Panasonic X60 Service Manual

EB-X60
ORDER NO. OMTD040201C8
ç 2004 Panasonic Mobile Communications Co., Ltd.
All rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and
distribution is a violation of law.
Personal Cellular Telephone
This service information is designed for experienced repair technicians only and is not designed for use by the general public.
It does not contain warnings or cautions to advise non-technical individuals of potential dangers in attempting to service a
product.
Products powered by electricity should be serviced or repaired only by experienced professional technicians. Any attempt to
service or repair the product or products dealt with in this service information by anyone else could result in serious injury or
death.
Y
WARNING
900 MHz 1800 MHz
Tx Frequency Range: 880 - 915 MHz 1710 -1785 MHz
Rx Frequency Range: 925 - 960 MHz 1805 -1880 MHz
Tx / Rx separation 45 MHz 95 MHz
RF Channel Bandwidth 200 kHz
Number of RF channels 174 374
Speech coding Full rate / Half rate / Enhanced Full rate
Operating temperature -10
°
C to +55 °C
Type Class 4 Handheld Class 1 Handheld
RF Output Power 2 W maximum 1 W maximum
Modulation GMSK (BT = 0.3)
Connection 8 ch / TDMA
Voice digitizing 13 kbps RPE-LTP / 13 kps ACLEP / 5.6 kps CELP / VSLEP
Transmission speed 270.833 kbps
Signal Reception Direct conversion
Antenna Impedance 50
Ω
(External Connector)
Antenna VSWR < 2.1 : 1
Dimensions Height : 75.5 mm
(Excluding antenna) Width : 44.5 mm
Depth : 27.3 mm
Volume 73 cc
Weight 85
g
Main Display LCD : 1286 x 128 pixels, 65,536 colours
Illumination 10 LEDs for Keypad Backlighting (White)
4 LEDs for LCD Backlighting (White)
3 LEDs for Sub LCD (Blue, Green, Orange)
Keys 16-key Keypad, Navigation key, 1 shutter key
SIM 3 V Plug-in type only
External DC Supply 5.8 V
Voltage
Battery 3.7 V nominal, 680mAh, Li-Ion
Standby Time 75 - 220 hrs
Talk Time 1.6 - 7.0 hrs
Talk and standby time will be dependent on network conditions, SIM card, backlight usage
and network condition.
R

i
COMPANY LIABILITY
Every care has been taken to ensure that the contents of this manual give an accurate representation of the equipment.
However, Panasonic Mobile Communications Co., Ltd. accepts no responsibility for inaccuracies which may occur and reserves
the right to make changes to the specification or design without prior notice. The information contained in this manual and all
rights in any design disclosed therein, are and remain the exclusive property of Panasonic Mobile Communications Co., Ltd.
Other patents applying to material contained in this publication:
CP8 PATENTS
Comments or correspondence concerning this manual should be addressed to:
Panasonic Mobile Communications Co., Ltd.
600, Saedo-cho, Tsuzuki-ku, Yokohama, 224-8539, Japan
CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-1
1.1. Purpose of the Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-1
1.2. Structure of the Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-1
1.3. Servicing Responsibilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-1
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-1
2.1. General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-1
2.2. Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-1
2.3. Handportable Main Kits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-1
3. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
3.1. General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
3.2. Controls and Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
3.3. Liquid Crystal Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
3.4. Text Entry (Edit) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-2
3.5. Features Menu Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
3.6. Glossary of Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-6
4. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-1
4.1. Tx Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-1
4.1.1. Frequency Error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-1
4.1.2. Modulation Phase Error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-1
4.1.3. Output RF Spectrum due to Modulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-1
4.1.4. Outout RF Spectrum due to Switching Transients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-1
4.1.5. Spurious Emissions at Antenna Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
4.1.6. Residual Peak Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
4.2. Rx Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
4.2.1. Sensitivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
5. TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-1
5.1. RF Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-1
5.1.1. RF Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-1
5.1.2. Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-1
5.2. Baseband Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
5.2.1. Baseband Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
5.2.2. Summary of Device/Circuit changes to achieve new features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
5.2.3. E-Gold + V3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-4
5.3.4. CPU Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-13
5.3.5. Main LCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-14
5.3.6. IrDA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-14
5.3.7. Polytone IC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-15

ii
5.2.8. Audio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-16
5.2.9. Power Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-17
5.2.10. UI Related Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-21
5.2.11. Power Consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-23
5.2.12. Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-24
5.2.13. External Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-26
6. DISASSEMBY / REASSEMBY INSTRUCTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-1
6.1. General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-1
6.1.1. ESD Handling Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-1
6.2. Disassemby . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-2
6.2.1. Lower Case Assembly and Main PCB Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-2
6.2.2. Upper Case Assembly/Module Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-3
6.2.3. Antenna Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-6
7. REPAIR PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-1
7.1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-1
7.2. Lead Free (PbF) solder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-1
7.3. External Testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-1
7.3.1. General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-1
7.4. Test Equipment Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-4
7.4.1. Equipment Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-4
7.5. Interfaces and Test Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-5
7.5.1. Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-4
7.5.2. LCD Module Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-6
7.5.3. SIM Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-7
7.5.4. Battery Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-7
7.5.5. Test Point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-8
7.5.6. Power On . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-9
8. SOFTWARE DOWNLOAD & ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-1
8.1. FlashTool update from Ver. 2.1 to Ver. 2.2 operation guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-1
8.1.1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-1
8.2. FlashTool update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-1
8.3. FlashTool operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-10
8.3.1. Download software file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-10
8.3.2. Static EEPROM data update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-11
8.3.3. Flash file system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-12
8.3.4. Download customization files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-13
8.3.5. Use ATE control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-13
8.3.6. COM port set-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-13
8.3.7. Start download . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-14
8.3.8. Program exit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-17
8.4. RF Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-19
8.4.1. System Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-19
8.4.2. P-test Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-19
8.4.3. Battery AD / Temperature AD Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-20
8.4.4. Battery Voltage AD Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-20
8.4.5. Battery Temperature AD Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-22
8.4.6. Tansmit Power Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-23
8.4.7. Rxlev Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-28
8.4.8. Data Overwrite Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-30
8.4.9. Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-32

iii
9. REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-1
9.1. Exploded View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-1
9.2. Mechanical Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-2
9.3. Main PCB Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-3
9.4. Upper Face PCB Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-6
9.5. Keypad PCB Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-7
9.6. Hinge PCB Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-7
9.7. Bulk Pack Items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-7
10. BLOCK DIAGRAMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-1
10.1. Block Diagram of Baseband . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-1
10.2. Block Diagram of RF Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-2
11. CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-1
11.1. Circuit Diagram of Main PCB (Baseband) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-1
11.2. Circuit Diagram of Main PCB (RF Band) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-2
11.3. Circuit Diagram of Upper Face PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-3
11.4. Circuit Diagram of Hinge PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-4
11.5. Circuit Diagram of Keypad PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-5
12. LAYOUT DIAGRAMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-1
12.1. Layout Diagram of Main PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-1
12.2. Layout Diagram of Upper Face PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-2
12.3. Layout Diagram of Hinge PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-3
12.4. Layout Diagram of Keypad PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-4
– 1–1 –
1. INTRODUCTION
WARNING
The equipment described in this manual contains polarised capacitors utilising liquid electrolyte. These devices are entirely safe provided
that neither a short-circuit nor reverse polarity connection is made across the capacitor terminals. FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS WARNING
COULD RESULT IN DAMAGE TO THE EQUIPMENT OR, AT WORST, POSSIBLE INJURY TO PERSONNEL RESULTING FROM
ELECTRIC SHOCK OR THE AFFECTED CAPACITOR EXPLODING. EXTREME CARE MUST BE EXERCISED AT ALL TIMES WHEN
HANDLING THESE DEVICES.
Caution
The equipment described in this manual contains electrostatic devices (ESDs). Damage can occur to these devices if the handling
procedures described in Section 4 are not adhered to.
Caution
This equipment may contain an internal battery in addition to the external battery packs. These batteries are recyclable and should be
disposed of in accordance with local legislation. They must not be incinerated, or disposed of as ordinary rubbish.
1.1. Purpose of the Manual
This Service manual contains the information and procedures required for installing, operating and servicing the Panasonic
GSM Personal Cellular Mobile Telephone system operating on GSM Digital Cellular Networks.
1.2. Structure of the Manual
The manual is structured to provide service engineering personnel with the following information and procedures:
1. General and technical information - provides a basic understanding of the equipment, kits and options, together with
detailed information for each of the major component parts.
2. Installation and operating information - provides instructions for unpacking, installing and operating the equipment.
3. Servicing information - provides complete instructions for the testing, disassembly, and reassembly of the product.
Step-by-step troubleshooting information is given to enable the isolation and identification of a malfunction, and thus
determine what corrective action should be taken. The test information enable verification of the integrity of the
equipment after any remedial action has been carried out.
4. Illustrated parts list - provided to enable the identification of all cosmetic and some electrical components, for the
ordering of replacement parts.
1.3. Servicing Responsibilities
The procedures described in this manual must performed by qualified service engineering personnel, at an authorized
service center.
The service engineering personnel are responsible for fault diagnosis and repair of all equipment described in this manual.

– 2–1 –
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1. General
This section provides a general description and kit composition details for the GSM Handportable Telephone system and
optional kits.
2.2. Features
The Panasonic Telephone Model EB-X60 is a high performance, small, light, handset for business and domestic use.
The following features are provided:
1.
Triple Rate, which includes Full Rate, Half rate and Enhanced Full Rate (EFR) speech, codec.
2.
Dual Band, E-GSM 900 and GSM 1800 operation.
Tegic T9 Text Entry.
3.
4. Voice Ringer.
5.
Desktop Hand free function comprising integral echo cancellation and noise suppression.
6.
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) Browser.
7. Backup Battery.
8.
Downloadable polyphonic melody ring tones.
9.
Clock, Calculator and Currency Converter.
2.3. Handportable Main Kit
1
2
3
Figure 2.1: Handportable Main Unit Kit Contents
Item Description
1 Main Unit
2 Battery Standard
3Travel Charger
– 3–1 –
3. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
3.1. General
This section provides a brief guide to the operation and facilities available on the telephone handset.
Refer to the Operating Instructions supplied with the telephone for full operational information.
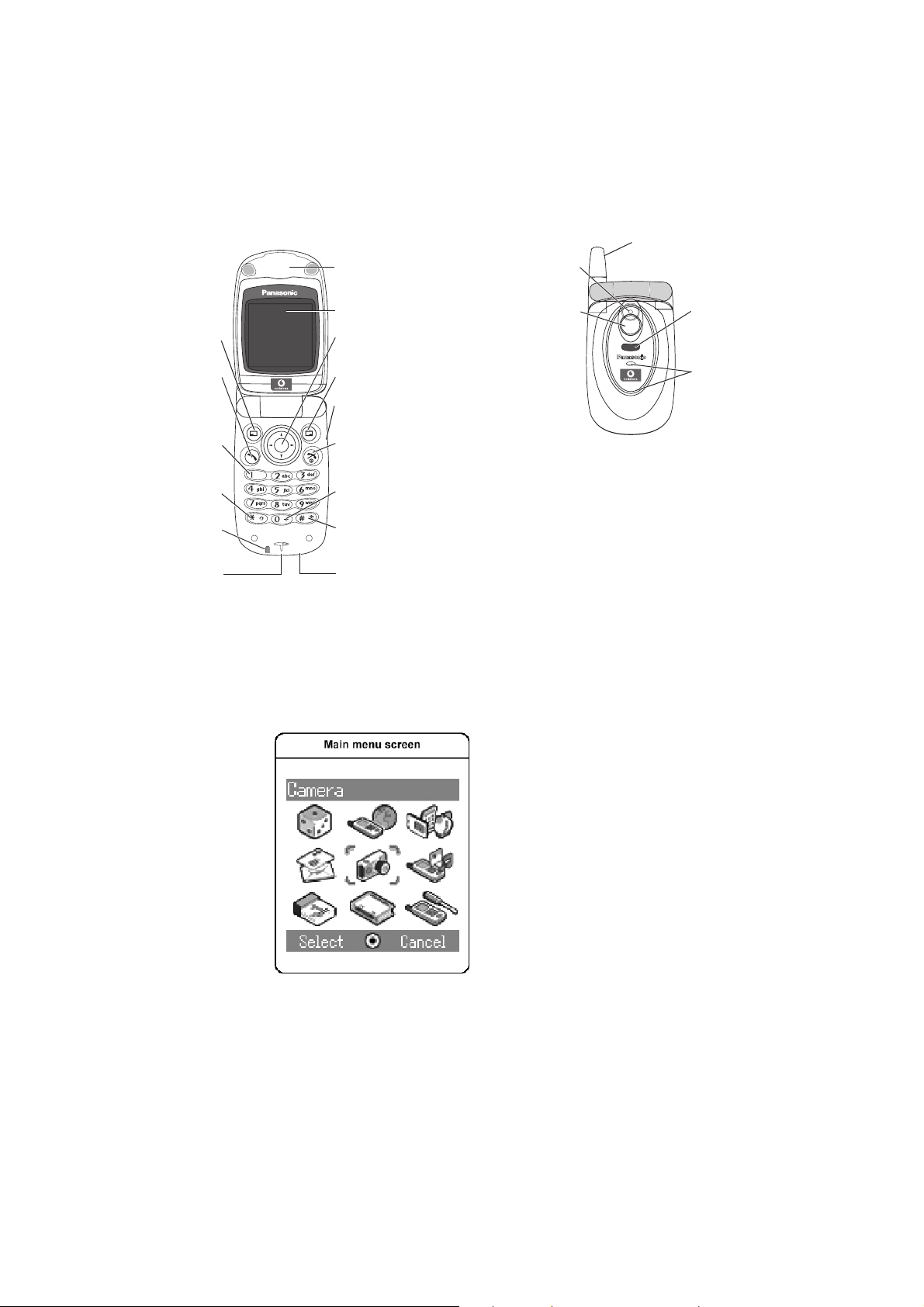
3.2. Controls and Indicators
Antenna
Earpiece
Camera Lens
Left Soft Key
Send Key
To answer a call or to
make an Outgoing Call
1Key/Vodafone mail Key
To press to call Vodafone mail
Asterisk Key International Dialling Prefix Key
Charging Indicator
Lights red during charging
Charging Connector
Main Display
Navigation Key
Selection/scroll/move key
Right Soft key
Multi Function Key
Camera/Shutter/Alert Mute
Power/End Key
Press and hold to switch your
phone on/off
Pause Key/Quiet mode Setting Key
Personal Handsfree Connector
Self Portrait Mirror
To see how you look when
taking a self portrait
Figure 3.1: Location of Controls and Indicators
3.3. Liquid Crystal Display
The telephone handset has a graphical chip on glass display. The following icons are available:
Infrared Port
Illumination
light
Figure 3.2: Liquid Crystal Display
– 3–2 –
3.4. Text Entry (Edit)
You can use alphanumeric characters to enter details into the Phonebook, to create text, email, message, etc.
Text Mode
Key
®
T9 (T9 , T9 or T9)
(Input language : English)
Alternatives . @ / – _ + 0 0/ (Hold)+
Punctuation
A B C (a b c) A B C 2 Γ Ä Å Æ Ç (a b c 2 ä å æ à) 2
D E F (d e f) D E F 3 ∆ É (d e f 3 é è) 3
G H I (g h i) G H I 4 Θ (g h i 4 ì) 4
J K L (j k l) J K L 5 Λ (j k l 5) 5
M N O (m n o) M N O 6 Ξ Ñ Ö Φ (m n o 6 ñ ö ø ò) 6
P Q R S (p q r s) P Q R S 7 Π Σ (p q r s 7 ß
T U V (t u v) T U V 8 Φ Ü (t y v 8 ü ù) 8
W X Y Z (w x y z) W X Y Z 9 Ψ Ω (w x y z 9) 9
Shift / (Hold) Input mode Shift / (Hold) Input mode change
Space / (Hold) Line feed
Delete text / (Hold) Delete all characters
Multi tap
(Input mode indicator : Abc, ABC or abc)
. , ? 1 ! " - : ; @ / * ( ) # + _ = [ ] { } ' ¡ ¿ & % \ ^ ~ | < > £ $ ¥ ¤
Space / (Hold) Character list
)
Space * # / (Hold) Line Feed # / (Hold) Line Feed
Numeric
(Input mode indicator : 0-9)
§
1
7
* / (Hold) Input mode change
NOTE : Displayed characters of T9 vary depending on the selected Input language.
®
– 3–3 –
3.5. Features Menu Structure
1. GAMES
2. MESSAGES
3. CALENDAR
GAMES
SETTINGS
CREATE NEW
INBOX
ARCHIVE
VOICEMAIL
CELL BROADCAST
SETTINGS
MEMORY STATUS
SOUND VOLUME
BACKLIGHT
VIBRATION
ONLINE SERVICE
MEMORY STATUS
RESET
INFORMATION
ON / OFF
READ MESSAGES
OPTIONS
MMS
SMS
MMS
SMS
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ASK
YES
NO
MMS
SMS
MMS
SMS
MMS
SMS
CALL MAILBOX
WEB MAIL
SET MAILBOX NUMBER
4. MY MEDIA PICTURES
SOUNDS
SHORTCUTS
TEXT TEMPLATES
MEMORY STATUS
5. CAMERA
6. CONTACTS CONTACTS LIST
ADD CONTACTS
CALLING LOG
SPEED DAIAL LIST
NEW GROUPS
ADVANCED MY NUMBER
SERVICE NUMBERS
STORED PICTURES
TAKE NEW PICTURE
STORED SOUNDS
RECORD NEW SOUND
CREATE MMS
INBOX (MMS)
CREATE SMS
INBOX (SMS)
PROFILES
ALARM
PHONE
SIM
MOBILE PROFILE
SIM PROFILE
GROUP SETTINGS
MEMORY STATUS
COPY FROM SIM
123
THRUCONNECT
NAVIGATOR
CALLBACK
CALL SCREEN ON
CALL SCREEN OFF
CUSTOMER CARE
DIRECTORY ASSIST
– 3–4 –
7. APPLICATIONS ALARM
SOUND RECORDER
INFRARED
OFF
0:00
ONCE
TYPE1
VOLUME 2
PROFILE
ONCE
EVERYDAY
WEEKDAYS
WEEKEND
PREINSTALLED
MY MEDIA
8. BROWSER
9. SETTINGS PROFILES
PANASONIC BOX
SOUND INCOMING TONE
VIBRATION ALERT
DISPLAY WALLPAPER PREINSTALLED
LANGUAGE
DATA COMMUNICATIONS
GSM NETWORK
OUTDOOR
CAR
NORMAL
QUIET
MEETING
MESSAGE TONE
RING VOLUME
KEY TONE
KEY VOLUME
WARNING TONE
ON
OFF
COLOUR THEME
CONTRAST
DISPLAY LANGUAGE
INPUT LANGUAGE
NEW SEARCH
SELECT NETWORK
SEARCH MODE
PREINSTALLED
MY MEDIA
PREINSTALLED
MY MEDIA
MY MEDIA
AUTOMATIC
MANUAL
TYPE1
TYPE2
TYPE3
TYPE4
CALLS CALL DIVERTS
CALL WAITING
SEND MY NUMBER
CALL DURATION
SECURITY
TIME AND DATE
PIN ENTRY
CHANGE PIN2
FIXED DIAL
CALL BARRING
TIME
DATE
ALL CALLS
WHEN BUSY
WHEN NO REPLY
WHEN UNREACHABLE
CANCEL CALL
STATUS CALL
NETWORK SET
ON
OFF
INCOMING
OUTGOING
ENABLE / DISABLE
CHANGE PIN
ENABLE
DISABLE
BAR OUTGOING CALLS
BAR FOREIGN CALLS
ONLY LOCAL & HOME
BAR INCOMING CALLS
CANCEL CALL
PASSWORD

– 3–5 –
SOUND
TYPE1
INCOMING TONE
MESSAGE TONE
RING VOLUME
KEY VOLUME
KEY VOLUME
WARNING TONE
PREINSTALLED
MY MEDIA
PREINSTALLED
MY MEDIA
TONE1
TONE2
TONE3
TONE4
ON
OFF
VIBRATION ALERT
DISPLAY WALLPAPER PREINSTALLED
LANGUAGE
DATA COMMUNICATIONS
GSM NETWORK
CALLS CALL DIVERTS
ON
OFF
COLOUR THEME
CONTRAST
DISPLAY LANGUAGE
INPUT LANGUAGE
NEW SEARCH
SELECT NETWORK
SEARCH MODE
MY MEDIA
AUTOMATIC
NORMAL
ALL CALLS
WHEN BUSY
WHEN NO REPLY
WHEN UNREACHABLE
CANCEL CALL
STATUS CALL
– 3–6 –
3.6. Glossary of Terms
Term Definition
DTMF Dual Tone Multiple Frequency tones. The numeric keys 0 to 9, and * and # will
generate different DTMF tones when pressed during conversation. These are
used to access voice mail, paging and home banking services.
GSM Global System for Mobile communications. The name given to the advanced
digital technology that the telephone uses.
Home network The GSM network on which subscription details are held.
Hot Key Dial Hot Key Dial allows quick access to numbers stored in the Phonebook of Service
Dial Number list. The source of the Hot Key Dial may be defined by the user or
preprogrammed by the Service Provide. It is most likely to be preprogrammed to
the Service Dial Numbers by the Service Provider.
Lock code Used for security of the telephone. Factory set to "0000".
Message Centre Where messages are sent before they are forwarded on to their destination. The
Message Centre telephone number may be programmed into the SIM or supplied
by the service provider.
Network operator The organisation responsible for operating a GSM network.
Password Used for the control of the call bar function. Supplied by the service provider.
PIN Personal Identification Number used for SIM security. Supplied by the service
provider.
PIN2 Personal Identification Number used for the control of Fixed Dial Memory and call
charge metering. Supplied by the service provider.
PUK/ PUK2 PIN/PIN2 Unblocking Key. Used to unblock the PIN/PIN2. Supplied by the
service provider.
Registration The act of locking on to a GSM network. This is usually performed automatically
by the telephone.
Roaming
Service Dia
Numbers
Service provider The organisation responsible for providing access to the GSM network.
SIM Subscriber Identification Module. A small smart-card which stores unique
Supplementary
service
Wild numbers Spaces in a stored telephone number. When the telephone number is recalled
The ability to use the telephone on networks other than the Home network.
Service Dial Numbers are predefined numbers that allow the user to access a set
of special services provided by the Service Provider. For example billing
information or access to Voice Mail.
subscriber and user-entered information such as Phone Book, Fixed Dial
Memory and short messages. Supplied by the service provider.
Network-controlled GSM functions supported by the telephone. Supplementary
services may only be available on a subscription bases.
pressing a numeric key will fill in a space. This can be used to restrict dialling to a
specific area.
– 4–1 –
4. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
4.1. Tx Characteristics
All data is applicable to E-GSM 900 and GSM 1800 except where stated.
4.1.1. Frequency Error
±0.1 ppm max., relative to base station frequency.
4.1.2 Modulation Phase Error
RMS: Equal to or less than 5 °
Peak: Equal to or less than 20 °
4.1.3. Output RF Spectrum due to Modulation
Offset from Centre Frequency (kHz) Maximum Level Relative to Carrier (dB)
±100 +0.5
±200 –30
±250 –33
±400 –60
±600 to 1800 –60
4.1.4. Output RF Spectrum due to Switching Transients
Offset from Centre Frequency (kHz)
E-GSM 900 GSM 1800
±400 –19 –22
±600 –21 –24
±1200 –21 –24
±1800 –24 –27
Measurement conditions for output RF spectrum measurements:
Frequency Span 0 Hz
Maximum Level (dBm)
Measurement Bandwidth: 30 kHz
Video Bandwidth: 30 kHz (modulation)
100 kHz (switching)
Average (Modulation) over 200 burst
Peak Hold (Switching) over 10 burst
– 4–2 –
4.1.5. Spurious Emissions at Antenna Connector
Frequency Range
100 kHz to 50 MHz – 10 kHz 30 kHz –36 –36
50 MHz to 500 MHz – 100 kHz 300 kHz –36 –36
500 MHz to 1 GHz 0 to 1 MHz 100 kHz 300 kHz –36 –36
1 GHz to 12.75 GHz 0 to 10 MHz 100 kHz 300 kHz –30 –30 (1.0 - 1.710 GHz)
Excl. relevant TX band > 10 MHz 300 kHz 1 MHz –30
E-GSM : 880 MHz to 915 MHz > 30 MHz 3 MHz 3 MHz –30 –36 (1.710 - 1.785 GHz)
DCS : 1710 MHz to 1785 MHz (off trom edge of
-and the Rx bands relevant Tx band) –30 (1.785 - 12.75 GHz)
925 MHz - 960 MHz
1805 MHz - 1880 MHz
Relevant TX band: 1.8 to 6.0 MHz 30 kHz 100 kHz –36 –36
E-GSM : 880 MHz to 915 MHz > 6.0 MHz 100 kHz 300 kHz –36 –36
DCS : 1710 MHz to 1785 MHz
Frequency
offset
Filter
Bandwidth
Approx
Video B/W
Limits (dBm)
E-GSM 900 GSM1800
4.1.6. Residual Peak Power
Equal to or less than 70 dBc (BW = 300 kHz)
4.2. Rx Characteristics
4.2.1. Sensitivity
■ E-GSM 900 Full Rate Speech
The reference sensitivity performance in terms of frame erasure, bit error, or residual bit error rates (whichever is
appropriate) is specified in the following table, according to the propagation conditions.
Channels Propagation conditions
TCH/FS FER 6.742*
class Ib (RBER) 0.42/
class II (RBER) 8.333 120,000 7.5 24,000 9.333 60,000 2.439 8,200
The reference sensitivity level is < –104 dBm.
TU high
Test Limit
error rate
%
α
α
Minimum
No of
samples
8,900 0.122*
1,000,000 0.41/ α20,000,000
Propagation conditionsRAPropagation conditionsHTStatic Conditions
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Test Limit
error rate
%
α
Minimum
No of
samples
164,000
NOTE : 1 < α < 1.6. The value of a can be different for each channel condition but must remain the same for FER and class
1b RBER measurements for the same channel condition.
– 4–3 –
■ E-GSM 900 Half Rate Speech
The reference sensitivity performance in terms of frame erasure, bit error, or residual bit error rates (whichever is
appropriate) is specified in the following table, according to the propagation conditions.
Channels Propagation conditions
TCH/FS (FER) 4.598 13,050
TCH/FS class Ib (BFI = 0) 0.404 148,500
TCH/FS class II (BFI = 0) 7.725 25,500 8.500 20,000 7.600 20,000
TCH/FS (UFR) 6.250 9,600
TCH/FS class Ib ((BFI or UFI) = 0) 0.269 227,000
TU high
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Propagation conditionsRAPropagation conditions
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Test Limit
error rate
%
HT
Minimum
No of
samples
■ GSM 1800 Full Rate Speech
The reference sensitivity performance in terms of frame erasure, bit error, or residual bit error rates (whichever is
appropriate) is specified in the following table, according to the propagation conditions.
Channels Propagation conditions
TU high
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Propagation conditionsRAPropagation conditionsHTStatic Conditions
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
TCH/FS FER 4.478*
class Ib (RBER) 0.32/
class II (RBER) 8.333 600,000 7.5 24,000 9.333 30,000 2.439 8,200
The reference sensitivity level is < –103 dBm.
NOTE: 1 < α < 1.6. The value of a can be different for each channel condition but must remain the same for FER and class
1b RBER measurements for the same channel condition.
α
α
13,400 0.122*
1,500,000 0.41/ α20,000,000
α
164,000
■ GSM 1800 Half Rate Speech
The reference sensitivity performance in terms of frame erasure, bit error, or residual bit error rates (whichever is
appropriate) is specified in the following table, according to the propagation conditions.
Channels Propagation conditions
TCH/FS (FER) 4.706 12,750
TCH/FS class Ib (BFI = 0) 0.426 141,000
TCH/FS class II (BFI = 0) 7.725 25,500 8.735 20,000 7.600 20,000
TCH/FS (UFR) 6.383 9,400
TCH/FS class Ib ((BFI or UFI) = 0) 0.291 206,000
TU high
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Propagation conditionsRAPropagation conditions
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Test Limit
error rate
%
HT
Minimum
No of
samples
– 4–4 –
■ Blocking:
Frequency
±
600 kHz to FR ± 800 kHz
FR
FR ± 800 kHz to FR ± 1,6 MHz
FR ± 1,6 MHz to FR ± 3 MHz
915 MHz to FR - 3 MHz
FR ± 3 MHz to FR 980 MHz
FR ± 600 KHz to FR ± 800 KHz
1785 MHz to FR - 3 MHz
835 MHz to < 915 MHz
> 980 MHz to 1000 MHz
100 KHz to < 835 MHz
> 1000 MHz to 12.75 GHz
100 KHz to 1705 MHz
> 1705 MHz to < 1785 MHz
> 1920 MHz to 1980 MHz
> 1980 MHz to 12.75 GHz
Small MS level in dBµVemf( )
E-GSM 900 GSM 1800
70
70
80
90
90
–
–
113
113
90
90
_
_
_
_
70
70
80
–
–
87
87
–
–
–
–
113
101
101
90
Measurement Conditions:
Wanted carrier is 3 dB above reference sensitivity.
Interferer is CW.
Spurious response exceptions:
Six exceptions are permitted IN band 915 - 980 MHz.
24 exceptions are permitted OUTSIDE band 915 - 980 MHz.
■ Intermodulation Characteristics
Interferer Level ( f1& f2) dBm Interferer Frequencies ( f1&f2 )
49 Wanted frequency= 2f1 - f2,
and [ f1 - f2] = 800 kHz
– 5–1 –
5. TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
5.1. RF Overview
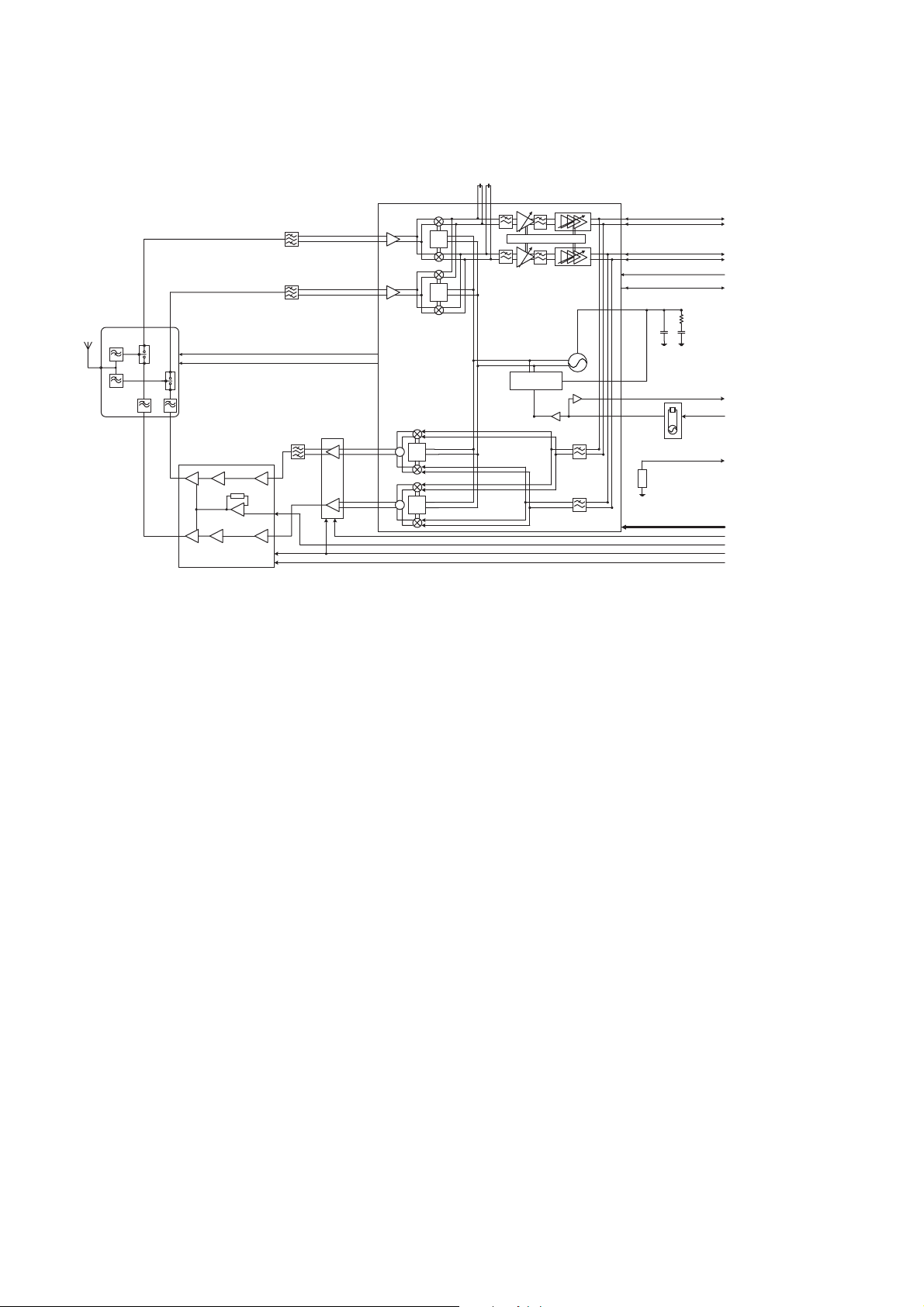
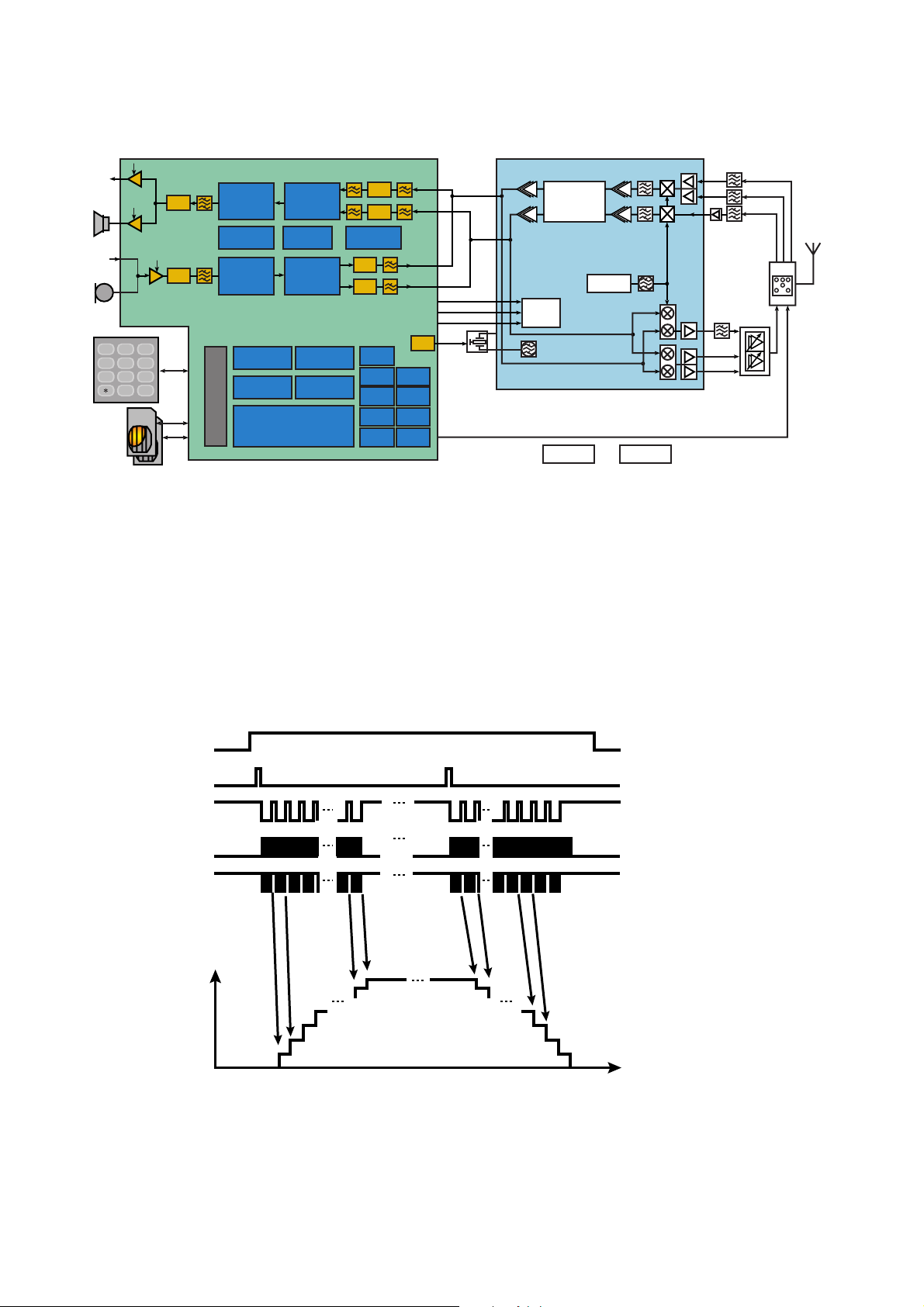
5.1.1. RF Block Diagram
FL201
Rx SAW Filter DCS
DCS1800
1805 - 1880 MHz
EGSM900
925 - 960 MHz
B7821
FL202
Rx SAW Filter EGSM
B7820
π
/2
1/2
π
/2
1/4
DC offset Compensation
U101
Transceiver IC
PMB6256V V1.1
I/IB
Q/QB
PLLON
AM_TRIG
DCS1800
1710 - 1785 MHz
VC2
VC1
S101
Antenna Switch module
LMSP54AA-117
EGSM900
880 - 915 MHz
U103
PA Module
RF3140
FL102
Tx SAW EGSM
EFCH897MMTE7
U102
Tx Limitter IC
PMB2256V V1.1
π
/2
+
1/4
π
/2
+
1/2
3420 - 3980 MHz
RF Synth
U301
TCXO module
MAA****A
26 MHz
13M_BB
AFC
TEMP
CLK/DA/EN
TXON
PALEVEL
BAND_SEL
TXON_PA
Figure 5.1. RF Block Diagram
5.1.2. Functional Description
The receiver is mainly composed of RF chipset and Front-end Module.
The RF chipset for the Dual-band receiver is the Transceiver IC U101 (PMB6256VV1.1) integrated a direct conversion receiver
with DC offset calibration circuitry. The PMB6256 contains the following circuit blocks.
8 EGSM900 and DCS1800 internal LNAs.
8 EGSM900 and DCS1800 down-conversion mixers/demodulators.
8 Channel filtering and base-band signal variable gain amplifiers with programmable gain control function.
The Antenna Switch Module S101 (LMSP54AA-117) is a dual-band antenna switch module. Two external SAW filters EL201
and FL202 (B7820 and B7821) for EGSM900 and DCS1800 are used to improve the isolation between 900MHz and 1800MHz.
The impedance of these two filters' output is 150 Ω balanced.
EGSM900/DCS1800
The input receiving signals into the LNAs coming from the SAWs provide out-band reflection.
However, the receiver is a direct conversion type, there is no need to concern about the image frequency blocking problem.

– 5–2 –
■ Transmitter Description
The main block for the dual-band transmitter is also the Transceiver IC U101 (PMB6256V V1.1) RF chipset.
The Transceiver IC U101 (PMB6256V V1.1)'s modulator is a direct-conversion architecture, so there are no Tx IF frequencies.
The Transceiver IC U101 (PMB6256V V1.1) contains the following Tx blocks:
8 Dual-band (EGSM900/DCS1800) IQ modulators with outputs at final frequencies, and integrated IQ uplink low pass filters.
8 Open collector outputs to the rest of the Tx chains.
The open collector outputs of the Transceiver IC U101 (PMB6256V V1.1) built up with two differential circuits, so called H3 filter,
are led to the Tx Limitter IC U102 (PMB2256 (Lumpi))'s dual-band amplifier/limiter. The Tx Limitter IC U102 (PMB2256V V1.1)'s
limiting function helps to reduce the AM ripple coming from the IQ modulators. The 900 MHz output signal from the Tx Limitter
IC U102 (PMB2256V V1.1) must pass through a Tx SAW filter FL102 (EFCH897MMTE7) before entering into the PA Module
U103 (RF3140) in order to ensure Tx noise in Rx-band satisfy GSM specifications. For 1800 MHz, the 11.10 specifications are
not very severe, so no SAW filtering is needed here. The signals are then attenuated through two attenuators to meet the drive
levels of the PA Module U103 (RF3140). Power control is managed through the control line PALEVEL.
Harmonics coming from this PA will also be removed inside the Front-End Module.
■ Synthesizer Description
The EB-X60's synthesizer is included in The transceiver IC U101 (PMB6256V V1.1). The internal VCO operates from 3.42 GHz
to 3.98 GHz, thus it is equivalent to 2 and 4 times of the DCS and EGSM frequencies. The registers, counters and phase
detectors for this synthesizer are included in The transceiver IC U101 (PMB6256V V1.1).
To meet GPRS's lock-up timing, the Transceiver IC U101 (PMB6256V V1.1) is included a switched frac-N and integer-N counter.
Also, it is included the facility for the switched bandwidth loop filter.
The TCXO module U301 (MAA3259A) generates 26 MHz in order to provide the reference clock to the transceiver IC and
base-band portion. As generated signal's frequency is changed by temperature, AFC functionality that base-band IC provides
control voltage and keeps frequency within a certain range is supported.
Moreover, there is a thermistor
reported RSSI.
RT101
(NCP15WD683J03RC) which is used for the temperature compensation of PA and the
■ DC Power Supplies
The PA runs directly from the battery and consumes no current when not transmitting. Two regulated 2.8 V lines
(RF2V8, VCC_VCXO) are provided for the rest of the RF circuitry from the
■ Antenna
Fixed helical typed antenna is utilized for EB-X60. Its length is 16 mm and located at the top of the lower unit.
It covers 900 MHz and 1800 MHz.
U2006 (PMB6810 V1.83
(E-POWER)).
– 5–3 –
5.2. Baseband Overview
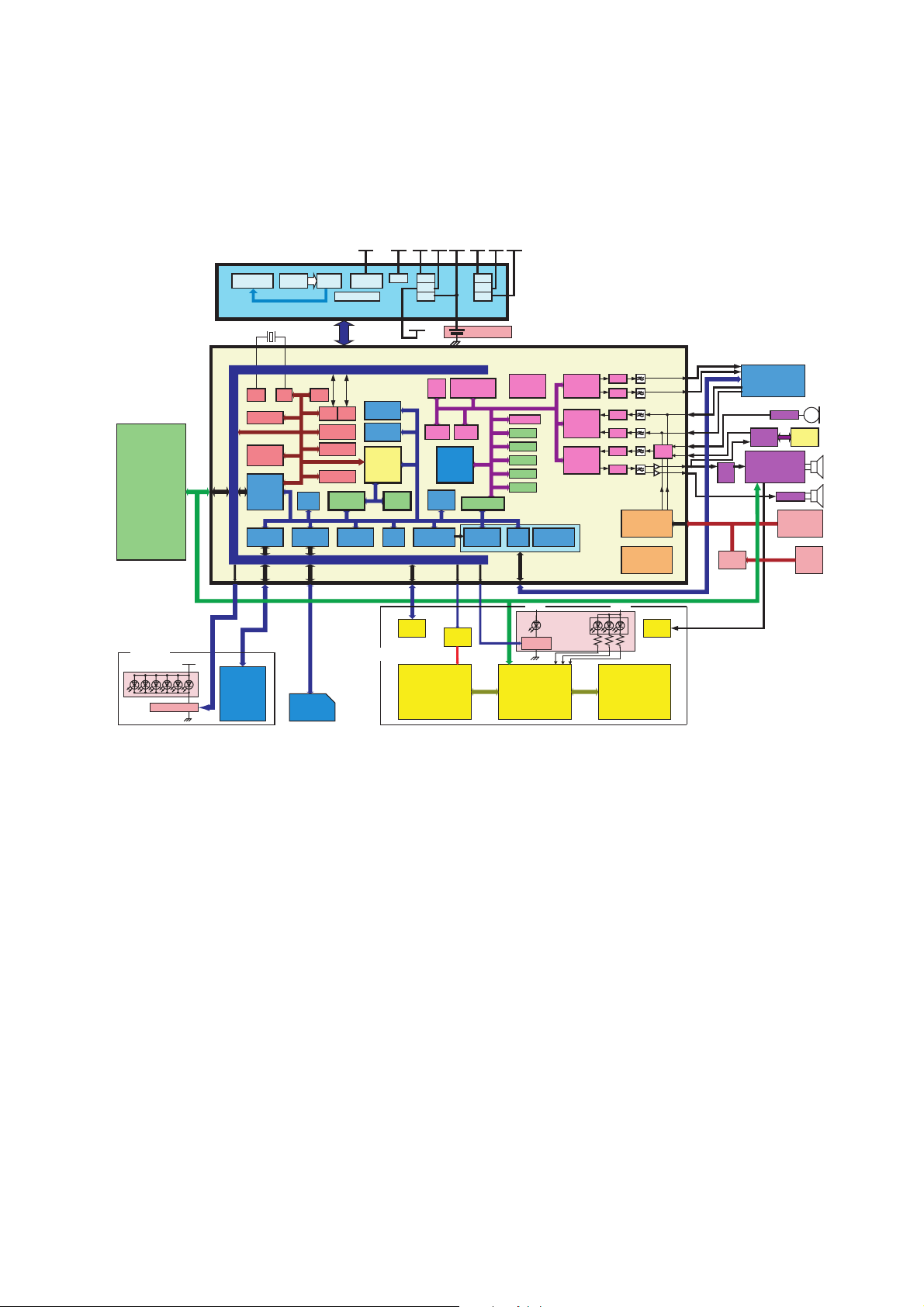
5.2.1. Baseband Block Diagram
The EB-X60 Baseband is based around a GSM chipset developed by Infineon chip set. The Infineon chipset consists of 2 chips,
one is a signal processing chip with DSP and CPU included the analogue baseband (e.g. RF, Audio, SIM), and the other is
U2006 (E-Power) which manages power supply and charge control.
U2008
MC-26426312-X
128-Mbit Flash
(64M+64M)
+
32-Mbit pSRAM
KEY Unit
KEY LED Curcuit
U2006
E-Power (PMB 6810)
A[23:0]
D[15:0]
KP[9:0]
VBAT
Key Pad
CHG
Charge Control
Osc.
CAPCOM
Multicore
Debug
Support
External
Bus & Port
Controller
Keypad
Interface
RTC
I2C bus
Interface
I2C
SIM card
Interface
SIM
VSSPW VANA VINT V3V VRTC
SDBB
Control
(Step-down)
Reference
I2C Bus
16 bit I/O Ports
SSC
ASC
ASC
0
1
GPT1/GPT2
Watchdog
Management
MMCI
ID Register
SRAM
256k x 8
GPRS Unit
Upper Unit
Clock
Generation
Power
MCU
C166S
LANA LINT
LSIM
LRTC
VSIM
PRAM
1k x 16
LPSA
System Timer
ASC0
DS3001
IrDA
GP2W0118YPS
Color LCD
128x128
STN 65Kcolor
F-51736GNCJ-MLW-AA
I2S
DSP
Timer1
Interface
GSM
OPTREX
Comm.Interface/
OAK78 DSP
Bus
Unit
Step up
DC/DC
LRF1
LRF2
LRF3
uCapacitor
DSP Serial
DAI
DSP
Timer2
Shared Memory
RF Control
VLED
D[7:0]
8080 I/F
VRF2 VRF3VRF1
Viterbi
HW
Accelerator
Cipher Unit
P ROM
P RAM
Y RAM
X RAM
X ROM
RF Control Block
RF Output
AFC
Power Control
Unit
VCHG VLOG
D[7:0]
A[2:1]
CHG LED
Curcuit
Companion IC
S1D13713B00B100
U2001
E-GOLD+ V3 (PMB 7850 V3)
DAC
GMSK
Modulator
DAC
Baseband
ADC
Filter/
Cordic-
ADC
Processor
ADC
DAC
Switch Matrix
Battery & Temp
Measurement
TAP Controller
JTAG
Boundary Scan
MUX
Voiceband
Filters
RX and TX
VIB
LBV10L-002
Camera
D[7:0]
Module
CIF CMOS
I2C Bus
SPK
Circuit
Charge
Circuit
RF Block
MIC Circuit
PHF
Circuit
U2011
Melody Gen.LSI
YMU759-QE2
REC Circuit
PHF
Battery
DC
Jack
Figure 5.2. Baseband Block Diagram
5.2.2. Summary of device/circuit changes to achieve the new features
■ Baseband Chipset U2001 (E-Gold + V3 / E-Power V1.83)
EB-X60 baseband block mainly consists of new baseband chipset IC2001, E-Gold + V3 and E-Power.
E-Gold + V3 is used C166S processor core with operating frequency up to 52 MHz. E-Gold + V3 is included the OAK DSP
core with operating frequency up to 78 MHz. Most of the digital sections are integrated in this chip, including C166S and
OAK core. E-Gold uses 0.13 µm process.
And also, E-Gold has the analogue interface of RF and audio. In previous chip set, these function is integrated the analogue
baseband LSI such as Omega, Nausica and IOTA. However, E-Gold + V3 is included the analogue block to save the package
size, die size, and parts price. Baseband analogue sections are integrated in this chip except for the power management and
charge control. The power management and charge control is integrated the E-Power LSI. This chip will take charge of voltage
regulators for baseband and RF block, and battery charge control.
E-Gold + V3 consists internal 2-Mbit SRAM. And EB-X60 will operate with 52 MHz MCU clock.
■ Memory
The ROM/RAM capacity of the EB-X60 external memory U2008 is 64-Mbit Flash + 64-Mbit Flash + 32-Mbit mobile SRAM.
A 3-chip stacked MCP (Multi-Chip Package) is used. The 2-Mb E-Gold + V3 internal SRAM is required together with the
external SRAM U2008.

– 5–4 –
■ Power Source
EB-X60 uses a 680 mAh Lithium-ion battery pack.
■ Main Colour STN LCD
A 65536 colour 128 x 128 pixels full-penetration STN LCD module by Optlex shall be adopted for the main LCD.
A S6B33B1 chipset is used for the LCD driver.
■ Integrated Camera
As one of the most characteristic features of the EB-X60 design, an integrated digital camera is introduced.
A CIF (352 x 288 pixels) size CMOS camera module. This camera module does not have an integrated SRAM nor a JPEG
encoder.
■ 16 polyphonic Melody Ringer
A new Melody generator IC ; U2011 YMU759B is used for the enhanced 16 polyphonic Melody ringer function with ADPCM.
Main features of the melody generator IC are as follows ;
8 16 multi-sounds
8 ADPCM decode function (possible to mix-play with melody data)
8 FIFO (512 byte for MIDI, 256 byte for ADPCM) and sequencer installed
8 0.4 W speaker amplifier integrated
■ IrDA
The IrDA transceiver function is added to EB-X60 to enable wireless data exchange with PCs and other handsets.
The IrDA DS3001 device used is a GP2W0118YPS.
■ RTC
EB-X60 has RTC function in U2001 E-Gold + V3 chip to provide time and calendar information, there is no need of an external
RTC IC. The RTC has following function.
Time counter (SEC, MIN, HOUR, WEEK, DAY, MONTH, and YEAR)
Daily/Weekly Alarm control
Time constant interrupt generator
High accuracy time correction control
■ Acoustic Components
EB-X60 will support desktop handsfree feature with DTMF speaker. The DTHF speaker is located in the bottom of the
handheld unit. Ringing tone also use this speaker. DTHF speaker is provided by Hoshiden. Its diameter is 14 mm.
■ Headset with remote switch
Due to the clamshell structure adopted for EB-X60, a headset with remote control switch is added the accessory line-up.
This will enable the user to receive, end or place a call without opening the clamshell of the headset.
5.2.3. U2001 E-Gold + V3 (BASEBAND CHIPSET, DIGITAL AND ANALOGUE CHIP)
The U2001 E-Gold + V3 manufactured by Infineon contains the DSP, CPU, GSM timing functions and many peripheral
functions, this LSI contains the interface circuits to the Audio, RF, SIM and auxiliary analogue functions.
■ DSP (OAK)
The DSP core is a 16-bit (data and program) high performance fixed-point DSP core and is designed for the mid to high-end
telecommunication applications, where low power and portability are still major requirements.
The core consists of a high performance central processing unit, including a full featured bit-manipulation unit, RAM and ROM
addressing units, and program control logic. The core has an improved set of DSP and general microprocessor functions to
meet the application requirements.
The DSP can be clocked at up to 78 MHz via a PLL contained within U2001 E-Gold+ V3.
Debugging access to the DSP is provided via the JTAG interface.

– 5–5 –
■ MCU (C166S)
o
The C166S controller core combines advantages of both RISC and CISC processors in advanced architecture which closely
couples on-chip memory and controller peripherals to the core in a very efficient way. This micro controller works in 32 bits or
16 bits instructions and on 32,16 or 8 bit data. The C166S architecture is based on RISC.
The core uses multiple variable register banks, and single cycle context switch support. The memory space us organised
logically as a van Neumann architecture, but physically the core uses multiple high bandwidth buses and core memory to
increase performance.
■ Memory interface
The U2001 E-Gold + V3 has a physical address space of 128-Mbit / 16-Mbyte. The actual amount of memory needed depends on
the features included in the product. The number of features also has an influence on the required memory access speed.
The memory data bus is 16 bit wide. The SRAM utilizes the BHEQ signal to support both 8 and 16 bits access for more
efficient use. The memory interface of the U2001 E-Gold + V3 supports 1.8 V or 2.6 V operation, allowing flexibility on the choice
memory components. EB-X60 adopted 2.6 V operation because the operation voltage of memory is 3.0 V operation.
The memory interface voltage level is selected by connecting the VDD2.0x supplies on E-Gold + to either V_SD or to VINT.
Maximum
Access Time [ns]
GSM stack, basic features 100 13MHz 0 ws 6.5
GSM stack, advanced features 70 26MHz 1 ws 8.67
GPRS stack 70 26MHz 1 ws 8.67
MCU
speed
Number of
write state
Eff. Bus
speed [MHz]
Memory Mapping:
0x00000
0x60000
0x80000
0x00000
0x60000
0x80000
SYSTEM Int. RAMSYSTEM Int. RAM
nCS4 Polytone ICnCS4 Polytone IC
nCS3 Companion ICnCS3 Companion IC
nCS2 Flash2
0x400000
nCS0 Flash1
0x400000
Initialize nCS2 and Not Use
or
Not Initialize _> nCS0
0x800000
0x800000
0xC00000
0xFFFFFF
nCS1 pSRAM
nCS1 pSRAM
0xC00000
nCS2 Flash2
nCS2 Flash2
0xFFFFFF
Normal Case Alternative Case
Figure 5.3. Memory Map
– 5–6 –
■ Clock Interface
The U2001 E-Gold + V3 clock generation unit is used to generate all major system clocks. There are two clock signals
connected to the clock generation unit.
8 32 kHz clock F32K
8 26 MHz clock F13/26M
The 32 kHz oscillator is used for the Real Time Clock block. As a power-saving feature the 32 kHz clock can be also used for
the MCU domain. The 32 kHz oscillator and the RTC block have its own power supply pads. It has the facility for a back-up
power source for when the main battery, etc. when the main battery is discharged or temporarily removed.
The 26 MHz clock is used as the major U2001 E-Gold + V3 clock reference. An on chip shaper is used to maintain the
low-swing input level on F13/26M. It can be powered-up with a delay (programmable in ECO block) related to the TCXO
power-up. This can slightly reduce overall power consumption.
CLKCTRL Clock Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
13/26 - - AFC32KEN - CPUPRE (2:0)
MHz_IN
76 5 4 3210
- CPUH AFCEN SX52M SXMEN CLKAEN SWCLK PLLUP
PLLUP :
SWCLK :
CLKAEN :
SXMEN :
SX52M :
AFCEN :
CPUH :
CPUPRE [2:0] :
AFC32KEN :
13/26MHz_IN :
CGURST Clock Generation Uint Reset Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
DSPSLOW 0 0 0 0 0 r r
76 5 4 3210
DSPRST :
SIMRST :
RTCRST :
DSPSLOW :
PLL Power Up Bit
PLL Clock Switch Bit
CLKANA Enable Bit
Coprocessor clock enable
Coprocessor clock switch
AFC Enable Bit
Enables 52 MHz operation of the CPU and serial interface
CPU Clock Prescale Factor
AFC clock enable during ECO eco sleeep mode
Configure the CGU for the operation with either 13 MHz or 26 MHz input
00 00RTCRST SIMRST DSPRST
DSP Reset Bit
SIM Card Interface Reset Bit
Real Time Clock Rest Bit
DSP slow-down control bit
The frequency of clk_pll depends on 13/26 MHZ_IN and DSPSLOW refers to the below table.
DSPSLOW 13/26 MHZ_IN Frequency of Input Frequency of Frequency of Frequency of
00 26 MHz 104 MHz 104 MHz 52MHz
01 13 MHz 104 MHz 104 MHz 52MHz
10 26 MHz 156 MHz 78 MHz 52MHz
11 13 MHz 156 MHz 78 MHz 52MHz
Clock F13/26M clk_pll clk_dsp clk_master

– 5–7 –
■ Interrupt and Exception Handler
An Interrupt and Exception Handler is responsible for managing all system and core exceptions.
There are four different kinds of exceptions that are executed in a similar way:
8 Interrupts generated by the Interrupt Controller (ITC)
8 DMA transfers issued by the Peripheral Event Controller (PEC).
8 Software traps caused by the TRAP instruction
8 Hardware traps issued by faults or specific system states
Normal Interrupt Processing
The CPU temporarily suspends the current program execution and branches to an Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) in order to
service an interrupt-requesting device. The current program status [Instruction Pointer (IP), Processor Status Word (PSW),
and in segmentation mode, the Code Segment Pointer (CSP)] is saved on the internal system stack.
A prioritization scheme with 16 priority levels and with 8 sub-levels (8 group levels) specifies the order of multiple
interrupt-request handling.
The maximum number of interrupt requests supported by the core architecture is 112 (configured in steps of 16).
Software and Hardware Traps
Trap functions are activated in response to special conditions that occur during the execution of instructions.
A trap can also be caused externally by the Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI) pin. Several hardware trap functions are provided
for handling erroneous conditions and exceptions that arise during the program execution. Hardware traps always have
highest priority and cause immediate system reaction. The software trap function is invoked by the TRAP instruction, which
generates a software interrupt for a specified interrupt vector. For all types of traps, the current program status is saved in the
system stack.
Interrupt Processing via the Peripheral Event Controller
A faster alternative to normal interrupt processing is servicing an interrupt requesting device by the C166S's integrated PEC.
Triggered by an interrupt request, the PEC performs a single-word or byte data transfer between any two memory locations
through one of 16 programmable PEC service channels. During a PEC transfer, the normal program execution of the CPU is
halted. No internal program status information needs to be saved. The same prioritization scheme is used for PEC service as
for normal interrupt processing.
■ General Purpose I/O
The MCU can configure the pin functionality of most of the pins after reset. Whether those pins show GPIO functionality or
one of the alternate functions ALT0 or ALT1 is defined by the PxCONF and PxALTSEL registers.
Because some of input functions appear on more than one pin, the PINSEL register must specify the respective pin. In case
of ASCx the active input needs to be set by the SxPISEL register of ASCx.
For peripherals which are not able to select or disable their input signal, the corresponding input signal must be enabled by
the INPEN register.
– 5–8 –
General purpose I/O lines usage
E-Gold + V3 pin name Ball EB-X60 use Description
HLDAQ/CC03IO/DSPIN0/T2IN U7 SDIR IrDA sensor enable/disable
T_OUT4/DSPIN0 G14 AM_TRIG Blocker detection in RF LSI
T_OUT5/CCI7IO G17 CAM_INT Companion IC interrupt detection
nCS0 A15 CSFLASH1 CS for FLASH1
nCS1 C16 CSMSRAM CS for MSRAM
nCS2/CC02IOB A17 CSFLASH2 CS for FLASH2
nCS3/EX4IN/DSPIN0/T4EUD D15 CSCAM CS for Companion IC
nCS4/DSPOUT E14 POLY_EN CS for Polytone IC
RESTR4/EX2IN/CLK32K L15 CAM32K CLK for Companion IC
MMCDAT L16 CAM_A[2] Command/data selection for Companion IC
LPAOUT0/CC05IO P8 OPDET Open/Close interrupt detection
CLKSXM/I2SWAO R17 POLYCLK Clock source for YAHAMA melody IC
T_OUT11/CC19IO H15 HOOK_KEY Hook key interrupt detection
CC02IO/nHOLD/DSPOUT1 D16 HS_DET Headset insert interrupt detection
LPAOUT1/I2SCAO U16 KEYLED Key LED control (ON/OFF)
RFSTR3/CC21IO K16 CUR_EN LCD backlight control (ON/OFF)
CC00IO/T3OUT R9 TRI_R Tri-color LED (Red) control (ON/OFF)
MTSR/SDA R16 TRI_B Tri-color LED (Blue) control (ON/OFF)
SSCCLK/SCI U17 TRI_G Tri-color LED (Green) control (ON/OFF)
RFSTR2/CC07IO K15 TOPLED1 Charge LED (Red) control (ON/OFF)
■ Specific I/O
Specific I/Os are reserved for the buzzer and keyboard.
Buzzer is not supported in EB-X60 because ringing tones are sounded through a speaker.
9 PWM
The U2001 E-Gold + V3 supports driving a ringer with a digital PWM signal RINGIN. Earpiece buffer one can be switched into
ringer mode by setting bit RINGSEL in the voiceband part of the analog control register.
The input to RINGIN can be selected by setting the bits RINS0 and RINS1 in the voiceband control register. The ringer input
signal is usually a pulse-width modulated signal which can be programmed conveniently.
9 Keypad Interface
The Keypad gives a 6 x 4 scan matrix allowing 24 keys. The keyboard interface provides a passive key detect function,
where a key press can be detected without activity scanning the matrix, thus enabling a fast key response, even when the
CPU is in idle. The scan period is every 4 msec.
If there is a need to support more than 24 keys, the key matrix can be extended by adding scan column output GPIO's.
The maximum key resistance is 2 kΩ, leakage between any two key matrix lines must be kept below 5 µA.
The End Key is also used to power on the phone it is allocated a complete ROW of the keyboard scan.
EB-X60 supports the VSCL games and keypad assignments for VSCL games refers to the below table.
Keypad assignments
Column 1 Column 2 Column 3 Column 4 Column 5 Column 6
KP0 KP1 KP2 KP3 KP4 KP5
Row 0 Left Up * 7 4 1
KP6 (Game C) (Game A)
Row 1 Send Center 0 8 5 2
KP7 (Fire) (Fire)
Row 2 Right Down # 9 6 3
KP8 (Game D) (Game B)
Row 3 Soft_1 Soft_2 Shutter
KP9 Bottom
– 5–9 –
■ I2C Bus Interface
A standard I2C-Bus interface is implemented, especially to control the Infineon power management device U2006 E-Power.
Operation of U2006 can be controlled completely by a set of control registers. E-Gold + can write to the control register via an
I2C-bus interface. Using the I2C-bus master interface on E-Gold + the system controller can control most functions of U2006
as soon as power is supplied to E-Gold +. Via the same interface E-Gold + can read status registers permitting monitoring of
the state of U2001, e.g. to detect the cause of a reset or whether an external supply voltage for battery charging is applied.
The controller may power-down the system or parts of it by writing to the appropriate control register. Powering down parts of
the system reduces stand-by power consumption of U2006 and may additionally reduce the power-down current of the
attached devices. The I2C-bus interface of E-Power is a pure slave interface. It permits fast-mode operation with clock
frequencies up to 400 kHz as described in the I2C-bus specification. Spike suppression is done by analogue filtering.
Error protection is used to prevent malfunction due to interference under adverse environmental conditions.
For this purpose an 8-bit CRC byte is appended to each command word. Only if the CRC has been verified by U2006 the
transferred command will be executed. Correct reception and execution of the transmitted command can be verified by
E-Gold + by reading back the transmitted CRC byte.
■ Timer / Watchdog Timer
The MCU general purpose timer blocks contain 9 16-bit timers and 16 capture compare channels with pulse width modulation
options. The Watchdog Timer provides programmable time-out periods derived from the CPU clock. If it is not served before
reaching time-out, the Watchdog Timer asserts a hardware reset.
■ UART (ASC : Asynchronous/Synchronous Serial Interface)
The U2001 E-Gold + V3 has two UART ports, ASC0 and ASC1. ASC0 with automatic baudrate detection running up to 3.28
Mbaud and IrDA DS3001 support up to 115.2 kBaud. ASC1 running up to 3.25 Mbaud and with IrDA support up to 115.2
kBaud. EB-X60 uses ASC0 port for serial interface in factory and software download. ASC1 port is used for DS3001 data
transmission.
ASC0 port Assignment
E-Gold + SIGNAL E-Gold+ Ball EB-X60 use I/O
TXD0 M15 Serial interface data TX O
RXD0 M16 Serial interface data RX I
ASC1 port Assignment
E-Gold + SIGNAL E-Gold+ Ball EB-X60 use I/O
TXD1 L14 IrDA interface serial data TX O
RXD1 L17 IrDA interface serial data RX I
nHLDA U7 IrDA module shutdown(L: Active, H:Shutdown) O

– 5–10 –
■ Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
The Chip Card Interface is a customized UART with additional features used for a 3 Volt Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
as specified by ISO 7816. It supports speed enhancement as specified in GSM 11.11 Phase 2+ with baud rates up to
100 kBaud. If the SIM card is disconnected, the chip card interface is able to power down the electrical contacts of the SIM
card automatically.
E-Gold + V3 features a GSM phase 11/11+ compliant SIM interface, providing support for 3 V normal and high-speed SIM
cards. 1.8 V cards are supported inherently, as 1.8 V cards according to specifications, must be able to work also at 3 V.
EB-X60 SIM interface is designed to support 3 V technology SIMs.
■ GSM Timer / RF Control
The GSM Timer and RF control modules are used to control all radio channel timings and to program external devices.
The main goal of the GSM timer is to off-load the MCU from scheduling periodic events within a TDMA frame. It provides
high flexibility in scheduling and executing events using a programmable RAM table and is able to generate timing and trigger
signals as well as interrupts to both the MCU and to the DSP. The RF Control Unit transmits user defined control information
to up to 5 devices via two separate serial interfaces. The RAM of the RF Control Unit holds up to 40 messages and 6 times
16 values for power amplifier ramping. The reference counter of the GSM Timer Unit is the TDMA counter of the TDMA
Compare Unit.
The TDMA counter is a programmable modulo 10000 D 15 bit counter, operated by a 0.461 µsec clock and allows to
measure the length of one TDMA frame (4.615 msec) with a resolution of one eights of a bit. The RAM of the GSM Timer
Unit contains the information at what time within a TDMA frame, one (or more) of the 26 output signals TRIG (25 : 0) change
its value (called timing compare value), and the new values of all output signals at this time. One timing compare value and
the corresponding TRIG (25:0) signal values are called timing event. The RAM operates like a FIFO. The TDMA Compare
Unit compares the last timing compare value of the FIFO with the TDMA counter value. When both values are identical, the
corresponding output values for TRIG (25 : 0) are read out of the RAM and taken over by the external signals. After a match,
the RAM address is incremented by the address generator of the RAM Control Block and the next timing compare value is
address decoder.
T_OUT Name Feature Ball EB-X60 Use Connection
T_OUT0 TXON F16 Transmitter block power control SmartiDC
T_OUT1 PLLON F14 Phase Lock Loop ON SmartiDC
T_OUT2 BAND_SEL F15 Band select GSM/DCS SmartiDC
T_OUT3 NC G16 No Connection
T_OUT4 AM_TRIG G14 AM signal detection SmartiDC
T_OUT5 CAM_INT G17 Camera Module interrupt Companion IC
T_OUT6 NC E17 No Connection
T_OUT7 DISP_RST F17 Display Reset Signal LCD Module
T_OUT8 TXON_PA G15 Power Amplifier ON Power Amplifier
T_OUT9 EP_INT H16 E-Power interrupt E-Power
T_OUT10 GND J14 Ground Ground
T_OUT11 HOOK_KEY H15 Hook Key detection on Personal HF Personal HF
T_OUT12 NC K17 No Connection
■ RTC
Real Time Clock block in U2001 E-Gold + V3 is used for EB-X60. The integrated RTC in the E-Gold + consumes only approx.
1 - 2 µA, hence backup can be provided simply by adding a large capacitance on the RTC supply.
In backup mode (E-Gold + powered off) with only the RTC running, the RTC will operate down to app. 1 V. EB-X60 has very
large backup capacitors. Thus, EB-X60 inserts a series resistor to avoid initial charging of the capacitor and clamps the RTC
supply, preventing the RTC circuit to work during E-Gold + initialization.
EB-X60 uses the micro capacitor instead of backup battery to save the cost and chip mount area.
The Transceiver IC U101 (PMB6256VV1.1) set does not support the backup function in these LSIs, it is necessary to add the
external regulator and power control circuit for backup battery charging.
The backup battery capacity is 50 µAh (2.6 V to 0.0 V discharge).
– 5–11 –
■ Uplink / Downlink I & Q
E-Gold + V3 performs GMSK modulation on Data samples received form DSP at 270 Kbits per second.
The I & Q signals are multiplexed to interface with the SMARTi RF IC.
Earpiece
Ringer
Car Kit
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
0 #
DAC
ADC
Speech
and Channel
Decoding
Viterbi HW
Accelerator
Speech
and Channel
Encoding
E-GOLD + V3
(PMB7850)
Realtime
Clock
GPRS Unit
2-Mbit SRAM
Infineon 16-Bit Core
Equalizer
OAK+
Modulator
C166S
GSMK
GSM
Timer
Power
Mgmt.
ADC
ADC
GSM
Cipher Unit
DAC
DAC
Interfaces
SSC
22
I C I S
DAI JTAG
MMC
Blue
tooth IF
ASC
IrDA
DAC
AFC
CLK
DAT
ENA
26 MHz
I
Q
RF Control
Compensation
Control
Logic
Automatic
GSM 900/1800
Offset
GSM 1900
SMARTi-DC-3
(PMB6257)
SAM
Fast PLL
only for
Tri-Band
Rx/Tx
Power
Amplifier
FLASHDisplay
Figure 5.4. Functional structure of the baseband Uplink / Downlink path
■ Power amplifier Ramp
The PA control ensures that the power ramp up and down sequences are generated. Each power ramp up/down sequence
consists of 16 values of 10-bit length which represents the shape of the rising (falling) edge of the desired ramping curve in
digital form. All 10-bit values will be delivered in serial manner to the power-ramping path of GAIM.
Shape
The Ramp Shape is defined by 16 steps, the shape can be defined differently for rising and falling ramps.
Typically a raised cosine shape will be used as a starting basis of the ramp shape.
TOUT(i)
trig_start
ramp up
ramp down
RFSTR(5)
GAIM_CLK
123 1516 1718 303132
GAIM_DATA
PAOUT
0 V
Figure 5.5. Raised and fall cosine for the PA ramp
– 5–12 –
■ AFC Control
The Automatic Frequency Control (AFC) Unit generates a pulse number modulated (PNM) signal which can be low pass
filtered externally to make a programmable DC voltage for controlling the external VCXO. The PNM signal repeats itself with
a period depending on the number of bits used in register AFCVAL.
For standard applications the upper 11-bit are used and the PNM signal repeats every 2048 13 MHz clock cycles.
(Approx. 158 µsec, frequency 6.35 kHz) For each 13 MHz clock input to the block, the output is driven to "1" or "0".
The ratio of the number of "1"s to "0"s output in a period is proportional to the value of the AFCVAL register. The "1"s are
distributed equally in a PNM period. No pulse deviates more from a perfect distribution by more than 1 input clock period. For
instance if the value 7 is programmed, the leading edge of the seven 77 nsec wide pulses are separated by 293, 293, 292,
293, 292, 293 and 292 clock periods, which is near the ideal value of 292.57. The equal spacing in a period ensures that most
of the energy in the signal appears at harmonics of 6.35 kHz, (in this case 7 x 6.35 kHz), and very little at 6.35 kHz. Because
of this the requirements for the low pass filter are considerably reduced compared to a pulse width modulated output or a
pulse number modulated signal with unequal distribution. In this example which uses 11-bits, the lowest frequency component
in the spectrum of any E-Gold + V3 PNM sequence is 6.35 kHz and has an effective amplitude of less than 1 LSB.
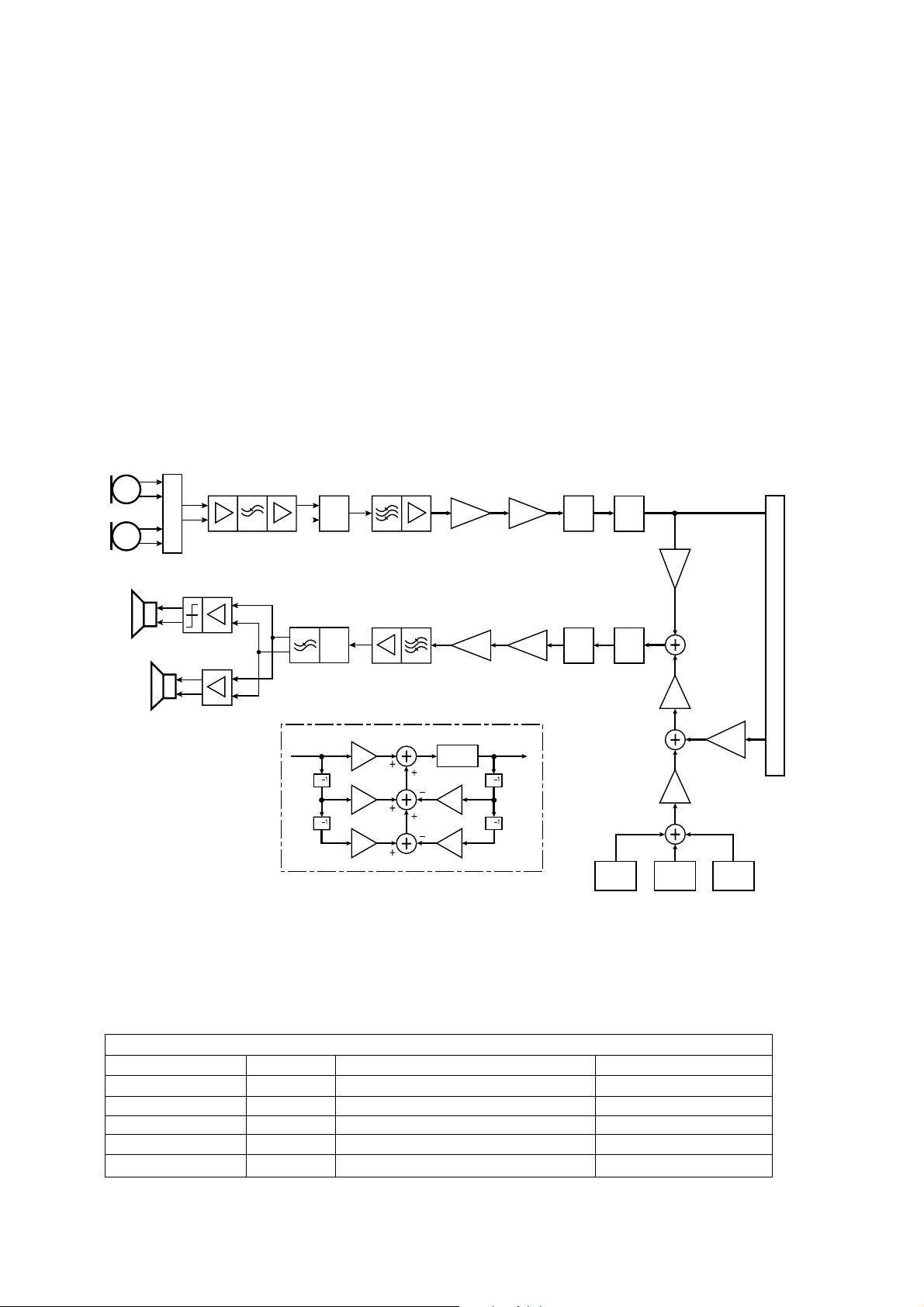
■ Audio
E-Gold + V3 provides the analogue interface for the digital audio samples processed by the DSP in E-Gold + V3.
Voice Uplink and Downlink path
1
MUX
ADC
Scal_In Scal_Mic
Biquad-
2
In #1
Biquad-
In #2
Side_
Tone
1
In #1
Biquad-
In #2
Tone
Generator
#1
Gain_
Out
Tone_
Mix
Tone
Generator
#2
Speech
_Mix
Tone
Generator
#3
VOICEBAND-SAMPLE-BUFFER
DAC
Scal_
Out
Scal_
Rec
Biquad-
2
Biquad-Filter
Input Output
a0
T
∗
a1
2
T
a2
Truncation
to 16 bits
2
∗
b1
b2
T
T
Figure 5.6. Voice ADC and DAC block diagram
■ Auxiliary A/D
E-Gold + V3 provides 5-input 10-bit A/D converters for monitoring. These inputs are available externally to monitor the main
battery voltage, charger voltage and charger current monitoring, ans so on.
The functions of the four external A/D inputs are as follows.
E-Gold+ V3 A/D inputs
E-Gold + input Pin No. Function Values
VBAT P1 Battery voltage
TBAT P2 Battery Temperature
TENV P3 Environment Temperature
TVCO H1 Quartz Temperature No connection in EB-X60
BTEC N2 Battery technology identification No connection in EB-X60
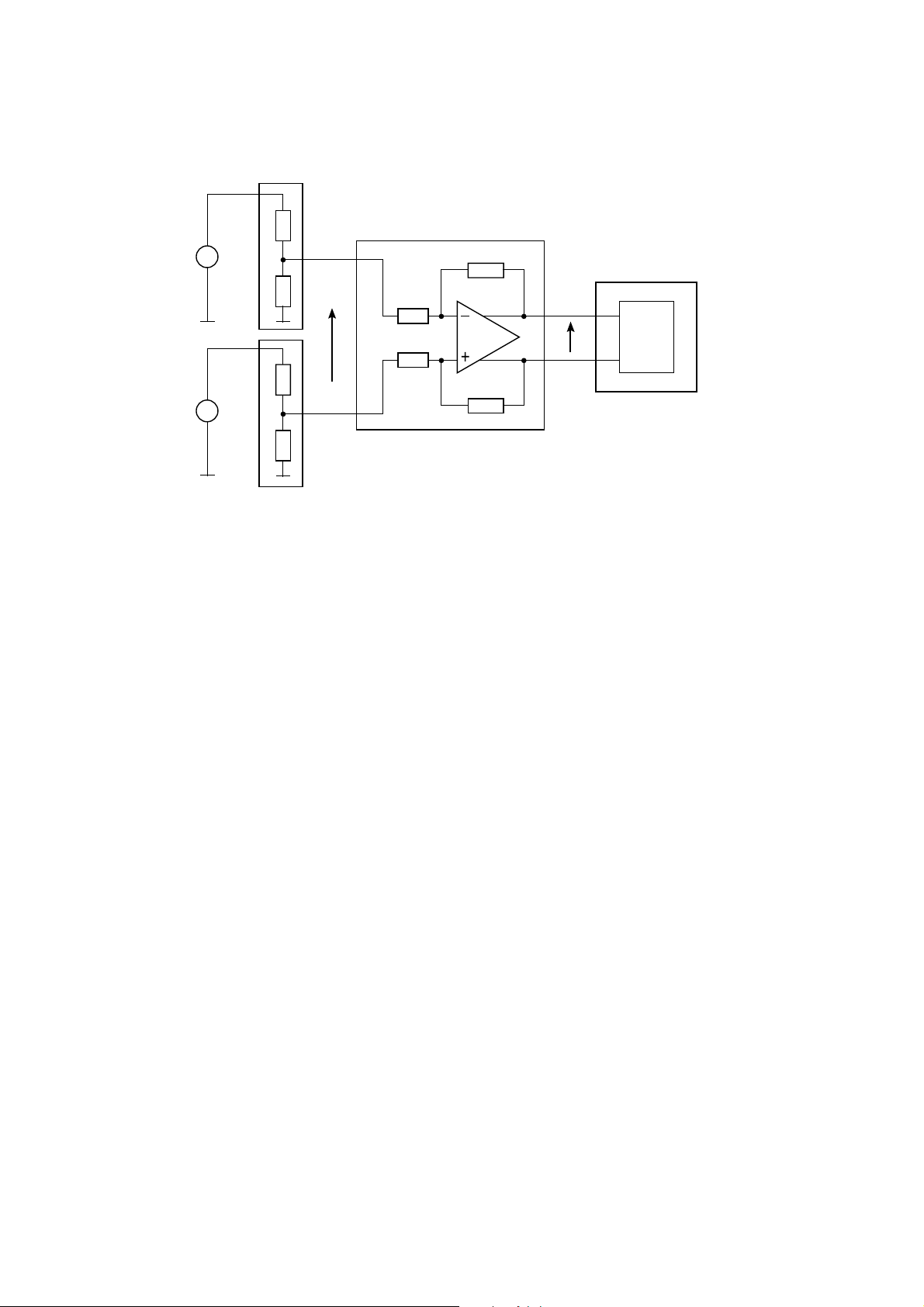
– 5–13 –
The figure shows an AD converter path, starting from the analog inputs, the buffer amplifier, the Σ∆ modulator and digital
decimating low-pass filter. The voltage is divided in an optional resistor divider to adapt to the input range of the
modulators, and the resulting voltage difference to the reference voltage Vref is converted to a 6.5 Mbit/s bitstream at the
output of the
Σ∆ modulator. This bitstream is converted to a 16-bit value in the decimating low pass filter.
R1
Σ∆
Vin
R2R3
V1
R5
R6
V2
Σ∆
R5
Vref
R4
Figure 5.7. AD Converter Path
8 Battery Temperature (TBAT) :
The battery packs used for EB-X60 contain a negative temperature coefficient thermistor. The basic parameters of the
thermistor are as follows:
R25 = 10 kΩ ± 1%
B = 3435K ± 1%
8 Calibration :
And EB-X60 has values of electrical volume for A/D calibration as follows.
Battery voltage : VBAT1, VBAT2
Battery temperature : TBAT1, TBAT2
Environment temperature : TENV1, TENV2
R6
5.2.4. CPU MEMORY
The memory is the second most expensive subsystem in the EB-X60 phone. To aid cost reduction multiple source
components are used where possible.
EB-X60 uses following memory configuration.
128 Mbits Flash memory organised as 4M x 16 + 4M x 16
EB-X60 uses Dual operation Flash memory + mobile RAM 3-chip stacked type MCP (Multi-Chip Package) to reduce chip
mount spaces. 36-Mbit RAM consists of 4-Mbit internal SRAM of E-Gold + V3 and 32-Mbit external mobile RAM on the
MCP device.
■ RAM Timing
This Timing chart is described in E-Gold + V3 specification:
36 Mbits RAM organised as 128k x 32 (Internal SRAM) + 2M x 16 (mobile RAM)
ABRIDGED APPROVAL FORM – PMB7850 Info Sheet
– 5–14 –
■ FLASH Timing
This Timing chart is described in E-Gold + V3 specification:
ABRIDGED APPROVAL FORM – PMB7850 Info Sheet
5.2.5. Main LCD
The LCD assembly is a subassembly comprising of LCD glass and driver chip on flexible PCB with connection to
the Upper unit PCB.
A 128 x 128 pixel graphical display is used to give maximum information.
It can display Chinese and large character sets.
The S6B33B1 display driver is used. This driver has Display RAM.
LCD glass size is as follows.
View area
Effective area
128 x 128 pixels
0.0200 mm
26.092 mm
26.099
30.4 mm
28.100 mm
0.204 mm
mm
0.204 mm
0.013 mm
Figure 5.8. LCD Glass Size
S6B33B1 driver is controlled by setting command register and display data register.
To send data or command to display driver, nCS; provided from companion IC; is used for chip select.
These register are assigned as follows.
Command register: $01C0:0000
Data register: $01C1:0000
These register are write access only.
5.2.6. IrDA
The IrDA module is mounted on the upper unit PCB. EB-X60 supports IrDA file transfer and object exchange, but does
not support IrDA dial-up.
In a special asynchronous mode of U2001 E-Gold+ V3, the ASC supports IrDA data transmissions up to 115.2 KBaud
with fixed or programmable IrDA pulse width. An autobaud detection unit allows to detect asynchronous data frames
with its baudrate andmode with automatic initialization of the baudrate generator and the mode control bits.
 Loading...
Loading...