Page 1

HOTWIRErM/SDSL and HDSL2
TERMINATION UNITS
MODELS 8747, 8777, AND 8779
USER’S GUIDE
Document No. 8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
Page 2

Copyright E 2000 Paradyne Corporation.
All rights reserved.
Printed in U.S.A.
Notice
This publication is protected by federal copyright law. No part of this publication may be copied or distributed,
transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any human or computer language in any form
or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, manual or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties without the
express written permission of Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Ave. N., Largo, FL 33773.
Paradyne Corporation makes no representation or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and specifically
disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Further, Paradyne Corporation
reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents hereof without
obligation of Paradyne Corporation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
Changes and enhancements to the product and to the information herein will be documented and issued as a new
release to this manual.
Warranty, Sales, Service, and Training Information
Contact your local sales representative, service representative, or distributor directly for any help needed. For
additional information concerning warranty , sales, service, repair, installation, documentation, training, distributor
locations, or Paradyne worldwide office locations, use one of the following methods:
H Internet: Visit the Paradyne World Wide Web site at www.paradyne.com. (Be sure to register your warranty at
www.paradyne.com/warranty.)
H Telephone: Call our automated system to receive current information by fax or to speak with a company
representative.
— Within the U.S.A., call 1-800-870-2221
— Outside the U.S.A., call 1-727-530-2340
Document Feedback
We welcome your comments and suggestions about this document. Please mail them to Technical Publications,
Paradyne Corporation, 8545 126th Ave. N., Largo, FL 33773, or send e-mail to userdoc@paradyne.com. Include
the number and title of this document in your correspondence. Please include your name and phone number if you
are willing to provide additional clarification.
Trademarks
ACCULINK, COMSPHERE, FrameSaver, Hotwire, and NextEDGE are registered trademarks of Paradyne
Corporation. MVL, OpenLane, Performance Wizard, and TruePut are trademarks of Paradyne Corporation. All other
products and services mentioned herein are the trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or registered
service marks of their respective owners.
Regulatory and Safety Information
Refer to the appropriate Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) manual for all regulatory notices and
safety information.
Printed on recycled paper
A
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 3

Contents
About This Guide
H Document Purpose and Intended Audience vii. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Document Summary vii. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Product-Related Documents viii. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 About the Hotwire 8747, 8777, and 8779 Termination Units
H M/SDSL and HDSL2 Overview 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Hotwire 87xx Termination Unit Features 1-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Network Configuration 1-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H SNMP Management Capabilities 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Management Information Base (MIB) Support 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SNMP Trap Support 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
H User Interface Access 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Management Serial Port Settings 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Logging In to the Hotwire DSLAM 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Initiating an ATI Session 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Screen Work Areas 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Navigating the Screens 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Keyboard Keys 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Screen Function Keys 2-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Switching Between Screen Work Areas 2-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Ending an ATI Session 2-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Exiting From the DSLAM Session 2-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
i
Page 4

Contents
3 Initial Startup and Configuration
H Overview 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Entering Identity Information 3-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Configuring the Unit 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration Options 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Accessing and Displaying Configuration Options 3-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Configuration Edit/Display 3-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Saving Configuration Options 3-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Restoring Access to the User Interface 3-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Resetting the Device 3-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Disabling AutoRate 3-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Resetting AutoRate 3-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Cross-Connecting Ports
H Overview 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Determining the Configuration 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Setting the Cross-Connect Modes 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Assigning Time Slots 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 IP Addressing
H Selecting an IP Addressing Scheme 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H IP Addressing Example 5-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Security
H Overview 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H ATI Access Levels 6-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Creating a Login 6-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Deleting a Login 6-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Controlling SNMP Access 6-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configurations Not Running IP Conservative Software 5-1. . . . . . . . . . .
All Configurations 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assigning SNMP Community Names and Access Types 6-5. . . . . . . . . .
Limiting SNMP Access through the IP Addresses of the Managers 6-5.
ii
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 5

7 Monitoring and Troubleshooting
H What to Monitor 7-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Viewing System and Test Status 7-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Health and Status Messages 7-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Self-Test Results Messages 7-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Status Messages 7-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Device Messages 7-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Viewing Network Error Statistics 7-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Viewing Network Performance Statistics 7-1 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Viewing DSX-1 Performance Statistics 7-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Viewing G.703 Performance Statistics 7-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Viewing LED Status 7-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Front Panel LEDs 7-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Changing the Meaning of the PORTS LEDs 7-20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Troubleshooting 7-21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Contents
8 Testing
H Accessing the Test Menu 8-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Running Network Tests 8-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Network Line Loopback 8-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Repeater Loopback 8-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTE Loopback 8-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote Send Line Loopback 8-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Send and Monitor 511 8-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Device Tests 8-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lamp Test 8-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Ending an Active Test 8-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Telco-Initiated Tests 8-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Telco-Initiated Line Loopback 8-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Telco-Initiated Payload Loopback 8-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Telco-Initiated Remote Line Loopback 8-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9 Transferring Code and Configurations Using TFTP
H Download Code 9-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Applying the Download 9-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Configuration Loader 9-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
iii
Page 6

Contents
A Configuration Options
H Overview A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Network Interface Options Menu A-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H DSX-1 Interface Options A-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H G.703 Interface Options A-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Copy Ports Options A-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H System Options A-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H System Clock A-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Cross-Connect A-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Set Cross-Connect Mode A-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assign Time Slots A-20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Management and Communication Options Menu A-23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Telnet Session Options A-23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General SNMP Management Options A-25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SNMP NMS Security Options A-27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SNMP Traps Options A-29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B Standards Compliance for SNMP Traps
H SNMP Traps B-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H ifIndex B-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H warmStart B-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H authenticationFailure B-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H linkUp and linkDown B-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Enterprise-Specific Traps B-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C Connector Pin Assignments
H Hotwire Termination Unit Front Panel 50-pin DTE Connector Pinouts C-1. .
H Model 8610, 8810, and 8820 DSLAM Telco 50-pin Connector Pinouts C-3.
iv
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 7

D Technical Specifications
E Cross-Connection Worksheets
H Using the Worksheets E-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H Port Connection Diagram E-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H DSX-1 Time Slot Assignments E-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H G.703 Time Slot Assignments E-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Glossary
Index
Contents
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
v
Page 8

Contents
This page intentionally left blank.
vi
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 9

About This Guide
Document Purpose and Intended Audience
This guide contains information needed to set up, configure, and operate Hotwire
Models 8747, 8777, and 8779 Multirate Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line
(M/SDSL) and High-bit-rate DSL second generation (HDSL2) Termination Units,
and is intended for installers and operators.
Document Summary
Section Description
Chapter 1 About the Hotwire 8747, 8777, and 8779 Termination Units.
Describes the Hotwire Termination Units’ features and
capabilities.
Chapter 2 Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface. Provides
instructions for accessing the user interface and navigating
the screens.
Chapter 3 Initial Startup and Configuration. Provides instructions for
configuring the unit.
Chapter 4 Cross-Connecting Ports. Provides instructions for
cross-connecting the time slots of the DSL and DTE ports.
Chapter 5 IP Addressing. Provides IP addressing requirements and
examples.
Chapter 6 Security. Presents procedures for creating a login, setting
the effective access levels, and controlling SNMP access.
Chapter 7 Monitoring and Troubleshooting. Describes using the LEDs,
status messages, and network statistics to monitor the unit
and diagnose problems.
Chapter 8 Testing. Provides instructions for running network, DSX-1,
and G.703 tests.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
vii
Page 10

About This Guide
Section Description
Chapter 9 Transferring Code and Configurations Using TFTP. Shows
how to upload and download firmware and configuration
files.
Appendix A Configuration Options. Contains all configuration options,
default settings, and possible settings.
Appendix B Standards Compliance for SNMP Traps. Contains SNMP
trap compliance information.
Appendix C Connector Pin Assignments. Lists the pin assignments for
the front panel DTE connector.
Appendix D Technical Specifications. Contains physical and regulatory
specifications, network and port interfaces, power
consumption values, and accessory part numbers.
Appendix E Cross-Connection Worksheets. Contains worksheets to help
plan and configure the cross-connection of DTE and DSL
ports.
Glossary Defines acronyms and terms used in this document.
Index Lists key terms, acronyms, concepts, and sections in
Product-Related Documents
Document Number Document Title
7970-A2-GB20 Hotwire M/SDSL, M/HDSL, and HDSL2 Standalone
8000-A2-GB22 Hotwire Management Communications Controller
8000-A2-GB29 Hotwire Management Communications Controller
8610-A2-GN10 Hotwire 8610 DSLAM Installation Instructions
8810-A2-GN11 Hotwire 8810 DSLAM Installation Instructions
8820-A2-GN20 Hotwire 8820 GranDSLAM Installation Guide
Contact your sales or service representative to order additional product
documentation.
alphabetical order.
Termination Units, Models 7944, 7945, 7974, 7975,
7976, 7984, 7985, and 7986, User’s Guide
(MCC) Card, IP Conservative, User’s Guide
(MCC) Card User’s Guide
viii
Paradyne documents are also available on the World Wide Web at
www.paradyne.com. Select Library → Technical Manuals.
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 11

About the Hotwire 8747, 8777, and 8779 Termination Units
M/SDSL and HDSL2 Overview
Hotwirer Multirate Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (M/SDSL) products
maximize customer service areas by varying the DSL line rate. This ensures
symmetric DSL connectivity over a wide range of telephone line distances and
transmission line qualities. Hotwire M/SDSL products transmit data over
14,000 feet (4.6 km) at rates up to 2.048 Mbps.
Hotwire High-bit-rate DSL second generation (HDSL2) products transmit data up
to 12,000 feet (3.9 km) at up to 1.544 Mbps.
1
Hotwire products support autorate. Units first synchronize to the highest line rate
that the 2-wire loop supports, and then automatically configure to the highest
multiple of 64 kbps supported by that line rate. Eight line rates are available. At all
rates, a 16 kbps management channel is available, which enables functions such
as firmware downloads to remote units. Units can also be configured manually to
full or fractional T1 or E1 rates.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
1-1
Page 12
About the Hotwire 8747, 8777, and 8779 Termination Units
Hotwire 87xx Termination Unit Features
The Hotwire 87xx Termination Unit is a circuit board mounted in a Hotwire 8610
or 8810 Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer (DSLAM), or 8820
GranDSLAM, and used to transport signals at high speeds over a twisted-pair
connection.
Model . . .
8747 HDSL2 ports DSX-1 ports
8777 M/SDSL ports DSX-1 ports
8779 M/SDSL ports G.703 ports
Hotwire 8747, 8777, and 8779 Termination Units have these standard features:
H Cross-Connection Capability. Any DSL port and time slot can be connected
to any DTE port and time slot.
H Embedded Operations Channel (EOC). Provides remote management via
SNMP or Telnet session capability over the DSL network.
H Asynchronous T erminal Interface (ATI). Provides a menu-driven
VT100-compatible terminal interface for configuring and managing the unit
locally or remotely by Telnet session.
H Local Management. Provides local management using the DSLAM
management card with a:
— Terminal or PC via the Management Serial port of the DSLAM
— NMS connection through the 10BaseT port
H Remote Management. Provides remote management:
Has eight . . . And eight . . .
1-2
— Out-of-band, using an external modem through the Management Serial
port of the DSLAM
— V ia Telnet over the EOC
H Alarm Indication. Activates front panel LEDs.
H Diagnostics. Provides the capability to diagnose device and network
problems and perform tests, including digital loopbacks, pattern tests, and
self-test.
H Device and Test Monitoring. Provides the capability of tracking and
evaluating the unit’s operation, including health and status, and error-rate
monitoring.
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 13
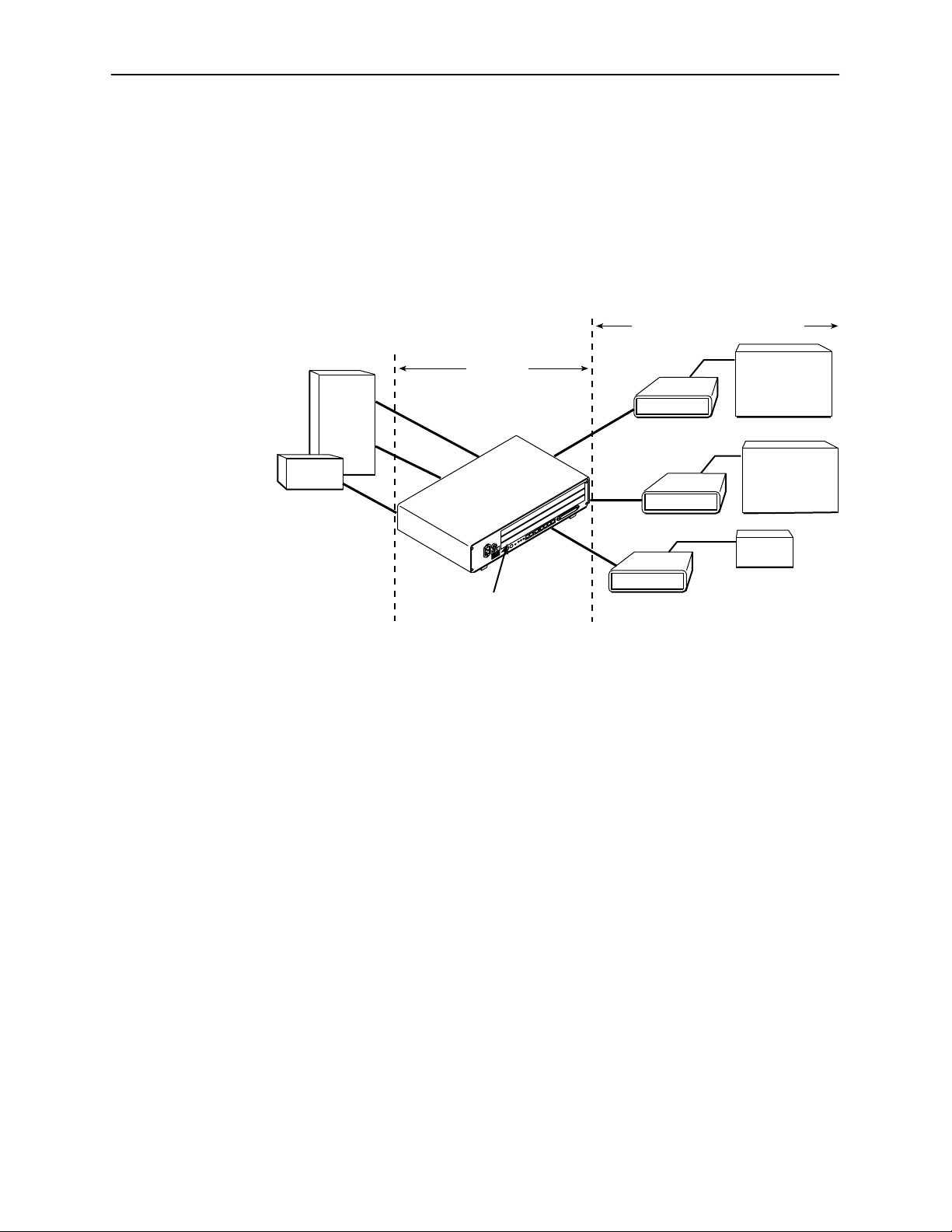
Network Configuration
Figure 1-1 shows a T1 network application using a Hotwire 87xx Termination Unit
for access concentration in a central office (CO). A frame relay switch and a
router are connected, through the termination unit, to partner units on the
customer premises (CP) supporting a T1 host or router, and frame relay
encapsulated or unframed data.
Frame
Relay
Switch
Router
DSX-1
DSX-1
About the Hotwire 8747, 8777, and 8779 Termination Units
Customer Premises (CP)
DSX-1
CO Site
1.544 Mb
DSX-1
7974
DSX-1
7974
EIA-530
7975
T1 Host
(Frame Relay
Encapsulated
Data)
Router
(Frame Relay
Encapsulated
Data)
Router
87xx T ermination Unit
in 8600 Series DSLAM
Figure 1-1. Sample CO-to-CP Configuration
99-16414-01
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
1-3
Page 14

About the Hotwire 8747, 8777, and 8779 Termination Units
SNMP Management Capabilities
Hotwire 87xx Termination Units support SNMP Version 1, and can be managed
by any industry-standard SNMP manager and accessed using SNMP by external
SNMP managers.
Management Information Base (MIB) Support
For a detailed description of supported MIBs, visit Paradyne’s Web site at
www.paradyne.com. The following MIBs are supported:
H MIB II (RFC 1213 and RFC 1573) – Defines the general objects for use with
a network management protocol in TCP/IP internets and provides general
information about the unit. MIB II is backward-compatible with MIB I.
H DS1/E1 MIB (RFC 1406) – Reports the performance status of the DSX-1 or
G.703 interface and supports the features found on the DSX-1 or G.703
Performance Statistics screen.
H Paradyne Enterprise MIB – Supports configuration, status, statistics, and
tests.
SNMP Trap Support
The Hotwire 87xx Termination Unit supports SNMP traps as shown in
Appendix B, Standards Compliance for SNMP Traps.
1-4
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 15

Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
User Interface Access
You can communicate with the asynchronous terminal interface (ATI) using one
of the following methods:
H Direct connection through the Management Serial port of the DSLAM (locally
or via an external modem).
H Telnet session using a Network Management System (NMS) connected to a
LAN/WAN port on the DSLAM.
2
H Telnet session through the Embedded Operations Channel (EOC).
NOTE:
Only one asynchronous terminal interface session can be active at a time,
and another user’s session cannot be forced to end. To automatically log out
a user due to inactivity, enable the Inactivity Timeout option (see Table A-11,
Telnet Session Options, in Appendix A, Configuration Options).
Security can limit ATI access several ways. To set up security or a login ID, refer
to Chapter 6, Security.
Management Serial Port Settings
Ensure that the device you connect communicates using these settings:
H Data rate set to 9.6 kbps.
H Character length set to 8.
H Parity set to None.
H Stop Bits set to 1.
8700-A2-GB20-00
Refer to the installation document for your DSLAM.
April 2000
2-1
Page 16
Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
Logging In to the Hotwire DSLAM
You can log in to the Hotwire DSLAM system using either a local
VT100-compatible terminal or a remote Telnet connection.
After you enter your user ID and password, the system displays the Hotwire
Chassis Main Menu. See your management card documentation for information
about selecting the unit from the card selection screen.
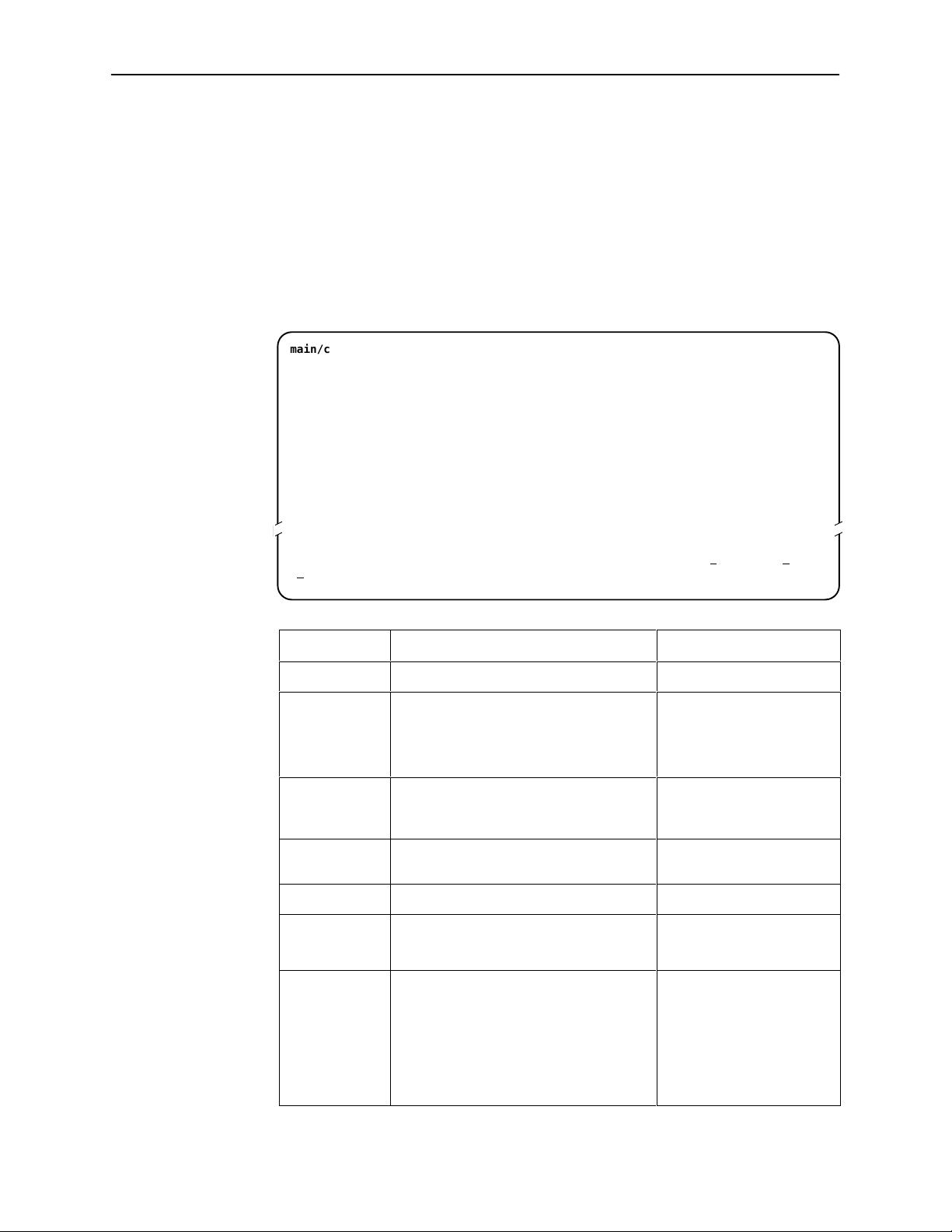
Initiating an ATI Session
The Main Menu screen is displayed on the screen unless a login ID and
password is required or the ATI is already in use.
If security is enabled on the Hotwire Termination Unit and you used Telnet to
access it directly (you did not log in through the management card), the system
prompts you for a login ID and password.
Login
Slot: 4
LOGIN
Login ID:
Enter Password:
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions E
Model: 87xx
xit
If you enter an invalid login ID and password after three attempts, the Telnet
session closes or the terminal connection returns to an idle state. Refer to
Chapter 6, Security.
If the ATI is already in use, the message connection refused is sent to a
terminal attempting Telnet access.
2-2
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 17
Screen
Area
Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
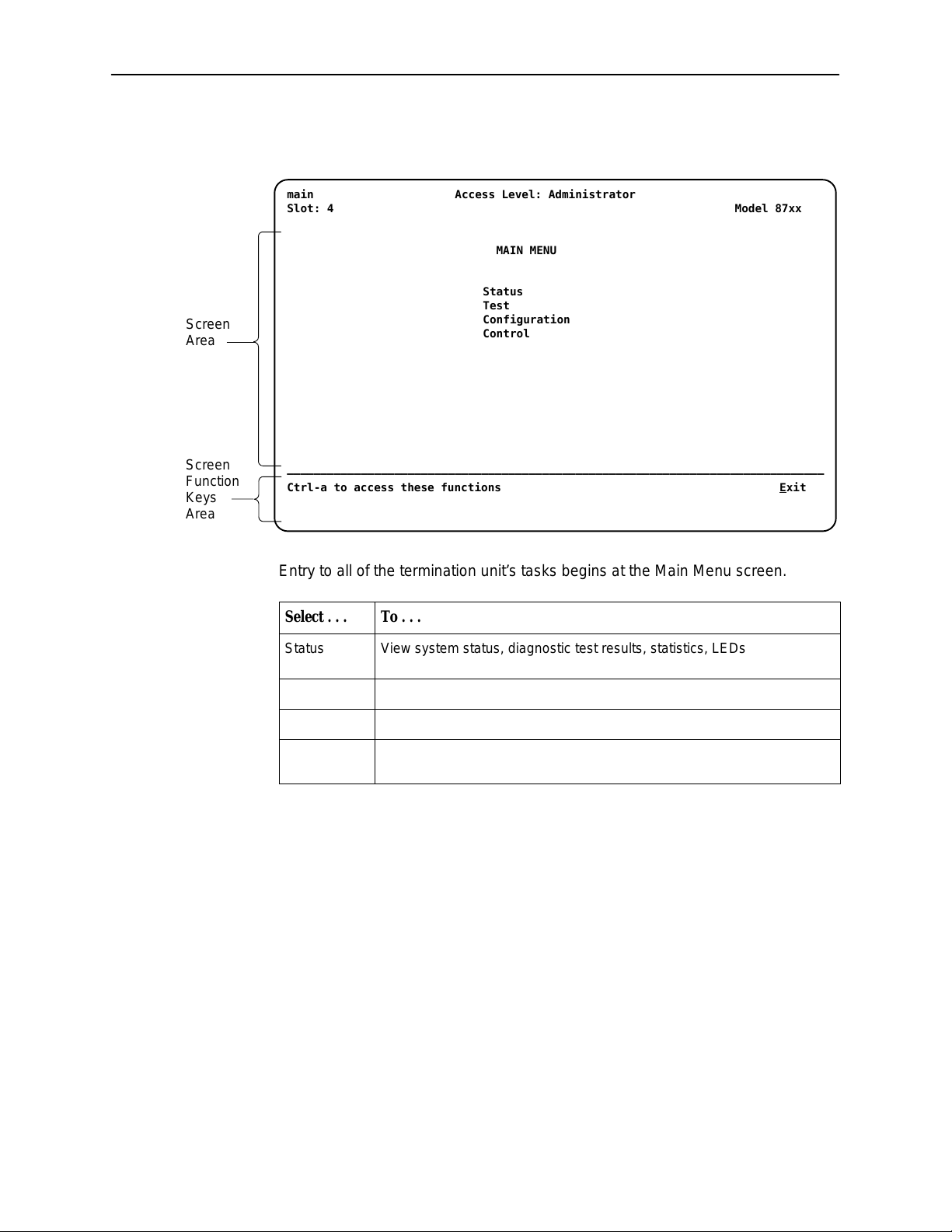
After you enter a valid login ID and password, the Main Menu appears.
main Access Level: Administrator
Slot: 4 Model 87xx
MAIN MENU
Status
Test
Configuration
Control
Screen
Function
Keys
Area
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions E
xit
Entry to all of the termination unit’s tasks begins at the Main Menu screen.
Select . . . To . . .
Status View system status, diagnostic test results, statistics, LEDs, and device
identity information.
Test Select, start, stop and cancel tests for the unit’s interfaces.
Configuration Display and edit the configuration options.
Control Change the device identity , administer logins, download new firmware, or
initiate a power-up reset of the unit.
What appears on the screens depends on your:
H Current configuration – How your unit is currently configured.
H Effective security access level – An access level that is typically set by the
system administrator for each interface and each user.
8700-A2-GB20-00
H Data selection criteria – What you entered in previous screens.
April 2000
2-3
Page 18
Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
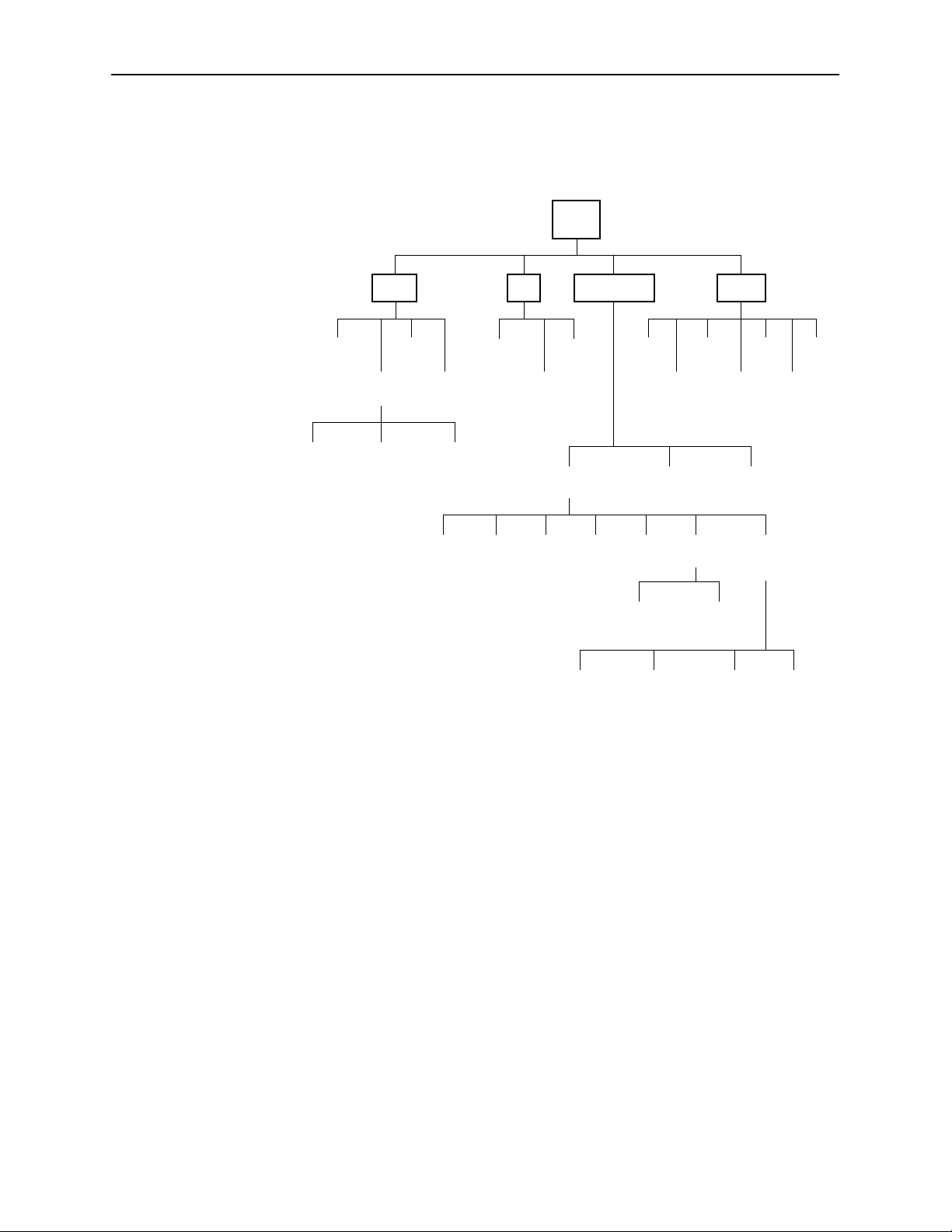
The following illustration shows the paths to the different ATI screens.
Main
System and
Test Status
Network
Error
statistics
Status Test
Display
LEDs
Performance
Statistics
Network
Performance
Statistics
Identity
DSX-1/G.703
Statistics
Network DSX-1/
Network and
DSX-1/G.703
Test
Current Configuration
G.703
Abort All
Tests
Device
Test
Edit/Display
Copy
Ports
Session
Configuration Control
System
Options
Telnet
Change
Identity
System
Clock
Set Cross
Connect Mode
General SNMP
Management
Download
Administer
Logins
Configuration
Loader
Cross
Connect
Code
Download
Default Factory
Assign
Time Slots
SNMP NMS
Security
Port
LEDs
Apply
Configuration
Communication
Reset
AutoRate
Management
and
SNMP
Reset
Device
Traps
99-16607
2-4
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 19

Screen Work Areas
There are two user work areas:
H Screen area – This is the area above the dotted line that provides the menu
H Screen function key area – This is the area below the dotted line that lists
Menu Path
Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
path, menus, and input fields.
The menu path appears as the first line on the screen. In this manual, the
menu path is presented as a menu selection sequence with the names of the
screens:
Main Menu →Configuration → Load Configuration From →Network
Interface Options
function keys specific to the screen, field value choices, and system
messages.
Input
Fields
Screen
Function
Keys
Field V alue
Choices
main/config/network
Slot: 4
Port: 2
NETWORK INTERFACE OPTIONS
Port Status Enable
Margin Threshold: –3db
Excessive Error Rate Threshold: 1E–5
AutoRate: Disable
DSL Line Rate: 1552 kbps
EIA-530 Payload Rate 1536
Transmit Attenuation 0dB
Peer IP Address: 111.255.255.000 Clear
Circuit Identifier:
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave
S
Select: 1E–4, 1E–5, 1E–6, 1E–7, 1E–8, 1E–9 LOS at Net, Pt 1
kbps
Model: 87xx
Clear
ainMenu Exit
System
Messages
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
2-5
Page 20

Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
Navigating the Screens
You can navigate the screens by:
H Using keyboard keys
H Using screen function keys
H Switching between the two screen work areas
Keyboard Keys
Use the following keyboard keys to navigate within the screen.
Press . . . To . . .
Ctrl-a Move cursor between the screen area and the screen function
Esc Return to the previous screen.
keys area below the dotted line at the bottom of the screen.
Tab Move cursor to the next field on the screen.
Backspace Move cursor to the previous field on the screen.
Enter Accept entry or display valid options on the last row of the screen
when pressed before entering data or after entering invalid data.
Ctrl-k T ab backwards (move cursor one field to the left).
Spacebar Select the next valid value for the field.
Delete (Del) Delete character that the cursor is on.
Up Arrow or Ctrl-u Move cursor up one field within a column on the same screen.
Down Arrow or Ctrl-d Move cursor down one field within a column on the same screen.
Right Arrow or Ctrl-f Move cursor one character to the right if in edit mode.
Left Arrow or Ctrl-b Move cursor one character to the left if in edit mode.
Ctrl-l Redraw the screen display, clearing information typed in but not
yet entered.
" Procedure
To make a menu or field selection:
2-6
1. Press the Tab key or the right arrow key to position the cursor on a menu or
field selection. Each selection is highlighted as you press the key to move the
cursor from position to position.
2. Press Enter. The selected menu or screen appears.
3. Continue Steps 1 and 2 until you reach the screen you want.
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 21
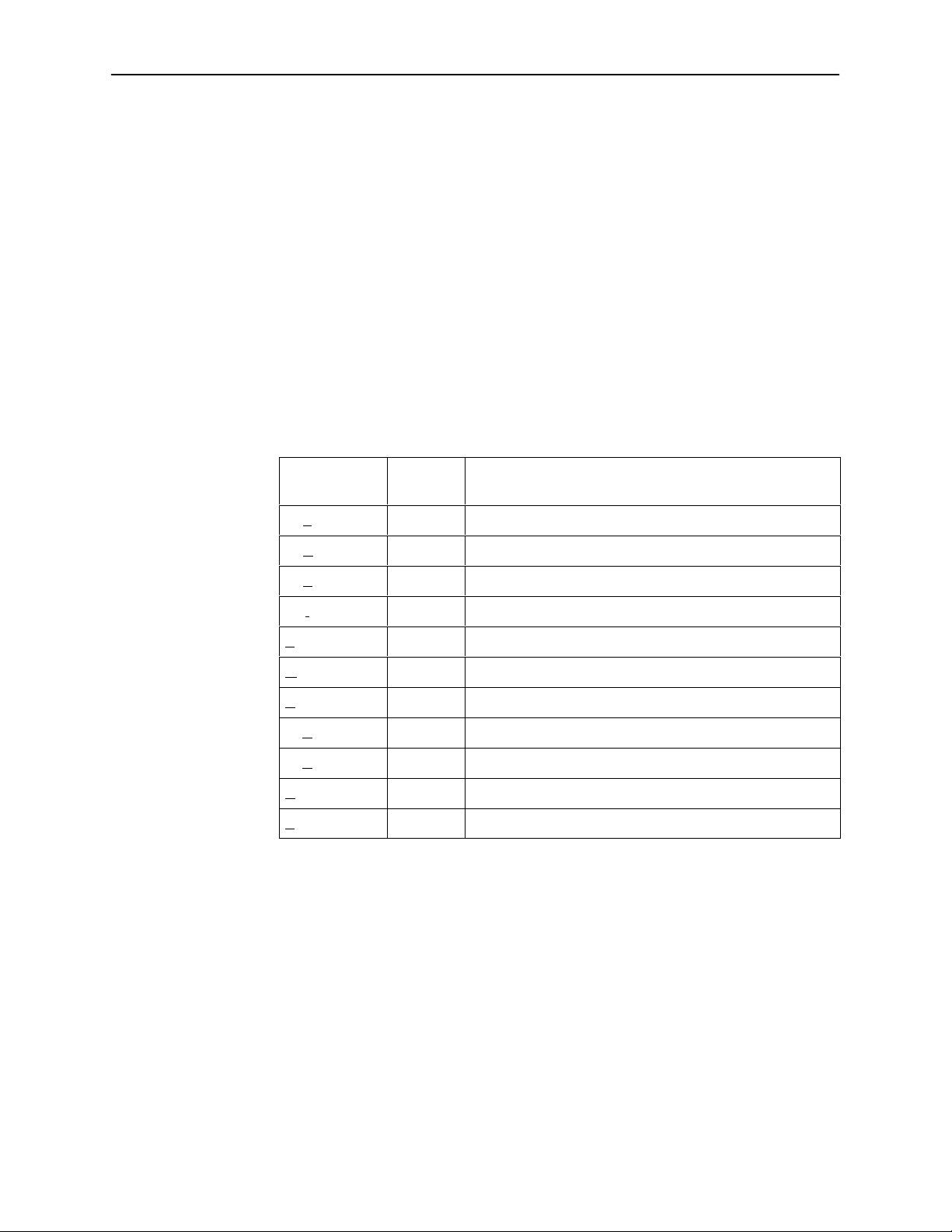
Screen Function Keys
Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
The current setting or value appears to the right of the field name. You can enter
information into a selected field by:
H Typing in the first letter(s) of a field value or command.
H Switching from the screen area to the screen function area below the dotted
line and selecting or entering the designated screen function key.
If a field is blank and the Field Values screen area displays valid selections, press
the spacebar and the first valid value for the field will appear. Continue pressing
the spacebar to scroll through other valid values.
All screen function keys located below the dotted line operate the same way
(upper- or lowercase) throughout the screens.
For the screen
function . . .
Select . . . And press Enter to . . .
ClrFar F or f Clear far-end network statistics and refresh the screen.
ClrNear N or n Clear near-end network statistics and refresh the screen.
ClrStats S or s Clear DSX-1 statistics and refresh the screen.
Delete L or l Delete data.
Exit E or e T erminate the asynchronous terminal session.
MainMenu M or m Return to the Main Menu screen.
New N or n Enter new data.
PgDn D or d Display the next page, or group of entries.
PgUp U or u Display the previous page, or group of entries.
ResetMon R or r Reset an active Monitor 511 test counter to zero.
Save S or s Save information.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
2-7
Page 22
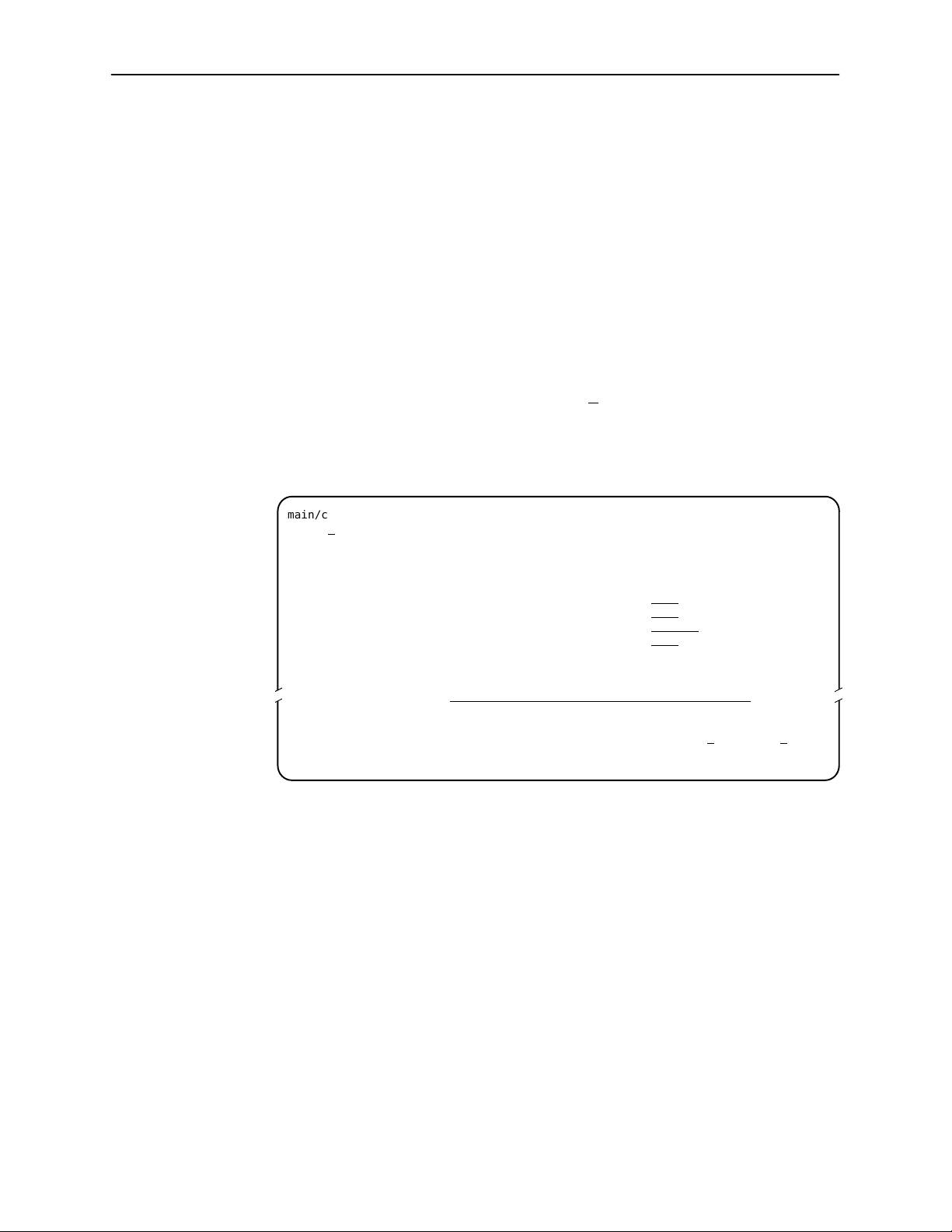
Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
Switching Between Screen Work Areas
Select Ctrl-a to switch between the two screen work areas to perform all screen
functions.
" Procedure
To access the screen function area below the dotted line:
1. Press Ctrl-a to switch from the screen area to the screen function key area
below the dotted line.
2. Select either the function’s designated (underlined) character or press the
Tab key until you reach the desired function key.
Example:
To save the current options, type s or S (S
3. Press Enter. The function is performed.
4. To return to the screen area above the dotted line, press Ctrl-a again.
ave).
main/config/network
Slot: 4
Port: 2
NETWORK INTERFACE OPTIONS
Margin Threshold: –3db
Excessive Error Rate Threshold: 1E–5
AutoRate: Disable
DSL Line Rate: 1552
Circuit Identifier: Clear
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
Model: 87xx
ainMenu Exit
2-8
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 23

Ending an ATI Session
Use the Exit function key from any screen to terminate the session.
" Procedure
To end a session with the asynchronous terminal interface:
1. Press Ctrl-a to go to the screen function key area below the dotted line.
2. Save changes if required. A confirmation message appears if you have made
but not saved changes to your configuration.
Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
3. Tab to E
through the management card, the Hotwire Chassis Card Selection menu
appears.
xit (or type e or E) and press Enter. If you have accessed the unit
Exiting From the DSLAM Session
You can manually log out of the system or, after five minutes of inactivity, the
system will automatically log you out.
" Procedure
To manually exit from the Hotwire DSLAM system:
1. Return to the Hotwire Chassis Main Menu by selecting Exit from either the
Hotwire – MCC menu or the Hotwire – DSL menu.
The Hotwire Card Selection menu appears.
2. Press Ctrl-z.
The Hotwire Chassis Main Menu appears.
3. From the Hotwire Chassis Main Menu, select Logout.
The system exits from the current login session on the Hotwire DSLAM.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
2-9
Page 24

Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
This page intentionally left blank.
2-10
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 25

Initial Startup and Configuration
Overview
This chapter provides instructions on how to access the system for the first time
and perform initial setup procedures. These procedures include:
H Providing initial unit identity information or changing existing identity
information.
H Accessing and displaying the current or factory default configuration options.
H Modifying current configuration options using the Configuration Edit/Display
menu.
3
H Saving your configuration option changes.
H Restoring access to the user interface in the event it is lost.
H Resetting the device.
This chapter also explains how to disable and reset AutoRate.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
3-1
Page 26
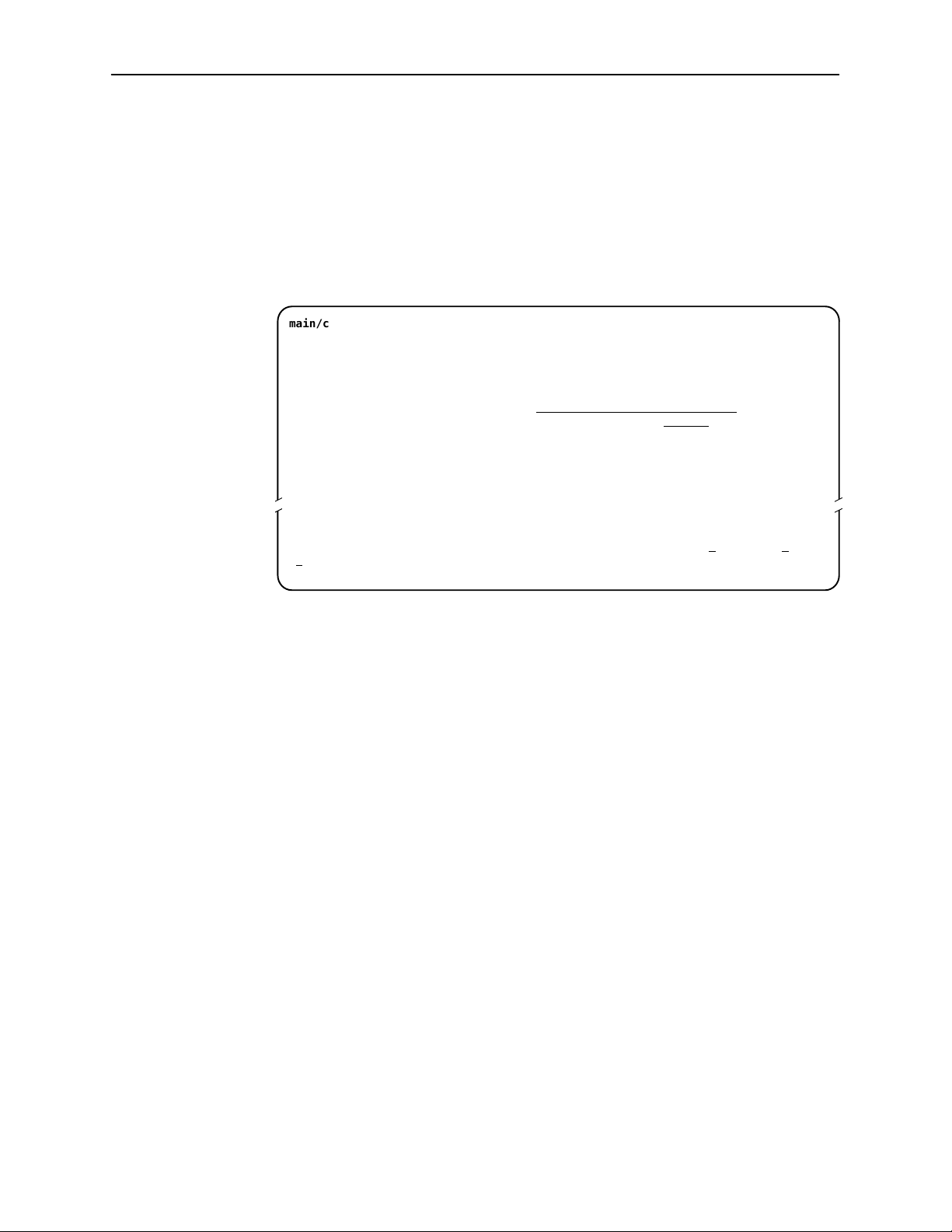
Initial Startup and Configuration
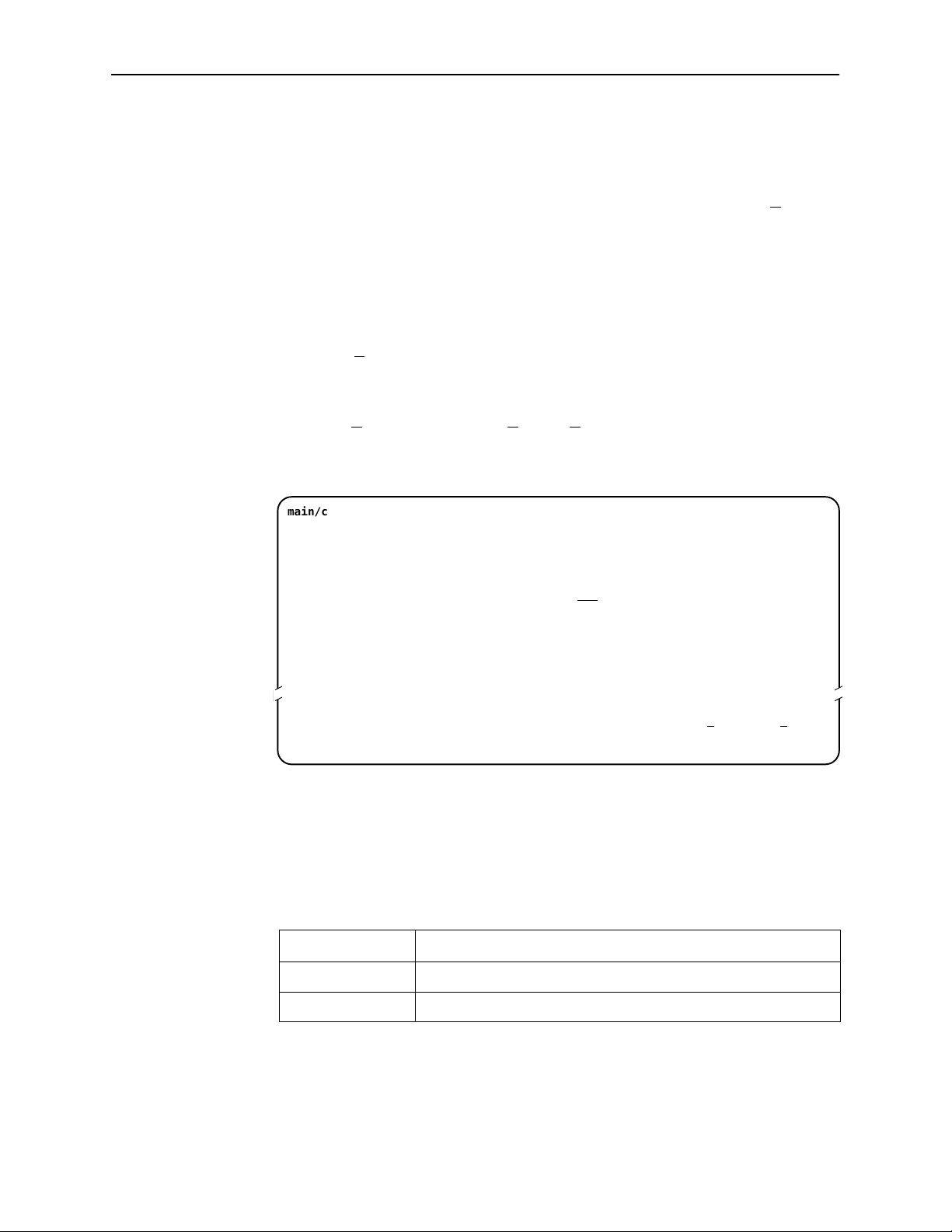
Entering Identity Information
After accessing your unit for the first time, use the Change Identity screen to
determine SNMP administrative system information that will be displayed on the
Identity screen of the Status branch. To access the Card Identity screen, follow
this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Control →Change Identity
main/control/change_identity
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
IDENTITY
System Name: Prez lllQJ98-001
System Location: Bldg. A412, 2nd Floor, Left cabinet
System Contact: L. Young 800-727-2396 pager 888-555-1212 Clear
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave
S
ainMenu Exit
Clear
Clear
The three System entry fields are alphanumeric and provide 128 characters for
each field. The System entries appear on the Identity display as shown above.
The SNMP System entry fields are:
H System Name: The general SNMP system name.
H System Location: The physical location of the SNMP-managed device.
H System Contact: Identification information, such as contact name, phone
number, or mailing address.
Valid entry values are any printable ASCII character. ASCII printable characters
include:
3-2
H Numeric 0–9
H Upper- or lowercase A–Z
H Space
H All ASCII symbols except the caret (^)
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 27

Initial Startup and Configuration
" Procedure
To enter Change Identity screen information:
1. Position the cursor in the System Name field. Enter a name unique in your
network to identify the SNMP managed node (or unit)
The maximum length of System Name is 128 characters.
2. Position the cursor in the System Location field. Enter the physical location of
the unit.
The maximum length of System Location is 128 characters.
3. Position the cursor in the System Contact field. Enter the name and contact
information for the person responsible for the unit.
The maximum length of System Contact is 128 characters.
4. Press Ctrl-a to switch to the screen function key area below the dotted line.
5. Select S
Configuring the Unit
Configuration option settings determine how the unit operates. Use the
Configuration branch of the asynchronous terminal interface menu to display or
change configuration option settings.
Configuration Options
The unit is shipped with factory settings in the Default Factory Configuration area.
You can find default information by:
H Referring to Appendix A, Configuration Options.
H Accessing the Configuration menu branch.
The unit has two sets of configuration option settings. The Current Configuration
matches the Default Factory Configuration until modified and saved by the user.
Configuration Option Area
ave and press Enter.
Description
8700-A2-GB20-00
Current Configuration The unit’s active set of configuration options.
Default Factory Configuration A read-only configuration area containing the factory
default configuration options.
If the factory default settings do not support your network’s configuration,
customize the configuration options for your application.
April 2000
3-3
Page 28
Initial Startup and Configuration
Accessing and Displaying Configuration Options
To display the configuration options, you must first load a configuration option set
into the edit area.
To load a configuration option set into the configuration edit area, follow this
menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration (Load Configuration From)
main/configuration
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
LOAD CONFIGURATION FROM:
Current Configuration
Configuration Loader
Default Factory Configuration
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ainMenu Exit
Make a selection by placing the cursor at your choice and pressing Enter.
If you select . . .
Current
Configuration
Configuration
Loader
Default Factory
Configuration
Then . . .
The selected configuration option set is loaded and the
Configuration Edit/Display menu screen appears.
The Configuration Loader screen is displayed allowing you to
upload or download configurations from a TFTP server.
The default factory configuration is loaded and the Configuration
Edit/Display menu screen appears.
3-4
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 29
Configuration Edit/Display
The Configuration Edit/Display screen appears when the current, customer, or
default configuration is loaded and allows groups of configuration options to be
displayed. To access the Configuration Edit/Display screen, follow this menu
selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Current Configuration
– or –
Main Menu →Configuration →Default Factory Configuration
main/config/edit
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
Initial Startup and Configuration
CONFIGURATION EDIT/DISPLAY
Network
DSX-1 | G.703
Copy Ports
System Options
System Clock
Cross-Connect
Management and Communication
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave
S
ainMenu Exit
Select . . . To Access the . . . To Configure the . . .
Network Network Interface Options, Table A-1 DSL interface ports.
DSX-1
G.703
Copy Ports Copy Ports Options, Table A-6 DSL network and DTE
System
Options
System Clock System Clock Options, Table A-8 LTU system clock options.
Cross-Connect Cross-Connect Mode Options, Table A-9
Management
and
Communication
DSX-1 Interface Options, Table A-4
DSX-1 interface ports
(Models 8747 and 8777).
G.703 Interface Options, Table A-5
G.703 interface ports
(Model 8779).
interface ports by copying
options from port to port.
System Options, Table A-7 General system options of
the unit.
DS1 and DS0
Assign Time Slots Options, Table A-10
Telnet Session Options, Table A-11
General SNMP Management Options,
Table A-12
cross-connect ports.
Management support of the
unit through SNMP and
Telnet.
SNMP NMS Security Options,
Table A-13
SNMP Traps Options, Table A-14
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
3-5
Page 30
Initial Startup and Configuration
Saving Configuration Options
When changes are made to the configuration options through the Configuration
Edit/Display branch, the changes must be saved to take effect. Use the S
or Save Configuration screen.
" Procedure
To save configuration options changes:
1. Press Ctrl-a to switch to the screen function key area below the dotted line.
ave key
2. Select S
ave and press Enter.
NOTE:
When Exit is selected before Save, or Save has been selected from any
menu in the Configuration/Edit branch, a Save Configuration screen appears
requiring a Yes or No response.
main/config/saveprompt
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
SAVE CONFIGURATION
Save Changes? No
WARNING:
An answer of “yes” will cause the system
to reset as if it had been powered off and on!
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
Command Complete
If the Telnet Session configuration option is changed, a message displays on the
Save Configuration screen warning that an answer of Yes will cause the Telnet
session to disconnect. Do not answer Yes unless you are prepared to disconnect.
ainMenu Exit
3-6
If the HDSL Mode configuration option is changed, the Save Configuration screen
bears the warning that an answer of Yes will cause the system to reset. Do not
answer Yes unless you are prepared to reset.
If you select . . .
Yes The configuration is saved.
No The Main Menu appears and changes are not saved.
Then . . .
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 31

Restoring Access to the User Interface
Improper configuration of the unit could render the user interface inaccessible. If
this occurs, access can be restored using the management card of the DSLAM.
" Procedure
To reset the DSL Card using the management card of the DSLAM:
1. Select Configuration →DSL Cards →Reset Slot.
2. Enter DSLnn, where nn is the slot number for the DSL card you wish to reset.
3. Enter Reset.
4. Enter Y if you want to clear NVRAM also, otherwise enter N.
5. Enter Y at the prompt to confirm.
NOTE:
When you enter Y, all data connectivity is interrupted.
Initial Startup and Configuration
Resetting the Device
If the user interface is functional, and you would like to reset the card without
removing the card from the DSLAM, follow this procedure.
" Procedure
To reset the card using the Control branch:
1. From the Main Menu, select Control →Reset Device.
2. The message Are you sure? appears.
3. Enter Yes.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
3-7
Page 32

Initial Startup and Configuration
Disabling AutoRate
The AutoRate function is controlled from the Network Interface Options screen
and allows you to enable or disable AutoRate. The AutoRate option is only
available if the unit is configured as an LTU. To access the Network Interface
screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Network
main/config/network
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
Port: 1
NETWORK INTERFACE OPTIONS
Margin Threshold: –3db
Excessive Error Rate Threshold: 1E–5
AutoRate Enable
Max DSL AutoRate 144
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave
S
" Procedure
The AutoRate option defaults to Enable. To disable AutoRate:
1. Position the cursor in the AutoRate field and press the spacebar.
The AutoRate field toggles to Disable and the DSL Line Rate field appears.
2. Enter a DSL Line Rate and press Enter.
Resetting AutoRate
The Reset AutoRate function of the Control branch causes the unit to repeat the
AutoRate sequence. The unit attempts to establish the DSL link at the highest
rate (or the value of DSL Line Rate, which represents the AutoRate ceiling when
AutoRate is enabled). If the link fails, the next lower rate is tried until the link is
established.
To access the Reset AutoRate screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
ainMenu Exit
3-8
Main Menu →Control →Reset AutoRate
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 33

Cross-Connecting Ports
Overview
Configuration of the cross-connections consists of the following steps:
- Determine how the ports will be connected and configured.
- On the Network Interface Options screen, enable if necessary the DSL ports
that will be in the cross-connection. The ports are enabled by default.
- On the DSX-1 or G.703 Interface Options screen, enable the DSX-1 or
G.703 ports that will be in the cross-connection. For G.703, specify whether
Time Slot 16 is used for signaling (voice mode).
4
- On the System Clock screen, configure the system clock.
- On the Cross-Connect Mode screen:
— Define all DS1 Bypass ports
— Define all DS1 Cross-Connect ports
— Define all DS0 Cross-Connect ports
- On the Assign Time Slots screen, configure the DS0 cross-connections.
This chapter describes the use of the Cross-Connect Mode and Assign Time
Slots screens. See Appendix A, Configuration Options, for information about
configuration options presented on the other screens.
Examples in this chapter show screens for DSX-1 models. The principles of
cross-connection are the same for G.703.
IMPORTANT:
All DSL time slots are available for cross-connect regardless of DSL
line rate, but all time slots are available for data transport only if the
DSL line rate is the full rate (1552 for DSX-1 or 2064 for G.703).
Configure only the time slots intended for use.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
4-1
Page 34

Cross-Connecting Ports
Determining the Configuration
The Hotwire cross-connect system allows you to connect the DSX-1 or G.703
ports to the DSL ports in a variety of ways:
H DS1 Bypass mode – The entire DSX-1 or G.703 interface is connected to
the DSL interface.
H DS1 Cross-Connect mode – The entire DSX-1 or G.703 interface is
connected to the DSL interface through cross-connect circuitry. Ports can be
switched through software.
H DS0 Cross-Connect mode – Any time slot of any DSX-1 or G.703 interface
can be connected to any time slot of any DSL interface. Time slots can be
individually allocated for voice or data.
The example in this chapter shows a DS0 cross-connection between DSX-1
Ports 1 and 2. DSX-1 Port 1 is dedicated to voice and Port 2 to data.
Port 1
X
❏ Voice
❏ Data
Port 2
❏ Voice
X
❏ Data
DSX-1
G.703
DSX-1
G.703
DS0
Cross-Connect
DSL
DSL
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
❏ Voice
X
❏ Data
Port 4
❏ Voice
X
❏ Data
Port 5
❏ Voice
X
❏ Data
Port 6
❏ Voice
X
❏ Data
Port 7
❏ Voice
X
❏ Data
Port 8
❏ Voice
X
❏ Data
DSX-1
G.703
DSX-1
G.703
DSX-1
G.703
DSX-1
G.703
DSX-1
G.703
DSX-1
G.703
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DSL
DSL
DSL
DSL
DSL
DSL
Port 3
Port 4
Port 5
Port 6
Port 7
Port 8
99-16603
4-2
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 35

NOTES:
Although the example in this chapter shows ports dedicated to voice or data,
a port can be configured for both voice and data.
In DS0 Cross Connect mode, for G.703 ports using Common Channel
Signaling (CCS), you must explicitly configure the cross-connections for Time
Slot 16 and related time slots.
You may find it useful to diagram your configuration. Appendix E,
Cross-Connection Worksheets, contains a skeleton diagram for this purpose. It
also contains worksheets for documenting your time slot cross-connections
before you begin to configure them.
Setting the Cross-Connect Modes
To access the Set Cross-Connect Mode screen, follow this menu selection
sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Load Configuration From →
Cross-Connect →Set Cross-Connect Mode
Cross-Connecting Ports
When the screen is first displayed, all ports are set to DS1 Bypass mode. In this
example, Ports 1 and 2 have been changed to DS0 Cross-connect, and Ports
3–8 have been changed to DS1 Bypass. Unassigned appears next to Ports 1
and 2 because time slots associated with the cross-connection have not yet been
assigned.
main/config/xconnect_mode
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
CROSS-CONNECT MODE
DSX-1 Port MODE DSL Port
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave Clear_All
S
1 DS0 Cross-connect
2 DS0 Cross-connect Unassigned
3 DS1 Bypass 3
4 DS1 Bypass
5 DS1 Bypass
6 DS1 Bypass
7 DS1 Bypass
8 DS1 Bypass
Assign_DS0s
Unassigned
4
5
6
7
8
ainMenu Exit
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
4-3
Page 36

Cross-Connecting Ports
Assigning Time Slots
You may find it helpful to map your cross-connection assignments on a
worksheet before configuring them in the unit. In the following example, the
worksheet for DSX-1 Port 1, odd-numbered time slots from DSL Ports 1 and 2
are assigned to the time slots of DSX-1 Port 1 and configured for voice.
Port Type
(D = DSL
X = DSX-1)
TS01
d (Data) or v (Voice)
Port Number
(1–8)
TS01 TS02 TS03 TS04 TS05 TS06 TS07
D
1 1
TS08 TS09 TS10 TS11 TS12 TS13 TS14
D
2 7
TS15 TS16 TS17 TS18 TS19 TS20 TS21
D
1 15
TS22 TS23 TS24
D
2 21
TS01 TS02 TS03 TS04 TS05 TS06 TS07
D
1 2
TS08 TS09 TS10 TS11 TS12 TS13 TS14
D
v
2 1
D
v
1 9
D
v
2 15
D
v
1 23
DSX-1 Port 2 is configured for data and is connected to the even-numbered time
slots of DSL Ports 1 and 2:
D
d
2 2
D
v
1 3
D
v
2 9
D
v
1 17
D
v
2 23
D
d
1 4
Time Slot
D
v
D
v
D
v
v
D
d
(1–24)
2 3
1 11
2 17
2 4
D
v
1 5
D
v
2 11
D
v
1 19
D
d
1 6
D
v
2 5
D
v
1 13
D
v
2 19
D
d
2 6
v
v
v
d
D
D
D
D
1 7
2 13
1 21
1 8
v
v
v
d
4-4
D
2 8
TS15 TS16 TS17 TS18 TS19 TS20 TS21
D
1 16
TS22 TS23 TS24
D
2 22
D
d
1 10
D
d
2 16
D
d
1 24
D
d
2 10
D
d
1 18
D
d
2 24
d
d
d
D
1 12
D
2 18
April 2000
D
d
2 12
D
d
1 20
D
d
1 14
D
d
2 20
d
d
D
2 14
D
1 22
8700-A2-GB20-00
d
d
Page 37

Cross-Connecting Ports
To access the Assign Time Slots screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Load Configuration From →
Cross-Connect →Assign Time Slots
When the screen is first displayed, port and time slot assignments are blank. The
following example shows the configuration for DSX-1 Port 1, transferred from the
worksheet.
main/config/cross_connect/timeslot
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
Port: 1
DSX-1
TS01 TS02 TS03 TS04 TS05 TS06 TS07
01 v D 2 01 v D 1 03 v D 2 03 v D 1 05 v D 2 05 v D 1 07 v
D 1
TS08 TS09 TS10 TS11 TS12 TS13 TS14
07 v D 1 09 v D 2 09 v D 1 11 v D 2 11 v D 1 13 v D 2 13 v
D 2
TS15 TS16 TS17 TS18 TS19 TS20 TS21
15 v D 2 15 v D 1 17 v D 2 17 v D 1 19 v D 2 19 v D 1 21 v
D 1
TS22 TS23 TS24
21 v D 1 23 v D 2 23 v
D 2
ASSIGN TIME SLOTS
Key: D = DSL, X = DSX-1
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave Clear_All
S
d = data, v = voice
ainMenu Exit
The following example shows the configuration for DSX-1 Port 2.
main/config/cross_connect/timeslot
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
Port: 2
DSX-1
TS01 TS02 TS03 TS04 TS05 TS06 TS07
02 d D 2 02 d D 1 04 d D 2 04 d D 1 06 d D 2 06 d D 1 08 d
D 1
TS08 TS09 TS10 TS11 TS12 TS13 TS14
08 d D 1 10 d D 2 10 d D 1 12 d D 2 12 d D 1 14 d D 2 14 d
D 2
TS15 TS16 TS17 TS18 TS19 TS20 TS21
16 d D 2 16 d D 1 18 d D 2 18 d D 1 20 d D 2 20 d D 1 22 d
D 1
TS22 TS23 TS24
22 d D 1 24 d D 2 24 d
D 2
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave Clear_All
S
ASSIGN TIME SLOTS
Key: D = DSL, X = DSX-1
d = data, v = voice
ainMenu Exit
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
4-5
Page 38

Cross-Connecting Ports
When the Cross-Connect Mode screen is displayed now, 1,2 appears next to
DSX-1 Ports 1 and 2 because time slots associated with the cross-connection
have been assigned.
main/config/xconnect_mode
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
CROSS-CONNECT MODE
DSX-1 Port MODE DSL Port
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave Clear_All
S
1 DS0 Cross-connect
2 DS0 Cross-connect 1,2
3 DS1 Bypass 3
4 DS1 Bypass
5 DS1 Bypass
6 DS1 Bypass
7 DS1 Bypass
8 DS1 Bypass
Assign_DS0s
1,2
4
5
6
7
8
ainMenu Exit
4-6
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 39

IP Addressing
Selecting an IP Addressing Scheme
Your IP addressing scheme depends in part whether the management card
controlling the chassis is running IP Conservative software.
Configurations Not Running IP Conservative Software
In a configuration not running IP Conservative software, the NTU’s network
interface IP address is assigned through the peer IP address of the LTU’s
Network Interface menu.
5
All Configurations
The termination unit is assigned an IP address and subnet through the DSLAM’s
Configuration → DSL Cards → Set IP Address menu. Once the address is
assigned, you can use the ATI to assign:
H Peer IP addresses to the DSL ports. These addresses are used as the IP
addresses of the remote units, and must be in the same subnet as the
DSLAM management card. See Table A-1, Network Interface Options, in
Appendix A, Configuration Options.
H An IP address for each NMS to act as a trap manager. See Table A-14,
SNMP Traps Options, in Appendix A, Configuration Options.
The NTU obtains its IP address when the PPP link is established over the EOC.
Use the ATI to assign:
H An IP address for each NMS. See Table A-13, SNMP NMS Security Options,
in Appendix A, Configuration Options.
H An IP address for the TFTP server you wish to use to upload and download
configurations. See Configuration Loader in Chapter 9, Transferring Code
and Configurations Using TFTP, and the documentation for your TFTP
server.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
5-1
Page 40

IP Addressing
Review the following information in preparation for selecting an IP addressing
scheme.
H Any legal host address is allowed for a given subnet. The address choice
within the subnet is arbitrary.
H A single route to a subnet is all that is needed to reach every device on a
subnet. The unit’s routing table supports a maximum of 20 routes.
IP Addressing Example
The following diagram shows IP addressing in a typical network. Note that:
H The Peer IP Address refers to the IP address of the unit configured as an
NTU.
H The Peer IP Address is assigned by the LTU.
DSLAM
MCC
MCC Backplane
Address = 126.35.1.1
MCC Backplane
Mask = 255.255.255.0
LTU Backplane
Address = 126.35.1.16
LTU
87xx
DSLAM
Peer IP Address Assignments
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.32
Port 1
Port 2
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.33
Port 3
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.34
Port 4
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.35
Port 5
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.36
Port 6
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.37
Port 7
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.38
Port 8
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.39
MCC
NTU
MCC Base
Address = 126.35.50.1
MCC Base Subnet
Mask = 255.255.255.0
79xx
NTU Backplane
Address = 126.35.50.17
79xx
79xx
79xx
79xx
79xx
79xx
99-16617
5-2
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 41

Security
Overview
6
The Hotwire 87xx Termination Unit provides several methods of limiting user
access to the ATI through option settings. You can:
H Enable the Telnet Login Required option.
H Limit the access by setting a Session Access Level option of Operator for the
Telnet Session.
H Disable the access with the Telnet Session option.
See Table A-11, Telnet Session Options, in Appendix A, Configuration Options.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
6-1
Page 42

Security
ATI Access Levels
The Hotwire Termination Unit has two access levels: Administrator and Operator.
The access level determines what functions are accessible, as shown in
Table 6-1.
Table 6-1. Access Levels
ATI Access to Menu Functions
Status Read-Only Read-Only
Test Full Access No Access
Configuration Full Access Read-Only
Control Full Access No Access
Access levels can be applied to Login IDs and Telnet sessions. When access is
through Telnet and a login is required for Telnet, the effective access level is the
more restrictive of the Telnet session access level or the login access level. (See
Table A-11, Telnet Session Options.)
When an access level of Operator is applied to Telnet sessions, a Login ID
with Administrator authority is effectively reduced to Operator. It is no longer
possible to change configuration options, and full access can be restored only by
reloading factory defaults. (See Restoring Access to the User Interface in
Chapter 3, Initial Startup and Configuration.)
Administrator Operator
6-2
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 43

Creating a Login
Logins apply to Telnet access directly to the ATI of the Hotwire Termination Unit.
The Administer Logins menu option is not presented when you access the unit
through the management card of the DSLAM.
Six login ID/password combinations are available. Each Login ID and Password
must be unique and include an access level.
" Procedure
Security
1. To create a login record, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Control →Administer Logins
main/control/admin_logins
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
ADMINISTER LOGINS Page 1 of 1
Login ID: newuser
Access Level: Administrator
Are You Sure? Yes
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
ave PgUp PgDnNew Delete
S
ESC for previous menu M
ainMenu Exit
2. Select New and press Enter. The Login Entry screen is displayed.
main/control/admin_logins
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
LOGIN ENTRY
Login ID: newuser
Password: e34t136
Re-enter Password: e34t136
Access Level: Administrator
New logins will not become permanent until saved
through the “ADMINISTER LOGINS” screen!
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions ESC for previous menu M
ave PgUp PgDnNew Delete
S
WARNING
ainMenu Exit
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
6-3
Page 44

Security
3. Create the login by entering the following fields. Login IDs and passwords are
case-sensitive.
On the Login Entry
screen, for the . . .
Login ID 1 to 10 ASCII printable characters (hex21 through 7E).
Password 1 to 10 ASCII printable characters that can consist of
Re-enter Password 1 to 10 ASCII printable characters that can consist of
Access Level Administrator, Operator
Enter . . .
Blanks are not allowed.
0–9, a–z, A–Z, # (pound), . (period), – (dash), and
/ (slash).
0–9, a–z, A–Z, # (pound), . (period),
– (dash), and / (slash).
NOTE:
Assign at least one Administrator-level Login ID. Full access is necessary
to make configuration option changes and administer logins.
Deleting a Login
" Procedure
4. Press Ctrl-a to switch to the screen function key area below the dotted line.
Select S
5. When Save is complete, Command Complete appears at the bottom of the
screen.
6. If additional logins are required, repeat Steps 3 through 5.
7. When all logins are entered, press Esc to return to the Administer Logins
screen.
8. Select S
1. To delete a login record, follow this menu selection sequence:
2. Select PgU
until you find the one to be deleted.
3. Once the correct record is displayed, select Del
4. To complete the delete action, select Save and press Enter.
When the deletion is complete, Command Complete appears at the bottom
of the screen. The number of login pages/records reflects one less record,
and the record following the deleted record appears.
ave and press Enter.
ave and press Enter.
Main Menu →Control →Administer Logins
p or PgDn and press Enter to page through login pages/records
ete and press Enter.
6-4
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 45

Controlling SNMP Access
There are three methods for limiting SNMP access.
H Disable the SNMP management option. Refer to Table A-12, General SNMP
Management Options, in Appendix A, Configuration Options.
H Assign SNMP community names and access types.
H Limit SNMP access through validation of the IP address of each allowed
SNMP manager.
Assigning SNMP Community Names and Access Types
The unit can be managed by an SNMP manager supporting SNMP. The
community name must be supplied by an external SNMP manager accessing an
object in the MIB.
To define SNMP community names, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Load Configuration From →Edit →
SNMP →General SNMP Management
Security
Refer to Table A-12, General SNMP Management Options, to:
H Enable SNMP Management.
H Assign the SNMP community names of the SNMP Managers that are allowed
to access the units Management Information Base (MIB).
H Specify Read or Read/Write access for each SNMP community name.
Limiting SNMP Access through the IP Addresses of the Managers
The unit provides an additional level of security through validation of the IP
addresses.
The SNMP Management option must be enabled. To control SNMP access with
IP addresses, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Management →Security Menu
Refer to Table A-13, SNMP NMS Security Options. The SNMP access can be
limited by:
H Enabling NMS IP address checking.
H Add each IP address and access level.
8700-A2-GB20-00
NOTE:
Do not change or delete the IP address or access level of the NMS
performing the sets or enable IP address checking prior to adding the NMS to
the table.
April 2000
6-5
Page 46

Security
This page intentionally left blank.
6-6
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 47

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
What to Monitor
This chapter presents information on how to diagnose problems, monitor unit
status, and assess performance by using the:
H System and Test Status screen
— Highest priority Health and Status message on the last line of all screens
— Self-test results messages
— Test status messages
7
H Device Messages displayed at the bottom of any ATI screen
H Network Error Statistics screen
H Network Performance Statistics screen
H DSX-1 or G.703 Statistics screen
H Display LEDs screen or LEDs on the unit’s front panel
H Troubleshooting table
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
7-1
Page 48

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Viewing System and Test Status
To view System and Test Status information, follow this menu selection
sequence:
Main Menu →Status → System and Test Status
main/status/system
Slot: 2 Model: 87xx
HEALTH AND STATUS SELF-TEST RESULTS TEST STATUS
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
LOS at Net, Pt n CPU Failed No Test Active
OOF at Net, Pt n Device Failed LLB Test Active, Pt n
EER at Net, Pt n Net DSL Failed, Pt n RLB Test Active, Pt n
LOS at DSX-1 Pt n DSX-1 Pt Failed, Pt n Lamp Test Active
Net Margin Threshold, Pt n Memory Failed DLB Test Active, Pt n
Device Failed yyyyyyyy Passed
Download Failed
SYSTEM AND TEST STATUS Page 1 of 1
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
ESC for previous menu M
ainMenu Exit
The System and Test Status screen has three sections:
H Health and Status – Displays messages in priority order (highest to lowest).
Refer to Table 7-1, Health and Status Messages.
H Self-Test Results – Results of the Diagnostic test run on the device itself.
Refer to Table 7-2, Self-Test Results Messages.
H Test Status – Currently active tests. Refer to Table 7-3, Test Status
Messages.
7-2
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 49

Health and Status Messages
The following messages appear in the first column of the System and Test Status
screen. The highest priority Health and Status message also appears on all ATI
screens on the bottom right.
Table 7-1. Health and Status Messages (1 of 3)
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Message
AIS at DSX-1,
Pt n
AIS at G.703,
Pt n
Device Failed
yyyyyyyy
Download Failed A firmware download was
EER at DSX-1,
Pt n
EER at G.703,
Pt n
What Message Indicates What To Do
An AIS (Alarm Indication
Signal) is being received by
the DSX-1 interface.
An AIS is being received by
the G.703 interface.
An internal error has been
detected by the operating
software. yyyyyyyy indicates
the 8-digit hexadecimal failure
code.
interrupted.
An EER condition has been
detected on the DSX-1
interface.
An EER condition has been
detected on the G.703
interface.
1. Verify that the unit’s line framing
and line coding are compatible.
2. Contact network provider.
1. Verify that the unit’s line framing
and line coding are compatible.
2. Contact network provider.
1. Provide the 8-digit failure code
shown (yyyyyyyy) to your service
representative.
2. Reset the unit to clear the
condition and message.
Repeat the download.
1. Verify the attached equipment
coding is compatible.
2. Contact network provider.
1. Verify that the network cable is
securely attached at both ends.
2. Verify proper NTU and LTU
configuration.
3. Contact network provider.
8700-A2-GB20-00
EER at Net, Pt n An EER (Excessive Error
Rate) condition has been
detected on the network
interface at Port n. The
condition is cleared when the
error rate falls below the
threshold value currently
configured.
Fallback Rate,
Pt n
IP Mismatch, Pt n The NTU and the LTU are
The L TU, set to AutoRate
enable, synchronized at a
lower rate when the line was
restored after an LOS.
operating in different NMS
management modes: one is
in IP Conservative mode and
one is not.
April 2000
1. Check the Network Performance
Statistics screen for possible line
impairments.
2. Set the unit to run at a lower DSL
line rate.
Reset AutoRate, or run at a fixed
rate.
In a DSLAM-to-DSLAM
configuration, use the same
software in the management cards
of both DSLAMs.
7-3
Page 50

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Table 7-1. Health and Status Messages (2 of 3)
Message What To DoWhat Message Indicates
LOF at DSX-1,
Pt n
LOF at G.703,
Pt n
LOS at DSX-1,
Pt n
LOS at G.703,
Pt n
An LOF (Loss Of Frame)
condition has been detected
on the DSX-1 interface. LOF
is declared when an OOF
state exists longer than 2.5
seconds.
An LOF condition has been
detected on the G.703
interface. LOF is declared
when any three consecutive
frame synchronization bits are
incorrect, frames not
containing the frame
alignment signal are received
with an error three times
consecutively, or, for CRC-4
framing, CRC multiframe bit
alignment fails.
An LOS (Loss Of Signal)
condition has been detected
on the DSX-1 interface. No
signal is being received on
Port n. LOS is declared when
175 consecutive zeros are
received.
An LOS condition has been
detected on the G.703
interface. No signal is being
received on Port n. LOS is
declared when 175
consecutive pulse
transmissions are received
with no pulse transitions.
1. Verify that the network cable is
securely attached at both ends.
2. Contact network provider.
1. Verify that the network cable is
securely attached at both ends.
2. Verify that the units line framing
and line coding are compatible.
3. Contact network provider.
1. Verify that the network cable is
securely attached at both ends.
2. Contact network provider.
1. Verify that the network cable is
securely attached at both ends.
2. Contact network provider.
7-4
LOS at Net, Pt n An LOS (Loss Of Signal)
condition has been detected
on the network interface. No
signal is being received on
Port n, possibly due to a local
network problem.
Mismatch Rate,
Pt n
Net Margin
Threshold, Pt n
The L TU, set to a fixed DSL
rate, is attempting to operate
at a rate the NTU is not
capable of.
The signal-to-noise margin
has exceeded the configured
threshold.
April 2000
1. Verify that the network cable is
securely attached at both ends.
2. Contact network provider.
Set the L TU to a compatible rate or
replace the NTU.
1. Check the Network Performance
Statistics screen for possible line
impairments.
2. Set the unit to run at a lower DSL
line rate.
3. Contact network provider.
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 51

Table 7-1. Health and Status Messages (3 of 3)
Message What To DoWhat Message Indicates
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
NTU TS16 Not
Supported
NTU/LTU
Mismatch, Pt n
OOF at Net, Pt n An Out Of Frame (OOF)
Primary Clock
Failed, Pt n
Primary System
Clock Failed
RAI at G.703,
Pt n
The L TU is configured for
TS16 signaling and the NTU
is not configured to support
TS16 signaling.
The NTU is not configured
compatibly with the L TU.
condition has been detected.
An OOF condition is declared
when 2 out of 4 frame
synchronization bits are in
error.
A failure has occurred in the
primary clock source for the
DSX-1 or G.703 port.
A failure has occurred in the
clock common to all
cross-connect circuitry.
An RAI (Remote Alarm
Indication) signal is being
received by the G.703
interface.
1. Verify endpoint is a G.703
product. EIA-530-A products do
not support signaling.
2. Replace endpoint or reconfigure
TS16 to data.
Configure units to match.
1. Check the Transmit Clock Source
configuration options. Do not set
both the local and remote unit to
Internal, External, or Loop timing.
2. Set the unit to run at a lower DSL
line rate.
3. Contact network provider.
1. Verify that the network cable is
securely attached at both ends.
2. Contact network provider.
Contact your service representative.
1. Check the status of the upstream
device.
2. Verify proper NTU and LTU
configuration.
Secondary
System Clock
Failed
System
Operational
Yellow Alarm at
DSX-1, Pt n
A failure has occurred in the
fallback clock for the system
clock.
There are no problems
detected.
A Yellow Alarm Indication
signal is being received by
the DSX-1 interface.
Contact your service representative.
1. Verify that the unit’s line framing
and line coding are compatible.
2. Contact network provider.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
7-5
Page 52

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
y
2.Call your service
y
2.Call your service
Self-Test Results Messages
The results of the last power-on or reset self-test appear in the middle column of
the System and Test Status screen.
Table 7-2. Self-T est Results Messages (1 of 2)
Message
CPU Fail The Central Processing Unit failed
CPU CPLD
Fail
Data Path
Fail, Pt n
DeviceFailed One or more of the unit’s integrated
DSL
Framer x Fail
DSL xcvr
Fail, Pt n
DSX-1
Failed, Pt n
DTE
Framer x Fail
DTE LIU x
Fail
What Message Indicates What To Do
internal testing.
The Complex Programmable Logic
Device serving the Central
Processing Unit failed.
The port shown failed to loop data on
the full data path test.
circuits has failed device-level
testing.
The DSL framer for Ports 1–4
(Framer A) or 5–8 (Framer B) failed.
The DSL transceiver failed on Port n.
The unit failed to internally loop data
on the DSX-1 Port n.
The DTE framer for Ports 1–4
(Framer A) or 5–8 (Framer B) failed.
The DTE Line Interface Unit for
Ports 1–2 (LIU A), 3–4 (LIU B), 5–6
(LIU C), or 7–8 (LIU D) failed.
1. Reset the unit and try again.
2. Call
our service
representative for assistance.
7-6
EEPROM
Fail
Failure
xxxxxxxx
FPGA Failed The Field Programmable Gate Array
G.703
Failed, Pt 1
Memory
Test n Fail
Passed No errors were detected. N/A
The unit failed Electrically Erasable
Programmable Read-Only Memory
verification.
An internal failure occurred.
(xxxxxxxx represents an 8-digit
hexadecimal failure code for use by
service personnel.)
serving all ports failed.
The unit failed to loop data on the
G.703 on Port n.
The unit failed memory data
verification (Test 1) or memory
address verification (Test 2).
April 2000
Record the failure code and
contact your service
representative.
1. Reset the unit and try again.
2. Call
our service
representative for assistance.
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 53

Table 7-2. Self-Test Results Messages (2 of 2)
re resentative for assistance
Message What To DoWhat Message Indicates
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Test Status Messages
PLD Failure An error was detected in a
Programmable Logic Device.
TSI CPLD
Fail
TSI Fail The Timeslot Interchanger failed.
The Complex Programmable Logic
Device serving the Timeslot
Interchanger failed.
1. Reset the unit and try again.
2. Call your service
representative for assistance.
1. Reset the unit and try again.
2. Call your service
representative for assistance.
.
The Test Status messages in the following table appear in the right column of the
System and Test Status screen.
Table 7-3. Test Status Messages
Test Status Message
511 Test Active, Pt n A 511 Test and Monitor is active on the DSL Port n network
DLB Test Active, Pt n A Data Terminal Loopback test is active on Port n.
Meaning
interface.
Lamp Test Active The Lamp Test is active, causing the LEDs on the front panel to
light.
LLB Test Active, Pt n A network Line Loopback test is active on Port n.
No Test Active No tests are currently running.
Remote LLB Dn
Active, Pt n
Remote LLB Up
Active, Pt n
RLB Test Active, Pt n A network Repeater Loopback test is active on Port n.
Telco LLB Active, Pt n A Telco-initiated Line Loopback is active on the specified
Telco PLB Active, Pt n A Telco-initiated Payload Loopback is active on the specified
A Remote Line Loopback Down command is being sent.
A Remote Line Loopback Up command is being sent.
DSX-1 port.
DSX-1 port.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
7-7
Page 54

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Device Messages
The Device Messages in Table 7-4, listed in alphabetical order, may appear in the
messages area at the bottom of the ATI screens.
Table 7-4. Device Messages (1 of 2)
Device Message
0.0.0.0 is an invalid
IP address
Access level is
Operator.
Configuration is
read-only.
Cannot Save – no
Login IDs with Access
Administrator
Command Complete Action requested has
Invalid Character (x) A nonprintable ASCII
Invalid Password Login is required and an
What Message Indicates What To Do
An IP address of all zeros
was entered.
The operator requested that
configuration options be
loaded, but does not have
authority to edit them.
All of the login IDs being
saved have an access level
below Administrator.
successfully completed.
character (x) has been
entered.
incorrect password was
entered; access is denied.
Enter a valid, non-zero IP
address.
If configuration options are to be
edited, use a Login ID that has
Administrator authority .
Change the access level of at
least one Login ID to
Administrator so that
configuration changes can be
made. (Operator-level users
cannot make configuration
changes.) Save the Login IDs.
No action needed.
Re-enter information using valid
characters.
H Try again.
H Contact your system
administrator to verify your
password.
7-8
Invalid – Send Pattern
Already Active
Invalid – [Test]
Already Active
Invalid Test
Combination
IP address not in MCC
subnet
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
A pattern test was already
in progress when the Start
field was selected.
The described test was
already in progress when
another selection was
made.
A loopback or pattern test
was in progress when Start
was selected to start
another test, or was active
on the same or another
interface when Start was
selected.
The Peer IP address
specified is not in the same
subnet as the MCC.
April 2000
H Allow test to continue.
H Select another test.
H Stop the test.
H Allow test to continue.
H Select another test.
H Stop the test.
H Wait until other test ends and
message clears.
H Abort all tests from the Test
menu screen.
H Stop the test from the same
screen the test was started
from.
Enter an IP address that is in the
same subnet as the MCC.
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 55

Table 7-4. Device Messages (2 of 2)
Device Message What T o DoWhat Message Indicates
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Limit of six Login IDs
reached
An attempt to enter a new
login ID was made, and the
limit of six login/password
combinations has been
reached.
No Security Records
to Delete
Delete was selected from
the Administer Login
screen, and no security
records had been defined.
Password Matching
Error – Re-enter
Password
Password entered in the
Re-enter Password field of
the Administer Logins
screen does not match
what was entered in the
Password field.
Please Wait Command takes longer
than 5 seconds.
Test Active A test is running and no
higher priority health and
status messages exist.
1. Delete another login/password
combination.
2. Re-enter the new login ID.
H No action needed.
H Enter a security record.
H Try again.
H Contact your system
administrator to verify your
password.
Wait until message clears.
H Contact service provider if test
initiated by the network.
H Wait until the other test ends
and message clears.
H Cancel all tests from the Test
screen.
H Stop the test from the same
screen the test was started
from.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
7-9
Page 56

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Viewing Network Error Statistics
The unit maintains error statistics on the network DSL interface for each port.
Port 1 is the default screen selection.
Statistics are maintained for up to 96 15-minute intervals (24 hours).
To view the Network Error Statistics, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Status →Performance →Network Error Statistics
main/status/performance/net_error
Slot: 4: Model: 87xx
NETWORK ERROR STATISTICS
Port: 2
Current Interval Timer: 002 Error Events Counter: 0034
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
–––ES––– –––SES––– ––FEBE–– –Complete–
Current Int: 000 000 000 000 000 000 Yes No
Interval 01
Interval 02 000 000 000 000 000 000 Yes Yes
Interval 03 000 000 000 000 000 000 Yes Yes
Interval 04
Interval 05 000 000 000 000 000 000 Yes Yes
Interval 06 000 000 000 000 000 000 Yes Yes
Interval 07
Near Far Near Far Near Far Near Far
000 000 000 000 000 000 Yes Yes
000 000 000 000 000 000 Yes Yes
000 000 000 000 000 000 Yes Yes
Worst Interval: 24 09 14 08 18 18
Near Tot(valid): 00010 00000 00000
Far Tot (valid): 00010 00000 00000
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl–a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
p PgDn ClrNear ClrFar
PgU
ainMenu Exit
Select a port 1–2 to view error statistics for the port. The default port is 1. Use the
virtual function keys to page through the intervals and clear statistics.
Network Error Statistics are collected for all ports for:
H ES (Errored Seconds): Seconds during which one or more ESF error events
occurred.
H SES (Severely Errored Seconds): Seconds during which more than
320 cyclic redundancy check (CRC) error events or at least one Out of Frame
(OOF) event occurred.
H FEBE (Far-End Block Errors): Errors reported by the remote equipment.
H Complete: Whether the interval register contains data for all 900 seconds of
the interval.
7-10
Use the virtual function keys to page through the intervals and clear statistics.
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 57

This Field . . . Contains . . .
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Current Interval
Timer
The number of seconds which have elapsed in the current
15-minute interval. Maximum value is 900 seconds (15 minutes).
This counter is reset every 15 minutes.
Error Events
Counter
A running total of CRC errors. Range 0–65535. This counter is
reset when the near-end data is cleared.
Current Int Performance data for the current 15-minute interval.
Interval xx Historical performance data for up to 96 15-minute intervals
(24 hours).
Worst Interval The number of the interval with the worst (highest) performance
data for both the near-end and far-end statistics. If two or more
intervals are equal, the oldest interval is displayed.
Near and Far TOT A running total of the near-end and far-end performance statistics.
Viewing Network Performance Statistics
Network performance statistics allow you to monitor the current status of the
network DSL operations. Performance statistics can assist you in determining the
duration of specific conditions and provide a historical context for problem
detection and analysis.
Statistics are maintained for up to 96 15-minute intervals (24 hours).
To view the Network Performance Statistics, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Status →Performance →Network Performance Statistics
main/status/performance/net_perf
Slot: 4: Model: 87xx
NETWORK PERFORMANCE STATISTICS
Port: 2
Current Interval Timer: 002 DSL Line Rate: 1552 kbps
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
––Mrgn–– ––XmtPw– ––RxGn–– –Complete–
Current Int: +02 +01 +03 +03 +02 +02 Yes Yes
Interval 01
Interval 02
Interval 03
Interval 04
Interval 05
Interval 06
Interval 07
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl–a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
p PgDn
PgU
Near Far Near Far Near Far Near Far
+02 +02 +03 +03 +02 +02 Yes No
+02 +01 +03 +03 +02 +02 Yes Yes
+02 +01 +03 +03 +02 +02 Yes Yes
+02 +01 +03 +03 +02 +02 Yes Yes
+02 +01 +03 +03 +02 +02 Yes Yes
+02 +01 +03 +03 +02 +02 Yes Yes
+02 +01 +03 +03 +02 +02 Yes Yes
Payload Rate: 1536 kbps
ainMenu Exit
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
7-11
Page 58

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Select a port (1–2) to view performance statistics for the port. The default port
is 1. Use the virtual function keys to scroll through the intervals
Use the virtual function keys to scroll through the intervals and clear statistics.
Network Performance Statistics are collected for all ports for:
H Mrgn: Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) Margin, the amount (in dB) that the
Receive signal has exceeded the value needed to maintain a Bit Error Rate
(BER) of 10
H XmtPw: The transmit power level.
H RxGn: The receiver gain level.
H Complete: Whether the interval register contains data for all 900 seconds of
the interval.
–7
or better.
This Field . . .
Current Interval
Timer
DSL Line Rate The rate of the DSL line.
Payload Rate The rate of data transfer.
Current Int Performance data for the current 15-minute interval.
Interval xx Historical performance data for up to 96 15-minute intervals
Contains . . .
The number of seconds which have elapsed in the current
15-minute interval. Maximum value is 900 seconds (15 minutes).
This counter is reset every 15 minutes.
(24 hours).
7-12
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 59

Viewing DSX-1 Performance Statistics
DSX-1 performance statistics allow you to monitor the current status of the DSX-1
interface operations when ESF framing is selected. Performance statistics can
assist you in determining the duration of specific conditions and provide a
historical context for problem detection and analysis. Statistics are maintained for
up to 96 15-minute intervals (24 hours).
To view the Network Performance Statistics, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Status →Performance →DSX-1 Performance Statistics
main/status/performance/DSX-1
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
Port: 2
Current Interval Timer: 2 Error Events Counter: 0000
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
––ES–– ––UAS–– ––SES–– ––BES–– ––CSS–– –LOFC– –Status–
DSX-1 PERFORMANCE STATISTICS
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Current Int: 000 000 000 000 000 000 Y
Interval 01
Interval 02
Interval 03
Interval 04
Interval 05
Interval 06
Interval 07
Worst Interval: 24 14 14 09 18 12
Tot (valid 96): 00010 00000 00000 00000 0020 0000
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl–a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
p PgDn ClrStats
PgU
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
ainMenu Exit
Select PgUp or PgDn to view the next or previous seven intervals, select ClrStats
to clear all statistics to zero.
DSX-1 Performance Statistics are collected for:
H ES (Errored Seconds): Seconds during which one or more error events
occurred.
H UAS (Unavailable Seconds): Seconds during which service is unavailable.
UAS is received at the start of 10 consecutive SES and cleared at the start of
10 seconds with no SES.
H SES (Severely Errored Seconds): Seconds during which 320 or more cyclic
redundancy check (CRC) error events or at least one Out of Frame (OOF)
event occurred.
8700-A2-GB20-00
H BES (Bursty Errored Seconds): Contains the number of bursty errored
seconds for the current interval. A bursty errored second is any second with
more than one but less than 320 CRC errors.
H CSS (Controlled Slip Seconds): Seconds during which one or more
controlled slips (as defined in TR 54016) occurred.
April 2000
7-13
Page 60

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
H LOFC (Loss of Frame Count): Contains the number of times that an LOF is
declared.
H Status: Contains the contents of the status events register. The status events
register maintains a history of specific events that have occurred during an
interval. V alues include:
— Y: Remote alarm indication signal (yellow alarm) received at the DSX-1
— L: Loss of signal detected at the DSX-1 interface
— E: Excessive error rate threshold exceeded
— F: Frame synchronization bit error detected
— V: Line code violation detected
— None: No significant events have occurred
interface
This Field . . .
Current Interval
Timer
Error Events
Counter
Current Int Performance data for the current 15-minute interval.
Interval xx Historical performance data for up to 96 15-minute intervals
Worst Interval Identifies the interval during which the most error events were
Contains . . .
The number of seconds which have elapsed in the current
15-minute interval. Maximum value is 900 seconds (15 minutes).
This counter is reset every 15 minutes.
A running total of CRC and OOF events. Total range = 0–65535.
This counter is reset when the statistics are cleared.
(24 hours) where the value of xx is from 01 to 96.
detected.
7-14
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 61

Viewing G.703 Performance Statistics
G.703 performance statistics allow you to monitor the current status of the
network DSL operations. Performance statistics can assist you in determining the
duration of specific conditions and provide a historical context for problem
detection and analysis.
Statistics are maintained for up to 96 15-minute intervals (24 hours).
To view the G.703 Performance Statistics, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Status →Performance →G.703 Statistics
main/status/performance/G.703
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
G.703 PERFORMANCE STATISTICS
Port: 2
Current Interval Timer: 004 Error Events Counter: 012
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
––ES–– ––UAS–– ––SES–– ––BES–– ––CSS–– –LOF– –Status–
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Current Int: 000 000 000 000 000 000 Y
Interval 01
Interval 02
Interval 03
Interval 04
Interval 05
Interval 06
Interval 07
Worst Interval: 24 14 14 09 18 12
Tot (valid 96): 00010 00000 00000 00000 0020 0000
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl–a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
PgU
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
000 000 000 000 000 000 none
ainMenu Exit
p PgDn ClrStats
Select a port to view the performance statistics. The default port is 1.
G.703 Performance Statistics are collected for all ports for:
H ES (Errored Seconds): Seconds during which one or more error events
occurred.
H UAS (Unavailable Seconds): Seconds during which service is unavailable.
UAS is received at the start of 10 consecutive SES and cleared at the start of
10 seconds with no SES.
8700-A2-GB20-00
H SES (Severely Errored Seconds): Seconds during which 805 or more cyclic
redundancy check (CRC) error events, 16 or more FAS errors, or at least one
Out of Frame (OOF) event occurred.
April 2000
7-15
Page 62

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
H BES (Bursty Errored Seconds): Contains the number of bursty errored
seconds for the current interval. A bursty errored second is any second with
more than one but less than 805 CRC errors (CRC Mode) or more than one
but less than 16 FAS errors (non-CRC mode).
H CSS (Controlled Slip Seconds): Seconds during which one or more
controlled slips (as defined in TR 54016) occurred.
H LOF (Loss of Frame Seconds): Contains the number of seconds that
contain one or more LOF events.
H Status: Contains the contents of the status events register. The status events
register maintains a history of specific events that have occurred during an
interval. V alues include:
— Y: Remote alarm indication signal received at the G.703 interface
— L: Loss of signal detected at the G.703 interface
— E: Excessive error rate threshold exceeded
— F: Frame synchronization bit error detected
— V: Line code violation detected
— None: No significant events have occurred
Use the virtual function keys to page through the intervals and clear statistics.
This Field . . .
Current Interval
Timer
Error Events
Counter
Current Int Performance data for the current 15-minute interval.
Interval xx Historical performance data for up to 96 15-minute intervals
Worst Interval The number of the interval with the worst (highest) performance
Tot A running total of the performance statistics.
Contains . . .
The number of seconds which have elapsed in the current
15-minute interval. Maximum value is 900 seconds (15 minutes).
This counter is reset every 15 minutes.
A running total of CRC errors. Range 0–65535. This counter is
reset when the statistics are cleared.
(24 hours).
data statistics. If two or more intervals are equal, the oldest
interval is displayed.
7-16
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 63

Viewing LED Status
The unit LEDs can be viewed on the Display LEDs Status screen, available
locally and remotely.
The LEDs are organized into three groups:
H System LEDs display the status of the unit
H DSX-1 or G.703 LEDs provide the status of the DTE interface
H DSL Loop LEDs display the activity on the DSL network
To view the Display LEDs status screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Status → Display LEDs
main/status/leds
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
DISPLAY LEDs
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
SYSTEM DSX-1|G.703 Port DSL LOOP
Alarm Off P1:Link Up P1:Link Up
Test Off P2:Link Up P2:Link Up
P3:Link Up P3:Disabledp
P4:Link Up P4:Link Up
P5:Link Up P5:Link Up
P6:Link Up P6:Link Up
P7:Link Up P7:Link Up
P8:Link Up P8:Link Up
ESC for previous menu M
ainMenu Exit
The LED status display screen is updated every 5 seconds.
Table 7-5 shows the meaning of the possible values for each LED represented.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
7-17
Page 64

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Table 7-5. Display LEDs Screen
Type
SYSTEM
DSX-1
PORT
G.703
PORT
Label Value is . . . Indicating . . .
Alarm On
Off
Test On
Off
P1
through
P8
P1
through
P8
Link Up
Link Down
LOF
EER
Yellow
AIS
Disabled
Link Up
Link Down
LOF
EER
RAI
AIS
Disabled
Device failure, Power-On Self-Test (POST)
failure, ports inoperable or unable to train.
No alarms.
Loopback test or 51 1 test pattern in progress.
No tests.
Recoverable signal present on the DSX-1
network.
No signal on the port.
The port has a Loss of Frame alignment.
The port has an Excessive Error Rate
condition.
The port received a Yellow Alarm.
The port received an Alarm Indication Signal.
The port has been administratively disabled.
Recoverable signal present on the G.703
network.
No signal on the port.
The port has a Loss of Frame alignment.
The port has an Excessive Error Rate
condition.
The port received a Remote Alarm Indication.
The port received an Alarm Indication Signal.
The port has been administratively disabled.
7-18
DSL LOOP P1
through
P8
Link Up
Link Down
Startup
OOF
Disabled
April 2000
DSL link is up.
DSL link is down.
DSL training in progress.
Out Of Frame condition.
The port has been administratively disabled.
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 65

Front Panel LEDs
The following table describes the meaning and states of the LEDs on the
SYSTEM
O
K
Alrm
Test
PORTS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
faceplate. PORTS LEDs represent the DTE or DSL ports depending on the Port
LEDs selection on the Control screen.
Type
SYSTEM
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
LED LED is . . .* Indicating . . .
OK
(Green)
Alrm
(Amber)
Test
(Amber)
On
Off
Slow cycling
Pulsing
On
Off
On
Slow cycling
Off
Normal operation; card functioning normally .
No power to card, or card failure.
Unit is in minimum mode and a download is
required.
Normal operation.
Device failure, Power-On Self-Test (POST) is
not complete, or an alarm was reported on a
DSL, DSX-1, or G.703 port.
No alarms.
Loopback test or 51 1 test pattern in progress.
POST in progress.
No tests.
M/SDSL
8747
99-16606
PORTS
(when
DSX-1 or
G.703
selected)
PORTS
(when DSL
selected)
1, 2, 3, 4,
5, 6, 7, 8
(Green)
1, 2, 3, 4,
5, 6, 7, 8
(Green)
On
Slow cycling
Fast cycling
Off
On
Slow cycling
Fast cycling
Off
Recoverable signal present on the DSX-1 or
G.703 network.
Yellow Alarm Indication (DSX-1) or Remote
Alarm Indication (G.703) present.
An OOF, LOF, EER, or AIS condition exists.
No signal on the port.
DSL link is up.
DSL training in progress.
OOF condition.
DSL link is down.
* Slow Cycling: LED turns off and on in equal duration once per second.
Fast Cycling: LED turns off and on in equal duration 5 times per second.
Pulsing: LED turns off momentarily once per second.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
7-19
Page 66

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Changing the Meaning of the PORTS LEDs
The PORTS LEDs on the front panel represent the status of the DSL network or
DTE ports depending on the Port LEDs configuration option. The LED display can
also be selected at any time through the Control branch.
" Procedure
To change the meaning of the PORTS LEDs using the Control branch:
1. From the Main Menu, select Control.
2. Move the cursor to the Port LEDs entry.
3. Toggle the selection using the spacebar.
4. Press Enter.
7-20
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 67

Troubleshooting
A
d
Chapter 8, Testing
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
The Hotwire Termination Unit is designed to provide you with many years of
trouble-free service. If a problem occurs, however, refer to Table 7-6 for possible
solutions. If an error message is displayed under Health and Status on the
System and Test Status screen, refer to Table 7-1, Health and Status Messages,
for recommended action.
Table 7-6. Troubleshooting (1 of 2)
Symptom
Alarm LED is on. A system failure has
Cannot access the
unit via the A TI.
Device Fail appears
on the System and
Test Status screen
under Self-Test
results.
Power-On Self-Test
fails. Only Alarm
LED is on after
power-on.
No power, or the
LEDs are not lit.
Possible Cause Solutions
occurred.
The terminal is not set up
for the correct rate or data
format, or the unit is
configured so it prevents
access.
The unit detects an internal
hardware failure.
The unit has detected an
internal hardware failure.
The unit is not properly
seated in the DSLAM.
There is no power to the
DSLAM.
Refer to Table 7-1, Health and
Status Messages, for
recommended action.
H Check the cable and
connections.
H Ensure that the unit is configured
properly in the DSLAM. Verify its
IP address.
H Reset the unit.
H Reset the unit.
H Contact your service
representative.
Verify that the unit is properly
inserted.
Verify that the DSLAM has power.
8700-A2-GB20-00
An LED is not lit. LED is out. Run the Lamp Test. If the LED in
question does not flash with the
other LEDs, then contact your
service representative.
Not receiving data. H The network or DTE port
cables are not
connected (check front
panel LEDs for more
information).
H
test is being execute
on the unit (check the
TEST LED on the front
panel).
H The far-end device is
offline.
April 2000
H Check network and DTE port
cables.
H Check Health and Status menu.
H Run Loopback tests. Refer to
p
H Stop the test or wait for the test
to end.
H Make sure the far-end device is
on.
.
7-21
Page 68

Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Table 7-6. Troubleshooting (2 of 2)
Symptom SolutionsPossible Cause
Not receiving data
on one or more time
slots.
The DSL line rate does not
support the number of DSL
time slots defined.
The associated port is
administratively disabled.
Match the number of DSL time slots
to the DSL line rate. See Tables A-2
and A-3 in Appendix A,
Configuration Options, for
information about maximum
payload rates for different DSL line
rates.
Check the Display LEDs screen to
determine if the port is disabled.
Enable the port if necessary using
the Network, DSX-1, or G.703
Interface Options screen.
7-22
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 69

Testing
Accessing the Test Menu
From the Test menu, you can run network tests, data port tests, and a front panel
lamp test.
To access the Test menu, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Test
8
main/test
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
TEST
Network & DSX-1 | G.703 Tests
Device Tests
Abort All Tests
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
Select . . . To . . .
Network & DSX-1 Tests
Network & G.703 Tests
Device Tests Start and stop the Lamp Test.
Abort All Tests To abort current tests excluding network-initiated
Start and stop tests on the DSX-1, G.703, or network
interface.
loopback tests. An aborted test may continue to run for
a few seconds as the abort command is sent to the
remote end and processed.
ainMenu Exit
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
8-1
Page 70

Testing
Running Network Tests
Network tests require the participation of your network service provider. To
access the Network Tests screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Test →Network & DSX-1 Tests
– or –
Main Menu →Test →Network & G.703 Tests
main/test/network_DSX1
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
Port: 1
Test Command Status Results
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Local Loopbacks
Network Line Loopback: Start Inactive 00:00:00
DSX-1 Repeater Loopback: Start Inactive 00:00:00
DSX-1 DTE Loopback: Start Inactive 00:00:00
NETWORK & DSX-1 TESTS
Remote Loopbacks
Send Line Loopback: Down
Pattern Tests
Send and Monitor 511 Stop Active 10:12:42 - Errors 99999+
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
esetMon
R
main/test/network_G703
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
Port: 2
Test Command Status Results
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Local Loopbacks
Network Line Loopback: Start Inactive 00:00:00
G.703 Repeater Loopback: Start Inactive 00:00:00
G.703 DTE Loopback: Start Inactive 00:00:00
Network Remote Loopbacks
Send Line Loopback: Down
Send Inactive 00:00:00
ainMenu Exit
NETWORK & G.703 TESTS
Send Inactive 00:00:00
8-2
Network Pattern Tests
Send and Monitor 511 Stop Active 11:37:52 - Errors 99999+
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
esetMon
R
April 2000
ainMenu Exit
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 71

Testing
Use the Command column to start or stop a test. When the Status column
shows that a test is Inactive, Start is displayed; when a test is Active, Stop is
displayed. Position the cursor at the desired Start or Stop command and press
Enter.
Selecting Abort All Tests from the Test menu will not disrupt a send and monitor
511 test.
The Results column displays the test duration.
When the Send and Monitor 511 test is active, R
error counter to zero.
esetMon is available to reset the
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
8-3
Page 72

Testing
Network Line Loopback
Network Line Loopback (LLB) loops the received signal on the network interface
back to the network without change. Also, for DSX-1 models:
H If the DSL port is in a DS0 cross-connection, corresponding DSX-1 time slots
H If the DSL port is in Bypass mode or a DS1 cross-connection, an AIS is sent
are sent all ones.
to the corresponding DSX-1 port.
CAP
DSL
Port
CAP T1/E1
FramerFramerTransceiver
LIU
AIS
DSX-1
or G.703
Port
99-16612
" Procedure
To run a Line Loopback:
1. Position the cursor at the Start command next to Network Line Loopback on
the Network & DSX-1 or Network & G.703 Tests screen.
2. Press Enter.
The Start command is changed to Stop.
3. To manually stop the test, verify that the cursor is positioned at the Stop
command.
4. Press Enter.
Network Line Loopback cannot be started when another loopback or pattern test
is in progress.
8-4
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 73

Repeater Loopback
Testing
Repeater Loopback (RLB) loops the signal being sent from the DTE port back to
the DTE port. Also, for DSX-1 models, if the DSX-1 port is in Bypass mode or a
DS1 cross-connection, the corresponding DSL port is sent all ones and data
received on the DSL link is ignored.
CAP
DSL
Port
AIS
CAP T1/E1
FramerFramerTransceiver
LIU
DSX-1
or G.703
Port
99-16613
" Procedure
To run a Repeater Loopback:
1. Position the cursor at the Start command next to Repeater Loopback on the
Network & DSX-1 or Network & G.703 Tests screen.
2. Press Enter.
The Start command is changed to Stop.
3. To manually stop the test, verify that the cursor is positioned at the Stop
command.
4. Press Enter.
A Repeater Loopback cannot be started when any other loopback test is in
progress.
8700-A2-GB20-00
NOTE:
Activating the Repeater Loopback test causes the Embedded Operations
Channel (EOC), used for management, to be lost to the remote unit.
April 2000
8-5
Page 74

Testing
DTE Loopback
DTE Loopback loops the DSX-1 or G.703 signal back to itself before the signal is
sent to the Framer. Also, for DSX-1 models:
H If the DSX-1 port is in a DS0 cross-connection, corresponding DSL time slots
are sent all ones.
H If the DSX-1 port is in Bypass mode or a DS1 cross-connection, all ones are
sent to the corresponding DSL port and data received on the DSL link is
ignored.
DSL
Port
CAP
All Ones
CAP T1/E1
FramerFramerTransceiver
LIU
DSX-1
or G.703
Port
99-16614
" Procedure
To run a DTE Loopback:
1. Position the cursor at the Start command next to DTE Loopback on the
Network & DSX-1 or Network & G.703 Tests screen.
2. Press Enter.
The Start command is changed to Stop.
3. To manually stop the test, verify that the cursor is positioned at the Stop
command.
4. Press Enter.
A DTE Loopback cannot be started when any other loopback test is in progress.
8-6
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 75

Remote Send Line Loopback
The local unit initiates this test by sending a line loopback Up or Down command
to the remote unit for 10 seconds. When the remote unit detects the loopback Up
command, it puts itself in line loopback and lights the front panel Test LED. The
remote unit remains in loopback until it receives a loopback Down command or
the remote unit’s test timeout value is exceeded. The Send Line Loopback tests
both units. External equipment can be used to verify the link.
Local Remote
Testing
LIU
Framer Framer Transceiver
" Procedure
To run a Remote Send Line Loopback:
1. Position the cursor at the Up or Down selection next to Send Line Loopback
on the Network & DSX-1 or Network & G.703 Tests screen.
2. Press the spacebar to select either Up or Down.
3. Position the cursor at the Send command next to Up or Down selection.
4. Press Enter.
The local unit stops sending the loopback command automatically after
10 seconds. You cannot stop the Remote Send Line Loopback test manually.
The Remote Send Line Loopback cannot be started when any other loopback or
a Send and Monitor 511 test is active on the network interface.
CAPCAPT1/E1
CAP
CAP T1/E1
FramerFramerTransceiver
LIU
AIS
DSX-1
or
G.703
Port
99-16615
8700-A2-GB20-00
Remote Send Line Loopback cannot be used in cross-connect mode.
April 2000
8-7
Page 76

Testing
Send and Monitor 511
The Send and Monitor 511 test causes the local and remote units to send a 511
test pattern to each other. Also, for DSX-1 models, all ones are sent to DSX-1
time slots connected to the DSL port being tested.
The front panel Test LEDs of both units light up during the test. The duration and
results of the test are displayed on the Network Test screen to the unit that
initiated the test.
NOTE:
The Send and Monitor 511 test is not a loopback test. Each unit
independently sends and monitors a 511 pattern.
AIS
LIU
Framer Framer
CAPT1/E1
CAP
511
Gen
511
Mon
Transceiver
511
Pattern
511
Pattern
CAP
511
Mon
511
Gen
Transceiver
CAP T1/E1
FramerFramer
LIU
AIS
99-16616
" Procedure
To run a Send and Monitor 511 test:
1. Position the cursor at the Start command next to Send and Monitor 511 on
the Network & DSX-1 or Network & G.703 Tests screen.
2. Press Enter.
The Start command is changed to Stop.
3. To manually stop the test, verify that the cursor is positioned at the Stop
command.
4. Press Enter.
When a Send and Monitor 511 test is active, a count of bit errors is displayed next
to the test duration, and the R
Type r or R or select the R
esetMon virtual function key is available for use.
esetMon virtual function key to reset the error count.
DSX-1
or
G.703
Port
8-8
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 77

Device Tests
Testing
The Device Tests branch is used to access the only card-level test, the Lamp
Test. To access the Device Tests screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Test →Device Tests
Lamp Test
main/test/card
DEVICE TESTS
Test Command Status
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Lamp Test: Start Inactive
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
Model: 87xx
ainMenu Exit
The Lamp Test determines whether all LEDs are lighting and functioning properly.
" Procedure
To test the LEDs:
8700-A2-GB20-00
1. Position the cursor at the Start command next to Lamp Test on the Device
Tests screen.
2. Press Enter.
The Start command is changed to Stop. During the Lamp Test, all LEDs blink
simultaneously every second. When you stop the Lamp Test, the LEDs are
restored to their normal condition.
3. To stop the Lamp Test, position the cursor at the Stop command.
4. Press Enter.
April 2000
8-9
Page 78

Testing
Ending an Active Test
Except for the Remote Send Line Loopback and Remote DCLB, a test initiated by
the user can be ended by the user. Tests can also be terminated automatically by
enabling the Test Timeout option from the System Options Menu.
H A Test Timeout option is available to automatically terminate a user-initiated
Loopback or Pattern test (as opposed to manually terminating a test) after it
has been running a specified period of time. The default is 10 minutes.
Refer to Table A-7, System Options, in Appendix A, Configuration Options.
H On each test screen is a Command column. To manually stop the test, press
Enter when the cursor is on the Stop command.
H Use the Abort All Tests selection from the Test menu to stop all tests running
on all interfaces, with the exception of network-initiated loopbacks. Command
Complete appears when all tests on all interfaces have been terminated.
An aborted test may continue to run for a few seconds as the abort command
is sent to the remote end and processed.
8-10
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 79

Telco-Initiated Tests
Hotwire 8747 and 8777 Termination Units support Telco-initiated tests as shown
in the following table.
Testing
Activation and
Deactivation
In-Band Signal Supported Not Applicable Not Supported
Bit-Oriented Supported Supported Supported
Message-Oriented Not Applicable Not Supported Not Applicable
Telco-Initiated Line Loopback
Hotwire 8747 and 8777 Termination Units support line loopback as specified in
AT&T TR 54016, AT&T TR 62411, and ANSI T1.403. A Telco-Initiated Line
Loopback loops the received signal on the DSX-1 interface back to the DSX-1
interface without modification. Framing, CRC, and FDL bits are returned
unaltered, and no BPVs or other line coding errors are removed. DSL time slots
mapped to the DSX-1 port are sent all ones.
DSL
All Ones
Port
Line Loopback Payload Loopback
CAP
CAP T1
LIU
FramerFramerTransceiver
Remote Line
Loopback
DSX-1
Port
Telco
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
99-16252
8-11
Page 80

Testing
Telco-Initiated Payload Loopback
The Hotwire 8747 and 8777 Termination Units support payload loopback as
specified in AT&T TR 54016 and ANSI T1.403. A Telco-initiated line loopback
loops the received signal on the DSX-1 interface back to the DSX-1 interface.
Framing, CRC, and FDL bits are regenerated at the point of the loopback, and
BPVs are removed. DSL time slots mapped to the DSX-1 port are sent all ones.
DSL
All Ones
Port
Telco-Initiated Remote Line Loopback
If Remote Telco Loopback is enabled, a Telco-Initiated Line Loopback loops
received data at the remote unit and passes it back to the Telco through the local
unit.
The following figure shows the data flow for a remote Telco-initiated payload
loopback.
Local Remote
CAPT1
CAP
CAP
CAP T1
FramerFramerTransceiver
CAP CAP T1
LIU
DSX-1
Port
99-16253
Telco
8-12
Telco
DSX-1
Port
LIU
Framer Framer Transceiver
Telco-Initiated Remote Line Loopback cannot be used in cross-connect mode.
DSL
April 2000
LIU
FramerFramerTransceiver
8700-A2-GB20-00
DSX-1
Port
AIS
99-16626
Page 81

Transferring Code and Configurations Using TFTP
Download Code
The Download Code screen allows you to download firmware from a TFTP
server. To access the Download Code screen, follow this menu selection
sequence:
Main Menu →Control →Download Code
9
main/control/download_code
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
DOWNLOAD CODE
Image File Name:
TFTP Server IP Address: 000
Destination: DSL1
Immediately Apply Download: No
Start Transfer: Yes
Packets Sent: 0000000
Packets Received: 0000000
Bytes Sent: 0000000
Bytes Received: 0000000
Transfer Status: Transfer Pending
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
.000.000.000 Clear
Clear
ainMenu Exit
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
9-1
Page 82

Transferring Code and Configurations Using TFTP
" Procedure
To download firmware:
1. Position the cursor in the Image File Name field. Type the name of the file to
be downloaded.
The file name may be a regular path name expression of directory names
separated by a forward slash (/) ending with the file name. The total path
name length can be up to 128 characters.
2. Position the cursor in the TFTP Server IP Address field. Enter the TFTP
server IP address.
The first three digits of the IP address cannot be 000 or greater than 223.
3. Position the cursor in the Immediately Apply Download field. If you would like
the download to be effective immediately, select Yes.
4. Position the cursor at the Start Transfer field. Use the spacebar to select Yes.
Press Enter.
When the data transfer is complete, the Transfer Status field changes to
Completed successfully.
Applying the Download
If you specified No (the default) in the Immediately Apply Download field in Step
3 above, you must now apply the download.
" Procedure
To apply the downloaded firmware:
1. Press the Escape key to return to the Control menu. Select Apply Download.
2. On the Apply Download screen, type Yes to reset the card and activate the
code.
9-2
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 83

Configuration Loader
The Configuration Loader screen allows you to upload configurations to and
download configurations from a TFTP server. To access the Configuration Loader
screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Configuration Loader
main/config/config_loader
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
Transferring Code and Configurations Using TFTP
CONFIGURATION LOADER
Image File Name:
TFTP Server IP Address: 000
TFTP Transfer Direction: Download from Server
Destination: DSL1
Start Transfer: Yes
Packets Sent: 0000000
Packets Received: 0000000
Bytes Sent: 0000000
Bytes Received: 0000000
Transfer Status: Transfer Pending
Activate new configuration? No
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
.000.000.000 Clear
Clear
ainMenu Exit
" Procedure
To upload or download a configuration:
1. Position the cursor in the Image File Name field. Type the name of the file to
be downloaded, or the name to be used for the file to be uploaded.
The file name may be a regular path name expression of directory names
separated by a forward slash (/) ending with the file name. The total path
name length can be up to 128 characters.
8700-A2-GB20-00
— DOS machine: If the TFTP server is hosted by a DOS machine, then
directory and filenames must consist of eight or less characters with an
optional suffix of up to three characters. The system will automatically
upload the configuration file and create directories and filenames as
needed.
— UNIX machine: If your server is hosted by a UNIX machine, the
configuration file you name must already exist. It will not be created on
the UNIX system by the TFTP server. It is critical that you work with your
system administrator to plan the naming conventions for directories,
filenames, and permissions so that anyone using the system has read
and write permissions.
April 2000
9-3
Page 84

Transferring Code and Configurations Using TFTP
2. Position the cursor in the TFTP Server IP Address field. Enter the TFTP
server IP address.
The first three digits of the IP address cannot be 000 or greater than 223.
3. Position the cursor in the TFTP Transfer Direction field. Use the spacebar to
select Download from Server or Upload to Server.
4. Position the cursor in the Destination field. Use the spacebar to select a
network destination for the TFTP server. Select DSL if the TFTP server
destination is the DSL link port or IMC (in-band management channel) if the
TFTP destination is the Management port of the management card.
5. Position the cursor at the Start Transfer field. Use the spacebar to select Yes.
Press Enter.
When the data transfer is complete, the Transfer Status field changes to
Completed successfully.
6. Position the cursor at the Activate new configuration? prompt and
select Yes to activate a new downloaded configuration. Press Enter.
NOTE:
The following options are not changed:
— DSL Mode and Telnet Session configuration options
— Peer IP address
You must change these settings with the appropriate configuration menus
after the new configuration is activated. See Table A-1, Network Interface
Options, Table A-7, System Options, and Table A-11, Telnet Session Options,
in Appendix A, Configuration Options.
9-4
April 2000
8700-A2-GB20-00
Page 85

Configuration Options
Overview
The tables in this appendix summarize the configuration options accessed when
you select Configuration on the Main Menu. The configuration options are
arranged into groups based upon functionality.
A
Select . . .
Network Network Interface Options, Table A-1 DSL interface ports.
DSX-1
G.703
Copy Ports Copy Ports Options, Table A-6 DSL network and DTE
System
Options
System Clock System Clock Options, Table A-8 LTU system clock options.
Cross-Connect Cross-Connect Mode Options,
Management
and
Communication
To Access the . . . To Configure the . . .
DSX-1 Interface Options, Table A-4
G.703 Interface Options, Table A-5
System Options, Table A-7 General system options of
Table A-9
Assign Time Slots Options, Table A-10
H Telnet Session Options, Table A-11
H General SNMP Management
Options, Table A-12
H SNMP NMS Security Options,
Table A-13
H SNMP Traps Options, Table A-14
DSX-1 interface ports
(Models 8747 and 8777).
G.703 interface ports
(Model 8779).
interface ports by copying
options from port to port.
the unit.
DS1 and DS0
cross-connect ports.
Management support of the
unit through SNMP and
Telnet.
8700-A2-GB20-00
NOTE:
All changes to configuration options must be saved. Refer to Saving
Configuration Options in Chapter 3, Initial Startup and Configuration.
April 2000
A-1
Page 86

Configuration Options
Network Interface Options Menu
For Network Interface Options, refer to Table A-1. To access the Network
Interface Options screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Current Configuration → Network
main/config/network
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
Port 2
Port Status Enable
Margin Threshold: 0db
Excessive Error Rate Threshold: 1E–6
AutoRate: Disable
DSL Line Rate: 1552 kbps
EIA-530 Payload Rate 1536
Transmit Attenuation 0dB
Peer IP Address: 111.255.255.000 Clear
DS0 Cross Connect Line Framing: ESF
NETWORK INTERFACE OPTIONS
kbps
Circuit Identifier: Clear
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave
S
ainMenu Exit
Table A-1. Network Interface Options (1 of 3)
Port Status
Possible Settings: Enable, Disable
Default Setting: Enable
Determines whether the port can be configured and used.
Enable – The port can be configured and used.
Disable – The port cannot be configured or used.
Margin Threshold
Possible Settings: –5db, –4db, –3db, –2db, –1db, 0db, 1db, 2db, 3db, 4db, 5db, 6db,
7db, 8db, 9db, 10db
Default Setting: 0db
Determines the level, expressed in decibels, at which a signal-to-noise margin condition
is recognized.
–5db to 10db – Sets the margin threshold to this value.
A-2
8700-A2-GB20-00April 2000
Page 87

Configuration Options
Table A-1. Network Interface Options (2 of 3)
Excessive Error Rate Threshold
Possible Settings: 1E–4, 1E–5, 1E–6, 1E–7, 1E–8, 1E–9
Default Setting: 1E–6
Determines the error rate at which an excessive error rate (EER) condition is
recognized. The rate is the ratio of the number of CRC errors to the number of bits
received in a certain period.
AutoRate
Possible Settings: Enable, Disable
Default Setting: Disable
Determines whether the unit automatically adjusts to the best line rate for conditions, or
is fixed at the rate in the DSL Line Rate field. The automatically set rate cannot exceed
Max DSL AutoRate.
H AutoRate is only available when the unit is configured as an LTU.
Enable – The LTU adjusts to the best line rate.
Disable – The LTU’s line rate is the DSL Line Rate selected.
DSL Line Rate
Possible Settings (Models 8747, 8777): 144, 272, 400, 528, 784, 1040, 1552
Default Setting: 1552
Possible Settings (Model 8779): 144, 272, 400, 528, 784, 1040, 1552, 2064
Default Setting: 2064
Determines the fixed line rate of the L TU when AutoRate is disabled. See Tables A-2
and A-3 for information about maximum payload rates for different DSL line rates.
H DSL Line Rate is only available when the unit is configured as an LTU and
AutoRate is disabled.
144 to 2064 – The fixed DSL Line Rate, in kbps.
Max DSL AutoRate
Possible Settings (Models 8747, 8777): 144, 272, 400, 528, 784, 1040, 1552
Default Setting: 1552
Possible Settings (Model 8779): 144, 272, 400, 528, 784, 1040, 1552, 2064
Default Setting: 2064
Determines the maximum rate the unit can AutoRate to. See Tables A-2 and A-3 for
information about maximum payload rates for different DSL line rates.
H Max DSL AutoRate is only available when the unit is configured as an LTU and
AutoRate is enabled.
144 to 2064 – The AutoRate ceiling, in kbps.
EIA-530 Payload Rate
Possible Settings: 64, 128
Default Setting: 128
Specifies the synchronous port speed of the remote NTU if the NTU is an EIA-530
model and the DSL line rate is 144 kbps. At higher line rates the EIA-530 NTU runs at
the highest payload rate possible.
H EIA-530 Payload Rate is only available when the unit is configured as an LTU.
64 or 128 – The synchronous port speed of the remote NTU, in kbps.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
A-3
Page 88

Configuration Options
Table A-1. Network Interface Options (3 of 3)
Transmit Attenuation
Possible Settings: 0dB, 3dB, 6dB
Default Setting: 0dB
Determines the amount the transmit power of the unit is reduced to accommodate a
short line length. 0dB denotes no attenuation.
0dB – The full transmit power is used.
3dB or 6dB – The transmit power is reduced the specified amount.
Peer IP Address (LTU Only)
Possible Settings: 001.000.000.000 – 223.255.255.255, Clear
Default Setting: 000.000.000.000
Specifies the peer IP address providing the remote management link on the DSL loop.
H Peer IP Address is only available when the unit is configured as an LTU and the
unit is in not running in IP Conservative mode.
Address Field – (001.000.000.000 – 223.255.255.255) – Enter an address for the peer
unit. The range for the first byte is 001 to 223, with the exception of 127. The range for
the remaining three bytes is 000 to 255. The IP address must be in the same subnet as
the MCC backplane address.
Clear – Clears the IP address and sets to all zeros.
DS0 Cross Connect Line Framing (Model 8777, L TU only)
Possible Settings: ESF, D4
Default Setting: ESF
Specifies the framing format to be used at the DSL interface for DS0 cross connects,
regardless of the framing format specified for the DSX-1 ports.
H DS0 Cross Connect Line Framing is only available on the Model 8777, only when
the unit is configured as an L TU, and only when the port is in a DS0 cross
connect.
ESF – ESF framing formatting is used for transmitted and received data over the DSL
Interface.
D4 – D4 framing format is used for transmitted and received data over the DSL
Interface.
Circuit Identifier
Possible Settings: [ASCII Text]
Default Setting: [blank]
Uniquely identifies the circuit number of the transmission vendor’s DSL line for
troubleshooting purposes.
[ASCII Text] – Enter a maximum of 128 characters. All printable ASCII characters
except ^ (caret) are allowed.
Clear – Clears the field.
A-4
8700-A2-GB20-00April 2000
Page 89

Configuration Options
Tables A-2 and A-3 provides the maximum payload rates achievable for each
DSL line rate and the number of time slots required to achieve that payload rate.
For G.703, the payload rate depends on whether you are using signaling (time
slots 0 and 16) or data only (time slot 0).
Table A-2. Payload Rates and DSL Line Rates for Models 8747 and 8777
DSX-1-to-DSX-1 (To
7974-A2, 8747, 8777)
DSL
Line
Rate
(kbps)
1552 1536 24 1536 24 1536 24
1040 1024 16 960 15 1024 16
784 768 12 704 11 768 12
528 512 8 448 7 512 8
400 384 6 320 5 384 6
272 256 4 – – 256 4
144 128 2 – – 128 2
Maximum
Payload
Rate
(kbps)
Time
Slots
DSX-1-to-DSX-1
(To 7974-A1, 8774)
Maximum
Payload
Rate
(kbps)
Time
Slots
DSX-1- to-EIA-530-A
Maximum
Payload
Rate
(kbps)
Table A-3. Payload Rates and DSL Line Rates for Model 8779
Voice Mode
G.703-to-G.703
Data Mode
G.703-to-G.703
Data Mode
G.703-to-EIA-530-A
Time
Slots
8700-A2-GB20-00
Maximum
DSL Line
Rate (kbps)
2064 1920 30 1984 31 1984 31
1552 1408 22 1472 23 1536 24
1040 896 14 960 15 1024 16
784 640 10 704 11 768 12
528 384 6 448 7 512 8
400 256 4 320 5 384 6
272 128 2 192 3 256 4
144 – – 64 1 128 2
Payload Rate
(kbps)
Time
Slots
April 2000
Maximum
Payload Rate
(kbps)
Time
Slots
Maximum
Payload Rate
(kbps)
Time
slots
A-5
Page 90

Configuration Options
DSX-1 Interface Options
For DSX-1 Interface Options (Models 8747 and 8777), refer to Table A-4. To
access the DSX-1 Interface Options screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Load Configuration From →DSX-1
main/config/DSX-1
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
Port 2
DSX-1 INTERFACE OPTIONS
Port Status: Enable
Line Coding: B8BS
Line Framing: ESF
Line Equalization: 0 -133
Excessive Error Rate Threshold: 1E-4
Primary Clock Source: DSX-1
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave
S
ainMenu Exit
Table A-4. DSX-1 Interface Options (1 of 2)
Port Status
Possible Settings: Enable, Disable
Default Setting: Enable
Determines whether the port can be configured and used.
Enable – The port can be configured and used.
Disable – The port cannot be configured or used. Configuration fields for the port are
inaccessible, no alarms or traps associated with the port are generated, and the LED
associated with the port is OFF.
Cross-connections are not cleared when a port is disabled.
Line Coding Format
Possible Settings: AMI, B8ZS
Default Setting: B8ZS
Specifies the line coding format to be used by the DSX-1 interface.
AMI – Indicates the line coding format used by the DSX-1 interface is Alternate Mark
Inversion (AMI).
B8ZS – Indicates the line coding format used by the DSX-1 interface is B8ZS.
A-6
8700-A2-GB20-00April 2000
Page 91

Configuration Options
Table A-4. DSX-1 Interface Options (2 of 2)
Line Framing
xx
Possible Settings: ESF, D4
Default Setting: ESF
Specifies the framing format to be used by the DSX-1 interface.
H Line Framing is only available when the unit is configured as an LTU. The NTU is
automatically configured to match the framing format used by the L TU.
ESF – ESF framing formatting is used for transmitted and received data over the
DSX-1 Interface.
D4 – D4 framing format is used for transmitted and received data over the DSX-1
Interface.
Line Equalization
Possible Settings: 0-133, 133-266, 266-399, 399-533, 533-655
Default Setting: 0-133
Compensates for signal distortion for a DSX-1 signal over a given distance.
0–133 feet – Provides equalization for a cable length up to 133 feet.
133–266 feet – Provides equalization for a cable length up to 266 feet.
266–399 feet – Provides equalization for a cable length up to 399 feet.
399–533 feet – Provides equalization for a cable length up to 533 feet.
533–655 feet – Provides equalization for a cable length up to 655 feet.
Excessive Error Rate Threshold
Possible Settings: 1E–4, 1E–5, 1E–6, 1E–7, 1E–8, 1E–9
Default Setting: 1E–4
Determines the error rate at which an excessive error rate (EER) condition is
recognized. The rate is the ratio of the number of CRC errors to the number of bits
received in a certain period.
1E–4 – 1E-9– The rate at which EER is recognized.
Primary Clock Source
Possible Settings: Internal, DSX-1
Default Setting: DSX-1
Specifies where the unit will derive its timing from.
H Primary Clock Source is available only when the unit is configured as an LTU and
the port is not cross-connected. If DSL Line Rate is set lower than 1552 kbps,
Primary Clock Source is forced to DSX-1 and cannot be changed.
Internal – Timing is derived from the internal oscillator.
DSX-1 – Timing is derived from the DSX-1 interface.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
A-7
Page 92

Configuration Options
G.703 Interface Options
For G.703 Interface Options (Model 8779), refer to Table A-5. To access the
G.703 Interface Options screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Load Configuration From →G.703
main/config/G.703
Slot: 4 Model: 87xx
Port: 2
G.703 INTERFACE OPTIONS
Port Status: Enable
Framing: Framed
Line Coding: HDB3
Line Framing: noCRC4
Time Slot 16: Data
Primary Clock Source: G703
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave
S
ainMenu Exit
Table A-5. G.703 Interface Options (1 of 2)
Port Status
Possible Settings: Enable, Disable
Default Setting: Enable
Determines whether the port can be configured and used.
Enable – The port can be configured and used.
Disable – The port cannot be configured or used. Configuration fields for the port are
inaccessible, no alarms or traps associated with the port are generated, and the LED
associated with the port is OFF.
Cross-connections are not cleared when a port is disabled.
Framing
Possible Settings: Framed, Unframed
Default Setting: Framed
Specifies whether G.704 framing is used for the G.703 interface.
Framed – The unit conforms to G.704 framing, using time slot 0.
Unframed – G.704 framing is disabled, and the port is forced to DS1 Bypass mode.
A-8
8700-A2-GB20-00April 2000
Page 93

Configuration Options
Table A-5. G.703 Interface Options (2 of 2)
Line Coding
Possible Settings: AMI, HDB3
Default Setting: HDB3
Specifies the line coding format to be used by the G.703 interface.
AMI – Indicates the line coding format used by the G.703 interface is Alternate Mark
Inversion (AMI).
HDB3 – Indicates the line coding format used by the G.703 interface is HDB3.
Line Framing
Possible Settings: CRC4, noCRC4
Default Setting: noCRC4
Specifies the framing format to be used by the G.703 interface.
H Line Framing is only available when the unit is configured as an LTU, AutoRate is
disabled, and the DSL Line rate is 2064 kbps. Otherwise the noCRC4 framing
format is used. The NTU is automatically configured to match the framing format
used by the L TU.
CRC4 – CRC4 framing formatting is used for transmitted and received data over the
G.703 Interface.
noCRC4 – Non-CRC4 framing format is used for transmitted and received data over the
G.703 Interface.
Time Slot 16
Possible Settings: Signaling-CAS, Signaling-CCS, Data
Default Setting: Signaling-CCS
Specifies whether the G.703 interface is used for voice or data.
Signaling-CAS – Time slot 16 contains Channel Associated Signaling (CAS)
information (the unit is in voice mode).
Signaling-CCS – Time slot 16 contains Common Channel Signaling (CCS) information
(the unit is in voice mode).
Data – Time slot 16 contains data (the unit is in data mode).
Primary Clock Source
Possible Settings: Internal, G.703
Default Setting: Internal
Determines the primary clock source for the unit.
H Primary Clock Source is available only when the unit is configured as an LTU.
Internal – Timing is derived from the internal oscillator.
G.703 – Timing is derived from the G.703 interface.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
A-9
Page 94

Configuration Options
Copy Ports Options
You can copy the configuration options of one DSX-1 interface and DSL loop to
another using the Copy Ports screen. For Copy Ports options, refer to Table A-6.
To access the Copy Ports screen, follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Load Configuration From →Copy Ports
main/config/copy
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
COPY PORTS
From: Port 1
To: Port 2
Perform Copy
Perform Copy Then Increment
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
ave
S
ESC for previous menu MainMenu Exit
Table A-6. Copy Ports Options
From: Port n
Possible Settings: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
Default Setting: 1
Controls the source of the configuration options.
1 to 8 – The configuration of the selected port is copied.
To: Port y
Possible Settings: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, All
Default Setting: 1
Controls the target of the configuration options.
1 to 8 – The configuration of the selected port is replaced. If Perform Copy Then
Increment is selected, the port number is incremented by 1 after the copy .
All – The configurations of all ports are replaced by the configuration of the selected
From: Port.
NOTE: Peer IP Address and Circuit Identifier are not copied.
A-10
8700-A2-GB20-00April 2000
Page 95

System Options
Configuration Options
For System Options, refer to Table A-7. To access the System Options screen,
follow this menu selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Load Configuration From →System
main/config/system
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
SYSTEM OPTIONS
DSL Mode: LTU
Test Timeout: Enable
Test Duration (min): 10
Telco Initiated Loopbacks: Enable (Models 8747, 8777)
Remote Telco Line Loopback: Disabled
G.703 Line Termination 120 Ohm
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave
S
(Models 8747, 8777)
(Model 8779)
ainMenu Exit
Table A-7. System Options (1 of 2)
DSL Mode
Possible Settings: LTU, NTU
Default Setting: LTU
Controls whether the unit is configured as a control unit or tributary unit.
LTU – The unit is configured as a control unit (Line Termination Unit).
NTU – The unit is configured as a tributary unit (Network Termination Unit). This unit will
request its IP address from the L TU during establishment of the PPP link.
NOTE: Changing this option will reset the card.
T est Timeout
Possible Settings: Enable, Disable
Default Setting: Enable
Allows tests to end automatically . The feature should be enabled when the unit is
remotely managed, so that control can be regained after a test is accidentally executed.
Enable – Loopback and pattern tests end when test duration is reached.
Disable – Tests run until manually terminated from the Network Tests screen or
remotely (network initiated tests). Refer to Running Network Tests in Chapter 8, Testing.
Test Duration (min)
Possible Settings: 1–120
Default Setting: 10
Number of minutes for a test to be active before automatically ending.
H Test Duration (min) option appears when Test Timeout is enabled.
1 to 120 – Amount of time in minutes for a test to run before terminating.
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
A-11
Page 96

Configuration Options
Table A-7. System Options (2 of 2)
T elco Initiated Loopback
Possible Settings (Models 8747, 8777): Enable, Disable
Default Setting: Enable
Determines if the unit will respond to Telco loopback commands on the DSX-1 interface.
See Telco-Initiated Tests in Chapter 8, Testing.
Enable – The unit will respond to Telco loopback commands.
Disable – The unit will not respond to Telco loopback commands.
Remote T elco Line Loopback
Possible Settings (Models 8747, 8777): Enable, Disable
Default Setting: Disable
Determines if the unit will perform a Telco initiated loopback on just the local unit or if
the loopback will be performed on the remote DSL unit. See Telco-Initiated Tests in
Chapter 8, Testing.
Enable – The loopback will be in the remote unit.
Disable – The loopback will be local.
G.703 Line T ermination
Possible Settings (Model 8779): 75 ohms, 120 ohms
Default Setting: 120 ohms
Specifies the impedance of the G.703 interface
75 ohms – The G.703 interface impedance is 75 ohms unbalanced.
120 ohms – The G.703 interface impedance is 120 ohms balanced.
A-12
8700-A2-GB20-00April 2000
Page 97

System Clock
Configuration Options
The Primary and Secondary System Clock References determine the clock used
by ports in a cross-connect configuration. For System Clock configuration
options, refer to Table A-8. To access the System Clock screen, follow this menu
selection sequence:
Main Menu →Configuration →Load Configuration From →System Clock
main/config/system_clock
Slot: 18 Model: 87xx
SYSTEM CLOCK
Primary System Clock Reference Internal
Secondary System Clock Reference Internal
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Ctrl-a to access these functions, ESC for previous menu M
ave
S
ainMenu Exit
All ports configured as system clock sources must be traceable to the same clock
reference. Ports in a cross-connect configuration that are not providing timing
themselves receive their timing from the system clock reference. All ports in a
cross-connect configuration are therefore synchronized to the system clock
reference.
The following table shows the system clock reference combinations permitted for
LTUs and NTUs. Choose the most accurate clock available for the Primary
System Clock Reference.
Device
LTU
If the Primary System Clock
Reference is . . .
DSX-1 or G.703 port in
cross-connect mode
DSX-1 or G.703 port in DS1
Bypass mode
The Secondary System Clock
Reference must be . . .
H DSX-1 or G.703 port in DS1 Bypass
mode, or
H Internal
H DSX-1 or G.703 port in DS1 Bypass
mode, or
H Internal
8700-A2-GB20-00
NTU
Internal Internal
DSL port in cross-connect mode DSL port in cross-connect mode
Internal Internal
April 2000
A-13
Page 98

Configuration Options
When a system clock source fails or is misconfigured, an alarm is reported.
Secondary clock failures are not reported unless the primary clock has also
failed. When the primary clock fails, clocking is switched to the secondary clock
source, if available. If a secondary clock is not available, the clock switches to
secondary holdover mode. In holdover mode, the system attempts to generate
timing which is consistent with the last clock reference. A switch is made back to
the primary clock when it becomes available.
Figure A-1 shows clocking in an LTU.
DSL
Transceiver
Framer
System Timing
Cross-Connect
System
Timing
Module
DSX-1/G.703 Port
Internal Oscillator
Figure A-1. System Timing
Figure A-2 shows sample system clock configurations.
Framer
DSX-1/
G.703
Driver
99-16627
A-14
8700-A2-GB20-00April 2000
Page 99

Configuration Options
G.703 Port 1
G.703 Port 2
G.703 Port 3
G.703 Port 4
G.703 Port 5
G.703 Port 6
G.703 Port 7
G.703 Port 8
G.703 Port 1
G.703 Port 2
G.703 Port 3
G.703 Port 4
G.703 Port 5
G.703 Port 6
G.703 Port 7
G.703 Port 8
LTU
Primary Clock*
DS0 or DS1
Cross Connect
Secondary Clock*
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
* Must be traceable to the same clock source
LTU
Primary Clock
DS0 or DS1
Cross Connect
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
G.703 Port 1
G.703 Port 2
G.703 Port 3
G.703 Port 4
G.703 Port 5
G.703 Port 6
G.703 Port 7
G.703 Port 8
G.703 Port 1
G.703 Port 2
G.703 Port 3
G.703 Port 4
G.703 Port 5
G.703 Port 6
G.703 Port 7
G.703 Port 8
LTU
DS0 or DS1
Cross Connect
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
NTU
DS0 or DS1
Cross Connect
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
G.703 Port 1
G.703 Port 2
G.703 Port 3
G.703 Port 4
G.703 Port 5
G.703 Port 6
G.703 Port 7
G.703 Port 8
8700-A2-GB20-00
LTU
Primary Clock*
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
Secondary Clock*
* Must be traceable to the same clock source
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
G.703 Port 1
G.703 Port 2
G.703 Port 3
G.703 Port 4
G.703 Port 5
G.703 Port 6
G.703 Port 7
G.703 Port 8
Figure A-2. System Clock Configuration Examples
April 2000
NTU
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
DS1 Bypass
00-16650
A-15
Page 100

Configuration Options
Table A-8. System Clock Options
Primary System Clock Reference
Possible Settings (L TU, Models 8747, 8777): DSX-1 Port 1, DSX-1 Port 2,
DSX-1 Port 3, DSX-1 Port 4, DSX-1 Port 5, DSX-1 Port 6, DSX-1 Port 7,
DSX-1 Port 8, Internal
Default Setting: Internal
Possible Settings (L TU, Model 8779): G.703 Port 1, G.703 Port 2, G.703 Port 3,
G.703 Port 4, G.703 Port 5, G.703 Port 6, G.703 Port 7, G.703 Port 8, Internal
Default Setting: Internal
Possible Settings (NTU): DSL Port 1, DSL Port 2, DSL Port 3,
DSL Port 4, DSL Port 5, DSL Port 6, DSL Port 7, DSL Port 8, Internal
Default Setting: Internal
Determines the source of system timing. Select the most accurate clock available.
DSX-1 or G.703 Port n – Timing is derived from the specified port. To be a valid clock
source, the port must be enabled and must derive its timing from the DSX-1 or G.703
network.
DSL Port n – Timing is derived from the specified port. The port must be enabled and in
a cross-connection.
Internal – Timing is derived from the internal oscillator, which provides a Stratum 4
reference.
Secondary System Clock Reference
Possible Settings (L TU, Models 8747, 8777): DSX-1 Port 1, DSX-1 Port 2,
DSX-1 Port 3, DSX-1 Port 4, DSX-1 Port 5, DSX-1 Port 6, DSX-1 Port 7,
DSX-1 Port 8, Internal
Default Setting: Internal
Possible Settings (L TU, Model 8779): G.703 Port 1, G.703 Port 2, G.703 Port 3,
G.703 Port 4, G.703 Port 5, G.703 Port 6, G.703 Port 7, G.703 Port 8, Internal
Default Setting: Internal
Possible Settings (NTU): DSL Port 1, DSL Port 2, DSL Port 3,
DSL Port 4, DSL Port 5, DSL Port 6, DSL Port 7, DSL Port 8, Internal
Default Setting: Internal
Determines the source of system timing if the primary system clock source fails. If the
secondary clock source fails, the unit switches to secondary holdover mode.
DSX-1 or G.703 Port n – Timing is derived from the specified port. To be a valid clock
source, the port must be enabled and must derive its timing from the DSX-1 or G.703
network.
DSL Port n – Timing is derived from the specified port. The port must be enabled and in
a cross-connection.
Internal – Timing is derived from the internal oscillator, which provides a Stratum 4
reference.
A-16
8700-A2-GB20-00April 2000
 Loading...
Loading...