
VDS Series PC Oscilloscopes
User Manual
WWW.O
WON.COM.HK

Dec. 2013 edition V1.3
Copy Right in this Manual © Lilliput Company. All rights Reserved.
The Lilliput's products are under the protection of the patent rights in America and other countries, including ones which have already obtained the patent rights and those which
are applying for. The information in this manual will replace all that in the materials published originally.
The information in this manual was correct at the time of printing. However, OWON will continue to improve products and reserves the rights to changes specification at any time
without notice.
OWON is the registered trademark of the Lilliput Company.
Headquarter:
Fujian Lilliput Optoelectronics Technology Co.,Ltd.: The mansion of optoelectronics, 19 Heming Road, Lantian industrial zone, Zhangzhou, Fujian, China
Tel :+86-596-2130430 Fax:+86-596-2109272
Web:
www.owon.com.hk Mail: Business Consulting: info@owon.com.hk
Sale service: service@owon.com.hk
Branch:
Xiamen Lilliput Technology Co.,Ltd.: the 5th floor, B Area, Chuangxin Mansion, Software Park, ZhenZhuWan, Huandao RD, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tel :+86-592-2575666 Fax:+86-592-2575669

General Warranty
Lilliput warrants that the product will be free from defects in materials and workmanship for a period of 3 years from the date of purchase of the product by
the original purchaser from the Lilliput Company. And the warranty period of accessories such as probe is 12 month. This warranty only applies to the
original purchaser and is not transferable to the third party. If the product proves defective during the warranty period, Lilliput either will repair the defective
product without charge for parts and labor, or will provide a replacement in exchange for the defective product. Parts, modules and replacement products
used by Lilliput for warranty work may be new or reconditioned to like new performance. All replaced parts, modules and products become the property of
Lilliput.
In order to obtain service under this warranty, Customer must notify Lilliput of the defect before the expiration of the warranty period. Customer shall be
responsible for packaging and shipping the defective product to the service center designated by Lilliput, and with a copy of customer proof of purchase.
This warranty shall not apply to any defect, failure or damage caused by improper use or improper or inadequate maintenance and care. Lilliput shall not be
obligated to furnish service under this warranty a) to repair damage resulting from attempts by personnel other than Lilliput representatives to install, repair
or service the product; b) to repair damage resulting from improper use or connection to incompatible equipment; c) to repair any damage or malfunction
caused by the use of non-Lilliput supplies; or d) to service a product that has been modified or integrated with other products when the effect of such
modification or integration increases the time or difficulty of servicing the product.
Please contact the nearest Lilliput's Sales and Service Offices for services or a complete copy of the warranty statement.
For better after-sales service, please visit www.owon.com.hk and register the purchased product online.
Excepting the after-sales services provided in this summary or the applicable warranty statements, Lilliput will not offer any guarantee for maintenance definitely declared or
hinted, including but not limited to the implied guarantee for marketability and special-purpose acceptability. Lilliput should not take any responsibilities for any indirect,
special or consequent damages.

Table of Contents
Table of Contents ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 4
VDS Oscilloscope Software Help ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 1
VDS1022(I)/ VDS2052(I) ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 1
VDS2062/VDS3102 ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 2
VDS2064/VDS3104 ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 2
I. PC Software USB Driver Install G uide ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 3
For Windows Vista or Window s 7 ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 3
For Windows XP or Windows 2000 .................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 7
II. User Interface........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 10
III. Operations Instruction ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 11
1.How to Set the Probe Attenuation Coefficient ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
2.How to Set the Ver t ical System ................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 12
3.How to Set the Horizontal System .............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 12
4.How to Set the Tr igg er System .................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
5.How to Set the Channels .............................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 15
6.How to Measure Aut omatically .................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 15
7.How to Implement Sampling Setup ............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 17
8.How to Measure with Cursors ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
9.How to Set the Display System ................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 19
10.Use Mathematical Manipulati on Function ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 21
11.How t o zoom the waveform ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 23
12.How to do Pass/Fail test ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 25
13.How to Record and Play a Waveform ...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 26
14.How to Implement the Utility setting ......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 27
15.How to Use Executive Buttons .................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 28
16.Use LAN Port ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 29
IV. Technical Specifications ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 32

VDS Oscilloscope Software Help
Welcome to VDS Oscilloscope softw ar e.
The supplied accessories of the oscilloscope include a Quick Guide. The Quick Guide of the oscilloscope and the following helps are for your
reference.
Minimum PC Requirements
Processor: Pentium(R) 4 2.4 GHz
Memory: 1GB
Disk space: 1GB minimum
Recommended PC Requirements
Processor: Pentium(R) Dual-Core 2.4 GHz
Memory: 2GB
Disk space: 1GB minimum
Other Requirements
Operating system: Windows XP(32-bit & 64-bit), Windows Vista(32-bit & 64-bit), Windows 7(32-bit & 64-bit)
Ports: USB2.0、USB1.1
Display Resolution: 1024 x 768
Ports Introduction
VDS1022(I)/ VDS2052(I)
1
3
4
5
2
Figure Ports of the Oscilloscope(take VDS1022 for instance)
1. USB port: Supply power by PC USB or the adapter; communicate with PC
2. Probe Compensation: Measurement signal (5V/1KHz) output
3. MULTI port: EXT trigger input, trigger output or Pass/Fail output
4. Signal input of Channel 2
5. Signal input of Channel 1
Note: VDS1022(I) represents two types of machines, they are VDS1022I and VDS1022. VDS1022I contains isolation, while VDS1022 does not
contain isolation. The same as VDS2052(I).
1

VDS2062/VDS3102
5
6
7
4
Figure: Ports of the Oscilloscope (take VDS3102 for instance)
1. RS-232C Port (optional)
2. USB port: Supply power by PC USB or the adapter; communicate with PC
3. LAN port (optional): Network port which can be used to connect with PC
4. Probe Compensation: Measurement signal (3.3V/1KHz) output
5. EXT trigger input, trigger output or Pass/Fail output
6. Signal input of Channel 2
7. Signal input of Channel 1
VDS2064/VDS3104
Figure: Ports of the Oscilloscope (take VDS3104 for instance)
1. Probe Compensation: Measurement signal (3.3V/1KHz) output
2. MULTI port: EXT trigger input, trigger output or Pass/Fail output
3. LAN port (optional): Network port which can be used to connect with PC
4. USB port: Supply power by PC USB or the adapter; communicate with PC
5. Signal input of Channel 4
6. Signal input of Channel 3
7. Signal input of Channel 2
8. Signal input of Channel 1
Note: If you use LAN port to communicate with PC, the oscil l osc op e shoul d be pow er ed by t he ada pter .
2

I. PC Software USB Driver Install Guide
Use the supplied USB cable to connect the oscilloscope with a PC through their USB ports.
Note: If you use a USB cable that is not supplied by us, som e problems su ch as connection error and signal dis turbing migh t
occur.
For Windows Vista or Windows 7
The Microsoft Windows Systems since Windows Vista or Windows 7, change a lot, which require a new installation guide of USB driver. Here it is.
During the whole installation, please assure that the device is running well and plugged into PC from USB.
Right click [Computer], you can find it on the desktop, or in [Start] menu.
in the pop up menu, click [Manage] and it will open a window named "Computer Management", as follow, in the left side click [Device Manager], it will show a devices tree in
the middle, and then click the last one button "Scan for hardware changes" in tool bar as follow, and if the device is running well and plugged into PC, computer will detect an
unknown device with a "!" icon.
Right click the unknown device icon, in the pop up menu click [Update Driver Software...],
In the open window, select [Browse my computer for driver software],
3
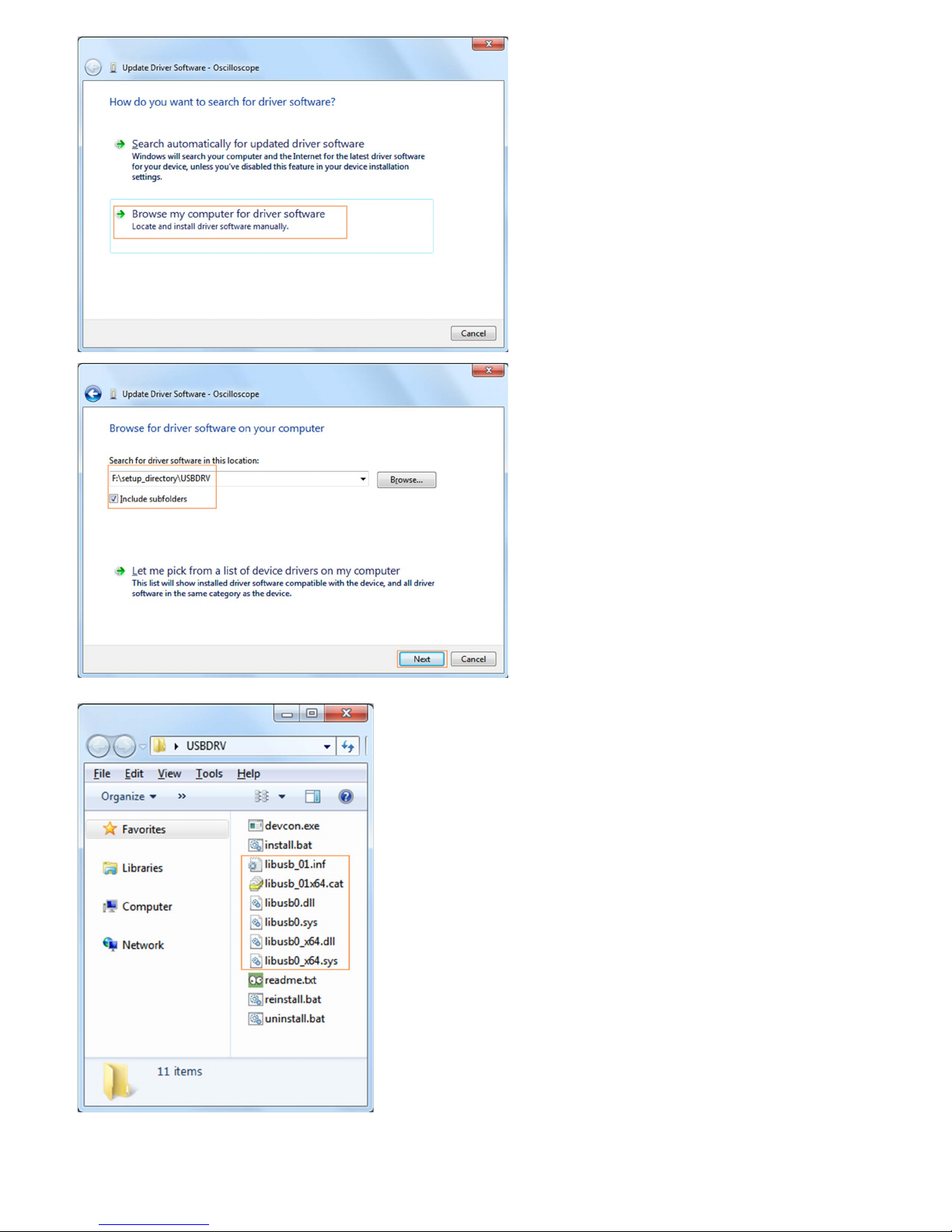
The next window, select a directory path for the driver software location, and click "Next",
Notice: the driver software location is a directory that is under the software setup folder named "USBDRV", and the contents inside are like these:
Or like this, than you should use the "USBDRV" directory to indicate the ".inf" file, and to the ".sys" or ".dll" file, you can indicate then in different directories like "x86", "ia64" or
"amd64" depending on the CPU, but most of time just x86 and amd64 are enough.
4
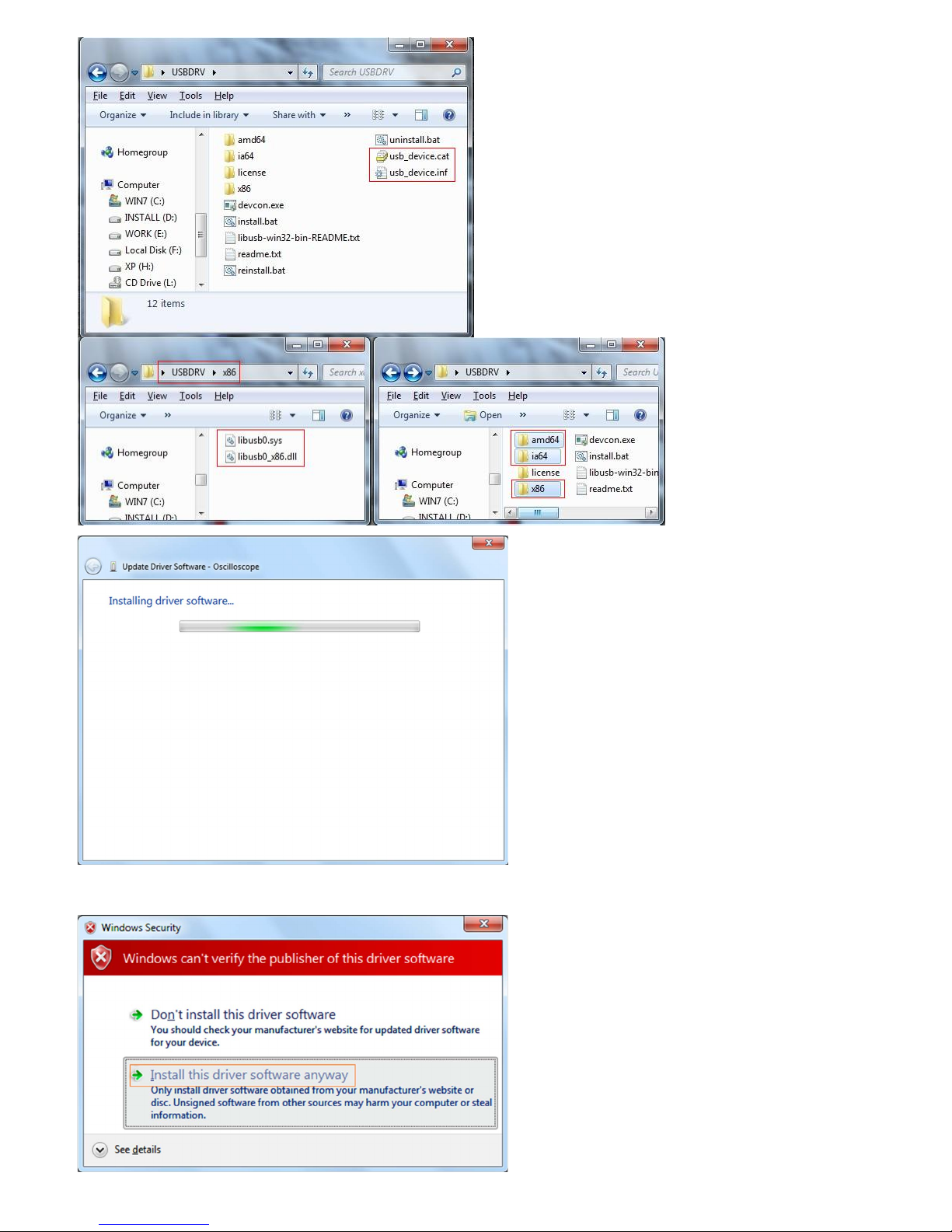
OK, back to the driver installing, after last "Next" step, the system is installing driver software for you, as follow,
In the course,
It(for Windows XP x86&x64, Windows Vista x86&x64, Windows 7 x86) may open a window named "Windows Security" as below, and just select "Install this driver software
anyway" to continue,
5
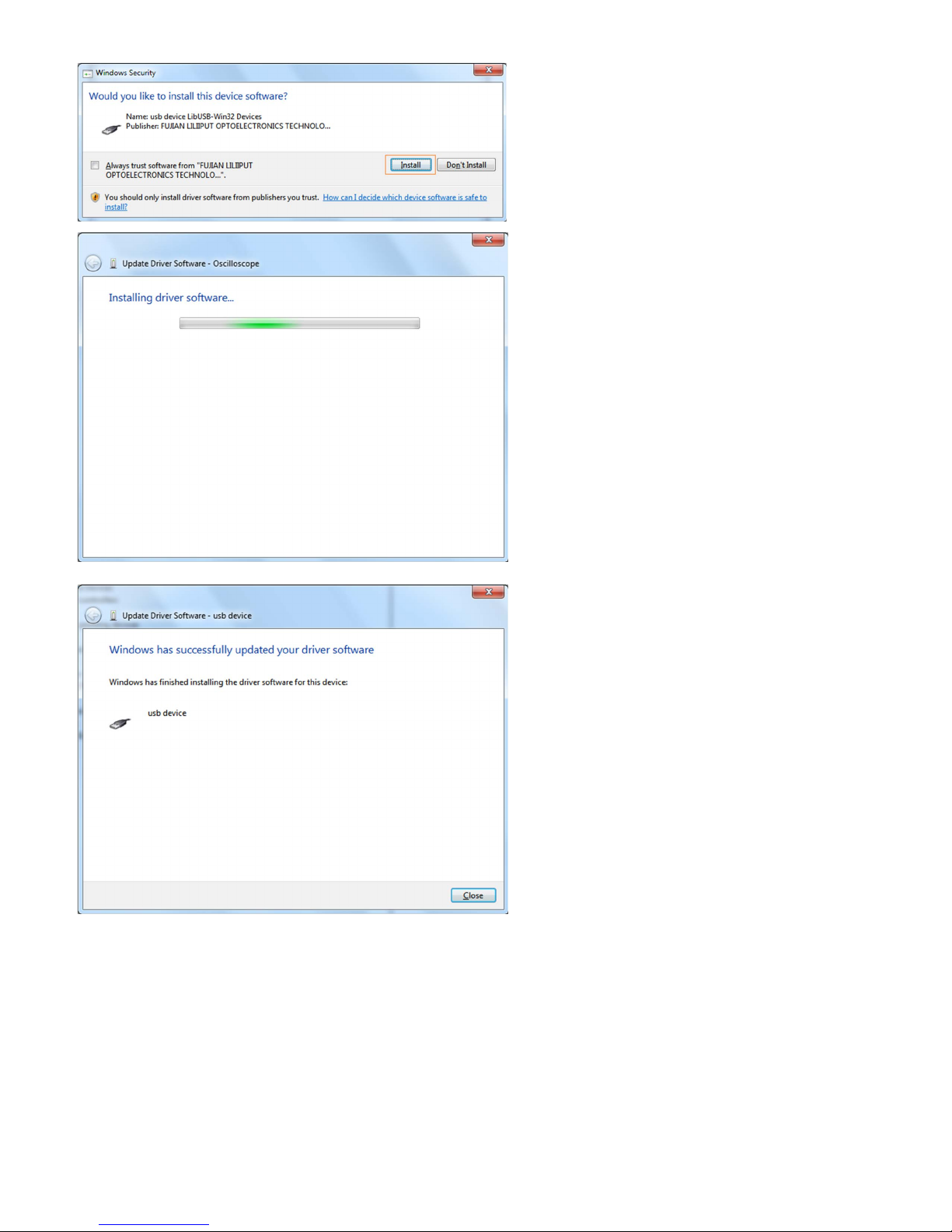
Or sometimes it(for Windows 7 x64) may open a window named "Windows Security" as below, and just click "Install" to continue,
And then continue installing,
And finish.
Now a successful installation window opens with information "Windows has successfully updated your driver software".
Close the window, have a look at the "Computer Management" window, you will find a device under [LibUSB-Win32 Devices], it should be like this:
6
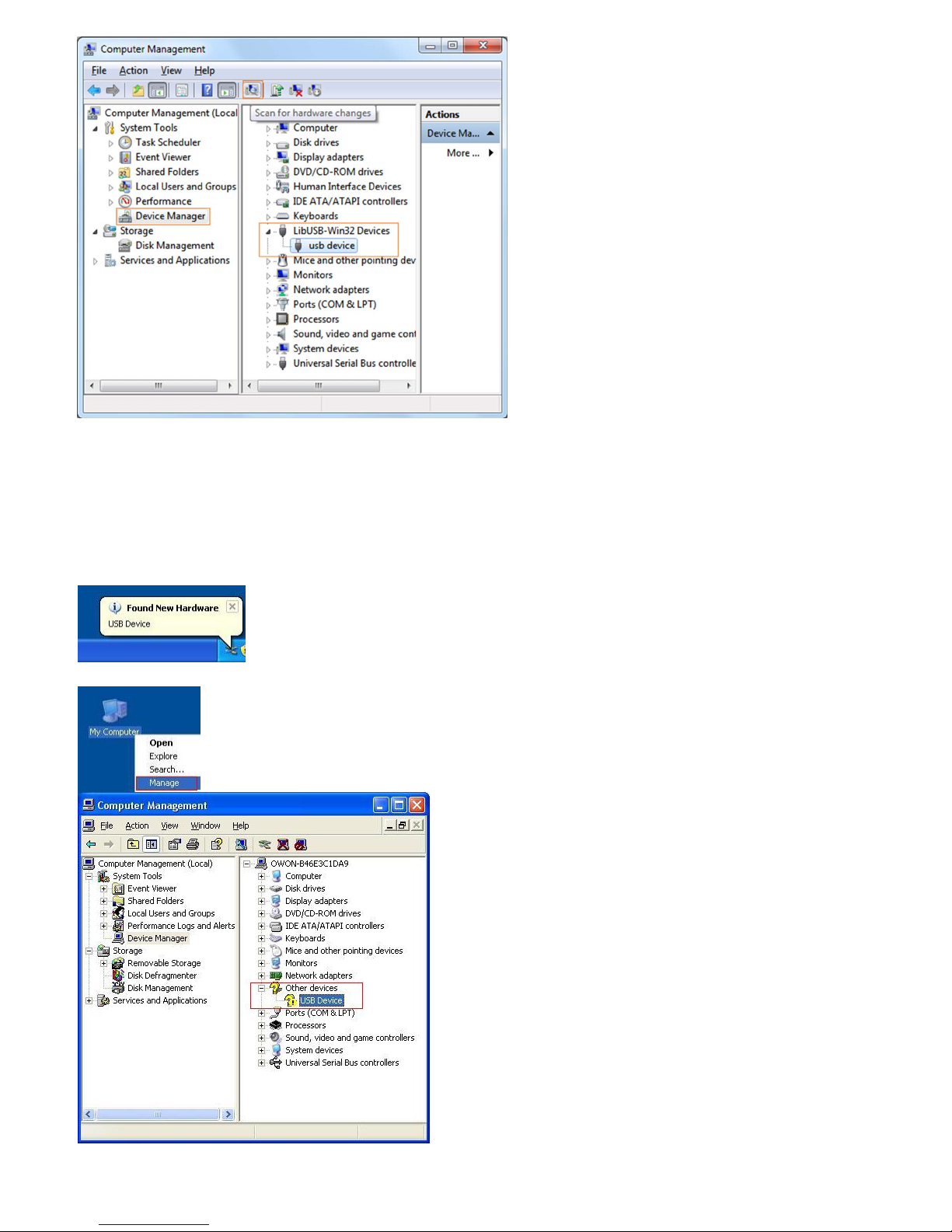
Now the USB driver will work.
For Windows XP or Windows 2000
For Windows XP or Windows 2000
Notice: for both x86 and x64.
Plug into the running well device to open [Found New Hardware Wizard] dialog.
Or you can right click [My Computer] and select [Manage], in the left area of opened [Computer Management] select [Device Manager] , double click the item [USB Device]
with "?" in the middle area to open the Wizard,
In the Wizard, select [No, not this time] ,
7
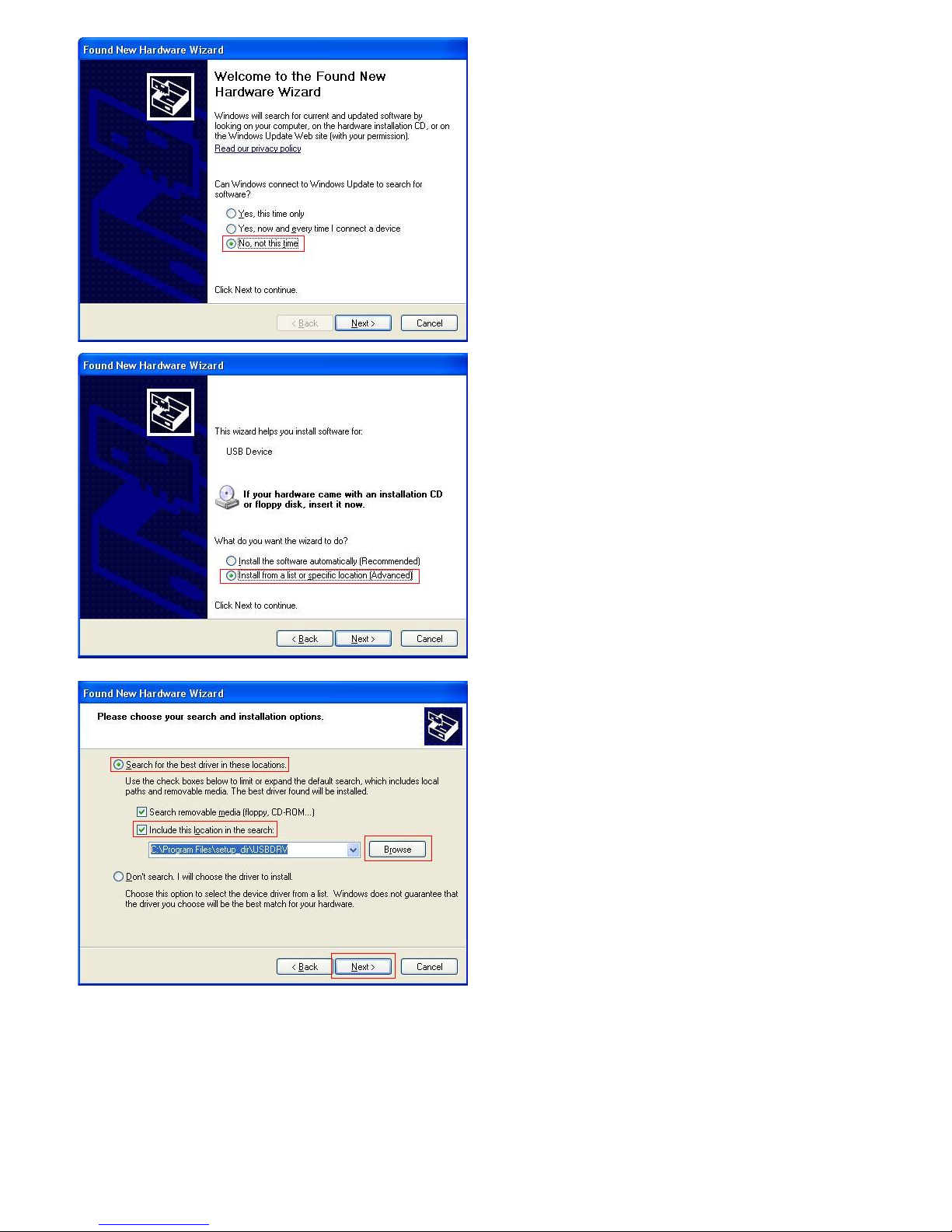
select [Install from a list or specific location(Advanced)] ,
select [Search for the best driver in these locations.] , then select [Include this location in the search] and indicate a directory location for USB driver which is named as
"USBDRV" and under the directory where you installed the program at,
Then the installation is running,
8

And complete,
And prompt as installed,
And show installed in [Device Management],
Now you can use the program and use if for USB communication.
If there is an early version of USB driver in your computer, you could try running "reinstall.bat" to fix, the file is under the directory of "USBDRV".
9

II. User Interface
1.
Waveform Display Area
2.
Display status, click to choose "Disconnect", "Install USB Driver" or "Connect LAN". Refer to the
instruction of the status after this list.
3.
The red pointer indicates the horizontal position for the trigger
4.
The pointer indicates the trigger position in the internal memory
5.
Measure time with cursors
6.
The two yellow dotted lines indicate the size of the viewing expanded window
7.
Auto set, see 15.How to Use Executive Buttons
8.
Run/Stop, see 15.How to Use Executive Buttons
9.
Single Trigger, see 15.How to Use Executive Buttons
10.
Back to Home menu
11.
Hide the menu
12.
Measure voltage with cursors
13.
The red pointer show s the trig g er lev el pos itio n f or CH 1 ( yel low for C H2). It c an be dr agg ed up and dow n.
14.
Function menu, click to show/hide
15.
Shortcut icon of resetting to factory settings, see "Default"
Shortcut icon of exporting waveform, see "Pause&Export"
Switch Three View/One View. In the Three View di
splay mode, the left top is XY mode widow, the
right top is FFT window.
Show/hide Function menu
16.
Trigger window, see 4.How to Set the Trigger System
17.
Sample and Period window, see 3.How to Set the Horizontal System
18/19. Channel window of CH2 and CH1, see 2.How to Set the Vertical System
20.
Display the measured type and v alue o f the correspondi ng cha nnel, see 6.H ow to Meas ure Auto matical ly
21.
Cursor measure window, see 8.How to Measure with Cursors
22/23. The yellow pointer shows the grounding datum point (zero point position) of the CH2 waveform. If
the pointer is not displayed, it means that this channel is turned off. (Red pointer is for CH1)
24.
The waveform of CH1
Keyboard Shortcuts
Space: Run/Stop
Enter: Auto set
Q:
The voltage division of Channel 1 decr eas es one
level
A: The voltage division o
f Channel 1 increases one
level
W: The voltage division of Channel 2 decreases
one level
10

S: The voltage division of Channel 2 increases one
level
←: Time base decreases one level
→: Time base increases one level
F1: Open this help document
Instruction of the status information
Auto
Automatic trigger mode
Ready
Ready for a trigger
Trig'd
Has trigged
Scan
Slow scan
Stop
Data acquisition stopped
Error
Error occurred
ReSyncing
Synchronize with the oscilloscope
again
AutoSet
In process of auto setting
The statuses of not staying connected with the oscilloscope:
Offline
No connection with the
oscilloscope
USBFound
Find available USB devices
USBDrvErr
USB drivers installed error
MachineNotSupport
Can not recognize the device
The statuses in the process of connecting with the oscilloscope:
Linking
Being connecting with the
oscilloscope
Connect
connect successfully
Match
Matching the model
Syncing
Sync the settings
III. Operations Instruction
Relevant operations of this software.
1.How to Set the Probe Attenuation Coefficient
The probe has several attenuation coefficients, which will influence the vertical scale factor of the oscilloscope.
To change or check the probe attenuation coefficient in the menu of oscilloscope:
(1) Click to show Function menu, choose "Channel".
(2) Set "Probe Rate" to the proper value corresponding to the probe.
This setting will be valid all the time before it is changed again.
Caution:
The default attenuation coefficient of the probe in the
software is
preset to 10X.
Make sure that the set value of the attenuation switch in the probe is
the same as the menu selection of the probe attenuation coefficient
in the software.
The set values of the probe switch are 1X and 10X.
Figure: Attenuation Switch
Caution:
When
the attenuation switch is set to 1X, the probe will limit the
bandwidth of the oscilloscope in 5MHz. To use the full bandwidth of
the oscilloscope, the switch must be set to 10X.
11

2.How to Set the Vertical System
You can set the corresponding parameters of vertical system in the Channel window (18/19 in II. User Interface).
In the voltage division list, you can select the proper value. Take VDS3102 for instance.
You can set the zero point position through the control bar to regulate of the vertical display position of the signal. You can also drag the zero
point position pointer (22, 23 in II. User Interface).
Drag the slider up to increase, down to decrease; the further from the center, the higher the changing speed is.
Keyboard Shortcuts
Q: The voltage division of Channel 1 decreases one
level
A:
The voltage division of Chann el 1 i ncr eases one level
W: The voltage division of Channel 2 decreases one
level
S: The voltage division of Channel 2 increases one level
Cymometer
It is a 6-digit cymometer. The cymometer can measure frequencies from 2Hz to the full bandwidth. Only if the measured channel has triggering
signal and in Edge mode, it can measur e frequency correctly. In the Single tri g ger mode, it is a one channel cymomet er and i t can only measure
the frequency of the triggering channel. In the ALT trigger mode, it is a two channel cymometer and it can measure the frequency of two
channels.
3.How to Set the Horizontal System
You can set the corresponding parameters of horizontal system in the Capture&period window (17 in II. User Interface).
You can use Horizontal Trigger Position cont r ol bar to a djus t th e hor i z ontal posi ti on o f the s ig nal in t he wav eform w indow . You c an also dr ag th e
red pointer to adjust it (3 in II. User Interface).
12

Note: Different machines have different ranges of time base, here just take VDS3102 for instance.
The further from the center, the higher the changing speed is.
Keyboard Shortcuts
←: Time base decreases one level
→
:
Time base increases one level
See also: 11.How to zoom the waveform
4.How to Set the Trigger System
Trigger determines when VDS starts to acquire data and display waveform. Once trigger is set correctly, it can convert the unstable display to
meaningful waveform.
When VDS starts to ac quire data, it will coll ect en oug h data to draw waveform on left of trigger point. VD S c o nti nu es t o ac q ui r e d ata while waiting
for trigger condition to occur. Once it detects a trigger it will acquire enough data continuously to draw the waveform on right of trigger point.
Click to show Function menu, choose "Trigger".
You can also click in the right bottom window to show it.
Trigger Control
The oscilloscope provides two trigger types: single trigger and alternate trigger.
Single trigger: Use a trigger level to capture stable waveforms in two channels simultaneously.
Alternate trigger: Trigger on non-synchronized signals.
The Single Trigger and Alternate Trigger menus are described respectively as follows:
Single trigger
1. In Trigger menu, choose "Single" (the chosen label has a mark).
2. Choose Source.
3. Choose Mode.
Single trigger has four modes: edge trigger, video trigger, slope trigger and pulse trigger.
Edge Trigger: It occurs when the trigger input passes through a specified voltage level with the specified slope.
Video Trigger: Trigger on fields or lines for standard video signal.
Slope Trigger: The oscilloscope begins to trigger according to the signal rising or falling speed.
Pulse Trigger: Find pulses with certain widths.
The four trigger modes in Single Trigger are described respectively as follows:
Edge Trigger
13

Choose Mode as "Edge". An edge trigger occurs on trigger threshold value of input signal. Select Edge trigger mode to trigger on rising edge or
falling edge.
Set in Trigger menu:
(1) Choose "Rise" to trigger on rising edge.
Choose "Fall" to trigger on falling edge.
(2) Click the voltage value after "Trigger" to show slider bar. You can also drag "13. Trigger point" in II. User Interface
.
(3) Choose Trig Mode.
Auto: Acquire waveform even no trigger occurs.
Normal: Acquire waveform when trigger occurs.
Single: When trigger occurs, acquire one waveform then stop.
(4) Set Hold Off: When trigger occurs, acquire one waveform then stop (100ns~10s).
Setting method: "+", "++", "+++" is the position of digit that will be changed. "+" represents the last digit, "++" represents the middle di g i t,
"+++" represents the first digit. Eg. When "+" is chosen, click ▲, the last digit will be increased by 1.
Click "Reset" to set Holdoff time as default value (100ns).
Set in Trigger window:
Force: Force to create a trigger signal and the function is mainly used in "Normal" and "Single" mode.
Video Trigger
Choose Mode as "Video" to trigger on fields or lines of NTSC, PAL or SECAM standard video signals.
(1) Select video modulation: NTSC, PAL or SECAM.
(2) Set trigger synchronization: Line, Field, Odd filed, Even filed or Line Number. When "Line Number" is selected, you can set the line
number.
(3) Set Hold Off. About the setting method, refer to Edge Trigger.
Slope Trigger
Choose Mode as "Slope" to set the oscilloscope as the positive/negative slope trigger within the specified time.
(1) Select slope condition.
(2) Set slope time.
(3) Set the High level upper limit and Low level lower limit.
(4) Set Trig Mode and Hold Off. About the setting method, refer to Edge Trigger.
Slew rate = (High level - Low level) / Settings
Pulse Width Trigger
Choose Mode as "Pulse". Pulse t rigg er occur s according to the w idth of puls e. The a bnormal signal s can be detect ed throug h setti ng up the pulse
width condition.
(1) Select pulse width condition and set time.
(2) Set trigger level.
(3) Set Trig Mode and Hold Off. About the setting method, refer to Edge Trigger.
Alternate trigger
Trigger signal comes from two vertical channels when alternate trigger is on. This mode is used to observe two unrelated signals. You can
choose different trigger modes for different channel s. The opt ions ar e as foll ows: edge, video, pulse or slope.
Set in Trigger menu:
1. In Trigger menu, choose "Alternate" (the chosen label has a mark).
2. Choose Source.
3. Choose Mode.
About the setting method of Mode and parameters, refer to Single trigger.
Note: In alternate trigger, only one channel at most can be set as Video mode. You can not choose Video in both channels. When VDS1022(I),
only channel 1 can be set as video mode.
Set in Trigger window:
14

Instruction of Trigger mode icon in Trigger window:
Rise in Edge mode
Fall in Edge mode
Synchronic trigger in video line
Synchronic trigger in video field
Synchronic trigger in video odd
filed
Synchronic trigger in video even field
Rising in Slope
Falling in Slope
+Pulse Width
-Pulse Width
5.How to Set the Channels
Click to show Function menu, choose "Channel". You can also click or in the Channel window on the left bottom. Or click ,
or in the Channel window on the left bottom when it is four- channel oscilloscope.
Fig. Dual channel setting Fig. Four channel setting
To turn on/off channels
Click to choose "CH1" or "CH2", check "On" to turn on the channel, uncheck it to turn off.
You can also click the channel switch in Channel window in left bottom. See figure below.
To invert a waveform
Waveform inverted: the displayed signal is turned 180 degrees against the phase of the earth potential.
Click to choose "CH1" or "CH2", check "Opposite" to invert the waveform, uncheck it to display normall y.
To set channel coupling
DC: Pass both AC and DC components of the input signal.
AC: Block the DC component of the input signal.
Ground: Disconnect the input signal.
You can also click the coupling mode to switch it. See fig ur e below.
To adjust the probe attenuation
For correct measurements, the attenuation coefficient settings in the operating menu of the Channel should always match what is on the probe
(see 1.How to Set the Probe Attenuation Coefficient ). If the attenuation coefficient of the probe is 1:1, the menu setting of the input channel
should be set to X1.
Some operations could be done in Channel window:
6.How to Measure Autom atically
Click to show Function menu, choose "Measure".
15

Automatic measurement works under this function. Totally twenty kinds of measurements. At most 8 types of measurements could be displ ay ed
on the bottom left of the screen. The osci llosc opes prov ide 20 par ameters for auto measure ment, inclu ding Vpp, Vmax, Vmi n, Vtop, V base, Vamp,
Vavg, Vrms, Overshoot, Preshoot, Freq, Period, Rise Time, Fall Time, Delay A→B , Delay A→B ,+Width, -Width, +Duty, -Duty.
Sho w All: Choose channel from the list on the right side of "Show All", a pop-up window will show all the measurement values.
Add measurement: Check the channel and measurement type. Measurement results display on the bottom left. You can add 8 types at most
for each channel. If 8 types are exceeded, the former option will be canceled. The measured values of two channels can be displayed
simultaneously.
Remove measurement: Uncheck the measurement type to remove it. Click "Remove All" to remove all measurements.
The automatic measurement of voltage parameters
The VDS series oscilloscopes provide automatic voltage measurements including Vpp, Vmax, Vmin, Vavg, Vamp, Vrms, Vtop, Vbase,
Overshoot and Preshoot. Figure below shows a pulse with some of the voltage measurement points.
Vpp: Peak-to-Peak Voltage.
Vmax: The maximum amplitude. The most positive peak volt ag e m easur e d over the entire waveform.
Vmin: The minimum amplitude. The most negative peak voltage measured over the entire waveform.
Vamp: Voltage between Vtop and Vbase of a waveform.
Vtop: Voltage of the waveform's flat top, useful for square/pulse waveforms.
Vbase: Voltage of the waveform's flat bas e, us e ful for sq uare/ p ul se waveforms.
Overshoot: Defined as (Vmax-Vtop)/Vamp, useful for squar e and pul s e waveforms.
Preshoot: Defined as (Vmin-Vbase)/Vamp, useful for square and pulse waveforms.
Average: The arithmetic mean over the entire waveform.
Vrms: The true Root Mean Square voltage over the entire waveform.
The automatic measurement of time parameters
The VDS series oscilloscopes prov ide ti me par ameters auto-measurements include Frequency, Period, Rise Time, F all Time, +Width, -Width,
Delay 1→2 , Delay 1→2 , +Duty and -Duty.
Figure shows a pulse with some of the time measurement points.
Rise Time: Time that the leading edge of the first pulse in the waveform takes to rise from 10% to 90% of its amplitude.
Fall Time: Time that the falling edge of the first pulse in the waveform takes to fall from 90% to 10% of its amplitude.
+Width: The width of the first positive pulse in 50% amplitude points.
-Width: The width of the first negative pulse in the 50% amplitude points.
Delay 1→2 : The delay between the two channels at the rising edge.
Delay 1→2 : The delay between the two channels at the falling edge.
+Duty: +Duty Cycle, defined as +Width/Period.
-Duty:-Duty Cycle, defined as -Width/Period.
16

7.How to Implement Sampling Setup
Click to show Function menu, choose "Sampling" to set sampling mode.
Sampling Mode
Description
Sampling
Normal sampling mode.
Peak Detect
Use to capture maximal and minimal samples. Finding highest and lowest
points over adjacent intervals. It
is used for the detection of the jamming
burr and the possibility of reducing the confusion.
Average
It is used to reduce the random and don't-care noises, with the editable
number (1≤ number ≤128) of averages.
Figure: Normal sampling mode display, in which no burr can be detected.
Figure: Peak Detect mode, under which the burrs on the falling edge of the square wave, can be detected and the noise is heavy.
Figure: The displayed waveform after the noise is removed under the Average Mode, in which the average number of 16 is set.
8.How to Measure with Cursors
17

Click to show Function menu, choose "Mark Cursor".
Normal mode
1. Choose source: choose the channel to be measured by cursors between CH1 and CH2.
2. Check measuremen t type: choose either Time cursor measurement or Voltage cursor measurement,or both.
Time cursor measurement: Tick on "Time" option, then two light red lines display along the vertical direction of the screen, which represent
Cursor 1 and Cursor 2.
Place the mouse pointer over Cursor 1 or Cursor 2, drag after the mouse pointer changing to , adjust the positions of Cursor 1 and Cursor 2
according to the waveform to be measured. The cursor increment window at the left bottom shows current time of the two cursors, absolute time
difference of the two cursors and frequency. (See figure below)
Voltage cursor measurement: Tick on "Voltage" option, then two light red lines which represent Cursor 1 and Cursor 2 display along the
horizontal direction.
Place the mouse pointer over Cursor 1 or Cursor 2, drag after the mouse pointer changing to , adjust the position of Cursor 1 and Cursor 2
according to the waveform to be measured. The cursor increment window on the bottom left shows current position of the two cursors, absolute
voltage amplitude difference of the two cursors and frequency. (See Figure below)
18

The cursor measurement for FFT mode
Check measurement type: choose either Amplitude Measurement or Frequency Measurement at the mode of FFT, or both at the same time.
Frequency Measurement: Tick on "Frequency", enter Home page->Math->FFT, then two light red lines represent Cursor 1 and Cursor 2 show
along the vertical direction on FFT window.
Place the mouse cursor on Cursor 1 or Cursor 2, drag after the mouse shape changing to , adjust the position of Cursor 1 and Cursor 2
according to the waveform to be measured. The cursor increment window on the bottom left of FFT window shows current frequency of the two
cursors, absolute frequency difference of the two cursors. (See figure below)
Vamp Measurement: Tick on "Amplitude", enter Home pa ge->Math->FFT, then two light red lines represent Cursor 1 and Cursor 2 show along
the horizontal direction on FFT window.
Place the mouse cursor on Cursor 1 or Cursor 2, drag after the mouse shape changing to , adjust the position of Cursor 1 and Cursor 2
according to the waveform to be measured. The cursor increment window on the bottom left of FFT window shows current position of the two
cursors, absolute voltage amplitude difference of the two cursors. (See figure below)
9.How to Set the Display Sy stem
Click to show Function menu, choose "Display".
19

Display Type
Click the button to choose the display type (the chosen button has a mark).
Vector: The space between the adjacent sampling points in the display is filled with the vector form.
Dots: Only the sampling points are displayed.
Figure: Display in the Vector Form
Figure: Display in the Dots Form
XY Mode
Check "XY Mode", the user interface is switched into Three View mode. Choose the first channel and the second channel. In XY mode widow,
the first channel is displayed in the horizontal axis and the second in the vertical axis.
Note: XY Mode only support 1K storage memory. The storage memory is set to 1K automatically.
Persistence
When the Persistence function is used, the persistence display effect of the picture tube oscilloscope can be simulated. The reserved original
data is displayed in fade color and the new data is in bright color.
Different persistence time can be chosen: Off, 0.5 second, 1second, 2seconds, 5seconds and Infinite.
20

When the "Infini te" option is set, the measuring points will be stored till the controlling value is changed.
Click "Clear" button, the persistence will be cleared.
Note:
If the time base, voltage division, deep memory is changed, or the channel is turned off/on, the persistence will be cleared automatically and
record the updated waveform.
Grid Brightness
Drag slider to adjust the brightness of grid in the Waveform Display Area.
10.Use Mathematical Manipulation Function
The Mathematical Manip ula tion function is used to show the results of the addition, multiplication, division and subtraction operations between
Channel 1 and Channel 2, and the FFT operation of Channel 1 or Channel 2.
Math of dual waveform
1. Turn on CH1 and CH2.
2. Click to show Function menu, choose "Math". Check "Math".
3. Choose the factors and operator. Select the voltage division of M. The software transforms the waveform data of the two factors into selec te d
voltage division of M and calculates. The green calculated waveform M is displayed in the screen.
Using FFT function
The FFT (fast Fourier transform) math function mathematically converts a time-domain waveform into its frequency components. It is very useful
for analyzing the input signal on Oscilloscope. You can match these frequencies with known system frequencies, such as system clocks,
oscillators, or power supplies.
FFT function in this oscilloscope transforms 2048 data points of the time-domain signal into its frequency components mathematically and the
final frequency contains 1024 points ranging from 0Hz to Nyquist frequency.
Taking the FFT operation for example, the operation steps are as follows:
1. Click to show Function menu, choose "Math". Check "FFT". The user interface is switched into Three View mode.
2. Set "Channel", "Window", "Format", "Scale", "Frequency Base".
3. You can drag anywhere in FFT window to move the signal up and down and side to side.
21

To select the FFT window
There are four FFT windows. Each one has trade-offs between frequency resolution and magnitude accuracy. What you want to measure and
your source signal characteristics help you to determine which window to use. Use the following guidelines to select the best window.
Type
Characteristics
Window
Hamming
Better solution for magnitude than Rectangle,
and good fo
r frequency as well. It has slightly
better frequency resolution than Hanning.
Recommend to use for:
Sine, periodic and narrow band random
noise.
Transients or bursts where the signal levels
before and after the event are significantly
different.
Rectangle
Best solution for frequency, wor st for magnit ude.
Best type for measuring the frequency spectrum
of non-repetitive
signals and measuring
frequency components near DC.
Recommend to use for:
Transients or bursts, the signal level before
and after the event are nearly equal.
Equal-
amplitude sine waves with
frequencies those are very close.
Broadband random noise with a relatively
slow varying spectrum.
Blackman
Best solution for magnitude, wor st for freq uency.
Recommend to use for:
Singl
e frequency waveforms, to find higher
order harmonics.
Hanning
Good for magnitude, but poorer frequency
resolution than Hamming.
Recommend to use for:
Sine, periodic and narrow band random
noise.
Transients or bursts where the signal levels
before
and after the event are significantly
different.
The figures below are examples for measuring sine wave with a frequency of 1kHz under the selection of four different windows for FFT:
Figure: Hamming window
22

Figure: Rectangle window
Figure: Blackman window
Figure: Hanning window
Notes for using FFT
Select "Scale" to magnify the FFT waveform if necessary.
Use the default dB scale for details of multiple frequencies, even if they have very different amplitudes. Use the Vrms scale to compare
frequencies.
DC component or off set c an c ause inc orr ect magnitude values of F FT w avefor m. To mi nimiz e the DC com pone nt, c hoos e AC Coupl in g on th e
source signal.
To reduce random noise and aliased components in repetitive or single-shot events, set the oscilloscope acquisition mode to average.
What is Nyquist frequency?
The Nyquist frequency is the hig hest freq uenc y that any real -time di git iz ing osci llos cope can acqui re wi thout ali asin g. Thi s freq uency is hal f of th e
sample rate. Frequencies above the Nyquist frequency will be under sampled, which causes aliasing. So pay more attention to the relation
between the frequency being sampled and measured.
Note:
In FFT mode, only support to set coupling, voltage division and zero position in Channel window, other operations are prohibited. If you want to
enter other menus, uncheck "FFT" first.
11.How to zoom the waveform
Click to show Function menu, choose "Display".
23

Main Time Base
The setting of the horizontal main time base is used to display the waveform.
Assist Set
A window area is defined by two cursors, which will be expanded to the full screen size in Window Expansion.
Choose W value from the combo box to adjust th e siz e o f this w i ndow area. Cli ck to show the slider bar. You c an adjust th e hor iz ontal
position of the area in main window by it.
Note: In Assist Set status, the time base and horizontal trigger position can not be set.
Window Expansion
Click "Zoom", the window area defined by two cursors will be expanded to the full screen size.
You can adjust the time base W and horizontal trigger position Tw of zoom window in the menu. You can also drag the red pointer to adjust the
horizontal trigger position (3 in II. User Interface).
You can also switch and set in Capture&period window as shown in the below.
24

12.How to do Pass/Fail test
The Pass/Fail function monitors changes of signals and output pass or fail signals by comparing the input signal that is within the pre-defined
mask.
Click to show Function menu, choose "Pass/Fail".
Detect whether the input sig nal i s w i thi n the l imi ts o f the r ul e, if it exceeds limits of the rule, it is "Fail"; otherwise it is "Pass". Also it can output fail
or pass signal by built-i n and co n fig ur able output port.
To run the test, read the following steps:
1.Choose channel: Options include CH1,CH2 and Math。
2.Set horizontal tolerance and vertical tolerance. You can adjust by or input directly.
3.Click "Create Rule".
4.Set output type: Choose "Pass" or "Fail". Check or uncheck "Ring", "Message Show" and "Stop Once" as needed.
Ring: The bell rings when it meets the rule.
Stop Once: Stop once it meets the rule.
Message Show: Display the counting message on the left top.
5.Enable switch on: Click "Enable".
6.Begin to test: Click "Run".
7.Stop testing: Click "Stop".
25

Save rule
Save: Save current rule.
Use: Load the selected rule in the list as the testing rule.
Remove: Remove the selected rule in the list.
13.How to Record and Pla y a Waveform
Wave Record function can record the input current wave. You can set the interval between recorded frames and get better analysis effect with
playback and storage function. The limit of the saved file size is 4000M. It will save the initial trig status, the time base, voltage division,
horizontal trigger position and zero position of each frame during recording.
Click to show Function menu, choose "Record".
Record
1. Choose "Record" tab on the top.
2. Click "Preset Save Path" to specify the save location. Waveform files have the suffix ".cap".
3. Set "Interval Time" and "End Frame". Interval Time refers to the interval between recorded frames. Interval Time ranges from 0 to 100000ms
and increment by 10ms.
4. Make the waveform in Run status.
5. Click "Begin Record". Counter starts to count the frame number.
6. Click "End Record" to stop recording, or wait until the Counter reaches the End Frame.
Note:
1.Waveforms of two channels can be recorded simultaneously.
2.You can turn on/off the channel s while recording. Only channels tu r ned on c a n be r ecorded. If a channel is turned o ff w hi le recording, there will
be no waveform of this channel after the frame when stopped.
Replay the waveform recorded
26

1. Choose "Play" tab on the top.
2. Click "From..." to choose the waveform file to be replayed.
3. Set the start frame "Sta" and end frame "End".
4. Set Interval Time for replaying.
5. Check "Cycle" to play back the waveform in a loop. Uncheck it to replay just once.
6. Click "Play". "Numbers" shows the current frame number that is replayed.
7. Click "Pause" to pause it.
8. Drag slider to display the frame you need.
Note:
1. If the software is in Run status, playing back will make the current acquisition stopped.
2. When replaying, entering other menu items will make the replay paused.
14.How to Implement the Utility setting
Click to show Function menu, choose "Utility".
Language
Choose the desired language.
Skin
Choose Black or Blue for interface skin. Then "Restart" button will appear. After clicking it, the software will be closed and restarted to apply the
new skin.
Open File
Choose BIN waveform file saved and open it, or just drag the file into the software interface to open it.
Print Preview
Click to open the Print Preview Window.
Instruction of the menu items in Print Preview Window:
File → Page Set: Set the page margins
Print: Enter printing window
Exit: Close the Print Preview Window
View →Page Transform: Switch the page orientation between landscape and portrait
Whole page: Display the full page on the screen
Face size: Display in actual size
Default Scale... : Display in a specified zoom factor
Show Wave Background: Check to display wave background color; uncheck to display preview paper background
Set Preview Page Background: Click to display color picker dialog box to set the color of preview page background
Save Image
27

Click to save screen shot as an image file in png, bmp or gif format.
Save/Refer
This function allows to store 8 reference waveforms. These waveforms can be displayed with the current waveform simultaneously. The recalled
waveform can't be adjusted. The source can be CH1, CH2 or Math.
To save the waveform of CH1 into object "a" and recall it, the steps are as follows:
1. Choose CH1 as source.
2. Choose "To Object" as "a".
3. Fill in "Object Rename", such as "sine". Click "OK". The object name is renamed as "a(sine)". This step can be skipped.
4. Click "save".
5. Select "a(sine)" from the list, tick "Show", the reference waveform will appear on the screen. The object name and relevant information will be
displayed on the top left. You can continue to choose another reference waveform to display. Click "Remove all" to clear all reference
waveforms on the screen.
If the chosen object has no stored waveform, it will display "No Saved" below.
Pause&Export
Export the waveform in to a file i n sp eci fied format accor di ng to c ur rent recor d leng th . You c an c hoose bi n, tx t, c sv , x ls as the format . You can also
click icon on the user interface to save it in the format specified in menu.
Self Cal
The self-calibration can make the oscilloscope reach the optimum condition rapidly to obtain the most accurate measurement value. You can
carry out this application program at any time. This program must be executed whenever the change of ambient temperature is 5℃ or over.
Before performing a self-calibration, disconnect all probes or wires from the input connector. After everything is ready, click "Self Cal".
Default
Click "Default" to call out the factory settings. You can also click icon on the user interface.
Help
Open this help document. You can press F1 as shortcut key.
Network
The oscilloscope could be connected to a PC via LAN port. For more details, see 16.Use LAN Port .
Tips Window
Choose a label among "Channel", "Capture&Period" or "Trigger" to view the guide for the new users.
Click anywhere in the help window to turn page.
If you do not want to display the guide automatically when running the software, check "Don't show again".
About
Display Version, Serial Number and Company website. Press "Update" button to detect update program on server.
Sync Trigger
Control the function of the port 5 in Ports of the Oscilloscope.
Trigger In: Input the trigger signal synchronously
Trigger Out: Output the trigger signal synchronously
Pass/Fail: Output high level when pass, output low level when fail.
15.How to Use Executive Buttons
Executive Buttons include AutoSet , Run/Stop / , Single Trigger . See 7, 8, 9 in II. User Interface.
AutoSet:
28

It's a very useful and quick way to apply a set of pre-set functions to the incoming signal, and display the best possible viewing waveform of the
signal and also works out some measurements for user as well.
The details of functions applied to the signal when using AutoSet are shown as the following table:
Function Items
Setting
Acquisition Mode
Current
Vertical Coupling
DC
Vertical Scale
Adjust to the proper division.
Horizontal Level
Middle
Horizontal Sale
Adjust to the proper division
Trigger Type
Current
Trigger Source
Show the minimum number of
channels.
Trigger Coupling
Current
Trigger Slope
Current
Trigger Level
Mid-point Setting
Trigger Mode
Edge
Display Format
YT
Run/Stop: Enable or disable sampling on input signals.
Single Trigger: You can set the trigger mode as single directly, so when trigger occurs, acquire one waveform then stop.
Keyboard Shortcuts
Enter: Auto set
Space: Run/Stop
16.Use LAN Port
Using the LAN port, the oscilloscope could be connected to a PC directly or through a router. Below introduces these two kind of connection
methods.
Connect directly via a LAN cable
1. View the network parameters of the computer
View the IP address of the computer to connect to. Assume the IP address is 192.168.1.71.
2.
Set the network parameters of the osci lloscope
(1)
Connect via USB and enter the menu: Use the supplied USB cable to connect the oscilloscope with a PC through their USB ports.
After connecting successfully, click to show Function menu, choose "Utility", click "Network".
(2)
Set IP and port of the oscilloscope: In Network menu, click "OK" to enter MachineNetSetting.
Choose the oscilloscope to be connected from the list. If it's not in the list, click "Refresh" to refresh the list.
Set IP, the first three bytes should be same as the IP address of the computer in step 1, the last byte should be different.
Here, we set it to
192.168.1.72. The range of the port value is 0~4000, here we set it to 3000.
29

(3)
Click "Rework" to restart the oscilloscope.
3.
Set the network parameters of the software
(1)
Supply power: Disconnect the USB cable from the computer. Connect it with the AC-DC adapter. Plug the adapter into an electrical
outlet to power the oscilloscope.
(2)
Connection: Plug in the LAN line to the LAN port of the oscilloscope; plug the other end into the LAN interface of the computer.
(3)
Set parameters in menu: Click to show Function menu, cho os e "Utility", click "Network". Set IP and Port
to the same value o f the
oscilloscope in step 2.
(4) Click "Connect".
Connect through a router
1. View the network parameters of the computer
View the network parameters of the computer to connect to. The Default gateway and Subnet mask should be set according to the
router.
Assume the parameters are as below:
IP address: 192.168.1.71
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Default gateway: 192.168.1.1
30

2.
Set the network parameters of the osci lloscope
(1)
Connect via USB and enter the menu: Use the supplied USB cable to connect the oscilloscope with a PC through their USB ports.
After connecting successfully, click to show Function menu, choose "Utility", click "Network".
(2)
Set the network parameters of the oscilloscope: In Network menu, click "OK" to enter MachineNetSetting.
Choose the oscilloscope to be connected from the list. If it's not in the list, click "Refresh" to refresh the list.
Set IP, the first three bytes should be same as the IP address of the computer in step 1, the last byte should be different. Here, we set it
to
192.168.1.72. The range of the port value is 0~4000, here we set it to 3000.
The Net mask and Gateway should be set according to the router.
(3)
Click "Rework" to restart the oscilloscope.
3.
Set the network parameters of the software
(1)
Supply power: Disconnect the USB cable from the computer. Connect it with the AC-DC adapter. Plug the adapter into an electrical
outlet to power the oscilloscope.
(2)
Connect to the router: Use a LAN cable to connect the oscilloscope with a router; the computer should be connected to the router too.
(3)
Set parameters in menu: Click to show Function menu, cho os e "Utility", click "Network". Set IP and Port
to the same value o f the
oscilloscope in step 2.
31

(4)
Click "Connect".
IV. Technical Specifications
Unless otherwise specified, the technical specifications applied are for VDS series only, and Probes attenuation set as 10X. Only if the
oscilloscope fulfills the following two conditions at first, these specification standards can be reached.
This instrument should run for at least 30 minutes continuously under the specified operating temperature.
If change of the operating temperature is up to or exceeds 5℃, do the "Self Cal" procedure in Utility menu
(see Self Cal).
Note: VDS1022(I) represents two types of machines, they are VDS1022I and VDS1022. VDS1022I contains isolation, while VDS1022 does
not contain isolation. The same as VDS2052(I).
Performance Characteristics
Instruction
Bandwidth
VDS1022(I)
25MHz
VDS2052(I)
50MHz
VDS2062
60MHz
VDS3102
100MHz
VDS2064
60MHz
VDS3104
100MHz
Channel
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
VDS2062
VDS3102
2 + 1 (*External)
VDS2064
VDS3104
4 + 1 (*External)
Acquisition
Mode
Normal, Peak detect, Averaging
Sample rate
(real time)
VDS1022(I)
Dual CH
100MS/s
Single CH
100MS/s
VDS2052(I)
Dual CH
250MS/s
Single CH
250MS/s
VDS2062
Dual CH
250MS/s
Single CH
500MS/s
VDS3102
Dual CH
500MS/s
Single CH
1GS/s
VDS2064
Four CH
125MS/s
32

Dual CH
250MS/s
Single CH
500GS/s
VDS3104
Four CH
250MS/s
Dual CH
500MS/s
Single CH
1GS/s
Input
Input coupling
DC, AC , Ground
Input impedance
1MΩ±2%, in parallel with 10pF±5pF
Probe attenuation
factor
1X, 10X, 100X, 1000X
Max. input voltage
VDS1022I
VDS2052I
400V (PK-PK) (DC + AC
PK-PK)
VDS1022
VDS2052
VDS2062
VDS3102
VDS2064
VDS3104
40V (PK-PK) (DC + AC PK-PK)
Channel –channel
isolation
50Hz: 100 : 1
10MHz: 40 : 1
Time delay
between
channel(typical)
150ps
Horizontal
System
Sampling rate
range
VDS1022(I)
Dual CH
0.5S/s~100MS/s
Single CH
0.5S/s~100MS/s
VDS2052(I)
Dual CH
0.5S/s~250MS/s
Single CH
0.5S/s~250MS/s
VDS2062
Dual CH
0.5S/s~250MS/s
Single CH
0.5S/s~500MS/s
VDS3102
Dual CH
0.5S/s~500MS/s
Single CH
0.5S/s~1GS/s
VDS2064
Four CH
0.5S/s~125MS/s
Dual CH
0.5S/s~250MS/s
Single CH
0.5S/s~500MS/s
VDS3104
Four CH
0.5S/s~250MS/s
Dual CH
0.5S/s~500MS/s
Single CH
0.5S/s~1GS/s
Interpolation
(sin x)/x
Max Record length
VDS1022(I)
Dual CH
≤Max
sampling rate
5K
Single CH
VDS2052(I)
Dual CH
≤Max
sampling rate
5K
Single CH
VDS2062
Dual CH
≤Max
sampling rate
10M
Single CH
VDS3102
Dual CH
≤Max
sampling rate
10M
Single CH
VDS2064
Four CH
≤Max
sampling rate
5M
Dual CH
Single CH
VDS3104
Four CH
≤Max
sampling rate
5M
Dual CH
Single CH
33

Scanning speed
(S/div)
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
VDS2062
VDS2064
5ns/div~100s/div,
step by 1~2~5
VDS3102
VDS3104
2ns/div~100s/div,
step by 1~2~5
Sampling rate /
relay time accuracy
±100ppm
Interval(△T)
accuracy
(DC~100MHz)
Single:
±(1 interval time+100ppm×reading+0.6ns);
Average>16:
±(1 interval time +100ppm×reading+0.4ns)
Vertical
system
A/D converter
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
VDS2062
VDS3102
8 bits resolution (2 Channels
simultaneously)
VDS2064
VDS3104
8 bits resolution (4 Channels
simultaneously)
Sensitivity
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
VDS2062
VDS2064
5mV/div~5V/div
VDS3102
VDS3104
2mV/div~5V/div
Displacement
VDS1022(I)
±10div
VDS2052(I)
±10div
VDS2062
±1V (5mV~100mV);
±50V (200mV~5V);
VDS3102
±1V(2mV~100mV);
±50V(200mV~5V);
VDS2064
±1V (5mV~100mV);
±50V (200mV~5V)
;
VDS3104
±2V(2mV~200mV);
±50V(500mV~5V);
Analog bandwidth
25MHz, 50MHz, 60MHz, 100MHz
Single bandwidth
Full bandwidth
Low Frequency
≥10Hz (at input, AC coupling, -3dB)
Rise time
VDS1022(I)
≤14ns (at input, Typical)
VDS2052(I)
≤7.0ns (at input, Typical)
VDS2062
≤5.8ns (at input, Typical)
VDS3102
≤3.5ns (at input, Typical)
VDS2064
≤5.8ns (at input, Typical)
VDS3104
≤3.5ns (at input, Typical)
DC accuracy
±3%
DC accuracy
(average)
Average≥16: ±(3% rdg + 0.05 div) for
△
V
Waveform inverted ON/OFF
34

Measurement
Cursor
△V and △T between cursors
Automatic
Vpp, Vmax, Vmin, Vtop, Vbase, Vamp,
Vavg, Vrms, Overshoot, Preshoot,
Freq,
Period, Rise Time, Fall Time, Delay
A→B , Delay A→B , +Width, -
Width,
+Duty, -Duty
Waveform Math +, -, *, / ,FFT
Lissajous
figure
Bandwi
dth
Full bandwidth
Phase
differen
ce
±3 degrees
Communicatio
n port
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
USB1.1
VDS2062
VDS3102
VDS2064
VDS3104
USB2.0, LAN (Optional)
Multi-function
Interface
Signal type
Synchronizing input, Synchronizing output,
Pass/Fail output, External trigger input
Level standard
TTL
*External refers to trigger in, trigger output or Pass/Fail output.
Trigger:
Performance Characteristics Instruction
Trigger level
range
Internal
±5 div from the screen center
Trigger level
Accuracy (typical)
Internal
±0.3div
EXT
TTL
Trigger
displacement
According to Record length and time base
Trigger Holdoff
range
100ns~10s
50% level setting
(typical)
Input signal frequency ≥50Hz
Edge trigger
slope Rising, Falling
Pulse trigger
Trigger condition
Positive pulse:>, <, =
negative pulse:>, <, =
Pulse Width range
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
VDS2062
VDS3102
VDS2064
VDS3104
30ns~10s
Video Trigger
Modulation
Support standard NTSC, PAL and
SECAM broadcast systems
Line number range 1-525 (NTSC) and 1-625 (PAL/SECAM)
Slope Trigger Trigger condition
Positive pulse:>, <, =
negative pulse:>, <, =
35

Performance Characteristics Instruction
Time setting
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
VDS2062
VDS3102
VDS2064
VDS3104
30ns~10s
Alternate Trigger
Trigger on CH1
Edge, Pulse, *Video, Slope
Trigger on CH2
Edge, Pulse, *Video, Slope
*Video: In alternate trigger, only one channel at most can be set as Video mode.
When VDS1022(I), in alternate trigger, only CH1 can be set as Video mode.
Output of the Probe Compensator
Performance
Characteristics
Instruction
Output Voltage
(Typical )
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
About 5V, with the Peak-to-Peak
voltage ≥1MΩ.
VDS2062
VDS3102
VDS2064
VDS3104
About 3.3V, with the Peak-to-
Peak
voltage ≥1MΩ.
Frequency (Typical )
Square wave of 1KHz
Power
Mains Voltage
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
5.0V/500mA
VDS2062(L)
VDS3102(L)
VDS2064
VDS3104
5.0V/1A
Power Consumption
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
<2.5W
VDS2062(L)
VDS3102(L)
VDS2064
VDS3104
<5W
Environment
Temperature
Working temperature: 0 ℃~ 40 ℃
Storage temperature: -20 ℃~ 60 ℃
Relative Humidity
≤ 90%
Height
Operating: 3,000 m
Non-operating: 15,000 m
Cooling Method
Natural convection
Mechanical Specifications
Dimension
VDS1022(I)
VDS2052(I)
170mm× 120mm×18mm (L*H*W)
VDS2062(L)
VDS3102(L)
VDS2064
VDS3104
190mm× 120mm×18mm (L*W*H)
Weight
About 0.26 kg
Interval Period of Adjustment:
One year is recommended for the calibration interval period.
36
 Loading...
Loading...