
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Translation of the original instructions
IKR 251
Compact Cold Cathode Gauge, FPM gedichtet
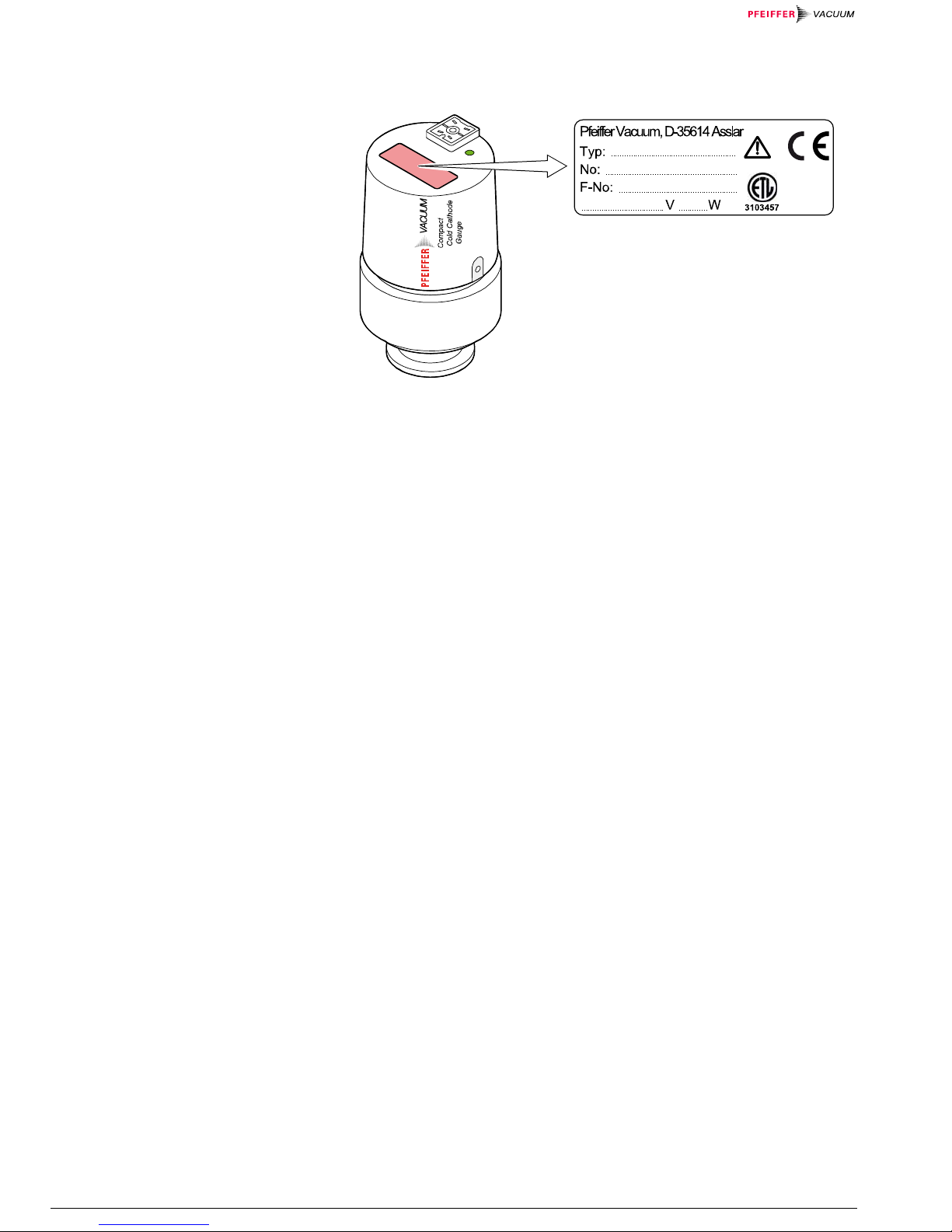
Product Identification
In all communications with Pfeiffer Vacuum, please specify the information given
on the product nameplate.
Validity
Intended Use
Functional Principle
This document applies to products with the following part numbers
PT R25 500 (DN 25 ISO-KF flange)
PT R25 501 (DN 40 ISO-KF flange)
PT R25 502 (DN 40 CF-F flange)
The part number can be taken from the product nameplate.
We reserve the right to make technical changes without prior notice.
The Compact Cold Cathode Gauge IKR 251 has been designed for vacuum
measurement in a pressure range of 2×10-9 1×10-2 hPa.
The IKR 251 can be used with a Pfeiffer Vacuum measurement unit for Compact
Gauges or with another evaluation unit.
Over the whole measurement range, the measuring signal is output as a logarithm
of the pressure.
If functions with a cold cathode ionization measurement circuit (according to the
inverted magnetron principle).
2 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251

Contents
Product Identification 2
Validity 2
Intended Use 2
Functional Principle 2
1 Safety 4
1.1 Symbols Used 4
1.2 Personnel Qualifications 4
1.3 Safety Information 4
1.4 Liability and Warranty 5
2 Technical Data 6
3 Installation 9
3.1 Vacuum Connection 9
3.1.1 Removing the Magnet Unit (Only for Gauges With CF Flanges) 10
3.2 Power Connection 11
3.2.1 Use With a Pfeiffer Vacuum Measurement Unit 11
3.2.2 Use With Another Evaluation Unit 11
4 Operation 13
5 Maintenance 14
5.1 Cleaning the Gauge / Replacing Parts 14
5.1.1 Disassembling the Gauge 15
5.1.2 Cleaning the Gauge 16
5.1.3 Reassembling the Gauge 16
5.1.4 Adjusting the Gauge 17
5.2 What to Do in Case of Problems 18
6 Removing the Gauge From the Vacuum System 18
7 Returning the Product 19
8 Accessories 19
9 Spare Parts 20
10 Disposal 20
Appendix 21
A: Conversion Table for Pressure Units 21
B: Measuring Signal vs. Pressure 21
C: Gas Type Dependence 22
ETL Certification 23
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 3
For cross references within this document, the symbol ( XY) is used, for
references to other documents, the symbol ( [Z]).

1 Safety
1.1 Symbols Used
1.2 Personnel Qualifications
1.3 Safety Information
DANGER
Information on preventing any kind of physical injury.
WARNING
Information on preventing extensive equipment and environmental damage.
Caution
Information on correct handling or use. Disregard can lead to malfunctions or
minor equipment damage.
Skilled personnel
All work described in this document may only be carried out by persons who
have suitable technical training and the necessary experience or who have been
instructed by the end-user of the product.
Adhere to the applicable regulations and take the necessary precautions for the
process media used.
Consider possible reactions between the materials ( 7) and the process
media.
Consider possible reactions of the process media due to the heat generated by
the product.
Adhere to the applicable regulations and take the necessary precautions for all
work you are going to do and consider the safety information in this document.
Before you begin to work, find out whether any vacuum components are con-
taminated. Adhere to the relevant regulations and take the necessary precautions when handling contaminated parts.
4 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251
DANGER
DANGER: magnetic fields
Strong magnetic fields can disturb electronic devices like heart
pacemakers or impair their function.
Maintain a safety distance of 10 cm between the magnet and the
heart pacemaker or prevent the influence of strong magnetic fields by
Pass on the safety information to other users.
antimagnetic shielding.

1.4 Liability and Warranty
Pfeiffer Vacuum assumes no liability and the warranty becomes null and void if the
custodian or third parties
disregard the information in this document
use the product in a non-conforming manner
make any kind of changes (modifications, alterations etc.) to the product
use the product with accessories not listed in the corresponding product
documentation.
The custodian assumes the responsibility in conjunction with the process media
used.
Gauge failures due to contamination or wear and tear, as well as expendable parts
(e.g. seals), are not covered by the warranty.
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 5

2 Technical Data
Admissible temperatures
Storage
Operation
Bakeout
-40 °C +65 °C
+5 °C +55 °C
+150 °C (without electronics unit and
magnetic shielding)
Relative humidity max. 80% at temperatures +31 °C
decreasing to 50% at +40 °C
Use indoors only
altitude up to 2000 m (6600 ft)
Measurement range (air, N2) 2×10-9 1×10-2 hPa
Accuracy
±30%
in the range 1×10-8 1×10-3 hPa
Reproducibility
Gas type dependence
±5%
in the range 1×10
Appendix C
-8
1×10-3 hPa
Adjustment The gauge is adjusted at the factory
and requires no maintenance.
Degree of protection IP 40
Maximum pressure (absolute) 1000 kPa
only for inert gases <55 °C
Supply
DANGER
The gauge may only be connected to supply or measurement units
that conform to the requirements of a grounded protective extra-low
Voltage at the gauge 15.0 30.0 VDC (max. ripple 1 Vpp)
Power consumption 2 W
Fuse1) 1 AT
The minimum voltage of the power supply must be increased proportionally to the
length of the measuring cable.
Voltage at the supply unit with
maximum cable length
Electrical connection Hirschmann compact connector
Tightening torque 0.2 Nm
Cable 5 poles plus screening
Maximum cable length 100 m (0.25 mm² conductor)
Operating voltage
(in the measuring chamber)
Operating current
(in the measuring chamber)
voltage (PELV). The connection to the gauge has to be fused.1)
16.0 30.0 VDC (max. ripple 1 Vpp)
type GO 6, 6 pins, male
150 m (0.34 mm² conductor)
500 m (1.0 mm² conductor)
3.3 kV
500 µA
6 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251
1)
Pfeiffer Vacuum measurement and control units for Compact Gauges fulfill
these requirements.
PT R25 500 (DN 25 ISO-KF)
Output signal (measuring signal)
Voltage range
0 V +10.5 V
Relationship voltage-pressure logarithmic, increase 1 V / decade
( Appendix B)
Error signals <0.5 V (no supply)
Output impedance
Normal load
Minimum load
2×10
100 k
10 k , short-circuit proof
Response time pressure dependent
p > 10-6 hPa
p = 10-8 hPa
<10 ms
1 s
Gauge identification
5.1 k resistor referenced to supply
common Figure 2
Grounding concept
Vacuum flange-measurement
common
Figure 2
connected via 10 k
(max. voltage differential
with respect to safety ±50 V
with respect to accuracy ±10 V)
Supply common-signal common conducted separately; differential
measurement recommended for cable
lengths 10 m
Materials exposed to the vacuum
Feedthrough isolation
Internal seals
Flange
Measuring chamber
Anode
Ignition aid
Internal volume
ceramic (Al2O3)
FPM75
stainless steel (1.4104)
stainless steel (1.4104)
Mo
stainless steel (1.4310/AISI 301)
20 cm³
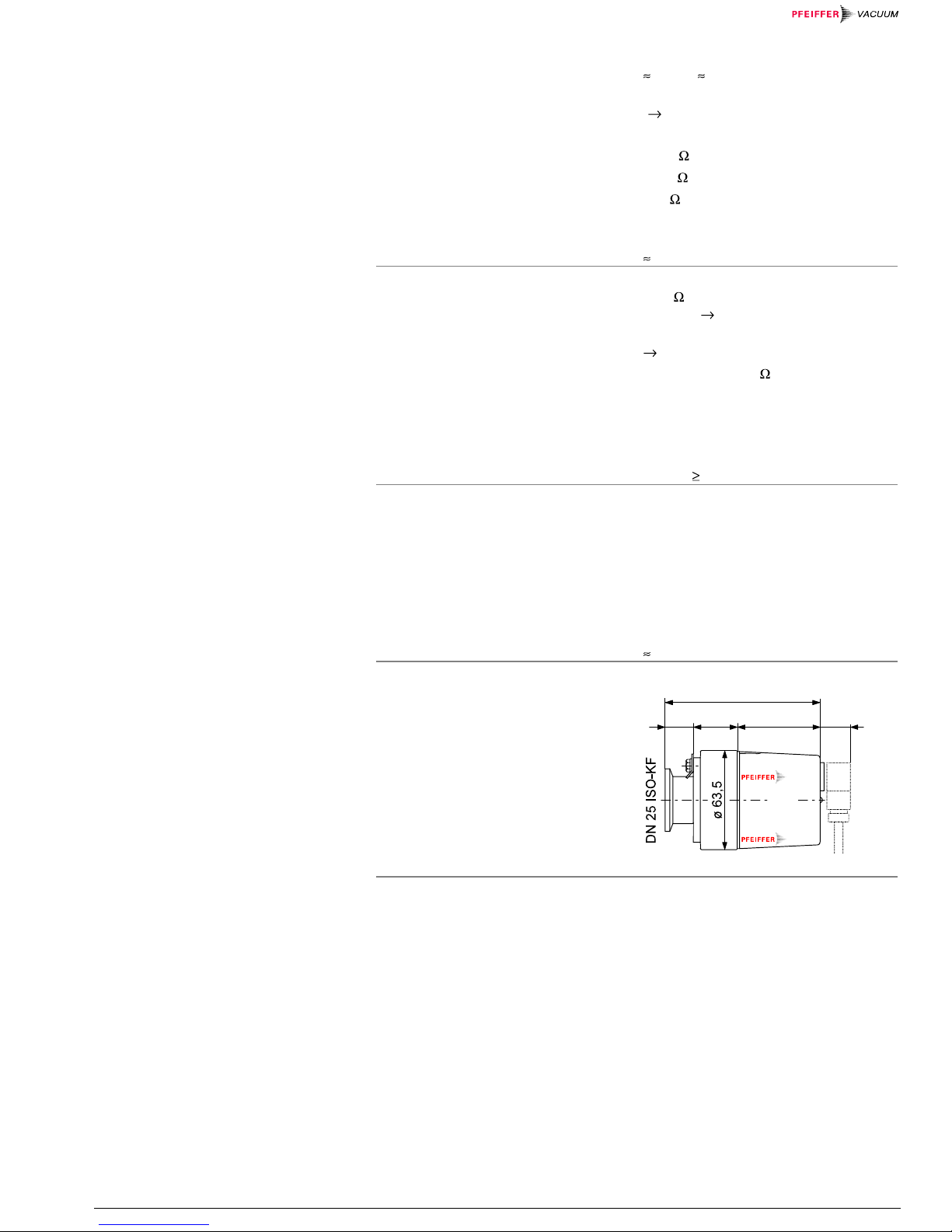
Dimensions [mm]
18
28
101
55 20
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 7
Weight 700 g
VAC UUM
Compact
ColdCathode
Gauge
VAC UUM
PT R25 501 (DN 40 ISO-KF)
PT R25 502 (DN 40 CF-F)
Materials exposed to the vacuum
Feedthrough isolation
Internal seals
Flange
Measuring chamber
Anode
Ignition aid
Internal volume
ceramic (Al2O3)
FPM75
stainless steel (1.4306/AISI 304L)
stainless steel (1.4104)
Mo
stainless steel (1.4310/AISI 301)
20 cm³
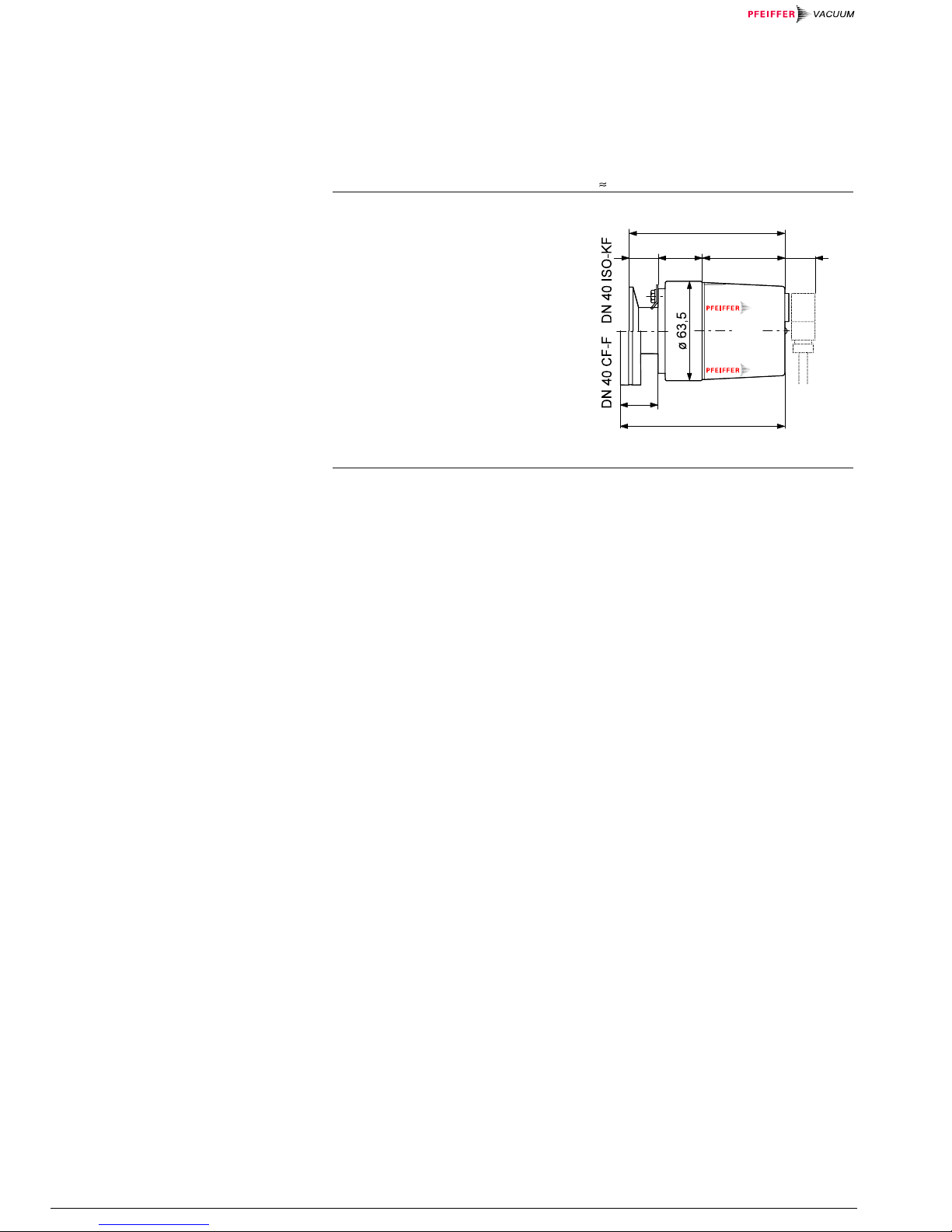
Dimensions [mm]
101.5
18.52428 55 20
VAC UUM
Compact
ColdCathode
Gauge
VAC UUM
107
Weight 700 g (DN 40 ISO-KF flange)
950 g (DN 40 CF-F flange)
8 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251

3 Installation
3.1 Vacuum Connection
Procedure
Caution
Caution: vacuum component
Dirt and damages impair the function of the vacuum component.
When handling vacuum components, take appropriate measures to
The gauge can be mounted in any orientation. However, it should be mounted so
that any particles present cannot penetrate into the measuring chamber ( 13).
See "Technical data" ( 6 ff.) for space requirements.
ensure cleanliness and prevent damages.
Remove the protective cap.
The protective cap will be
needed for maintenance work.
Make the flange connection.
When making a CF flange connection, it
can be advantageous to temporarily
remove the magnet unit
( section 3.1.1).
DANGER
DANGER: overpressure in the vacuum system >250 kPa
KF flange connections with elastomer sealing rings (e.g.
O-rings) cannot withstand such pressures. Process media can
thus leak and possibly damage your health.
Use sealing rings provided with an outer centering ring.
DANGER
DANGER: overpressure in the vacuum system >100 kPa
If clamps are opened unintentionally injury can be caused by
catapulted parts.
Use the type of clamps which can only be opened and closed
by means of a tool (e.g. hose clip clamping ring).
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 9

3.1.1 Removing the Magnet
Unit (Only for Gauges
With CF Flanges)
Tools required
Procedure
DANGER
The gauge must be electrically connected to the grounded
vacuum chamber. The connection must conform to the requirements of protective connection according to EN 61010:
CF flanges fulfill this requirement
For gauges with KF flanges, use a conductive metallic
clamping ring.
WARNING
WARNING: electric arcing
Helium may cause electric arcing with detrimental effects on the
electronics of the product.
Before performing any tightness tests put the product out of
Allen wrench AF 1.5
Open-end wrench AF 7
operation and remove the electronics unit.
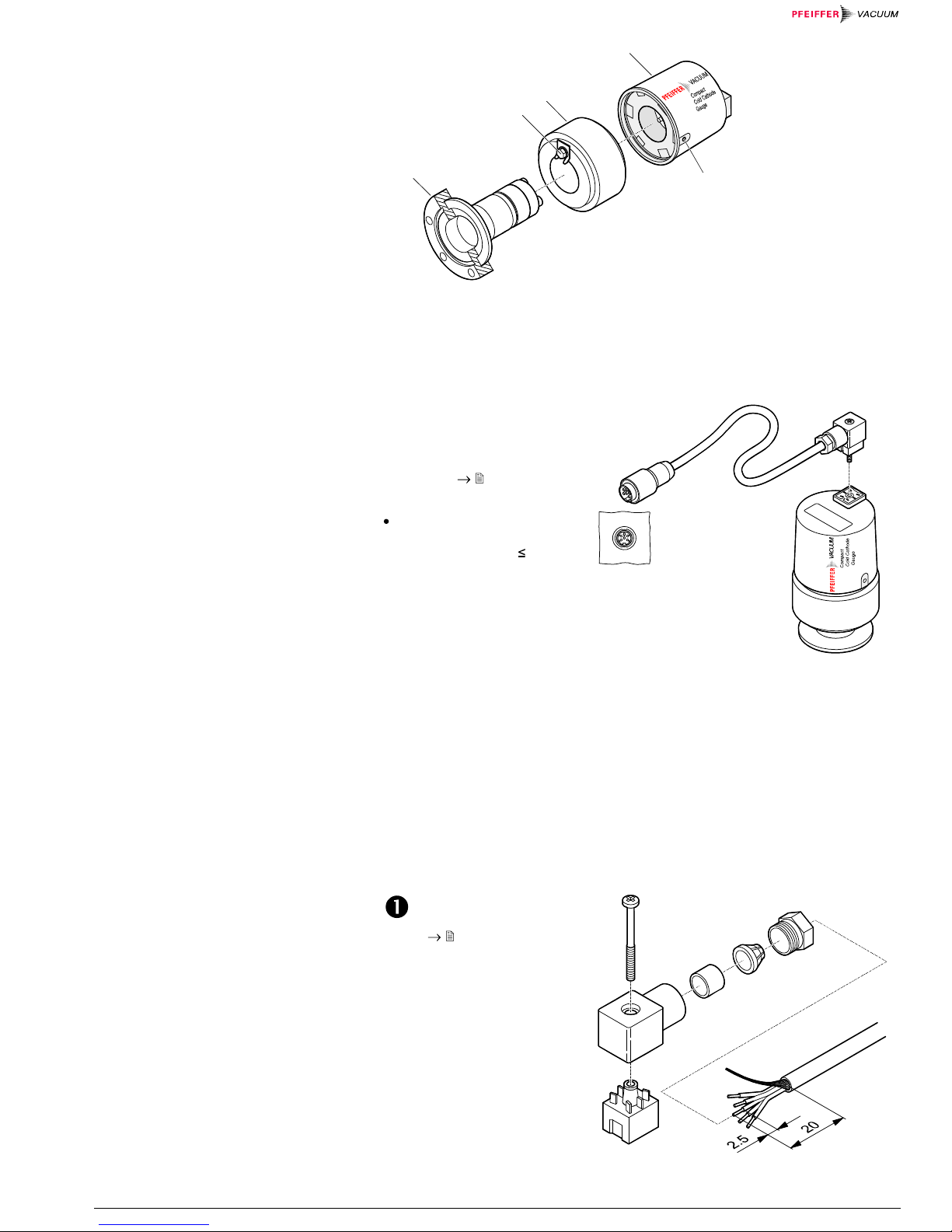
Unfasten the hexagon socket set screw (1) on the side of the electronics
unit (2) ( Figure 1).
Remove the electronics unit.
Unfasten the hexagon head screw (3) on the magnet unit (4) and remove
the magnet unit.
Caution
The magnetic force and the tendency to tilt make it more
difficult to separate the magnet unit and the measuring chamber
(7).
Make the flange connection between the gauge and the vacuum system.
Remount the magnet unit and lock it with the hexagon head screw (3).
Carefully mount the electronics unit (2).
Push the electronics unit up to the mechanical stop and lock it with the
hexagon socket set screw (1).
10 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251
2
4
3
3.2 Power Connection
3.2.1 Use With a
Pfeiffer Vacuum
Measurement Unit
7
Figure 1
If the gauge is used with a
Pfeiffer Vacuum measurement
unit for Compact Gauges, a
corresponding connection cable
is required ( 19).
Secure the cable at the
gauge with the screw
(tightening torque 0.2 Nm).
1
3.2.2 Use With Another
Evaluation Unit
Procedure
The gauge can also be operated with other evaluation units. In this case, an
individual connection cable must be made.
For cable lengths up to 10 m (with a conductor cross-section of 0.34 mm2), the
measuring signal can be read directly between the positive signal output (pin 2)
and the supply common (pin 5) without the degree of accuracy being lowered. For
longer measurement cable lengths, we recommend a differential measurement
between the signal output and the signal common (pin 3) (as a result of the voltage
drop along the supply cable ground lead, the common mode signal is approx. 1.0 V
at the maximum permissible cable length).
Prepare the connector
(Ordering number
19).
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 11

Solder the connection cable according to the diagram.
10
10
5.1 k
10k
2
3
1
4
5
6
V
Figure 2: Power connection
Pin 1 identification
Pin 2 signal output
(measuring signal)
Pin 3 signal common
Pin 4 supply
Pin 5 supply common
Pin 6 screen
2
3
4
5
Connector, soldering side
WARNING
The supply common (pin 5) and screen (pin 6) must be
connected to the supply unit with protective ground.
Incorrect connection, incorrect polarity, or inadmissible supply
Reassemble the connector.
Plug in the connector.
Secure the cable on the gauge
with the screw (tightening torque
0.2 Nm).
voltages can damage the gauge.
+
+
1
6
12 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251

4 Operation
Gas type dependence
Ignition delay
Contamination
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 13
As soon as the required voltage is applied, the measuring signal is available
between pins 2 and 3. ( Appendix B for the relationship between the measuring
signal and the pressure).
The green lamp on the gauge
indicates the operating state:
Supply voltage present.
No supply voltage.
Caution
Turn on the gauge only at pressures <10-2 hPa to prevent excessive
contamination.
If you are using a Pfeiffer Vacuum measurement unit for Compact
Gauges with at least two gauge connections, the cold cathode gauge
The measuring signal depends on the type of gas being measured. The curves are
accurate for dry air, N2, O2 and CO. They can be mathematically converted for
other gases ( Appendix C).
If you are using a Pfeiffer Vacuum measurement unit for Pfeiffer Vacuum Compact
Gauges, you can enter a calibration factor to correct the measurement value
displayed ( of that measurement unit).
An ignition delay occurs when cold cathode gauges are switched on. The delay
time increases at low pressures and for clean, degassed gauges it is typically:
10-7 hPa 0.1 minute
10-8 hPa 1 minute
2×10-9 hPa 5 minutes
The ignition is a statistical process. Already a small amount of depositions on the
inner surfaces can have a strong influence on it.
Gauge failures due to contamination or wear and tear, as well as expendable parts
(e.g. seals), are not covered by the warranty.
Gauge contamination is influenced by the process media used as well as any
existing or new contaminants and their respective partial pressures. Continuous
operation in the range of 10-4 hPa ... 10-2 hPa can cause severe contamination as
well as reduced up-time and maintenance cycles. With constantly low pressures
(< 1×10-6 hPa), the gauge can be operated for more than one year without cleaning
(cleaning the gauge 16).
In general, contamination of the gauge leads to deviations of the measured values:
In the low pressure range (p < 1×10-3 hPa), the pressure indication is usually
too low (as a consequence of the contamination of the cold cathode system). In
case of severe contamination, instabilities can occur (layers of the measuring
chamber peel off). Contamination due to isolating layers can even lead to a
complete failure of the discharge.
Contamination can to a certain extent be reduced by:
geometric protection (e.g. screenings, elbows) against particles that spread
rectilinearly
mounting the flange of the gauge at a place where the partial pressure of the
pollutants is particularly low.
Special precautions are required for vapors deposited under plasma (of the cold
cathode measuring system). It may even be necessary to temporarily switch of the
gauge while vapors occur.
can be controlled, for example, by a Pirani gauge.

5 Maintenance
5.1 Cleaning the Gauge /
Replacing Parts
Tools / material required
Gauge failures due to contamination or wear and tear, as well as expendable parts
(e.g. seals), are not covered by the warranty.
DANGER
DANGER: contaminated parts
Contaminated parts can be detrimental to health and environment.
Before you begin to work, find out whether any parts are contaminated. Adhere to the relevant regulations and take the necessary precautions when handling contaminated parts.
DANGER
DANGER: cleaning agents
Cleaning agents can be detrimental to health and environment.
Adhere to the relevant regulations and take the necessary precautions
when handling and disposing of cleaning agents. Consider possible
Allen wrench AF 1.5
Allen wrench AF 3
Open-end wrench AF 7
Pliers for circlip
Polishing cloth (400 grain) or Scotch-Brite
Tweezers
Cleaning alcohol
Mounting tool for ignition aid
Ignition aid
FPM seal (11) for anode feedthrough
reactions with the product materials ( 7).
14 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251
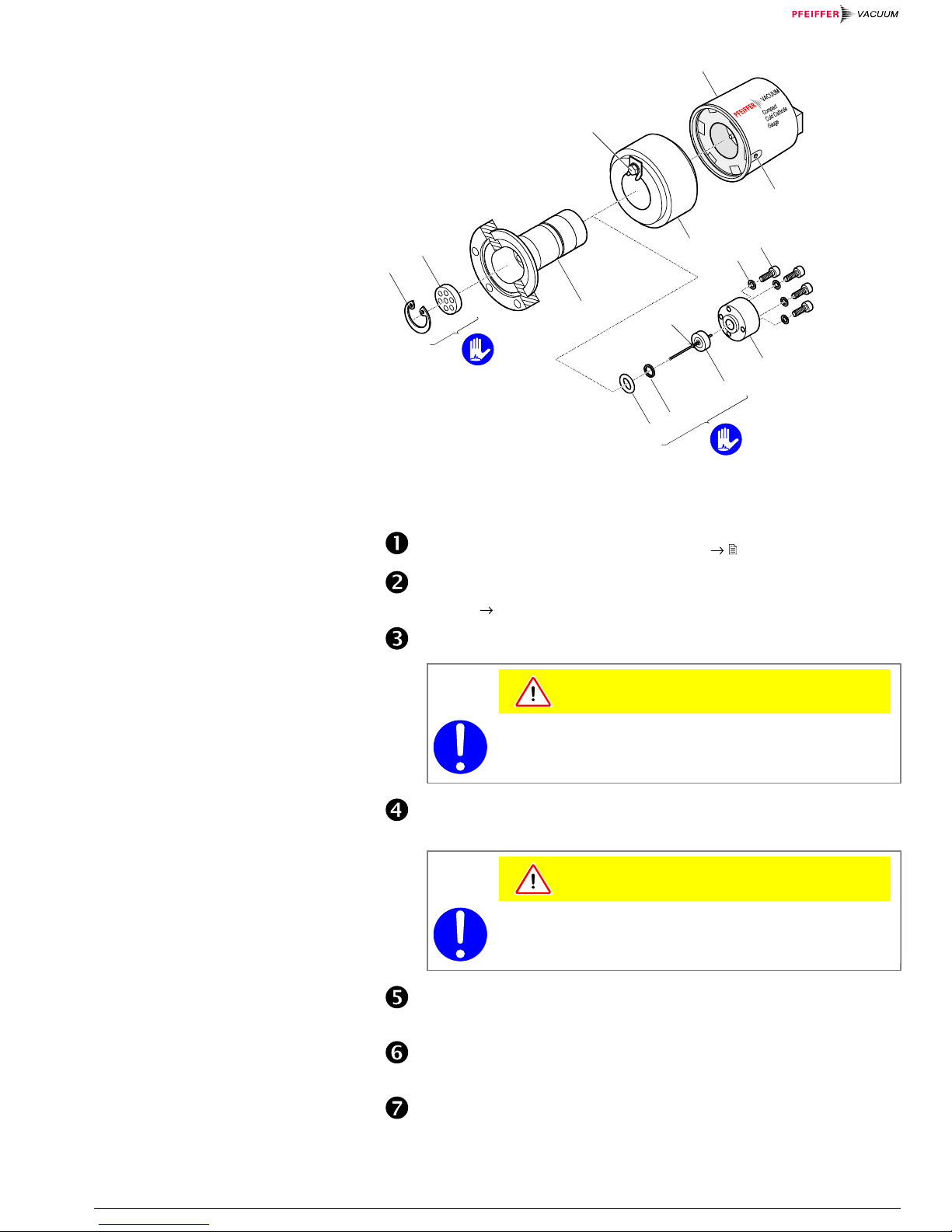
5.1.1 Disassembling the Gauge
2
3a,b,c
1
Procedure
6
5
Figure 3
4
7
10a
11
12
8
8a
9
10
Remove the gauge from the vacuum system ( 18).
Unfasten the hexagon socket set screw (1) on the side of the electronics
unit (2) ( Figure 3).
Remove the electronics unit.
Caution
The cover of the electronics unit cannot be removed.
Unfasten the hexagon head screw (3) on the magnet unit (4) and remove
the magnet unit.
Caution
The magnetic force and the tendency to tilt make it more
difficult to separate the magnet unit and the measuring chamber
(7).
Remove the circlip (5) as well as the polarity insert (6) from the measuring
chamber.
Remove the four (or two) hexagon socket screws (8) incl. lock washers (8a)
on the back of the measuring chamber.
Carefully remove the following items in this order: pressure piece (9),
complete anode (10), FPM seal (11) incl. support ring (12).
The parts can now be cleaned or replaced.
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 15

5.1.2 Cleaning the Gauge
Procedure
Using a polishing cloth rub the inside walls of the measuring chamber and
the polarity insert to a bright finish.
Caution
The sealing surfaces must only be worked concentrically.
Rinse the measuring chamber and the polarity insert with cleaning alcohol.
Allow both to dry.
Cleaning or replacing the anode:
Remove the old ignition aid (10a) with tweezers ( Figure 3).
Using a polishing cloth rub the anode pin to a bright finish.
Caution
Do not bend the anode. Do not carry out mechanical work on
the ceramic part.
5.1.3 Reassembling the Gauge
Procedure
Rinse the anode with cleaning alcohol.
Allow the anode to dry.
Insert a new ignition aid (10a) into the mounting tool.
Carefully press the anode (clean or new) centered and parallel to the tool
axis into the ignition aid and insert it to a depth of approx. 15 mm. The final
positioning is established after the anode is installed.
Anode
Ignition aid
Mounting tool
Insert the FPM seal (11) with the support ring (12) centered into the
measuring chamber. The sealing surface, seal, and ceramic part must be
clean ( Figure 3).
16 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251
Carefully insert the anode (10) incl. ignition aid (10a) into the measuring
chamber.
Carefully place the pressure piece (9) on the measuring chamber and
tighten it uniformly with the four (or two) hexagon socket screws (8) incl.
lock washers (8a) until the stop position is reached.

Position the ignition aid (10a) by pushing the mounting tool over the anode
pin until the mechanical stop is reached.
Remove the particles in the measuring chamber with dry nitrogen (be
careful to hold the measuring chamber with the flange pointing downwards).
Slide the polarity insert (6) into the measuring chamber up to the
mechanical stop.
Place the circlip (5) snugly fitting on the polarity insert.
Caution
Visually check that the anode pin is centered over the middle
hole of the polarity insert (max. eccentricity = 0.5 mm).
If possible perform a leak test (leak rate <10
-9
hPa l/s).
WARNING
WARNING: electric arcing
Helium may cause electric arcing with detrimental effects on the
electronics of the product.
Before performing any tightness tests put the product out of
operation and remove the electronics unit.
Mount the magnet unit (4) and lock it with the hexagon head screw (3).
Carefully slide the electronics unit (2) on the magnet unit until the
mechanical stop is reached.
Fasten the electronics unit (2) by means of the hexagon socket set
screw (1).
5.1.4 Adjusting the Gauge
DANGER
Due to missing ground connection in conjunction with missing
or not correctly tightened hexagon socket set screw (1) dangerous contact voltage will occur and electronic components will
The gauge is factory-calibrated and requires no maintenance. It must be replaced
in the event of a defect ( 20).
be damaged.
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 17
5.2 What to Do in Case of
Problems
Problem Possible cause Correction
Measuring signal
No supply voltage. Turn on the power
continually < 0.5 V and
green lamp is OFF.
Measuring signal
Supply voltage too low. Increase the supply
continually < 0.5 V and
green lamp is ON Electronics unit defective. Replace the electronics
Measurement signal
continually in the range of
Vacuum chamber pressure
< 2×10-9 hPa.
0.5 ... 1.8 V (underrange). Gas discharge has not
ignited.
Measuring signal unstable. Gauge contaminated. Clean the gauge
6 Removing the Gauge From the Vacuum System
supply.
voltage ( 6).
unit ( 6).
Wait until the gas discharge ignites
( 5 minutes at a
pressure of 10-9 hPa).
( 16).
Procedure
DANGER
DANGER: contaminated parts
Contaminated parts can be detrimental to health and environment.
Before you begin to work, find out whether any parts are contaminated. Adhere to the relevant regulations and take the necessary precautions when handling contaminated parts.
Caution
Caution: vacuum component
Dirt and damages impair the function of the vacuum component.
When handling vacuum components, take appropriate measures to
ensure cleanliness and prevent damages.
Deactivate the gauge.
Unplug the connector.
18 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251

Detach the gauge from the
vacuum apparatus.
Place the protective cap.
7 Returning the Product
8 Accessories
WARNING
WARNING: forwarding contaminated products
Products returned to Pfeiffer Vacuum for service or repair should, if
possible, be free of harmful substances (e.g. radioactive, toxic, caustic
or microbiological). Otherwise, the type of contamination must be
declared.
Adhere to the forwarding regulations of all involved countries and forwarding companies and enclose a completed contamination declara-
*)
Form under www.pfeiffer-vacuum.de
Products that are not clearly declared as "free of harmful substances" are decontaminated at the expense of the customer.
tion *).
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 19
Ordering number
Cable for connection to Pfeiffer Vacuum
measurement unit for Compact Gauges
3 m
6 m
10 m
Socket Hirschmann GO 6 WF,
6 contacts, angled, female
Magnetic shielding
PT 44 850-T
PT 448 251-T
PT 448 252-T
B 470 7283 MA
PT 443 155-X

9 Spare Parts
3a,b,c
6
5
Always include the following information with your spare parts order:
Type of product
Manufacturing number according to nameplate
Position, description, and ordering number according to spare parts list
The following parts are available as spare parts sets:
Pos. Description Ordering number
Maintenance set, consisting of:
2
12
11
10a
1× support ring
1× O-ring FPM75 10.82 × 1.78
3× ignition aid
BN 846 239-T
1× O-ring FPM75 3.69 × 1.78
(not used with IKR)
1
4
8
8a
Repair set, including:
12
11
10
10a
1× support ring
1× O-ring FPM75 10.82 × 1.78
1× anode, complete
3× ignition aid
7
11
10a
9
10
12
Set of ignition aids, including:
10a
10× ignition aid
Mounting tool for ignition aid BG 510 600
2 Electronics unit IKR 251 PT 120 160-T
BN 846 252-T
BN 845 995-T
Measuring system, complete
DN 25 ISO-KF flange
DN 40 ISO-KF flange
DN 40 CF-F flange
BN 846 462-T
BN 846 463-T
BN 846 464-T
Exchange gauge
(return defective gauge to Pfeiffer Vacuum)
DN 25 ISO-KF flange
DN 40 ISO-KF flange
DN 40 CF-F flange
PT R25 500-A
PT R25 501-A
PT R25 502-A
10 Disposal
20 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251
WARNING
WARNING: substances detrimental to the environment
Products, operating materials etc. may have to be specially disposed
of.
For environmentally compatible disposal, please contact your nearest
Pfeiffer Vacuum Service Center.

Appendix
A: Conversion Table for
Pressure Units
B: Measuring Signal vs.
Pressure
Conversion formulae
mbar bar Pa hPa kPa Torr
mbar 1 1×10-3 100 1 0.1 0.75
bar 1×103 1 1×105 1×103 100 750
Pa 0.01 1×10-5 1 0.01 1×10-3 7.5×10-3
hPa 1 1×10-3 100 1 0.1 0.75
kPa 10 0.01 1×103 10 1 7.5
Torr
mm HG
1.332 1.332×10-3133.32 1.3332 0.1332 1
1 Pa = 1 N/m2
U-c
p = 10
U = c + log10 p
mm HG
Conversion curves
p U c
[hPa] [V] 10.5
[µbar] [V] 7.5
[Torr] [V] 10.625
[mTorr] [V] 7.625
[micron] [V] 7.625
[Pa] [V] 8.5
[kPa] [V] 11.5
where U Measurement signal
p Pressure
c, d Constant (dependent
on pressure unit)
Pressure p
1E+00
1E01
1E02
1E03
1E04
valid in the range 2×10-9 hPa < p
1.5×10-9 Torr < p
2×10-7 Pa < p
< 1×10-2 hPa
< 7.5×10-3 Torr
< 1 Pa
Pa
hPa
Torr
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 21
1E05
1E06
1E07
1E08
1E09
1E10
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5 6.5 7.5 8.5 9.5 10.52.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0
Measuring signal U [V]

Conversion table
C: Gas Type Dependence
Measuring
signal U [V]
[hPa]
Pressure p
[Torr]
< 0.5 Sensor error
0.5 ... 1.8 Underrange
1.8
2.5
3.5
4.5
5.5
6.5
7.5
8.5
2.0×10-9
1.0×10-8
1.0×10-7
1.0×10-6
1.0×10-5
1.0×10-4
1.0×10-3
1.0×10-2
1.5×10-9
7.5×10-9
7.5×10-8
7.5×10-7
7.5×10-6
7.5×10-5
7.5×10-4
7.5×10-3
8.5 ... 10.5 Overrange
Indicated pressure (gauge calibrated for air)
p (hPa)
4
2
-3
10
8
6
4
2
-4
10
8
6
4
2
-5
10
8
6
4
2
-6
10
8
6
4
2
-7
10
-7
10
-6
10
642
-5
10
642
Xe Kr
-4
10
642
Luft / Air
Ar
10
642
CO
-3
[Pa]
2.0×10-7
1.0×10-6
1.0×10-5
1.0×10-4
1.0×10-3
1.0×10-2
0.1
1.0
O
2
N
2H2
-2
10
642
p
(hPa)
eff
22 BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251

Indication range below 10-5 hPa
In the range below 10-5 hPa, the pressure indication is linear. For gases other than
air, the pressure can be determined by means of a simple conversion formula:
p
= K × indicated pressure
eff
where gas type K
air (N2, O2, CO) 1.0
Xe 0.4
Kr 0.5
Ar 0.8
H2 2.4
Ne 4.1
He 5.9
These conversion factors are average values.
Caution
A mixture of gases and vapors is often involved. In this case, accurate
determination is only possible with a partial pressure measurement
instrument, e.g. a quadrupole mass spectrometer.
ETL Certification
RECOGNIZED
COMPONENT
3103457
ETL LISTED
The product IKR 251
conforms to the UL Standard UL 61010-1
is certified to the CAN/CSA Standard C22.2 No. 61010-1
BG 5151 BEN / D (2017-07 ) IKR 251 23

VACUUM SOLUTIONS FROM A SINGLE SOURCE
Pfeiffer Vacuum stands for innovative and custom vacuum solutions worldwide,
technological perfection, competent advice and reliable service.
COMPLETE RANGE OF PRODUCTS
From a single component to complex systems:
We are the only supplier of vacuum technology that provides a complete product portfolio.
COMPETENCE IN THEORY AND PRACTICE
Benefit from our know-how and our portfolio of training opportunities!
We can support you with your plant layout and provide first-class on-site-service worldwide.
Are you looking for a
perfect vacuum solution?
Please contact us:
Pfeiffer Vacuum GmbH
Headquarters Germany
T +49 6441 802-0
info@pfeiffer-vacuum.de
www.pfeiffer-vacuum.com
bg515 1ben/ d
 Loading...
Loading...