Page 1

ATM Line Cards
Models 8955, 8965, 8968, and 8985
User’s Guide
Document No. 8900-A2-GB20-30
June 2004
Page 2

Copyright © 2004 Paradyne Corporation.
All rights reserved.
Printed in U.S.A.
Notice
This publication is protected by federal copyright law. No part of this publication may be copied or distributed,
transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any human or computer language in any form
or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, manual or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties without the
express written permission of Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Ave. N., Largo, FL 33773.
Paradyne Corporation makes no representation or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and specifically
disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Further, Paradyne Corporation
reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents hereof without
obligation of Paradyne Corporation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
Changes and enhancements to the product and to the information herein will be documented and issued as a new
release to this manual.
Warranty, Sales, Service, and Training Information
Contact your local sales representative, service representative, or distributor directly for any help needed. For
additional information concerning warranty, sales, service, repair, installation, documentation, training, distributor
locations, or Paradyne worldwide office locations, use one of the following methods:
Internet: Visit the Paradyne World Wide Web site at www.paradyne.com. (Be sure to register your warranty at
www.paradyne.com/warranty.)
Telephone: Call our automated system to receive current information by fax or to speak with a company
representative.
— Within the U.S.A., call 1-800-870-2221
— Outside the U.S.A., call 1-727-530-2340
Document Feedback
We welcome your comments and suggestions about this document. Please mail them to Technical Publications,
Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Ave. N., Largo, FL 33773, or send e-mail to userdoc@paradyne.com. Include
the number and title of this document in your correspondence. Please include your name and phone number if you
are willing to provide additional clarification.
Trademar ks
ACCULINK, COMSPHERE, FrameSaver, Hotwire, MVL, NextEDGE, OpenLane, and Performance Wizard are
registered trademarks of Paradyne Corporation. GranDSLAM, GrandVIEW, Hotwire Connected, ReachDSL, and
TruePut are trademarks of Paradyne Corporation. All other products and services mentioned herein are the
trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or registered service marks of their respective owners.
Regulatory and Safety Information
Refer to the appropriate Broadband Access Concentrator (BAC) installation guide for all regulatory notices and safety
information.
A June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 3

Contents
About This Guide
Document Purpose and Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iii
Document Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iii
Product-Related Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iv
1 About the ATM Line Cards
ATM Line Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
ATM Line Card Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
ATM Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Endpoint Support Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Sample Network Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
SNMP Management Capabilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Management Information Base (MIB) Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
SNMP Trap Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
2 Accessing the SCP Card Web Interface
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Logging Into the Web Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Help Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Ending a Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
3 Configuration Using the Web Interface
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Configuring Spectrum Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Configuring ReachDSL Ports (8955) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Configuring ADSL Ports (8965, 8968) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Configuring SHDSL Ports (8985) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
Configuring Line Profiles (8955, 8965, 8968). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Creating Line Profiles for Ports (8985) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Configuring Alarm Threshold Profiles (8955, 8965, 8968) . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Creating Alarm Threshold Profiles for Model 8985 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
Configuring Cross Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
Default Mappings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 i
Page 4

Contents
Configuring ATM Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Configuring Traffic Profiles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
4 Monitoring
What to Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Front Panel LEDs (Models 8955, 8965, and 8985) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Front Panel LEDs (Model 8968). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
5Diagnostics
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Lamp Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Loopback Test (Model 8985 Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Adding a Port-to-Port Cross Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
Adding a Slot-to-Slot Cross Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
6 Maintenance Procedures
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Uploading and Downloading a Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Resetting the Configuration to Default Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Resetting the Configuration to Downloaded Settings . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Downloading and Switching Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
Downloading Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
Switching Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
Restarting the Line Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
A Connector Pin Assignments
8620 and 8820 Telco Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Model 8968 Line Card Telco Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
B Technical Specifications
Index
ii June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 5

About This Guide
Document Purpose and Intended Audience
This guide contains information needed to configure and operate the Models
8955-B1, 8965-B2, 8968-B1, and 8985-B2 ATM line cards, and is intended for
installers and operators. Basic installation information can be found in the AT M
Line Cards, Models 8955, 8965, 8968, and 8985, Installation Instructions.
Document Summary
Section Description
Chapter 1, About the ATM Line
Cards
Chapter 2, Accessing the SCP
Card Web Interface
Chapter 3, Configuration Using
the Web Interface
Chapter 4, Monitoring Describes how to locate information about a line card
Chapter 5, Diagnostics Provides instructions for running a lamp test and
Chapter 6, Maintenance
Procedures
Appendix A, Connector Pin
Assignments
Appendix B, Tec hn ic al
Specifications
Index Lists key terms, acronyms, concepts, and sections in
Describes the cards’ features and capabilities.
Provides instructions for accessing the user interface.
Provides instructions for configuring the line cards.
and its status.
loopback test.
Provides instructions for uploading or downloading a
configuration, downloading firmware, and resetting the
card.
Lists the pin assignments for the Broadband Access
Concentrator (BAC) Telco connectors.
Contains physical and regulatory specifications, and
power consumption values.
alphabetical order.
A master glossary of terms and acronyms used in Paradyne documents is
available on the World Wide Web at www.paradyne.com. Select Support →
Technical Manuals → Technical Glossary.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 iii
Page 6
About This Guide
Product-Related Documents
Complete documentation for this product is available online at
www.paradyne.com. Select Support → Technical Manuals.
Document Number Document Title
6381-A2-GN10 Hotwire ReachDSL Modem, Model 6381 with Inline Phone Filter,
6390-A2-GK40 Hotwire ReachDSL Modem, Model 6390 with Inline Phone Filter,
6390-A2-GN10 Hotwire ReachDSL Modem, Model 6390 with Inline Phone Filter,
7890-A2-GB22 GrandVIEW EMS User’s Guide
8000-A2-GB30 8620 and 8820 Broadband Access Concentrator SNMP
8400-A2-GB20 Shelf Concentration and Processing (SCP) Card with ATM
Installation Instructions
Installation and Operation Supplement
Installation Instructions
Reference
Uplink User’s Guide
8400-A2-GB21 Shelf Concentration and Processing (SCP) Card with IP Uplink
User’s Guide
8400-A3-GB21 8620 and 8820 Broadband Access Concentrator TL1 Interface
Reference
8400-A3-GB22 8620 and 8820 Broadband Access Concentrator Command Line
Interface Reference
8620-A2-GN20 8620 Broadband Access Concentrator Installation Guide
8820-A2-GN20 8820 Broadband Access Concentrator Installation Guide
8900-A2-GZ40 ATM Line Cards, Models 8955, 8965, 8968, and 8985,
Installation Instructions
To order a paper copy of a Paradyne document, or to speak with a sales
representative, please call 1-727-530-2000.
iv June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 7

About the ATM Line Cards
ATM Line Cards
The 8955, 8965, 8968, and 8985 Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Line Cards
are circuit boards mounted in an 8620 or 8820 Broadband Access Concentrator
(BAC) and used to transport ATM cells at high speeds over a single twisted-pair
connection or, optionally, two twisted-pair connections (8985 only).
Model 8955 supports ReachDSL. It automatically adjusts to the highest rate
the loop can support, from 32 to 2176 kbps. It has 24 ports.
Models 8965 and 8968 support Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL).
They can be set to adapt to the line conditions at startup, or set to the following
fixed rates depending on line code:
1
— G.lite: 64 to 3008 kbps downstream and 32 to 512 kbps upstream.
— G.dmt, ANSI T1.413, ADSL2, and ADSL2+: 32 to 8000 kbps downstream
and 32 to 832 kbps upstream.
— ADSL2: 32 to 16000 kbps downstream and 32 to 1056 kbps upstream.
— ADSL2+: 32 to 29000 kbps downstream and 32 to 2200 kbps upstream.
The Model 8965 has 24 ports and the Model 8968 has 48 ports.
Model 8985 supports Single-pair High-speed Digital Subscriber Line
(SHDSL). It can be set to adapt to the line conditions at startup, or set to a
fixed line rate from 192 to 2304 kbps (or 384 to 4608 kbps with two wire pairs).
It has 24 ports.
The 8955, 8965, 8968, and 8985 line cards are configured and managed using the
Shelf Concentration and Processing (SCP) card.
Part of Paradyne’s Hotwire Connected™ program, the cards interoperate with
third-party DSL endpoints providing end users with the ability to select the best
equipment to fit their application. The line cards also integrate support for multiple
DSL services on a single card.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 1-1
Page 8

1. About the ATM Line Cards
ATM Line Card Features
The ATM Line Cards have these standard features:
Alarm indication. Activates front panel LEDs.
Diagnostics. Provides lamp test and SHDSL line loopback (8985).
Device and test monitoring. Provides the capability of tracking and
evaluating the unit’s operation, including health and status, and error-rate
monitoring.
Software upgrade. Supports software upgrades using FTP.
ATM Features
The cards’ ATM features include:
Classes of service. Supports traffic management service categories
necessary to support voice and data applications:
—CBR
— rt-VBR
— nrt-VBR
— UBR (only class of service supported for the Model 8955)
Auto configuration. Two Virtual Channel Connections (VCCs) per port are
automatically configured, providing data and voice services.
Multiple virtual circuits. Up to 250 additional VCCs can be configured by the
user and assigned among the DSL ports.
ATM statistics. Maintains statistics for:
— Total cells received
— Total cells transmitted
— Total cells dropped
— Loss of cell delineation events
— Cells with uncorrectable HEC
Endpoint Support Features
The cards’ endpoint support features include:
Third-party endpoint support. Models 8965, 8968, and 8985 line cards
support third-party endpoints through the Hotwire Connected program,
including Integrated Access Devices (IADs) and data-only endpoints from
numerous industry-leading vendors. The Model 8985 card supports third-party
endpoints using the ITU SHDSL standard. A list of Paradyne’s SHDSL
partners is available on the World Wide Web at www.paradyne.com. Select
Company → Partners → Hotwire Connected Interoperability Program.
1-2 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 9
Model 6381 and 6390 Modem support. Models 8955, 8965, and 8968 line
cards support the Model 6381 Modem. The Model 8955 line card also
supports the discontinued Model 6390 Modem.
Model 8300 Modem support. The Model 8985 line card supports the
Model 8300 Modem.
Automatic rate adaptation. The card and the endpoint negotiate the best
rate, limited if desired by the user, through automatic rate adaptation.
Sample Network Configurations
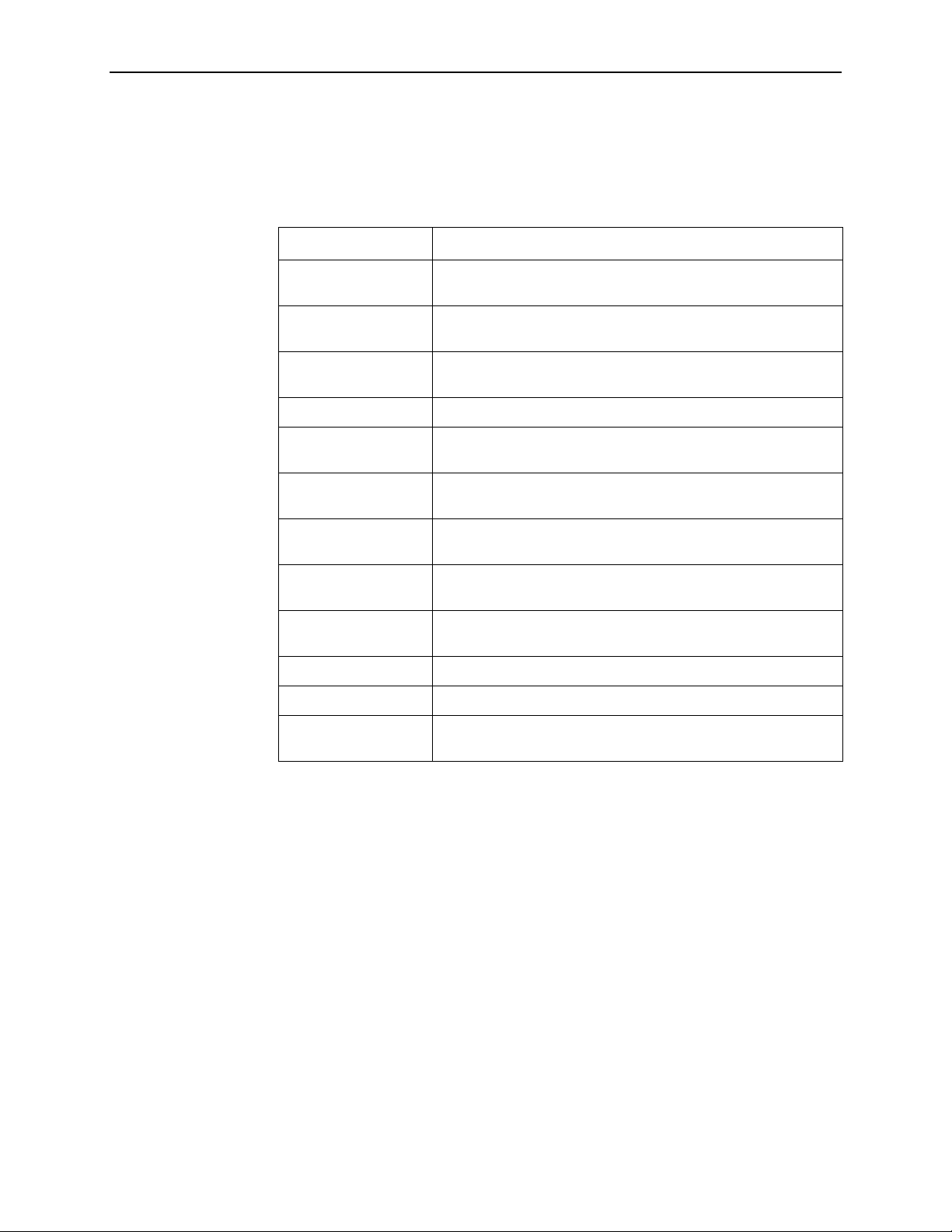
Figure 1-1 shows the ATM Line Card used to carry voice over DSL.
1. About the ATM Line Cards
ISP
Corporate
Site
PSTN Voice
Traffic
Voice
Gateway
AT M
Network
ATM Cells
Hotwire ATM
Line Card
SCP Card
ATM Cells
DSL
8820 BAC
Customer Premises
LAN
Integrated
Access
Device
(IAD)
04-17444-01
Figure 1-1. Endpoint with Voice Interfaces
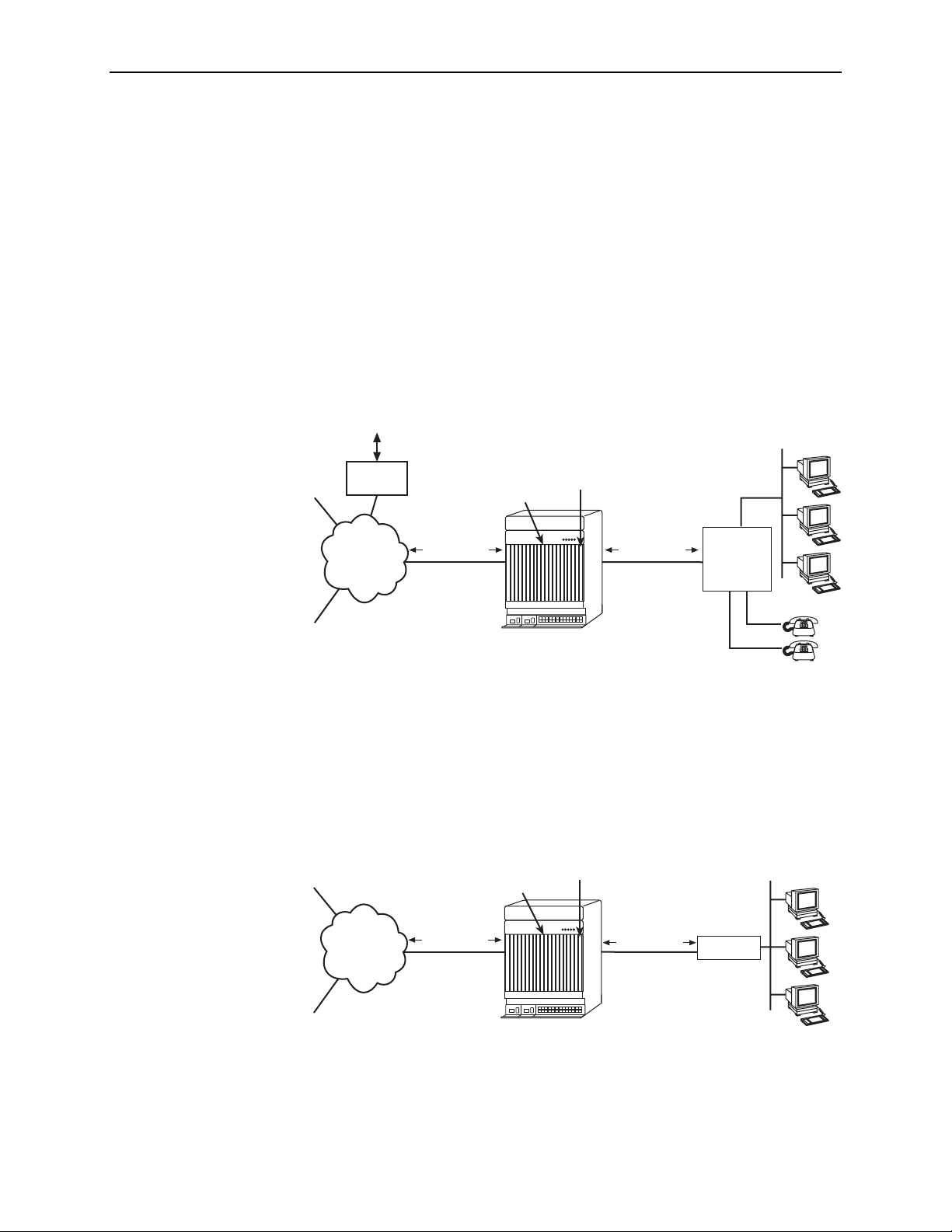
Figure 1-2 shows a configuration in which the endpoints include a router to provide
data encapsulation.
ISP
Hotwire ATM
Line Card
SCP Card
Customer Premises
LAN
AT M
Network
Corporate
Site
ATM Cells
Figure 1-2. Router Endpoint
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
8820 BAC
ATM Cells
DSL
Router
04-17443-01
1-3
Page 10

1. About the ATM Line Cards
SNMP Management Capabilities
The ATM Line Cards support SNMP Version 1, and can be managed by
Paradyne’s GrandVIEW
®
or any industry-standard SNMP manager.
Management Information Base (MIB) Support
For a detailed description of supported MIBs, visit Paradyne’s Web site at
www.paradyne.com. The following MIBs are supported:
ATM Forum SNMP M4 Network Element View (af-nm-0095.001)
Definitions of Managed Objects for the ADSL Lines (RFC 2662)
Definitions of Managed Objects for ATM Management (RFC 2515)
Definitions of Managed Objects for HDSL2 and SHDSL Lines
(draft-ietf-adslmib-hdsl2-10.txt)
Definitions of Textual Conventions and OBJECT-IDENTITIES for ATM
Management (RFC 2514)
Evolution of MIB II Interfaces (RFC 2863)
ADSL Extension MIB (Models 8965 and 8968) (draft-ietf-adslmib-adslext.txt)
SHDSL MIB (Model 8985 only) (draft-ietf-adslmib-hdsl2.txt)
Entity MIB Using SMIv2 (RFC 2037)
SNMP Trap Support
MIB II and the Interfaces Group MIB (RFC 1213, RFC 2233)
Paradyne enterprise MIBs for:
— xDSL Interface
—SLE Device Control
— SLE Device Health and Status
— MaxVciVpi-MIB Table
—IF-MIB Table
— ATM VPL Statistics Table
The ATM Line Cards support SNMP traps as shown in the 8620 and 8820
Broadband Access Concentrator SNMP Reference.
1-4 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 11

Accessing the SCP Card Web Interface
Introduction
The ATM line cards can be configured and monitored using:
The SCP card’s Command Line Interface (see the 8620 and 8820 Broadband
Access Concentrator Command Line Interface Reference) or TL1 interface
(see the 8620 and 8820 Broadband Access Concentrator TL1 Interface
Reference)
GrandVIEW EMS 4.1 or above (see the GrandVIEW EMS User’s Guide)
SNMP using another EMS (see the 8620 and 8820 Broadband Access
Concentrator SNMP Reference)
2
The web interface of the Shelf Concentration and Processing (SCP) card.
Logging Into the Web Interface
To access the web interface:
Procedure
1. Open your web browser. (Internet Explorer Version 6 or above is
recommended.)
2. Type http:// and the IP address of the SCP card into the Address field of your
browser window. For example:
The default address is 10.10.10.10.
3. A login window appears. Enter the User ID and Password, and click on OK.
The web interface screen appears. The web interface screens consist of a
header, a menu frame, and a content frame.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 2-1
Page 12
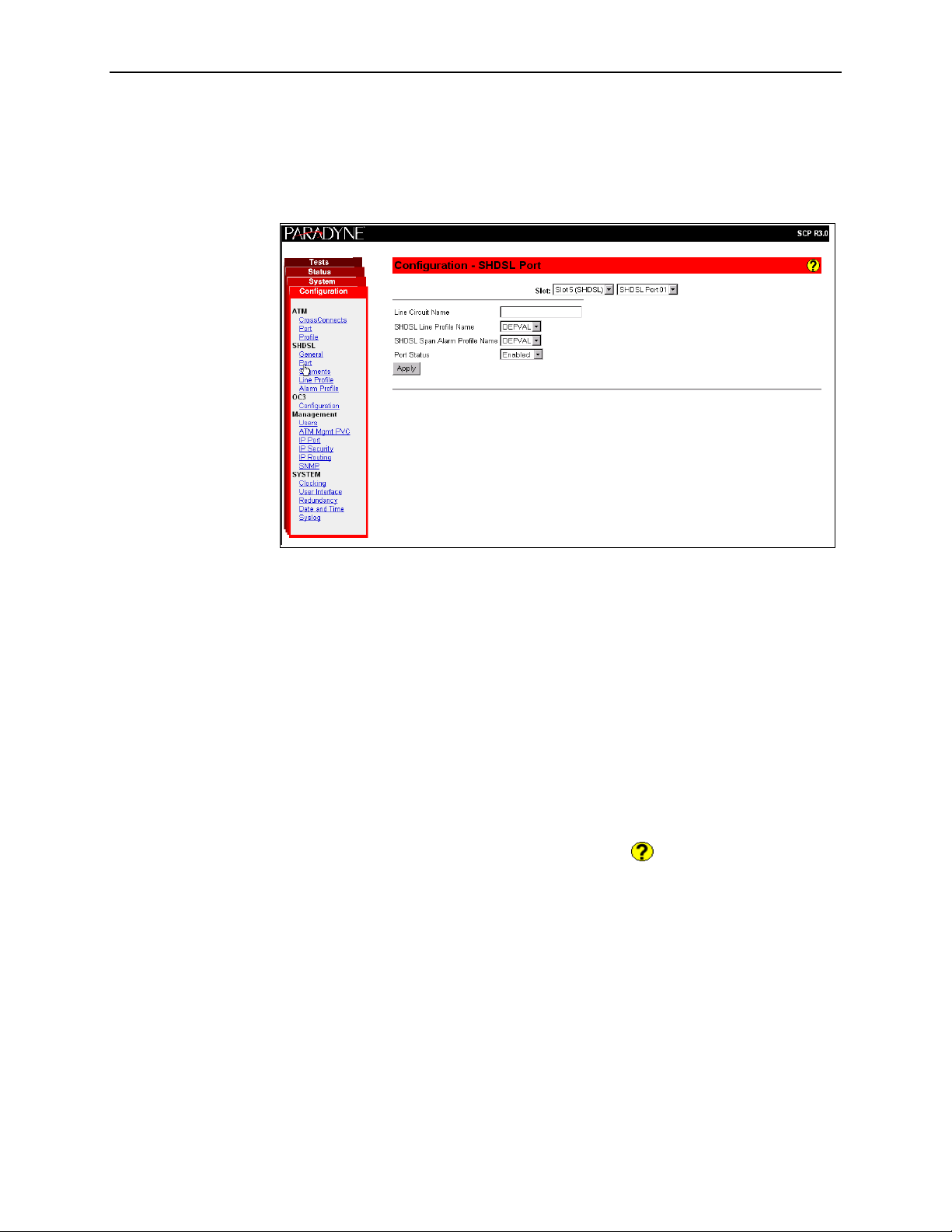
2. Accessing the SCP Card Web Interface
4. Click on the Configuration menu tab. The configuration screens available in
the contents frame depend on the types of line cards and type of SCP card
installed in the chassis. The Configuration - SHDSL Port screen is displayed
here.
Help Button
Ending a Session
All main screens of the web interface can be reached by clicking on hyperlinks in
the four menus:
Configuration – Configure the system and interfaces
Status – Display statistics, status, performance information, and contents of
memory
System – Display system information, download firmware, back up
configurations, and reset the SCP card
Tests – Start and stop tests
For more information about any screen, click on the Help button on the screen.
Help is displayed in a new window.
To end a session, close your web browser. This prevents an unauthorized user
from accessing the system using your user name and password.
2-2 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 13
Configuration Using the Web Interface
Overview
This chapter provides instructions on how to configure the ATM line cards using
the SCP card’s web interface.
If you would like to configure the
card using . . . See the . . .
3
The BAC’s TL1 Interface (when an
SCP card with an ATM uplink is used)
The BAC’s router-like command line
interface (when an SCP card with an IP
uplink is used)
GrandVIEW EMS 4.1 or above GrandVIEW EMS User’s Guide
SNMP using another EMS 8620 and 8820 Broadband Access
Configuring Spectrum Management
Use the Configuration - DSL General screen to enable and disable Spectrum
Management. When Spectrum Management is enabled, the maximum transmit
speeds and maximum transmit power are limited to meet local spectrum
management guidelines.
Procedure
To enable or disable Spectrum Management:
1. Select Disable or Enable from the drop-down list.
2. For the 8985 line card, additionally select the Spectrum Management Region:
8620 and 8820 Broadband Access
Concentrator TL1 Interface Reference
8620 and 8820 Broadband Access
Concentrator Command Line Interface
Reference
Concentrator SNMP Reference
— ANSI T1417 – To select American National Standards Institute T1.417
definitions
— ANFP ND 1602 – To select Access Network Frequency Plan ND1602
definitions
3. Click on Apply.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 3-1
Page 14
3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Configuring ReachDSL Ports (8955)
Use the Configuration - DSL Port screen to set parameters for a DSL port on the
8955 ReachDSL line card.
Procedure
To configure a ReachDSL port:
1. Select a Port from the drop-down list and click on Select. Current values for
the port are displayed.
2. Enter or select the following fields:
Field Description
Line Circuit Name Enter a name from 1 to 255 characters long to indicate to
whom the port is assigned. The following values are
reserved and cannot be used: AVAILABLE (port is not
assigned), and FAULTY (port is faulty and can not be
assigned).
Line Code The Line Code parameter currently has no effect on a
ReachDSL card.
DSL Line Profile Name Enter the name of a DSL line profile to set rates for the
port.
DSL Alarm Profile Name Enter the name of a DSL alarm profile to set alarm
thresholds for the port.
Equivalent Working Length Specify the estimated length of the DSL line. This used to
limit transmit rates and maximum transmit power settings
according to local spectrum management guidelines.
Max Tx Power Specify the maximum transmit power setting for the
ATU-C. The allowable Maximum Transmit Power range
may be limited according to local spectrum management
guidlines. The actual transmit power level will be based
upon the symbol rate selected to maximize the transmit
data rate and may be lower than the Maximum Transmit
Power level configured.
Far End Max Tx Power Specify the maximum transmit power setting for the
ATU-R. The allowable Maximum Transmit Power range
may be limited according to local spectrum management
guidlines. The actual transmit power level will be based
upon the symbol rate selected to maximize the transmit
data rate and may be lower than the Maximum Transmit
Power level configured.
Port Status Select Enabled, Disabled, or Reset from the drop-down
list to determine the status of the port.
3. Click on Apply.
3-2 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 15
Configuring ADSL Ports (8965, 8968)
Use the Configuration - DSL Port screen to set parameters for an ADSL port on
the 8965 or 8968 line card.
Procedure
To configure an ADSL port:
1. Select a Port from the drop-down list and click on Select. Current values for
the port are displayed.
2. Enter or select the following fields:
Field Description
Line Circuit Name Enter a name from 1 to 255 characters long to indicate to
whom the port is assigned. The following values are
reserved and cannot be used: AVAILABLE (port is not
assigned), and FAULTY (port is faulty and can not be
assigned).
3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Line Code Select a line code:
MultiMode - The port uses the line code of its partner
modem
ANSI T1.413 - The port uses DMT modulation
ITU G.dmt Annex A - The port uses G.992.1 Annex A
modulation
ITU G.dmt Annex B - The port uses G.992.1 Annex B
modulation
ITU G.lite - The port uses G.992.2 modulation
ADSL2 Annex A - The port uses G.992.3 Annex A
modulation
ADSL2+ Annex A - The port uses G.992.5 Annex A
modulation
DSL Line Profile Name Enter the name of a DSL line profile to set rates for the
port.
DSL Alarm Profile Name Enter the name of a DSL alarm profile to set alarm
thresholds for the port.
ADSL2 PSD Profile Name Select a PSD profile from the drop-down list.
ADSL2+ PSD Profile Name Select a PSD profile from the drop-down list.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
3-3
Page 16

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Field Description
Power Management Specify whether power management is supported on this
port:
Enabled - Power management is enabled
Disabled - Power management is disabled
Power management refers to the following modes, defined
in the ADSL2 specification:
L2 low power: Power consumption is reduced at the
local unit when there is no traffic. Entry to and exit from
L2 low power mode happens so quickly that it is
undetectable by the user.
L3 low power: The port enters sleep mode during
extended periods of inactivity, saving power at both the
local and remote units.
Power Management State
Enabling
Select the line states that the port may autonomously
switch to on this line:
Idle – L3 low-power mode
Low Power – L2 low power mode
Both – Both L2 and L3 low power modes
None – Power management is disabled
L0 Time Specify the minimum number of seconds allowed between
an exit from the low power (L2) state and the next entry into
the low power state.
L2 Time Specify the minimum number of seconds allowed between:
An entry into the low power (L2) state and the first
power trim in the low power state
Two consecutive power trims in the low power state
Port Status Select Enabled, Disabled, or Reset from the drop-down list
to determine the status of the port.
3. Click on Apply.
3-4 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 17

Configuring SHDSL Ports (8985)
Use the Configuration - SHDSL Port screen to set parameters for a DSL port on
the 8985 line card.
Procedure
To configure a DSL port:
1. Select a Port from the drop-down list and click on Select. Current values for
the port are displayed.
2. Enter or select the following fields:
Field Description
Line Circuit Name Enter a name from 1 to 255 characters long to indicate to
3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
whom the port is assigned. The following values are
reserved and cannot be used: AVAILABLE (port is not
assigned), and FAULTY (port is faulty and can not be
assigned).
SHDSL Line Profile Name Enter the name of a DSL line profile to set rates for the
port.
SHDSL Alarm Profile Name Enter the name of a DSL alarm profile to set alarm
thresholds for the port.
Equivalent Working Length Specify the estimated length of the line. The length is
used to limit transmit rates according to local spectrum
management guidelines.
Port Status Select Enabled, Disabled, or Reset from the drop-down
list to determine the status of the port.
3. Click on Apply.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
3-5
Page 18

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Configuring Line Profiles (8955, 8965, 8968)
Use the Configuration - Line Profiles screens to define line profiles to be assigned
to ports.
To create a line profile for ReachDSL and ADSL ports:
1. Click on Create New Profile. The ADSL Profile Create screen appears.
2. Enter or select the following fields:
Field Description
Profile Name Specify a name for this line profile.
Latency Select the channel the following rates are effective for:
Fast or Interleaved.
For ADSL, S=1/2 encoding is not supported when
Latency is set to Fast. For ADSL2, S=1/2 is supported in
both modes.
Downstream / Near End Profile
Max Rate (kbps) Enter a maximum rate from 0 to 65535.
Min Rate (kbps) Enter a minimum rate from 0 to 65535.
Max Delay Select the maximum delay allowed for the interleaved
channel, in milliseconds.
Max Additional Noise Margin Select the maximum additional noise margin.
Min Noise Margin Select the minimum noise margin.
Target Noise Margin Select a target noise margin.
Max Spectrum Density This is set to 40 dBm/Hz.
Rate Adaptive Mode Select a rate adaptive mode:
Manual - Manually selected at startup
Init - Automatically selected at startup
Dynamic - Automatically selected at run time
Upstream / Far End Profile
Max Rate (kbps) Enter a maximum rate from 0 to 65535.
Min Rate (kbps) Enter a minimum rate from 0 to 65535.
Max Delay Select the maximum delay allowed for the interleaved
channel, in milliseconds: 1, 4, or 16.
To obtain the fastest rate downstream for ADSL (not
ADSL2) endpoints that support S=1/2 encoding, set
Latency to Interleaved and Max Delay to 1 ms.
Max Additional Noise Margin Select the maximum additional noise margin.
Min Noise Margin Select the minimum noise margin.
Target Noise Margin Select a target noise margin.
3-6 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 19

3. Click on Apply.
Creating Line Profiles for Ports (8985)
Procedure
To create a line profile for SHDSL ports:
1. Click on Create New Profile. The SHDSL Profile Create screen appears.
2. Enter or select the following fields:
Field Description
Profile Name Specify a name for this line profile.
Max Rate Enter a maximum rate from 192 to 2304 kbps.
Min Rate Enter a minimum rate from 192 to 2304 kbps.
3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Mode Select the regional setting supported, as specified by
ITU-T G.991.2:
Annex A
Annex B
Both
Remote Management Select Enable or Disable from the drop-down list to
determine whether remote management is supported for
the network element this profile is assigned to.
Reference Clock Select the timing source from the drop-down list:
System – Clocking is provided by the backplane. (The
backplane clock is configured on the Configuration System - Clocking screen.)
Local – Clocking is provided by an onboard oscillator.
Target Margin Enter a target noise margin from 2–15 dBm, or None.
Interface Select an interface from the drop-down list:
Wire Pair 1 – The profile applies to Wire Pair 1.
Wire Pair 2 – The profile applies to Wire Pair 2.
Select Wire Pair 1 if this profile is to be used for ports that
use only one wire pair.
3. Click on Apply.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
3-7
Page 20

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Configuring Alarm Threshold Profiles (8955, 8965, 8968)
Use the Configuration - Alarm Threshold Profiles screen to define sets of alarm
thresholds that you can apply to DSL ports.
To create an alarm threshold profile for a ReachDSL or ADSL line card:
1. Click on Create New Profile. The Alarm Threshold Profile Create screen
appears.
2. Enter or select the following fields:
Field Description
Profile Name Specify a name for this alarm profile.
Downstream / Near End Alarm Profile
Loss of Frame Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous message are sent if the
number of LOFS events in a 15-minute interval meets or
exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
Loss of Power Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous messages are sent if
the number of LPRS events in a 15-minute interval meets
or exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
Errored Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous message are sent if the
number of ES events in a 15-minute interval meets or
exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
Severely-Errored Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous message are sent if the
number of SES events in a 15-minute interval meets or
exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
Unavailable Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous message are sent if the
number of UAS events in a 15-minute interval meets or
exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
Increasing Rate SNMP rate change trap and TL1 autonomous message
are sent if the current rate is greater than or equal to the
previous rate plus this threshold (0–65535 kbps, where 0
disables the messages).
Decreasing Rate SNMP rate change trap and TL1 autonomous message
are sent if the current rate is less than or equal to the
previous rate minus this threshold (065535 kbps, where 0
disables the messages).
Upstream / Far End Alarm Profile
Loss of Frame Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous message are sent if the
number of LOFS events in a 15-minute interval meets or
exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
3-8 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 21

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Field Description
Loss of Signal Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous message are sent if the
number of LOSS events in a 15-minute interval meets or
exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
Loss of Link Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous message are sent if the
number of LOLS events in a 15-minute interval meets or
exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
Errored Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous message are sent if the
number of ES events in a 15-minute interval meets or
exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
Severely-Errored Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous message are sent if the
number of SES events in a 15-minute interval meets or
exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
Unavailable Seconds SNMP trap and TL1 autonomous message are sent if the
number of UAS events in a 15-minute interval meets or
exceeds the selected value (0–900 seconds, where 0
disables the messages).
Increasing Rate SNMP rate change trap and TL1 autonomous message
are sent if the current rate is greater than or equal to the
previous rate plus this threshold (065535 kbps, where 0
disables the messages).
Decreasing Rate SNMP rate change trap and TL1 autonomous message
are sent if the current rate is less than or equal to the
previous rate minus this threshold (065535 kbps, where 0
disables the messages).
Init Failure Specify whether initialization failure generates
InitFailureTrap messages as specified in RFC 2662.
Yes - Enable Initialization Failure Trap messages.
No - Disable Initialization Failure Trap messages.
3. Click on Apply.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
3-9
Page 22

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Creating Alarm Threshold Profiles for Model 8985
Procedure
To create an alarm threshold profile for an SHDSL line card:
1. Click on Create New Profile. The Alarm Threshold Profile Create screen
appears.
2. Enter or select the following fields:
Field Description
Profile Name Specify a name for this alarm profile.
Loop Attenuation Threshold Specify a loop attenuation alarm threshold of 0–127 dB.
An SNMP Loop Attenuation crossing trap message and a
TL1 autonomous message may be sent if the current loop
attenuation reaches or exceeds this threshold. A Loop
Attenuation alarm will also be declared when the current
Loop Attenuation exceeds this value. A value of 0 disables
event notifications for the condition.
SNR Margin Specify an SNR Margin alarm threshold of 0–15 dB. An
SNMP Margin crossing trap message and a TL1
autonomous message may be sent if the current SNR
Margin reaches or drops below this threshold. An SNR
Margin alarm will also be declared when the current SNR
Margin has dropped below this value. A value of 0
disables event notifications for the condition.
Errored Seconds Specify an ES threshold of 0–900 seconds. An SNMP ES
trap message and a TL1 autonomous message may be
sent if the number of ES events in a 15-minute interval
equals or exceeds the selected value. At most one SNMP
and one TL1 notification will be sent per interval per
device. A value of 0 disables event notifications for the
condition.
Severely-Errored Seconds Specify an SES threshold of 0–900 seconds. An SNMP
SES trap message and a TL1 autonomous message may
be sent if the number of SES events in a 15-minute
interval equals or exceeds the selected value. At most one
SNMP and one TL1 notification will be sent per interval
per device. A value of 0 disables event notifications for the
condition.
Code Violations Specify a Code Violations threshold of 0–900 seconds. An
SNMP code violations trap message and a TL1
autonomous message may be sent if the number of Code
Violations in a 15-minute interval equals or exceeds this
threshold. At most one SNMP and one TL1 notification will
be sent per interval per device. A value of 0 disables event
notifications for the condition.
3-10 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 23

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Field Description
Loss of Sync Word Seconds Specify a Loss of Sync Word Seconds threshold of 0–900
seconds. An SNMP LOSWS trap message and a TL1
autonomous message may be sent if the number of
LOSWS in a 15-minute interval equals or exceeds this
threshold. At most one SNMP and one TL1 notification will
be sent per interval per device. A value of 0 disables event
notifications for the condition.
Unavailable Seconds Specify an Unavailable Seconds threshold of 0–900
seconds. An SNMP UAS trap message and a TL1
autonomous message may be sent if the number of UAS
events in a 15-minute interval equals or exceeds the
selected value. At most one SNMP and one TL1
notification will be sent per interval per device. A value of
0 disables event notifications for the condition.
3. Click on Apply.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
3-11
Page 24

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Configuring Cross Connections
Use the Configuration - Cross Connect screen to establish or delete Virtual
Channel Connections (VCCs) by port or by slot. Connections may be established
between any combination of:
Subtended ports
DSL ports
Network interface (uplink)
Default Mappings
A DSL port’s data VPI/VCI is always 0,35.
Default VC mappings to the SCP card for data service may be determined so:
VPI is 2 for ports 1–24 and 3 for ports 25–48
VCI is (Slot * 24) + (Port number up to 24) + 7
Port numbers 25 through 48 are reduced (by 24) to 1 through 24, respectively, in
calculating VCI. So the VCI for Slot 3, Port 1 is the same as the VCI for Slot 3,
Port 25:
Slot 3, Port 1: 3*24 + 1 + 7 = 80
Slot 3, Port 25: 3*24 + 25 – 24 + 7 = 80
Adding a Port-to-Port Cross Connection
Procedure
To create a cross connection between specified ports:
1. On the Configuration - Cross Connect screen, click on Create New Cross
Connect. The Configuration - Cross Connect Create screen appears.
2. Enter or select the following fields:
Field Description
Port A
Slot Select from the drop-down list the slot where the card
associated with this port resides.
Port Select the port for the cross-connection.
VPI Enter the VPI for this side of the cross-connection.
Start VCI Enter the first VCI for this side of the cross-connection.
3-12 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 25

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Field Description
End VCI Enter the last VCI for this side of the cross-connection.
Segment End Point Select True or False from the drop-down list to signify
whether this connection is the segment endpoint. This field
determines if the port card will function as an endpoint for
ATM OAM loopbacks. If False, the port card will loop back a
cell only if its location ID matches the preconfigured
location ID. (See Configuring ATM Ports on page 3-16.) All
other loopback cells are passed to the next segment.
Port B
Slot Select from the drop-down list the slot where the card
associated with this port resides.
Port Select the user port for the cross-connection.
VPI Enter the VPI for the user side of the cross-connection.
Start VCI Enter the first VCI for the user side of the cross-connection.
End VCI Enter the last VCI for the user side of the cross-connection.
Segment End Point Select True or False from the drop-down list to signify
whether this connection is the segment endpoint. This field
determines if the port card will function as an endpoint for
ATM OAM loopbacks. If False, the port card will loop back a
cell only if its location ID matches the preconfigured
location ID. (See Configuring ATM Ports on page 3-16.) All
other loopback cells are passed to the next segment.
Profiles
Port B to Port A Profile Select a profile for upstream traffic.
Port A to Port B Profile Select a profile for downstream traffic.
3. Click on Apply.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
3-13
Page 26

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Adding a Slot-to-Slot Cross Connection
Procedure
To create a range of VCCs between specified slots and the SCP card:
1. On the Configuration - Cross Connect screen, click on Create Cross Connect
by Slot. The Configuration - Cross Connect - Slot screen appears.
2. Enter or select the following fields:
Field Description
Start Slot Select from the drop-down list the first slot in a range to
End Slot Select from the drop-down list the last slot in a range to
Start Port Select from the drop-down list the first port in a range to
have connections established to the SCP card.
have connections established to the SCP card. It may be
the same as the Start Slot.
have a connection established to the SCP card. The
range of ports will be applied to all slots selected.
End Port Select from the drop-down list the last port in a range to
have a connection established to the SCP card. It may be
the same as the Start Port. The range of ports will be
applied to all slots selected.
Slot VPI Enter the VPI of this circuit.
Slot VCI Enter the VCI of this circuit.
Segment End Point (Slot) Select True or False from the drop-down list to signify
whether this connection is the segment endpoint. This
field determines if the port card will function as an
endpoint for ATM OAM loopbacks. If False, the port card
will loop back a cell only if its location ID matches the
preconfigured location ID. (See Configuring ATM Ports on
page 3-16.) All other loopback cells are passed to the
next segment.
SCP VPI Enter the VPI of this range of VCCs.
SCP Start VCI Enter the first VCI of this range of VCCs.
Segment End Point Select True or False from the drop-down list to signify
whether this connection is the segment endpoint. This
field determines if the port card will function as an
endpoint for ATM OAM loopbacks. If False, the port card
will loop back a cell only if its location ID matches the
preconfigured location ID. (See Configuring ATM Ports on
page 3-16.) All other loopback cells are passed to the
next segment.
Upstream Profile Select a profile for upstream traffic.
Downstream Profile Select a profile for downstream traffic.
3-14 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 27

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
For example, if:
Start Slot is 1 and End Slot is 2
Slot VPI and VCI are 0 and 35
SCP VPI and Start VCI are 2 and 32
The VCCs created have the following VPI,VCI values:
Slot
SCP Card
Slot 1 Port 1 0,35 → 2,32
Port 2 0,35 → 2,33
| | |
Port 24 0,35 → 2,55
Slot 2 Port 1 0,35 → 2,56
Port 2 0,35 → 2,57
| | |
Port 24 0,35 → 2,79
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
3-15
Page 28

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Configuring ATM Ports
Use the Configuration - ATM Port screen to associate a DSL port or the T1/E1 port
with an ATM segment location. ATM segment location ID is a 16-octet field that
identifies this ATM interface for OAM F5 loopbacks. When a segment F5 OAM
loopback cell is received, the destination segment location in the cell is compared
to the segment location ID for the port. If the destination location ID matches the
location ID or is all ones, the cell is looped back to the source. If there is not a
match, the cell passes through the card.
Procedure
To associate a port with an ATM segment location:
1. Select a Slot and Port from the drop-down lists, and click on Select.
2. Enter an ATM Segment Location ID. The value must be 32 hexadecimal
characters or ALLONES. Allowed values are restricted per ITU-T1.610 as
follows:
— The first byte must be 01, 02, 03, FF or 6A.
— If the first octet is FF, then octets 2–16 must also be FF.
— If the first octet is 6A, then octets 2–16 must also be 6A.
3. Click on Apply.
3-16 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 29

Configuring Traffic Profiles
Use the Configuration - Profile Traffic Descriptor screen to define, modify, and
delete ATM traffic profiles.
To create a traffic profile:
1. On the Configuration - Profile Traffic Descriptor screen, click on Create New
Profile. The first Configuration - Profile Traffic Descriptor Create screen
appears.
2. Select a Class of Service (CoS) from the drop-down list:
— UBR - Unspecified Bit Rate
— CBR - Constant Bit Rate
— nrt-VBR - Non-Real-Time Variable Bit Rate
— rt-VBR - Real-Time Variable Bit Rate
3. The Configuration - Profile Traffic Descriptor Create - CoS screen appears.
What fields are displayed depends on the Class of Service. Enter or select:
3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
Field Description
Profile Name Enter a name for this profile.
PCR Enter a Peak Cell rate from 0 to 351566.
SCR Enter a Sustainable Cell Rate from 0 to 351566.
CDVT Enter a Cell Delay Variation Tolerance from 0 to 100000.
If you enter 0, a CDVT value is automatically calculated.
MDCR Enter a Minimum Desired Cell Rate from 0 to 351566.
MBS Enter a Maximum Burst Size from 0 to 351566.
Tagging Select Yes or No from the drop-down list to determine if
tagging is allowed for this profile.
Traffic Policing Select Yes or No from the drop-down list to determine if
traffic policing is allowed for this profile.
Packet Discard Select Yes or No from the drop-down list to determine if
partial packet discards are allowed for this profile.
Shaping Select Yes or No from the drop-down list to determine if
shaping is allowed for this profile.
4. Click on Apply.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
3-17
Page 30

3. Configuration Using the Web Interface
3-18 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 31

Monitoring
What to Monitor
This chapter presents information on how to monitor unit status and assess
performance.
Table 4-1, Location of ATM Line Card Information, shows on which web interface
screens you can find information useful in reporting and diagnosing problems.
Table 4-1. Location of ATM Line Card Information (1 of 2)
4
Field Screen
Code Violation alarm Status - DSL or SHDSL Performance
DC Continuity Fault alarm Status - DSL or SHDSL Performance
Errored Second alarm Status - DSL or SHDSL Performance
Errored Seconds Status - DSL or SHDSL Statistics
Firmware Revision System - Firmware or
System - Slot Information
Hardware Revision System - Slot Information
Loop Attenuation Status - DSL or SHDSL Performance
Loss of Synchronization Word alarm Status - DSL or SHDSL Performance
Loss of Synchronization Word Seconds Status - DSL or SHDSL Statistics
Model Number System - Slot Information
No Neighbor Present alarm Status - DSL or SHDSL Performance
Protocol Initialization Failure alarm Status - DSL or SHDSL Performance
Serial Number System - Slot Information
Severely Errored Second alarm Status - DSL or SHDSL Performance
Severely Errored Seconds Status - DSL or SHDSL Statistics
SNR Margin Defect alarm Status - DSL or SHDSL Performance
Syslog Status - Syslog
System Contact System - System Information
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 4-1
Page 32

4. Monitoring
Table 4-1. Location of ATM Line Card Information (2 of 2)
Field Screen
System Location System - System Information
System Name System - System Information
Unavailable Second alarm Status - DSL or SHDSL Performance
Unavailable Seconds Status - DSL or SHDSL Statistics
Unknown Cell Log Status - Unknown Cell Log
For example, to view the system log, click on Syslog under Status in the web
interface menu frame. The Status - System Log screen appears.
Use the online Helps to obtain information about the System and Status displays.
4-2 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 33

Front Panel LEDs (Models 8955, 8965, and 8985)
The following table describes the meaning and states of the LEDs on the front
panel of the Model 8955, 8965, and 8985 line cards.
4. Monitoring
SYSTEM
OK
Alrm
Test
ATM BUS
TX
RX
LOC
DSL PORT
1/13
2/14
3/15
4/16
PORT
5/17
6/18
7/19
8/20
PORT
9/21
10/22
11/23
12/24
ALT BANK
13-24
1-12
SYSTEM
OK
Alrm
Test
SYS BUS
TX
RX
LOC
DSL PORT
1/13
2/14
3/15
4/16
PORT
5/17
6/18
7/19
8/20
PORT
9/21
10/22
11/23
12/24
ALT BANK
13-24
1-12
SYSTEM
OK
Alrm
Test
ATM BUS
TX
RX
LOC
DSL PORT
1/13
2/14
3/15
4/16
PORT
5/17
6/18
7/19
8/20
PORT
9/21
10/22
11/23
12/24
ALT BANK
13-24
1-12
Type LED LED is . . . *
SYSTEM OK Green, On
Off
Green,
Pulsing
Green,
Fast Blinking
Alrm Amber, On
Off
Test Amber, On
Off
Amber,
Fast Blinking
ATM BUS
or
SYS BUS
DSL PORT 1/13–12/24 Green, On
TX Off
Green,
Fast Blinking
RX Off
Green,
Fast Blinking
LOC Amber, On
Off
Off
Green,
Slow Blinking
Green,
Fast Blinking
Indicating . . .
Card failure. System processing
functions have stopped.
No power to card.
Card functioning normally.
Firmware download needed.
Alarm is present on the card. ATM
interface is not being detected.
Normal operation, no alarms.
Te s t i n p r o gr e s s .
Normal operation, no tests.
Self-test is in progress.
Inactive.
Cells are being transmitted.
Inactive, link down.
Cells are being received.
Loss Of Clock. Bus clock signal is
not present.
Normal operation.
Good signal, unit is trained.
Port is disabled.
Port is in test, or is down.
Port is training.
ALT BANK Off
AT M
ReachDSL
8955
ATM
ADSL2+
8965
AT M
SHDSL
8985
Amber,
03-17424
04-17425-01
03-17426
Fast Blinking
* Pulsing: LED turns off momentarily once per second.
Slow Blinking: LED turns on momentarily once per second.
Fast Blinking: LED turns off and on in equal duration 4 times per second.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
The ports not currently displayed
by the port status LEDs are
functioning normally or are
disabled.
One of the ports not currently
being displayed by the port status
LEDs is down, in test, or in training
mode.
4-3
Page 34

4. Monitoring
Front Panel LEDs (Model 8968)
The following table describes the meaning and states of the LEDs on the front
panel of the Model 8968 line card. The card has 24 LEDs to show the state of DSL
ports. Depending on the setting of the switch on the face of the card, the LEDs
reflect the state of ports 1–24 or 25–48.
SYSTEM
OK
Alrm
Test
25 - 48 1 - 24
1/25
11/35
13/37
23/47
25-48
1-24
Type LED LED is . . . *
SYSTEM OK Green, On
Indicating . . .
Card failure. System processing
functions have stopped.
Off
Green,
No power to card.
Card functioning normally.
Pulsing
Green,
Firmware download needed.
Fast Blinking
Alrm Amber, On
Alarm is present on the card. ATM
interface is not being detected.
Off
Test Amber, On
Off
Amber,
Normal operation, no alarms.
Te s t i n p r o gr e s s .
Normal operation, no tests.
Self-test is in progress.
Fast Blinking
2/26
12/36
14/38
DSL PORT 1/25–24/48 Green, On
Off
Green,
24/48
Slow Blinking
Green,
Good signal, unit is trained.
Port is disabled.
Port is in test, or is down.
Port is training.
Fast Blinking
* Pulsing: LED turns off momentarily once per second.
Slow Blinking: LED turns on momentarily once per second.
Fast Blinking: LED turns off and on in equal duration 4 times per second.
ADSL2+
8968
04-17507
4-4 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 35

Diagnostics
Overview
5
The ATM line cards provide the following diagnostic tools:
Lamp Test on page 5-1
— Tests the front panel LEDs on a line card.
Loopback Test (Model 8985 Only) on page 5-2
— Performs Loopback test on the SHDSL span of the network for
Model 8985 cards.
Lamp Test
Use the Tests - Lamp Test screen to verify that the front panel LEDs on line card
are functional.
Procedure
To test the LEDs:
1. Select a Slot from the drop-down list.
2. Click on Start Lamp Test. The button changes to Stop Lamp Test, and power is
applied to all LEDs on the card’s front panel.
3. When you have checked the LEDs, click on Stop Lamp Test.
If all LEDs did not light up, contact your service representative.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 5-1
Page 36

5. Diagnostics
Loopback Test (Model 8985 Only)
Use the Tests - SHDSL Loopbacks screen to start and stop line loopback tests.
Procedure
To run a SHDSL loopback test:
1. Click on Configure Test(s). The SHDSL Loopback Tests setup screen appears.
2. Select a Slot from the drop-down list.
3. For any port and direction (STUC or STUR), click on the associated Payload
Loopback button if you want the loopback to include a data payload.
4. For any port and direction, click in the Start box if you want the entity to be
included in the loopback tests.
5. Click on Start Selected. The button changes to Stop Selected.
6. When you have completed testing, click on Stop Selected.
5-2 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 37

Maintenance Procedures
Overview
This chapter provides instructions on how to perform miscellaneous maintenance
procedures:
Uploading and Downloading a Configuration on page 6-2
Downloading and Switching Firmware on page 6-4
Restarting the Line Card on page 6-5
6
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 6-1
Page 38

6. Maintenance Procedures
Uploading and Downloading a Configuration
Your configuration options for the BAC reside in a file in memory on the SCP
card. This file may be saved for purposes of disaster recovery by uploading it to
an FTP (File Transfer Protocol) server. A configuration file may be restored by
downloading it from an FTP server.
Use the System - Save and Restore screen to:
Save (upload) the configuration to an external file using FTP.
Restore (download) the configuration from an external file using FTP. A
downloaded configuration file remains in the memory of the SCP card until it is
overwritten by another downloaded configuration file, or until the SCP card is
reset to factory defaults.
Reset the SCP card using factory default configuration settings
Reset the SCP card using downloaded configuration settings
Procedure
To upload and download configurations:
1. In the Configuration (FTP) box, set the parameters as shown in the following
table.
Configuration (FTP) Parameters
FTP Server IP Address Specify the network address of the FTP server where
the configuration is to be uploaded to or downloaded
from. For example: 137.90.128.10
User Name Specify a user name accepted by the FTP server. For
example: admin
Password Specify a password accepted by the FTP server. For
example: admnpass
Filename Specify the name or pathname of the configuration file.
For example: /configs/may_2003_backup.cfg
2. Click on the:
— Download button to copy a configuration file to the SCP card
— Upload button to back up the configuration file to a server
A Configuration Transfer Status frame is displayed showing the filename, server
address, number of bytes transferred, and the Transfer Status.
When the download or upload is complete, Transfer Status changes to "Transfer
completed successfully."
6-2 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 39

Resetting the Configuration to Default Settings
Procedure
To reset the running configuration to the default settings:
1. In the Configuration Reset box, click on Reset to Factory Defaults. Any
configuration options you have modifed are replaced with default values.
Resetting the Configuration to Downloaded Settings
Procedure
To reset the running configuration to the settings in the downloaded file:
1. In the Configuration Reset box, click on Reset to Downloaded file. Any
configuration options you have modifed are replaced with the values in
the downloaded file.
6. Maintenance Procedures
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
6-3
Page 40

6. Maintenance Procedures
Downloading and Switching Firmware
Use the System - Firmware screen to upgrade firmware or switch versions of
firmware in the chassis.
The SCP card has two banks of firmware: the running firmware and alternate
firmware. When firmware is downloaded, it is downloaded to the alternate
firmware bank. Switching firmware versions changes the running firmware to the
dormant (alternate) firmware, and the alternate firmware to the active (running)
firmware.
Downloading Firmware
Procedure
To download new firmware from an FTP server to the SCP card:
1. Enter or select the appropriate parameters in the Firmware Download box as
shown in the following table.
Firmware Download Parameters
FTP Server IP Address Specify the network address of the FTP server where
the firmware is to be downloaded from. For example:
137.90.128.10
User Name Specify a user name accepted by the FTP server. For
example: admin
Password Specify a password accepted by the FTP server. For
example: admnpass
Filename Specify the name or pathname of the firmware file. For
example: /scp_030145.fpi
2. Click on Download. The firmware is downloaded. A Firmware Download
Status frame is displayed showing the filename, server address, number of
bytes transferred, and the Transfer Status.
When the download is complete, Transfer Status changes to "Transfer
completed successfully."
6-4 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 41

Switching Firmware
6. Maintenance Procedures
Procedure
To switch between the firmware currently running and alternate firmware stored in
the unit:
1. Verify that the Running Firmware and Alternate Firmware displayed in the
Firmware box are different versions.
2. Click on the Switch button. The unit is reset and:
— The Running Firmware becomes the alternate firmware
— The Alternate Firmware becomes the running firmware
3. Delete the cache used by your web browser before logging into the SCP card:
— With Internet Explorer, select Tools -> Internet Options. On the General
tab, in the Temporary Internet Files box, click on Delete Files.
— With Netscape, select Edit -> Preferences. Click on Advanced, then click
on Cache. On the Cache page, click on Clear Memory Cache, then click
on Clear Disk Cache.
4. If you upgrade an 8965 or 8968 line card from a firmware level prior to 3.01.06,
you must reset the card. See Restarting the Line Card, below.
Restarting the Line Card
The System - Restart screen allows you to reset a line card or SCP card and clear
its statistics.
This is a software reset that does not power down the unit. However, all links are
dropped, and the restarted line card retrains with its DSL endpoint.
Procedure
To restart a card:
1. Select a Slot from the drop-down list and click on Select.
2. Click on the Restart button.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
6-5
Page 42

6. Maintenance Procedures
6-6 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 43

Connector Pin Assignments
8620 and 8820 Telco Connector Pinouts
For 24-port line cards, the Telco 50-pin connectors
on the back of the 8620 BAC chassis (numbered
1–3) and the 8820 BAC chassis (numbered 1–18)
provide the 2-wire loop interface from each DSL
port to either the POTS splitter shelf or, if the loop
is not being shared with POTS, then to the Main
Distribution Frame (MDF). The following table lists
the pin assignments for each of these interfaces.
A
Pin
Number 50
Connector Pins
Port
Port 1 1, 26 Port 13 13, 38
Port 2 2, 27 Port 14 14, 39
Port 3 3, 28 Port 15 15, 40
Port 4 4, 29 Port 16 16, 41
Port 5 5, 30 Port 17 17, 42
Port 6 6, 31 Port 18 18, 43
Port 7 7, 32 Port 19 19, 44
Port 8 8, 33 Port 20 20, 45
Port 9 9, 34 Port 21 21, 46
Port 10 10, 35 Port 22 22, 47
Port 11 11, 36 Port 23 23, 48
Port 12 12, 37 Port 24 24, 49
(Tip, Ring) Port
Connector Pins
(Tip, Ring)
Pin
Number 1
00-16714
Pins 25 and 50 are not used.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 A-1
Page 44

A. Connector Pin Assignments
Model 8968 Line Card Telco Connector Pinouts
The Telco 50-pin connectors on the faceplate of
the Model 8968 line card provide the 2-wire loop
interface from each DSL port to either the POTS
splitter shelf or, if the loop is not being shared with
POTS, then to the Main Distribution Frame (MDF).
The following table lists the pin assignments for
each of these interfaces.
The bottom connector (Connector 1) services
ports 1–24 and the top connector (Connector 2)
services ports 25–48
Pin
Number 50
Pin
Number 1
00-16714
Connector 1
Port
Port 1 Port 25 1, 26 Port 13 Port 37 13, 38
Port 2 Port 26 2, 27 Port 14 Port 38 14, 39
Port 3 Port 27 3, 28 Port 15 Port 39 15, 40
Port 4 Port 28 4, 29 Port 16 Port 40 16, 41
Port 5 Port 29 5, 30 Port 17 Port 41 17, 42
Port 6 Port 30 6, 31 Port 18 Port 42 18, 43
Port 7 Port 31 7, 32 Port 19 Port 43 19, 44
Port 8 Port 32 8, 33 Port 20 Port 44 20, 45
Port 9 Port 33 9, 34 Port 21 Port 45 21, 46
Port 10 Port 34 10, 35 Port 22 Port 46 22, 47
Port 11 Port 35 11, 36 Port 23 Port 47 23, 48
Port 12 Port 36 12, 37 Port 24 Port 48 24, 49
Connector 2
Port
Connector Pins
(Tip, Ring)
Connector 1
Port
Connector 2
Port
Connector Pins
(Tip, Ring)
Pins 25 and 50 are not used.
A-2 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 45

Technical Specifications
Table B-1. ATM Line Card Technical Specifications (1 of 2)
Specifications Criteria*
Size Length: 25.4 cm (10 in)
Weight
Model 8955
Model 8965
Model 8968
Model 8985
B
Height: 31.1 cm (12.3 in)
Width: 2.0 cm (0.8 in)
0.9 kg (2.0 lbs)
0.6 kg (1.4 lbs)
0.9 kg (2.0 lbs)
0.6 kg (1.4 lbs)
Approvals
Safety Certifications Refer to the equipment’s label for approvals on product.
Power
Model 8955
Model 8965
Model 8968
Model 8985
Physical
Environment
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Relative humidity
Shock and vibration
* Technical specifications are subject to change without notice.
The ATM Line Card requires –48 VDC power input. The –48
VDC power is distributed through the BAC backplane.
Maximum Power Dissipation:
27 watts
27 watts
61 watts
45 watts
0° to 50° C (32° to 122° F)
–20° to 70° C (–4° to 158° F)
5% to 85% (noncondensing)
Withstands normal shipping and handling.
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 B-1
Page 46

B. Technical Specifications
Table B-1. ATM Line Card Technical Specifications (2 of 2)
Specifications Criteria*
Line Code
Model 8955
Models 8965 and 8968
Model 8985
DSL Line Rates
Model 8955
Models 8965 and 8968
Model 8985
ReachDSL
ANSI (ANSI T1.413-1998)
G.dmt (ITU G.992.1)
G.lite (ITU G.992.2)
ADSL2 (ITU G.992.3)
ADSL2+ (ITU G.992.5)
G.shdsl (ITU G.991.2)
32–2176 kbps
Downstream:
32–29000 kbps for ADSL2+
32–16000 kbps for ADSL2
32–8000 kbps for G.dmt and ANSI
64–3008 kbps for G.lite
Upstream:
32–2200 kbps for ADSL2+
32–1056 kbps for ADSL2
32–832 kbps for ADSL2, ADSL2+, G.dmt, and ANSI
32–512 kbps for G.lite
192–2304 kbps (384–4608 kbps with two wire pairs)
* Technical specifications are subject to change without notice.
B-2 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 47

Index
Numerics
8955
alarm threshold profiles, 3-8
configuring ports, 3-2
description, 1-1
line profiles, 3-6
8965
alarm threshold profiles, 3-8
configuring ports, 3-3
description, 1-1
line profiles, 3-6
8968
alarm threshold profiles, 3-8
configuring ports, 3-3
connectors, A-2
description, 1-1
LEDs, 4-4
line profiles, 3-6
8985
alarm threshold profiles, 3-10
configuring ports, 3-5
description, 1-1
line profiles, 3-7
loopback tests, 5-2
A
ADSL
configuring ports, 3-3
line profiles, 3-6
alarms
threshold profiles, 3-8, 3-10
where displayed, 4-1
applications
multiple protocols, 1-3
voice over DSL, 1-3
ATM
ports, configuring, 3-16
statistics, 1-2
C
classes of service, 1-2
Code Violation alarm, 4-1
configuration, 3-1
ADSL ports, 3-3
alarm threshold profiles, 3-8, 3-10
ATM ports, 3-16
cross connections, 3-12
example of network, 1-3
line profiles, 3-6
ReachDSL ports, 3-2
saving, 6-2
SHDSL ports, 3-5
tab, 2-2
traffic profiles, 3-17
upload and download, 6-2
cross connections, 3-12
D
data rate
adaptation, 1-3
DC Continuity Fault alarm, 4-1
dimensions, B-1
documents, related, iv
downloading
a configuration, 6-2
firmware, 6-4
DSL ports
ADSL, 3-2
ReachDSL, 3-2
SHDSL, 3-5
E
ending a session, 2-2
endpoint support, 1-2
environment requirements, B-1
Equivalent Working Length, 3-5
Errored Second alarm, 4-1
Errored Seconds, 4-1
example network, 1-3
F
features, 1-2
firmware
download, 6-4
revision number, 4-1
fornt panel LEDs, 4-3
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004 IN-1
Page 48

Index
G
glossary, iii
GrandVIEW, 1-4
H
Hardware Revision, 4-1
Help, 2-2
L
lamp test, 5-1
LEDs, 4-3
line profiles
ADSL, 3-6
ReachDSL, 3-6
SHDSL, 3-7
login, 2-1
logout, 2-2
Loop Attenuation, 4-1
loopback test, 5-2
Loss of Synchronization Word alarm, 4-1
Loss of Synchronization Word Seconds, 4-1
M
maintenance procedures, 6-1
menus, 2-2
described, 2-1
MIBs
list of supported, 1-4
Model 8620 and 8820 connectors, A-1
Model 8968 connectors, A-2
Model Number, 4-1
monitoring, 4-1
N
network example, 1-3
No Neighbor Present alarm, 4-1
O
online Help, 2-2
overview
ADSL, 1-1
ATM line cards, 1-1
card features, 1-2
device features, 1-2
maintenance procedures, 6-1
ReachDSL, 1-1
SHDSL, 1-1
tests, 5-1
user interfaces, 2-1, 3-1
user’s guide, iii
P
performance, 4-1
physical environment requirements, B-1
pin assignments, A-1–A-2
port-to-port cross connections, 3-12
Power Management (ADSL2), 3-4
power requirements, B-1
product-related documents, iv
profiles
alarm threshold, 3-8, 3-10
line, 3-6
traffic, 3-17
Protocol Initialization Failure alarm, 4-1
R
ReachDSL
line profiles, 3-6
related documents, iv
reset
card, 6-5
to downloaded settings, 6-3
to factory defaults, 6-2
restart card, 6-5
restoring configuration from server, 6-2
S
save configuration to server, 6-2
saving a configuration, 6-2
screens, how to use, 2-1
Serial Number, 4-1
Severely Errored Second alarm, 4-1
Severely Errored Seconds, 4-1
SHDSL
line profiles, 3-7
loopback, 5-2
ports, 3-5
size of card, B-1
slot-to-slot cross connections, 3-14
SNMP
general management capabilities, 1-4
MIBs supported, 1-4
trap support, 1-4
SNR Margin Defect alarm, 4-1
software reset, 6-5
spectrum management, 3-1
speeds
automated adjustment, 1-3
status, 4-1
Syslog status, 4-1
IN-2 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
Page 49

Index
System
Contact, 4-1
Location, 4-2
Name, 4-2
T
technical manuals, iv
technical specifications, B-1
Telco 50-pin connectors, A-1–A-2
test, 5-1
LEDs, 5-1
procedures, 5-1
SHDSL, 5-2
threshold profiles, 3-8, 3-10
traffic profiles, 3-17
traps, 1-4
U
Unavailable Second alarm, 4-2
Unavailable Seconds, 4-2
Unknown Cell Log, 4-2
uploading a configuration, 6-2
user interface
configuration of card, 3-1
how to use, 2-1
monitoring, 4-1
V
voice over DSL, 1-3
W
web interface
accessing, 2-1
menu tabs, 2-2
website, Paradyne technical manuals, iv
weight of card, B-1
8900-A2-GB20-30 June 2004
IN-3
Page 50

Index
IN-4 June 2004 8900-A2-GB20-30
 Loading...
Loading...