Panasonic CT-2017F Service Manual
ORDER NO. MT NC020410A1
B1
Service Manual
Color Television
S
m
i
p
l
i
f
i
e
d
Simplified Manual
(NA7DM)
Panasonic
Model
CT-2017F AP391
Chassis
This Simplified Service Manual is issued to add listed models to the Main Service Manual order No.
MTNC010303C1(CT-20R6E). A set of schematics, unique settings and a complete parts list are included in this
Manual.
Please file and use this Simplified Service Manual together with Main Service Manual, order No. MTNC010303C1 .
“WARNING! This ServiceManualis designed forexperiencedrepairtechnicians only and is not designedfor use bythe general public.
It does not contain warnings or cautions to advise non-technical individuals of potential dangers in attempting to service a product.
Productspowered byelectricityshouldbeservicedorrepairedonlybyexperiencedprofessionaltechnicians.Anyattempttoservice
or repair the product or products dealt with in this Service Manual by anyone else could result in serious injury or death.”
The service technician is requiredtoreadand follow the “Safety Precautions”and“Important Safety Notice” in this Main Manual.
Copyright2002by Matsushita Electric Corporation of
America. All rights reserved. Unauthorized copying
and distribution is a violation of law.
Important Safety Notice
Special components are used in this television set which are important for safety. These parts are identified on the
schematic diagram by the symbol and printed in BOLD TYPE on the replacement part list. It is essential that
these critical parts are replaced with the manufacturer’s specified replacement part to prevent X-ray radiation,
shock, fire or other hazards. Do not modify the original design without the manufacturer’s permission.
Safety Precautions
General Guidelines
An Isolation Transformer should always be used
during the servicing of a receiver whose chassis is not
isolated from AC power line. Use a transformer of
adequate power rating as this protects the technician
from accidents resulting in personal injury from
electrical shocks. It will also protect the Receiver from
being damaged by accidental shorting that may occur
during servicing.
When servicing, observe the original lead dress,
especially in the high voltage circuit. Replace all
damaged parts (also parts that show signs of
overheating.)
Always Replace Protective Devices,suchas
fishpaper, isolation resistors and capacitors, and
shields after servicing the Receiver. Use only
manufacturer’s recommended rating for fuses, circuits
breakers, etc.
High potentials are present when this Receiver is
operating. Operation of the Receiver without the rear
cover introduces danger for electrical shock. Servicing
should not be performed by anyone who is not
thoroughly familiar with the necessary precautions
when servicing high-voltage equipment.
Extreme care should be practiced when Handling the
Picture Tube. Rough handling may cause it to implode
due to atmospheric pressure. (14.7 lbs per sq. in.). Do
not nick or scratch the glass or subject it to any undue
pressure. When handling, use safety goggles and
heavy gloves for protection. Discharge the picture
tube by shorting the anode to chassis ground (not to
the cabinet or to other mounting hardware). When
discharging connect cold ground (i.e. dag ground lead)
to the anode with a well insulated wire or use a
grounding probe.
Avoid prolonged exposure at close range to unshielded
areas of the picture tube to prevent exposure to
X-ray radiation.
The Test Picture Tube used for servicing the chassis
at the bench should incorporate safety glass and
magnetic shielding. The safety glass provide shielding
for the tube viewing area against X-ray radiation as
well as implosion. The magnetic shield limits the X-ray
radiation around the bell of the picture tube in addition
to the restricting magnetic effects. When using a
picture tube test jig for service, ensure that the jig is
capable of handling 35kV without causing
X-ray radiation.
Before returning a serviced receiver to the owner,
the service technician must thoroughly test the unit to
ensure that is completely safe to operate. Do not use a
line isolation transformer when testing.
Leakage Current Cold Check
Unplug the AC cord and connecta jumper between the
two plug prongs.
Measure the resistance between the jumpered AC plug
and expose metallic parts such as screwheads,
antenna terminals, control shafts, etc.
If the exposed metallic part has a return path to the
chassis, the reading should be between 240kΩ and
5.2MΩ. If the exposed metallic part does not have a
return path to the chassis, the reading should be
infinite.
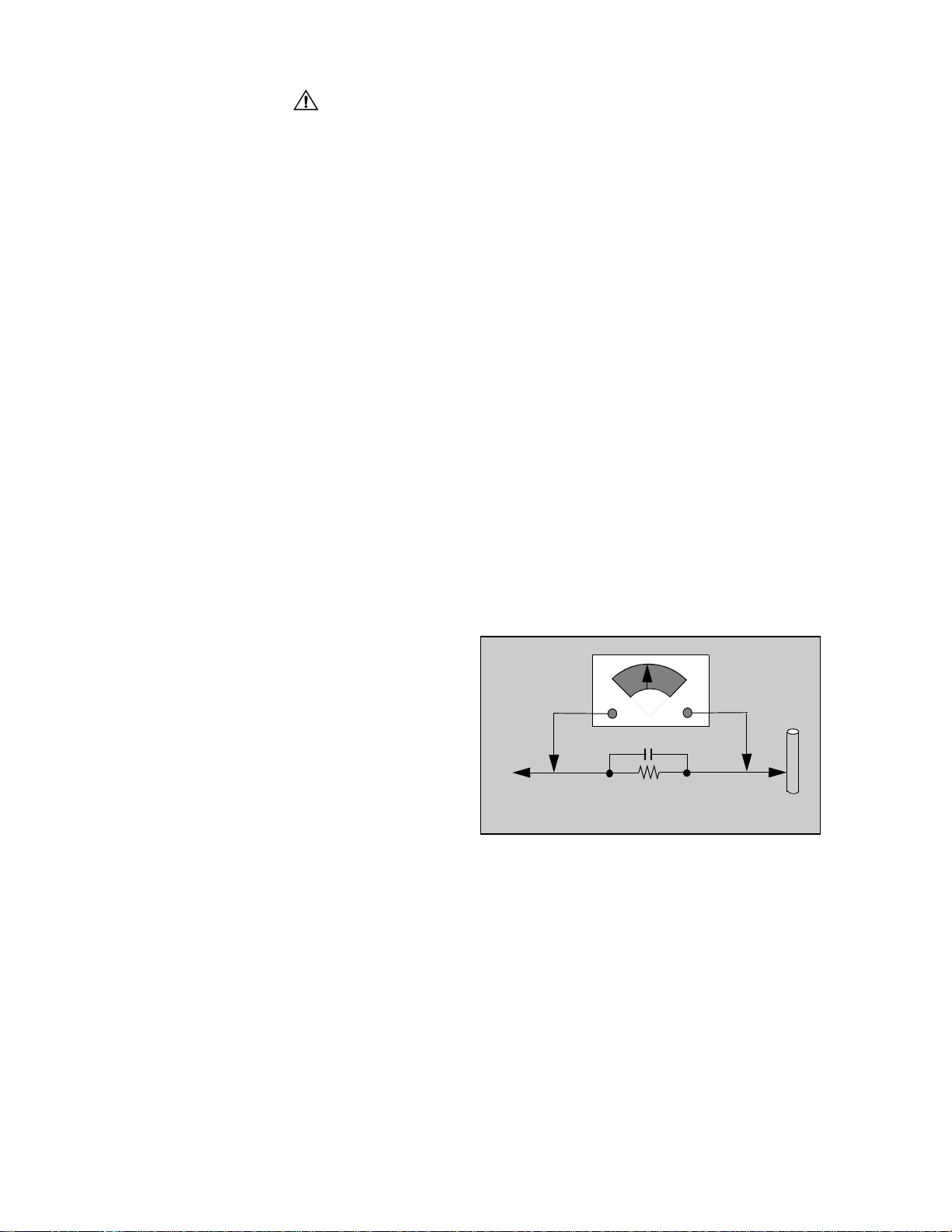
Leakage Current Hot Check (Fig. 1)
Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use
an isolation transformer during the check.
Connect a 1.5kΩ 10 watt resistor in parallel with a
0.15µF capacitor between an exposed metallic part
and ground. Use earth ground, for example a
water pipe.
Using a DVM with a 1000 ohms/volt sensitivity or
higher, measure the AC potential across the resistor.
Repeat the procedure and measure the voltage
present with all other exposed metallic parts.
Verify that any potential does not exceed 0.75 volt
RMS. A leakage current tester (such a Simpson Model
229, Sencore Model PR57 or equivalent) may be used
in the above procedure, in which case any current
measure must not exceed 0.5 milliamp. If any
measurement is out of the specified limits, there is a
possibility of a shock hazard and the Receiver must be
repaired and rechecked before it is returned to the
customer.
AC VOLTMETER
COLD
WATER
PIPE
(GROUND)
0.15µF
TO
INSTRUMENT’S
EXPOSED METAL
PARTS
1500Ω,10 W
Figure 1. Hot Check
X-ray Radiation
WARNING: The potential source of X-ray radiation in the
TV set are the High Voltagesection and the picture tube.
Refer to X-RAY PROTECTON CIRCUIT CHECK in
Service Notes in this manual to confirm HHS Volt age.
High Voltage (CRT Anode)
Confirm Anode voltage is within limits:
Set the BRIGHTNESS, PICTURE, SHARPNESS and
COLOR to minimum (To obtaina dark image). Measure
High Voltage. It should be:
26.60±1. 25 kVfor CT-2017F
If the upper limit is out of tolerance, immediate service
and correction is required.
Note: It is important to use an accurate,
calibrated high voltage meter.
.
-2-
About lead free solder (PbF)
Note: Lead is listed as (Pb) in the periodic table of elements.
In the information below, Pb will refer to Lead solder, and PbF will refer to Lead Free Solder.
The Lead Free Solder used in our manufacturing process and discussed below is (Sn+Ag+Cu).
That is Tin (Sn), Silver (Ag) and (Cu) although other types are available.
This model uses Pb Free solder in it’s manufacture due to environmental conservation issues. For
service and repair work, we’d suggest the use of Pb free solder as well, although Pb solder may be
used.
PCBs manufactured using lead free solder will have the PbF within a leaf Symbol stamped on the
back of PCB.
Caution
• Pb free solder has a higher melting point than standard solder. Typically the melting
point is 50 ~ 70 °F(30~40°C) higher. Please use a high temperature soldering iron
and set it to 700 ± 20 °F(370± 10 °C).
• Pb free solder will tend to splash when heated too high (about 1100 °For600°C).
If you must use Pb solder, please completely remove all of the Pb free solder on the
pins or solder area before applying Pb solder. If this is not practical, be sure to heat the
Pb free solder until it melts, before applying Pb solder.
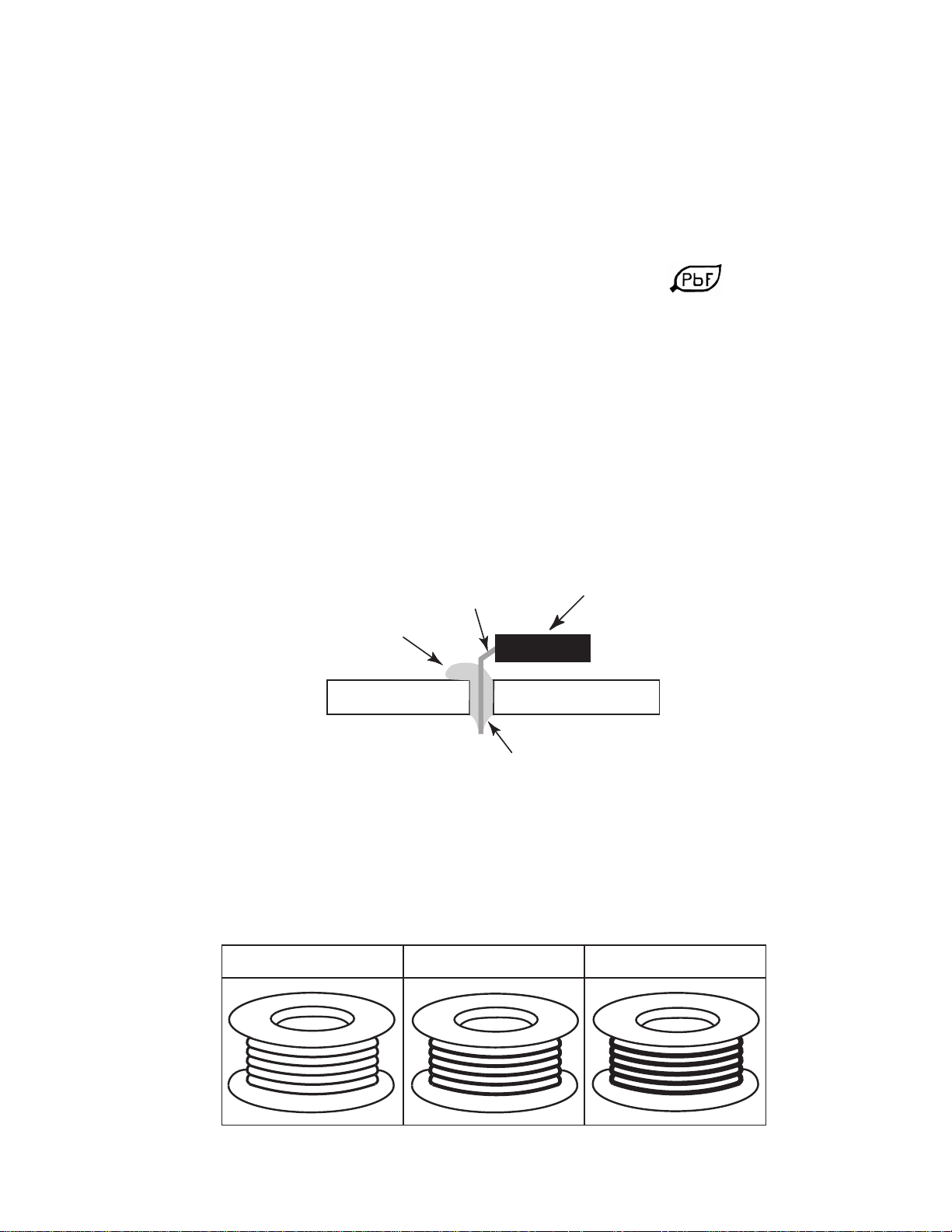
• After applying PbF solder to double layered boards, please check the component side
for excess solder which may flow onto the opposite side. (see figure below)
remove all of the
excess solder
component
pin
component
slice view
solder
Suggested Pb free solder
There are several kinds of Pb free solder available for purchase. This product uses Sn+Ag+Cu
(tin, silver, copper) solder. However, Sn+Cu (tin, copper), Sn+Zn+Bi (tin, zinc, bismuth) solder
canalsobeused.
0.3mm X 100g
0.6mm X 100g 1.0mm X 100g
-3-

ImportantSafetyNotice...................2
Safety Precautions .................2
About Lead Free Solder (PbF) ........3
ServiceNotes...........................5
X-Ray protection circuit check .........6
ReceiverFeatureTable ...................7
AudioSignalPathBlockDiagram..........13
VideoSignalPathBlockDiagram..........14
PartsList..............................16
SchematicNotes........................22
Schematics
Location of Controls (Receiver)
Receiver Front Control Panel .........8
DisassemblyforService..................9
MainComponentsLocation ..............11
A-Board ...........................24
C-Board ...........................32
Voltages and Waveforms
Voltages (A,C-Boards)..............29
Waveforms.......................31
Layouts
A,C-Boards ........................34
-4-
Service Notes
Note: These components are affixed with glue. Be careful not to break or damage any foil under the
component or at the pins of the ICs when removing. Usually applying heat to the component for a short time
while twisting with tweezers will break the component loose.
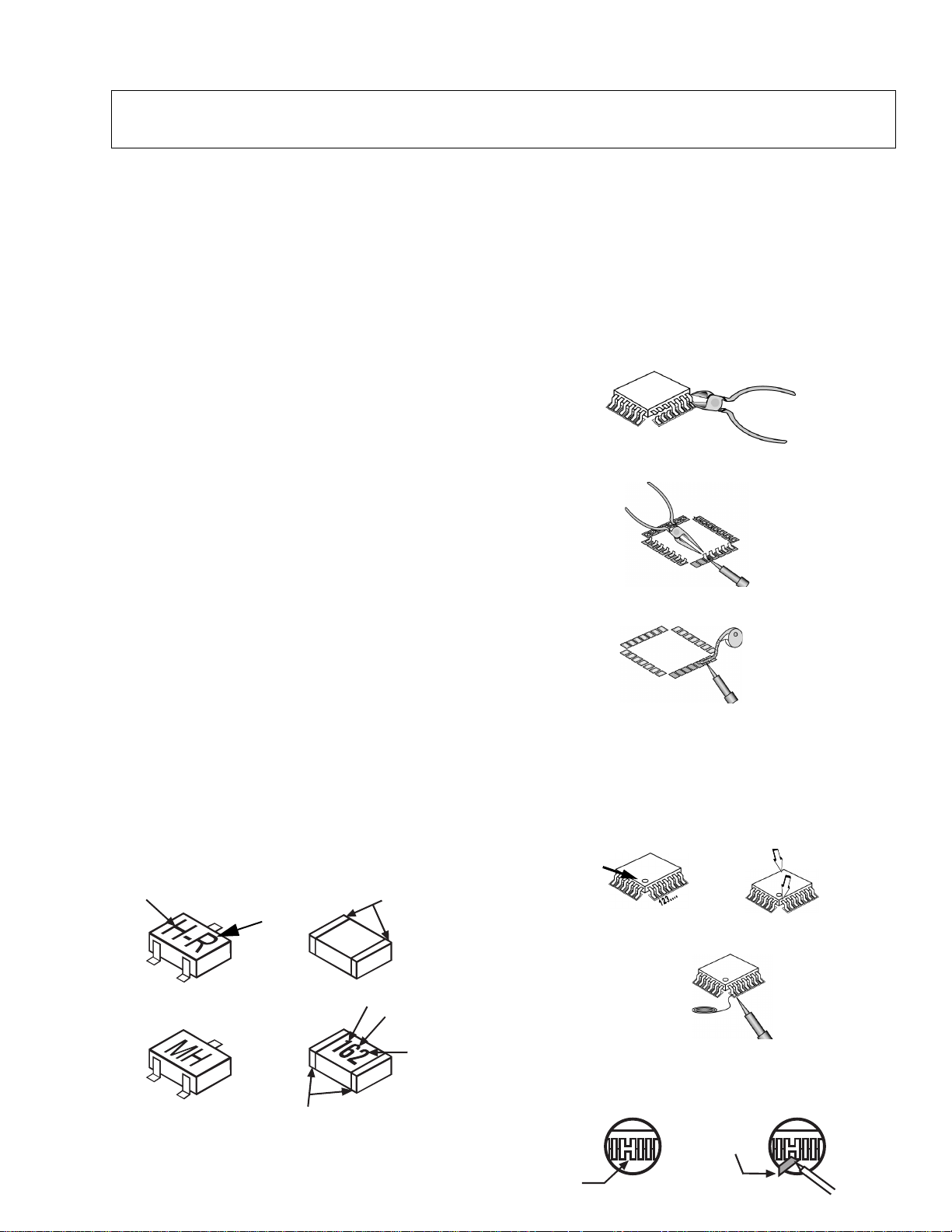
Leadless Chip Component
(surface mount)
Chip components must be replaced with identical chips
due to critical foil track spacing. There are no holes in
the board to mount standard transistors or diodes.
Some chips capacitor or resistor board solder pads
may have holes through the board, however the hole
diameter limits standard resistor replacement to 1/8
watt. Standard capacitor may also be limited for the
same reason. It is recommended that identical
components be used.
Chip resistor have a three digit numerical resistanc e
code - 1st and 2nd significant digits and a multiplier.
Example: 162 = 1600 or 1.6kΩ resistor, 0 = 0Ω (jumper).
Chip capacitors generally do not have the value
indicated on the capacitor. The color of the component
indicates the general range of the capacitance.
Chip transistors are identified by a two letter code. The
first letter indicates the type and the second letter, the
grade of transistor.
Chip diodes have a two letter identification code as per
the code chart and are a dual diode pack with either
common anode or common cathode. Check the parts
list for correct diode number.
Component Removal
1. Use solder wick to remove solder from component
end caps or terminal.
2. Without pulling up, carefully twist the component
with tweezers to break the adhesive.
3. Do not reuse removed leadless or chip
components since they are subject to stress
fracture during removal.
Chip Component Inst allation
1. Put a small amount of solder on the board
soldering pads.
2. Hold the chip component against the soldering
pads with tweezers or with a miniature alligator clip
and apply heat to the pad area with a 30 watt iron
until solder flows. Do not apply heat for more than
3 seconds.
TYPE
b
e
ANODES
MH DIODE
Chip Components
GRADE
c
TRANSISTOR
COMMON
CATHODE
SOLDER
CAPS
CAPACITOR
1ST DIGIT
RESISTOR
SOLDER
CAPS
2ND DIGIT
MULTIPLIER
=1600 = 1.6k
How to Replace Flat-IC
- Required Tools -
• Soldering iron • De-solder braids
• Sharpen pliers (wire
cutters and long nose)
1. Cut the pins ofthe defective IC with the wire cutters
pliers, and remove it completely away from the
board. If the IC is glued to the board, apply hot air
to complete the removal. CAUTION- Do not pull or
twist the pliers, may damage the soldering pads in
the board.
Flat-IC
2. UsingtheSolderingIronandthelongnosepliers,
remove the IC pins that still attached to the board.
3. Using the De-solder braid and the Soldering Iron,
remove the solder from the board soldering pads.
4. Position the new Flat-IC in place (apply the pins of
the Flat-IC to the soldering pads where the pins
need to be soldered). Properly determine the
positions of the soldering pads and pins by
correctly aligning the polarity symbol. Start aligning
and soldering Pin No.1, then align and solder the
pin in the apposite corner of the IC, this will help to
align the rest of the pins.
Polarity
Symbol
5. Solder all pins to the soldering pads using a fine
tipped soldering iron.
Solder
6. Check with a magnifier for solder bridge between
the pins or for dry joint between pins and soldering
pads. To remove a solder bridge, use a de-solder
braid as shown in the figure below.
Solder
Bridge
-5-
• Magnifier
Soldering
Iron
De-Solder
Braid
Soldering
Iron
Soldering
Iron
De-Solder
Braid
Soldering
Iron

Service Notes (Continued)
IMPORTANT: To protect against possible damage to
the solid state devices due to arcing or static discharge,
make certain that all ground wires and CTR DAG wire
are securely connected.
CAUTION: The power supply circuit is above earth
ground and the chassis cannot be polarized. Use an
isolation transformer when servicing the Receiver to
avoid damage to the test equipment or to the chassis.
Connect the test equipment to the proper ground ( ) or
( ) when servicing, or incorrect voltages will be
measured.
Procedure:
1. Connect receiver to Isolator Transformer.
2. Apply a monoscope pattern.
3. In Service Mode. (Refer to Service Mode Section)
Select Register C0b.
4. Measure TP5 (TPs port close to tuner). Compare
the measure of TP5 and set the data for C0b
according the following table
TP 5
MEASURE (V)
DATA TO
C0b (Hex)
WARNING: This Receiver has been designed to meet
or exceed applicable safety and X-ray radiation
protection as specified by government agencies and
independent testing laboratories.
To maintain original product safety design standards
relative to X-ray radiation and shock and fire hazard,
parts indicated with the symbol on the schematic
must be replaced with identical parts. Order parts from
the manufacturer’s parts center using the parts
numbers shown in this service manual, or provide the
chassis number and the part reference number.
For optimum performance and reliability, all other parts
should be replaced with components of
identical specification.
X-RAY PROTECTION CIRCUIT CHECK
This test must be performed as final check before the
Receiver is returned to the customer. If Voltage is out of
tolerance, immediate service and correction is required
to insure safe operation and to prevent the possibility of
premature component failure.
Equipment needed to check the protection circuit:
1. Isolator transformer.
2. High voltage meter.
3. Short jumper.
4. Diode connection jumper
Use similar diode than D823, refer to parts list for
part No., (Diode should support at least 150V.)
0 ~ 0.93 00
0.93 ~ 0.97 01
0.97 ~ 1.01 02
1.01 ~ 1.05 03
1.05 ~ 1.09 04
1.09 ~ 1.13 05
1.13 ~ 1.17 06
1.17 ~ 1.21 07
5. Exit Service Mode and turn Receiver OFF.
6. Connect a jumper from TPD16 to TPD17.
7. Connect the
Diode jumper
,cathodetoTPD14
(COLD GND), anode to TPD15 (HOT GND).
8. Apply 75 V AC to the AC input of the Insulator
transformer.Turn receive ON.
9. Set PICTURE and BRIGTHNESS to minimum.
10. Increase the AC voltage at the input of Insulator
transformer and confirm the HHS Voltage is 32kV,
at the point set starts to loose sync,
11. Reset picture controls to original levels.
12. Turn the set OFF, and remove all jumpers and
connections from chassis.
-6-
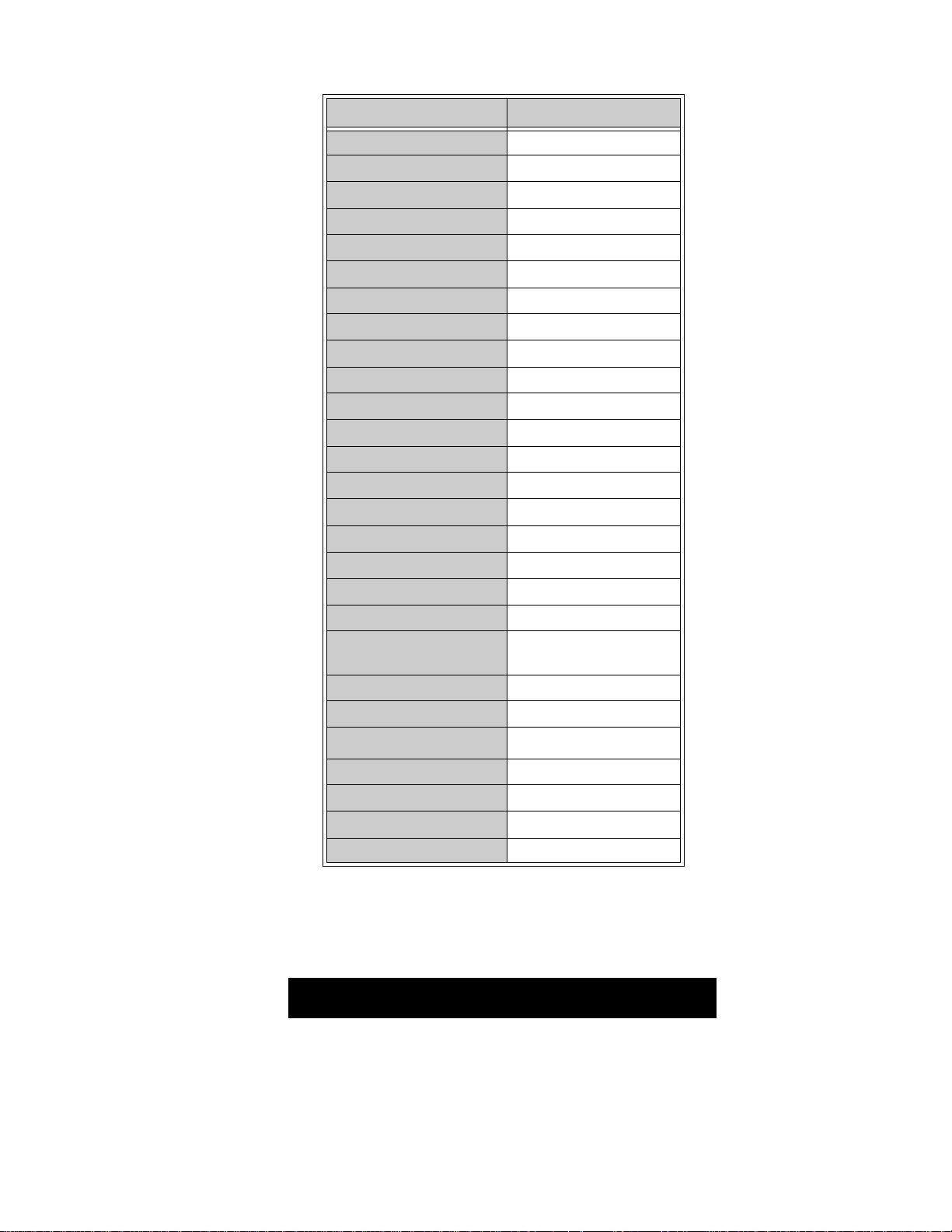
Receiver Feature Table
FEATURE\MODEL CT-2017F
Chassis No AP391
Family NA7DM
Receiving System NTSC
# of channels 181
Menu language ENG/SPN/FRN
Closed Caption X
V-Chip USA/CANADA
75 Ω input X
Remote Model # EUR501450
Picture tube Type PANABLACK
Picture tube Supplier SAMSUNG
Comb Filter 2DIG
V/A norm V
MTS/SAP/DBX X
Built-in audio power 1.5Wx2 (10%)
# of speakers 2
AI Sound X
A/V in (rear/front) 1(1/1)
EPJ/HPJ/MISC HPJ
Dimensions mm
(WxDxH) in
Weight (kg/lbs) 20/44.09
Power source (V/Hz) 120/60
Anode voltage
Video input jack 1Vp-p 75Ω, phono
Audio input jack 500mV rms, 47KΩ
A-Board TNP2AH040 DH*
C-Board TNP2AA106 AF*
515.7x490.5x461.7
20.30x19.31x18.17
26.6
±1.25 kV
Table 1. ReceiverFeatures
*Note: When ordering a Board, add and ” S” after the Board suffix application.
Example, If Order A-Board for CT-2017F, should be ordered as: TNP2AH040S.
Specifications are subject to change without notice or obligation.
Dimensions and weights are approximate.
-7-

Location of Controls (Receiver)
Figure 2. Location of Controls (Receiver).
POWER VOLUME CHANNEL ACTION TV/VIDEO
1 2 4 53
Quick Reference Control Operation
Quick Reference
Control Operation
1
Power Button - Press to turn ON or OFF.
Volume Buttons - Press to adjust Sound Level, or to adjust Audio Menus, Video
2
Menus, and select operating features when menus are displayed
Channel Buttons - Press to select programmed channels. Press to highlight desired
features when menus are displayed. Also use to select Cable Converter box channels
3
after programming Remote Control Infra-red codes (the TV/AUX/CABLE switch must
be set in CABLE position).
Remote Control
Sensor
(Actualappearance
may vary)
HPJ & A/V
Jacks
Action Button - Press to display Main Menu and access On Screen feature and
4
Adjustment Menus.
5
TV/Video Button - Press to select TV or Video Input.
-8-
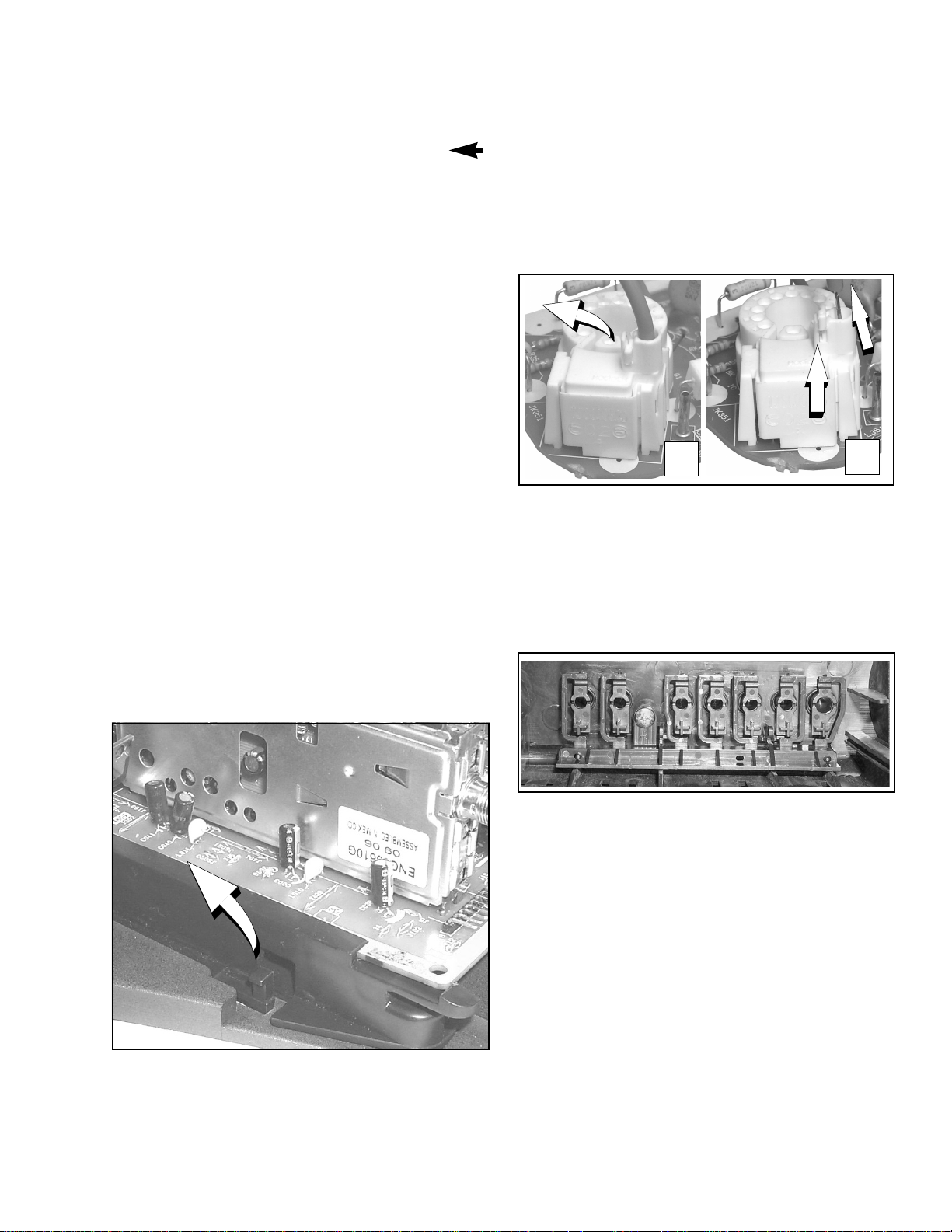
Dissasembly for Service
Back Cover
Remove all the screws marked with an arrow( )
from the back of the receiver.
Note: Screw configuration, type, and number of
screws vary depending on the model of the
Receiver serviced and the application; various
models are covered in this Manual. Use same
hardware when reassembling the receiver.
• 2 screws at the top edge of the Receiver.
• 2 screws at the lower corners of the Receiver.
• 1 screw by the A/V jacks.
• 1 screw by the Fly-back assembly.
A-Board - Main Chassis
1. Pull carefully the tab in the chassis rail, at the left
side of the main chassis, this will release the rail
from the cabinet. See Fig 3.
2. Slide the chassis and rail completely out of the
guide rails of the cabinet.
3. Stand the receiver on its edge. The underside of
the board is completely accessible for component
replacement.
Note: Some tie-wraps that secure the wire
dressings may need to be unfastened for chassis
removal.
4. When reassembly, place the chassis rail on the
cabinet, then place the main chassis, be sure is in
the rails at both sides, then push all the way to the
front.
C-Board - CRT Output
Plugs into the socket on the CRT neck.
To release the Focus wire, use a flat tool to release
the tab in the socket,
Release” on page 9
remove the wire by pulling away the socket
re-insert, close the wire-look by pushing until is
secured with the tab, and insert the wire into the
socket
See Fig. 4“Focus Wire
,Apull the wire-look up and
A
Figure 4. Focus Wire Release
Speakers
Speakers are secured to the cabinet’s front with 2
screws in diagonal (opposite corners).
Keyboard Push Button Assembly
Fastened to the inside of the cabinet front with 1
screw.
B,
B
To
Figure 3. Chassis Rail Detail
Disassembly for CRT Replacement
1. Discharge the CRT as instructed in the Safety
Precautions (see page 2).
2. Disconnect the yoke (DY) plug and degaussing coil
(DEG) plug from the main board.
3. Unplug the CRT 2nd anode button.
4. Remove the C-Board from the CRT base and
unplug the black wire (CRT dag ground) C10.
5. Disconnect Speakers plug SP from the A-Board.
6. Lift the Main Chassis (A-Board) completely out with
theCRTBoardattached.
-9-
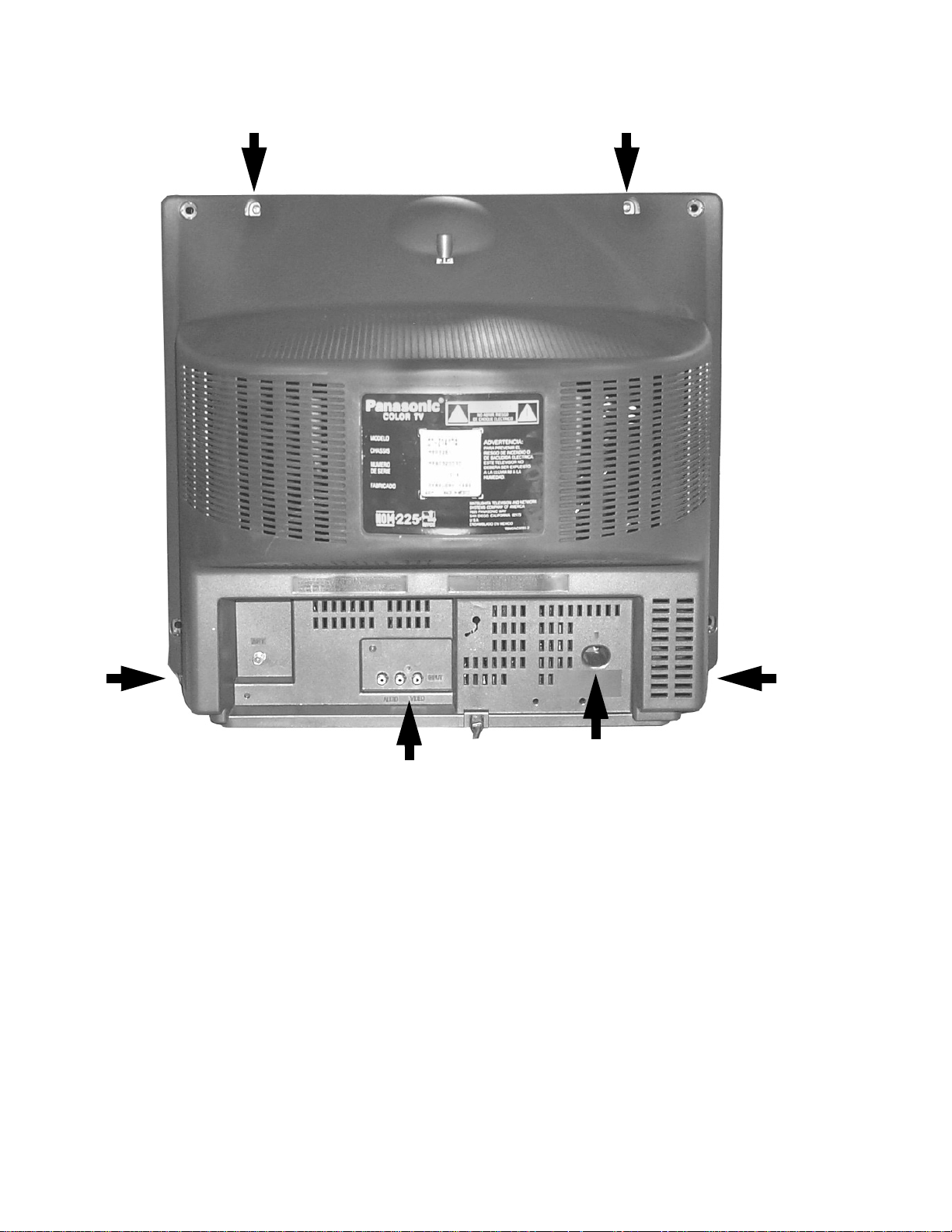
Back Cover Disassembly
Figure 5. Back Cover Removal
• 2 Screws at the top edge
• 1 Screw in each lower corner
• 1 Screw by the A/V Jacks
• 1 Screw by the Flyback Assembly.
-10-
CRT
(Secured to Cabinet
by4ScrewsonCorners)
Yoke
Wedge
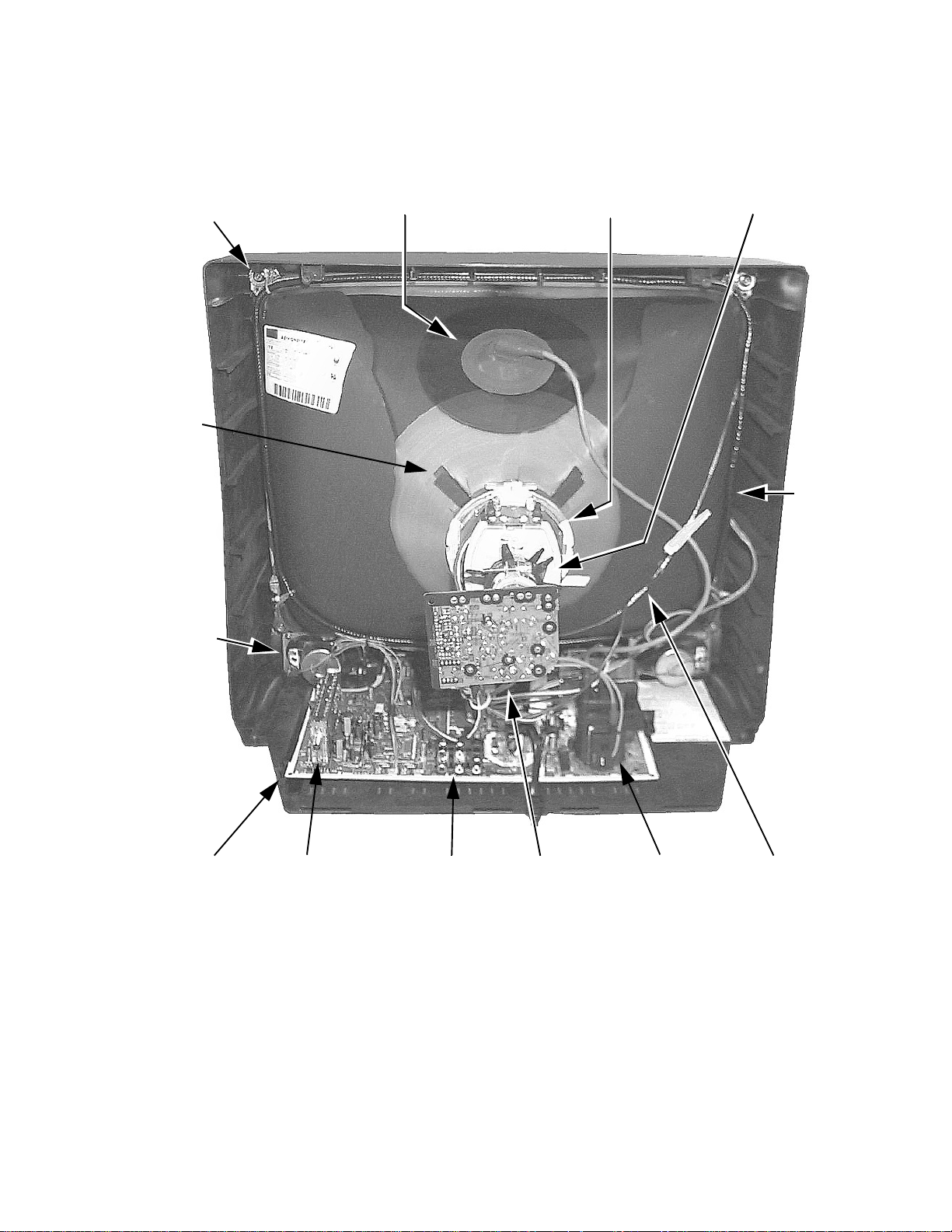
Main Components Location
ANODE
(HIGH VOLTAGE)
Deflection Yoke
DY
CY
Convergence Yoke
Degaussing
Coil
Speakers
Secured by
2 Screws
A-Board
Main Chassis
Tuner A/V
JACKS
Figure 6. Rear View
C-Board
CRT Panel
Flyback Dag Ground
-11-
 Loading...
Loading...