Pentair E110-14-H/D, E54-30-H/D, E70-23V-H/D, E75-25-H/D, E80-20V-H/D Installation And Service Manual
...Page 1

E SERIES
RECIPROCATING PUMP
INSTALLATION AND SERVICE MANUAL
NOTE! To the installer: Please make sure you provide this manual to the owner of the equip ment or to the responsible
party who maintains the system.
Part # 26850A004 | © 2015 Pentair Ltd. | 10/23/15
Page 2

GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
SUGGESTED MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
CAUTION: Positive displacement pumps must have a
proper size and operable type of pressure regulating
valve or pressure relief valve piped into the discharge
line. This is mandatory to prevent damage to pump
and piping or possible injury to personnel. Do not
install any valves or shut-off devices in the bypass line
from pressure regulator to tank or supply.
CAUTION: All pumps should be installed level. For
mobile applications the maximum angle of intermittent
operation should be no more than 5 degrees in any
one direction.
CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65 WARNING:
accessories contain chemicals known to the
State of California to cause cancer, birth
defects or other reproductive harm.
This product and related
BELT DRIVE SEWER CLEANERS
With belt drives, the pulley on both the engine and
pump should be located as closely as possible to the
bearing to reduce bearing and shaft bending loads.
Make sure that all bolts, nuts, set screws and keys
are properly tightened. On multiple V-belt drives, a
complete set of belts should be installed when making
a replacement.
STARTING PUMP
Fill pump crankcase with recommended oil to the
level mark on the oil saber. Oil recommendations are
covered in lubrication section of pump instructions.
Replace all drain plugs in pump and piping. Inspect
tank to be sure that no foreign material is in tank
or suction line. Fill tank at least half full or connect
suction to water supply. Open valve (if present) in
suction line. Avoid prolonged dry operation which
may cause excessive wear on cylinders and piston
packing. Be sure that an operating pressure gauge
is located in the discharge line. Make sure all
valves, including spray gun or nozzles, are open in
the discharge line. Spray gun may be anchored to
discharge back into the tank. Completely back off
pressure adjusting screw on the pressure regulating
valve.
After starting, close discharge valve or spray gun
slowly while watching pressure gauge to make sure
relief valve or unloader is operating properly. Adjust
relief valve or unloader to desired pressure. See
regulator instructions. Cycle nozzles or gun on and
off to be sure that pressure adjustment and regulator
operation is satisfactory. Nozzle capacity should
not exceed 90% of pump capacity for satisfactory
regulator operation. Avoid freezing by draining all
water from pump and system in cold weather.
Check oil level – Daily
Drain at operating temperature to prevent
contamination from settling.
Drain and change oil – 300 hrs.
Inspect frequently for leakage; replace before 500
hours if any cylinder exceeds 10 drops per minute
leakage. Packing may not look badly worn but will
often be shiny and hard and won’t seal well.
Replace piston packing – 500 hrs.
Replace if cracks and heavy wear are present.
Inspect valves and springs – 500 hrs.
Inspect connecting link bearing inserts – 1000 hrs.
Replace at first signs of fatigue or wear to prevent
damage to crankshaft.
Inspect crankshaft tapered roller bearings – 2000 hrs.
LUBRICATION
Fill gear case with Mobilgear 630 or equivalent 80W90
oil to 6-1/2 qts for 1000-1800 pinion rpm range and
7-1/2 qts for 600-999 rpm range. Maintain oil level at
mark on oil dipstick.
NOTE: Slow speed operation of Myers® reciprocating
pumps can be accomplished by adding additional oil
to the crankcase. The higher level compensates for
lack of splash lubrication at slow speeds. Some slight
leakage may occur around crossheads and dipstick/
vent area with additional oil.
IMPORTANT: After first 30 hours of operation drain
oil from gear case (preferably drain at operating
temperature), replace plug and refill crankcase with
new oil. Change oil every 300 hours thereafter. Check
oil level daily and add oil as needed.
ADDITIVES FOR CRANKCASE OIL
Use of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is optional as an
additive to the petroleum-based gear case oil in back
geared pumps and speed reducers manufactured
by Myers. Do not use this additive with synthetic
oil. It is so effective in reducing wear and friction that
power train life may be doubled between overhauls.
SERVICE
Disengage clutch, disconnect electrical leads to motor
or remove spark plug leads on engine.
2
Page 3

REMOVING PACKING
REMOVING CYLINDERS
Move assembly to front end of cylinder (top dead
center). Remove valve assembly if required to provide
clearance. Remove cap screw with an Allen wrench.
Retract piston rod. Pull packing assembly out or push
by rotating crankshaft by hand.
REMOVING PISTON
After removing the nuts, clamp and cylinder cap,
move piston assembly to front end of cylinder (top
dead center). Remove valve assembly if required, to
provide clearance. Remove cap screw with a 12mm
(.472") across flats Allen wrench or use the removal
tool. Use the removal tool to screw into the piston hub
and then pull piston assembly out, using momentous,
backward-forward motion with the sliding handle bar
against the bolted-anchored end.
CAUTION: Also inspect cylinders for linear grooving
by running your thumbnail circumferentially around
bore of cylinder. If any grooving is detected also
replace cylinders. New packing will rapidly cut or wear
out in grooved cylinders.
INSTALLING CUP
First remove packing as outlined previously. Rotate
crankshaft until piston rod is in rear position. Insert
puller through inside of cylinder and pilot over piston
rod. Insert disc into slots on puller. Slip plate over
threads on puller. Screw nut on thread on puller and
snug up. Tighten nut until liner breaks loose. Loosen
nut and slip disc out of slots. Remove puller and
repeat to remove other cylinders.
CYLINDER INSTALLATION
Reasonable care and judgment should be used
when installing the new cylinder. Clean out any
accumulation of loose rust or corrosion in cylinder
body. Install a new O-ring in groove on tapered
portion of cylinder, lubricate O-ring with oil or grease
for ease in insertion. Position cylinder carefully by
hand to avoid cutting the O-ring. Drive into position
firmly with a wooden block and mallet. Never use a
hydraulic press; excessive force can cause damage
and make cylinders very difficult to remove for later
replacement.
REMOVING SEATS: WING GUIDED
VALVES
Assemble cup onto hub. Lubricate the outside of the
assembly with Molykote® or other grease for ease in
insertion – do not use a graphite type grease.
When installing each cup assembly, rotate crankshaft
until piston rod is at forward position. Place O-ring in
position in piston hub using a small amount of grease
to hold in place.
NOTE: Apply Loctite® RC35 to capscrew prior to
piston installation. Follow instructions on label and
make certain threads in piston rod are clean and free
of any grease or oil.
Assemble capscrew, etc., into piston assembly and
push into cylinder. Torque the capscrew to 50 ft/lbs
using a hexagonal socket attachment 12mm (.472")
across flats.
INSTALLING PACKING
Assemble V-rings onto stud. Lubricate the outside of
the assembly with Molykote® or other grease for ease
in insertion – do not use a graphite type grease. When
installing each V-ring assembly, rotate crankshaft until
piston rod is at forward position. Place copper gasket
in position in stud using a small amount of Permatex®
to hold in place. Apply Loctite® RC35 to cap screw
prior to piston installation. Follow instructions on label
and make certain threads in piston rod are clean and
free of any grease or oil. Assemble cap screw, etc.,
into piston assembly and push into cylinder. Torque
the cap screw to 50 ft/lbs using a hexagonal socket
attachment 3/8" across flats.
Remove valve caps, and cylinder caps, which provide
access to suction and discharge valves. Remove the
stainless steel cage which serves as a valve guide and
spring retainer. Remove cage, spring and valve from
the pump fluid end.
Suction valve seats are removed as above except two
stud lengths are joined using coupling.
REPLACEMENT OF VALVES
Inspect tapered valve seat bore in fluid end for rust
and wipe out excess with a rag. Place a new lower
seat in tapered hole. Drive lower seat firmly into place
and repeat for upper seat being sure to also inspect
the tapered bore for rust.
IMPORTANT: Both the valve seat O.D. and tapered
bore I.D. must be very clean.
Reassemble valve, spring and cage, and confirm that
springs are in correct location. When upper and lower
valve seats are the same size, the heavier spring is
installed on upper or discharge valve.
NOTE: Be sure that cage is tightened onto valve seat.
Inspect seals on valve and cylinder caps. Replace if
seals show signs of wear.
3
Page 4

REPLACING PISTON ROD SEALS
The rod seal assembly contains two seals, two oil
seals with lips facing the power end. The oil seal
can be replaced without taking the fluid end off by
removing the cylinder and piston to allow access for
oil seal housing. Unscrew two Allen screws and place
into the other two tapped holes. Gradually screw
them in to push oil seal housing off the retainer. After
assembling new seals in oil seal housing an assemble
thimble should be used on the end of the crosshead
rod for sliding oil seal housing back into the retainer.
Check gasket and replace if damaged.
An assembly thimble should be used on small end of
the piston rod to expand sealing edge as it is pushed
on. The thimble should be machined from high carbon
steel and polished on the exterior to reduce possibility
of seal lip damage.
REMOVING CRANKSHAFT AND PINION
SHAFT
Remove piston assemblies. Remove connecting
link caps and move the link-crosshead assembly
as far forward as possible. Secure separation of the
crankshaft gear and gear case so that crankshaft will
be held in place against pinion shaft. Remove both
crankshaft bearing caps. Hold crankshaft at ring gear
and left-hand link journal to prevent dropping into
bearing bores and remove from gear case by moving
crankshaft to the right until left end can be swung
free.
To remove pinion shaft, remove bearing cap bolts.
Tap the end of the pinion shaft extension to remove
the bearing cup at the opposite end. After removing
the pinion shaft, the remaining bearing cup can be
removed by gently tapping against the peripheral
edge of the cup.
REPLACING PINION SHAFT AND
SHIMMING BEARINGS
After installing the link-crosshead assemblies and
moving them toward the fluid end as far as possible,
press bearing cones onto both ends of the pinion
shaft, being sure bearing seats completely against
stop on shaft. Place pinion and bearing cone
assembly into the crankcase, positioning the pinion
gear over the crankshaft gear. Carefully “hand” press
bearing cups into both sides of the crankcase. Tap
cups until bearing cups and cone come together and
pinion is in the proper location in the crankcase. Press
shaft seal into bear/seal cap. Be sure the seal lip in
both caps are installed with the lip inward towards the
center of the crankcase. Install right bearing/seal cap
with two .003" thick shims and tighten cap screws.
Install left bearing/seal cap with one .015" thick and
one .003" thick shim and tighten screws. Rotate the
pinion shaft back and forth and apply about 15 lbs. of
axial force to properly seat the tapered roller bearings.
Measure the end play by using a dial indicator.
Subtract recommended end play of .005" to .009"
from the actual end play. This is the amount of shim
that must be removed. After excess shim thickness
has been removed, replace left cap and retighten
cap screws. Measure end play again and repeat if
necessary.
REPLACING CRANKSHAFT AND
SHIMMING BEARINGS
Press the bearing cups into the caps. Place one
cap into position on the right side with cap screws
engaged about one turn. Install crankshaft, left end
first, and push both bearing caps into place. Extreme
care should be exercised to avoid damage to gear
teeth, bearings and link journals.
For quiet operation and long life, the crankshaft and
bearings must be installed with .003" to .005" in
preload. To adjust, loosen the four cap screws on the
pinion shaft bearing cap.
Place about .045" shim on the right crankshaft
bearing cap, tighten the five cap screws. Install the
left cap without shims, secure with two cap screws at
13 ft/lbs and rotate the crankshaft. Retorque the cap
screws. Repeat three times to properly seat tapered
roller bearings. Measure (adjacent to the cap screws)
the shim gap remaining between the bearing cap and
the gear case. The required shim thickness for this
cap is equal to the average gap measurement plus
.022". Insert correct shim thickness under left bearing
cap and tighten cap screws. Install connecting links
and caps and torque cap screws to 40 ft/lbs.
Important - Check for adequate side clearance of links
on crankshaft. Some shims must be moved from one
end to the other until sideways movement of all links
can be seen.
Check torque of cap screws on all bearing caps.
RECONDITIONED CRANKSHAFTS
When the crank throws are slightly damaged, they can
sometimes be reconditioned for further use. This can
be done by sandpapering and polishing until all ridges
are completely removed. The final polishing operation
should be with very fine emery cloth. If the surface is
badly damaged, the crankshaft can often be salvaged
by “metalizing” the crank throw and then regrinding
and polishing to the original diameter.
4
Page 5
SERVICING CONNECTING LINKS
CROSSHEAD AND PISTON RODS
The connecting rod link is furnished with replaceable
split sleeve bearing inserts at the crank throw. Do
not attempt to refit connecting links to the crankshaft
bearings by filing or grinding the mating faces of the
link cap where it contacts the link. Always be sure
that the proper side of the link is placed upward when
attaching it to the crankshaft. The upper side contains
an oil hole at the crosshead end of the link. This oil
hole must be up to allow proper oil feeding to the
crosshead pin bushing. The wrist pin is press-fitted
into crosshead and slip-fitted through the bronze
bushing. Use arbor press to force in the wrist pin.
Check to see if link is free to rotate after the wrist pin
is pressed in. Verify that both sides of the wrist pin do
not protrude beyond the crosshead.
The crosshead end of the connecting link is fitted
with a bronze bushing. New replacement links are
obtained, these bushings are reamed to the proper
size for immediate installation. If only the bushing
is replaced, it may be necessary to ream the new
bushing to the proper inside diameter after it is
pressed into the link. When placing the bushing on the
link be sure that the oil holes in the bushing and link
are in line after the bushing is pressed into position.
Repair parts for the crosshead and piston rod are
supplied as a complete unit. If either of these parts
become worn, it is necessary to replace both the
crosshead and piston rod. Under normal conditions
a crosshead will not wear, nor will the bore of the
crankcase wear to the extent that oversize crossheads
will be required. A clearance of .002" to .004" is
standard for the crosshead.
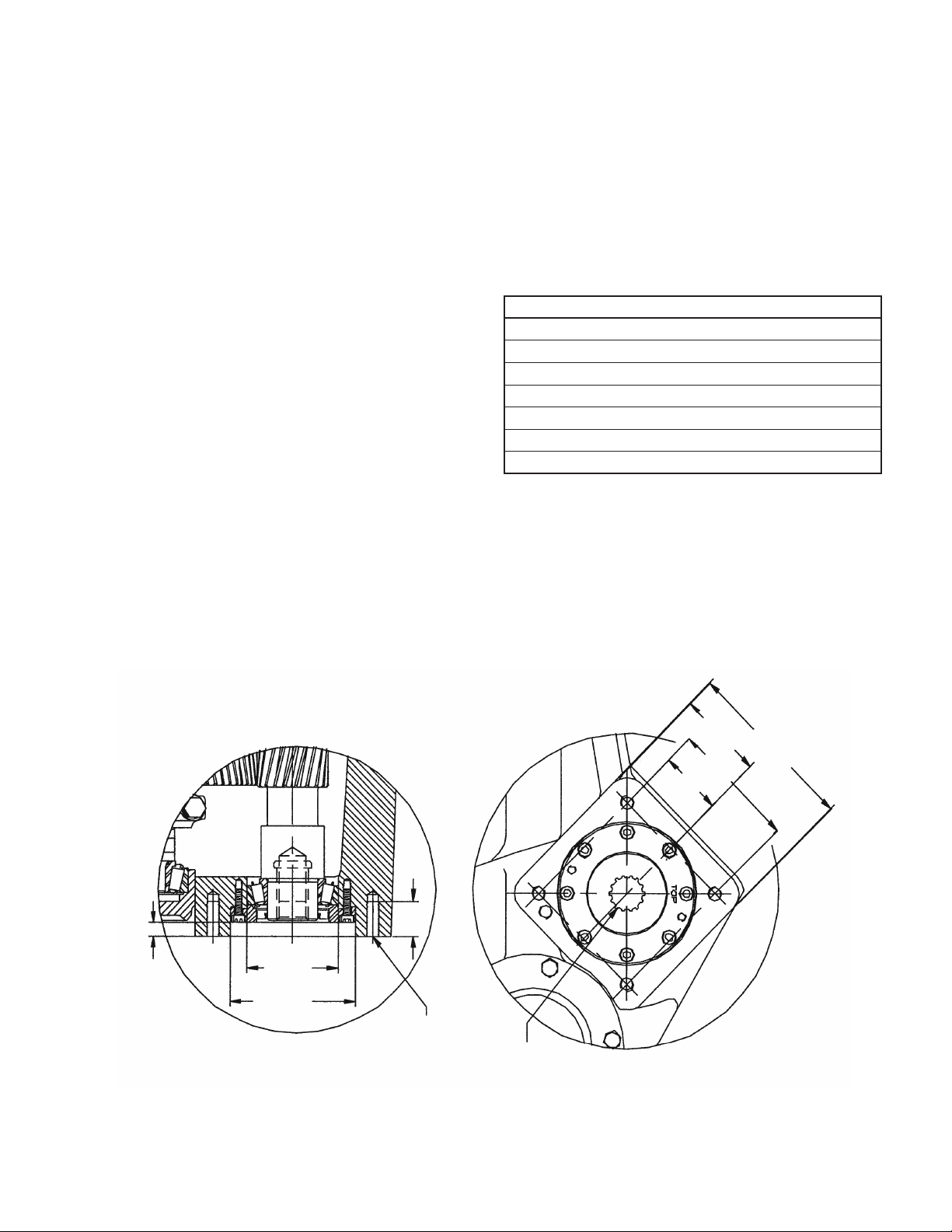
RECOMMENDED TORQUE (foot-pounds)
Fastener Location
Link Bearing Caps – 40
Crankshaft End Caps – 20
Pinion Bearing End Caps – 20
Cap Screw, 3/4 (Fluid End to Power End) – 250
Cap Screw, 5/8 (Fluid End to Power End) – 150
Cylinder Cap Clamps (Front) – 200
Valve Cap Clamps (Top) – 100
DIMENSIONS, S.A.E. “C” FACE MOUNTING
.540 Pilot Depth
NOTE: Measurements in inches
3.636 DIA.
3.625 DIA.
5.0000 DIA.
5.0020 DIA.
1-3/8
1/2-20UNF-2B
4 (Holes)
14 tooth 12/24
Pitch Involute Spline
2-1/4
3-5/64 TYP.
6-5/32 TYP.
4-1/2 TYP.
TYP.
5
Page 6

THE PUMP MUST BE INSTALLED WITH A PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE IN DISCHARGE LINE
TROUBLESHOOTING
Pump fails to build pressure with discharge closed
Failure to hold pressure with discharge open
Pump is noisy
Pump gets hot
Pressure gauge shows abnormal fluctuation
POSSIBLE CAUSE OF PROBLEM
1. Pump not primed X
2. Valve closed in suction line X X
3. Suction line or sediment chamber clogged X X X
4. Air leak in suction line X X X
5. Pressure regulator valve badly worn or not properly adjusted X X
6. Broken valves or springs X X X
7. Pump packing or valves badly worn X X X
8. Pressure regulator bypassed by open #1 valve X X
9. Pump cylinder body cracked X X X
10. Water in crankcase X
11. Worn connecting link inserts or wrist pin bushings X X
12. Lack of oil in crankcase X X
13. Foaming mixture in tank X X X
14. Regulator plunger sticking X
15. Foreign matter under pump valve X X X
16. Loose piston rod X
17. Improper preload of crankshaft bearings X X
Explanation of the Service Chart
1. Pump priming is usually not necessary when the
pump is installed correctly. However, there are certain
conditions which may make it necessary to prime the
pump to get the pumping action started. Priming will
be required when it is impossible for the piston to
displace the air in the pump and replace it with water.
This could be caused by a high suction lift, the valves
being stuck on the seat or by valves sticking due to
extreme corrosion. A pump will not prime readily if
someone has tampered with the valve springs causing
them to exert undue pressure of the valve plates
against the valve seats.
2. A gate valve is sometimes installed in the suction
line between a tank or pressure line and the pump
sediment chamber. It will shut off the supply source
in order to clean the sediment chamber or to perform
pump repairs. If this valve is partially or fully closed, it
will interfere with the flow of water to the pump suction.
This also may cause severe knocking and vibration
of the pump because the water cannot flow into the
cylinder cavities fast enough.
3. A sediment chamber should be installed in the suction
line between the gate valve and the pump suction. The
strainers in these sediment chambers are to allow a
free flow of liquid to the pump. If the strainers become
severely clogged, they will completely stop the flow of
liquid to the pump.
4. Any piston pump operating at a high pressure will not
perform properly or quietly if a mixture of air and water
is allowed to enter the pump suction. A small air leak
in the suction line will cause the pump to knock and
vibrate excessively by allowing the pump to draw a
certain amount of water mixed with air on each stroke
of the piston. A large air leak will cause the pump to
lose prime after which it cannot be reprimed until the air
leak is stopped. Air leaks may occur at the joints of the
suction line piping, at the gate valve in the suction line,
at the gasket sealing the cap on the sediment chamber,
by a crack in the suction wall of the cylinder body, or by
air drawing past the packing on the suction stroke if the
packing is badly worn.
6
Page 7

5. If the pressure regulator internal bypass valve is
worn, it will allow too much of the pump capacity to
be bypassed and recirculated back to the tank. By
examining the flow from this valve with the discharge
turned on, it can be determined whether or not the
valve is worn. If a heavy flow continues when the
discharge is turned on, it is usually a good indication of
a worn valve and should be replaced.
6. A broken pump valve or spring will often prevent one
cylinder from functioning properly resulting in a rough
pulsing discharge, a knocking sound and a loss of
capacity. If not repaired immediately, the rough running
pump can cause mechanical damage to itself or other
system components.
7. Worn packing, valves or valve seats will cause a
severe drop in pump capacity pressure. Worn packing
is detected by water leakage and should be replaced
immediately. Water getting in the pump crankcase
will cause severe corrosion of the bearings and cause
rapid wear. Worn valves can be detected by visual
examination of each valve assembly. Abrasive liquid will
cause wire cuts which begin as a very small groove, but
increases rapidly once the valve starts to leak through
this groove. If the valves are replaced as soon as they
start to show this cutting action, it will prevent the valve
seat from becoming cut in a similar manner.
8. If a portion of the pump delivery is allowed to bypass
because the #1 control valve is not completely
closed, there may not be adequate flow to develop
full pressure. This will cause rapid wear in the control
valve. Any excess flow should be bypassed only by
the pressure regulator.
9. Pump cylinder bodies withstand an extreme amount
of shock and pulsation while in operation. If the
pump is allowed to freeze, by not being drained, the
freezing may crack the cylinder body walls in almost
any location. If the crack occurs on the suction valve
or cylinder portion of the body, it may allow a small
amount of air to enter on the suction stroke and cause
noisy operation or a decrease in pumping capacity. If
the crack develops in the walls between the cylinder
cavities or discharge valve cavity, it may allow the water
to flow from one cavity to the adjacent cavity and cause
uneven displacement.
10. Water may accumulate in the pump crankcase from
two sources; leakage of packing or an accumulation
of condensation/moisture inside the crankcase due to
changes in weather or the repeated heating and cooling
of the pump. Pumps used consistently, running for a
considerable period of time to heat the oil and other
working parts, will not normally accumulate water by
condensation. Replace the packing as soon as it starts
to leak.
11. Worn connecting link bearings are caused by unusual
or adverse operating conditions and are seriously
affected by corrosion if water is present in the
crankcase. They will wear out from overheating if
the oil is not high quality or clean. Drain, clean and
refill with new oil at the specified interval and prior to
any storage period. Replace link inserts as soon as
any wear is noticed to avoid damage to crankshaft
journals.
12. Low oil in the crankcase can quickly cause failure of
the pumps power end and result in extensive repairs.
Oil level should be checked periodically during normal
operation and during all maintenance work.
13. A foaming mixture will sometimes have the same
effect as a small air leak in the suction line. This is
because various quantities of the foam are drawn
through the suction line into the pump disrupting the
normal flow of water.
14. Pressure regulators can become sluggish due to the
plunger sticking or fitting too tightly in the cylinder.
This may happen by an accumulation of chemicals
collecting in and around the plunger or from excessive
corrosion of the plunger parts. To check this condition,
remove and clean the plunger and cover the parts with
a waterproof grease before assembling. The pressure
regulator may chatter or vibrate excessively due to
an unstable operation from nozzling in the high or low
capacity range of the regulator. The range should be at
least 50% to 90% of pump capacity.
15. If foreign matter becomes lodged between the pump
valve and valve seat, a drastic drop in capacity and
considerable surge or pulsation will occur in the
discharge line. Examine each valve if this occurs.
16. Noisy pump operation may be caused by a loose
piston rod in the crosshead. This noise usually
has a regular cadence timed with each stroke. If
this happens, always replace both the rod and the
crosshead.
17. Increased preload to the crankshaft bearings will
reduce bearing life, require more power and generate
more heat. Insufficient preload may cause a knock,
timed with the crankshaft rotation. Check for loose
bolts on the crankshaft end caps or adjust shims to
obtain proper bearing preload. Worn roller bearings will
continue to run but will introduce wear particles into
the oil.
7
Page 8

E54-30-H/D, E70-23-H/D, E80-20-H/D, E110-14-H/D
8
Page 9

E70-23V-H/D, E75-25-H/D, E80-20V-H/D, E80-25-H/D
47
46
76
75
74
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
78
79
80
55
92
53
51
52
50
45
45
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
73
48
11
36
35
34
33
49
77
9
Page 10

HYDRAULIC DRIVE POWER END
10
Page 11

E SERIES – HYDRAULIC DRIVE – PARTS LIST
Item Description Qty. Eng. No.
1 CASE, GEAR 1 04625E100
2 SHIM, PLASTIC, PINK, .015" 6 05068A016
3 SHIM, PLASTIC, GREEN, .003" 6 05068A018
4 O-RING, 5-1/8" O.D. 2 05876A098
5 WASHER, SEAL 10 14946A003
6 SCREW, CAP 3/8"-16 UNC x 1" 18 19101A013
7 CAP, BEARING, CRANKSHAFT 2 04624B004
8 CUP, BEARING, CRANKSHAFT 2 05675A013
9 CONE, BEARING, CRANKSHAFT 2 05674A021
10* CRANKSHAFT, W/75 TEETH GEAR
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25 AND E75-25) 1 27937C022
E80-25 AND E75-25 1 27937C044
11 PACKING E70-23V, E75-25 AND E80-25 3 18922A000
PACKING E80-20V 3 18922A004
12 OIL SEAL, 2" 2 05710A046
13 CAP, OPEN, PINION 2 04742B101
14 CUP, BEARING, PINION 2 05675A019
15 CONE, BEARING, PINION 2 05674A020
16 SHIM, .015" THK., PINK 2 05863A023
17 SHIM, .003" THK., GREEN 4 05863A024
18* SHAFT, PINION, 19 TEETH 1 27938B040
19 COVER 1 26588B000
20 SCREW, HEX HD., 1/2"-20 UNF x 3/4" 4 19103A054
21 SCREW, CAP, 5/16"-24 UNF x 1" 16 06106A048
22 CROSSHEAD ASSEMBLY
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25 AND E75-25) 3 06211B042
E80-25 AND E75-25 3 06211B044
23 LINK, WITH BUSHING & SCREWS 3 17042C002
BUSHING, WRIST PIN 3 B01619A000K
WASHER, LOCK 6 05454A004
SCREW, CAP 6 19103A016
24 WRIST PIN 3 M01525A001
25 BEARING, TWO HALVES 3 15245A101K
26 PLUG, DRAIN, MAGNETIC, 3/4-14 1 17481A002
27 GASKET, LID, SPECIAL SHAPE 1 06201C000
28 SCREW, CAP 5/16"-18 x 7/8" ST. 8 19100A033
29 O-RING, OIL GAUGE 1 110-000110-201
30 GAUGE, OIL & O-RING (ITEM 29) 1 17360A011K
31 LID, GEAR CASE 1 04561B000
32 NIPPLE, SPECIAL VENT 1 17995A000
33 CAP, PIPE 1 05737A002
34 SLINGER, NEOPRENE 3 05059A263
35 SCREW, CAP, HEX, 5/8-11 UNC x 2 4 19105A008
36 SCREW, SKT. HD. 10-32 UNF x 1/2" 6 06106A034
37 HOUSING, OIL SEAL 3 24959A000
38 SPRING, SEAL RETAINER 3 M01643A000
39 GASKET, SEAL HOUSING, 2.312 O.D. 3 05059A434
40 GASKET, VELLUMOID, 3.50 O.D. 3 05059A058
41 RETAINER, OIL SEAL HOUSING 3 24958A000
42 OIL SEAL, U CUP, VITON
43 SCREW, SKT. HD. 3/4-10UNC x 2-1/2" 4 06106A038
44 WASHER, LOCK, 3/4" 4 05454A003
45 SCREW, DRIVE, .133 x 5/16" 6 045800011
46 PLUG, PIPE, 3" NPT 2 03210A000
47 PLUG, PIPE, 1" NPT 3 05022A043
48 PLUG, PIPE, 1/2" NPT 3 05022A015
49 BODY, CYLINDER
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25 AND E75-25) 1 18639F008
E80-25 AND E75-25 1 18639F007
50 LID, CYLINDER (PONY ROD COVER) 1 M01520A000
51 CLAMP, LID 2 26842A000
52 SCREW, MACH. 1/4-20 UNC x 1/2" 2 148850001
®
6 22835A003
Item Description Qty. Eng. No.
53 O-RING, 1-1/4" O.D. 3 110-000024-218
54 PISTON HUB E54-30 3 7206-0354-00A
E70-23 3 7206-0393-00A
E110-14 3 7206-0358-00A
55 LINER, CYL. E54-30 1.750 I.D. 3 26849A000
E70-23 2.000 I.D. 3 20851A001
E75-25 2.000 I.D. 3 26849A001
E80-20 2.125 I.D. 3 20851A004
E110-14 2.500 I.D. 3 M01512A003
56 PISTON, CUP, E54-30 1.750" O.D. 3 7206-0361-00A
E70-23 2.000 O.D. 3 7206-0392-00A
FLAT BACK E110-14 2.500 O.D. 3 7203-0617-00A
57 RETAINER, PISTON E54-30 3 7206-0356-00A
E70-23 3 7206-0394-00A
E110-14 3 7206-0389-00A
58 SCREW, CAP, .551" M-14 METRIC 3 16654A006
59 O-RING, 2-15/16" O.D.,CYL. LINER 3 05876A095
60 SEAL, RING, VALVE CAP
(ALL MODELS EXCEPT E80-25) 3 26862A001
SEAL, RING, VALVE CAP E80-25 0 05876A064
61 CAP, VALVE
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25 AND E75-25) 3 26848A000
E80-25 AND E75-25 3 17390A000
62 CLAMP, 5/8" STUD, VALVE CAP 3 20848A000
63 STUD, 5/8-11 UNC x 3-5/16 LG. 6 05659A560
64 NUT, HEX 5/8"-11 UNC 6 19109A046
65 CAGE, VALVE 6 7203-0544-00B
66 SPRING, VALVE 6 7206-0302-00A
67 VALVE, GUIDE 6 7203-0542-00A
68 INSERT, VALVE, POLYURETHANE 6 7203-0546-00A
69 O-RING, VALVE, 2.004 O.D. 6 110-000032-201
70 SEAT, VALVE 6 7203-0543-00B
71 SEAL, RING, CYLINDER CAP
(ALL MODELS EXCEPT E80-25) 3 7202-0041-00A
SEAL, RING, CYLINDER CAP E80-25 3 05876A096
72 CAP, CYLINDER
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25 AND E75-25) 3 26805A000
E80-25 AND E75-25 3 26805A001
73 SPRING 3 20853A000
74 CLAMP, 7/8" STUD, CYLINDER CAP 3 20856A000
75 STUD, 7/8"-14 UNF x 4-1/2" 6 05659A089
76 NUT, HEX, 7/8-14 UNF 6 19109A072
77 PLUG, PIPE, 1-1/4" NPT 1 05022A041
78 PRESSURE RING E70-23V AND E75-25 3 18921A000
PRESSURE RING E80-20V, E80-25 3 20854A000
79 RETAINER, SPRING 3 20852A003
80 FOLLOWER E70-23V AND E75-25 3 18932A002
FOLLOWER E80-20V, E80-25 3 20855A000
PISTON BODY E70-23V AND E75-25 3 18924A004
PISTON BODY E80-20V, E80-25 3 20850A011
SPRING; VALVE 316 SST
(FOR E80-25 AND E75-25) 3 11829A000
SPRING; VALVE DISCHARGE DP PUMP
(FOR E80-25 AND E75-25) 3 11829A001
SCREW; CAP 1-1/4 LG 3/8-16 SHOULDER,
FOR VALVE (FOR E80-25 AND E75-25)
RETAINER, SPRING FOR VALVE
(FOR E80-25 AND E75-25) 6 18833A003
VALVE, ACETAL 2.063 DIA
(FOR E80-25 AND E75-25) 6 18834A005
SEAT; VALVE (FOR E80-25 AND E75-25) 6 18835A008
* When purchasing the crankshaft or pinion on units built prior to 07/12, both
items will need to be replaced due to an improvement in design.
11
6 18832A004
Page 12

42
63
73
74
71
47
46
48
21
72
67
70
69
68
66
65
64
75
36
35
34
37
40
39
38
41
54
55
51
49
50
52
53
62
60
61
57
58
59
56
25
22
23
24
44
43
45
45
F
L
26
32
33
31
28
27
29
30
E70-23, E80-20 SHAFT DRIVE
Pre-June 2008
12
Page 13

E70-23, E80-20 SHAFT DRIVE
47
46
76
75
74
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
78
79
80
55
92
53
51
52
50
45
45
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
73
48
11
36
35
34
33
49
77
Post-June 2008
13
Page 14

SHAFT DRIVE POWER END
20164B020
20
16
5
6
19
17
10
8
9
1
3
4
5
7
6
2
18A
15
18
16
14
12
13
11
17
14
Page 15

E SERIES – SHAFT DRIVE – PARTS LIST
Item Description Qty. Eng. No.
1 CASE, GEAR 1 04625E010E
2 SHIM, PLASTIC, PINK, .015" 6 05068A016
3 SHIM, PLASTIC, GREEN, .003" 6 05068A018
4 O-RING, 5-1/8" O.D. 2 05876A098
5 WASHER, SEAL 18 14946A003
6 SCREW, CAP 3/8"-16 UNC x 1" 18 19101A013
7 CAP, BEARING, CRANKSHAFT 2 04624B004
8 CUP, BEARING, CRANKSHAFT 2 05675A013
9 CONE, BEARING, CRANKSHAFT 2 05674A021
10* CRANKSHAFT, W/75 TEETH GEAR
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25) 1 27937C022
E80-25 1 27937C044
11 KEY, SQ. 3/8 x 3/8 x 2-1/2 1 05818A048
12 OIL SEAL, 1-5/8" 1 05710A017
13 CAP, OPEN, PINION 1 04563A001
14 CUP, BEARING, PINION 2 05675A009
15 CONE, BEARING, PINION 2 05674A013
16 SHIM, .015" THK., PINK
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25) 4 05231A075
E80-25 2 05863A023
17 SHIM, .003" THK., GREEN
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25) 4 05231A074
E80-25 4 05863A024
18* SHAFT, PINION, 19 TEETH 1 27938B020
18A SPACER 1 20164B022A
19 CAP, CLOSED, BEARING, PINION 1 04741B001
20 PLUG, PIPE, 1/2" NPT, SQ. HD. 1 05022A039
21 CLAMP, 7/8" STUD, CYLINDER CAP 3 20856A000
22 CROSSHEAD ASSEMBLY
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25) 3 06211B042
E80-25 3 06211B044
23 LINK, WITH BUSHING & SCREWS 3 17042C002K
BUSHING, WRIST PIN 3 B01619A001
WASHER, LOCK 6 05454A004
SCREW, CAP 6 19103A016
24 WRIST PIN 3 M01525A001
25 BEARING, TWO HALVES 3 15245A101K
26 PLUG, DRAIN, MAGNETIC, 3/4-14 1 17481A002
27 GASKET, LID, SPECIAL SHAPE 1 06201C000
28 SCREW, CAP 5/16"-18 x 7/8" ST. 8 19100A033
29 O-RING, OIL GAUGE 1 110-000110-201
30 DIPSTICK, OIL LEVEL & O-RING (ITEM 29) 1 7206-0094-00K
31 LID, GEAR CASE 1 04561B000
32 NIPPLE, SPECIAL VENT 1 17995A000
33 CAP, PIPE 1 05737A002
34 SLINGER, NEOPRENE 3 05059A263
35 SCREW, CAP, HEX, 5/8-11 UNC x 2 4 19105A008
36 SCREW, SKT. HD. 10-32 UNF x 1/2" 6 06106A034
37 HOUSING, OIL SEAL 3 24959A000
38 SPRING, SEAL RETAINER 3 M01643A000
39 GASKET, SEAL HOUSING, 2.312 O.D. 3 05059A434
40 GASKET, VELLUMOID, 3.50 O.D. 3 05059A058
41 RETAINER, OIL SEAL HOUSING 3 24958A000
42 OIL SEAL, U CUP, VITON
43 SCREW, SKT. HD. 3/4-10 UNC x 2-1/2" 4 06106A038
44 WASHER, LOCK, 3/4" 4 05454A003
45 SCREW, DRIVE, .133 x 5/16" 6 045800011
46 STUD, 7/8"-14 UNF x 4-1/2" 6 05659A089
47 NUT, HEX, 7/8-14 UNF 6 19109A072
48 PLUG, PIPE, 1-1/4" NPT 1 05022A041
49 BODY, CYLINDER
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25) 1 18639F008
E80-25 1 18639F007
50 LID, CYLINDER (PONY ROD COVER) 1 M01520A000
51 CLAMP, LID 2 26842A000
52 SCREW, MACH. 1/4-20 UNC x 1/2" 2 148850001
53 O-RING, 1-1/4" O.D. 3 110-000024-218
®
6 22835A003
Item Description Qty. Eng. No.
54 PISTON HUB E54-30 3 7206-0354-00A
E70-23 3 7206-0393-00A
E80-20 3 7206-0396-00A
E110-14 3 7206-0358-00A
55 LINER, CYL. E54-30 1.750 I.D. 3 26849A000
E70-23 2.000 I.D. 3 20851A001
E70-23V/E80-25 2.000 I.D. 3 26849A001
E80-20 2.125 I.D. 3 20851A004
E80-20V 2.125 I.D. 3 20851A004
E110-14 2.500 I.D. 3 26849A003
56 PISTON, CUP, E54-30 1.750" O.D. 3 7206-0361-00A
E70-23 2.000 O.D. 3 7206-0392-00A
E80-20 2.125 O.D. 3 7206-0395-00A
FLAT BACK E110-14 2.500 O.D. 3 7203-0617-00A
57 RETAINER, PISTON E54-30 3 7206-0356-0A
E70-23 3 7206-0394-00A
E80-20 3 7206-0397-00A
E110-14 3 7206-0359-00A
58 SCREW, CAP, .551" M-14 METRIC 3 16654A006
59 O-RING, 2-15/16" O.D.,CYL. LINER 3 05876A095
60 SEAL, RING, VALVE CAP
(ALL MODELS EXCEPT E80-25) 3 26862A001
SEAL, RING, VALVE CAP E80-25 3 05876A064
61 CAP, VALVE
(ALL E SERIES EXCEPT E80-25) 3 26848A000
E80-25 3 17390A000
62 CLAMP, 5/8" STUD, VALVE CAP 3 20848A000
63 STUD, 5/8-11 UNC x 3-5/16 LG. 6 05659A560
64 NUT, HEX 5/8"-11 UNC 6 19109A046
65 CAGE, VALVE 6 7203-0544-00B
66 SPRING, VALVE 6 7206-0302-00A
67 VALVE, GUIDE 6 7203-0542-00A
68 INSERT, VALVE, POLYURETHANE 6 7203-0546-00A
69 O-RING, VALVE, 2.004 O.D.
E70.23V AND E110-14 6 110-000032-201
E54-30 AND E80-20V 6 05876A236
70 SEAT, VALVE 6 7203-0543-00B
71 SEAL, RING, CYLINDER CAP
(ALL MODELS EXCEPT E80-25) 3 7202-0041-00A
SEAL, RING, CYLINDER CAP E80-25 3 05876A096
72 CAP, CYLINDER 3 26805A000
73 PLUG, PIPE, 3" NPT 2 03210A000
74 PLUG, PIPE, 1" NPT 3 05022A043
75 PLUG, PIPE, 1/2" NPT 3 05022A015
76 SPRING 3 20853A000
77 PACKING E70-23V 3 18922A000
PACKING E80-20V 3 18922A004
PACKING E80-25 3 18922A000
PRESSURE RING E70-23V 3 18921A000
PRESSURE RING E80-20V 3 20854A000
PRESSURE RING E80-25 3 18921A000
RETAINER, SPRING 3 20852A003
FOLLOWER E70-23V 3 18923A002
FOLLOWER E80-20V 3 20855A000
FOLLOWER E80-25 3 18923A002
PISTON BODY E70-23V 3 18924A004
PISTON BODY E80-20V 3 20850A011
PISTON BODY E80-25 3 18924A004
SPRING; VALVE 316 SST (E80-25) 3 11829A000
SPRING; VALVE DISCHARGE DP PUMP
(E80-25) 3 11829A001
SCREW; CAP 1-1/4 LG 3/8-16 SHOULDER,
FOR VALVE (E80-25)
RETAINER, SPRING FOR VALVE (E80-25) 6 18833A003
VALVE, ACETAL 2.063 DIA (E80-25) 6 18834A005
SEAT; VALVE (E80-25) 6 18835A008
* When purchasing the crankshaft or pinion on units built prior to 07/12, both
items will need to be replaced due to an improvement in design.
6 18832A004
15
Page 16

STANDARD LIMITED WARRANTY
the date of shipment from Pentair Myers or 18 months from the manufacturing date, whichever occurs first – provided
that such products are used in compliance with the requirements of the Pentair Myers catalog and technical manuals.
or maintain the unit in accordance with the printed instructions provided; (b) to failures resulting from abuse, accident
CENTRIFUGAL & RECIPROCATING PUMPS
Pentair Myers® warrants its products against defects in material and workmanship for a period of 12 months from
During the warranty period and subject to the conditions set forth, Pentair Myers, at its discretion, will repair or
replace to the original user, the parts that prove defective in materials and workmanship. Pentair Myers reserves the
right to change or improve its products or any portions thereof without being obligated to provide such a change or
improvement for prior sold and/or shipped units.
Seals, piston cups, packing, plungers, liners and valves used for handling clear, fresh, nonaerated water at a
temperature not exceeding 120ºF are warranted for ninety days from date of shipment. All other applications are
subject to a thirty day warranty. Accessories such as motors, engines and auxiliary equipment are warranted by
the respective manufacturer and are excluded in this standard warranty. Under no circumstance will Pentair Myers
be responsible for the cost of field labor, travel expenses, rented equipment, removal/reinstallation costs or freight
expenses to and from the factory or an authorized Pentair Myers service facility.
This limited warranty will not apply: (a) to defects or malfunctions resulting from failure to properly install, operate
or negligence; (c) to normal maintenance services and parts used in connection with such service; (d) to units that
are not installed in accordance with applicable local codes, ordinances and good trade practices; (e) if the unit is
moved from its original installation location; (f) if unit is used for purposes other than for what it is designed and
manufactured; (g) to any unit that has been repaired or altered by anyone other than Pentair Myers or an authorized
Pentair Myers service provider; (h) to any unit that has been repaired using non factory specified/OEM parts.
Warranty Exclusions: PENTAIR MYERS MAKES NO EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES THAT EXTEND BEYOND THE
DESCRIPTION ON THE FACE HEREOF. PENTAIR MYERS SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Liability Limitation: IN NO EVENT SHALL PENTAIR MYERS BE LIABLE OR RESPONSIBLE FOR CONSEQUENTIAL,
INCIDENTAL OR SPECIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM OR RELATED IN ANY MANNER TO ANY PENTAIR MYERS
PRODUCT OR PARTS THEREOF. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR PROPERTY DAMAGE MAY RESULT FROM IMPROPER
INSTALLATION. PENTAIR MYERS DISCLAIMS ALL LIABILITY, INCLUDING LIABILITY UNDER THIS WARRANTY, FOR
IMPROPER INSTALLATION. PENTAIR MYERS RECOMMENDS INSTALLATION BY PROFESSIONALS.
Some states do not permit some or all of the above warranty limitations or the exclusion or limitation of incidental or
consequential damages and therefore such limitations may not apply to you. No warranties or representations at any
time made by any representatives of Pentair Myers shall vary or expand the provision hereof.
1101 MYERS PARKWAY
ASHLAND, OHIO, USA 44805
419-289-1144
WWW.FEMYERS.COM
Warranty Rev. 12/13
 Loading...
Loading...