Page 1

Parallels
Parallels Business
Automation Standard
Provider's guide
Release 4.3
(c) 1999-2013
Page 2

Copyright Notice
Parallels IP Holdings GmbH
Vordergasse 59
8200 Schaffhausen
Switzerland
Tel: + 41 52 632 0411
Fax: + 41 52 672 2010
Copyright © 1999-2013 Parallels IP Holdings GmbH. and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This product is protected by United States and international copyright laws. The product's underlying
technology, patents, and trademarks are listed at http://www.parallels.com/trademarks
Microsoft, Windows, Windows Server, Windows NT, Windows Vista, and MS-DOS are registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Mac is a registered trademark of Apple, Inc.
All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3
Contents
Preface 10
About This Guide ....................................................................................................................................... 10
Audience .......................................................................................................................................... 10
Typographi cal Convent i ons ............................................................................................................. 10
Feedback .......................................................................................................................................... 11
Meet the Parallels Business Automation - Standard 12
Parallels Business Automation - Standard Advantages .............................................................................. 12
Parallels Business Automation - Standard Users ........................................................................................ 15
Browsers Compatible with Pa rallels Business Automation - Standard ...................................................... 15
Connecting to Parallels Business Automation - Standard Browser-Based Tools ....................................... 16
Parallels Business Automation - Standard I nterface Features .................................................................... 16
Navigation................................................................................................................................................... 16
Main Screen ................................................................................................................................................ 17
Adding a Comment to the Parallels Business Automation - Standard Object ............................................ 18
General Configuration of Parallels Business Automation - Standard 19
Checking Provider Account Contacts ......................................................................................................... 20
Setting Up Access Permission s for Parallels Business Automation - Standard Users ................................ 21
Setting Up Messenger and S/MIME Signing for E-mail ............................................................................ 23
Selecting Regional Settings ........................................................................................................................ 24
Language ......................................................................................................................................... 24
Default Time Zone .......................................................................................................................... 24
First Day of Week ........................................................................................................................... 24
Currency .......................................................................................................................................... 24
Available Languages ....................................................................................................................... 25
Customizing the Onscreen Help in Control Panel ...................................................................................... 25
Securing the Parallel s Business Automation - Standard Tools Using SSL ................................................. 26
Getting the SSL Certificate .............................................................................................................. 27
Enabling SS L for Parallels Business Automation - Standard Tools ................................................ 27
Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 28
Registering Virtuozzo or Plesk Nodes ........................................................................................................ 30
Plesk Nodes Specific Settings ..................................................................................................................... 32
Virtuozzo Nodes Specific Settings ............................................................................................................. 35
Managing Parallels Server Nodes ............................................................................................................... 35
Registering Parallels Server Nodes ................................................................................................. 36
Managing Virtual Machines ............................................................................................................ 37
Managing Parallels Automation Services ................................................................................................... 38
Parallels Automation Integrati on Guidelines ................................................................................... 39
I. Configuring PA Node................................................................................................................... 39
II. Registering PA Node in PBAS. .................................................................................................. 39
III. Creating Service Template(s) in POA. ...................................................................................... 39
IV. Synchronizing POA Service Templates. ................................................................................... 39
V. Creating POA Hosting Plan. ....................................................................................................... 39
Managing Parallels Automation Nodes ........................................................................................... 40
Managing PA Subscriptions ............................................................................................................ 51
PA Synchro nization Setup ............................................................................................................... 52
Page 4

Sitebuilder Management ............................................................................................................................. 52
Sitebuilder Services Provisioning .................................................................................................... 54
Connecting Sitebuilder Nodes ......................................................................................................... 56
Setting Up Sitebuilder ..................................................................................................................... 57
Managing Sitebuilder Nodes ........................................................................................................... 58
Managing Sitebuilder Plans ............................................................................................................. 59
Managing Sitebuilder Sites .............................................................................................................. 60
Managing Dedicated Servers ...................................................................................................................... 61
Registering Data Centers ................................................................................................................. 62
Registering Racks in Data Centers .................................................................................................. 62
Registeri ng Switches ....................................................................................................................... 63
Registering Dedicated Server .......................................................................................................... 64
Activating Dedicated Server Subscription ....................................................................................... 66
Managing Nodes by Groups ....................................................................................................................... 67
Selling Licenses .......................................................................................................................................... 68
Managing Key Administrator Plug-Ins............................................................................................ 69
Selecting License Classes to Provide .............................................................................................. 70
Managing Licenses .......................................................................................................................... 71
Allocating IP Addresses .............................................................................................................................. 76
Supervising Service Le vel .......................................................................................................................... 77
Configuri ng Traffic Classes ........................................................................................................................ 78
Setting Up Domains Registration 80
How to Start Registering Dom a ins Online ................................................................................................. 80
Configuri ng Domain Registratio n Plug-Ins ................................................................................................ 81
Top Level Domains Assignment ................................................................................................................ 82
Setting Registrar Prices ............................................................................................................................... 83
Selecting Both the Default Domain and the Domain for Trial Containers Hostnames ............................... 86
Allowing Domain Transfer P er Registrar TLDs ......................................................................................... 87
Configuri ng Default Records for Zone Files (DNS Templates) ................................................................. 88
Specifying Name Server Sets...................................................................................................................... 89
Registering Name Servers ............................................................................................................... 89
Managing Name Server ................................................................................................................... 90
Changing Name Server Type........................................................................................................... 90
Registering Internationalized Domain Names ............................................................................................ 92
Adjusting D NS General S ettings ................................................................................................................ 93
Managing Contacts Used for Domain Registration .................................................................................... 96
Specifying Whois Servers ........................................................................................................................... 97
Setting Up HTTP Whois Search ...................................................................................................... 97
Viewing Incoming and Outgoing Domain Registration E-mails ................................................................ 98
Setting Up Billing System 99
Understanding the Parallels B usiness Automation - Standard Billing System ......................................... 100
Calculations for the Services Provided .......................................................................................... 102
System-Wide Billing Settings ................................................................................................................... 102
Invoice Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 103
Consolidated Invoices Processing ................................................................................................. 105
Pricing and Discounts ............................................................................................................................... 107
Managing Prices ............................................................................................................................ 108
Setting Credit Terms ................................................................................................................................. 109
Configuri ng Taxation ................................................................................................................................ 111
Configuri ng Fraud Pr otection ................................................................................................................... 112
Adjusting Anti-Fraud Plug-ins General Settings ........................................................................... 112
Managing Accounts and Documents Held Up by Anti-Fraud Filters ............................................ 113
Configuri ng Credit Car d Payment Plug-ins .............................................................................................. 115
What Payment Plug-Ins are Available ........................................................................................... 115
How to Configure a Payment Plug-In ........................................................................................... 115
Page 5
Activatin g Payment Plug-Ins and Making Them Available for Resellers ..................................... 115
Security With CVV and AVS ........................................................................................................ 116
Configuri ng Bank Tra nsfer Payment Plug-ins .......................................................................................... 117
Using Specific Accounting ....................................................................................................................... 118
Russian Accounting Options ......................................................................................................... 119
Managing Payment Methods 121
Configuri ng Encryption for Payment Methods ......................................................................................... 122
Managing Recurring P ayments ................................................................................................................. 123
How a Payment Method Can be Added .................................................................................................... 124
Managing Credit Cards ............................................................................................................................. 124
How to Start Accepting Credit Card s ............................................................................................ 125
Managing Bank Accounts ......................................................................................................................... 126
How to Start Accepting Bank Transfers ........................................................................................ 126
Adding Bank Account Manually ................................................................................................... 126
Changing Bank Account Attributes in Parallels Business Automation - Standard Database ........ 127
Viewing Transaction Log ......................................................................................................................... 128
Removing a Payment Method ................................................................................................................... 128
Managing Hosting Plans 129
Hosting Plans Categories .......................................................................................................................... 130
Hosting Plan Groups ................................................................................................................................. 131
Hosting Plan Types ................................................................................................................................... 133
Hosting Plan Resources ............................................................................................................................ 134
Creating Hosting Plans ............................................................................................................................. 135
Creating POA Hosting Plan ........................................................................................................... 138
Upgrading Hosting Pla ns .......................................................................................................................... 140
Adding Custom Services to a Ho sting Plan .............................................................................................. 142
Managing Hosting Pla ns by Versions ....................................................................................................... 144
Creating a Hosting Plan on the Basi s of an Existing One ......................................................................... 145
Promoting Hosting Plans .......................................................................................................................... 145
Calculations for the Hosting Plan Change ................................................................................................ 146
Managing Online Store 147
New Store Configuration Basics ............................................................................................................... 150
Hosting Plans Presentation and Purchase Wizard ......................................................................... 150
Domains Registration Feature s ...................................................................................................... 154
Opening the New Store.................................................................................................................. 154
Switching Between the Old and the New Store ............................................................................. 155
Enable New Store for Resellers ..................................................................................................... 155
Page 6

Configuri ng and Opening Store ................................................................................................................ 156
Managing Resellers' Stores ....................................................................................................................... 156
For the Old Store: Customizing Store U sing File Manager ...................................................................... 157
Managing Accounts 163
Users ......................................................................................................................................................... 164
User Roles ................................................................................................................................................. 164
Permissions ............................................................................................................................................... 164
Creating Accounts .................................................................................................................................... 165
Entering Use r Agreeme nt ......................................................................................................................... 166
Assigning a Tax Zone ............................................................................................................................... 168
Granting a Discount .................................................................................................................................. 169
Adjusting Account Balance ...................................................................................................................... 170
Viewing the Account Billing History ....................................................................................................... 170
Managing the Set of Events a Customer Receives E-Mail Notifications .................................................. 171
Managing Account Contacts by Versions ................................................................................................. 172
Changing a Customer Billing Da y ............................................................................................................ 173
Managing Resellers 175
Entering Reseller Agr eement .................................................................................................................... 175
Managing Pre-Defined Reseller Configurations ....................................................................................... 176
Creating Reseller Account ........................................................................................................................ 177
Assigning Partner Discount to Reseller Account ...................................................................................... 180
Assigning Discount to Reseller Account .................................................................................................. 181
Hiding Reseller's URL .............................................................................................................................. 182
Creating Hosting Plan for Rese lle r ........................................................................................................... 183
Managing Receivables 184
Understanding Parallels B usiness Auto mation - Standard Billing Wor kflow .......................................... 185
Viewing and Operating Receivables ......................................................................................................... 186
Processing Offline P ayments and Changing Payment Method ..................................................... 187
Increasing Accounts Balance by Online Payment or Bank Transfer ............................................. 188
Editing Orders and Invoices .......................................................................................................... 189
Issuing Invoices Manua lly ............................................................................................................. 189
Reopening Cutoff Invoi ces ............................................................................................................ 190
Processing Documents Paid by Credit Cards ............................................................................................ 190
Setting Transactions Approval and Processing Mode .................................................................. 191
Page 7

Processing Document s Paid by Bank Transfers........................................................................................ 193
Refunding Documents Paid by Credit Cards ............................................................................................ 194
Recreating Orders With Updated Tax Rates ............................................................................................. 194
Managing Statements ................................................................................................................................ 195
Printing out Documents ............................................................................................................................ 196
Managing Subscriptions 197
Understanding Subscription Types and Statuses ...................................................................................... 198
Renewing Subscriptions ........................................................................................................................... 200
Managing Subscription Grace Period ....................................................................................................... 201
Terminating Subscriptions ........................................................................................................................ 202
Changing Account for Subscription .......................................................................................................... 203
Upgrading Dedicated Third-Party Subscriptions ...................................................................................... 204
Sending Subscription Notification ............................................................................................................ 204
Synchronizing Customer System With Subscription ................................................................................ 205
Managing Resold Subscriptions ............................................................................................................... 205
Managing Subscription Attrib utes ............................................................................................................ 209
Managing Payables in Reseller Control Center 210
Viewing Balance of Reseller Account Payable ........................................................................................ 211
Increasing Reseller Account Balance ....................................................................................................... 211
Managing Financial Documents Issued by HSP ....................................................................................... 212
Managing Orders ........................................................................................................................... 212
Paying HSP Invoices ..................................................................................................................... 213
Viewing Payments ......................................................................................................................... 213
Viewing Adj ust me nts .................................................................................................................... 214
Viewing Statements Issued by HSP .......................................................................................................... 214
Viewing Billing Reports 215
Accountin g R eports .................................................................................................................................. 216
Taxation Reports ....................................................................................................................................... 217
Managing Containers 218
Managing Both OS and Application Templates for Containers................................................................ 218
Managing Standard Templates ...................................................................................................... 219
Managing EZ Templates ............................................................................................................... 220
Importing Templates from Hardware Nodes ................................................................................. 221
Removing Application Template from Hardware Node ................................................................ 221
Application Template Prop e rties ................................................................................................... 222
OS Templates ................................................................................................................................ 226
Managing Container Applications Upgrades ................................................................................. 227
Creating More Application T emplates .......................................................................................... 227
Setting Up Both Trial Containers and Co ntainers Backups Creatio n ....................................................... 228
Keeping Container Root Passwords in Parallels Business Automation - Standard Database ................... 228
Backups Management ............................................................................................................................... 229
Creating Container .................................................................................................................................... 230
Operating Co nta i ner .................................................................................................................................. 232
Migrating Container ...................................................................................................................... 234
Repairing Container ....................................................................................................................... 236
Recreating Container With Ability to Change OS ......................................................................... 237
Page 8
Managing Plesk Clients and Domains 238
Setting Up Trial Plesk Do mains Cre a tion ................................................................................................. 239
Plesk Applications Vault Mana gement ..................................................................................................... 240
Creating a Plesk Domain .......................................................................................................................... 242
Creating a Plesk Client ............................................................................................................................. 243
Managing Domains 245
Configuri ng Domain Registratio n Plug-Ins .............................................................................................. 247
Understanding Domains Management in Parallels Business Automat ion - Standard............................... 249
Registeri ng a Domain fr om Control Center .............................................................................................. 251
Selecting Both the Default Domain and the Domain for Trial Containers Hostnames ............................. 252
Promoting Domains Registration .............................................................................................................. 253
Transferring or Registering Domains in Parallels Business Automation - Standard ................................ 254
Sorting Out D omains Transferred Away .................................................................................................. 257
Domain General Information .................................................................................................................... 258
Managing DNS Records Suppliers ........................................................................................................... 261
Managing a Domain Zone File ................................................................................................................. 261
Updating Domain Owner Contacts ........................................................................................................... 261
Managing SSL Certificates 262
Configuri ng SS L Cert i fica tes Plug-Ins ..................................................................................................... 263
Managing SSL Certificates Pro visioning .................................................................................................. 264
Editing or Re-Issuing Certifica te ................................................................................................... 265
Managing Certificate Contacts ...................................................................................................... 268
Viewing SSL Certificates Transaction Log .............................................................................................. 269
Support and Administration 270
Using the Problem Viewer ........................................................................................................................ 270
Trouble Ticket System .............................................................................................................................. 271
Configuri ng Parallels Business Automation - Standard Trouble Tic ket Syste m ........................... 271
Using the Screens Viewer ......................................................................................................................... 273
Using the Mass Mailer .............................................................................................................................. 273
Managing Parallels Business A utomation - Standard Objects Description Templates ............................. 274
Managing Events ...................................................................................................................................... 275
Service Logging In to Resellers and Customers Tools ............................................................................. 277
Using the Maintenance Mode for your Hardware Nodes ......................................................................... 277
Managing the User Password Strength ..................................................................................................... 277
Updating Parallels Business Automation - Standard ................................................................................ 278
Monitoring the Vital Services Status ............................................................................................. 280
Checking Paralle ls Business Automation - Standard Database Integrity .................................................. 281
Setting the Statistics Storage Per iod ......................................................................................................... 283
Tasks Management ................................................................................................................................... 283
Viewing Log Files .................................................................................................................................... 284
Log Level Set tings ......................................................................................................................... 284
Using the Action Log .................................................................................................................... 285
Parallels Business Automation - Standard Profiling ...................................................................... 286
XML-Based Data Import and Export........................................................................................................ 286
Resolving Data Conflicts 287
Resolving Container Subscript ions Registration Conflicts ....................................................................... 288
Synchronizing the Plesk Subscription on a Node and in Parallels Busi ness Auto mation - Standard
Database .................................................................................................................................................... 289
Resolving Parallels Automatio n Conflicts ................................................................................................ 290
Resolve PA Subscriptions not Registered in PBAS ...................................................................... 291
Page 9
Resolve PA Subscriptions Registere d in PBAS but Absent in PA ................................................ 292
Marketing and Affiliate Programs 293
Managing Campaigns ............................................................................................................................... 293
Configuri ng Ca mpa i gns ................................................................................................................. 294
Managing Affiliates ....................................................................................................................... 299
Managing Affiliates Payment Requests ......................................................................................... 303
Viewing Campaigns Report ........................................................................................................... 304
Setting Up External Payments Li mitations .................................................................................... 305
Configuri ng your Store to Collect Referrals Statistics .............................................................................. 305
Customizing the Parallels Business Automation - Standard Tools Appearance ....................................... 306
Customizing Customer Control Panel Skin ................................................................................... 307
Customizing Provide r Control Center Skin ................................................................................... 308
Applying S kins .............................................................................................................................. 310
Integration and Customization Opportunities 311
Parallels Business Automation - Standard API and Customization .......................................................... 311
Application Templates Creati on ............................................................................................................... 312
Parallels Business Automation - Standard Internal Licensing 313
Installing License Certificates................................................................................................................... 314
PBAS License Details ............................................................................................................................... 315
Getting Technical Support 317
An Overvie w of Parallels Technica l Support............................................................................................ 317
Questions for Technical Suppor t .............................................................................................................. 317
How to Send Support Questions ............................................................................................................... 318
Index 319
Page 10
10
About This Guide .................................................................................................................. 10
Items you must select, such
as menu options, command
Titles of chapters, sections,
C
HAPTER
1
Preface
In This Chapter
About This Guide
This Guide describes the most important and frequently-used Parallels Business Automation Standard working scenarios including initial settings for the system.
Note: The PDF-version of this Guide is an overview of the Parallels Business Automation Standard overall functionality and is not to be used as a thorough howto. For details see contextsensitive HTML help (the Help link at the upper right corner of every screen).
Audience
This gu ide is addressed to Hosting Service Providers and helps both to evaluate the product and
get acquainted with Parallels Business Automation - Standard.
T ypographical Conventions
Before you start using this guide, it is important to understand the documentation conventions
used in it.
The following kinds of formatting in the text identify special information.
Formatting convention Type of Information Example
Special Bold
buttons, or items in a list.
and subsect ions.
Go to the System tab.
Read the Basic Administration
chapter.
Page 11

Preface 11
Italics
Used to emphasize the
importance of a point, to
introduce a term or to
designate a command line
is to be
The names of commands,
The license file is located in
Preformatted
other programming
# ls –al /files
Preformatted Bold
What you type, contrasted
screen computer
# cd /root/rpms/php
Names of keys on the
Key combinations for which
the user must press and hold
Monospace
placeholder, which
replaced with a real name or
value.
files, directories, and do main
names.
The system supports the so
called wildcard character
search.
the
http://docs/common/
licenses directory.
CAPITALS
KEY+KEY
On-screen computer output in
your command-line sessions;
source code in XML, C++, or
languages.
with onoutput.
keyboard.
down one ke y and the n press
another.
total 14470
SHIFT, C TRL, ALT
CTRL+P, ALT+F4
Feedback
If you have found a mistake in this guide, or if you have suggestions or ideas on how to improve
this guide, please send your feedback using the online form at
http://www.parallels.com/en/support/usersdoc/. Please include in your report the guide's title,
chapter and section titles, and the fragment of text in which you have found an error.
Page 12

12
Parallels Business Automation - Standard Interface Features............................................... 16
Parallels Plesk Control Panel
and Parallels Plesk Sitebuilder
Parallels Plesk Sitebuilder
C
HAPTER
2
Meet the Parallels Business Automation Standard
Parallels Business Automation - Standard is an end-to-end solution for h os ting service providers
(HSPs) and Internet Data Centers covering full life-cycle of HSP/IDC operations. Parallels
Business Automation - Standard allows HSPs to drastically decrease the cost of operating
hosting business while increasing revenues, developing new reseller channels, and improving
usage of hardware and personnel resources.
In This Chapter
Parallels Business Automation - Standard Advantages ........................................................ 12
Parallels Business Automation - Standard Users .................................................................. 15
Browsers Compatible with Parallels Business Automation - Standard ................................ 15
Connecting to Parallels Business Automation - Standard Browser-Based Tools ................. 16
Parallels Business Automation Standard Advant ages
Parallels Business Automation - Standard includes everything a company needs to run a
successful and profitable hosting business from advanced technology and tools to manage your
servers and overall infrastructure to billing, sales channel management, and e-commerce
application:
The full range of services supported:
Domain registration
Plesk Domain hosting
Virtuozzo Container hosting
licenses
support
Dedicated servers for resellers
Dedicated or Co-location
Miscellaneous
Page 13

Meet the Parallels Business Automation - Standard 13
Powerful Container
IPs allocation and DNS
Integrated trouble ticketing and
Maintenance automation and
Discounts, promotions, coupon
Customizable notifications and
Credit Cards processing through over 30 payment gateways (new added
Complete infrastructure management:
management
administration
Flexible self-provisioning
Integrated complete billing solution:
Customizable online store
Country-specific accounting
Automated recurring invoicing
Private label resellers
monthly):
Server-/client-side backups
External Helpdesks support
more
codes
Taxation with tax exemption
Automated upgrades/downgrades
more
integrated with fraud screening
flexible manual approval rules
refunds, reversals, credits
sensitive data is encrypted
delayed capture
CVV/AVS verification and more
Page 14

Meet the Parallels Business Automation - Standard 14
source and commercial
Application templates creation
Bank transfer payments for German (DTAUS), Spanish (Norma 19), and Netherlands
(ClieOp3) standards: flexible batch management with approval queues.
Domain registrations through over 25 domain registrars (new added monthly):
Wide range of Operating Systems and Applications for Container hosting:
Centralized management
Automated upgrades
Over 50 applications
Easy customization and integration:
Customizable PHP based store
Notifications custom ization
Customizable menu items
Colors, logos, page content
Create your own plug-ins
Redhat, Fedora, Suse, Debian
Open-
applications
Game servers and more
guide
Powerful API
Advanced multi-language
support
XML data export/import tools
Everything in one box!
Page 15
Meet the Parallels Business Automation - Standard 15
Parallels Business Automation Standard Users
The following Account types exist within Parallels Business Automation - Standard:
Provider Account (only one Account of such type can exist). This Account is registered
during Parallels Business Automation - Standard installation and it always has the ID=1. All
registered persons that have role in Provider Account are considered as Provider staff
members with particular access permissions to Parallels Business Automation - Standard
Provid e r C on trol Center. The number of Provider staff members that can concurrently log in
to the Provider Control Center is defined by the Parallels Business Automation - Standard
license.
Reseller Account. Reseller Accounts are registered using the Account Director > Reseller
Manager. The number of Reseller Accounts is defined in the Parallels Business Automation
- Standard License. All registered persons that have role in Reseller Account are considered
as Reseller staff members with particular access permissions to Parallels Business
Automation - Standard Reseller Control Center.
Customer Account. Customer Accounts are being registered using the Account Director >
Customer Manager. Customer Accounts can be of two types: personal or business. All
persons associated with Customer Account have access to Parallels Business Automation Standard Control Panels.
Browsers Compatible with Paral l els Business Automation - Standard
The following browsers are fully compatible with Parallels Business Automation - Standard
web-based tools:
Firefox 3.6 and above
Microsoft Internet Explorer 7 and above
Safari 5.0 and above for Mac
Google Chrome 8.0 and above
Note 1: Pop-up blocking in your browser should be disabled.
Note 2: Session and permanent cookies in your browser should be enabled.
Page 16

Meet the Parallels Business Automation - Standard 16
Connecting to Parallels Business
Automation - Standard BrowserBased Tools
To connect to the Parallels Business Automation - Standard tools, enter into your browser the
Management Node hostname and append the tool index (http://hostname/index). If no
tool index is specified, then nothing to be appended to open the tool:
Tool Tool index
Public Site
Old Online Store hspc
New Online St ore shop
Provider Control Center pcc
Reseller Control Center rcc
Control Panel cp
My Control Panel mycp
The SSL protocol can be enabled separately for each of Parallels Business Automation Standard web-based tools. The SSL configuration is available both in Provider and Reseller
Control Centers.
Note: To connect to the My Control Panel, it is necessary to create a Container subscription, log
in to the Control Panel, then create a user (if System Administrator Control Panel Application is
installed inside Container) or a mailbox in multiple domains (if Workgroup Administrator
Control Panel is installed inside Container). After this you can log in to the My Control Panel
with the e-mail address as a login and a user regula r password.
Parallels Business Automation Standard Inter f ace Features
Navigation
To use one or another Parallels Business Automation - Standard component or tool, please use
the namespace tree located in the left pane.
Control Centers specific:
You can hide/display the namespace tree by clicking on the slider at the vertical bar that
separates the left and the right parts of the screen.
Page 17

Meet the Parallels Business Automation - Standard 17
When you start your Parallels Business Automation - Standard session, the path (chain of links)
appears at the top of the screen. These links provide the "breadcrumb navigation" and show you
the path to your actual location within the Parallels Business Automation - Standard. By
clicking on these links, you can be one or more (depending on your location) levels up.
Main Screen
The right pane of Parallels Business Automation - Standard screen serves for operating
components selected from the namespace tree. The main screen shows the Parallels Business
Automation - Standard Directors' or Managers' dashboards, lists of objects, single objects'
properties, or other related data.
Each Parallels Business Automation - Standard component (Director or Manager) has its own
dashboard. Moreover, the Parallels Business Automation - Standard has its dashboard that may
be considered as 30,000-foot view of tools and operations. So, a dashboard is the Parallels
Business Automation - Standard component 'front-page' that provides you with the most
important statistics and a place to start including:
Shortcuts to the lists of objects.
Information about the number of objects with separate counters for the objects in different
states like Active Accounts, Accounts on Hold, Running Containers, etc.
Shortcuts for the creation of new objects that fall into the functionality of Parallels Business
Automation - Standard component selected.
To facilitate operating the lists of objects you can use:
Search particular item within the list or filter the items by a particular property. The Search
and filter bar is located at the top of each list.
Hide/Show search and filter bars, action bars, tables and create/edit forms sections. Their
hide/show status is retained throughout the session.
Change Sorting Order. To this effect, click on the column-heading you want to sort by. In
this case, the special pointer (small triangle) appears at the top of each column. This triangle
indicates current sorting order: peak-up or peak-down for ascending and descending order
respectively. Repeating click on the same link in column-heading changes sorting order
from ascending to descending (and conversely) within single property.
Change List Size. It is possible to set the listing to 20, 40, or 80 items per page. Appropriate
links are above the list, to the right. Special links for viewing pages (page numbers,
next,last) are also provided and you can find them both at the beginning and the end of the
list.
Export lists to Excel. Parallels Business Automation - Standard allows you to export data
from any list in Parallels Business Automation - Standard to Excel, thus facilitating data
operations. The information is exported from the whole list, not only from the visible part.
For example, if you have set the listing to 40 items per page and the whole list includes 100
entries, you will get an excel format document covering 100 items. The
icon is located above and under the lists.
Set columns visibility. You can choose the columns to be displayed in the list tables by
clicking on the
entries in the drop-down menu. You are also allowed to set the columns order by drag-anddropping the column titles.
icon above and under the list and enabling/disabling the corresponding
Export to Excel
Page 18

Meet the Parallels Business Automation - Standard 18
In order to immediately bring the screen content in correspondence with actual state of affairs,
you can Refresh the screen using the button located at the upper right corner of the screen.
The Help button located at the upper right corner of each screen shows the context-sensitive
HTML help.
Screen ID is located at the upper-right corner of each screen. Screen ID allows to refer to a
screen for customization purposes or in the problem report. In addition, each screen ID is a
clickable link that leads the the Screens Viewer and allows getting a screen alias immediately.
Adding a Comment to the Parallels Business Automation - Standard Object
You can add a free-form comment to almost any of Parallels Business Automation - Standard
object. To this effect click on the Add comment link at the upper-right c orne r of an objec t vie w
form.
Page 19
19
Securing the Parallels Business Automation - Standard Tools Using SSL ........................... 26
C
HAPTER
3
General Configuration of Parallels Business Automation - Standard
When you log in to the Parallels Business Automation - Standard Provider or Reseller Control
Center first time, the Setup Wizard helps you to make the most important initial settings.
Please check the initial configuration of the Parallels Business Automation - Standard
installation:
Submit/edit the company name and sender e-mail address (messenger) used in notifications.
Set data retention rules both for system events (on page 275) and logs (on page 284).
Make the regional settings including the interface language, set the first day of week
(monday or sunday), the default time zone to bound system events and logs, select the
system-wide currency.
Set up secure communications (turn on SSL, generate CSR, install signed secure
certificate).
In addition, to facilitate the operations (like domain registration) performed on behalf of the
default Provider account created in Parallels Business Automation - Standard (for Provider
Control Center users only), it is necessary to check and adjust if needed, the contact information
containing in the default Provider account.
Note: The special Getting Started checklist is provided for Resellers.
In This Chapter
Checking Provider Account Contacts ................................................................................... 20
Setting Up Access Permissions for Parallels Business Automation - Standard Users .......... 21
Setting Up Messenger and S/MIME Signing for E-mail ...................................................... 23
Selecting Regional Settings................................................................................................... 24
Customizing the Onscreen Help in Control Panel ................................................................ 25
Page 20

General Configuration of Parallels Business Automation - Standard 20
Checking Provider Account Contacts
Please fill all the fields in the default Accounts’ profile (contacts, etc.). This is necessary for
successful domains registration since the information from an Account profile is being
transferred to a Registrar if you, for example, decide to register a domain (on page 251) for one
of your own accounts.
Note: Editing the Account profile and contacts does not mean creation of new Parallels
Business Automation - Standard Users. In other words, it does not affect login credentials.
To edit the Provider Account contacts, click the topmost item in the Navigation tree (in the left
pane) and select the Company Profile tab and then click the Contacts tab.
Page 21

General Configuration of Parallels Business Automation - Standard 21
Setting Up Access Permissio ns for
Parallels Business Automation Standard Users
To log in to Parallels Business Automation - Standard, a registered user must have a role in one
of accounts registered in Parallels Business Automation - Standard. This role gains a user
particular access permissions to particular Parallels Business Automation - Standard tools. It is
possible to set permissions only if a user is associated with a particular account. Users that are
not associated with an account cannot log in to Parallels Business Automation - Standard tools.
In Parallels Business Automation - Standard, editable access permissions are set for Control
Center users only. Customers that have access to Control Panel can gain only one role
(Customer Administrator) that allows working in Control Panel, and in this case the set of tools
available depends on the applications included in customer's subscription, but not on the role.
For the clean installation, there is a set of default roles both for Provider and Reseller staff
members (i.e., registered users under Provider or Reseller account).
Provider can edit access permissions for every role and add new roles both for Provider staff
members and Reseller staff m em bers.
Resellers can only view the access permissions set for each Reseller staff role.
Basic Notions
Users
Users (staff members, customers, and resellers) permissions are identified by Accounts. Each
person is associated with one Account and may have different sets of access permissions within
that Account. An Account can have multiple Users associated with it. Staff members are users
registered within the Provider Account.
User Roles
Roles are assigned to a User within the Account. A Role defines a set of access permissions to
the Parallels Business Automation - Standard tools. In the Parallels Business Automation Standard there are three customizable roles for Provider staff members and three for Reseller
staff members. The set of permissions in each Role is defined by Provider. Customers get the
default and non-customizable role of Control Panel Administrator.
Permissions
Permissions are assigned per Role, not per individual user. Permissions are assigned separately
to Roles available for HSP staff members and Resellers.
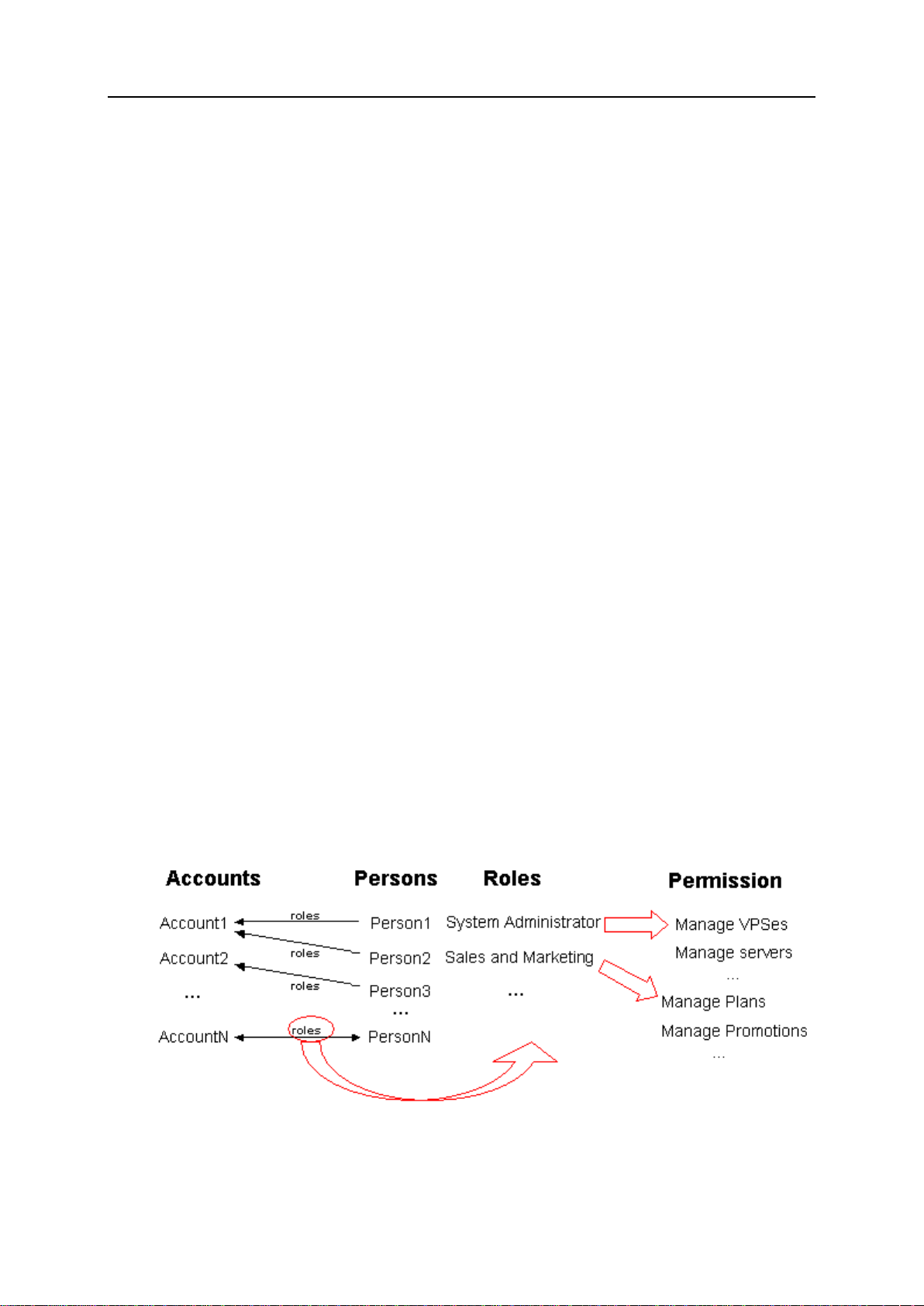
How Permissions Control is Organiz ed
Page 22
General Configuration of Parallels Business Automation - Standard 22
Only Provider can edit access permissions from the Parallels Business Automation - Standard
Provid er contr ol Center. And the Reseller Control Center allows Resellers to view permissions
set for Reseller staff members roles (Operations Administrator, Sales and Marketing,
Accountant, etc.) by Provider.
Resellers can read this section to get acquainted with the Parallels Business Automation Standard security model and the mechanism of roles assignment.
Account is the basic Parallels Business Automation - Standard security notion. All operations
performed within the system are connected with different Accounts. A person registe red wit hin
an Account can gain the certain access permissions to Parallels Business Automation - Standard
tools, depending on the type of Account.
The following Account types exist in Parallels Business Automation - Standard system:
Provider Account (only one Account of such type can exist in your Parallels Business
Automation - Standard system). This Account is created during the Parallels Business
Automation - Standard installation. All persons associated with Provider Account are
considered as Provider staff members with particular access permissions to Parallels
Business Automation - Standard Provider Control Center. The number of Provider staff
members that can concurrently log in to the Provider Control Center is defined by the
Parallels Business Automation - Standard license.
Reseller Account. Reseller Accounts are registered using the Account Director > Reseller
Manager. The number of Reseller Accounts is defined in the Parallels Business Automation
- Standard License. All persons associated with Reseller Account are considered as Reseller
staff members and can be granted a particular role (i.e., access permissions) within Parallels
Business Automation - Standard Reseller Control Center.
Customer Account. Customer Accounts are registered using the Account Director >
Customer Manager. Customer Accounts can be of two types: personal or business. All
persons associated with Customer Account have access to Parallels Business Automation Standard Control Panels.
Access permissions per user role can be set in the Configuration Director > Security Manager.
Roles per account can be assigned registered persons in the Configuration Director > Security
Manager > All Users. Select a user and then select the Accounts tab.
Figure 1: PBAs Security Model
Page 23

General Configuration of Parallels Business Automation - Standard 23
Setting Up Messenger and S/MIME Signing for E-mail
Parallels Business Automation - Standard provides an opportunity to automatically generate and
send e-mail notifications to Provider Administrator and other HSP staff members (for example,
about resources overusage or nodes outages) or to HSP Customers (for example, if Subscription
period is about to expire). The set of events that can be followed by e-mail notifications is readonly and defined in the Event Manager (on page 275). The component that automatically
generates and sends e-mail notifications is called 'Messenger'. Notifications themselves may be
configured for a certain number of events that take place within Parallels Business Automation Standard system and tracked by the Event Manager.
Each message (including automatically generated ones) shall have the 'From' field. For
automatically-sent messages (or notifications) the 'From' field should contain the sender name
and e-mail of a messenger. In addition, you can enable or disable e-mail notifications sending
and select the e-mail messages encoding (character set). Finally, you can configure e-mail
messages S/MIME signing. To set the messenger, go to the Configuration Director >
Miscellaneous Settings > E-Mail Setup.
Page 24

General Configuration of Parallels Business Automation - Standard 24
Selecting Regional Settings
To make regional settings, go to the Configuration Director > Miscellaneous Settings > Regional
Settings.
The regional settings include:
The language;
The default time zone;
The calendar settings (the first day of week);
The system-wide currency.
Selecting languages available for your customers to switch the interface.
Language
The language setting allows you to set the system-wide language of the Parallels Business
Automation - Standard interface.
Default Time Zone
In respect to registration of the events that happen within the system, the Parallels Business
Automation - Standard database is bound to GMT. This means that automatically-generated
notifications and system messages (for example, about subscriptions expiration dates) may
occur to be hardly understandable for the customers that reside in the other time zones.
Thus, the Parallels Business Automation - Standard provides an opportunity of setting different
time zones for different Customers (or Resellers). This can be done during creation of a new
Account or later. The special time zone can be set for each user associated with an Account.
After this, all the time-related data (in Action Log, Event Manager, or automatically-generated
notifications) will be bound to the User’s time zone, without the need for him (or her) to
recalculate time.
However, if most of your prospect customers will reside in the single time zone, it is quite
reasonable to set default time zone for the newly registered persons.
First Day of Week
You can select the day a week starts. For example, this setting is used when setting the weekly
time interval in the Billing Reports (on page 216) view.
Currency
You can set the system-wide currency (for all financial documents and Hosting Plan prices).
Resellers can set the own currency and enter the cross rate between the Provider currency and
Reseller currency. This feature is very useful for selling through international channels as well
as having separate branches in different countries around the world.
Page 25

General Configuration of Parallels Business Automation - Standard 25
Note: Parallels Business Automation - Standard is a single-currency system. In other words
automatic currency recalculations are not available. If you change the system-wide currency,
you will have the unified currency sign, fractional part format, etc., however you will need to
recalculate all prices manually. For example, most of domain-registration Plug-Ins support US
Dollar only as an accounting currency. Thus, in order to update domain-registration prices
correctly the system-wide currency should be US Dollar by prices update, otherwise the new
prices will not be used in Parallels Business Automation - Standard billing.
Available Languages
Check the boxes next to language names to allow your customers to switch the interface into
these languages. The list of languages in this section is comprised of the languages shipped
within separate language packs with Parallels Business Automation - Standard kit and installed
during the Parallels Business Automation system configuration.
Customizing the Onscreen Help in Control Panel
Each screen of the Parallels Business Automation - Standard Control Panels is provided with a
short onscreen help topic.
If needed, you can edit the onscreen help topics for each screen of the Control Panels your
customers use. To this effect, login to the Control Panel (yourcompany.com/cp) using one of the
logins of your Provider Account (as a staff member). In this case, on almost every Control
Panel screen (excluding dashboards) a special "question-mark" icon appears at the upper right
corner of the screen.
Click
text appears. Type the text and click the Update button.
From the Provider Control Center you can hide or show the onscreen help and show/hide in the
source HTML of each Parallels Business Automation - Standard screen the special metatags
used to mark the Parallels Business Automation - Standard screen elements (called controls).
Usage of these metatags is described in details in the Parallels Business Automation - Standard
SDK.
at the screen you want to add a help topic for. The popup window with the help bar
Page 26

General Configuration of Parallels Business Automation - Standard 26
Securing the Par al l els Business Automation - Standard Tools Using SSL
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) provides a level of security and privacy for those wishing to
conduct secure transactions over the Internet. Introduced to the Internet market by Netscape
Communications, the SSL protocol protects HTTP transmissions over the Internet by adding a
layer of encryption . This insures that your transactions are not subject to "sniffing" by a third
party.
SSL provides visitors of your website with the confidence to communicate securely via an
encrypted session. For companies wishing to conduct secure e-commerce, such as receiving
credit card numbers or other sensitive information online, SSL is essential.
Important: SSL Setup for Resellers
SSL certificate is generated per vendor domain name. For provider, this domain name is
Management Node hostname, by default.
Resellers use the same domain as their provider until a reseller URL is not hidden (on page
182). Thus, if a reseller with not hidden URL tries to generate an SSL Certificate request, the
same domain as provider's one will be used. This can corrupt provider's SSL settings. That is
why Parallels Business Automation - Standard does not allow SSL setup for resellers with not
hidden URL - the SSL Setup item is not available in RCC menu in this case.
To make SSL Setup available for a reseller, provider should do the following:
1. Hide reseller URL (on page 182) to provide a reseller with own domain name, which makes
it possible to generate an SSL Certificate for this reseller.
2. Make sure that Reseller Administrator permissions allow managing SSL. To this effect, go
to the Configuration Director > Security Manager > Setup, select Reseller Permissions tab,
and then select Reseller Administrator role. Open the Configuration Director > Miscellaneous
settings item and make sure that the SSL Setup check box is selected. After this, SSL setup
will become available for all resellers in Reseller Control Center.
Page 27

General Configuration of Parallels Business Automation - Standard 27
Getting the SSL Certificate
For SSL to work a valid signed SSL certificate is required. Certificates are a standard way of
binding a public key to a name. Public key encryption is a technique that uses a pair of
asymmetric keys for encryption and decryption. Each pair of keys consists of a public key and a
private key. The public key is made public by distributing it widel y. The private key is never
distributed; it is always kept secret. Data that is encrypted with the public key can be decrypted
only with the private key. Conversely, data encrypted with the private key can be decrypted
only with the public key. This asymmetry makes public key cryptography so useful.
You can generate a self-signed certificate and use it for some time until the certificate “signed”
by a trusted external authority: VeriSign (http://www.verisign.com) or Thawte
(http://www.thawte.com) will be ready.
Note: Netscape and Mozilla browsers automatically detect whether a website uses encryption of
transmitted data or not (as for Internet Explorer, please encourage your website visitors who use
IE to use Internet Explorer 5.0 or later). Thus, if you use a self-signed certificate, your website
visitors will be notified that your website uses encryption, but the authority that signed a
certificate is not recognized. So if you intend to conduct e-commerce at your website, it is better
to obtain an SSL certificate signed by VeriSign or Thawte
To obtain the SSL certificate:
1. Generate Certificate Request in the Configuration Director > Miscellaneous Settings > SSL
Setup > Certificate Request tab.
2. After the Certificate request is generated, you can do one of the following:
Copy the Certificate Request and send it to the Certificate Authority to obtain the signed
Certificate and import it later;
Generate self-signed Certificate and use it for som e time.
3. Restart Apache on your Management Node. Please note that in this case your Management
Node will be not available for some time. So if you already have customers by the moment
of importing the SSL Certificate, your customer's Containers will also become offline till
Apache on your Management Node restarts.
Enabling SSL for Parallels Business Automation - Standard T ools
You can enable the SSL protocol separately for the Provider Control Center and Reseller
Control Canter, Control Panels, website, and your online store.
To enable the SSL protocol, go to the Configuration Director > Miscellaneous Settings > SSL
Setup. Select the the Enable SSL tab. You can enable the SSL prot ocol by c hecking t he Enable
SSL in Parallels Business Automation > Standard Web Tools boxes next to the name(s) of the
web tools (Control Centers, Control Panels, store, etc.).
Page 28

28
C
HAPTER
4
Managing Parallels Business Automation
- Standard Services and Data Center
The tools for your Data Center management are collected under the Service Director.
In spite of the fact that Parallels Business Automation - Standard operates the virtual-server
farm, a Data Center should be understood in common sense, i.e., as a centralized storage facility
to retain database information related to decision-making processes.
In general, Parallels Business Automation - Standard Data Center activity includes the
following:
Servers (Nodes) management.
DNS and IP addresses management.
Service level managem ent.
The hardware configuration to run Parallels Business Automation - Standard includes one
computer for Management Node and two or more computers for Hardware Nodes.
A Management Node is a computer (or a specially configured Virtuozzo Container) used for
management. It runs services for web-based management interface and the database containing
information about customers and services. The Management Node also establishes connection
with domain registrars and payment gates.
A Hardware Node is a computer that runs the software (Virtuozzo, Plesk, etc.) that provides
services for customers or a third-party software (server lease, collocation or dedicated hosting).
Dedicated third-party servers can be grouped into racks. A rack in Parallels Business
Automation - Standard is a logical container, it is just a record in the Parallels Business
Automation - Standard database. Logical racks can follow the actual servers grouping at your
Data Center.
The Parallels Business Automation - Standard Data Center management tools allow managing
the following servers:
Servers that run Parallels Plesk Control Panel that can be used for Plesk Domains or Clients
provisioning for customers and sold as dedicated servers. Plesk servers can also be installed
inside Virtuozzo Containers.
Servers that run Parallels Virtuozzo Containers that can be used for Virtuozzo Containers
provisioning for customers and sold as dedicated servers.
Servers that run Parallels Server Bare Metal that can be used for Virtual Machines
provisioning.
Servers that run Parallels Plesk Sitebuilder allowing a HSP to sell Sitebuilder services.
Page 29

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 29
Third-party servers (server lease, collocation, dedicated servers). These servers cannot be
managed directly from the Parallels Business Automation - Standard web-based interface,
but in this case, the Parallels Business Automation - Standard takes care of all the billing
matters including creation of dedicated subscription, charging a customer, issuing the
renewal order, sending notifications, etc.
In Parallels Business Automation - Standard, the Virtuozzo, Plesk, or Sitebuilder servers are
called Nodes. And third-party servers are called Servers.
Nodes and third-party servers can be registered and managed using the Service Director and,
depending on a server designation, using the Plesk Manager, Virtuozzo Manager, Parallels Server
Manager, Sitebuilder Manager, or Servers Manager for Plesk, Virtuozzo, Parallels Server Bare
Metal, Sitebuilder, or third-party serv ers resp ec tively .
Virtual Plesk Nodes (Parallels Plesk Control Panel installed inside a Virtuozzo Container) are
registered automatically as the Plesk nodes, after the Plesk Virtual Node subscription is
activated.
In This Chapter
Registering Virtuozzo or Plesk Nodes .................................................................................. 30
Plesk Nodes Specific Settings ............................................................................................... 32
Virtuozzo Nodes Specific Settings ........................................................................................ 35
Managing Parallels Server Nodes ......................................................................................... 35
Managing Parallels Automation Services ............................................................................. 38
Sitebuilder Management ....................................................................................................... 52
Managing Dedicated Servers ................................................................................................ 61
Managing Nodes by Groups ................................................................................................. 67
Selling Licenses .................................................................................................................... 68
Allocating IP Addresses ........................................................................................................ 76
Supervising Service Level..................................................................................................... 77
Configuring Traffic Classes .................................................................................................. 78
Page 30

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 30
Registering Virtuozzo or Plesk Nodes
When a Virtuozzo or Plesk node is registered in Parallels Business Automation - Standard, this
means that a connection is established to this node and a certain data exchange is possible
between a node and the Parallels Business Automation - Standard database. To make a node
registration possible, a node must be up and running and available over a network.
Beginning with PBAS 4.1 Virtuozzo 4.6 is fully supported without compatibility mode.
A registered node may become unavailable because of outages on a node itself or network
connection loss. When a registered node becomes available, the connection is re-established
automatically.
It is possible to break the connection to a node (i.e., unregister it) by one click. It this case
connection to a node will remain established, but events on a node will stop synchronizing with
Parallels Business Automation - Standard database and thus, creation of new Containers or
Plesk Clients/Domains from Parallels Business Automation - Standard web-based interface will
become impossible.
Registered Virtuozzo nodes allow a wider range of operations: manage applications installed,
operate Containers (create new, start, stop, delete, etc.), manage Containers backups, manage
trial Containers creation settings, adjust traffic shaping and allow name-based Containers
creation (on page 35). Registered Plesk nodes allow viewing and adding new Plesk Clients or
Domains and setting permissions for trial Plesk Domains creation.
If Plesk Virtual node is registered, it is necessary to:
Make sure that Virtuozzo node that hosts Container for a Plesk Virtual node is registered in
PBAS.
After Plesk Virtual node registration, go to Service Director > Plesk Manger > Nodes, select
the node and:
Select Virtuozzo node name for a Plesk Virtual node from Hardware Node list.
Enter the ID of Virtuozzo Container where Plesk is installed into the CTID field.
To view the list of Virtuozzo or Plesk nodes connected to Parallels Business Automation Standard, click Nodes either on Virtuozzo Manager or Plesk Manager submenu under the Service
Director.
The list of nodes displays the following:
ID - Numerical identifier, assigned to the Hardware Node.
Shortname - Hardware node friendly name.
IP Address - Current IP address assigned to a node.
The number of subscriptions on a Hardware Node:
For Virtuozzo Nodes - the Accts column shows the number of Containers on a node. If
the number of Containers is limited, then the current number and the maximal allowed
number of Containers will be shown, e.g., "40 of 100" means that a node runs 40
Containers of the 100 allowed.
Page 31

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 31
For Plesk Nodes - Domains and Clients columns show the number of Plesk domains
existing on a Node.
New Accts - Whether it is allowed to create more subscriptions on a Node. Green tick
indicates that yes, red cross - that not.
Platform - the software installed on a node.
Version:
For Virtuozzo nodes the full version of the VzAgent running on a node.
For Plesk nodes - the OS installed and the full version of Plesk Server Administrator
installed on a node.
Reg. Status - The current Hardware Node status in respect to its manageability via your
Control Center web-based interface:
Registered - the connection with a Hardware Node was established successfully, a
Hardware Node is fully manageable;
Conflicts - the data found on a node does not correspond to the data existing in Parallels
Business Automation - Standard database or some other problems occurred during
registration. To resolve the data conflicts, you can use the special tool provided in
Parallels Business Automation - Standard - Conflicts Resolver (on page 287).
Unregistered - t he connection with a Hardware Node is not established but a Hardware
Node configuration is stored in the Parallels Business Automation - Standard database.
Such a Hardware Node cannot be managed from Parallels Business Automation Standard web-based interface.
Availability - Current status of a node in respect to establishing connection to it. Unavailable
node usually means some kind of hardware or network problems on a node.
For Virtuozzo node:
SLM - Whether a Virtuozzo node uses a SLM resource management type (Yes) or old-
style UBC or UBC combined with SLM (No).
VSwap - Whether a Virtuozzo node uses a new VSwap memory management type.
For Plesk node:
Physical - Whether a Plesk node is a physical server (Yes) or is installed inside a
Virtuozzo Container (No).
Owner - An Account which owns a Hardware Node, if any.
To register a new node, click the New Node button. Click here to read more about nodes
registration.
Page 32

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 32
Plesk Nodes Speci f ic Settings
A Plesk node properties are grouped under several tabs:
Summary
Availability. Current status of a node in respect to establishing connection to it. Unavailable node
usually means some kind of hardware or network problems on a node.
Registration Status:
Registered - the connection with a Hardware Node was established successfully, a
Hardware Node is fully manageable;
Conflicts - the data found on a node does not correspond to the data existing in Parallels
Business Automation - Standard database or some other problems occurred during
registration. To resolve the data conflicts, you can use the special tool provided in
Parallels Business Automation - Standard - Conflicts Resolver (on page 287).
Unregistered - the connection with a Hardware Node is not established but a Hardware
Node configuration is stored in the Parallels Business Automation - Standard database.
Such a Hardware Node cannot be managed from Parallels Business Automation Standard web-based interface.
Upgrading - the status informs that recently Plesk upgrade took place at a node. In this
case PBAS executes tasks to adjust Plesk subscriptions data. This status occurs
automatically as soon as PBAS detects upgrade at a Plesk node. Applicable to Plesk
nodes only.
Page 33

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 33
Allow new accounts. Whether new Parallels Business Automation - Standard accounts are
allowed to create subscriptions on this node. Green tick - yes, red cross - no. You can change
this setting under the General Settings tab.
Accounts. The number of accounts that currently have subscription(s) on this node.
Plesk Domains. The number of Plesk domains currently existing on this node. Domains are
sorted by hosting plans, such as: the name of hosting plan - the number of domains based on this
hosting plan.
Plesk Clients. The number of Plesk clients currently existing on this node. Clients are sorted by
hosting plans, such as: the name of hosting plan - the number of clients based on this hosting
plan.
General Settings
Here you can:
Transparently log in to the Plesk Admin Control Panel for the node - just click on the Login
to Plesk link.
View or hide Plesk Administrator password. To view password, click on the Show
Password link. To hide the password again, click on the Hide Password link.
To change password, and other settings click the Edit button:
Attention: The Plesk node General Settings form includes some advanced settings: network
configuration and Plesk virtual node (Container) related settings. We do not recommend to
change these settings if you are not absolutely sure what must be entered instead of the existing
values.
Hardware Node name. Here you can edit the Plesk node friendly name (this is not a
hostname, this name is just used in Parallels Business Automation - Standard to refer to the
node.
Allow new accounts. Check this box to allow creating clients or domains on this node for
new Parallels Business Automation - Standard ac counts, i.e., for accounts that do not have
any subscriptions on this node yet. To disallow this, clear the box.
Maximum number of domains. If you want to limit the allowable number of domains to be
created on the node, then enter the maximal allowed number of domains into this field.
Leave the field empty to impose no limitations on the number of domains on this node.
You can type a new Plesk Administrator password for this node into the two fields below
(type and retype the password).
Synchronize DNS. This box defines whether the changes made to DNS configuration on the
Plesk node will be automatically synchronized with Parallels Business Automation Standard DNS (and conversely) or not. We recommend to keep this box checked.
Synchronize domains and clients. This setting enables or disables automated
synchronization of Plesk domains and clients on the node with Parallels Business
Automation - Standard database. If the box is cleared, then synchronization is disabled and
manual creation of Plesk client or domain on the Plesk node will not be noticed by Parallels
Business Automation - Standard. We strongly recommend to keep this box checked.
Network settings:
Page 34

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 34
Hostname. Plesk node hostname. If you are not sure what hostname must be entered,
leave this field as is. If the field contents was unintentionally deleted and you do not
know what to enter instead, you can enter the Plesk node IP address. Later you can
change the IP into the correct hostname. Do not enter the incorrect hostname into this
field, because this will break the transparent logging in to the Plesk Admin Panel from
Parallels Business Automation - Standard interface.
IP address. Plesk node IP address. Here you can reassign another IP address to the Plesk
node. To do this, just enter this new IP into this field. Important: A new IP address
must be from the set of IPs assigned to the node and this IP address must be shared.
After IP address reassignment, all Plesk domains existing on the node and all domains
created in future on this node will be moved to this new IP address.
Plesk Container Properties. This group of fields appear only for virtual Plesk nodes, i.e., the
nodes that are installed inside a Virtuozzo Containers:
Hardware Node. The friendly name of Virtuozzo node that hosts the Container running
Plesk Server Administrator. You may need to re-specify Hardware Node if Plesk
Container was migrated on another Hardware Node.
Container ID. Numerical identifier of Container that runs Plesk Server Administrator. For
example, you may need to re-specify the Container ID if a Container was migrated to
another Hardware Node and started there with another ID.
Owner. The name of account owning the Plesk node. If no owner is specified, then the node
is assigned to Provider account. Otherwise, the name of owning Reseller account is shown.
Please note that if any clients or domains have been already created on the node, then it is
not possible to reassign the node to another account, because this will cause a lot of conflicts
in billing.
Hardware. The Plesk node hardware configuration. You can adjust any parameter.
Comment. Free-form comment.
Maintenance. If you need to take a certain hardware node offline for maintenance or upgrade
you can bring a Hardware Node into a special maintenance mode that temporarily disables
management of Plesk domains hosted on this Hardware node from the Control Panel:
You can check the Do not allow customers to manage their domains from CP box to
disable Plesk domains management from Control Panel.
Note: This setting affects domains hosted on the selected Hardware Node only. Note that
you can compose a Mass Mailer (on page 273) for customers on that specific Hardware
Node.
In the Warning Message field you can type the text of the system message to be shown to
your customers when domains management is disabled but they try to perform an
operation under domain(s) You can leave this field empty to use the default system
message.
Page 35

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 35
Accounts
Accounts registered in Parallels Business Automation - Standard accounts that own Plesk clients
or domains hosted on this node are enlisted under this tab.
Plesk Domains
Plesk domains existing on the node are shown here.
Plesk Clients
Plesk clients existing on the node are shown here.
Virtuozzo Nodes Specific Settings
The most wide management opportunities are provided in Parallels Business Automation Standard for servers that run Virtuozzo (Virtuozzo nodes). For example, you can set up the
traffic shaping for a Virtuozzo node or allow creation the name-based Containers.
Managing Paral lels Server Nod es
PBAS allows establishing connection to servers that run Parallels Server Bare Metal and
provisioning Virtual Machines to customers.
Note: PBAS supports registration of PSBM slave nodes only.
To view the list of Parallels Server nodes connected to Parallels Business Automation Standard, open Service Director submenu and then click Nodes either on Parallels Server
Manager submenu.
To register a new Parallels Server Node, click New Node.
The list of Parallels Server nodes displays the following:
ID - Numerical identifier, assigned to the Hardware Node.
Shortname - Hardware node friendly name.
IP Address - Current IP address assigned to a node.
New Accounts - Whether it is allowed to create more subscriptions on a Node. Green tick
indicates that yes, red cross - that not.
Platform - the software installed on a node. Parallels Server.
Version - the full version of the VzAgent running on a node.
Reg. Status - The current Hardware Node status in respect to its manageability via your
Control Center web-based interface:
Registered - the connection with a Hardware Node was established successfully, a
Hardware Node is fully manageable.
Page 36

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 36
Unregistered - the connection with a Hardware Node is not established but a Hardware
Node configuration is stored in the Parallels Business Automation - Standard database.
Such a Hardware Node cannot be managed from Parallels Business Automation Standard web-based interface.
Availability - Current status of a node in respect to establishing connection to it. Unavailable
node usually means some kind of hardware or network problems on a node.
Registering Parallels Server Nodes
To register a new Parllels Server node:
1. Open Service Director submenu and then click Nodes either on Parallels Server Manager
submenu. The list of registered Parallels Server nodes (if any) is displayed.
2. Click the New Node button. Parallels Server node registration wizard starts.
3. Enter the connection settings:
a Type the node hostname or IP address into the Hostname (IP Address) field.
b Enter the user root password to the Parallels server into the Parallels Server root
password field.
4. Click Next. PB AS establishes connection to the node and fetches its parameters. The node
configuration settings pre-filled with node parameters is displayed. Adjust the node
parameters:
a Hardware node name - Hardware Node alphanumeric identifier, any combination of
letters and (or) digits you consider convenient to refer to a Hardware Node within your
Parallels Business Automation - Standard system. A Hardware Node short name will be
used both in the lists of Parallels Business Automation - Standard objects (Hardware
Nodes and Containers) and other Hardware Nodes related operations (for example,
assigning IP Pool to a Hardware Node).
b To allow creation new Virtual Machines at the node, tick the Allow New Virtual Machines
check box.
Note: Information about Virtual Machines created at the node before registration in PBAS is
not passed. Take into account the node current load before allowing new Virtual Machines
creation.
c Enter the maximal number of Virtual Machines allowed at the node into the Maximum
number of virtual machines (leave empty for the unlimited type) field.
d The Hostname field is pre-filled with IP address or hostname of the node. You can
adjust the node hostname.
e You can adjust the Operating system installed at the node. The OS name fetched during
establishing connection to the node is shown in the OS field.
f Operating system build number is shown in the OS release field. If needed, you can
adjust it.
g If needed, adjust the node hardware configuration shown in the Hardware sec tion o f the
form.
h If needed, type a free-form comment into the Comment field.
5. Click Save.
Page 37

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 37
Managing Virtual Machines
Virtual Machines are managed under Service Director > Parallels Server Manger > Virtual
Machines.
The current implementation of PBAS - PSBM integration brings several limitations of Virtual
Machines management:
A Virtual Machine can be created from online store only, upon a sales order.
Virtual Machines created at a PSBM node before registration of this node in PBAS are not
visible from PBAS and information about these Virtual Machines is not passed. PBAS
Conflict Resolver does not support Virtual Machines conflicts resolution.
Virtual Machines templates are not managed in PBAS. A Virtual Machine template is to be
entered manually. Thus, it is very important to specify the exact template name in a Virtual
Machine hosting plan.
Virtual Machines resources management tools are not supported by now. Thus, a Virtual
Machine resources allocation cannot be billed and/or changed.
Virtual Machines traffic is not calculated.
Customers that subscribed for Virtual Machine hosting plan can manage Virtual Machine using
Parallels Power Panel. Transparent logging in to Parallels Power Panel is possible directly from
PBAS Customer Control Panel, following the link Parallels Power Panel located at the System
zone of the Control Panel.
The list of Virtual Machines displays the following:
ID - Virtual Machine ID assigned in PBAS.
Name - Virtual Machine hostname.
IP Addresses - IP addresses (both IPv4 aqnd IPv6) allocated for a Virtual Machine.
Account - The name of account that owns Virtual Machine.
Status - Virtual Machine current status.
Node - Hostname or IP address of PSBM server that runs a Virtual Machine.
To operate Virtual Machines, select Virtual Machine by putting a tick into check box next to its
(their) name(s) and use controls:
Start - Start Virtual Machine.
Stop - Stop Virtual Machine.
Restart - Restart Virtual Machine .
Synchronize - Set Virtual Machine administrator password and IP address. This operation is
needed if password and/or IP allocation has been changed and it is necessary to pass them to a
Virtual Machine. Virtual Machines are synchronized every hour by a scheduled task, the
statuses are updated. This control allows synchronizing Virtual Machines on demand.
Page 38

38
PA Synchronization Setup .................................................................................................... 52
C
HAPTER
5
Managing Parallels Automation Services
PBAS allows establishing connection to servers that run Parallels Operations Automation
(POA) and Parallels Plesk Automation (PPA) to provide the services to customers.
In This Chapter
Parallels Automation Integration Guidelines ........................................................................ 39
Managing Parallels Automation Nodes ................................................................................ 40
Managing PA Subscriptions .................................................................................................. 51
Page 39

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 39
Parallels Automation Integration Guidelines
This section describes what should be done to integrate POA or PPA with PBAS and then to
start providing the services using PBAS.
I. Configuring P A Node
For POA: Log in to POA Control Panel. Configure POA node (on page 42).
For PPA: Log in to PPA Control Panel. Configure PPA node (on page 45).
II. Registering P A Node in PBAS.
Log in to PBAS Provider Control Panel, Service Director > Parallels Automation Manager >
Nodes
Register POA node (on page 43)
Register PPA node (on page 46)
III. Creating Service T emplate(s) in POA.
Log in to the PA node Control Panel
Create Service Template.
IV . Synchronizing POA Service T emplates.
In PBAS Provider Control Center go to Service Director > Parallels Automation Manager >
Nodes. Select the POA node. Switch to the POA Service Templates tab. Synchronize service
templates (on page 50).
V. Creating POA Hosting Plan.
In PBAS Provider Control Center go to Billing Director > Product Manager > Hosting Plans.
Create POA hosting plan (on page 138).
Page 40

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 40
Managing Parallels Automation Nodes
Before registering a node, it is necessary to configure it in a way that allows connecting to
PBAS:
Configure POA (on page 42) node
Configure PPA (on page 45) node
PA service templates that allow selling PA resources via PBAS are configured at POA side and
then synchronized with PBAS (on page 50).
The list of PA nodes displays the following:
ID. The node numeric identifier assigned in PBAS. Click to view the node settings.
Shortname. The node friendly name used in PBAS to refer to the node. Click to view the
node settings.
POA Manager API address. POA API URL. Configured in POA and later used in PBAS
during POA node registration.
Frontend hostname. URL to POA UI server.
Platform. POA software installed at the node.
Reg. Status. Current status of the POA node in respect to its ability to connect to PBAS:
Registered. PBAS is registered at POA node. POA can connect to PBAS.
Unregistered. PBAS is not registered at POA node. POA cannot connect to PBAS.
Availability. The node status in respect to the ability of PBAS to connect to POA:
Available. PBAS can connect to POA node.
Not available. PBAS cannot connect to POA node.
Owner. PBAS account that owns POA node.
To register a new POA node (on page 40), click the New Node button.
Registering PA Node
PA nodes are registered in PBAS using the same wizard. However nodes pre-configuration
differs for POA and PPA platform.
Please click the link below to get the needed help page displayed:
I'm registering POA node (on page 40)
I'm registering PPA node (on page 44)
Registering POA Node
Shortly, POA node registration consists of the steps:
1. Configure POA node (on page 42):
a Configure system properties.
b Install DNS plug-in.
c Configure POA API.
Page 41

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 41
2. Register POA node in PBAS (on page 43).
3. Set up PBAS as primary DNS set (on page 47).
Page 42

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 42
POA Node Pre-Configuration Before Registration
For POA 5.5 this
field must be left
For POA versions
below 5.5, specify
PBAS Customer
Control Panel
In this section we do not provide the paths to POA components, but mention only the settings
that require configuration. For more information refer to POA documentation.
To configure POA system parameters:
1. Log in to POA Provider Control Panel.
2. Edit the System Properties as follows:
Ability to add domains from customer CP
Domain registrar status default va lue
Allow to use services from different subscriptions on domain
Allow to move domains between subscriptions
Customers management fro m POA UI
Allow using of several dots in domain name
IDN Domains Support
Ability to remove domains from customer CP*
*Recommended setting.
External login URL
Ready
empty.
URL:
http://<PBAS
_hostname>/c
p
Stay in POA Control Panel. Now we install DNS plug-in for PBAS.
To install DNS plug-in:
For POA 5.0.1 with hotfix (http://kb.parallels.com/en/9440 ) installed:
1. Go to Hardware Nodes list.
2. Select the POA system node. This node has
system node ID or hostname. The node details are displayed.
3. Select the Packages tab. The list of packag es insta lled at POA node is display ed.
4. Click the Install Package button.
in the System column. Click on the
Page 43

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 43
5. Select the PBASDNS package. Click the Install button.
For POA 5.2 and above:
1. Go to Service Controllers. The list of service controllers is displayed.
2. Click the Install Service Controller button.
3. Select PBASDNS Service Controller. Follow the wizard.
Stay in POA Control Panel. Now we configure API connection.
To configure API:
1. Go to Public API Manager. The Public API Manager Summary is displayed.
2. Click the Edit button. Adjust settings:
a Check the SSL box.
b Check the HTTP Authentication box. This is optional, but strongly recommended.
c Set Accept connections to Only from allowed networks.
3. Click the Submit button.
4. Select the Allowed Networks tab. Click the Add button. Fill the form:
a Type the PBAS node IP address into the IP Address field.
b Type the 255.255.255.255 mask into the Netmask field.
5. Click the Submit button.
6. Select the Summary tab.
7. Make sure that POA API is running: if the Start button is shown, click it to start API. If only
Stop button is shown, this means that API is already running.
8. Write down or save in a file the Access Point URL shown at the Summary screen. This URL
will be needed to register POA node in PBAS.
POA node pre-configuration is finished. Proceed with POA node registration in PBAS.
POA Node Registration
Before registering POA node it is necessary to configure POA (on page 42).
To register POA node in PBAS:
1. Log in to PBAS Control Center.
2. Go to Service Director > Parallels Automation Manager > Nodes. The list of registered POA
nodes (if any) is displayed.
3. Click the New Node button. POA node registration wizard starts.
4. Enter the connection parameters:
a Enter the POA API URL you have got as Access Point after POA API configuration (on
page 45) into the POA Manager API address (Example https://HOSTNAME:8440/RPC2)
field.
b Enter the POA UI node (frontend hostname) into the Frontend hostname (Example
http://HOSTNAME:8080) field.
c Enter the POA node administrator login into the POA user field.
Page 44

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 44
d Enter the POA node administrator password into the POA password field.
5. Click Next. POA node settings are displayed:
a Ent er the friendly name for POA node into the Hardware Node name field. This name
will be used in PBAS to refer to the POA node.
b If needed, you can adjust POA API URL and POA frontend hostname.
6. The DNS resource regex (case-insensitive) field is pre-filled with POA resource class name.
This regexp is used to detect DNS resource on POA side by resource class. In most cases
this field should not be changed.
7. Enter a free-form description of POA node into the Comment field.
8. Click Save.
To POA Integration Guidelines (on page 39)
Registering PPA Node
Shortly, PPA node registration consists of the steps:
1. Configure PPA node (on page 45)
a Configure system properties.
b Install DNS plug-in (if needed).
c Configure POA API.
2. Register PPA node in PBAS (on page 46).
3. Set up PBAS as primary DNS set (on page 47).
Page 45

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 45
PPA Node Pre-Configuration Before Registration
Leave this field
In this section we do not provide the paths to PPA components, but mention only the settings
that require configuration. For more information refer to PPA documentation.
To configure PPA system param et er s:
1. Log in to PPA Control Panel.
2. Edit the System Properties as follows:
Ability to add domains from customer CP
Domain registrar status default va lue
Allow using of several dots in domain name
Allow to move domains between subscriptions
Customers management fro m POA UI
IDN Domains Support
Ability to remove domains from customer CP*
*Recommended setting.
External login URL
Stay in PPA Control Panel. Now we shall check if it is needed to install DNS plug-in for PBAS.
Ready
empty.
To check the DNS plug-in and install it if needed:
1. Go to Service Nodes. The list of servers involved in PPA deployment is displayed.
2. Select the PPA management node. Click on the management node ID or hostname. The
node details are displayed.
3. Select the Packages tab. The list of packages installed at PPA node is displayed.
4. Search for the PBASDNS package. If it is found in the packages list, this means that it is
already installed; in this case skip the further steps and proceed with API configuration later
in this topic.
5. If the package is not found, click the Install Package button.
6. Select the PBASDNS package. Click the Install button.
Stay in PPA Control Panel. Now we configure API connection.
To configure API:
1. Go to Public API Manager. The Public API Manager Summary is displayed.
2. Click the Edit button. Adjust settings:
a Check the SSL box.
b Check the HTTP Authentication box. This is optional, but strongly recommended.
Page 46

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 46
c Set Accept connections to Only from allowed networks.
3. Click the Submit button.
4. Select the Allowed Networks tab. Click the Add button. Fill the form:
a Type the PBAS node IP address into the IP Address field.
b Type the 255.255.255.255 mask into the Netmask field.
5. Click the Submit button.
6. Select the Summary tab.
7. Make sure that PPA API is running: if the Start button is shown, click it to start API. If only
Stop button is shown, this means that API is already running.
8. Write down or save in a file the Access Point URL shown at the Summary screen. Thi s UR L
will be needed to register PPA node in PBAS.
PPA node pre-configuration is finished. Proceed with PPA node registration in PBAS.
PPA Node Registration
Before registering PPA node it is necessary to configure PPA (on page 45).
To register PPA node in PBAS:
1. Log in to PBAS Control Center.
2. Go to Service Director > Parallels Automation M anager > Nodes. The list of registered PA
nodes (if any) is displayed.
3. Click the New Node button. PA node registration wizard starts.
4. Enter the connection parameters:
a Enter t he PPA API URL you have got as Access Point after POA API configuration (on
page 45) into the POA Manager API address (Example https://HOSTNAME:8440/RPC2)
field.
b Enter the PPA UI node (frontend hostname) into the Frontend hostname (Example
http://HOSTNAME:8443) field.
c Enter the PA node administrator login into the User field.
d Enter the PA node administrator password into the Password field.
5. Click Next. PA node settings are displayed:
a Enter the friendly name for PA node into the Hardware Node name field. This name will
be used in PBAS to refer to the PA node.
b If needed, you can adjust PA API URL and PA frontend hostname.
Page 47

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 47
6. The DNS resource regex (case-insensitive) field is pre-filled with PA resource class name.
This regexp is used to detect DNS resource on PA side by resource class. In most cases this
field should not be changed.
7. Enter a free-form description of PA node into the Comment field.
8. Click Save.
To PA Integration Guidelines (on page 39)
Setting PBAS DNS as Primary for Parallels Automaion Services
To provide PA services, it is required to set up PBAS as primary DNS. This is done by means of
the DNS Hosting resource configuration.
In this section, we do not provide the paths to PA components, but mention only the settings
that require configuration. For more information refer to PA documentation.
In POA, there is no pre-configured Service Templates. Thus, you will need to create the DNS
Hosting resource, configure it properly, and add it to Service Templates.
In PPA, the default Service Templates are shipped. So, in this case, you will need to adjust the
existing DNS Hosting resource or create a new one and add it to the Service Templates you are
planning to use with PBAS.
How DNS settings are synchronized between PA and PBAS
As soon as PBAS is set as primary DNS, every 2 minutes PBAS checks for the changes in
domain zones at PA side and synchronizes all the changes.
However, the periodical check is not enough if there is the need for bulk synchronization of all
DNS data kept at PA side.
To synchronize the PA node, go to Service Director > Parallels Automation Manager > Nodes,
select the PA node, then select the General Settings tab and click Synchronize DNS.
To synchronize domain zones per PA subscripiton, go to Service Director > Parallels Automation
Manager > Subscripitons, select the subscription and click Synchronize DNS.
The required configuration of Activation Parameters for the DNS Hosting reso urce (other
parameters are not critical, you may leave defaults):
Auto host domains: Yes.
First nameserver: PBAS name server.
If you already have created Service Templates in PA with DNS Hosting resource
misconfigured, and have synchronized the Service Templates with PBAS, then there are three
ways to fix it:
1. Replace the existing DNS Hosting resource with a correct new one in Service
Templates.
In PA:
a Add new DNS Hosting resource and configure it as required.
b Drop the old DNS Hosting resource from Service Templates.
Page 48

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 48
c Add the new DNS Hosting resource configured correctly to Service Templates.
In PBAS:
d Propagate the changes to PBAS: Go to Service Director > Parallels Automation Manager
> Nodes, select the PA node, then select the Service Templates tab and click Synchronize
service templates.
e Renew hosting plans: Go to Billing Director > Product Manager > Hosting Plans, sel ect
the PA hosting plan, then select the Billable Resources tab. Click Edit. W hen the Billable
Resources list is displayed for editing, just click Save.
2. Change the existing DNS Hosting resource. Changes will be propagated to all Service
Templates that use this resource.
In PA:
a Open the list of all Resources available in the PA installation.
b Select the DNS Hosting resource. Confiugre its Activation Parameters as required.
In PBAS: No actions needed, changes are applied automatically.
3. Change the existing DNS Hosting resource per Service Template. Changes will be
applied only to the Service Template you have adjusted.
In PA:
a Open the list of all Service Templates.
b Select the Service Template and then se lec t the Resources tab.
c Click on the DNS Hosting resource name. Confiugre its Activation Parameters as
required.
In PBAS: No actions needed, changes are applied automatically.
PA Node Settings
PA node settings are grouped as follows:
Summary. The node status and statistics on subscriptions/service templates. Read-only.
General Settings. The node connection settings. Here you can edit connection settings,
unregister the node or delete information about the node from PBAS.
Service Templates. View service templates available at the node, synchronize service
templates with PBAS.
Resources. All resources available in the frame of service templates at the POA node. PA Node Summary
The PA node Summary displays the status and statistics on subscriptions/service templates:
Availability. The node status in respect to the ability of PBAS to connect to PA:
Available. PBAS can connect to PA node.
Not available. PBAS cannot connect to PA node.
Registration Status. Current status of the PA node in respect to its ability to connect to
PBAS:
Registered. PBAS is registered at PA node. PA can connect to PBAS.
Unregistered. PBAS is not registered at PA node. PA cannot connect to PBAS.
Page 49

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 49
Subscriptions. The number of subscriptions at PA node.
Service Templates. The number of service templates at PA node.
PA Node General Settings
POA node General Settings display the connection settings:
Hardware Node ID. The node numeric identifier assigned in PBAS.
Hardware Node name. The node friendly name used in PBAS to refer to the node. Click to
view the node settings.
User. PA node administrator login. If the Login to PCP button is available, click to
transparently log in to the Node administrator panel.
API address. PA API URL. Configured in PA and later used in PBAS during PA node
registration.
Frontend hostname. The URL to PA UI server.
DNS resource regex (case-insensitive). POA resource class name. This regexp is used to
detect DNS resource on POA side by resource class. In most cases this field should not be
changed.
Reseller Service Template. The name of the Reseller Service Template created at PA node.
Reseller service template defines the set of PA resources available for reseller.
Comment. A free-form description of POA node.
Buttons (viewing the node settings):
Cancel. Back to the list of POA nodes (when editing the node settings - back to view
screen).
Synchronize DNS. Synchronize all the zone files stored at the PA node with PBAS. All the
DNS records except for NS are synchronized.
Unregister. Unregister the node; PBAS cannot connect to unregistered node. If the node is
unregistered, then the Connect button is shown; click Connect to retry registering the node.
Delete. Disconnect and delete all the information about POA node from PBAS.
Edit. Edit the node settings. When editing the node settings, the Update button is used to
save the node settings.
Page 50

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 50
PA Node Service Templates
PA service templates are created at PA node and then synchronized with PBAS. To PA
Integration Guidelines (on page 39).
Synchronized service templates are used to create POA hosting plans (on page 138) in PBAS.
To fetch the service templates from PA node to PBAS, click the Synchronize service templates
button. After a service template is synchronized, it appears in the PBAS Service Templates list.
Service templates automated synchronization is scheduled under Service Director > Parallels
Automation Manager > Setup.
Resources included in the POA service templates are shown under the Resources tab.
Important: The DNS Host ing resource should be configured to point at PBAS name servers as
primary DNS set.
To view the list of resources included in a service template, click on this service template ID or
name. The list of resources is shown under the Resources tab, but filtered according to the
service template you have selected.
POA Node Resources
The PA resources available with PA service templates synchronized with PBAS are shown
under the Resources tab.
For more details about PA resources, refer to POA or PPA documentation.
Page 51

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 51
Managing P A Subscriptions
POA subscriptions are managed in the same way as other subscriptions in PBAS. To get all the
options applicable to subscriptions, go to Account Director > Subscription Manager >
Subscriptions and filter the list down to POA subscriptions. For more details, refer to PBAS
online help (on page 197).
In addition, POA subscriptions are grouped under Service Director > Parallels Automation
Manager > Subscriptions.
To synchronize subscriptions with hosting plans, click Synchronize subscriptions. Subscriptions
automated synchronization is scheduled under Service Director > Parallels Automation Manager
> Setup.
In some cases, for example if the subscripiton has been added to PBAS by Conflict Resolver (on
page 290), DNS data is not properly synchronized with PBAS. It is possible to synchronize the
subscripiton DNS data stored at PA side, with PBAS:
1. Click on the subscripiton name in the list. The subscripiton details open.
2. Click Synchronize DNS.
The list of PA subscriptions displays the following:
ID. Subscription ID assigned in PBAS. Click to view subscription summary.
Subscription name. The name of hosting plan or domain name.
Account Name. Name of the account that owns the subscription.
Node name. Friendly name of PA node, where the subscription is created.
Service Template Name. The name of service template used for hosting plan the subscription
is based on.
Status. Subscription current status:
Active. Subscription is available for PBAS and can be synchronized or managed.
Offline. Subscription is not available for PBAS and cannot be synchronized or managed.
Page 52

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 52
P A Synchronization Setup
The following data is synchronized with PA:
Statuses of subscriptions,
Resource usage,
Service Templates.
DNS
Synchronization setup allows scheduling synchronization between PA and PBAS.
Note: DNS data is synchronized every 2 minutes. DNS synchronization schedule cannot be
changed.
To change synchronization schedule, click Edit.
Subscriptions synchronization period (hours). How often (in hours) PA subscriptions are
synchronized with PBAS.
Subscriptions usage statistic synchronization period (hours). How often (in hours) PA
subscriptions resources usage is synchronized with PBAS.
Service templates synchronization period (hours). How often (in hours) PA service templates
are synchronized with PBAS.
Sitebuilder Management
Sitebuilder (http://www.parallels.com/en/products/sitebuilder/) is an easy to use web application
designed to create and manage websites. Parallels Business Automation - Standard provides
integration with Parallels Plesk Sitebuilder 2.1.1, 3.0.1, 4.x for Unix/Linux and Parallels Plesk
Sitebuilder 2.0.5, 3.2.1, 4.x for Windows.
Important: Sitebuilder for Windows sites publishng
Sitebuilder for Windows sites are published on Plesk hosting only.
Sitebuilder for Windows sites are published into the /sitebuilder/ folder created
over the document root folder. The index file containing auto-redirect to the
/sitebuilder/ folder is created automatically and placed to Plesk Domain
document root. These settings are PBAS defaults, they cannot be changed; PBAS
default publishing settings always override Sitebuilder publishing settings.
Page 53

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 53
This chapter describes the Sitebuilder Manager integrated in Parallels Business Automation Standard Control Center. Sitebuilder Manager is used to administer Sitebuilder nodes, plans and
sites and provide Sitebuilder services as an add-on within hosting plans. After nodes
registration, Sitebuilder sites can be designed and published using the Parallels Business
Automation - Standard Control Panel (see Parallels Business Automation - Standard
Subscriber's guide for details). For more details about Sitebuilder services provisioning in
Parallels Business Automation - Standard, please see the next topic (on page 54).
Important: When preparing Parallels Plesk Sitebuilder for integration with Parallels Business
Automation - Standard, please only install Parallels Plesk Sitebuilder itself and a Parallels Plesk
Sitebuilder license. Do not configure anything additionally in Parallels Plesk Sitebuilder
Administrator Control Panel. For example, DO NOT ADD HOSTS. When a Sitebuilder node is
connected to Parallels Business Automation - Standard, everything is done automatically. Thus,
any additional configuration on a Sitebuilder node side may cause problems. For example, if
host(s) is(are) manually specified in a Sitebuilder node Administrator Control Panel, publishing
sites from Parallels Business Automation - Standard fails. To avoid this, always do minimal
configuration on Sitebuilder nodes that are planned to be connected to Parallels Business
Automation - Standard.
Sitebuilder Nodes (on page 58) are registered and modified in Service Director > Sitebuilder
Manager > Nodes panel of Sitebuilder Manager. On the Nodes panel, you can search the existing
nodes by name or ID, view the list of nodes, modify nodes and register new ones.
On the Plans (on page 59) panel you can search plans by name or ID, add, remove or modify
Sitebuilder plans.
On the Sites (on page 60) panel, you can search and view the sites on the Sitebuilder server.
On the Setup (on page 57) panel, you can view available Sitebuilder modules and templates.
Page 54

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 54
Sitebuilder Services Provisioning
There are two types of sites in Sitebuilder: trial web sites and regular web sites:
A trial web site is a site with limited functionality. Trial sites cannot be published. They are
created for users who use Sitebuilder for the first time. Also trial site has a time life of 30
days. If the trial web site is not transferred into regular web site upon expiration of its timelife this trial site is terminated.
A regular web site is a site with a full functionality and ready for publishing.
Parallels Business Automation - Standard automatically transfers trial Sitebuilder sites into
regular after a customer pays the corresponding order.
Sitebuilder integration with Parallels Business Automation - Standard allows the following
scheme for Sitebuilder services provisioning:
After Sitebuilder Manager is set up and Sitebuilder nodes are registered and synchronized,
you can create Sitebuilder service offerings called Plans.
Plans then can be included in hosting plans to be sold at your online store. Hosting plan
types the Sitebuilder service can be included are: Virtuozzo Container, Plesk Client, Plesk
Domain, Plesk Virtual Node. Sitebuilder services can be included in a hosting plan either
during creation or later, under the Sitebuilder tab within a hosting plan properties.
By design, the Sitebuilder service is always included in a Hosting Plan price. You can only
set the fees for additional Sitebuilder sites, over the number included in a Sitebuilder plan.
Thus, you can take the Sitebuilder service price into account when setting both setup and
recurring fees for the Hosting Plan you want to in clu d e Sitebu ild er serv ic es in.
When a customer subscribes for a hosting plan with Sitebuilder service, two variants of
Sitebuilder site hosting are available:
If a customer has already passed the Sitebuilder site creation Wizard on one of your
registered Sitebuilder nodes, he/she already has a trial Sitebuilder site with the unique
code (called site alias) assigned. In this case, when a customer buys hosting with
Sitebuilder services, he/she can check the box next to a Sitebuilder service offering,
enter a Sitebuilder site alias when subscribing to a hosting plan and assign this
Sitebuilder site to his/her subscription. Later, after an order is paid and subscription is
activated, a customer can host this Sitebuilder site on his/her Container or Plesk domain.
If a customer has no Sitebuilder sites by the moment of hosting plan purchase, he/she
can check the box next to a Sitebuilder service offering and get a trial Sitebuilder site
anyway, without the need for entering a site alias or passing a Sitebuilder Wiz ard. I n this
case, a trial and empty Sitebuilder site will be created automatically (the same option is
available from Control Panel). The main designation of such empty site is to reserve a
site alias for a customer and let customer save time and get Sitebuilder site already on a
hosting plan purchase stage. A customer can later pass the Sitebuilder Wizard for this
special empty Sitebuilder site.
Page 55

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 55
A Sitebuilder site remains trial till a customer pays for hosting. After payment is received, a
customer Sitebuilder site automatically becomes regular and a customer can host this site on
his/her hosting (Container or Plesk domain) and publish it as soon as his/her subscription is
activated. If a customer does not pay for hosting, a trial Sitebuilder site keeps remaining trial
and if an order is not paid by the date a trial site lifetime expires (30 days after creation), this
site is removed.
Notes about Sitebuilder site troubleshooting by a customer:
Only actually existing sites with valid site aliases are shown in Provider Control Center.
Corrupted and deleted sites are shown in customer Control Panel and a customer can decide
whether to permanently delete such a site.
If a Sitebuilder site creation has failed (for example, due to technical problems on a Sitebuilder
node), then the site status (shown in Control Panel only) is Pending and a customer can recreate
this site from the Control Panel or delete it and get the refund for the Sitebuilder services.
If a Sitebuilder site becomes not available due to its deletion on a Sitebuilder node, and this is
not a customer fault or intention, then the site status (shown in Control Panel only) is Conflicts
and a customer can delete the information about this site from Parallels Business Automation Standard database and get the refund for the Sitebuilder services.
Sitebuilder Installation:
Sitebuilder requires installation on a dedicated physical or virtual node. For Sitebuilder
installation instructions, please refer to the Sitebuilder original documentation.
After installation, do the following to s etup and configure Sitebuilder Manager:
1. Register Sitebuilder node(s), assign logins/passwords and URLs. In case the nodes are to be
transferred to Resellers, associate the nodes with them.
2. Configure the message to be shown on the Publish screen of the Sitebuilder Wizard on a
node. This message must help customers that do not yet have hosting for their Sitebuilder
sites to get to your shop and buy hosting compatible with their sites.
3. Synchronize nodes, if required. Generally, synchronization is performed automatically after
registration, however, if you enable or disable some templates or modules on a node using
the native Sitebuilder Administrator Control Panel, you must synchronize a node with
Parallels Business Automation - Standard database to make the newly enabled templates or
modules available.
4. Create Sitebuilder plans and synchronize them to Sitebuilder nodes. In respect to Sitebuilder
plans, such synchronization allows you to compare the set of templates/modules declared in
a plan with an actual set of templates/modules available on each of Sitebuilder nodes
registered in Parallels Business Automation - Standard. After such synchronization, you can
see the match between plans and nodes and can decide upon the templates/modules that
miss on nodes to provide services declared in plans.
5. Go to Provider Control Center > Billing Director > Product Manager > Hosting Plans and
associate Sitebuilder with hosting plans as follows:
Click on a hosting plan.
Click on the Sitebuilder tab.
Under the Sitebuilder tab, click the Edit button.
Check the Sitebuilder enabled box to enable Sitebuilder services for the selected hosting
plan.
Page 56

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 56
Select a Sitebuilder plan to be included into the hosting plan.
Click the Save button to confirm or the Cancel button to return to the previous menu.
Note: If a reseller clones a Provider's plan, Sitebuilder settings for this hosting plan are reset to
default (not enabled by default).
Connecting Sitebuilder Nodes
The connection to a Sitebuilder node is established using the special management interface
called Remote Admin. Thus, for successful Sitebuilder node registration in Parallels Business
Automation - Standard, the Remote Admin must be installed on a node before you start
registering it. For more details about the Remote Admin installation, please refer to the
Sitebuilder documentation.
Note: The Sitebuilder administrator account login and password are used by Parallels Business
Automation - Standard also for establishing connection to a Sitebuilder node API (Remote
Admin).
By default, Sitebuilder has only one administrator account: For Sitebuilder 2.x or 3.x
administrative user name root and the password sitebuilder; for Sitebuilder 4.x
administrative user name admin and the password admin. These login and password are used
for initial logging in to the Sitebuilder Admin Panel.
For security purposes, before registering a Sitebuilder node, we strongly recommend to log in to
the Sitebuilder Admin Panel on this node and change the default administrator login/password.
Parallels Business Automation - Standard allows granting access to a single Sitebuilder node
both to a Provider account and a number of reseller accounts at the same time. In Provider
Control Center a node registered for several accounts looks like a separate node assigned to a
single reseller account. In Reseller Control Center such Sitebuilder node behaves like a
dedicated node assigned to reseller. To grant access to a Sitebuilder node to a reseller account,
log in to the Sitebuilder Admin Control Panel and create a reseller. Then get back to the
Provider Control Center and register this Sitebuilder node as a new one but with URLs that use
this reseller domains. At the same time, assign this Sitebuilder node to a corresponding reseller
account registered in Parallels Business Automation - Standard.
To register a Sitebuilder Node, open the Service Director submenu and select the Sitebuilder
Manager. Click Nodes on the Sitebuilder Manager submenu.
Page 57

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 57
Setting Up Sitebuilder
The Sitebuilder Manager Setup informs you about all Sitebuilder add-ons (programs like
guestbook or photo gallery called modules and web page templates) available at all Sitebuilder
nodes registered.
The list of modules (or templates) displays the following:
Modules (or Templates) - depending on the tab you select. - The list of modules or templates
named according to the Sitebuilder naming convention. You cannot change these names,
they are shown exactly as were fetched. Please, refer to the Sitebuilder documentation to
know more about each module or template.
Note: You can see the palette and style of each template using the Preview link pla ced in
brackets next to each template name.
Sitebuilder nodes friendly names you have assigned them during registration in Parallels
Business Automation - Standard. The green tick next to a node name means that a given
module or template is available on a node. Red cross next to a node name means that a
module or a template is disabled on a node. The synchronization status is shown for the
moment of the latest synchronization for each node.
The process of fetching the information about templates and modules available on a Sitebuilder
node is called synchronization. Normally, each node is synchronized automatically right after
registration (on page 56).
Important notes about Sitebuilder Nodes Synchronization:
After a Sitebuilder node is registered, its synchronization is performed as follows:
Manually. Using the Synchronize button at a node General Settings or Configuration screen.
Please keep in mind that when you edit a Sitebuilder node configuration and save it, the
changes are not automatically synchronized with a node, but just saved in the Parallels
Business Automation - Standard database. To synchronize changes, you need to click the
Synchronize button. This is done intentionally to save your time, because if a Sitebuilder
node runs many sites, synchronization may take long (an hour or more). So the idea was to
let you start synchronization when you really need this.
Automatically. By means of a periodical task. The periodical task synchronizes the status
of all registered Sitebuilder nodes every 5 minutes and performs sites synchronization for all
registered Sitebuilder nodes every 8 hours. You can change the nodes status synchronization
period in Action Log - Tasks Queue.
Page 58

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 58
Please note that Parallels Business Automation - Standard does not provide tools that allow
enabling/disabling templates or modules on Sitebuilder nodes. Thus, if you want to enable or
disable some templates or modules, you must do this using the original Sitebuilder Admin
Control Panel.
After the composition of enabled templates/modules on a Sitebuilder node have been changed,
there are two ways to synchronize Sitebuilder node to refresh the data about a node in Parallels
Business Automation - Standard database and make a newly enabled templates/modules
available for Sitebuilder plans you create in Parallels Business Automation - Standard:
1. Synchronize either templates or modules for all Sitebuilder nodes registered by one click.
To this effect, click the Modules or Templates tab to synchronize modules or templates
respectively and then click the Synchronize button.
2. Per node as this described later in this guide.
Managing Sitebuilder Nodes
Sitebuilder Nodes are managed under the Service Director > Sitebuilder Manager i n the Nodes
panel. You can register a new node (on page 56), edit or remove a node.
The list of Sitebuilder nodes displays the following:
ID. A node numerical identifier assigned to a node on registration in Parallels Business
Automation - Standard automatically.
Name. A node friendly name. An arbitrary alphanumerical identifier assigned manually to a
node. Used just to recognize a node when working in Parallels Business Automation Standard web-based interface.
Vendor. The name of the account that owns a node. A node can be assigned either to a
Provider administrative account. or to a reseller account. After a node is assigned, the
Sitebuilder services provided by this node can be sold on behalf of the owning account. i.e.,
either in the provider store, or in the store that belongs to the reseller account a node is
assigned to.
Sites. The number of Sitebuilder sites hosted on a node.
Wizard URL. The URL to the Sitebuilder five-step website creation wizard on a node.
Availability. The status a node currently has:
Available. A node is online, up and running. Ready to provide Sitebuilder services
having been managed via the Parallels Business Automation - Standard web-based
interface.
Not available. A node either is offline or down. The connection with a node is broken
and Sitebuilder services provisioning using this node is not possible.
To view or adjust a node settings, click on a node ID or name.
Page 59

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 59
Managing Sitebuilder Plans
A Sitebuilder plan is an add-on that can be included in hosting plans as an additional service
offering. When you enable Sitebuilder for a hosting plan, you set both the setup and monthly
fee, the number of websites included and price per additional website, over the included set.
Sitebuilder services can be included as a special offering in the following hosting plan types:
Virtuozzo Container - several websites can be provided.
Plesk Client - several websites can be provided.
Plesk Domain - one website can be provided.
Note: For hosting plans that allow creating several Sitebuilder websites, the number of websites
is limited only by a disk size and the number of websites stated for a given Plesk Client or
Container.
Sitebuilder plans can be added to hosting plans either during creation (if Sitebuilder services are
available, the Sitebuilder related step is included into a hosting plan creation wizard) or later,
under the Sitebuilder tab in hosting plan settings.
The list of Sitebuilder plans displays the following:
ID. A plan numerical identifier assigned to all objects in Parallels Business Automation -
Standard automatically.
Name. The title a plan is referred to in Parallels Business Automation - Standard. A plan
name can be changed under the General tab in a plan settings.
Pages. The maximal number of pages allowed for websites created under a plan.
Modules. The number of Sitebuilder programs (modules) included in a plan. You can view
the list of modules included and/or include/exclude modules to/from a plan, under the
Modules tab in a plan settings.
Templates. The number of Sitebuilder website style templates included in a plan . You can
view the list of templates included and/or include/exclude templates to/from a plan, under
the Templates tab in a plan settings.
Sites. The number of westites created under a plan.
To add a plan Click the New Sitebuilder Plan button.
Page 60

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 60
Managing Sitebuilder Sites
All Sitebuilder websites created on all Sitebuilder nodes registered in Parallels Business
Automation - Standard are shown under the Sites item on the Sitebuilder Manager submenu. You
can view, activate/deactivate sites on the Sitebuilder server.
You can search sites by ID, Code, Domain, Account ID, and Subscription.
Sites can be filtered by Type and status (Active/Inactive). The information about the sites created
on a Sitebuilder node using the original Sitebuilder Admin Control Panel or using other tools
different from Parallels Business Automation - Standard is fetched during node synchronization.
The list of Sitebuilder sites displays the following:
ID. The numerical identifier assigned automatically to a site in Parallels Business
Automation - Standard.
Site Alias. A site code assigned by Sitebuilder. This code is called site alias in terms of
Sitebuilder.
Node. The friendly name of Sitebuilder node a site is hosted on.
Vendor. The name of Sitebuilder administrator or reseller (registered directly on a
Sitebuilder node) that officially provides a site.
Plan. The name of Parallels Business Automation - Standard Sitebuilder plan, under which a
site was created. N/A means that a site was created outside Parallels Business Automation Standard (e.g., using the Sitebuilder Admin Control Panel) and is not related to any of
Sitebuilder plans existing in Parallels Business Automation - Standard.
Domain. The hostname of Container or Plesk domain or client a site is hosted on. N/A
means that a site was created, but not reassigned to Parallels Business Automation Standard hosting yet.
Account name. The name of Parallels Business Automation - Standard account owning a
site.
Trial. A site type. In Sitebuilder all sites are trial first. A trial site has a valid code and can be
filled with content using Sitebuilder wizard, but cannot be published. To be published, a
Sitebuilder site must have the regular type. Parallels Business Automation - Standard
automatically turns trial sites into regular after the corresponding order is paid. Red cross in
this column means that a site is regular, green tick means that a site is trial.
Status. A site status in respect to Sitebuilder services. Can be one of the following:
Active. Sitebuilder can be launched for this site and all operations over a site are
available.
Disabled. Sitebuilder cannot be launched for a site. Site management is suspended.
Important: Troubleshooting Sitebuilder Sites
If a Sitebuilder site provisioning has failed because of some temporal problems at a
Sitebuilder node (node unavailability, temporarily dns problem, etc.) it is possible to
manually restart site provisioning. In this case, a site settings are synchronized with its
configuration (templates, modules, etc.) stored in a customer subscription. To this effect,
click the Republish button at a site details screen.
Page 61

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 61
To view site settings click on a Site ID or Site Alias. The site details appear on the screen. You
can deactivate a site by clicking the Deactivate button.
Note: For Sitebuilder versions starting from 3.x.x the selected sites deactivation is not
supported. Thus for sites created on Sitebuilder 3.x.x the Deactivate button is not shown. For
such sites it is possible to deactivate a Sitebuilder user, which deactivates all sites this user
owns.
To view details on Account owning a site, click the account information link. You will be taken
to Top > Account Director > Customer Manager. To view detailed information about a
Subscriptio n that in c lu des a Sitebuilder site, click the subscription information link.
Managing Dedicated Servers
Dedicated servers that run some third-party software (different from Virtuozzo or Plesk) are
managed separately in Parallels Business Automation - Standard using a special set of tools for
dedicated hosting services provisioning including the following:
Creation of hosting plans for dedicated hosting offerings. Such a hosting plan defines the
following server properties:
Both setup and recurring fees for service.
The scheme for traffic accounting by classes.
Number and prices for static IP addresses that can be assigned to a server.
Server configuration and available upgrades for a customer can be outlined using
custom attributes (for RAM, disk space, etc.) assigned to a hosting plan.
In addition, it is possible to sell different application licenses at a separate fees.
Dedicated servers registration in Parallels Business Automation - Standard, which allows
saving the most general properties of a server in the Parallels Business Automation Standard database and, when the corresponding order is placed and paid by a customer,
creating a dedicated subscription for a particular server.
Dedicated servers grouping by Data centers and racks in each Data Center. In addition it is
possible to group servers by switches used.
Dedicated servers management tools are grouped under Servers Manager of the Service Director.
Page 62

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 62
Registering Data Centers
Data Centers registration in Parallels Business Automation - Standard serves for accounting
purposes and does not provide any connection to a Data Center facilities. When you register a
Data Center, a record in Parallels Business Automation - Standard database is created. After
this, you can register racks and switches by your Data Centers and finally, register dedicated
servers located in each Data Center.
To register a Data Center:
1. Click Data Centers on the Servers Manager submenu. The list of Data Centers registered (if
any) appears on the screen.
2. Click the New Data Center button.
3. Fill the form that appears:
a Type the Data Center name into the Identification field. This is the name the Data center
will be referred to in Parallels Business Automation - Standard database. You can enter
any alphanumerical name (number of words and upper/lower case is not critical).
b You can specify the Data Center location (country, city, address) in a free form in the
Location field.
c And into the Comment fi eld you can enter some additional information about the Data
Center.
4. Click the Save button.
Registering Racks in Data Centers
You may have considerable number of servers in your Data Center, and in order to facilitate
servers management, you can save in the Parallels Business Automation - Standard database
your racks capacity, location, and load.
From Parallels Business Automation - Standard standpoint, a rack is a logical container used for
accounting purposes. A rack may be considered as an object within Parallels Business
Automation - Standard. This means that if you do not have any material racks at your Data
Center, you can group your Hardware Nodes into logical racks just for better manageability. On
the other hand, the set of racks you create in Parallels Business Automation - Standard may
follow the actual configuration of a Data center.
To view/edit the racks configuration, or add/delete a rack, click Racks on t he Servers Manager
submenu and selecrt a rack from the list.
To register a new rack:
1. Click Racks on the Servers Manager submenu. The list of racks registered (if any) appears
on the screen.
2. Click the New Rack button.
3. Fill the form that appears:
a Type the name of the Rack into the Identification field. This is the name the rack will be
referred to in Parallels Business Automation - Standard database. You can enter any
alphanumerical name (number of words and upper/lower case is not critical).
Page 63

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 63
b You can enter a rack capacity into the Capacity field. This is an optional Parallels
Business Automation - Standard rack attribute representing the maximal number of
servers this rack can contain. Similarly to a material rack capacity, this attribute is
measured in Units (U). An Parallels Business Automation - Standard logical rack does
not have any capacity restrictions.
c You can specify the rack actual location by selecting the Data Center a rack is located in
from the Data Center drop-down menu.
d You can register servers located on this rack right away. To this effect, click the Add
button on the Dedicated Servers part of the form and select one or more servers from the
list that appears in the popup window. As you click on a server name, it appears in the
list. Add servers and close the popup list. In case of mistake or if you want to re-group
servers, you can remove a server from the list and detach it from the rack, To this effect,
select a server. To select several servers in series, hold down SHIFT, and then click the
first and last server names of the group. To select several servers that are nonadjacent in
the list, hold down CTRL, and click a server name. To remove the selected servers from
the rack, click the Remove button.
e Comment - any comment you consider useful.
4. Click the Save button.
Registering Switches
To facilitate traffic accounting and servers allocation, you can save the information about
switches located in your Data Centers in Parallels Business Automation - Standard database.
To register a new switch:
1. Click Switches on the Servers Manager submenu. The list of switches registered (if any)
appears on the screen.
2. Click the New Switch button.
3. Fill the form that appears:
a Type the name of the switch into the Identification field. This is the name the switch will
be referred to in Parallels Business Automation - Standard database. You can enter any
alphanumerical name (number of words and upper/lower case is not critical).
b Type the number of ports in the switch into the Total number of ports field.
c Type the switch manufacturer name into the Brand field.
d Enter the switch model specification into the Model field.
e You can specify the switch actual location by selecting the Data Center a switch is
located in from the Data Center drop-down menu.
f You can register servers connected to the switch right away. To this effect, click the Add
button on the Dedicated Servers part of the form and select one or more servers from the
list that appears in the popup window. As you click on a server name, it appears in the
list. Add servers and close the popup list. In case of mistake or if you want to re-group
servers, you can remove a server from the list and detach it from the rack, To this effect,
select a server. To select several servers in series, hold down SHIFT, and then click the
first and last server names of the group. To select several servers that are nonadjacent in
the list, hold down CTRL, and click a server name. To remove the selected servers from
the rack, click the Remove button.
Page 64

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 64
g Comment - any comment you consider useful.
h In the fields located in the SNMP Settings part of the form, you can enter the SNMP
(Simple Network Management Protocol) data for the switch:
Read-Only Community String. The switch SNMP community string, i.e., a string used as
a switch password that allows a read-only access to a switch over the network.
IP address for SNMP management. The switch IP address.
4. Click the Save button.
Registering Dedicated Server
Dedicated servers cannot be physically managed using the Parallels Business Automation Standard web-based interface. However, you can save the detailed information about a server
(location in a rack, form factor, switch used, IP address(es) assigned) in Parallels Business
Automation - Standard database for accounting purposes.
Dedicated servers are accounted by racks and switches used, but not by Data Centers they are
located in. However, a server location can be defined by a rack and a switch since racks and
switches are bound to particular Data Centers.
After a server is registered, you can create dedicated subscription in accordance with the order
placed by a customer.
To register a server designated for dedicated hosting service provisioning:
1. Click Dedicated Servers on the Servers Manager submenu. The list of dedicated servers
registered (if any) appears on the screen.
2. Click the New Dedicated Server button.
3. Fill the form that appears:
a Type the name of the server into the Identification field. This is the name the server will
be referred to in Parallels Business Automation - Standard database. You can enter any
alphanumerical name (number of words and upper/lower case is not critical).
b Enter the server size in Units into the Form factor field.
c You can optionally specify the administrator login and password in Administrator login
name and Administrator password fields.
d If you already have registered the rack the server is located, you can add the information
about the rack the server belongs to the other information. To this effect, select the
needed rack from the Rack drop-down menu.
e If you already have registered the switch the server uses, you can add the information
about this switch. To this effect, select the needed switch from the Switch drop-down
menu and type the number of port the server is connected into the Port: field.
f The Subscription part of the form serves for activating a subscription for this server.
Dedicated subscriptions can be activated only manually (on pa ge 66). By default, when
you register a new server, the option button is set to Not assigned. You can register as
many unassigned dedicated servers as you need. When you get an order and a pending
subscription for a dedicated hosting, you can set the option button to Assign dedicated
server to existing subscription, click the Select button and chose the subscription. After
this, when you save changes, a subscription will be automatically activated.
Page 65

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 65
g One or more IP addresses from your IP pool can be assigned to the dedicated server. To
make IP addresses assignment possible, your IP addressed must be registered in the
Parallels Business Automation - Standard database (on page 76). To assign an IP
address click the Add button on the IP Addresses part of the form and select one or more
IP addresses from the list that appears in the popup window. As you click on an IP
address, it appears in the list. Add IP addresses and close the popup list. In case of
mistake or if you want to reassign IP address(es), you can remove one or more IP
addresses from the list and release them. To this effect, select an IP address. To select
several IP adresses in series, hold down SHIFT, and then click the first and last IP
addresses of the group. To select several IP addresses that are nonadjacent in the list,
hold down CTRL, and click an IP address. To release the selected IP addresses click the
Remove button.
h To automatically send an e-mail notification to a server owner in case an IP address was
assigned to the server, check the Notify dedicated server owner about IP addresses
assignment box.
i Comment - any comment you consider useful.
4. Click the Save button.
Page 66

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 66
Activating Dedicated Server Subscription
To activate the Dedicated subscription go to the Service Director > Servers Manager > Dedicated
Servers.
Dedicated server subscriptions can be activated only manually.
Say, you have created and offered in your store the dedicated hosting plan for such a server.
When a customer places and pays an order for this hosting plan, the subscription is
automatically created in Parallels Business Automation - Standard. This subscription is in the
Pending state, because it awaits for particular dedicated server assignment.
In hosting plans, dedicated servers configuration is defined by custom attribute values specified
for a hosting plan (on page 142).
When you assign a dedicated server to a subscription, Parallels Business Automation - Standard
automatically checks every item of a corresponding order in respect to an ordered server
configuration and in case an ordered configuration does not match an assigned server
configuration, Parallels Business Automation - Standard warns you. In this case, you can check
the available dedicated servers configuration, if needed, upgrade or downgrade one of them to
match the ordered configuration, then adjust the dedicated server registration parameters in
Parallels Business Automation - Standard or register a server and after this, try to activate a
dedicated subscription once again.
Advanced custom attributes system and dedicated servers configuration auto-check during
subscription activation considerably facilitates dedicated hosting provisioning:
All third-party servers in your data center can be accounted and registered in Parallels
Business Automation - Standard database in accordance with servers actual location and
configuration.
Automated server configuration check during dedicated subscription activation facilitates
dedicated servers assignment and servers accounting.
Automated billing for dedicated hosting upgrade: You can specify a dedicated server
configuration in hosting plan and allow a customer to select each parameter within a certain
range during initial purchase and later order upgrade or downgrade for his/her dedicated
server by selecting one or another option in a corresponding custom attribute (disk space,
RAM, etc.).
If a hardware Node was not registered yet, then register it. Select a
Hardware Node
and edit its
General Settings: assign an owner account and create a subscription (or assign a server to
existing subscription).
If an a ssigned server configuration does not match an ordered configuration, Parallels Business
Automation - Standard allows assigning a server anyway, but leaves a server in Not
Synchronized status till a server configuration will be brought in correspondence with an
ordered configuration.
Page 67

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 67
Managing Nodes by Groups
Servers (also referred as nodes) registered in Parallels Business Automation can be united into
groups for better management. Such grouping provides an additional way to assign nodes for
services provisioning (per hosting plan) and allocate IP addresses. IP addresses allocation is
associated with nodes groups by assigning an IP pool to a nodes group, in the same way as an IP
pool can be allocated to a type of hosting. In addition, you can group nodes by location
(datacenters, etc.).
Nodes are grouped by types. Only nodes of the same type can be included in a group. It is
possible to create as many nodes groups as needed. First you create a group and then add
(remove) nodes into (from ) it.
To add a nodes group:
1. Open the Service Director submenu, expand the Manager folder that corresponds to type of
nodes you want to group (Plesk, Virtuozzo, Parallels Server, Dedicated Servers). Select
Node Groups.
2. Click New Node Group. Fill the form:
a Type a group name into the Name field. This is the name the group will be referred to
when associating with hosting plan or IP pool.
b Type a short description of the group into the Description field.
c Enter a free-form comment into the Comment field.
3. Click Save.
As a group is created, you can add or remove nodes, or remove this group. Removing a group
cancels nodes logical grouping.
To add node to group:
1. Click on a group name.
2. Switch to the Nodes tab.
3. Click Add Nodes. The list of all the nodes that belong to the type you have selected appears
on the screen.
4. Select the nodes you want to add by checking the box next to nodes' names.
5. Click Add Nodes.
Page 68

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 68
Selling Licenses
Parallels Business Automation - Standard allows selling Parallels Plesk Control Panel, Parallels
Plesk Sitebuilder, Parallels Virtuozzo Container, and some other types of licenses as a part of
services included in the following types of hosting plans:
Dedicated node.
Dedicated Plesk server.
Virtuozzo Container (in case a hosting plan includes the Plesk Server Administrator
application). A Virtuozzo Container behaves like a Plesk server, but is not registered in
Parallels Business Automation - Standard as a Plesk node.
Plesk Server in Virtuozzo Container (Plesk Virtual Node). A Virtuozzo Container behaves
like a Plesk server, and is registered in Parallels Business Automation - Standard as a Plesk
node.
Miscellaneous.
The special plug-in for licenses issuing (Parallels Key Administrator) that can be installed
similarly to the other plug-ins makes it possible to request licenses on a customer order. The
plug-in can be configured both for working in online and offline mode.
The requisites and keys necessary for Parallels Key Administrator (Parallels KA) to work online
are issued by Parallels. Depending on a HSP needs, Parallels can issue a special key for a
particular license class or for a number of license classes.
Tools for license services management are grouped under the Service Director > License
Manager. The list of licenses classes available for the Parallels partner if shown under the
License Manager > Licenses.
Page 69

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 69
Managing Key Administrator Plug-Ins
To use the Parallels Key Administrator services, please, contact your vendor and complete a
client agreement to get the Parallels Key Administrator client login. Using this login, you can
log in to the Parallels Key Administrator GUI and manage your licenses and this login is also
used to set up the Key Administrator plug-in that allows requesting licenses online.
Note: There can be different Parallels Key Administrator client logins that allow issuing
licenses of different classes. If you have different client logins and if you want to sell different
license classes using the Parallels Business Automation - Standard tools, then you should
configure several KA plug-in configurations.
The KA plug-in can be configured both for online licenses issuing and manual licenses upload.
You can configure a number of KA plug-ins. However, to sell licenses, it is required to
configure at least one plug-in, because configuring a KA plug-in is the only way to define the
set of license classes you will sell.
Immediately after a KA plug-in configuration is saved, Parallels Business Automation Standard starts executing a special task that fetches the list of license classes. Only after the list
of license classes is fetched a KA plug-in is considered as configured and gets a 'Configured'
status, i.e., ready for use.
The list of license classes is available for every KA plug-in below the License Classes and
Properties tab.
For offline KA plug-in configurations the list of license classes is taken from the Parallels
Business Automation - Standard database and thus, it is the same for any offline KA plug-in
configuration. This list of license classes includes the full set of license types the Parallels KA
provides, so after the list of license classes is fetched, it is necessary to do a post-configuration
and select the license classes to sell in accordance with the client agreement completed with
Parallels Key Administrator .
For online KA plug-in configurations the list of license classes is requested online directly from
the KA server and since a client requisites are passed to KA, the returned list of license classes
corresponds to a client permissions stated in a client agreement. Thus, for online KA plug-ins
additional check and post-configuration of the license classes list is possible but not necessary.
To add a new KA plug-in configuration, click the New plug-in button.
The list of KA plug-ins displays the following:
ID. A numerical identifier assigned to a KA plug-in configuration in the Parallels Business
Automation - Standard database.
Plug-in name. The KA plug-in configuration name assigned in Parallels Business
Automation - Standard. A pug-in is referred
Configured. This column shows whether a KA plug-in is ready for use or not:
- A plug-in is ready for use, all the necessary data is entered and saved, the list of
license classes is fetched.
- A plug-in is not ready for use. Either some data is missing in a plug-in
configuration, or (for online plug-is) no connection with KA server, or the list of license
classes is not fetched.
Page 70

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 70
Selecting License Classes to Provide
A 'License Class' is a particular version of a particular licensed product. For example, Plesk 7.5
Reloaded (TM). Licenses are issued in the frame of a license class, starting from a single license
and up to a license pack that includes several identical licenses.
After all the data necessary for new Parallels Key Administrator (KA) plug-in configuration is
saved, Parallels Business Automation - Standard starts executing a special task that fetches the
list of license classes allowed for this particular plug-in. Only af ter the li st of license c lasses is
fetched a KA plug-in is considered as configured and gets a 'Configured' status, i.e., ready for
use. The list of license classes appears under the License Classes and Properties tab within a
plug-in configuration settings.
The set of license classes is read-only in respect to the number of license classes, their
composition and each class properties.
For offline Parallels Key Administrator (KA) plug-in configurations the set of license classes
available is taken from the Parallels Business Automation - Standard database and in this case,
the license classes list normally includes all license classes available at Parallels KA. For offline
KA plug-ins you must manually select the license classes to sell, in accordance with the client
agreement you have completed with Parallels KA.
For offline KA plug-in configurations the set of license classes available can be changed (for
example, new classes can be added to the list) by installing a simple upgrade. The upgrade is
developed and conducted by Parallels.
For online KA plug-in configurations the set of license classes available is fetched online after
a plug-in is configured from the KA server and in this case, the set of license classes will
automatically correspond to your KA client agreement, because it is checked by your client
login and password. Online KA plug-in configuration allows updating the list of license classes
online. In this case, if Parallels Key Administrator has started supporting new license classes,
they appear in the list, and if some license classes support has been discontinued, such license
classes are removed from the list. Existing configuration of license classes availability stays
without changes. To update the list of license classes online, use the Reconfigure button located
below the list of license classes.
You can enable a license class to make it possible to include the corresponding licenses in
hosting plans and sell them. Please note that only enabled license classes can be included in
hosting plans.
Each license class can include a variety of license types (for example, different number of
domains for Plesk licenses), additional features, and additional keys. Additional keys are
complementary licenses that can be sold together with license that belongs to a license class. A
license class configuration with all its features and additional keys (if any) is visible from
hosting plan settings, under the Licenses tab or at the 'Licenses' step in a hosting plan creation
wizard.
To make licenses of a particular class available for sale:
1. Select Service Director > License Manager > Plug-Ins. The list of all configured KA plug-ins
appears on the screen.
2. Click on the name of the KA plug-in you would like to configure license classes for.
Page 71

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 71
3. As the KA plug-in settings appear on the screen, click on the License Classes and Properties
tab.
Note: If you have selected a KA plug-in configured to get licenses online, the list of license
classes can be updated online. To this effect, click the Reconfigure button located at the
bottom of the list. Offline KA plug-ins do not have such a button.
4. Scroll the list of license classes that appears on the screen up to the end and click the Edit
button.
5. To allow a license class for selling, check the box next to a license class name. To disable a
license class for hosting plans, clear the box next to a license class name.
6. To save changes, click the Update button.
Managing Licenses
Licenses provisioning sch eme is the follo win g:
Customer orders a hosting plan with license in store and pays the order.
After this, subscription creation starts. At the same moment, a license file image called
license re qu est i s added to the Parallels Business Automation - Standard database. A license
request contains all the information about an ordered license. A license request is submitted
to Parallels Key Administrator to get a license key and after this, a license file(s). In the
course of an order completion, License(s) provisioning is the last thing, it starts after all the
other services included in a subscription are ready for use.
Online licenses issuing is a quick procedure in case the Parallels Key Administra tor (KA)
server is available. A KA plug-in sends a license request to the (KA) server. In return, the
KA server issues a license key (a license alphanumerical identifier) and sends is to the plugin. Then, using an issued license key, the KA server generates a license file and sends it to
Parallels Business Automation - Standard. Finally, the KA plug-in tries to install a license
into a customer subscription. In case installation fails, provider can install a license file for a
customer manually.
In case licenses are uploaded manually, provider can view license requests in the list.
Then provider clicks on a license request ID and gets a license request details displayed.
After this, a license key(s) and file(s) can be uploaded manually to the Parallels B usiness
Automation - Standard database. Finally, provider manually installs a license into a
customer subscription.
Page 72

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 72
Licenses are displayed in a list below a tab where the name of KA plug-in used to issue these
licenses is shown. If you use several KA plug-ins, then licenses are collected into a several lists
below several tabs, grouped by plug-ins used for issuing.
To upload or request a new license (on page 74), click the New License button.
The list of licenses displays the following:
ID. The numerical identifier assigned to a license in the Parallels Business Automation -
Standard database. ID is assigned from the moment when a license request appears.
Key Number. A license identifier issued by Parallels Key Administrator. If a license key
number is not shown, this means that only a license request presents. A license key can be
issued by a license request.
Subscription. If a license is assigned to a customer subscription, then this subscription name
is shown. If no subscription shown, then a license is unused. If the Not Assigned is displayed
in the Subscription column, this means that a license has been ordered for a subscription of
Dedicated Server type, but this subscription is still in the Pending state awaiting for manual
assignment of a dedicated server.
License Class. The name and version of a licensed software. There may be a variety of
license types for a particular software product, for example Plesk licenses with different
number of domains or clients or Virtuozzo licenses with different number of Containers.
That is why software type is called as License Class.
Status. A license current status tells what has been done to a license and what can be done
to it at the moment. A license possible statuses are:
Pending. Only a license request is stored in the Parallels Business Automation -
Standard database. There is neither a license key, nor a license file. First, a license key is
to be obtained. To get a license key, click on a license request ID. After a license request
details appear on the screen, click the Issue License button.
Issued. A license key is issued and is stored in the Parallels Business Automation -
Standard database. There is no license file yet. To get a license file, click on a license
ID. After a license details appear on the screen, click the Retrieve button.
Retrieved. A license file(s) (together with a license key) is in the Parallels Business
Automation - Standard database. A license file is ready for passing to a customer or for
sale, if there is no order for a license. However, a license file is still at the Management
Node. It is possible to download it at your local computer. To this effect, click on a
license ID. After a license de tails appear on t he screen, clic k the Download to Desktop
button. After a license file is downloaded, it can be manually passed to a customer or
installed into a customer subscription. In addition, there is an intermediate status
Retrieving. It means that a license retrieval is in process. Normally, this status occurs for
a very short time. However, if something impedes a license retrieval process, for
example, connection between KA plug-in and KA server is broken, then a license may
stay in the Retrieving status for some time.
Terminated. A license is cancelled at the Parallels KA side. This status only means that a
license is marked as terminated at the Parallels KA side. There is no online tools for
licenses termination in customers subscriptions.
Uploaded. A license is manually uploaded into the Parallels Business Automation -
Standard database using the offline KS plug-in.
Installed. A license is installed in a customer subscription. There is an additional status
Installing. It means that a license is in process of installation into a customer
subscription.
Page 73

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 73
Expired. A license has been issued using the Monthly bill type and its expiration period
is over. Expired licenses cannot be used anymore.
Activated. This status occurs for licenses (some Sitebuilder and Virtuozzo versions) that
require activation after a license key is issued. Such licenses can be retrieved only after
activation.
Bill Type. How a license is to be paid. Can be one of the following:
Monthly. License is purchased for the period of one month with one-month Parallels's
Software Update Service (SUS), i.e. the abili t y of upgrading a license. Monthly paymen t
is required, if a subscription is not renewed in time, license(s) are deactivated and cannot
be sold to customers.
Purchase. Licenses are purchased for an unlimited period with one-time payment and
one year SUS. In this case, licenses never expire.
Page 74

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 74
Uploading Licenses
A new licence is added in the two steps.
After you click the New License button at the screen showing the list of Licenses, first you select
the product you would like to get a new license for, in other words, you select a License Class.
Then you select a license capacity.
Selecting a License Class
The list of License Classes that appears at the screen corresponds to the set of License classes
allowed for the KA plug-in you use to request a license.
1. Set the option button to the product you would like to get a new license for. It is possible to
select only one License Class, but several licenses of this class can be ordered.
2. Enter the number of licenses of the selected License Class you want to request into the
Number of Licenses field located below the list of License Classes.
3. Click the Next button.
Specifying a new license capacity
Licenses of each License Class have a particular configuration settled by the issuer - the
Parallels Key Administrator. For offline KA plug-ins licenses configuration is fetched from the
Parallels Business Automation - Standard database, and for online KA plug-ins it is taken online
from the Parallels Key Administrator server.
Depending on a License class (i.e., a licensed product), a license configuration differs.
Some licenses are a single file without any additional features, other licenses may be of a
different capacity (for example, Parallels Plesk Control Panel license may be for different
number of domains, Virtuozzo licenses may be for different number of Containers) and include
a number of additional features, a license may also include additional license keys (gameserver
or anti-virus) and a number of additional features may be available both as a standalone
services and in the frame of one of another additional license key. Additional license keys are
separate licenses, but they are included in a basic license and shipped together with it.
Additional keys and features are sold as included or complementary services in the frame of a
license. Prices and conditions for licenses and additional keys/features are specified per hosting
plan.
1. The settings related to the basic license are grouped at the License Properties bar. Specify a
license capacity (if any variants are at your choice).
a Set the option button to a needed capacity.
b If any additional features are available for the license, check the boxes next to the
features names to request the license with these features. If you do not need a feature in
the license, leave the box next to its name clear.
Page 75

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 75
2. If any additional licenses are available with the basic license, then the options related to
each additional license key is brought to a separate bar and a licensed product name if
written on this bar.
a To include an additional license key into a basic license, check the box next to the
licenses product name. If you do not include an additional license into the basic one,
leave the box clear.
b If any additional features are available with the additional license key, these features are
specified below the licensed product name. To include an additional feature in the basic
license you are going to request, check the box next to a feature name, otherwise - leave
this box clear. If an additional license has its own capacity, then set the option button to
the needed capacity in the same way as for the basic license.
3. To request a new license, click the Issue License button.
Page 76

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 76
Allocating IP Addresses
Note: This section describes the IP addresses management available from the Provider Control
Center. The special paragraph is devoted to IP addresses management for Resellers, using the
Reseller Control Center.
The IP addresses assets assigned to the Parallels Business Automation - Standard cluster are
managed by groups (IP pools).
It is possible allocate IP addresses of types:
IPv4 - standard 32 bit IP address of xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx format.
IPv6 - new 128 bit IP addressing of xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx format. A
group of xxxx represents the 16-bit hexadecimal value, for example,
4FDE:0000:0000:0002:0022:F376:FF3B:AB3F.
It is by design that in PBAS interface IPv6 addresses are always shown compressed and letters
in lower case. At the same time, IPv6 addresses can be entered in PBAS in any format:
compressed or not; in upper case or in lower case. Anyway, the IPv6 address will be shown
compressed and in lower case.
For example, the IPv6 address 4FDE:0000:0000:0002:0022:F376:FF3B:AB3F will be shown as
4fde::0002:0022:f376:ff3b:ab3f.
Provider can add IP pools using the Service Director > IP Manager. To add an IPv4 IP pool, click
the New IP Pool button. To add an IPv6 IP pool, click the New IPv6 Pool button.
The IP Manager allows you to automate the configuration of IP address properties such as
addresses of the DNS servers and default gateways for Containers.
You can define only static allocation within each IP pool. Static IP addresses are allocated
permanently and can be released only manually.
Using the IP Manager you can track the usage of IP addresses in the frame of services provided.
The list of leases is provided for each IP pool. This list shows which Containers are using
particular IP addresses.
To restrict usage of certain IP addresses within an IP pool, you can create exclusions that cover
a single IP address or series of IP addresses.
IP pools can be assigned to specific resel lers or hardw are nodes o r types of hos ting:
Assigning an IP pool to a specific type of hosting means that IP addresses from this IP pool
will be used for provisioning of particular type of services. This assignment is exclusive,
i.e., it is not possible to assign an IP pool to several types of hosting. You can allocate an IP
pool for:
Virtuozzo Containers.
Name-based Virtuozzo Containers.
Plesk Domain or Client hosting.
Virtual Machines
Page 77

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 77
Dedicated servers.
Assigning an IP pool to a reseller means that customers of this reseller will use IP addresses
from the IP pool assigned.
Assigning an IP pool to a Hardware Node means that IP addresses from the IP pool
assigned will be allocated, for example, to Containers hosted on this Hardware Node
only.This is extremely useful if you have different network segments in your infrastructure.
In this case, you can assign particular IP pools to corresponding Hardware Nodes in
segment. In case Containers will be migrated from one Hardware Node to another, IP
addresses will be reassigned automatically.
Assigning an IP pool to a group of nodes means that IP addresses from the IP pool assigned
will be allocated, for example, to Containers hosted on nodes included in this group.
Supervising Service Level
The Service Level Manager provides a mechanism for checking the current resource utilization
throughout Containers and Hardware Nodes. Using the Service Director > Service Level
Manager, you can:
View the both the current resources consumption and the resources usage history for every
Container or every Hardware Node. Go to the Service Director - Service Level Manager.
Select Virtuozzo Container or Hardware Nodes. For every Container or Hardware Node you
an view the current resources usage (the Current Values tab) or resource usage history
(Statistics tab). This feature is very useful if, for example your customer believes that some
resource was under-delivered. In this case you can settle a customer's doubts by checking
the total resource usage during a particular period and daily or hourly consumption for a
given period of time.
View traffic usage statistics for third-party dedicated servers.
Set the thresholds in percents for disk space and traffic that when exceeded are reported into
the list of Containers that are approaching limits. To this effect, go to the Service Level
Manager - Setup. To view the list of Containers that have exceeded the threshold percentage
of promised disk space and traffic, select Container approaching limit.
Note: When traffic or disk space usage for a Container approaches the limits set in the Service
Level Manager, the corresponding event is registered by the Parallels Business Automation Standard Event Manager (namely, Traffic is nearly used up and Disk space is nearly used up, to
find these events, filter the list by the Subscription object type). Thus, you can attach an action
to such events, for example, e-mail notification or SMS message to your staff member.
Finally, you can configure traffic accounting by classes in the Service Director > Service
Level Manager > Traffic Classes.
Page 78

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 78
Configuring Traffic Classes
The Parallels Business Automation - Standard service level management tools allow you to
track the inbound and outbound network traffic for Plesk clients and domains, Containers, and
physical dedicated servers. In order to provide the ability to distinguish between domestic and
international traffic, a concept of network classes is introduced. It is important to fully
understand this notion, because network classes IDs are used in the values of some network
traffic parameters. A network class is a range of IP addresses for which traffic is counted and
charged.
Parallels Business Automation - Standard allows having up to 15 different network classes
specified. Each class can contain one or more IP address ranges.
Classes 1 and 2 have special meanings. Class 1 defines the IP address range for which no
accounting is done. Usually, it corresponds to the Virtuozzo Hardware Node subnet (the Node
itself and its Containers). Setting up Class 1 is not required; however, its correct setup improves
performance.
Class 2 is defined to match any IP address. It must be always present in the network classes
definition file. Other classes should be defined after Class 2. They represent exceptions from the
"matching-everything" rule of Class 2.
Traffic classes IDs are assigned automatically and cannot be changed later.
Important: A traffic class configuration must be passed to a Hardware Node and stored there in
a special network configuration file, so a Hardware Node could 'know' what traffic data must be
accounted and passed to Parallels Business Automation - Standard. The procedure of passing a
traffic class to a Hardware Node is called 'Synchronization'. Virtuozzo for Unix allows
accounting traffic by all the traffic classes, and Plesk as well as Virtuozzo for Windows allow
accounting t he overall traffic only, i.e., by the Class 2. Please keep in mind that a traffic class
must be synchronized with a Node to make traffic accounting by this class possible. Traffic
classes synchronization can be initiated using the Synchronize traffic classes button at the traffic
classes list screen, or its current synchronization state can be checked at the Synchronization
details tab within a traffic class details.
The tools for traffic classes management are grouped under the Service Director - Service Level
Manager - Traffic Classes.
The order of traffic accounting follows the order of traffic classes in the list shown at the Traffic
Classes screen.
Note: Traffic accounting by classes can be set for all hosting plan types (except Miscellaneous
and Domain Registration). For all types of Virtuozzo Unix hosting plans (Container, Dedicated
Virtuozzo server, Plesk server in Container) and dedicated hosting all traffic classes are
applicable. For Plesk (Dedicated Plesk Server, Plesk Client, Plesk Domain) and Virtuozzo for
Windows hosting plan types only Class 2 is applicable.
To add a network class:
1. Click Traffic Classes on the Service Level Manager submenu. The list of all traffic classes
appears on the screen.
Page 79

Managing Parallels Business Automation - Standard Services and Data Center 79
2. Click the Add Traffic Class button.
3. Fill the form that appears:
a Enter the traffic class friendly name into the Traffic Class Name field.
b To perform the traffic accounting by the class and make it possible to define the traffic
accounting by this class for hosting plans, you need to enable the traffic class by
checking the Enabled box.
c You can add a free-form comment into the Description field.
4. Click the OK button. The newly created traffic class properties appear on the screen. They
display all the data entered for the class plus one more property - the used fie ld. T his f ield
shows whether a class is used in hosting plan(s) or not (green tick -yes, used, red cross - not
used). If a traffic class is used in at least one hosting plan, it cannot be deleted.
5. Click the IP Ranges tab to define the range(s) of IP addresses to be accounted.
6. Click the Add IP range button.
7. Fill the form that appears:
a Type the starting IP address into the IP range and the netmask in the bit form into the
Range prefix field.
b You can add the detailed description of the IP range into the Description field.
8. Click the OK button.
Page 80

80
C
HAPTER
6
Setting Up Domains Registration
This chapter advises how to start registering domains online and make the most general settings
necessary for a successful domain registration. The daily tasks connected with the domain
management are described later in this guide (on page 245).
In This Chapter
How to Start Registering Domains Online ............................................................................ 80
Configuring Domain Registration Plug-Ins .......................................................................... 81
Top Level Domains Assignment ........................................................................................... 82
Setting Registrar Prices ......................................................................................................... 83
Selecting Both the Default Domain and the Domain for Trial Containers Hostnames......... 86
Allowing Domain Transfer Per Registrar TLDs ................................................................... 87
Configuring Default Records for Zone Files (DNS Templates) ........................................... 88
Specifying Name Server Sets ................................................................................................ 89
Registering Internationalized Domain Names ...................................................................... 92
Adjusting DNS General Settings .......................................................................................... 93
Managing Contacts Used for Domain Registration .............................................................. 96
Specifying Whois Servers ..................................................................................................... 97
Viewing Incoming and Outgoing Domain Registration E-mails .......................................... 98
How to Start Registering Domains Online
Parallels Business Automation - Standard allows establishing connection with Internet
Registrars via the pluggable modules (plug-ins).
To configure domain registration plug-ins, please register your reseller account with the
corresponding Registrars and obtain all the necessary pre-requisites. After this, you can go to
the Service Director > Domain Manager > Plug-Ins and configure domain plug-ins.
To register a domain manually, from the Provider Control Center, select Service Director >
Domain Manager > Domains > New Domain button.
You can assign both the default domain and the domain used for trial subscriptions (for
customers to create subdomains), as well as use the other advanced domain settings.
Page 81

Setting Up Domains Registration 81
Configuring Domain Registration Plug-Ins
For the fresh Parallels Business Automation - Standard installation, Parallels Inc. offers a set of
plug-ins for establishing a connection with the domain registrars, so you just have to key in the
necessary information into simple forms. Please note that in this case, you should open the
Account with the registrars where you want to register your domains and receive your own
logins, private keys and other data, depending on the Registrar's internal rules.
Domain registration plug-ins are shipped as RPM modules independent from Parallels Business
Automation - Standard functionality.
After installation, a plug-in becomes available in Parallels Business Automation - Standard as a
selectable type for a new domain registration plug-in configuration. To add a domain
registration plug-in based on one of a standard configurations, it is enough to go to Service
Director > Domain Manager > Plug-ins, click New Plug-in, enter a new plug-in configuration
name and select a configuration type. After this, a plug-in configuration form appears on the
screen . The o nly thi ng to do a fter this - fill the form and save the configuration. The number of
plug-ins that can be added on the basis of the same standard configuration is not limited.
Note1: The Parallels Business Automation - Standard installation owner defines the set of
domain registration plug-ins available for each reseller.
The list of domain registration plug-ins (to domain registries and registrars) shipped with
Parallels Business Automation - Standard is available at the Parallels official website
(http://www.parallels.com/en/products/hspcomplete/templates/domain).
Note2: If you are planning to use OpenSRS services for the online domain registration, then
Port 55000 for OpenSRS (horizon.opensrs.net) should be opened on the Management Node. In
the case if you intend to use eNom services for the online domain registration, then Port 80 for
eNom should be opened on the Management Node (the host should be agreed with eNom).
Please, make sure that the RPM packages necessary for online domains registration are installed
(refer to the Parallels Business Automation - Standard Installation Gu id e ).
You can view the Plug-in lookup state in the Domain lookup mode field of the Plugin Setup
window. The mode may be as follows:
registrar API is used for lookup (green indicator)
WHOIS lookup is used; all plug-in's TLDs are assigned to some WHOIS (green indicator)
WHOIS lookup is used; and some TLDs are not assigned to any WHOIS (yellow indicator);
TLDs which are not assigned to WHOIS servers are listed in 'Comment' field
WHOIS lookup is used; no TLDs are assigned to WHOIS servers (red indicator)
Note: Many registrars accept requests from known hosts only and require that you specify the
client IP address (i.e, your Management Node IP address) in your account profile. Please, clarify
this issue with registrars' support before you start using a domain plug-in.
Page 82

Setting Up Domains Registration 82
Important: The ability for resellers to use the own configuration of domain plug-ins is defined
in Reseller Configuration (on page 176). Reseller Configuration can be assigned in reseller
account General Settings.
Top Level Domains Assignment
You have already configured (on page 81) one or more domain registration plug-ins.
Before activating domain plug-ins and start registering domains, it is necessary to correctly
configure the set of Top Level Domains (TLDs, like .com, .net, org, etc) available for domains
registration for each domain plug-in, i.e., specify what TLDs supported by each registrar.
Since the set of TLDs supported by one or another Registrar can change (new TLDs can be
added or some TLDs can be cancelled by a Registrar), TLDs can be manually added or removed
for each domain registration plug-in. Provider can change the TLDs set for domain plug-ins in
an arbitrary manner. Thus, Provider is finally responsible for correct TLDs assignment.
The same TLD can be assigned to a number of domain registration plug-ins, which allows
saving in Parallels Business Automation - Standard the conditions of domain registration in the
same TLD offered by a number of registrars.
A registrar that will actually provide domain registration in one or another TLD can be selected
per domain registration hosting plan. When you change registrar in a hosting plan, customers
who have already registered domains with a previous registrar keep using their domains on the
same conditions and new customers start registering domains with a newly set registrar. Thus,
changes in a domain registration hosting plan is not followed with creation of a hosting plan
version.
In a few words, the scheme of TLDs assignment in Parallels Business Automation -
Standard is the following:
1. Go to Service Director > Domain Manager > Plug-Ins.
2. Select a plug-in.
3. Select the Prices tab from a plug-in settings.
Note: For plug-ins that support the online prices update, the Update Prices but ton is sh own
below the list of TLDs. You can click this button and get the prices online. For other plugins you must know out the actual registrar prices and enter them manually.
4. Click the New TLD button.
5. Enter a new TLD name and select a plug-in (i.e., a registrar). (Select a plug-in you want to
add TLD(s) for. Click Next.
6. Specify the conditions of domains registration. Click Update.
Note: You can add the same TLD(s) to several Registrars and then select an active registrar
in hosting plan settings.
Page 83

Setting Up Domains Registration 83
For the registrars that do not support the online prices update it is only possible to manually
enter your retail prices:
Contact a Registrar and know out the prices. Then go to Operations Director > Domain
Manager > Plugins, select the plug-in and then select the Prices tab. Click on the TLD name
and type your own retail prices.
Setting Registrar Prices
Prices for domain registration are set per registrar. After you set registrar prices, a TLD is
considered as configured for a given registrar and you can select the corresponding plug-in as
supporting registry for a TLD in hosting plans.
To set prices for a TLD, select a plug-in, select the Prices tab, and then click on a TLD name or
click the New TLD button.
To set the registrar prices:
1. Select registration periods available and set prices:
a To allow domain registration period, check the box next to the period name. To mark a
period as not supported, clear this box. Only supported registration periods are shown in
domain registration hosting plans TLD settings. As you check the box next to a
registration period the fields where you can enter prices become activated.
b For each supported period, enter a registrar's one-time fee for domain registration into
the Registration cost field and enter the registrar's recurring fee into the Renewal cost
field.
2. Adjust the domains Transfer Settings. To allow transferring domains registered in the
selected TLD and enable the form fields where you can enter your retail price for the
transfer, check the Allow domain transfers box. To disallow transfer, clea r this bo x. As you
allow transfer, the fields where you can enter transfer prices become activated:
a Enter the registrar's one-time fee for domain transfer service into the Transfer cost field.
b Transfer includes domain renewal. To renew domain registration under this registrar
right after a domain is transferred, select the renewal period from the Period drop-down
menu. In case of transfer, your prices set in hosting plan for domain renewal will be
applied.
3. Set the domain Renewal Limitations:
a If the registrar allows domain renewal at any moment without respect to the time
remaining before registration period is over, set the option button to Renewal is allowed
at any time.
b If the registrar regulates domain renewal time frame, check the relevant box to select the
condition:
If the registrar allows domain renewal only after a particular time has passed after
domain registration, check the not earlier than _ days after domain registration date box
and enter the period in days.
If the registrar allows domains renewal only when a particular time remains before
registration period is over, check the not earlier than _ days before domain registration
date box and enter the period in days.
Page 84

Setting Up Domains Registration 84
If the registrar allows domains renewal after a domain registration period is over only
during several days, check the not later than_ days after domain expiration date box and
enter the period in days.
4. Specify the DNS zone startup settings:
a Create DNS zone before domain registration. This option is required for correct domain
registration processing for some registrars, which start checking a customer name
servers right after a domain registration request is received. In this case, if a customer
have his/her name servers not configured properly by the moment of domain registration
order placement, a registrar sends an error response. If this option is enabled (the box is
checked) then a zone file is created in Parallels Business Automation - Standard before
sending a domain registration request to a registrar. Name servers synchronization
process starts automatically and Parallels Business Automation - Standard periodically
checks name servers in respect to their readiness to resolve a domain. A zone file is
checked several times with a certain period and these settings can be adjusted specially.
In case the check fails a corresponding record specifying the number of failed attempt
and the period when the next check is to be performed is added to the Action Log. In
case a check is successful (i.e., name servers are ready to serve a domain), the
registration request is sent to registrar. As soon as you check this box the fields where
you can enter DNS startup and check limit become activated.
b DNS zone startup time limit. This option limits the overall time that can be used for name
servers readiness check. If the time is over and name servers are not ready (zone file is
still not created), then domain registration request is sent without respect to a zone file
creation. Please enter the time limit in minutes.
c The number of attempts to check DNS zone. The overall number of attempts Parallels
Business Automation - Standard performs to check the name server readiness. The
checks frequency is calculated automatically, in a nonlinear way, taking in account some
specific features of the synchronization process.
5. Use your contacts for customer's domains registration. Here you can specify what contact
information will be asked during domain registration at a given Registrar in a TLD you have
selected. The value of contact data required and its format considerably differs depending on
Registrar. Some Registrars require a rather specific data. To simplify domain registration
procedure for your customers, you can replace Registrar's contacts form with your own one
(a so called base contacts) that have a standard format.
You can create your contacts (up to 10 for one account name) under Domain Manager >
Setup > Contacts tab. All of the contacts created by you are included in the drop-down
menus next to contacts' names.
The number and names of contacts offered here may vary depending on a Registrar. The
most typical set is Owner Contact, Administrative Contact, Billing Contact, and Technical
Contact.
To create a new contact, click the Create new button. A new contact will be available for
selection for all contact types right after you save it.
To create a new contact on the basis of an existing one, select a contact you want to base
upon from the drop-down menu. The Create copy button activates. Click the Create copy
button. The contact form appears. Adjust the contact data in the form and save changes. The
new contact will be added with an new name ( the auto-incremented numeric prefix added
to the name of contact).
To hide the contact type from a customer, and thus make this contact a read-only, check the
Force box next to the contact type name.
Page 85

Setting Up Domains Registration 85
6. To save changes, click the Update button.
Page 86

Setting Up Domains Registration 86
Selecting Both the Default Domain and the Domain for Trial Containers Hostnames
After you register at least one domain for HSP Company (Provider Account) within your
Parallels Business Automation - Standard system, you should set default domain so that your
prospect customers could register for their subscriptions the subdomains in this domain.
In this case, you should have the list of all domains (Domains screen) displayed. After domain(s)
registration, the list of all domains will be displayed automatically. Otherwise, please click the
Domains link on the Navigation tree or Registered D om ains link at Domain Manager dashboard.
The list of domains displays the following:
Domain. The name of a domain;
Account. The name of an Account a domain was registered for;
Added by. This column shows the name of a User (staff member or a Customer) that h ad
added a domain, and consequently, points to the origin of domain Order (Provider Control
Center or HSPstore). Since several Users can be associated with an Account, this additional
information helps you to manage domains;
Registrar. The Internet Registrar, a company that registered a domain;
Exp. date. The date a domain registration period expires;
Zone Created. Whether an appropriate zone file is created for this domain. In other words,
the green tick in this column indicates that a domain is successfully registered in Parallels
Business Automation - Standard (appropriate Order is completed, and a domain is
manageable). Red cross - that a domain is not registered (domain Order is not paid yet, and
a zone file is not created).
Click on the domain name registered for Provider Account. Domain details will be displayed.
In order to set the default domain, its General Info (namely, Policy settings) should be edited
appropriately. Thus, click the Edit button.
Default domain will be offered to your customers in online store to create subdomains. In case
your prospect customer does not have registered domain or does not intend to register new
domain, he (or she) will definitely use the default offered. Therefore, in order to set domain as
default, you should allow customers (at least Provider’s ones) to register subdomains in this
domain. To this effect, please set the radio button to one of the positions that allow registering
subdomains.
In addition, you can allow registering hostnames for trial Containers. If the Use domain for trial
Container checkbox marked, then this domain will be offered to your customers in HSPstore.
You certainly can set several domains as default ones and allow several domains to be used for
trial Containers. At the same time you can set several domains both as default ones and
available for trial Containers.
Page 87

Setting Up Domains Registration 87
To confirm settings, click the OK button. Changes will be immediately applied to subscription
cycle at your HSPstore.
Allowing Domain Transf er Per Registrar TLDs
Domains transfer can be allowed or disallowed as a system-wide option, in store settings.
However, if you allow domains transfer in general, you still can narrow the set of domains
allowed for transfer by selecting particular TLDs which transfer is allowed for. You can select
TLDs allowed for transfer for each domain registration plug-in.
To select TLDs allowed for transfer, go to the Service Director > Domain Manager > Plug-Ins.
Select a plug-in and then click the TLDs tab. Select a TLD from the list that appears and check
the Allow domain transfers box. As you allow transfer, the fields where you can enter transfer
prices become activated:
Enter the registrar's one-time fee for domain transfer service into the Transfer cost field.
Transfer includes domain renewal. To renew domain registration right after a domain is
transferred, select the renewal period from the Period drop-down menu. In case of transfer,
your prices set in hosting plan for domain renewal will be applied.
Page 88

Setting Up Domains Registration 88
Configuring Default Records for Zone Files (DNS Templates)
Using the DNS template, you can set the pre-defined configuration of resource records in a zone
file created on domains registration in Parallels Business Automation - Standard.
Note: Default SOA records are bound to TLDs and configured in Domain Manager > Setup -SOA
Defaults.
DNS templates are bound to Domain Registration hosting plans. When you add a hosting plan
(any type except for One-Time Fee Item type), you should always select the corresponding DNS
template.
To add a DNS template, please go to the Service Director - Domain Manager > DNS Templates.
To facilitate configuration of services on a domain, DNS Template types have been introduced.
Now you can create DNS templates that can be used in a particular hosting plan types.
One of the DNS templates within each type should be marked as default. The default DNS
template is applied to zone files in case no DNS template has been specially assigned.
The DNS template of the Common type is applied to hosting plan types that do not have a
special type of DNS template.
The list of DNS templates displays the following:
ID. The numerical identifier automatically assigned to a DNS template in Parallels Business
Automation - Standard.
DNS Template. The DNS template name assigned by you. This name is used in Parallels
Business Automation - Standard to just refer to a DNS template.
Account. The name of an account a DNS template has been added by.
Type. The type of hosting plan a DNS template is used for.
Default. The green tick in this column means that a DNS template is the default one and is to
be applied to zone files if no other DNS templates are specified. Red cross - that a DNS
template is not the default one and is to be applied in accordance with a manual assignment
to a hosting plan. The default DNS template is also can be used while restoring a domain
zone file from the Parallels Business Automation - Standard database. To use the default
DNS template for zone files restoring, set this in Domain Manager > Setup.
Page 89

Setting Up Domains Registration 89
Specifying Name Server Sets
For the fresh Parallels Business Automation - Standard installation, by default you have two
Provider name servers grouped into one set - the default name servers set.
You can use the default name servers set or you can add more name servers and create more
name servers sets.
It is possible to install and configure name servers directly from the Provider Control Center
web-based interface.
The default name servers set can be se lected in the Service Director > Domain Manager > Setup.
Name servers set are specified per Domain-Registration Hosting Plan.
Registering Name Servers
To manage name servers and name servers sets, select Domain Manager from the Service
Director submenu and then click Name Servers on the Domain Manager menu.
To add more name servers:
1. Click the Name Servers tab. The list of name servers appears on the screen.
2. Click the New Name Server button. The wizard that helps to add a name server starts.
3. Type the name server name and select the type:
a Type the name server friendly name (not hostname) into the Title field.
b Set the radio button to the type of name server:
Non-manageable name server. If you want to register a third-party name server that
answers the Parallels Business Automation - Standard DNS requests, but does not
support automated zone files synchronization. For example, you can use this type of
registration for your secondary name server.
Name server to be managed over SSH. If you want to register the physical name server
and if you want changes made to a domain (e.g., if more hostnames were added) to be
automatically synchronized with appropriate zone files on this name server.
Important: If you register a name server managed by SSH, please make sure that hostname
of this name server is resolved correctly on your Management Node. In this case, you can
enter an IP address instead of a hostname, but this is not recommended.
4. Click the Next bu tton and follow the wizard.
Page 90

Setting Up Domains Registration 90
Managing Name Server
o the list of name servers (when viewing name
server information) or to exit the edit mode without
Change name server type (manageable or not) and
Name Server Properties:
Title. Name server reference name.
Status. Server current status.
Hostname. Name server hostname.
IP Address. Name server IP address.
Account. The name of the account that owns the name server.
Name server is managed by Parallels Business Automation - Standard:
For SSH-managed name servers:
Use IP address instead of hostname for SSH connection:
Path to named configuration file. The path to the named configuration file on the name server
SSH protocol version. Version of SSH protocol.
Establishing Connection Timeout. The connection timeout interval in seconds into the field.
Button Click To
Cancel
Check Status
- yes, managed.
- no, not managed.
- IP is used.
- hostname is used.
Get back t
saving changes (when editing).
Update name server status.
Change NS Type
settings (on page 90).
Delete
Edit
Delete information about name server from PBAS.
Edit name server settings (keeping its type unchanged).
Changing Name Server Type
Change name server type:
1. Fill the form:
a Type the name server new name into the Title field.
Page 91

Setting Up Domains Registration 91
b To make name server available for zones addition/update, check the Name server is
available box. To temporarily disallow zones synchronization, clear this box.
c Select the name server new type:
Non-manageable name server. If you want to register it as a third-party name server that
answers the Parallels Business Automation - Standard DNS requests, but does not
support automated zone files synchronization. For example, you can use this type of
registration for your secondary name server.
Name server to be managed over SSH. If you want to register it as the physical name
server and if you want changes made to a domain (e.g., if more hostnames were added)
to be automatically synchronized with appropriate zone files on this name server.
a Check the respective box to register the name server with domain registrar(s) , if
available.
2. Click Next to proceed.
3. Fill the form:
If you have selected non-manageable server type, click to get the instruction.
If you have selected name server managed over SSH, click to get the instruction.
4. Click Save to apply and save your changes.
Page 92

Setting Up Domains Registration 92
Registering Internationalized Domain Names
An Internationalized Domain Name (IDN) is a standard for the domains that can contain
characters other than the 36 basic ASCII ones permitted to date (a-z, 0-9, and -). Thi s includes
Latin letters with umlauts, accents and other diacritics, but it goes further than that and allows
using completely different alphabets, such as the Greek and Cyrillic ones, as well as Chinese
letters and characters.
Parallels Business Automation - Standard does not call for any specific configuration to start
registering IDNs. A domain name entered as a Unicode string is converted into a permitted
ASCII domain name.
A system called Internationalizing Domain Names in Applications (IDNA)
(http://ietf.org/rfc/rfc3490.txt?number=3490) was adopted as the chosen Internet standard for
IDNs. The IDNA algorithm transforms domain names which include letters that are not
available in ASCII into the format that can be handled by normal name servers. This
transformation algorithm is based on the Punycode ASCII encoding of normalized (Nameprep)
Unicode strings.
Note: The IDNA standard requires that the user who would like to view an IDN, has an IDN
compatible application (browser, mail client, etc). The lists of such applications are available
over the web.
Nameprep is the process of normalization, case-folding, etc. applied to a text before it is suitable
to represent a domain name. Nameprep is defined in RFC 3491
(http://ietf.org/rfc/rfc3491.txt?number=3491).
Punycode defined in RFC 3492 (http://ietf.org/rfc/rfc3492.txt?number=3492) is the special
encoding of Unicode strings into the limited character set supported by the DNS. The encoding
is applied separately to each component of a domain name which is not represented solely
within the ASCII character set, and a reserved prefix 'xn--' is added to the translated Punycode
string.
Thus, an IDN always has two forms: one with special characters and the other in pure ASCII
also called ACE (ASCII Compatible Encoding) or Punycode.
This ACE string is then entered into the DNS. The introduction of IDN means that in this case
the entry in DNS is no longer identical with the domain name.
Not all the world’s Top Level Domains (TLDs) are going to take on all these special letters and
characters! Each registry responsible for a TLD is to decide for itself which subset to admit for
the domains under it. In doing so, it strikes a balance between the limitations imposed by the
standard and the particular needs of its local Internet Community. So please, keep this in mind
when enabling INDs registration in Parallels Business Automation - Standard as system-wide
option and then selecting TLDs per domain registration plug-ins.
Page 93

Setting Up Domains Registration 93
Note: Some letters are not included in the IDNA Standard, such as the German ' ' (called
'scharfes s' or 'eszett'), which should be written as 'ss' instead. The eszett is a letter that is totally
unique to the German alphabet. Unlike other letters, it has no upper case form, because it never
occurs at the beginning of a word. The eszett is always normalized as 'ss' and thus, is typically
shown as 'ss' in registered domain names. For example, wei
.com will not be transformed to
xn--wei-abc.com. Rather, it must be written as weiss.com and therefore is classified as a normal
domain.
You can enable registering IDNs globally, as a system-wide setting, in Service Director - Domain
Manager - Setup.
Adjusting DNS General Settings
To adjust DNS general settings:
1. Open the Service Director submenu and select Domain Manager.
2. Click on the Setup on the Domain Manager submenu.
3. Click the General tab. The Domain Manager General setup form appears on the screen.
4. Click the Edit button. The screen reloads with the General setup for editing;
5. Fill the form:
a Select the default name servers set from the Default name servers set drop-down menu.
This is the set to be used by default to register domains for Containers, for web hosting.
Thus, only manageable name server sets are available as default ones.
Note: The default name servers set is used only if the active domain-registration plug-in is
configured to use Provider DNS. If the active plug-in is configured to use the Registrar
DNS, then this setting is ignored.
b Use DNS Template for switching to DNS Hosting. Parallels Business Automation -
Standard supports DNS hosting (when a domain zone file is created at Parallels
Business Automation - Standar d name servers). Put a tick in this box to use the default
DNS template for zone files creation in such cases.
c Default MX priority. This option is used for mail setup for owners of subdomains
registered in Provider default domain (i.e., a domain does not belong to a customer). For
example, when a customer buys Container and registers for this Container a domain in
Provider's default domain, the corresponding MX record pointing to a customer's
Container is created in the Provider default domain zone file. This allows receiving email for a customer.And the Default MX priority allows setting the priority for this mail
exchanger. Typically this is a low priority, so the number specified should be not very
small (for example, 255).
d Default record TTL. The default time-to-live assigned to resource records in zone files.
The next two options allow controlling the reverse DNS records (PTR) creation for Plesk
Domains and Containers. PTR (pointer) records are the reverse of A records: whereas the
latter maps names to addresses, PTR addresses map addresses to names.
Note: These two options are available for Provider Control Center only and affect Provider
and all Resellers.
Page 94

Setting Up Domains Registration 94
e Import PTR records from Plesk. It is possible to switch the primary DNS synchronization
source from Plesk DNS to Parallels Business Automation - Standard and conversely.
This is done per Plesk hosting plans, on the Permissions Setup step. When Plesk DNS is
set as a primary source (the Manage DNS permission is enabled) all the DNS records
are imported from Plesk to Parallels Business Automation - Standard DNS. There can be
many PTR records in Plesk zones since shared IP addresses are widely used. If you do
not want to import all these PTR records into Parallels Business Automation - Standard,
you can clear this box and this will override the 'Mange DNS' permission for all Plesk
zones.
f Create PTR records for Containers. For Containers PTR records are added automatically
if this option is enab le d.
PTR records are created automatically for every IP address assigned to a Container. If a
Container has several domains assigned, then PTR records are created only for default
domain, so every IP has only one PTR record.
PTR record that points to a Container default domain name is created for default IP
address only.
For non-default IP addresses PTR record is auto-generated according to the rule: an IP
address converted into four hex values is appended before default domain name to get a
unique record. For example, for IP address 10.26.141.37 the domain name in PTR
record will look as 0a1a8d25.domain.com, where domain.com is a Container default
domain name. This rule ensures that IP points to unique domain name, which allows
avoiding possible rejection of mail by anti-SPAM systems.
Note: A rec ord s f or non-default IP addresses are created similarly as PTR records: an IP
address converted into four hex values is appended before default domain name to get a
unique A record.
For security reasons, on IP address release, all PTR records created for this IP address
are removed automatically.
To enable or disable this option, check or clear the box respectively. Note that is this
option is disabled, then management of PTR records from Control Panel becomes
disabled as well.
Note: PTR records can be created by customers only for IPs that have reverse zones
configured. You should create reverse zones for IPs under Service Director > Domain
Manager > Domains, Reverse DNS tab. Please make sure that reverse zones are configured
before enabling PTR records management for customers.
g Manage PTR records for Containers in Control Panel. This option is used to
allow/disallow customers adding PTR records for Containers from Control Panel. If this
option is enabled, then Reverse DNS link appears within the Domain Management
section under the System tab for Container subscriptions. Customer can add/edit/delete
as many PTR records as needed for IPs that are allocated to his/her Container(s). To
enable or disable this option, check or clear the box respec tiv ely .
h Name Server Synchronization Timeout. The period of time in seconds allowed for name
servers synchronization. If synchronization takes longer, the NS synchronization task
fails by timeout. The default timeout is 180 sec. Please note that if you have many
domains, synchronization may fail by timeout. In this case, the timeout should be
increased.
Page 95

Setting Up Domains Registration 95
i Available periods. Select domain registration periods that will be shown on the Prices
form for each TLD. To make a period available, check the box next to a period name.
To disallow a period, clear the box next to this period name.
j Allow customers to enter International Domain Names (IDN). Parallels Business
Automation - Standard supports Internationalized Domain Names (on page 92)
registration and here you can allow or disallow your customers to register IDNs. To
allow IDNs registration, check this box. To disallow IDNs, clear this box.
k Domain Data Consistency. These options allow auto-fixing domains expiration date
mismatch between PBAS and Registrar. If a domain expiration date is unknown for a
transferred domain, Parallels Business Automation - Standard automatically sets this
date to one year starting from domain transfer moment. To ensure the correctness of
domains registration expiration date stored in Parallels Business Automation - Standard
database, you can configure the auto-check of domain expiration date at Registrar. If
this option is enabled, Parallels Business Automation - Standard will run a periodical
task trying to contact a Registrar and get the domain expiration date confirmation. If a
Registrar does not reply, Parallels Business Automation - Standard will tr y to check a
domain expiration date via whois.
To configure the domain expiration date validation, put a tick into the Run domains real
expiry date checking box and enter how frequently (in days) the check is to be
performed. In addition, you can set the order of domain expiration date auto-fixing in
case this date is incorrect and does not considerably differ from a correct date (not
greater that one month).
To configure the periodical checking of the domains status, put a tick into the Run
domains status checking every box and enter how frequently (in days) the check is to be
performed.
Note: The domains that have the status "transferred away", will be shown under the
Service Director > Domain Manager > Domains, the Domains required attention tab (on
page
257), and you may terminate the remaining domain subscriptions there.
To enable this auto-fix, put a tick into the Autofix if expiry date mismatch is less or equal
to box and enter the maximal difference in days into the relevant field.
To limit the number of domains checked by a single task, enter how many domains are
checked into the Number of domains to check at a time field.
6. Click the OK button.
Page 96

Setting Up Domains Registration 96
Managing Con t acts Used for Domain Regis t rat ion
The composition and format of contact data required for domains registration differs depending
on Registrar. Some Registrars require a rather specific data. To simplify domain registration
procedure for your customers, you can replace Registrar's contacts form with your own one (a
so called base contacts) that have a standard format.
Base contacts usage is provided by a special methods used in plug-in. For more information
about domain plug-ins API, please see the Parallels Business Automation - Standard SDK.
Provider contacts are managed under Domain Manager > Setup > Contacts tab.
Customer contacts are managed under the Contacts tab within an account properties.
To replace Registrar contacts with your own contacts form, go to Domain Manager > Plug-Ins >
select a plug-in, then click the Prices tab. Select a TLD. The number and names of contacts
offered here may vary depending on a Registrar. The most typical set is Owner Contact,
Administrative Contact, Billing Contact, and Technical Contact.
The contacts list displays the following:
ID - contact numerical identifier assigned in Parallels Business Automation - Standard
database.
Contact name - contact name a contact is referred to.
Company name - the company name specified in the contact. Available for business
contacts only (i.e., contacts for enterprises).
First name - first name specif ied in a contac t.
Last name - last name specified in a contact.
Type - a contact type (Business - for enterprise, Personal - for person).
To edit or remove an existing contact, click on a contact name and after a contact view form
appears on the screen, click the Edit button to edit, Delete - to remove a contact.
To create a new contact, click the Create button. A new contact will be available for selection
for all contact types right after you save it.
The form for a new contact creation is standard and the same for every contact. Form fields are
pre-filled with the contact data fetched from your Administrative account:
Account Type. Select the account type (Business or Personal). This selection defines the
contact type.
Company name. Available only if you select the Business account type. Enter the name of
company.
Contact name. The contact name for reference.
E-mail. Contact e-mail.
Name. Enter the first and last names of the contact person.
Address. Enter the postal address (without city).
Page 97

Setting Up Domains Registration 97
City. Enter the city name.
State (US or Canada). If you select USA or Canada country, select the state.
State (other countries). You can optionally specify the state or province for countries other
than USA or Canada.
Country. Select country.
Zip/postal code. Enter the zip code.
Phone. Enter the contact phone number.
Fax. Enter the fax number.
To save the contact, click the Update button.
Specifying Whois Servers
You can form a list of Whois servers in Parallels Business Automation - Standard and after this
bind each of top level domains to one of more Whois servers.
Note: It is possible to set up the whois with HTTP protocol enabled.
To add a whois server, select Service Director - Domain Manager - Setup - Whois Servers.
To assign a whois server to a TLD, go to the Service Director - Domain Manager - Setup and then
select the TLDs tab. Select the TLD and assign one or more whois servers (from the set formed
before in Parallels Business Automation - Standard) to a given TLD.
Setting Up HTTP Whois Search
To set up the whois search for a plug-in, you need to:
1. Contact your Registrar support and ask them to register the IP address of the computer that
runs Parallels Business Automation - Standard (your Management Node). Without this
registration all requests sent by the plug-in will be rejected by the Registry.
2. In the Parallels Business Automation - Standard Control Center register a separate whois
server for Registrar and configure it prop er ly:
a Select Service Director - Domain Manager - Setup.
b Click the Whois Servers tab on the Setup menu.
c Click the New Whois Server button.
d On the New Whois Server form that appears check the Use http protocol box. Some fields
will become unavailable (Port, Command prefix, Command suffix, Drop TLD in
request). Enter a new whois server friendly name into the Title field. And into the Whois
server you must enter the URL to whois query.
A domain name will be added to the query automatically.
Set the option button to Use 'domain not found' pattern. Enter the usual pattern for a
whois server into the field next to this option, e.g. Domain does not exist.
3. Click the Save button.
Page 98

Setting Up Domains Registration 98
Viewing Incoming and Outgoing Domain Registration E-mails
You may need to view the domain registration log e-mails. This gives ability to review history
of sent messages as well as troubleshoot processing of incoming messages triggering domain
registration within the Parallels Business Automation - Standard (such as messages sent by
domain registrar modules communicating via email-based protocol). The e-mail
senders/recipients are:
Billing
Event Manager
Mass Mailer
Domain registration plug-ins that use e-mail to communicate with Internet Registrar.
Trouble tickets
The log can be viewed at Configuration Director - Logging and Errors - E-mails Log. Here yo u
can view the inbox mail at the Incoming Mail tab and the outbox mail at the Outgoing Mail tab.
For your convenience it has been designed with the following columns:
ID - unique ID assigned to the e-mail;
Subject - the subject of the e-mail;
Accepted/Sent for Incoming Mail and Outgoing Mail respectively - the date of the message
acceptance/dispatch;
Status - the status of the message;
By now the e-mails are assigned the following statuses:
Processed - the e-mail has been processed all right;
Error - the e-mail processing has failed;
Skipped - the e-mail has arrived to the right address but the system does not know how
to handle it or chooses not to process it;
Unknown - the handler has failed to assign any of the above statuses to it. The handler
does not how to respond to the e-mail.
Handler - Parallels Business Automation - Standard module processing this e-mail.
Page 99

99
Using Specific Accounting ................................................................................................... 118
C
HAPTER
7
Setting Up Billing System
This chapter describes how to set up Parallels Business Automation - Standard Billing System:
prices and discounts, credit terms, taxation, fraud protection, credit card processing and other
billing features and tools.
In This Chapter
Understanding the Parallels Business Automation - Standard Billing System ..................... 100
System-Wide Billing Settings ............................................................................................... 102
Invoice Settings ..................................................................................................................... 103
Pricing and Discounts ........................................................................................................... 107
Setting Credit T erms ............................................................................................................. 109
Configuring Taxation ............................................................................................................ 111
Configuring Fraud Protection ............................................................................................... 112
Configuring Credit Card Payment Plug-ins .......................................................................... 115
Configuring Bank Transfer Payment Plug-ins ...................................................................... 117
Page 100

Setting Up Billing System 100
Understanding the Parallels Business Automation - Standard Billing System
Parallel s Bus iness Automation - Standard billing system is supported by the Billing Director that
provides financial management of the following client categories: Resellers and Customers. For
settlement purposes, Accounts are created for each category. Parallels Business Automation Standard billing provides a single-currency settlement and accounting system. A system-wide
currency can be selected per Control Center (one currency for Provider and another currencies
for Resellers, the exchange rate can be set per Reseller). In order to change the system-wide
currency, select Configuration Director - Miscellaneous Settings - Regional Settings.
Hosting Plan is the basic account unit that used for calculation of money equivalent of services
provided. A subscription period can be selected by customers from offered by Hosting Service
Provider (one month, three months, six months, and year). Services provided in accordance with
a Hosting Plan are paid in advance, in accordance with resource-specific quotes. Resources
overusage is paid either in advance or at the end of subscription period.
Note: In Parallels Business Automation - Standard billing, the billing cycle equals to one month
by default. This means that statements and resource overusage invoices are generated for each
subscription each month. There are no mentions about billing cycles in Parallels Business
Automation - Standard web-based interface.
Invoices are generated in accordance with Subscription terms. Account balance is calculated on
the basis of actual resource usage and payment(s) received. Account balance is calculated every
hour (by default).
Current Account balance is regularly compared with customer credit limit. Depending on
Billing Manager settings and Account balance, the following operations can be performed:
Notification about negative Account balance can be generated and sent to a customer;
Negative balance and credit limit control, generating reports on Accounts in debt;
Suspending subscriptions associated with Accounts in debt in the case of credit limit
overrun;
For Virtuozzo Container subscriptions, changing a Container parameters (available
resources limitation) in the case of resourc e overus age.
Basic Notions
Subscriptions
A Subscription holds terms of contract between Hosting Service Provider and a customer.
Changes in Provider prices do not affect terms of Subscription. This means that prices for the
Hosting Plan purchased remain changeless up to the end of subscription period.
However, if additional Applications or Containers were purchased, or a Subscription was
upgraded to a higher version of the same hosting plan, then Subscription terms may change.
Documents
 Loading...
Loading...