Page 1

Radian Series Inverter/Charger
GS8048A
GS4048A
Installation Manual
Page 2

Address:
Corporate Headquarters
Arlington, WA 98223 USA
European Office
Schwabach, Germany
Telephone:
+1.360.435.6030
+1.360.435.6019 (Fax)
+49.9122.79889.0
Email:
Support@outbackpower.com
Website:
http://www.outbackpower.com
About OutBack Power Technologies
OutBack Power Technologies is a leader in advanced energy conversion technology. OutBack products include
true sine wave inverter/chargers, maximum power point tracking charge controllers, and system communication
components, as well as circuit breakers, batteries, accessories, and assembled systems.
Grid/Hybrid™
As a leader in off-grid energy systems designed around energy storage, OutBack Power is an innovator in
Grid/Hybrid system technology, providing the best of both worlds: grid-tied system savings during normal or
daylight operation, and off-grid independence during peak energy times or in the event of a power outage or an
emergency. Grid/Hybrid systems have the intelligence, agility and interoperability to operate in multiple energy
modes quickly, efficiently, and seamlessly, in order to deliver clean, continuous and reliable power to residential
and commercial users while maintaining grid stability.
Contact Information
17825 – 59th Avenue N.E.
Suite B
+1.360.618.4363 (Technical Support)
Hansastrasse 8
D-91126
+49.9122.79889.21 (Fax)
Disclaimer
UNLESS SPECIFICALLY AGREED TO IN WRITING, OUTBACK POWER TECHNOLOGIES:
(a) MAKES NO WARRANTY AS TO THE ACCURACY, SUFFICIENCY OR SUITABILITY OF ANY TECHNICAL OR OTHER
INFORMATION PROVIDED IN ITS MANUALS OR OTHER DOCUMENTATION.
(b) ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR LOSS OR DAMAGE, WHETHER DIRECT, INDIRECT,
CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL, WHICH MIGHT ARISE OUT OF THE USE OF SUCH INFORMATION. THE USE OF
ANY SUCH INFORMATION WILL BE ENTIRELY AT THE USER’S RISK.
OutBack Power Technologies cannot be responsible for system failure, damages, or injury resulting from
improper installation of their products.
Information included in this manual is subject to change without notice.
Notice of Copyright
Radian Series Inverter/Charger Installation Manual © 2013 by OutBack Power Technologies. All Rights Reserved.
Trademarks
OutBack Power, the OutBack Power logo, FLEXpower ONE, and Grid/Hybrid are trademarks owned and used by
OutBack Power Technologies, Inc. The ALPHA logo and the phrase “member of the Alpha Group” are trademarks
owned and used by Alpha Technologies Inc. These trademarks may be registered in the United States and other
countries.
Date and Revision
February 2014, Revision A
Part Number
900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 3

Table of Contents
Introduction ................................................................................................. 3
Audience ................................................................................................................................................................................. 3
Welcome to OutBack Power Technologies ................................................................................................................. 3
Components and Accessories ......................................................................................................................................... 4
Planning ...................................................................................................... 5
Applications ........................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Input Modes ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
Renewable Energy ............................................................................................................................................................... 6
Battery Bank ........................................................................................................................................................................... 7
Generator ................................................................................................................................................................................ 9
Maintenance Bypass Switching ................................................................................................................................... 10
Installation ................................................................................................. 11
Location and Environmental Requirements ............................................................................................................ 11
Dimensions .......................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Tools Required .................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Mounting .............................................................................................................................................................................. 13
Component Mounting...................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Removing Front Cover .................................................................................................................................................... 16
Terminals and Ports .......................................................................................................................................................... 17
Wiring .................................................................................................................................................................................... 19
Grounding ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 19
DC Wiring ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 20
AC Wiring ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 22
Accessory Wiring ................................................................................................................................................................................. 25
AUX Wiring ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 26
Generator Control .............................................................................................................................................................................. 27
AC Configurations ............................................................................................................................................................. 31
Single-Inverter ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 31
Multiple-Inverter AC Installations (Stacking) ........................................................................................................................... 33
Functional Test ................................................................................................................................................................... 38
Preventative Maintenance ............................................................................................................................................. 38
Symbols, Terms, and Definitions .................................................................. 39
Symbols Used ..................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Definitions ............................................................................................................................................................................ 39
Index ......................................................................................................... 41
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 1
Page 4

Table of Contents
List of Tables
Table 1 Components and Accessories ......................................................................................................... 4
Table 2 Battery Bank Elements ....................................................................................................................... 8
Table 3 Ground Conductor Size and Torque Requirements .............................................................. 19
Table 4 DC Conductor Size and Torque Requirements ....................................................................... 21
Table 5 Terms and Definitions ...................................................................................................................... 39
List of Figures
Figure 1 Radian Series Inverter/Charger .................................................................................................. 3
Figure 2 Radian Inverter and Accessories ............................................................................................... 4
Figure 3 Applications (Example) ................................................................................................................. 5
Figure 4 Bypass Switching .......................................................................................................................... 10
Figure 5 Bypass Switching for Multiple Inverters ............................................................................... 10
Figure 6 Dimensions ..................................................................................................................................... 11
Figure 7 System Dimensions ..................................................................................................................... 12
Figure 8 Installing the Mounting Plate ................................................................................................... 13
Figure 9 Mounting the Inverter ................................................................................................................ 14
Figure 10 Mounting for System Components ........................................................................................ 15
Figure 11 Removing the Front Cover ........................................................................................................ 16
Figure 12 DC Terminals, Ribbon Cables, and Auxiliary Terminals ................................................... 17
Figure 13 AC Terminals, Ports, and Ground Bus .................................................................................... 18
Figure 14 Chassis Ground TBB ..................................................................................................................... 19
Figure 15 GS8048A and GS4048A Battery Terminals ........................................................................... 20
Figure 16 DC Cable Hardware (Radian inverter) .................................................................................... 21
Figure 17 AC Terminals .................................................................................................................................. 22
Figure 18 AC Sources ...................................................................................................................................... 24
Figure 19 Accessory Connections .............................................................................................................. 25
Figure 20 ON/OFF Jumper and Connections.......................................................................................... 25
Figure 21 AUX Connections for Vent Fan (Example)............................................................................ 26
Figure 22 AUX Connections for Diversion (Example) .......................................................................... 27
Figure 23 Two-Wire Generator Start (RELAY AUX)................................................................................ 28
Figure 24 Two-Wire Generator Start (12V AUX) ..................................................................................... 28
Figure 25 Three-Wire Generator Start (Example) .................................................................................. 29
Figure 26 Single-Inverter AC System ......................................................................................................... 31
Figure 27 Single-Inverter AC Wiring with GS Load Center ................................................................. 32
Figure 28 OutBack Communications Manager and System Display .............................................. 33
Figure 29 Example of Parallel Stacking Arrangement (Three Inverters)........................................ 35
Figure 30 Parallel Wiring ................................................................................................................................ 36
Figure 31 Parallel Wiring with GSLC .......................................................................................................... 37
2 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 5
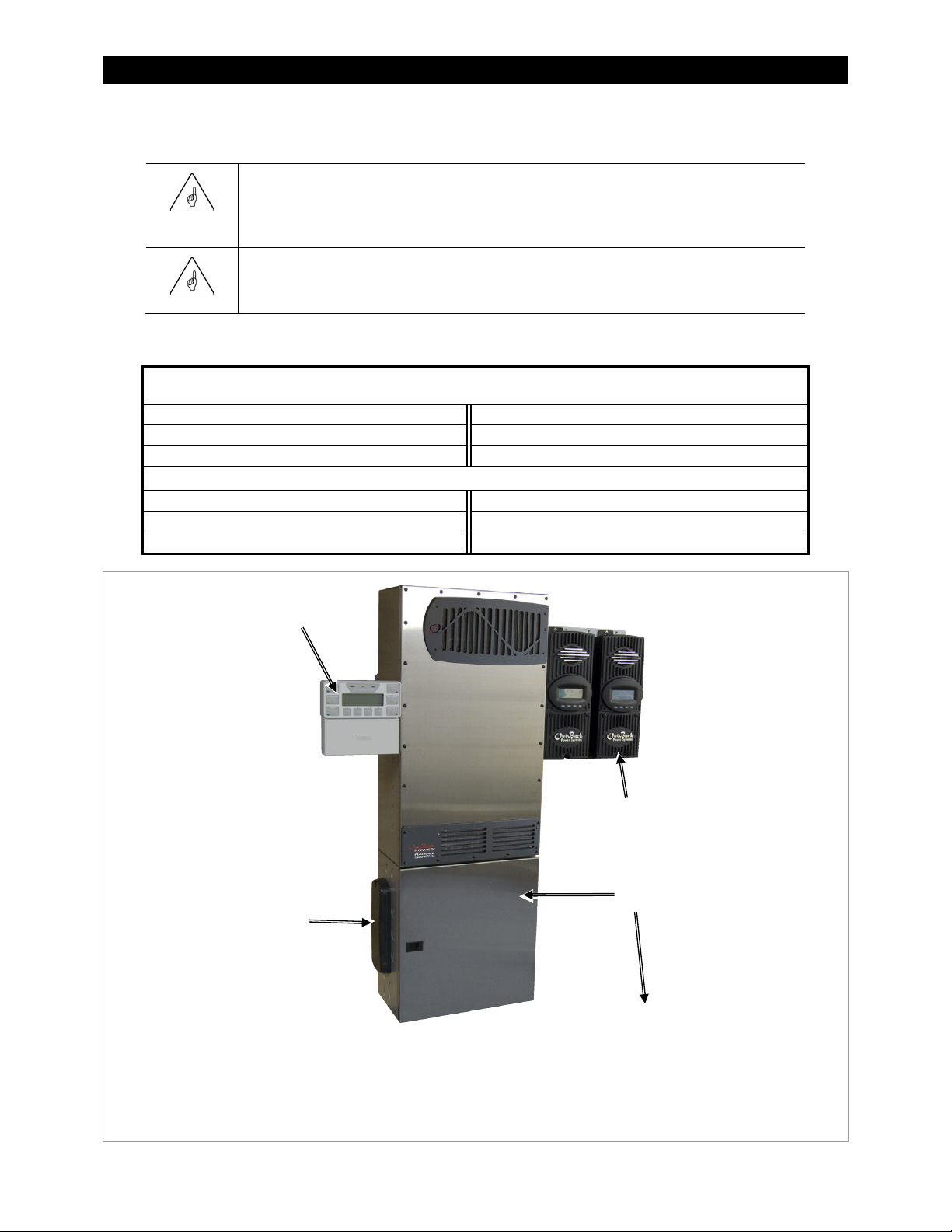
Audience
Designed to be integrated as part of an OutBack
This book provides instructions for the physical installation and wiring of this product.
These instructions are for use by qualified personnel who meet all local and governmental code
requirements for licensing and training for the installation of electrical power systems with AC and DC
voltage up to 600 volts. This product is only serviceable by qualified personnel.
Welcome to OutBack Power Technologies
Thank you for purchasing the OutBack Radian Series Inverter/Charger. This product offers a complete
power conversion system between batteries and AC power. It can provide backup power, sell power
back to the utility grid, or provide complete stand-alone off-grid service.
Grid/Hybrid™ system
Battery-to-AC inverting which delivers split-phase power
(100/200 Vac to 120/240 Vac at 60 or 50 Hz)
Model GS8048A can continuously produce 8 kVA (33 Aac)
Model GS4048A can continuously produce 4 kVA (16 Aac)
Mounts easily with supplied mounting plate
All terminals exit at the bottom of the inverter, allowing the
installer to use a single distribution box; the GS Load Center
(GSLC) is specifically designed for this purpose
Uses spring-based AC terminals instead of screw-based
terminals; this eliminates torque requirements and periodic
re-tightening
Uses the MATE3™ System Display and Controller (sold
separately) for user interface as part of a Grid/Hybrid system
Uses the HUB™ Series Communications Manager for
networking as part of a Grid/Hybrid system
Features versatile mounting locations for the MATE3, HUB,
FLEXmax charge controller, and GSLC
The venting on the cover allows mounting of multiple Radian
inverters side by side with minimal clearance between them
Up to 10 Radian inverter/chargers can be stacked together
Introduction
Figure 1 Radian Series Inverter/Charger
: This product has a settable AC output range. In this book, many references to the output refer
NOTE
to the entire range. However, some references are made to 120/240 Vac or 60 Hz output. These are
intended as examples only.
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 3
Page 6
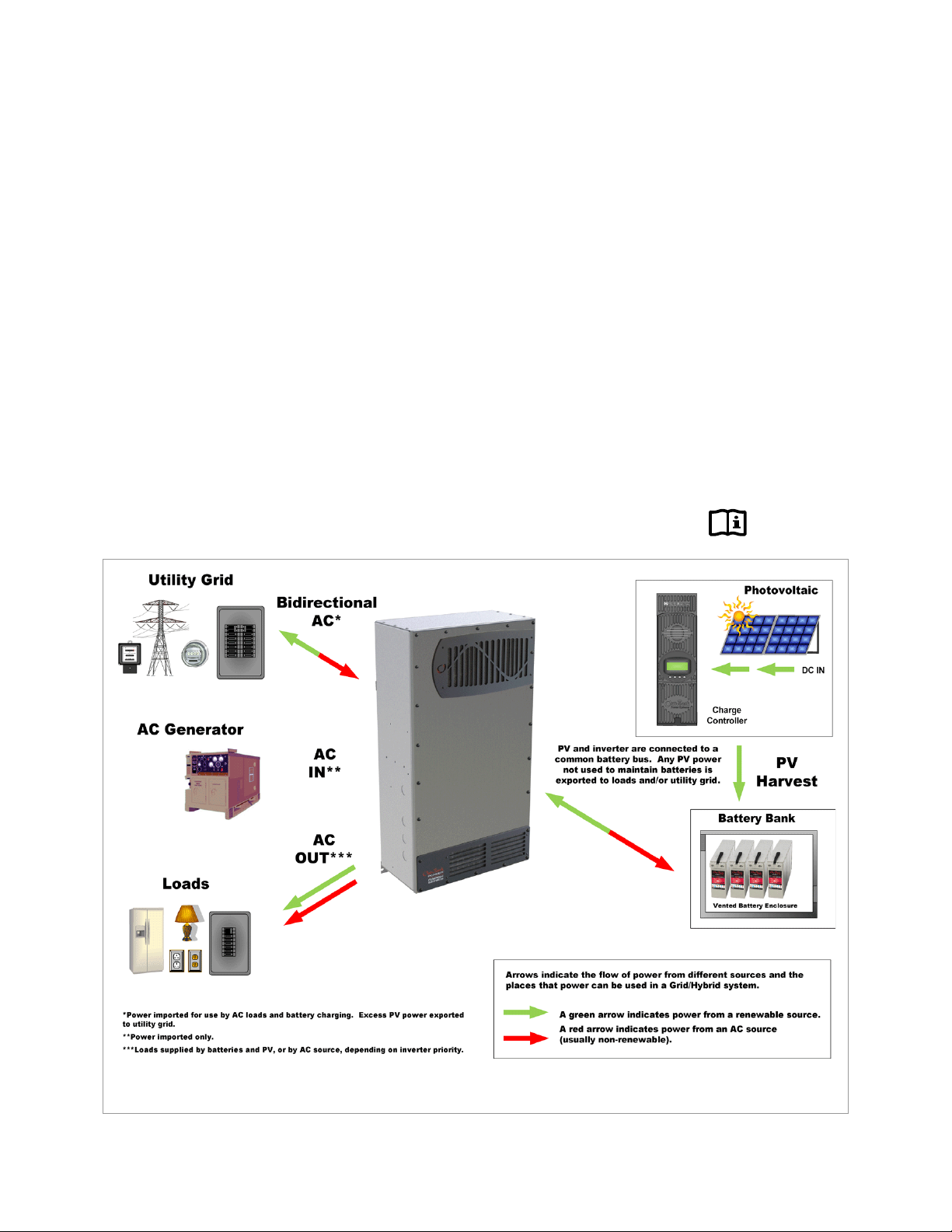
Introduction
IMPORTANT:
Controller. Use of these products is not supported with the Radian Series.
IMPORTANT:
This product is not stackable with the GS8048 inverter. See page 32.
Mounting Bracket
Optional Components for Attachment to Radian Inverter
NOTE: The system display is required if any Radian functions
GSLC
HUB
MATE3 System Display
Components and Accessories
This product is not compatible with the OutBack MATE or MATE2 System Display and
Table 1 Components and Accessories
Included in Box
Radian Series Installation Manual (this book) RTS (Remote Temperature Sensor)
Radian Series Operator’s Manual Hardware Kit
MATE3 System Display and Controller FLEXmax Series Charge Controller
FW-MB3 (MATE3 bracket) FW-CCB or FW-CCB2 (charge controller brackets)
GSLC (GS Load Center) series HUB Series Communications Manager
Communications
Manager
need adjustment from the factory default settings.
Figure 2 Radian Inverter and Accessories
4 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Charge Controllers
Page 7
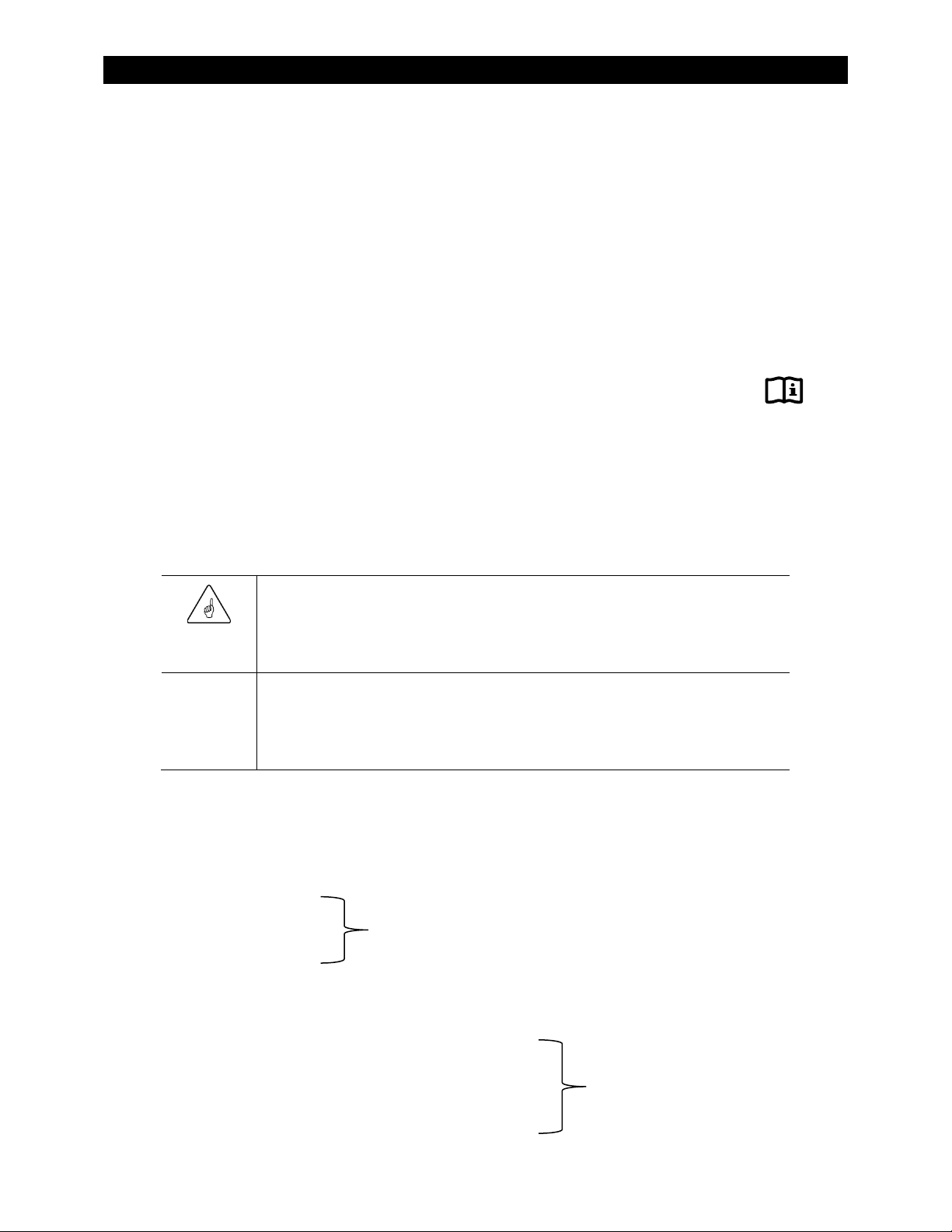
Planning
Applications
The Radian Series Inverter/Charger is intended for both off-grid and grid-interactive (Grid/Hybrid)
applications. It is designed to use a battery bank to store energy. It can work in conjunction with
photovoltaic (PV) modules to harvest solar energy, as well as wind turbines and other renewable
sources. These sources charge the battery, which in turn is used by the inverter.
The Radian inverter has two sets of AC input terminals. Two AC sources, such as a gas or diesel
generator and the utility grid, can be connected to the inverter. Other combinations of AC sources
are possible.
NOTE:
although this can be changed.
The Radian inverter’s settings can be changed to accommodate many applications.
The inverter can only accept one source at a time. The input marked
has priority,
Grid
Figure 3 Applications (Example)
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 5
Page 8

Planning
Input Modes
The Radian inverter has seven modes of operation. These modes determine how the Radian interacts
with an AC source. Each mode has functions and priorities that are intended for a designated
application. Each of the Radian’s two AC inputs can be set to a different operating mode, so that
different applications can be supported.
Generator
imperfect AC waveform. The Radian can charge from the generator even when the generator is undersized
or substandard.
Support
other limitations may require temporary assistance to run very large loads. The Radian adds inverter and
battery power to the AC source to ensure that the loads receive the power they require.
Grid Tied
batteries above a selected “target” voltage, the Radian inverter will send the excess energy to any loads. If
the loads do not use all the excess energy, then the Radian will return (sell) that energy to the utility grid.
UPS
interruption when switching between AC input and batteries. The response speed has been increased so
that if an AC disconnect occurs the response time will be minimized.
Backup
have specialty requirements such as selling or support. The AC source will flow through the Radian inverter
to power the loads unless power is lost. If power is lost, then the Radian inverter will supply energy to the
loads from the battery bank until the AC source returns.
Mini Grid
renewable energy. The system will run off the renewable energy until the battery voltage falls to a specified
low level. When this occurs, the Radian inverter will connect to the utility grid to power the loads. The
Radian inverter will disconnect from the utility grid when the batteries are sufficiently recharged.
Grid Zero:
renewable energy. The system will remain connected to the utility grid, but will only draw power from it
when no other power is available. The default power sources are the batteries and renewable energy, which
attempt to “zero” the use of the AC source. The batteries are discharged and recharged while remaining
grid-connected.
: This mode is intended for a wide range of AC sources, including generators with a rough or
: This mode is intended for systems using the utility grid or a generator. AC source size, wiring, or
: This mode is intended for grid-interactive systems. When renewable energy sources charge the
: This mode is intended for systems primarily intended to maintain power to the loads without any
: This mode is intended for systems that have the utility grid or a generator available, but do not
: This mode is intended for systems that have the utility grid as an input and a sizable amount of
This mode is intended for systems that have the utility grid as an input and a sizable amount of
See the Radian Series Inverter/Charger Operator’s Manual for additional information on these modes,
including the reasons and considerations for using each mode.
Renewable Energy
The Radian Series Inverter/Charger cannot connect directly to photovoltaic arrays, wind turbines,
or other renewable sources. As a required part of a Grid/Hybrid system, the batteries are the inverter’s
primary source of power. However, if the renewable sources are used to charge the batteries, the
inverter can use their energy by drawing it from the batteries.
The renewable source is always treated as a battery charger, even if all of its power is used
immediately. The renewable source must have a charge controller or some way to prevent
overcharging. OutBack Power’s FLEXmax family of charge controllers can be used for this purpose, as
can other products.
The GSLC will receive the mechanical and electrical connections for up to two FLEXmax charge
controllers. It can receive the electrical connections for two FLEXmax Extreme charge controllers.
6 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 9
Planning
IMPORTANT:
factory default settings, may cause the batteries to be undercharged or overcharged.
CAUTION: Hazard to Equipment
product warranty. (Sealed batteries may be an exception.)
Any losses are essentially amp-hour
stem cannot use.
increased to account for losses.
These are the most basic
Battery Bank
When planning a battery bank, consider the following:
Cables:
will determine the placement of the battery bank. Other local codes or regulations may apply and may take
priority over OutBack recommendations.
Battery Type: The Radian inverter/charger uses a three-stage charge cycle.
~ The cycle was designed for lead-chemistry batteries intended for deep discharge. These include
~ Each stage of the charging cycle can be reconfigured or omitted from the cycle if necessary.
~ The Radian inverter/charger is designed to work with a 48-volt battery bank. Before constructing a
Charger Settings and Maintenance:
usually recommended for safety reasons. It may be necessary to use a fan to ventilate the battery enclosure.
Batteries must be regularly maintained according to the instructions of the battery manufacturer.
Recommendations for battery cable size and length are shown on page 20. The maximum length
batteries for marine, golf-cart, and forklift applications. They also include gel-cell batteries and
absorbed glass-mat (AGM) batteries. OutBack Power recommends the use of batteries designed
specifically for renewable energy applications. Automotive batteries are strongly discouraged and will
have a short life if used in inverter applications.
This programming is performed using the system display. The charger can be customized to charge a
wide range of battery technologies including nickel, lithium-ion, and sodium-sulfur batteries.
battery bank, confirm the nominal voltage of individual batteries.
A vented battery enclosure may be required by electric code and is
Bank Size:
accurately as possible, beginning with the items below. This avoids underperformance or wasted capacity.
These ten items are obtainable in different places, summarized in Table 2 on the next page. Some of the
information is specific to the site or application. Some can be obtained from the battery manufacturer.
Information on OutBack products is available from OutBack Power Technologies or its dealers.
A. Size of load:
B. Daily hours of use:
C. Days of autonomy:
D. Application: This often helps define or prioritize the previous three items. Off-grid systems often
require enough capacity to last for an extended period before recharging. Grid-connected systems
frequently need only enough capacity for short-term backup during outages.
E. Conductor efficiency: Wire size and other factors
will waste power due to resistance and voltage drop.
Typical acceptable efficiency is 96 to 99%.
F. Inverter efficiency: Radian specifications list
“Typical Efficiency” to help estimate operating loss.
Battery charger settings need to be correct for a given battery type. Always follow
battery manufacturer recommendations. Making incorrect settings, or leaving them at
Batteries can emit vapors which are corrosive over long periods of time. Installing the
inverter in the battery compartment may cause corrosion which is not covered by the
Battery bank capacity is measured in amp-hours. Determine the required bank specifications as
and essential factors used
capacity that the sy
The battery bank size can be
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 7
Page 10

Planning
G. System DC voltage: The Radian inverter
1) A ÷ [E x F] 1000 ÷ (0.98 x 0.93) = 1097.2 W
Table 2 Battery Bank Elements
Item
Source of information
A. Load Size
Site-specific
B. Daily Hours
Site-specific
C. Days of Autonomy
Site-specific
D. Application
Site-specific
E. Conductor Efficiency
Site-specific
F. Inverter Efficiency
Inverter manufacturer
G. System Vdc
Inverter manufacturer
H. Battery Vdc
Battery manufacturer
I. Capacity
Battery manufacturer
J. Maximum DoD
Battery manufacturer
requires nominal 48 Vdc to operate.
H. Battery voltage: Most individual battery
voltages are less than the system DC voltage.
The batteries need to be placed in series to
deliver the correct voltage.
I. Capacity: Battery capacity, which is measured
in amp-hours, is not usually a fixed number.
It is specified based on the rate of discharge.
For example, the OutBack EnergyCell 200RE is
rated at 154.7 Ahr when discharged at the
5-hour rate (to terminal voltage 1.85 Vpc). This is a high rate of discharge that would hypothetically
drain the battery in 5 hours. The same battery is rated at 215.8 Ahr when used at the 100-hour rate.
Use the appropriate discharge rate (correlated to the expected loads) to measure the capacity of a
battery. Use battery specifications for terminal voltage 1.85 Vpc whenever possible.
J. Maximum depth of discharge (DoD): Most batteries cannot be discharged below a certain level
without damage. The bank requires enough total capacity to keep this from happening.
To Calculate Minimum Battery Bank Size (refer to Table 2 for letter designations):
1. The load size, item A, is measured in watts. Compensate this figure for efficiency loss. Multiply the
conductor efficiency by the inverter efficiency (E x F). (These items are represented as percentages,
but may be displayed as decimals for calculation.) Divide item A by the result.
2. Convert the compensated load into amperes (Adc). Divide the step 1 result by the system voltage
(item G).
3. Determine the daily load consumption in ampere-hours (amp-hours, or Ahr). Multiply the step 2
result by the daily usage hours (item B).
4. Adjust the total for required days of autonomy (the days the system must operate without
recharging) and the maximum DoD. Multiply the step 3 result by C and divide by J.
The result is the total amp-hour capacity required for the battery bank.
5. Determine the number of parallel battery strings required. Divide the Ahr figure from step 4 by the
individual battery capacity (I). Round the result to the next highest whole number.
6. Determine the total number of batteries required. Divide the system voltage by the battery voltage
(G ÷ H). Multiply the result by the step 5 result.
The result is the total required quantity of the chosen battery model.
EXAMPLE #1
A. Backup loads: 1.0 kW (1000 W)
B. Hours of use: 8
C. Days of autonomy: 1
D. Grid-interactive system (GS4048A inverter)
E. Conductor efficiency: 98% (0.98)
F. Inverter efficiency: 93% (0.93)
G. System voltage: 48 Vdc
H. Batteries: OutBack EnergyCell 220GH (12 Vdc)
I. Capacity at 8-hour rate: 199.8 Ahr
J. Maximum DoD: 80% (0.8)
8 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
2) 1 ÷ G 1097.2 ÷ 48 = 22.9 Adc
3) 2 x B 22.9 x 8 = 182.9 Ahr
4) [3 x C] ÷ J [182.9 x 1] ÷ 0.8 = 228.6 Ahr
5) 4 ÷ I 228.6 ÷ 199.8 = 1.14 (rounded to 2)
6) [G ÷ H] x 5 [48 ÷ 12] x 2 strings = 8 batteries
Page 11
Planning
EXAMPLE #2
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
1) A ÷ [E x F] 1750 ÷ (0.97 x 0.93) = 1939.9 W
A. Backup loads: 1.75 kW (1750 W)
B. Hours of use: 8
C. Days of autonomy: 2
D. Off-grid system (GS4048A inverter)
E. Conductor efficiency: 97% (0.97)
F. Inverter efficiency: 93% (0.93)
G. System voltage: 48 Vdc
H. Batteries: OutBack EnergyCell 200RE (12 Vdc)
I. Capacity at 8-hour rate: 167.5 Ahr
J. Maximum DoD: 50% (0.5)
2) 1 ÷ G 1939.9 ÷ 48 = 40.4 Adc
3) 2 x B 40.4 x 8 = 323.3 Ahr
4) [3 x C] ÷ J [323.3 x 2] ÷ 0.5 = 1293.3 Ahr
5) 4 ÷ I 1293.3 ÷ 167.5 = 7.7 (rounded to 8)
6) [G ÷ H] x 5 [48 ÷ 12] x 8 strings = 32 batteries
Generator
These Radian models can work with any “split-phase” generator that delivers reliable AC power at the
appropriate voltage and frequency. They cannot work with a single-phase or three-phase generator.
Use of a three-phase generator with this equipment may damage either the inverter or
the generator. This damage to the inverter is not covered by the product warranty.
The Radian inverter/charger can provide a start signal to control an automatic start generator. If automatic
generator starting is required, the generator must be an electric-start model with automatic choke. It
should have two-wire start capability. For other configurations, additional equipment may be required.
In any configuration, the inverter may need to be programmed using the system display.
Perform all programming according to the specifications of the generator and the required operation of the
inverter. Parameters to be programmed may include generator size, automatic starting requirements, and
potential fluctuations in generator AC voltage.
Generator Sizing
A generator should be sized to provide enough power for all the loads and the battery charger.
Available generator power may be limited by ratings for circuit breakers and/or generator connectors.
The maximum allowed AC circuit breaker size is 50 Aac per Radian inverter/charger.
The generator must be able to provide current to all inverters. Minimum generator wattage
recommended to be twice the wattage of the inverter system. Many generators may not be able to
maintain AC voltage or frequency for long periods of time if they are loaded more than 80% of
rated capacity.
A generator that is to be installed in a building usually should not have a bond between the neutral and
ground connections. The generator should only be bonded if there is a specific need. Installations in North
America are expected to bond the neutral and ground at the main electrical panel. See page 22 for more
information on neutral-ground bonding.
1
is usually
1
This is the wattage value after deratings for the following: peak versus continuous power, load power factor considerations,
fuel type, altitude, and ambient temperature.
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 9
Page 12

Planning
WARNING: Shock Hazard or Equipment Damage
inappropriate places. This could create an electric shock hazard or damage the equipment.
AC Source
AC Loads
GSLC Bypass
Inoperative
Inverter
Input Wiring
Output Wiring
AC Source
AC Loads
Output Wiring
Inactive Radian Inverters
GSLC Bypass Devices
(not to be used)
External Bypass Device
Input Wiring
Maintenance Bypass Switching
Inverter systems are often equipped with AC maintenance bypass switches or interlocks. If the
inverter system ever needs to be shut down or removed, the AC sources and loads must be
disconnected. A bypass device allows the AC source to deliver power directly to the loads, bypassing
the inverter. This can minimize disruption to the system and avoids the need for extensive rewiring.
Radian
Figure 4 Bypass Switching
The GS Load Center (GSLC) can be equipped with bypass circuit breakers for this purpose. However, if
multiple Radian inverters are stacked in a single system, then the GSLC bypass kits should not be used.
The bypass function must be simultaneous for all inverters. The GSLC bypass kits operate
independently, not simultaneously.
Both manual and automatic double-throw bypass switches are commonly available in a range of sizes
and options. These are highly recommended for systems with more than a single inverter.
Using independent bypass devices on multiple inverters can result in power being routed to
Figure 5 Bypass Switching for Multiple Inverters
10 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 13

Installation
Enclosure Height 28” (71.1 cm)
Mounting Hole Spacing 1.97" (5.0 cm)
Enclosure
Height with
Flange
29.1” (74 cm)
Width 16” (40.6 cm)
Depth
The dimensions of an assembled system with mounting plate and GSLC are shown on the next page.
Location and Environmental Requirements
Radian Series Inverter/Chargers must be located in a weather-proof enclosure or enclosed area. It is
not designed for exposure to water or excessive wind-blown dust and debris. It carries an Ingress
Protection (IP) rating of 20 and a Relative Humidity (RH) rating of 93%.
The Radian inverter must be wall-mounted in an upright position. The inverter is not approved for
mounting in any other position or orientation.
Recommended minimum clearance is 2 to 4 inches (5 to 10 cm) for the front and top of the inverter.
The sides and bottom may be enclosed or obscured with no restriction when mounting accessory devices or
one other Radian inverter. If more than two Radian inverters are installed side by side with the GSLC, the
inverters should be separated by at least 0.9 inches (2.3 cm) to accommodate the GSLC hinged doors.
The Radian inverter will function best if operated in a temperature range of -4°F to 77°F (–20°C to 25°C). At
temperatures up to 122°F (50°C), all inverter components meet their specifications, but the inverter’s power
is derated. It can function in environments as cold as –40°F (–40°C) and as warm as 140°F (60°C), but it may
not meet all component specifications. This temperature range also applies to storage.
The specifications are listed in the Radian Series Inverter/Charger Operator’s Manual.
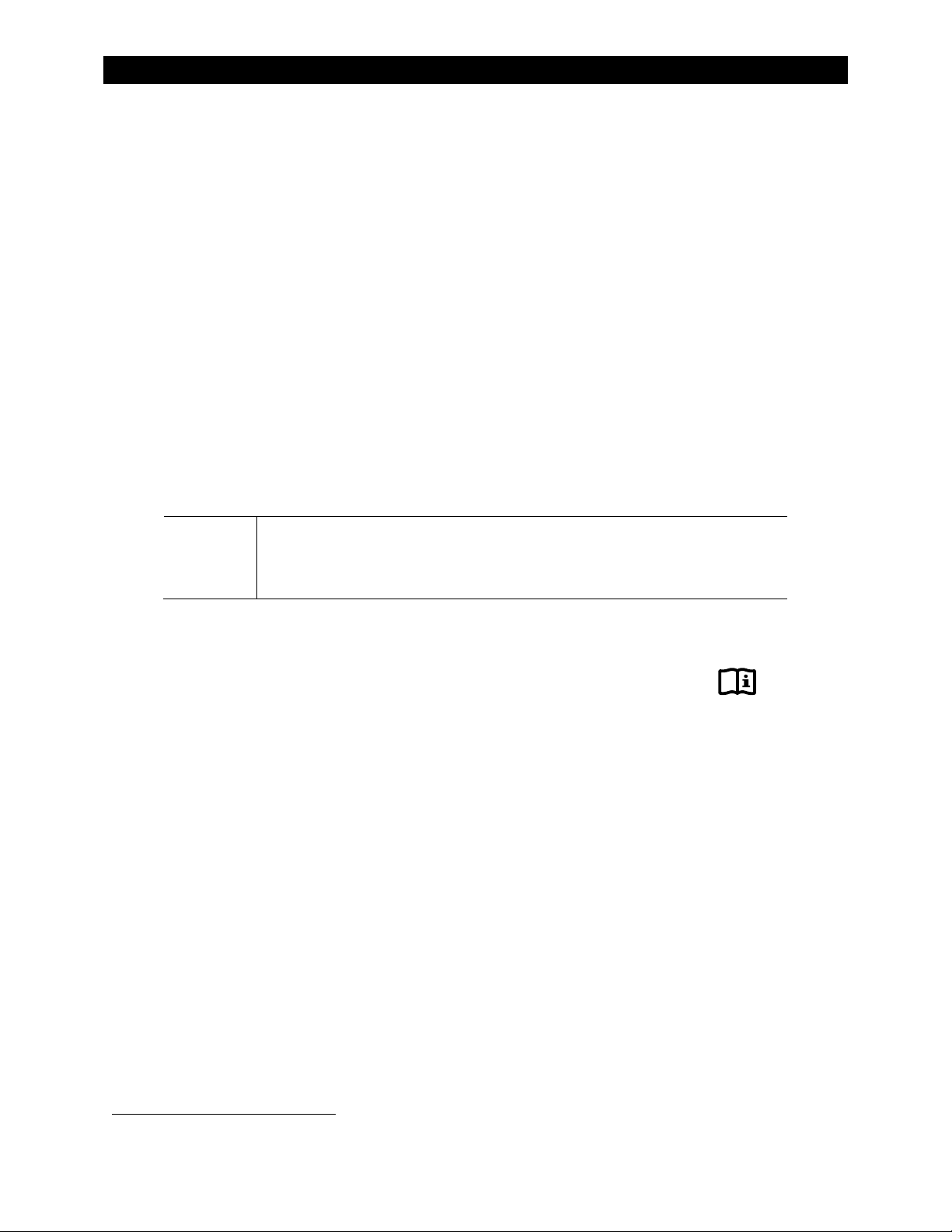
Dimensions
8.75"
(22 cm)
Figure 6 Dimensions
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 11
Page 14
Installation
Width 16.0” (40.6 cm)
0.45” (1.1 cm)
0.45” (1.1 cm)
13.7”
28”
29.0”
12.5”
45.0”
8.75”
(22.2 cm)
14.0” (35.6 cm)
This illustration can be used as a
(114.3 cm)
(71.1 cm )
(73.7 cm)
(31.8 cm)
basic template for planning layouts,
marking mounting holes, etc.
when installing a system.
12 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
The requirements for mounting the
Radian inverter are described
beginning on the next page.
Figure 7 System Dimensions
Page 15
Installation
IMPORTANT:
with inadequate fasteners.
The Radian inverter is mounted using these
Continued on the next page…
16.0” (40.6 cm)
Mounting Plate
8.0” (20.3 cm)
4.1”
5.0”
(12.7 cm)
Insulated screwdriver set; should include
DVM or Voltmeter
Tools Required
The following tools may be required for this installation:
Wrench and socket sets; should include torque and ratchet
wrenches; also reversible (stubby) wrenches for narrow access
Wire cutters/strippers
a #2 Phillips screwdriver 15 to16” long
Long-nose pliers
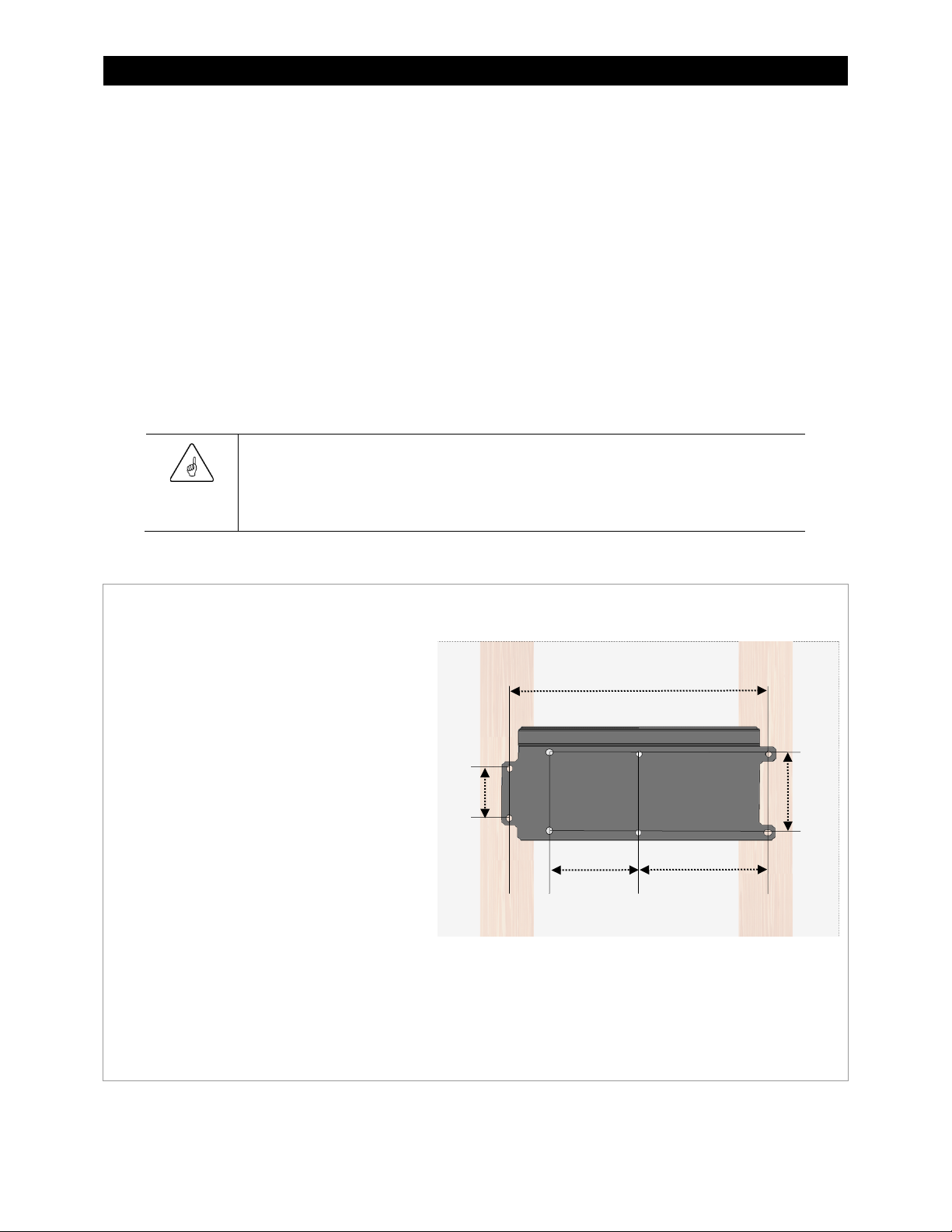
Mounting
Two or more people may be needed to install the Radian inverter/charger due to its weight.
Mount and secure each component before attaching any wiring. Local or national wiring codes may require
the bottom of the inverter to be enclosed. The GS Load Center was specifically designed for this purpose.
Avoid large air gaps behind the Radian inverter/charger and its mounting plate. These can result in louder
mechanical noise during heavy inverting or charging. Mount the plate on a flat, solid mounting surface.
Use correct fasteners to secure the mounting plate and the Radian inverter/charger to the
mounting surface. OutBack cannot be responsible for damage to the product if it is attached
The Radian inverter/charger comes equipped with a mounting plate, as shown in Figure 8.
steps.
1. The mounting plate is to be screwed or
bolted directly to a solid mounting surface
such as wall studs. (See Figure 8.) Lag
screws are provided for this purpose.
~ The plate is designed to mount on wall
studs with a spacing of 16” (40.6 cm).
If the studs have a different spacing,
plywood or similar material should be
installed over the studs. This material
should be1/2” size or thicker. The
mounting plate can be installed on the
plywood surface.
~ If multiple Radian inverter/chargers are
being installed, all mounting plates
should be installed first. The inverters
can be mounted and secured one at a
time when this is done.
(10.4 cm)
6.0” (15.2 cm)
Figure 8 Installing the Mounting Plate
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 13
Page 16

Installation
Radian Inverter
Mounting Plate
mounting flange may be used.
2. Place the Radian inverter against the wall and slide it
directly over the upper lip of the mounting plate. The
WARNING: Shock Hazard
chassis may involve metal-to-metal contact or separate ground wires.
…continued from the previous page…
inverter’s mounting flange should come to rest within the
lip so that it hangs securely.
To assist in alignment, dimples have been placed on the
side of the unit to mark the lower edge of the flange. In the
picture to the left, the two X symbols show the location of
the dimples.
3. Align the left edge of the inverter with the left edge of the
mounting plate. This will expose the right edge of the plate,
allowing easy installation of another Radian inverter/charger in
the future. All additional inverters are mounted to the right of
the existing unit.
The unit shown to the right is not aligned with the mounting
plate, as the plate is still visible. In this example, it should slide
to the left so that the plate is entirely covered.
NOTE: If the GS Load Center is used with the Radian inverter,
the following step should be omitted.
4
. Once aligned, secure the Radian inverter to the stud using a lag
screw (provided) in the left corner of the inverter’s bottom
flange. Securing the inverter this way will prevent it from
dislodging from the mounting plate in the event of an
earthquake or similar event.
NOTE: The left corner is used for securing the inverter to a stud.
If the Radian inverter is mounted on plywood or a similar
wide-area mounting surface as shown, any of the slots in the
When the inverter is used with other metal chassis, make sure that all chassis are
grounded appropriately. (See the grounding instructions on page 18.) Grounding other
14 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Figure 9 Mounting the Inverter
Page 17

Installation
For the FLEXmax charge controller:
For the MATE3:
To fit on the
left side, the MATE3 requires
the FW
b
the upper and lower left side
to attach the FW
more information, see the
FW
For the HUB:
To fit on the
the HUB uses two mounting holes and
three knockouts.
NOTE: The OutBack FLEXmax Extreme should be installed on the wall to either side of the
Component Mounting
The top of the GS Load Center (GSLC) connects to the
bottom of the Radian inverter using four keyhole slots. The
keyhole slots fit over four screws on the bottom of the inverter
that secure the GSLC to the inverter when they are tightened.
(The long screwdriver recommended on page
13 may
be needed to reach these screws.) The GSLC should
be secured to the wall using screws or wall anchors.
The GSLC also makes a mechanical connection to the
Radian using bus bars that bolt to the inverter’s DC
terminals. Other connections are wired as necessary.
Several system components can mount directly onto the Radian
inverter or the GSLC. The MATE3 System Display and the HUB
Communications Manager can easily be mounted on the left side
of the system. Up to two FLEXmax 60 or 80 charge controllers can
be mounted on its right side.
: The FLEXmax controller requires mounting brackets
NOTE
(see below). The conduit provided with these brackets is long
enough to wire the FLEXmax directly to the GSLC. Additional
conduit may be necessary when mounting on the inverter. The
image on the right shows GSLC mounting. See Figure 2 on page 4
for other configurations.
Radian inverter’s
-MB3 mounting
racket. Holes are provided on
-MB3. For
-MB3 instruction sheet.
Radian inverter’s left side,
GSLC for direct wiring access and does not require additional brackets.
Figure 10 Mounting for System Components
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 15
To fit on the Radian inverter’s right side, the FLEXmax
charge controllers require the FW-CCB or FW-CCB2
mounting brackets. To accommodate many possible
mounting requirements, four sets of mounting holes
have been provided for the brackets.
Page 18

Installation
Removing Front Cover
Cover
Plate
Plate
The front cover must be removed in order to access the Radian inverter’s AC terminals and other
connections. These include the Remote and Batt Temp ports, as well as several sets of auxiliary
terminals.
Twenty-two machine screws are located around the perimeter. Remove these screws with a #2
Phillips screwdriver. Once they are removed, the cover can be lifted off.
: The screws which secure the plastic plates to the cover do not need to be removed.
NOTE
Screws
Screws
(x22)
NOTE:
initial installation. The remaining screws are included in the hardware kit.
16 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Screws
Figure 11 Removing the Front Cover
The Radian inverter may ship with only a few screws installed to make it easier to perform the
Page 19

Installation
WARNING: Shock Hazard and Equipment Damage
handling. This damage is not covered under the unit’s warranty.
12V AUX: Delivers 12 Vdc up to
0.7
be switched on and off for many
functions. See page 26 for details.
SWITCH INV eceives wires for a
manual
inverte
NOTE:
overrides these terminals when installed.
(See above.)
RELAY AUX: Relay contacts with no
voltage (
The relay can be
many functions. See page 26 for details.
ON/OFF INV JUMPER (J3): Overrides the
DC TERMINALS Connects to the battery cables and DC system. There are
two DC
requires separate cables and separate overcurrent protection. See page
for instructions.
RIBBON CABLES Connects the Radian’s power
modules and control board. See Warning below.
The functions for each set of AUX contacts can be programmed
using the system di
Terminals and Ports
positive and two DC negative terminals. Each DC positive terminal
20
10 amps at 250 Vac or 30 Vdc).
switched on and off for
splay.
amps (8.4 watts). The output can
Figure 12 DC Terminals, Ribbon Cables, and Auxiliary Terminals
It may be necessary to remove the ribbon cables in the course of servicing the Radian. (This is detailed in
the Radian service manual.) The cables must never be removed until all power has been disconnected from
the Radian for a minimum of one minute. If the cables are removed prematurely, the Radian’s capacitors
will retain a sizable charge, which can cause electrical shock or severe equipment damage during normal
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 17
SWITCH INV terminals when installed. When
installed, the inverter is ON. The ON or OFF
states can then only be controlled by the MATE3.
NOTE: J3 is installed to the ON position during
manufacture, but the Radian inverter is given an
external OFF command at the same time. Its
initial state will be OFF.
on/off switch to control the
r. See page 25 for instructions.
The ON/OFF INV jumper (J3)
Page 20

Installation
WARNING: Shock Hazard
Manual for the shutdown procedure before removing the covers.
AC TERMINAL BLOCK
REMOTE and BATTERY TEMP
CONTROL WIRING TERMINAL
BLOCK
variety of functions
ge
terminal descriptions.
GROUND BUS
: Receives control wires for a
nerator control. See facing page for
Receives AC input wires
for two input sources (L1,
L2, and neutral for each).
Also receives AC output
wires (L1, L2, and neutral).
All neutral wires are
electrically common. See
page
, including
22 for instructions.
PORTS: Receive the RJ45 and
RJ11 plugs from the MATE3
system display and Remote
Temp Sensor. See page
instructions.
25 for
Figure 13 AC Terminals, Ports, and Ground Bus
18 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
After installation, do not remove the covers while the inverter has any source of power. See the Operator’s
Receives ground wires
from multiple
locations. See page
for instructions.
19
Page 21

Installation
Wiring
WARNING: Shock Hazard
WARNING: Shock Hazard
GSLC is also equipped with its own bond, which may need to be removed.)
IMPORTANT:
discussed extensively.
The inverter’s ground terminal bus bar (TBB) may be used for
It will be necessary to remove knockouts from the chassis to run wires. Bushings are included with the
hardware kit to protect the wires. Make sure to install these bushings in the holes.
Use copper wire only. Wire must be rated at 75°C or higher.
Grounding
This unit meets the IEC requirements of Protection Class I.
The unit must be connected to a permanent wiring system that is grounded
according to the IEC 60364 TN standard.
The input and output circuits are isolated from ground. The installer is responsible
for system grounding according to all applicable codes.
For safety, the neutral and ground conductors should be mechanically bonded.
OutBack does not bond these conductors within the inverter. Make sure that no
more than one bond is present in the AC system at any time. Some codes require
the bond to be made at the main panel only.
The GS Load Center (GSLC) is equipped with a neutral-ground bond. If bonding is
required to be in another location, the bond in the GSLC may need to be removed.
For all installations, the negative battery conductor should be bonded to the grounding
system at only one point. If the OutBack GFDI is present, it can provide the bond. (The
Most OutBack products are not designed for use in a positive-grounded system. If it is
necessary to build a positive-grounded system with OutBack products, contact OutBack
Technical Support at
online forum at
+1.360.618.4363
www.outbackpower.com/forum/
Table 3 Ground Conductor Size and Torque Requirements
Terminal Location Minimum Conductor Size Torque Requirements
Ground TBB
making all ground connections to other parts of the system.
Examples include inverter equipment grounding, generator
grounding, load panel grounding, and main earth ground
wire. When the GSLC is used, make a connection from the
inverter to the ground TBB in the GSLC.
This TBB accepts up to #4 AWG (0.033 in²) or 25 mm² wire.
#8 AWG (0.013 in²) or 10 mm² 25 in-lb (2.8 Nm)
before proceeding. Additionally, consult the
, where this subject has been
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 19
Figure 14 Chassis Ground TBB
Page 22

Installation
DC Wiring
WARNING: Shock Hazard
Use caution when working in the vicinity of the inverter’s battery terminals.
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
Never reverse the polarity of the battery cables. Always ensure correct polarity.
CAUTION: Fire Hazard
See the hardware diagrams on page 21.
IMPORTANT:
IMPORTANT:
The terminals on the right
must not
be connected to battery power.
The Radian inverter has four battery cable terminals, two positive
and two negative. Each terminal is a threaded hole which accepts
a hex bolt (provided). Notes on assembly and cabling are shown
on the next
GS8048A
GS4048A
The installer is responsible for providing overcurrent protection. Install a
The DC terminals must be encased in an enclosure to meet NEC requirements.
Table 4 contains OutBack’s recommendations for minimum cable sizes. Other
circuit breaker or overcurrent device on each DC positive (+) conductor to
protect the DC system.
Never install extra washers or hardware between the mounting surface
and the battery cable lug. The decreased surface area can build up heat.
The GS Load Center (GSLC) meets this requirement.
codes may supersede OutBack’s requirements. Consult local codes for final
size requirements.
page.
The Radian GS8048A contains two internal power modules, each with its own
set of DC terminals. Both sets of terminals
power for the inverter to work correctly.
The Radian GS4048A contains a single power module which occupies the
space on the left. Although it has two pairs of terminals, only the pair on the
left is functional. The battery cables must be connected to these terminals.
be connected to battery
must
Figure 15 GS8048A and GS4048A Battery Terminals
20 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 23

Installation
Table 4 DC Conductor Size and Torque Requirements
GS8048A
104
2/0 AWG 0.105 in²) or 70 mm²
175 Adc/AIC 10kA
104
If the battery cables are connected directly to the Radian
All GSLC models connect the battery negative cables to the shunt, which is threaded for 3/8” bolts. See image D.
Battery Cable
Flat Washer
M8-1.25 Hex Bolt
Mounting
Lock Washer
Battery
M8-1.25 Hex Bolt
Lock Washer
Flat
DC
Positive
Nut
Flat Washer
GS-SBUS
Battery
Cable Lug
Flat Washer
Lock Washer
Shunt
DC Disconnect
Battery
Battery Monitor
Ring Terminal
Charge
Flat Washer
Lock Washer
Nut
M8 Stud
A
3/8” Hex Bolt
Inverter Nominal DC Amps
(Minimum, per breaker)
(Derated 125%)
GS4048A
Conductor Size
(Minimum, per breaker)
2/0 AWG 0.105 in²) or 70 mm² 175 Adc/AIC 10kA
Breaker Size
Terminal Location Torque Requirements
Inverter DC Terminals 60 in-lb (6.9 Nm)
When installing DC cables:
Make certain DC circuit breakers are turned to the off position, or fuses are removed, before proceeding.
Battery positive (+) and negative (–) cables should not exceed 10 feet (3 m) each to reduce voltage loss and other effects.
The modular construction of the GS8048A requires the use of two DC circuit breakers or fuses.
The cables for each overcurrent device must
Install all overcurrent devices on the positive cable.
Tie, tape, or twist positive and negative cables together to reduce self–inductance. Run positive and negative cables
NOTE
all cases the battery cable lug must be the first item installed. It must make solid contact with the surface.
Battery Terminals See battery manufacturer’s recommendations
be sized appropriately. Alternately, a single cable or bus may be used
each
if sized to the minimum total ampacity. The cables listed above are for each inverter in a system. In a multiple-inverter
system, each inverter requires its own cables and overcurrent devices of the size indicated.
through the same knockouts and conduit.
: Do not install hardware in a different order from the illustrations shown in
Error! Reference source not found.
. In
inverter, the hardware should be arranged as shown in image A.
The inverter’s battery terminal is a threaded hole which accepts
a hex bolt (provided). The battery cable lug must have a
0.79 cm (5/16") diameter hole.
If the inverter is installed with the GS Load Center (GSLC),
follow GSLC instructions for cable and hardware installation.
The hardware should be arranged according to the appropriate image below.
GSLC models used with the GS8048A inverter are equipped with a DC positive (+) plate. The plate accepts an M8 hex
bolt and nut. See image B.
GSLC models used with the GS4048A inverter do not use the DC positive plate. The cable lugs are connected to the
DC disconnect, which uses a threaded M8 stud. See image C.
Cable Lug
Controller Ring
Terminal
Surface
Lug
Cable Lug
(+) Plate
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 21
Figure 16 DC Cable Hardware (Radian inverter)
Page 24

Installation
AC Wiring
WARNING: Shock Hazard
WARNING: Fire Hazard
connected.
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
power source.
IMPORTANT:
maximum size to meet NEC or other code requirements.
AC Out
(L1, L2, Neutral)
Grid In
(L1, L2, Neutral)
Generator In (L1, L2, Neutral)
The neutral and ground conductors should be mechanically bonded.
Do not install the GS4048A using a load center that has multiwire branch circuits
The Radian inverter cannot be connected to a three-phase source (utility grid or
generator). The L1 and L2 inputs cannot be connected to two lines of a three-phase
The installer is responsible for providing overcurrent protection. The AC input and
output must be protected with branch-rated circuit breakers of up to 50 Aac
Ensure there is no more than one AC neutral-ground bond at any time.
Local or national codes may require the bond to be made at the main panel
only. The GS Load Center (GSLC) is equipped with its own bond, which may
need to be removed.
All system wiring must comply with national and local codes and regulations.
The Radian inverter/charger’s AC terminal block has nine positions for AC wires. The minimum
2
recommended wire size is #8 AWG (0.013 in
specific conditions. The largest size that can be used with the terminals is #6 AWG (0.021 in
2
16 mm
wire.
) or 10 mm2. Larger wire gauges may be required for
2
) or
The inverter makes its AC connections using spring-loaded clamps. It is necessary to strip
approximately ½ inch (1.3 cm) of insulation from the end of each wire. Other tools are not required.
22 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Figure 17 AC Terminals
Page 25

Installation
WARNING: Shock Hazard
Operator’s Manual for more information.
The terminals labeled L1 and
L2 GRID
are used to connect to the two utility grid “hot” wires. The L1
and L2 wires are usually black and red respectively, and read 120 Vac each when measured with
respect to neutral. In a standard service, L1 and L2 are 180 degrees out of phase and should read 240
Vac when measured from one to the other.
The L1 and
L2 GEN
terminals are used to connect to the “hot” wires on a 120/240 Vac generator.
Three neutral (N) terminals are available. These terminals are electrically common. Any of them can
be used to connect to neutral wires from various parts of the system. The most common connections
are to the neutral bus on the main panel or utility grid service, the neutral bus on the output load
panel, the neutral bus in the GSLC, and the neutral wire from a generator.
The Radian can accept input voltages that range between (nominal) 100/200 Vac and 120/240 Vac
(split-phase only). The range of input acceptance may need to be adjusted to the nominal voltage of
the system so that inappropriate voltages are not accepted.
The AC source(s) can power both battery charger and loads if sized correctly. Use the source
amperage and the charger size to determine actual maximum draw. Size the input circuit breakers
according to these specifications.
The terminals labeled
are used to connect the Radian inverter to the load circuits. These
OUT
terminals also transfer power from an input source if it is available. (See the next page.) Size the load
circuit breakers accordingly.
A Ground Terminal Bus Bar (TBB) is also available if multiple ground connections are needed (see
Figure 14 on page 19).
During an error shutdown, the inverter’s output terminals are not live. However,
if the inverter recovers from a shutdown, the terminals will become live without
notice. Several error shutdowns can be recovered automatically, including
Battery V, High Battery V
section and the list of error messages in the Radian Series Inverter/Charger
, and
Over Temperature.
Low
See the Troubleshooting
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 23
Page 26

Installation
AC Sources
IMPORTANT:
The inverter’s transfer relay is normally set to provide inverter power to the output.
The conditions for AC acceptance are defined by the inverter’s programmed settings and AC input
mode. The relay will switch to transfer the AC source power to the output when the AC acceptance
conditions are met.
The Radian inverter has connections for two AC sources,
(generator) and
GEN
GRID
, for ease of
installation. Each source is transferred with a separate relay. However, internally it can only connect
to one AC source at a time. It cannot use both utility grid and generator power at the same time. If
presented with two sources of power, the default setting is to accept the source connected to the
terminals. The source priority can be changed using the system display.
GRID
NOTE:
The terminals are labeled due to common conventions, not inverter requirements. The
GEN
terminals can accept grid power if necessary. The opposite is also true. Each input can accept any AC
source as long as it meets the requirements of the Radian and the selected input mode, with the
following exception.
The generator must be connected to the
MATE3’s Advanced Generator Start (
auxiliary function. If the input priority is set to
energized, an automatically controlled generator will shut down. This prevents an
automatic generator from working correctly when using the
: If an AC source is present on the priority input, the second input cannot accept another source
NOTE
AGS
for any reason. This is true even if the inverter has not accepted the priority source. The behavior is
the same whether the first source was rejected for quality issues or because of programmed settings.
In Figure 18, the arrow between the output neutral and ground wires indicates that these two wires
have been bonded together, usually at the main electrical panel. Only one bond should be made
between neutral and ground at any time. See pages 19 and 22. If a generator is present in a
permanent installation, the generator’s neutral and ground should be isolated.
terminals if using either the
GEN
) function or the Radian’s
and the
GRID
GRID
GRID
GenAlert
terminals are
terminals.
24 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Figure 18 AC Sources
Page 27

Installation
Accessory Wiring
RTS cable
telephone)
The upper board has ports for both the
See the Operator’s Manual
MATE3 or HUB cable
CAT5 non-crossover)
System Display
port
RTS port
MATE
port
Additional
Ports
When a HUB Communications Manager occupies the inverter’s Remote
The
ON/OFF INV
jumper bridges two pins. This jumper (J3) parallels the
Jumper On
Jumper Off
ON/OFF INV
Remote Temperature Sensor (RTS) and the
system display. The system display port is
labeled Remote. The RTS port is labeled
Battery Temp.
If a HUB Communications Manager is in use, it
occupies the inverter’s Remote port. The
system display plugs into the HUB product.
(RJ11, 4-conductor,
(RJ45, 8-conductor,
port, the system display connects directly to the HUB’s MATE port.
Inverters connect to communications manager ports 1 and above.
Charge controllers and other devices connect to additional ports after
the last inverter is connected. See Stacking on page 27 for information
on connecting inverters.
Figure 19 Accessory Connections
two
Switch INV
connections is closed, the inverter is on. (Although the jumper is
factory-installed to the on position, the inverter is given an off command
before leaving the factory and will initially be off.)
If the Radian is inverting, removing the
terminals on the terminal block. If either set of
jumper will turn it off. To remove the
jumper, use long-nose pliers or a
similar tool.
for functional information on the RTS.
Once the plastic
has been removed, the Switch INV
terminals on the terminal block can be
used to wire a manual on/off switch.
These terminals can also be used to
control an Emergency Power Off (EPO)
device instead of a standard switch.
Figure 20 ON/OFF Jumper and Connections
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 25
jumper
Page 28

Installation
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
lack of protection is not covered by the Radian warranty.
12V AUX
Fan
AUX Wiring
The Radian inverter has two sets of terminals which can respond to different criteria and control many
functions. These include cooling fans, vent fans, load diversion, fault alarms, and the Advanced
Generator Start (AGS) function.
The
12V AUX
terminals are a switched 12 Vdc power supply. They can control any of the Auxiliary
Output functions available in the system display (MATE3).
The
12V AUX
terminals can supply up to 0.7 amps at 12 Vdc (8.4 watts). This is sufficient to drive a
small fan or a relay controlling a larger device. The terminals accept wire up to #14 AWG (0.0032 in²) or
2.5 mm². This circuit contains electronic overcurrent protection, which resets after being overloaded.
No additional fuses are required for the 12V AUX terminals.
The
RELAY AUX
terminals are “dry” relay contacts with no voltage. Their most common function is to
serve as a switch for the start circuit of an automatic generator using the generator control functions.
However, they can be programmed for other auxiliary functions as well. These terminals can conduct
up to 10 amps at up to 30 Vdc or 250 Vac.
This circuit has no overcurrent protection. A fuse of no larger than 10 amps must
be installed to protect the circuit. Since the internal circuitry of the
terminals does not incorporate overcurrent protection, it is the responsibility
AUX
of the installer to ensure the circuit is protected. Internal failure that results from
RELAY
Each set of terminals has its own set of programmed criteria.
NOTE:
independent functions. For example, the
while the
The menus for each set of terminals have identical options available, but can control
terminals can be used for generator control,
12V AUX
RELAY AUX
terminals can simultaneously be used to control a vent fan in the battery box.
The control logic for the terminals is not always located in the same device. Radian Auxiliary functions
are located within the inverter itself and are described with other inverter functions. Although
inverter-based functions require the system display for programming, they will function even if the
display is removed. However, AGS programming is located within the system display and will not
work if the display is removed. Other devices may also be able to control the terminals.
For generator control, see page 27.
In this example, the
drive a 12-volt vent fan. The + and – wires on the
fan are connected to the AUX terminals.
NOTE: If another device is used, such as a larger
fan, it must not draw more than 0.7 amps.
terminals directly
Figure 21 AUX Connections for Vent Fan (Example)
26 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 29

Installation
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
lack of protection is not covered by the Radian warranty.
In this example, the 12V AUX terminals drive a
relay that diverts wind power. The relay’s coil is
Relay
Element
Turbine
NOTE: Relays and elements shown are examples only
connected to the 12V AUX terminals. When the
AUX function closes the relay (based on battery
voltage), the relay diverts the excess wind power
to a water heating element.
and may vary depending on the installation.
Figure 22 AUX Connections for Diversion (Example)
Generator Control
Either set of Radian AUX terminals can provide a signal to control an automatic-start generator.
The control function can be
Advanced Generator Start
AGS can start the generator using settings from the system display, or it can use battery readings from
the FLEXnet DC battery monitor. Alternately, the control function can be
function based directly in the Radian inverter.
The choice of control function depends on system needs and the capabilities of each device.
The generator must be an electric-start model with automatic choke. It is recommended to have
“two-wire” start capability.
The
RELAY AUX
terminals can most easily perform two-wire generator start. A two-wire-start
generator is the simplest type, where the cranking and starting routine is automated. It usually has a
single switch with two positions that is turned ON to start, OFF to stop.
Two-Wire-Start (RELAY AUX Terminals)
The
RELAY AUX
This method is only advised if the generator’s starting circuit is triggered by continuity. (This circuit
must use fewer than 10 amps.)
terminals can be wired in place of the generator’s start switch as shown in Figure 23.
(AGS), which is situated in the system display.
Gen Alert
, which is a simpler
This circuit has no overcurrent protection. A fuse of no larger than 10 amps must
be installed to protect the circuit. Since the internal circuitry of the
terminals does not incorporate overcurrent protection, it is the responsibility of
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 27
the installer to ensure the circuit is protected. Internal failure that results from
RELAY AUX
Page 30

Installation
Starting
Switch
Two-Wire-Start
Generator
Starting
Generator
Battery
Relay
Relay
Two-Wire-Start
12V AUX Terminals
In other cases, or in the case of a three-wire-start generator, the inverter should use the
12V AUX
terminals instead, in conjunction with a three-to-two wire converter. (See pages 28 and 29.)
Figure 23 Two-Wire Generator Start (RELAY AUX)
Two-Wire-Start (12V AUX Terminals)
The 12 Vdc signal provided by the
12V AUX
signal. It is not usually recommended to connect the
use the
12V AUX
terminals to energize the coil of a 12 Vdc automotive or similar relay.
terminals can be switched on and off to provide a start
terminals directly to the generator, but to
AUX
The OutBack FLEXware Relay Assembly depicted in Figure 24 is sold for this purpose. The relay
contacts can serve in place of the generator’s start switch. The battery shown below is depicted for
clarity. Usually it is part of the generator’s internal starting circuit and is not an external component.
The drawing below is one example of a possible arrangement. Specific arrangements, relays, and
other elements depend on the requirements of the installation and of the generator.
Coil
Contacts
Terminals
Generator
28 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Figure 24 Two-Wire Generator Start (12V AUX)
Page 31

Installation
Atkinson
GSCM-Mini
Three-Wire-Start
12V AUX Terminals
Three-Wire-Start
A “three-wire-start” generator has two or more starting circuits. It usually has a separate switch or
position for cranking the generator. A three-wire generator has fewer automated functions than a
two-wire. It usually requires multiple controls for starting, running, or stopping. The inverter
terminals cannot control this type of generator without using a three-wire to two-wire conversion kit.
Atkinson Electronics
(http://atkinsonelectronics.com)
is one company that makes these kits. The
Atkinson GSCM-Mini is intended to work with OutBack inverters.
NOTE:
The
12V AUX
If the
AUX
The conversion kit requires a 12-volt signal which the
RELAY AUX
terminals may be used to operate the conversion kit, as shown in Figure 25 .
terminals are being used for another purpose, it may be necessary for the
terminals cannot provide.
RELAY AUX
terminals to control an external relay and 12-volt source in conjunction with the conversion kit. The
wiring and requirements for this arrangement will depend on the circumstances.
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 29
Generator
Figure 25 Three-Wire Generator Start (Example)
Page 32

Installation
NOTES:
30 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 33

Installation
AC Configurations
1. The Radian inverter has separate neutral connections for grid input, generator input, and output. These are electrically common. If an
2. Maintenance bypass switching assemblies are commonly used so that the inverter can be taken offline, if necessary, withou
NOTES:
Single-Inverter
Figure 26 (below) shows the general wiring of the Radian inverter and the AC system connected to it.
This figure is not a physical representation of the inverter and does not depict the GSLC.
Figure 27 (see next page) shows the locations of AC and network connections. This figure is a physical
diagram for wiring the GSLC, network components, and external AC devices with the inverter.
All overcurrent devices in permanent installations must be sized for 50 Aac or less.
All wiring in permanent installations must be sized for 50 Aac or more.
All output circuit breakers must be sized appropriately for loads and inverter wattage.
The Radian inverter has wiring connections for two AC sources, but it can only accept one source at a time.
external neutral bus exists (as shown in the AC Load Panel above), not all of the Radian neutral connections need to be made.
down the entire system. These assemblies usually include an interlock mechanism that isolates AC lines from each other. This figure
shows the general design of a bypass system.
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 31
Figure 26 Single-Inverter AC System
t shutting
Page 34

Installation
1. Ground wiring is not shown for reasons of simplicity. Regardless, this system must be connected to a grounded, permanent wiring
2. The Radian inverter has separate neutral connections for grid input, generator input, and output. These are
3. The GSLC AC circuit breakers are designed as a maintenance bypass switching assembly. The assembly can be used so that the inverter
NOTES:
system. See page 19.
external neutral bus exists (as shown in the GSLC), not all of the Radian neutral connections need to be made. In this example, only the
Grid neutral terminal on the inverter is connected.
can be taken offline, if necessary, without shutting down the entire system. This figure shows the connections of a bypass system.
Figure 27 Single-Inverter AC Wiring with GS Load Center
electrically common. If an
32 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 35

Installation
Port 1
MATE3 Port
MATE3
HUB4
Stacking Connections
Stacking requires an
Multiple-Inverter AC Installations (Stacking)
Installing multiple inverters in a single AC system supports larger loads than a single inverter can
handle. This requires stacking. Stacking refers to how the inverters are wired within the system and
then programmed to coordinate activity. Stacking allows all units to work together as a single system.
The GS4048A and GS8048A models can stack up to ten units in parallel.
OutBack communications manager and a system display.
A system of four or fewer units may use the HUB4 Communications Manager.
A system of up to ten units requires either the HUB10 or HUB10.3 Communications Manager.
All interconnections between the products are made using CAT5 non-crossover cable.
Each inverter must be assigned a stacking mode, “master” or “slave”, depending on the configuration.
The master provides the primary output phase. Other inverters in the system base their phase on that of the
master. If the master shuts off, all other inverters also shut off.
The master must sense and connect to an AC source before other inverters can connect. In all cases, the
master inverter must be connected to port 1 on the communications manager.
In a parallel-stacked system, the master tends to be the most heavily used unit.
Only one slave mode, “OutBack”, is available for the GS8048A and GS4048A. This mode is used for inverters
stacked in parallel.
All slave inverters are in phase with the master. The slave outputs are pulse-width-matched to be precisely
synchronized with the master inverter. This avoids potential backfeed.
OutBack slaves can be placed in Power Save mode when not in use. They are activated by the master
inverter as needed. For this reason, the master is normally the only inverter to enter Search mode.
Connect all units other than the master to ports 2 and above on the communications manager.
The system display may have other port restrictions pertaining to stacking. In general, it is always
important to keep track of units and ports for programming purposes.
Programming involves using the system display to assign a status and stacking value to the inverter
on each port. The stacking assignments can be changed at any time as long as the master is
connected to port 1.
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 33
Figure 28 OutBack Communications Manager and System Display
Page 36

Installation
IMPORTANT:
Neither the GS8048A nor the GS4048A can stack with the previous model GS8048.
The GS8048 can share a HUB product with the others if it is wired independently.
The GS8048A can be stacked with the GS4048A using HUB products. To optimize
the Power Save function, GS4048A inverters should have higher rank numbers than
any GS8048A inverter. This is true regardless of the quantity of either model. In
addition, the GS4048A should not be the master inverter in a mixed system.
The master inverter must always be connected to port 1 on the communications
manager. Connecting it elsewhere, or connecting a slave to port 1, will result in
backfeed or output voltage errors which will shut the system down immediately.
Installing multiple inverters without stacking them (or stacking them incorrectly)
will result in similar errors and shutdown.
Although stacking allows greater capacity, the loads, wiring, and overcurrent
devices must still be sized appropriately. Overloading may cause circuit breakers to
open or the inverters to shut down.
34 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 37

Installation
Parallel Stacking (Dual-Stack and Larger)
24 kVA
8 kVA
8 kVA
120/240 Vac
8 kVA
In parallel stacking, two or more inverters are stacked to create a single, common AC bus as shown in
Figure 29.
The slave outputs are controlled directly by the master and cannot operate independently.
All inverters share a common input (AC source) and run loads on a common output.
Slave inverters can go into Power Save mode when not in use. The master will activate individual slaves
based on load demand. This reduces idle power consumption and improves system efficiency.
Up to ten inverters may be installed in a parallel arrangement. The example on this page shows three
inverters. The wiring diagrams on the next few pages show two.
Figure 30 (see page 36) shows the general wiring of the Radian inverters and the AC system connected
to them. This figure is not a physical representation of the inverters and does not depict the GSLC.
Figure 31 (see page 37) shows the locations of AC and network connections. This figure is a physical
diagram for wiring the GSLC, network components, and external AC devices with each inverter.
120/240 Vac
120/240 Vac
120/240 Vac
Figure 29 Example of Parallel Stacking Arrangement (Three Inverters)
When installing a parallel system, the following rules must be observed.
Parallel stacking requires the system display and a communications manager.
One inverter, and one inverter only, is always the master and is programmed as
Master
display. This is the default setting.
The master must be connected to port 1 of the communications manager. Other inverters must not be
selected as master.
All slave inverters, regardless of number, should be selected as
All overcurrent devices must be sized for 50 Aac or less.
All wiring must be sized for 50 Aac or more.
All output circuit breakers must be sized appropriately for loads and inverter wattage.
The AC input (generator or utility grid) must be a split-phase output at the proper voltage and frequency.
The input/output bypass kit for the GS Load Center cannot be used. See page 10 for more information.
during programming.
Slave
in the MATE3 system
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 35
Page 38

Installation
1.
2. Maintenance bypass switching assemblies are commonly used so that the inverter can be taken offline, if necessary, withou
3. When multiple inverters are stacked, the GS Load Center (GSLC) for each inverter can be wi
NOTES:
The Radian inverter has separate neutral connections for grid input, generator input, and output. These are electrically common. If an
external neutral bus exists (as shown in the AC Load Panel above), not all of the Radian neutral connections need to be made.
down the entire system. These assemblies usually include an interlock mechanism that isolates AC lines from each other. This figure
shows the general design of a bypass system.
conduit box and AC load center. However, the GSLC bypass switching assemblies are only sized for single inverters and cannot work in
conjunction with each other. The GSLC bypass assemblies should not be used with multiple inverters present. (See page
external bypass assembly must be used instead. Larger external assemblies are available from other manufacturers.
red together to serve as a common input
Figure 30 Parallel Wiring
36 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
t shutting
10.) An
Page 39

Installation
1. Ground wiring is not shown for reasons of simplicity. Regardless, this system must be connected to a grounded, permanent wiring
2
3
NOTES:
system. See page 19.
. The Radian inverter has separate neutral connections for grid input, generator input, and output. These are electrically common. If an
external neutral bus exists (as shown in the GSLC), not all of the Radian neutral connections need to be made. In this example, only the
Grid neutral terminal on each inverter is connected.
. The bypass assembly in each GSLC cannot be used with multiple inverters and is not depicted here. External bypass assemblies are
available from other manufacturers. See page
Figure 31 Parallel Wiring with GSLC
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 37
10.
Page 40

Installation
Functional Test
Once the mounting, wiring, and other installation steps are completed, proceed to the Radian Series
Inverter/Charger Operator’s Manual. The Operator’s Manual has steps for system commissioning. These
include powering up and performing a functional test on the inverter system, as well as powering
down and adding new devices to an existing system.
Refer to the MATE3 System Display and Controller Owner’s Manual (or the appropriate system display
manual) for programming instructions and menus.
Preventative Maintenance
The Radian inverter requires almost no regular maintenance. However, OutBack recommends the
following items on a periodic basis:
Check all electrical connections periodically for tightness using the torque values from pages 19 through 22.
Check the fan screens on each module and clear them of any debris.
38 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 41

Symbols, Terms, and Definitions
WARNING: Hazard to Human Life
CAUTION: Hazard to Equipment
IMPORTANT:
recommendations in such a notation could result in voiding the equipment warranty.
MORE INFORMATION
Inverter/Charger Installation Manual. Another common reference is the system display manual.
Table 5 Terms and Definitions
Term
Definition
12V AUX
Auxiliary connection that supplies 12 Vdc to control external devices.
AC
Alternating Current; refers to voltage produced by the inverter, utility grid, or generator
AIC
Ampere Interrupting Capacity; the rated maximum current a circuit breaker can
interrupt without damage
AGS
Advanced Generator Start
AS
Australian Standards
DC
Direct Current; refers to voltage produced by the batteries or renewable source
DVM
Digital Voltmeter
Symbols Used
This type of notation indicates that the hazard could be harmful to human life.
This type of notation indicates that the hazard may cause damage to the equipment.
This type of notation indicates that the information provided is important to the
installation, operation and/or maintenance of the equipment. Failure to follow the
When this symbol appears next to text, it means that more information is available in other
manuals relating to the subject. The most common reference is to the Radian Series
Definitions
The following is a list of initials, terms, and definitions used with this product.
Communications
manager
Multi-port device such as the OutBack HUB4, HUB10, or HUB10.3, used for connecting
multiple OutBack devices on a single remote display; essential for stacking inverters
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 39
Page 42

Terms and Definitions
Table 5 Terms and Definitions
Term
Definition
EPO
Emergency Power Off; a switching product used for emergency shutdown
GFDI
Ground Fault Detector Interruptor; a safety device for PV systems
GND
Ground; a permanent conductive connection to earth for safety reasons; also known as
Chassis Ground, Protective Earth, PE, Grounding Electrode Conductor, and GEC
Grid/Hybrid™
System technology which optimizes both grid-interactive and off-grid options
Grid-interactive,
grid-intertie, grid-tie
Utility grid power is available for use and the inverter is a model capable of returning
(selling) electricity back to the utility grid
GSLC
GS Load Center; the wiring box for the Radian (GS) inverter
HUB
A line of OutBack communications manager products
IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission; an international standards organization
MATE3
An OutBack system display, used for monitoring, programming and communicating
with the inverter
NEU
AC Neutral; also known as Common
Off-grid
Utility grid power
is not
available for use
PV
Photovoltaic
RELAY AUX
Auxiliary connection that uses switch (relay) contacts to control external devices.
RTS
Remote Temperature Sensor; accessory that measures battery temperature for charging
System display
Remote interface device (such as the MATE3), used for monitoring, programming and
communicating with the inverter; also called “remote system display”
Three-phase, 3-phase
A type of utility electrical system with three “hot” lines, each 120° out of phase;
respect to each other equaling the line voltage multiplied by 1.732
Utility grid
The electrical service and infrastructure supported by the electrical or utility company;
Neutral-to-ground
bonding
Split-phase A type of utility electrical system with two “hot” lines 180° out of phase, common in
A mechanical connection between the AC neutral (Common) bus and the ground (PE)
bus; this bond makes the AC neutral safe to handle
North America; each line typically carries 120 Vac (or the nominal line voltage) with
respect to neutral and 240 Vac with respect to each other
each carries the nominal line voltage with respect to neutral; each carries voltage with
also called “mains”, “utility service”, or “grid”
40 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 43

A
Index
F
AC Inputs ............................................................. 5, 18, 22, 24
AC Wiring ........................................................................ 18, 22
Advanced Generator Start (AGS) .................................. 26
Applications ............................................................................. 5
AUX ............................................................................ 17, 26, 39
B
Battery Bank............................................................................. 7
Sizing .................................................................................... 8
Bypass ..................................................................................... 10
C
Clearance ............................................................................... 11
Communication Cables .................................................... 33
Communications Manager ............................... 25, 33, 39
Components ............................................................................ 4
Conductor Size
AC Conductors ............................................................... 22
DC Conductors .............................................................. 21
Ground Conductors ..................................................... 19
Cover ....................................................................................... 16
Features .................................................................................... 3
FLEXmax ............................................................................ 4, 15
FLEXmax Extreme ............................................................... 15
Front Cover ............................................................................ 16
G
Generator ........................................................................ 24, 35
Applications ...................................................................... 5
Automatic Control ........................................................ 26
Requirements ............................................................. 9
Three-Wire ................................................................. 29
Two-W
ire ............................................................. 27, 28
Sizing.................................................................................... 9
Wiring ................................................................................ 22
GFDI ................................................................................... 19, 40
Grid-Interactive .................................................................... 40
Grounding ...................................................................... 18, 19
GSLC ............................................................... 4, 10, 12, 15, 40
H
HUB ........................................................................ 4, 15, 33, 40
D
DC Terminals ................................................................. 17, 21
DC Wiring ............................................................................... 20
Definitions ............................................................................. 39
Dimensions
Inverter ............................................................................. 11
System............................................................................... 12
Diversion Control................................................................ 27
Drawings
Multiple AC Sources .................................................... 24
Parallel-Stacked System ............................................. 35
Transfer Relay ................................................................. 24
DVM .................................................................................. 13, 39
E
Environmental Requirements........................................ 11
EPO .................................................................................... 25, 40
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 41
I
IEC ...................................................................................... 19, 40
Input Modes ............................................................................ 6
J
Jumper J3 ........................................................................ 17, 25
L
Location .................................................................................. 11
M
Maintenance Bypass .......................................................... 10
Maintenance Checks.......................................................... 38
MATE and MATE2 .................................................................. 4
Page 44

Index
MATE3 ................................................................... 4, 15, 18, 40
AUX .................................................................................... 26
Stacking ............................................................................ 33
Mounting
Components ................................................................... 15
Dimensions .............................................................. 11, 12
Orientation ...................................................................... 11
Plate ............................................................................ 13, 14
Multiple AC Sources .......................................................... 24
N
Neutral-Ground Bonding ..................................... 9, 19, 22
P
Parallel Stacking .................................................................. 35
Ports, RJ45 and RJ11 ................................................... 18, 25
R
Remote System Display ................................................... 40
Remote Temperature Sensor (RTS) .................. 4, 18, 25
Renewable Energy ................................................................ 6
Ribbon Cables ...................................................................... 17
S
Stacking .................................................................................. 33
Parallel .............................................................................. 35
Switch ............................................................................... 17, 25
Symbols Used ....................................................................... 39
System Display .................................................. 4, 25, 35, 40
T
Temperatures ....................................................................... 11
Terms and Definitions ....................................................... 39
Tools Required ..................................................................... 13
Torque Requirements
DC Terminals ................................................................... 21
Ground Terminals ......................................................... 19
Transfer Relay ....................................................................... 24
U
Utility Grid ................................................................ 24, 35, 40
Applications ...................................................................... 5
Wiring ................................................................................ 22
W
Wiring
AC Connections ...................................................... 18, 22
AUX Connections .......................................................... 26
DC Connections ............................................................. 20
Ground Connections ............................................ 18, 19
Parallel Inverters ............................................................ 35
Single Inverter ................................................................ 31
42 900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 45

THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK.
Page 46

THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK.
900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Page 47

THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK.
900-0160-01-00 Rev A 45
Page 48

Masters of the Off-Grid.™ First Choice for the New Grid.
Corporate Headquarters
+1.360.435.6030
European Office
+49.9122.79889.0
17825 – 59th Avenue N.E.
Suite B
Arlington, WA 98223 USA
900-0160-01-00 Rev A
Hansastrasse 8
D-91126
Schwabach, Germany
 Loading...
Loading...