • Apache Axis is
an implementation of the SOAP (“Simple Object Access Protocol”) used for communications between
various PGP products is provided under the Apache license found at http://www.apache.org/licenses/
LICENSE-2.0.txt. • mx4j, an open-source implementation of the Java Management Extensions (JMX),
is released under an Apache-style license, available at http://mx4j.sourceforge.net/docs/ch01s06.html.
• jpeglib version 6a is based in part on the work of the Independent JPEG Group. (http://www.ijg.org/)
• libxslt the XSLT C library developed for the GNOME project and used for XML transformations is
distributed under the MIT License http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html. • PCRE version
4.5 Perl regular expression compiler, copyrighted and distributed by University of Cambridge. ©1997-2006.
The license agreement is at http://www.pcre.org/license.txt. • BIND Balanced Binary Tree Library and
Domain Name System (DNS) protocols developed and copyrighted by Internet Systems Consortium,
Inc. (http://www.isc.org) • Free BSD implementation of daemon developed by The FreeBSD Project, ©
1994-2006. • Simple Network Management Protocol Library developed and copyrighted by Carnegie
Mellon University © 1989, 1991, 1992, Networks Associates Technology, Inc, © 2001- 2003, Cambridge
Broadband Ltd.© 2001- 2003, Sun Microsystems, Inc., © 2003, Sparta, Inc, © 2003-2006, Cisco, Inc and
Information Network Center of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, © 2004. The license
agreement for these is at http://net-snmp.sourceforge.net/about/license.html. • NTP version 4.2 developed
by Network Time Protocol and copyrighted to various contributors. • Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
developed and copyrighted by OpenLDAP Foundation. OpenLDAP is an open-source implementation of
the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). Copyright © 1999-2003, The OpenLDAP Foundation.
The license agreement is at http://www.openldap.org/software/release/license.html. • Secure shell
OpenSSH version 4.2.1 developed by OpenBSD project is released by the OpenBSD Project under
a BSD-style license, available at http://www.openbsd.org/cgibin/cvsweb/src/usr.bin/ssh/LICENCE?
rev=HEAD. • PC/SC Lite is a free implementation of PC/SC, a specification for SmartCard integration is
released under the BSD license. • Postfix, an open source mail transfer agent (MTA), is released under
the IBM Public License 1.0, available at http://www.opensource.org/licenses/ibmpl.php. • PostgreSQL,
a free software object-relational database management system, is released under a BSD-style license,
available at http://www.postgresql.org/about/licence. • PostgreSQL JDBC driver, a free Java program
used to connect to a PostgreSQL database using standard, database independent Java code, (c)
1997-2005, PostgreSQL Global Development Group, is released under a BSD-style license, available
at http://jdbc.postgresql.org/license.html. • PostgreSQL Regular Expression Library, a free software
object-relational database management system, is released under a BSD-style license, available at
http://www.postgresql.org/about/licence. • 21.vixie-cron is the Vixie version of cron, a standard UNIX
daemon that runs specified programs at scheduled times. Copyright © 1993, 1994 by Paul Vixie; used
by permission. • JacORB, a Java object used to facilitate communication between processes written in
Java and the data layer, is open source licensed under the GNU Library General Public License (LGPL)
available at http://www.jacorb.org/lgpl.html. Copyright © 2006 The JacORB Project. • TAO (The ACE
ORB) is an open-source implementation of a CORBA Object Request Broker (ORB), and is used for
communication between processes written in C/C++ and the data layer. Copyright (c) 1993-2006 by
Douglas C. Schmidt and his research group at Washington University, University of California, Irvine, and
Vanderbilt University. The open source software license is available at http://www.cs.wustl.edu/~schmidt/
- 4 -
Page 5

ACEcopying. html. • libcURL, a library for downloading files via common network services, is open source
software provided under a MIT/X derivate license available at http://curl.haxx.se/docs/copyright.html.
Copyright (c) 1996 - 2007, Daniel Stenberg. • libuuid, a library used to generate unique identifiers, is
released under a BSD-style license, available at http://thunk.org/hg/e2fsprogs/?file/fe55db3e508c/lib/uuid/
COPYING. Copyright (C) 1996, 1997 Theodore Ts’o. • libpopt, a library that parses command line options,
is released under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License available at http://directory.fsf.org/
libs/COPYING.DOC. Copyright © 2000-2003 Free Software Foundation, Inc. • gSOAP, a development
tool for Windows clients to communicate with the Intel Corporation AMT chipset on a motherboard, is
distributed under the GNU Public License, available at http://www.cs.fsu.edu/~engelen/soaplicense.html.
• Windows Template Library (WRT) is used for developing user interface components and is distributed
under the Common Public License v1.0 found at http://opensource.org/licenses/cpl1.0.php. • The Perl Kit
provides several independent utilities used to automate a variety of maintenance functions and is provided
under the Perl Artistic License, found at http://www.perl.com/pub/a/language/misc/Artistic.html.
Export Information
Export of this software and documentation may be subject to compliance with the rules and regulations
promulgated from time to time by the Bureau of Export Administration, United States Department of
Commerce, which restricts the export and re-export of certain products and technical data.
Limitations
The software provided with this documentation is licensed to you for your individual use under the terms of
the End User License Agreement provided with the software. The information in this document is subject
to change without notice. PGP Corporation does not warrant that the information meets your requirements
or that the information is free of errors. The information may include technical inaccuracies or typographical
errors. Changes may be made to the information and incorporated in new editions of this document, if and
when made available by PGP Corporation.
Notices
- 5 -
Page 6

PGP Endpoint Application Control
- 6 -
Page 7

Table of Contents
Preface: About This Document................................................................13
Typographical Conventions.......................................................................................... 13
Getting Assistance........................................................................................................13
Chapter 1: PGP Endpoint Application Control Overview......................15
Product Overview..........................................................................................................15
Server, Database and Client Process..........................................................................17
System Requirements...................................................................................................18
Minimum Hardware Requirements........................................................................18
Supported Operating Systems..............................................................................19
Supported Databases............................................................................................20
Other Software Requirements...............................................................................21
Recommended Configuration................................................................................21
Client Supported Languages.................................................................................22
Chapter 2: Using Application Control.....................................................23
Getting Started with PGP Endpoint Application Control...............................................23
The File Authorization Setup Process..........................................................................24
Accessing the Management Server Console...............................................................26
Logging In to the Management Server Console................................................... 26
Logging Out of the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console.........................27
Common Functions within the Management Server Console...................................... 27
Viewing the Management Server Console............................................................28
Common Conventions...........................................................................................28
Using the Management Server Console Control Panel........................................29
Resizing and Repositioning Panels.......................................................................30
Organizing Columns for Display............................................................................30
Using the File Menu..............................................................................................32
Using the View Menu............................................................................................32
Using the Tools Menu...........................................................................................33
Using the Reports Menu....................................................................................... 33
- 7 -
Page 8

Table of Contents
Chapter 3: Using the Authorization Wizard............................................39
Chapter 4: Using Modules........................................................................47
Using the Explorer Menu...................................................................................... 34
Using the Window Menu.......................................................................................35
Using the Help Menu............................................................................................ 35
PGP Endpoint Application Control Modules..........................................................36
License Expiration.........................................................................................................36
Working with the Authorization Wizard........................................................................ 39
Authorizing Executable Files.................................................................................40
Working with Scan Explorer.........................................................................................48
Creating a File Scanning Template ..................................................................... 48
Scanning Files on a Client Computer...................................................................50
Comparing Scans..................................................................................................52
Modifying File Authorization..................................................................................54
Working with the Exe Explorer ....................................................................................54
Setting Up the Exe Explorer Default Options........................................................55
Adding a File Group..............................................................................................56
Renaming a File Group.........................................................................................57
Deleting a File Group............................................................................................57
Working with User Explorer..........................................................................................58
About File Groups................................................................................................. 58
File Group by User Tab.......................................................................................58
The User by File Group Tab.................................................................................63
Working with Database Explorer..................................................................................66
The Files Tab........................................................................................................ 67
The Groups Tab....................................................................................................70
Working with Log Explorer........................................................................................... 73
The Log Explorer Window.....................................................................................74
Navigation Control Bar..........................................................................................74
Column Headers....................................................................................................75
Log Explorer Templates........................................................................................83
Select and Edit Templates Dialog.........................................................................89
Template Settings Dialog......................................................................................92
- 8 -
Page 9

Table of Contents
Criteria/Properties Panel......................................................................................105
Results Panel/Custom Report Contents..............................................................105
Upload Latest Log Files...................................................................................... 109
Chapter 5: Using Tools...........................................................................111
Synchronizing Domains..............................................................................................112
Synchronizing Domain Members.........................................................................112
Synchronizing Domain Users..............................................................................113
Database Clean Up.................................................................................................... 114
Deleting Database Records.................................................................................114
Defining User Access................................................................................................. 116
Assigning Administrators.....................................................................................118
Defining Administrator Roles...............................................................................118
Assigning Administrator Roles.............................................................................121
Defining Default Options.............................................................................................122
Default Options Page.......................................................................................... 122
Default Option Precedence Rules.......................................................................130
Changing Default Options................................................................................... 138
Managing Path Rules................................................................................................. 138
Creating a Path Rule for All Users..................................................................... 140
Creating a Path Rule for a User or User Group................................................. 143
Modifying a Path Rule.........................................................................................146
Deleting a Path Rule...........................................................................................148
Defining a Trusted Owner...................................................................................150
Deleting a Trusted Owner...................................................................................152
Defining Spread Check...............................................................................................153
Enabling Spread Check.......................................................................................154
Sending File Authorization Updates to Computers.................................................... 154
Sending Updates to All Computers ....................................................................154
Sending Updates to a Single Computer..............................................................155
Working with Standard File Definitions...................................................................... 156
Importing Standard File Definitions..................................................................... 157
Exporting File Authorization Settings..........................................................................158
Exporting Settings................................................................................................159
Importing Settings................................................................................................159
- 9 -
Page 10

Table of Contents
Chapter 6: Using Reports.......................................................................163
Working with Endpoint Maintenance..........................................................................160
Creating Endpoint Maintenance Tickets..............................................................161
About Reports.............................................................................................................163
Reporting by User Role..............................................................................................163
Working with Reports................................................................................................. 164
Opening a Report................................................................................................164
Closing a Report..................................................................................................164
Saving a Report...................................................................................................164
Printing a Report................................................................................................. 165
Available Reports.................................................................................................165
File Groups by User............................................................................................166
User by File Group..............................................................................................167
User Options........................................................................................................168
Machine Options..................................................................................................169
Client Status........................................................................................................ 170
Server Settings....................................................................................................171
Chapter 7: Using the Client Deployment Tool Tool............................. 173
PGP Endpoint Client Deployment Window................................................................ 174
Packages Panel...................................................................................................174
Packages Menu...................................................................................................175
Computers Panel.................................................................................................176
Computers Menu.................................................................................................176
Creating Deployment Packages.................................................................................177
Adding Computers......................................................................................................180
Deploying Packages...................................................................................................182
Querying Client Status................................................................................................186
Appendix A: PGP Endpoint Administrative Tools................................189
Using the PGP Endpoint Authorization Service Tool................................................. 189
Scheduling Domain Synchronization..........................................................................193
Manage Administrator Rights..................................................................................... 195
Using PGP Endpoint with Novell................................................................................196
- 10 -
Page 11

Table of Contents
Using Novell Shared Data File Directory............................................................ 197
Running the Novell Synchronization Script.........................................................198
Opening Firewall Ports............................................................................................... 199
Open Ports by Firewall Exception.......................................................................199
Open Ports by Active Directory Policy................................................................200
- 11 -
Page 12

Table of Contents
- 12 -
Page 13

Preface
About This Document
This User Guide is a resource written for all users of PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1.
This document defines the concepts and procedures for installing, configuring, implementing,
and using PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1.
Tip:
PGP documentation is updated on a regular basis. To acquire the latest version of this or
any other published document, please refer to the PGP Support Portal Web Site (https://
support.pgp.com).
Typographical Conventions
The following conventions are used throughout this documentation to help you identify various
information types.
Convention Usage
bold Buttons, menu items, window and screen objects.
bold italics Wizard names, window names, and page names.
italics New terms, options, and variables.
UPPERCASE SQL Commands and keyboard keys.
monospace File names, path names, programs, executables, command
syntax, and property names.
Getting Assistance
Getting Product Information
Unless otherwise noted, the product documentation is provided as Adobe Acrobat PDF files
that are installed with PGP Endpoint. Online help is available within the PGP Endpoint product.
Release notes are also available, which may have last-minute information not found in the
product documentation.
- 13 -
Page 14

Preface
Contacting Technical Support
• To learn about PGP support options and how to contact PGP Technical Support, please visit
the PGP Corporation Support Home Page (http://www.pgp.com/support).
• To access the PGP Support Knowledge Base or request PGP Technical Support, please visit
PGP Support Portal Web Site (https://support.pgp.com).
Note:
You may access portions of the PGP Support Knowledge Base without a support agreement;
however, you must have a valid support agreement to request Technical Support.
• For any other contacts at PGP Corporation, please visit the PGP Contacts Page (http://
www.pgp.com/company/contact/index.html).
• For general information about PGP Corporation, please visit the PGP Web Site (http://
www.pgp.com).
• To access the PGP Support forums, please visit PGP Support (http://
forums.pgpsupport.com). These are user community support forums hosted by PGP
Corporation.
- 14 -
Page 15

Chapter
1
PGP Endpoint Application Control Overview
In this chapter:
• Product Overview
• Server, Database and
Client Process
• System Requirements
PGP Endpoint application and device control solutions
include:
• PGP Endpoint Device Control, which prevents
unauthorized transfer of applications and data by
controlling access to input and output devices, such as
memory sticks, modems, and PDAs.
• PGP Endpoint Device Control client for Embedded
Devices, which moves beyond the traditional desktop
and laptop endpoints to a variety of platforms that
include ATMs, industrial robotics, thin clients, set-top
boxes, network area storage devices and the myriad
of other systems running Microsoft® Windows XP
Embedded.
• PGP Endpoint Application Control, which delivers
granular control of application execution in an enterprise
environment.
• PGP Endpoint Application Control Terminal Services
Edition, which extends application control to Citrix® or
Microsoft Terminal Services ® environments that share
applications among multiple users.
• PGP Endpoint Application Control Server Edition, which
delivers application control to protect enterprise servers,
such as web servers, e-mail servers, and database
servers.
®
Product Overview
PGP Endpoint software is based on a multi-tier software architecture that processes and stores
data for Application Control and Device Control. Users can interact with the application through
- 15 -
Page 16

PGP Endpoint Application Control
the client interface. A separate Management Server Console provides a user interface for
network administrators.
The primary components of the PGP Endpoint Application Control solution are:
• The PGP Endpoint database which serves as the central repository of authorization
information for devices and applications.
• One or more Administration Servers that communicate between the database, the protected
clients, and the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console.
• The PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, which provides the administrative user
interface for the PGP Endpoint Administration Server.
• The PGP Endpoint client, which is installed on each computer, either endpoint or server, that
you want to protect.
The following figure illustrates the relationships between the PGP Endpoint components.
Figure 1: PGP Endpoint Component Relationships
- 16 -
Page 17

PGP Endpoint Application Control Overview
Server, Database and Client Process
The Administration Server communicates between the database and the protected client
computers.
The following describes the communication process flow between the Administration Servers,
database, and clients when using Application Control.
Figure 2: Application Control Process Flow
- 17 -
Page 18

PGP Endpoint Application Control
System Requirements
The following sections describe the minimum system requirements necessary for successful
installation of PGP Endpoint 4.4 SR1 and the languages supported by the client.
Important: For installation or upgrade to PGP Endpoint version 4.4 SR1:
• You must have a new license file that is valid specifically for version 4.4.
• Existing license files issued before PGP Endpoint version 4.4 will not work with the PGP
Endpoint Administration Server and may cause your Administration Servers to stop working.
The PGP Endpoint 4.4 license must be installed before you install or upgrade the PGP
Endpoint database, and then the Administration Server.
• Request a new license file using the Downloads tab on the PGP Licensing and Entitlement
Management System (LEMS) ( https://lems.pgp.com/account/login) .
Minimum Hardware Requirements
The minimum PGP Endpoint hardware requirements depend upon your service network
environment, including the type of database supported, the number of Administration Servers
you need support a distributed network, and the number of subscribed clients.
The hardware requirements for PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1 vary depending upon
the number of servers and clients you manage. The following minimum hardware requirements
will support up to:
• 200 connected PGP Endpoint clients for PGP Endpoint Device Control
• 50 connected PGP Endpoint clients for PGP Endpoint Application Control
Table 1: Minimum Hardware Requirements
PGP Endpoint Component Requirement
Database
Administration Server
• 1 GB (4 GB recommended) memory
•
Pentium® Dual-Core CPU processor or AMD equivalent
• 3 GB minimum hard disk drive
• 100 MBits/s NIC
• 512 MB (1 GB recommended) memory
•
Pentium® Dual-Core CPU or AMD equivalent
• 3 GB minimum hard disk drive
• 100 MBits/s NIC
- 18 -
Page 19

PGP Endpoint Component Requirement
PGP Endpoint Application Control Overview
Management Server Console
Client
• 512 MB (1 GB recommended) memory
• 15 MB hard disk drive for installation, and 150 MB
additional for application files
• 1024 by 768 pixels for display
• 256 MB (1 GB recommended) memory
• Pentium Dual-Core CPU or AMD equivalent
• 10 MB hard disk drive for installation, and several
additional GB for full shadowing feature of PGP Endpoint
Device Control
• 100 MBits/s NIC
Supported Operating Systems
PGP Endpoint supports multiple Microsoft Windows operations systems for the Administration
Server, Management Server Console, database, and client.
The operating system requirements for PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1 components
are outlined as follows.
Table 2: Operating System Requirements
PGP Endpoint Component Requirement
Database
One of the following:
•
Microsoft Windows ® XP Professional Service Pack 2 or
higher (SP2+) (32-bit)
• Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2) (64-bit)
•
Microsoft Windows Server® 2003 Service Pack 2 (SP2)
(32- and 64-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 (64 bit only)
Administration Server One of the following:
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003 SP2 (32-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 (64 bit only)
- 19 -
Page 20

PGP Endpoint Application Control
PGP Endpoint Component Requirement
Management Server Console One of the following:
Client One of the following:
• Microsoft Windows XP Professional SP2+ (32-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003 SP2 (32-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 (64 bit only)
•
Microsoft Windows Vista™ SP1+ (32- and 64-bit)
• Microsoft Windows 7 (32- and 64-bit)
•
Microsoft Windows® Server 2000 Service Pack 4 or higher
(SP4+) (32-bit)
• Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional SP4+ (32-bit)
• Microsoft Windows XP Professional Service Pack 2 or
higher (SP2+) (32- and 64-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003 SP2 (32- and 64-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 (64 bit only)
• Microsoft Windows Vista SP1+ (32- and 64-bit)
• Microsoft Windows 7 (32- and 64-bit)
• Microsoft Windows XP Embedded (XPe) Service Pack 2
(SP2) (32-bit)
• Microsoft Windows Embedded Point of Service (WEPOS)
(32-bit)
• Microsoft Windows XP Tablet PC Edition (32-bit)
•
Citrix Access Gateway™ 4.5
•
Citrix Presentation Server™ 4.0 for Windows Server 2003
SP1/SR2+ (32-bit)
• Citrix Presentation Server 4.5 for Windows Server 2003
SP1/SR2+ (32- and 64-bit)
Supported Databases
PGP Endpoint supports multiple releases of Microsoft® SQL Server® . You should choose
the database instance required by your network operating environment and the number of
Administration Server s and subscribed clients the application must support.
The database requirements for PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1 components are
outlined as follows.
- 20 -
Page 21

Table 3: Database Requirements
PGP Endpoint Application Control Overview
PGP Endpoint
Component
Database One of the following:
Requirement
•
Microsoft SQL Server® 2005 Service Pack 2 or higher (SP2+)
(32-bit and 64-bit)
• Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express Edition SP2+ (32-bit and
64-bit)
• Microsoft SQL Server 2008
• Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Express Edition
Other Software Requirements
The PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1 release requires the following additional
software.
Additional software requirements for PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1 components are
outlined as follows.
Table 4: Other Software Requirements
PGP Endpoint Component Requirement
Database No additional software requirements.
Administration Server
Install Microsoft® Certificate Authority for PGP Endpoint
Device Control encryption, if you will be encrypting Windows
user accounts. See Microsoft Certificate Authority (http://
technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc756120.aspx) for
additional information about certificates.
Management Server Console Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributable Package.
Client No additional software requirements.
Recommended Configuration
To maximize PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1 for operation in a Microsoft Windows
environment, you should configure your network environment database and client components
using the following suggested configurations.
The recommended configurations for PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1 components
are outlined as follows. These settings represent the usual default settings, but should be
confirmed before beginning PGP Endpoint installation.
- 21 -
Page 22

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Table 5: Recommended Configuration
PGP Endpoint Component Requirement
Database
Administration Server None recommended.
Management Server Console None recommended.
Client
• Change the Windows Event Viewer settings to 1024 KB
and choose to overwrite events as necessary.
• Change Windows Performance settings to prioritize for
background applications.
• If you are using Active Directory, configure a
corresponding Domain Name System (DNS) server as
Active Directory (AD) integrated and create a reverse
lookup zone, to provide for name resolution within the
PGP Endpoint Management Server Console.
• Configure NIC to receive IP from DHCP service.
• Change the Windows Event Viewer settings to 1024 KB
and choose to overwrite events as necessary.
Client Supported Languages
The PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1 client supports multiple languages in text format.
The PGP Endpoint Application Control 4.4 SR1 client is supported in the following languages:
• English
• French
• Italian
• German
• Spanish
• Japanese
• Simplified Chinese
• Traditional Chinese
• Russian
• Dutch
• Portuguese
• Swedish
- 22 -
Page 23

Chapter
2
Using Application Control
In this chapter:
• Getting Started with PGP
Endpoint Application
Control
• The File Authorization
Setup Process
• Accessing the
Management Server
Console
• Common Functions within
the Management Server
Console
• License Expiration
The Management Server Console allows the user to
communicate with an Administration Server to send and
retrieve file authorization data from the database. The data
is sent from the server to a client, thereby establishing
application control on the client. The Management Server
Console provides direct access to system management,
configuration, file authorization, reporting, and logging
functions.
Getting Started with PGP Endpoint Application Control
Get started with Application Control by installing the application, which includes all server and
database components, the Management Server Console, and the clients. Then you use the
Management Server Console to define user and device permissions for encryption of removable
storage devices.
You must begin the installation process with a clean machine that fulfills the minimum software
and hardware requirements. You must resolve all hardware and software conflicts prior installing
- 23 -
Page 24

PGP Endpoint Application Control
PGP Endpoint solutions and install the latest operating system and database service packs.
Refer to the following processes to identify tasks when installing Application Control.
Figure 3: PGP Endpoint Installation
The File Authorization Setup Process
After successfully installing Application Control, an administrator uses the Management Server
Console to configure and define user access permissions and file authorization rules required in
a PGP Endpoint environment that specify which executable files, scripts, and macros each user
can use, as described by the following process flow.
You can use standard Microsoft file definitions to quickly build a
central file authorization list for executable files, macros, and scripts.
- 24 -
Page 25

Using Application Control
You can assign administrator access rights using the User Access
tool. An Administrator has restricted access to the Management
Server Console and can be assigned various administrative roles by
an Enterprise Administrator.
After defining Administrator roles, you can use the User Access tool
to assign the defined roles to Administrators.
File groups simplify the process of administering large numbers of
executable, script, and macro files for users. Instead of individually
authorizing files, you can logically group files together logically by
creating file groups.
PGP Endpoint verifies which file group is associated with an
executable, script, or macro and whether the user has permission for
the file group. You can assign specific permissions to local users and
user groups. Only authorized applications and scripts assigned to a
user or a user group can run on the client.
After creating file groups and parent-child relationships you want to
use, you can assign file groups to users or user groups.
You can create a template and scan a target computer running the
client. You can scan all files on a computer, or you can create a
template to scan selected directories or specific file types for example,
*.exe, *.com, *.dll, *.ocx, *.sys, *.drv, *.cpl, *.vbs, *.js, to reduce the
scan time required.
After you create the necessary file groups and required parent-child
relationships, you can assign executable files, scripts, and macros to
file groups.
Activating Execution blocking prohibits user access to unauthorized
files. Local authorization is permitted only for the administrators and
LocalSystem account.
Once you identify all your files, categorize them into file groups, and assign the file groups to
users or user groups, these files are centrally authorized and immediately available to be run by
all allowed users.
- 25 -
Page 26

PGP Endpoint Application Control
When a user wants to run an executable, script, or macro, the following actions take place
automatically:
• A file that is identified as an executable, script, or macro, by the operating system is stored in
the PGP Endpoint database ready for execution (but not actually executed).
• A file is identified by PGP Endpoint as an executable, script, or macro, has the entire file
content checked to determine its digital signature (hash) before being allowed to execute by
the operating system.
• The digital signature is compared to those of the authorized files that can be run (stored in a
central file authorization list).
• If and only if, the file corresponds exactly to a file in the central file authorization list, that
is, the digital signatures are identical, and the file is authorized for execution for the user or
machine that requested it, the file is executed.
Accessing the Management Server Console
Access to the Administration Server is controlled using the login and logout functions
provided by the Management Server Console. Only authorized administrators may access the
Administration Server.
The Management Server Console is a Windows application that conforms to standard
conventions. From the Management Server Console, you navigate through the system with
menu bars, scroll bars, icons, lists, and checkboxes.
Logging In to the Management Server Console
You access the application by logging in to the Management Server Console.
1. Select Start > Programs > PGP > Endpoint Security > PGP Endpoint Management
Server Console.
Step Result: Each time you access the Management Server Console, the Connect to PGP
Endpoint Management Server Console dialog appears.
2. From the Administration Server drop-down list, select the Administration Server you want
to connect to.
You can type the server name as an IP address with port if required in square brackets,
NetBios name, or fully qualified domain name in the Administration Server field.
3. Select one of the following options:
Option Description
Use current user
By default the system connects to the Administration
Server using your credentials.
- 26 -
Page 27

Using Application Control
Option Description
Log in as Type the user name in the Username field and type the
password in the Password field.
Tip: Prefix the user name by a computer workstation
name and backslash for a local user, and by a domain
name and backslash for domain users.
4. Click OK.
Step Result: The Connect to PGP Endpoint Management Server Console dialog closes.
Result: The PGP Endpoint Management Server Console window opens.
Logging Out of the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console
When you log out from the Management Server Console you can choose to terminate the
adminstrative session or disconnect from the Administration Server.
1. To disconnect from the Administration Server, select File from the navigation bar.
2. Select one of the following options:
Option Description
Disconnect The Management Server Console remains open.
Exit The PGP Endpoint Management Server Console closes.
Result: The Disconnect or Exit action terminates your current administrative session.
Common Functions within the Management Server Console
PGP Endpoint uses standard browsing conventions and navigational functions.
Features specific to the Management Server Console include menu selections for Modules,
Tools, and Reports. From the console, you can access the PGP Endpoint Control Panel
features that you have administrative user access for. You can use the navigation bar to access
administrative options and PGP Endpoint control features.
- 27 -
Page 28

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Viewing the Management Server Console
The Management Server Console graphically displays the administrative user features for the
application.
The Management Server Console window is divided into four panels:
• The Control Panel provides access to PGP Endpoint modules, tools, reports, and help
functions.
• The main panel displays a window for the module currently selected from the Control Panel.
Modules remain open and arranged as stacked tabs until closed.
• The Connection panel shows information about the current user. You can use the scrollbar
to navigate through the text.
• The Output panel displays system processing information and error messages.
You can also view the following bars in the Management Server Console window:
• The navigation bar provides access to different PGP Endpoint functions and commands.
Some of these commands and functions depend on the module you are currently using.
• The status bar displays information about the condition of the console.
Figure 4: Management Server Console
Common Conventions
This application supports conventions common to most Windows applications.
Table 6: Common User Interface Conventions
Screen Feature Function
Entry Fields Type data into these fields, which allow the system to retrieve
matching criteria or to enter new information.
- 28 -
Page 29

Using Application Control
Screen Feature Function
Drop-Down Menus Displays a list to select preconfigured values.
Command Buttons Perform specific actions when clicked.
Check Boxes A check box is selected or cleared to enable or disable a feature.
Some lists also include a Select All check box that lets you select all
the available listed items on that page.
Radio Buttons Select the button to select an item.
Sort Data presented in tables can be sorted by ascending (default)
or descending order within a respective column by clicking on a
(enabled) column header.
Mouseovers Additional information may be displayed by hovering your mouse
pointer over an item.
Auto Refresh Where present and when selected, the auto refresh function
automatically refreshes the page every 15 seconds.
Scrollbars Drag to see additional data that does not fit the window.
Tabs Click on the tab name to switch to different information related to the
specific page or dialog.
Bread Crumb Where present and when selected, names the page you are
currently viewing, that page's parent page (if applicable), and the
navigation menu item that opened the displayed page. If viewing a
page that is child to another page, you can view the parent page by
clicking the bread crumb, which also serves as a link, allowing you to
retrace your steps.
Tip: All list pages support right-click.
Using the Management Server Console Control Panel
The Control Panel, adjacent to the Management Server Console main window, provides
access the Modules, Tools, Reports, and Help administrative user features.
You can perform the following tasks using the Control Panel:
• Use the application control Modules to administer routine PGP Endpoint control tasks.
• Generate Reports for users, file groups, PGP Endpoint clients, and administrator actions.
• Perform system administrative tasks using Tools.
• Get Help.
- 29 -
Page 30

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Resizing and Repositioning Panels
You can resize and reposition the Management Server Console panels.
You can customize the appearance of the main window as follows:
• Drag a panel, by selecting the title bar, to any position on the main page.
• Float a panel in any position in the window, to share the main window with open Modules.
• Dock a panel to minimize the appearance in the main window. The docked panel appears as
a tab at the edge of the main window.
• Scroll across an active panel.
• Close an active panel by clicking the Close icon.
• Double click a panel title bar to return to the original position on the main screen.
• Right-click a floating panel title bar to display a drop down menu to restore, move, size,
minimize, maximize, or close the panel.
Use the icons listed in the following table to resize or reposition a panel:
Table 7: Resizing and Repositioning Panels
Icon Function
Float a panel
Dock a panel
Scroll left or right
Close an active panel
Organizing Columns for Display
You can customize the graphical display for columns in the Log Explorer module.
You can reorganize columns by headings only for the Log Explorer module.
1. Select the Log Explorer module from the PGP Endpoint Control Panel.
Step Result: The Explorer window opens for the module you select.
2. Right-click the table header row of the Explorer main window.
Step Result: A right-mouse menu opens showing all available columns for display. The
menu options shown vary according to the PGP Endpoint control module you
select and your license type.
3. Select a column name from the list. A check beside the column name enables the column for
display in the Explorer window.
- 30 -
Page 31

4. To organize columns, select Choose Columns....
Step Result: The Choose Columns dialog opens.
Using Application Control
Figure 5: Choose Columns Dialog
5. Choose any of the following options from the Choose Columns dialog:
Item Description
Column Select or clear the check box for a column. You can
modify the column width in the Width of selected column
field.
Move Up Shifts the column name description up one place in the
dialog list.
Move Down Shifts the column name description down one place in the
dialog list.
Hide Masks the column display.
Show Displays the column.
6. Click OK.
Result: The Choose Columns dialog closes. The Explorer window shows the selected
columns and associated attributes.
- 31 -
Page 32

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Using the File Menu
The File menu displays options for managing the Administration Server from the main window.
You can also print and save the contents displayed in the main window of the Management
Server Console.
The following table describes the File menu items and functions:
Table 8: File Menu
Menu Item Description
Connect Establishes communication between the PGP Endpoint
Disconnect Detaches the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console from the
Save as Saves the contents of the main window in .html format for exporting
Print Prints the active report window.
Management Server Console and a PGP Endpoint Administration
Server connected to another computer or user.
current PGP Endpoint Administration Server.
data to any .html compliant application.
Exit Exits the current PGP Endpoint Management Server Console
administrative session.
Using the View Menu
The View menu displays options for controlling the appearance of the main panel within the
Management Server Console.
The following table describes the View menu items and functions:
Table 9: The View Menu
Menu Item Description
Modules Shows a submenu for selecting a module.
Control Panel Shows or hides the menu for selecting Modules, Tools, Reports, and
Help.
Output Shows or hides the Output window, which displays a log of system
activity.
Connection Shows or hides the Connection window, which displays real-time
system operating information.
Status bar Shows or hides the status bar.
- 32 -
Page 33

Using Application Control
Using the Tools Menu
The Tools menu displays a list of tasks for performing user and database administration.
The following table describes the Tools menu items and functions:
Table 10: Tools Menu
Menu Item Description
Synchronize
Domain Members
Database
Maintenance
User Access Defines PGP Endpoint Enterprise Administrators and Administrators by
Default Options Changes the default option settings for users and computers.
Path Rules Uses file paths and trusted owners to define which applications can run.
Spread Check Prevents the spread of self-propagating code by disabling suspicious
Send Updates to
All Computers
Send Updates to Transmits the latest setting and permission changes to specific
Import Standard
File Definitions
Export Settings Places file authorization settings in an external file that can be sent to
Updates the PGP Endpoint database using a current list of users and
groups for a domain or machine.
Deletes log and computer database scan files created before a
specified date.
allowing you to assign access rights for setting permissions and viewing
audit information for administrator actions.
executables that have been locally authorized on multiple computers.
Transmits the latest setting and permission changes to all managed
devices. Changes can be sent manually or automatically when
computers restart or at the next login event.
computers on the network.
Imports files and associated digital signatures for Windows operating
systems supported by the PGP Endpoint application.
PGP Endpoint clients working offline to update file authorization lists.
Endpoint
Maintenance
Creates and saves maintenance tickets for computers and computer
groups that allows modification of protected files and registries for PGP
Endpoint clients.
Using the Reports Menu
The Reports menu displays options to save or print information about Application Control
system operations.
The following table describes the Reports menu items and functions:
- 33 -
Page 34

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Table 11: Reports Menu
Menu Item Description
File Groups by
User
Users by File
Shows one or more users and groups the assigned files groups assigned to
file groups.
Shows one or more file groups assigned to users and groups.
Group
User Options Shows all the user options defined in the system.
Machine
Shows all the computer options defined in the system.
Options
Client Status Shows the hardening options, client version, and log and policy file status.
Server
Shows how your Administration Server is configured.
Settings
Using the Explorer Menu
The Explorer menu displays options that vary based upon the module selected in the Control
Panel.
The following tables describe the Explorer menu items and functions.
Note: There is no Explorer menu for the User Explorer module.
Table 12: Database Explorer Module Menu
Menu Item Description
Assign Changes the file group assignment.
Manage File Groups Adds, renames, or deletes a file group.
Choose Columns Organizes the panels columns.
Table 13: Exe Explorer Module Menu
Menu Item Description
Map Network Drive Assigns a drive letter to a shared resource on a network.
Disconnect Network
Drive
Removes the drive letter assigned from any shared resource on a
network to prevent users from browsing without credentials.
Assign Changes the file group assignment.
Manage File Groups Adds, renames, or deletes a file group.
Choose Columns Organizes the panels columns.
- 34 -
Page 35

Using Application Control
Table 14: Log Explorer Module Menu
Menu Item Description
Fetch log Obtains the latest log data from a client.
Manage File Groups Adds, renames, or deletes a file group.
Table 15: Scan Explorer Module Menu
Menu Item Description
Perform Scan Scans a computer to identify executable files, scripts and macros
to be authorized.
Select Scans Provides the option to compare two scans.
Assign Changes the file group assignment.
Manage File Groups Adds, renames, or deletes a file group.
Choose Columns Organizes the panel columns.
Using the Window Menu
The Window menu provides options to control the navigation and display of open windows
within the Management Server Console.
The following table describes the Window menu options.
Table 16: Window Menu
Menu Item Description
Cascade Displays open windows in an overlapping arrangement.
Tile Displays open windows in a side-by-side arrangement.
Using the Help Menu
The Help menu displays option for using help features.
The following table describes the Help menu items and functions.
Table 17: Help Menu
Menu Item Description
Contents Displays the Contents tab of the Help file.
Search Finds a specific topic in the Help file.
Index Displays the Help index page.
- 35 -
Page 36

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Menu Item Description
About Displays information about your installed version of PGP
PGP on the Web Redirects to the PGP home page for up-to-date information,
PGP Knowledgebase Provides direct access to the PGP knowledge base, a source
PGP Endpoint Application Control Modules
The Application Control Modules provide access to the functions necessary for configuring
and managing and are grouped into several modules, represented by the icons in the Modules
section of the Control Panel.
The PGP Endpoint Application Control Modules provide access to the functions necessary for
configuring and managing PGP Endpoint and are grouped into five modules, represented by the
icons in the Modules section of the Control Panel:
Table 18: PGP Endpoint Application Control Modules
Module Icon Description
Endpoint.
resources, and support.
of tips, questions and answers, and how-to articles.
Database
Explorer
Exe Explorer Builds a list of executable files, scripts, and macros that are
Log Explorer Shows logs of applications, scripts, and macros that were run,
Scan Explorer Scans a computer or domain to identify executable files, scripts,
User Explorer Links users or user groups with file groups, granting permission
Shows the list of executable files, scripts, and macros that
are stored in the PGP Endpoint database and manages file
assignment details.
allowed to run on PGP Endpoint clients, and assigns files to file
groups.
files for which access was denied, and files authorized locally.
and macros to be authorized, and assigns files to a file group
using templates.
to use the files assigned to file groups.
License Expiration
A license expiration Warning message displays, if you are a subscription user, when you log in
to the Management Server Console.
The following table describes the types of license expiration warnings.
- 36 -
Page 37

Using Application Control
Expiration Period Warning Message Frequency
Expired The license has expired. Once
Less than one day
Less than 60 days The license will expire in x days. Once per day
More than 60 days No message. Not applicable
Note: When you must renew or add a license, contact your PGP representative.
The license will expire in x hours.
The license will expire in x minutes.
Once per hour
- 37 -
Page 38

PGP Endpoint Application Control
- 38 -
Page 39

Chapter
3
Using the Authorization Wizard
In this chapter:
• Working with the
Authorization Wizard
PGP Endpoint allows the operating system determine
whether a file is executable and then checks the digital
signature against the central file authorization list. PGP
Endpoint provides several strategies for authorizing
executable files, scripts, and macros including:
• Central authorization using digital signatures.
• Central authorization using file paths and trusted owners.
• Local authorization providing local users limited rights to
authorize executable files, scripts, and macros to run on
a specific user computer.
Scripts and macros are more difficult to identify than
executables files. PGP Endpoint recognizes and centrally
manages the following types of scripts and macros:
• VBScripts and JScripts that are interpreted by the
Windows Script Host that have the .vbs or .js extension.
• Scripts interpreted by cscript.exe and wscript.exe.
• Visual Basic scripts that run within Microsoft Office and
other host applications.
The Authorization Wizard Wizard is an administrative tool
that you can use to build an initial list of centrally authorized
application files.
Working with the Authorization Wizard
The Authorization Wizard tool is used for performing an initial inventory of existing software
applications that can be authorized for use.
The Authorization Wizard tool provides a simple method for scanning existing files and
directories on a computer to add files to the central authorization list. The wizard can
- 39 -
Page 40

PGP Endpoint Application Control
automatically assign scanned files with existing digital signatures to file groups. Alternatively,
scanned files without a digital signature can be processed manually to create digital signatures
and then assign these files to file groups. The wizard can also expand compressed files during
the scanning process, identify or create digital signatures, and then assign these files to files
groups.
The Authorization Wizard:
• Searches for executable files from a specific source, as a computer hard drive, network
share (UNC path), or CD/DVD-ROM.
Executable file sources include the following:
• Windows operating systems, applications, and service packs
• Self-extracting ZIP archives
• RAR, MSI, and Microsoft CAB files
• Creates digital signatures for selected files.
• Records the digital signatures in the PGP Endpoint database.
The Authorization Wizard does not scan for scripts or macros.
Restriction: The Authorization Wizard does not expand setup.exe files and incorrectly
classifies them as a single executable file instead of an auto-extraction file.
Authorizing Executable Files
You can use the Authorization Wizard to scan a reference computer to build an initial list of
centrally authorized files.
1. Select Windows Start > Programs > PGP > Endpoint Security > Authorization Wizard.
Step Result: The Authorization Wizard dialog opens.
2. Click Next.
- 40 -
Page 41

Using the Authorization Wizard
The wizard advances to the Options - Authorization Wizard dialog.
Figure 6: Options - Authorization Wizard Dialog
3. Enter the name of a computer to connect to the Administration Server, using one of the
following options:
• Type the server name (my_server)
• Type the server IP address (192.168.1.1)
• Click different user name to use other server connection credentials (another dialog
opens and you type the user name and password)
Attention: When you can only leave certain non-standard ports open in your firewall,
you need to specify the server TCP port number between square brackets, for example:
server[1234].
a) Click Check Server to verify the connection.
4. Select or clear the Process known files automatically check box as follows:
Option Description
Select Add existing files to the database that match an existing
database entry with a different digital signature, and
assign the files to existing file groups.
Clear Identify unknown files and process them manually.
5. Click Next.
- 41 -
Page 42

PGP Endpoint Application Control
6. To browse to the root directory that you want to scan for executable files, select one of the
following options, then click the ellipsis adjacent to the Source field.
Option Description
Directory If you are scanning from a directory
File If you are scanning from a file or compressed archive file.
7. To select the temporary directory where the wizard can expand compressed files, click the
ellipsis adjacent to the Extract temporary files to: field.
Figure 7: Options - Authorization Wizard Dialog
Caution: If the Free space for extraction falls below 100 MB, you receive a message
prompting you to create more free disk space.
- 42 -
Page 43

Using the Authorization Wizard
8. Click Start.
Step Result: The Source Selection - Authorization Wizard - Connected dialog opens.
The wizard searches the source directory or file and lists the number of files
found.
Figure 8: Source Selection - Authorization Wizard - Connected Summary
9. Click Next.
If you select the Process known files automatically option, the wizard processes all
executable files and assigns them to corresponding file groups. If a matching filename exists
- 43 -
Page 44

PGP Endpoint Application Control
in the database and is assigned to a file group, the wizard assigns the new file definition to
the same file group. The results are summarized as follows:
• Number of files processed
• Number of files assigned to file groups
• Number of files as duplicates of previously assigned files
Step Result: The Scanning - Authorization Wizard - Connected Summary dialog opens.
Figure 9: Scanning - Authorization Wizard - Connected Summary
10.Click Next.
Step Result: The Assigning Files - Authorization Wizard - Connected dialog opens.
The wizard lists files that are not assigned to file groups because they
- 44 -
Page 45

Using the Authorization Wizard
do not match existing filenames in the database or cannot be processed
automatically.
Figure 10: Assigning Files - Authorization Wizard - Connected Dialog
11.To manually assign the unknown file(s) to a file group, select one or more file names from the
File Name list.
12.Click the Suggested File Group drop-down list or File Groups to select a file group for
assignment.
13.Click Next.
Step Result: The new file definitions are added to the database.
14.Click Finish.
You may select the Restart the wizard to add more files or CDs option.
Result: The selected files are assigned to file groups.
After Completing This Task:
You may need to update user access permissions to enable users or user groups to run newly
authorized applications.
- 45 -
Page 46

PGP Endpoint Application Control
- 46 -
Page 47

Chapter
4
Using Modules
In this chapter:
• Working with Scan
Explorer
• Working with the Exe
Explorer
• Working with User
Explorer
• Working with Database
Explorer
• Working with Log Explorer
Depending on the task, you may use one of the following
modules in the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console
Control Panel:
• Exe Explorer to explore a few directories or files.
• Database Explorer to explore previously authorized files
already stored in the database.
• User Explorer to manage user and user group
assignments to file groups.
• Scan Explorer to explore a computer using a predefined
scanning template.
• Log Explorer to explore and analyze user activity logs.
- 47 -
Page 48

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Working with Scan Explorer
Using the Scan Explorer module you can create a template and scan a target computer that
runs the client.
A scanning template provides a foundation for you to quickly build a centrally authorized list from
the files scanned on a client computer, using a reference computer, and authorize applications.
Figure 11: Scan Explorer Main Window
Creating a File Scanning Template
You can create a template to identify new file authorization changes to make when new software
is installed.
You can scan for files by creating a template with the following rules:
• Scan all executables matching the pattern *.exe or *.dll in the %SYSTEMROOT% directory
and subdirectories.
• Scan all files matching the pattern *.exe or *.dll in the %PROGRAMFILES% directory and
subdirectories.
- 48 -
Page 49

Using Modules
1. From the Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Scan Explorer > Perform
New Scan > Create New Template.
Step Result: The Create New Template dialog opens.
Figure 12: Create New Template Dialog
2. In the New Template name: field, enter the name for the new template.
3. Click Add.
Step Result: The New Rule dialog opens.
Figure 13: New Rule Dialog
- 49 -
Page 50

PGP Endpoint Application Control
4. In the Scan files matching the pattern (use * wildcard for all files) field, enter the name
patterns to use for scanning.
Caution: When you specify wildcard masks, for example: *.com, you can miss scanning for
files that do not use standard file extensions such as: *.exe, or *.dll, and so forth. The result
is that these types of files will not be authorized, which means that these applications will not
work or work properly.
5. In the In directory field, enter the path name for the directory you want to scan.
6. Select one or more of the following options:
Option Description
Include subdirectories Scan subdirectories of the root directory.
Scan executables Scan for executable files and ignore all other file types.
The scan also searches for 16-bit executables.
Attention: If you do not select the Scan Executables
option, you must specify the *.exe and *.sys for the
matching pattern to scan for these types of files.
7. Click OK.
Step Result: The New rule dialog closes and the rules you define appear on the Rules
box.
8. Click Save.
Result: The Perform New Scan dialog lists the new template in the From Template drop-
down list.
Scanning Files on a Client Computer
You can scan all files on a computer, or you can create a template to scan selected directories
or specific file types for example, *.exe, *.com, *.dll, *.ocx, *.sys, *.drv, *.cpl, *.vbs, *.js, to reduce
the scan time required.
Prerequisites:
Before you scan a computer, create a file scanning template.
1. From the Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Scan Explorer.
Step Result: The Scan Explorer window opens.
- 50 -
Page 51

2. Click Perform New Scan.
Step Result: The Perform New Scan dialog opens.
Using Modules
Figure 14: Perform New Scan Dialog
3. In the From Template field, select a template from the drop-down list.
4.
Click on the ellipsis button adjacent to the On Computer field.
a) Type the computer name.
b) Click Search or Browse.
c) Select the computer from the list.
d) Click OK.
You can type the computer name directly or use wildcard, such as * and ?.
Step Result: The Select Computer dialog opens.
- 51 -
Page 52

PGP Endpoint Application Control
5. Click Start Scan.
Step Result: The Perform New Scan dialog opens.
Figure 15: Perform New Scan Dialog - Comment
6. Enter a name or comment to distinguish this scan in the Comment field.
7. Click OK.
Result: PGP Endpoint scans the specified file directories, calculates digital signatures for
all executable files, scripts, and macros, and adds these digital signatures to the
database. The results are shown in the Scan Explorer main window as follows.
Figure 16: Scan Explorer Window
Comparing Scans
You can compare a scan, performed before installing a new application, to a scan performed
after the installation process is complete. Alternatively, you can compare different scans to
identify files associated with separate applications.
Prerequisites:
Before you can compare two scans, you must perform at least two separate scans.
- 52 -
Page 53

1. In the Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Scan Explorer.
Step Result: The Scan Explorer window opens.
2. Click Select Scans.
Step Result: The Select Scans dialog opens.
Using Modules
Figure 17: Select Scans Dialog
3. In the Show scans made from template field, select a template from the drop-down list.
4. In the First Scan panel:
a) Select a computer name from the drop-down list.
b) Select the name of your first scan from the drop-down list.
5. In the Second Scan panel:
a) Select a computer from the drop-down list.
b) Select the name of for your second scan from the drop-down list.
6. Click OK.
Result: The system compares the two scans and lists the results in the Scan Explorer
window. Each file is assigned a status as follows:
• Added - The file was added between the first and second scans.
• Different - The file has been modified since the previous scan. The file has the
same filename but a different digital signature and may be a newer version.
• Original - The file remains unchanged from the previous scan. This output only
shows when comparing the same scan.
- 53 -
Page 54

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Modifying File Authorization
After scanning a computer to identify executable files, scripts, and macros, or comparing two
scans to identify updates, you can change file assignment details so users can work with a new
or upgraded application.
The purpose of the scan is to identify changes made when installing a new application, so you
can assign new or modified files to a specific file group, or remove them.
Tip: You can use the right-click menu to filter a scan and show only <Not Authorized> files or
Show all files.
1. Select the files.
2. Right-click the list.
3. From the shortcut menu shown, select own the following options.
• Assign to File Group
• Remove from File Group
Result: After changing the file group assignment, the applications use is denied or allowed,
depending of the action specified in the User Explorer module.
Working with the Exe Explorer
You can use the Exe Explorer module to create a list of executable files, scripts, and macros
that you want to authorize.
Use Exe Explorer for a newly configured reference computer to ensure that only clean files
are authorized. The reference computer does not have to be the same computer that the
Management Server Console is installed on. You can browse the network and select any
available computer as your reference. You may manually assign macros and scripts to the
central file authorization list using the Exe Explorer module, although PGP recommends that
you do this using the Log Explorer module.
Before using the Exe Explorer module, you must set up the default options for this module. The
default options determine the way PGP Endpoint searches computer directories and how results
are displayed. When you choose the root directory of a computer, the search process creates a
list of all executable files, scripts, and macros on the computer. This process can be slow and is
typically done when you want to check all the applications installed on a computer.
Restriction: Only administrators with defined user access rights can use the Exe Explorer
module.
- 54 -
Page 55
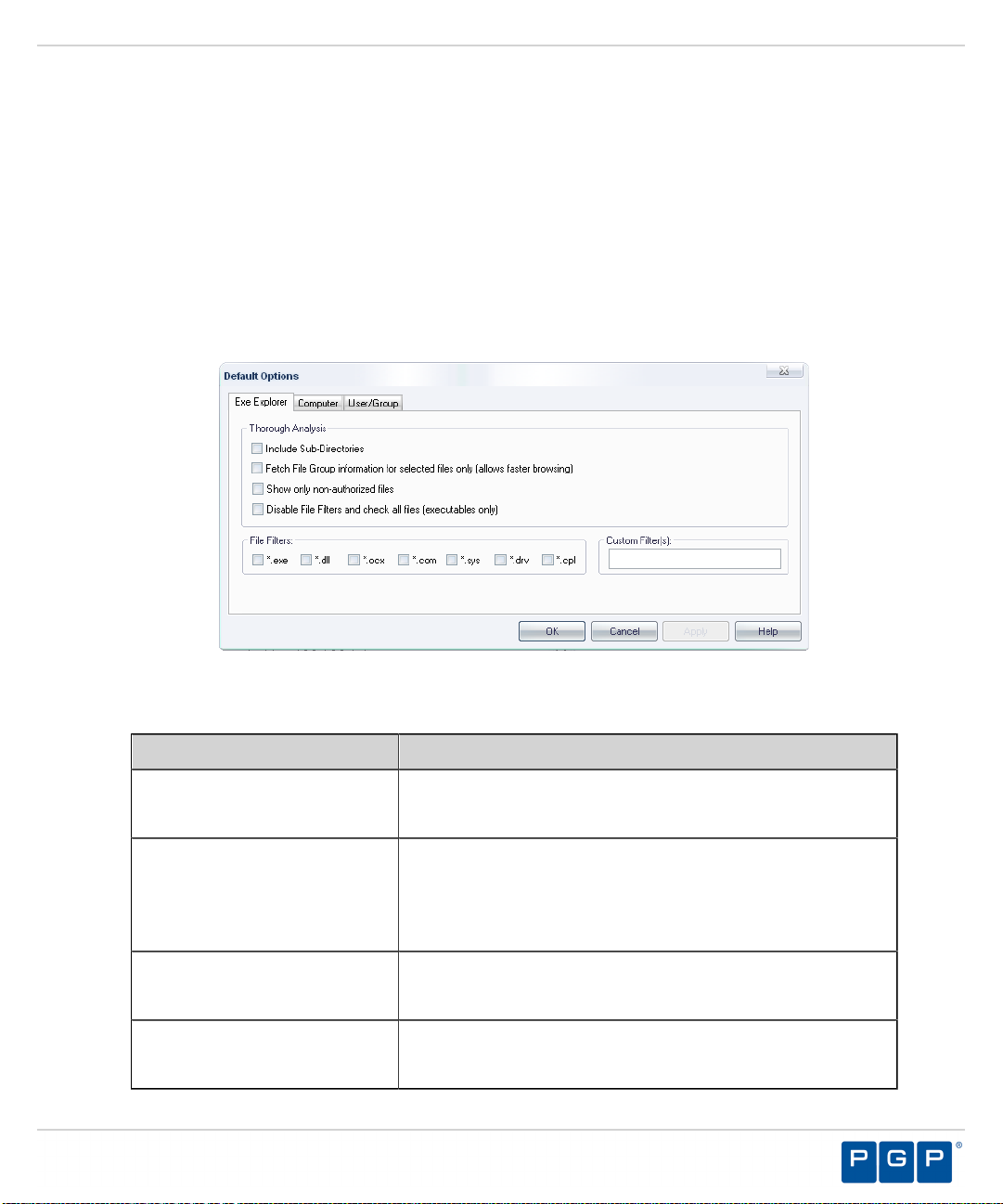
Setting Up the Exe Explorer Default Options
The Exe Explorer searches computer directories for executable files, scripts, and macros.
1. From the Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Exe Explorer.
Step Result: The Exe Explorer window opens.
2. From the PGP Endpoint Control Panel, select Tools > Default Options.
Step Result: The Default Options dialog opens.
3. Select the Exe Explorer tab.
Using Modules
Figure 18: Default Options Dialog - Exe Explorer Tab
4. Select or clear one or more of the following check boxes:
Option/button Description
Include SubDirectories
Fetch File Group
information for selected
files only (allows faster
browsing)
Show only non-authorized
files
Disable file filters and check
files (executable only)
Defines the directories to search. Select to search for files
from a named directory and sub-directories.
Displays the file group information for all files or only
selected files. Select search only for files with standard file
extensions and display file group information only for files
you select.
Displays previously authorized files. Select to filter
previously authorized files and show the remaining files.
Checks for all files or files with specific extensions. Select
to search for files with standard file extensions.
- 55 -
Page 56

PGP Endpoint Application Control
5. To search for files with:
• One or more non-standard file extensions, deselect the Disable File Filters and check
all files (executables only) check box and enter the custom file extension(s) in the
Custom Filter(s) field. Separate entries using semi-colons with no spaces.
• Specific file extensions, deselect the Disable File Filters and check all files
(executables only) check box and select the file extensions from the File Filters panel.
Result: The Exe Explorer module window changes to reflect the default options you select.
Adding a File Group
File groups simplify the process of administering large numbers of executable, script, and macro
files for users. Instead of individually authorizing files, you can logically group files together
logically by creating file groups.
1. In the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Exe Explorer
> Explorer > Manage File Groups.
Step Result: The File Group Management dialog opens.
2. Click Add File Group.
Step Result: The Add File Group dialog opens.
Figure 19: Add File Group Management Dialog
3. Enter the name of the file group in the File Group field.
4. Click OK.
Step Result: The file group is added to the File Groups list.
5. Click Close.
Result: The file group is added to the list. You can now assign files to the new file group.
Note: You must grant dedicated accounts such as LocalSystem the right to
use the appropriate file groups containing services. For example, if you create
- 56 -
Page 57

Using Modules
a Windows File Group where you place all operating system executable files
(including Windows services that run with the LocalSystem account), you should
grant LocalSystem the right to use this Windows file group.
Renaming a File Group
You can rename an existing file group.
1. In the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Exe Explorer
> Explorer > Manage File Groups.
Step Result: The File Group Management dialog opens.
2. Select a file group to rename.
3. Click Rename File Group.
4. Type a new file group name.
5. Click OK.
6. Click Close.
Step Result: The File Group Management dialog closes.
Result: The file group is renamed.
Deleting a File Group
You can delete an existing file group.
1. In the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Exe Explorer
> Explorer > Manage File Groups.
Step Result: The File Group Management dialog opens.
2. Select the file group you want to delete.
3. Click Delete File Group.
Step Result: The Delete File Group dialog opens and shows the authorized users and
user groups, and associated files.
4. Click OK.
5. Click Close.
Step Result: The File Group Management dialog closes.
Result: The file group is removed from the database.
Note: Deleting a file group may remove parent-child dependencies for related file
authorizations.
- 57 -
Page 58

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Working with User Explorer
You can use the User Explorer module to control user access to authorized software.
Many enterprises differentiate between types of users to control user access to software
applications. Controlling user access to applications reduces the risk associated with malicious
software applications. The User Explorer main window is divided in two tab pages where you
can:
• Link users and user groups with the file groups containing files authorized for users, using
the File Groups by User tab.
• Assign specific authorizations to users and groups, synchronize domains, and change
options, using the Users by File Group tab.
About File Groups
Associating file groups with domain user groups reduces administrative burden because new
user group members inherit application authorization assigned to the parent file group.
The users, groups, and computers assigned to each domain file group are defined within
domain controllers as follows.
• You can authorize users directly or indirectly through a user group assignment.
• A user can be a member of more than one user group. A user group member is authorized to
use the applications that are approved for the associated user groups.
• Users can have indirect authorization assignments resulting from creating parent-child
relationships.
• When you assign a system group or system user a file authorization, the authorization is
assigned to the associated users for every computer in your network.
• You can authorize a global user groups to use an application. Any member of a global user
group is then indirectly authorized through domain user groups to use that application.
File Group by User Tab
You can use the File Group by User tab to group administrative actions based on user access.
Using the File Groups by User tab you can:
• Associate users and user groups to file groups.
• Change user, user group, and computer options.
• Send updates to computers.
• Synchronize local users, user groups, and domain member information.
• View indirect file group assignments.
- 58 -
Page 59

The File Groups by User tab consists of the following panels:
• Users, Groups, Computers and Domains
• File Groups
Figure 20: File Groups by User Tab
The following table describes the key elements in the Users, Groups, Computers and
Domains panel:
Table 19: Users, Groups, Computers and Domains Panel
Using Modules
Name Description
Users, Groups, Computers and
Domains field
Type a name to add to the list of available users,
groups, computers, and domains.
Add Adds a name to the list of users, groups, computers,
and domains names.
Users; Groups; Computers;
Domains check box
Users, groups, computers and
domains list
Includes or excludes from the list of available users,
groups, computers, and domains.
Lists the selected users, groups, computers, and
domains.
The following table describes the key elements in the File Groups panel:
Table 20: File Groups Panel
List Name Description
Authorized Lists authorized files groups for the user or user group
selected from the list. This list may include indirect
authorizations created by parent-child relationships.
Not Authorized Lists files groups not authorized for the user or user group
selected from the list.
- 59 -
Page 60

PGP Endpoint Application Control
List Name Description
Indirectly Authorized
through Domain Groups
Lists file groups and domain user groups that specify the
domain user groups that indirectly authorize other file
groups to the user or user group selected from the list.
You can expand and collapse the hierarchy structure for an object in the Name column, to
browse for the specific users or user groups that you want to create file group assignments for.
The following table describes the key elements in the Users, Groups, Computers and
Domains list:
Table 21: Users, Groups, Computers and Domains List Columns
Column Description
Name The name of the user, user group, computer, or domain.
Location Windows or Novell domain; only for computers or domains.
Type Description of the list item like computer, global user, domain,
and so on.
Note: The LocalSystem user group is a built-in user group used to run services on Microsoft
Windows 2000, XP, 2003, and Vista ® operating systems. Windows Vista also uses the builtin LocalService and NetworkService user groups to run services.
Assigning File Groups to Users
After creating file groups and parent-child relationships you want to use, you can assign file
groups to users or user groups.
1. In the Management Server Console, select View > Modules > User Explorer.
Step Result: The User Explorer window opens.
2. Select the File Groups by User tab.
3. In the Users, Groups, Computers and Domains panel, select a user or user group.
4. Select one or more file groups from the Not Authorized list.
5. Select one of the following options:
Command Action
Authorize Adds the selected file group to the list of file groups
directly authorized for the selected user or user group.
- 60 -
Page 61

Command Action
Authorize All Adds the names of file listed as Not Authorized to file
groups directly authorized for the selected user or user
group.
Note: Changes to file authorizations or user membership for a file group can remove users
that are indirectly authorized for a file group.
Result: The user or user group is now assigned to the designated file group.
After Completing This Task:
You can send the updated authorization(s) immediately to the client computers using the
Control Panel > Tools > Send Updates option. If you do not send updates to protected
clients, they automatically receive updates when they restart or at next user log in.
Removing File Groups from Users
You can remove file group assignments by user or user group.
1. In the Management Server Console, select View > Modules > User Explorer.
Using Modules
Step Result: The User Explorer window opens.
2. Select the File Groups by User tab.
3. In the Users, Groups, Computers and Domains panel, select a user or user group.
4. Select one or more file groups from the Authorized list.
5. Select one of the following options:
Command Action
Remove Deletes the selected file group from the list of file groups
directly authorized for the chosen user or user group.
Remove All Deletes the file group names listed as Authorized from
file groups directly authorized for the selected user or user
group.
Result: The selected file group is no longer authorized for the chosen user or user group.
After Completing This Task:
You can send the updated authorization(s) immediately to the client computers using the
Control Panel > Tools > Send Updates option. If you do not send updates to protected
clients, they automatically receive updates when they restart or at next user log in.
- 61 -
Page 62

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Changing the User Explorer Options
You can access the Default Options tool from the User Explorer using a shortcut menu.
1. From the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > User
Explorer.
Step Result: The User Explorer window opens.
2. Select the File Groups by User tab.
3. In the Users, Groups, Computers and Domains panel, right-click to select user, user
group, or computer in the Name column.
Step Result: A right-mouse menu appears.
4. Select Options from the shortcut menu.
Step Result: The Default Options dialog opens.
Result: You have a shortcut to access the Default Options dialog directly from the User
Explorer module to the Control Panel > Tools > Default Options for changing
user, user group, and computer options.
Synchronizing Local Users and User Groups
An administrator must manually import and synchronize local user and user groups to add them
to the database, when the users and groups are not part of the existing domain.
The PGP Endpoint database contains only domain users by default, so local users and groups
must be added separately.
Restriction: Only an Enterprise Administrator can synchronize Novel Organization Units (OU)
local user and user group domain information.
1. In the Management Server Console, select View > Modules > User Explorer.
Step Result: The User Explorer window opens.
2. Select the File Groups by User tab.
3. In the Users, Groups, Computers and Domains panel, right-click to select a local computer
on the Name column.
Step Result: A right-mouse menu appears.
4. Select Synchronize Local Users/Groups from the context menu.
The PGP Endpoint Management Server Console shows you an error message if the
computer being synchronized is offline.
Step Result: The operation result appears in the Output window.
Result: The local user and user groups information is synchronized and imported to the
database.
- 62 -
Page 63

Using Modules
The User by File Group Tab
You can use the User by File Group tab to group administrative actions based on file groups.
Using the Users by File Group tab you can:
• Associate file groups to users and user groups.
• View file group assignments.
• Change user and user group options.
The Users by File Group tab consists of the following panels:
• File Groups
• Associated Users
Figure 21: The Users by File Group Tab
The following table describes the key elements for the Users by File Group tab:
Table 22: Users by File Group Tab Elements
List Name Description
File Groups Lists the existing file groups including file groups imported
when using the Standard File Definitions or file groups
created by a PGP Endpoint administrator.
Associated Users Shows the list of users or user groups directly or indirectly
authorized to use the file group select from the File Groups
list.
Restriction: For a Microsoft Windows 2000 default configuration, some of the global users
and user groups are pre-defined members of the system groups: Administrators, Everyone,
Power Users, and Users. When a computer joins a domain, the domain group is set by
- 63 -
Page 64

PGP Endpoint Application Control
default as member of the system group for that computer. In the User Explorer module,
the system groups on each computer are assigned to the same sets of authorized system
file groups.However, you can change the domain for members of system groups on a per
computer basis. File groups authorized to global members of system groups do not appear in
the Indirectly Authorized Through Domain Groups list when you view the authorizations for a
domain user or domain group, although the authorizations may exist on a per computer basis.
The following table describes the key elements in the Associated User list:
Table 23: Associated Users List Columns
Column
Name The name of the user, user group, computer,
Location Windows or Novell domain; only for
Type Description of the list item such as computer,
Note: The LocalSystem user group is a built-in user group used to run services on Microsoft
Windows 2000, XP, 2003, and Vista ® operating systems. Windows Vista also uses the builtin LocalService and NetworkService user groups to run services.
or domain.
computers or domains.
global user, domain, and so forth.
Assigning Users to a File Group
You can assign specific permissions to local users and user groups. Only authorized
applications and scripts assigned to a user or a user group can run on the client. PGP Endpoint
verifies which file group is associated with an executable, script, or macro and whether the user
has permission for the file group.
1. From the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > User
Explorer.
Step Result: The User Explorer window opens.
2. Select the User by File Group tab.
3. In the File Groups list, select a file group.
4. Click Add.
Step Result: The Select Group, User, Local Group, Local User dialog opens.
5. Click Search.
Step Result: The Name column list the user group, user, local user group, and local user
names.
6. Select one or more user or user group names from the list.
- 64 -
Page 65

7. Click OK.
Step Result: The Select Group, User, Local Group, Local User dialog closes.
Result: The file group is assigned to the designated user or user group.
After Completing This Task:
You can send the updated authorization(s) immediately to the client computers using the
Control Panel > Tools > Send Updates option. If you do not send updates to protected
clients, they automatically receive updates when they restart or at next user log in.
Removing Users from a File Group
You can remove individual users or groups of users from existing file groups.
1. From the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > User
Explorer.
Step Result: The User Explorer window opens.
2. Select the User by File Group tab.
3. In the File Groups list, select a file group.
4. In the Associated Users list, select one or more users or user groups.
5. Select one of the following options:
Using Modules
Command Action
Remove Deletes the link for the file group assignment from the
selected file group.
Remove All Deletes the link for the file group assignment for users and
user groups from the selected file group.
Result: The designated user or user group link is deleted from the file group assignment.
After Completing This Task:
You can send the updated authorization(s) immediately to the client computers using the
Control Panel > Tools > Send Updates option. If you do not send updates to protected
clients, they automatically receive updates when they restart or at next user log in.
- 65 -
Page 66

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Working with Database Explorer
The Database Explorer module is the primary tool for viewing and managing database records
as well as creating and maintaining file group relationships.
You can use the Database Explorer to:
• Administer file group assignments.
• Manage file groups.
• View database records.
• Administer file group relationships.
The PGP Endpoint database serves as the central repository of authorization information for:
• Authorized executable files, scripts, and macros.
• Digital signatures that uniquely identify the authorized files.
• File groups.
• File group parent-child relationships.
• Authorized users and user groups.
The Database Explorer module consists of two tab pages:
• The Files tab shows you all files stored in the PGP Endpoint database. You can assign files
to file groups.
• The Groups tab allows you to manage file group relationships.
When working in either tab you can access the Explorer menu to manage file groups, and the
Tools menu to do database maintenance.
On the Files tab page you can see the following columns and fields:
Table 24: Files Tab Column Descriptions
Column Description
File Name Object used to filter the result query for the Database Explorer main
page, used in combination with the File Group field, which field
accepts wildcard.
File Group Field used to filter the result query in the Database Explorer main
page to select the required file group from the list or use with <All>,
and is used in combination with the File Group field.
ID Unique system file identifier.
File Name Full file name.
Extension File extension.
Original Path Full path from where the file was first scanned.
- 66 -
Page 67

Column Description
File Group The assigned file group. <Not Authorized> if the file has not been
assigned.
Hash The calculated digital signature as stored in the database.
File Type Shows the file category: Executable, macro, or script.
On the Groups tab page you can see the following panels and columns:
Table 25: Groups Tab Column Descriptions
Item Description
File Groups This panel has the top-level file groups. Those file groups with a lock
cannot be deleted.
Relationships This panel shows all available relationships.
Name The file group name n the File Group or Relationship panel.
Type Relationship type: Child, Parent, Child (indirect), Parent (indirect).
Using Modules
The Files Tab
The Database Explorer page shows the internal system ID, filename, extension, path, file
group assignment, and parent-child relationships between file groups for each file on the Files
tab.
The Database Explorer module displays a list of all the files stored in the PGP Endpoint
database with a valid digital signature.
Figure 22: Database Explorer Files Tab
- 67 -
Page 68

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Assigning Files to File Groups
After you create the necessary file groups and required parent-child relationships, you can
assign executable files, scripts, and macros to file groups.
1. In the Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Database Explorer.
2. Select the file(s) to assign to a file group.
3. Right-click the file selection.
4. Select the Assign to File Group option.
Step Result: The Assign Files to a File Group dialog opens.
Figure 23: Assign Files to File Groups Dialog
Table 26: Assign Files to File Groups Columns
Column Description
File Name of the file including extension.
File Path Complete file path name, including the drive.
Current File Group The file group to which the file currently belongs.
Suggested File
Group
Files that are not assigned to a file group are
designated as <Not Authorized>.
A proposed file group based on the file name. A
file having the same name as another file in the
database is suggested to belong to the same file
group as the initial file.
- 68 -
Page 69

Using Modules
5. Select a file group from the drop-down list in the Suggested File Group column.
6. Click OK.
Result: The file(s) are now assigned to the designated file group.
Note: You can assign a script or macro to a file group as a script, as distinguished
from an executable file.
Changing File Assignments
You can modify file lists and group assignments periodically.
You may need to modify your file lists or assignments when:
• New software has been installed on your protected endpoints, and you wish to permit users
access to the new applications.
• Updated versions of existing software are provided, and you want users to use the new
versions.
• An executable file, script, or macro has become corrupted or is no longer appropriate, and
you want to prevent users from running the application.
• Multiple users are locally authorizing files that are centrally denied, as reported in the log
files.
Viewing Database Records
The Database Explorer module displays a list of the executable, script, and macro files, digital
signatures, and assigned file groups stored in the PGP Endpoint database.
1. From the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Database
Explorer.
Step Result: The Database Explorer page opens.
Figure 24: Database Explorer Module
- 69 -
Page 70

PGP Endpoint Application Control
2. Select the Files tab.
3. Type a file name in the File name field. You can use wild cards (* and ?).
4. Select a file group from the File Group list.
5. Click Search.
Result: You can view the files stored in the database including the digital signature and file
group assignment.
Caution: Your request may process slowly when you have a large PGP Endpoint
database.
Saving the Database Records
You can save database records as a Comma Separated Value *.csv files that you can use with
third-party reporting tools.
1. Use the File > Save as command.
Step Result: The Windows Save as dialog opens.
2. Select the file location and name.
3. Click Save.
Result: The records are saved as a Comma Separated Value *.csv file. You can import the
file information to a third party reporting tool.
The Groups Tab
You use the Groups tab to manage parent-child relationships between file groups.
Creating Parent-Child Relationships
You administer parent-child relationships between file groups using the Database Explorer
Groups tab.
Prerequisites:
You must create parent and child file groups before creating parent-child relationships.
Parent-child relationships may be direct or indirect. A direct relationship exists when a file
group has a direct line of descendants between parent and child file groups. All other file group
relationships are indirect relationships.
1. From the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Database
Explorer.
Step Result: The Database Explorer page opens.
2. Select the Groups tab.
3. Select the desired group from the File Groups list.
- 70 -
Page 71

Using Modules
4. To assign a relationship, by selecting a file group from the Relationships list and click one of
the following:
• Add child
• Add parent
• Remove
Step Result: The Type column changes from Available to:
• Child
• Parent
• Child (Indirect)
• Parent (Indirect)
Result: The parent-child relationship associations are shown with one of the following icons
indicating the relationship status:
Table 27: File Group Relationship Status Icons
Icon Description
The file group is a parent of the one selected in the File Groups
panel.
The file group is child of the one selected in the File Groups
panel.
The file group is an indirect parent of the one selected in the File
Groups panel.
The file group is an indirect child of the one selected in the File
Groups panel.
A file group created by a PGP Endpoint administrator that can be
deleted or renamed.
A file group created by the program that is blocked and cannot be
deleted.
Note: You cannot delete indirect relationships, you must first proceed to the
directly related file group and then remove the relationship.
The following examples demonstrate hierarchical parent-child file group
relationships.
- 71 -
Page 72

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Example:
The file group 16 Bit Applications is the parent of Accessories, and also has
indirect child Alternative and CAD software:
Figure 25: File Group Parent Relationship
The File Group Accounting is the child of Marketing who also has an indirect
child Payroll:
Figure 26: File Group Child Relationship
This is the consequence of the following parent-child assignments:
Figure 27: File Group Parent-Child Relationship
When assigning the file group Payroll to a user or user group; there is also an
indirect assignment because of this relationship:
Figure 28: File Group Indirect Assignment
You can view indirect parent-child relationship assignments by using the File
Groups by User tab of the User Explorer module.
- 72 -
Page 73

Using Modules
Working with Log Explorer
Every endpoint protected by PGP Endpoint generates activity logs for administrator and userdefined client actions. The information in these logs is sent to the PGP Endpoint Administration
Server and can be viewed through the Log Explorer module of the PGP Endpoint Management
Server Console.
Every endpoint protected by PGP Endpoint generates activity logs that record application
attempts, denials, and, optionally, authorizations. In addition, all tasks performed in the PGP
Endpoint Management Server Console also generate audit logs showing actions carried out by
administrators, such as changing user access rights and file group permissions.
If you have appropriate administrative privileges, you can use the Log Explorer module to view
logs of executable files, scripts, and macros:
• That have been executed or denied by central authorization.
• That were executed or denied by local authorization.
• For a designated user, computer, or filename by matching pattern.
With the Log Explorer module you can also:
• Sort, add criteria, define columns, create templates, and organize information.
• Monitor the activities of administrators using audit log information.
• Save the results of querying log entries.
• Generate on-demand or automatic reports containing details of granted or denied
applications or administrator actions.
• Generate custom reports using templates.
- 73 -
Page 74
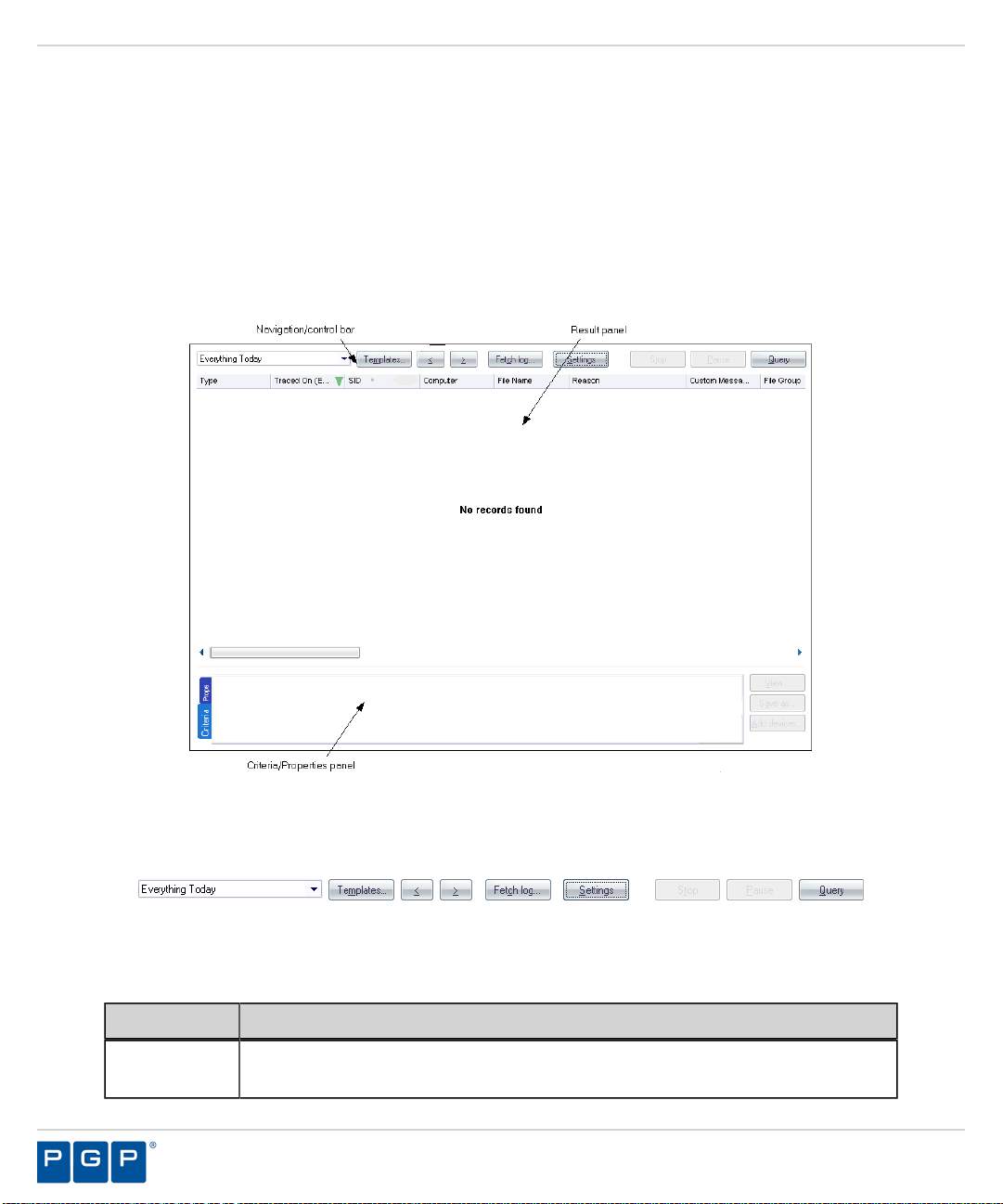
PGP Endpoint Application Control
The Log Explorer Window
The Log Explorer window is the primary mode for administrator interaction with Log Explorer
module features.
The Log Explorer window consists of the following components:
• Navigation control bar
• Results panel
• Criteria/Properties panel
Figure 29: Log Explorer Window
Navigation Control Bar
You can use the navigation control bar to select a template or navigate and control your results.
Figure 30: Navigation/Control Bar
The following table describes the features of the navigation control bar.
Table 28: Log Explorer Navigation Control Bar
Control Description
Templates Create a new template or select from your recently used templates list, shown
as a drop-down list.
- 74 -
Page 75

Using Modules
Control Description
Previous Allows you to navigate backward to the previous query result list stored
internally, when you are performing multiple queries.
Next Allows you to navigate forward to the query result list stored internally, when
you are performing multiple queries.
Query Retrieves all log entries that match the criteria defined in the current template.
Column Headers
The column headers display the title of the columns.
In addition to displaying column titles, you can use column headers to:
• Sort results to classify the results and display them in a specified order depending on the
value for the log entry (or log entries) in one or more columns.
• Show/hide columns to determine what information is displayed for each result in the report.
• Change the size of the displayed columns by dragging the column header dividers to the left
or right.
• Change the order in which the columns are displayed by dragging and dropping the column
titles in the column headers.
• Group log entries to display a single report row corresponding to multiple log entries grouped
according to the values in one column.
• Display computed columns to display calculated values such as a count of the number of log
entries in a grouped result, the maximum value, minimum value, sum of values, or average
value.
• You can make changes to the columns to display different information from the log entries
without re-executing the query.
• You can also use the column context menu to access the advanced query settings for the
template.
Note: Any on-the-fly changes you make to the column headers are saved in the current
template that you are using.
Show/Hide Columns
You can show or hide selected columns of log entry information.
Prerequisites:
You must select a template that displays query results in the Log Explorer window.
- 75 -
Page 76

PGP Endpoint Application Control
1. Right-click the column header row to display the field names for the fields displayed in the
Results panel.
Step Result: A right-mouse menu appears showing all the column names.
Figure 31: Columns Right-Mouse Menu
2. Click a field name showing a check mark to hide the column, or a field name without a check
mark to show the column.
Result: The names of the columns that you selected are shown or hidden in the Results
panel.
Group Log Entries
You can group multiple log entries into single report rows according to the values in one or more
column log entries.
Prerequisites:
You must select a template that displays query results in the Log Explorer window.
- 76 -
Page 77

Using Modules
1. Right-click the column header row to display the field names for the fields displayed in the
Results panel.
Step Result: A right-mouse menu appears showing all the column names.
Figure 32: Columns Right-Mouse Menu
2. Select Group by from the menu.
- 77 -
Page 78

PGP Endpoint Application Control
3. Check the column you want to group your template query results by.
Figure 33: Group By Option
Result: The log report results are grouped by the column you selected. Primary groups are
denoted by a green circle shown in the column title when a column is used to group
results, as illustrated by the following:
Figure 34: Column Title Primary Group
- 78 -
Page 79

Using Modules
You can repeat the above procedure to create sub groups. Secondary subgroups
are denoted by a blue circle with the number 2 shown in the column title when a
column is used to group results, as illustrated by the following:
Figure 35: Column Title Subgroup
Computed Columns
You can include computed columns in your report.
Prerequisites:
You must select a template that displays query results in the Log Explorer window.
You can show additional information alongside predefined log entry columns, corresponding to
additional information stored in the client activity logs.
1. Right-click the column header row to display the field names for the fields displayed in the
Results panel.
Step Result: A right-mouse menu appears showing all the column names.
Figure 36: Columns Right-Mouse Menu
- 79 -
Page 80

PGP Endpoint Application Control
2. Select the Computed Columns option.
The operations supported for computed columns are:
Table 29: Computed Columns Operations
Operation Description
Count Calculates the number of log entries for a value type, such as Count
(Device Class) that shows how many log entries contain device
information. Count (Any) shows the total number of log entries.
Min Calculates the minimum value in a column for a set of results.
Max Calculates the maximum value in a column for a set of results.
Sum Calculates the sum of numerical data for a set of results; valid only for the
File Size column.
Average Calculates the numerical average of numerical data for a set of results;
valid only for the File Size column.
Note: These operations do not apply to all columns.
- 80 -
Page 81

Using Modules
3. Select the type of calculation you want to perform from the Computed Columns sub menu.
Figure 37: Computed Columns Menu
4. Select the column shown in the Results panel that contains the data you want to calculate
computed values for.
Result: The Log Explorer window shows the calculated column results.
- 81 -
Page 82

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Clear Columns Settings
You can reset columns to original values by clearing the sort and group filters.
1. Right-click the column header row to display the field names for the fields displayed in the
Results panel.
Step Result: A right-mouse menu appears showing all the column names.
Figure 38: Columns Right-Mouse Menu
- 82 -
Page 83

2. Select the Current Column option.
Using Modules
Figure 39: Reset Column Groups Headings
3. Select Unsort or Ungroup.
Result: The selected column groupings are reset according to your selection.
Log Explorer Templates
The operation of the Log Explorer module is based on templates that allow you generate
custom reports containing results that match specific criteria.
You use the Log Explorer templates to change criteria options, column size and order, columns
are displayed in the Results panel and custom reports, and the whole sets of configurable
options to create templates. A template is a set of rules used when displaying audit and activity
log data in the Log Explorer.
- 83 -
Page 84

PGP Endpoint Application Control
You can create your own templates or use predefined templates created by PGP. You can save
customized templates for future use.
Note: The list of predefined templates depends upon your license type. Predefined Templates
PGP provides a set of predefined templates used by the Log Explorer, based on commonly
used audit queries.
You can use the following predefined templates.
Table 30: Log Explorer Predefined Templates
Template Name Shows Prerequisite
Applications denied today All applications that
have been denied for
the day.
Applications locally
authorized today
All applications that
have been locally
authorized for the day.
Applications often denied
this week
The most often denied
applications for the
week.
Audit by Administrator
'adm'
All actions performed by
a specific administrator.
This only applies to user for which
the Execution Blocking option is
properly configured.
Entries are only logged when the
Execution Log option is properly
configured.
This only applies to user for which
the Execution Blocking option is
properly configured.
You must enable the Local
Authorization option for each
computer you want to audit.
This only applies to user for which
the Execution Blocking option is
properly configured.
Entries are only logged when the
Execution Log option is properly
configured.
You must change the “adm” user
to an actual administrator in the
Template Settings dialog. The
result is classified by user.
Audit for PC xyz Audit trace for a specific
computer.
- 84 -
You must change the “xyz”
computer to an actual computer in
the Template Settings dialog.
Page 85

Template Name Shows Prerequisite
Using Modules
Audit for user 'abcd' Audit trace for a specific
user.
Audit today Daily audit trace. No action is required.
Everything today Everything that
happened for the day.
Hardening violations this
month
Relaxed logon apps this
week
Users denied acc. to regedit
this week
All client hardening
violations detected for
the month.
All relaxed logon
applications done for the
month.
The user tried to run
Windows regedit utility
and access was denied.
You must change the “abcd”
user to an actual computer in the
Template Settings dialog.
No action is required.
You must configure the Client
Hardening option.
This only applies to user for which
the Execution Blocking option is
properly configured.
Entries are only logged when the
Execution Log option is properly
configured.
You must configure the Relaxed
Logon option for each user that
you want to audit.
This only applies to user for which
the Execution Blocking option is
properly configured.
Users denied app. device
this week
All applications and
device denied this for
the week.
- 85 -
Entries are only logged when the
Execution Log option is properly
configured.
This only applies to user for which
the Execution Blocking option is
properly configured.
Entries are only logged when the
Execution Log option is properly
configured.
You must enable the Device Log
option.
Page 86

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Template Name Shows Prerequisite
Users denied apps this
month
All applications denied
by user for the month.
This only applies to user for which
the Execution Blocking option is
properly configured.
Entries are only logged when the
Execution Log option is properly
configured.
Create New Template
The Log Explorer provides extended capability for creating custom audit query templates.
You can created customized templates that represent specific query criteria.
1. From the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Log
Explorer > Template.
Step Result: The Select and edit templates dialog opens.
Figure 40: Select and Edit Templates Dialog
- 86 -
Page 87

2. Click New.
Step Result: The Templates settings dialog opens, which consists of three tabs:
• General tab
• Simple Query tab
• Schedule tab
Using Modules
Figure 41: Template Settings Dialog
3. Select the General tab.
4. Enter a name for the new template in the Template name field.
5. Type a brief description of the template in the in the Description field.
6. Select one of the following options:
Option Description
Private The new template will only be accessible to the owner and
Enterprise Administrators.
Published The template can be used by any user but can only be
edited by the owner and Enterprise Administrators.
- 87 -
Page 88

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Option Description
Shared The template can be accessed, used, and edited by any
7. Select the Simple Query tab to specify your query columns and criteria.
These criteria determine which log entries are shown as results in the Log Explorer report,
and the information that is displayed.
To select log entries that match certain criteria, select the column to which the criteria apply,
by clicking on the appropriate box, clicking (ellipsis) in the Criteria column, and specify
what you want to match entry details to.
You can choose which information to display for each entry, the display size of the columns
and how the results are grouped or sorted in particular ways.
Note: If you select the Count column then the results are automatically grouped.
8. Click Execute Query.
If you click OK, the window closes and then you will need to click Execute from the Select
and Edit Templates dialog.
user.
Step Result: The Template settings dialog closes and you see the results in the Log
Explorer window.
Result: The template is stored when you execute the query.
- 88 -
Page 89

Using Modules
Select and Edit Templates Dialog
The Select and edit templates dialog is used to select, add, edit, import, export, schedule, and
run templates.
Figure 42: Select and Edit Templates Dialog
The Select and edit templates columns are described in the following table:
Column Description
Name Lists all existing templates that you can access.
Selected Indicates whether the template is currently selected.
Owner The template owner with full rights to use and edit the template.
Permissions Indicates whether the template can be viewed or changed by
users other than the Owner.
Scheduled Indicates whether the template is used to create automatic
reports periodically.
Format Delivery Indicates whether schedule reports are e-mailed or where the
reports are stored.
- 89 -
Page 90

PGP Endpoint Application Control
When you right-click the main panel of the Select and edit templates dialog, the Templates
right-mouse menu is shown:
Figure 43: Templates Menu
Note: The options available in the Templates menu depend on whether you have a template
selected when you opened the menu.
You can use the Templates menu to:
• Create a new template or clone an existing template.
• Change the settings of a selected template.
• Delete a selected template.
• Import templates in XML format or legacy format (*.tmpl) from the registry.
• Export a selected template to an XML file.
• Execute a query to retrieve all log entries that match the criteria defined in the currently
selected template, and display these in the Log Explorer window.
• Filter the templates shown in the Select and Edit Templates dialog.
Filtering Templates
You can create subsets of the templates listed in the Select and Edit Templates dialog.
You can select multiple filtering criteria to narrow the focus of template sets shown, thereby
reducing the number of templates that are listed.
1. From the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Log
Explorer > Templates.
Step Result: The Select and Edit Templates dialog opens.
- 90 -
Page 91

2. Click Filter.
Step Result: The Filter dialog opens.
Figure 44: Filter Dialog
3. Select one or more of the following options:
Option Description
Private Shows templates visible only to the template owner and
Enterprise Administrator.
Published Shows templates visible to all Management Server
Console users within your system that can only
be changed by the template owner and Enterprise
Administrator.
Using Modules
Shared Shows templates viewed and changed by any
Management Server Console users within your system.
Non-scheduled Shows templates used to generate specific reports.
Scheduled Shows templates automatically run periodically to
generate regular reports. These are saved in a shared
folder on your network or e-mailed to specified recipients.
Created by others Shows templates created by users other than the
Enterprise Administrator.
4. Click OK.
Result: A subset of all available templates is shown.
- 91 -
Page 92

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Template Settings Dialog
The Template settings dialog is used to define the settings used for a new template, or a
template selected from the Select and edit templates dialog:
You can use the Template settings dialog to:
• Name a new template using the General tab and specify who is allowed to use and edit the
template by selecting the Private, Published, or Shared options.
• Choose whether the template is used to generate reports automatically on a periodic basis
by setting the parameters in the Schedule tab and selecting Generate scheduled reports.
• Specify complex selection and display settings for the template by using the Advanced View
with the Query & Output tab.
• Schedule the production of periodic reports using a template using the Schedule tab.
• Define the format of scheduled reports using the Schedule tab.
• Choose who you want the reports to be e-mailed to using the Schedule tab.
• Execute the query specified by the template and display the results in the main Log Explorer
window.
• Save the changes made to the template settings.
Figure 45: Template Settings Dialog
- 92 -
Page 93

Using Modules
General Tab
The General tab is displayed by default when the Template settings dialog opens and is used
to define general template use conditions.
You can use the General tab to:
• Define the template name in the Template name field.
• Describe the template in the Description field.
• Define the user access type as:
• Private - Template can be used only by the Owner and Enterprise Administrators.
• Published - Template can be used by any user but can only be edited by the Owner and
Enterprise Administrators.
• Shared - Template can be used and edited by any user.
Simple Query Tab
The Simple Query tab is displayed by default when the Template settings dialog opens and is
used define simple template query conditions.
Using the Simple Query tab,you can:
• Show/hide columns by selecting or deselecting the column names in the Columns list.
Step Result: The column name moves to the top section of the list when you check it.
• Change the display size of a column by:
a) Selecting a row.
b) Clicking Size.
c) Typing a new size.
• Sort ascending/descending:
a) Click the Sort/Group by cell of the row corresponding to the appropriate results column
(or highlight the row and click Sort/Group By).
b) Choose either Ascending or Descending from the drop-down list options.
c) If you want to sort the results of the query by the values in more than one column, select
the multi-column sorting box and choose the columns that you want to sort your results by
in turn.
• Group results according to the value in a particular column:
a) Click the Sort/Group by cell of the row corresponding to the appropriate results column
(or select the row and click Sort/Group By).
b) Choose the Group by option from the drop-down list.
When grouping results, all log entries in the Log Explorer Results panel/custom report
are compiled into single entries corresponding to the unique values in the column. In the
following figure, results are grouped according to their File Type value. The ellipses indicate
- 93 -
Page 94

PGP Endpoint Application Control
hidden log entries and the Count column indicates how many log entries have the same File
Type.
Figure 46: Grouping Results in the Query
• Define the column display order using Move up and Move down commands.
- 94 -
Page 95

Using Modules
Schedule Tab
The Schedule tab is displayed by default when the Template settings dialog opens and is
used scheduling report generation.
The Schedule tab is used to define the following:
• Start and end dates between which reports are automatically generated using the Schedule
template.
• How often the report is generated and the pattern for production. For example, you can
choose report generation on a daily or weekly basis for specific days, every few hours, or on
a monthly basis.
• Who and where the information is sent, or stored, and the format.
Restriction: You cannot schedule a log report unless have the necessary administrative rights.
If you do not have administrative rights, you will see that the options are grayed-out and you
receive a warning message.
Figure 47: Schedule Tab
- 95 -
Page 96

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Scheduling a Report
Using a template, you can schedule automatic report generation by specifying the report
frequency and report recipients.
1. From the PGP Endpoint Management Server Console, select View > Modules > Log
Explorer > Templates.
Step Result: The Select and edit template dialog opens.
2. Choose the template from the list.
3. Click Settings.
Step Result: The Template settings dialog opens.
4. Select the Schedule tab.
5. Select the Generate scheduled reports option.
6. In the Range of recurrence panel:
a) Select the starting date and hour.
b) You may select the End by option and select and ending date and hour.
7. In the Delivery targets panel:
a) Click New.
Step Result: The Edit target dialog opens.
Figure 48: Edit Target Dialog
b) Select the Method from the drop-down list.
- 96 -
Page 97

c) If you select the Share method, click Browse.
Step Result: The Browse for Folder dialog opens.
Figure 49: Browse for Folder
d) Select a shared folder.
e) Click OK.
Step Result: The Edit target dialog opens.
Using Modules
Figure 50: E-mail Options
f) If you selected E-mail as method, specify the To, Cc, From recipients, and Mail server
(SMTP) in the Edit target dialog.
g) Click Ping to test the connection.
h) If you select the Apply for every target option, the Mail server field for every delivery
target changes and you lose any existing information. You must be careful when setting
e-mail delivery options. If not correctly set, the report may be sent to the junk mail folder.
- 97 -
Page 98

PGP Endpoint Application Control
The specified mail server should accept anonymous connections so that the reports
delivery option works properly.
i) Click OK.
Step Result: The Edit target dialog closes. The Schedule tab of the Template settings
dialog opens. The Schedule tab is used to define whether reports are sent
via mail or saved in a shared folder on the network.
8. In the Format field:
a) Select the file Format from the drop-down list.
b) Change the Output extension, as necessary.
9. In the Recurrence pattern panel:
a) Select a frequency option from the list shown.
Step Result: The right panel changes to reflect your selection.
10.Click OK.
11.Click Close.
Result: The selected template is ready to generate a regularly schedule report that is
archived on a shared folder or sent by e-mail as an attachment.
Criteria
You specify the criteria you want to use for a particular template using one or more contextdependent Criteria dialogs.
Criteria narrow the query results you. Typically, the more specific you are with your search
criteria, the fewer results are returned.
Criteria choices range from a fixed value the Criteria dialog displays to a free text data field
where you can use wild cards to delimit the criteria. Others dialogs contain Select or Search
commands, for example, when specifying criteria involves matching one or more computers or
users.
The Criteria dialog list is displayed when log entry fields contain one of a fixed set of values.
Figure 51: Criteria Dialog
- 98 -
Page 99

Using Modules
The free-text Criteria dialog is used to filter the query results based on any text that you type in.
Figure 52: Free-text Criteria Dialog
The time Criteria dialog is used to search for log entries that were produced, or uploaded to the
server, at a certain date/time.
Figure 53: Time Criteria Dialog
After you define the criteria used in your template, they are displayed in the Criteria column of
the Template settings dialog.
Figure 54: Example Criteria settings
Specify Criteria Type
You can view the device access event types by specifying log entry Type criteria.
The Computer, Traced on, and Transferred on fields are shown in the logs for every event
associated with input/output device access, as described in the following table.
- 99 -
Page 100

PGP Endpoint Application Control
Table 31: Log Explorer Criteria by Type
Criteria by Type Logged Event Additional Information
MEDIUM-INSERTED Occurs when a user inserts
a CD/DVD in the computer
drive or removable media
reader.
DEVICE-ATTACHED Occurs when a device is
connected to a computer.
READ-DENIED Occurs when a user attempts
to access an unauthorized
device.
Device type name of the
device medium.
Volume label is the medium
tag.
Medium hash is the hash
number for the inserted
medium.
Other is the inserted medium
serial number.
None.
Device type name of the
device medium.
Volume label is the medium
tag.
File Name is the name of
the file the user attempted to
read.
User Name is the name of
the user who attempted to
access the device.
WRITE-DENIED Occurs when a user attempts
to write a file to a read-only
device.
- 100 -
Process Name is the
application used to access
the device.
Other is the exact access
mask, in hexadecimal format,
used to access the device.
Device type name of the
device medium.
Volume label is the medium
tag.
 Loading...
Loading...