PEERLESS Series 63, Series 64 Installation, Operation & Maintenance Manual

63/64
™
Boilers
Series
Gas
Installation,
Operation &
Maintenance
Manual

USING THIS MANUAL 1
A. MANUAL ORGANIZATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
B. SPECIAL ATTENTION BOXES . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1. PREINSTALLATION 2
A. GENERAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
B. CODES & REGULATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
C. ACCESSIBILITY CLEARANCES . . . . . . . . . . .2
D. CLEARANCE FROM COMBUSTIBLE
CONSTRUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
E. AIR COMBUSTION AND VENTILATION . . . .3
F. INSTALLATION SURVEY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
G. PLANNING THE LAYOUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
2. BOILER PLACEMENT & ASSEMBLY 7
A. PACKAGED BOILER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
B. KNOCKDOWN BOILERS – SPLIT BLOCK . . .7
C. KNOCKDOWN BOILERS – ASSEMBLED
BLOCKS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
D. KNOCKDOWN BOILERS – CONTROL &
MANIFOLD ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
E. KNOCKDOWN BOILERS – FLUE COLLECTOR
ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
F. KNOCKDOWN BOILERS – HYDROSTATIC
TESTING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
G. KNOCKDOWN BOILERS – ASSEMBLE
JACKET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
3. VENTING 11
A. CHIMNEY OR VENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
B. AUTOMATIC VENT DAMPER
INSTALLATION – GENERAL . . . . . . . . . . . .11
C. BOILER REMOVAL FROM COMMON
VENTING SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
4. BOILER PIPING 13
A. WATER BOILER PIPING – SINGLE
BOILER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
B. WATER BOILER PIPING – MULTIPLE
BOILERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
C. STEAM BOILER PIPING – SINGLE
BOILER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
D. STEAM BOILER INDIRECT WATER HEATER
PIPING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
E. STEAM BOILER PIPING – MULTIPLE
BOILERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
5. FUEL PIPING 16
A. INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
B. OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
6. CONTROLS & TRIM 18
A. WATER BOILER CONTROLS & TRIM . . . . .18
B. STEAM BOILER CONTROLS & TRIM . . . . .19
7. ELECTRICAL 20
A. CONNECT SUPPLY WIRING . . . . . . . . . . . .20
B. MOUNT REMAINING CONTROLS . . . . . . . .20
C. INSTALL CONTROL WIRING . . . . . . . . . . . .21
D. WIRING DIAGRAM INDEX . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
8. BOILER OPERATION 32
A. SYSTEM INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
B1. FILL THE BOILER (WATER BOILERS) . . . . .32
B2. FILL THE BOILER (STEAM BOILERS) . . . . .32
C. LIGHTING INSTRUCTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
D. PILOT CHECK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
E. MAIN BURNER CHECK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
F. CONTROLS CHECK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
G. PURGING AIR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
H. CHECK SYSTEM PRESSURE . . . . . . . . . . . .33
I. CLEAN THE BOILER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
J. BOILER SHUT-DOWN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
9. MAINTENANCE 39
A. GENERAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
B. DAILY MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
C. WEEKLY MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
D. MONTHLY MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
E. ANNUAL MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
F. AS REQUIRED MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . .41
10. TROUBLESHOOTING 42
11. BOILER DIMENSIONS & RATINGS 45
12. REPAIR PARTS 47
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
USING THIS MANUAL
A. INSTRUCTION MANUALS
The Series 63/64™ Installation, Operation &
Maintenance Manual is divided into four basic sections:
1. Preinstallation (Section 1)
2. Installation (Sections 2 through 8)
3. Start-Up (Section 9)
4. Maintenance (Section 10)
B. SPECIAL ATTENTION BOXES
Throughout this manual special attention boxes are
provided to supplement the instructions and make
special notice of potential hazards. The definition
of each of these categories, in the judgement of
PB Heat, LLC are as follows.
USING THIS MANUAL
Indicates special attention is needed, but not directly
related to potential personal injury or property
damage.
NOTICE
Indicates a condition or hazard which will or can
cause minor personal injury or property damage.
CAUTION
DANGER
Indicates a condition or hazard which will cause
severe personal injury, death or major property
damage.
Indicates a condition or hazard which may cause
severe personal injury, death or major property
damage.
WARNING

2
PREINSTALLATION
A. GENERAL
Series 63/64™ boilers are supplied knocked down for field
assembly or completely assembled as packaged boilers.
All items should be inspected for damage upon receipt
and any damage reported to the trucker and wholesaler.
All components should be stored in a clean dry area.
Carefully read these instructions before beginning work.
Understand all aspects of the installation. Contact PB
Heat sales representative or customer service for help in
answering questions.
This boiler must be installed by a qualified contractor.
The boiler warranty may be voided if the boiler is not
installed correctly.
A hot water boiler installed above radiation level or as
required by the Authority having jurisdiction, must be
provided with a low water cut-off device either as part of
the boiler or at the time of installation.
B. CODES & REGULATIONS
1. All work should be performed in strict accordance
with the requirements of state and local regulating
agencies and codes dealing with boiler installations.
2. In the absence of such local requirements the
following should govern.
a. ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code, Section
IV – “Heating Boilers”
b. ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code, Section
VI – “Recommended Rules for the Care and
Operation of Heating Boilers”
c. ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54 – “National Fuel Gas
Code”
d. ANSI/NFPA 70 – “National Electrical Code”
e. ASME CSD-1 – “Controls & Safety Devices for
Automatically Fired Boilers”
f. ANSI/NFPA 211 – “Chimneys, Fireplaces, vents,
and Solid Fuel Burning Appliances”
3. Where required by the authority having jurisdiction,
the installation must conform to the Standard for
Controls and Safety Devices for Automatically Fired
Boilers, ANSI/ASME CSD-1.
C. ACCESSIBILITY CLEARANCES
The following recommendations allow for reasonable
access to the boiler. Local codes or special conditions
may require greater clearances.
1. For servicing the boiler provide not less than 24"
from the side of the boiler where limit and level
controls are mounted.
2. For servicing the burners provide not less than 24"
from the front of the boiler.
3. The remaining clearances should be 6" from all sides.
D. CLEARANCES FROM COMBUSTIBLE
CONSTRUCTION
Boiler Models 63-03 through 63-06
1. The design of this boiler is certified for alcove
installation with the following clearances to
combustible construction.
a. Sides: 6"
b. Top: 30"
c. Front: 18"
d. Rear: 6"
e. Single Wall Vent Pipe: 6"
Boiler Models 64-07 through 64-12
2. The design of this boiler is certified for installation
with the following clearances to combustible
construction. Boiler must be installed in an area large
in comparison to the boiler.
a. Sides: 24"
b. Top: 30"
c. Front: 18"
d. Rear: 24"
e. Single Wall Vent Pipe: 6"
3. All Models
a. Single wall vent pipe must be at least 6" away
from combustible construction.
b. For installation on non-combustible flooring only.
c. If it is necessary to build a non-combustible floor
pad on top of an existing combustible floor,
construct pad as described in the Installation of
Specific Equipment Chapter of National Fuel Gas
Code Handbook.
1. PREINSTALLATION
Do not install this boiler on carpeting.
WARNING
Do not install this boiler on combustible flooring. Boiler
installation on combustible flooring is a fire hazard.
WARNING
E. AIR FOR COMBUSTION AND
VENTILATION
1. Adequate combustion air and ventilation air must be
provided for this appliance in accordance with the
section of the National Fuel Gas Code entitled, “Air
for Combustion and Ventilation” or applicable
provisions of the local building code. Subsections 2
through 8 as follows are based on the National Fuel
Gas Code requirements.
2. Required Combustion Air Volume:
The total required
volume of indoor air is to be the sum of the required
volumes for all appliances located within the space.
Rooms communicating directly with the space in
which the appliances are installed and through
combustion air openings sized as indicated in
Subsection 3 are considered part of the required
volume. The required volume of indoor air is to be
determined by one of two methods.
a. Standard Method: The minimum required
volume of indoor air (room volume) shall be 50
cubic feet per 1000 BTU/Hr (4.8 m
3
/kW). This
method is to be used if the air infiltration rate is
unknown or if the rate of air infiltration is known
to be greater than 0.6 air changes per hour. As
an option, this method may be used if the air
infiltration rate is known to be between 0.6 and
0.4 air changes per hour. If the air infiltration rate
is known to be below 0.4 then the Known Air
Infiltration Rate Method must be used. If the
building in which this appliance is to be installed
is unusually tight, PB Heat recommends that the
air infiltration rate be determined.
b. Known Air Infiltration Rate Method: Where
the air infiltration rate of a structure is known, the
minimum required volume of indoor air for
appliances other than fan assisted and for the
Series 63/64™ Boiler shall be determined as
follows:
where:
I
other
= Input of appliances other than fan
assisted in Btu/hr
ACH = air change per hour (percent of the
volume of the space exchanged per
hour, expressed as a decimal)
For fan assisted appliances, calculate the required
volume of air using the following equation:
I
fan
= Input of the fan assisted appliances in
Btu/hr
Note: These calculations are not to be used for
infiltration rates greater than 0.60 ACH.
3. Indoor Air Opening Size and Location:
Openings
connecting indoor spaces shall be sized and located
as follows:
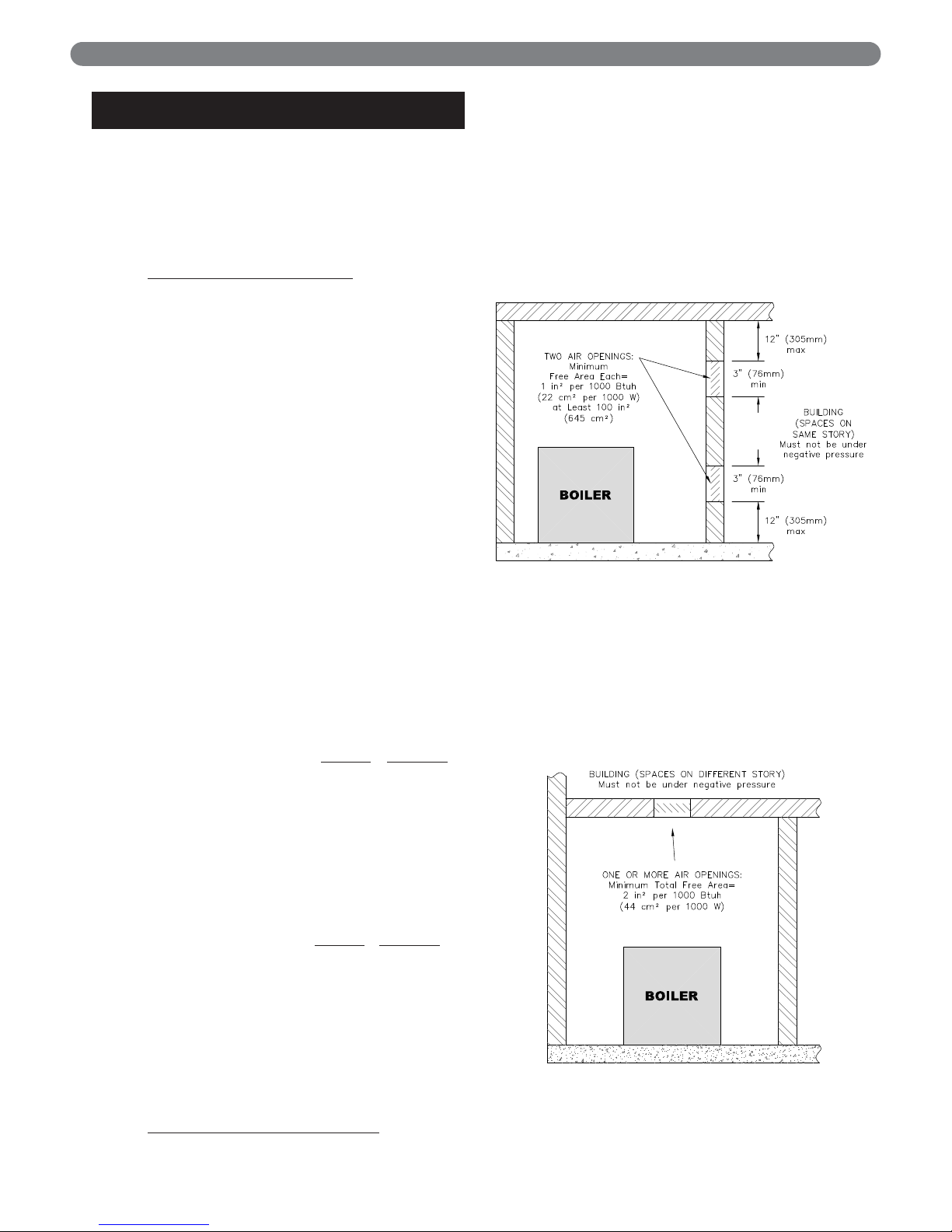
a. Combining spaces on the same floor:
Provide two permanent openings communicating
with additional spaces that have a minimum free
area of 1 in
2
per 1000 Btu/hr (22 cm2per 1000 W)
of the total input rating of all gas fired equipment
but not less than 100 in
2
(645 cm2). One
opening is to begin within 12 inches (305 mm)
from the top of the space and the other is to
begin within 12 inches (305 mm) from the floor.
The minimum dimension of either of these
openings shall be 3 inches (76 mm). See Figure
1.1 for an illustration of this arrangement.
b. Combining spaces on different floors:
Provide one or more permanent openings
communicating with additional spaces that have
a total minimum free area of 2 in
2
per 1000
Btu/hr (44 cm
2
per 1000 W) of total input rating
of all equipment. See Figure 1.2 for an
illustration of this arrangement.
Figure 1.1: Air Openings – All Air from Indoors
on the Same Floor
Figure 1.2: Air Openings – All Air from Indoors
on Different Floors
15 ft
3
I
fan
ACH 1000
Btu
/
hr
Required Volume
fan
=
21 ft
3
I
other
ACH 1000
Btu
/
hr
Required Volume
other
=
⎛
⎜
⎝
⎛
⎜
⎝
⎛
⎜
⎝
⎛
⎜
⎝
3
4
PREINSTALLATION
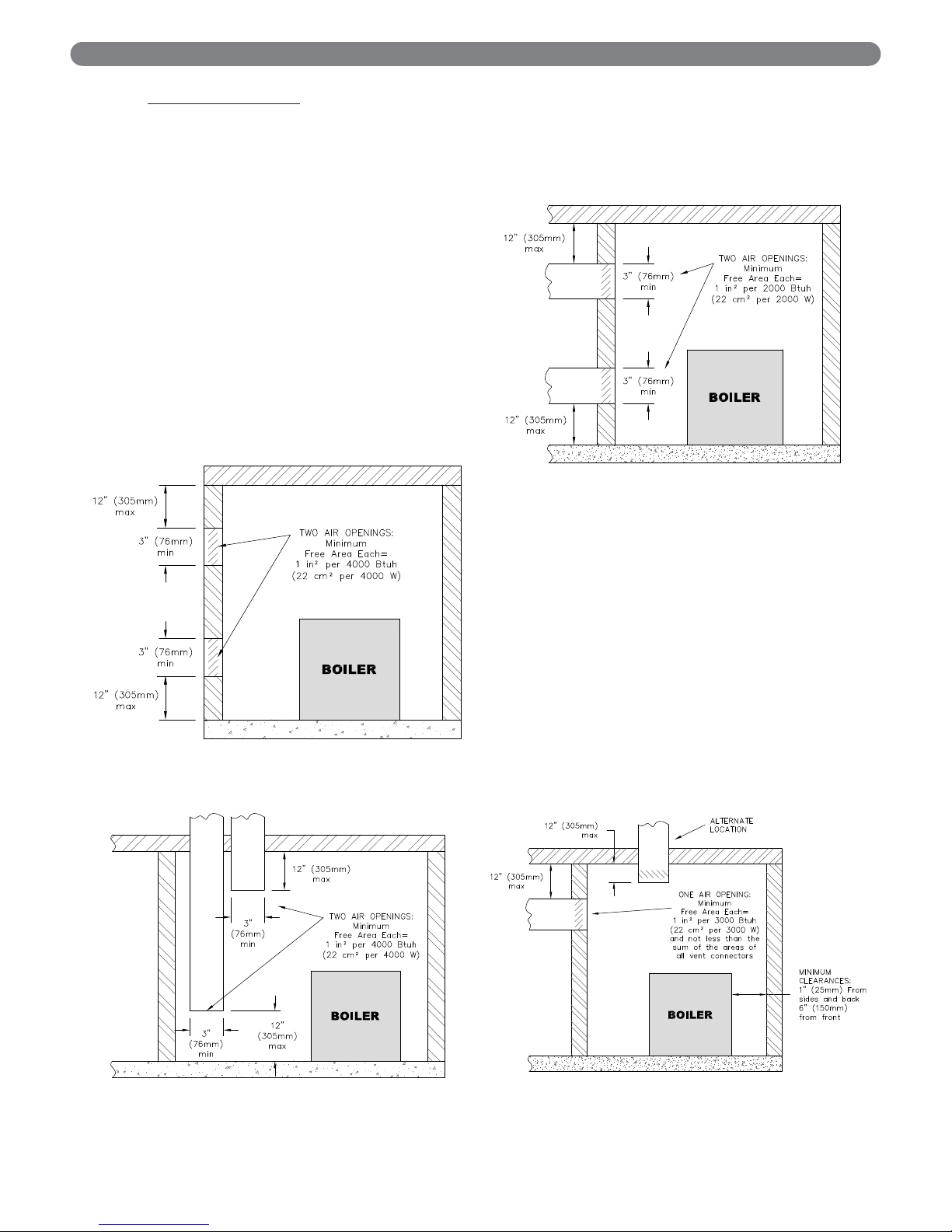
4. Outdoor Combustion Air: Outdoor combustion air is
to be provided through one or two permanent
openings. The minimum dimension of these air
openings is 3 inches (76 mm).
a. Two Permanent Opening Method: Provide
two permanent openings. One opening is to
begin within 12 inches (305 mm) of the top of
the space and the other is to begin within 12
inches (305 mm) of the floor. The openings are
to communicate directly or by ducts with the
outdoors or with spaces that freely communicate
with the outdoors. The size of the openings shall
be determined as follows:
i. Where communicating directly or through
vertical ducts with the outdoors each opening
shall have a minimum free area of 1 in
2
per
4000 Btu/hr (22 cm
2
per 4000 W) of total
input rating for all equipment in the space.
See Figure 1.3 for openings directly
communicating with the outdoors or Figure
1.4 for openings connected by ducts to the
outdoors.
ii. Where communicating with the outdoors
through horizontal ducts, each opening shall
have a minimum free area of 1 in
2
per 2000
Btu/hr (22 cm
2
per 2000 W) of total rated
input for all appliances in the space. See
Figure 1.5.
b. One Permanent Opening Method: Provide
one permanent opening beginning within 12
inches (305 mm) of the top of the space. The
opening shall communicate directly with the
outdoors, communicate through a vertical or
horizontal duct, or communicate with a space
that freely communicates with the outdoors. The
opening shall have a minimum free area of 1 in
2
per 3000 Btu/hr of total rated input for all
appliances in the space and not less than the
sum of the cross-sectional areas of all vent
connectors in the space. The gas-fired equipment
shall have clearances of at least 1 inch (25 mm)
from the sides and back and 6 inches (150 mm)
from the front of the appliance. See Figure 1.6
for this arrangement.
Figure 1.4: Air Openings – All Air from Outdoors
through Vertical Ducts
Figure 1.5: Air Openings – All Air from Outdoors
through Horizontal Ducts
Figure 1.6: Air Openings – All Air from Outdoors
through One Opening
Figure 1.3: Air Openings – All Air Directly from
Outdoors

5
5. Combination Indoor and Outdoor Combustion Air: If
the required volume of indoor air exceeds the
available indoor air volume, outdoor air openings or
ducts may be used to supplement the available
indoor air provided:
a. The size and location of the indoor openings
comply with Subsection 3.
b. The outdoor openings are to be located in
accordance with Subsection 4.
c. The size of the outdoor openings are to be sized
as follows:
where:
A
req
= minimum area of outdoor openings.
A
full
= full size of outdoor openings calculated
in accordance with Subsection 4.
V
avail
= available indoor air volume
V
req
= required indoor air volume
6. Engineered Installations:
Engineered combustion air
installations shall provide an adequate supply of
combustion, ventilation, and dilution air and shall be
approved by the authority having jurisdiction.
7. Mechanical Combustion Air Supply:
a. In installations where all combustion air is
provided by a mechanical air supply system, the
combustion air shall be supplied from the
outdoors at the minimum rate of 0.35 ft
3
/min per
1000 Btu/hr (0.034 m
3
/min per 1000 W) of the
total rated input of all appliances in the space.
b. In installations where exhaust fans are installed,
additional air shall be provided to replace the
exhaust air.
c. Each of the appliances served shall be
interlocked to the mechanical air supply to
prevent main burner operation when the
mechanical air supply system is not in operation.
d. In buildings where the combustion air is provided
by the mechanical ventilation system, the system
shall provide the specified combustion air rate in
addition to the required ventilation air.
8. Louvers & Grills:
a. The required size of openings for combustion,
ventilation, and dilution air shall be based on the
net free area of each opening.
i. Where the free area through a louver or grille
is known, it shall be used in calculating the
opening size required to provide the free area
specified.
ii. Where the free area through a louver or grille
is not known, it shall be assumed that wooden
louvers will have 25% free area and metal
louvers and grilles will have 75% free area.
iii. Nonmotorized dampers shall be fixed in the
open position.
b. Motorized dampers shall be interlocked with the
equipment so that they are proven in the full
open position prior to ignition and during
operation of the main burner.
i. The interlock shall prevent the main burner
from igniting if the damper fails to open
during burner startup.
ii. The interlock shall shut down the burner if
the damper closes during burner operation.
9. Combustion Air Ducts
a. Ducts shall be constructed of galvanized steel or
an equivalent corrosion- resistant material.
b. Ducts shall terminate in an unobstructed space,
allowing free movement of combustion air to the
appliances.
c. Ducts shall serve a single space.
d. Ducts shall not serve both upper and lower
combustion air openings where both such
openings are used. The separation between ducts
serving upper and lower combustion air
openings shall be maintained to the source of
combustion air.
e. Ducts shall not be screened where terminating in
an attic space.
f. Horizontal upper combustion air ducts shall not
slope downward toward the source of the
combustion air.
g. The remaining space surrounding a chimney
liner, gas vent, special gas vent, or plastic piping
installed within a masonry, metal, or factory built
chimney shall not be used to supply combustion
air.
h. Combustion air intake openings located on the
exterior of buildings shall have the lowest side of
the combustion air intake opening at least 12
inches (305 mm) above grade.
V
avail
1 –
V
req
A
req
= A
full
x
⎛
⎜
⎝
⎛
⎜
⎝

6
F. INSTALLATION SURVEY
For new and existing installations, a Water Installation
Survey or a Steam Installation Survey is available from
PB Heat, LLC. The surveys will provide information on
how the boiler works with your specific system and will
provide an overview of boiler system operation in
general.
You can also use this survey to locate system problems
which will have to be corrected. To obtain copies of
these Surveys, contact your PB Heat representative or
download them from PeerlessBoilers.com.
G. PLANNING THE LAYOUT
Prepare sketches and notes of the layout to minimize the
possibility of interferences with new or existing
equipment, piping, venting and wiring.
PREINSTALLATION
Liquefied Petroleum (LP) is heavier than air and may
collect or “pool” in a low area in the event of a leak
from defective equipment. This gas may then ignite,
resulting in a fire or explosion.
WARNING
7
BOILER PLACEMENT & ASSEMBLY
A. PACKAGED BOILER
1. Remove the crate top and sides and remove any
loose cartons.
2. Lift the boiler from the crate pallet. Move the boiler to
the location determined in Chapter 1: Pre-installation.
3. Proceed to Chapter 3: Piping the Boiler.
B. KNOCKDOWN BOILERS – SPLIT BLOCK
ASSEMBLY MODELS 64-07 TO 64-12
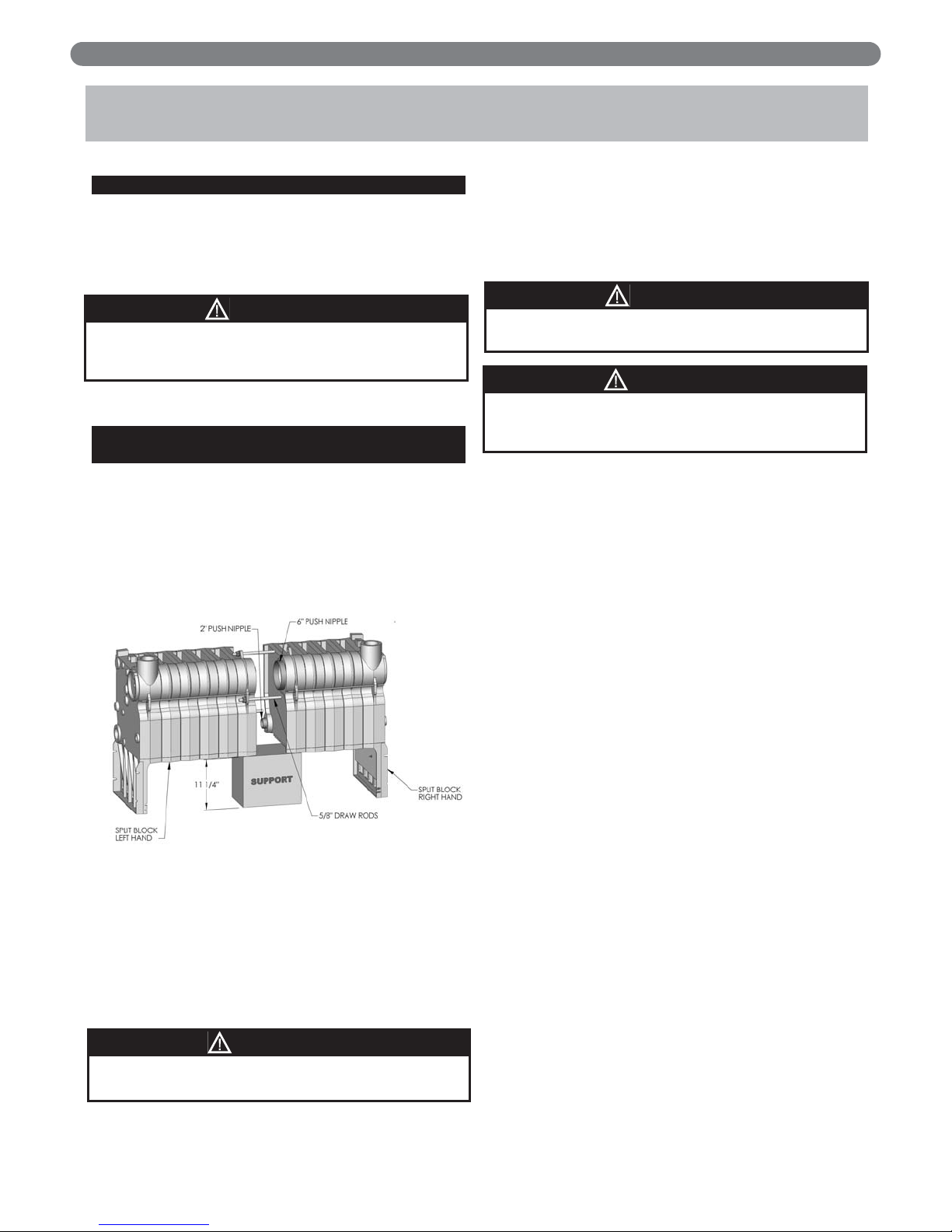
1. The boiler sections and base on Model 63-03 to 63-06
are factory assembled. If the boiler is 63-03 through
63-06 begin assembly as described in step 2.C,
Knockdown Boilers: Assembled Blocks.
2. Move each block of cast iron sections off of the
shipping pallets and support them as shown in
Figure 2.1.
3. Clean nipple ports using a wire brush. Make certain
there are no burrs around the outside edge of the ports.
If necessary, remove any burrs on the edges using a
round file (be careful not to score the nipple port).
4. Spread a thin coat of TFE TITE Nipple Sealant in
the nipple ports.
5. Insert the push nipples into the nipple ports of one of
the split block ends. Make sure the nipples are clean
and free of burrs. Use a block of wood to protect the
surface of the nipple while setting the nipple into the
nipple port with a hammer. Assure that the nipple is
firmly seated in the nipple port before proceeding.
6. Apply silicone sealant to the rope groove to hold the
rope in place during assembly. Press 1/2" diameter
rope into the rope groove.
7. Assure the nipples are perpendicular to the sections
and that the blocks are aligned properly.
8. Insert draw rods through the lugs provided on the
mating intermediate sections. Use 5/8" draw rods as
shown in Figure 2.1.
9. Before starting to draw the sections together, apply
lubricating oil to the threads.
10. Tighten the hex nuts and draw the boiler sections
together evenly until the small pads on each of the
mating sections are in contact:
·
Periodically measure the gap at all four corners
of the section to make sure the sections are
drawing together evenly – gaps measured at
all four corners should not vary more than
1/8". Turn wrench no more than 3-4 times before
moving to the next nut (this equates to about an
1/8" draw-up).
·
Using similar torque on each nut, gradually
increase the torque as the sections are drawn
closer together. Maximum allowable torque
on the draw rod nuts is 80 foot-pounds.
Typically only 30 to 60 foot-pounds is required to
pull together evenly drawn sections.
·
If one corner resists moving, loosen the draw
rods on the other corners to help pull the subject
corner into proper alignment.
2. BOILER PLACEMENT & ASSEMBLY
Never apply nipple sealer on the nipples. Apply only
in nipple ports.
NOTICE
Be careful not to damage the burner tray when
removing the boiler from the pallet. If necessary,
remove the burner tray before moving the boiler.
NOTICE
Figure 2.1: Block Assembly
Never hit the nipple directly with a hammer. This will
damage the nipple and cause leaks.
NOTICE
If the nipple is not fully seated in the nipple port,
damage to the nipple may occur when the sections
are drawn together.
NOTICE
8
BOILER PLACEMENT & ASSEMBLY
11. If the sections do not draw together using the torque
specified above, the block must be separated and the
nipples replaced before reassembly is attempted.
12. The sections may alternatively be drawn together
using long 5/8" rods along with cast iron washers
through the nipple ports. Two large cast iron washers
(51163), two small cast iron washers (51165) and
two long 5/8" NPT rods are required (not provided).
Do not attempt to draw sections together without the
cast iron washers.
C. KNOCKDOWN BOILERS: ASSEMBLED
BLOCKS
1. If shipping pallet is still attached, move the
assembled block off of the pallet.
2. Move the assembled block to the location determined
in Chapter 1: Pre-installation. The location should
be on a level foundation as near to the chimney as
possible and centralized with respect to the heating
system.
3. Attach the base front/rear insulated panels to the cast
iron block assembly as shown in Figure 2.2 using
3/8" carriage bolts and 3/8" hex nuts.
4. Attach the base lower rear panel to the cast iron block
assembly using 3/8" carriage bolts and hex nuts.
D. KNOCKDOWN BOILERS: CONTROL &
MANIFOLD ASSEMBLY
1. Remove the burner tray assembly from the burner
and controls carton.
2. Check burners to assure that they are seated
correctly in the burner tray rear support.
3. For Series 64™ boilers, assemble the 90° elbow and
return bend to the manifold assembly.
4. Remove the gas valve manifold components from
the burner tray and controls carton and connect
them to the burner manifold. Refer to Figure 5.2
through 5.5 in Section 5 for the specific Gas Train
Manifold Configuration.
5. Slide the burner tray under the cast iron block
assembly and attach to the end sections using the 1/4"
carriage bolts and nuts provided. (See Figure 2.2).
6. Attach the base burner access panel to the base front
panel assembly with two #10 x 1/2" sheet metal
screws (See Figure 2.2).
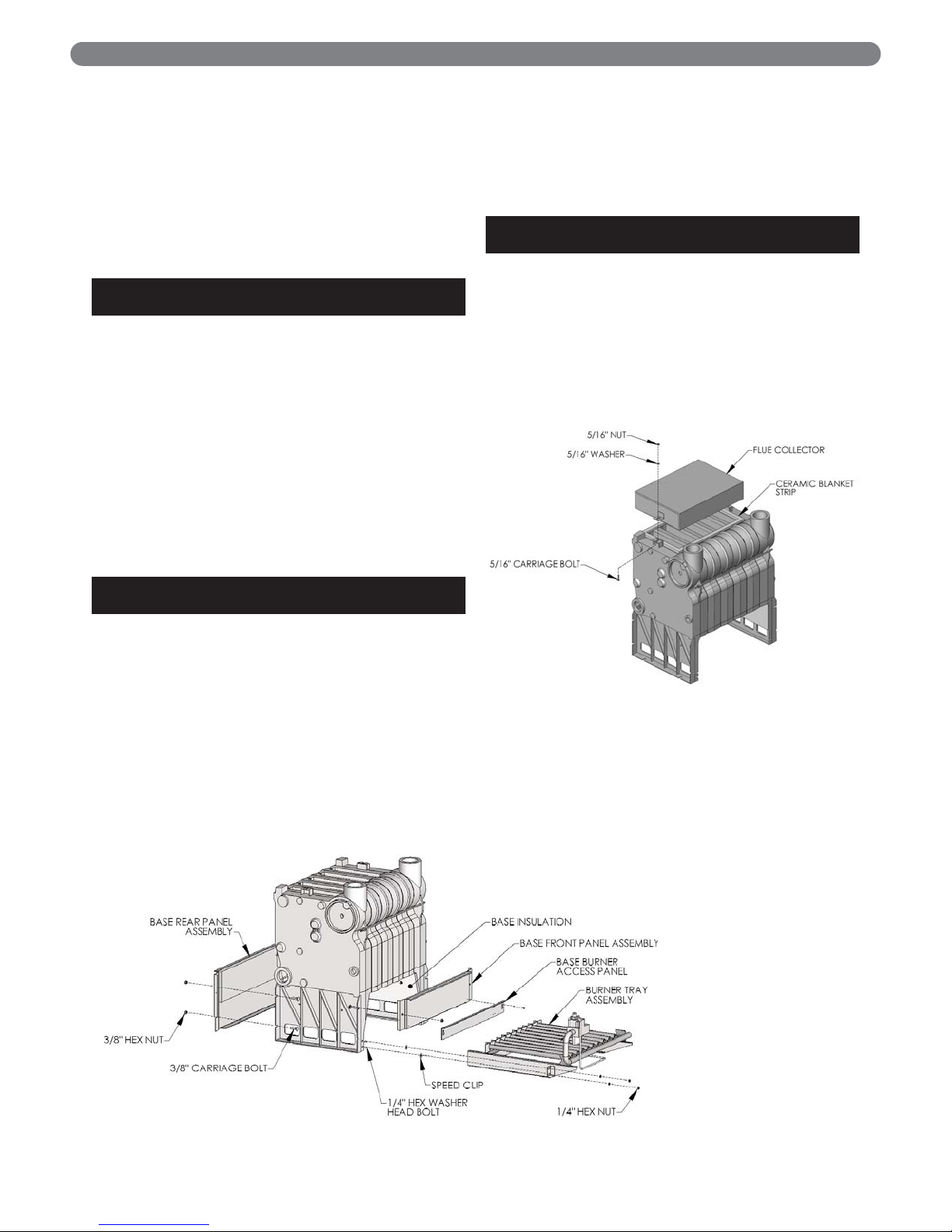
E. KNOCKDOWN BOILERS: FLUE
COLLECTOR ASSEMBLY
1. Remove the flue collector and ceramic blanket strip
insulation from burner and controls carton.
2. Lay the ceramic blanket strip on top of the boiler
using care not to block any flue passageways.
3. Insert the two 1/4"-20 carriage bolts provided with
boiler into the lugs on top of the boiler end sections
as shown in Figure 2.3.
4. Attach the flue collector to the bolts with the flat
washers and hex nuts provided. Tighten the nuts
snugly.
Figure 2.3: Flue Collector Attachment
Figure 2.2: Base Panel Attachment
9
F. KNOCKDOWN BOILER: HYDROSTATIC
TESTING
1. Install the pressure gauge and drain valve in the right
hand end section.
2. Install a water supply line with a shut-off valve in the
right hand end section.
3. Install an air vent valve on the boiler relief valve
connection.
4. Plug all open tappings in the boiler.
5. Fill the boiler with water, venting air from the top of
the unit as the water level rises.
6. Pressurize the boiler from 75 to 85 psig. Do not
exceed 85 psig.
7. Maintain pressure while inspecting the boiler
thoroughly for leaks.
8. After inspection is complete, drain the boiler and
remove plugs from tappings that are to be used.
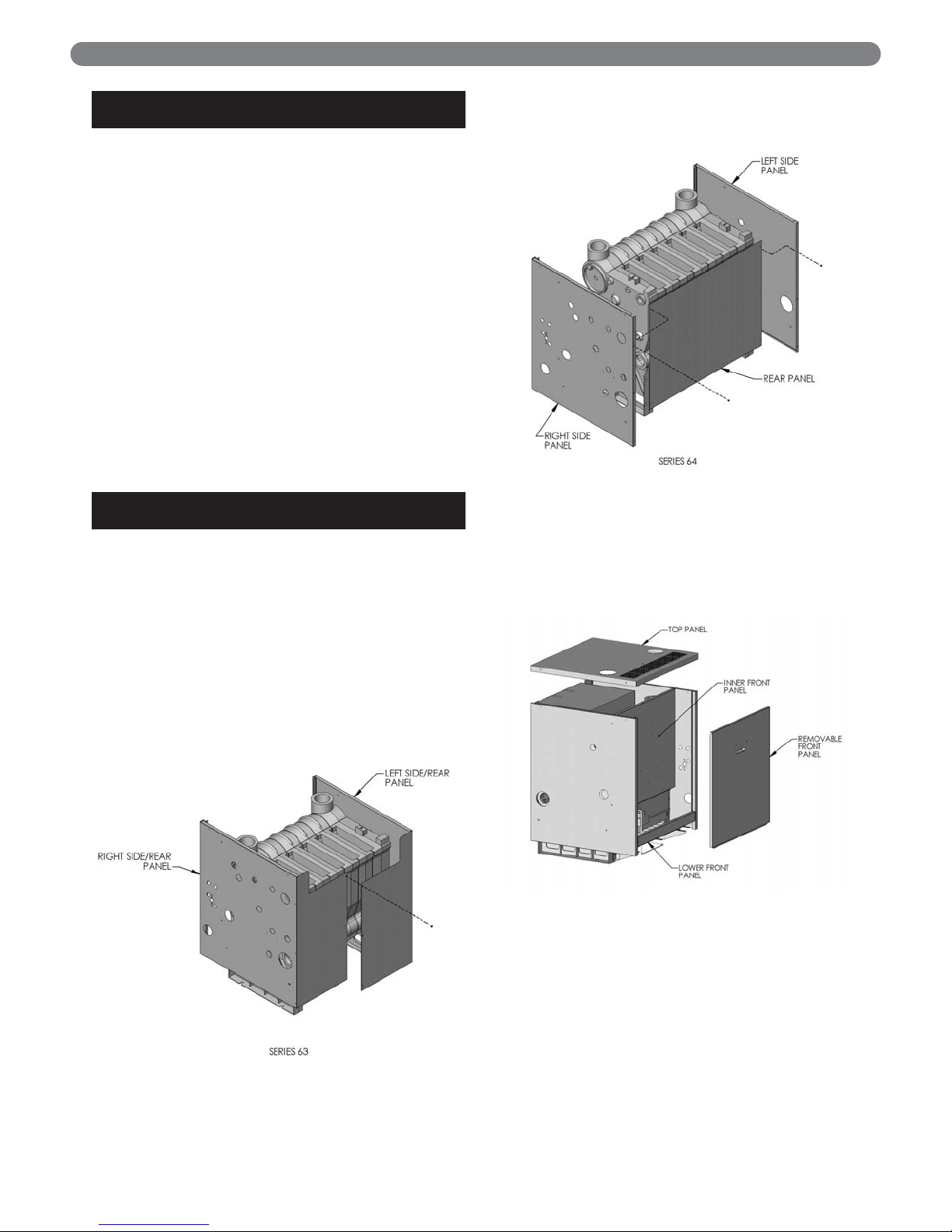
G. KNOCKDOWN BOILER: ASSEMBLE
JACKET
1. The Series 63™ boilers employ a wrap-around style
jacket while the Series 64™ boilers use an individual
back panel.
2. Align the clearance holes on the side panels with the
mounting holes in the base front & back plates and
attach with #10 x 1/2" sheet metal screws.
3. Wrap-Around Jacket: Bend the side jacket panels
at the perforations to form the back of the jacket.
The left side should overlap the right for proper
attachment. Connect the two panels with three
#10 x 1/2" sheet metal screws. See Figure 2.4.
4. Back Panel Jacket: Position the back jacket panel
inside the flange of the side jacket panels and attach it
with six #10 x 1/2" sheet metal screws. See Figure 2.5.
5. Position the Inner Front Panel between the side
panels and align the mounting holes on the side
flanges with the clearance holes on the side panels.
Attach with four #10 x 1/2" sheet metal screws
provided. See Figure 2.6.
6. Attach the Lower Front Panel to the bottom front of
the side Jacket Panels with two #10 x 1/2" sheet
metal screws. See Figure 2.6.
BOILER PLACEMENT & ASSEMBLY
Figure 2.4: Jacket Assembly, Series 63™ Boilers
Figure 2.5: Jacket Assembly, Series 64™ Boilers
Figure 2.6: Jacket Panel Attachment
10
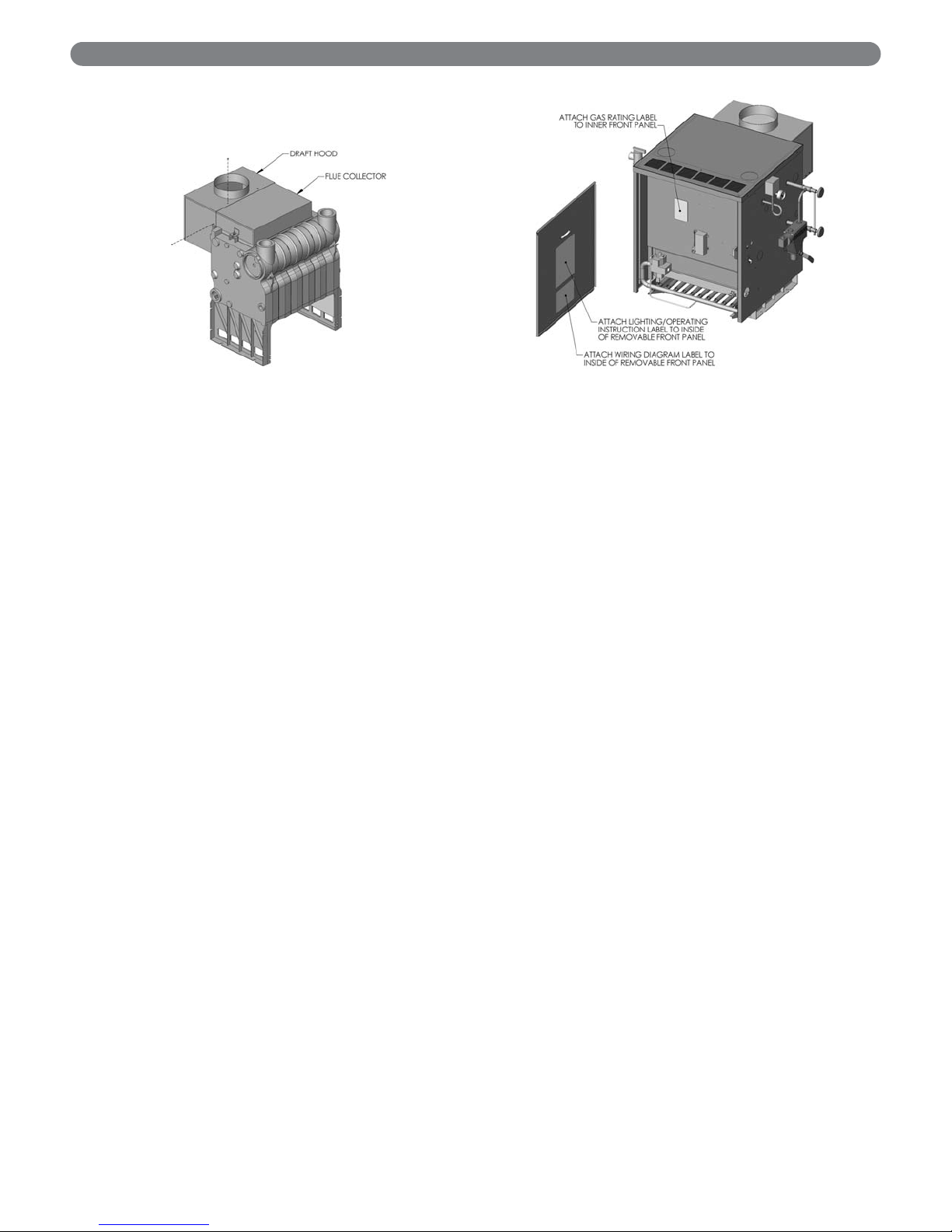
7. Attach the Draft Hood to the Flue Collector using
#10 x 1/2" sheet metal screws provided. Refer to
Figure 2.7.
8. Position the Top Jacket Panel so that the flanges
overlap the Side Jacket Panels and the air louvers are
at the front of the boiler. Attach with six #10 x 1/2"
sheet metal screws. See Figure 2.6.
9. Remove the following data plates or labels from the
manila envelope that contains the Instruction
Manual:
- Boiler Rating Label
- Lighting/Operating Instruction Label
- Wiring Diagram Label
Attach labels as shown in Figure 2.8.
10. Insert the top edge of the Front Jacket Panel beneath
front flange of the Top Jacket Panel and against the
top of the Lower Front Panel.
Figure 2.7: Draft Hood Attachment
Figure 2.8: Label & Rating Plate Locations
BOILER PLACEMENT & ASSEMBLY
11
A. CHIMNEY OR VENT
1. Inspect the existing chimney or vent system. Make
sure it is in good condition. Inspect chimney liner
and repair or replace if necessary.
2. The vent system and installation must be in
accordance with Venting of Equipment chapter of
the current edition of the National Fuel Gas Code,
ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54, or applicable provisions of
the local building codes.
3. Chimney/Vent Operation: The vent system must be
sized and installed to provide the draft needed to
remove all combustion products. If the vent system
does not provide enough draft, combustion products
will spill into the building from the draft hood relief
opening. If spillage of combustion products occurs,
check the vent system, the combustion and
ventilation openings and make sure the boiler room
is never under negative pressure.
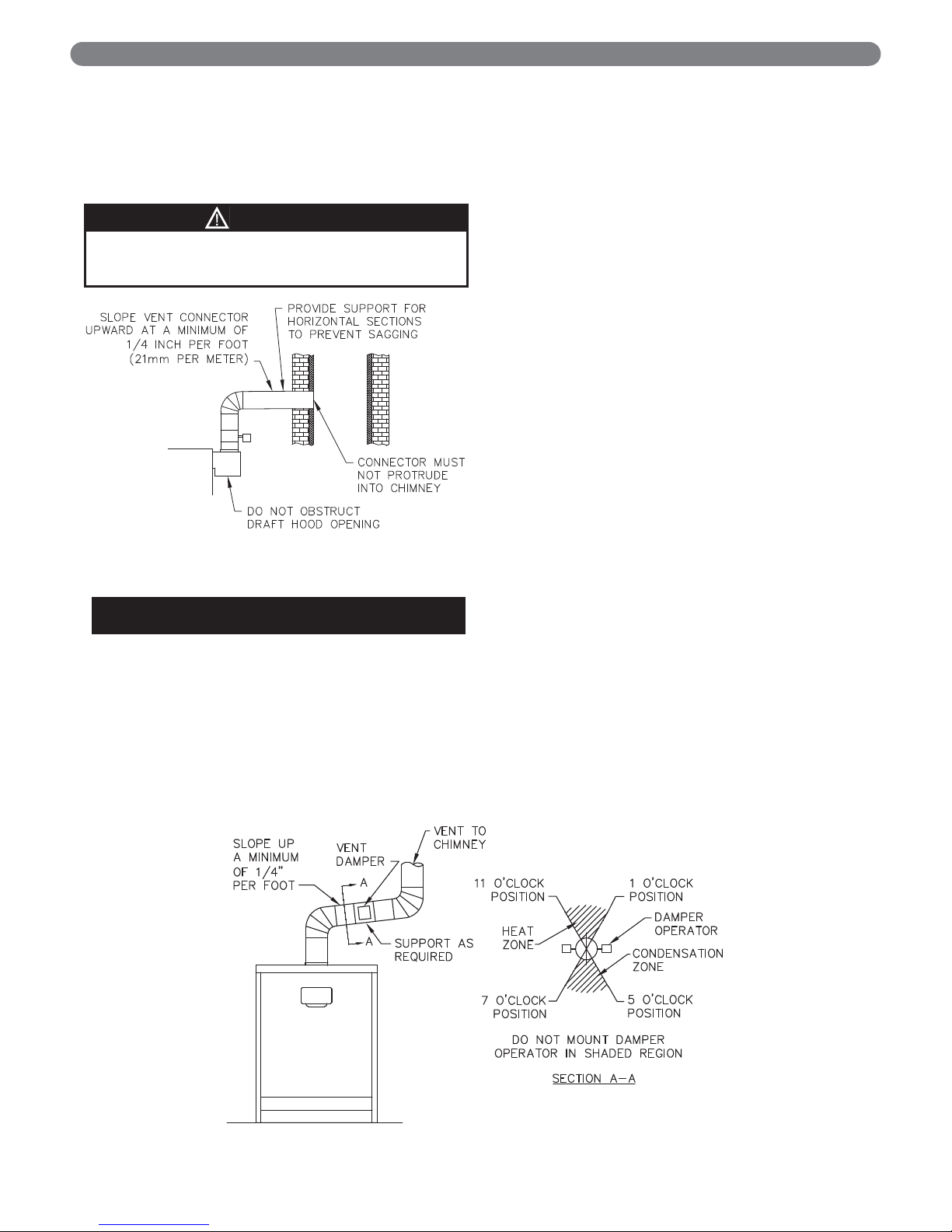
4. Vent Connection to Boiler:
a. Support the weight of the vent system
independently of the boiler draft hood. The draft
hood is not designed to carry structural loading.
b. Provide support of the vent connector
(breeching) at maximum 12 foot intervals to
prevent sagging and to provide a minimum
upward slope of 1/4" per foot.
c. Do not connect the vent for this boiler into any
vent system which operates with positive
pressure.
d. The vent connector must be single wall steel or
Type B double wall vent pipe. The vent
connector must be Type B double wall if it is
located in or passes through cold areas. The vent
connector must extend into, but not beyond, the
inside wall of the chimney.
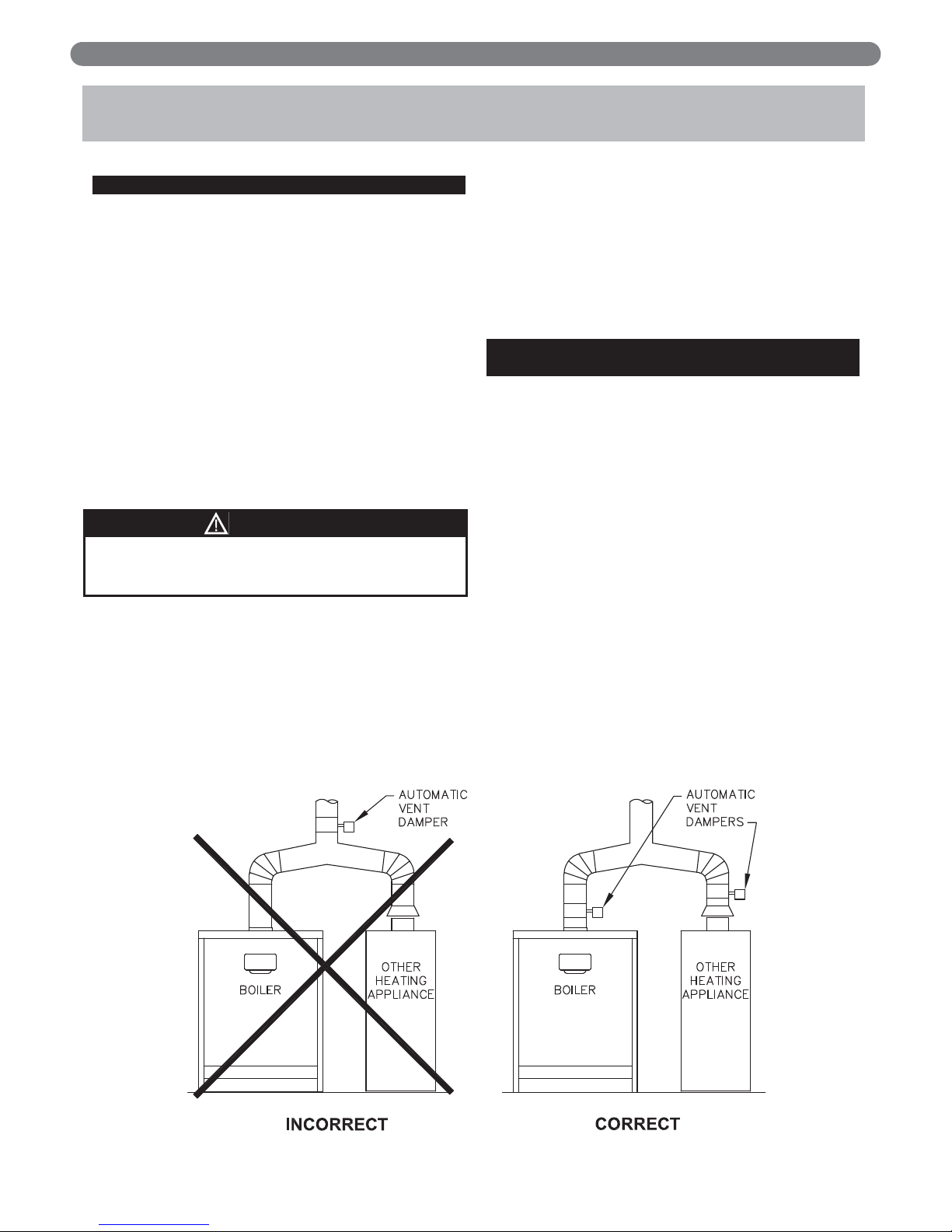
B. AUTOMATIC VENT DAMPER
INSTALLATION – GENERAL
1. Do not use one vent damper to control two or more
heating appliances. See Figure 3.1.
2. Follow these and the installation instructions
included with the vent damper. Observe the cautions
and warnings that accompany all instructions.
3. Provide minimum 6 inch (152 mm) clearance
between automatic vent damper and combustible
construction. Increase clearance if required by vent
damper manufacturer’s instructions. Provide
adequate space for vent damper access and service.
4. The automatic vent damper can be mounted directly
onto the draft hood outlet or in vent piping close to
the boiler.
See Figure 3.2 for installation with vent damper
mounted in vertical position. See Figure 3.3 for
installation with vent damper mounted in horizontal
position. Mount the unit to avoid excessive heat on
the operator or condensation drips into the operator.
Figure 3.1: Venting Multiple Appliances
Failure to provide adequate venting can result in
severe personal injury or death.
WARNING
3. VENTING
12
VENTING
a. Orient the vent damper operator to facilitate
connection of the vent damper harness to
knockout on right side of boiler.
b. Orient vent damper direction arrow in direction
of vent gas flow. Direction arrow must be visible
from front of boiler.
C. BOILER REMOVAL FROM COMMON
VENTING SYSTEM
When an existing boiler is removed from a common
venting system, the common venting system is likely to
be too large for proper venting of the remaining
appliances connected to it.
At the time of removal of an existing boiler, follow these
steps with each appliance remaining connected to the
common venting system placed in operation, while the
other appliances remaining connected to the common
venting system are not in operation:
a. Seal any unused openings in the common venting
system.
b. Visually inspect the venting system for proper size
and horizontal pitch and determine there is no
blockage or restriction, leakage, corrosion and other
deficiencies which could cause an unsafe condition.
c. Insofar as is practical, close all building doors and
windows and all doors between the space in which
the appliances remaining connected to the common
venting system are located and other spaces of the
building. Turn on any clothes dryers and any
appliance not connected to common venting system.
Turn on any exhaust fans, such as range hoods and
bathroom exhausts, so they will operate at maximum
speed. Do not operate a summer exhaust fan. Close
fireplace dampers.
d. Place in operation the appliance being inspected.
Follow the lighting instructions. Adjust thermostat so
appliance will operate continuously.
e. Test for spillage at the draft hood relief opening after
5 minutes of main burner operation. Use the flame
of a match or candle, or smoke from a cigarette,
cigar, or pipe.
f. After it has been determined that each appliance
remaining connected to the common venting system
properly vents when tested as outlined above, return
doors, windows, exhaust fans, fireplace dampers and
any other gas-burning appliance to their previous
conditions of use.
g. Any improper operation of the common venting
system should be corrected so that the installation
conforms with the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1/NFPA 54 or CAN/CGA B149 Installation
Codes. When resizing any portion of the common
venting system, the common venting system should
be resized to approach minimum size as determined
using the appropriate tables located in the chapter
“Sizing of Category I Venting Systems,” of the
National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54 or
CAN/CGA B149 Installation codes.
Figure 3.2: Venting with Vent Damper in
Vertical Position
Figure 3.3: Venting with Vent Damper in Horizontal Position
Damper must be in open position when appliance
main burner is operating.
CAUTION
13
BOILER PIPING
A. WATER BOILER PIPING – SINGLE
BOILER
1. Refer to the PB Heat Water Installation Survey and
Hydronics Institute Residential Hydronic Heating
Installation Design Guide.
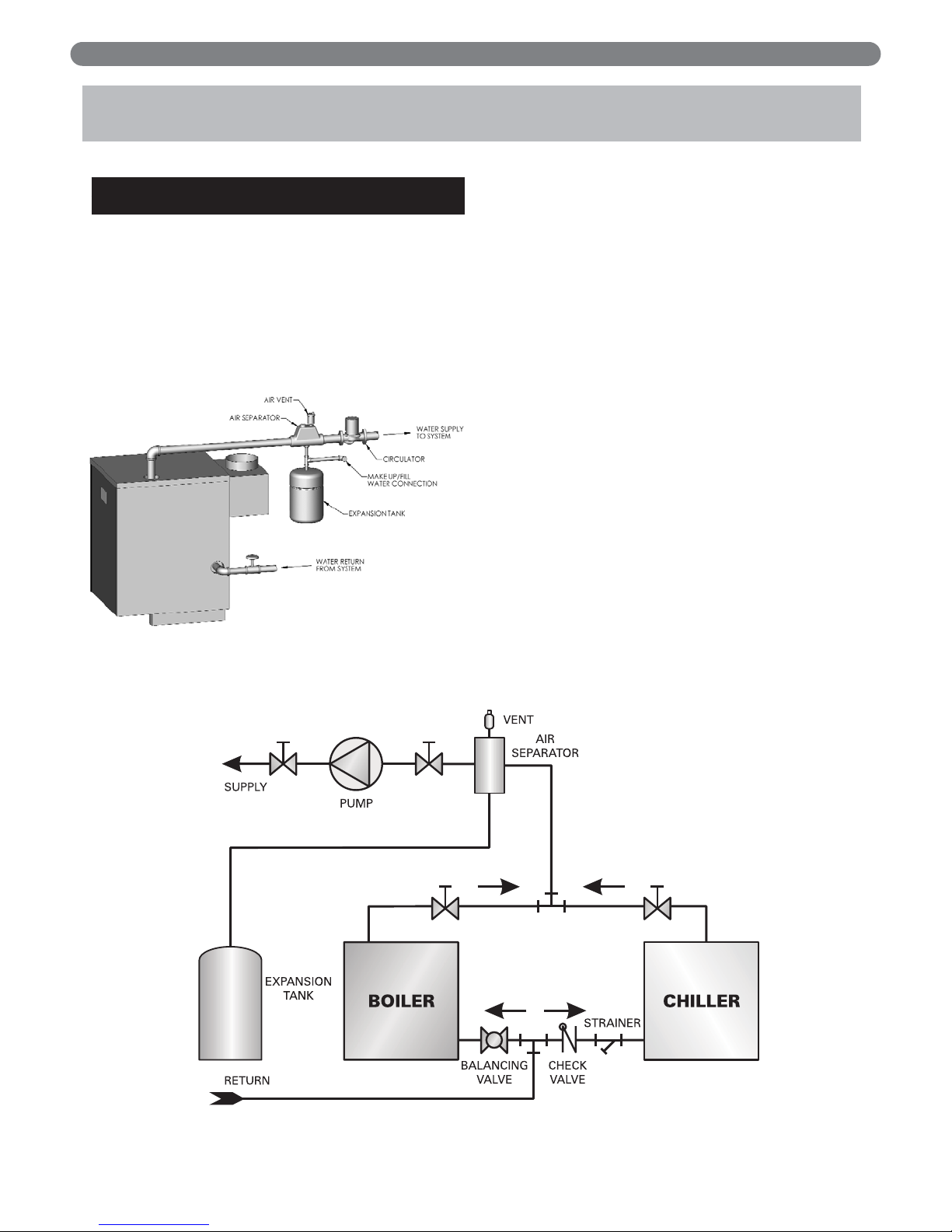
2. Figure 4.1 shows typical supply and return piping for
a boiler system. If the system expansion tank is
located on the boiler loop, it should be located on the
supply side of the boiler with the system circulator
pumping away from the expansion tank connection.
3. If the boiler is piped in a secondary loop separate
from the system expansion tank, the boiler circulator
should be located on the return side of the boiler
pumping away from the common piping.
4. Return water should not reach the boiler return
connection at less than 130°F under normal
operating conditions. If the system return
temperature is expected to be below 130°F the boiler
should be piped in a secondary loop with a bypass
arrangement to assure water returning to the boiler is
above 130°F. For more information on bypass piping
consult the PB Heat Water Installation Survey.
5. If the boiler and distribution system is used in
conjunction with a refrigeration system, pipe the
chilled medium in parallel with the boiler and
provide isolation valves to prevent chilled water form
entering the boiler. See Figure 4.2.
6. If the boiler is connected to a heating coil in a forced
air combination heating and cooling system, install
flow control valves to prevent gravity circulation of
the boiler water during cooling cycles.
7. A hot water boiler installed above radiation level or
as required by the Authority having jurisdiction, must
be provided with a low water cut-off device either as
part of the boiler or at the time of installation.
4. BOILER PIPING
Figure 4.1
Figure 4.2: Piping to Isolate Boiler from Chilled Medium on Chiller Systems

14
BOILER PIPING
B. WATER BOILER PIPING – MULTIPLE
BOILERS
Refer to the PB Heat Water Installation Survey and
Hydronics Institute Residential Hydronic Heating
Installation Design Guide for guidance on multiple boiler
installations.
C. STEAM BOILER PIPING – SINGLE
BOILERS
1. Refer to the PB Heat Steam Installation Survey and
Hydronics Institute Residential Hydronic Heating
Installation Design Guide for guidance.
2. Install steam supply pipes as shown in Figure 4.3 for
Model 63-03 to 64-07 and Figure 4.4 for Model 64-08
to 64-12. The minimum quantity and size of supply
pipes are indicated in Table 4.1.
3. Pipe the steam header a minimum of 24" above the
normal water line using swing joints to attach the
risers into the steam header.
4. Use threaded fittings for manifold piping to provide
flexibility for thermal expansion.
5. Connect the equalizing line as shown in Figure 4.3
or 4.4 assuring that the reducing elbow is facing
down and that any bushings are vertical to prevent
water build-up in the steam header.
Figure 4.3: Steam Piping – Single Supply
Connection
Use swing joints to attach to the header to avoid
damage to the boiler due to thermal expansion and
contraction of steam header pipe.
NOTICE
Figure 4.4: Steam Piping – Dual Supply
Connections
• Do not use bushings or concentric reducers in the
horizontal header piping. This will prevent water
from dropping into the equalizer and cause water
carryover into the steam piping.
• Do not reduce the size or number of steam supply
risers below the minimum shown in Table 4.1.
Insufficient or undersized risers can cause damage
to the boiler.
• Do not use a bullhead tee to provide steam supply
to the system. This will cause water carryover into
the steam piping.
NOTICE
Use Threaded Fittings for Manifold Piping
Use Threaded Fittings for Manifold Piping
 Loading...
Loading...