Panasonic X700 Service Manual

ORDER NO. PMCE041201C8
EB-X700
EB-X701
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
Digital Cellular Phone
900 MHz 1800 MHz 1900 MHz
Tx Frequency Range: 880 - 915MHz 1710 -1785 MHz 1850 - 1910 MHz
Rx Frequency Range: 925 - 960 MHz 1805 -1880 MHz 1930 - 1990 MHz
Tx / Rx separation 35 MHz 75 MHz
RF Channel Bandwidth 200 kHz
Number of RF channels 174 374
Speech coding Full rate/Half rate/Enhanced Full rate
Operating temperature -10 °C to +55 °C
Type Class 4 Handheld Class 1 Handheld Class 1 Handheld
RF Output Power 2 W maximum 1 W maximum 1 W maximum
Modulation GMSK (BT = 0.3)
Connection 8 ch / TDMA
Voice digitizing 13 kbps RPE-LTP / 13 kbps ACLEP / 5.6 kbps CELP / VSLEP
Transmission speed 27
Signal Reception Direct conversion
Antenna VSWR < 2.5 : 1
Dimensions
(excluding antenna)
Volume 89 c c
Weight 107 g
Main Display LCD, 176 x 208 pixels, 65,000 colours
Sub Display LCD, 64 x 96 pixels, 56,000 colours
Illumination
Keys 21-key Keypad, Navigation key, 1 memo key
SIM
External DC Supply
Voltage
Battery 3.7 V nominal, 780mAh, Li-Ion
Standby Time
Talk Time
Talk and standby time will be dependent on network conditions, SIM card, backlight usage
and network condition.
Height: 97 mm
Width: 49 mm
Depth: 24 mm
16 LEDs for Keypad Backlighting (14 Blue & 2 White)
4 LEDs for LCD Backlighting (White)
2 LEDs for Sub LCD (White)
1.8 V & 3 V Plug-in type only
5.8 V
250 hrs
6 hrs
60 MHz
299
This service information is designed for experienced repair technicians only and is not designed for use by the general public.
It does not contain warnings or cautions to advise non-technical individuals of potential dangers in attempting to service a
product.
Products powered by electricity should be serviced or repaired only by experienced professional technicians. Any attempt to
service or repair the product or products dealt with in this service information by anyone else could result in serious injury or
death.
Revision : 00
WARNING
2004 Panasonic Mobile Communications Co., Ltd.
All rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and
R
distribution is a violation of law.

Limitation of Panasonic’s Liability
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The contents in this Manual (and which otherwise may be included in product packaging) are provided "AS IS" without any
warranty, express, implied, or otherwise. Panasonic Mobile Communication Co., Ltd. ("PMC"), for itself, PMC’s parent
company, and PMC’s affiliates, factories, and licenso rs, disc la im s all warrant ies , wheth er ex pres s, imp lie d, or oth erwis e. This
disclaimer includes, but is not limited to, implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, noninfringement of intellectual property or other violation of rights, and any warranties arising from any course of dealing, usage
or trade practice.
Commercially reasonable care has been taken to ensure that the contents of this manual give an accurate representation of
the product(s). H o w eve r, PMC accepts no responsibility for inaccuracies which m ay o cc ur. PMC res erv es th e right, in its sole
discretion, to m odi fy the content in this m an ua l w i th or without notice to You. PMC shall not be liable to You in connection with
any such modification of the materials in this manual. The proprietary rights to the PMC content, programs and materials
incorporated or provided herein are the property of PMC or other rights holders, such as PMC’s licensors. You may use this
manual only for personal, non-commercial purposes ("Limited Use"). Except for the foregoing Limited Use, all other uses are
prohibited, and other uses may constitute infringement of copyright and/or other proprietary rights.
All claims for enforcement, breach, or violation of responsibilities or rights shall be governed by the laws of Japan. Any claims
under consumer protection laws, unfair competition laws, and in tort, shall be governed by the laws of the country of Your
residence. PMC has no liability or obligations to you or any other party for claims that are disclaimed herein or are otherwise
beyond PMC’s reasonable control. In the event that any provision is held to be unenforceable, then the remaining provisions
will remain in full force and effect, and the unenforceable provision will be replaced with an enforceable provision that most
closely approximates the intent and economic effect of such severed provision. All controversies and disputes arising out of
or relating to this manual shall be submitted to the Tokyo District Court in Tokyo, Japan as the Court of first instance. You
hereby irrevocably consent to the exclusive jurisdiction of such Court. Any failure by PMC to exercise or enforce its rights
under the Terms of Use shall not constitu te a wai ve r of such righ ts.
"Panasonic" is a registered tradema rk of Mat sush ita Ele ctric Indu strial Co., Lt d. ("MEI"), PMC ’s parent company. Neithe r Your
purchase of this Panasonic product nor Your use of any related materials, including this manual, constitutes a grant of any
license to use the Panasonic or related marks, names, or logos.
The information contained in this manual or other materials provided with product packaging and all rights in any design(s)
disclosed therein, are and remain the exclusive property of PMC or its licensors. The technology contained in the product
and/or required for proper operation of the product may be owned by PMC, its parent company, or PMC’s affiliates, factories,
or licensors or may be used under license arrangements with licensors or other organizations. No use or other rights, other
than the use of the product as intended, is granted or intended.
Copyright ©2004 Panasonic Mobile Communications Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Comments or correspondence concerning this manual should be addressed to:
Panasonic Mo bile Communications Co., Ltd.
600, Saedo-cho, Tsuzuki-ku, Yokohama, 224-8539, Japan
- i -

1. INTRODUCTION
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
WARNING
The equipment described in this manual contains polarised capacitors utilising liquid electrolyte. These devices are entirely safe provided
that neither a short-circuit nor reverse polarity connection is made across the capacitor terminals. FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS WARNING
COULD RESULT IN DAMAGE TO THE EQUIPMENT OR, AT WORST, POSSIBLE INJURY TO PERSONNEL RESULTING FROM
ELECTRIC SHOCK OR THE AFFECTED CAPACITOR EXPLODING. EXTREME CARE MUST BE EXERCISED AT ALL TIMES WHEN
HANDLING THESE DEVICES.
WARNING
A Naphthalene-based resin paste is used to bond underfill components on this phone. When heated, this paste may give off traces of
Naphthalene.
Therefore, it is recommended that work on the PCB be carried out in a well-ventilated area, especially when using hot air blowers or
soldering irons.
The following components are bonded using the paste:
OMAP310 (U200) ; S-Gold (U100) ; Bluetooth IC (U201)
Caution
The equipment described in this manual contains electrostatic devices (ESDs). Damage can occur to these devices if the handling
procedures described in Section 4 are not adhered to.
Caution
This equipment may contain an internal battery in addition to the external battery packs. These batteries are recyclable and should be
disposed of in accordance with local legislation. They must not be incinerated, or disposed of as ordinary rubbish.
1.1. Purpose of the Manual
This Service Manual contains the information and procedures required for installing, operating and servicing the Panasonic GSM
Personal Cellular Mobile Telephone system operating on GSM Digital Cellular Networks.
1.2. Structure of the Manual
The manual is structured to provide service engineering personnel with the following information and procedures:
1. General and technical information - provides a basic understanding of the equipment, kits and options, together with detailed
information for each of the major component parts.
2. Installation and operating information - provides instructions for unpacking, installing and operating the equipment.
3. Servicing information - provides complete instructions for the testing, disassembly, repair and reassembly of each major
component part. Step-by-step troubleshooting information is given to enable the isolation and identification of a malfunction,
and thus determine what corrective action should be taken. The test information enables verification of the integrity of the
equipment after any remedial action has been carried out.
4. Illustrated parts list - provided to enable the identification of all equipment components, for the ordering of spare/replacement
parts.
1.3. Servicing Responsibilities
The procedures described in this manual must be performed by qualified service engineering personnel, at an authorised
service centre.
The service engineering personnel are responsible for fault diagnosis and repair of all equipment described in this manual.
– 1-1 –

2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Unless stated otherwise, references in this manual to X700 also apply to X701.
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
2.1. General
This section provides a general description and kit composition details for the Digital Cellular Phone and optional kits.
2.2. Telephone Handset Main Kit
12 3
Figure 2.1: Telephone Handset Main Unit Kit Contents
Item Description Model Number
1 Main Unit EB-X700
2 Battery, Standard EB-BSX700EU
EB-BSX700US
EB-BSX700CN
3 Travel Charger EB-CAX70EU
EB-CAX70US
EB-CAX70CN
EB-CAX70UK
EB-CAX70AU
2.3. Features
The Panasonic Phone Model EB-X700 and EB-X701 are high performance, small, light, telephone handsets for business and
domestic use on General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) running on GSM networks. The following features are provided:
• Triple Band, EGSM 900, GSM 1800 and GSM 1900 operation.
• Triple Rate, which includes Full Rate, Half rate and Enhanced Full Rate (EFR) speech, codec.
• GPRS-compatible (Class 10).
• 65,000-color Thin Film Transistor (TFT) Main Display and 56,000-colour LCD Sub-Display.
• Integrated Digital Camera.
• Multimedia Message Service (MMS) and Short Message Service (SMS) messaging.
• POP3-compliant email client.
• Tegic T9 Text Entry.
• Bluetooth connectivity.
• Infrared communications port (IrDA).
• Voice Recorder.
• WAP 2.0 and WAP 1.2.1 compliant Browser.
• Backup Battery.
• 40-voice polyphonic ringtones.
• Downloadable pictures, animations and polyphonic melody ring tones.
• Clock, Calculator and Unit Converter.
– 2-1 –

3. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
3.1. General
This section provides a brief guide to the operation and facilities available on the telephone handset. Refer to the Operating
Instructions supplied with the telephone for full operational information.
3.2. Controls and Indicators
Left Softkey
- Perform action named in lower left of display.
- Shortcut to open preset application in standby mode.
- To lock the keypad, press , then press .
- To unlock the keypad, press , then press .
Edit Key
- Select Dictionary for predictive text including insert and edit
word, or alpha mode or number mode.
- Insert numbers and symbols.
- Change writing language.
- Mark multiple items in a list.
Send Key
- Make a call.
- Recall recently dialled numbers.
- Press and hold in standby mode to activate Voice commands.
Send Key
- Make a calls.
* Key
- In standby mode, press and hold to switch Photolight on or off.
- In edit mode, press to open special character table.
- In numeric and standby modes, press repeatedly for *, p, w,
and + characters.
- In dictionary mode, scroll to other word choices when word is
underlined.
Applications Key
- Enter the main applications menu area.
- Return to standby mode.
- Press and hold to view currently open applications.
Navigation Key
- Press outside edges to scroll up , down , left or right
to move through menus and text.
- Press canter to select option.
- Take a picture in Camera mode by pressing .
Right Softkey
- Perform action named in lower right of display.
- Shortcut to open preset application in standby mode.
Clear Key
- Erase character in edit mode.
- Delete highlighted entered item.
End Key
- Ends call. Return to standby mode.
Silent Mode Key
- From standby mode, press and hold to switch Silent mode on/off.
- In edit mode, shift to upper and lower case letters, or press twice
briefly to turn on/off Dictionary for predictive text.
Power Key
- Press and hold to switch phone on or off.
- Press to choose different ringtones, lock the keypad, lock the
phone, or eject miniSD card.
Zero Key
- In standby mode, press and hold to enter + character for dialling.
- In edit mode, enter space.
Left Softkey
Edit Key
Send Key
Application
Key
* Key
Browser Key
Microphone
Figure 3.1: Phone overview; Open-view
Earpiece
Main Display
Right Softkey
Navigation Key
Clear Key
End Key
Silent Mode /
# Key
Power Key
Zero Key
− 3-1 −

Camera Lens
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
Multibutton
Infrared Port
miniSD Card
Pocket
Camera Lens
- Point at subject of photo.
Multibutton
- From external display, turns on backlight for 15 seconds, or if
backlight is already on, brings up status icons.
Personal Handsfree
and TTY Connector
Indicator Light and
Photolight
External Display
and Viewfinder
- Turns off ringer during an incoming call.
- Take a picture.
Infrared Port
- Transfer data between the phone and other devices with an
infrared connection.
Accessory Connector
- Plug in most EB-X700 accessories here.
Personal Handsfree and TTY Connector
- Plug in Personal Handsfree Headset and TTY accessory here.
Indicator Light
Accessory
Connector
- Remains on during charging.
- Flash to indicate incoming calls.
Photolight
- In standby mode, press and hold to switch Photolight on or off.
External Display and Viewfinder
- Displays clock. Press Multibutton twice to view status icons.
- In Camera mode, acts as viewfinder if flip is closed.
Figure 3.2: Phone Overview; External View
− 3-2 −

3.3. Liquid Crystal Displays
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The telephone handset has two liquid Crystal Displays - a colour display for main operation and a colour sub-display for a
quick review of phone status.
Signal strength
icon
Wallpaper
Left Softkey
selection area
Network that phone
is currently using
Time
Network name
Main Display
Battery charge
level icon
Date
Right Softkey
selection area
Network that phone
is currently using
Signal strength
Phone Status
icon
Phone Status
Sub-Display
icon area
Network name
Time and
date area
Battery charge
level icon
icon area
Figure 3.3: Main & Sub Liquid Crystal Displays
3.4. Alpha Mode Entry
3.4.1. Character Set / Key Assignments
Alpha Mode entry is used to enter alphanumeric characters in to the Phonebook, Short Messages and Greeting Message
areas.
Each time a key is pressed, it will display the next character. When another key is pressed, or no key is pressed for a short
time, the cursor will move to the next position.
In alpha mode choose from:
First letter capital All capitals
Lower case
To enter symbols, press Edit key and select Insert symbol.
To enter text at a flashing cursor:
1. Press the number keys associated with the planned letters repeatedly until the planned letters appear on screen.
2. Editing actions for each key and shortcuts:
Enter space.
Enter punctuation by pressing repeatedly.
Erase a character.
Press and hold to switch between text and
number modes.
Press to scroll through upper case, lower case,
and first letter capital mode.
Switch to number mode.
Insert symbols.
Change writing language.
Press outer edges to scroll up, down, left, and
right through text.
3.4.2. Editing Alpha Entry
Press outer edges to scroll up, down, left, and right through text.
Pressing will delete the character to the left of the cursor.
− 3-3 −

3.5. Features Menu Structure
V
G
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
Note that some features are SIM and/or Network dependent.
Games N/A Games
More Games (games under ’Extras’ menu) Micro Golf
Micro Golf Balloon Headed Boy
Ballon Headed Boy More Games
Vodafone live! Orange Menu N/A
Vodafone live! Orange World
Enter URL Backup
Bookmarks Update
What’s New Help
Games SIM Tool Kit
Ringtones PacketVideo
Pictures
Themes
News
Sports
Media Album
Applications Extras Tools
Postcards QuickOffice Calculator
SIM Tool Kit Calculator Converter
App. Manager Micro Golf Notepad
Calculator File Manager Rec or der
Converter Converter To-Do
Recorder Ballon Headed Boy miniSD
File Manager Help App Manager
QuickOffice Recorder File Manager
Photobase
Voice Commands ...Conversatio ns Photolight (Flashli ght )
RealOne Player ...Friends SIM Tool Kit (if applic ab le)
Shortcuts ...Chat Rooms
Help Notepad
Messages Messaging Messages
Create Message
Inbox
Drafts ...Write Message ...Write Message
Sent ...Inbox ...Inbox
Email Inbox ...Documents (My Folders) ...Documents (My Folders)
Vodafone Messenger ...Mailbox ...Mailbox
Voicemail ...Drafts ...Drafts
My Folders ...Sent items ...Sent items
Media Album / Live! Studio ...Outbox . .. O utb ox
Outbox ...Delivery Repo rt ...Delivery Report
Delivery Report
Camera Camera Camera
Take Picture (lauches Camera app) (lauches Camera app)
Record Video
Photolight
My Items Media Media
Pictures Gallery Media Gallery
….GMS Pictures
……….individua l pi c ture file (uncorrupte d)
created - process ing ) ……….individual picture file (uncorrupted ) ……….individual picture file (uncorrupted)
……….individua l pi c ture file (corrupted)
….MMS background images
….Wallpaper ….MMS background images ….MMS background images
Sounds
…Digital Tones
……..individual aud io file … . individual video file ….individual vid eo fi le
…Simple Tones
……..individual aud io file … . individual audio file ….individual audio file
Videos Photobase Real One
….individual vi deo file
Organiser Calendar Calendar
Calendar (Launches Calendar app) (Launches Calendar app)
Alarm Clock
To-Do
Notes
odafone Orange
Chat
To-Do
Photolight (Flas h li ght)
Voice Mail Voice Mail
Messages Messages
Chat Chat
...Conversations ...Conversations
...Friends ...Friends
...Chat Rooms ... Chat Rooms
Pictures Pictures
….GMS Pictures ….GMS Pictures
processing) processing)
……….individual picture file (corrupt ed) ……….individual picture file (corrupted)
….wallpaper ….wallpaper
Videos Videos
Sounds Sounds
RealOne Photobase
Video Recorder Video Recorder
eneric
Help
Figure 3.4: Features Menu Structure (continued on next page)
− 3-4 −

Contacts Address Book Contacts
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
Contacts List (Launches Contacts app) (Launches Contacts app)
Create Contact
Call Log
Speed Dial
Settings Settings Settings
Profiles Ringtones Ringtones
Themes Phone Themes
General
...Phone ...Call ...Device
...Call ...Connection ...Call
...Date & Time ...Date & Time ...Connecti on
...Connection ...Security ...Date & Time
...Security ...Call Divert ...Security
...Call Diverts ...Barrings …Call Divert
...Call Barring ...GSM Network ...Barrings
...Network ...Accessories ...GSM Network
...Enhancement
Connectivity Themes Clock
...Infrared SpeedDial SpeedDial
...Bluetooth App Manager Voice Commands
...Modem Clock About
...Conn Mgr Voice Mail
...SyncML Voice Commands
...Dev Mgr About
...Conn Test
...USB
miniSD
Voice Commands
About
N/A Connectivity Connectivity
(Connectivity options under 'Settings' menu
VF Messenger N/A N/A
Conversations (Chat found under 'Messaging' menu) (Chat found under 'Messages' menu)
Friends
Chat Rooms
Shortcuts Favourites Favourites
Inbox Notes Notes
Notes Calendar Calendar
Calendar Inbox Inbox
Vodafone Live! Download more games
Ringtones Download more ringtones
Pictures Download more pictures
Games Download more videos
N/A Browser N/A
(Browser found under 'Vodafone Live!' menu) portal)
N/A
(Call Logs found under 'Contacts' menu)
N/A N/A QuickOffice
(QuickOffice found under 'Applications' menu) (QuickOffice found under 'Options' menu)
…Device
miniSD
Bluetooth Browser
Infrared Operator
FaxModem Bluetooth
Conn Mgr Infrared
SyncML SyncML
Dev Mgr De v Mg r
USB Conn Mgr
Download more applications
Call Logs Call Logs
Call Register Call Register
Call Timers Call Timers
GPRS Counter GPRS Counter
General Settings
...Accessories
FaxModem
USB
(Browser found under 'Connectivity' menu)
(Launches QuickOffice app)
Figure 3.5: Features Menu Structure
− 3-5 −

3.6. IMEI and Software Identification
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
To check the IMEI number of the phone:
Press: * # 0 6 #
To identify the software version installed on the phone:
Press: * # 9 9 9 9 # within five seconds of switching on.
3.7. SIM Personalisation
3.7.1 Introduction
SIM personalisation wil l li mi t the us e of t he te lep ho ne to a s ing le SI M, a SIM s up pli ed b y o ne Ne twork/ Sub-net w ork / Serv ice
Provider or a SIM purchased by a company (corporation). If a personalised handset contains a SIM that is from a different
source, it will d isplay the messag e “SIM ERROR” when switch ed on. This perso nalisation is sometimes ref erred to as SIM
lock or SIM latch.
3.7.2 Testing
To test a personalised handset when the user has not supplied the SIM, a SIM configured for test purposes (e.g. test SIM or
soft SIM) should be used. The mobile will recognise that the SIM is for testing purposes only and operate as normal.
3.7.3 Personalisation Function
Personalisation is activated during manufacture. Enabling / disabling is available by entering a special key sequence
immediately af ter pow er on . Once the enabl e / disable men u is s hown it i s p ossible to s elec t the ty pe of pe rso nalis ation. When
personalisation is enabled it is only possible to disable it if the mobile contains a SIM and the 8 or 16 digit Control Key (CK) is
known. For security reasons, when CK is enabled, it cannot be read by the user.
There are two special key sequences to enter the enable / disable menu:
Key Sequence
Notes
Can only disable personalisation
Can both enable and disable personalisation
3.7.4 Disabling Procedure
1. Press
2. Scroll up / down
"SIM" for SIM Personalisation
"Network" for Network Personalisation
"Sub-Network" for Sub-Network Personalisation
"ServiceProvider" for Service Provider Personalisation, or
"Corporate" for Company Personalisation.
3. Press
4. Enter the 8 or 16 digit Control Key and press
5. Confirm by entering the 8 or 16 digit Control Key again and press
to select:
or
The display will confirm which type of Personalisation has been disabled.
− 3-6 −

3.7.5 Enabling Procedure
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
1. Press
2. Scroll up / down
"SIM" for SIM Personalisation
"Network" for Network Personalisation
"Sub-Network" for Sub-Network Personalisation
"ServiceProvider" for Service Provider Personalisation, or
"Corporate" for Company Personalisation.
3. Press
4. Enter the 8 or 16 digit Control Key and press
5. Confirm by entering the 8 or 16 digit Control Key again and press
The display will confirm which type of Personalisation has been enabled.
to select:
− 3-7 −
4. TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
4.1. RF Overview
4.1.1 General Specifications
The telephone is a triple band product incorporating three switchable transceivers, GSM 900 (EGSM 900) band,
GSM 1800 (DCS 1800) band, and GSM 1900 (PCS 1900) band. The transmit and receive bands are given in the table below:
Tx Rx
EGSM 900 880-915 MHz 925-960 MHz
DCS 1800 1710-1785 MHz 1805-1880 MHz
PCS 1900 1850-1910MHz 1930-1990MHz
Other notable technical features are as follows:
EGSM 900 GSM 1800 G SM 1900
Rx Bandwidth 35 MHz 75 MHz 60MHz
Tx Bandwidth 35 MHz 75 MHz 60MHz
Duplex Spacing 45 MHz 95 MHz 80MHz
Number of Channels 174 374 299
ARFCN (Channel Numbers) 975 - 1023 512- 885 512 - 810
0 - 124
1st Tx Channel 880.2 MHz 1710.2 MHz 1850.2MHz
(Ch 975) (Ch 512) (Ch 512)
Last Tx Channel 914.8 MHz 1784.8 MHz 1909.8MHz
(Ch 124) (Ch 885) (Ch 810)
1st Rx Channel 925.2 MHz 1805.2 MHz 1930.2MHz
(Ch 975) (Ch 512) (Ch 512)
Last Rx Channel 959.8 MHz 1879.8 MHz 1989.8MHz
(Ch 975) (Ch 512) (Ch 810)
Maximum calibrated Tx Power, Voice Call 32.25 dBm 29.25 dBm 29.25 dBm
(Class 4) (PL5) (Class 1) (PL0) (Class 1)
Minimum calibrated Tx Power, Voice Call 5.0 dBm 0.0 dBm 0.0 dBm
(PL19) (PL15) (PL15)
4.1.2 Description of PCBs
The handset, which is in the form of a clamshell, contains three printed circuit boards. The main PCB is based on an 8 layer
methodology, constructed using ALIVH-G material. It carries all the RF components on the top half and the baseband
components (Logic circuits) on the lower half. The key pad is mounted on the reverse side of the main PCB. The RF circuit
area is shielded by two metal screens. One compartment contains the Antenna Switch Module (ASM), Power Amplifier
Module (PAM), TX SAW filter and limiter amplifier. The other shielded compartment contains the transceiver IC (Smarti-DC +),
TCXO, 3rd Harmonic (H3) filters, and the RX SAW filters. The logic and Bluetooth circuits are shielded by one screen each.
The second PCB is a flexible printed circuit. One side of its assembly consists of all the components and connectors required
for the sub LCD module, camera and main display. The third is a 4 layer PCB constructed using FR4 material. This board
contains the mini-SD and SIM card holders, as well as the vibrator.
− 4-1 −

4.1.3 Bl ock Diagram
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
Figure 4.1: RF Block Diagram
4.1.4 Frequency Plan
Rx: 925 - 960 MHz
RFLO VCO
3520 - 3840 MHz
Tx: 880 - 915 MHz
1/4
I, Q output to
baseband
925 - 960 MHz
880 - 915 MHz
I, Q output from
baseband
Rx: 1805 - 1880 MHz
RFLO VCO
1/2
3420 - 3760 MHz
Tx: 1710 - 1785 MHz
Figure 4.2: Frequency Plan
I, Q output to
baseband
1805 - 1880 MHz
1710 - 1785 MHz
I, Q output from
baseband
Rx: 1930 - 1990 MHz
3700 - 3980 MHz
Tx: 1850 - 1910 MHz
1/2
I, Q output to
baseband
1930 - 1990 MHz
1850 - 1910 MHz
I, Q output from
baseband
4.1.5 Synthesiser
The transceiver IC U500 is capable of supporting quad-band operation (GSM 850, EGSM 900, DCS 1800, and PCS 1900),
but X700 only supports EG S 900 , DCS 1800 , an d PCS 190 0. G SM 850 is n ot used . The transceiver IC has a synthesizer and
VCO for generating appropriate signals for the transmitter and receiver. Channel data is transferred to U500 from the
baseband IC by three-wire bus (Data, Clock and Strobe). Signal output is divided by 4 for EGSM 900 and by 2 for DCS 1800/
PCS 1900. Synthesizer lock time is approximately 130 µs. An external TCXO is used to generate a 26 MHz reference signal
for the transceiver and logic blocks. Automatic Frequency Control (AFC) is employed to maintain stability over changes in
temperature.
− 4-2 −

4.1.6 Antenna
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The antenna is a fixed helical type and is designed for a triple band operation (EGSM 900, DCS 1800 and PCS 1900).
4.2. Transmitter
4.2.1 Functional Description
Figure 4.3: Transmitter Block Diagram
The transceiver IC U500 supports quadrature modulation and employs direct modulation. The differential I/Q inputs from
thebaseband circuit are up-converted to the transmit frequency by the quadrature modulator. The required signal path is
selected (EGSM 900 or DCS 1800/ PCS 1900). The transceiver output level is approximately 0 dBm.
The modulated outputs pass through third harmonic filters, FL500 and FL501, to the quad band limiter amplifier U501.
In EGSM operation, the differential outputs from the limiter amplifier pass into the TX SAW filter where they are converted into
a single-ended signal. The SAW filter also attenuates the Tx noise. In the case of PCS and DCS, the differential to singleended conversion takes place in the limiter amp and the output is passed into the input of the PAM U503. The PAM contains an
integrated power control function and therefore does not require any additional external components to implement the
Automatic PowerControl (APC) loop. The TX output from the PAM is applied to the ASM U502 which provides a connection
path via the RFconnector to the external antenna.
− 4-3 −

4.3. Receiver
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
4.3.1. Functional Description
ANTENNA
U502
ANTENNA
SWITCH
MODULE
FL502
SAW
FILTER
FL503
SAW
FILTER
FL504
SAW
FILTER
QUAD BAND TRANSCEIVER
LNA
GSM 850
1/4
LNA
EGSM 900
LNA
DCS 1800
1/2
LNA
PCS 1900
VCO
U500
PGA
AMP
BASSBAND
LOW PASS
FILTER
IR
IRX
QR
QRX
Figure 4.4: Receiver Block Diagram
The main building block for the receiver is the transceiver IC U500 which includes a direct conversion receiver with in-phase and
quadrature demodulation. The antenna passes the received signal to the antenna port of the Antenna Switch Module U502.
The U502 switches the signal to the corresponding receive port (EGSM 900, DCS 1800 or PCS 1900). The unbalanced output
signal from the U502 is routed through a 50 ohm PCB trace to the appropriate Rx SAW filter, FL502, FL503 or FL504.
The SAW filter converts the unbalanced signal to a balanced signal and also attenuates any out-of-band blocking signals.
The balanced output from the SAW filter are routed through 75 ohm balanced PCB traces to the LNA input of the transceiver
U500. A balanced matching network has been provided between the Rx SAW output and the LNA input in order to provide an
optimum LNA noise figure (NF). The output of the LNA is then converted directly to baseband frequency by a quadrature
demodulator mixer. The local oscillator (LO) signal presented to the mixer is provided by an internal VCO and it's frequency is
either divided by four (EGSM 900) or by two (DCS 1800 and PCS 1900) before reaching the mixer. After the RF signal is
converted into a baseband signal, the resulting in-phase and quadrature signals are fed into two baseband low pass filters.
These filters provide suppression of in-band blocking signals and adjacent channel interferers. The passband of the filters is
optimized for low group delay ripple. The baseband signal is then amplified by a Programmable variable Gain Amplifier (PGA)
within U500. The in-phase and quadrature baseband signals are then offset to a DC offset level of 1.35 V.
– 4-4 –

4.4. Baseband Overview
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
4.4.1 Introduction
The X700 architecture consists of two main sections; a GSM Modem to handle the speech coding and air interface protocol,
and an Applications Processor to provide the MMI, peripherals support and to execute software applications. Here the GSM
Modem is described, also commonly known as the Baseband section:
The functionality of the GSM Modem is primarily implemented by the Infineon S-Gold ASIC (PMB8870), supported by the
Infineon Power Management IC (PMIC) called S/M-Power (PMB86811), with functionality extended by the Panasonic
Companion IC (AN32061A). The PMIC and the Companion IC are discussed separately in a later section.
S-Gold’s Baseband circuits in the X700 architecture perform the following functions:
GSM Channel Equalization
•GSM Channel Coding / Decoding
•Speech Coding / Decoding
•GPRS (Packet) Support
•Data Encryption
•Basestation Synchronization & Frequency Locking (AFC)
•RF Scheduler and Transmit Power Control
•Real Time Clock (for Day/Date & Idle-Mode Power Saving)
•Audio and Tone Synthesis/Generation (except Ring-Tones, Music & Audio Samples)
•PCM Audio Routing to/from Application Processor & Bluetooth Module
•SIM Interface and Management
•Power Supply and Battery Management (including Charging)
•PWM Generation (Control of the Main & Sub-Display Backlights, and Camera Photolight Intensity)
•IPC Communication with the Application Processor (running the Man-Machine Interface)
•Provision of Application Processor 13MHz Clock, Reset and Handshaking Signals
•Miscellaneous Support (Clamshell Flip Sensor, Headset Detect & HS Send/End, Battery Temperature)
The GSM Modem (S-Gold) can be viewed as a module, performing the aforementioned tasks, generally under the control of
the Application Processor. S-Gold executes its own locally stored code from 4MB of Flash, with 1MB of SRAM provided in a
stacked Flash & RAM package to save PCB area. S-Gold receives instructions at UART1 from the ApplicationProcessor
via the Primary Inter-Processor Communication (IPC-PRIMARY) serial link. The Application Processor is discussed
separately.
At phone power-up, S-Gold boots from its external Flash memory, initializes the Modem as a whole into an idle state,
and supplies the divided-by-2 system clock to the Application Processor, which then boots-up after reset is released by S-Gold.
Once the Application Processor has booted, it then takes overall control of the entire system.
− 4-5 −

Application
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
Proccessor
RST_OUT
USB I/F
UART3 I/F
IRDA_SD
SD/MMC I/F
SD_SW1
VSIM1
VSIM_SW
UART1
IPC_GPIO
AP_CLK_REQ
LOW_PWR
McBSP1
McBSP2
32KHz
AP_RST
AP_WAS_RSR
UART2
IrDA
SD Card
FLASH
4MB
SRAM
1MB
SIM
Flip Sensor
IPC
32KHz
CLK32K
GPIO86
EINT0
VLSD
EBU I/F
(CS0,CS1)
CC_VZ_N
SIM I/F
OP_DET
UART1
CC2CC3IO
I2S2
SSC0
CLKOUT1
VDD_RTC2
USART0
CC0CC4 IO
(KP_IN4)
KP_OUT2
RTC
POAKOUT1
KP_IN0
Modem
Proccessor
DIF_D4
DIF_D3
SOAKOUT0
M8
M9
M2
M1
DIF_D5
MICP2/N2
EPREF
EPPA1/2
MICP1/N1
EPP1/N1
CC1CC4IO
CC1CC0IO
CC1CC2IO
VBATT
CURRENT
BATT_TEMP
RF_TEMP
CIC_IRQ
HH MIC
HH SPK
I2C
Vmain
RTCONT
PM_INT
NRESET
VCXO_EN
RF I/F
F26M
/HS_DET
HS_SND_ENDKP_IN6
BT_CLK_PU
BT_RST
I2S1
PWM_MAIN
PWM_SUB
PWM_FLASH
VINT
LOW_PWR
ON
LRF3_EN
ON
COMPANION
PMIC
USB
UART3
USART0
VDCDC
VBATT Vmain
VDD_RTC3
VDD_RTC2
VLSD
IC
VLBB3
HS_SND_END
BATT_TEM
HF SPK
VBUS
EXT_PWR
VIB
SLED1
SLED2
LED
VRF1
VRF2
VRF3
HS_MIC
HS_SPK
/HS_DET
M
RF_TEMP
I/O CN
Mono HS
Battery
840 mAh
EXT_PWR
Paging LED
Alert LED
Keypad LED
VACC
VBUS
VBATT
VACC
Vmain
VRF1
VRF2
RF
VRF2
BT_CLK
BT_CLK_REQ
Bluetooth
VRF3
Figure 4.5: Baseband Block Diagram
4.5. Modem
4.5.1. Base-Station Synchronisation & AFC
The Modem attempts to locate valid network service by monitoring the received RF signals to "camp-on" an available network.
In this "Idle" mode the Modem only receives at precise intervals (paging channel time slots), listening for incoming voice calls
and data packets; at all other times the Modem RF sub-system is powered-down to conserve battery life.
The base-station network signals to the Modem the exact intervals at which any incoming transmission may be expected.
Frequency tuning (channel selection and frequency-drift correction) is achieved by the Automatic Frequency Control system
by slightly adjusting the frequency of the 26 MHz Voltage-Controlled Temperature-Compensated Crystal Oscillator (the
VCTCXO is located in the RF section and not shown in the block diagram above). The VCTCXO is the master clock reference
from which the RF frequencies are generated and most of the Modem logic is clocked, and is located in the RF section of the
design, having the part reference Y500.
– 4-6 –

4.5.2. RF Scheduler and Transmit Power Control
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
S-Gold has a GSM System Interface Block which incorporates in hardware a GSM Timer which is programmed by the Modem
software to activate sections of the RF sub-system when required for reception during the paging channel timeslots, and an RF
Ramp Controller which additionally switches-on and ramps-up the transmit RF power amplifier when in a voice call sending
data packets. By only activating the necessary parts of the system when required, battery life is extended considerably.
The table below shows how these circuits are connected:
System Timer Signal Name Description Notes
T_OUT0 TX_ON_PA TX Power Amp
On/Off Control
T_OUT1 TX_ON_DRV Alternate source for
Driver Enable,
primary source is
SmartiDC+.
T_OUT2 VC1 Antenna Switch Control 1.
T_OUT3 VC2 Antenna Switch Control 2.
T_OUT4 VC3 Antenna Switch Control 3.
T_OUT5 Not currently connected.
T_OUT6 (R) (MODE) Future use for EDGE. Reserved - Not currently connected.
T_OUT7 BAND_SELECT Alternate source for
Band Select, primary
source is SmartiDC+.
T_OUT8 (R) (TX-EDGE) Future use for EDGE. Reserved - Not currently connected.
T_OUT9 Not currently connected.
T_OUT10 Not currently connected.
T_OUT11 BT_CLK_REQ Used as GPIO for When BT module powers up, the
Pull Up. BT_CLK_REQ is an input with weak pulldown.
This PU is needed to provide the
clock to BT module to boot-strap the clock
enable. Used as a GPIO function only.
T_OUT12 (R) (CRAM_MODE) Future use for CRAM GPIO function – not currently connected.
mode selection.
4.5.3. Real Time Clock (RTC)
The Real Time Clock block (located inside S-Gold) performs several functions. It is used to time the intervals between paging
slots when the handset is otherwise shut-down, to save power, and also to maintain the current date and time. Since the RTC
Block is clocked by its own low frequency (32,768 Hz) crystal, it consumes very little power, and is relied upon to keep track
of elapsed time whenever the handset is in power saving mode (when the main 26 MHz VCTCXO is switched-off).
Prior to being used to accurately time successive paging slots, it is calibrated against the very accurate 26 MHz VCTCXO to
± 1 count (± 1/32768 s), thus allowing a low-cost low-accuracy crystal to accurately time short intervals.
The Power Management sub-system (discussed separately) incorporates a small 3V battery (button-type cell) which is kept
charged to allow the RTC to continue to maintain the current date and time during recharging or replacement of the main
handset battery. A 2.1 V regulator then provides a constant voltage to the RTC Block, with the 3V battery voltage providing
sufficient headroom for the battery to discharge over while providing the required RTC back-up time.
4.5.4. Audio & Tone Synthesis/Generation
The DSPs inside S-Gold also generate the DTMF (Dual-Tone-Multi-Frequency) signalling tones used to communicate over
the air interface with the POTs network or other equipment, in addition to performing voice encoding & decoding, and
channel encoding & decoding.
The Modem S-Gold also incorporates an analog audio block, which provides an analog electrical interface for connecting
the microphone, speakers and headset to. Note that the audio transducers are actually indirectly connected via the Power
Management Block, since this allows multiple audio transducers to be multiplexed to S-Gold, and for the signals to the
speakers to be buffered and amplified.
– 4-7 –

4.5.5. PCM Audio Routing to/from Application Processor & Bluetooth
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
Although the Modem handles the speech audio to and from the microphone and handset / hands-free loudspeakers, MP3decoding, voice-recognition, high-quality ring-tones and other synthesised audio are handled or generated by the Application
Processor. These are passed between the Modem and Application Processor via the dedicated digital PCM bus called
IPCAUDIO (Inter-Processor Communication - Audio). This is a 4 line bus (IPCAUD-CLK, IPCAUD-TX, IPCAUD-RX and
IPCAUDSYNC), with the Modem always being the IPCAUD Bus Master. Various sample rates are supported, depending upon
the quality of the audio, from 8kSamples/s to 48kSamples/s.
Bluetooth audio support is also provided by the separate, highly-integrated Bluetooth ASIC (U504). Audio at Samples/s is
passed between S-Gold and the Bluetooth ASIC in digital PCM format via PCM-CLK, PCM-IN, PCM-OUT and PCM- SYNC.
The Bluetooth ASIC is always the PCM Bus Master.
4.5.6. Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
The Modem supports the SIM Card (Subscriber Identity Module) interface. The Power Management Sub-System has been
designed to provide 2.8 V or 1.8 V supplies to the SIM, although the software may only support 2.8 V SIMs. The power to the
SIM can be switched off by S-Gold's CC_VZ_N output, which allows additional power savings, while the rest of the Modem
remains powered-up and operational.
4.5.7. Power Supply and Battery Management (inc. Charging)
The Modem handles the battery charging algorithm, which is started when a charger is inserted into the handset. It also provides
an indication of the battery voltage (and hence an estimate of the remaining capacity) for display to the User. It automatically
switches between fast charging and trickle charging (battery full maintenance).
4.5.8. PWM Generation (Main & Sub-Display Backlights & Photolight)
Since S-Gold incorporates a set of Capture-Compare (CAPCOM) functions, these are utilised to produce Pulse-WidthModulated digital logic-level outputs, each with a variable duty-cycle. These outputs can be used to vary the intensity of the LCD
backlights, and operate at a high frequency with an increasing proportion of the time at a high logic level corresponding to an
increased drive provided to each respective backlight:
The PWM signal controlling the brightness of the Main LCD backlight is provided by CC1CCIO4;
The PWM signal controlling the brightness of the Sub LCD backlight is provided by CC1CCIO0;
The PWM signal controlling the brightness of the Camera Photo-light is provided by CC1CCIO2.
The camera photolight is provided in the handset so that images may be captured at low light levels. The Photolight drive level
is variable so that the appropriate amount of illumination may be selected for the best quality low-light image capture.
4.5.9. IPC Communication
The Modem and Application Processor systems communicate via the asynchronous serial IPC-PRIMARY bus (Inter-Processor
Communication - Primary), over lines IPCPRI-TX, IPCPRI-RX, IPCPRI-RTS and IPCPRI-CTS.
4.5.10. Application Processor Clock, Reset & Hand-shaking
In the EB-X700 architecture, the Modem is responsible for providing the Application Processor with a 13 MHz clock, and the
necessary reset and control handshaking signals. At initial power-up, the Modem (S-Gold) boots itself, while holding the
Application Processor in reset. After a short time, the Modem provides the 13 MHz clock to the Application Processor, and
releases the reset line (AP-RST). The Application Processor then boots, and assumes control of the handset (including the
Modem).
A handshaking mechanism is provided to allow the Application Processor to signal to the Modem that it no longer requires the
13 MHz clock (via line AP-CLK-REQ), allowing the Modem to switch-off the VCTCXO for power-saving, if the Modem also does
not require the system clock.
A further hand-shaking mechanism is provided for the Application Processor to signal to the Modem that an error and reset
event occurred in the Application Processor, requiring an overall system reset to recover (via line AP-WAS-RST). This allows
the handset to take the appropriate automatic reset and reboot action necessary to return functionality to the User.
– 4-8 –

4.5.11. Miscellaneous Support
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The Flip Sensor (U400) is a magneto-resistive device which changes its output logic level in the presence of a magnetic field.
When the clamshell is closed, a magnet in the upper part of the handset aligns with U400 mounted on the main PCB, causing
the logic level to change to High. This is sensed by S-Gold at KP-IN4, and this information is relayed to the Application
Processor to switch off the Main LCD and its backlight to save power (while switching on the Sub-LCD), as well causing the
S-Gold to disable the handset audio circuits to prevent acoustic feedback. Note that S-Gold's keypad interface function is not
used, and instead purely functions as General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO).
Insertion or removal of a personal Handsfree (ear-bud & microphone) is detected by S-Gold via a logic level change on HSDET.
This accessory incorporates a headset cord-mounted switch, which when pressed shorts HS-SEND/END to ground, signalling
to S-Gold that a call is to be answered or ended, as appropriate.
S-Gold also has an internal analogue-to-digital conversion block. This is used for a number of analogue sensing functions,
such as charge current monitoring (for charging status detection), battery temperature monitoring (for safety), and RF system
temperature monitoring (for calibration adjustment for accuracy).
4.5.12. Modem Memories
The Modem has dedicated non-volatile NOR Flash and volatile asynchronous SRAM memories, separate from the
Application Processor memories. The Flash is needed to retain and execute the Modem software, which is primarily used
to control Modem reception and transmission across the RF air interface.
Upon initial power-up of the Modem, S-Gold boots from an internal boot memory, determining whether to continue to boot
from the external Flash for normal handset operation, or whether to initiate re-programming.
Both the individual Flash and SRAM silicon die are located in a single stacked Multi-Chip Package (MCP) in order to
save PCB area, with the (joint) component designation U102. The MCP is organised as 32 Mbits of Flash (2M address
locations x 16 bits wide data) plus 8Mbits SRAM (512k locations x 16 bits wide data). The Flash supports 52MHz burst
operation for speed. Both memories operate at 1.8 V for low power.
4.6. Baseband Overview (Application Processor)
4.6.1. AT Command Communication with GSM Modem S-GOLD
The Application Processor and Modem processor communicate via the asynchronous serial IPC-PRIMARY bus (InterProcessor Communication - Primary), over lines IPCPRI-TX, IPCPRI-RX, IPCPRI-RTS and IPCPRI-CTS, a part of IPC
communication link. AT commands are transferred between two processors to link the smart phone software running on
the application processor side with the Modem software running on the Modem processor side.
4.6.2. PCM Audio Routing to/from S-GOLD
In the EB-X700 architecture design, the Modem is responsible for providing the Application Processor with a 13 MHz
clock, and the necessary reset control handshaking signals. At initial power-up, the Modem (S-Gold) boots itself, while
holding the Application Processor in reset. After a short time, the Modem provides the 13 MHz clock to the Application
Processor, and releases the reset line (AP-RST). The Application Processor then boots, and assumes control of the
handset (including the Modem).
A reset handshaking mechanism is provided for the Application Processor to signal to the Modem that an error and
reset event occurred in the Application Processor, requiring an overall system reset to recover (via line AP-WAS-RST).
This allows the handset to take the appropriate automatic reset and reboot action necessary to return functionality to
the User.
– 4-9 –

4.6.3. Reset and Sleep/Wakeup Handshaking Signals with Modem
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
In the EB-X700 architecture design, the Modem is responsible for providing the Application Processor with a 13MHz clock, and
the necessary reset control handshaking signals. At initial power-up, the Modem (S-Gold) boots itself, while holding the
Application Processor in reset. After a short time, the Modem provides the 13 MHz clock to the Application Processor, and
releases the reset line (AP-RST). The Application Processor then boots, and assumes control of the handset (including the
Modem).
A reset handshaking mechanism is provided for the Application Processor to signal to the Modem that an error and reset
event occurred in the Application Processor, requiring an overall system reset to recover (via line AP-WAS-RST). This allows
the handset to take the appropriate automatic reset and reboot action necessary to return functionality to the User.
A sleep/wakeup hand-shaking mechanism is also provided to allow the Application Processor go to sleep mode and signals
the Modem that it no longer requires the 13 MHz clock (via line AP-CLK-REQ), then the Modem will switch off the 13 MHz
clock but maintains 32 kHz clock to the Application processor. The Modem will also switch-off the VCTCXO for power-saving
if the Modem does not require the system clock. Furthermore, the IPCPRI-RTS line is also used for Modem processor to
wakeup the application processor, and the IPCPRI-CTS line is also used for the application processor to wakeup the Modem
processor.
4.6.4. Memory Management
The Application processor has dedicated non-volatile NOR Flash and volatile SDRAM memories, separate from the Modem
memories. The Flash is needed to retain and execute the smart phone software and desired user data. Upon initial
power-up of the EB-X700 phone, the Application processor boots from the boot-loader in the Flash memory once the
13 MHz clock is supplied and the reset line is released by the Modem processor.
Both the individual Flash and SDRAM silicon die are located in a single stacked Multi-Chip Package (MCP) in order to save
PCB area, with the (joint) component designation U203. The MCP is organized as 48-Mbyte of Flash (32-Mbyte is enabled by
CS0 and 16-Mbyte is enabled by CS3) plus 16-Mbyte SDRAM.
4.6.5. Keypad
The keypad interface supports up to 6 columns by 5 rows, but only a 5 x 5 keypad matrix is used for EB-X700 design.
The keypad scanning algorithm and de-bounce time is software controlled for event detection on both key press and key
release. The keypad is managed under 32 kHz clock to allow a keypad interrupt to be detected even in the sleep mode.
Besides 6 x 5 keypad matrix, a dedicated on/off key is also provided for powering up (short key press) or powering down
(long key press) the EB-X700 phone.
TP416
S403
EDIT
S404
W@P
S405
SF1
S406
CLR
S407
OK
S408
1
S409
2
S410
3
S411
SND
S412
M1
S413
4
S414
5
S415
5
S416
UP
S417
DOWN
S418
7
S419
8
S420
9
S421
LEFT
S422
RIGHT
S423
*
S424
0
S425
#
S426
END
S427
M2
TP413
TP414
TP415
TP417
TP419
TP420
TP421
TP422
TP423
TP424
PW-ON
KBI-R0
KBI-R1
KBI-R2
KBI-R3
KBI-R4
KBO-C0
KBO-C1
KBO-C2
KBO-C3
KBO-C4
KBO-C5
KEYBL-PWM
VMAIN
TP431
TP433
PAD FOR KEYPAD
S428
TP418
Figure 4.6: Keypad
– 4-10 –
TP425

4.6.6. Bluetooth Module
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The bluetooth module U201 provides short range (typical 10 meters or less) connectivity from the hanset to bluetooth-enabled
devices such as headsets, car kits, and personal computers for transfer of voice and data.
The Application processor controls the initialization of the bluetooth module through the UART2 interface (BT-RX, BT-TX, BtRTS and BT-CTS) and a reset line (GPIO13) BT-RST controls bluetooth reset.
Bluetooth system clock is supplied by a buffered 26MHz source built in to the RF chip SMARTI DC+, which has an on/off
function controlled by the BT-CLK-REQ signal line.
A PCM audio connection from U201 connects via the 4-wire I2S1 port of Modem processor S-GOLD, which uses 13-bit linear
PCM.
4.6.7. IrDA
The IrDA transceiver interface is provided by the UART3 port of the Application processor to support the slow IrDA with data
rate from 2.4kbps to 115.2kbps (IrDA-1.0 standard). The IrDA transceiver module can be set to low power mode using GPIO8
IrDA-SD-MODE control line.
4.6.8. SD Card
The SD interface of the Application processor supports Mini SD card operation at either 1-bit bus mode or 4-bit bus mode.
The Mini SD card used for X700 handset provides a convenient compact storage device for saving the data files, such
as pictures taken from the camera or the video clips loaded from PC and play back to the main LCD of the handset.
Mini SD card interface supports SD card hot insertion and removal, which is implemented by a mechanical switch built-in to
the Mini SD connector.
– 4-11 –

4.6.9. Main LCD Module
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The main LCD module has 176 x 208 pixels TFT display with 65K colour resolution. The Application processor provides 16-bit
interface for RGB pixel data transfer and a 3-wire (LCD-SCL, LCD-SDO and MAINLCD-CS/GPIO12) serial interface (McBSP3)
for the module register settings.
8.9439.31 ACTIVE AREA
0.063
0.189
RGB
0.189
51.50
A
33.26 ACTIVE AREA
39.90
Figure 4.7: Main LCD Dimensions
The backlighting for the main LCD module is provided by +13 V DCDCOUT voltage of Companion IC, which has an on/off
function programmed by an I2C link provided by the Modem processor.
The partial display mode is supported by the main LCD module to reduce the power consumption of the display.
Shown below is of all four configurations the LCD driver is capable.
The main LCD module can be set to standby mode by programming the main LCD register to turn-off/reset mode for the best
power savings whenever it is not in use.
MASKS1
MASKE1
MASKS2
MASKE2
non-display
display non-display
non-display
MASKS1
MASKE1
MASKS2 : FFh
MASKE2 : FFh
non-display
display
display
MASKS1
MASKE1
MASKS2 : FFh
MASKE2 : FFh
non-display
display
MASKS1
MASKE1
display
MASKS2 : FFh
MASKE2 : FFh
Figure 4.8: LCD Module Standby Mode
– 4-12 –

4.6.10. Sub-LCD Module
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The Sub LCD module has 96x64 pixel CSTN display with 65K colour resolution. The Application processor provides a 3-wire
(LCD-SCL, LCD-SDO and SUBLCD-CS/GPIO6) serial interface (McBSP3) for the 16-bit RGB pixel data transfer or the module
register settings.
The backlighting for the Sub LCD module is provided by +13 V DCDCOUT voltage of Companion IC, which has an on/off
function programmed by an I2C link provided by the Modem processor. The Sub LCD module can be set to standby mode by
programming the Sub LCD register to turn-off and then pull the LCD-NRST/GPIO11 line to logic low for the best power savings
whenever it is not in use.
64
Non-Display Area
Display Area
Non-Display Area
Figure 4.9: Sub-LCD Dimensions
96
4.6.11. Camera Module
The camera module is uses a 13MHz clock that is supplied by the camera interface of Application Processor. The camera
interface also provides 8-bit parallel interface to receive the RGB or YCrCb pixel data from the camera module, and an I2C
interface to read or write the registers of the camera module.
The full resolution of the camera module is VGA 640x480 pixels, which is YCrCb data format used for snapshot and required by
JPEG compress and store. The image resizing can be done by programming the related registers for QVGA (320 x 240),
CIF (352 x 288) or QCIF (176 x 144) decimation. QCIF is used for camera viewfinder mode.
Whenever the Sub LCD module is used for camera viewfinder mode, the QQQVGA (80 x 60) resizing should be done by the
Application processor.
Whenever the camera module is not used, the camera sensor readout function should be disabled and the STANDBY pin should
be set for power saving.
The following image processing can be done in the camera module:
Colour recovery and correction Auto white balance and auto black
Sharpening Auto flicker detection
Gamma correction On the fly defect correction
Lens shading correction Digital zoom (2 x)
Aperture correction and interpolation Auto color saturation and control
Auto exposure
4.6.12. USB
The Application processor supports full speed (12 MHz) USB functionality as a Client USB Function Peripheral as defined in
USB 1.1 standard. The USB host uses USB Type A connector to connect to the USB data cable accessory. When USB cable
is connected to the X700 handset, the USB function controller of the Application processor shall detect the VBUS voltage
provided by the host USB, and start running the USB program to support the USB communication link with the USB host.
– 4-13 –

4.7. Bluetooth Module
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The X700 handset contains a Bluetooth module centered on Cambridge Silicon Radio’s (CSR) BlueCore3-ROM IC
(U201).This provides short range (typically 10 meters or less) connectivity from the handset to Bluetooth-enabled devices
such asheadsets, car kits, and personal computers in order to transfer voice and/or data. Shown below is the block diagram
of the X700 Bluetooth interface.
BT-Antenna
U200
OMAP310
U100
PMB8870
SGOLD
IPC
I2S1
Serial I/F
AFC
UART2_TX
UART2_RX
UART2_CTS
UART2_RTS
GPIO12
I2S1_CLK0
I2S1_TX
I2S1_RX
I2S1_WA0
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
VCXO_EN
DIF-D7
(I2S1-WA1)
FSYS
VRF3
SPI_CSB
SPI_CLK
SPI_MOSI
SPI_MISO
USB_D+
USB_D-
UART_RX
UART_TX
UART_RTS
UART_CTS
BT_RST
PIO[4]
PIO[5]
PCM_CLK
PCM_IN
PCM_OUT
PCM_SYNC
U201
VBT18
1.8V
Bluetooth
BC313143A
VBT18 VBT18
TX_A
TX_B
RF_IN
AIO[2]
AIO[1]
AIO[0]
PIO[0]
PIO[1]
PIO[3]
PIO[6]
PIO[7]
PIO[8]
PIO[9]
PIO[10]
PIO[11]
XTAL_OUT
XTAL_IN
PIO[2]
BT-CLK-REQ
BT26M
(26MHz)
Bluetooth RF
Balun/
Vmain
VDDPW
VDDB
SDBB
VDDC
Vmain
VDDRF
VCXO_EN
VRF1
VRF1
VRF2
Filter
PMB8611
1.8v,850mA
1.5v,170mA
1.5v,220mA
2.85v,250mA
2.85v,10mA
2.65v,150mA
RF Sub-System
EN
EN
PMB6258
VCTCXO
AFC
U304
PMIC
SDBB
LBB1
LBB2
LRF1
LRF2
LRF3
26MHz
SDBB
VLBB1
VLBB2
VRF1
VRF2
VRF3
U500
The Bluetooth IC connects to the UART2 interface on OMAP which provides the control and data interface to the application
processor.The 4-wire UART connection (TXD, RXD, RTS, CTS) uses the BlueCore Serial Protocol (H5) with error detection
and re-transmission.
The PCM audio connection from Bluetooth is connected to the I2S1 port on SGOLD. The PCM interface (with BT as the
Master) is configured for a 256kHz bit-clock and an 8kHz sync rate.
The Bluetooth chip is powered by the VRF3 (2.65v @ 150mA) regulator supplied by the SM-PWR IC. VRF3 supplies the I/O
block as well as an integrated 1.8v @ 100mA regulator (VBT18). This (VBT18) is used to power the RF portion, analog
section, core and memory of the Bluetooth sub-system.
Figure 4.10: Bluetooth Module
− 4-14 −

The BT chip requires a 26MHz clock that is provided by an internal buffer in the RF Smarti DC+ IC. The buffer receives the
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
26MHz signal from a VCTCXO and is enabled by BT_CLK_REQ (PIO2). Once the BT IC is powered-up, the BT-CLK-REQ
signal will be pulled high by an internal pull-up. The BT-CLK-REQ line also goes to the SM-Power IC where it is used to
turnon the VRF2 supply (power for VCTCXO).
The Bluetooth IC reset is generated by the application processor (GPIO13). This is a logic low signal (~2.7V when high).
After power-up, Persistent Store-Key (PS-Keys) settings are sent to the Host Controller Interface (HCI) firmware to initialize
BLUETOOTH. These settings (PCM configuration, BT address, etc.…) are stored in the OMAP memory and downloaded to
the BT IC upon initialization. The 6-byte Bluetooth Address will be programmed during manufacture.
The CSR Bluetooth IC has a Deep Sleep mode. In this mode, the 26MHz clock (BT-CLK-REQ goes low) and much of the
analog circuitry is shut down to save power. The BT IC will automatically enter this mode when idle (no BT activity detected).
The device's timing is maintained by an internal, 1kHz slow clock. The chip will wake every 1.28 seconds to check for BT
activity. When the host sends a packet to the BlueCore3 while it is in Deep Sleep, the activity on the UART will wake the IC.
Then, with the BCSP protocol, the packet is resent after a delay.
− 4-15 −
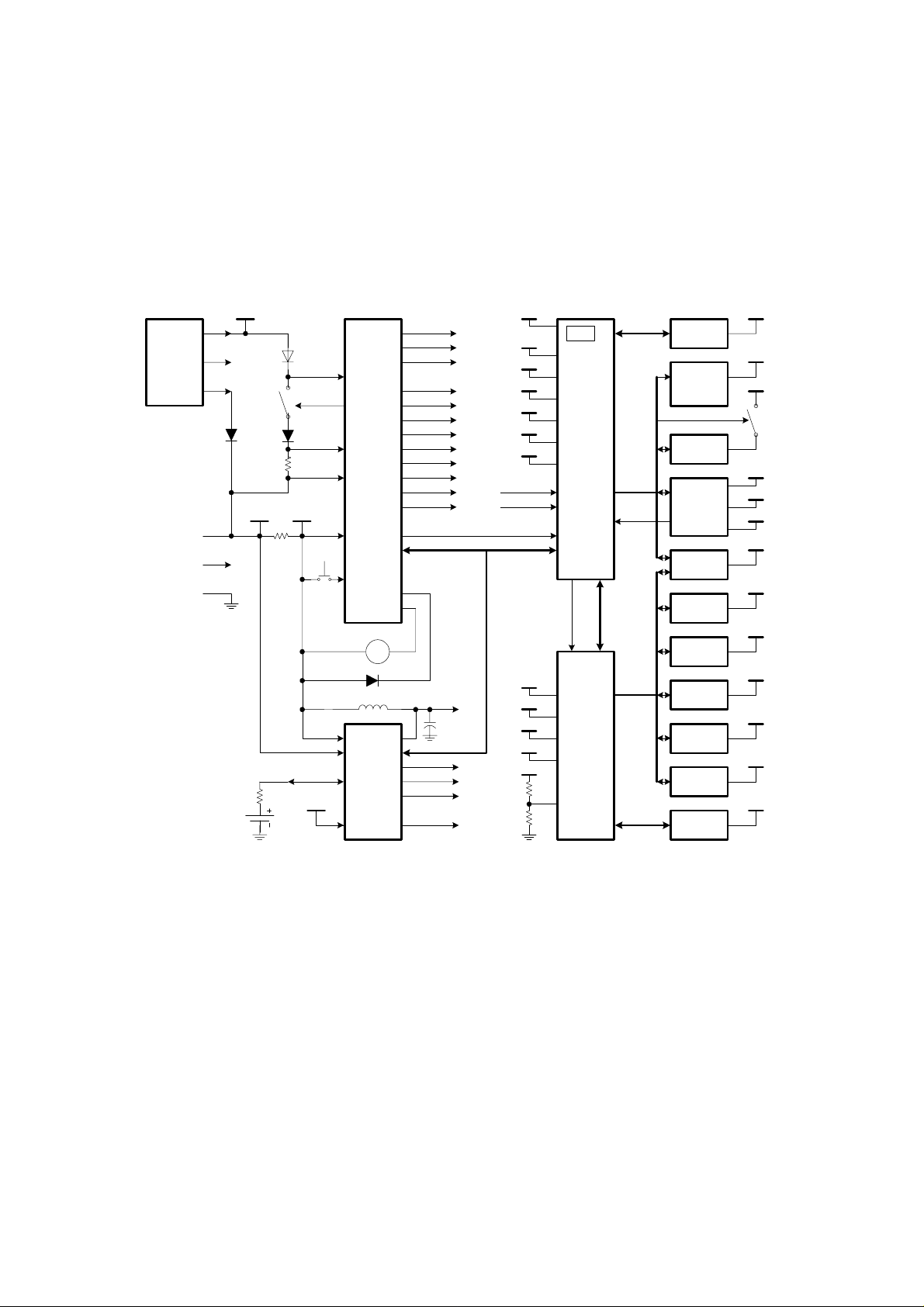
4.8. Power Supplies
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
4.8.1 Introduction
The power management block primarily consists of SM-PWR (U304) and Companion IC (U300). U304 is a highly integrated
power management ASIC with a complete on/off logic and charging control, regulators, LED drivers, 8-ohm speaker and
vibrator driver. The companion IC is an ASIC that complements U304 providing the additional functionality like back-up battery
charging, audio switching including stereo/mono headset, boost converter and additional regulators.
J300
I/O CN
P300
Li-ION
Battery
780
mAH
D303
VBUS
VACC
BATT
TEMP
R327
BT300
EXT_PWR
VBATT
Charging
CKT
D302
Q301
D301
R321
VMAIN
R313
PWR
KEY
VIB
Keypad, Alert, Charging LED
SDBB
U304
SM-
PWR
M
U300
Com-
panion
IC
SDBB
VLBB1
VLBB2
VINT
VSIM1
V28
VSD
VUSB
VANA
VRF1
VRF2
VRF3
RESET_N
I2C and Control I/F
LED
SLED1/2
VIB
DCDCOUT
SENSEOUT
VRTC2VRTC3
VAUDIO
VLBB3
VRTC2
SDBB
VLBB1
VLBB2
VINT
VSIM1
VANA
BATT_TEMP
SENSEOUT
CLK(13MHz, 32kHz)
SDBB
VLBB3
V28
VUSB
VBUS
R252
R251
AP_RST
RTC
U100
SGOLD
Control I/F
IPC and
U200
OMAP
F26M
U102
MEMORY
Backlight
Main/Sub/
Photo
SIM
RF
U201
Bluetooth
Mini-SD
Sub-LCD
Main-LCD
Camera
IrDA
U203
MEMORY
DCDCOUT
Q401
VSIM1
SW
SDBB
VSIM1
VBATT
VRF1
VRF2
VRF3
VSD
V28
V28
V28
V28
SDBB
The Power Management Block consists of the following sections:
1. Power Source
2. Power Control Logic
3. System Power Supply
4. Battery Charging & Monitoring
5. Accessory Detection
4.8.2 Power Source
The main battery is a single Lithium-Ion 780mAH(Li-Ion) cell with 3.7v nominal voltage. The RTC back-up battery is a LithiumIon 0.5mAH coin cell with 3.0v nominal voltage. The charger supported is a 5.6v±0.4v, 700mAH
Figure 4.11: Power Supply and Related Sub-System Block Diagram
− 4-16 −

4.8.3 Power Control Logic
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The power on sequence can be initiated when a valid battery voltage is applied (VBATT>3.1).
One of following conditions start the Power Up sequ enc e.
1. Power key is pushed for more than 1,000 ms
2. Application of a charger voltage EXT_PWR > 4.0V
3. Real Time Clock alarm generated by U100 (SGOLD) RTCOUT=1
The Power Up sequence is as follows:
1. U304 band gap reference is activated.
2. U304 checks VBATT voltage. If VBATT > 3.1 then power-up, Else check for VBATT while power-up event is valid.
3. The following U304 regulators are en abl ed in sequen ce : VRF2, SDBB, VLBB2 , VLBB1, VINT, VANA , VSIM1 , V28, VSD,
VUSB.
4. After U304 VINT is enabled, U300 VLBB3 is also enabled.
5. After U304 VUSB is enabled, U304-41 (INTOUT) will go low followed by U304-48 (RESET_N) going high releasing U100
SGOLD from reset.
6. U100 boot code will determine if the power-up sequence is valid. If valid then provide clock to U200 (13MHz and 32kHz)
and release U100 from reset (AP_RST); Else send ALL_OFF command to U304 to power-down the system.
7. U200 power-up to complete the turn-on sequence.
The power-down sequence of the phone is as follows:
1. Power-down sequence is initi ated by th e dete ction of a v alid SW 428 ON /OFF key press or a low b attery voltag e condit ion
has been detected.
2. U200 determines that a valid power-down sequence was detected.
3. U200 disables both active hardware and software application.
4. After U200 power-down sequence is completed, a command to U100 is sent to disable U304.
5. U100 initiates its power-down sequence then resets U200 and remove clock.
6. After U100 power-down sequence is completed, an ALL_OFF command to U304 is sent to disable all regulators.
− 4-17 −

4.8.4. System Power Supply
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The following is the summary of the power supplies provided by SM-PWR (U304).
Power Supply Description Input Supply Rating
SDBB Memory core and I/O Supply VMAIN 1.80 V ± 0.12 V, 850 mA
(U102, U203)
VLBB1 U100 DSP core supply SDBB 1.50 V ± 0.09 V, 170 mA
VLBB2 U100 ARM core supply SDBB 1.50 V ± 0.09 V, 300 mA
VINT U100 I/O and peripheral supply VMAIN 2.72 V ± 0.10 V, 135 mA
VANA U100 Analog circuit supply VMAIN 2.65 V ± 0.09 V, 220 mA
VSIM1 U100 SIM I/O and SIM card supply VMAIN 2.85 V ± 0.10 V or
VSIM1_SW Switched SIM card supply (On/off VSIM1 1.80 V ± 0.09 V, 22 mA
control by U100)
V28 U200 I/O and peripheral supply VMAIN 2.85 V ± 0.09 V, 200 mA
(Main/Sub LCD, Camera, IrDA)
VSD Mini-SD power supply VMAIN 2.85 V ± 0.10 V, 135 mA
(serially set to 2.85v after powerup)
VUSB U200 USB I/F supply VMAIN 3.10 V ± 0.10 V, 45 mA
VRF1 RF regulated supply VMAIN 2.70 V ± 0.10 V, 260 mA
(serially enabled after power-up)
VRF2 Y500 (26MHz) VCXO supply VMAIN 2.70 V ± 0.10 V, 10 mA
VRF3 U201 Bluetooth supply VMAIN 2.7 V ± 10 V, 150 mA
(serially enabled after power-up)
The following is the summary of the power supplies provided by Companion IC (U300).
Power Supply Description Input Supply Rating
VLBB3 U200 ARM core supply SDBB 1.50 V ± 0.09 V, 300 mA
DCDCOUT 13 V Boost Converter for driving VMAIN 13.00 V ± 0.09 V, 170 mA
Main/Sub backlight LED and
Camera Photo-light
VAUDIO U300 Audio circuit supply VMAIN 2.70 V ± 0.08 V, 100 mA
VRTC3 Back-up battery charging supply VMAIN 3.00 V ± .09 V, 10 mA
VRTC2 U100 RTC supply VRTC3 2.10 V ± 0.06 V, 2 mA
– 4-18 –

4.8.5. Battery Charging and Monitoring
PROVISIONAL ISSUE
The estimated battery capacity is displayed as a LCD battery icon. It is derived from battery voltage and current consumption
measurements made by U100 as shown below:
Icon Status VBATT
Icon Status VBATT
7 4.07 V < VBATT < 4.20 V
6 3.95 V < VBATT < 4.07 V
5 3.85 V < VBATT < 3.95 V
4 3.70 V < VBATT < 3.85 V
3 3.65 V < VBATT < 3.70 V
2 3.60 V < VBATT < 3.65 V
1 3.45 V < VBATT < 3.60 V
Low Voltage Alarm 3.35 V < VBATT < 3.45 V
HW Shutdown VBATT < 2.9 V ± 0.06 V
When a deeply discharged battery is used, a pre-charging circuit is automatically enabled for trickle charging when a charger is
connected. Also the charging (RED) LED is automatically enable even though the unit is not active. Only after the battery has
sufficient charge that it will automatically enter normal charging operation.
Only approved chargers can be used with the handset. By using only approved chargers and the unique Panasonic J300
connector no additional circuitry is provided within the unit to protect from charger voltage exceeding the design limit of 7.0 V.
4.8.6. Accessory Detection
The phone supports detection of an USB data cable through the presence of VBUS in the I/O connector.
– 4-19 –
 Loading...
Loading...