Panasonic TH-58PX600U, TH-50PX600U, TH-42PX600U, TH-58PX60U, TH-50PX60U Training Manual
...
Panasonic Services Company
TH
9
Gen. Plasma Display Television
National Training
1
Models Comparison
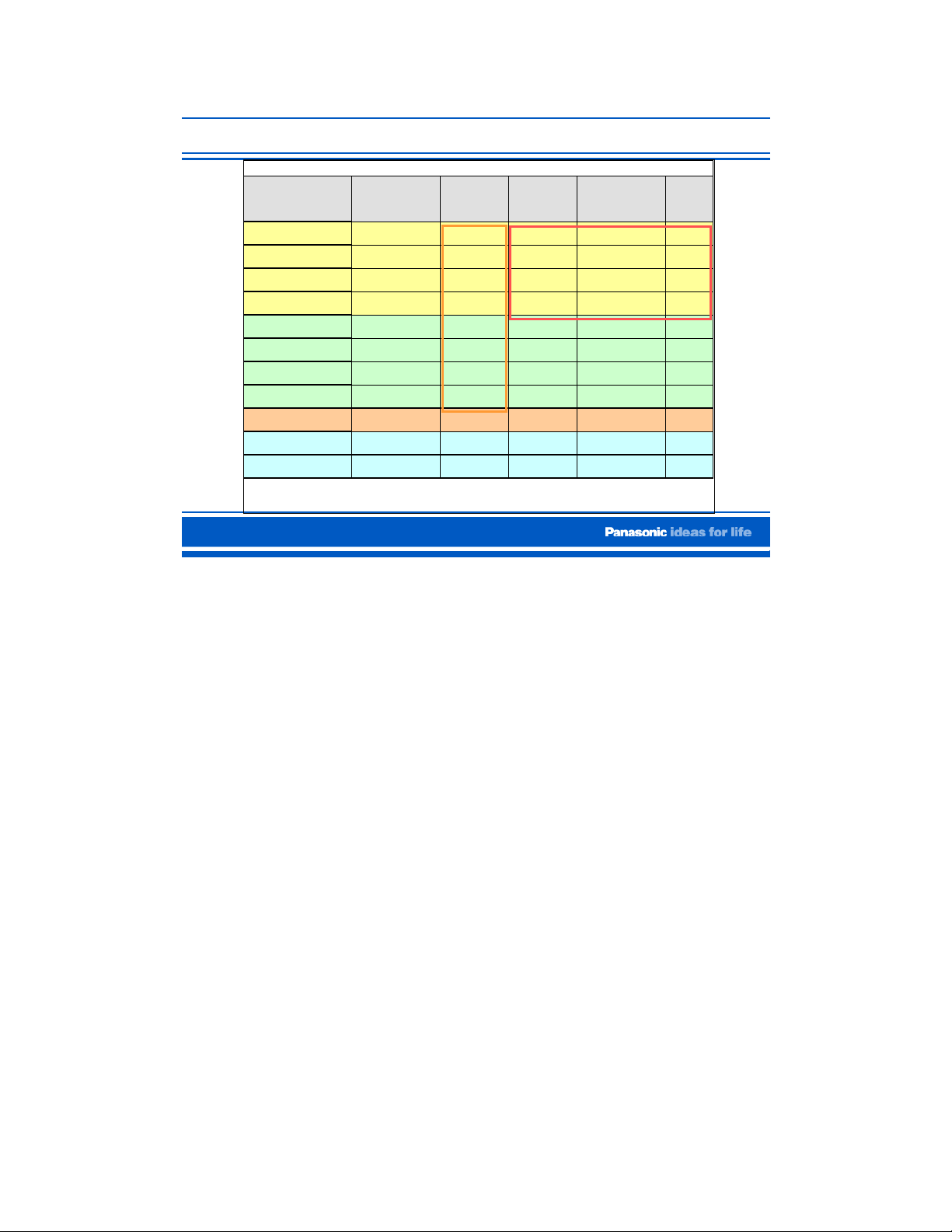
Comparison Table
MODEL Resolution SD Card
TH-65PX600U 1920x1080p
TH-58PX600U 1366x768p
TH-50PX600U 1366x768p
TH-42PX600U 1024x768p
TH-58PX60U 1366x768p
TH-50PX60U 1366x768p
TH-42PX60U
TH-37PX60U 1024x720p
TH-42PD60U
TH-50PX6U
TH-42PX6U 1024x768p
1024x768p
852x480p
1366x768p
TV-
Guide
EPG
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes No No No
Yes No No No
Yes No No No
Yes No No No
No No No No
No No No No
No No No No
CableCARD
slot in the
Tuner
PC
Input
This table is a comparison between the different models of this line of plasma televisions.
Beside having all the features found on the PX60U models, the PX600U models have some
unique features like TV Guide EPG, CableCARD Slot, and PC Input.
Only the 65PX600 has 1080p resolution. All other 2006 models will take a 1080p input but
display it in their native resolution.
2
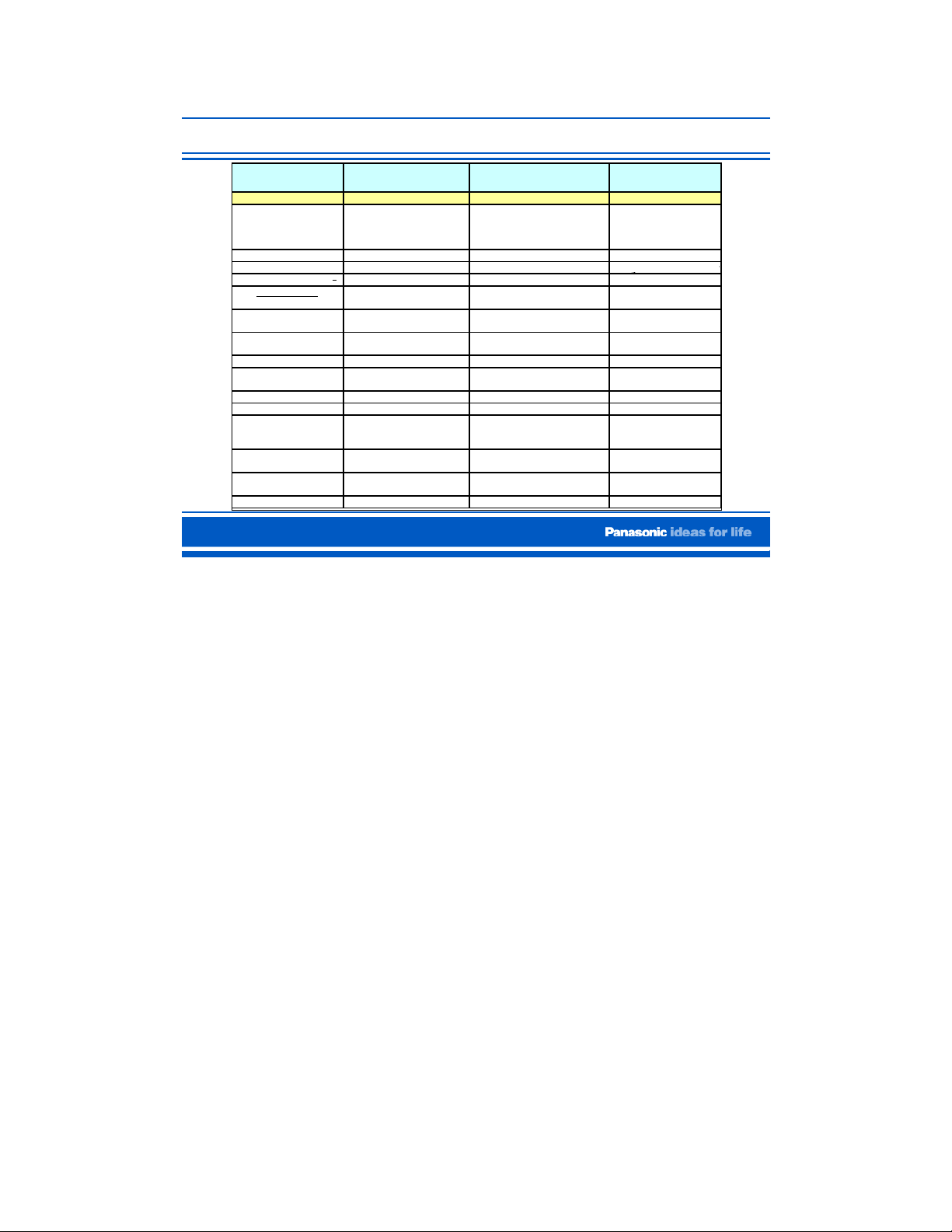
Input/Output (Jacks)
INPUT/OUTPUT:
Tuners
Photo Viewer Yes (SD Slot) Yes (SD Slot) No
SD Card Slot Yes (J PEG Photo Viewer ) Yes (JPEG Photo Viewer) Yes (JPEG Photo Viewer
CableCARD Ready 5 Yes No No
HDMI-HDCP
Interface
Analog Audio Input
(for HDMI)
Composite Video
Input
S-Video Input 3 (2 rear, 1 front) 3 (2 rear, 1 front) 2 rear
Audio Input (for
Video)
PC Input (RGB-VGA) Yes No No
Audio Input (for PC) Yes No No
Component Video
Input [Y, PB(CB),
PR(CR)]
Audio Input (for
Component Video)
Composite Video
Output
Audio Output 1 rear 1 rear 1 rear
TH-42/50/58/65
PX600U
NTSC (Standard analog
broadcasts)
ATSC/QAM (SDTV and
HDTV broadcasts)
2 rear 2 rear 1rear
1 rear 1 rear 1 rear
3 (2 rear, 1 front) 3 (2 rear, 1 front) 2 rear
3 (2 rear, 1 front) 3 (2 rear, 1 front) 2 rear
2 rear 2 rear 2 rear
2 rear 2 rear 2 rear
1 rear 1 rear 1 rear
37/42/50/58PX60U
ATSC/QAM (SDTV and HDTV
TH-
NTSC (Standard analog
broadcasts)
broadcasts)
TH-42PD60U
NTSC (Standard analo g
broadcasts)
ATSC/QAM (SDTV and
HDTV broadcasts)
No
This table shows the input signals available for each line of plasma TV.
3
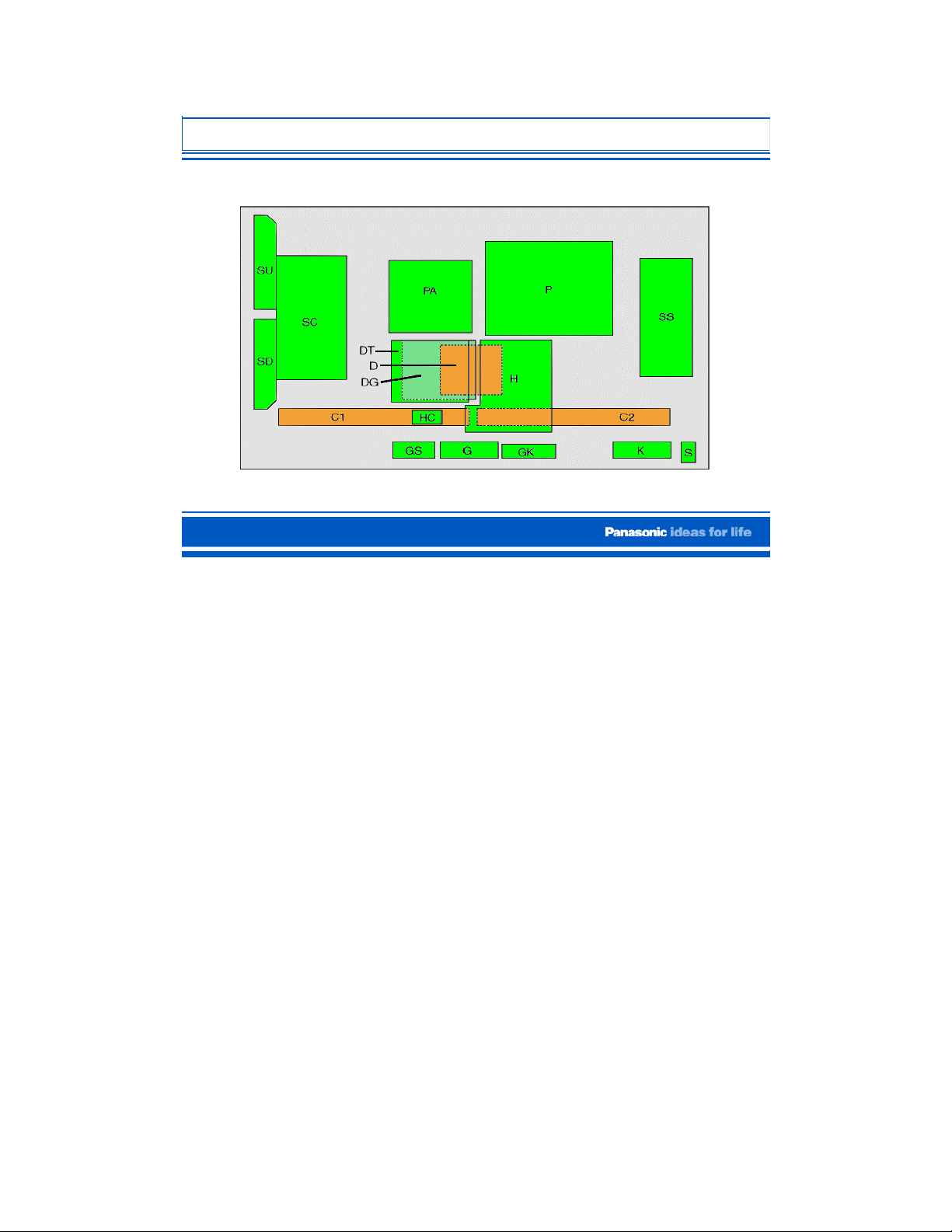
42PX60 Board Layout
4
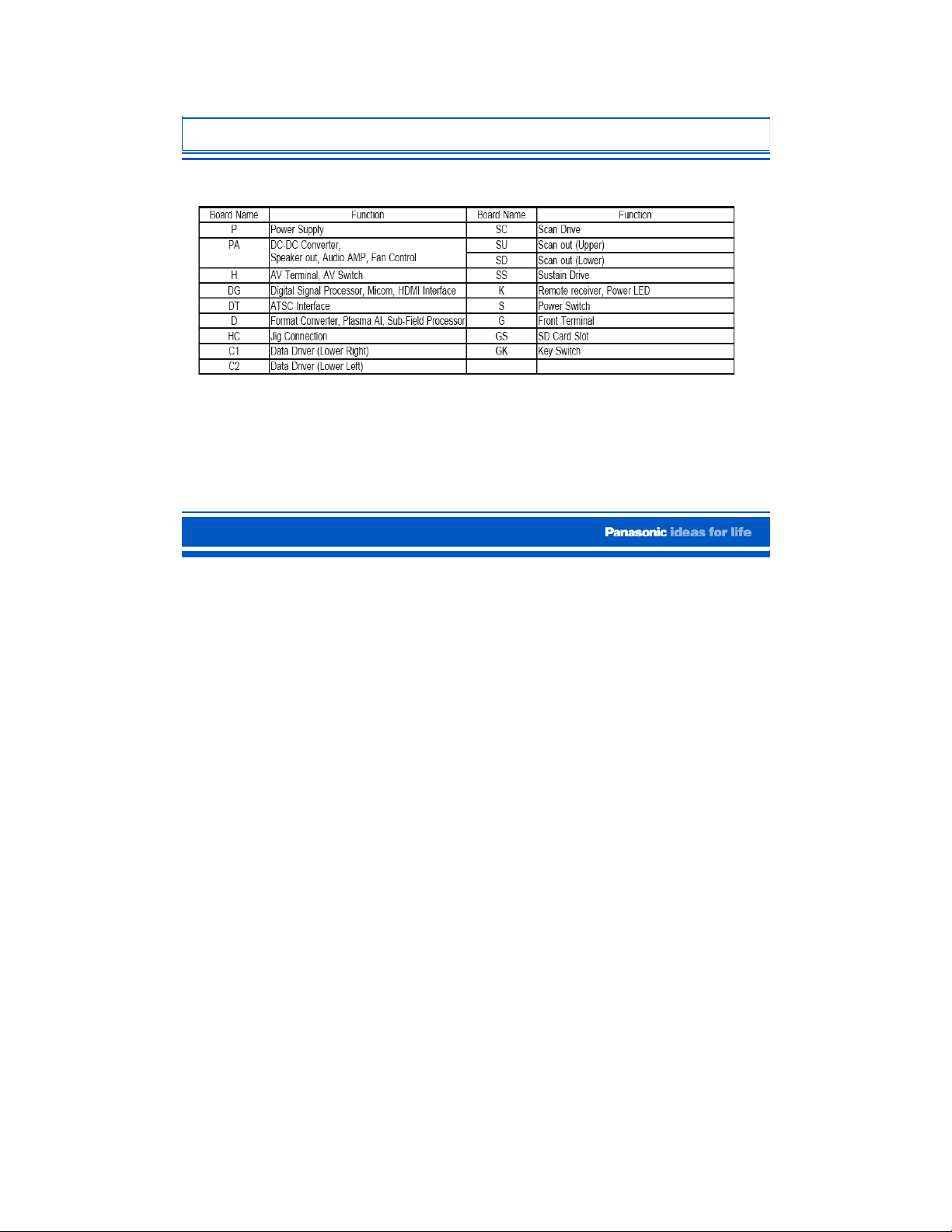
42PX60 Board Description
5

Getting Familiar With The New Plasma TV
Before this generation of plasma TV, Panasonic has always used the double scan system in
their HD plasma TV. In this generation, the 37” and the 42” HD models utilized the single
scan system.
The earlier production of HD 42” models have 3 fans and the HD 50” models contain 4
fans. Normally there will only be 2 fans in the HD 42” models and 3 fans in the HD 50”
models.
6
Differences Between 8thand 9thGenerations
1. No Data Drive Circuit Boards (C Boards) for 37” and
42” models (PD60U, PX6U, PX60U, & PX600U) at
the top of the TV.
2. The PA board is back where it originally was in the 6
Generation models.
3. No PB board (Fan Drive and Audio +B)
4. No Z board (Audio Amp.)
5. The D board is now hidden under the DG board.
6. No DV board
7. Different Digital Tuner (Optical Jack is on the right)
8. The SD and SU boards are flipped, showing the
component side.
th
The differences between the 8thand the 9thgeneration are explained here.
7

D board Location
The purpose of this picture is to show the new location of the D board, which seats below
the DG and the DT boards. Unlike the previous generation, there’s not any access to this
board.
8
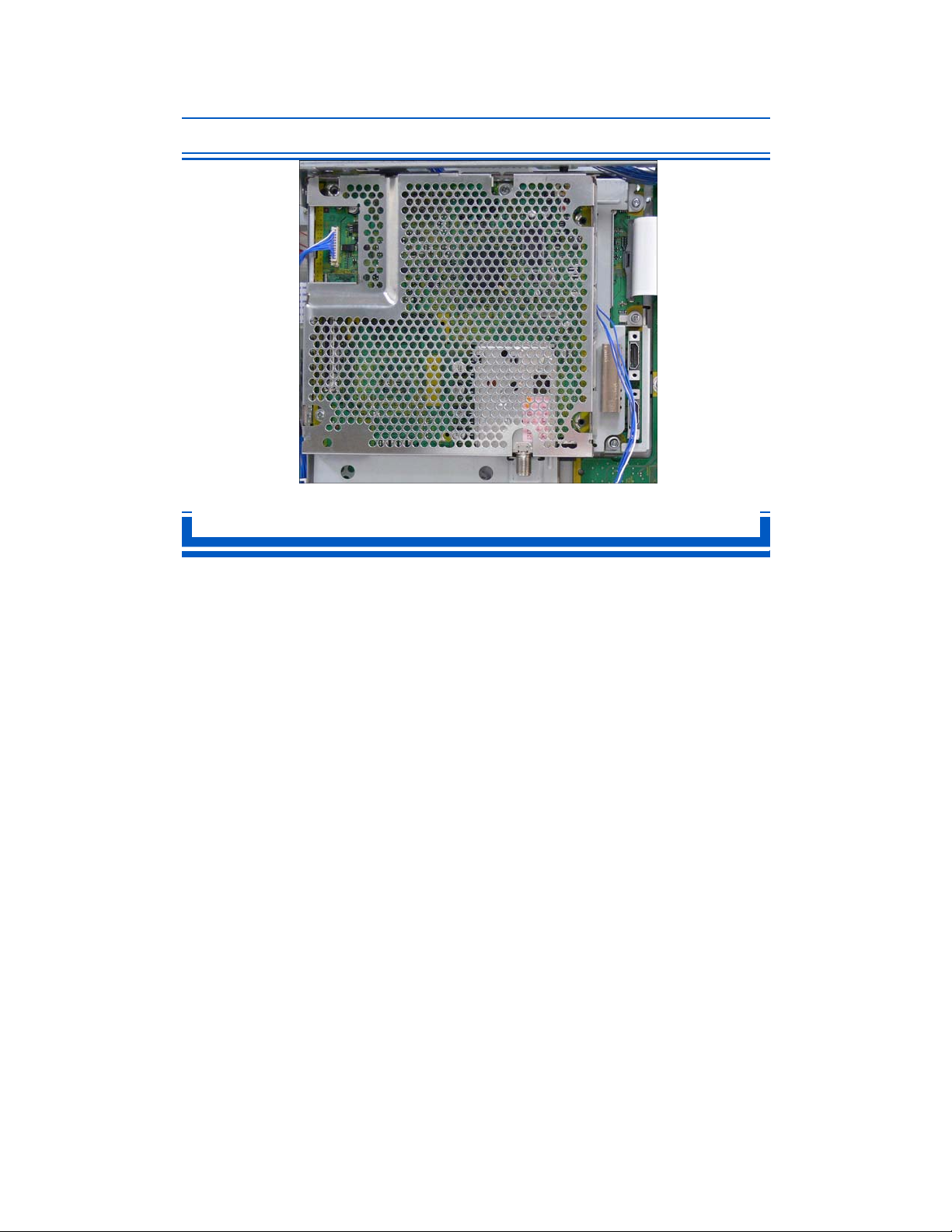
Digital Tuner/HDMI Connector
When an ATSC channel is selected, the output of the DIGITAL AUDIO OUT jack
is Dolby Digital. When a NTSC channel is selected, the output is PCM.
Since the TV does not have a DV board, this picture shows the new location of the HDMI
connectors (2). These connectors are located on the DG board. The previous models only
had 1 HDMI connector.
9

SC, SU, and SD Boards
The component side of the SU and SD boards is now visible without removal.
10

Inputs
This picture shows the CableCARD slot, the Antenna terminal, the HDMI input connectors,
and the PC input connector.
11

HDAVI
HDAVI control
Enables unified control between compatible Panasonic products
connected via the HDMI cable, so you can, for instance, control
multiple compatible Panasonic A/V products from a single
remote.
The new EZ-Sync
This might look like just another so-called universal remote.
But universal remotes are really not 'universal' at all. What
they do is combine a bunch of incompatible controllers into
one case. Playing a DVD with a DTS soundtrack with a
universal remote requires pushing just as many buttons as
using three separate remotes.
12

"With EZ-Sync, you press one button and
• The TV turns on
• The DVD player turns on
• The home theater surround sound system turns
on and automatically selects the right inputs
and settings to use for the DVD."
13
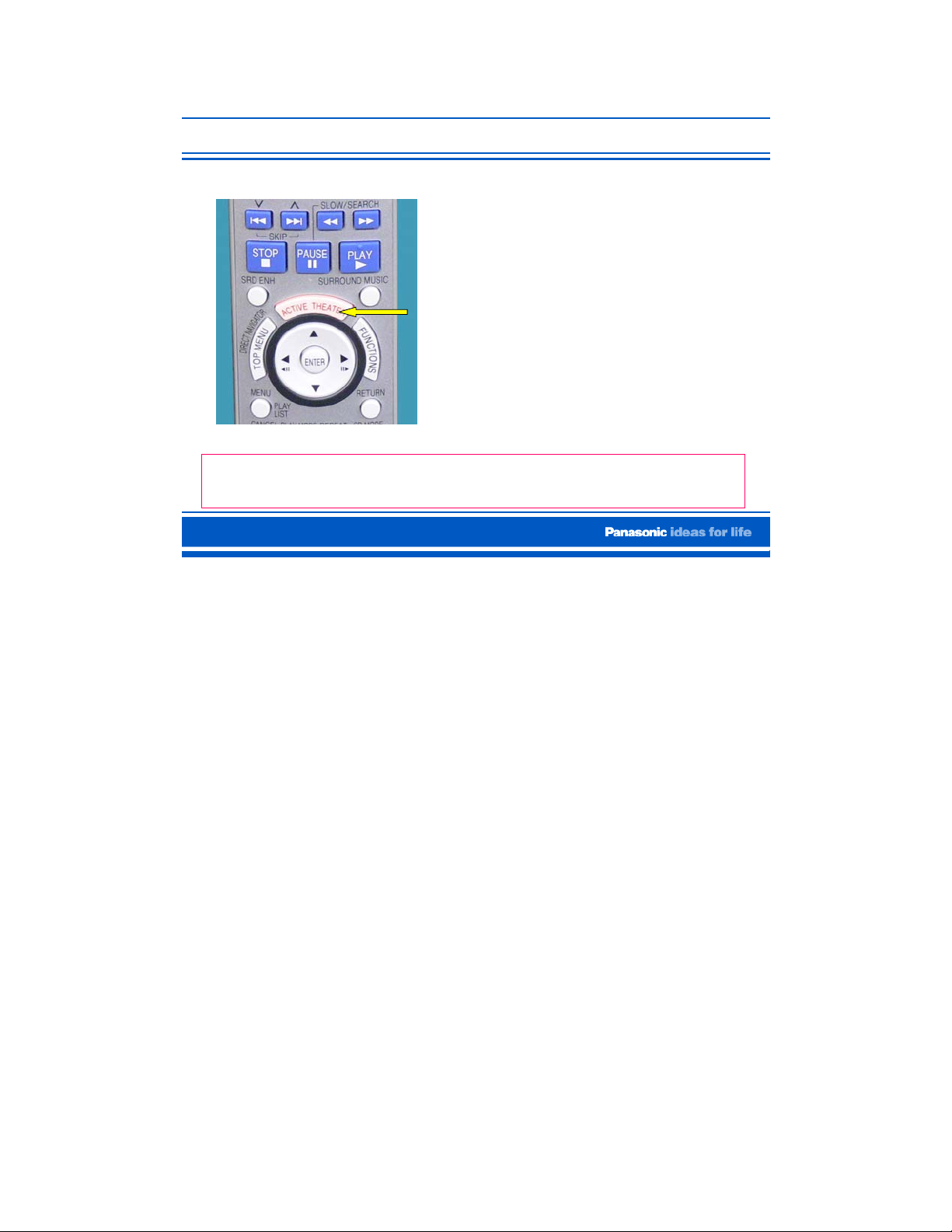
Control with HDMI “HDAVI Control”
Home theater’s Remote Control
• Connect the Compatible
Home Theater (SA-HT940)
using the HDMI connector.
• Turn on the HT and the TV
individually to first establish
communication.
• If there is a disc in the unit
and the “Active Theater”
button on the HT is pressed,
the HT turns on, it starts to
play the disc, and the TV turns
on with HDMI input selected.
In the OI, they refer to the “Active Theater” button as the
“One Touch Play” button.
14
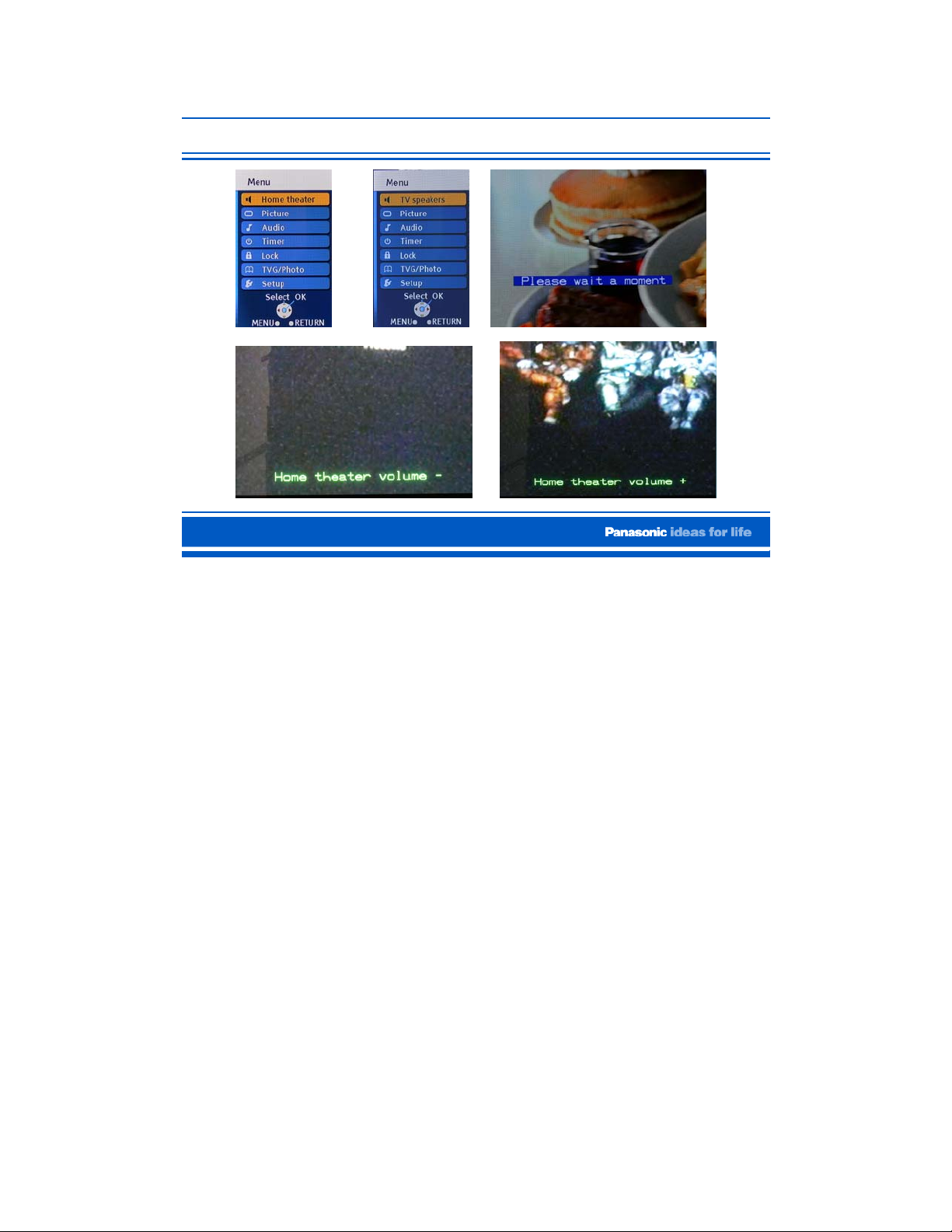
Control with HDMI “HDAVI Control”
Under normal condition, the menu does not show the “Home Theater” option. This option is
added to the menu when the TV is connected to a HDAVI compatible Panasonic home
theater unit.
This feature allows you to control the home theater’s volume by using the TV’s remote
control.
15
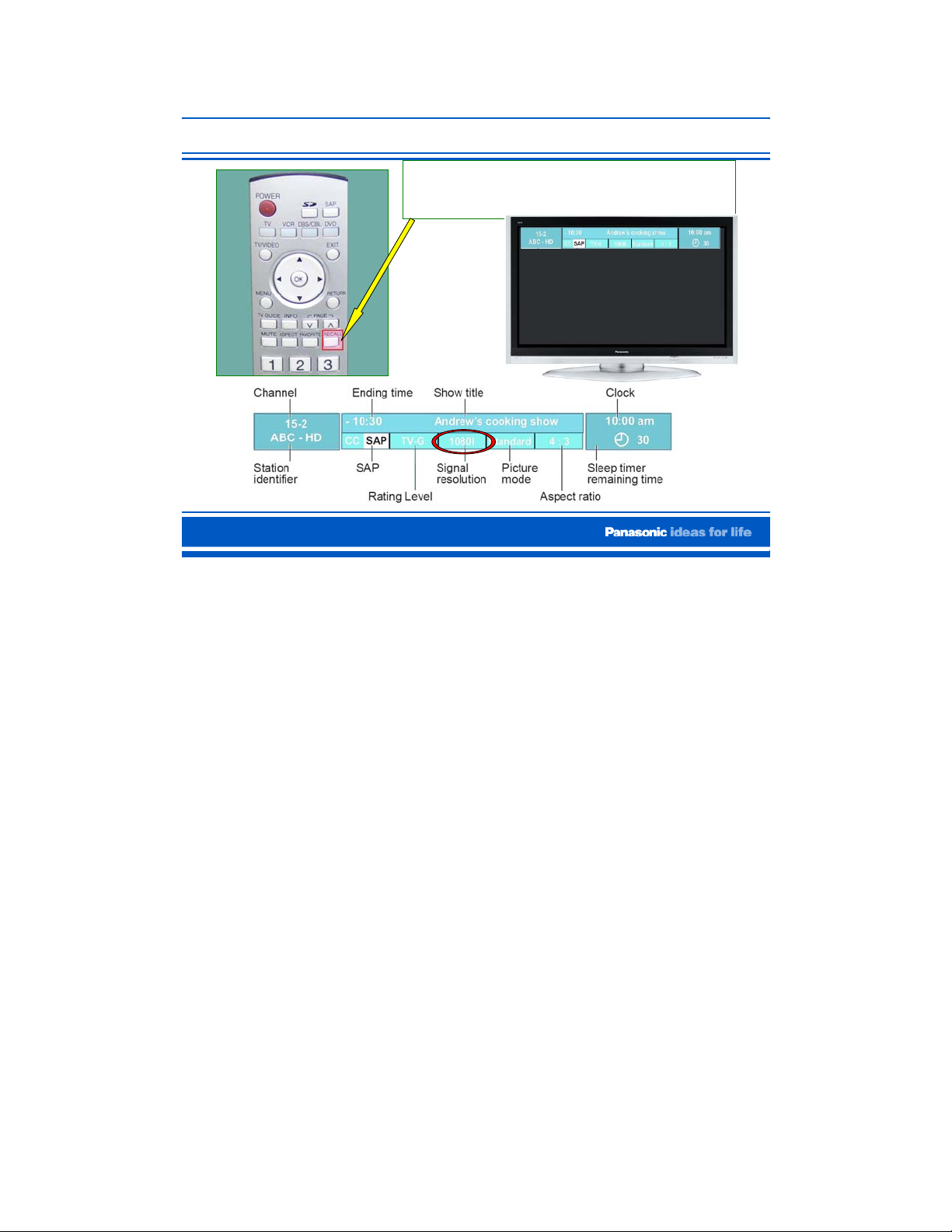
How Do I know the Format of the Signal Received?
Press the “Recall” button on
the Remote Control
In previous models, information that could only be seen in the serviceman mode menu is is
now available by pressing the “RECALL” button on the remote control.
16

SD Card (PX60U &PX600U)
Compliant card type
(maximum capacity)
• SD Card (2 GB)
Mini SD Card (1 GB)
(requiring mini SD
Card adapter)
This light can
be turned off
from the menu
Recycle the Power if the TV won’t read the card
The PX60U and the PX600U models are equipped with a SD card slot for photo viewing
purposes. The maximum card capacity is now 2GB for SD card and 1 GB for mini SD card.
The mini SD card requires a SD card adapter.
The SD card slot on the PX600U models has a light that turns on when a card is inserted.
The menu provides option to turn this feature off or on.
Note: Firmware upgrade can also be done through the SD card slot.
PX600
Only
17

Power Supply
Power Supply
18
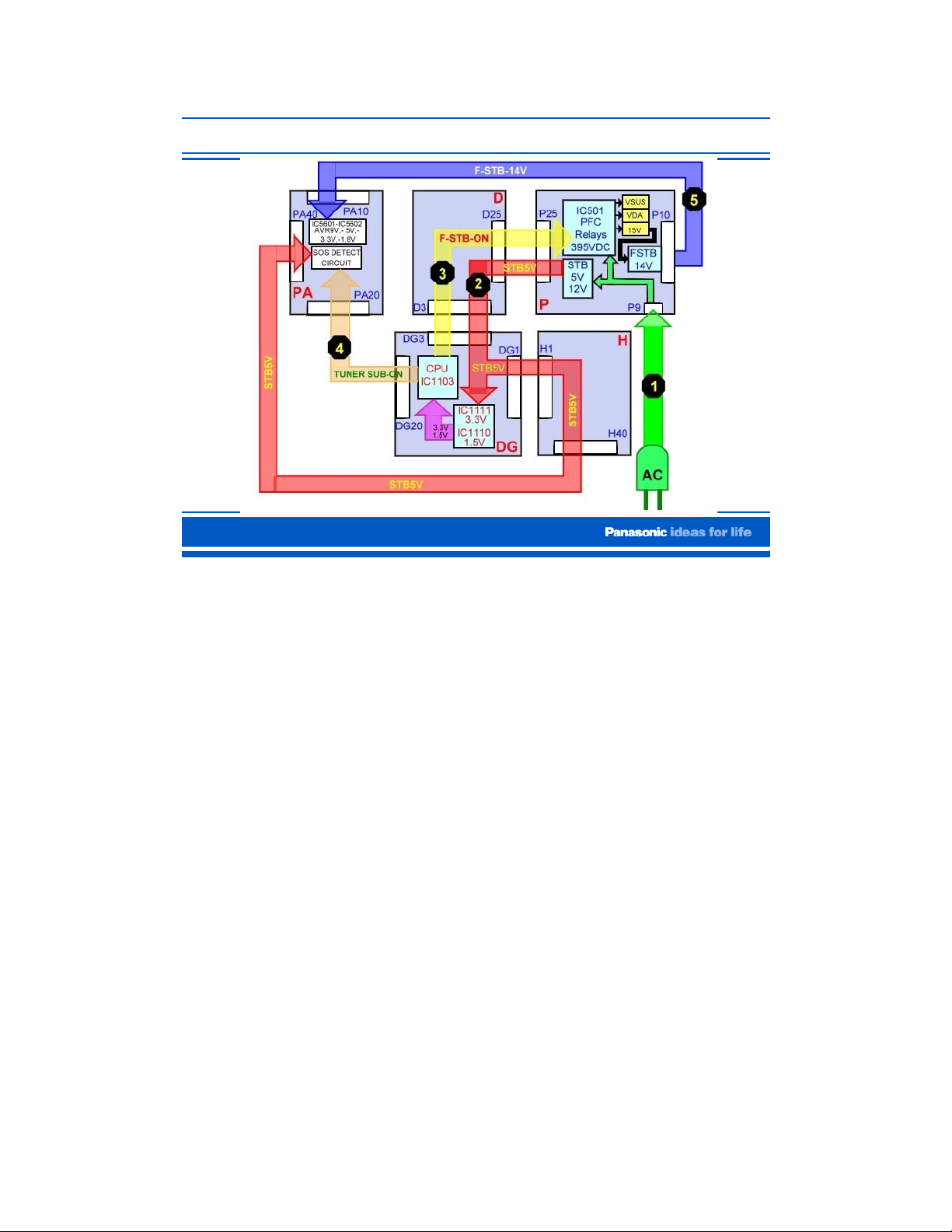
Standby Block Part1
This block diagram shows the sequence of events that takes place inside the TV during
standby.
When the TV is plugged in:
1. AC is applied to the power supply board (P) through connector P9. The AC is applied to
the standby circuit to produce STB12V and STB5V. The STB12V is only used to turn
on a circuit whose function is to allow the output of the STB5V through connector P25.
2. The STB5V passes through the D board via the connectors D25 and D3 and enters the
DG, the H, and the PA boards. The STB5V is applied to a 3.3V and a 1.5V regulator
circuit to power the Main CPU (IC1103) on the DG board.
3. When IC1103 receives 3.3V and 1.5V, it outputs a command that is provided to both the
P and the PA board. This command only lasts approximately 15 seconds. The command
applied to the P board is called “F-STB-ON” and it is routed through the D board via
connectors D3 and D5. The function of this command is to turn on the circuit that
generates the “F-STB-14V” in the P board.
4. The command applied to the PA board through connector PA20 is called “TUNERSUB-ON”. The function of this command along with the STB5V from connector PA40,
is activate the “SOS DETECT” circuit in the PA board.
5. The F-STB14V from connector P10 on the P board is applied to the PA board through
connector PA10. This voltage is applied to a regulator circuit that generates: SUB9V,
SUB5V, and SUB3.V.
19

Standby Block Part 2
6. The STB9V and STB5V from the PA board are provided to the Main CPU IC1103 on
the DG board as 9V detect and 5V detect lines. If any of these voltages is missing, the
TV goes into shutdown and the power LED blinks 10 times as soon as the unit is
plugged into the wall outlet. The STB9V and the STB5V are also applied to the DT.
7. The H board also receives STB9V and STB5V with the addition of the SUB3.3V. The
SUB9V is applied to a DC-DC converter to generate the BT30V.
8. The BT30V is connected to the DT board via the DG board through connectors DG1 and
DG22.
20
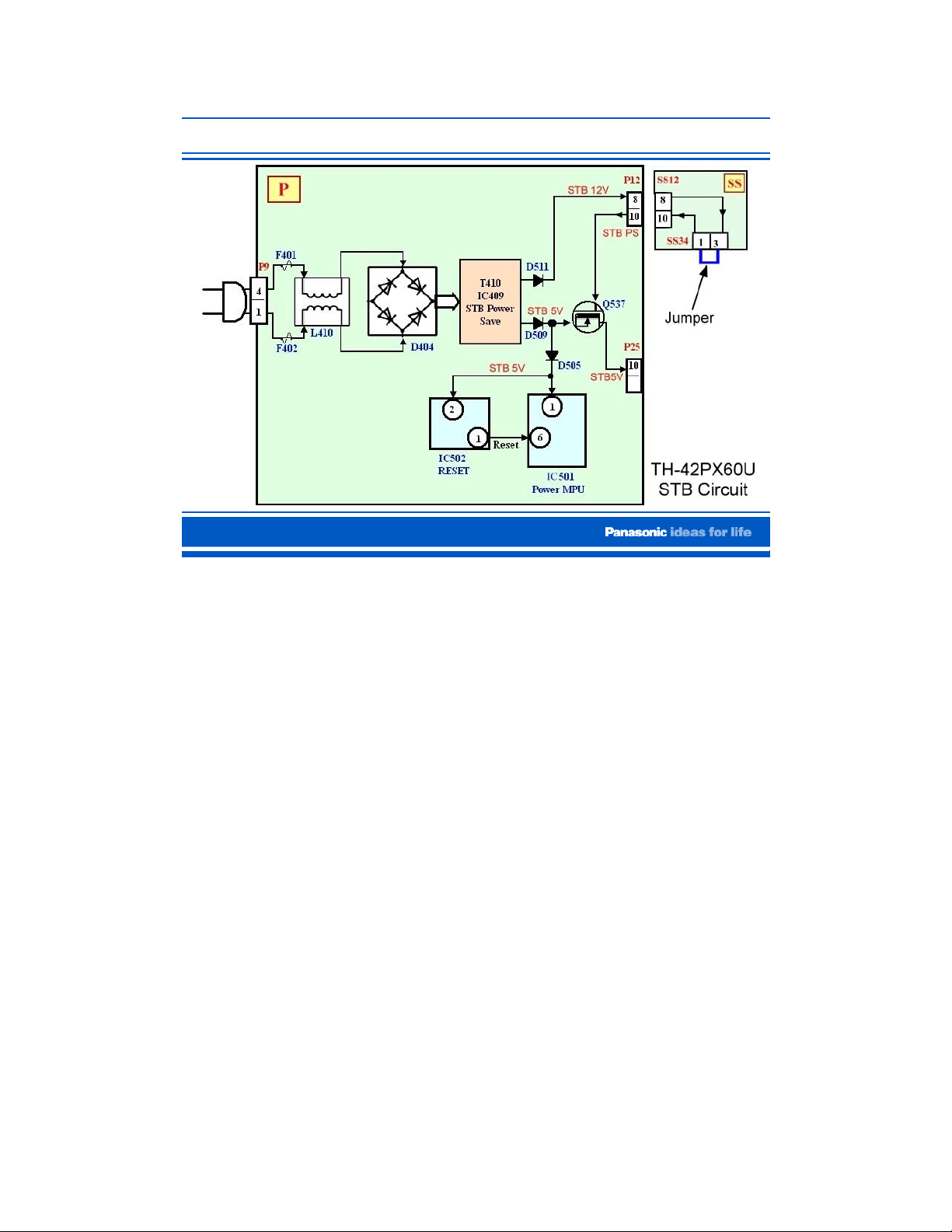
Power Supply (Standby Circuit)
This is a sequence of events that take place during the standby operation.
The AC from connector P9 is filtered by the line filter L410 and then it is rectified by
the bridge rectifier D404. The DC from D404 is applied to the standby circuit (T410,
IC409) where 12V and 5V are developed.
The STB5V is applied to pin 1 of the Power MPU IC IC501 and pin 2 of the Reset IC,
IC502.
The STB5V is also applied to the source of Q537 and the STB12V is applied to the
gate of the transistor to turn it on. As a result, the STB5V comes out on pin 10 of
connector P25.
21
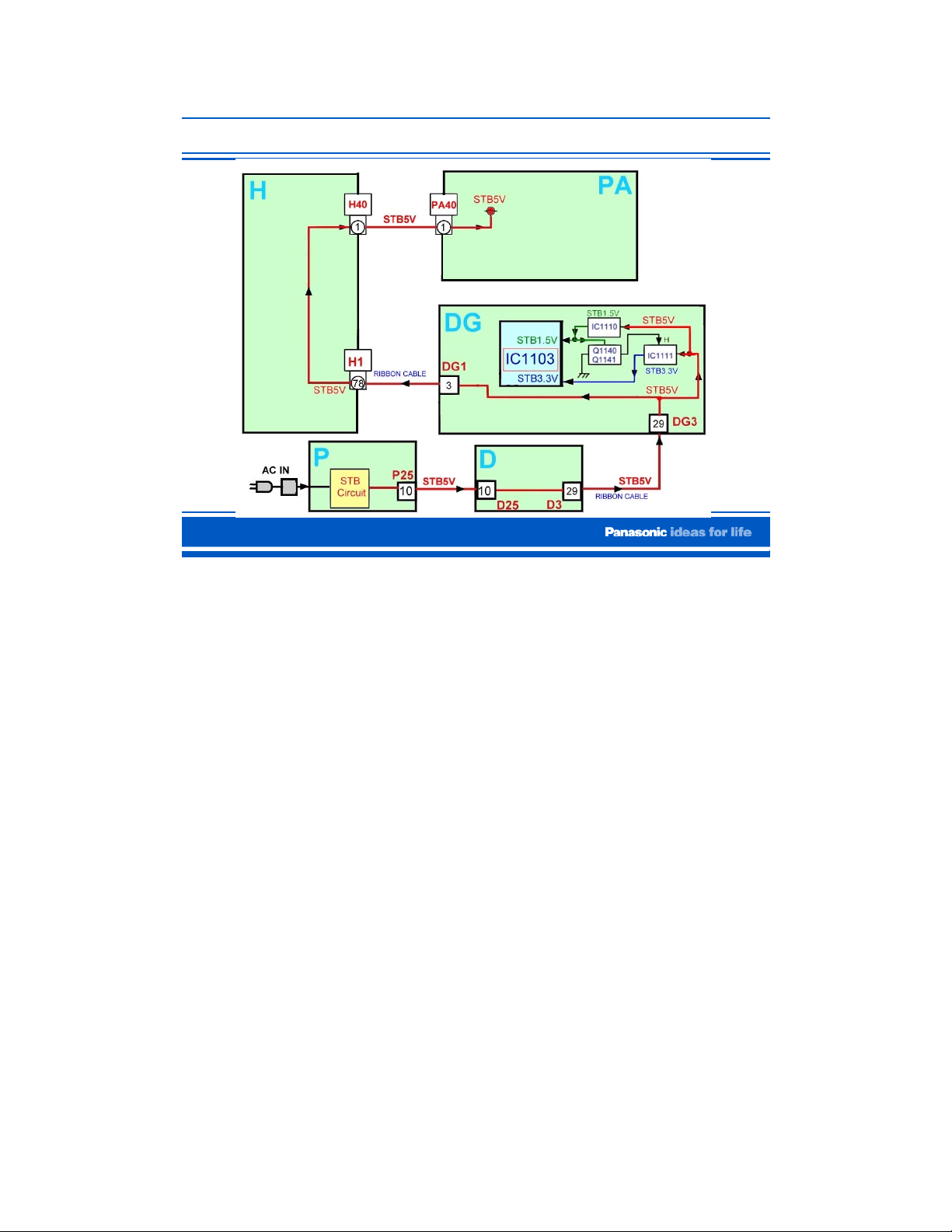
STB5V Distribution
The STB5V is routed through the D board to be connected to the DG board. In the DG
board, the STB5V is used to generate the 1.5V and the 3.3V to power the CPU (IC1103).
The STB5V is also routed through the H board and applied to the PA SOS detect circuit.
The explanation for the circuit that generates the STB3.3V and STB1.5V is covered in the
next slide.
22

Power Supply (Standby Circuit)
The STB5V from the P board is connected to the D board via connector D25. From there, it
is provided to the DG board via pin 29 of connector DG3.
On the DG board, the STB5V is connected to a 3.3V regulator, and a 1.5V regulator.
IC1110 provides the STB1.5V to the CPU IC1103 and the switching circuit consisting of
Q1140 and Q1141. The switching circuit outputs a high to turn on the STB3.3V regulator
(IC1111).
The 3.3V from IC1111 is provided to the CPU IC1103.
When IC1103 receives both 1.5V and 3.3V, it sends out a 3.2V command out of pin 216.
This command is provided to two different circuits and is given a different name in each of
these circuits. It first goes to pin 8 of connector DG20 under the name of “Tuner-Sub-ON”
and from there it goes to connector PA20 on the PA board to activate the protection circuit
of the PA board.
This command also goes to pin 27 of connector DG3 under the name of “F-STB-14V ON”.
From there it goes to pin 13 of connector D25/P25 of the power supply circuit (P board).
23
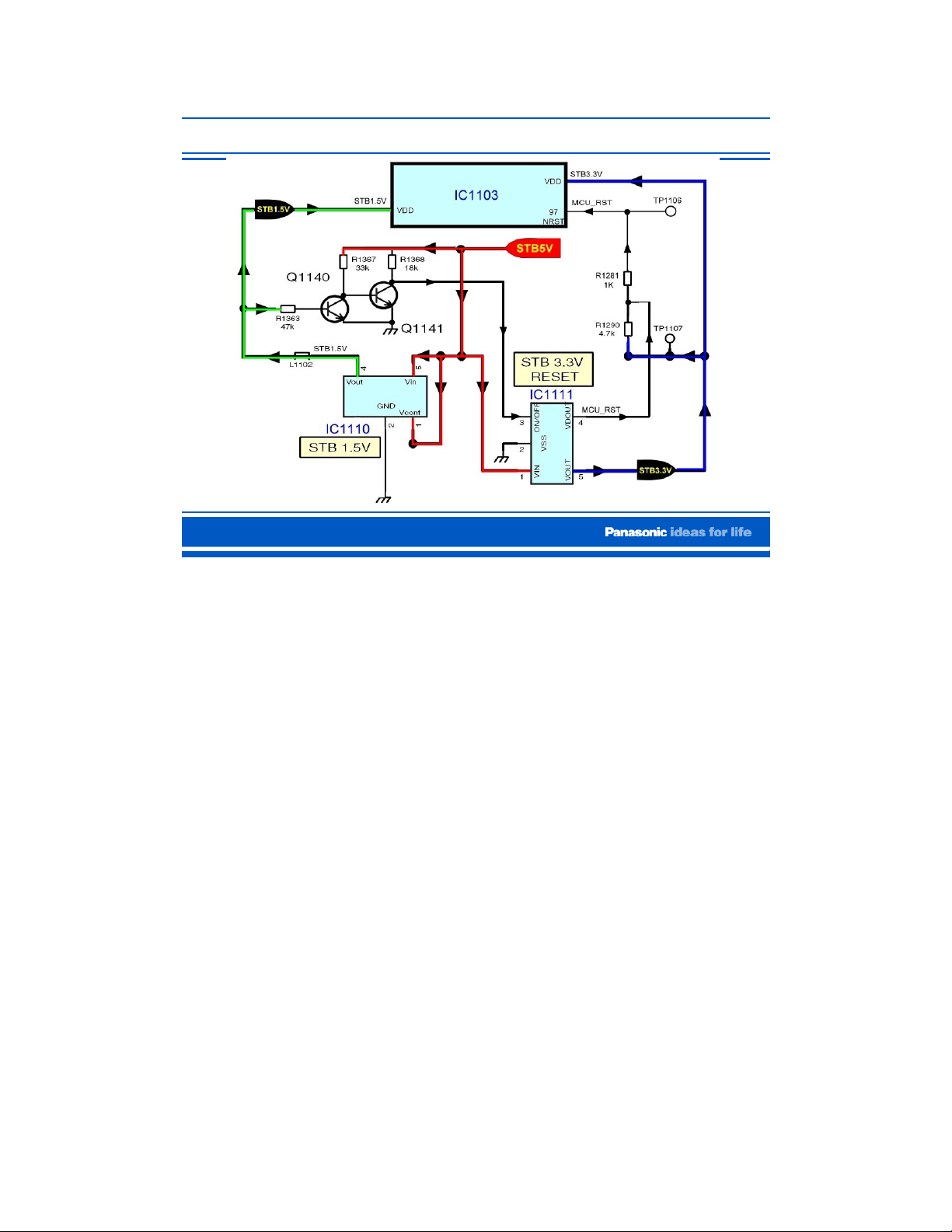
STB5V, STB3.3V, and STB1.5V
This is a schematic diagram of the STB3.3V, and STB1.5V regulators. To understand the
operation of the circuit, see the explanation of the previous slide.
24
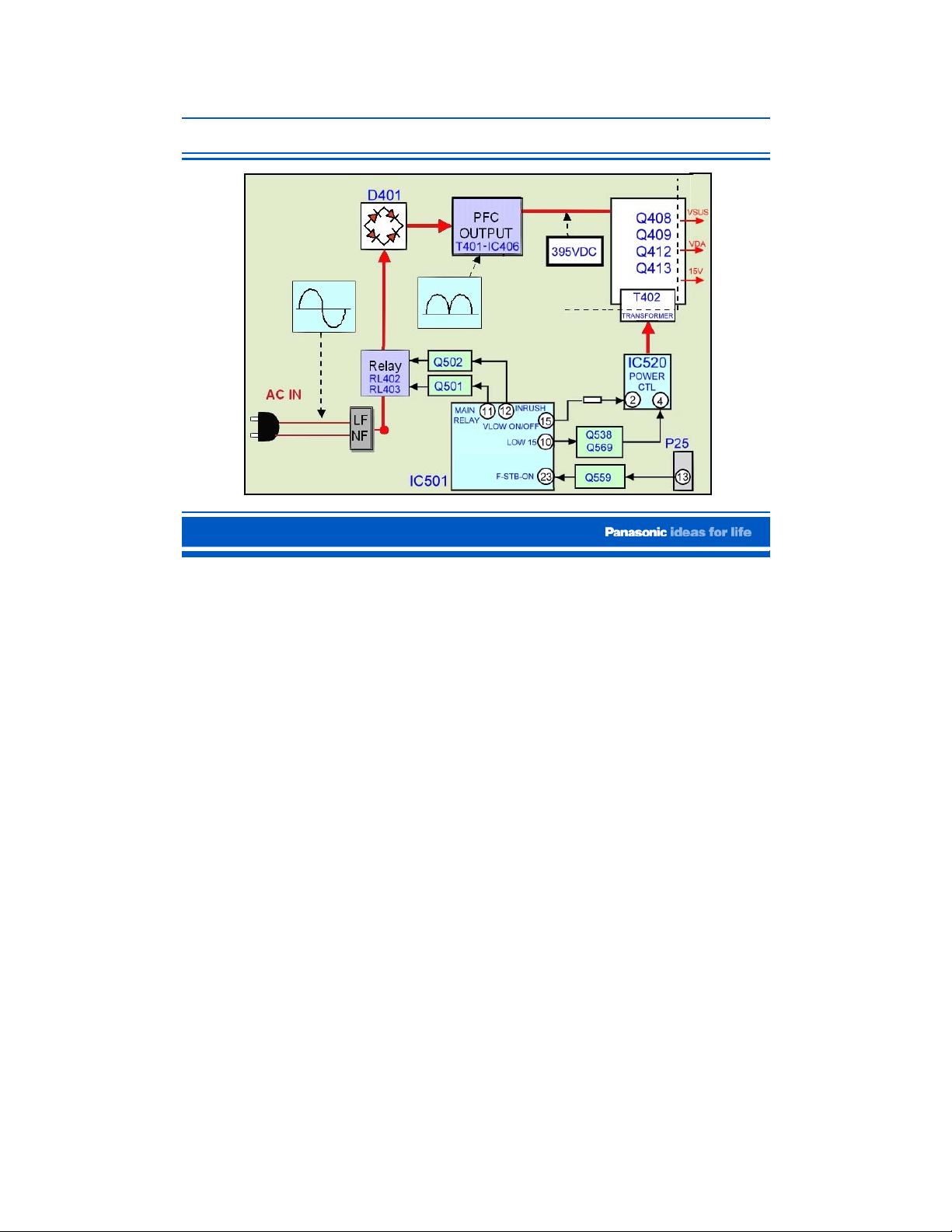
F-STB-ON (Primary)
The F-STB-ON voltage (3.2) from pin 13 of connector P25 is applied to pin 23 of the Power
CPU (IC501) on the P board.
IC501 sends out commands to first turn on the primary circuit of the power supply, and then
the circuit that allows the FSTB14V to develop on the secondary circuit.
1. The relay commands (high) from pins 11 and 12 of IC501 are used to trigger the relays
RL402 and RL403. The incoming AC passes through the relays and enters the bridge
rectifier D401. The DC voltage from D401 is applied to the Power Factor Control (PFC)
circuit (T401 and IC406). The PFC outputs 395VDC is applied to the switching circuit
(Q408, Q409, Q412, and Q413). The operation of this switching circuit is controlled by
the transformer T402 which is driven by the power control IC, IC520.
2. A low from pin 10 and a high from pin 15 of IC501 are used to turn on the power
control IC (IC520) to energize the primary of transformer T402 and allow the switching
circuit to drive transformer T404 (not shown in the diagram.
3. The secondary circuit of transformer T404 outputs the VSUS, VDA, and 15V voltage
sources.
25
 Loading...
Loading...