Panasonic SBWA-500-PP Service manual

PSG1006031CE
Wireless Subwoofer Unit
Model No. SB-WA500PP
Product Color: (K)...Black Type
A6
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Safety Precautions ----------------------------------------------- 3
1.1. General Guidelines---------------------------------------- 3
1.2. Before Repair and Adjustment ------------------------- 4
1.3. Protection Circuitry ---------------------------------------- 4
1.4. Safety Part Information----------------------------------- 4
2 Warning-------------------------------------------------------------- 5
2.1. Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD)
to Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices---------- 5
2.2. Service caution based on Legal restrictions -------- 6
3 Service Navigation ----------------------------------------------- 7
3.1. Service Information --------------------------------------- 7
4 Specifications ----------------------------------------------------- 8
5 Location of Controls and Components ------------------- 9
5.1. Main Unit Key Button Operations---------------------- 9
6 Self diagnostic and special mode setting ---------------10
6.1. Service Mode ----------------------------------------------10
7 Disassembly and Assembly Instructions ---------------11
7.1. Disassembly flow chart----------------------------------12
7.2. Main Parts Location Diagram--------------------------12
7.3. Disassembly of Side Panel Unit ----------------------13
PAG E PAG E
7.4. Disassembly of Passive Radiator ------------------- 14
7.5. Disassembly of Woofer Speaker (SP61) ---------- 15
7.6. Disassembly of Amp Module Assembly ----------- 16
7.7. Disassembly of AC Inlet P.C.B. ---------------------- 17
7.8. Disassembly of SMPS Module P.C.B. ------------- 17
7.9. Disassembly of Digital Receiver (RX) Module
P.C.B. ------------------------------------------------------- 18
7.10. Disassembly of ID Switch P.C.B. and D-Amp
P.C.B. ------------------------------------------------------- 19
7.11. Replacement of Switch Regulator IC (IC5200)
---------------------------------------------------------------- 20
8 Service Position ------------------------------------------------- 23
8.1. Checking and Repairing of D-Amp P.C.B. --------- 23
9 Voltage Measurement & Waveform Chart--------------- 24
9.1. D-AMP P.C.B. --------------------------------------------- 24
9.2. Waveform Chart ------------------------------------------ 24
10 Illustration of IC’s, Transistors and Diodes ------------ 25
11 Block Diagram --------------------------------------------------- 27
11.1. RECEIVER BLOCK DIAGRAM----------------------- 27
12 Wiring Connection Diagram--------------------------------- 29
© Panasonic Corporation 2010. All rights reserved.
Unauthorized copying and distribution is a violation of
law.

13 Schematic Diagram Notes ----------------------------------- 31
14 Schematic Diagram--------------------------------------------- 33
14.1. D-AMP CIRCUIT ----------------------------------------- 33
14.2. ID SWITCH CIRCUIT, AC INLET CIRCUIT ------- 34
15 Printed Circuit Board ------------------------------------------ 35
15.1. D-AMP P.C.B., ID SWITCH P.C.B., AC INLET
P.C.B.-------------------------------------------------------- 35
16 Exploded View and Replacement Parts List -----------37
16.1. Exploded View and Mechanical replacement
Parts List --------------------------------------------------- 37
16.2. Electrical Replacement Parts List -------------------- 40
2

1 Safety Precautions
1.1. General Guidelines
1. When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or
damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, ensure that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly
installed.
3. After servicing, check for leakage current checks to prevent from being exposed to shock hazards.
1.1.1. Leakage Current Cold Check
1. Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two prongs on the plug.
2. Using an ohmmeter measure the resistance value, between the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabinet part on
the equipment such as screwheads, connectors, control shafts, etc. When the exposed metallic part has a return path to the
chassis, the reading should be between 1MΩ and 5.2Ω. When the exposed metal does not have a return path to the chassis,
the reading must be
1.1.2. Leakage Current Hot Check
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an isolation transformer for this check.
2. Connect a 1.5kΩ, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15μF capacitors, between each exposed metallic part on the set and a
good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in Figure 1.
3. Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the voltage at each point.
5. Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the above measurements.
6. The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or equivalent)
may be used to make the hot checks, leakage current must not exceed 1/2 milliamp. should the measurement is outside of
the limits specified, there is a possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be repaired and re-checked before it is
returned to the customer.
3

1.2. Before Repair and Adjustment
DO NOT SHORT-CIRCUIT DIRECTLY (with a screwdriver blade, for instance), as this may destroy solid state devices.
After repairs are completed, restore power gradually using a variac, to avoid overcurrent.
• Current consumption at AC 120 V, at 60 Hz in NO SIGNAL mode, at volume minimum, SEL: DVD, no link, take before 10s
should be ~200 mA.
1.3. Protection Circuitry
The protection circuitry may have operated if either of the following conditions are noticed:
• No sound is heard when the power is turned on.
• Sound stops during a performance.
The function of this circuitry is to prevent circuitry damage if, for example, the positive and negative speaker connection wires are
"shorted", or if speaker systems with an impedance less than the indicated rated impedance of the amplifier are used.
If this occurs, follow the procedure outlines below:
1. Turn off the power.
2. Determine the cause of the problem and correct it.
3. Turn on the power once again after one minute.
Note:
When the protection circuitry functions, the unit will not operate unless the power is first turned off and then on again.
1.4. Safety Part Information
Safety Parts List:
There are special components used in this equipment which are important for safety.
These parts are marked by in the Schematic Diagrams & Replacement Parts List. It is essential that these critical parts should
be replaced with manufacturer’s specified parts to prevent shock, fire or other hazards. Do not modify the original design without
permission of manufacturer.
Safety Ref. No. Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
68 RGNX1154-K SPEC LABEL
80 N0AB6GY00007 SMPS MODULE P.C.B.
PCB1 REPX0771C RX MODULE P.C.B.
PCB2 REPX0770C TX MODULE P.C.B.
PCB5 REPX0865DA AC INLET P.C.B. (RTL)
P5701 K2ABYA000001 AC INLET
L1001 G0B340J00002 LINE FILTER
4

2Warning
2.1. Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) to Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by electricity. Such components commonly are called Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and semiconductor “chip” components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage caused by
electro static discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equiped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap,
which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equiped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as aluminium foil, to prevent electrostatic charge build up or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder remover device. Some solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static (ESD protected)” can
generate electrical charge to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminium foil or comparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize body motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD) sufficient
to damage an ES device).
5
2.2. Service caution based on Legal restrictions
2.2.1. General description about Lead Free Solder (PbF)
The lead free solder has been used in the mounting process of all electrical components on the printed circuit boards used for this
equipment in considering the globally environmental conservation.
The normal solder is the alloy of tin (Sn) and lead (Pb). On the other hand, the lead free solder is the alloy mainly consists of tin
(Sn), silver (Ag) and Copper (Cu), and the melting point of the lead free solder is higher approx.30 degrees C (86°F) more than that
of the normal solder.
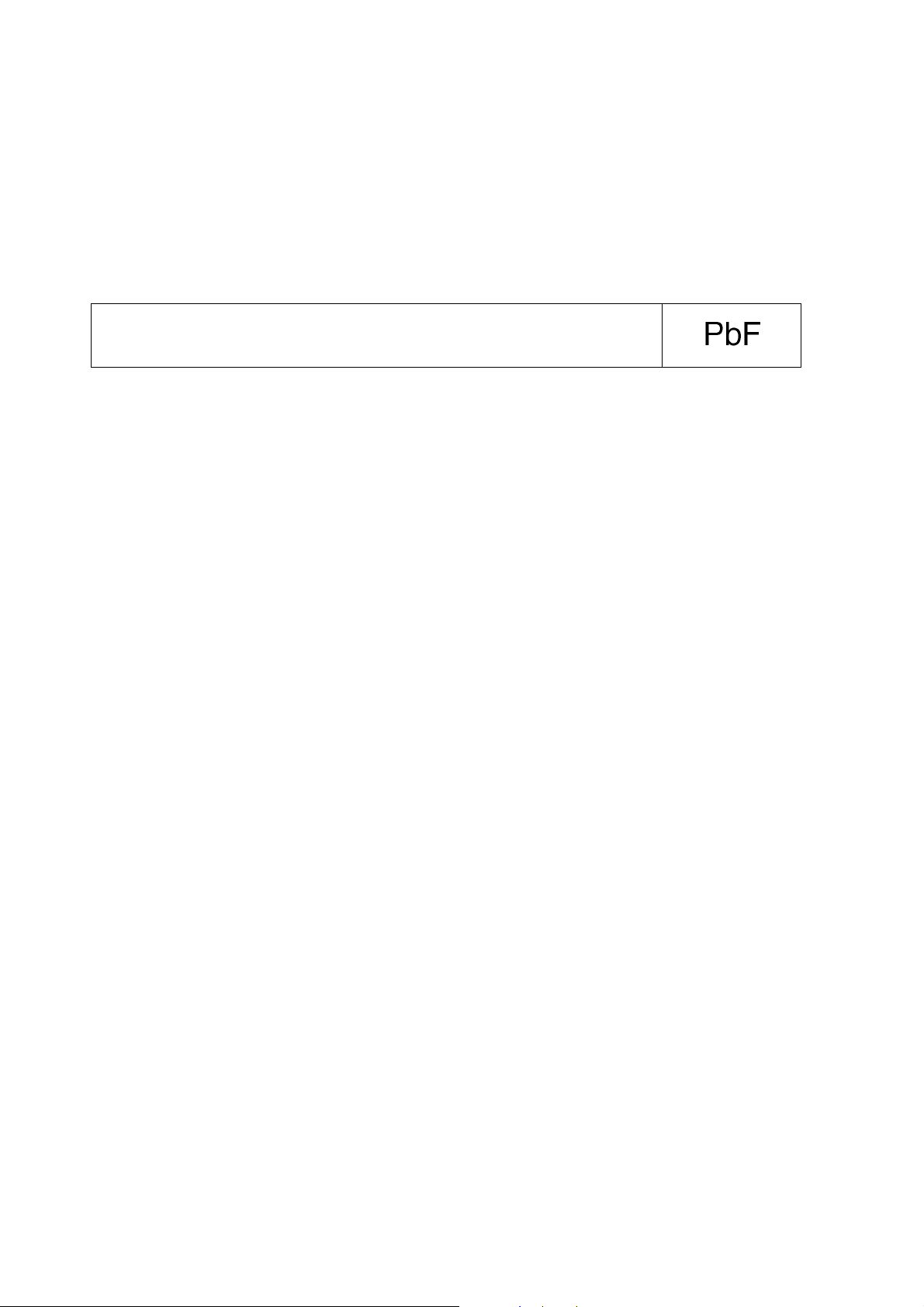
Definition of PCB Lead Free Solder being used
The letter of “PbF” is printed either foil side or components side on the PCB using the lead free solder.
(See right figure)
Service caution for repair work using Lead Free Solder (PbF)
• The lead free solder has to be used when repairing the equipment for which the lead free solder is used.
(Definition: The letter of “PbF” is printed on the PCB using the lead free solder.)
• To put lead free solder, it should be well molten and mixed with the original lead free solder.
• Remove the remaining lead free solder on the PCB cleanly for soldering of the new IC.
• Since the melting point of the lead free solder is higher than that of the normal lead solder, it takes the longer time to melt the
lead free solder.
• Use the soldering iron (more than 70W) equipped with the temperature control after setting the temperature at 350±30 degrees
C (662±86°F).
Recommended Lead Free Solder (Service Parts Route.)
• The following 3 types of lead free solder are available through the service parts route.
RFKZ03D01K-----------(0.3mm 100g Reel)
RFKZ06D01K-----------(0.6mm 100g Reel)
RFKZ10D01K-----------(1.0mm 100g Reel)
Note
* Ingredient: Tin (Sn), 96.5%, Silver (Ag) 3.0%, Copper (Cu) 0.5%, Cobalt (Co) / Germanium (Ge) 0.1 to 0.3%
6

3 Service Navigation
3.1. Service Information
This service manual contains technical information which will allow service perssonnel’s to understand and service this model.
Please place orders using the parts list and not the drawing reference numbers.
If the circuit is changed or modified, this information will be followed by supplement service manual to be filed with original service
manual.
3.1.1. Power supply
This model uses Switching Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Module for powering the receiver unit. It is replaceable as an assembly
unit. (Part No : N0AB6GY0007) Do not attempt to repair or its component on board.
3.1.2. Digital Transmitter Unit / Digital Receiver Module (Rx) P.C.B. Replacement
1. This Model uses Digital Transmitter Unit & Digital Receiver Module (Rx) P.C.B. for the wireless transmission of signals.
2. After replacement of either Digital Transmitter Unit or Digital Receiver Module (Rx) P.C.B., ID setting is required.
Refer to section 6.1 Service Mode Table 1 for the procedures for ID setting.
7

4 Specifications
Q GENERAL
Power consumption: Active subwoofer : 20 W
Power consumption in off mode: Active subwoofer : Approx. 0.2 W
Power supply: AC 120 V, 60 Hz
Dimensions (W x H x D):
Active subwoofer : 250 mm x 323 mm x 356 mm (9 27/32” x 12 23/32” x 14 1/32”)
Mass:
Active subwoofer : Approx. 6.7 kg (14.8 lbs)
Operating temperature range: 0°C to +40°C (+32°F to +104°F)
Operating humidity range: 20% to 80% RH (no condensation)
Q AMPLIFIER SECTION
RMS Output Power
Subwoofer ch: 120 W per channel (8 Ω), 100 Hz, 10% THD
Total RMS Dolby Digital mode power: 240 W
FTC Output Power
Subwoofer ch: 37 W per channel (8 Ω), 40 Hz to 120 Hz, 1% THD
Total FTC Dolby Digital mode power: 87 W
Q SPEAKER SECTION
ACTIVE SUBWOOFER
Type: 1 way 1 speaker system (Kelton type)
Woofer: 16 cm (6 1/2”) Cone type
Passive radiator: 25 cm (10”)
Output sound pressure: 78 dB/W(1m)
Frequency range: 35 Hz to 180 Hz (-16dB)
40 Hz to 160 Hz (-10dB)
Note:
1. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
2. Total harmonic distortion is measured by the digital spectrum analyzer.
8

5 Location of Controls and Components
5.1. Main Unit Key Button Operations
9
6 Self diagnostic and special mode setting
This unit is equipped with features of self-diagnostic & special mode setting for checking the functions & reliability.
Special Note : Checking of the reliability (ageing) & changer operation must be carry out to ensure good working condi-
tion in unit.
6.1. Service Mode
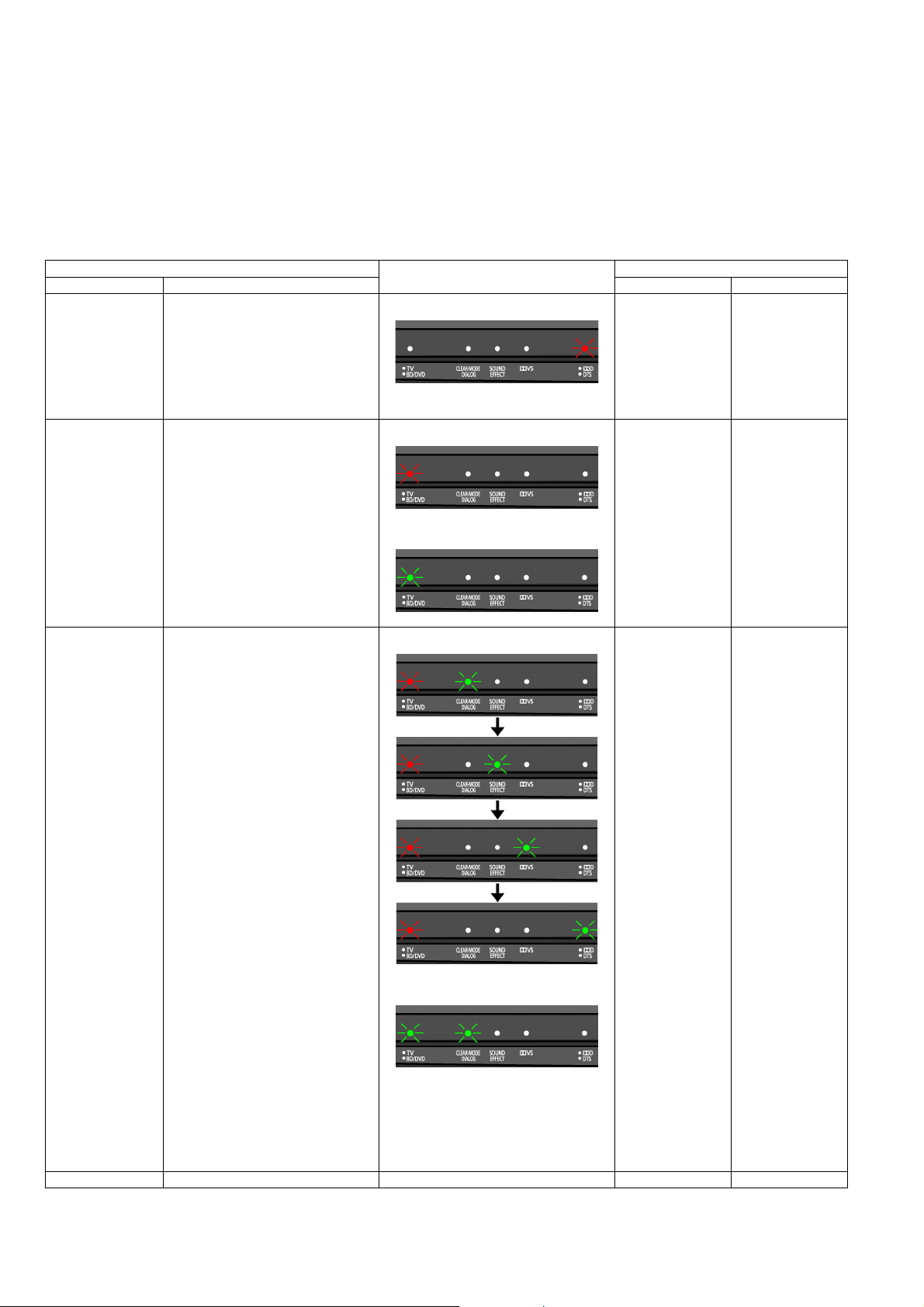
Service Mode Table 1
To pair Transmitter Unit & Wireless Subwoofer Unit
Item Main Unit LED Display Key Operation
Mode Name Description Main Unit Remote Control
Service Mode 1. Power on both Main Unit & Wireless
Subwoofer Unit
2. Press & hold [VOL +],[VOL -] follow
by [POWER] simultaneously on the
Main Unit.
[DTS] LED (Red) will light up.
Pairing Mode 1. Enter into Service Mode.
2. Press [SUBW -] for 2 secs on the
Remote Control.
Note:
Unit will go into "Pairing Mode" for only
1 min.
After 1 min, it will return to Service
Mode.
During Pairing
Mode
No Link Condition:
[BD/DVD] LED will light up & other 4
LEDs ([CLEAR-MODE DIALOG],
[SOUND EFFECT], [DVS], [DD]) will
run 1 by 1 shifting for 1 min & return to
Service Mode.
No Link Condition:
Link Condition:
No Link Condition:
[VOL +] [VOL -]
[POWER]
[SUBW -]
Link Condition:
[TV] LED will light up & other 4 LEDs
([CLEARMODE DIALOG], [SOUND
EFFECT], [DVS], [DD]) will run 1 by 1
shifting for 1 min & return to Service
Mode.
Note:
Pairing is auto configured.
If auto configuration failed, press [ID]
button on the Wireless Subwoofer Unit
during the "Under Pairing Mode".
Exit Mode 1. Press [POWER] on the Main Unit.
Link Condition:
4 Green LEDs running will be same as
above.
10

7 Disassembly and Assembly Instructions
Caution Note:
• This section describes the disassembly and/or assembly procedures for all major printed circuit boards & main components for
the unit. (You may refer to the section of “Main components and P.C.B Locations” as described in the service manual)
• Before carrying out the disassembly process, please ensure all the safety precautions & procedures are followed.
• During the disassembly and/or assembly process, please handle with care as there may be chassis components with
sharp edges.
• Avoid touching heatsinks due to its high temperature after prolong use. (See caution as described below)
• During disassembly and assembly, please ensure proper service tools, equipments or jigs is being used.
• During replacement of component parts, please refer to the section of “Replacement Parts List” as described in the
service manual.
• Select items from the following indexes when disassembly or replacement are required.
• Disassembly of Side Panel Unit
• Disassembly of Passive Radiator
• Disassembly of Woofer Speaker (SP61)
• Disassembly of Amp Module Assembly
• Disassembly of AC Inlet P.C.B.
• Disassembly of SMPS Module P.C.B.
• Disassembly of Digital Receiver (RX) Module P.C.B.
• Disassembly of ID Switch P.C.B. and D-Amp P.C.B.
• Replacement of Switch Regulator IC (IC5200)
11

7.1. Disassembly flow chart
The following chart is the procedure for disassembling the casing and inside parts for internal inspection when carrying out the servicing.
To assemble the unit, reverse the steps shown in the chart below.
7.2. Main Parts Location Diagram
12
7.3. Disassembly of Side Panel Unit
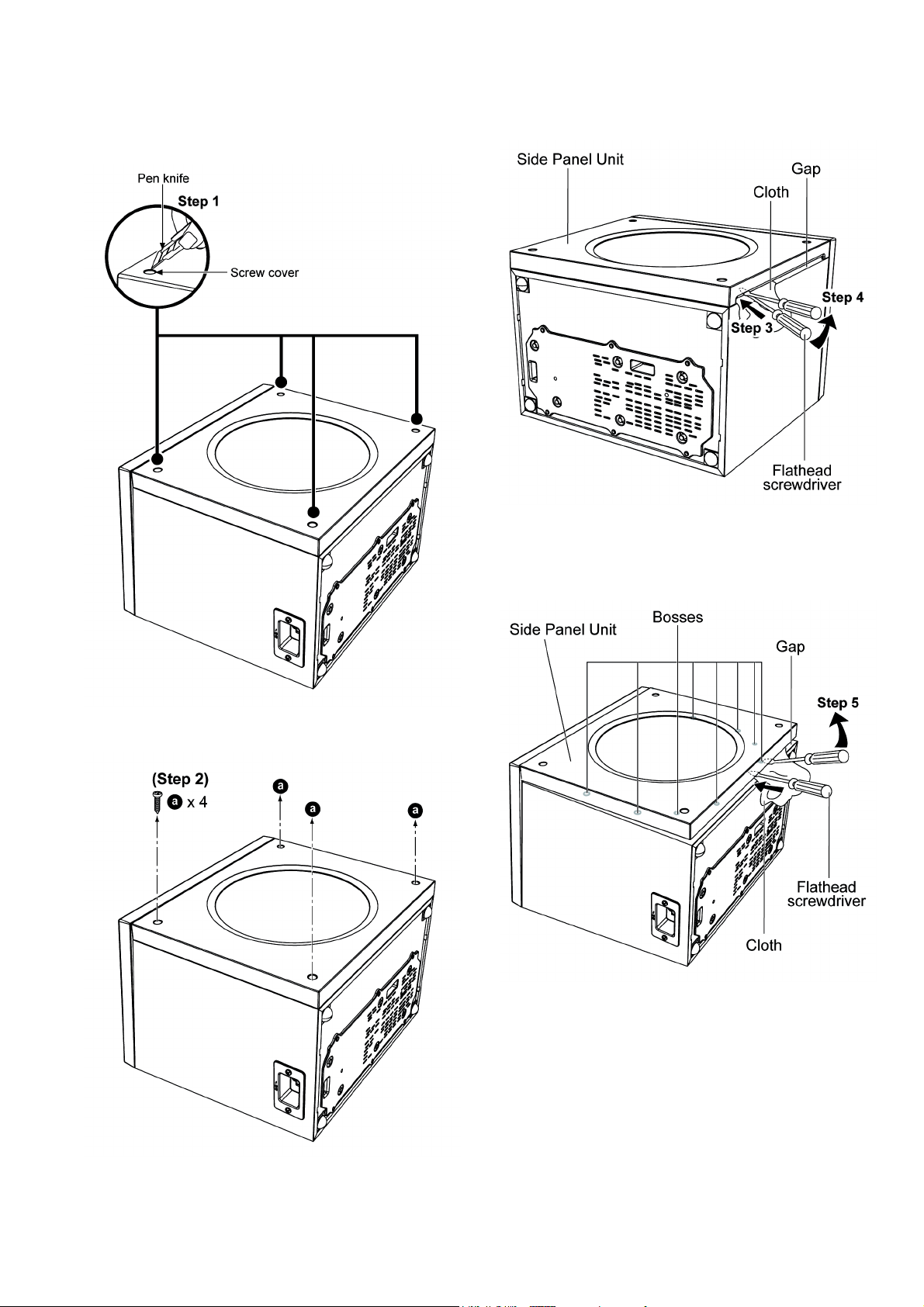
Step 1 : Peel off the screw covers by using the pen knife.
Caution : Place it in original location during assembling.
Step 3 : Insert the flathead screwdriver into the gap of the Side
Panel Unit.
Step 4 : Lift up the Side Panel Unit slightly.
Step 5 : Insert two flathead screwdriver at the gap and apply
force to gently push out the Side Panel Unit as shown.
Caution : Do not exert too much force as it may damage
the Side Panel Unit.
Step 2 : Remove 4 screws.
13
 Loading...
Loading...