Page 1

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Page 2

Safety Precautions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Observe the following notices to ensure personal safety or to prevent accidents.
To ensure that you use this product correctly, read this User’s Manual thoroughly before use.
Make sure that you fully understand the product and information on safety.
This manual uses two safety flags to indicate different levels of danger.
WARNING
If critical situations that could lead to user’s death or serious injury is assumed by
mishandling of the product.
-Always take precautions to ensure the overall safety of your system, so that the whole
system remains safe in the event of failure of this product or other external factor.
-Do not use this product in areas with inflammable gas. It could lead to an explosion.
-Exposing this product to excessive heat or open flames could cause damage to the lithium
battery or other electronic parts.
CAUTION
If critical situations that could lead to user’s injury or only property damage is
assumed by mishandling of the product.
-To prevent excessive exothermic heat or smoke generation, use this product at the values
less than the maximum of the characteristics and performance that are assured in these
specifications.
-Do not dismantle or remodel the product. It could cause excessive exothermic heat or smoke
generation.
-Do not touch the terminal while turning on electricity. It could lead to an electric shock.
-Use the external devices to function the emergency stop and interlock circuit.
-Connect the wires or connectors securely.
The loose connection could cause excessive exothermic heat or smoke generat ion.
-Do not allow foreign matters such as liquid, flammable materials, metals to go into the inside
of the product. It could cause excessive exothermic heat or smoke generation.
-Do not undertake construction (such as connection and disconnection) while the power
supply is on. It could lead to an electric shock.
Copyright / Trademarks
-This manual and its contents are copyrighted.
-You may not copy this manual, in whole or part, without written consent of
Industrial Devices SUNX Co., Ltd.
-Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in th e United States and other
countries.
-All other company names and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective owners.
Panasonic
PLC_ORG
Page 3
Introduction
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Thank you for buying a Panasonic product. Before you use the product, please carefully read
the installation instructions and the users manual, and understand their contents in detail to
use the product properly.
Types of Manual
There are different types of user's manual for the FP7 series, as listed below. Please refer to
a relevant manual for the unit and purpose of your use.
The manuals can be downloaded on our website.
Unit name or purpose of
use
FP7 Power Supply Unit
FP7 CPU Unit
ons for Built-in
Instructi
LAN Port
ons for Built-in
Instructi
COM Port
FP7 Extension Cassette
(Communication)
(RS-232C/RS485 type)
FP7 Extension Cassette
(Communication)
(Ethernet type)
FP7 Extension (Function)
Cassette
Analog Cassette
FP7 Digital Input/Output Unit FP7 Digital Input/Output Unit Users Manual WUME-FP7DIO
FP7 Analog Input Unit FP7 Analog Input Unit Users Manual WUME-FP7AIH
FP7 Analog Output Unit FP7 Analog Output Unit Users Manual WUME-FP7AOH
FP7 High-speed counter Unit FP7 High-speed counter Unit Users Manual WUME-FP7HSC
FP7 Pulse Output Unit FP7 Pulse Output Unit Users Manual
FP7 Positioning Unit FP7 Positioning Unit Users Manual WUME-FP7POSP
FP7 Serial Communication
Unit
PHLS System PHLS System Users Manual WUME-PHLS
Programming Software
FPWIN GR7
Manual name Manual code
FP7 CPU Unit Users Manual (Hardware) WUME-FP7CPUH
FP7 CPU Unit Command Reference Manual WUME-FP7CPUPGR
FP7 CPU Unit Users Manual
(Logging Trace Function)
FP7 CPU Unit Users Manual (Security Function) WUME-FP7CPUSEC
FP7 CPU Unit Users Manual
(LAN Port Communication)
FP7 series Users Manual (SCU communication) WUME-FP7COM
FP7 series Users Manual (Communication
cassette Ethernet type)
FP7 Analog Cassette Users Manual
FP7 series Users Manual (SCU communication) WUME-FP7COM
FPWIN GR7 Introduction Guidance WUME-FPWINGR7
WUME-FP7CPULOG
WUME-FP7LAN
WUME-FP7CCET
WUME-FP7FCA
(Upcoming)
WUME-FP7PG
(Upcoming)
Page 4

Table of Contents
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Table of Contents
1. Functions of Units and Restrictions on Combination.....1-1
1.1 Features and Functions of Units ............................................................ 1-2
1.1.1 Functions of Units....................................................................................1-2
1.1.2 Types of Unit...........................................................................................1-3
1.1.3 Types of Cassette ...................................................................................1-3
1.1.4 Applications that can be Used in Each Port............................................1-3
1.2 Overview of Communication Functions..................................................1-4
1.2.1 PLC Link Functions (MEWNET-W0).......................................................1-4
1.2.2 MEWTOCOL Master/Slave Communication...........................................1-5
1.2.3 MODBUS RTU Master/Slave Communication........................................1-6
1.2.4 General-Purpose Communication...........................................................1-7
1.3 Restrictions on Units Combination.........................................................1-8
1.3.1 Restrictions on the Number of Installed Units.........................................1-8
1.3.2 Restrictions on the Combination of Extension Cassettes (Communication
Cassettes)...............................................................................................1-8
1.3.3 Restrictions on Communication Functions to be Used ...........................1-8
1.3.4 Unit to be Used and Applicable Versions of CPU Unit and FPWIN GR71-8
1.3.5 Restrictions on Consumption Current.....................................................1-9
2. Names and Functions of Parts ..........................................2-1
2.1 Names and Functions of Parts............................................................... 2-2
2.1.1 Communication Port of CPU Unit............................................................2-2
2.1.2 Parts Names and Functions of Serial Communication Unit....................2-3
3. Wiring the COM. Port..........................................................3-1
3.1 Attaching a Communication Cassette....................................................3-2
3.1.1 Attachment Instructions...........................................................................3-2
ii
Page 5

Table of Contents
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.2 Wiring of COM Port Terminal Block........................................................3-3
3.2.1 Suitable Wires and Tools........................................................................3-3
3.2.2 Applicable Cable.....................................................................................3-4
3.2.3 Wiring Method.........................................................................................3-5
3.3 Wiring for CPU Unit (GT Power Supply and COM0 Port).......................3-6
3.3.1 Handling of GT Power Supply Terminals................................................3-6
3.3.2 Terminal Layouts and Examples of Wiring .............................................3-6
3.4
Wiring for Communication Cassettes COM.1 to COM.4 Ports...............3-8
3.4.1 Communication Cassette AFP7CCS1 (RS-232C, 1-Channel Insulated
Type).......................................................................................................3-8
3.4.2 Communication Cassette AFP7CCS2 (RS-232C, 2-channel insulated
type) ........................................................................................................3-9
3.4.3 Communication Cassette AFP7CCM1 (RS-422 / RS-485, 1-Channel
Insulated Type) .....................................................................................3-12
3.4.4 Communication Cassette AFP7CCM2 (RS-422 / RS-485, 2-Channel
Insulated Type) .....................................................................................3-15
3.4.5 Communication Cassette AFP7CCS1M1 (RS-232C 1-Channel + RS-485
1-Channel Insulated Type)....................................................................3-19
4. I/O Allocation .......................................................................4-1
4.1 Input/Output Signals Used for Communication.......................................4-2
4.1.1 I/O Allocation of CPU Unit.......................................................................4-2
4.1.2 I/O Allocation of Serial Communication Unit...........................................4-4
4.2 Registration in I/O Map...........................................................................4-6
4.2.1 Settings Using FPWIN GR7 (For CPU with built-in SCU).......................4-6
4.2.2 Settings Using FPWIN GR7 (For Serial Communication Unit) ...............4-6
5. Setting and Confirming Communication Conditions.......5-1
5.1 Setting Applications and Communication Conditions.............................5-2
5.1.1 Applications to be Set for Each Port .......................................................5-2
5.1.2 Conditions to be Set for Each Port..........................................................5-2
iii
Page 6

Table of Contents
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.2 Setting Communication Conditions........................................................5-3
5.2.1 Settings Using FPWIN GR7 (For CPU with built-in SCU).......................5-3
5.2.2 Settings Using FPWIN GR7 (For Serial Communication Unit) ...............5-4
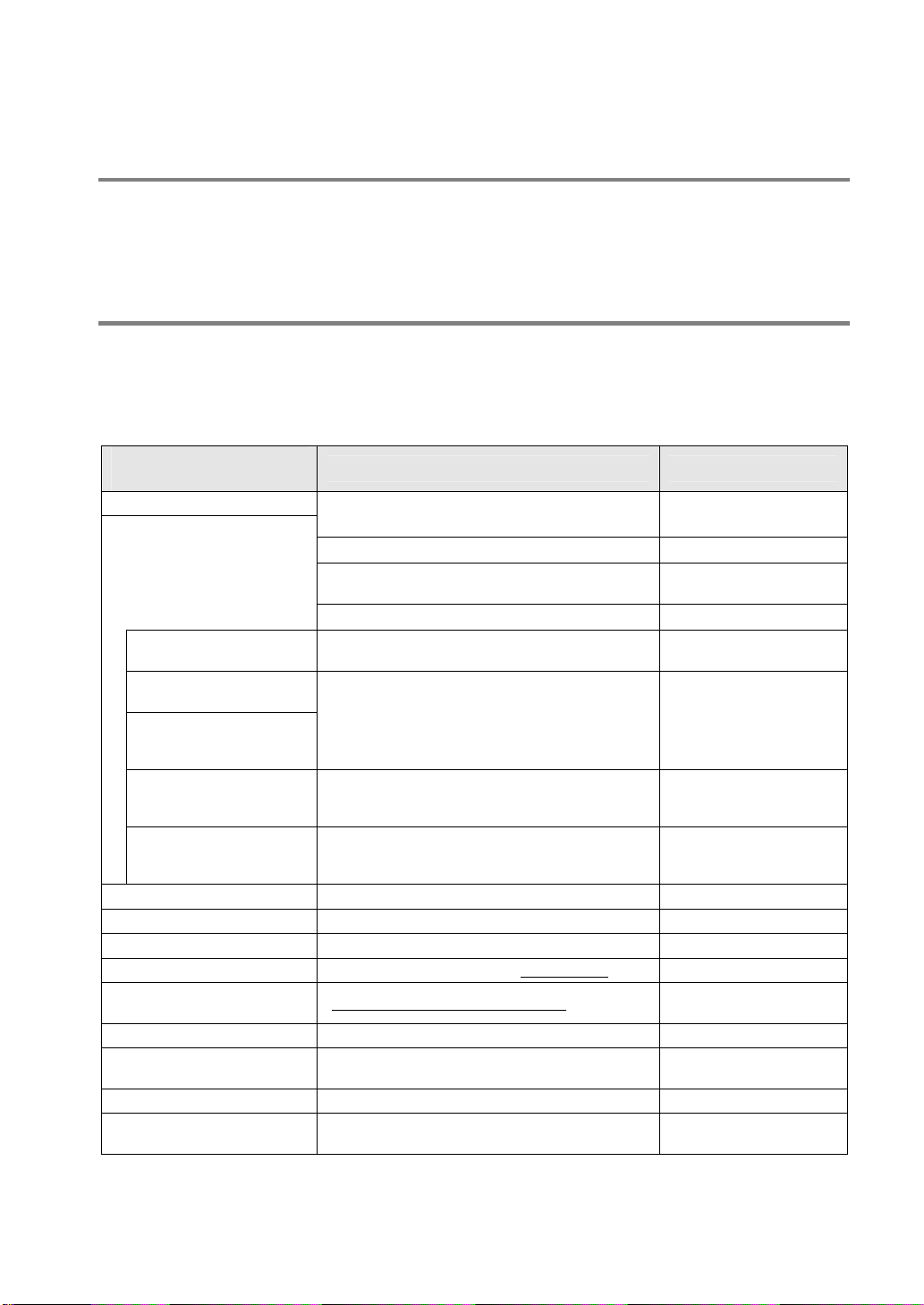
6. PLC Link...............................................................................6-1
6.1 Operation of PLC link MEWNET-W0...................................................... 6-2
6.1.1 Overview of PLC Link Operation.............................................................6-2
6.1.2 Operation of Link Relays and Link Registers..........................................6-3
6.2 Configuration Required for PLC Link...................................................... 6-4
6.2.1 Setup Procedure (For CPU with built-in SCU)........................................6-4
6.2.2 Setup Procedure (For Serial Communication Unit).................................6-5
6.2.3 List of Setting Items.................................................................................6-6
6.3 Setting Items for PLC Link...................................................................... 6-7
6.3.1 Station No. Setting ..................................................................................6-7
6.3.2 Max. Station No. Setting..........................................................................6-7
6.3.3 Memory Block Numbers for Link Relays and Link Registers to be Used6-8
6.3.4 Range of Use of Link Relays and Range of Use of Link Registers ........6-8
6.3.5 Starting No. for Link Relay Send Area and Sending Size.......................6-9
6.3.6 Starting No. for Link Register Send Area and Sending Size.................6-10
6.4 PLC Link Response Time..................................................................... 6-12
6.4.1 Response Time of 1 Transmission Cycle..............................................6-12
6.4.2 Response Time When There is a Station Yet to be Added ..................6-14
7. MEWTOCOL Master/Slave Communication...................... 7-1
7.1 Configuration.......................................................................................... 7-2
7.1.1 Setting Communication Conditions.........................................................7-2
7.2 List of MEWTOCOL / MEWTOCOL7 Supporting Commands................ 7-3
7.2.1 List of MEWTOCOL Commands.............................................................7-3
7.2.2 List of MEWTOCOL7 Commands...........................................................7-3
iv
Page 7

Table of Contents
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7.3 MEWTOCOL-COM Master Communication (RECV)..............................7-4
7.3.1 Read Data from an External Device .......................................................7-4
7.3.2 RECV Instruction (When MEWTOCOL-COM is Used)...........................7-7
7.4 MEWTOCOL-COM Master Communication (SEND)..............................7-8
7.4.1 Write Data into an External Device.........................................................7-8
7.4.2 SEND Instruction (When MEWTOCOL-COM is Used).........................7-11
8. MODBUS RTU Master/Slave Communication..................8-1
8.1 Configuration ..........................................................................................8-2
8.1.1 Setting Communication Conditions.........................................................8-2
8.2 List of MODBUS RTU Supported Commands........................................8-3
8.2.1 List of MODBUS Function Codes............................................................8-3
8.3 MODBUS RTU Master Communication (RECV)....................................8-4
8.3.1 Read Data from an External Device .......................................................8-4
8.3.2 RECV Instruction (MODBUS Function Code Specified Type)................8-7
8.3.3 RECV Instruction (MODBUS Function Code Unspecified Type)............8-8
8.4 MODBUS RTU Master Communication (SEND)....................................8-9
8.4.1 Write Data into an External Device.........................................................8-9
8.4.2 SEND Instruction (MODBUS Function Code Specified Type)..............8-12
8.4.3 SEND Instruction (MODBUS Function Code Unspecified Type)..........8-13
9. General-Purpose Communication .....................................9-1
9.1 Operation of General-Purpose Communication......................................9-2
9.1.1 Read Data from an External Device .......................................................9-2
9.1.2 Write Data into an External Device.........................................................9-2
9.2 Configuration ..........................................................................................9-3
9.2.1 Setting Communication Conditions.........................................................9-3
9.3 Sending Operation..................................................................................9-4
9.3.1 Overview of Sending Operation..............................................................9-4
v
Page 8

Table of Contents
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
9.3.2 Contents of Sent Data.............................................................................9-6
9.3.3 GPSEND (General-Purpose Communication Sending Instruction)........9-7
9.3.4 Precautions on Sending Data .................................................................9-8
9.4 Receiving Operation...............................................................................9-9
9.4.1 Overview of Receiving Operation............................................................9-9
9.4.2 Contents of Received Data ...................................................................9-12
9.4.3 Precautions on Receiving Data.............................................................9-12
9.4.4 Operations of the "Reception done copy" flag and multiplex reception9-13
9.4.5 GPRECV (General-Purpose Communication Receiving Instruction) ...9-14
9.5 Sending/Receiving Flag Operation....................................................... 9-15
9.5.1 No Header (Start Code), Terminator (End Code) "CR": .......................9-15
9.5.2 Start Code "STX", End Code "ETX":.....................................................9-16
10. Troubleshooting...............................................................10-1
10.1 Self-diagnostic Function....................................................................... 10-2
10.1.1 CPU Unit’s Operation Monitor LED.......................................................10-2
10.1.2 Operation at the Time of Error..............................................................10-2
10.1.3 Serial Communication Unit's Operation Monitor LE D...........................10-3
10.2 What to DO If an Error Occurs (For Each Communication Mode) ...... 10-4
10.2.1 When Using PLC Link Function ............................................................10-4
10.2.2 When Using MEWTOCOL/ MEWTOCOL7/ MODBUS-RTU Function..10-4
10.2.3 When Using General-purpose Communication Function......................10-5
10.3 Checking Status with PMGET Instruction ............................................ 10-6
10.3.1 Specifications of PMGET Instruction.....................................................10-6
10.3.2 List of Communication Parameters.......................................................10-6
10.4 Clearing Errors Using User Programs.................................................. 10-9
10.4.1 Clearing Errors Using User Programs...................................................10-9
vi
Page 9

Table of Contents
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
11. Specifications ...................................................................11-1
11.1 Communication Function Specifications...............................................11-2
11.1.1 CPU Unit Communication Specifications..............................................11-2
11.1.2 Extension Cassette Comm unication Specifications..............................11-4
11.2 MEWTOCOL-COM Format...................................................................11-5
11.2.1 MEWTOCOL-COM Command Format .................................................11-5
11.2.2 MEWTOCOL-COM Response Format..................................................11-7
11.3 MEWTOCOL7-COM Format.................................................................11-9
11.3.1 MEWTOCOL7-COM Command Format ...............................................11-9
11.3.2 MEWTOCOL7 Response Format.......................................................11-11
11.4 MODBUS RTU Format .......................................................................11-13
11.4.1 MODBUS RTU Command Format......................................................11-13
11.4.2 MODBUS RTU Response Format ......................................................11-14
vii
Page 10

Table of Contents
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
viii
Page 11

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1
Functions of Units and
Restrictions on Combination
Page 12

Functions of Units and Restrictions on Combination
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1.1 Features and Functions of Units
1.1.1 Functions of Units
CPU Unit
One
communication
cassette can be
attached.
COM.0 port is
equipped as standard.
(For 3-wire RS-232C)
Serial Communication Unit
Two
communication
cassettes can be
Removable serial communication cassettes are used.
Selectable from five communication cassettes in conformity with communication standards
of RS-232C, RS-422 and RS-485. (Sold separately)
One communication cassette can be attached to the CPU unit, and two communication
cassettes to the serial communication unit.
The CPU unit includes a COM.0 port as standard equipment.
The CPU unit includes a RS-232C port (3-wire type) for the connection with a programmable
display and a power supply as standard equipment.
Four communication modes are available.
The PC link, MEWTOCOL, MODBUS RTU and general-purpose communication modes are
provided, and many serial communication devices can be connected by the combination of
communication cassettes.
1-2
Page 13
1.1 Features and Functions of Units
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1.1.2 Types of Unit
Types of unit that can perform serial communication
Name Model no.
AFP7CPS4E
CPU Unit
Serial Communication Unit AFP7NSC
(Note 1) The COM.0 port equipped in the CPU unit is a terminal block especially for RS-232C (3-wire type).
AFP7CPS3E
AFP7CPS3
Communication ports that can be allocated
COM.0 COM.1 COM.2 COM.3 COM.4
● ● ●
● ● ● ●
1.1.3 Types of Cassette
Types of communication cassette
Model no. Communication interface
AFP7CCS1 1-channel RS-232C
AFP7CCS2
AFP7CCM1 1-channel RS-422 / RS-485
AFP7CCM2 2-channel RS-422 / RS-485
AFP7CCS1M1
(Note 1) For AFP7CCS2, select and use either 3-wire 2-channel RS-232C or 5-wire 1-channel RS-232C. Switching
should be performed using a switch on the Communication Cassette.
(Note 2) For AFP7CCM1 and AFP7CCM2, select and use either RS-422 or RS-485. Switching should be performed
using a switch on the Communication Cassette.
(Note 3) For AFP7CCS1M1, both 1-channel RS-485 and 3-wire 1-channel RS-232C can be used.
3-wire 2-channel RS-232C
5-wire 1-channel RS-232C
1-channel RS-485
3-wire 1-channel RS-232C
Communication ports that can be allocated
COM.0 COM.1 COM.2 COM.3 COM.4
● ●
● ● ● ●
● ●
● ●
● ● ● ●
● ●
● ●
1.1.4 Applications that can be Used in E ach Port
Available functions for each communication port
Communication function to be used
PLC link
MEWTOCOL7-COM (Note 1)
MEWTOCOL-COM
MODBUS-RTU
General-purpose communication
(Note 1) In MEWTOCOL7-COM, there is no master communication function.
Master
Slave
Master
Slave
Communication ports that can be allocated
COM.0 COM.1 COM.2 COM.3 COM.4
●
● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
1-3
Page 14
Functions of Units and Restrictions on Combination
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1.2 Overview of Communication Functions
1.2.1 PLC Link Functions (MEWNET-W0)
Overview of function
A system can be configured for the PLC link (MEWNET-W0).
Exclusive internal relays “link relays (L)” and data registers “link registers (LD)” are shared
between the connected PLCs.
Among up to 16 PLCs, data can be exchanged with 1,008 link relay points and 128 link
register words.
Applications of PLC Link Functions (MEWNET-W0)
Among our FP series PLC, it can be used for link functions with the following models. It is also
capable of 1:1 communication via RS-232C port.
FP-X0 (L40MR / L60MR)
FP0R (RS485 type)
FPΣ (Using Communication cassette RS-485 type)
FP-X (Using Communication cassette RS-485 type)
FP2 Multi Communication Unit (Using Communication cassette RS-485 type)
1-4
Page 15
1.2 Overview of Communication Functions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
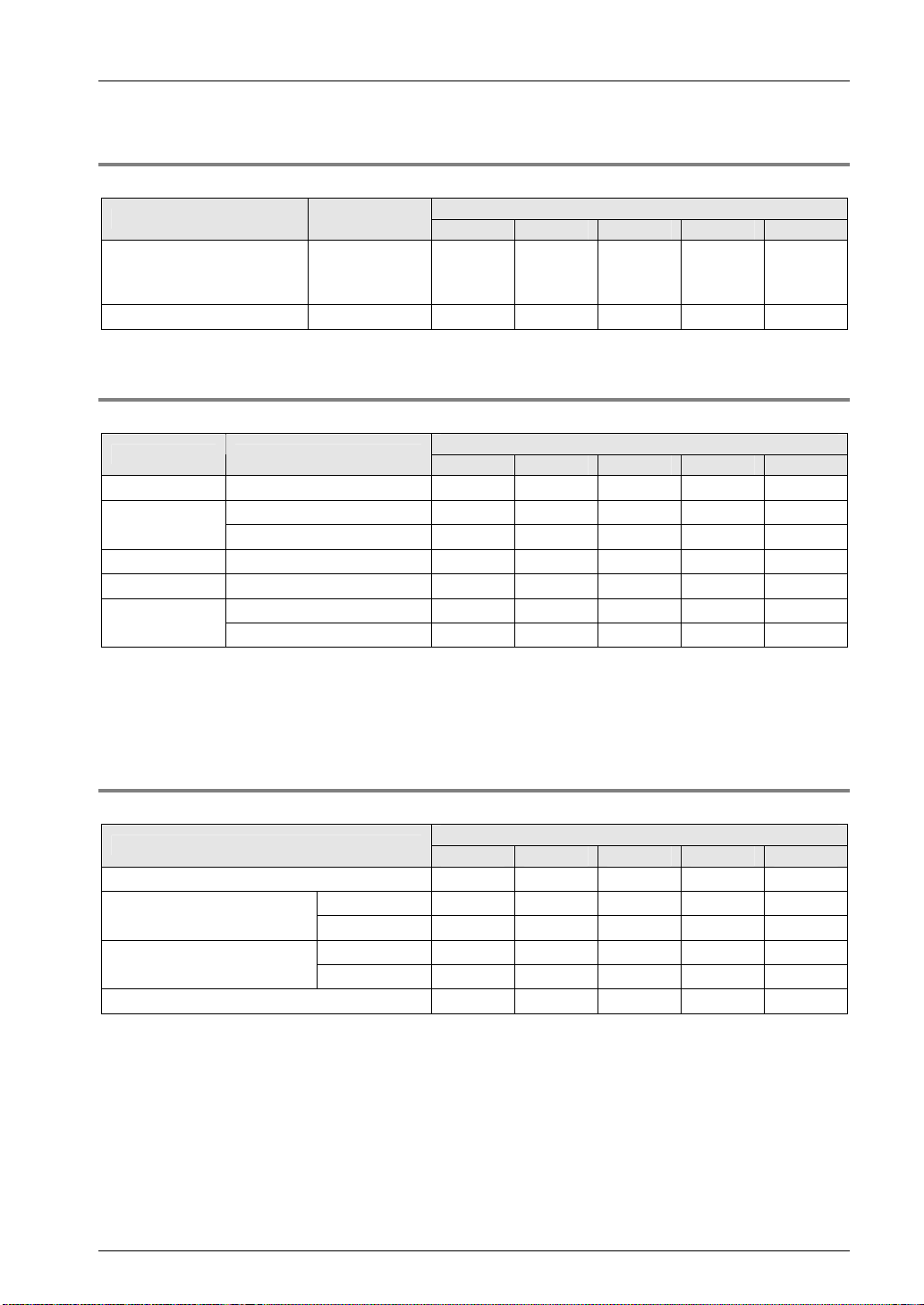
1.2.2 MEWTOCOL Master/Slave Communication
Overview of function
Execute communication using MEWTOCOL-COM, a communication protocol used by our PLC.
In master communication, PLC executes communication by sending commands to devices that
support MEWTOCOL, and receiving responses. Me ssages in accordance wit h the protocol are
automatically generated by PLC. In the user program, read ing and writin g can be done simply by
specifying the station no. an d memory a ddress an d executi ng SE ND/RECV instru ction s.
Slave communication is performed when the computer or display connected to PLC has th e
sending right, and sends commands, and PLC returns responses. In slave communication, PLC
responds automatically, so no program concerning com mu nic ation i s necessary on the P LC side.
The data size that can be sent or received in a single communication is up to 507 words for
register transmission (up to 1,014 words for MEWTOCOL7-COM) and 1 bit for bit transmission.
Master function
Slave function
Examples of applications of MEWTOCOL master communication
This is used for connection with a device that supports our PLC's protocol MEWTOCO L.
Programmable controller FP series
Displacement sensor HL series
Eco power meter KW series
Examples of applications of MEWTOCOL slave communication
This is used for connection with a device that supports our PLC's protocol MEWT OCOL-COM
master communication.
Programmable displays made by various manufacturers
1-5
Page 16
Functions of Units and Restrictions on Combination
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
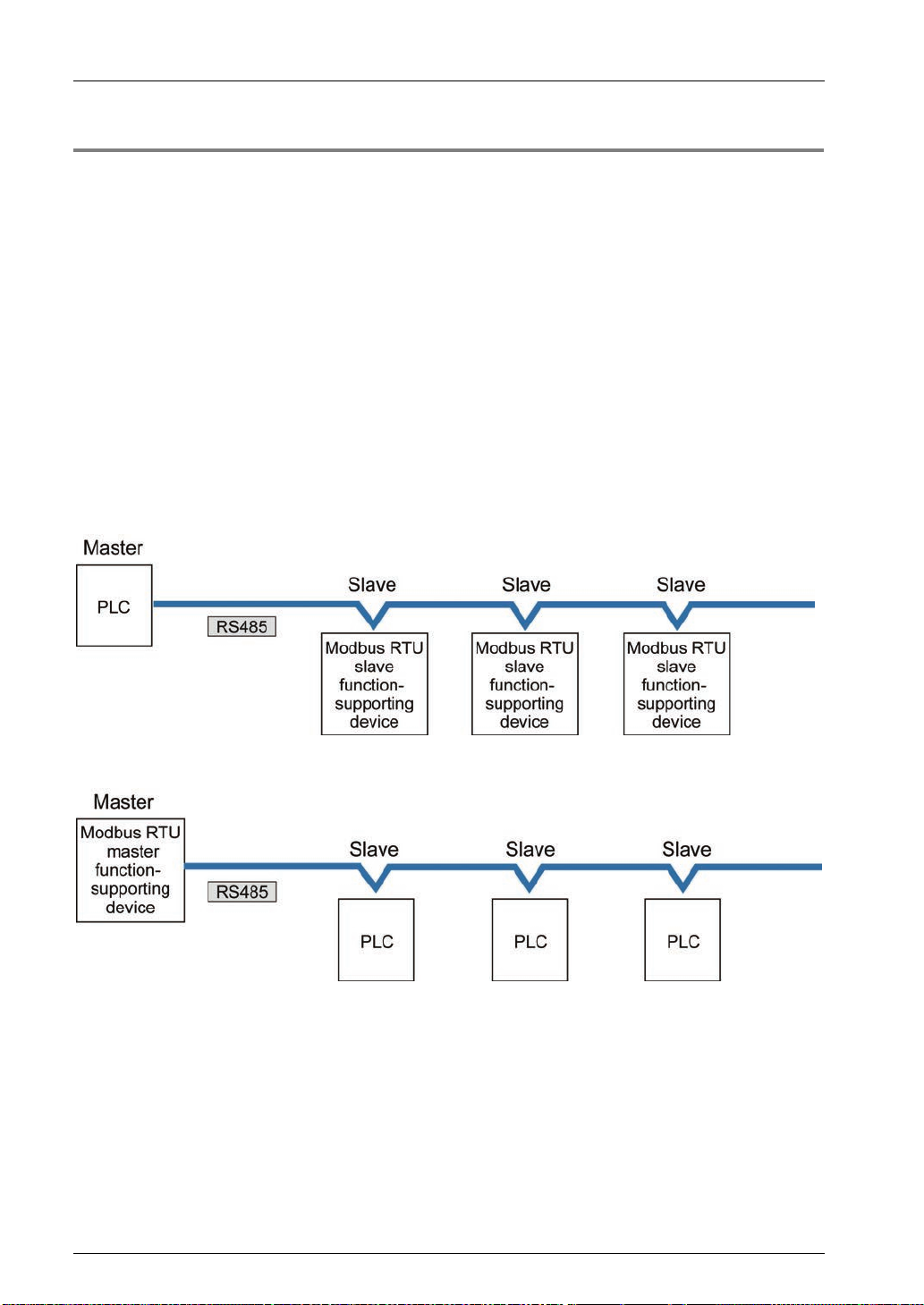
1.2.3 MODBUS RTU Master/Slave Communication
Overview of function
This is used for communicating with other devices that support the MODBUS RTU protocol.
In master communication, communication is performed when the master unit sends
instructions (command messages) to slave units and the slave unit returns responses
(response messages) according to t he instructions. Messages in accordance with the
protocol are automatically generated by PLC. In the user program, reading and writing can
be done simply by specifying the station no. and memory address and executing
SEND/RECV instructions.
Slave communication is performed when the higher device connected to PLC has the
sending right, and sends commands, and PLC returns responses. In slave communication,
PLC responds automatically, so no program concerning comm unication is necessary on the
PLC side.
The data size that can be sent or received in a single communication is up to 127 words for
register transmission and 2,040 bit for bit transmission.
Master function
Slave function
Examples of applications of MODBUS-RTU master communication
This is used for connection with a device that supports the MODBUS-RTU protocol.
Thermoregulator KT series
Devices from other manufacturers that support MODBUS-RTU
Examples of applications of MODBUS-RTU slave communication
This is used when access is made from the higher device using MODBUS-RTU commands.
1-6
Page 17
1.2 Overview of Communication Functions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
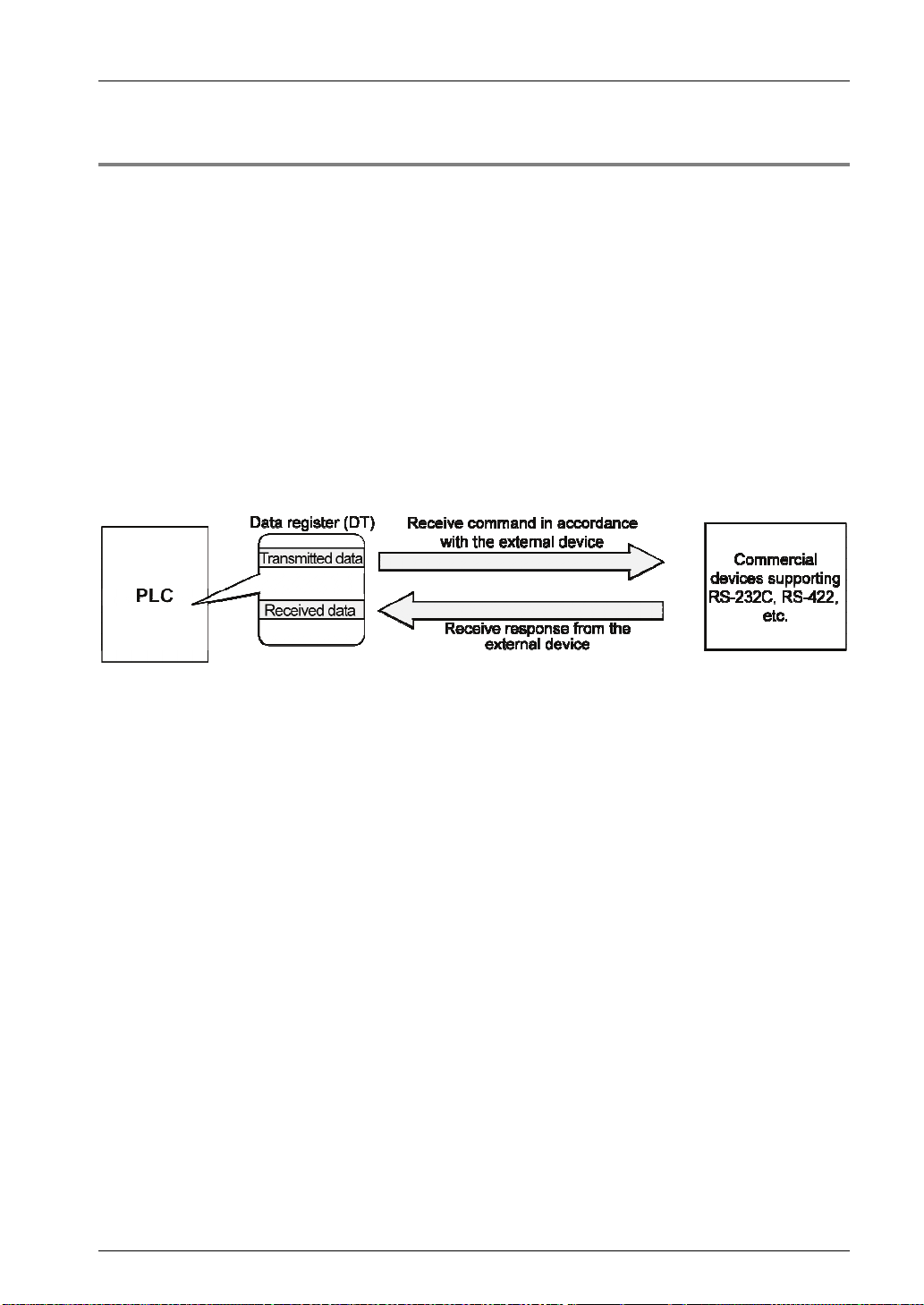
1.2.4 General-Purpose Communication
Overview of function
General-purpose communication is used when PLC executes communication in accordan ce
with the protocol of the partner device.
Formulation and sending of command messages to the partner device, and reception
processing of responses from the partner device, are performed by the user program.
Sending/receiving of data with an external device is executed via given operation memory
(e.g. data register).
Data are sent by converting commands in accordance with the partner device as strings into
ASCII text, setting them into a given data register, and executing GPSEND instruction.
Response received from the partner device is temporarily saved in the buffer. Based on the
reception done flag, GPRECV instruction is executed. The ASCII strings can be converted
into numerical data, etc. as necessary, by the user program.
The data size that can be sent or received in a single communication is up to 4,096 bytes.
(including control codes)
Applications of general-purpose communication
This is used for connection with devices made by differing manufacturers that have dedicated
communication protocols.
1-7
Page 18
Functions of Units and Restrictions on Combination
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1.3 Restrictions on Units C ombination
1.3.1 Restrictions on the Number of Installed Units
There are following restrictions depending on units to be used.
Unit type Number of installed units Remarks
Serial Communication Unit Max. 8 units
1.3.2 Restrictions on the Combination of Extension Cassettes
(Communication Cassettes)
One communication cassette can be attached to the CPU unit, and two communication
cassettes to the serial communication unit.
The FP7 communication cassette (Ethernet type) can be attached to the CPU only. It cannot
be attached to the serial communication unit (SCU).
1.3.3 Restrictions on Communication Functions to be Used
There are the following restrictions on functions to be used when using the SCU or ET-LAN
that is built in the CPU unit, or the serial communication unit (SCU).
Function to be used Restrictions
Up to two communication ports can be used. For using two ports, allocate
PLC link function
MEWTOCOL-COM master
MODBUS-RTU master
MEWTOCOL-COM slave
MEWTOCOL7-COM slave
MODBUS-RTU slave
General-purpose
communication
different link areas to them.
CPU with built-in SCU (COM.1 port)
Serial communication unit (COM.1 port)
A maximum of 16 communication ports and the number of connections in
combination can be used simultaneously.
CPU with built-in SCU (COM.1 port to COM. 2 port)
Serial communication unit (COM.1 port to COM.4 port)
CPU with built-in ET-LAN (User connections 1 to 16)
A maximum of 15 communication ports and the number of connections in
combination can be used simultaneously.
CPU with built-in SCU (COM.1 port to COM. 2 port)
Serial communication unit (COM.1 port to COM.4 port)
CPU with built-in ET-LAN
(System connections 1 to 4 / User connections 1 to 16)
There is no restriction.
1.3.4 Unit to be Used and Applicable Versions o f CPU Unit and FPWIN GR 7
For using the unit, the following versions of CPU unit and FPWINGR7 are required.
Unit type
FP7 Serial Communication Unit Ver.1.2 or later Ver.1.3 or later
Applicable versions
CPU unit FPWINGR7
Remarks
1-8
Page 19
1.3 Restrictions on Units Combination
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1.3.5 Restrictions on Consumption Current
Including other units, the consumption current should be within the allowable capacity of a
power supply unit.
Unit's consumption current table (24 V)
Product name Model number
196k steps, Built-in Ethernet
function
CPU Unit
When attaching
Extension Cassette
(Communication
Cassette) to CPU
Unit
(Note 1) (Note 2)
Serial Communication Unit AFP7NSC 50 mA or less
When attaching
Extension Cassette
(Communication
Cassette) to Serial
Communication Unit
(Note 1) (Note 2)
(Note 1) The consumption currents listed in the Extension Cassette column indicate the increased amount of the
CPU's consumption current which increases when each extension cassette is added.
(Note 2) The consumption current of extension cassette (communication cassette) varies according to the unit to
which the cassette is attached (CPU or serial communication unit).
120k steps, Built-in Ethernet
function
120k steps, No Ethernet function AFP7CPS3 200 mA or less
RS-232C x 1ch AFP7CCS1 35 mA or less
RS-232C x 2ch AFP7CCS2 60 mA or less
RS-422 / 485 x 1ch AFP7CCM1 60 mA or less
RS-422 / 485 x 2h AFP7CCM2 90 mA or less
RS-232C x 1ch
RS-422 / 485 x 1ch
Ethernet AFP7CCET 35 mA or less
RS-232C x 1ch AFP7CCS1 20 mA or less
RS-232C x 2ch AFP7CCS2 40 mA or less
RS-422 / 485 x 1ch AFP7CCM1 30 mA or less
RS-422 / 485 x 2h AFP7CCM2 60 mA or less
RS-232C x 1ch
RS-422 / 485 x 1ch
AFP7CPS4E 200 mA or less
AFP7CPS3E 200 mA or less
AFP7CCS1M1 70 mA or less
AFP7CCS1M1 50 mA or less
Consumption
current (mA)
REFERENCE
For information on the restrictions on the combination of units, also refer to FP7 CPU
Unit User's Manual (Hardware).
1-9
Page 20

Functions of Units and Restrictions on Combination
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1-10
Page 21

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
2
Names and Functions of
Parts
Page 22
Names and Functions of Parts
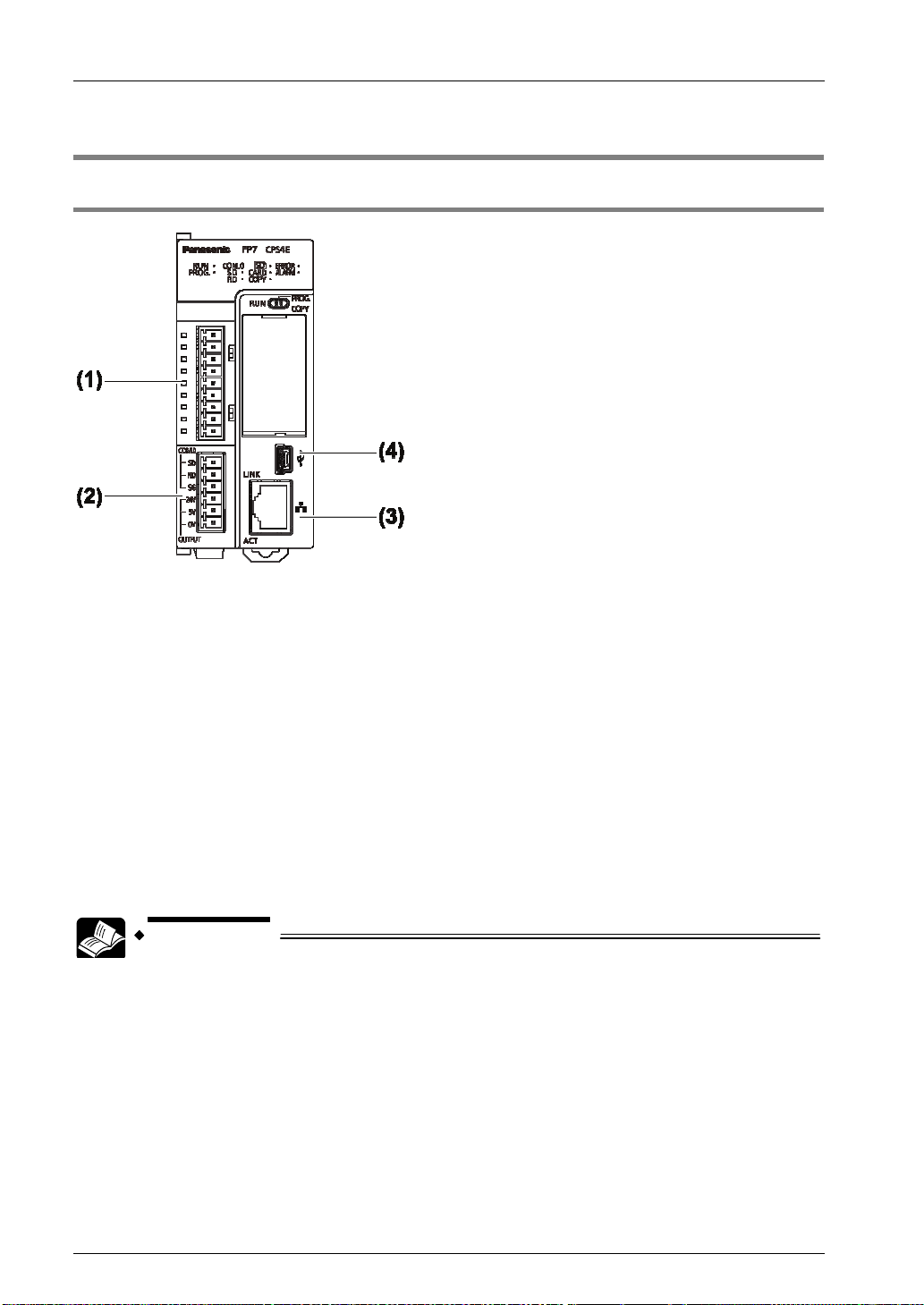
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
2.1 Names and Functions of Parts
2.1.1 Communication Port of CPU Unit
(In the above figure, a communication cassette is attached to the COM.1 and COM.2 ports.)
Names and Functions of Parts
(1) COM.1 and COM.2 ports
Attach a separately sold communication cassette to use these ports. A blank cover is fitted
when the unit is shipped.
(2) COM.0 port, GT power supply terminals
This is an RS-232C port that is equipped to a standard model of CPU unit. It is equipped with
power supply terminals (5 VDC and 24 VDC) to which a GT series programmable display can
be connected.
(3) LAN port
This is equipped to a standard model of CPU unit. This is used for connection to Ethernet.
(4) USB port
This is equipped to a standard model of CPU unit. This is used for connecting tool software.
REFERENCE
For details of the communication method using LAN port, refer to FP7 CPU
Unit User's Manual (LAN port communication).
For details of the communication using Communication cassette (Ethernet
type) AFP7CCET, refer to FP7 series User's Manual (Communication
cassette Ethernet type).
2-2
Page 23
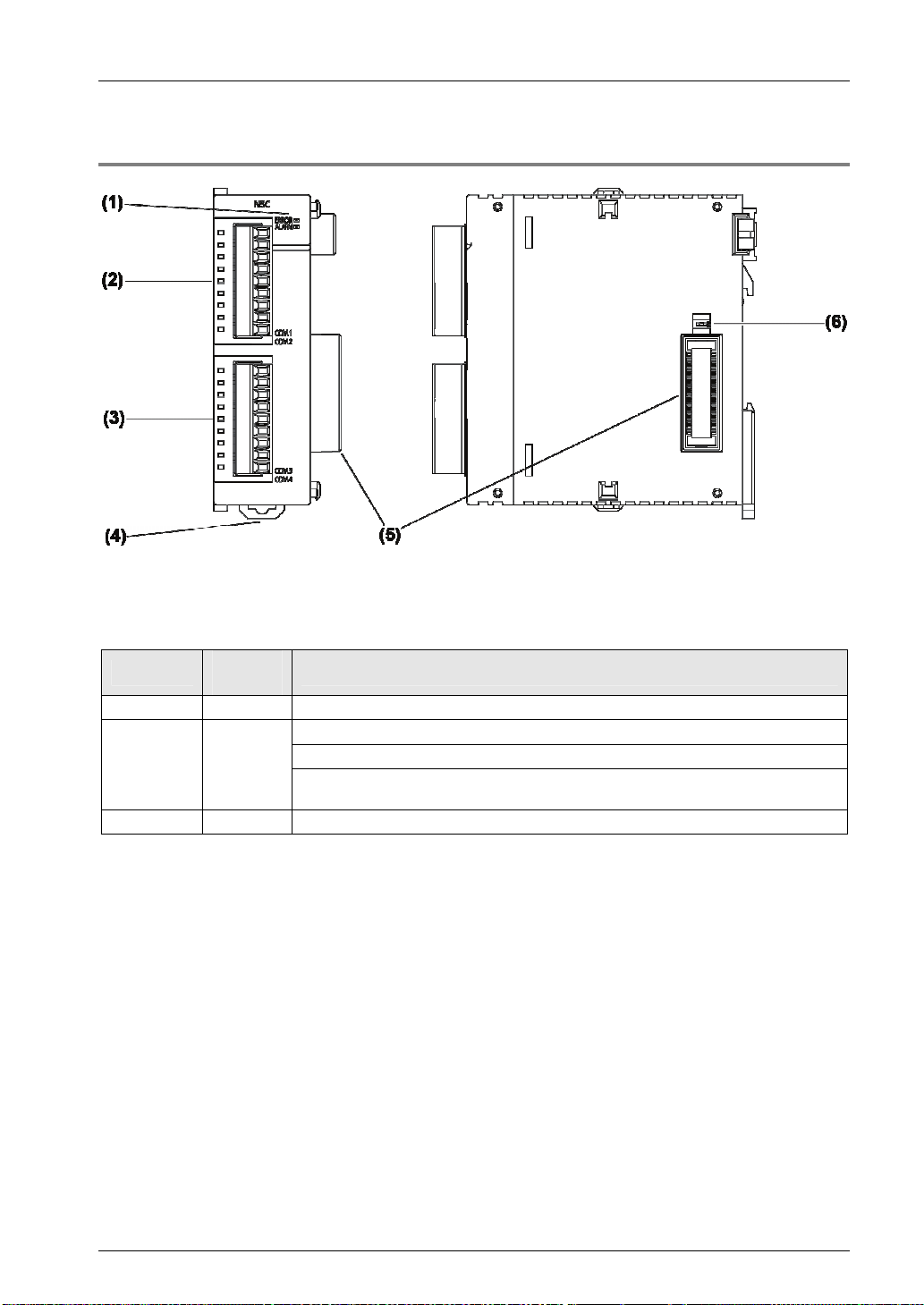
2.1 Names and Functions of Parts
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
2.1.2 Parts Names and Functions of Serial Communication Unit
(In the above figure, two communication cassettes are attached.)
Names and Functions of Parts
(1) Operation monitor LEDs
Display
- Blue Lights when the power supply of the CPU unit is on.
ERROR Red
ALARM Red Lights when an error occurs in hardware.
LED
color
Description
Lights when the configuration setting is incorrect, or a communication error occurs.
Flashes when the factory acceptance test switch is on. (Flashing cycle: 100 ms)
Flashes when an extension cassette that cannot be used is installed. (Flashing
cycle: 500 ms)
(2) COM.1 and COM.2 ports
Attach a separately sold communication cassette to use these ports. No blank cover is fitted
when the unit is shipped.
(3) COM.3 and COM.4 ports
Attach a separately sold communication cassette to use these ports. A blank cover is fitted
when the unit is shipped.
(4) DIN hook
This is used to fix the unit to a DIN rail.
(5) Unit connector
This is used to connect the internal circuit of an I/O unit or advanced unit.
(6) Factory acceptance test switch
This is used for factory acceptance test. Do not turn it on.
2-3
Page 24

Names and Functions of Parts
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
2-4
Page 25

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3
Wiring the COM. Port
Page 26
Wiring the COM. Port
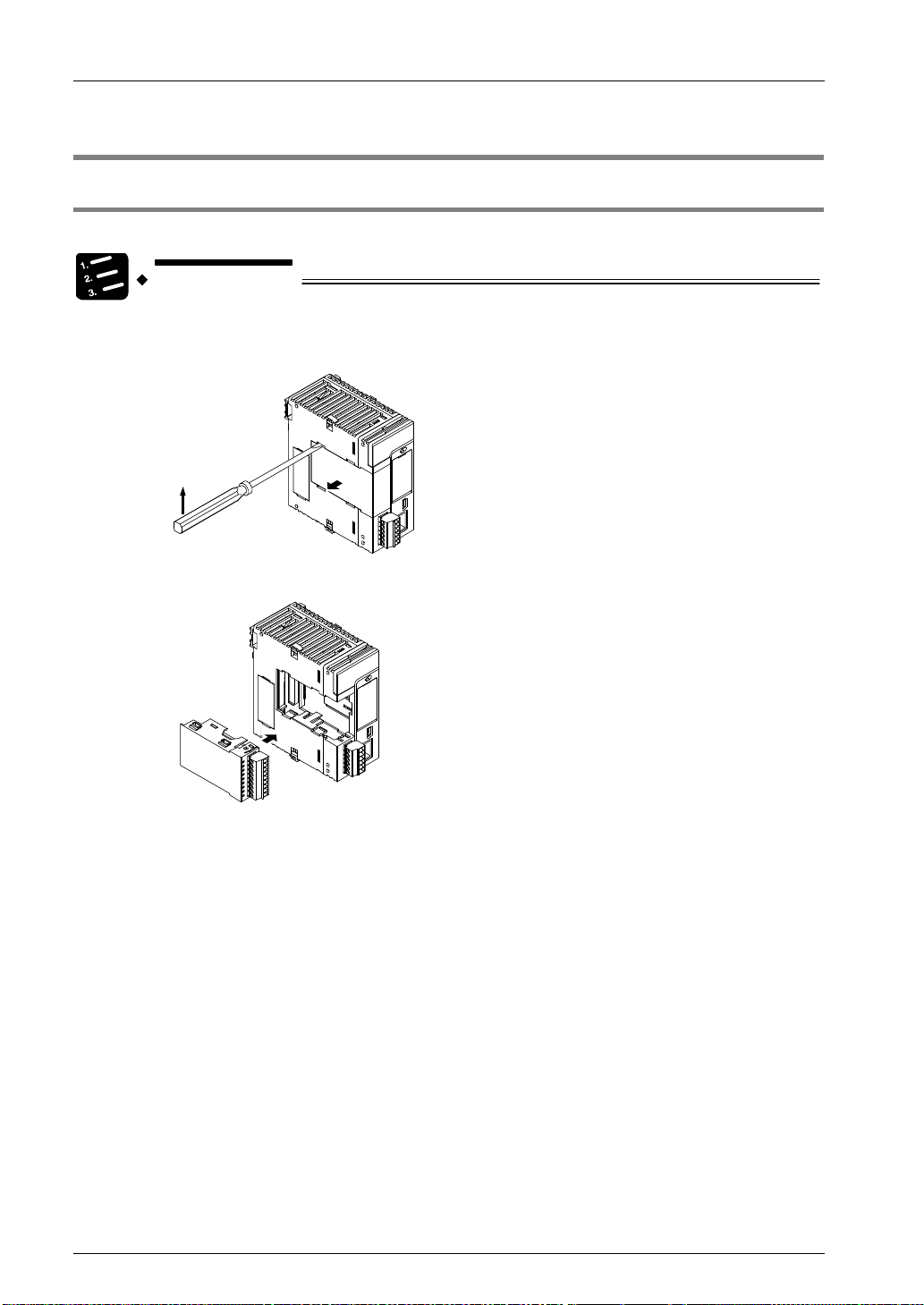
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.1 Attaching a Communication Cassette
3.1.1 Attachment Instructions
When an optional Communication Cassette is to be used, attach it in the following procedures.
PROCEDURE
1. Using a flathead screwdriver, remove the cover on the side of the CPU unit.
You will find four toggles.
2. Attach a desired Communication Cassette.
The illustration is the CPU unit. As for the Serial Communication Unit, the
attachment procedure is the same.
3-2
Page 27
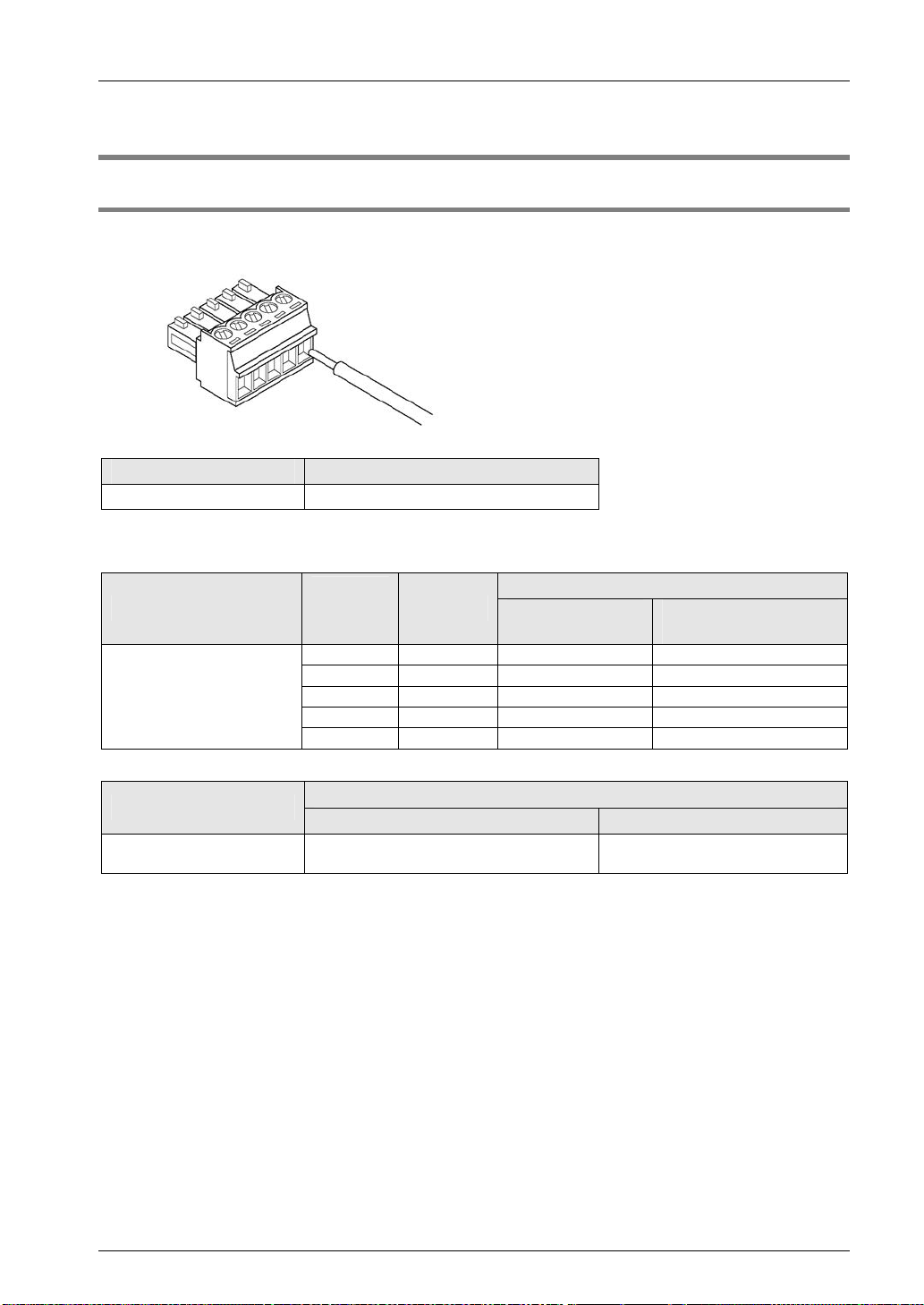
3.2 Wiring of COM Port Terminal Block
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.2 Wiring of COM Port Terminal Blo ck
3.2.1 Suitable Wires and Tools
A screw-down connection type for terminal block is used for the communication port. Use the
following items for wiring.
Suitable wires (strand wire)
Size Nominal cross-sectional area
AWG #28 to 16 0.08 mm2 to 1.25 mm2
Pole terminal with a compatible insulation sleeve
If a pole terminal is being used, the following models should be used.
Part no.
With insulating
sleeve
Without insulating
sleeve
Manufacturer
Phoenix Contact
Crosssectional
area
0.25 mm2 AWG #24 AI 0.25-6 BU A 0.25-7
0.34 mm2 AWG #22 AI 0.34-6 TQ A 0.34-7
0.50 mm2 AWG #20 AI 0.5-6 WH A 0.5-6
0.75 mm2 AWG #18 AI 0.75-6 GY A 0.75-6
1.00 mm
Size
2
AWG #18 - A 1-6
Pressure welding tool for pole terminals
Manufacturer
Phoenix Contact
Model no.
Part no. Product no.
CRIMPFOX 6 1212034
Screwdriver for terminal block
To tighten the terminals, use a screwdriver by Phoenix Contact (model No. SZS 0.4 x 2.5,
product No. 1205037, blade size 0.4 x 2.5) or our screwdriver (part No. AFP0806). The
tightening torque should be 0.22 to 0.25 N·m.
3-3
Page 28
Wiring the COM. Port
-
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.2.2 Applicable Cable
Use a cable as prescribed below.
Suitable wires (strand wire): For RS-232C / RS-422 communication
Conductor Insulator
Classifi-
cation
Cross-sectional
view
Size
Resistance
value
(at 20°C)
Material
Thick-
ness
Cable
diam.
Sample
appropriate
cable
Shielded
multi-core
cable
Shield
Conductor
Cover
Insulator
0.3 mm2
(AWG22)
or larger
Max.
58.8 Ω/km
Vinyl
chloride
Max.
0.3 mm
Suitable wires (strand wire): For RS-485 communication
Conductor Insulator
Classifi0c
ation
Cross-sectional
view
Size
Resistance
value
Material
Thick-
ness
(at 20°C)
2
Max.
16.8 Ω/km
Max.
33.4 Ω/km
2
Max.
25.1 Ω/km
Polyethylene
Polyethylene
Polychlorinated
biphenyl
Max.
0.5 mm
Max.
0.5 mm
Max.
0.6 mm
Shielded
twisted
pair
VCTF
Shield
Conductor
Conductor
NOTES
1.25 mm
(AWG16)
Cover
or larger
Insulator
0.5 mm2
(AWG20)
or larger
Cover
0.75 mm
(AWG18)
Insu
lator
or larger
Use shielded twisted pair cables.
Use only one type of transmission cable. Do not mix more than 1 type.
Twisted pair cables are recommended in noisy environments.
When using shielded cable with crossover wiring for the RS-485
transmission line, grounded one end.
Approx.
6.6 mm
Cable
diam.
Approx.
8.5 mm
Approx.
7.8 mm
Approx.
6.6 mm
Onamba Co. Ltd.
ONB-D6 × 0.3 mm
2
Sample
appropriate
cable
Hitachi Cable, Ltd.
KPEV-S1.25 mm
1P
Belden Inc., 9860
Hitachi Cable, Ltd.
KPEV-S0.5 mm
1P
Belden Inc., 9207
VCTF0.75 mm2 × 2C
(JIS)
2
×
2
×
3-4
Page 29
3.2 Wiring of COM Port Terminal Block
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
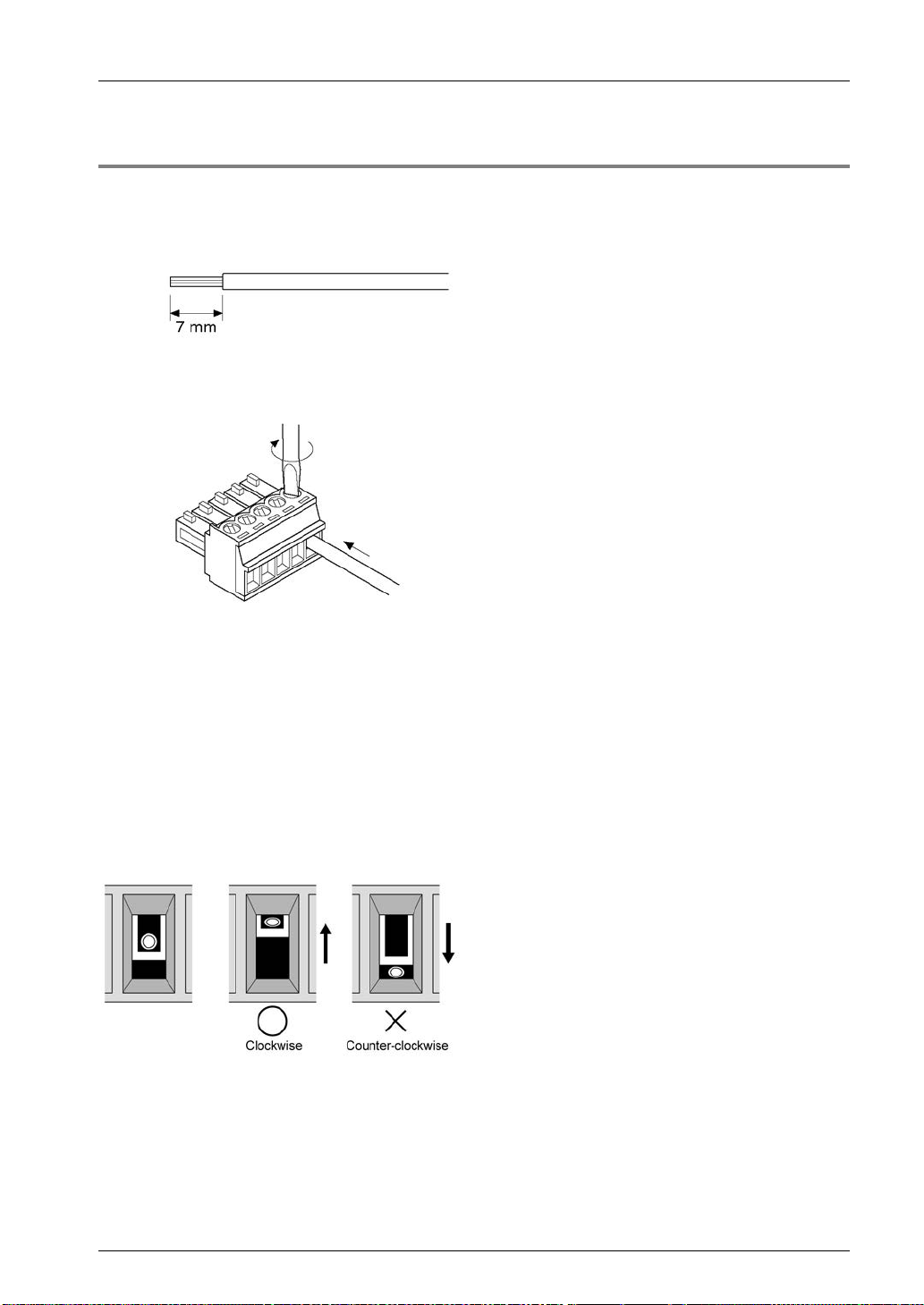
3.2.3 Wiring Method
Wiring method
(1) Remove a portion of the wire’s insulation.
(2) Insert wire into terminal hole until it stops. Tighten screw clockwise to fix wire in place.
(The tightening torque: 0.22 to 0.25 N·m (2.3 to 2.5 kgf·cm))
Precautions on wiring
The following precautions should be observed, to avoid broken or disconnected wire s.
When removing the wire’s insulation, be careful not to scratch the core wire.
Do not twist the wires to connect them.
Do not solder the wires to connect them. The solder may break due to vibration.
After wiring, make sure stress is not applied to the wire.
In the terminal block socket construction, if the wire is fastened upon counter-clockwise
rotation of the screw, the connection is faulty. Disconnect the wire, check the terminal hole,
and then re-connect the wire.
3-5
Page 30
Wiring the COM. Port
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.3 Wiring for CPU Unit (GT Power Supply and COM0 Port)
3.3.1 Handling of GT Power Supply Terminals
GT power supply terminals can be used as power supply terminals for the GT series of our
programmable displays.
In accordance with the model to be used, use either 5V DC or 24V DC.
NOTES
GT power supply terminals (5V DC / 24V DC) are design exclusively for the
GT series of our programmable displays. Do not use the terminals for other
devices.
GT power supply terminals and COM0 port (RS-232C) are insulated inside.
3.3.2 Terminal Layouts and Examples of Wiring
Layout for GT power supply terminals and COM0 port terminals
Terminal
no.
1 COM.0 SD Sent data
2 RD Received data
3 SG Signal Ground -
4 OUTPUT 24V 24V 5 5V 5V 6 0V 0V -
Terminal part
Symbol
Functions
that can be
allocated
Signal direction
PLC →
External device
PLC ←
External device
Ports that can be
allocated
in the software
COM.0
-
3-6
Page 31

3.3 Wiring for CPU Unit (GT Power Supply and COM0 Port)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Example of wiring (in the case of GT02 5V DC type)
COM.0 port terminal / GT power supply terminal
FP7 CPU unit
Terminal
No.
4
GT power
supply
Terminal part symbolSignal name
COM.0
OUTPUT
SDSent Data 1
RDRecei ved Data2
SGSignal Ground3
24V
5V5
0V6
to GT +
terminal
to GT terminal
From 5 V
terminal
From 0 V
terminal
Example of wiring (in the case of GT series 24V DC type)
COM.0 port terminal / GT power supply terminal
Terminal
No.
4
FP7 CPU unit
GT power
supply
Terminal part symbolSignal name
COM.0
OUTPUT
SDSent Data 1
RDRecei ved Data2
SGSignal Ground3
24V
5V5
0V6
From 24V
terminal
From 0V
terminal
to GT +
terminal
to GT terminal
GT02 / GT02L series
5V DC type
Terminal
part symbol
Signal name
Functional Ground
Sent Data SD
Received DataRD
Signal GroundSG
GT series
24V DC type
Terminal
part symbol
Signal name
Functional Ground
Sent Data SD
Received DataRD
Signal GroundSG
5 V+
0 V-
NCRS
NCCS
24V+
0V-
NCRS
NCCS
NOTE
The terminal layout on the display side differs for the existing models GT01
series.
3-7
Page 32

Wiring the COM. Port
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.4
Wiring for Communication Cassettes COM.1 to COM.4 Ports
3.4.1 Communication Cassette AFP7CCS1
(RS-232C, 1-Channel Insulated Type)
Terminal layout
Terminal
no.
1 CH1 SD SD SD: Sent Data
2 RD RD
3 - SG
4 - 9 - - - - -
(Note) Do not connect anything to Terminals No.4 through No.9.
LED part
Symbol
Terminal
part
Symbol
Functions
that can be
allocated
RD: Received
Data
SG: Signal
Ground
Signal
direction
PLC →
External device
PLC ←
External device
-
Ports that can be
allocated
in the software
COM.1
Example of wiring
Terminal
No.
AFP7CCS1
Terminal
part symbol
Signal name
Sent Data 1
Received Data 1
Signal Ground
Functions
SDSD1
RDRD2
SGSG3
Partner
Signal nameSymbol
Received DataRD
Sent DataSD
Signal GroundSG
3-8
Page 33

3.4 Wiring for Communication Cassettes COM.1 to COM.4 Ports
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.4.2 Communication Cassette AFP7CCS2
(RS-232C, 2-channel insulated type)
Setting of Application Switch
Applications for use can be switched using a switch on the backplane for Communication
Cassette AFP7CCS2. Settings can be confirmed with LED lamps at the front of the cassette.
3-wire 2-channel RS-232C
5-wire 1-channel RS-232C (RS/CS controlled)
3-9
Page 34

Wiring the COM. Port
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Terminal layout (in th e setting of 3-wire 2-channel RS-232C)
Terminal
no.
1 CH1 SD SD SD: Sent Data
2 RD RD
3 - SG
4 CH2 SD / R SD SD: Sent Data
5 RD / C RD
6 - SG
7 MODE - - - -
8 3-Wire - - - 9 5-Wire - - - -
(Note 1) Route between CH1 and CH2 are insulated inside.
(Note 2) Do not connect anything to Terminals No.7 through No.9.
LED part
Symbol
Terminal
part
Symbol
Functions
that can be
allocated
RD: Received
Data
SG: Signal
Ground
RD: Received
Data
SG: Signal
Ground
Signal
direction
PLC →
External device
PLC ←
External device
PLC →
External device
PLC ←
External device
-
Ports that can be
allocated
in the software
COM.1
COM.2
Example of wiring (in the setting of 3-wire 2-channel RS-232C)
Terminal
No.
Terminal
part symbol
AFP7CCS2
Signal name
Sent Data 1
Received Data 1
Signal Ground
Sent Data 2
Received Data 2
Signal Ground
Functions
SDSD1
RDRD2
SGSG3
SDSD4
RDRD5
SGSG6
Partner 1
Signal nameSymbol
Received DataRD
Sent DataSD
Signal GroundSG
Partner 2
Signal nameSymbol
Received DataRD
Sent DataSD
Signal GroundSG
3-10
Page 35

3.4 Wiring for Communication Cassettes COM.1 to COM.4 Ports
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Terminal layout (in th e setting of 5-wire 1-channel RS-232C RS/CS controlled)
Terminal
no.
1 CH1 SD SD SD: Sent Data
2 RD RD
3 - SG
4 CH2 SD / R SD
5 RD / C RD
6 - SG - - -
7 MODE - - - 8 3-Wire - - - 9 5-Wire - - - -
(Note) Do not connect anything to Terminals No.6 through No.9.
LED part
Symbol
Terminal
part
Symbol
Functions
that can be
allocated
RD: Received
Data
SG: Signal
Ground
RS: Request to
Send
CS: Clear to
Send
Signal
direction
PLC →
External device
PLC ←
External device
PLC →
External device
PLC ←
External device
Ports that can be
allocated
in the software
COM.1
Example of wiring (in the setting of 5-wire 1-channel RS-232C RS/CS controlled)
Terminal
No.
AFP7CCS2
Terminal
part symbol
Signal name
Sent Data
Received Data
Signal Ground
Request to Send
Clear to Send
Functions
SDSD1
RDRD2
SGSG3
RSSD4
CSRD5
Symbol
RD
SD
SG
RS
CS
Partner
Signal name
Received Data
Sent Data
Signal Ground
Request to Send
Clear to Send
3-11
Page 36

Wiring the COM. Port
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.4.3 Communication Cassette AFP7CCM1
(RS-422 / RS-485, 1-Channel Insulated Type)
Setting of application switch
Applications for use can be switched using a switch on the backplane for Communication
Cassette AFP7CCM1. Settings can be confirmed with LED lamps at the front of the cassette.
Settings for termination resistance selector switch
On the surface of Communication Cassette AFP7CCM2 is located a termination resistance
selector switch.
When RS-422 is used: Turn ON the switch.
When RS-485 is used: Turn ON the switch only when it is the end unit.
3-12
Page 37

3.4 Wiring for Communication Cassettes COM.1 to COM.4 Ports
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Terminal layout (in th e setting of RS-485)
Terminal
no.
1 CH1 SD + / S Transmission line (+) 2 RD - / S Transmission line (-) 3 485 + / R Transmission line (+) 4 422 - / R Transmission line (-) 5 - 9 - - - - -
(Note 1) In the setting of RS-485, Terminal No.1 and Terminal No.3, and Terminal No.2 and Terminal No.4 are
respectively connected inside. They can be used as terminals for crossover wiring for the transmission cable.
(Note 2) Do not connect anything to Terminals No.5 through No.9.
LED part
Symbol
Terminal
part
Symbol
Functions that can
be allocated
Signal
direction
Ports that can be
allocated
in the software
COM.1
Example of wiring (in the setting of RS-485)
AFP7CCM1
No.
Terminal part
symbol
Signal name
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
Functions
++ / S1
--/ S2
++ / R3
--/ R4
Terminal
Terminal
+
-
Terminal
+
-
Partner 1
Signal name
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
Partner 2
Signal name
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
3-13
Page 38

Wiring the COM. Port
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Terminal layout (in th e setting of RS-422)
Terminal
no.
1 CH1 SD + / S Sent Data (+)
2 RD - / S Sent Data (-)
3 485 + / R Received Data (+)
4 422 - / R Received Data (-)
5 - 9 - - - - -
(Note) Do not connect anything to Terminals No.5 through No.9.
LED part
Symbol
Terminal
part
Symbol
Functions that
can be
allocated
Signal
direction
PLC →
External device
PLC →
External device
PLC ←
External device
PLC ←
External device
Ports that can be
allocated
in the software
COM.1
Example of wiring (in the setting of RS-422)
AFP7CCM1
No.
Terminal part
symbol
Signal name
Sent Data (+)
Sent Data (-)
Received Data (+)
Received Data (-)
Functions
SD (+)+ / S1
SD (-)-/ S2
RD (+)+ / R3
RD (-)-/ R4
Terminal
Terminal
RD (+)
RD (-)
SD (+)
SD (-)
Partner
Signal name
Received Data (+)
Received Data (-)
Sent Data (+)
Sent Data (-)
3-14
Page 39

3.4 Wiring for Communication Cassettes COM.1 to COM.4 Ports
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.4.4 Communication Cassette AFP7CCM2
(RS-422 / RS-485, 2-Channel Insulated Type)
Setting of application switch
Applications for use can be switched using a switch on the backplane for Communication
Cassette AFP7CCM2. Settings can be confirmed with LED lamps at the front of the cassette.
Settings for termination resistance selector switch
On the surface of Communication Cassette AFP7CCM2 is located a termination resistance
selector switch.
When RS-422 is used: Turn ON the switch.
When RS-485 is used: Turn ON the switch only when it is the end unit.
3-15
Page 40

Wiring the COM. Port
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Terminal layout (in th e setting of RS-485)
Terminal
no.
1 CH1 SD + / S Transmission line (+) 2 RD - / S Transmission line (-) 3 485 + / R Transmission line (+) 4 422 - / R Transmission line (-) 5 - - - - 6 CH2 SD + / S Transmission line (+) 7 RD - / S Transmission line (-) 8 485 + / R Transmission line (+) 9 422 - / R Transmission line (-) -
(Note 1) In the setting of RS-485, Terminal No.1 and Terminal No.3, and Terminal No.2 and Terminal No.4 are
respectively connected inside. They can be used as terminals for crossover wiring for the transmission cable.
(Note 2) In the setting of RS-485, Terminal No.6 and Terminal No.8, and Terminal No.7 and Terminal No.9 are
respectively connected inside. They can be used as terminals for crossover wiring for the transmission cable.
(Note 3) Do not connect anything to Terminal No.5.
(Note 4) Route between CH1 and CH2 are insulated inside.
LED part
Symbol
Terminal
part
Symbol
Functions that can
be allocated
Signal
direction
Ports that can
be allocated
in the software
COM.1
COM.2
3-16
Page 41

3.4 Wiring for Communication Cassettes COM.1 to COM.4 Ports
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Example of wiring (in the setting of RS-485)
Terminal
No.
5
AFP7CCM2
Terminal
part symbol
-
Signal name
Transmission line 1 (+)
Transmission line 1 (-)
Transmission line 1 (+)
Transmission line 1 (-)
NC
Transmission line 2 (-)
Functions
++ / S1
--/ S2
++ / R3
--/ R4
NC
+Transmission line 2 (+)+ / S6
-Transmission line 2 (-)-/ S7
+Transmission line 2 (+)+ / R8
--/ R9
Transmission line 1 Partner 1
Terminal
+
-
Signal name
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
Transmission line 1 Partner 2
Terminal
+
-
Signal name
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
Transmission line 2 Partner 1
Terminal
+
-
Signal name
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
Transmission line 2 Partner 2
Terminal
+
-
Signal name
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
3-17
Page 42

Wiring the COM. Port
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Terminal layout (in th e setting of RS-422)
Terminal
no.
1 CH1 SD + / S Sent Data (+)
2 RD - / S Sent Data (-)
3 485 + / R Received Data (+) PLC ← External device
4 422 - / R Received Data (-) PLC ← External device
5 - - - - 6 CH2 SD + / S Sent Data (+)
7 RD - / S Sent Data (-)
8 485 + / R Received Data (+) PLC ← External device
9 422 - / R Received Data (-) PLC ← External device
(Note 1) Do not connect anything to Terminal No.5.
(Note 2) Route between CH1 and CH2 are insulated inside.
LED part
Symbol
Terminal
part
Symbol
Functions that
can be allocated
Signal direction
PLC → External device
PLC → External device
PLC → External device
PLC → External device
Ports that can be
allocated
in the software
COM.1
COM.2
Example of wiring (in the setting of RS-422)
AFP7CCM2
No.
5
Terminal
part symbol
-
Signal name
Sent Data 1 (+)
Sent Data 1 (-)
Received Data 1 (+)
Received Data 1 (-)
Received Data 2 (-)
Functions
SD (+)+ / S1
SD (-)-/ S2
RD (+)+ / R3
RD (-)-/ R4
SD (+)Sent Data 2 (+)+ / S6
SD (-)Sent Data 2 (-)-/ S7
RD (+)Received Data 2 (+)+ / R8
RD (-)-/ R9
Terminal
Terminal
RD (+)
RD (-)
SD (+)
SD (-)
Terminal
RD (+)
RD (-)
SD (+)
SD (-)
Partner 1
Signal name
Received Data (+)
Received Data (-)
Sent Data (+)
Sent Data (-)
Partner 2
Signal name
Received Data (+)
Received Data (-)
Sent Data (+)
Sent Data (-)
3-18
Page 43

3.4 Wiring for Communication Cassettes COM.1 to COM.4 Ports
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.4.5 Communication Cassette AFP7CCS1M1 (RS-232C 1-Channel + RS-485
1-Channel Insulated Type)
Settings for termination resistance selector switch
A termination resistance selector switch is locate d on the RS-485 side of the surface of
Communication Cassette AFP7CCS1M1. Turn ON the switch only when it is the end unit.
Terminal
no.
1 CH1 SD + Transmission line (+) 2 RD - Transmission line (-) 3
4
5 - 6
7 CH2 SD SD Sent data 8 RD RD Received data 9 SG SG Signal ground -
(Note 1) Terminal No.1 and Terminal No.3, and Terminal No.2 and Terminal No.4 are respectively connected inside.
(Note 2) Do not connect anything to Terminals No.5 and No.6.
LED part
Symbol
-
Terminal
part
Symbol
+ Transmission line (+) -
- Transmission line (-) -
- - - -
Functions that
can be allocated
Signal
direction
Ports that can be
allocated
in the software
COM.1
COM.2
3-19
Page 44

Wiring the COM. Port
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Example of wiring
Terminal
No.
5
6
AFP7CCS1M1
Terminal
part symbol
-
-
Signal name
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
NC
Signal Ground
Functions
++ / S1
--/ S2
++ / R3
--/ R4
NC
NCNC
SDSent DataSD7
RDReceived DataRD8
SGSG9
RS-485 Partner 1
Terminal
+
-
Signal name
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
RS-485 Partner 2
Terminal
+
-
Signal name
Transmission line (+)
Transmission line (-)
RS-232C partner
Terminal
RD
SG
Signal name
Received Data
Sent DataSD
Signal Ground
3-20
Page 45

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3
I/O Allocation
Page 46

I/O Allocation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
4.1 Input/Output Signals Used for Communication
4.1.1 I/O Allocation of CPU Unit
Input signal
Input
signal
X0 For COM.1 Port
X1 For COM.2 Port
X2 For COM.0 Port
X3 - Not used Do not use this.
X4 For COM.1 Port
X5 For COM.2 Port
X6 For COM.0 Port
X7 - Not used Do not use this.
X8 For COM.1 Port
X9 For COM.2 Port
XA For COM.0 Port
XB - Not used Do not use this.
XC For COM.1 Port
XD For COM.2 Port
XE For COM.0 Port
XF - Not used Do not use this.
X10 For COM.1 Port
X11 For COM.2 Port
X12 For COM.0 Port
X13
X14 For COM.1 Port
X15
- X1F
(Note 1) The general-purpose communication reception done (copy) flag is effective after the execution of the RECV
Communication
port
- Not used Do not use this.
- Not used Do not use this.
instruction until one of the following instructions is executed. This flag does not remain ON across several scans.
Execute 1: END instruction (scan header), and 2: RECV instruction
Name Description
Generalpurpose
communication
Reception
done flag
Generalpurpose
communication
Reception
done (copy)
flag
Generalpurpose
communication
Clear to send
flag
Master
communication
Clear to send
flag
Reset done
CTS signal
monitor
When the unit completes the data reception,
it turns on (1).
Waiting for data reception: 0, Reception
completed: 1
It turns on (1) if there are copied data when
GPRECV instruction is executed. It turns off
(0) when END instruction is executed.
(Note 1)
Reading completed: 1
No data to be read: 0
It turns on (1) when the unit is set to the
general-purpose communication mode. It
turns off (0) in other modes.
It turns on (1) when the unit is set to modes
other than the PLC link mode or generalpurpose communication mode. It turns off (0)
in other modes.
When the communication channel is reset
under the output Y10 - Y12, the flag is
turned on (1) once the resetting operation is
completed.
Resetting done: 1
Y10 - Y12 is off: 0
Status of the CTS signal sent from the
device communicating with.
Clear to send from COM.1 port = 0
Cannot send from COM.1 port = 1
The RTS signal can be controlled with Y14.
Effective
operation
mode
Generalpurpose
communication
Generalpurpose
communication
Generalpurpose
communication
MEWTOCOL
MODBUS-RTU
Generalpurpose
communication
When RS/CS is
set to valid in
Communication
Block COM.1.
4-2
Page 47

4.1 Input/Output Signals Used for Communication
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Output signal
Output
signal
Y0 For COM.1 Port
Y1 For COM.2 Port
Y2 For COM.0 Port
Y3
- Y7
Y8 For COM.1 Port
Y9 For COM.2 Port
YA For COM.0 Port
YB - Undefined
YC For COM.1 Port
YD For COM.2 Port
YE For COM.0 Port
YF - Undefined
Y10 For COM.1 Port
Y11 For COM.2 Port
Y12 For COM.0 Port
Y13 - Undefined
Y14 For COM.1 Port
Y15 Y1F
(Note 1) When transmission is completed within one scan, it turns off when the GPSEND instruction is executed in
Communication
port
- Undefined
- Undefined
the subsequent scan.
Name Description
Sending done
result
Generalpurpose
communication
Sending active
flag
Master
communication
Sending active
flag
Request to
reset CH
Output RTS
signal
Reports the results of sending in master
communication or general-purpose
communication.
Normal completion: 0, Abnormal completion:
1
Do not turn on "undefined". (Default setting is
0.)
It turns on (1) during sending in the general-
purpose communication mode.
(Note 1)
Sending done: 0, Sending: 1
Do not turn on "undefined". (Default setting is
0.)
It turns on (1) during sending in the master
communication mode.
Sending done: 0, Sending: 1
Do not turn on "undefined". (Default setting is
0.)
By turning on (1) Y10 - Y12, the
communication channel can be reset.
Without a request to reset = 0, With a
request to reset = 1
After ON (1) is output and the completion of
the reset is confirmed by X10 - X12, return to
OFF (0). The reset is performed only once
when this signal rises.
This function can be used to delete
unnecessary received data or to clear errors
before starting normal reception.
1:Sending canceled
2:Reception canceled
3:Re-set communication parameters
4:Clear error information (only for errors that
can be cleared)
Do not turn on "undefined". (Default setting is
0.)
By turning on (1) this output, RTS is
controlled.
Transmission from the device communicating
with is permitted = 0
Transmission from the device communicating
with is prohibited = 1
Monitor the CTS signal from the device
communicating with using X14.
Do not turn on "undefined". (Default setting is
0.)
Effective
operation
mode
MEWTOCOL
MODBUS-RTU
Generalpurpose
communication
Generalpurpose
communication
MEWTOCOL
MODBUS-RTU
Generalpurpose
communication
When RS/CS is
set to valid in
Communication
Cassette
COM.1
-
NOTE
Each contact in the table above is used for reading the operation status. Do
not write over it with a user program. (excluding Y10 - Y12 and Y14)
4-3
Page 48

I/O Allocation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
4.1.2 I/O Allocation of Serial Commun ication Unit
Input signal
Input
signal
X0 For COM.1 Port
X1 For COM.2 Port
X2 For COM.3 Port
X3 For COM.4 Port
X4 For COM.1 Port
X5 For COM.2 Port
X6 For COM.3 Port
X7 For COM.4 Port
X8 For COM.1 Port
X9 For COM.2 Port
XA For COM.3 Port
XB For COM.4 Port
XC For COM.1 Port
XD For COM.2 Port
XE For COM.3 Port
XF For COM.4 Port
X10 For COM.1 Port
X11 For COM.2 Port
X12 For COM.3 Port
X13
X14 For COM.1 Port
X16 For COM.3 Port
X15,
X17
- X1F
(Note 1) The general-purpose communication reception done (copy) flag is effective after the execution of the RECV
(Note 2): The I/O numbers actually allocated are the numbers based on the starting word number allocated to the unit.
Communication
port
For COM.4 Port
- Not used Do not use this.
instruction until one of the following instructions is executed. This flag does not remain ON across several scans.
Execute 1: END instruction (scan header), and 2: RECV instruction
Example) When the starting word number for the unit is "10", the general-purpose communication reception
done flag for COM.1 port is X100.
Name Description
Generalpurpose
communication
Reception
done flag
Generalpurpose
communication
Reception
done (copy)
flag
Generalpurpose
communication
Clear to send
flag
Master
communication
Clear to send
flag
Reset done
CTS signal
monitor
When the unit completes the data reception,
it turns on (1).
Waiting for data reception: 0, Reception
completed: 1
It turns on (1) if there are copied data when
GPRECV instruction is executed. It turns off
(0) when END instruction is executed.
(Note 1)
Reading completed: 1
No data to be read: 0
It turns on (1) when the unit is set to the
general-purpose communication mode. It
turns off (0) in other modes.
It turns on (1) when the unit is set to modes
other than the PLC link mode or generalpurpose communication mode. It turns off (0)
in other modes.
When the communication channel is reset
under the output Y10 - Y13, the flag is
turned on (1) once the resetting operation is
completed.
Resetting done: 1
Y10 - Y12 is off: 0
Status of the CTS signal sent from the
device communicating with.
Clear to send from COM.1/COM.3 port = 0
Cannot send from COM.1/COM.3 port = 1
The RTS signal can be controlled with
Y14/Y16.
Effective
operation
mode
Generalpurpose
communication
Generalpurpose
communication
Generalpurpose
communication
MEWTOCOL
MODBUS-RTU
Generalpurpose
communication
When RS/CS is
set to valid in
Communication
Cassette
COM.1/COM.3
4-4
Page 49

4.1 Input/Output Signals Used for Communication
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Output signal
Output
signal
Y0 For COM.1 Port
Y1 For COM.2 Port
Y2 For COM.3 Port
Y3 For COM.4 Port
Y4
- Y7
Y8 For COM.1 Port
Y9 For COM.2 Port
YA For COM.3 Port
YB For COM.4 Port
YC For COM.1 Port
YD For COM.2 Port
YE For COM.3 Port
YF For COM.4 Port
Y10 For COM.1 Port
Y11 For COM.2 Port
Y12 For COM.3 Port
Y13 For COM.4 Port
Y14 For COM.1 Port
Y16 For COM.3 Port
Y15
Y17
- Y1F
(Note 1) When transmission is completed within one scan, it turns off when the GPSEND instruction is executed in
(Note 2): The I/O numbers actually allocated are the numbers based on the starting word number allocated to the unit.
Communication
port
- Undefined
- Undefined
the subsequent scan.
Example) When the starting word number for the unit is "10", the sending done result flag for COM.1 port is
Y100.
Name Description
Reports the results of sending in master
Sending done
result
Generalpurpose
communication
Sending active
flag
Master
communication
Sending active
flag
Request to
reset CH
Output RTS
signal
communication or general-purpose
communication.
Normal completion: 0, Abnormal completion:
1
Do not turn on "undefined". (Default setting is
0.)
It turns on (1) during sending in the general-
purpose communication mode.
(Note 1)
Sending done: 0, Sending: 1
It turns on (1) during sending in the master
communication mode.
Sending done: 0, Sending: 1
By turning on (1) Y10 - Y13, the
communication channel can be reset.
Without a request to reset = 0, With a request
to reset = 1
After ON (1) is output and the completion of
the reset is confirmed by X10 - X13, return to
OFF (0). The reset is performed only once
when this signal rises. This function can be
used to delete unnecessary received data or
to clear errors before starting normal
reception.
1:Sending canceled
2:Reception canceled
3:Re-set communication parameters
4:Clear error information (only for errors that
can be cleared)
By turning on (1) this output, RTS is
controlled.
Transmission from the device communicating
with is permitted = 0
Transmission from the device communicating
with is prohibited = 1
Monitors the CTS signal from the device
communicating with using X14/X16.
Do not turn on "undefined". (Default setting is
0.)
Effective
operation
mode
MEWTOCOL
MODBUS-RTU
Generalpurpose
communication
Generalpurpose
communication
MEWTOCOL
MODBUS-RTU
Generalpurpose
communication
When RS/CS is
set to valid in
Communication
Cassette
COM.1/COM.3
-
NOTE
Each contact in the table above is used for reading the operation status. Do
not write over it with a user program. (excluding Y10 - Y14 and Y16)
4-5
Page 50

I/O Allocation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
4.2 Registration in I/O Map
4.2.1 Settings Using FPWIN GR7 (For CPU with built- in SCU)
For the CPU with built-in SCU, there is no need to set with FPWIN GR7 because the
following fixed areas are allocated.
No. of occupied words
Unit type Model number
CPU Unit CPU with built-in SCU Common
4.2.2 Settings Using FPWIN GR7 (For Serial Communica tion Unit)
The explanation below shows the case that the serial communication unit is registere d in the
slot number 1.
(No. of occupied points)
Input Output
2 words (32 points)
WX0 - WX1 Fixed
2 words (32 points)
WY0 - WY1 Fixed
PROCEDURE
1. Select "Options" > "FP7 Configuration" in the menu bar.
The "FP7 Configuration" dialog box appears.
2. Select "I/O map" in the left pane.
The "I/O map" dialog box is displayed.
3. Double-click Slot No. 0.
The "Unit selection [Slot No. 0]" dialog box is displayed.
4. Select "CPU unit" for Unit type, and select a CPU unit used for Unit name,
and press [OK] button.
The CPU unit is registered. Only CPU unit can be registered in Slot No. 0. Slot
No.1 and subsequent numbers cannot be set unless Slot No. 0 is set.
4-6
Page 51

5. Double-click Slot No. 1 in the "I/O map" dialog box.
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
The "Unit selection [Slot No. 1]" dialog box is displayed.
4.2 Registration in I/O Map
6. Select "Communications" for Unit type, and select "SCU unit" for Unit name,
and press [OK] button.
"SCU unit" is registered in the I/O map.
The set conditions are reflected in the project being edited.
4-7
Page 52

I/O Allocation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
4-8
Page 53

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5
Setting and Confirming
Communication Conditions
Page 54

Setting and Confirming Communication Conditions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.1 Setting Applications and Communication Conditions
5.1.1 Applications to be Set for Each Port
Available functions for each communication port
Communication function to be used
PLC link
MEWTOCOL7-COM (Note 1)
MEWTOCOL-COM
MODBUS-RTU
General-purpose communication
(Note 1) In MEWTOCOL7-COM, there is no master communication function.
Master
Slave
Master
Slave
COM.0 COM.1 COM.2 COM.3 COM.4
5.1.2 Conditions to be Set for Each Port
Communication condition
Communication port Setting range Default
1 - 99 (MEWTOCOL-COM)
Station no.
Baud rate 300,600,1200,2400,4800,9600,19200,38400,57600,115200,230400 9600
Data length 7 bits, 8 bits 8 bits
Parity None, Odd, Even Odd
Communica
tion format
RS/CS controlled No/Yes Invalid
Send Waiting 0 to 100 ms 0 ms
Modem initialization Invalid, Valid, Re-initialization Invalid
(Note) Communication conditions that can be set vary by the mode to be used (PLC link, MEWTOCOL
communication, MODBUS-RTU, general-purpose communication).
Stop bit 1 bit, 2 bits 1 bit
End code CR, CR+LF, ETX , or time (0.01 ms – 100 ms, by the unit of 0.01 ms) CR
Start code With STX, Without STX
1 - 999 (MEWTOCOL7-COM)
1 - 247 (MODBUS-RTU)
Allocated communication port
●
● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
1
Without
STX
5-2
Page 55

5.2 Setting Communication Conditions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.2 Setting Communication Conditions
5.2.1 Settings Using FPWIN GR7 (For CPU with built- in SCU)
Applications and communication conditions for each communication port should be set using
the tool software FPWIN GR7.
PROCEDURE
1. From the menu bar, select "Option" > "FP7 Configuration".
The "FP7 Configuration" dialog box opens.
2. Select "Built-in SCU".
Setting items for "Built-in SCU" appear.
3. Specify communication conditions and press [O K] button.
Set conditions are incorporated into the project that is being edited.
5-3
Page 56

Setting and Confirming Communication Conditions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.2.2 Settings Using FPWIN GR7 (For Serial Communica tion Unit)
Applications and communication conditions for each communication port should be set using
the tool software FPWIN GR7.
The explanation below shows the case that the serial communication unit is registered in the
slot number 1.
PROCEDURE
1. Select "Options" > "FP7 Configuration" in the menu bar.
The "FP7 Configuration" dialog box appears.
2. Select "I/O map" in the left pane.
The "I/O map" dialog box is displayed.
3. Select the Slot No. in which SCU unit is registered in the "I/O map" dialog box,
and press the "Advanced" button.
The "SCU Unit Settings" dialog box is displayed.
4. Select COM No. in the left pane.
Setting items available for each COM. number are displayed.
5. Set communication conditions, and press [OK] button.
The set conditions are reflected in the project being edited.
5-4
Page 57

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6
PLC Link
Page 58

PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.1 Operation of PLC link MEWNET-W 0
6.1.1 Overview of PLC Link Operation
“Link relays (L)” and data registers “link registers (LD)” are shared between the connected
PLCs.
If the link relay contact for one PLC goes on, the same link relay also goes on in each of the
other PLCs connected to the network.
Likewise, if the contents of a link register are rewritten in one PLC, the change is made in the
same link register of each of the other PLCs connected to the network.
(Station no.1) (Station no.2) (Station no.3) (Station no.4)
Send area
Receive area
No.1 No.1 No.1
No.2
Receive area
Send area
Receive area
No.2 No.2
Receive area
Send area
No.3No.3No.3
Receive area
PLC PLC PLC PLC
RS485
6-2
Page 59

6.1 Operation of PLC link MEWNET-W0
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.1.2 Operation of Link Relays and Link Registers
Link relay
If the link relay L0 in unit No.1 is turned on, the status change is fed back to the link relay L0
with the same number in other units, and R0 in the other units is output.
R0
L0
L0
Y0
L0
Y0
L0
Y0
PLC PLC PLC PLC
RS485
R0
F0, MV, K10 0 , LD0
No.1 Link register
LD 0 100
No.2 Link register
LD 0 100 LD 0 100 LD 0 100
Link register
If the constant 100 is written into LD0 of the source station no.1, LD0 of the other station no.2
is also changed to the constant 100.
No.3 Link register No.4 Link register
6-3
Page 60

PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.2 Configuration Required for PLC Link
6.2.1 Setup Procedure (For CPU with built-in SCU)
In order to use the PLC link function, setting of communication conditions and allocation of
memories are required.
Settings should be performed by the programming tool FPWIN GR7.
PROCEDURE
1. From the menu bar, select "Option" > "FP7 Configuration".
The "FP7 Configuration" dialog box appears.
2. From the left pane of the dialog box, select "Built-in SCU".
Setting items for each COM port are displayed.
3. Select "PLC link" from "Communication mode" in setting items under "COM1
settings".
Setting items for PLC link become valid.
4. Specify conditions to be allocated to each setting item for "Station no." and
"PLC link settings" under "COM1 settings", and press [OK] button.
The settings are registered in the project.
6-4
Page 61

6.2 Configuration Required for PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.2.2 Setup Procedure (For Serial Communication Unit )
In order to use the PLC link function, setting of communication conditions and allocation of
memories are required.
Settings should be performed by the programming tool FPWIN GR7.
The following procedure describes the case that the serial communication unit has been
already registered in the I/O map.
PROCEDURE
1. Select "Options" > "FP7 Configuration" in the menu bar.
The "FP7 Configuration" dialog box appears.
2. From the left pane of the dialog box, select “I/O map”.
The "I/O map" dialog box is displayed.
3. Select a unit used for PLC link, and press [Advanced] button.
The "SCU Unit Settings" dialog box is displayed.
4. Select "COM.1 settings" from the left pane, and select "PLC link" in
"Communication mode".
差し替え
5. Set conditions assigned to each item in "PLC link settings", and press [OK]
button.
The settings are registered in the project.
REFERENCE
For details of PLC link settings, please see explanation on the next page onward.
6-5
Page 62

PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.2.3 List of Setting Items
List of setting items (COM1 settings)
Setting items
Communication mode PLC link
Station no. 1 - 16
Baud rate 115200 bps
Data length 8 bit
Parity Odd
Stop bit 1 bit
RS/CS Invalid
Send waiting time 0
Start code STX Invalid
Terminator setting CR
Terminator judgment time 0
Modem initialization Do not initialize
List of setting items (PLC link settings)
Setting items Setting range Setting method
Memory block numbers for link relays and
link registers to be used
Maximum station no. to be used for PLC
link
Range of link relays used 0 to 64 words
Range of link registers used 0 to 128 words
Starting no. for link relay send area 0 to 63
Size of link relay send area 0 to 64 words
Starting No. for link register send area 0 to 127
Size of link register send area 0 to 127 words
Settings when the PLC link
function is used
0 or 1
0 to 16
Remark
Set a specific station no. for PLC to be
connected to the PLC link.
Regardless of settings in FPWIN GR7,
the FP7 CPU unit itself performs automatic
settings.
Specify the device No. range for link relays
and link registers to be used in a block.
Set the Max. station no. for PLC to be
connected to the PLC link.
Specify the device No. range for link relays
and link registers to be used.
NOTE
When you want to change the communication mode set in the PLC link to
another mode, download the changed project to the CPU unit in FPWIN GR7,
and turn on power to the FP7 CPU unit again.
6-6
Page 63

6.3 Setting Items for PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.3 Setting Items for PLC Link
6.3.1 Station No. Setting
In the PLC link where multiple PLCs are connected to the transmission line, station no.
should be set to identify each PLC.
Station nos. are the numbers to identify the different PLCs on the same network. The same
number must not be used for more than one PLC on the same network.
6.3.2 Max. Station No. Setting
Set the Max. station no. for PLC to be connected to the PLC link.
The smaller the Max. station no. is, the shorter the relative transmission time becomes.
NOTES
Station nos. should be set sequentially and consecutively, starting from 1,
Set the same value for the Max. station no. for all PLCs connected to the
with no breaks between them. If there is a missing station no., the
transmission time will be longer.
same PLC link.
6-7
Page 64

PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.3.3 Memory Block Numbers for Link Relays and Link Regist ers to be Used
The memory area of link relays and link registers are divided into the area for PLC link 0 and
the area for PLC link 1, which can respectively use up to 1024 link relay points (64 words)
and up to 128 link register words.
Specify "0" when the former memory block is used, and specify "1" when the latter memory
block is used.
Configuration of link area
6.3.4 Range of Use of Link Relays and Range of U se of Link Registers
Specify the memory area range for link relays and link registers to be used.
Link relays and link registers that do not use the link function can be used in place of internal
relays and data registers.
E.g. Examples of setting the range of use (in the case of PLC link 0)
The figure below indicates a case where the link relay range of use is set to "50" (50 words,
WL0 - WL49) and the link register range of use is set to "100" (100 words, LD0 - LD99).
If all the link relays are used in the PLC link 0 area, set the link relay range of use to "64" (64
words), and all the link register range of use to "128" (128 words).
6-8
Page 65

6.3 Setting Items for PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.3.5 Starting No. for Link Relay Send Area and Sending Size
The memory areas for link relays are divided into send areas and receive areas.
The link relays are transmitted from the send area to the receive area of a different PLC.
Link relays with the same numbers as those on the sending side must exist in the receive
area on the receiving side.
E.g. Example of setting the starting No. for link relay send area and the sending size (in
the case of memory block No.0)
List of setting items (PLC link settings)
Setting items
Memory block numbers for link
relays and link registers to be
used
Maximum station no. to be used
for PLC link
Range of link relays used
Starting no. for link relay send
area
Size of link relay send area
Setting
range
0 or 1 0 0 0 0
0 to 16
0 to 64
words
0 to 63
0 to 64
words
No.1 No.2 No.3 No.4
Station no. and setting method
4 4 4 4
64 64 64 64
0 20 40 0
20 20 24 0
6-9
Page 66

PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.3.6 Starting No. for Link Register Send Area and Sending Size
The memory areas for link registers are divided into send areas and receive areas.
The link registers are sent from the send area to the receive area of a different PLC. Link
registers with the same numbers as those on the sending side must exist in the receive area
on the receiving side.
E.g. Example of setting the starting No. for link register send area and the sending size
(in the case of memory block No.0)
List of setting items (PLC link settings)
Setting items
Memory block numbers for link
relays and link registers to be used
Maximum station no. to be used for
PLC link
Range of link registers used for
PLC link
Starting No. for link register send
area
Size of link register send area
Setting
range
0 or 1
0 to 16
0 to 128
words
0 to 127
0 to 127
words
Station no. and setting method
No.1 No.2 No.3 No.4
0 0 0 0
4 4 4 4
128 128 128 128
0 40 80 0
40 40 48 0
NOTES
If a mistake is made when allocating a link area, be aware that an error will
result, and communication will be disabled.
Avoid overlapping send areas.
6-10
Page 67

6.3 Setting Items for PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
In the example shown below, there is an area between No. 2 and No. 3 link relays
which is overlapped, and this will cause an error, so that communication cannot be
carried out.
The allocations shown below are not possible, neither for link relays nor for
link registers.
Send area is split on a single PLC
Send and receive areas are split into multiple segments
6-11
Page 68

PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.4 PLC Link Response Time
6.4.1 Response Time of 1 Transmission Cycle
The maximum value for the transmission time (T) of one cycle can be calculated using the
following formula.
Calculation formula
(1) Ts (transmission time per station)
Calculation
formula
Ts = Scan time + Tpc (PLC link sending time)
Tpc = Ttx (sending time per byte) x Pcm (PLC link sending byte size)
Ttx = 1 / (transmission speed kbps × 1000) × 11ms … Approx. 0.096 ms at 115.2 kbps
Pcm = 23 + (number of relay words + number of register words) x 4 (4 times based on ASCII
code)
(2) Tlt (link table sending time)
Calculation
formula
Tlt = Ttx (sending time per byte) x Ltm (link table sending size)
Ttx = 1 / (transmission speed kbps × 1000) × 11 ms … Approx. 0.096 ms at 115.2 kbps
Ltm = 13 + 2 × n (n = No. of added stations)
(3) Tso (Master station scan time)
This should be confirmed using the programming tool.
(4) Tlk (link addition processing time)
Calculation
formula
When there is no station that is yet to be added to the link, Tlk = 0
Tlk = Tlc (link addition command sending time) + Twt (addition waiting time)
+ Tls (sending time for command to stop transmission if link error occurs) + Tso (master station
scan time)
Tlc = 10 x Ttx (sending time per byte)
Ttx = 1 / (transmission speed kbps × 1000) × 11ms … Approx. 0.096 ms at 115.2 kbps
Twt = Default value: 400 ms
Tls = 7 x Ttx (sending time per byte)
Ttx = 1 / (transmission speed kbps × 1000) × 11ms … Approx. 0.096 ms at 115.2 kbps
Tso = Master station scan time
6-12
Page 69

Example of calculation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Condition Calculation process
16 units connected to the link; no
station yet to be added
Where Max. station no. = 16,
1
Relays/registers are equally
allocated, and
Scan time for each PLC is set at 1
ms:
16 units connected to the link; no
station yet to be added
Where Max. station no. = 16,
2
Relays/registers are equally
allocated, and
Scan time for each PLC is set at 5
ms:
16 units connected to the link; 1
station yet to be added
Where Max. station no. = 16,
3
Relays/registers are equally
allocated, and
Scan time for each PLC is set at 5
ms:
8 units connected to the link; no
station yet to be added
Where Max. station no. = 8,
4
Relays/registers are equally
allocated, and
Scan time for each PLC is set at 5
ms:
2 units connected to the link; no
station yet to be added
Where Max. station no. = 2,
5
Relays/registers are equally
allocated, and
Scan time for each PLC is set at 5
ms:
2 units connected to the link; no
station yet to be added
Where Max. station no. = 2,
6
Where 32 relay points and 2W
registers are equally allocated,
and scan time for each PLC is set
at 1 ms:
Ttx = 0.096
Each Pcm = 23 + (4 + 8) × 4 = 71 bytes
Tpc = Ttx × Pcm = 0.096 × 71 ≈ 6.82 ms
Each Ts = 1 + 6.82 = 7.82 ms
Tlt = 0.096 × (13 + 2 × 16) = 4.32 ms
Ttx = 0.096
Each Pcm = 23 + (4 + 8) × 4 = 71 bytes
Tpc = Ttx × Pcm = 0.096 × 71 ≈ 6.82 ms
Each Ts = 5 + 6.82 = 11.82 ms
Tlt = 0.096 × (13 + 2 × 16) = 4.32 ms
Ttx = 0.096
Each Ts = 5 + 6.82 = 11.82 ms
Tlt = 0.096 × (13 + 2 × 15) ≈ 4.13 ms
Tlk = 0.96 + 400 + 0.67 + 5 ≈ 407 ms
Note: Default value for the addition
waiting time: 400 ms
Ttx = 0.096
Each Pcm = 23 + (8 + +16) × 4 = 119
bytes
Tpc = Ttx × Pcm = 0.096 × 119 ≈ 11.43
ms
Each Ts = 5 +11.43 = 16.43 ms
Tlt = 0.096 × (13 + 2 × 8) ≈ 2.79 ms
Ttx = 0.096
Each Pcm = 23 + (32 + +64) × 4 = 407
bytes
Tpc = Ttx × Pcm = 0.096 × 407 ≈ 39.072
ms
Each Ts = 5 + +39.072 = 44.072 ms
Tlt = 0.096 × (13 + 2 × 2) ≈ 1.632 ms
Ttx = 0.096
Each Pcm = 23 + (1 + +1) × 4 = 31 bytes
Tpc = Ttx × Pcm = 0.096 × 31 ≈ 2.976 ms
Each Ts = 1 + +2.976 = 3.976 ms
Tlt = 0.096 × (13 + 2 × 2) ≈ 1.632 ms
6.4 PLC Link Response Time
Response time of 1
transmission cycle
(T)
T Max. = Ts + Tlt + Tso
7.82 × 16 + 4.32 + 1
= 130.44 ms
T Max. =Ts+Tlt+Tso
11.82×16+4.32+5
=198.44ms
T Max. = Ts + Tlt + Tso
+ Tlk
11.82 × 15 + 4.13 + 5 +
407
= 593.43 ms
T Max. = Ts + Tlt + Tso
16.438 + 2.79 + 5
= 139.23 ms
T Max. = Ts + Tlt + Tso
44.072 × 2 + 1.632 + 5
= 94.776 ms
T Max. = Ts + Tlt + Tso
3.976 × 2 + 1.632 + 1
= 10.584 ms
6-13
Page 70

PLC Link
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.4.2 Response Time When There is a Station Ye t to be Added
If there are stations that have not been added to the link, the Tlk time (link addition
processing time) increases, and with this the transmission cy cle time will be longer.
NOTE
“Stations that have not been added (stations yet to be added)” refers to
stations between No.1 and the Max. station no. that are not connected, or
those that are connected but whose power supply has yet to be turned on.
6-14
Page 71

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
MEWTOCOL
Master/Slave Communication
7
Page 72

MEWTOCOL
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
7.1 Configuration
7.1.1 Setting Communication Conditions
Configuration
Setting items Default Specification range Remark
Communication
mode
Station no. 1
Baud rate 9600 bps
Data length 8 bits 8 bits
Parity Odd Odd
Stop bit 1 bit 1 bit
RS/CS Invalid Invalid / Valid
Send waiting time
(set value × 0.01
ms)
Start code STX Invalid Terminator setting CR Terminator
judgment time
(set value × 0.01
ms)
Modem initialization
(Note 1) In MEWTOCOL communication, the following setting items need not to be specified.
Start code, terminator setting, terminator judgment time, PLC link setting
MEWTOCOLCOM
0
0 -
Do not
initialize
MEWTOCOL-COM
MEWTOCOL7-COM
MEWTOCOL-COM: 0 - 99
MEWTOCOL7-COM: 0 - 999
300 / 600 / 1200 / 2400 / 4800 /
9600 / 19200 / 38400 / 57600 /
115200 / 230400
0 - 10000
(0 - 100 ms)
Do not initialize / Initialize while
performing settings / Reinitialize while performing
settings
Master communication is not
possible using MEWTOCOL7.
Set a specific station no. for PLC to
be connected to the PLC link. Set a
value that does not overlap with
other devices.
Set the baud rate to match that of
devices to be connected.
The setting must be done according
to the devices connected.
In general, the default values (8-bit
length, odd parity, and 1-stop bit)
should be used.
Set this when it is necessary to
delay response to the partner
device in slave communication.
No need to specify.
Perform settings only when a
modem is to be connected. Perform
settings for start-up modem
initialization.
7-2
Page 73

7.2 List of MEWTOCOL / MEWTOCOL7 Supporting Commands
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7.2 List of MEWTOCOL / MEWTOCOL7 Supporting Commands
7.2.1 List of MEWTOCOL C ommands
Commands to be used
Type of instruction Code Description
RC Reads ON/OFF status of contact.
Read contact area
Write contact area
Read data area RD Reads the contents of a data area.
Write data area WD Writes data to a data area.
Register or Reset
contacts monitored
Register or Reset
data monitored
Monitoring start MG Monitors a registered contact or data using MC and MD.
Preset contact area
(fill command)
Preset data area
(fill command)
Read the status of PLC RT
Abort AB Aborts reception of multiple frame responses before completion.
(Note) Some devices are not accessible due to format restrictions of MEWTOCOL-COM communication commands.
(RCS) - Specifies only one point.
(RCP) - Specifies multiple contacts.
(RCC) - Specifies a range in word units.
WC Turns ON or OFF the contact.
(WCS) - Specifies only one point.
(WCP) - Specifies multiple contacts.
(WCC) - Specifies a range in word units.
MC Registers the contact to be monitored.
MD Registers the data to be monitored.
SC Embeds the area of a specified range in a 16-point on/off pattern.
SD Writes the same contents to the data area of a specified range.
Reads the specifications of the programmable controller and error
codes if an error occurs.
7.2.2 List of MEWTOCOL7 Commands
Commands to be used
Type of instruction Code Description
Read data area MMRD Reads the contents of a data area.
Write data area MMWT Writes data to a data area.
REFERENCE
For details of MEWTOCOL commands, please see 11.2 MEWTOCOL-COM
Format and 11.3 MEWTOCOL7-COM Format.
7-3
Page 74

MEWTOCOL
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
7.3 MEWTOCOL-COM Master Communication (RECV)
7.3.1 Read Data from an External Device
Instructions
In master communication, PLC has the sending right, and executes communication by
sending commands to devices that support MEWTOCOL, and receiving responses.
Messages in accordance with the protocol are automatically generated by PLC. In the user
program, reading and writing can be done simply by specifying the station no. and memory
address and executing SEND/RECV instructions.
PLC
DT100 100
DT101 0
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Command message
%01#RD0040000401 (BCC) C
%01$RD64000000 (BCC) C
R
R
External device sup por ting
MEWTOCOL-COM
DT00400 100
DT00401 0
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Response message
Specify and read station no. and address based on RECV instruction
Sample program
Send commands from the COM1 port of the CPU unit, read data from the data area of an
external device (station no. 1) DT400 - DT401, and write the content into PLC's data register
DT100 - DT101.
Confirm that the unit is in the master mode (XC), and that the sending process is not in
progress for the same port (YC), and start up the SEND instruction.
In the UNITSEL instruction, specify the slot No. (U0) and the COM. port No. (U1).
In the RECV instruction, specify and execute the partner station no. (U1), initial address
(DT400), No. of data (U2), and initial address on the PLC side to save data (DT100).
R0
R100
DF
()
XC YC
Master
communication
Clear to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
R100
Execute
RECV
UNITSEL U0 U1
S1 S2
RECV.US DT0U2 DT100U1 DT400
S1 S2 n D1 D2
(Note) The unit number and COM port number in the above program is applied when the COM.1 port of the CPU unit
is used.
Starting conditions for RECV
execution
Clear to send flag: ON
Sending active flag: OFF
Settings for communication port
S1: Slot 0
S2: COM1
RECV processing
S1: Partner station no. (U1)
S2: Data address (DT400)
n: No. of data (U2)
D1: Data saving area (DT100)
D2: Execution result code (DT 0)
7-4
Page 75

Timing chart
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7.3 MEWTOCOL-COM Master Communication (RECV)
Master communication
Clear to send flag
(XC, XD, XE, XF )
Master communication
Sending active flag
(YC, YD, YE, YF)
Execute RECV
Master communication
Sending done result flag
(Y0, Y1, Y2, Y3)
Sending data
Response reception
processing
Confirm ON
Confirm OFF
I/O allocation (For CPU Unit)
COM port no.
1 2 0
XC XD XE
YC YD YE
Y0 Y1 Y2
Name Explanation
Master
communication Clear
to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
Sending done result
flag
Conditions to enable execution of RECV
instruction
Clear to send flag (XC, XD, XE, XF): ON
Sending active flag (YC, YD, YE, YF): OFF
Sending active flag (YC, YD, YE, YF):
Sending data: ON, Sending done: OFF
Sending done result flag (Y0, Y1, Y2, Y3):
Normal completion: OFF
Abnormal com p le ti on: ON
Turns ON when MEWTOCOL-COM, MEWTOCOL7, or
MODBUS-RTU is set for the communication mode, and the unit
is in the RUN mode.
Turns ON during sending data based on SEND/RECV
instruction.
Turns OFF when the sending process is completed.
Reports completion result of sending data in general-purpose
communication or master communication.
(Normal completion: 0, Abnormal completion: 1)
I/O allocation (For Serial Communication Unit)
COM port no.
1 2 3 4
XC XD XE XF
YC YD YE YF
Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3
(Note 1) Each contact is used for reading the operation status. Do not write over it with a user program.
Name Explanation
Master
communication
Clear to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
Sending done result
flag
Turns ON when MEWTOCOL-COM, MEWTOCOL7, or
MODBUS-RTU is set for the communication mode, and the
unit is in the RUN mode.
Turns ON during sending data based on SEND/RECV
instruction.
Turns OFF when the sending process is completed.
Reports completion result of sending data in genera-purpose
communication or master communication.
(Normal completion: 0, Abnormal completion: 1)
7-5
Page 76

MEWTOCOL
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
KEY POINTS
Specify the port targeted for communication, using UNITSEL instruction
immediately before SEND/RECV instruction.
Master communication is only valid when MEWTOCOL or MODBUS is
selected. Confirm that the "Master communication Clear to send flag" (XC XF) for the targeted channel is ON, and execute SEND/RECV instruction.
You cannot execute other SEND/RECV instruction for a communication port
in master communication. Confirm that the "Master communication Sending
active flag" (YC - YF) is OFF, and execute instruction.
You cannot execute SEND/RECV instruction for a port in slave
communication.
If no response is received, the "Master communication Sending active flag"
(YC - YF) remains ON throughout the timeout setting time specified in CPU
configuration.
Up to 16 SEND/RECV instructions can be executed simultaneously for
different COM. ports.
7-6
Page 77

7.3 MEWTOCOL-COM Master Communication (RECV)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7.3.2 RECV Instruction (When MEWTOCOL-COM is Used )
Instruction format
Items Settings Setting range
i Specify the operation unit. US / SS
S1 Specify the partner station no. 1 - 99
S2
n Specify the No. of sent data. (Note 3)
D1
D2
(Note 1) Transmission methods vary by the type of device to be specified for the operands [S2] and [D1].
(Note 2) Bit device DT, n and LD, n cannot be specified for the header of the sender data in the partner node.
(Note 3) The No. of sent data is on a word basis for register transmission, and on a bit basis for bit transmission.
(Note 4): Device that can be specified for [D2] are: WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD. Saved as one word in the specified area.
0: Normal completion
1: Communication port is being used for master communication
2: Communication port is being used for slave communication
3: No. of master communication instructions that can be used simultaneously has been exceeded
4: Sending timeout
5: Response reception timeout
6: Received data error
Specify the device initial address of the source node data area in the partner
node. (Note 1)( Note 2)
Specify the device initial address of the receiver node data area in the source
node. (Note1)
Specify the device area in the source node to save the execution result code
(one word). (Note 4)
Device to be specified for [S2] and [D1]
0 - 99999
1 - 509 words
or 1 bit
(Note1)
-
Transmission
method
16 bit device: WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD
1 bit device: X; Y; R; L; DT,n; LD, Bit transmission
Register
transmission
7-7
Page 78

MEWTOCOL
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
7.4 MEWTOCOL-COM Master Communication (SEND)
7.4.1 Write Data into an Externa l Device
Instructions
In master communication, PLC has the sending right, and executes communication by
sending commands to devices that support MEWTOCOL, and receiving responses.
Messages in accordance with the protocol are automatically generated by PLC. In the user
program, reading and writing can be done simply by specifying the station no. and memory
address and executing SEND/RECV instructions.
PLC
DT100 100
DT101 0
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Command message
%01#WDD004000040164000000 (BCC) C
%01$WD (BCC) C
R
External device sup por ting
MEWTOCOL-COM
R
DT00400 100
DT00401 0
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Response message
Specify and write station no. and address based on SEND instruction
Sample program
Send commands from the COM1 port of the CPU unit, and write the content of PLC's data
register DT100 - DT101 into the data area of an external device (station no. 1) DT400 DT401.
Confirm that the unit is in the master mode (XC), and that the sending process is not in
progress for the same port (YC), and start up the SEND instruction.
In the UNITSEL instruction, specify the slot No. (U0) and the COM. port No. (U1).
In the SEND instruction, specify and execute the sender initial address (DT100), No. of data
(U2), "Transmit to" station no. (U1), and initial address (DT400).
R0
DF
()
R100
(Note) The unit number and COM port number in the above program is applied when the COM.1 port of the CPU unit
is used.
XC YC
Master
communication
Clear to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
UNITSEL U0 U1
SEND.US DT0U1 DT400DT100 U2
S1 n D1 D2 D3
R100
Execute
SEND
S1 S2
SEND execution condition
Clear to send flag: ON
Sending active flag: OFF
Settings for communication port
S1: Slot 0 (U0)
S2: COM1 (U1)
SEND process
S: Data saving area (DT100)
n: No. of sent data (U2)
D1: Area code of the receiver (U1)
D2: "Forward to" address (DT400)
D3: Execution result code (DT0)
7-8
Page 79

Timing chart
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7.4 MEWTOCOL-COM Master Communication (SEND)
Master communication
Clear to send flag
(XC, XD, XE, XF )
Master communication
Sending active flag
(YC, YD, YE, YF)
Execute SEND
Master communication
Sending done result flag
(Y0, Y1, Y2, Y3)
Sending data
Response reception
processing
Confirm ON
Confirm OFF
I/O allocation (For CPU Unit)
COM port no.
1 2 0
XC XD XE
YC YD YE
Y0 Y1 Y2
Name Explanation
Master
communication
Clear to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
Sending done
result flag
Conditions to enable execution of SEND
instruction
Clear to send flag (XC, XD, XE, XF): ON
Sending active flag (YC, YD, YE, YF): OFF
Sending active flag (YC, YD, YE, YF):
Sending data: ON, Sending done: OFF
Sending done result flag (Y0, Y1, Y2, Y3):
Normal completion: OFF
Abnormal completion: ON
Turns ON when MEWTOCOL-COM, MEWTOCOL7, or
MODBUS-RTU is set for the communication mode, and the unit is
in the RUN mode.
Turns ON during sending data based on SEND/RECV instruction.
Turns OFF when the sending process is completed.
Reports completion result of sending data in general-purpose
communication or master communication. (Normal completion: 0,
Abnormal completion: 1)
I/O allocation (For Serial Communication Unit)
COM port no.
1 2 3 4
XC XD XE XF
YC YD YE YF
Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3
(Note 1) Each contact is used for reading the operation status. Do not write over it with a user program.
Name Explanation
Master
communication
Clear to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
Sending done result
flag
Turns ON when MEWTOCOL-COM, MEWTOCOL7, or
MODBUS-RTU is set for the communication mode, and the
unit is in the RUN mode.
Turns ON during sending data based on SEND/RECV
instruction.
Turns OFF when the sending process is completed.
Reports completion result of sending data in genera-purpose
communication or master communication.
(Normal completion: 0, Abnormal completion: 1)
7-9
Page 80

MEWTOCOL
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
KEY POINTS
Specify the port targeted for communication, using UNITSEL instruction
immediately before SEND/RECV instruction.
Master communication is only valid when MEWTOCOL or MODBUS is
selected. Confirm that the "Master communication Clear to send flag" (XC XF) for the targeted channel is ON, and execute SEND/RECV instruction.
You cannot execute other SEND/RECV instruction for a communication port
in master communication. Confirm that the "Master communication Sending
active flag" (YC - YF) is OFF, and execute instruction.
You cannot execute SEND/RECV instruction for a port in slave
communication.
If no response is received, the "Master communication Sending active flag"
(YC - YF) remains ON throughout the timeout setting time specified in CPU
configuration.
Up to 16 SEND/RECV instructions can be executed simultaneously for
different COM. ports.
7-10
Page 81

7.4 MEWTOCOL-COM Master Communication (SEND)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7.4.2 SEND Instruction (When MEWTOCOL-COM is Used)
Instruction format
Setting
items
i Specify the operation unit. US / SS
S Specify the header of the source node data area. (Note 1) -
n Specify the No. of sent data.
D1 Specify the partner station no. (Note 2) (Note 3) 0 - 99
D2
D3
(Note 1) Transmission methods vary by the type of device to be specified for the operands [S] and [D2].
(Note 2) The No. of sent data is on a word basis for register transmission, and on a bit basis for bit transmission.
(Note 3) When "0" is specified for partner station no., global transmission is applied. In this case, no response
message is received from the partner side.
(Note 4) Bit device DT, n and LD, n cannot be specified for the header of the receiver data in the partner node.
(Note 5): Device that can be specified for [D3] are: WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD. Saved as one word in the specified area.
0: Normal completion
1: Communication port is being used for master communication
2: Communication port is being used for slave communication
3: No. of master communication instructions that can be used simultaneously has been exceeded
4: Sending timeout
5: Response reception timeout
6: Received data error
Settings Setting range
1 - 507 words
or 1 bit
Specify the initial address of the receiver node data area in the partner
node. (Note 4)
Specify the device area in the source node to save the execution result
code (one word).
Device to be specified for [S2] and [D1]
0 - 99999
(Note 5)
Transmission
method
16 bit device: WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD
1 bit device: X, Y, R, L, DT, n, LD, n Bit transmission
Register
transmission
7-11
Page 82

MEWTOCOL
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
7-12
Page 83

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
MODBUS RTU
Master/Slave Communication
8
Page 84

MODBUS RTU
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
8.1 Configuration
8.1.1 Setting Communication Conditions
Configuration
Setting items Default Specification range Remark
Communication mode
Station no. 1 0 - 247
Baud rate 9600
Data length 8 bits 8 bits
Parity Odd Even
Stop bit 1 bit 1 bit
RS/CS Invalid Invalid / Valid
Send waiting time
(set value × 0.01 ms)
Start code STX Invalid Terminator setting CR Terminator judgment
time
(set value × 0.01 ms)
Modem initialization Do not initialize -
(Note 1) In MODBUS communication, the following setting items need not to be specified.
Start code, terminator setting, terminator judgment time, modem initialization, PLC link setting
MEWTOCOLCOM
0 0 - 10000
0 -
MODBUS-RTU Specify "MODBUS-RTU".
300 / 600 / 1200 / 2400 /
4800 / 9600 / 19200 /
38400 / 57600 / 115200
Set a specific station no. for PLC to
be connected to the PLC link. Set a
value that does not overlap with
other devices.
The setting must be done
according to the devices
connected.
The setting must be done
according to the devices
connected. In general, 8-bit length,
even parity, and 1-stop bit is used.
Set this when it is necessary to
delay response to the partner
device in slave communication.
Use the unit in the default setting
as indicated on the left.
8-2
Page 85

8.2 List of MODBUS RTU Supported Commands
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
8.2 List of MODBUS RTU Supported Commands
8.2.1 List of MODBUS Function Codes
Table of supported commands
Code Name (MODBUS) Name
01 Read Coil Status Read Y and R Coils 0X
02 Read Input Status Read X Contact 1X
03 Read Holding Registers Read DT 4X
04 Read Input Registers Read WL and LD 3X
05 Force Single Coil Write Single Y and R 0X
06 Preset Single Register Write DT 1 Word 4X
08 Diagnostics Loopback Test 15 Force Multiple Coils Write Multiple Y's and R's 0X
16 Preset Multiple Registers Write DT Multiple Words 4X
22 Mask Write 4X Register Write DT Mask 4X
23 Read/Write 4X Registers Read/Write DT 4X
(Note 1) Types of MODBUS function codes vary by instructions to be used.
Remarks
(Reference No.)
FP7 supported
functions
●
●
●
●
●
●
-
●
●
-
-
Correspondence table for MODBUS reference No. and device No.
MODBUS reference No.
000001-002048 0000-07FF Y0-Y127F Coil
002049-034816 0800-87FF R0-R2047F
Input 100001-108192 0000-1FFF X0-X511F
Holding register 400001-465536 0000-FFFF DT0- DT65535
300001-301024 0000-03FF WL0-WL1023 Input register
302001-318384 07D0-47CF LD0-LD16383
(Note 1) The table above indicates correspondence between the MODBUS reference numbers for accessing from a
higher device to FP7 using the MODBUS protocol, and the operation device numbers of FP7.
Data on BUS
(hexadecimal)
PLC device number
8-3
Page 86

MODBUS RTU
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
8.3 MODBUS RTU Master Communication (RECV)
8.3.1 Read Data from an External Device
Instructions
In master communication, PLC has the sending right, and executes communication by
sending commands to devices that support MODBUS-RTU, and receiving responses.
Messages in accordance with the protocol are automatically generated by PLC. In the user
program, reading and writing can be done simply by specifying the station no. and memory
address and executing SEND/RECV instructions.
PLC
DT100 100
DT101 0
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Command message
(Hex) 01 03 00 00 00 02 (CRC)
(Hex) 01 03 04 00 64 00 00 (CRC)
External device
supporting Modbus-RTU
40001 100
40002 0
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Response message
Specify and read station no. and address based on RECV instruction
Sample program
Send co mmands from the COM1 port of the CPU unit, read data from the data area o f an external
device (station no. 1) 40001 - 40002, and write the content into PLC's data register DT100 - DT101.
Confirm that the unit is in the master mode (XC), and that the sending process is not in
progress for the same port (YC), and start up the SEND instruction.
In the UNITSEL instruction, specify the slot No. (U0) and the COM. port No. (U1).
In the RECV instruction, specify and execute the partner device station no. (U1), MODBUS
command and partner device station no. to be used (H0301), initial address (40001), No. of
data (U2), and initial address on the PLC side to save data (DT100). For the address of the
partner device, please check operating instructions, etc. of the relevant device.
R0
R100
DF
()
XC YC
Master
communication
Clear to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
R100
Execute
RECV
UNITSEL U0 U1
S1 S2
RECV.US DT0U2 DT100H0301 H0
S1 S2 n D1 D2
(Note 1) Operand [S1] of RECV instruction is specified by combining two hexadecimal digits of MODBUS function
code with two hexadecimal digits of partner device station no.
(Note 2) When the partner device is FP series PLC, Operand [S2] of RECV instruction can be specified using the
Device No.
(Note 3) The unit number and COM port number in the above program is applied when the COM.1 port of the CPU
unit is used.
Starting conditions for REC V
execution
Clear to send flag: ON
Sending active flag: OFF
Settings for com m u ni cat i on port
S1: Slot 0 (U0)
S2: COM1 (U1)
RECV processing
S1: MODBUS code (H03) and
partner device station no. (H01)
S2: Partner device address (H0)
(corresponds to H0: 40001)
n: No. of data (U2)
D1: Data saving area (DT100)
D2: Execution result code (DT0)
8-4
Page 87

Timing chart
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
8.3 MODBUS RTU Master Communication (RECV)
Master communication
Clear to send flag
(XC, XD, XE, XF )
Master communication
Sending active flag
(YC, YD, YE, YF)
Execute RECV
Master communication
Sending done result flag
(Y0, Y1, Y2, Y3)
Sending data
Response reception
processing
Confirm ON
Confirm OFF
I/O allocation (For CPU Unit)
COM port no.
1 2 0
XC XD XE
YC YD YE
Y0 Y1 Y2
Name Explanation
Master
communication
Clear to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
Sending done
result flag
Conditions to enable execution of RECV
instruction
Clear to send flag (XC, XD, XE, XF): ON
Sending active flag (YC, YD, YE, YF): OFF
Sending active flag (YC, YD, YE, YF):
Sending data: ON, Sending done: OFF
Sending done result flag (Y0, Y1, Y2, Y3):
Normal completion: OFF
Abnormal com p le ti on: ON
Turns ON when MEWTOCOL-COM, MEWTOCOL7, or
MODBUS-RTU is set for the communication mode, and the unit is
in the RUN mode.
Turns ON during sending data based on SEND/RECV instruction.
Turns OFF when the sending process is completed.
Reports completion result of sending data in general-purpose
communication or master communication. (Normal completion: 0,
Abnormal completion: 1)
I/O allocation (For Serial Communication Unit)
COM port no.
1 2 3 4
XC XD XE XF
YC YD YE YF
Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3
(Note 1) Each contact is used for reading the operation status. Do not write over it with a user program.
Name Explanation
Master
communication
Clear to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
Sending done result
flag
Turns ON when MEWTOCOL-COM, MEWTOCOL7, or
MODBUS-RTU is set for the communication mode, and the
unit is in the RUN mode.
Turns ON during sending data based on SEND/RECV
instruction.
Turns OFF when the sending process is completed.
Reports completion result of sending data in genera-purpose
communication or master communication.
(Normal completion: 0, Abnormal completion: 1)
8-5
Page 88

MODBUS RTU
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
KEY POINTS
Specify the port targeted for communication, using UNITSEL instruction
immediately before SEND/RECV instruction.
Master communication is only valid when MEWTOCOL or MODBUS is
selected. Confirm that the "Master communication Clear to send flag" (XC XF) for the targeted channel is ON, and execute SEND/RECV instruction.
You cannot execute other SEND/RECV instruction for a communication port
in master communication. Confirm that the "Master communication Sending
active flag" (YC - YF) is OFF, and execute instruction.
You cannot execute SEND/RECV instruction for a port in slave
communication.
If no response is received, the "Master communication Sending active flag"
(YC - YF) remains ON throughout the timeout setting time specified in CPU
configuration.
Up to 16 SEND/RECV instructions can be executed simultaneously for
different COM. ports.
8-6
Page 89

8.3 MODBUS RTU Master Communication (RECV)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
8.3.2 RECV Instruction (MODBUS Function Code Specified Type)
Instruction format
Operand
Items Settings Setting range
i Specify the operation unit. US / SS
Specify the MODBUS function codes and partner station no. to be used. (Note 1) (Note 2)
Higher
S1
S2 Specify the source MODBUS address in the partner node. H0 - HFFFF (0 - 65535)
n Specify the No. of sent data. (Note 3)
D1
D2
(Note 1) Operand [S1] is specified by combining two hexadecimal digits of MODBUS function code with two
(Note 2) Based on the types of device specified in operand [D1], the transmission methods and MODBUS function
byte
Lower
byte
Specify the device initial address of the receiver node data area in the
source node. (Note 2)
Specify the device area in the source node to save the execution result
code (one word).
hexadecimal digits of partner station no.
E.g. Specify "H030F" when MODBUS function code is 03 (Read Holding Registers) and station no. is 15.
codes that can be used vary.
Device to be specified
for [D1]
16 bit device
WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD
1 bit device
X, Y, R, L, DT, n, LD, n
(Note 3) The No. of sent data is on a word basis for register transmission, and on a bit basis for bit transmission.
(Note 4): Device that can be specified for [D2] are: WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD. Saved as one word in the specified
area.
0: Normal completion
1: Communication port is being used for master communication
2: Communication port is being used for slave communication
3: No. of master communication instructions that can be used simultaneously has been exceeded
4: Sending timeout
5: Response reception timeout
6: Received data error
Two hexadecimal digits that indicate the MODBUS
function code
Two hexadecimal digits that indicate the station no. H1 - HF7 (1 - 247)
Transmission
Values that can be specified in higher
method
H1: Read Coil Status (01)
Register
transmission
Bit transmission
H2: Read Input Status (02)
H3: Read Holding Registers (03)
H4: Read Input Registers (04)
H1: Read Coil Status (01)
H2: Read Input Status (02)
H1 - H4 (1 - 4)
1 - 127 words
1 - 2040 bits
-
(Note 3)
bytes of [S1]
8-7
Page 90

MODBUS RTU
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
8.3.3 RECV Instruction (MODBUS Function Code Unspecified Type)
Instruction format
Operand
Items Settings Setting range
i Specify the operation unit. US / SS
S1 Specify the partner station no. H1 - HF7 (1 - 247)
S2
n Specify the No. of sent data.
D1
D2
(Note 1) Types of devices and transmission methods to be specified for operands [S2] and [D1], and MODBUS
(Note 2) Bit device L; DT, n; and LD, n cannot be specified for the header of the sender data in the partner node.
(Note 3) The No. of sent data is on a word basis for register transmission, and on a bit basis for bit transmission.
(Note 4): Device that can be specified for D1 are: WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD.
(Note 5): Device that can be specified for D2 are: WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD. Saved as one word in the specified area.
Specify the device initial address of the source node data area in the
partner node.
Specify the device initial address of the receiver node data area in the
source node.
Specify the device area in the source node to save the execution result
code (one word).
function codes to be used for instruction execution vary.
Device to be specified
for [S2] and [D1]
16 bit device
WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD
1 bit device
X, Y, R, L, DT, n, LD, n
0: Normal completion
1: Communication port is being used for master communication
2: Communication port is being used for slave communication
3: No. of master communication instructions that can be used simultaneously has been exceeded
4: Sending timeout
5: Response reception timeout
6: Received data error
Transmission
method
Register
transmission
Bit transmission
MODBUS function codes
to be used for instruction execution
Read Coil Status (01)
Read Input Status (02)
Read Holding Registers (03)
Read Input Registers (04)
Read Coil Status (01)
Read Input Status (02)
H0 - HFFFF (0 - 65535)
(Note 1) (Note 2)
1 - 127 words
1 - 2040 bits
(Note 3)
(Note 1) (Note 4)
(Note 5)
8-8
Page 91

8.4 MODBUS RTU Master Communication (SEND)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
8.4 MODBUS RTU Master Communication (SEND)
8.4.1 Write Data into an Externa l Device
Instructions
In master communication, PLC has the sending right, and executes communication by
sending commands to devices that support MODBUS-RTU, and receiving responses.
Messages in accordance with the protocol are automatically generated by PLC. In the user
program, reading and writing can be done simply by specifying the station no. and memory
address and executing SEND/RECV instructions.
PLC
DT100 100
DT101 0
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Command message
(Hex) 01 10 00 00 00 02 04 00 64 00 00 (CRC)
(Hex) 01 10 00 00 00 02 (CRC)
External device
supporting Modbus-RTU
40001 100
40002 0
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Response message
Specify and write station no. and address based on SEND instruction
Sample program
Send commands from the COM1 port of the CPU unit, and write the content of PLC's data
register DT100 - DT101 into the data area of an external device (station no. 1) 40001 - 40002.
Confirm that the unit is in the master mode (XC), and that the sending process is not in
progress for the same port (YC), and start up the SEND instruction.
In the UNITSEL instruction, specify the slot No. (U0) and the COM. port No. (U1).
In the SEND instruction, specify and execute the PLC initial address (DT100), No. of data
(U2), MODBUS function code to be used (16: H10), partner device station no. (H01), and
initial address (H0). For the address of the partner device, please check operating
instructions, etc. of the relevant device.
R0
DF
()
R100
(Note 1) Operand [S1] of SEND instruction is specified by combining two hexadecimal digits of MODBUS function
code with two hexadecimal digits of partner device station no. When the MODBUS function code is 16, specify
H10 for [D1].
(Note 2) When the partner device is FP series PLC, Operand [S2] of SEND instruction can be specified using the
Device No.
(Note 3) The unit number and COM port number in the above program is applied when the COM.1 port of the CPU
unit is used.
XC YC
Master
communication
Clear to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
UNITSEL U0 U1
SEND.US DT0H1001 H0DT100 U2
S n D1 D2 D3
R100
Execute
SEND
S1 S2
SEND execution conditions
Clear to send flag: ON
Sending active flag: OFF
Settings for communication port
S1: Slot 0 (U0)
S2: COM1 (U1)
SEND process
S: Data saving area (DT100)
n: No. of sent da ta ( U2)
D1: MODBUS code (H10) and
partner device station no. (H01)
D2: "Transmit to" address (H0)
D3: Execution result code (DT0)
8-9
Page 92

MODBUS RTU
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
Timing chart
Master communication
Clear to send flag
(XC, XD, XE, XF )
Master communication
Sending active flag
(YC, YD, YE, YF)
Execute SEND
Master communication
Sending done result flag
(Y0, Y1, Y2, Y3)
Sending data
Response reception
processing
Confirm ON
Confirm OFF
I/O allocation (For CPU Unit)
COM port no.
1 2 0
XC XD XE
YC YD YE
Y0 Y1 Y2
Name Explanation
Master
communication Clear
to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active flag
Sending done result
flag
Conditions to enable execution of SEND
instruction
Clear to send flag (XC, XD, XE, XF): ON
Sending active flag (YC, YD, YE, YF): OFF
Sending active flag (YC, YD, YE, YF):
Sending data: ON, Sending done: OFF
Sending done result flag (Y0, Y1, Y2, Y3):
Normal completion: OFF
Abnormal completion: ON
Turns ON when MEWTOCOL-COM, MEWTOCOL7, or
MODBUS-RTU is set for the communication mode, and the unit
is in the RUN mode.
Turns ON during sending data based on SEND/RECV
instruction.
Turns OFF when the sending process is completed.
Reports completion result of sending data in general-purpose
communication or master communication. (Normal completion:
0, Abnormal completion: 1)
I/O allocation (For Serial Communication Unit)
COM port no.
1 2 3 4
XC XD XE XF
YC YD YE YF
Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3
(Note 1) Each contact is used for reading the operation status. Do not write over it with a user program.
8-10
Name Explanation
Master
communication
Clear to send flag
Master
communication
Sending active
flag
Sending done
result flag
Turns ON when MEWTOCOL-COM, MEWTOCOL7, or
MODBUS-RTU is set for the communication mode, and the unit
is in the RUN mode.
Turns ON during sending data based on SEND/RECV
instruction.
Turns OFF when the sending process is completed.
Reports completion result of sending data in genera-purpose
communication or master communication.
(Normal completion: 0, Abnormal completion: 1)
Page 93

8.4 MODBUS RTU Master Communication (SEND)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
KEY POINTS
Specify the port targeted for communication, using UNITSEL instruction
immediately before SEND/RECV instruction.
Master communication is only valid when MEWTOCOL or MODBUS is
selected. Confirm that the "Master communication Clear to send flag" (XC XF) for the targeted channel is ON, and execute SEND/RECV instruction.
You cannot execute other SEND/RECV instruction for a communication port
in master communication. Confirm that the "Master communication Sending
active flag" (YC - YF) is OFF, and execute instruction.
If no response is received, the "Master communication Sending active flag"
(YC - YF) remains ON throughout the timeout setting time specified in CPU
configuration.
You cannot execute SEND/RECV instruction for a port in slave
communication.
Up to 16 SEND/RECV instructions can be executed simultaneously for
different COM. ports.
8-11
Page 94

MODBUS RTU
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
8.4.2 SEND Instruction (MODBUS Function Code Specified Type)
Instruction format
Operand
Items Settings Setting range
i Specify the operation unit. US / SS
S Specify the header of the source node data area. (Note 1) -
n Specify the No. of sent data. (Note 1) (Note 2)
Specify the MODBUS command and partner station no. to be used. (Note 3) (Note 4)
D1
D2
D3
(Note 1) Based on the types of device specified in operand [S] and the No. of sent data specified in [n], the
Specify the header of the MODBUS address in the receiver data area in
the partner node.
Specify the device area in the source node to save the execution result
code (one word).
transmission methods and MODBUS function codes that can be used vary.
Higher
byte
Lower
byte
Types of device
to be specified in [S]
Two hexadecimal digits that indicate the
MODBUS function code
Two hexadecimal digits that indicate the station
no.
Transmission
method
No. of sent
data
Values that can be specified in
[n]
H6: Preset Single Register (06)
16 bit device
WX, WY, WR, WL, DT,
LD
1 bit device
X, Y, R, L, DT, n, LD,n
(Note 2) The No. of sent data [n] is on a word basis for register transmission, and on a bit basis for bit transmission.
(Note 3) Operand [D1] is specified by combining two hexadecimal digits of MODBUS function code with two
hexadecimal digits of partner station no.
E.g. Specify "H100A" when MODBUS function code is 16 (Preset Multiple Registers) and station no. is 10.
(Note 4) When "0" is specified for partner station no., global transmission is applied. In this case, no response
message is received from the partner side.
(Note 5): Device that can be specified for [D3] are: WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD. Saved as one word in the specified area.
0: Normal completion
1: Communication port is being used for master communication
2: Communication port is being used for slave communication
3: No. of master communication instructions that can be used simultaneously has been exceeded
4: Sending timeout
5: Response reception timeout
6: Received data error
Register
transmission
Bit
transmission
1
2 - 127
1
2 - 2040 HF: Force Multiple Coils (15)
HF: Force Multiple Coils (15)
H10: Preset Multiple Registers (16)
HF: Force Multiple Coils (15)
H10: Preset Multiple Registers (16)
H5: Force Single Coil (05)
HF: Force Multiple Coils (15)
1 - 127 words
1 - 2040 bits
H5, H6, HF, H10
H0 - HF7 (0 - 247)
H0~HFFFF (0 - 65535)
(Note 5)
higher bytes of [D1]
8-12
Page 95

8.4 MODBUS RTU Master Communication (SEND)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
8.4.3 SEND Instruction (MODBUS Function Code Unspecified Type)
Instruction format
Operand
Items Settings Setting range
i Specify the operation unit. US / SS
S Specify the header of the source node data area. (Note 1)
n Specify the No. of sent data. 1 - 127 words, 1 - 2040 bits (Note 2)
D1 Specify the partner station no. H0 - HF7 (0 - 247) (Note 3)
D2
D3
(Note 1) Types of devices and transmission methods to be specified for operands [S] and [D2], and MODBUS
Specify the initial address of the receiver node data area
in the partner node.
Specify the device area in the source node to save the
execution result code (one word).
function codes to be used for instruction execution vary.
Types of device
to be specified in [S]
16 bit device
WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD
Transmission
method
Register transmission
H0 - HFFFF (0 - 65535) (Note 4)
(Note 5)
MODBUS function codes
to be used for instruction execution
Force Multiple Coils (15)
Preset Multiple Registers (16)
1 bit device
X, Y, R, L, DT, n, LD, n
(Note 2) The No. of sent data [n] is on a word basis for register transmission, and on a bit basis for bit transmission.
(Note 3) When "0" is specified for partner station no., global transmission is applied. In this case, no response
message is received from the partner side.
(Note 4) 16 bit device WX, WL, and LD; and 1 bit device X; L; DT, n; and LD, n cannot be specified for the header of
the receiver data in the partner node.
(Note 5): Device that can be specified for [D3] are: WX, WY, WR, WL, DT, LD. Saved as one word in the specified area.
0: Normal completion
1: Communication port is being used for master communication
2: Communication port is being used for slave communication
3: No. of master communication instructions that can be used simultaneously has been exceeded
4: Sending timeout
5: Response reception timeout
6: Received data error
Bit transmission Force Multiple Coils (15)
8-13
Page 96

MODBUS RTU
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Master/Slave Communication
8-14
Page 97

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
9
General-Purpose
Communication
Page 98

General-Purpose Communication
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
9.1 Operation of General-Purpose Communication
9.1.1 Read Data from an External Device
Read data from a partner device
In general-purpose communication, communication is executed by sending commands that
suit the partner device, and receiving responses. Command messages are sent by
formulating a data table for message in accordance with the protocol, on the given data
register, and subsequently executing GPSEND instruction.
PLC
External device
Send command message
DT100 U 4
DT101 H 42 41
DT102 H 44 43
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
ABCD (CR)
1 2 3 4 (CR)
40001 2 1
40002 4 3
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Receive response message
Send command based on GPSEND instruction
Receive response based on GPRECV instruction
9.1.2 Write Data into an Externa l Device
Write data into a partner device
In general-purpose communication, communication is executed by sending commands that
suit the partner device, and receiving responses. Command messages are sent by
formulating a data table for message in accordance with the protocol, on the given data
register, and subsequently executing GPSEND instruction.
PLC
DT100 U 6
DT101 H 42 41
DT102 H 44 43
DT103 H 32 31
Send command message
ABCD 1 2 (CR)
XYZ (CR)
Receive response message
External device
40001 2 1
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Send command based on GPSEND instruction
Receive response based on GPRECV instruction
KEY POINTS
There is no relevance between the operation of transmission by GPSEND
instruction and the operation of reception by GPRECV instruction. The CPU
with built-in SCU unit is always clear to receive data.
9-2
Page 99

9.2 Configuration
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
9.2 Configuration
9.2.1 Setting Communication Conditions
Configuration
Setting items Default Specification range Remark
Communication
mode
Station no. 1 1 - 999 Settings are not necessary.
Baud rate 9600
Data length 8 bits 7 bit / 8 bits
Parity Odd None / Odd / Even
Stop bit 1 bit 1 bit / 2 bits
RS/CS Invalid Invalid / Valid
Send waiting
time
(unit: 0.01 ms)
Start code STX Invalid Invalid / Valid
Terminator
setting
Terminator
judgment time
(unit: 0.01 ms)
Modem
initialization
(Note 1) In general-purpose communication, the following setting items need not to be specified.
Station no., PLC link
MEWTOCOL-COM
0 0 - 10000
CR
0
Do not initialize
General-purpose
communication
300 / 600 / 1200 / 2400
/ 4800 / 9600 / 19200 /
38400 / 57600 / 115200
/ 230400
CR / CR+LF / Time /
ETX
0 - 10000
(0 - 100 ms)
Do not initialize /
Initialize while
performing settings /
Re-initialize while
performing settings
Specify "general-purpose
communication".
The setting must be done according to
the devices connected.
Set to "Valid" only when Communication
Cassette AFP7CCS2 is used in a 5-wire
mode.
Set this when it is necessary to delay
response to the partner device.
The setting must be done according to
the devices connected.
In cases where "Time" is specified in the
terminator setting, set the time for judging
the terminator.
Perform settings only when a modem is
to be connected. Perform settings for
start-up modem initialization.
9-3
Page 100

General-Purpose Communication
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
9.3 Sending Operation
9.3.1 Overview of Sending Operation
Instructions
Sending in the general-purpose communication is performed by formulating a data table for
sending on the given operation memory, and subsequently executing GPSEND instruction.
PLC
External device
Send message/data
DT100 U 5
DT101 B A
DT102 D C
DT103 ・・E
ABCDE (CR)
Send data based on GPSEND
instruction
00001 ・・・・・・・・
00002 ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・ ・・・・・・・・
Sample program
Confirm that the unit is in the general-purpose communication mode (X8), and that the
general-purpose sending process is not in progress for the same port (Y8), and start up the
sending program.
In the SSET instruction, convert a given message into an ASCII text string, and specify the
number of strings to be sent in the data register DT100, and the message to be sent from
the data register DT101.
In the UNITSEL instruction, specify the slot No. (U0) and the COM. port No. (U1).
In the GPSEND instruction, specify and execute the header of the table where the message
to be sent is saved (DT101) and the No. of characters (DT100).
R0
R100
R100
R100
DF
()
General purpose
communication
Clear to send flag
DF
()
X8 Y8
General-purpose
communication
Sending active flag
SSET DT100“ABCDE”
GPSEND . US
R101
S1 S2
R100
UNITSEL U1U0
S1 S2
DT101 DT0DT100
SnD
GPSEND execution conditions
Clear to send flag: ON
Sending active flag: OF F
Data conversion
S1: Sent Data
S2: Save Sent Data
DT100: No. of Sent Characters
DT101 onward: Sent Data
Settings for communication port
S1: Slot 0 (U0)
S2: COM1 (U1)
SEND processing
S: Header of Sent Data (DT101)
n: No. of Sent Characters (DT100)
D: Execution Result Code (DT0)
Y8 R101
()
DF /
(Note) The unit number and COM port number in the above program is applied when the COM.1 port of the CPU unit
is used.
9-4
Confirm sending completion
Reset GPSEND execution
conditions
 Loading...
Loading...