Page 1
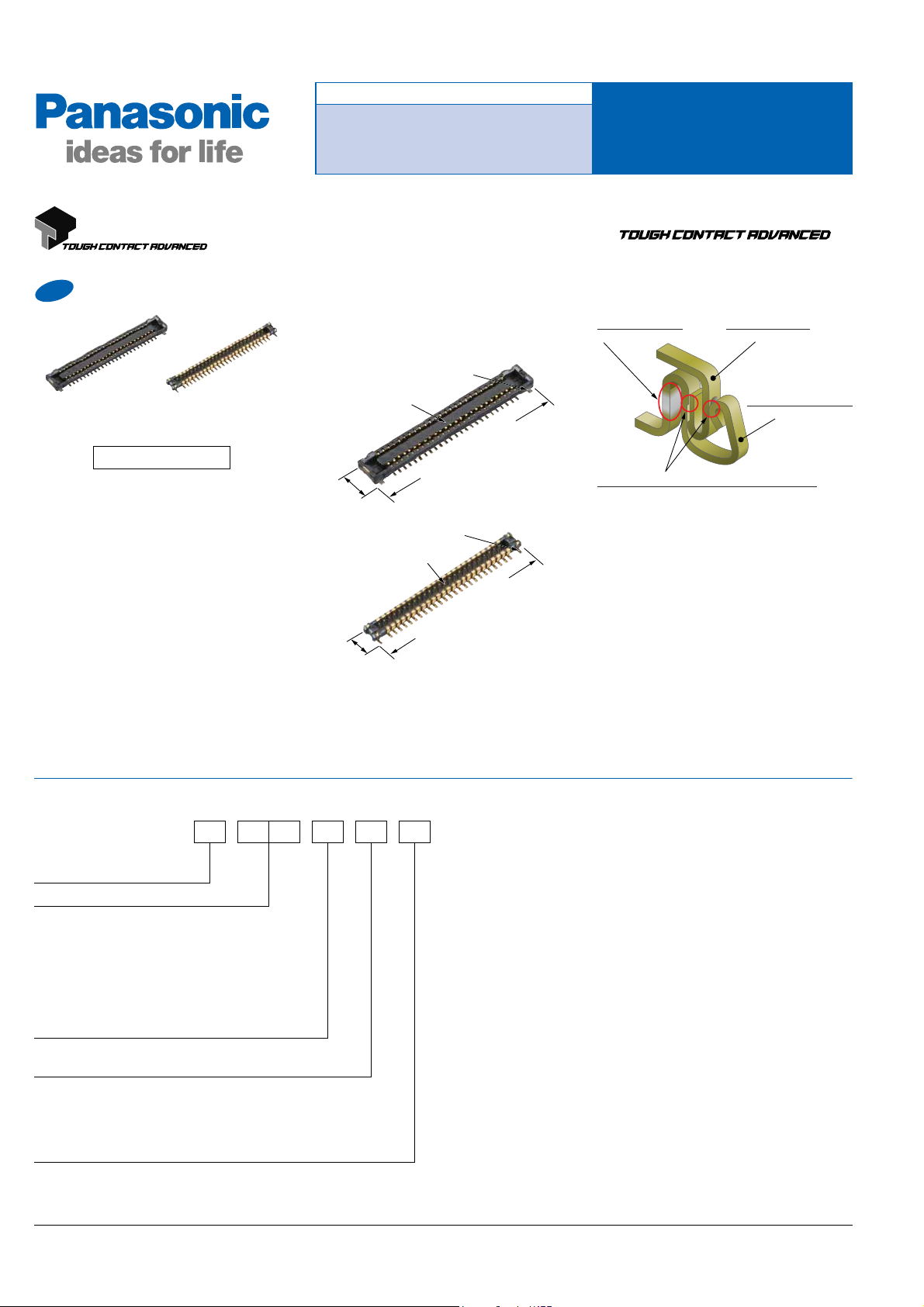
AXE1/AXE2
Bellows contact
construction
(Against dropping!)
Ni barrier
construction
(Against solder rise!)
Porosity treatment
(Against corrosive gases!)
V notch and Double contact constructions
(Against foreign particles and flux!)
For board-to-FPC
New
Socket Header
RoHS compliant
Narrow pitch connectors
(0.4mm pitch)
FEATURES
1. Mated width: 2.2 mm and Mated
height: 0.8 mm, 1.0 mm and 1.5 mm
When mated, the footprint is reduced by
approx. 12% from A4S series (50 pin
contacts), contributing to the functionality
enhancement and size reduction of end
equipment.
Soldering terminals
at each corner
Suction face: 0.6mm*
2.2mm
Suction face: 0.7mm*
1.8mm
* Suction face size for the 1.0 mm/1.5 mm mated
height type: Socket — 0.64 mm, Header — 0.76 mm
2. Improves degree of design freedom
(Mated height of 0.8 mm, 1.0 mm, or
1.5 mm with the same foot pattern)
12.5 mm (50 pin contacts)
Socket
Soldering terminals
at each corner
11.8 mm (50 pin contacts)
Header
A4US Series
3. “ ”
ensures high resistance to various
environments in lieu of its spacesaving footprint.
4. Simple lock structure provides
tactile feedback to ensure excellent
mating/unmating operation feel.
5. Soldering terminals at each corner
enhance mounting strength.
6. Gull-wing-shaped terminals to
facilitate visual inspections.
APPLICATIONS
Suitable for board-to-FPC connections
in mobile equipment that requires size
and thickness reduction and
functionality enhancement.
ORDERING INFORMATION
AXE 42
1: Socket
2: Header
Number of pins (2 digits)
Mated height
<Socket>
1: 0.8 mm
2: 1.0 mm/1.5 mm
<Header>
1: 0.8 mm
2: 1.0 mm
3: 1.5 mm
Functions
2: Without positioning bosses
Surface treatment (Contact portion / Terminal portion)
<Socket>
4: Base: Ni plating, Surface: Au plating (for Ni barrier available)
<Header>
4: Base: Ni plating, Surface: Au plating
Panasonic Corporation Automation Controls Business Unit industrial.panasonic.com/ac/e/
ACCTB4E 201201-T1
Page 2
AXE1/AXE2
PRODUCT TYPES
Mated height Number of pins
10 AXE110124 AXE210124
14 AXE114124 AXE214124
18 AXE118124 AXE218124
20 AXE120124 AXE220124
24 AXE124124 AXE224124
0.8mm
1.0mm
1.5mm
Notes: 1. Order unit:
For volume production: 1-inner carton (1-reel) units
Samples for mounting check: 50-connector units. Please contact our sales office.
2. The above part numbers are for connectors without positioning bosses, which are standard. When ordering connectors with positioning bosses, please contact our
sales office.
3. Please contact us for connectors having a number of pins other than those listed above.
30 AXE130124 AXE230124
36 AXE136124 AXE236124
40 AXE140124 AXE240124
50 AXE150124 AXE250124
60 AXE160124 AXE260124
70 AXE170124 AXE270124
80 AXE180124 AXE280124
10 AXE110224 AXE210224
20 AXE120224 AXE220224
34 AXE134224 AXE234224
40 AXE140224 AXE240224
60 AXE160224 AXE260224
80 AXE180224 AXE280224
20 AXE120224 AXE220324
60 AXE160224 AXE260324
80 AXE180224 AXE280324
Socket Header Inner carton (1-reel) Outer carton
Part number Packing
5,000 pieces 10,000 pieces
SPECIFICATIONS
1. Characteristics
Item Specifications Conditions
Rated current 0.30A/pin contact (Max. 5 A at total pin contacts)
Rated voltage 60V AC/DC
Electrical
characteristics
Mechanical
characteristics
Environmental
characteristics
Lifetime
characteristics
Unit weight
Breakdown voltage 150V AC for 1 min.
Insulation resistance Min. 1,000MΩ (initial) Using 250V DC megger (applied for 1 min.)
Contact resistance Max. 90mΩ
Composite insertion force Max. 0.981N/pin contacts × pin contacts (initial)
Composite removal force Min. 0.165N/pin contacts × pin contacts
Contact holding force
(Socket contact)
Ambient temperature –55°C to +85°C No freezing at low temperatures. No dew condensation.
Soldering heat resistance
Storage temperature
Thermal shock resistance
(header and socket mated)
Humidity resistance
(header and socket mated)
Saltwater spray resistance
(header and socket mated)
H2S resistance
(header and socket mated)
Insertion and removal life 30 times
No short-circuiting or damage at a detection current of 1 mA
when the specified voltage is applied for one minute.
Based on the contact resistance measurement method
specified by JIS C 5402.
Min. 0.20N/pin contacts
Peak temperature: 260°C or less (on the surface of
the PC board around the connector terminals)
300°C within 5 sec. 350°C within 3 sec. Soldering iron
–55°C to +85°C (product only)
–40°C to +50°C (emboss packing)
5 cycles,
insulation resistance min. 100MΩ,
contact resistance max. 90mΩ
120 hours, insulation resistance min. 100MΩ,
contact resistance max. 90mΩ
24 hours, insulation resistance min. 100MΩ,
contact resistance max. 90mΩ
48 hours, contact resistance max. 90mΩ
60 pin contacts Socket (h = 0.8mm: 0.03g, h = 1.0/1.5mm: 0.04g)
Header (h = 0.8mm: 0.01g, h = 1.0mm: 0.02g, h = 1.5mm: 0.03g)
Measuring the maximum force.
As the contact is axially pull out.
Infrared reflow soldering
No freezing at low temperatures. No dew condensation.
Sequence
0
1. –55 °C, 30 minutes
−3
2. ~ , Max. 5 minutes
+3
3. 85 °C, 30 minutes
0
4. ~ , Max. 5 minutes
Bath temperature 40±2°C,
humidity 90 to 95% R.H.
Bath temperature 35±2°C,
saltwater concentration 5±1%
Bath temperature 40±2°C, gas concentration 3±1 ppm,
humidity 75 to 80% R.H.
Repeated insertion and removal speed of max. 200 times/
hours
ACCTB4E 201201-T1
Panasonic Corporation Automation Controls Business Unit industrial.panasonic.com/ac/e/
Page 3
AXE1/AXE2
2. Material and surface treatment
Part name Material Surface treatment
Molded
portion
Contact and
Post
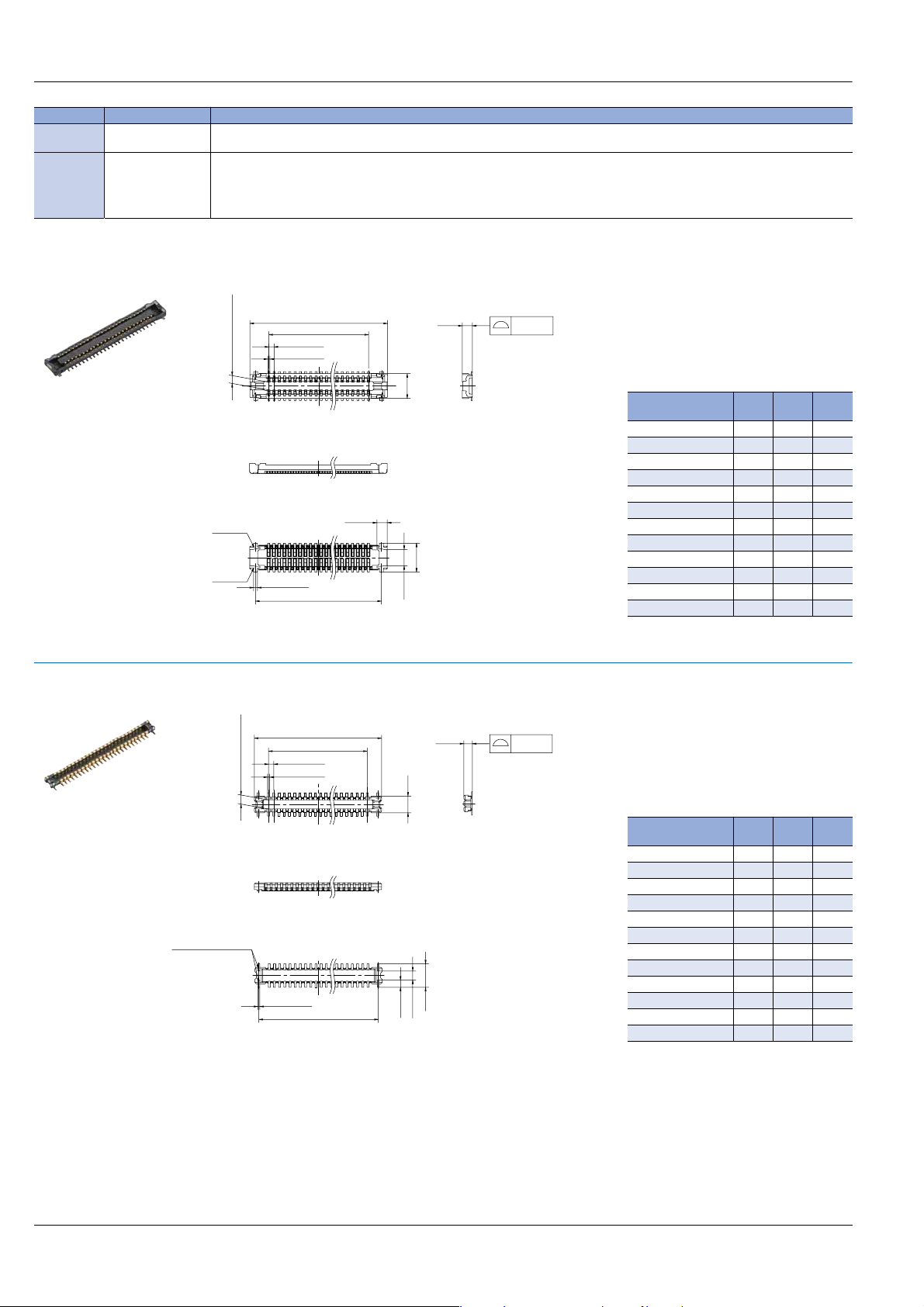
DIMENSIONS (Unit: mm)
Socket (Mated height: 0.8 mm)
LCP resin
(UL94V-0)
Copper alloy
—
Contact portion:
Terminal portion: Base: Ni plating, Surface: Au plating (except the terminal tips)
Base: Ni plating, Surface: Au plating
The socket terminals close to the portion to be soldered have nickel barriers (exposed nickel portions).
Soldering terminals: Sockets: Base: Ni plating, Surface: Pd+Au flash plating (except the terminal tips)
Headers: Base: Ni plating, Surface: Au plating (except the terminal tips)
Terminal coplanarity
(Contact and
soldering terminals)
0.60 (Suction face)
Y (Note)
Z (Note)
0.40±0.05
0.15±0.03
0.30±0.03
A
B±0.1
C±0.1
0.77
1.90
(0.80)
2.20
1.24
General tolerance: ±0.2
Note: Since soldering terminals are built into the body, the Y and Z parts are connected electrically.
Header (Mated height: 0.8 mm)
Terminal coplanarity
(Post and
soldering terminals)
General tolerance: ±0.2
0.70 (Suction face)
Soldering terminals
0.40±0.05
0.15±0.03
0.15±0.03
A
B±0.1
C±0.1
1.28
(0.54)
(0.72)
0.65
1.80
(Soldering terminals portion)
0.08
0.08
Dimension table (mm)
Number of pins/
dimension
10 4.5 1.6 3.6
14 5.3 2.4 4.4
18 6.1 3.2 5.2
20 6.5 3.6 5.6
24 7.3 4.4 6.4
30 8.5 5.6 7.6
36 9.7 6.8 8.8
40 10.5 7.6 9.6
50 12.5 9.6 11.6
60 14.5 11.6 13.6
70 16.5 13.6 15.6
80 18.5 15.6 17.6
Dimension table (mm)
Number of pins/
dimension
10 3.8 1.6 3.2
14 4.6 2.4 4.0
18 5.4 3.2 4.8
20 5.8 3.6 5.2
24 6.6 4.4 6.0
30 7.8 5.6 7.2
36 9.0 6.8 8.4
40 9.8 7.6 9.2
50 11.8 9.6 11.2
60 13.8 11.6 13.2
70 15.8 13.6 15.2
80 17.8 15.6 17.2
A B C
A B C
Panasonic Corporation Automation Controls Business Unit industrial.panasonic.com/ac/e/
ACCTB4E 201201-T1
Page 4

Socket (Mated height: 1.0 mm and 1.5 mm)
AXE1/AXE2
0.64
Y (Note)
Z (Note)
(Suction face)
0.40±0.05
0.15±0.03
0.30±0.03
A
B±0.1
C±0.1
(0.80)
0.97
1.96
2.20
1.30
General tolerance: ±0.2
Note: Since soldering terminals are built into the body, the Y and Z parts are connected electrically.
Header (Mated height: 1.0 mm)
0.76
A
B±0.1
0.40±0.05
0.15±0.03
(Suction face)
0.85
Terminal coplanarity
0.08
(Contact and
soldering terminals)
Terminal coplanarity
0.08
(Post and
soldering terminals)
Dimension table (mm)
Number of pins/
dimension
10 4.5 1.6 3.6
20 6.5 3.6 5.6
34 9.3 6.4 8.4
40 10.5 7.6 9.6
60 14.5 11.6 13.6
80 18.5 15.6 17.6
A B C
Soldering terminals
Header (Mated height: 1.5 mm)
Soldering terminals
0.76
(Suction face)
0.15±0.03
0.40±0.05
0.15±0.03
0.15±0.03
C±0.1
A
B±0.1
C±0.1
1.36
0.77
(0.515)
1.80
(Soldering terminals portion)
General tolerance: ±0.2
1.80
(Soldering terminals portion)
Terminal coplanarity
0.08
(Post and
soldering terminals)
1.35
1.36
(0.50)
(0.80)
General tolerance: ±0.2
Dimension table (mm)
Number of pins/
dimension
10 3.8 1.6 3.2
20 5.8 3.6 5.2
34 8.6 6.4 8.0
40 9.8 7.6 9.2
60 13.8 11.6 13.2
80 17.8 15.6 17.2
Dimension table (mm)
Number of pins/
dimension
20 5.8 3.6 5.2
60 13.8 11.6 13.2
80 17.8 15.6 17.2
A B C
A B C
Socket and Header are mated
Header
0.80±0.1
Socket Socket Socket
ACCTB4E 201201-T1
Header
1.00±0.1
Panasonic Corporation Automation Controls Business Unit industrial.panasonic.com/ac/e/
Header
1.50±0.1
Page 5

AXE1/AXE2
2.20±0.03
0.90±0.03
2.20±0.03
0.50±0.03
(0.85)
(0.65)
0.40±0.03
0.80±0.03
0.28±0.03
0.23±0.03
0.80±0.01
0.23±0.01
2.07±0.01
(0.76)
0.55±0.01
2.07±0.01
1.03±0.01
(0.52)
0.40±0.01
0.20±0.01
EMBOSSED T APE DIMENSIONS (Unit: mm)
• Specifications for taping
(In accordance with JIS C 0806-3:1999. Ho w ever, not applied to
the mounting-hole pitch of some connectors.)
Tape I Tape II
Leading direction after packaging
+0.3
−0.1
(C)
(1.75)
1.5
(4.0)
(2.0)
8.0
+0.1
0
dia.
(A±0.3)(A )
(B)
(C)
(1.75)
(4.0)
(2.0)
8.0
1.5
+0.1
0
dia.
• Dimension table (Unit: mm)
Type/Mated height Number of pins Type of taping A B C D Quantity per reel
Common for sockets and headers:
0.8mm, 1.0mm and 1.5mm
Max. 24 Tape I 16.0 — 7.5 17.4 5,000
30 to 70 Tape I 24.0 — 11.5 25.4 5,000
80 Tape II 32.0 28.4 14.2 33.4 5,000
• Connector orientation with respect to embossed tape feeding direction
Direction
of tape progress
Type
Socket Header
• Specifications for the plastic reel
(In accordance with EIAJ ET-7200B.)
(D±1)
380 dia.
Common for A4US
Top cover tape
Embossed carrier tape
Embossed mounting-hole
Taping reel
NOTES
1. Design of PC board patterns
Conduct the recommended foot pattern
design, in order to preserve the
mechanical strength of terminal solder
areas.
2. Recommended PC board and metal
mask patterns
Connectors are mounted with high pitch
density, intervals of 0.35 mm, 0.4 mm or
0.5 mm.
In order to reduce solder bridges and
other issues make sure the proper levels
of solder is used.
The figures to the right are recommended
metal mask patterns. Please use them as
a reference.
3. See the common “NOTES FOR
USE” on the next page for other points
to be noted.
Note: There is no indication on this product regarding top-bottom or left-right orientation.
• Socket (Mated height: 0.8 mm, 1.0
mm and 1.5 mm)
Recommended PC board pattern (TOP VIEW)
0.40±0.03
2.60±0.03
1.04±0.03
(0.78)
Recommended metal mask opening pattern
Metal mask thickness: When 120µm
2.60±0.01
1.04±0.01
(0.78)
0.23±0.03
0.80±0.03
1.45±0.03
(Terminal opening ratio: 70%)
(Metal-part opening ratio: 100%)
0.40±0.01
0.20±0.01
0.80±0.01
1.45±0.01
: Insulatin area
(0.50)
C0.30
(0.40)
C0.30
0.20±0.03
1.70±0.01
1.60±0.03
2.50±0.01
• Header (Mated height: 0.8 mm, 1.0
mm and 1.5 mm)
Recommended PC board pattern (TOP VIEW)
Recommended metal mask opening pattern
Metal mask thickness: When 120µm
(Terminal opening ratio: 70%)
(Metal-part opening ratio: 73%)
Panasonic Corporation Automation Controls Business Unit industrial.panasonic.com/ac/e/
ACCTB4E 201201-T1
Page 6

NOTES FOR USE
Connector mounting
When the working environment is dry, be
careful for static buildup.
The buildup of static electricity
occasionally causes the products to cling
to the taping material. To prevent static
buildup, it is recommended that you
maintain the relative humidity of your
working environment at 40 to 60%, while
eliminating static using an ionizer or other
means.
Soldering
1) Manual soldering.
• Due to the connector’s low profile, if an
excessive amount of solder is applied to
this product during manual soldering, the
solder may creep up near the contact
points, or solder interference may cause
imperfect contact.
• Make sure that the soldering iron tip is
heated within the temperature and time
limits indicated in the specifications.
• Flux from the solder wire may adhere to
the contact surfaces during soldering
operations. After soldering, carefully
check the contact surfaces and clean off
any flux before use.
• Be aware that a load applied to the
connector terminals while soldering may
displace the contact.
• Thoroughly clean the iron tip.
2) Reflow soldering
• Screen-printing is recommended for
printing paste solder.
• To determine the relationship between
the screen opening area and the PCboard foot pattern area, refer to the
diagrams in the recommended patterns
for PC boards and metal masks. Make
sure to use the terminal tip as a reference
position when setting.
Avoid an excessive amount of solder
from being applied, otherwise,
interference by the solder will cause an
imperfect contact.
Terminal
• Consult us when using a screen-printing
thickness other than that recommended.
• Depending on the size of the connector
being used, self alignment may not be
possible. Accordingly, carefully position
the terminal with the PC board pattern.
Paste
solder
PC board
foot pattern
• The recommended reflow temperature
profile is given in the figure below
Recommended reflow temperature profile
Upper limit (Soldering heat resistance)
Temperature
Lower limit (Solder wettability)
260°C
230°C
180°C
150°C
Preheating
60 to 120 sec.
Peak temperature
220°C
200°C
25 sec.
70 sec.
Time
• The temperature is measured on the
surface of the PC board near the
connector terminal.
• Certain solder and flux types may cause
serious solder creeping. Solder and flux
characteristics should be taken into
consideration when setting the reflow
soldering conditions.
3) Reworking on a soldered portion
• Finish reworking in one operation.
• For reworking of the solder bridge, use
a soldering iron with a flat tip. Do not add
flux, otherwise, the flux may creep to the
contact parts.
• Use a soldering iron whose tip
temperature is within the temperature
range specified in the specifications.
Do not drop or handle the
connector carelessly. Otherwise, the
terminals may become deformed due
to excessive force or applied
solderability may be degraded during
reflow.
Do not insert or remove the
connector when it is not soldered.
Forcibly applied external pressure on
the terminals can weaken the
adherence of the terminals to the
molded part or cause the terminals to
lose their evenness.
Excessive prying-force applied to
one end may cause product breakage
and separation of the solder joints at
the terminal.
When removing the connector, be
sure not to tilt the connector
exceeding 15 degrees widthwise.
Excessive force applied for insertion
in a pivot action as shown may also
cause product breakage.
Align the header and socket positions
before connecting them.
or less
15 degrees
AXE1/AXE2
When cutting or bending the PC
board after mounting the connector,
be careful that the soldered sections
are subjected to excessive forces.
The soldered areas should not be subjected to forces.
Notes when using a FPC.
When the connector is soldered to an
FPC board, during insertion and removal
forces may be applied to the terminals
and cause the soldering to come off. It is
recommended to use a reinforcement
board on the backside of the FPC board
to which the connector is being
connected. Mak e sure that the reinforcing
plate is larger than the outline of the
recommended PC board pattern (Outline
+ approx. 1 mm). The reinforcing plate is
made of glass epoxy or polyimide that is
0.2 to 0.3 mm thick.
This connector employs a simple locking
structure. However, the connector may
come off depending on the size and
weight of the FPC, layout and reaction
force of FPC, or by drop impact. Make
sure to fully check the equipment’s
condition. To prevent any problem with
loose connectors, adopt measures to
prevent the connector from coming off
inside the equipment.
Other Notes
When coating the PC board after
soldering the connector (to prevent the
deterioration of insulation), perform the
coating in such a way so that the coating
does not get on the connector.
The connectors are not meant to be used
for switching.
Please refer to the latest product
specifications when designing your
product.
ACCTB4E 201201-T1
Panasonic Corporation Automation Controls Business Unit industrial.panasonic.com/ac/e/
Page 7

NO TES FOR USING ADVANCED SERIES
NARROW -PITCH CONNECT ORS
Connector mounting
Excessive mounter chucking force may
deform the molded or metal part of the
connector. Consult us in advance if
chucking is to be applied.
Soldering
1) Manual soldering.
• Due to the connector’s low profile, if an
excessive amount of solder is applied
during manual soldering, the solder may
creep up near the contact points, or
solder interference may cause imperfect
contact.
• Make sure that the soldering iron tip is
heated within the temperature and time
limits indicated in the specifications.
• Flux from the solder wire may adhere to
the contact surfaces during soldering
operations. After soldering, carefully
check the contact surfaces and clean off
any flux before use.
• Be aware that a load applied to the
connector terminals while soldering may
displace the contact.
• Thoroughly clean the iron tip.
2) Reflow soldering
• Screen-printing is recommended for
printing paste solder.
• To determine the relationship between
the screen opening area and the PCboard foot pattern area, refer to the
diagrams in the recommended patterns
for PC boards and metal masks. Make
sure to use the terminal tip as a reference
position when setting. A v oid an excessiv e
amount of solder from being applied,
otherwise, interference by the solder will
cause an imperfect contact.
Terminal
Paste
solder
PC board
foot pattern
• Consult us when using a screen-printing
thickness other than that recommended.
• Depending on the size of the connector
being used, self alignment may not be
possible. Accordingly, carefully position
the terminal with the PC board pattern.
• The recommended reflow temperature
profile is given in the figure below
Recommended reflow temperature profile
Upper limit (Soldering heat resistance)
Temperature
Lower limit (Solder wettability)
260°C
230°C
180°C
150°C
Preheating
60 to 120 sec.
Peak temperature
220°C
200°C
25 sec.
70 sec.
Time
• The temperature is measured on the
surface of the PC board near the
connector terminal.
• Some solder and flux types may cause
serious solder creeping. Solder and flux
characteristics should be taken into
consideration when setting the reflow
soldering conditions.
• When performing reflow soldering on
the back of the PC board after reflow
soldering the connector, secure the
connector using, for example, an
adhesive (Double reflow soldering on the
same side is possible)
3) Reworking on a soldered portion
• Finish reworking in one operation.
• For reworking of the solder bridge, use
a soldering iron with a flat tip. Do not add
flux, otherwise, the flux may creep to the
contact parts.
• Use a soldering iron whose tip
temperature is within the temperature
range specified in the specifications.
Do not drop or handle the
connector carelessly. Otherwise, the
terminals may become deformed due
to excessive force or applied
solderability may be degraded during
reflow.
Do not insert or remove the
connector when it is not soldered.
Forcibly applied external pressure on
the terminals can weaken the
adherence of the terminals to the
molded part or cause the terminals to
lose their evenness.
Excessive prying-force applied to
one end may cause product breakage
and separation of the solder joints at
the terminal.
When removing the connector, be
sure not to tilt the connector
exceeding 15 degrees widthwise.
Excessive force applied for insertion
in a pivot action as shown may also
cause product breakage.
Align the header and socket positions
before connecting them.
or less
15 degrees
When cutting or bending the PC
board after mounting the connector,
be careful that the soldered sections
are subjected to excessive forces.
The soldered areas should not be subjected to forces.
Notes when using a FPC.
• When the connector is soldered to an
FPC board, during insertion and removal
forces may be applied to the terminals
and cause the soldering to come off. It is
recommended to use a reinforcement
board on the backside of the FPC board
to which the connector is being
connected. Mak e sure that the reinforcing
plate is larger than the outline of the
recommended PC board pattern (Outline
+ approx. 1 mm). The reinforcing plate is
made of SUS, glass epoxy or polyimide
that is 0.2 to 0.3 mm thick.
This connector employs a simple locking
structure. However, the connector may
come off depending on the size and
weight of the FPC, layout and reaction
force of FPC, or by drop impact. Make
sure to fully check the equipment’s
condition. To prevent any problem with
loose connectors, adopt measures to
prevent the connector from coming off
inside the equipment.
Other Notes
When coating the PC board after
soldering the connector (to prevent the
deterioration of insulation), perform the
coating in such a way so that the coating
does not get on the connector.
The connectors are not meant to be used
for switching.
Please refer to the latest product
specifications when designing your
product.
(Common)
ACCTB11E 201201-T
Panasonic Corporation Automation Controls Business Unit industrial.panasonic.com/ac/e/
 Loading...
Loading...