Page 1

INSTALLATION/OPERATION
IX Series Network Camera
Sarix™ Technology
C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 2

Contents
Important Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Legal Notice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Regulatory Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Video Quality Caution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Open Source Software Notice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Compatible Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Product Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Product Label . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Service Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Camera Configuration Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Minimum System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Accessing the IP Camera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Frame Rate Notice Regarding User-Selected Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Cat5 Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Alarm, Relay, and 24 VAC Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Logging On to the Camera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Live Video Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Live Video Page Icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Keyboard Shortcuts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Selecting a Stream . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Primary Stream and Secondary Stream. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
QuickView Stream . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Event Stream . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Unicast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Multicast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Taking a Snapshot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Settings Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Accessing the Camera Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
System Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Changing the Device Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Configuring DHCP Time Server Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Configuring Manual Time Server Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Customizing the Appearance of the Text Overlay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Generating a System Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Rebooting the Camera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Restoring All Camera Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Downloading a Full Backup of Camera Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Uploading a Backup File to Restore Camera Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Downloading Snapshots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Deleting Snapshots. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Network Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Changing the Hostname . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Turning On DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Turning Off DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Selecting the Secure Sockets Layer Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Generating a Certificate Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
C2950M-G (4/12) 3
Page 3

Generating a Self-Signed Certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Enabling Secure Shell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Configuring the 802.1x Port Security Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Selecting SNMP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Configuring SNMP V2c . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Configuring SNMP V3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Imaging Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Configuring the Orientation of the Scene. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Changing the Digital Processing Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Selecting Auto Exposure Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Selecting Manual Exposure Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Day Night Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Day Night Auto and Manual Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Day Night Auto Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Day Night Manual Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Configuring Auto Focus Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Configuring Manual Focus Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Setting Tone Map Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Selecting Auto White Balance Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Selecting Manual White Balance Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Turning On Window Blanking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Turning Off Window blanking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Deleting a Window Blanking Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
A/V Streams Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Selecting a Video Preset Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Configuring a Custom Video Stream Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Compression Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Available Camera Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Image Rate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Bit Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
I-Frame Interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Quality of Service for Differentiated Services Code Point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Endura Signing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Advanced Sharpening . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Selecting the Audio Configuration Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Users Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Selecting the Users and Groups Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Creating a New User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Editing a User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Deleting a User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Events Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Creating an Alarm Event Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Creating an Analytic Event Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Creating a System Event Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Creating a Timer Event Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Editing an Event Source. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Deleting an Event Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Handlers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Creating an Event Handler: Send Email. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Creating an Event Handler: Write JPEG to SD Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Creating an Event Handler: Upload JPEG to FTP Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Creating an Event Handler: Open/Close Relay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Editing an Event Handler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Deleting an Event Handler. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Example Handler Filter Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Analytic Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
4 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 4

Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Profile Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Creating a New Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Revising a Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Deleting a Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Behaviors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Configuring a Behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Zones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Draw Zone Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Drawing a Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Deleting a Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Adaptive Motion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Scene Setup for Adaptive Motion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Selecting Adaptive Motion Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Camera Sabotage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Scene Setup for Camera Sabotage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Selecting Camera Sabotage Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
IXS0 Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
IX30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
C2950M-G (4/12) 5
Page 5

List of Illustrations
1 Camera Connections and Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
2 Remove Back Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3 Product Label . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4 Lens Pin Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
5 Ferrite Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
6 Attaching the 2.5 mm Stereo Headphone Plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
7 Cat5 Cable Pin Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
8 Alarm, Relay, and 24 VAC Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
9 Relay Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
10 Supervised Alarm Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
11 Supervised Alarm Input Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
12 Unsupervised Alarm Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
13 Normally Closed and Normally Open Unsupervised Alarm Input Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
14 Alarm Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
6 C2953M-G (4/12)
Page 6

Important Notices
LEGAL NOTICE
SOME PELCO EQUIPMENT CONTAINS, AND THE SOFTWARE ENABLES, AUDIO/VISUAL AND RECORDING CAPABILITIES, THE IMPROPER USE OF
WHICH MAY SUBJECT YOU TO CIVIL AND CRIMINAL PENALTIES. APPLICABLE LAWS REGARDING THE USE OF SUCH CAPABILITIES VARY
BETWEEN JURISDICTIONS AND MAY REQUIRE, AMONG OTHER THINGS, EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM RECORDED SUBJECTS. YOU
ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE FOR INSURING STRICT COMPLIANCE WITH SUCH LAWS AND FOR STRICT ADHERENCE TO ANY/ALL RIGHTS OF
PRIVACY AND PERSONALTY. USE OF THIS EQUIPMENT AND/OR SOFTWARE FOR ILLEGAL SURVEILLANCE OR MONITORING SHALL BE DEEMED
UNAUTHORIZED USE IN VIOLATION OF THE END USER SOFTWARE AGREEMENT AND RESULT IN THE IMMEDIATE TERMINATION OF YOUR
LICENSE RIGHTS THEREUNDER.
REGULATORY NOTICES
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
RADIO AND TELEVISION INTERFERENCE
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits of a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However there is no guarantee that the interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try
to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
You may also find helpful the following booklet, prepared by the FCC: “How to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems.” This
booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington D.C. 20402.
Changes and Modifications not expressly approved by the manufacturer or registrant of this equipment can void your authority to operate this
equipment under Federal Communications Commission’s rules.
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
VIDEO QUALITY CAUTION
FRAME RATE NOTICE REGARDING USER-SELECTED OPTIONS
Pelco systems are capable of providing high quality video for both live viewing and playback. However, the systems can be used in lower quality
modes, which can degrade picture quality, to allow for a slower rate of data transfer and to reduce the amount of video data stored. The picture
quality can be degraded by either lowering the resolution, reducing the picture rate, or both. A picture degraded by having a reduced resolution
may result in an image that is less clear or even indiscernible. A picture degraded by reducing the picture rate has fewer frames per second,
which can result in images that appear to jump or move more quickly than normal during playback. Lower frame rates may result in a key event
not being recorded by the system.
Judgment as to the suitability of the products for users’ purposes is solely the users’ responsibility. Users shall determine the suitability of the
products for their own intended application, picture rate and picture quality. In the event users intend to use the video for evidentiary purposes in
a judicial proceeding or otherwise, users should consult with their attorney regarding any particular requirements for such use.
OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE NOTICE
This product includes certain open source or other software originated from third parties that is subject to the GNU General Public License (GPL),
GNU Library/Lesser General Public License (LGPL) and different and/or additional copyright licenses, disclaimers, and notices.
The exact terms of GPL, LGPL, and some other licenses are provided to you with this product. Please refer to the exact terms of the GPL and LGPL
at http://www.fsf.org (Free Software Fou ndation) or http://www.opensource.org (Open Source Initiative) regarding your rights under said license.
You may obtain a complete corresponding machine-readable copy of the source code of such software under the GPL or LGPL by sending your
request to digitalsupport@pelco.com; the subject line should read Source Code Request. You will then receive an email with a link for you to
download the source code.
This offer is valid for a period of three (3) years from the date of the distribution of this product by Pelco.
C2950M-G (4/12) 7
Page 7

Introduction
The IX Series camera is a network-based camera with a built-in, Web-based viewer for live streaming to a standard Web browser (Microsoft
Internet Explorer
®
or Mozilla
®
behaviors, which can be configured and enabled using a standard Web browser.
The camera features open architecture connectivity to third-party software. Pelco offers an application programming interface (API) and software
development kit (SDK) that enables third-party systems to interface with Pelco's IP cameras. The camera is also compatible with Endura
DX Series, and Digital Sentry
The camera supports up to three compression formats and many resolutions. The two standard compression formats include H.264 and MJPEG.
MPEG-4 is also available with IXS0 models. The dual streams can be configured to a variety of resolutions, frame rates, and bit rates.
The camera includes 0.5 and 3.1 megapixel (MPx) models available in two camera styles: color or day/night. The day/night models have a
mechanical IR cut filter that increases camera sensitivity in low light situations. The camera uses a 1/3-inch imager and accommodates
CS-mount lenses.
The camera also includes built-in Power over Ethernet (PoE), which supplies power to the camera through the network. If PoE is not available, the
camera is prewired for 24 VAC.
COMPATIBLE SYSTEMS
The device can also be used with an Endura, DX Series, or Digital Sentry system. It also works with many third-party systems with Pelco’s API
and the ONVIF API. For detailed instructions on configuring the device using one of these systems, refer to the manual shipped with the system.
Go to partnerfirst.pelco.com for a list of compatible products and partners.
MODELS
Firefox®). All camera models are preloaded with Pelco’s Adaptive Motion Detection and Camera Sabotage
®
systems to record, manage, configure, and view multiple live streams.
®
®
,
IXS0C Sarix IX Series, network camera, 0.5 MPx standard definition color
IXS0DN Sarix IX Series, network camera, 0.5 MPx standard definition day/night
IX30DN Sarix IX Series, network camera, 3.1 MPx day/night
Getting Started
Before installing your camera, thoroughly familiarize yourself with the information in this section.
NOTES:
• Pelco recommends connecting the camera to a network that uses a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server to address devices.
• Do not use a network hub when configuring the network settings for the camera.
• To ensure secure access to the IP camera, place the camera behind a firewall when it is connected to a network.
PARTS LIST
Qty Description
1Camera
1 Ferrite (for Class B compliance)
1 6-pin connector
1 IX Series Quick Start Guide
1 Resource disc
3 MAC address labels (extra)
Installation tools and the following parts are needed but not supplied
:
Qty Description
1 Lens (use either a megapixel or standard auto iris lens, depending on the camera model)
1 Service cable (IX-SC)
1 Mounting hardware
8 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 8
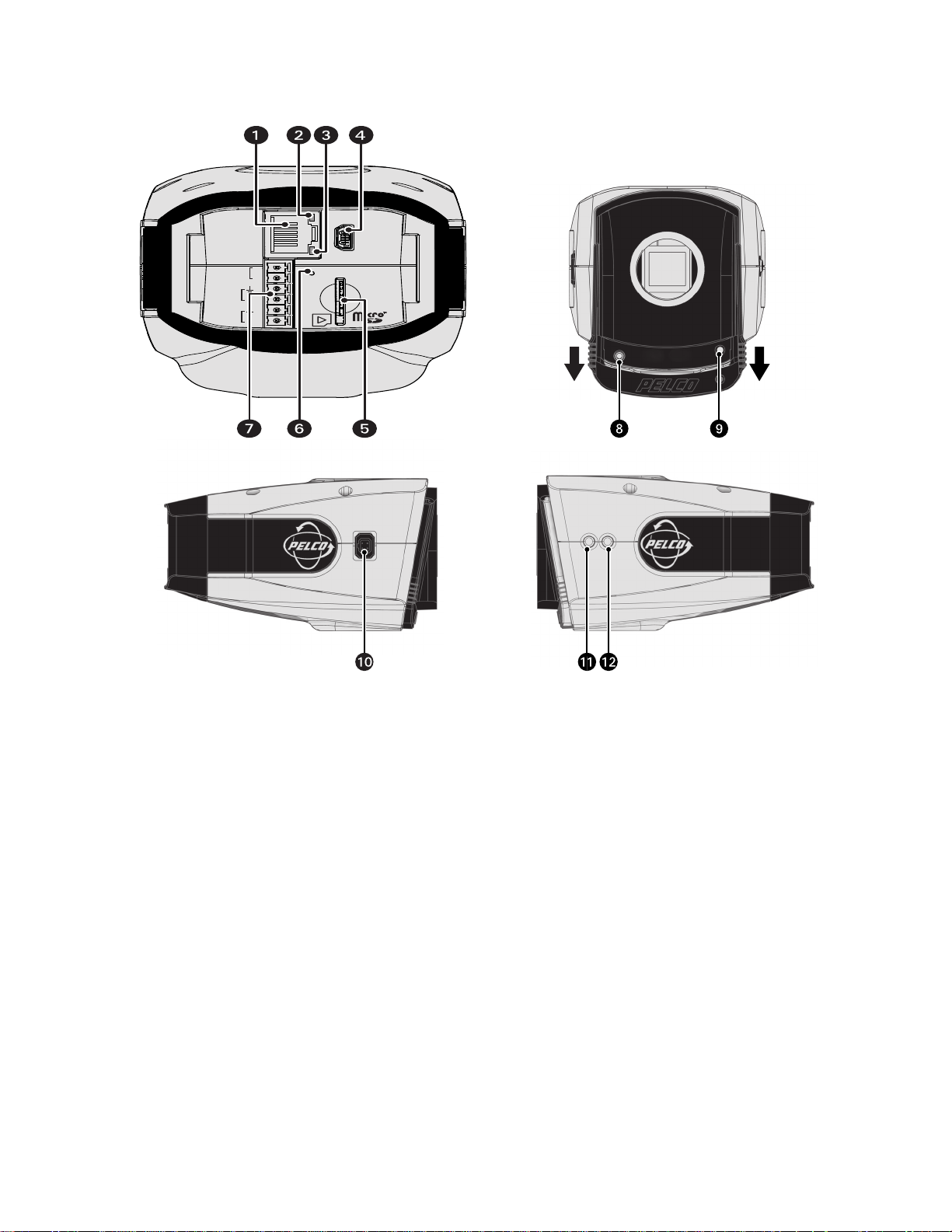
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
ACC
PoE
LINK
RESET
AC
24V~
RELAY
R1
ALARM
A1
FV
(FRONT COVER
OPENED)
Figure 1. Camera Connections and Features
ì
RJ-45 Network Port: Connects the camera to the IP network. Also supplies power to the camera through the network using PoE. If PoE is
not available, the camera is prewired for 24 VAC.
î
Ethernet Activity LED: Flashes green to indicate that data is being transmitted or received by the camera.
ï
Ethernet Link LED: Glows solid amber to indicate that a live network connection is established.
ñ
Accessory Port: For use with compatible Pelco accessories.
ó
24 VAC Power, Relay, and Alarm Connections: Supports 24 VAC as the power source, one relay that can be used to control an external
circuit, and one alarm for physical input into the system.
r
Reset Button: Reboots the camera or restores the camera’s factory default settings. This button is recessed. Using a small tool, such as a
paper clip, press and release the reset button once to reboot the camera. Press and hold the reset button until the green light inside the
SD card slot flashes orange to restore the camera to the factory default settings.
s
Mini SD Card Slot: Saves a snapshot image to a mini SD card based on alarm activity.
NOTE: The mini SD card must be formatted as FAT32. Other formats are not compatible with the camera.
t
Service Port: Outputs analog video. Use this port at the installation site to set up the field of view and to focus the camera. When a
service cable is connected to the camera, video to the IP stream is disabled (refer to Service Cable on page 13).
u
Power LED: Glows solid amber and then flashes green during the configuration sequence; glows solid green after the sequence is
complete. The LED can be disabled (refer to System T ab on page 23). If this LED glows red (solid or flashing), contact Pelco Product Support
at 1-800-289-9100 (USA and Canada) or +1-559-292-1981 (international) for assistance.
C2950M-G (4/12) 9
Page 9
~í
DC01234 SN:123-4567
00:15:C5:3A:84:DB
IX30-C3 A1.0
US
LISTED
C
N15007
AMPS
390mA
MAX
VOLTS
24V~
ITE
15KT
Auto Iris Lens Connector: Controls the amount of light allowed through the lens. Insert the 4-pin connector from the DC drive auto iris
lens into this connector
~â
Auto Back Focus Button: Sets the auto back focus mechanism. Press the button once to center the auto back focus mechanism and to
fully open the iris. Press and hold the button for three seconds to start the auto back focus mechanism and to focus the camera.
~ä
NTSC/PAL Button: Toggles the service port between NTSC and PAL formats.
PRODUCT LABEL
The product label lists the model number, date code, serial number, and Media Access Control (MAC) address. This information might be required
for setup. To access the product label remove the back cover of the camera (refer to Figure 2 and Figure 3).
Figure 2. Remove Back Cover
Figure 3. Product Label
10 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 10
Installation
Pin DC (AID) Auto Iris Lens
1 Control coil negative (–)
2 Control coil positive (+)
3 Drive coil positive (+)
4 Drive coil negative (–)
NOTE: Megapixel lenses are designed and tested to deliver optimal image quality to megapixel cameras. A standard definition lens installed on
a megapixel camera will limit the resolution of the camera and create poor image quality.
1. Install the lens.
a. Remove the cover from the lens mount.
b. Screw the lens onto the lens mount. Be careful to prevent dust from entering the space between the lens and the imager. If necessary,
use clean, compressed air to remove any foreign matter (refer to the instructions shipped with the lens). Make sure the lens does not
touch the camera imager when installed.
c. Connect the auto iris lens to the 4-pin connector located on the side of the camera. Refer to Figure 4 for the pin connections for the
auto iris lens connector.
3
12
2. Use a standard screw to mount the camera in the desired location. The maximum thread depth is 0.25 inches (6.4 mm). The camera can be
mounted from either the top or bottom, depending on the type of camera mount used in your installation.
NOTE: When installing inside an enclosure, mount the camera in an inverted position to allow easy access to the service port. Use the
camera software to reconfigure the camera orientation for normal operation (refer to Configuring the Orientation of the Scene on page 32).
3. Connect the power wiring using one of the following options:
• Connect the network cable to RJ-45 network port on the back of the camera.
• If the network has no PoE, connect a 24 VAC Class 2 power supply to the 24 VAC power connector.
Refer to Wiring on page 14 for more information.
4
Figure 4. Lens Pin Connections
C2950M-G (4/12) 11
Page 11

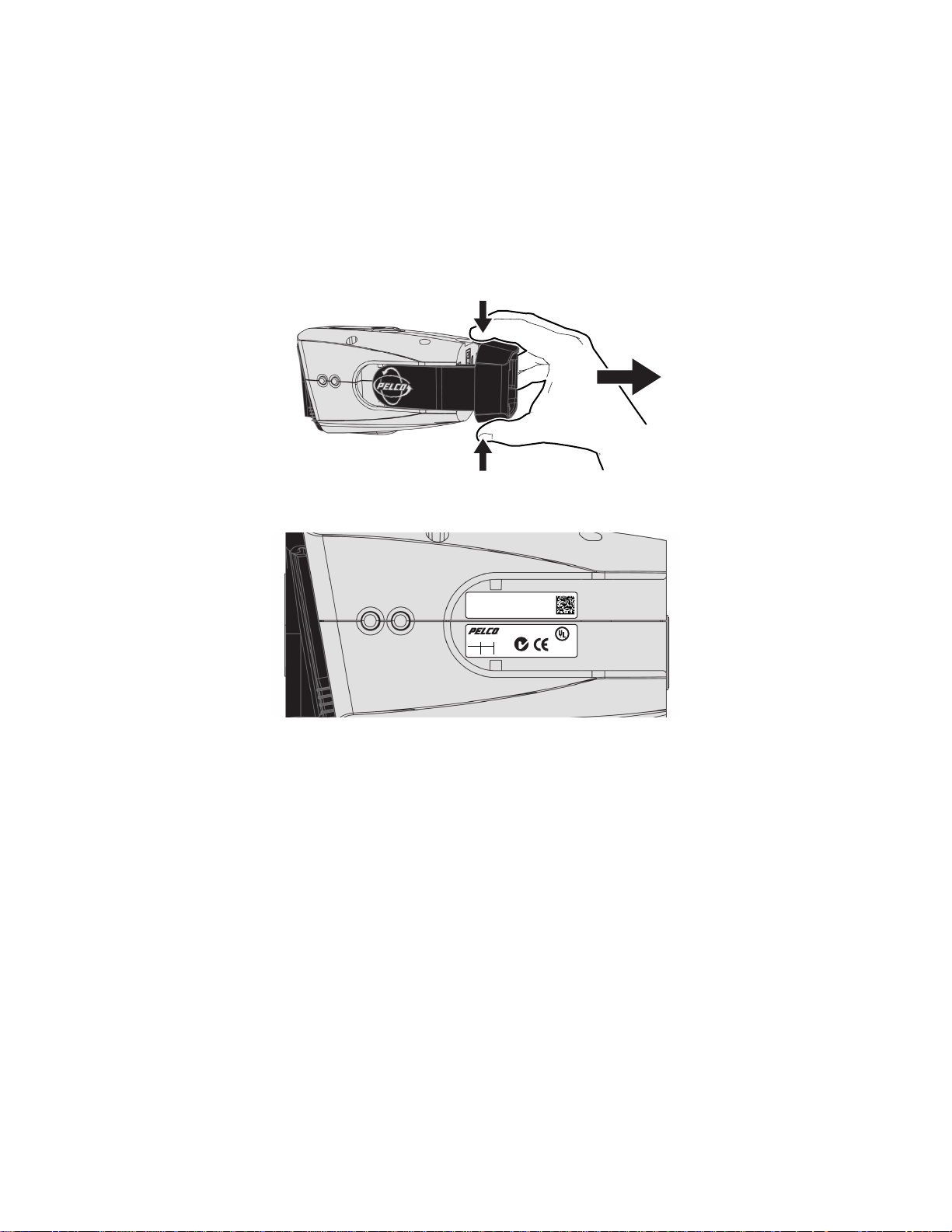
4. For FCC Class B installations, attach the supplied ferrite to the network cable (refer to Figure 5.) The ferrite should be installed on the cable
approximately 1 inch (2.54 cm) from the camera’s RJ-45 network port.
Figure 5. Ferrite Installation
WARNING: The ferrite must be installed for the camera to meet FCC Class B compliance standards. Failure to correctly install the ferrite
might cause harmful interference to radio communications.
5. Connect the necessary wiring for alarms and relays (refer to Wiring on page 14).
6. Apply power to the camera. The camera will complete a configuration sequence; the green LED flashes five times per second for
approximately two minutes, and then turns solid after the sequence is complete.
NOTE: If the camera is not connected to a DHCP server and DHCP is enabled, the configuration sequence might take up to five minutes to
complete.
7. View the camera image using the service port or a Web browser.
8. Focus the lens:
a. Press the auto back focus button once to center the focus mechanism. The button is located on the side of the camera.
b. Manually adjust the zoom and focus of the lens to the desired field of view (refer to the instructions shipped with the lens).
c. Press and hold the back focus button for three seconds to start the auto back focus mechanism.
12 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 12
SERVICE CABLE
The camera includes a service port that outputs camera video. Use it at the installation site to set up the field of view and to focus the camera.
Pelco offers an optional service cable (IX-SC) that connects directly to the service port. The service cable has a male BNC output for most
standard viewers.
NOTE: The ICS-SC and CST150 are not compatible with this camera. If you have any questions about service cable compatibility, contact
Pelco Product Support at 1-800-289-9100 (USA and Canada) or +1-559-292-1981 (international).
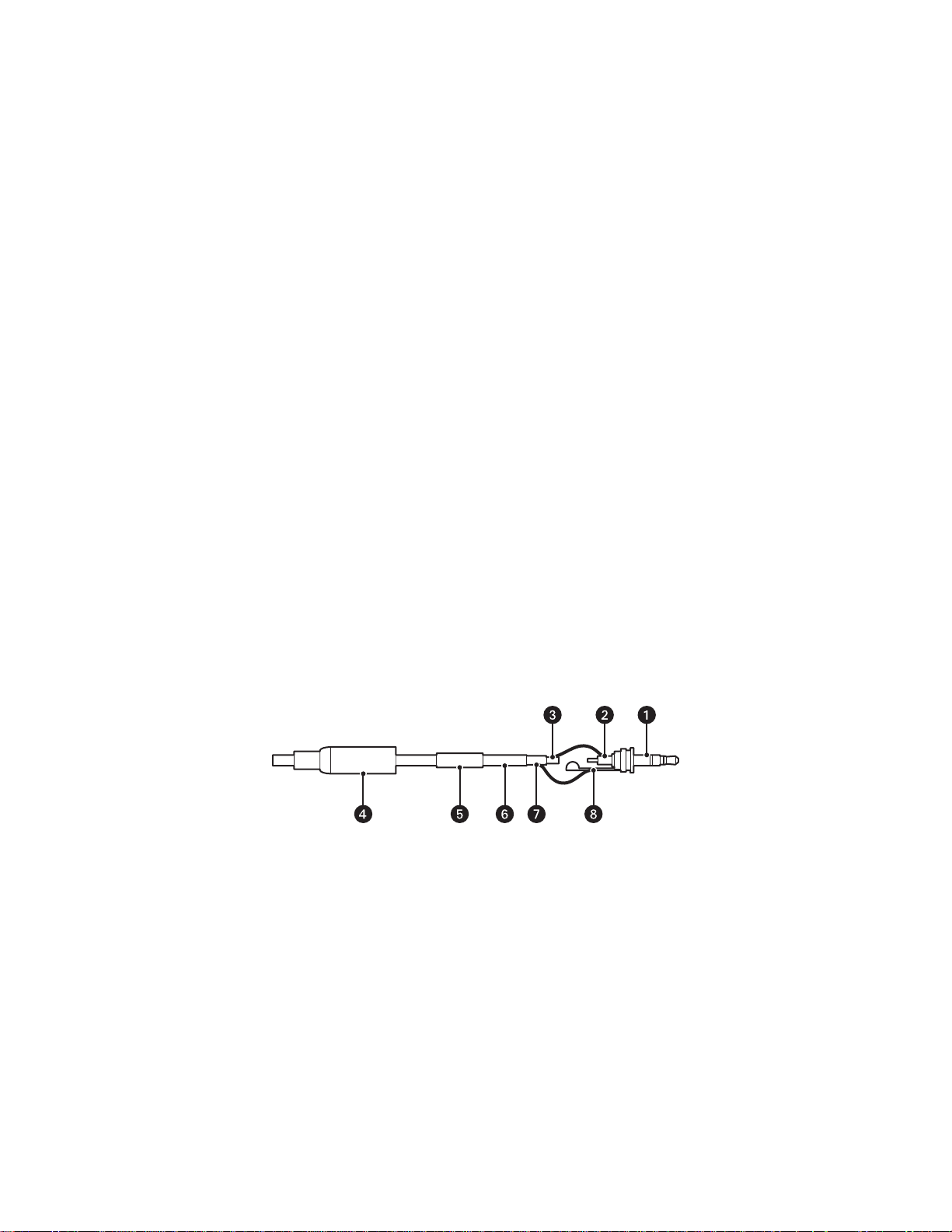
To assemble a service cable for the camera, purchase the following items from an electronics supply store:
Qty Description
1 2.5 mm stereo plug (male)
1 CPM 88 miniature coaxial connector
1 RG174/U coaxial cable
1 1/8-inch shrink fit tubing, 1/2-inch long
To assemble the cable:
1. Attach the CPM 88 miniature coaxial connector to one end of the cable. Follow the directions supplied with the miniature coaxial connector.
2. Attach the 2.5 mm stereo plug to the other end of the coaxial cable (refer to the figure below):
a. Remove the support sleeve from the plug.
b. Slip the shrink fit tubing and support sleeve over the end of the cable.
c. Prepare the cable:
(1) Strip back the outer jacket 0.318 inch (8.06 mm) inch from the end of the cable.
(2) Pull back the coaxial braid shield.
(3) Strip back the insulating material 0.125 inch (3.18 mm) inch to expose the center conductor.
d. Solder the center connector of the cable to the shoulder pin of the plug.
e. Heat the shrink fit tubing around the center conductor and shoulder pin
f. Pull the coaxial braid shield back through the crimp pin and solder it to the top of the crimp pin arm.
g. Crimp the end of the crimp pin around the cable.
h. Reassemble the support sleeve and the plug.
Figure 6. Attaching the 2.5 mm Stereo Headphone Plug
ì
2.5 mm Stereo Plug
î
Plug Shoulder Pin
ï
Center Conductor
ñ
Support Sleeve
C2950M-G (4/12) 13
ó
Shrink Fit Tubing
r
Coaxial Cable
s
Coaxial Braid Shield
t
Crimp Pin Arm
Page 13
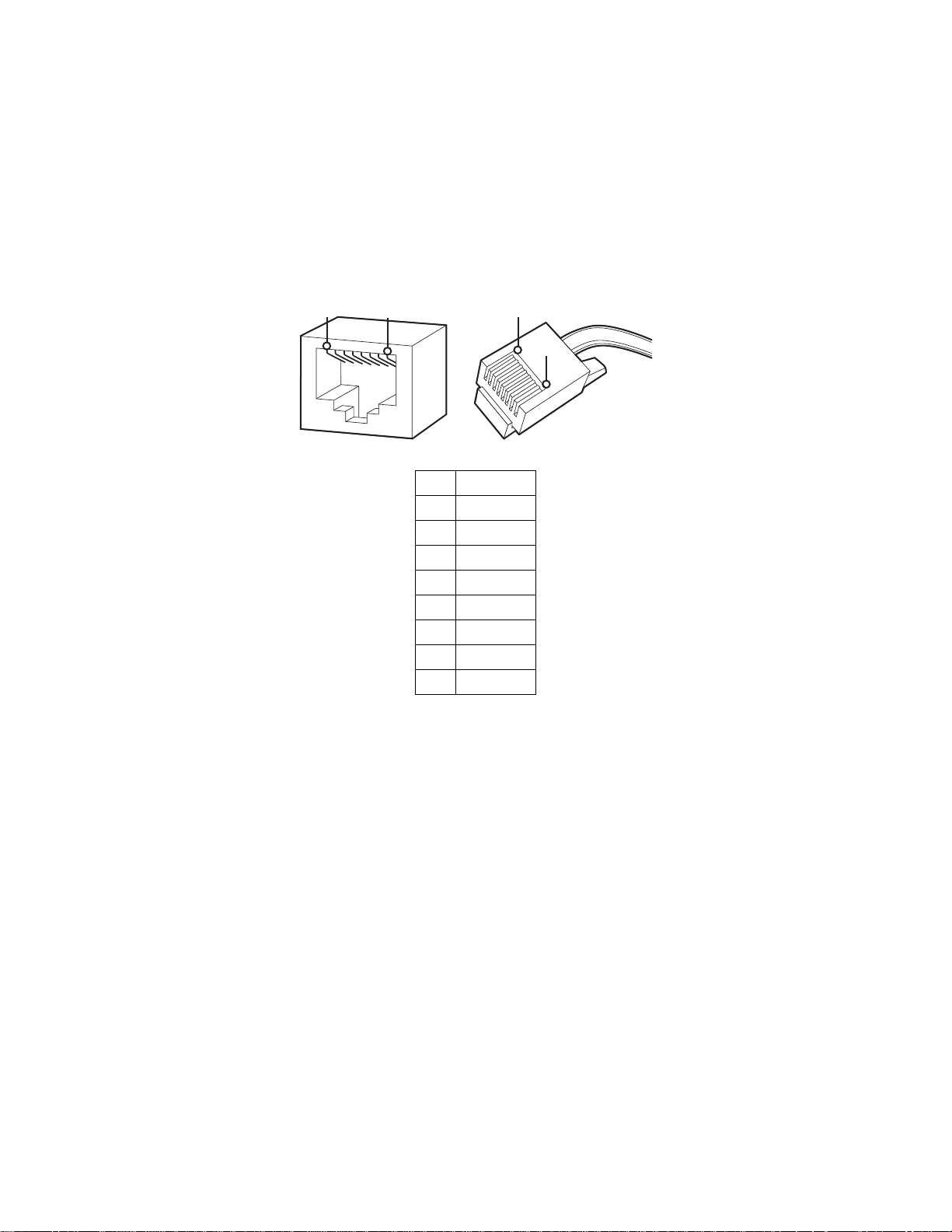
WIRING
8
8
1
1
CAT5 CABLE
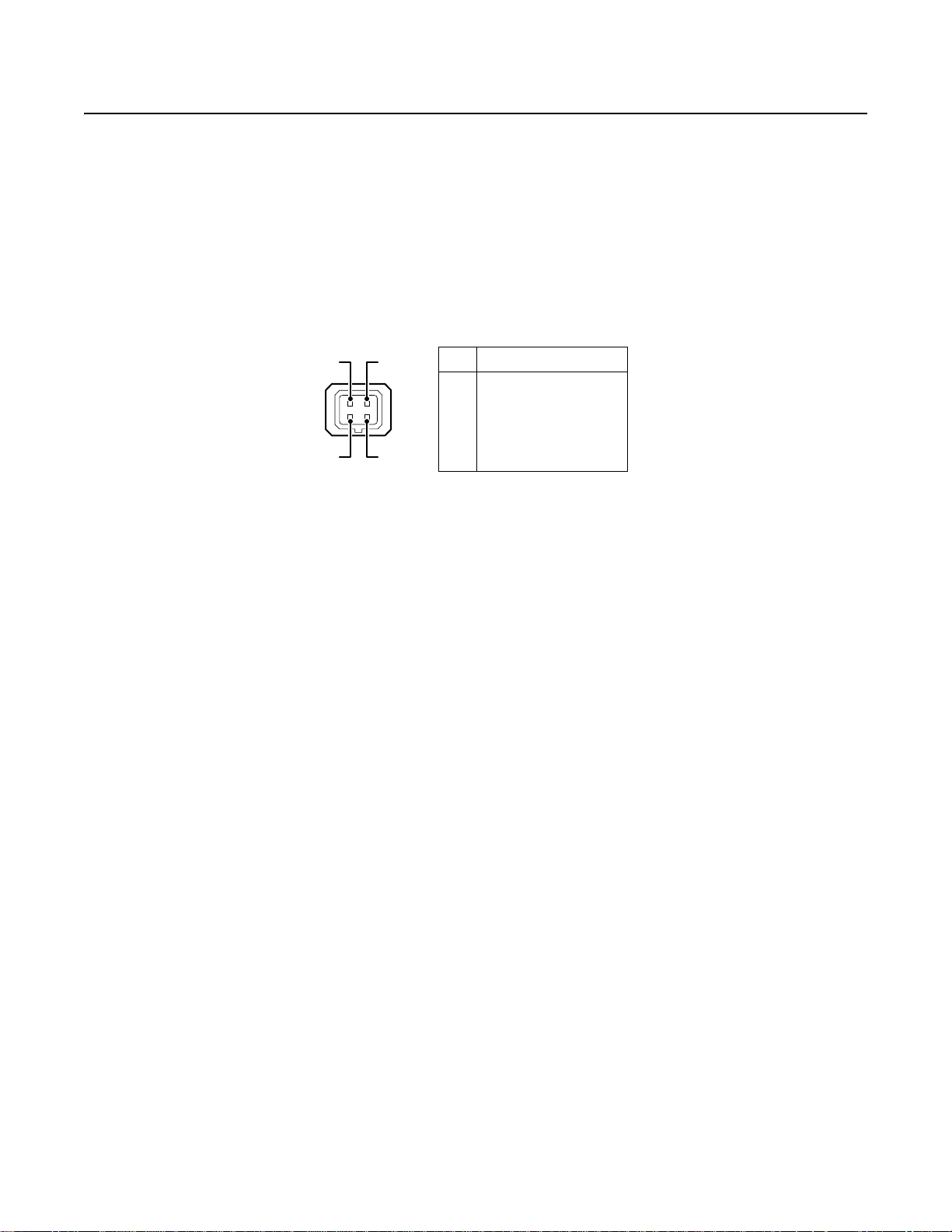
Connect a Cat5 cable to an RJ-45 network connector (not supplied). The 8-pin connector includes video and PoE for the camera.
PoE (IEEE 802.3af) injects power over the same cabling that carries the network data, eliminating the need for a separate power supply. This
simplifies the installation and operation of the camera without affecting network performance.
NOTE: The camera will autosense and configure itself to use either a crossover cable or a straight cable.
Refer to Figure 7 for pin descriptions.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Pin Function
1TX+
2TX–
3 RX+
4PoE 1-2
5PoE 1-2
6 RX–
7PoE 3-4
8PoE 3-4
Figure 7. Cat5 Cable Pin Descriptions
14 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 14
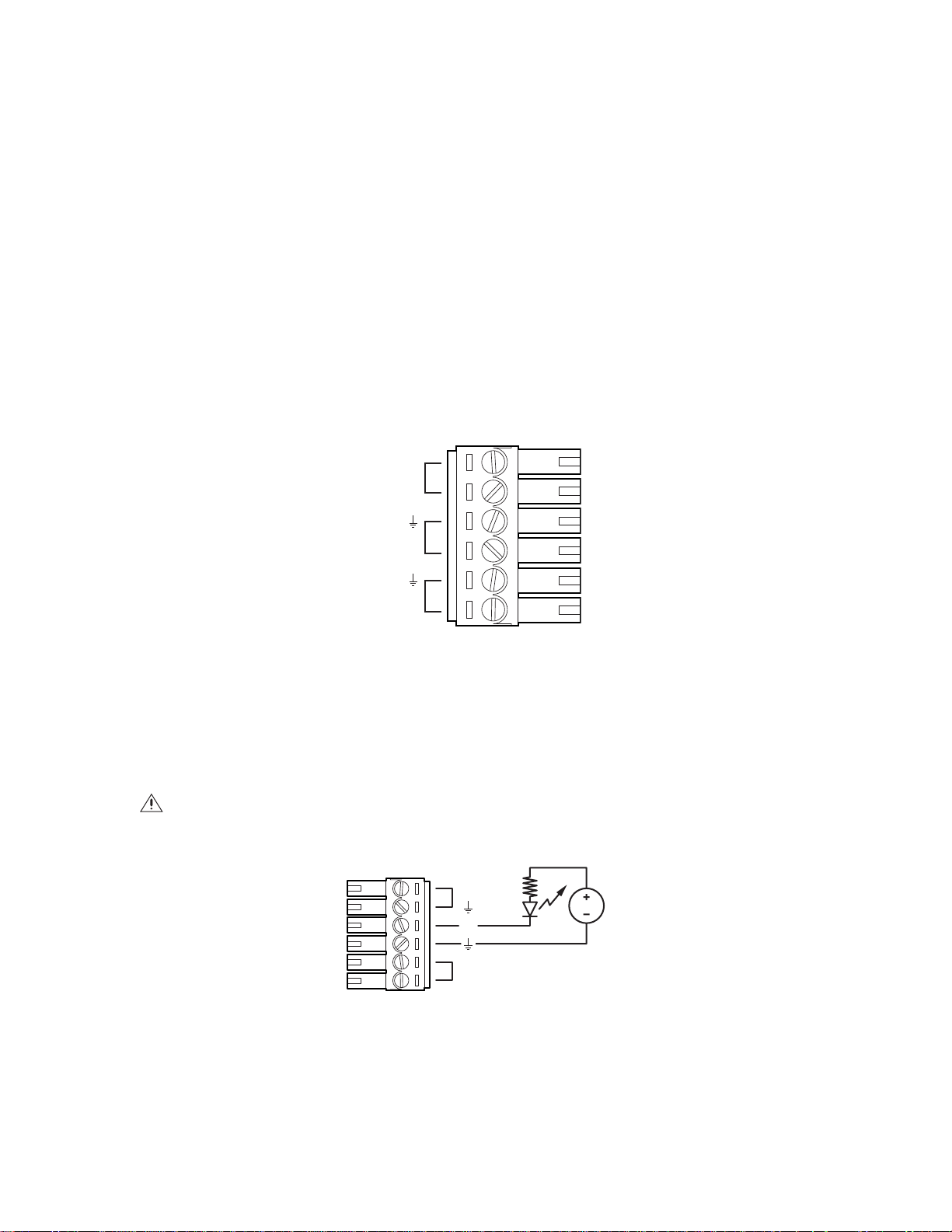
ALARM, RELAY, AND 24 VAC CONNECTOR
24V~
RELAY
R1
ALARM
A1
12 VDC, 150 mA MAX
24V~
R1
A1
Single Camera Wiring
If PoE is not available:
1. Connect the alarm, relay, and 24 VAC wires to the supplied mating connector (refer to Figure 8).
NOTE: Only use the 24 VAC wires if PoE is not available.
2. When finished, attach the mating connector to the green connector on the back of the camera.
Multiple Camera Wiring
If you are operating the camera using 24 VAC and you are wiring more than one camera to the same transformer:
1. Connect one side of the transformer to pin 1 of the 2-position terminal block on all modules.
2. Connect the other side of the transformer to pin 2 of the terminal block on all modules.
NOTE: Failure to connect all modules identically might introduce video noise for some installations.
Figure 8. Alarm, Relay, and 24 VAC Connector
Connecting a Relay Device
The camera has an output for activating an external device. It supports both momentary and continuous relay operation.
You can operate the relay interactively during an active connection, or it can operate automatically to coincide with certain events. Typical
applications include turning on lights or other electrical devices or activating a door, gate, or lock.
WARNING: Do not exceed the maximum rating of 12 VDC, 0.15 A.
Figure 9 shows how to wire the relay with its power source to the camera.
Figure 9. Relay Wiring
C2950M-G (4/12) 15
Page 15
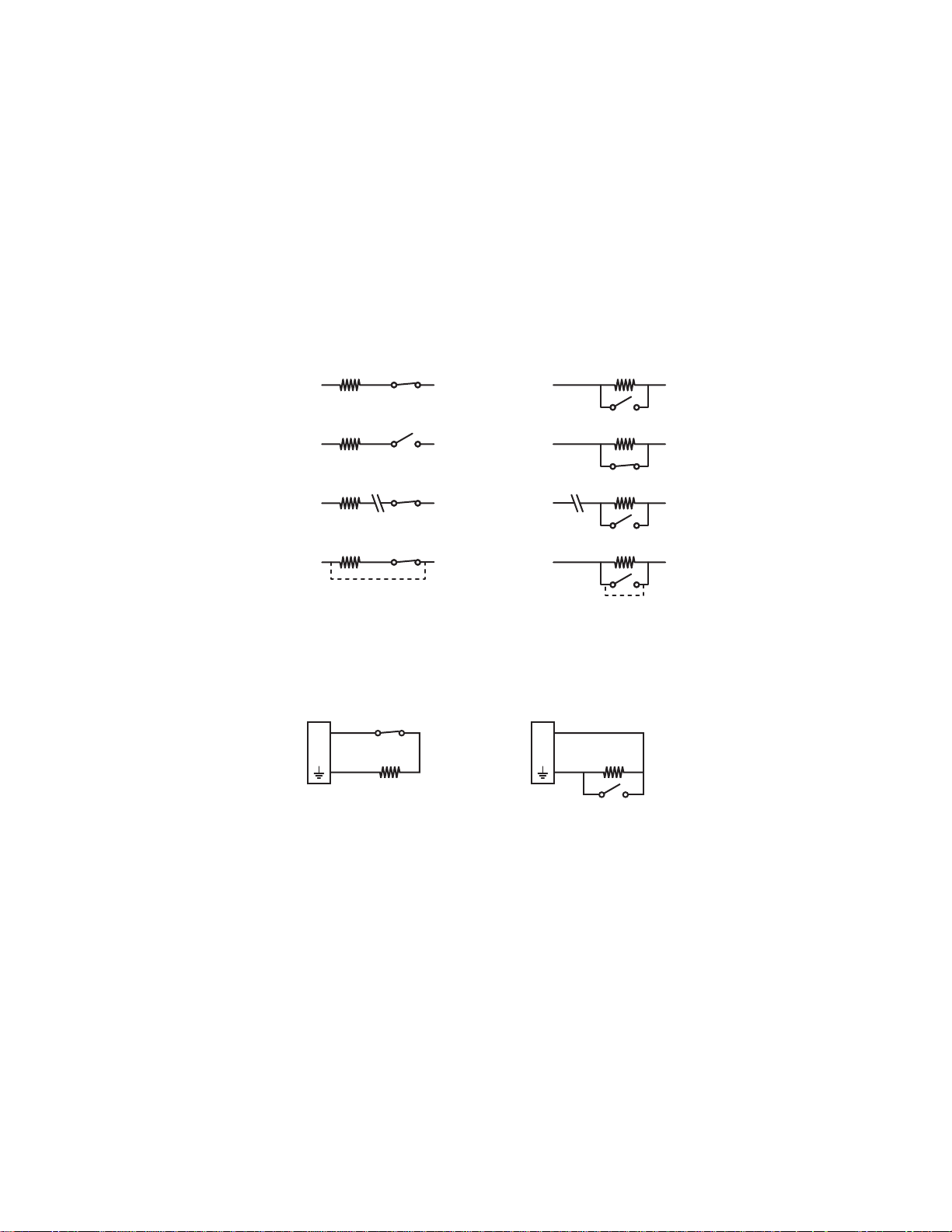
Connecting Alarms
+V
+V
+V
+V
+V
+V
+V
+V
BYPASS
CUT
BYPASS
CUT
1 KΩ
1 KΩ
1 KΩ
1 KΩ
1 KΩ
1 KΩ
1 KΩ
1 KΩ
GND
ALARM
GND
ALARM
GND
NO ALARM
GND
ALARM
GND
ALARM
GND
ALARM
GND
NO ALARM
GND
ALARM
NORMALLY OPENNORMALLY CLOSED
1 KΩ
A
1
1 KΩ
A
1
NORMALLY OPENNORMALLY CLOSED
The camera provides an alarm input for external signaling devices, such as door contacts or motion detectors. Both normally open and normally
closed devices are supported.
Supervised Alarms
When an alarm is configured as a supervised alarm, the camera maintains a constant electrical current through the alarm circuit
(3.3 VDC, 1 ohm). If the alarm circuit length changes, due to an electrical short or a bypass, the voltage fluctuates from its normal state and
activates an alarm.
NOTE: Install the 1-kohm resistor as close to the switch as possible.
Figure 10 illustrates the alarm and no alarm conditions of a supervised alarm input. Whether the alarm is normally closed or normally open,
neither a cut nor a bypass can defeat these alarms.
Figure 10. Supervised Alarm Conditions
Figure 11 illustrates the wiring configuration for supervised alarm inputs.
Figure 11. Supervised Alarm Input Wiring
16 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 16
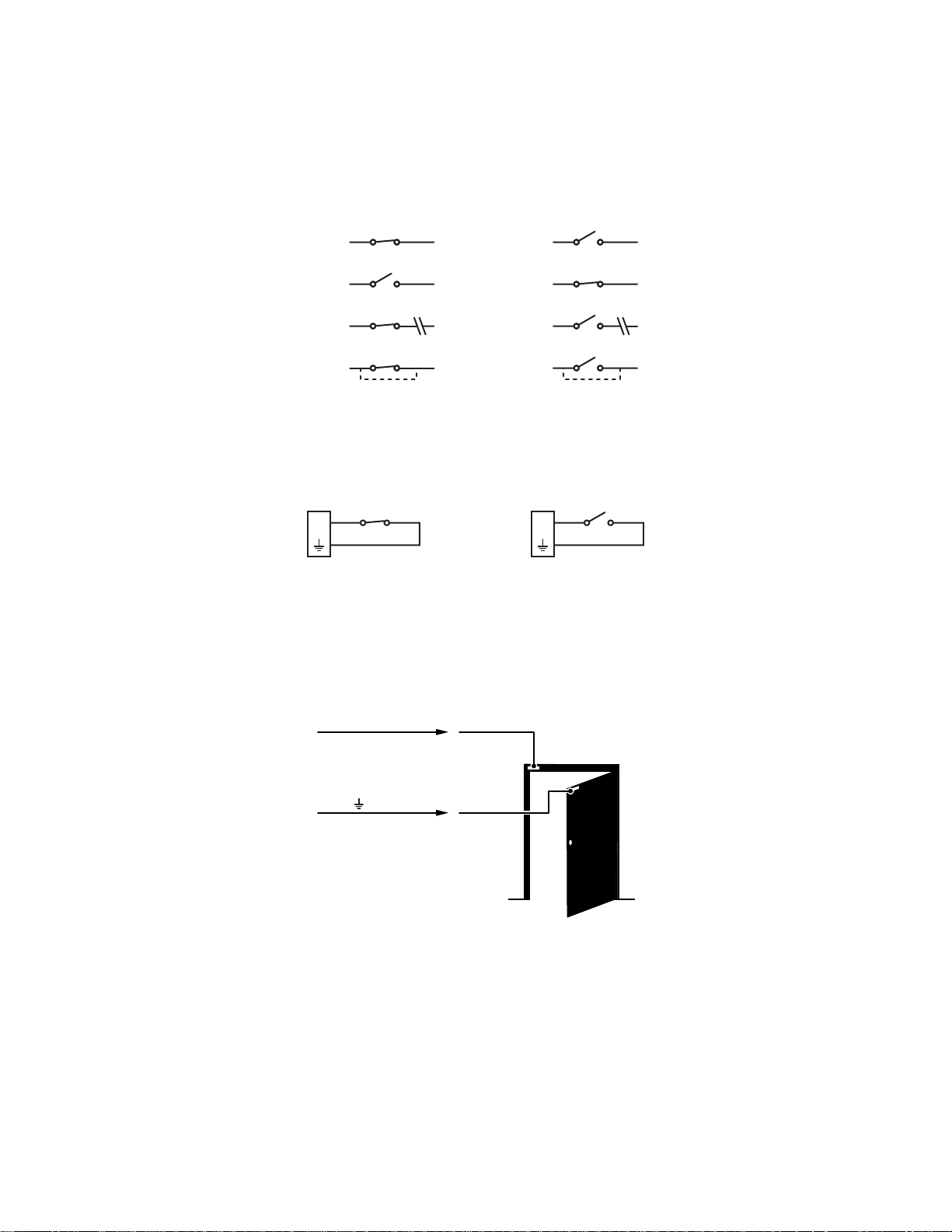
Unsupervised Alarms
+V
+V
+V
+V
+V
+V
+V
+V
BYPASS
CUT
BYPASS
CUT
GND
ALARM
GND
ALARM
GND
NO ALARM
GND
NO ALARM
GND
NO ALARM
GND
ALARM
GND
NO ALARM
GND
ALARM
NORMALLY OPENNORMALLY CLOSED
A1A1
NORMALLY OPENNORMALLY CLOSED
ALARM
ALARM A1
When an alarm is configured as an unsupervised alarm, the camera only activates an alarm when the normal alarm state (open or closed)
changes.
Figure 12 illustrates the alarm and no alarm conditions of an unsupervised alarm input.
Figure 12. Unsupervised Alarm Conditions
Figure 13 illustrates the wiring configuration for unsupervised alarm inputs.
Figure 13. Normally Closed and Normally Open Unsupervised Alarm Input Wiring
NOTE: A normally closed alarm input can be defeated with a bypass; a normally open input can be defeated with a cut.
Alarm Connections
Figure 14 shows how to wire the camera to an alarm.
Figure 14. Alarm Connections
C2950M-G (4/12) 17
Page 17

Operation
CAMERA CONFIGURATION SEQUENCE
Once the device is installed and power is applied, the device will start a configuration sequence: the green LED flashes five times per second for
approximately two minutes, indicating that the boot cycle is complete and the device is on line.
NOTE: If the device is not connected to a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server and DHCP is enabled, the configuration sequence
might take up to five minutes to complete.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• Network Tab on page 26
• Turning On DHCP on page 27
• Turning Off DHCP on page 27
MINIMUM SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
Network and processor bandwidth limitations might cause the video stream to pause or appear pixilated when additional Web-interface users
connect to the camera. Decrease the images per second (ips), resolution, compression, or bit rate settings of the Web interface video streams to
compensate for network/processor limitations.
®
Processor: Intel
Operating system: Microsoft
Pentium® 4 microprocessor, 1.6 GHz
®
Windows® XP, Windows Vista®, Windows 7® or Mac® OS X 10.4
Memory: 512 MB RAM
Network interface card: 100 megabits (or greater)
Monitor: Minimum of 1024 x 768 resolution, 16- or 32-bit pixel color resolution
Web browser: Internet Explorer
Media player: Pelco Media Player or QuickTime
Mac OS X 10.4 (or later)
NOTES:
• Pelco Media Player is recommended for control, smoothness, and reduced latency as compared to QuickTime.
• This product is not compatible with QuickTime version 7.6.4 for Windows XP or Windows Vista. If you have this version installed on your PC,
you will need to upgrade to QuickTime version 7.6.5.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• Compression Standards on page 40
• Available Camera Resolution on page 41
• Image Rate on page 41
• Bit Rate on page 41
®
7.0 (or later) or Mozilla® Firefox® 3.0 (or later)
®
7.6.5 for Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7; or QuickTime 7.6.4 for
18 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 18

ACCESSING THE IP CAMERA
The first time you access the camera, the live video page appears. By default, you are viewing the video as a public user and only have access to
the single stream live view.
If, for security purposes, users should not be allowed to view video without first logging on to the camera, change the permissions for public
users.
LOGGING ON TO THE CAMERA
1. Open the Web browser.
2. Type the camera’s IP address in the browser address bar.
NOTE: If you do not know the camera’s IP address, you can locate it using the Pelco Device Utility software.
3. Click the Login button in the navigation bar; a dialog box appears.
4. Type your user ID and password.
NOTE: If you are logging on to the camera as the administrator for the first time, the default User ID and Password are admin
(all lowercase). For security purposes, be sure to change the password after you log on for the first time.
5. Click Log In.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• System Tab on page 23
• Network Tab on page 26
• Imaging Tab on page 31
• A/V Streams Tab on page 39
• Users Tab on page 43
• Events Tab on page 45
C2950M-G (4/12) 19
Page 19

Live Video Page
The live video page allows you to manage the way you view live video and capture images. You can also view live video from this page and
access menus on the navigation bar (based on user permissions).
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• Live Video Page Icons on page 20
• Keyboard Shortcuts on page 20
• Taking a Snapshot on page 22
• Settings Page on page 22
LIVE VIDEO PAGE ICONS
Viewable icons are based on user permissions.
Select Stream: Selects the viewable video stream that is displayed in live view (primary or secondary) and selects unicast or multicast
settings.
Maximize Viewing Area: Scales the image to the full size of the browser. To resize the video pane to normal view, click the
Show Toolbar button in the upper-right corner of the window.
Show Toolbar: Returns the window to normal view. This option is only available after the window has been set to maximize the
viewing area.
Open Stream in New Window: Opens the video in a scalable, independent window. Opening the video in a separate window allows
you to view the video while other applications are running. This window can be minimized, maximized, or closed using the title bar
buttons of the active window. The window can also be resized by dragging the lower-right corner of the window.
Take a Snapshot: Captures the image displayed in the video pane and then saves it as a JPEG file.
KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS
Several keyboard shortcuts are available when viewing live video from Microsoft® Internet Explorer® and the Pelco Media Player. These
keyboard shortcuts display different overlays on a video pane and provide quick access to a specific function.
Keyboard Shortcut Function
SHIFT + A Displays analytics information for the current active behavior.
SHIFT + S Displays details about the live video such as image rate, resolution, and transmission rate.
SHIFT + T Displays the current date and time.
These keyboard shortcuts are not available when viewing video with Apple
Table A. Keyboard Shortcuts
®
Quicktime®.
20 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 20

SELECTING A STREAM
1. Click the Select Stream button.
2. Select one of the following stream options from the Select Stream page:
Primary Stream: To select this stream, click the button next to Primary Stream.
Secondary Stream: To select this stream, click the button next to Secondary Stream.
QuickView Stream: To select this stream, click the button next to QuickView Stream.
Event Stream: To select this stream, click the button next to Event Stream.
NOTE: If the secondary stream has not been configured, only Primary Stream, Event Stream, and QuickView Stream are available.
3. Select one of the following options to adjust the stream settings:
MPEG-4 or H.264 compression: Select the video transmission type from the Transmission drop-down menu. Available settings include
Unicast and Multicast. Select the media player from the Player drop-down menu. Available settings include Pelco Media Player or
QuickTime.
JPEG compression: Select the image rate for the stream from the Image Rate drop-down menu. The available settings for the primary
and secondary streams depend on the Image Rate setting. The QuickView Stream has only two image rate settings: 2 ips and 1 ips.
4. Click the Select button to save the stream settings.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• QuickView Stream on page 21
• Multicast on page 22
• Primary Stream and Secondary Strea m on page 21
• QuickView Stream on page 21
• Compression Standards on page 40
• Image Rate on page 41
PRIMARY STREAM AND SECONDARY STREAM
The Primary Stream and Secondary Stream are video streams that include compression, resolution, image rate, and bit rate settings. The streams
can be set up using a video preset setting, or they can be customized using the video configuration settings.
A video preset is a predefined video configuration that offers a good balance between video performance and bandwidth usage. For easy stream
configuration, use the Video Preset page located in the drop-down menu of the A/V Streams Tab.
To customize the Primary Stream or Secondary Stream use the Video Configuration page located in the drop-down menu of the A/V Streams Tab.
Configurable settings include the stream name, compression standard, resolution setting, image rate, and bit rate. The default names for the
streams are Primary Stream and Secondary Stream; however, if these stream names have been changed, the new names will replace the default
names (Primary Stream and Secondary Stream) on the Select Stream page.
QUICKVIEW STREAM
The QuickView Stream is a predefined JPEG video stream with a lower resolution. This low resolution, low frame rate stream is displayed when
the Imaging Tab settings are configured. This allows users to view changes to exposure, white balance, and tone map settings as they are
configured and before the settings are saved.
The QuickView Stream is also ideal for users who are connected to a network with processor bandwidth limitations that might cause a high
resolution, high frame rate video stream to pause or appear pixilated.
The aspect ratio of the QuickView Stream mirrors that of the Primary Stream. The only stream setting that is selectable is the framerate: 2 ips
or 1 ips.
C2950M-G (4/12) 21
Page 21

EVENT STREAM
The Event Stream displays a list of alerts triggered by a running behavior (analytic). The alert includes a screen capture, the profile that was
triggered, and the zone where the alert was detected. For the Event Stream to work you must have a behavior profile running. To set up and run
behaviors, use the Analytic Configuration page located in the drop-down menu of the Events Tab.
UNICAST
A unicast transmission sends a separate video stream to each user that is requesting data. Although multiple users might request the same data
from the camera at the same time, duplicate video streams are transmitted to each user. Every unicast user that connects to the camera
consumes additional processing power, which limits the number of simultaneous users who can access the camera.
The camera supports a maximum of 20 simultaneous users.
MULTICAST
A multicast transmission sends data to multiple users at the same time using one transmission stream. Each multicast user that connects to the
camera consumes no additional processing power; therefore, multicast video streams can be sent to an unlimited number of simultaneous users.
TAKING A SNAPSHOT
1. Click the “Take a Snapshot” button.
2. The File Download dialog box opens, and the following message appears: “Do you want to open or save this file?”
3. Select one of the following options:
Open: Your computer’s photo editing program opens and displays the screen image. This function is available only when using
Microsoft
Save: The image is saved as a JPEG file on your computer.
Cancel: The captured image is not saved or displayed and the dialog box closes.
NOTE: If you are using JPEG, the captured image will be the size of the largest MJPEG stream. If you are using MPEG-4 or H.264, the image is
captured using the QuickView Stream, which is approximately VGA resolution.
®
Internet Explorer® 7.0 (or later) or Mozilla® Firefox® 3.0 (or later).
SETTINGS PAGE
Depending on user permissions, the Settings page allows you to manage camera system settings, set up users, configure events, and control the
camera.
NOTE: The Settings menu might not be available if the user does not have permission to access this feature.
ACCESSING THE CAMERA MENUS
1. Log on to the camera.
2. Click the Settings link in the navigation bar located in the upper-right corner of the page; a list of menu tabs appears.
3. Place the mouse pointer over a tab to display a list of submenus.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• System Tab on page 23
• Network Tab on page 26
• Imaging Tab on page 31
• A/V Streams Tab on page 39
• Users Tab on page 43
• Events Tab on page 45
22 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 22

System Tab
Use the System tab to change the device name, configure the time settings, set up the text overlay for the live view, display system information,
and access snapshots generated by event handlers. You can also use the System tab to generate a system log, reboot the camera, or restore the
camera’s factory default settings.
General Settings
The General Settings page includes configurable fields for the device name, time server, and text overlay settings. The device name is the
user-friendly description of the camera displayed in the gray area near the top of screen. The time server is an external server that uses
Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize the camera date and time settings. The text overlay settings allow you to customize the appearance
of the Web browser by displaying the device name and the date and time at the top or bottom of the live view.
You can also use the General Settings page to turn the camera’s power LED on or off and to configure the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
server to send an email notification when an event handler is activated.
NOTE: Consult your network administrator for information on configuring email notification on your local network.
Backup and Restore Settings
Once the camera settings have been configured for optimal scene display, use the backup feature to save the camera settings. If the camera
settings are changed and inadvertently result in a less desirable image, use the restore setting to restore the camera to the previously saved
settings.
NOTE: This feature is not intended for the configuration of multiple units or for firmware upgrades.
Information Settings
The System Information page fields are read-only and include the firmware version, hardware version, model number, and serial number of the
system. This information is typically required by Pelco Product Support for troubleshooting purposes.
Snapshot Viewer
The Snapshot Viewer page displays a list of snapshots saved to the SD card when a “Write JPEG to SD Card” event handler is activated. From
this page, you can open, download, or delete snapshots from the SD card. There are 100 snapshots displayed per page.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• Changing the Device Name on page 23
• Customizing the Appearance of the Text Overlay on page 24
• Generating a System Log on page 24
• Rebooting the Camera on page 24
• Restoring All Camera Defaults on page 25
CHANGING THE DEVICE NAME
1. Place your mouse pointer over the System tab.
2. Select General Settings from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the Device Name box and highlight the text.
4. Type a user-friendly name into the Device Name box (2 to 63 characters). A user-friendly name makes it easier to recognize the device on
the network. Examples of user-friendly names are Front Door, Lobby, or Parking Lot.
5. Click Save to save the new device name, or click Reset to restore to the previously saved device name.
C2950M-G (4/12) 23
Page 23

CONFIGURING DHCP TIME SERVER SETTINGS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the System tab.
2. Select General Settings from the drop-down menu.
3. Select DHCP in the Time Server field.
NOTE: Select DHCP if the camera is connected to a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) network that has time server properties
configured. Selecting this option automatically synchronizes the camera with the time server. If the DHCP network’s time server properties
are not configured or the network does not have a time server, you will need to configure the DHCP settings manually.
4. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
CONFIGURING MANUAL TIME SERVER SETTINGS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the System tab.
2. Select General Settings from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the Manual button in the Time Server section.
4. Type the IP address of the time server in the Time Server text box. The time server is an external server that uses
Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize the camera date and time settings.
5. Configure the Time Zone option by selecting the continent and the region that are closest to the camera’s location.
NOTE: If your location observes a form of daylight saving time, the system will automatically change the time on the associated dates.
6. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
CUSTOMIZING THE APPEARANCE OF THE TEXT OVERLAY
1. Click the System tab.
2. Select General Settings from the drop-down menu.
3. Set the Text Overlay settings:
Date/Time Overlay: Select Show to display the date and time in the live view overlay. The default setting is Hide.
Camera Name Overlay: Select Show to display the device name in the live view overlay. The default setting is Hide.
4. Select the display position for the overlay from the Position drop-down menu. Selections include Top Right, Top Center, Top Left, Bottom
Right, Bottom Center, and Bottom Left.
5. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
GENERATING A SYSTEM LOG
1. Click the System tab.
2. Click the Generate System Log button to create a system log that can be used by Pelco Product Support for troubleshooting. Contact Pelco
Product Support at 1-800-289-9100 (USA and Canada) or +1-559-292-1981 (international).
REBOOTING THE CAMERA
1. Click the System tab.
2. Select General Settings from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the Reboot Camera button to restart the camera. Rebooting the camera does not change the configured camera settings.
24 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 24

RESTORING ALL CAMERA DEFAULTS
WARNING: This process cannot be undone; all user and custom settings will be lost.
1. Click the System tab.
2. Select General Settings from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the Restore All Camera Defaults button to restore the camera’s factory default settings.
NOTE: If the camera is not connected to a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) network, the IP address settings for the camera will be
lost and the server will not recognize the camera. DHCP On is the default setting for the camera IP address.
Refer to the following section for more information:
• Turning Off DHCP on page 27
DOWNLOADING A FULL BACKUP OF CAMERA SETTINGS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the System tab.
2. Select Backup & Restore from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the Download Now button. A file download dialog box appears on the screen.
4. Click Save and then select where you want to save the file.
UPLOADING A BACKUP FILE TO RESTORE CAMERA SETTINGS
1. Click the System tab.
2. Select Backup & Restore from the drop-down menu.
3. Click on the Browse button. A Choose File to Upload dialog box opens.
4. Select the file you want to upload.
5. Click the Open button.
6. Click the Upload and Restore button.
DOWNLOADING SNAPSHOTS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the System tab.
2. Select Snapshot Viewer from the drop-down menu.
3. Download snapshots in one of the following ways:
• Download one snapshot: Click “download” next to the individual snapshot.
• Download all snapshots: Click the Download button in the upper-right corner to download all snapshots on that page.
4. Follow the file download instructions on your screen to open or save the JPEG files.
DELETING SNAPSHOTS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the System tab.
2. Select Snapshot Viewer from the drop-down menu.
3. Delete snapshots in one of the following ways:
• Delete one snapshot: Click “delete” next to the individual snapshot.
• Delete all snapshots: Click the Delete All button in the upper-right corner to delete all snapshots from the camera’s SD card.
4. Click OK in the dialog box to delete the JPEG files.
C2950M-G (4/12) 25
Page 25

NETWORK TAB
Use the Network tab to change the camera’s general network settings, select the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) settings, enable Secure Shell (SSH),
configure 802.1x port security, and select Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) settings.
General Network Settings
The General Network page includes configurable and read-only fields for network communication settings. Available settings include the
Hardware Address, Hostname, IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, and DNS Servers.
You can also enable or disable the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server from the General Network page. DHCP automatically
assigns an IP address to the device if there is a DHCP server on the network. If DHCP is set to On, the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS
server settings are read-only text. If DHCP is set to Off, these settings must be manually changed. The default camera setting for DHCP is On.
SSL Settings
To ensure security on the Internet, all Web browsers provide several security levels that can be adjusted for sites that use SSL technology to
transmit data. SSL encrypts communications, making it difficult for unauthorized users to intercept and view user names and passwords.
SSL requires signed certificates to determine if the Web browser accessing the camera has the required authentication. The camera can
generate a certificate signing request (CSR) that can be sent to a certificate authority for a signature (for example, VeriSign
a self-signed certificate using the Generate Self-Signed Certificate option.
®
), or it can generate
SSH Settings
SSH is a user-enabled protocol that allows Pelco Product Support to log on to and service the camera for advanced troubleshooting purposes.
From this page, users with the appropriate permissions can enable or disable SSH access to the camera.
802.1x
802.1x is a port security that authenticates devices that want to establish a point-to-point access through a wired or wireless port using
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). This port-based authentication method prevents unauthorized access to a Local Area Network (LAN)
through a physical port. For example, when a device is connected to a network port, the network switch will ask the device for authentication.
If the credential is accepted when the device sends a credential to the network switch, the network switch will open the port for normal use.
If authentication fails, the device is prevented from accessing information on the port.
SNMP
SNMP is an application layer protocol used to manage TCP/IP-based networks from a single workstation or several workstations. The camera
supports SNMP versions 2c and 3 and can be configured to send data using a trap.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• Changing the Hostname on page 27
• Turning On DHCP on page 27
• Turning Off DHCP on page 27
• Selecting the Secure Sockets Layer Mode on page 28
• Generating a Certificate Request on page 28
• Generating a Self-Signed Certificate on page 29
• Enabling Secure Shell on page 29
• Configuring the 802.1x Port Security Settings on page 29
• Selecting SNMP Settings on page 30
26 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 26

CHANGING THE HOSTNAME
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select General from the drop-down menu.
3. Click in the Hostname box and highlight the text.
4. Type a user-friendly name into the Hostname box (1 to 21 characters) using alphanumeric characters. A user-friendly name makes it easier
to recognize the device on the network. Numeric-only names are not allowed.
5. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
TURNING ON DHCP
The default Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) setting for the camera is DHCP On. If the DHCP option is set to Off, complete the
following steps to reset it to On.
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select General from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the On option for DHCP.
4. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
NOTE: If the camera is not connected to a DHCP server but DHCP is set to On, the default IP address 192.168.0.20 on subnet mask 255.255.255.0
is automatically assigned to the camera. After the first camera is connected and assigned the default IP address, the system will automatically
look for other cameras on the auto IP address system and assign IP addresses in sequential order as required. For example, if three cameras are
connected to a network without a DHCP server, the first camera will be assigned address 192.168.0.20, the second camera will be assigned
address 192.168.0.21, and the third camera will be assigned address 192.168.0.22.
TURNING OFF DHCP
WARNING: Contact your network administrator to avoid any network conflicts before setting or changing the IP address of the device.
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select General from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Off option for the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
4. Change the following network settings as required:
IP Address: The address of the camera connected to the network.
Subnet Mask: The address that determines the IP network that the camera is connected to (relative to its address).
Gateway: The router that accesses other networks.
DNS Servers: The addresses of the dedicated servers that translate the names for Web sites and hostnames into numeric IP addresses.
5. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
C2950M-G (4/12) 27
Page 27

SELECTING THE SECURE SOCKETS LAYER MODE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select SSL from the drop-down menu.
3. Select one of the following modes:
Required: A signed Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate must be installed, and a secure URL that begins with the protocol name “https:”
must be used to access the camera. Sensitive data is always encrypted during transmission. A URL that begins with the “http:” protocol
rather than the “https:” protocol will be redirected to the secure URL automatically.
NOTE: Beginning with firmware version 1.8.2, this field cannot be modified in the Web browser. To select or clear the Required mode, you
must use the ONVIF or Pelco API call. Doing so avoids placing the camera into a mode in which it would no longer work with a connected
VMS system.
Optional: A signed SSL certificate must be installed, but a secure URL that begins with the protocol name “https:” is optional when
accessing the camera. You can also access the camera using a standard URL with the “http:” protocol, but sensitive data is not encrypted
during transmission. To ensure that sensitive data is encrypted, you must use a secure URL with the “https:” protocol.
Disabled (default): Turns off access to the Web client through SSL. Sensitive data will not be encrypted during transmission.
NOTE: If the SSL mode is set to disabled, you cannot access the camera using a URL that begins with an “https:” protocol. Your Web
browser displays an error message if you do not type the camera URL correctly.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• Generating a Certificate Request on page 28
• Generating a Self-Signed Certificate on page 29
GENERATING A CERTIFICATE REQUEST
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select SSL from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the Install Certificate button located at the bottom of the SSL Configuration page. The Select Certificate Install Method option buttons
appear on the page.
4. Select Generate Certificate Request, and then click Next. The Certificate Request Form opens.
5. Fill in all of the fields, and then click Generate Request. The following progress message appears on the page: “Generating certificate
signing request, please wait.”
6. Send the CSR, which looks like an encrypted block of undecipherable text, to a third-party certificate authority of your choice for a
signature.
7. After you receive the signed certificate, click the Install Certificate button to upload the signed certificate to the device.
8. After the certificate is uploaded, select the desired mode.
9. Click Save.
NOTE: Depending on the third-party certificate authority that signed your certificate, you might need to renew your certificate after a specified
amount of time. Consult the certificate authority for more details.
28 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 28

GENERATING A SELF-SIGNED CERTIFICATE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select SSL from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the Install Certificate button located at the bottom of the SSL Configuration page. The Select Certificate Install Method option buttons
appear on the page.
4. Select the “Generate Self-signed Certificate” option, and then click Next. The “Self-signed Certificate Information Form” opens.
5. Fill in all of the fields, and then click Generate Request. The following progress message appears on the page: “Your changes are being
applied. This process might take up to 3 minutes.” After three minutes, the certificate is uploaded to the device.
6. After the certificate is uploaded, select the desired mode.
7. Click Save.
NOTE: Self-signed certificates are valid for one year. The certificate’s expiration date is listed in the Installed Certificate information section.
If the certificate has expired and you attempt to access the camera using a secure URL, the Web browser displays a message. Repeat this
procedure to generate and upload a new certificate.
ENABLING SECURE SHELL
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select SSH from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Enabled check box.
4. Click in the Password box and type a password (4 to 16 alphanumeric characters). Passwords are case-sensitive.
NOTE: The default username is “root” and cannot be changed. The username and password are required when accessing the camera
through a third-party SSH client.
5. Click in the “Re-type Password” box and retype your password.
6. Click the Save button to save the password and enable SSH, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without
saving it.
CONFIGURING THE 802.1X PORT SECURITY SETTINGS
WARNING: To prevent network conflicts, contact your network administrator before configuring the 802.1x port security settings.
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select 802.1x from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the On option for the 802.1x Port Security. The default setting for 802.1x is Off.
4. Select the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) method from the Protocol drop-down menu. Supported EAP methods include EAP-MD5,
EAP-PEAP, EAP-TLS, and EAP-TTLS.
5. Type the information required for the selected 802.1x authentication method.
6. Connect the PC to a 802.1x secured switch with like authentication protocols.
7. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
C2950M-G (4/12) 29
Page 29

SELECTING SNMP SETTINGS
WARNING: The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) settings are advanced controls. Consult your network administrator to
obtain the required information to configure SNMP settings.
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select SNMP from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the SNMP Version: None, V2c, or V3. None disables the SNMP configuration and is the default setting.
NOTE: SNMP V2c and SNMP V3 configuration settings are independent of each other, but only one SNMP version can be active at a time.
CONFIGURING SNMP V2C
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select SNMP from the drop-down menu.
3. Select V2c as the SNMP Version.
4. Type the community name in the Community String box. The default name for the Community String is ”public.”
5. Configure the Trap Configuration settings.
Address: Type the host name or IP address of the recipient of the trap message.
Community String: Type the name of the community that should receive the trap message.
6. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
CONFIGURING SNMP V3
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Network tab.
2. Select SNMP from the drop-down menu.
3. Select V3 as the SNMP Version.
4. Type the SNMP user name in the SNMP user field.
5. Select the encryption algorithm for authentication from the Authentication drop-down menu: None, MD5, or SHA. If you use authentication
method MD5 or SHA, type a password in the text box to the right of the selected Authentication encryption.
6. Select the privacy encryption algorithm setting from the Privacy drop-down menu: None, DES, or AES. If you use privacy method DES or
AES, type a password in the text box to the right of the selected Privacy encryption.
7. Configure the address for the Trap Configuration. The Address is the host name or IP address of the recipient of the trap message.
8. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
30 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 30

Imaging Tab
Use the Imaging tab to change the camera’s general image settings, adjust the camera exposure, program the focus mechanism, adjust the tone
map settings to increase scene detail, tune the white balance settings for scenes with fluctuating lighting conditions, or define window blanking
privacy areas.
General Imaging Settings
General imaging settings include adjustments for camera orientation and digital processing. The Orientation settings reconfigure the image
180 degrees horizontally and 180 degrees vertically. Use these settings when installing the camera in an inverted position. If the orientation is
not adjusted, the image will display upside down and mirrored.
Digital processing settings can be set to Auto or Manual to adjust the camera’s sharpness, saturation, and contrast. When set to Auto, the
camera continually delivers the best possible image by automatically adjusting the digital processing settings based on the scene. Auto is the
default setting. Manual digital processing is recommended only for indoor applications that have a single, unchanging primary light source.
Exposure Settings
Exposure is the amount of light detected by the camera sensor. A scene with correct exposure settings has adequate detail and contrast between
white and dark values. An image with too little or too much exposure eliminates detail in the scene. The camera features Auto and Manual
exposure settings. Auto exposure automatically sets the amount of light detected by the camera sensor based on settings for light control,
exposure compensation, and the day and night exposure times. Manual exposure sets the amount of light detected by the camera sensor based
on a user-defined setting. Manual exposure is recommended only for indoor applications that have a single, unchanging primary light source.
Auto is the default setting.
Focus Settings
Focus sets the back focus to the center focal point of the scene. The camera can be configured to back focus automatically or manually. Auto
focus automatically back focuses the camera on the subject in the center of the scene. Manual focus turns off the auto focus mechanism and
locks the camera at a user-specified position. The manual focus setting is recommended only for indoor applications that have a single,
unchanging primary light source. The Focus page also includes Full Range Auto-Focus, Quick Auto-Focus, and a Factory Defaults.
Tone Map Settings
Tone map balances the brightest and darkest sections of a scene to produce an image with more balanced lighting and more detail. This is
accomplished, in part, when the device maps the 10-bit input sensor data (0 to 1023 bits) into 8-bit output RGB values (0 to 255 bits).
White Balance Settings
White balance settings define how the camera processes video images to render true colors in a scene. White balance is especially effective in
scenes with changing lighting conditions or in scenes with more than one type of light source. For example, scenes that benefit from white
balance correction are outdoor scenes, indoor scenes that include a window or door that opens to the outdoors, or indoor scenes that include
both incandescent and fluorescent lighting.
Window Blanking Settings
Window blanking is used to conceal user-defined privacy areas. A blanked area appears on the screen as a solid gray window. The camera can
handle up to four blanked windows as long as the total blanked area does not exceed 50 percent of the field of view.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• Configuring the Orientation of the Scene on page 32
• Changing the Digital Processing Settings on page 32
• Selecting Auto Exposure Settings on page 32
• Selecting Manual Exposure Settings on page 34
• Day Night Settings on page 34
• Configuring Auto Focus Settings on page 35
• Configuring Manual Focus Settings on page 36
• Setting Tone Map Options on page 36
• Selecting Auto White Balance Settings on page 37
C2950M-G (4/12) 31
Page 31

• Selecting Manual White Balance Settings on page 37
• Turning On Window Blanking on page 38
• Turning Off Window blanking on page 38
• Deleting a Window Blanking Area on page 38
CONFIGURING THE ORIENTATION OF THE SCENE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select General from the drop-down menu.
3. Select one of the following options:
• Click the “Flip left-to-right” box to rotate the camera image 180 degrees horizontally.
• Click the “Flip top-to-bottom” box to rotate the camera image 180 degrees vertically.
CHANGING THE DIGITAL PROCESSING SETTINGS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select General from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the mode: Manual or Auto. Auto is the default.
4. Move the slider to the left or right to change the following settings:
Sharpness AdjustSharpness: Controls the clarity of detail in a scene. Move the slider to the right to increase the sharpness; move the
slider to the left to decrease the sharpness. Increasing the sharpness also increases the image noise. The auto range of adjustment is
–100 to 100; the auto default setting is 0 (zero). The manual range of adjustment is 0 to 100; the manual default setting is 50.
Saturation AdjustSaturation: Controls how intense or vivid the colors are in a scene. Move the slider to the right to increase the
saturation level; move the slider to the left to decrease the saturation level. The auto range of adjustment is –100 to 100; the auto default
setting is 0 (zero). The manual range of adjustment is 0 to 100; the manual default setting is 50.
Contrast AdjustContrast: Controls gradations between the darkest and lightest portions of the scene. Move the slider to the right to
increase the contrast; move the slider to the left to decrease the contrast. The auto range of adjustment is –100 to 100; the auto default
setting is 0 (zero). The manual range of adjustment is 0 to 100; the manual default setting is 50.
Brightness AdjustBrightness: Controls the lighting detail in a scene. Move the slider to the right to lighten the image; move the slider to
the left to darken the image. The auto range of adjustment is –100 to 100; the auto default setting is 0 (zero). The manual range of
adjustment is 0 to 100; the manual default setting is 50.
SELECTING AUTO EXPOSURE SETTINGS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select Exposure from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Auto mode.
4. Select the Light Control method: Digital Exposure or Auto-Iris Exposure.
Digital Exposure: This setting automatically adjusts the sensor exposure time depending on the light level at the scene. For very bright
scenes, the exposure time is very short and, as the scene becomes less bright, the exposure time is increased until the maximum exposure
time is reached. Digital Exposure is the default setting and provides the best image quality for the majority of scenes.
Auto-Iris Exposure: This setting automatically adjusts the lens iris depending on the light level at the scene. For this setting, the sensor
exposure time is fixed. Select Auto-Iris if the video shows flickering or rolling bands due to 50 Hz or 60 Hz lighting. Most lighting situations
do not require this setting.
5. Select the Exposure Optimization setting: Normal or Action. These are optimizations of the Digital Exposure control.
32 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 32

Normal: This setting is for very bright scenes and exposure time is very short. As the scene becomes less bright, the exposure time is
increased until the maximum exposure time is reached. Normal is the default setting.
Action: This setting operates similar to Normal except the short exposure times are used for both bright and mid-level lighting. This
minimizes the blur in video caused by moving objects. For very low light scenes, Action optimization operates the same as Normal,
increasing the exposure time until the maximum exposure time is reached.
6. Color cameras only: Set the Exposure Compensation setting. Move the slider bar to the right to brighten the video, or move it to the left to
darken the video. The exposure compensation range is –100 to 100; the default setting is 0 (zero).
7. Day/night cameras only: Set the Day Exposure Compensation and Night Exposure Compensation.
Day Exposure Compensation: This setting controls the brightness of the video when the camera is in Day (Color) mode. Move the slider
bar to the right to brighten the video, or move it to the left to darken the video. The exposure compensation range is –100 to 100; the
default setting is 0 (zero).
Night Exposure Compensation: This setting controls the brightness of the video when the camera is in Night (black-white) mode. Move
the slider bar to the right to brighten the video, or move it to the left to darken the video. The exposure compensation range is –100 to 100;
the default setting is 0 (zero).
8. Color cameras only: Set the Max Exposure Time and Night Max Exposure Time.
Max Exposure Time: This setting controls the maximum time in milliseconds that an image is exposed during daytime conditions.
Decreasing Max Exposure Time reduces the blur caused by fast moving objects as the light dims, but it also reduces the light sensitivity of
the camera. The exposure range is 1 to 500 msec; the default setting is 33.3 msec.
Night Max Exposure Time: This setting controls the maximum time in milliseconds that an image is exposed during dim light, such as
nighttime conditions. Increase this time to increase the light sensitivity of the camera. The exposure range is 1 to 500 msec; the default
setting is 120 msec.
9. Day/night cameras only: Set the Day Max Exposure Time and Night Max Exposure Time.
Day Max Exposure Time: This setting controls the maximum time in milliseconds that an image is exposed when the camera is in
Day (Color) mode. Decreasing Max Exposure Time reduces the blur caused by fast moving objects as the light dims, but it also reduces the
light sensitivity of the camera. The exposure range is 1 to 500 msec; the default setting is 33.3 msec.
Night Max Exposure Time: This setting controls the maximum time in milliseconds that an image is exposed when the camera is in
Night (black-white) mode. Increase this time to increase the light sensitivity of the camera. The exposure range is 1 to 500 msec; the
default setting is 120 msec.
10. Day/night cameras only: Set the Day Exposure Time and the Night Exposure Time.
Day Exposure Time: This setting is the maximum time in milliseconds that an image is exposed during daytime conditions. Decreasing
exposure time decreases the light sensitivity of the scene and reduces the blur caused by fast moving objects; however, it increases the
amount of noise in the scene. The day maximum exposure time range is 1 to 500 msec; the default setting is 33.3 msec.
Night Exposure Time: This setting is the maximum time in milliseconds that an image is exposed during nighttime (black-white)
conditions. Increase the exposure time to increase light sensitivity of the scene. The night maximum exposure time range is 1 to 500 msec;
the default setting is 120 msec.
11. Day/night cameras only: Set the Day Night mode to Auto or Manual.
Auto: This setting automatically controls the IR cut filter determined by the Transition Level and the Transition Detect settings.
Manual: This setting sets the IR filter to a fixed position. The filter can be set to the Day (color) position or the Night (black-white) position.
Refer to the following section for more information:
• Day Night Settings
on page 34
C2950M-G (4/12) 33
Page 33

SELECTING MANUAL EXPOSURE SETTINGS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select Exposure from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Manual mode.
4. Move the Analog Gain slider to the desired position. Increasing the gain increases the brightness of the image, but it also increases the
amount of noise in the image. The analog gain range is 1.00 to 15.75; the default setting is 1.00.
5. Move the Exposure Time slider to the desired position. This setting is the maximum time in milliseconds that the sensor is exposed to the
light. Decreasing the maximum exposure time decreases the light sensitivity. The exposure time range is 0.01 to 1000 msec; the default
setting is 15 msec.
6. Day/night cameras only: Set the Day Night Position setting.
Day: Sets the IR filter to the Day (color) position.
Night: Sets the IR filter to the Night (black-white) position.
Refer to the following section for more information:
• Day Night Settings on page 34
DAY NIGHT SETTINGS
The Day Night mode controls the position of the IR cut filter, which determines the color or black-white setting of the camera. The Day Night
mode settings change depending on the Exposure settings. If the camera is set to Auto Exposure mode, the Day Night mode can be set to Auto or
Manual and all of the respective settings are available. If the camera is set to Manual Exposure, the only available Day Night mode setting is
Position, which sets the IR filter to either the Day (color) position or the Night (black-white) position.
34 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 34

DAY NIGHT AUTO AND MANUAL MODES
DAY NIGHT AUTO MODE
The Day Night Auto mode setting automatically controls the IR cut filter depending on the Transition Level and Transition Detect Time settings.
T ransition Level: Determines when the camera changes from day mode (color) to night mode (black-white). Move the slider to the left or right
to change the transition level to a lighter or darker setting. Select a lighter transition level setting if you want the camera to change modes at a
high lux setting. Use the default setting of 4 for normal day/night operation. Use a darker transition level to change modes at a low lux setting.
Table B. Lux Transition Points for Incandescent Lighting
Transition Leve l
Lighter 1 50 ~ 25 lux
Darker 5 3.125 ~ 1.5 lux
Tra nsition Detect Time (sec): Controls the length of time the camera is exposed to a light level before it changes to color or black-white mode.
This setting is useful for dark scenes where a bright light is momentarily introduced in the scene (for example, when a car with its headlights
turned on passes the camera scene).
DAY NIGHT MANUAL MODE
The Day Night Manual mode sets the IR cut filter to a fixed position depending on the Position setting. Available settings include Day and Night.
Day: Sets the IR filter to the Day (color) position.
Night: Sets the IR filter to the Night (black-white) position.
NOTE: Position is the only available Day Night setting if the camera exposure is set to Manual.
CONFIGURING AUTO FOCUS SETTINGS
Day to Night
Setting
2 25 ~ 12.5 lux
3 12.5 ~ 6.25 lux
4 6.25 ~ 3.125 lux
Transition Point
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select Focus from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Auto mode.
4. Set the Temperature Change Refocus setting. The camera is programmed to run a quick automatic focus sequence when the internal
temperature sensor of the camera detects an environmental temperature change of 41°F (5°C). This focus sequence adjusts the center
focal point of the scene to maintain optimal focus. The default setting is On; select Off to turn off this setting.
5. Day/night cameras only: Set the Day/Night Switch Refocus setting. The default setting for the Day/Night Switch Refocus is Off. Select On
if the camera’s focal length is greater than ~25 mm or the night scene uses mostly IR lighting. The best method to determine if the day/night
refocus should be enabled is to test the camera with the daytime light conditions, and then test it again with the nighttime light conditions.
When enabled (On) this setting refocuses the camera when the camera changes from day mode (color) to night mode (black-white) or vice
versa. For example, if the camera changes from day mode to night mode, the imager automatically adjusts the back focus for the change in
light.
6. If required, use one of the following buttons to adjust the focus:
Full Range Auto-Focus: The camera starts a full-range search to find the optimal focal point for the scene.
Quick Auto-Focus: The camera searches for the optimal focal point in a limited range.
Restore Setings to Defaults: The camera resets the auto focus to the factory default setting.
C2950M-G (4/12) 35
Page 35

CONFIGURING MANUAL FOCUS SETTINGS
NOTE: It is recommended to set the focus to Manual when using analytics. If the focus is set to Auto, significant background changes will occur
when the camera automatically adjusts to different points within a scene resulting in frequently changing image sharpness. This may cause
problems with scene recognition, which will suspend analytics operation or cause false alarms.
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select Focus from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Manual mode.
4. Set one of the following settings:
Day Manual Focus Position: (Available only with day/night cameras.) This is the position of the focus mechanism when the IR cut filter
is applied. The day mode focus position range is 0 to 100.
Night Manual Focus Position: (Available only with day/night cameras.) This is the position of the focus mechanism when the IR cut filter
is removed. The night mode focus position range is 0 to 100.
Manual Focus Position: (Available only with color cameras.) This is the manual setting of the focus mechanism. The focus range is
0to100.
5. Set the Manual Focus Position. The focus range is 0 to 100.
6. If required, click the Restore Settings to Defaults button to reset the focus to the factory default setting.
SETTING TONE MAP OPTIONS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select Tone Map from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Optimization setting:
Normal (H.264): If the compression standard for the primary stream is H.264, set Optimization to Normal (H.264). This is the default
setting.
Photographic (JPEG): If the compression standard for the primary stream is JPEG, set Optimization to Photographic (JPEG).
4. Move the Tone Map sliders to adjust the following image settings:
Black Clip Percent: Adjusts the percent of pixels set to black. Move the slider to the right to darken the scene by increasing the number
of pixels that are mapped to absolute black. The black clip percent range is 0 to 25; the default setting is 0.5.
White Clip Percent: Adjusts the percent of pixels set to white. Move the slider to the right to lighten the scene by increasing the number
of pixels that are mapped to absolute white. The white clip range is 0 to 25; the default setting is 0.5.
Gamma Correction: Adjusts the details in the light and dark areas of the scene. Move the slider to the left to expose more detail in the
light areas of the scene; move the slider to the right to expose more detail in the dark areas of the scene. The gamma corrector range is
0.1 to 3.0; the default setting is 2.2.
5. If required, click the Restore Settings to Defaults button to reset the Tone Map to the factory default setting.
36 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 36

SELECTING AUTO WHITE BALANCE SETTINGS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select White Balance from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Auto mode.
4. Move the sliders to adjust the following settings in Auto mode:
Red Gain Adjust: Adjusts the image output in the red range. Move the slider to the right to increase the red level; move the slider to the
left to decrease the red level. As you move the slider, you will see the color change on your monitor. The auto range of adjustment is
–1.0 to 1.0; the default setting is 0 (zero).
Green Gain Adjust: Adjusts the image output in the green range. Move the slider to the right to increase the green level; move the slider
to the left to decrease the green level. As you move the slider, you will see the color change on your monitor. The auto range of adjustment
is –1.0 to 1.0; the default setting is 0 (zero).
Blue Gain Adjust: Adjusts the image output in the blue range. Move the slider to the right to increase the blue level; move the slider to
the left to decrease the blue level. As you move the slider, you will see the color change on your monitor. The auto range of adjustment is
–1.0 to 1.0; the default setting is 0 (zero).
5. If required, click the Restore Settings to Defaults button to reset the white balance to the factory default setting.
SELECTING MANUAL WHITE BALANCE SETTINGS
NOTE: Manual white balance is recommended only for indoor applications that have a single, unchanging primary light source.
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select White Balance from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Manual mode.
4. Move the sliders to adjust the following settings in Manual mode:
Red Gain: Adjusts the image output in the red range. Move the slider to the right to increase the red level; move the slider to the left to
decrease the red level. As you move the slider, you will see the color change on your monitor. The manual range of adjustment is 0 to 32;
the default setting is 1.
Green Gain: Adjusts the image output in the green range. Move the slider to the right to increase the green level; move the slider to the
left to decrease the green level. As you move the slider, you will see the color change on your monitor. The manual range of adjustment is
0 to 32; the default setting is 1.
Blue Gain: Adjusts the image output in the blue range. Move the slider to the right to increase the blue level; move the slider to the left to
decrease the blue level. As you move the slider, you will see the color change on your monitor. The manual range of adjustment is 0 to 32;
the default setting is 1.
5. If required, click the Restore Settings to Defaults button to reset the white balance to the factory default setting.
C2950M-G (4/12) 37
Page 37

TURNING ON WINDOW BLANKING
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select Window Blanking from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the On option for Window Blanking.
4. Draw a window in the Live Preview area of the page:
a. Hold down the left mouse button.
b. Drag the mouse diagonally across the area you want to blank.
c. A color-coded box appears in the Edit Window section of the page that is the same color as the window drawn in the Live Preview
area.
NOTE: Up to four blanked windows can be defined, but the blanked area cannot exceed 50 percent of the field of view.
5. To resize the window, click and drag one or more of the points until the window is the desired shape and size.
6. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
TURNING OFF WINDOW BLANKING
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select Window Blanking from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Off option for Window Blanking.
4. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
DELETING A WINDOW BLANKING AREA
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Imaging tab.
2. Select Window Blanking from the drop-down menu.
3. In the Edit Window area of the page, click the check box next to the window blanking area you want to delete.
4. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
38 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 38

A/V Streams Tab
Use the A/V Streams tab to configure the video and audio streams for the camera. The A/V Streams tab includes a Video Presets page, a Video
Configuration page, and an Audio Configuration page.
Video Presets
The Video Preset page includes three fully-configured video presets, which include primary and secondary video stream settings for easy setup.
These presets may also be used as a starting point for a custom video configuration. These preset configurations vary depending on camera
model.
Video Configuration
The Video Configuration page allows you to customize the compression, resolution, image rate, and bit rate of the video streams. The default
names for the streams are Primary Stream and Secondary Stream. Although each stream can be configured independently, the settings of one
stream can limit the options available to the other stream, depending on the processing power used.
NOTE: Always configure the primary stream before the secondary stream. The primary stream should always be the most resource-intensive of
the streams.
Audio Configuration
The Audio Configuration page allows you to setup an external audio device. The default setting for Audio is disabled, which means that no audio
is transmitted from the camera. When enabled, audio is transmitted from the camera to the PC. Based on your system configuration, images and
audio may not be synchronized.
Not all camera models are equipped with an internal audio device. Refer to the specifications for your camera model for information.
NOTE: Improper use of audio/visual recording equipment may subject you to civil and criminal penalties. Applicable laws regarding the use of
such capabilities vary between jurisdictions and may require, among other things, express written consent from the recorded subjects. You are
solely responsible for insuring strict compliance with such laws and for strict adherence to any/all rights of privacy and personalty.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• Selecting a Video Preset Configuration on page 39
• Configuring a Custom Video Stream Configuration on page 40
• Compression Standards on page 40
• Available Camera Resolution on page 41
• Image Rate on page 41
• Bit Rate on page 41
• I-Frame Interval on page 42
• Quality of Service for Differentiated Services Code Point on page 42
• Endura Signing on page 42
SELECTING A VIDEO PRESET CONFIGURATION
1. Place your mouse pointer over the A/V Streams tab.
2. Select the Video Presets option from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear your selection without saving it.
C2950M-G (4/12) 39
Page 39

CONFIGURING A CUSTOM VIDEO STREAM CONFIGURATION
1. Place your mouse pointer over the A/V Streams tab.
2. Select Video Configuration from the drop-down menu.
3. Click both of the Clear buttons to delete the primary and secondary streams settings.
4. Optional: In the Primary Stream section, type a user-friendly name in the Name box (2 to 64 characters). A user-friendly name makes it
easier to recognize the stream (for example, Live and Recording).
5. Configure the Compression Standard, Resolution, Image Rate, and Bit Rate settings for the primary stream.
NOTE: The compression standard, resolution, image rate, and bit rate settings are dependent on each other. You must first decide the
priority setting before you configure a stream. For example, if you want an image rate of 30 ips, set the image rate before you configure the
other settings.
6. Repeat steps 3 to 5 for the Secondary stream.
7. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
COMPRESSION STANDARDS
JPEG: A commonly used video compression scheme, also known as MJPEG. JPEG has the least impact on the camera’s processor, but it requires
the most bandwidth.
MPEG-4 (available only with 0.5 megapixel model): A full-motion video standard used by most DVD recorders. MPEG-4 is less
processor-intensive than JPEG, but it uses more bandwidth than H.264.
H.264: A new version of MPEG-4 compression used in high-definition video players such as Blu-ray
processor-intensive, but it requires the least amount of bandwidth.
™
and HD-DVD. H.264 is the most
40 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 40

AVAILABLE CAMERA RESOLUTION
Refer to the following table for the resolution capabilities of your camera model.
Table C. Available Camera Resolution
Camera Model 0.5 Megapixel 3.1 Megapixel
— 2048 x 1536
— 1920 x 1080
— 1600 x 1200
— 1280 x 1024
— 1280 x 960
— 1280 x 720
800 x 600 800 x 600
704 x 576 —
704 x 480 —
Available
Resolutions
640 x 512 640 x 512
640 x 480 640 x 480
640 x352 640 x 352
480 x 368 480 x 368
480 x 272 480 x 272
352 x 240 —
352 x 288 —
320 x 256 320 x 256
320 x 240 320 x 240
320 x 176 320 x 176
IMAGE RATE
The image rate is the number of images per second (ips) available for the video stream configuration. Available image rates depend upon the
model of the device that you are using.
NOTE: The maximum image rate setting might not be obtainable due to the compression standard and the resolution of the stream.
Refer to the following section for more information:
• Specifications on page 59
BIT RATE
The bit rate is the quality of the video stream (rendered in kilobits per second). The higher the value, the higher the video quality and bandwidth
required.
NOTE: When you change any of the video stream configuration settings, the camera automatically adjusts the bit rate. If you manually reduce
the bit rate lower than the camera's automatic setting, the image quality might be reduced and the stream selection options might be limited.
C2950M-G (4/12) 41
Page 41

I-FRAME INTERVAL
The I-frame interval configures the number of partial frames that occur between full frames in the video stream. For example, in a scene where a
door opens and a person walks through, only the movements of the door and the person are stored by the video encoder. The stationary
background that occurs in the previous partial frames is not encoded, because no changes occurred in that part of the scene. The stationary
background is only encoded in the full frames. Partial frames improve video compression rates by reducing the size of the video. As the I-frame
interval increases, the number of partial frames increases between full frames. Higher values are only recommended on networks with high
reliability. This setting is only available with H.264 and MPEG-4 compression standards.
QUALITY OF SERVICE FOR DIFFERENTIATED SERVICES CODE POINT
Quality of Service (QoS) for Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) is a code that allows the network to prioritize the transmission of different
types of data. This setting is only available with H.264 and MPEG-4 compression standards.
NOTES:
• If you are not familiar with DSCP, contact your network administrator before changing this setting.
• Your network must be configured to use QoS. If you are unsure if your network is QoS-aware, contact your network administrator.
ENDURA SIGNING
Enabling the Endura Signing feature allows an Endura® system to authenticate video from an Endura recorded stream. This setting is only
available with H.264 and MPEG-4 compression standards.
ADVANCED SHARPENING
The Advanced Sharpening setting enhances picture detail by sharpening the edges in the picture. When this mode is enabled, there is a trade-off
between image quality and the resources required for processing power. The maximum camera resolution and image rate will not be available,
but the edges of the image seem sharper. Only use this setting if you cannot achieve the sharpness level you want by adjusting the digital
processing settings of the camera. The default setting for Advanced Sharpening is Off.
SELECTING THE AUDIO CONFIGURATION SETTINGS
To use audio with the camera if it does not have built-in audio support, you must connect an audio device to the accessory port. Once the device
is connected, audio can only be enabled through the primary stream.
Audio and video may not be synced when viewing and listening to the primary stream through a Web browser. You may experience a
three-second delay in video when viewing the primary stream with audio.
NOTE: Improper use of audio/visual recording equipment may subject you to civil and criminal penalties. Applicable laws regarding the use of
such capabilities vary between jurisdictions and may require, among other things, express written consent from the recorded subjects. You are
solely responsible for insuring strict compliance with such laws and for strict adherence to any/all rights of privacy and personalty.
1. Place your mouse pointer over the A/V Streams tab.
2. Select the Audio Configuration option from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Enabled option in the Audio section.
4. Select the encoding method for the audio device from the Encoding drop-down box. Available encoding methods are PCMU, PCMA, and
PCM16. The default setting is PCMU.
5. If required, click the button next to Mute to mute the audio device.
NOTE: Do not use the mute button on an audio device, as it will override the audio software settings. To mute the audio device, select the
Mute option located on the Audio Configuration page.
6. Set the sensitivity of the input level by moving the Input Level slider. Move the slider to the right to increase the sensitivity level; move it to
the left to decrease the sensitivity level. For example, if the camera is installed in a noisy environment or the connected microphone has a
built-in line amplifier, set the sensitivity to a low setting. The setting range is 0 to 100.
7. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
42 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 42

Users Tab
Use the Users tab to create and manage user accounts and to change the way the camera manages the users settings.
General Settings
Use the General Settings page to set the public user access level. This access level is a predefined set of user permissions that allows the
camera to be accessed without logging on. Available permission levels depend upon the model of the device that you are using.
The General Settings page also allows you to change the way the camera manages users and groups settings. These settings can be managed on
a camera-to-camera basis or by using a centralized server to apply changes to multiple cameras.
Users
User accounts are created to limit the permissions of individuals who are logged onto the camera. The Users page also includes four predefined
access level settings that include Administrator, Manager, Operator, and Viewer permissions.
Refer to the following sections for more information.
• Selecting the Users and Groups Settings on page 43
• Creating a New User on page 44
• Editing a User on page 44
• Deleting a User on page 44
SELECTING THE USERS AND GROUPS SETTINGS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Users tab.
2. Select General Settings from the drop-down menu.
3. Select a Public User Access level setting.
4. Select one of the following User and Group Management modes:
Local Mode: The camera manages its users and groups locally. Any changes to users and groups affect only the camera that you are
accessing. Standalone is the default setting.
Remote Mode: The camera uses a centralized Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) or Active Directory server to manage users
and groups. In this mode, the Users and Groups page is disabled and all management is done on the central server.
WARNING: Remote Mode settings are advanced controls. Consult your network administrator to obtain the required information to
configure remote settings.
5. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
C2950M-G (4/12) 43
Page 43

CREATING A NEW USER
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Users tab.
2. Select Users from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the Access Level for the user.
Admins: Permissions include access to all camera settings.
Managers: Permissions include access to all settings except this user cannot modify user permissions or restore factory default settings.
Viewers: Permissions include view video.
4. Click in the Username box and type a user name (2 to 23 alphanumeric characters). User names are not case-sensitive and are saved in
lowercase characters.
5. Click in the Password box and type a password (4 to 16 alphanumeric characters). Passwords are case-sensitive.
6. Click in the Retype Password box and retype your password.
7. Click the Save button to save the settings and create a new user (the new user profile appears in the box on the left side of the page), or
click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
EDITING A USER
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Users tab.
2. Select Users from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the user profile that you want to edit from the box on the left side of the page.
4. If required, select a different Access Level for the user.
5. Double-click in each of the text boxes to highlight the text. Type the new information in each text box.
NOTE: The Username cannot be modified; this text box is read-only.
6. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
DELETING A USER
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Users tab.
2. Select Users from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the user profile that you want to delete from the defined users section located in the box on the left side of the page.
4. Click the Delete User button. A dialog box appears with the message “Are you sure you want to delete this user?”
5. Click OK. The user profile is deleted from the defined user profiles section.
NOTE: The “admin” user cannot be deleted.
44 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 44

Events Tab
Use the Events tab to configure camera events and analytics.
Events are activated by user-defined event sources that tell the device how to react when an event occurs. Event handlers are the actions that
the device takes when an event occurs. For example, a system source can be configured to send email to an operator if the system shuts-down
and restarts.
Sources
The camera supports an input alarm source, an analytic source, a system source, and a timer source. The Alarm source is the camera input for an
external signaling device, such as a door contact or motion detector. The Analytics source triggers when any configured behavior is detected. The
System source is activated when the camera restarts. The Timer source is a user-defined event that activates an event after a specified amount
of time. For example, the timer can be activated every 60 seconds to save an image to an SD card.
Handlers
The device supports a Send Email handler, a “Write JPEG to SD Card handler,” and an “Upload JPEG to FTP Server handlers.” The Send Email
handler sends an email to a defined email address when an event is activated. The “Write JPEG to SD Card” saves a JPEG of the activated event
to an SD card. The “Upload JPEG to FTP Server” saves a JPEG of the activated event to a defined FTP server.
Analytic Configuration
Pelco analytics can be configured and enabled using a standard Web browser. The device is preloaded with Pelco’s Camera Sabotage behavior,
which detects contrast changes in the field of view. An alarm is triggered if the lens is obstructed with spray paint, a cloth, or covered with a lens
cap. Any unauthorized repositioning of the camera also triggers an alarm.
Pelco analytics are also compatible with Endura
documentation for instructions on how to configure and enable Pelco analytics.
®
or a third-party system that supports alarms using Pelco’s API. Refer to the specific product
NOTE: Analytic alerts can be seen in the event stream, but alarms are only transmitted through Pelco’s API.
C2950M-G (4/12) 45
Page 45

SOURCES
An event is a configured camera function that is automatically activated by an event source. The camera supports the following types of event
sources:
Alarm: The camera supports one alarm source if the device’s General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) alarm input is configured. If the Pelco Alarm
accessory is connected to the device’s accessory port, the device can support alarm and auxiliary relay sources.
Analytics: An analytic source will activate a user-defined event handler when an analytic alert is detected.
System: A system source is activated when the camera restarts.
Timer: A timer source is a user-defined event. The user can configure the timer to activate an event after a specified amount of time.
For example, the timer can be activated to save an image to an SD card every 60 seconds.
CREATING AN ALARM EVENT SOURCE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Sources from the drop-down menu.
3. Click in the Name box and type a user-friendly name (2 to 23 alphanumeric characters).
4. Select Alarm from the Type drop-down menu.
5. Select the alarm you want to trigger when an event occurs from the Alarm drop-down menu.
6. Select either true or false from the Supervised drop-down menu.
7. Click the Submit button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
CREATING AN ANALYTIC EVENT SOURCE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Sources from the drop-down menu.
3. Click in the Name box and type a user-friendly name (2 to 23 alphanumeric characters).
4. Select Analytics from the Type drop-down menu.
5. Click the Submit button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
CREATING A SYSTEM EVENT SOURCE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Sources from the drop-down menu.
3. Click in the Name box and type a user-friendly name (2 to 23 alphanumeric characters).
4. Select System from the Type drop-down menu.
5. Select the Boot check box to activate an event when the camera reboots.
6. Click the Submit button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
46 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 46

CREATING A TIMER EVENT SOURCE
1. Place you mouse over the Events tab.
2. Select Sources from the drop-down menu.
3. Click in the Name box and type a user-friendly name (2 to 23 alphanumeric characters).
4. Select Timer from the Type drop-down menu.
5. Click in the Frequency box and type a number. Select seconds, minutes, hours, or days from the Frequency drop-down menu.
6. Click the Submit button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
EDITING AN EVENT SOURCE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Sources from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the source profile that you want to delete from the defined source box located on the left side of the page.
4. Make any necessary changes to the available fields.
5. Click the Submit button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
DELETING AN EVENT SOURCE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Sources from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the source profile that you want to delete from the defined source box located on the left side of the page.
4. Click the Delete Source button. A dialog box appears with the message “Are you sure you want to delete the source?”
5. Click OK. The source profile is deleted from the defined source box.
C2950M-G (4/12) 47
Page 47

HANDLERS
Event handlers are the actions that the camera takes when an event occurs. The camera supports the following event handlers:
Send Email: Sends an email to a defined email address when an event is activated. The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server must be
configured to accept the camera’s IP address.
Write JPEG to SD Card: Saves a JPEG of the activated event to an SD card. An SD card must be installed in the device for this handler to
function.
NOTE: The SD card must be formatted as FAT32. Other formats are not compatible with the camera.
Upload JPEG to FTP Server: Saves a JPEG of the activated event to a defined FTP server.
Open/Close Relay: Sends a signal to an external device when an alarm or relay is triggered.
CREATING AN EVENT HANDLER: SEND EMAIL
NOTE: To use email notification, the camera must be connected to a local area network (LAN) that maintains an SMTP mail server. Consult your
network administrator for information on configuring email notification on your local network.
1. Configure the SMTP server to send email.
2. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
3. Select Handler from the drop-down menu.
4. Click in the Name box and type a user-friendly name (2 to 23 alphanumeric characters).
5. Select Send Email from the Type drop-down menu.
6. Click in the text boxes (To, From, Subject, and Message), and then type the necessary information in each text box.
7. Select the JPEG Snapshot box if you want to send a JPEG as an attachment.
8. Select the Attach Raw Event Data box if you want the email to include extra data about the event. For example, select this box if the event
is triggered by an alarm and you want to receive data about the state, time, or type of alarm.
9. If you do not want the handler activated every time an event occurs, set filters for the handler.
a. Select the day(s) of the week on which you want emails to be sent.
b. Type times in the Start and End boxes for the days you have selected. Use time values in 24-hour notation (for example, use 0800 for
8:00 a.m., 1600 for 4:00 p.m.).
10. Select one or more event sources to send an email when those event sources are activated.
11. Click the Submit button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
Refer to the following sections for more information:
• System Tab on page 23
• Example Handler Filter Setup on page 51
48 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 48

CREATING AN EVENT HANDLER: WRITE JPEG TO SD CARD
1. Install an SD card in the SD card slot located on the back of the camera.
NOTE: The SD card must be formatted as FAT32. Other formats are not compatible with the camera.
2. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
3. Select Handlers from the drop-down menu.
4. Click in the Name box and type a user-friendly name (2 to 23 alphanumeric characters).
5. Select “Write JPEG to SD Card” in the Type drop-down menu.
6. The JPEG files saved to the SD card will be given file names that correspond to the date and time of the event. Select a time standard from
the “File name” drop-down menu.
7. Click in the Size limit box and type a number. Select Kilobytes, Megabytes, or Gigabytes from the Size Limit drop-down menu.
NOTE: Do not select a size limit that is larger than the amount of memory on the SD card. For example, if the SD card is 2 MB, do not
exceed 2 MB in the Size Limit box.
8. If you do not want the handler activated every time an event occurs, set filters for the handler.
a. Select the day(s) of the week on which you want JPEGs saved to the SD card.
b. Type times in the Start and End boxes for the days you have selected. Use time values in 24-hour notation (for example, use 0800 for
8:00 a.m., 1600 for 4:00 p.m.).
9. Select one or more sources to save a JPEG to the SD card when those event sources are activated.
10. Click the Submit button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
Refer to the following section for more information:
• Example Handler Filter Setup on page 51
CREATING AN EVENT HANDLER: UPLOAD JPEG TO FTP SERVER
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Handlers from the drop-down menu.
3. Click in the Name box and type a user-friendly name (2 to 23 alphanumeric characters).
4. Select “Upload JPEG to FTP Server” in the Type drop-down menu.
5. Click in the Server box and type the server address (1 to 32 alphanumeric characters).
6. Click in the Username box and type the user’s name (1 to 32 alphanumeric characters).
7. Click in the Password box and type a password (4 to 16 alphanumeric characters).
8. Click in the Base Path box and type the base path (1 to 32 alphanumeric characters).
9. The JPEG files uploaded to the FTP server will be given file names that correspond to the date and time of the event. Select a time standard
from the “File name” drop-down menu.
10. If you do not want the handler activated every time an event occurs, set filters for the handler.
a. Select the day(s) of the week on which you want JPEGs saved to the FTP server.
b. Type times in the Start and End boxes for the days you have selected. Use time values in 24-hour notation (for example, use 0800 for
8:00 a.m., 1600 for 4:00 p.m.).
11. Select one or more sources to save a JPEG to the FTP server when those event sources are activated.
12. Click the Submit button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
Refer to the following section for more information:
• Example Handler Filter Setup on page 51
C2950M-G (4/12) 49
Page 49

CREATING AN EVENT HANDLER: OPEN/CLOSE RELAY
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Handlers from the drop-down menu.
3. Click in the Name box and type a user-friendly name (2 to 23 alphanumeric characters).
4. Select Open/Close Relay in the Type drop-down menu.
5. Select either GPIO or the serial number of the relay device from the Relay Bank drop-down menu.
6. Select the relay you want to trigger when an event occurs from the Relay drop-down menu.
7. Move the On Time slider to set the amount of time that the relay will remain open. The time range is 0.1 to 200 seconds;
the default setting is 0.1.
8. Move the Off Time slider to set the amount of time that the relay will remain closed. The time range is 0.1 to 200 seconds;
the default setting is 0.1.
9. Click in the Pulse Count box and type a number.
10. If you do not want the handler activated every time an event occurs, set filters for the handler.
a. Select the day(s) of the week on which you want the relay opened/closed.
b. Type times in the Start and End boxes for the days you have selected. Use time values in 24-hour notation (for example, use 0800 for
8:00 a.m., 1600 for 4:00 p.m.).
11. Select one or more event sources to open/close the relay when those event sources are activated.
12. Click the Submit button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
Refer to the following section for more information:
• Example Handler Filter Setup on page 51
EDITING AN EVENT HANDLER
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Handlers from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the handler profile that you want to delete from the defined handler box located on the left side of the page.
4. Make any necessary changes to the available fields.
5. Click the Submit button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
DELETING AN EVENT HANDLER
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Handlers from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the handler profile that you want to delete from the defined handler box located on the left side of the page.
4. Click the Delete Handler button. A dialog box appears with the message “Are you sure you want to delete the handler?”
5. Click OK. The handler profile is deleted from the defined handler box.
50 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 50

EXAMPLE HANDLER FILTER SETUP
If you do not want a handler activated every time an event occurs, use the filter fields to limit handlers. For example, you only want a handler
activated when an event occurs after business hours. Your business is open Monday through Saturday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m., and it is closed on
Sunday.
1. Create a handler for Monday through Saturday:
a. Select the day filter fields Monday through Saturday.
b. Type 0000 in the Start box and 0800 in the End box.
c. Click the plus button (+) to add another time range. Type 1800 in the second Start box and type 2400 in the second End box.
d. Select the source(s) that activates the handler.
e. Click the Submit button to save the handler.
2. Create a second handler for Sunday:
a. Select Sunday from the day filter fields.
b. Do not set a Start time or End time as this is a 24-hour event.
c. Select the source(s) that activates the handler.
d. Click the Submit button to save the second handler.
C2950M-G (4/12) 51
Page 51

Analytic Configuration
To configure an analytic behavior using a standard Web browser, you must create a profile, select the behavior for the profile, and then create the
zones to be monitored by the behavior.
NOTES:
• This section explains how to configure and enable Pelco analytics using a Web browser.
• Analytic alerts can be seen in the event stream, but alarms are only transmitted through Pelco’s API.
PROFILES
A profile defines the scene attributes of a behavior including scene type, background movement, and noise sensitivity. When configured properly,
a profile will accurately detect behavior violations and decrease the number of triggered false alarms.
PROFILE SETTINGS
For each behavior, you can create several custom profiles that contain different settings. These settings include:
Name: Assigns a descriptive name to the profile to make it easier to recognize and locate. Consider naming profiles based on their function.
Scene type: Sets the scene type of the profile. Available settings include Indoor and Outdoor.
Background: Defines the background movement of the scene. Available settings include Still or Noisy. If the background is stable, with few
moving objects, set the background to Still. If the background is busy, with many moving objects, select Noisy.
Fine tuning: Defines the zone violation sensitivity. Available settings include Conservative, Normal, or Aggressive. Conservative is the least
sensitive setting and reduces the amount of triggered false alarms, but it could miss some zone violations. Aggressive is the most sensitive
setting and detects all suspect objects, but it could trigger more false alarms. Normal falls between conservative and aggressive sensitivity and
provides moderate results.
Sensitivity: Defines the minimum motion an object can move before a behavior is activated. Settings range from 1 (low) to 10 (high). The
selected setting identifies any movement lower than the defined setting as noise, and ignores it. The higher the setting, the greater the chance
for a false alarm. A lower setting reduces the chance for a false alarm, but it could result in missed violations.
CREATING A NEW PROFILE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Analytic Configuration from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the New button located in the Select Profile section.
4. Type a descriptive name for the profile in the Name box located in the Profile Settings section.
NOTE: Consider naming profiles based on their function. A more descriptive name makes it easier to recognize and locate a profile.
5. Select the Scene Type, Background, Fine Tuning, and Sensitivity settings from the drop-down menus located in the Profile Settings section.
6. Click the Calibrate Scene button to calibrate the scene.
NOTE: Set the perspective settings to reflect the camera’s angle. This information will make the object sizes you set on the next tab more
meaningful and help reduce the number of false alarms.
7. Select the behavior for the profile from the “Select Behaviors” section.
8. Configure the settings for the behavior.
9. Click the Save button to save the profile. The new profile name appears in the Select Profile section.
52 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 52

REVISING A PROFILE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Analytic Configuration from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the profile name from the Select Profile section. The settings for the profile appear.
4. Make the required changes to the profile settings.
5. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
DELETING A PROFILE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Analytic Configuration from the drop-down menu.
3. Select the profile name from the Select Profile section.
4. Click the Delete button located in the Select Profile section.
5. A dialog box opens and the following message appears: “Are you sure you want to delete the profile?”
6. Click the OK button to delete the profile.
BEHAVIORS
Behaviors analyze objects within the camera’s field of view and are configured to detect and trigger alarms automatically when specific activity
is detected. Examples of behaviors include Camera Sabotage, which detects contrast changes in the field of view and triggers an alarm if the
lens is obstructed or if the camera is repositioned; Adaptive Motion, which detects and tracks objects that enter a user-defined zone; and Object
Counting, which counts the number of objects that enter a defined zone.
CONFIGURING A BEHAVIOR
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Analytic Configuration from the drop-down menu.
3. Select a profile from the Select Profile section.
4. Select the behavior for the profile from the “Select behaviors” section.
5. Check the Activate Behavior box located in the “Settings for [behavior name]” section.
If the camera has enough resources, the behavior activates and a check mark appears to the left of the selected behavior(s), which is
located in the “Select behaviors” section.
If the camera does not have enough resources, the following message and instructions appear: “The camera does not have enough
processing power to activate this behavior. To free up needed resources, turn off one of the other behaviors or reconfigure the video
streams.”
6. Set up the zones for the behavior.
7. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
C2950M-G (4/12) 53
Page 53

ZONES
A zone is a defined boundary or area that is monitored by a configured behavior. A zone can be defined by a box, polygon, or line. If a box or
polygon is drawn to define the zone, any motion against the alarmed direction will trigger an alarm. If a line is drawn to define the zone, any
motion that crosses the line against the alarmed direction will trigger an alarm.
DRAW ZONE TOOLS
Box: Tracks objects that move against the alarmed direction in a defined zone.
Polygon: Tracks objects that move against the alarmed direction in a defined zone.
Line: Tracks objects that cross a line (trip wire) against the alarmed direction.
Exclude Zone Box Tool: Ignores objects inside a defined zone.
Exclude Zone Polygon Tool: Ignores objects inside a defined zone.
Object Size Filter: Sets the minimum and maximum object size for a zone.
Drawing a Box
1. Hold down the left mouse button.
2. Drag the mouse pointer diagonally across the area you want to define with a box.
3. A color-coded box appears to the right of the preview pane in the “Zone list.” The Zone box is the same color as the box drawn in the
preview pane.
4. To resize the box, click and drag one or more of the points until the box is the desired shape and size.
5. To move the box, click inside the box and drag it to the desired location.
Drawing a Polygon
NOTE: A polygon is drawn with six points.
1. To define the first point of the polygon, click anywhere in the preview pane while holding down the left mouse button.
2. Drag the mouse pointer across the preview pane, and then release the mouse button to define the second point of the polygon.
3. Click the second point and drag the mouse pointer across the preview pane. Release the mouse button to define the third point of
the polygon.
4. Repeat this process to define points four and five.
5. To define the sixth point and to close the polygon, you must double-click the first point again.
6. To resize the polygon, click and drag one or more of the points until the polygon is the desired shape and size.
7. To move the polygon, click inside the polygon and drag it to the desired location.
54 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 54

Drawing a Line
NOTE: A line is drawn with two points.
1. Click the Line tool.
2. To define the first point of the line, click anywhere in the preview pane while holding down the left mouse button.
3. Drag the mouse pointer across the preview pane, and then release the mouse button to define the second point of the line.
4. A color-coded box appears to the right of the preview pane in the “Zone list.” The Zone box is the same color as the line drawn in the
preview pane.
5. To resize the line, click and drag one of the points of the line until it is the desired length.
6. To move the line, click the line and drag it to the desired location.
7. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
Drawing an Exclude Zone Box
1. Click the Exclude Zone Box tool.
2. Click anywhere in the preview pane while holding down the left mouse button.
3. Drag the mouse pointer diagonally across the area you want to exclude with a box.
4. To resize the box, click and drag one or more of the points until the box is the desired shape and size.
5. To move the box, click inside the box and drag it to the desired location.
6. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
Drawing an Exclude Zone Polygon
NOTE: A polygon is drawn with six points.
1. Click the Exclude Zone Polygon tool.
2. To define the first point of the polygon, click anywhere in the preview pane while holding down the left mouse button.
3. Drag the mouse pointer across the preview pane, and then release the mouse button to define the second point of the polygon.
4. Click the second point and drag the mouse pointer across the preview pane. Release the mouse button to define the third point of
the polygon.
5. Repeat this process to define points four and five.
6. To define the sixth point and to close the polygon, you must double-click the first point again.
7. To resize the polygon, click and drag one or more of the points until the polygon is the desired shape and size.
8. To move the polygon, click inside the polygon and drag it to the desired location.
9. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
C2950M-G (4/12) 55
Page 55

Drawing an Object Size Filter
1. Click the Object Size Filter tool. The Minimum and Maximum object size boxes appear.
2. Click and drag one or more of the points of the Minimum object size box until it is the desired shape and size. Objects in the scene that are
smaller than the Minimum object size will not be detected.
3. Click and drag one or more of the points of the Maximum object size box until it is the desired shape and size. Objects in the scene that are
larger than the Maximum object size will not be detected.
4. This setting applies only to the Object Counting behavior: Click and drag one or more of the points of the Average object size box until it is
the desired shape and size. Setting the Average object size increases the accuracy of the Object Counting behavior.
For example, if you want to detect people and you set the Average object size for an average-sized human, the behavior will accurately
count two people when two people are walking side-by-side. If you want to detect people and you set the Average object size as
significantly larger than an average-sized human, the behavior will mistakenly count two people who are walking side-by-side as only
one person.
5. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
DRAWING A ZONE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Analytic Configuration from the drop-down menu.
3. Click a behavior located in the “Select behaviors” section.
4. Check the Activate Behavior box located in the “Settings for [behavior name]” section. A check mark appears to the left of the selected
behavior(s) located in the “Select behaviors” section.
5. Use the draw tools to define the zone.
6. Set the behavior-specific settings for the zone.
7. To draw another zone, repeat steps 5 and 6.
8. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
DELETING A ZONE
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Analytic Configuration from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the behavior located in the “Select behaviors” section that you want to modify.
4. The settings for the behavior are displayed in the “Settings for [behavior name]” section.
5. In the “Zone list” area of the page, click the check box next to the zone you want to delete.
6. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
56 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 56

ADAPTIVE MOTION
The Adaptive Motion behavior detects and tracks objects that enter a scene, and then it triggers an alarm when the objects enter a user-defined
zone. The objects are monitored until they exit the scene.
The Adaptive Motion behavior is designed to work indoors and outdoors to track a few moving objects in uncrowded fields of view. The behavior
learns the background scene over time and adjusts to changing conditions like snow, fog, wind, and rain.
Analytics events, including Adaptive Motion, are displayed on the live video page when viewing the Event stream. You must configure both an
analytics event source and the appropriate event handlers in order to receive notifications when an Adaptive Motion alarm is triggered.
SCENE SETUP FOR ADAPTIVE MOTION
Install the camera in a ceiling or against a wall with the lens pointing at a slight downward angle, above regular motion activity.
The ideal scene for Adaptive Motion behavior is one with light traffic and a clean background. If heavy traffic or a busy background is
unavoidable, place the user-defined zone in a relatively stable area.
Avoid crowded scenes where people move in all directions or stand in one place for long periods of time.
NOTE: Objects that are very small may not be classified as the correct object type. This could result in false alarms or alarms not being triggered.
If objects appear too small in the scene, zoom in on the particular zone of interest or move the camera closer to the zone of interest to increase
the relative size of the objects in the scene.
SELECTING ADAPTIVE MOTION SETTINGS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Analytic Configuration from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the profile that you want to use from the Select Profile list.
4. Click Adaptive Motion from the Select Behaviors list.
5. Click the Activate Behavior check box to enable Adaptive Motion for the selected profile.
6. Use the zone draw tools to draw one or more zones of interest in the video pane.
7. After you have defined the desired zones, adjust the following zone settings:
Name: A descriptive name makes the zone easier to distinguish when viewing detection messages.
Direction: Detects and tracks moving objects and people that move in a specified direction within the defined zone.
Enable alarm: Turns on the zone alarm, which displays a log of analytics events in the Event stream on the live video page. Alarms can
also trigger an event handler if sources and handlers are configured for analytics.
Alarm severity: Defines the severity of an alarm to allow the prioritization of alarms.
Dwell time: Defines the amount of time that an alarm remains activated after the alarm-triggering object exits the zone.
8. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
C2950M-G (4/12) 57
Page 57

CAMERA SABOTAGE
The Camera Sabotage behavior detects scene changes or contrast changes in the field of view. An event or alarm is triggered if the lens is
obstructed by spray paint, a cloth, or if it is covered with a lens cap. Any unauthorized repositioning of the camera also triggers an event or alarm.
SCENE SETUP FOR CAMERA SABOTAGE
Install the camera in a high position, looking down on the scene. The field of view should be as large as possible. A small field of view could
result in the view being blocked by an adjacent object.
Avoid scenes with a dark, uniform background; low lighting; and large moving objects.
SELECTING CAMERA SABOTAGE SETTINGS
1. Place your mouse pointer over the Events tab.
2. Select Analytic Configuration from the drop-down menu.
3. Click the profile that you want to use from the Select Profile list.
4. Click Camera Sabotage from the Select Behaviors list.
5. Click the Activate Behavior check box to enable Camera Sabotage for the selected profile.
6. Adjust the following zone settings:
Delay before alarm: Defines the delay between the time a violation is detected and the actual trigger of an event or alarm. If the violation
does not continue past the delay period, an event or alarm does not trigger. If the violation lasts longer than the delay period, an event or
alarm is triggered. The default setting is 3 seconds.
Alarm severity: Defines the severity of an alarm to allow the prioritization of alarms.
7. Click the Save button to save the settings, or click the Reset button to clear all of the information you entered without saving it.
58 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 58

Specifications
IXS0 SERIES
MODELS
IXS0C SVGA 0.5 MPx network color camera
IXS0DN SVGA 0.5 MPx network day/night camera
GENERAL
Imaging Device
16:9 Aspect Ratio 1/3-inch (effective)
4:3 and 5:4 Aspect Ratios 1/4-inch (effective)
Imager Type CMOS
Imager Readout Progressive scan
Maximum Resolution 800 x 600
Signal-to-Noise Ratio 50 dB
Auto Iris Lens Type DC drive
Electronic Shutter Range 1 ~ 1/100,000 sec
Wide Dynamic Range 60 dB
White Balance Range 2,000° to 10,000°K
Sensitivity f/1.2; 2850°K; SNR >24 dB
Color (33 ms) 0.50 lux
Color SENS (500 ms) 0.12 lux
Mono (33 ms) 0.25 lux
Mono SENS (500 ms) 0.03 lux
ELECTRICAL
Port RJ-45 connector for 100Base-TX
Auto MDI/MDI-X
Cabling Type Cat5 or better for 100Base-TX
Power Input 24 VAC or PoE (IEEE 802.3af class 3)
Power Consumption
(camera only) <6 W
Input Current
PoE <200 mA maximum
24 VAC <295 mA nominal; <390 mA maximum
Local Storage Mini SD
Alarm Input 10 VDC maximum, 5 mA maximum
Relay Output 12 VDC maximum, 150 mA maximum
Service Port External 3-connector, 2.5 mm provides NTSC/PAL video output
MECHANICAL
Lens Mount CS mount, adjustable
Camera Mount 0.25-inch (0.64 cm) UNC-20 screw, top and bottom of camera housing
C2950M-G (4/12) 59
Page 59

VIDEO
Video Encoding H.264 base profile, MPEG-4, and MJPEG
Video Streams Up to 2 simultaneous streams; the second stream is variable based on the setup of the primary stream
Frame Rate Up to 30, 25, 24, 15, 12.5, 12, 10, 8, 7. 5, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2.5, 2, 1
(dependent upon coding, resolution, and stream configuration)
Available Resolutions
Resolution Maximum IPS
MPx Width Height Aspect Ratio MJPEG H.264 Base Profile MPEG-4
0.5 800 600 4:3 30 25 N/A
0.4 704 576 4CIF (PAL) 25 25 25
0.3 704 480 4CIF (NTSC) 30 30 30
0.3 640 512 5:4 30 30 30
0.3 640 480 4:3 30 30 30
0.3 640 352 16:9 30 30 30
0.2 480 368 4:3 30 30 30
0.2 480 272 16:9 30 30 30
0.1 352 288 CIF (PAL) 25 25 25
0.1 352 240 CIF (NTSC) 30 30 30
0.1 320 250 5:4 30 30 30
0.1 320 240 4:3 30 30 30
0.1 320 176 16:9 30 30 30
Supported Protocols TCP/IP, UDP/IP (Unicast, Multicast IGMP), UPnP, DNS, DHCP, RTP, RTSP, NTP, IPv4, SNMP, QOS, HTTP,
HTTPS, LDAP (client), SSH, SSL, SMTP, FTP, and 802.1x (EAP)
Users
Unicast Up to 20 simultaneous users depending on resolution settings (2 guaranteed streams)
Multicast Unlimited users H.264 or MPEG-4
Security Access Password protected
Software Interface Web browser view and setup
Pelco System Integration Endura 1.5 or later (MPEG-4) or Endura 2.0 or later (H.264); Digital Sentry 4.2 IP bundle 3 or later; DX8100
Series 2.0 or later; and DVR5100 version 1.5.4 or later
Open API Pelco API or ONVIF v1.02
ENVIRONMENTAL
Operational Temperature 14° to 122°F (–10° to 50°C)
Storage Temperature 14° to 158°F (–10° to 70°C)
Storage Humidity 20% to 90%, noncondensing
PHYSICAL
Dimensions 5.4" D x 3.1" W x 3.0" H
(13.7 x 7.9 x 7.6 cm)
Weight (without lens) 1.14 lb (0.52 kg)
60 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 60

IX30
MODEL
IX30DN 3.1 MPx network day/night camera
GENERAL
Imaging Device 1/3-inch (effective)
Imager Type CMOS
Imager Readout Progressive scan
Maximum Resolution 2048 x 1536
Signal-to-Noise Ratio 50 dB
Auto Iris Lens Type DC drive
Electronic Shutter Range 1 ~ 1/100,000 sec
Wide Dynamic Range 60 dB
White Balance Range 2,000° to 10,000°K
Sensitivity f/1.2; 2,850°K; SNR >24dB
Color (33 ms) 0.50 lux
Color SENS (500 ms) 0.12 lux
Mono (33 ms) 0.25 lux
Mono SENS (500 ms) 0.03 lux
ELECTRICAL
Port RJ-45 connector for 100Base-TX
Auto MDI/MDI-X
Cabling Type Cat5 or better for 100Base-TX
Power Input 24 VAC or PoE (IEEE 802.3af class 3)
Power Consumption
(camera only) <6 W
Current Consumption
PoE <200 mA maximum
24 VAC <295 mA nominal; <390 mA maximum
Local Storage Mini SD
Alarm Input 10 VDC maximum, 5 mA maximum
Relay Output 12 VDC maximum, 150 mA maximum
Service Port External 3-connector, 2.5 mm provides NTSC/PAL video output
MECHANICAL
Lens Mount CS mount, adjustable
Camera Mount 0.25-inch (0.64 cm) UNC-20 screw, top and bottom of camera housing
C2950M-G (4/12) 61
Page 61

VIDEO
Video Encoding H.264 base profile and MJPEG
Video Streams Up to 2 simultaneous streams; the second stream is variable based on the setup of the primary stream.
Frame Rate Up to 30, 25, 24, 15, 12.5, 12, 10, 8, 7. 5, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2.5, 2, 1
(dependent on the coding, resolution, and stream configuration)
Available Resolutions
Resolution Maximum IPS
MPx Width Height Aspect Ratio MJPEG H.264 Base Profile
3.1 2048 1536 4:3 10 3
2.1 1920 1080 16:9 15 5
1.9 1600 1200 4:3 15 6
1.3 1280 1024 5:4 20 8
1.2 1280 960 4:3 20 8
0.9 1280 720 16:9 30 11
0.5 800 600 4:3 30 25
0.3 640 512 5:4 30 30
0.3 640 480 4:3 30 30
0.3 640 352 16:9 30 30
0.2 480 368 4:3 30 30
0.2 480 272 16:9 30 30
0.1 320 256 5:4 30 30
0.1 320 240 4:3 30 30
0.1 320 176 16:9 30 30
Supported Protocols TCP/IP, UDP/IP (Unicast, Multicast IGMP), UPnP, DNS, DHCP, RTP, RTSP, NTP, IPv4, SNMP, QOS, HTTP,
HTTPS, LDAP (client), SSH, SSL, SMTP, FTP, and 802.1x (EAP)
Users
Unicast Up to 20 simultaneous users depending on resolution settings (2 guaranteed streams)
Multicast Unlimited users H.264 or MPEG-4
Security Access Password protected
Software Interface Web browser view and setup
Pelco System Integration Endura 2.0 or later, Digital Sentry 4.2 IP bundle 3 or later
Open API Pelco API or ONVIF v1.02
ENVIRONMENTAL
Operational Temperature 14° to 122°F (–10° to 50°C)
Storage Temperature 14° to 158°F (–10° to 70°C)
Storage Humidity 20% to 90%, noncondensing
PHYSICAL
Dimensions 5.4" D x 3.1" W x 3.0" H
(13.7 x 7.9 x 7.6 cm)
Weight (without lens) 1.14 lb (0.52 kg)
62 C2950M-G (4/12)
Page 62

PRODUCT WARRANTY AND RETURN INFORMATION
WARRANTY
Pelco will repair or replace, without charge, any merchandise proved defective in
material or workmanship for a period of one year after the date of shipment.
Exceptions to this warranty are as noted below:
• Five years:
– Fiber optic products
– Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) transmission products
– CC3701H-2, CC3701H-2X, CC3751H-2, CC3651H-2X, MC3651H-2, and
MC3651H-2X camera models
• Three years:
– FD Series and BU Series analog camera models
– Fixed network cameras and network dome cameras with Sarix
– Sarix thermal imaging products (TI and ESTI Series)
– Fixed analog camera models (C20 Series, CCC1390H Series, C10DN Series,
and C10CH Series)
– EH1500 Series enclosures
– Spectra
– Spectra HD dome products
– Camclosure
®
IV products (including Spectra IV IP)
®
IS Series integrated camera systems
– DX Series video recorders (except DX9000 Series which is covered for a
period of one year), DVR5100 Series digital video recorders, Digital Sentry
Series hardware products, DVX Series digital video recorders, and NVR300
Series network video recorders
®
– Endura
– Genex
Series distributed network-based video products
®
Series products (multiplexers, server, and keyboard)
– PMCL200/300/400 Series LCD monitors
– PMCL5xxF Series and PMCL5xxNB Series LCD monitors
• Two years:
– Standard varifocal, fixed focal, and motorized zoom lenses
– DF5/DF8 Series fixed dome products
®
– Legacy
– Spectra III
Series integrated positioning systems
™
, Spectra Mini, Spectra Mini IP, Esprit®, ExSite®, ExSite IP, and
PS20 scanners, including when used in continuous motion applications
– Esprit Ti and TI2500 Series thermal imaging products
– Esprit and WW5700 Series window wiper (excluding wiper blades)
– CM6700/CM6800/CM9700 Series matrix
– Digital Light Processing (DLP
®
) displays (except lamp and color wheel). The
lamp and color wheel will be covered for a period of 90 days. The air filter is
not covered under warranty.
®
technology
•Six months:
– All pan and tilts, scanners, or preset lenses used in continuous motion
applications (preset scan, tour, and auto scan modes)
Pelco will warrant all replacement parts and repairs for 90 days from the date of
Pelco shipment. All goods requiring warranty repair shall be sent freight prepaid
to a Pelco designated location. Repairs made necessary by reason of misuse,
alteration, normal wear, or accident are not covered under this warranty.
Pelco assumes no risk and shall be subject to no liability for damages or loss
resulting from the specific use or application made of the Products. Pelco’s liability
for any claim, whether based on breach of contract, negligence, infringement of
any rights of any party or product liability, relating to the Products shall not exceed
the price paid by the Dealer to Pelco for such Products. In no event will Pelco be
liable for any special, incidental, or consequential damages (including loss of use,
loss of profit, and claims of third parties) however caused, whether by the
negligence of Pelco or otherwise.
The above warranty provides the Dealer with specific legal rights. The Dealer may
also have additional rights, which are subject to variation from state to state.
If a warranty repair is required, the Dealer must contact Pelco at (800) 289-9100 or
(559) 292-1981 to obtain a Repair Authorization number (RA), and provide the
®
following information:
1. Model and serial number
2. Date of shipment, P.O. number, sales order number, or Pelco invoice number
3. Details of the defect or problem
If there is a dispute regarding the warranty of a product that does not fall under
the warranty conditions stated above, please include a written explanation with
the product when returned.
Method of return shipment shall be the same or equal to the method by which the
item was received by Pelco.
RETURNS
To expedite parts returned for repair or credit, please call Pelco at (800) 289-9100
or (559) 292-1981 to obtain an authorization number (CA number if returned for
credit, and RA number if returned for repair) and designated return location.
All merchandise returned for credit may be subject to a 20 percent restocking and
refurbishing charge.
Goods returned for repair or credit should be clearly identified with the assigned
CA or RA number and freight should be prepaid.
Revised 1-12-12
The materials used in the manufacture of this document and its components are compliant to the requirements of Directive 2002/95/EC.
This equipment contains electrical or electronic components that must be recycled properly to comply with Directive 2002/96/EC of the European Union
regarding the disposal of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). Contact your local dealer for procedures for recycling this equipment.
REVISION HISTORY
Manual # Date Comments
C2950M 1/09 Original version.
C2950M-A 5/09 Added periodic refocus and day/night refocus features to the operation section.
C2950M-B 10/09 Added Sarix 1.3 software features to the operation section.
C2950M-C 1/10 Added Sarix 1.4 software features to the operation section.
C2950M-E 8/10 Added Sarix 1.6 software features to the operation section.
C2950M-F 12/10 Removed obsolete camera models. Added Sarix 1.7 software features to the operation section. Added ONVIF information.
C2950M-G 4/12 Added Sarix 1.8.2 software features to the operation section.
Pelco, the Pelco logo, and other trademarks associa ted with Pelco products referred to in this publication are trademarks of Pelco, Inc. or its affilia tes. © Copyright 2012, Pelco, Inc.
All other product names and services are the property of their respective companies. All rights reserved.
ONVIF and the ONVIF logo are trademarks of ONVIF Inc.
Product specifications and availability are subject to change without notice.
Page 63

www.pelco.com
Pelco by Schneider Electric 3500 Pelco Way Clovis, California 93612-5699 United States
USA & Canada Tel (800) 289-9100 Fax (800) 289-9150
International Tel +1 (559) 292-1981 Fax +1 (559) 348-1120
 Loading...
Loading...