
Model No. SA-AKX92PH
Product Color: (K)...Black Type
Please refer to the original service manual for:
O CD Mechanism Unit (BRS1C), Order No. PSG1102001CE
O Speaker system SB-AKX92PU-K, Order No. PSG1103049CE
PSG1103015CE
CD Stereo System
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Safety Precautions----------------------------------------------- 3
1.1. General Guidelines---------------------------------------- 3
1.2. Before Use -------------------------------------------------- 3
1.3. Caution For Fuse Replacement ------------------------ 3
1.4. Before Repair and Adjustment ------------------------- 4
1.5. Protection Circuitry---------------------------------------- 4
1.6. Safety Parts Information --------------------------------- 5
2 Warning-------------------------------------------------------------- 6
2.1. Prevention of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
to Electrostatic Sensitive (ES) Devices -------------- 6
2.2. Precaution of Laser Diode------------------------------- 7
2.3. Service caution based on Legal restrictions--------8
2.4. Handling Precautions for Traverse Unit-------------- 9
3 Service Navigation----------------------------------------------11
PAGE PAGE
3.1. Service Information-------------------------------------- 11
4 Specifications ----------------------------------------------------12
5 Location of Controls and Components------------------ 13
5.1. Main Unit Key Button Operation----------------------13
5.2. Remote Control Key Button Operation ------------- 14
5.3. Media Information---------------------------------------- 15
6 Self-Diagnostic and Special Mode Setting -------------16
6.1. Cold-Start --------------------------------------------------16
6.2. Doctor Mode Table---------------------------------------17
6.3. Reliability Test Mode (CD Mechanism Unit
(BRS1C))--------------------------------------------------- 19
6.4. Self-Diagnostic Mode -----------------------------------20
6.5. Self-Diagnostic Error Code Table--------------------21
6.6. Sales Demonstration Lock Function ---------------- 22
© Panasonic Corporation 2011. All rights reserved.
Unauthorized copying and distribution is a violation
of law.

7 Troubleshooting Guide----------------------------------------23
7.1. Troubleshooting Guide for F61 and/ or F76 -------23
7.2. Part Location ----------------------------------------------24
7.3. D-Amp IC Operation & Control -----------------------28
8 Service Fixture & Tools---------------------------------------30
8.1. Service Tools and Equipment-------------------------30
9 Disassembly and Assembly Instructions---------------31
9.1. Disassembly Flow Chart--------------------------------32
9.2. Main Components and P.C.B. Locations-----------33
9.3. Disassembly of Top Cabinet---------------------------34
9.4. Disassembly of Tuner P. C.B.--------------------------35
9.5. Disassembly of Front Panel Unit ---------------------35
9.6. Disassembly of Jupiter P.C.B.-------------------------37
9.7. Disassembly of Panel P.C.B.--------------------------38
9.8. Disassembly of Remote Sensor P.C.B.-------------40
9.9. Disassembly of USB P.C.B. ---------------------------40
9.10. Disassembly of Music Port P.C.B. -------------------41
9.1 1 . Disassembly of CD Lid----------------------------------42
9.12. Disassembly of Main P.C.B.---------------------------43
9.13. Replacement of Voltage Regulator IC
(IC2010) ----------------------------------------------------44
9.14. Disassembly of D-Amp P.C.B.------------------------45
9.15. Replacement of Audio Digital Amp IC
(IC5000) ----------------------------------------------------47
9.16. Replacement of Audio Digital Amp IC
(IC5400) ----------------------------------------------------48
9.17. Replacement of Audio Digital Amp IC
(IC5200) ----------------------------------------------------49
9.18. Replacement of Audio Digital Amp IC
(IC5300) ----------------------------------------------------50
9.19. Disassembly of SMPS P.C.B.-------------------------51
9.20. Replacement of Regulator IC (IC5701)-------------52
9.21. Replacement of Rectifier Diode (D5702)-----------54
9.22. Replacement of Rectifier Diode (D5801)-----------56
9.23. Replacement of Rectifier Diode (D5802)-----------57
9.24. Replacement of Rectifier Diode (D5803)-----------58
9.25. Disassembly of CD Mechanism Unit (BRS1C)---59
9.26. Disassembly of Rear Panel----------------------------61
9.27. Disassembly of Voltage Selector P.C.B.------------62
9.28. Disassembly of Surround D-Amp P.C.B.-----------63
9.29. Replacement of Audio Digital Amp IC
(IC5900) ----------------------------------------------------65
10 Replacement of Traverse Unit------------------------------67
10.1. Disassembly of Traver se Unit-------------------------67
10.2. Assembly of Traverse Unit-----------------------------69
10.3. Disassembly of CD Servo P.C.B.---------------------71
11 Service Position -------------------------------------------------74
11.1. Checking and Repairing of Main P.C.B. ------------ 74
11.2. Checking and Repairing of D-Amp P.C.B. ---------74
11.3. Checking and Repairing of Surround D-Amp
P.C.B.--------------------------------------------------------75
11.4. Checking and Repairing of Panel P.C.B.-----------75
11.5. Checking and Repairing of Jupiter P.C.B.----------76
11.6. Checking and Repairing of SMPS P.C.B.---------- 77
11.7. Checking and Repairing of CD Servo P.C.B.------78
12 Voltage & Waveform Chart-----------------------------------79
12.1. CD Servo P.C.B.------------------------------------------79
12.2. Main P.C.B. (1/3)-----------------------------------------80
12.3. Main P.C.B. (2/2)-----------------------------------------81
12.4. Main P.C.B. (3/3)-----------------------------------------82
12.5. Panel P.C.B.-----------------------------------------------82
12.6. Music Port P.C.B.---------------------------------------- 83
12.7. Tuner P.C.B.----------------------------------------------- 83
12.8. Jupiter P.C.B. (1/3)-------------------------------------- 84
12.9. Jupiter P.C.B. (2/3)-------------------------------------- 85
12.10. Jupiter P.C.B. (3/3)-------------------------------------- 86
12.1 1. D-AMP P.C.B.--------------------------------------------- 87
12.12. Surround D-AMP P.C.B. ------------------------------- 88
12.13. SMPS P.C.B.---------------------------------------------- 88
12.14. Waveform Table------------------------------------------ 89
13 Illustration of ICs, Transistor and Diode---------------- 91
14 Simplified Block Diagram------------------------------------ 93
14.1. Overall Simplified Block Diagram-------------------- 93
14.2. D-Amp Block Diagram---------------------------------- 94
15 Block Diagram--------------------------------------------------- 95
15.1. Servo & System Control------------------------------- 95
15.2. IC Terminal Chart---------------------------------------- 97
15.3. Audio-------------------------------------------------------- 98
15.4. Power Supply--------------------------------------------100
16 Wiring Connection Diagram -------------------------------102
17 Schematic Diagram-------------------------------------------103
17.1. Schematic Diagram Notes ---------------------------103
17.2. CD Servo Circuit ----------------------------------------105
17.3. Main Circuit-----------------------------------------------107
17.4. Panel Circuit ---------------------------------------------115
17.5. Music Port Circuit---------------------------------------117
17.6. Remote Sensor, USB, Tuner & Voltage Circuit -118
17.7. Jupiter Circuit --------------------------------------------119
17.8. D-Amp Circuit--------------------------------------------123
17.9. Surround D-Amp Circuit ------------------------------125
17.10. SMPS Circuit---------------------------------------------126
18 Printed Circuit Board-----------------------------------------128
18.1. CD Servo P.C.B.----------------------------------------128
18.2. Main P.C.B.-----------------------------------------------129
18.3. Panel P.C.B.----------------------------------------------130
18.4. Music Port, Remote Sensor, USB & Tuner
P.C.B. ------------------------------------------------------131
18.5. Jupiter P.C.B.--------------------------------------------132
18.6. D-Amp P.C.B.--------------------------------------------133
18.7. SMPS, Surround D-Amp & Voltage Selector
P.C.B. ------------------------------------------------------134
19 Terminal Function of ICs------------------------------------135
19.1. IC2003 (RFKWMAKX92M0): IC MICROPROCESSOR -------------------------------------------135
19.2. IC6001(C0HBB0000057): IC FL Driver-----------136
20 Exploded View and Replacement Parts List----------137
20.1. Exploded View and Mechanical Replacement
Parts List--------------------------------------------------137
20.2. Electrical Replacement Parts List ------------------143
2
1 Safety Precautions
1.1. General Guidelines
1. Wh en servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or
damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, see to it that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly
installed.
3. After servicing, carry out the following leakage current checks to prevent the customer from being exposed to shock hazards.
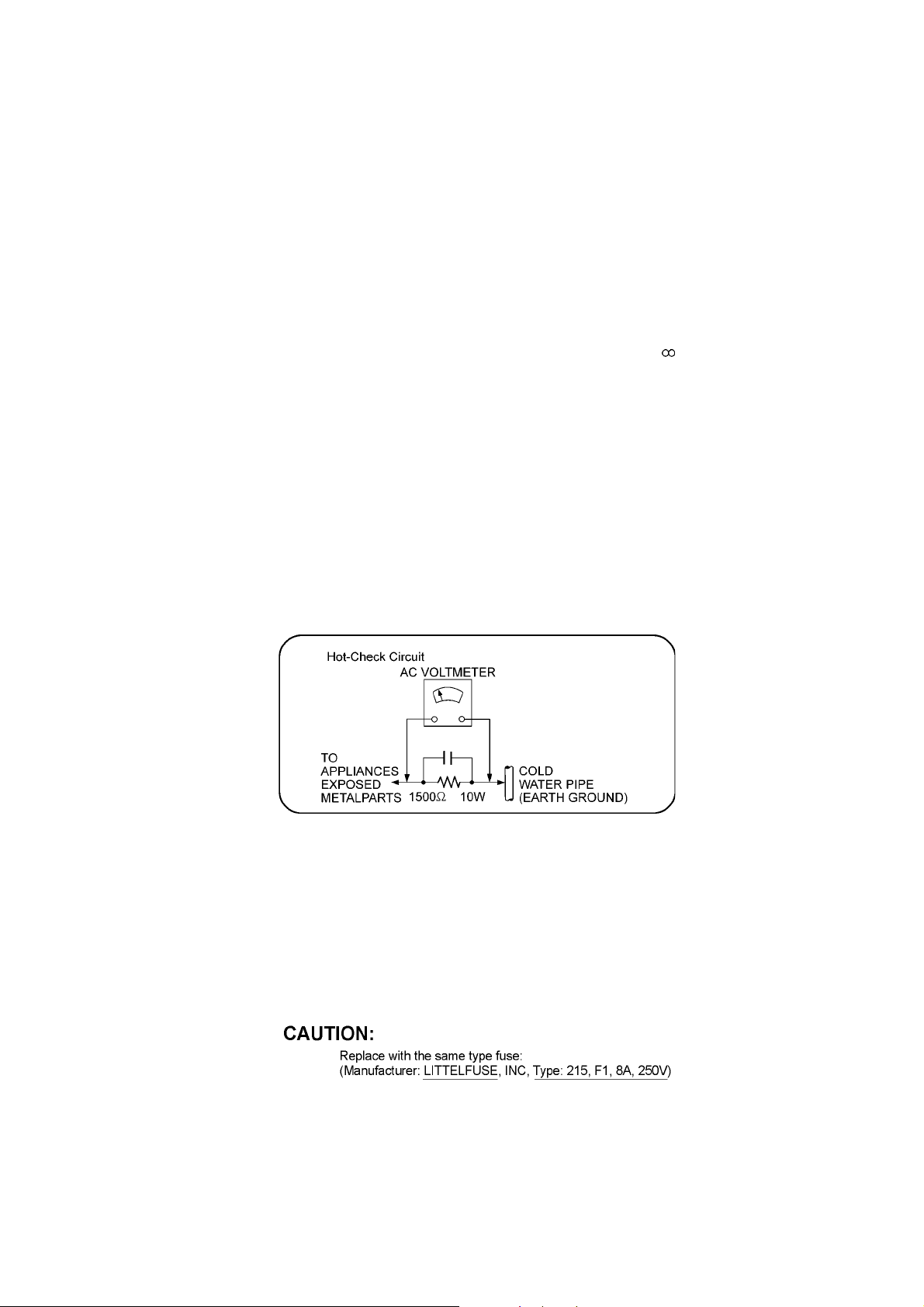
1.1.1. Leakage Current Cold Check
1. Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two prongs on the plug.
2. Measure the resistance value, with an o hmmeter, between the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabinet part on
the equipment such as screwheads, connectors, control shafts, etc. When the exposed metallic part has a return path to th e
chassis, the reading should be between 1MΩ and 5.2MΩ.
When the exposed metal does not have a return path to the chassis, the reading must be
1.1.2. Leakage Current Hot Check
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an isolation transformer for this check.
2. Connect a 1.5kΩ, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15µF capacitors, between each exposed metallic part on the set and a
good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in Figure 1.
3. Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the voltage at each point.
5. Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the above measurements.
6. Th e potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or equivalent)
may be used to make the hot checks, leakage current must not exceed 1/2 milliamp. In case a measurement is outside of the
limits specified, there is a possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be repaired and rechecked before it is
returned to the customer.
Figure 1
1.2. Before Use
Be sure to disconnect the mains cord before adjusting the voltage selector.
Use a minus(-) screwdriver to set the voltage selector (on the rear panel) to the voltage setting for the area in which the unit will be
used. (If the power supply in your area is 110V ~ 127V or 220V ~ 240V, set to the “110V ~ 127V or 220V ~ 240V” position.)
Note that this unit will be seriously damaged if this setti ng is not made correctly. (There is no voltage selector for some countries,
the correct voltage is already set.)
1.3. Caution For Fuse Replacement
3

1.4. Before Repair and Adjustment
Disconnect AC power to discharge unit AC Capacitors as such (C5700, C5701, C5703, C5704, C5705, C5708) through a 10 Ω, 10
W resistor to ground.
Caution:
DO NOT SHORT-CIRCUIT DIRECTLY (with a screwdriver blade, for instance), as this may destroy solid st ate devices.
After repairs are completed, restore power gradually using a variac, to avoid overcurrent.
Current consumption at AC 110~127 V / 220~240 V, 50/60 Hz in Power ON, FM T uner, No Signal, Volume minimal mode should be
~ 900 mA.
1.5. Protection Circuitry
The protection circuitry may have operated if either of the following conditions are noticed:
• No sound is heard when the power is turned on.
• Sound stops during a performance.
The function of this circuitry is to prevent circuitry damage if, for example, the positive and negative speaker connection wires are
“shorted”, or if speaker systems with an impedance less than the indicated rated impedance of the amplifier are used.
If this occurs, follow the procedure outlines below:
1. Turn off the power.
2. Determine the cause of the problem and correct it.
3. Turn on the power once again after one minute.
Note:
When the protection circuitry functions, the unit will not operate unless the power is first turned off and then on again.
4
1.6. Safety Parts Information
Safety Parts List:
There are special components used in this equipment which are important for safety.
These parts are marked by in the Schematic Diagrams, Exploded View & Replacement Parts List. It is essential that these
critical parts should be replaced with manufacturer’s specified parts to prevent shock, fire or other hazards. Do not modify the
original design without permission of manufacturer.
Safety Ref No. Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
4 REXX1122 1P BLACK WIRE (VOLTAGE SELECTOR-SMPS)
5 REXX1123 1P RED WIRE (VOLTAGE SELECTOR-SMPS)
8 RGRX1008E-A REAR PANEL
14 RKMX1011-K TOP CABINET
301 RAEX1033Z-V TRAVERSE ASS'Y
A2 K2CQ2CA00007 AC CORD
A3 RQTX1300-M O/I BOOK (Sp)
PCB10 REPX0886G SMPS P.C.B. (RTL)
PCB11 REPX0886G VOLTAGE SELECTOR P.C.B. (RTL)
DZ5701 ERZV10V511CS ZNR
S5701 K0ABCA000007 SW VOLTAGE SELECTOR
L5701 G0B932H00002 LINE FILTER
T5701 G4DYZ0000049 SWITCHING TRANSFORMER
T5751 ETS19AB2E6AG SWITCHING TRANSFORMER
T6000 G4DYA0000214 SUB TRANSFORMER
PC5701 B3PBA0000503 PHOTO COUPLER
PC5702 B3PBA0000503 PHOTO COUPLER
PC5720 B3PBA0000503 PHOTO COUPLER
PC5799 B3PBA0000503 PHOTO COUPLER
F1 K5D802BNA005 FUSE
TH5702 D4CAA2R20001 THERMISTOR
TH5860 D4CC11040013 THERMISTOR
TH5861 D4CC11040013 THERMISTOR
TH5900 D4CC11040013 THERMISTOR
P5701 K2AA2B000011 AC INLET
R5708 ERJ8GEYJ155V 1.5M 1/4W
R5709 ERJ8GEYJ155V 1.5M 1/4W
C5700 F1BAF471A013 470pF
C5701 F0CAF104A105 0.1uF
C5703 F0CAF224A105 0.22uF
C5704 F1BAF471A013 470pF
C5705 F1BAF471A013 470pF
C5708 F1BAF1020020 1000pF
5

2Warning
2.1. Prevention of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) to Electrostatic Sensitive
(ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components commonly are called Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and
semiconductor "chip" components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component da mage
caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap,
which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, p lace the assembly on a cond ucti ve surface su ch as a luminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static (ESD protected)” can
generate electrical charge sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil or comparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
Caution:
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the
brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lif ting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD) suf-
ficient to damage an ES device).
6
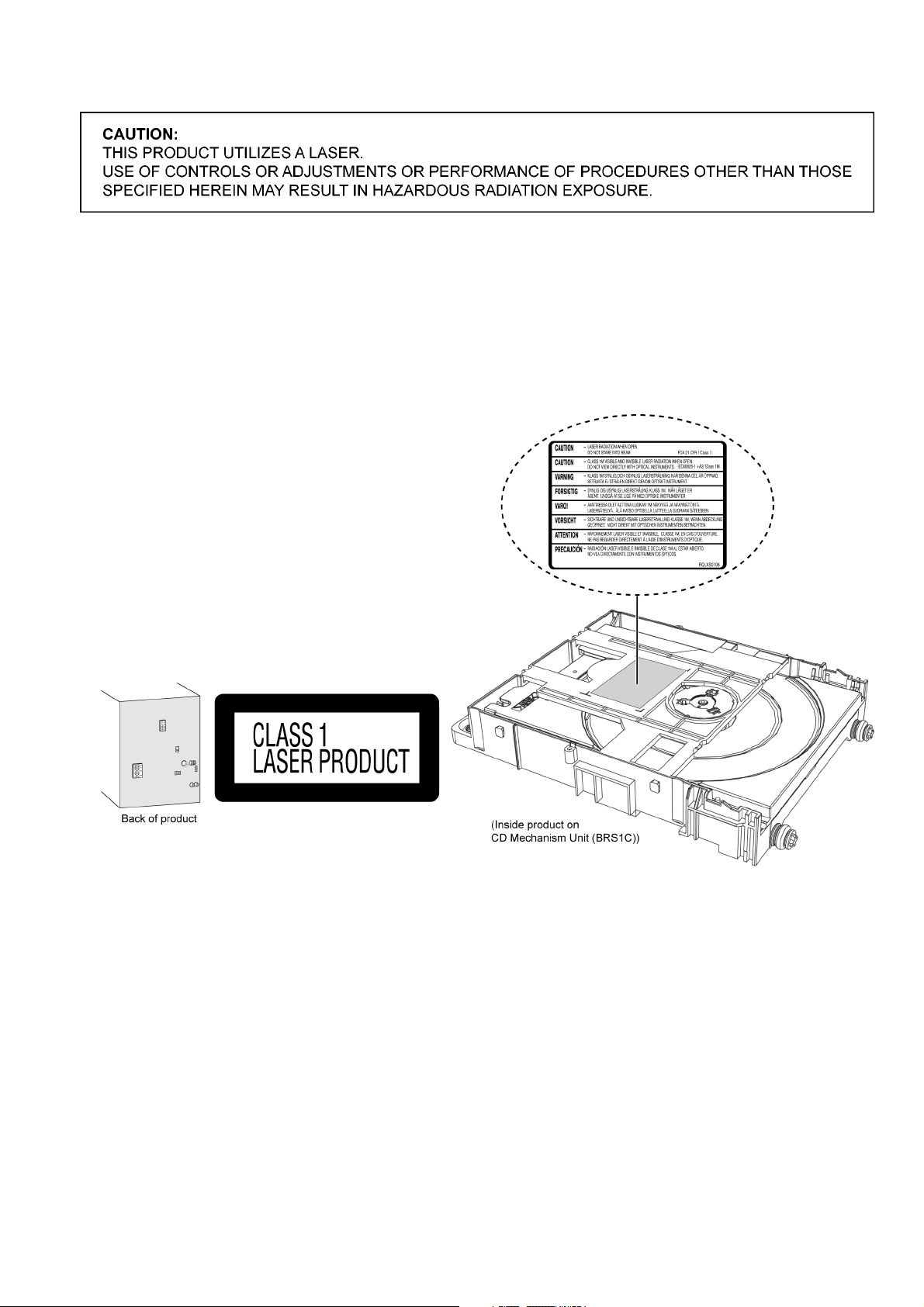
2.2. Precaution of Laser Diode
Caution:
This product utilizes a laser diode with the unit turned “on”, invisible laser radiation is emitted from the pickup lens.
Wavelength: 790 nm (CD)
Maximum output radiation power from pickup: 100 µW/VDE
Laser radiation from the pickup unit is safety level, but be sure the followings:
1. Do not disassemble the pickup unit, since radiation from exposed laser diode is dangerous.
2. Do not adjust the variable resistor on the pickup unit. It was already adjusted.
3. Do not look at the focus lens using optical instruments.
4. Recommend not to look at pickup lens for a long time.
7

2.3. Service caution based on Legal restrictions
2.3.1. General description about Lead Free Solder (PbF)
The lead free solder has been used in the mounting process of all electrical compone nts on the printed circuit boards used for this
equipment in considering the globally environmental conservation.
The normal solder is the alloy of tin (Sn) and lead (Pb). On the other hand, the lead free solder is the alloy mainl y consists of tin
(Sn), silver (Ag) and Copper (Cu), and the melting point of the lead free solder is higher approx.30 degrees C (86°F) more than that
of the normal solder.
Definition of PCB Lead Free Solder being used
The letter of “PbF” is printed either foil side or components side on the PCB using the lead free solder.
(See right figure)
Service caution for repair work using Lead Free Solder (PbF)
• The lead free solder has to be used when repairing the equipment for which the lead free solder is used.
(Definition: The letter of “PbF” is printed on the PCB using the lead free solder.)
• To pu t lead free solder, it should be well molten and mixed with the original lead free solder.
• Remove the remaining lead free solder on the PCB cleanly for soldering of the new IC.
• Since the melting point of the lead free solder is higher than that of the normal lead solder, it takes the longer time to melt the
lead free solder.
• Use the soldering iron (more than 70W) equi pped with the temperature co ntrol after setting the temp erature at 350±30 degrees
C (662±86°F).
Recommended Lead Free Solder (Service Parts Route.)
• The following 3 types of lead free solder are available through the service parts route.
RFKZ03D01K-----------(0.3mm 100g Reel)
RFKZ06D01K-----------(0.6mm 100g Reel)
RFKZ10D01K-----------(1.0mm 100g Reel)
Note
* Ingredient: tin (Sn), 96.5%, silver (Ag) 3.0%, Copper (Cu) 0.5%, Cobalt (Co) / Germanium (Ge) 0.1 to 0.3%
8
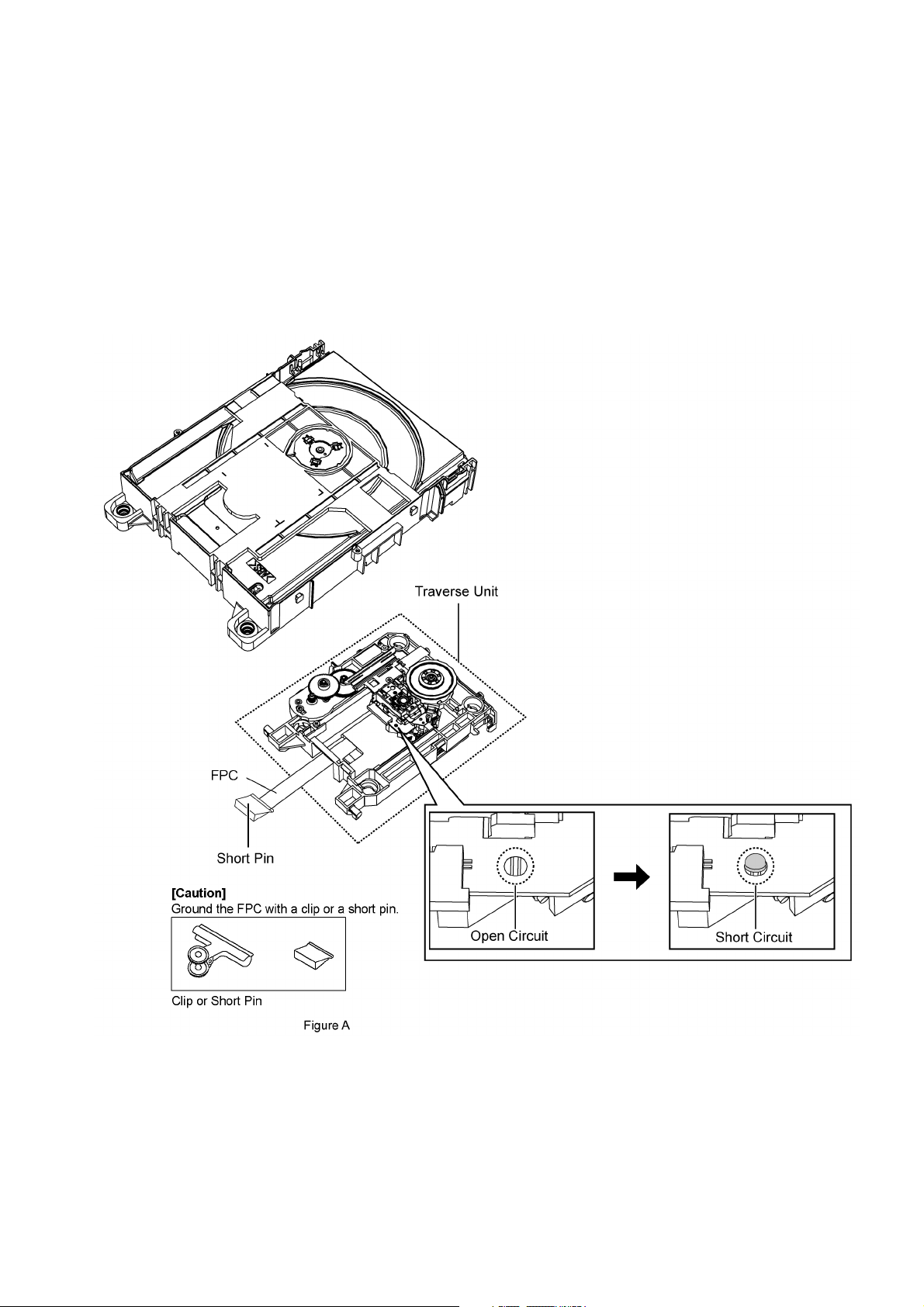
2.4. Handling Precautions for Traverse Unit
The laser diode in the optical pickup unit may break down due to static electricity of clothes or human b ody. Special care must be
taken avoid caution to electrostatic breakdown when servicing and handling the laser diode in the traverse unit.
2.4.1. Cautions to Be Taken in Handling the Optical Pickup Unit
The laser diode in the optical pickup un it may be damaged due to electrostatic discharge generating from clothes or human body.
Special care must be taken avoid caution to electrostatic discharge damage when servicing the laser diode.
1. Do not give a considerable shock to the optical pickup unit as it has an extremely high-precise structure.
2. To prevent the laser diode from the electrostatic discharge damage, the flexible cable of the optical pickup unit removed
should be short-circuited with a short pin or a clip.
3. The flexible cable may be cut off if an excessive force is applied to it. Use caution when handling the flexible cable.
4. The antistatic FPC is connected to the new optical pickup unit. After replacing the optical pickup unit and connecting the flexible cable, cut off the antistatic FPC.
9
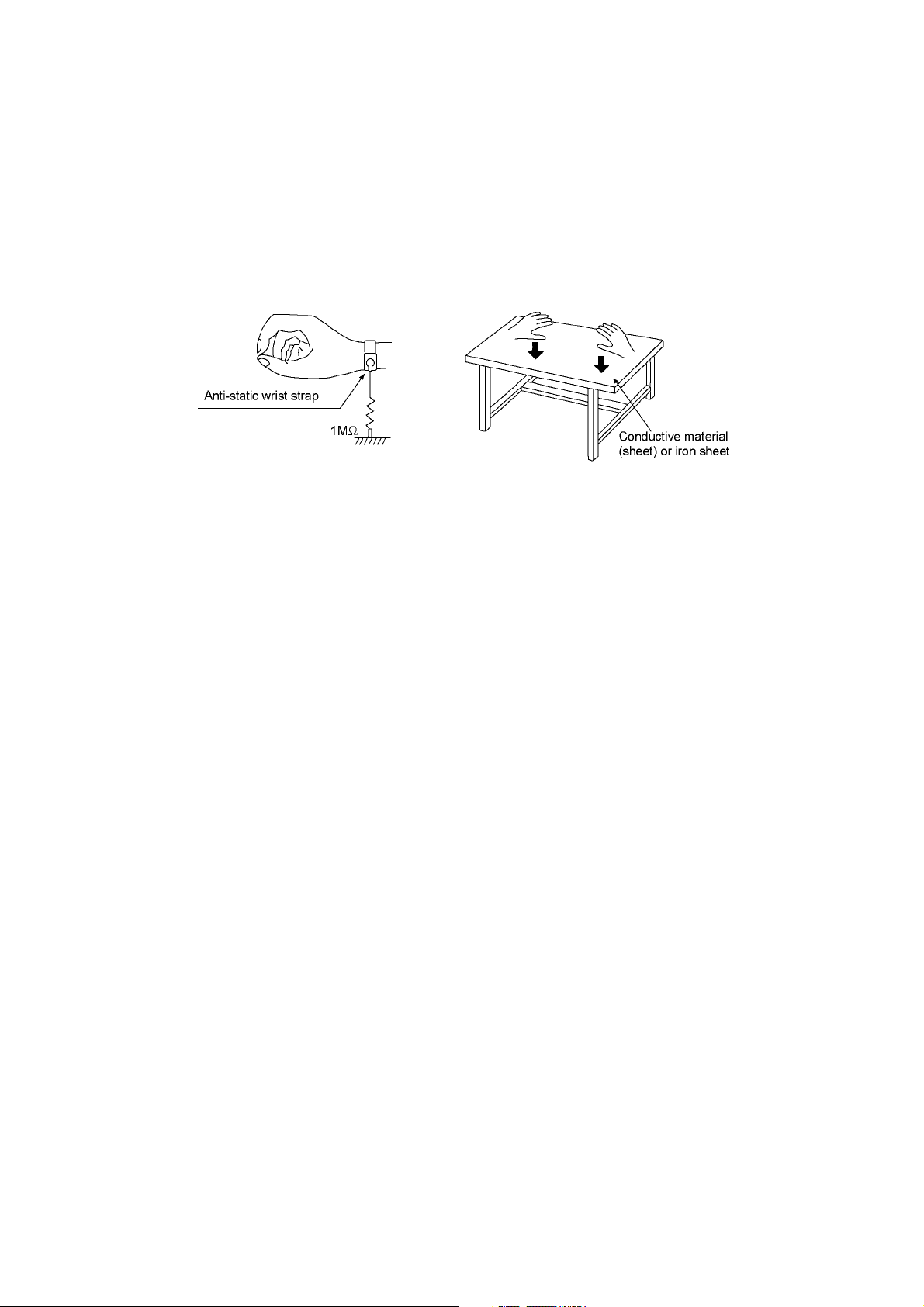
2.4.2. Grounding for electrostatic breakdown prevention
Some devices such as the DVD player use the optical pickup (laser diode) and the optical pickup will be damaged by static electricity in the working environment. Proceed servicing works under the working environment where grounding works is completed.
2.4.2.1. Worktable grounding
1. Put a conductive material (sheet) or iron sheet on the area where the optical pickup is placed, and ground the sheet.
2.4.2.2. Human body grounding
1. Use the anti-static wrist strap to discharge the static electricity form your body.
10

3 Service Navigation
3.1. Service Information
This service manual contains technical information which will allow service personnel’s to understand and service this model.
Please place orders using the parts list and not the drawing reference numbers.
If the circuit is changed or modified, this information wil l be fol lowed by supplemen t service manual to be filed with original se rvice
manual.
• CD Mechanism Unit (BRS1C):
1) This model uses CD Mechanism Unit (BRS1C).
• Micro-processor:
1) The following components are supplied as an assembled part.
- Micro-processor IC, IC2003 (RFKWMAKX92M0)
• Speaker System:
1) This model uses Speaker System, SB-AKX92PU-K.
11

4 Specifications
Q AMPLIFIER SECTION
RMS output power stereo mode
Front Hi (both ch driven)
110 W per channel (5 Ω), 1 kHz, 10% THD
Front Lo (both ch driven)
140 W per channel (4 Ω), 1 kHz, 10% THD
Surround Ch 140 W per channel (4 Ω), 1 kHz, 10% THD
Subwoofer Ch 300 W per channel (8 Ω), 1 kHz, 10% THD
Total RMS stereo mode power 1380 W
Q FM/AM TUNER, TERMINALS SECTION
Preset station FM 30 stations
AM 15 stations
Frequency Modulation (FM)
Frequency range 87.50 to 108.00 MHz (50 kHz step)
Antenna terminal (s) 75 Ω (unbalanced)
Amplitude Modulation (AM)
Frequency range 522 to 1629 kHz (9 kHz step)
520 to 1630 kHz (10 kHz step)
Headphone jack
T erminal Stereo, 3.5 mm jack
Output level (CD, 1 kHz, –20 dB) 0.7 mW + 0.7 mV, 32 Ω (Max)
Mic jack
Sensitivity 0.7 mV, 1.1 kΩ
Terminal Mono, 3.5 mm jack (1 system)
Music port (front)
Sensitivity 100 mV, 4.7 kΩ
Terminal Stereo, 3.5 mm jack
AUX Input RCA pin jack
(Use 128 kbps, approximately 1 song = 4 mins)
Q GENERAL
Power supply AC 110 to 127 V, 220 to 240 V, 50/60 Hz
Power Consumption 165 W
Dimensions (W x H x D) 220 mm x 334 mm x 249 mm
Mass 3.6 kg
Operating temperature range 0 °C to +40 °C
Operating humidity range 35 % to 80% RH
(no condensation)
Power Consumption in standby mode 0.3 W (Approximate)
Notes
1. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Mass and dimensions are approximate.
2. Total harmonic distortion is measured by the digital spectrum
analyzer.
Q System: SC-AKX92PH-K
Main Unit: SA-AKX92PH-K
Front Speakers: SB-PF92PH-K
Surround speakers: SB-PS92PU-K
Subwoofer 1 (with Vol control): SB-WAKX93PUK
Subwoofer 2: SB-WAKX92PUK
Q DISC SECTION
Discs played (8 cm or 12 cm)
(1) CD-Audio (CD-DA)
(2) CD-R/RW (CD-DA, MP3* formatted disc)
(3) MP3*
*MPEG-1 layer 3
Pick up
Wavelength 790 nm(CD)
Audio output (Disc)
Number of channels 2 (FL, FR)
FL = Front left channel
FR = Front right channel
Q USB SECTION
USB Port
USB standard USB 2.0 full speed
Media file format support MP3 (*.mp3)
USB device file system FAT12, FAT16, FAT32
USB Port power 500 mA (max)
Bit Rate 16 kbps to 320 kbps (playback)
USB recording
Bit Rate 128 kbps, 192 kbps, 320 kbps
USB recording speed 1x,4x (CD only)
recording file format MP3 (*.mp3)
Q INTERNAL MEMORY SECTION
Memory
Memory size 4 GB
Memory File format MP3 (*.mp3)
Memory recording
Bit Rate 128 kbps, 192 kbps, 320 kbps
Memory Recording speed 1x,4x, (CD only)
Recording file format MP3 (*.mp3)
Capacity of total song recoreded 1000 song
12
5 Location of Controls and Components
5.1. Main Unit Key Button Operation
13

5.2. Remote Control Key Button Operation
14

5.3. Media Information
15

6 Self-Diagnostic and Special Mode Setting
6.1. Cold-Start
Here is the procedure to carry out cold-start or initialize to shipping mode.
1. Unplug AC power cord
2. Press & hold [POWER] button
3. Plug AC power cord while [POWER] button being pressed
FL Display will show “_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _”
4. Release [POWER] button
16
6.2. Doctor Mode Table
6.2.1. Doctor Mode Table 1
Doctor Mode
Micro-P Version
Display
Item
DescriptionMode Name
To enter into Doctor Mode
To check the firmware version
for Jupiter & Microprocessor IC.
Display 1 will display for 2 secs,
followed by display 2.
Display 1:
Display 2:
FL Display
Key Operation
Front Key
1.In CD Mode:
Press [ ] button on main
unit follow by [4] and [7] on
remote control.
2.To exit, press [OK] button on
remote control or press
[POWER, /I] button on main
unit or remote control.
In Doctor Mode:
1.Press [2] button on
remote control.
Jupiter
Micro-P
Version
Micro-processor
Version
17
6.2.2. Doctor Mode Table 2
Cold Start
Volume Setting
Check
FL Display
Check
CD Open
Check
BRS1C Reliability
Test (Traverse)
Item
DescriptionMode Name
To active cold start upon next AC
power up when reset start is execute
the next time.
To check the volume setting of a main
unit.
To check the FL segment display
All segment will light up while all LED
blink at 0.5s,intervals.(if any)
To excute CD Open operation.
To determine CD Mechanism BRS1C
Access Inner & Outer disc operation.
In this mode,ensure the CD is in the
main unit.
Note: Refer to Section 6.3 Fig 2. for
process flow.
FL Display
Press [7]: VOL50
Press [8]: VOL35
Press [9]: VOL0
Press [PLAY/RADIO MODE]: VOL30
The counter will
increment by one.
When reach 9999
will change to 0000
Cancellation Display
Volume
Key Operation
Front Key
In Doctor Mode:
1. Press [DISPLAY/-DIMMER]
button on remote control.
In Doctor Mode:
1. Press [7],[8],[9],
[PLAY MENU/RADIO
MENU] button on remote
control.
In Doctor mode:
1. Press [1] button on
remote control.
In Doctor mode:
1. Press [DEL] button on
remote control.
In Doctor Mode:
1. Press [10] [1] [2] button
on remote control.
2. To cancel, press [0]
on remote control.
BRS1C Reliability
Test
(Combination)
BRS1C Reliability
Test (Loading)
To determine CD Mechanism Unit
(BRS1C) Open/Close & Access Inner &
Outer Disc Operation.
In this mode,ensure the CD is in the
main unit.
Note: Refer to Section 6.3 Fig 3. for
process flow.
To determine CD Mechanism Unit
(BRS1C) Open/Close operation.
In this mode, the tray will open &
close.
Note: Refer to Section 6.3 Fig 1 for
process flow.
In Doctor Mode:
1. Press [10] [1] [5] button
on remote control.
The counter will
increment by one.
When reach 9999
will change to 0000
Cancellation Display
2. To cancel, press [0]
on remote control.
In Doctor Mode:
1. Press [10] [2] [1] button
on remote control.
The counter will
increment by one.
When reach 9999
will change to 0000
Cancellation Display
2. To cancel, press [0]
on remote control.
18
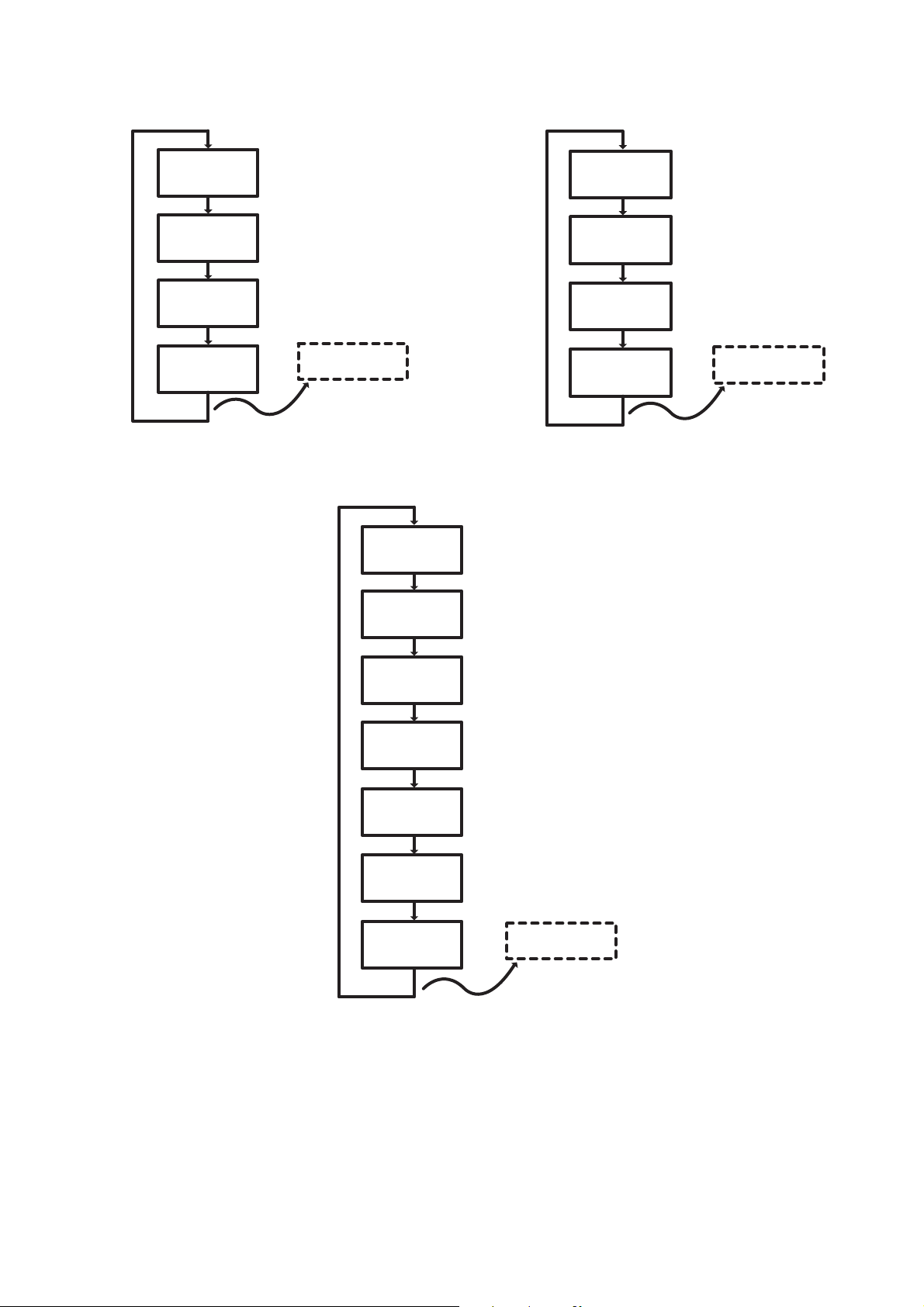
6.3. Reliability Test Mode (CD Mechanism Unit (BRS1C))
Below is the process flow chart of the aging test for the CD Mechanism Unit (BRS1C).
OPEN
Operation
OPEN wait
fot 1 s
CLOSE
Operation
CLOSE wait
for 4s
Fig. 1. Reliability Test (Loading)
Count up
First Track
Access
First Track
Play 10 s
First Track
Access
First Track
Play 5 s
Last Track
Access
Last Track
Play 5 s
Fig. 2. Reliability Test (Traverse)
Count up
Last Track
Access
Last Track
Play 10 s
Open
Operation
Open wait
for 1 s
CLOSE
Operation
Fig. 3. Reliability Test (Combination)
Count up
19
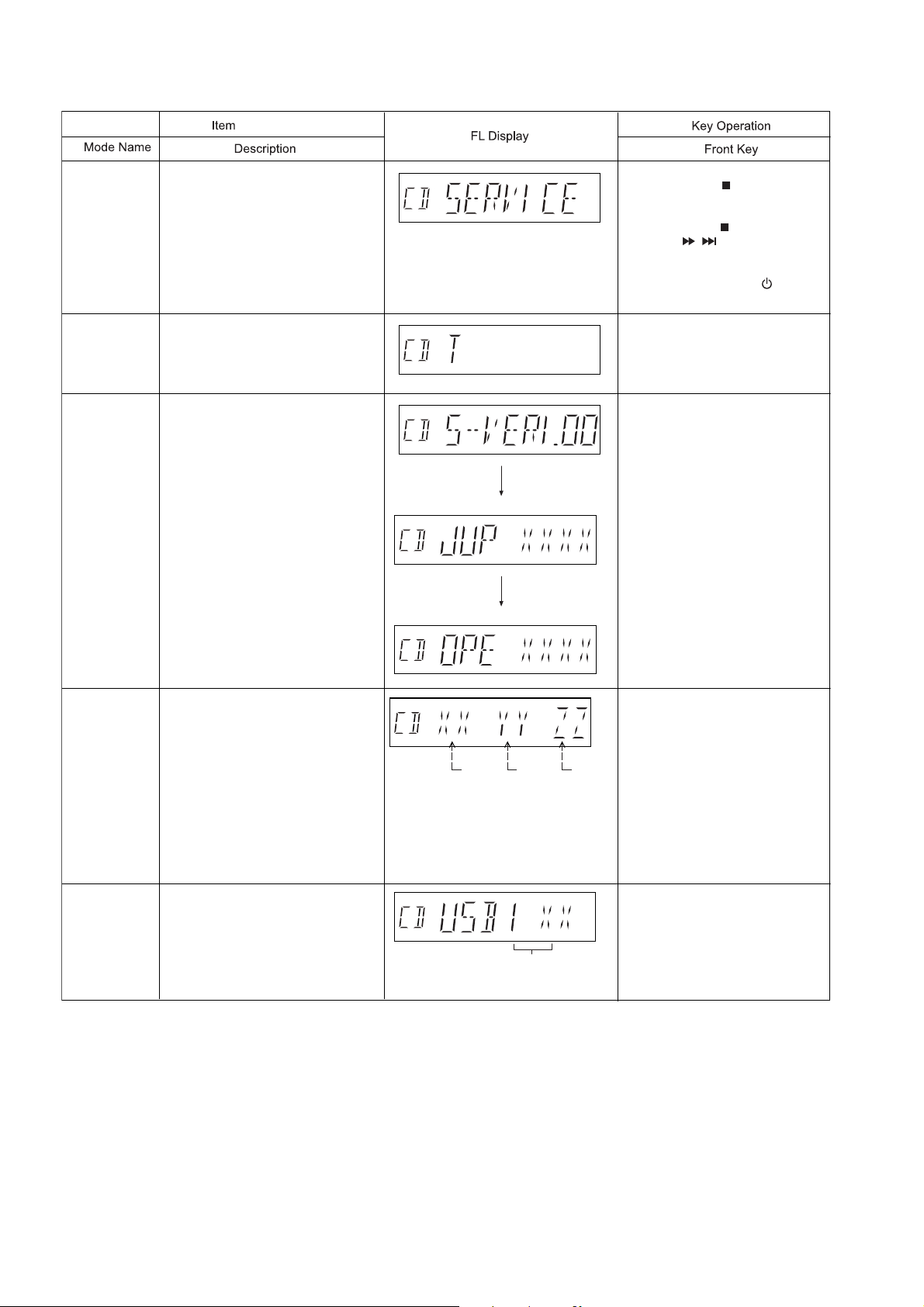
6.4. Self-Diagnostic Mode
Service Mode
Error Code
History
Software
Display
Version.
To enter into Service Mode
Checking the records for Error Code.
If there’s no error code.Display will
remain as [T ]
To check for following:
1)System Version.
2)Jupiter Micro-processor Version.
In CD Mode:
1.Press and hold [ ] button on
main unit for 2 secs.
2.Do not release [ ] button, press
and hold [ / ] on the remote
control for 2 secs.
3.To exit, press [POWER, ]
button on main unit.
In Service Mode:
1.Press button [1] on remote control.
2.To clear history,press & hold [0] for
5 seconds or more
In Service Mode:
1.Press button [2] on remote control.
2.Press button [2] on remote control.
/l
Display of AD
value of main
body key
USB Error
Code History
3) Opecon Version.
To check the AD input value In Service Mode:
XX: AN2 input value (2 hexadecimal
value digits) --> KEY1
YY: AN3 input value (2 hexadecimal
value digits) --> KEY2
ZZ: AN4 input value (2 hexadecimal
value digits) --> KEY3
To check for USB error Codes.
History
number
3.Press button [2] button on remote
control.
1.Press button [ 4 ] on remote
control for 2 secs.
AN4AN3AN2
In Service Mode:
1.Press button [5] on remote control.
2.To clear history,press & hold [0] for
5 seconds or more.
20
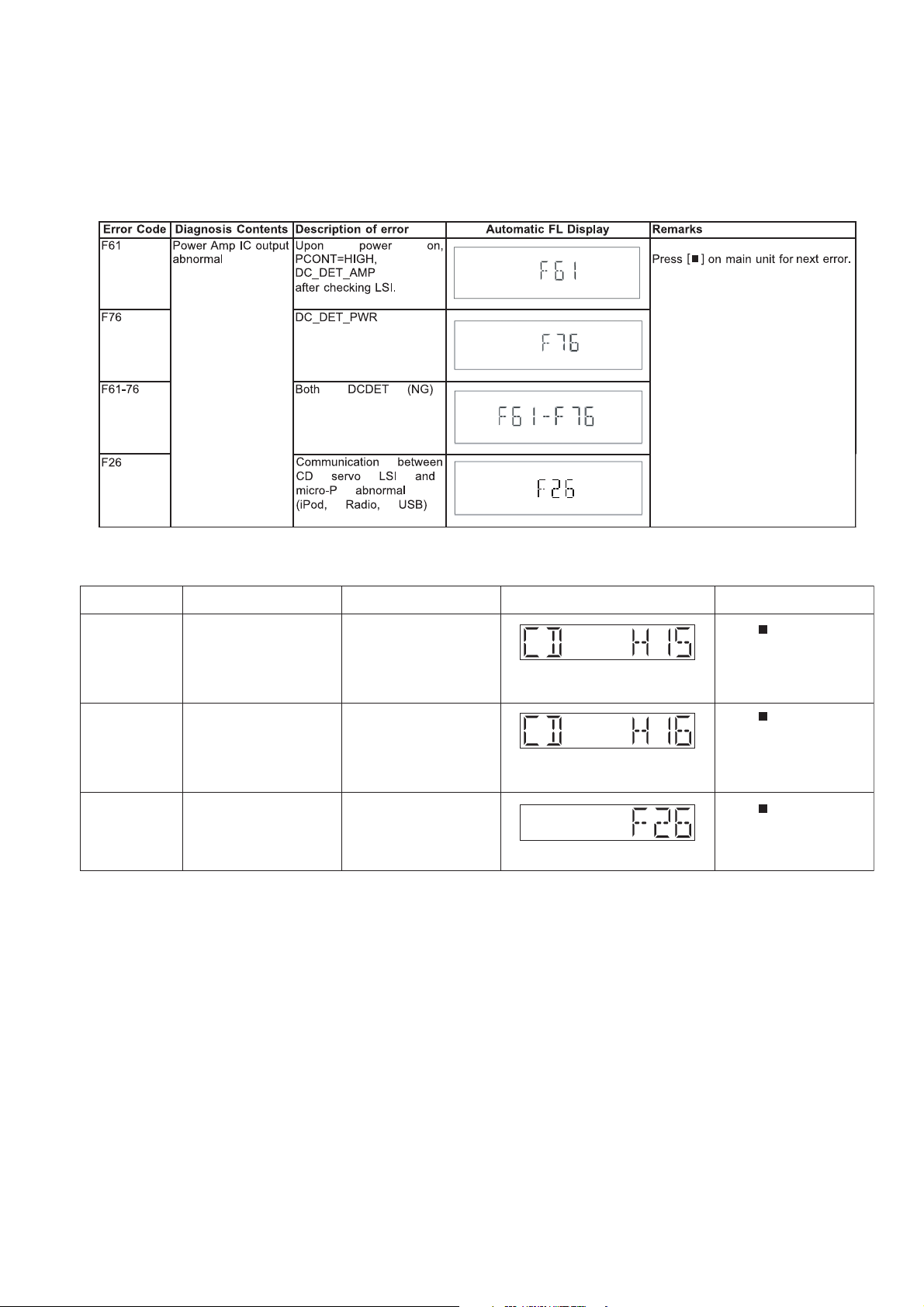
6.5. Self-Diagnostic Error Code Table
Self-Diagnostic Function (Refer Section 6.4. Self-Diagnostic Mode) provides information on any problems occurring for the unit and
its respective components by displaying the error codes. These error code such as U**, H** and F** are stored in memory and held
unless it is cleared.
The error code is automatically display after entering into self-diagnostic mode.
6.5.1. Power Supply Error Code Table
6.5.2. CD Mechanism Error Code Table (CD Mechanism Unit (BRS1C))
Error Code Diagnostic Contents Description of error Automatic FL Display Remarks
CD H15 CD Open Abnormal During operation
CD H16 CD Closing Abnormal During operation
F26 Communication between
CD servo LSI and micro-p
abnormal.
POS_SW_R On fail to be
detected with 4 sec. Error
No. shall be clear by force
or during cold start.
POS_SW_CEN On fail to
be detected with 4 sec.
Error No. shall be clear by
force or during cold start.
During switch to CD function, if SENSE = “L” within
failsafe time of 20ms.
Press [
next error.
Press [
next error.
Press [
next error.
] on main unit for
] on main unit for
] on main unit for
21
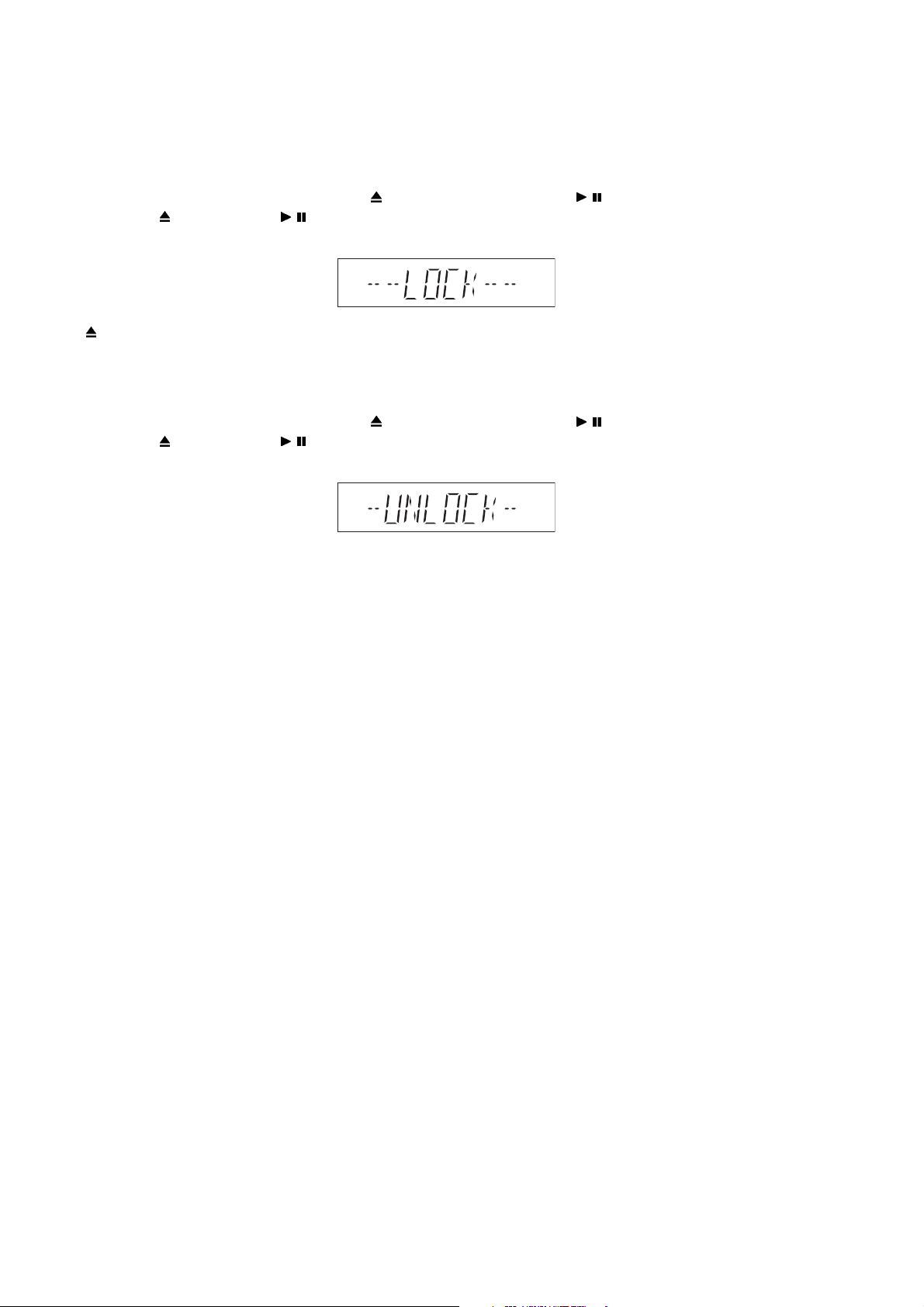
6.6. Sales Demonstration Lock Function
6.6.1. Entering into sales Demo Mode
Here is the procedures to enter into Sales Demonstration Lock.
Step 1: Turn on the unit.
Step 2: Select to any mode function, press and hold [
Step 3: Hold both [
Step 4: The display will show upon entering into this mode.
OPEN/CLOSE] and [ / ] keys for 5 sec.
OPEN/CLOSE] key and follow by [ / ] key pressed within 0.5 sec.
Note: [
OPEN/CLOSE] button is invalid and the main unit displays “LOCKED” while the lock function mode is entered.
6.6.2. Cancellation
Step 1: To cancel only can be triggered in CD Mode and Volume 19.
Step 2: Select to any mode function, press and hold [
Step 3: Hold both [
Step 3: The display will show after exit from this mode.
OPEN/CLOSE] and [ / ] keys for 5 sec.
OPEN/CLOSE] key and follow by [ / ] key pressed within 0.5 sec.
22
7 Troubleshooting Guide
7.1. Troubleshooting Guide for F61 and/ or F76
This section illustrates the checking procedures when upon detectin g th e error of “F61” and “F76” after power up of the unit.It is for
purpose of troubleshooting and checking in SMPS,D-Amp & Main P.C.B..
Symptom Remarks
Set cannot ON 1 AC Cord 1 Faulty AC Cord, Loose connection
2 AC Inlet, P5701 2 P5701 solder crack, dry joint.
3 Fuse, F1 3 Fuse, F1 Open
4 Photocoupler 4 PC5702/PC5799 solder crack.
PC5702, PC5799 Dry joint, short circuit, open circuit.
5 Switching IC, IC5701 5 IC5701 Faulty.
6 Switching IC, IC5799 6 IC5799 Faulty.
Set can ON 1 Speaker Output 1a Faulty speaker unit, Loose connection, Short.
then F61
2 D-AMP circuit
Set can ON 1 Transformer T5701 1a Short circuit between Pin 14 and Pin 15.
then F76 1b Short circuit between Pin 15 and Pin 16.
2 DC-DC Circuit 2a Check cable wire connection between connector
1b Check output IC (Pin 10 & 14) which have DC Voltage
at speaker output short to Vdd/Vss.
2a D-Amp IC5000, IC5200, IC5300, IC5400 defective.
Check PWM output at pin 10, 14 of D-Amp IC.
Check + VDD/SS supply at pin 4 & 20 of D-Amp IC.
Check pin 1 (OSC) & pin 23 (MODE) of D-Amp IC.
Check pattern crack and solderability.
2b D-AMP IC, IC5900 defective.
(DC voltage of +/-30V detected at speaker output)
1c Short circuit between Pin 16 and Pin 17.
ZJ2007(At Main P.C.B) & connector CN5802
(At SMPS P.C.B)
2b Voltage regulator IC (IC2010) & DC/DC Converter IC
(IC2011) faulty.
Possible Fault(s)Checking Items
Refer to
section 7.2.1
Fig.1 SMPS P.C.B..
Refer to section
7.2.3 Fig 3 D-Amp
P.C.B..
Refer to section
7.2.4 Fig 4
Surround
D-Amp P.C.B..
Refer to
section 7.2.1
Fig.1 SMPS P.C.B..
Refer to
section 7.2.2
Fig.2 Main P.C.B..
3 Photocoupler 3 PC5720 solder crack.
Set can ON 1 Rectifier D5801 1a Improper contact between D5801 to Heatsink
working normally Rectifier D5802
for some time 2 Thermistor TH5860 1b Set trigger temperature protection.
then F76
PC5720 dry joint, short circuit, open circuit.
Improper contact between D5802 to Heatsink
Refer to
section 7.2.1
Fig.1 SMPS P.C.B..
23
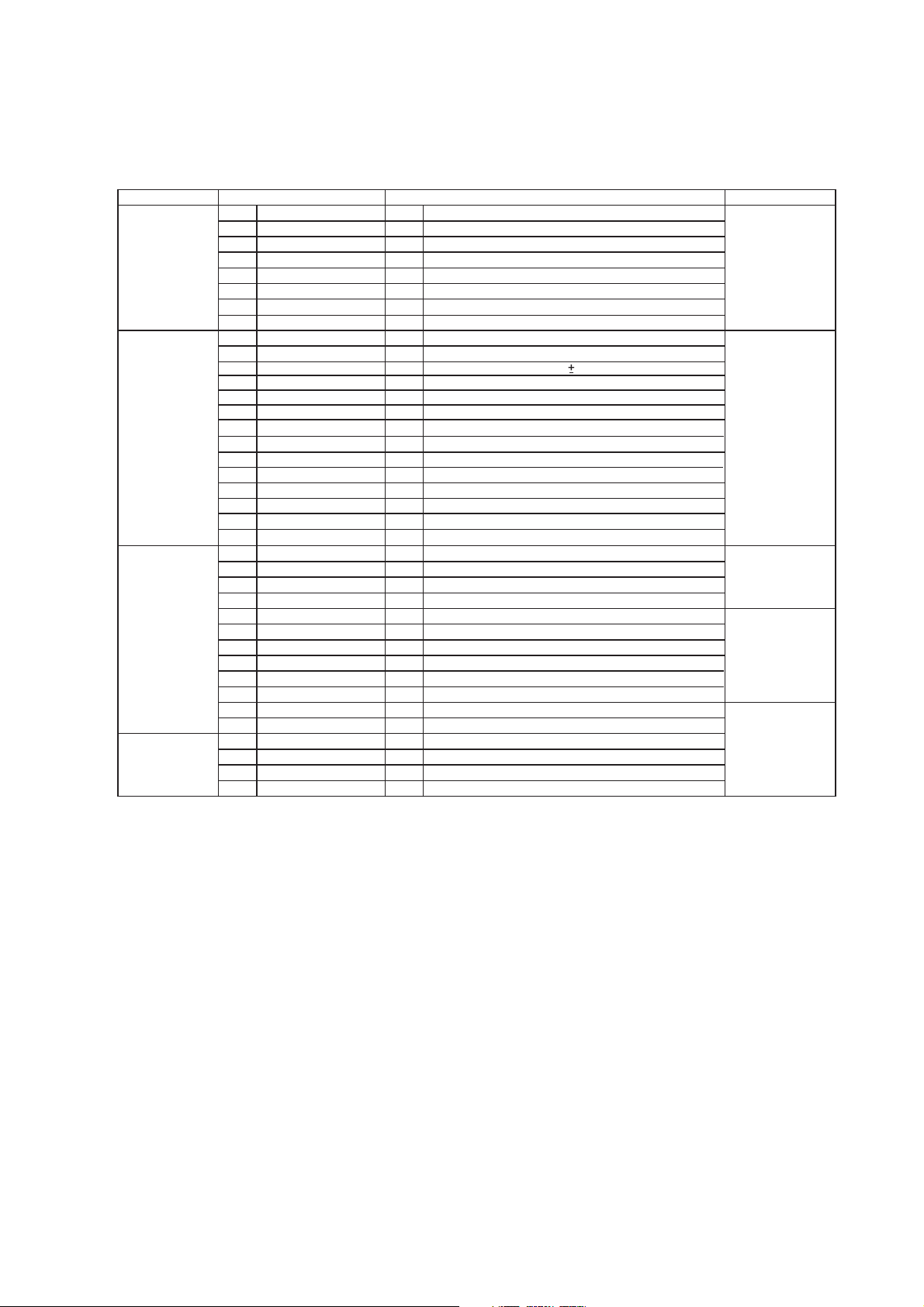
7.2. Part Location
7.2.1. SMPS P.C.B.
Switching Regulator
IC: IC5701
AC Inlet:
P5701
Switching
Regulator IC:
IC5799
Thermistor:
TH5860
Fuse:
F1
Photocoupler:
PC5702, PC5799
Transformer:
T5701
Rectifier Diode:
D5801, D5802
Connector:
CN5802
Photocoupler:
PC5720
Fig. 1 SMPS P.C.B.
24
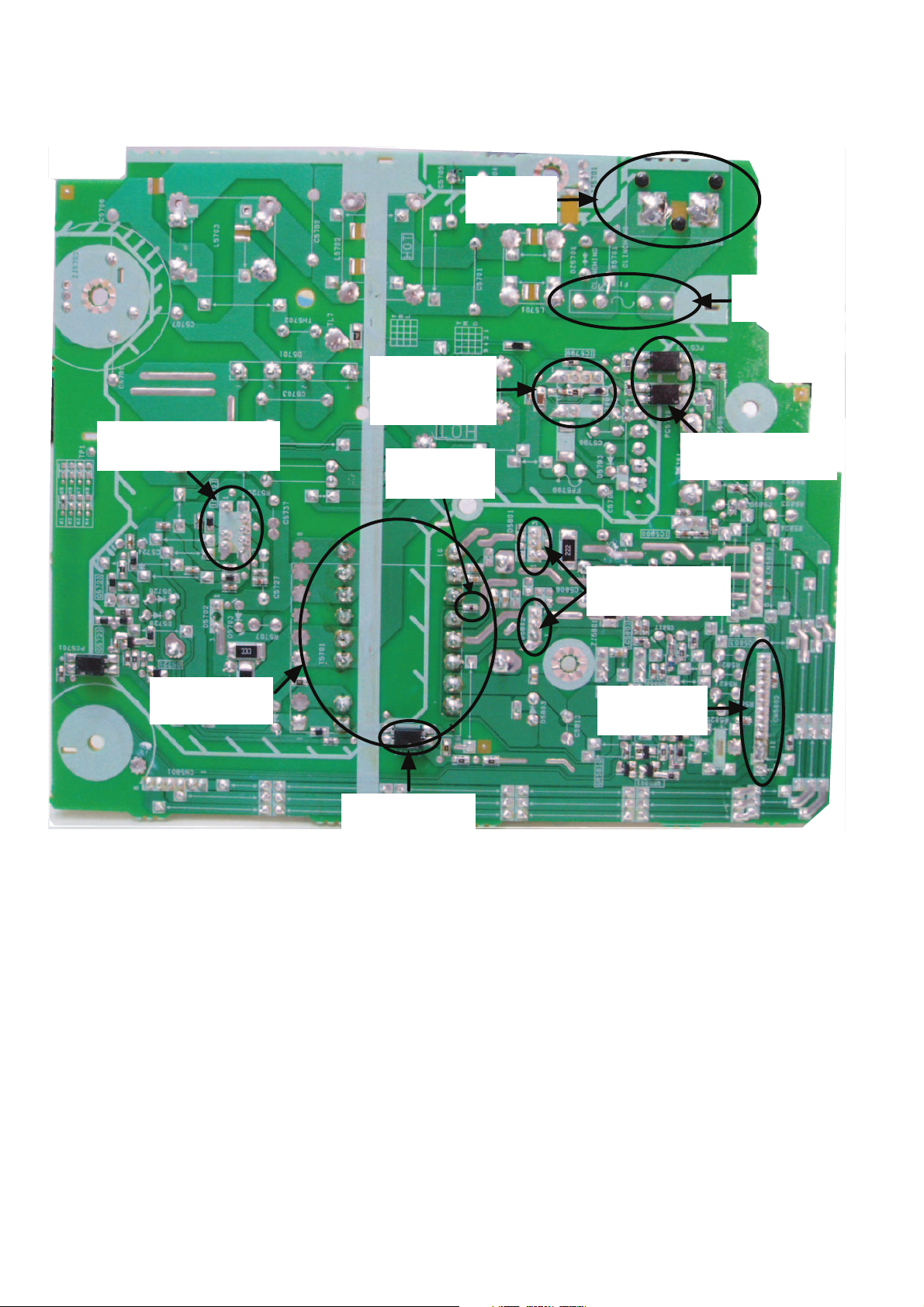
7.2.2. Main P.C.B.
Voltage Regulator IC:
IC2010
DC/DC Converter IC:
IC2011
Connector:
ZJ2007
Fig. 2 Main P.C.B.
25
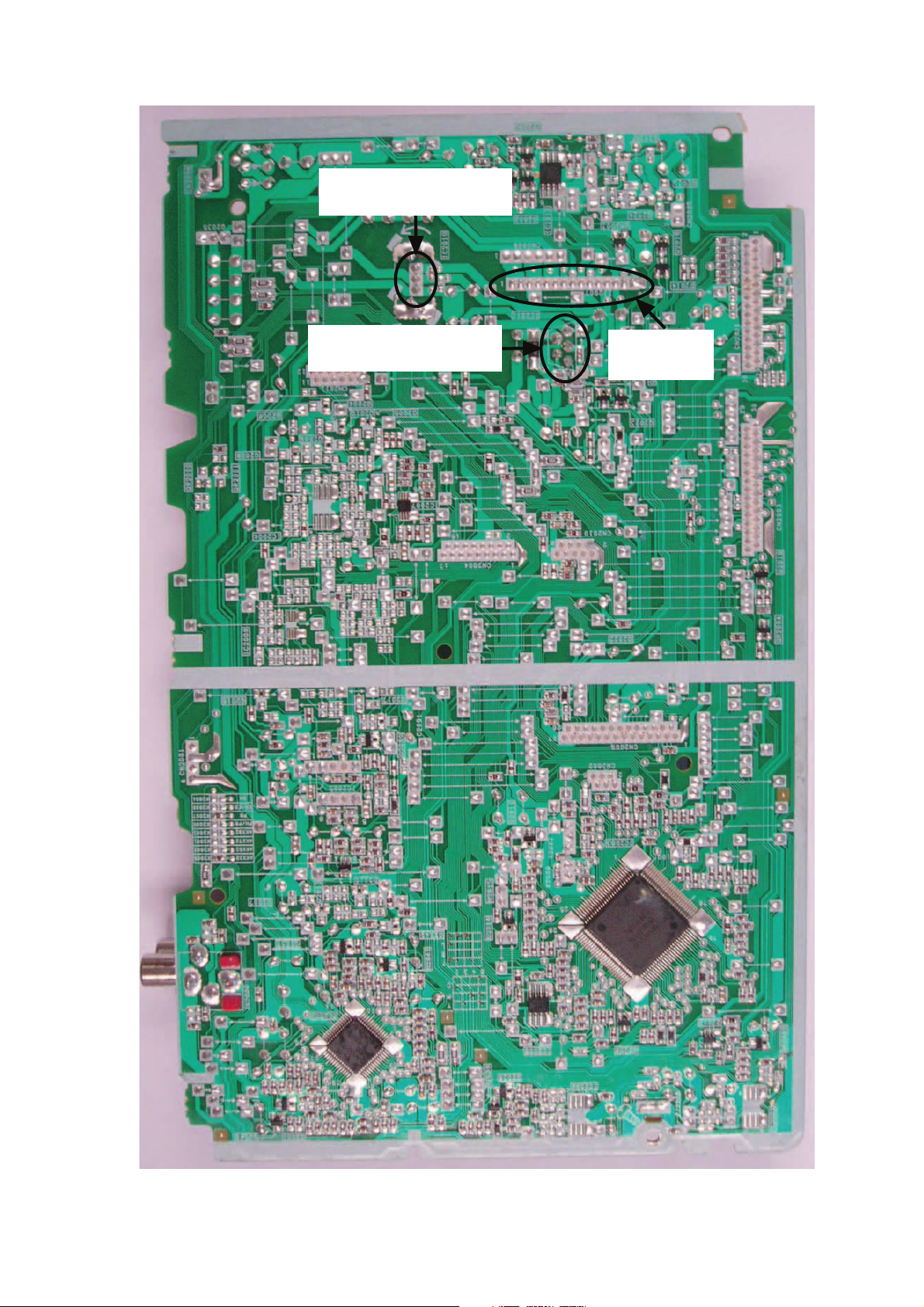
7.2.3. D-Amp P.C.B.
Audio Digital
Amp IC: IC5400
Audio Digital
Amp IC: IC5000
Audio Digital
Amp IC: IC5300
Audio Digital
Amp IC: IC5200
Fig. 3 D-Amp P.C.B.
26
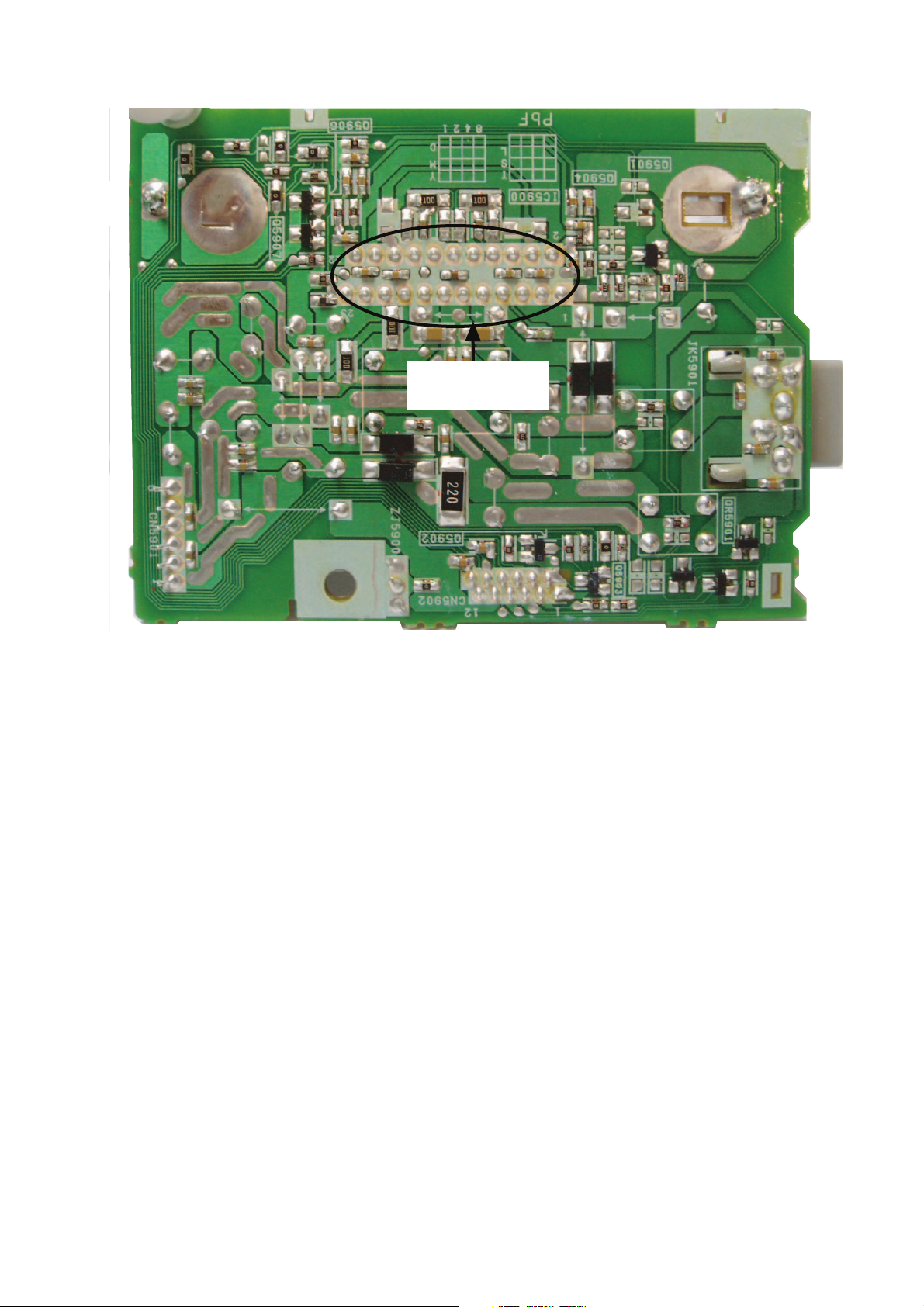
7.2.4. Surround D-Amp P.C.B.
Audio Digital
Amp IC: IC5900
Fig. 4 Surround D-Amp P.C.B.
27
7.3. D-Amp IC Operation & Control
D-AMP IC Operation & Control
1) D-AMP IC (C1AB00000497) was used for this model.
2) Three control pins (signal send from micro-processor IC) were used to control the D-AMP IC
operation such as muting, standby and normal operation. They are described as below: -
No Pin no Signal name Function
1 4 F_HOP Frequency Hop control.
2 6 MODE_DA Digital Amp On/Off control.
3 3 MUTE_F Digital Amp Muting control
Table 1: Digital AMP Pin Control.
Here is detailed description of the three control pins for the D-AMP IC
A) MODE_DA & MUTE_F were used to switch the D-AMP IC in the following muting status:
x L(Low/OFF): Standby / OFF
x H (High/ON): Operating or Mute
Below is the logic for the two pins used for the control of the D-AMP IC.
No MODE_DA MUTE_F Digital AMP IC mode status
1 L X OFF (0V)
2 H H Mute (2.5V)
3 H L Operating(5V)
Table 2: Digital AMP IC Mode Status.
Note: Standby/OFF condition of D.AMP IC is available / activated only during the following
event: Switching of Frequency Hoping, power off and start up (when the unit is undergoing
the transition from standby to normal operation mode)
B) F_HOP is used to control the D-AMP operation to avoid interference with AM source by
controlling the frequency source used. It will switch from one frequency to the other, depending on
the tuned AM frequency.
For 9 KHz Step
AM Band Frequency F_HOP Switching Frequency
522 ~ 558 L 301
567 ~ 639 H 350
648 ~ 855 L 301
864 ~ 945 H 350
954 ~ 1152 L 301
1161 ~ 1242 H 350
1251 ~ 1449 L 301
1458 ~ 1539 H 350
1548 ~ 1629 L 301
Table 3: F_HOP Control during 9 kHz Step
For 10 KHz Step
AM Band Frequency F_HOP Switching Frequency
520 ~ 560 L 301
570 ~640 H 350
650 ~ 860 L 301
870 ~ 950 H 350
960 ~ 1160 L 301
28

1170 ~ 1250 H 350
1260 ~ 1450 L 301
1460 ~ 1540 H 350
1550 ~ 1710 L 301
Table 4: F_HOP Control during 10 kHz Step
Note: During activating, the 3 control pins namely MUTE_F, MUTE_A and MODE_DA must
be used to cover the “Pop” sound cause by F-HOP switching.
29

8 Service Fixture & Tools
8.1. Service Tools and Equipment
Prepare service tools before process service position.
Service Tools Remarks
Main P.C.B. (ZJ2007) - SMPS P.C.B. (CN5802) REXX1206 (15P Cable Wire)
30
 Loading...
Loading...