Page 1

Radian Series Inverter/Charger
GS7048E
GS3548E
Operator’s Manual
Page 2

Address:
Corporate Headquarters
Arlington, WA 98223 USA
European Office
Schwabach, Germany
Telephone:
+1.360.435.6030
+1.360.435.6019 (Fax)
+49.9122.79889.0
Email:
Support@outbackpower.com
Website:
http://www.outbackpower.com
About OutBack Power Technologies
OutBack Power Technologies is a leader in advanced energy conversion technology. OutBack products include true sine
wave inverter/chargers, maximum power point tracking charge controllers, and system communication components, as well
as circuit breakers, batteries, accessories, and assembled systems.
Grid/Hybrid™
As a leader in off-grid energy systems designed around energy storage, OutBack Power is an innovator in Grid/Hybrid system
technology, providing the best of both worlds: grid-tied system savings during normal or daylight operation, and off-grid
independence during peak energy times or in the event of a power outage or an emergency. Grid/Hybrid systems have the
intelligence, agility and interoperability to operate in multiple energy modes quickly, efficiently, and seamlessly, in order to
deliver clean, continuous and reliable power to residential and commercial users while maintaining grid stability.
Contact Information
17825 – 59th Avenue N.E.
Suite B
+1.360.618.4363 (Technical Support)
Hansastrasse 8
D-91126
+49.9122.79889.21 (Fax)
Disclaimer
UNLESS SPECIFICALLY AGREED TO IN WRITING, OUTBACK POWER TECHNOLOGIES:
(a) MAKES NO WARRANTY AS TO THE ACCURACY, SUFFICIENCY OR SUITABILITY OF ANY TECHNICAL OR OTHER
INFORMATION PROVIDED IN ITS MANUALS OR OTHER DOCUMENTATION.
(b) ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR LOSS OR DAMAGE, WHETHER DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL OR
INCIDENTAL, WHICH MIGHT ARISE OUT OF THE USE OF SUCH INFORMATION. THE USE OF ANY SUCH INFORMATION WILL BE
ENTIRELY AT THE USER’S RISK.
OutBack Power Technologies cannot be responsible for system failure, damages, or injury resulting from improper
installation of their products.
Information included in this manual is subject to change without notice.
Notice of Copyright
Radian Series Inverter/Charger Operator’s Manual © 2014 by OutBack Power Technologies. All Rights Reserved.
Trademarks
OutBack Power, the OutBack Power logo, FLEXpower ONE, and Grid/Hybrid are trademarks owned and used by OutBack
Power Technologies, Inc. The ALPHA logo and the phrase “member of the Alpha Group” are trademarks owned and used by
Alpha Technologies Inc. These trademarks may be registered in the United States and other countries.
Date and Revision
February 2014, Revision A (firmware revision 001.005.xxx)
Part Number
900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 3
Table of Contents
Introduction ................................................................................................. 5
Audience ................................................................................................................................................................................. 5
Symbols Used ........................................................................................................................................................................ 5
General Safety ....................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Welcome to OutBack Power Technologies ................................................................................................................. 6
Inverter Functions ................................................................................................................................................................ 6
GS7048E ................................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
GS3548E ................................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
Inverter Controls ................................................................................................................................................................... 8
On/Off Switch ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
MATE3 System Display and Controller ......................................................................................................................................... 8
Commissioning ............................................................................................ 9
Functional Test ...................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Pre-startup Procedures ....................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Startup ...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Powering Down ................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Adding New Devices ......................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Firmware Updates .............................................................................................................................................................................. 12
Operation .................................................................................................. 13
Inverter Functionality ...................................................................................................................................................... 13
Description of AC Input Modes .................................................................................................................................... 13
Generator ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Support ................................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Grid Tied ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 15
UPS ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
Backup .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Mini Grid ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 18
Grid Zero ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 19
Description of Inverter Operations ............................................................................................................................. 22
Inverting ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 22
DC and AC Voltages .................................................................................................................................................................................... 22
AC Frequency ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 23
Search ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 23
Input ........................................................................................................................................................................................................ 24
AC Current Settings ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
AC Source Acceptance ............................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Generator Input ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 26
Transfer ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 26
Battery Chargin .................................................................................................................................................................................... 27
Charge Current ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 27
Charge Cycle .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 27
Charging Graphs .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 28
Charging Steps.............................................................................................................................................................................................. 29
New Charging Cycle .................................................................................................................................................................................... 31
Equalization ................................................................................................................................................................................................... 33
Battery Temperature Compensation ..................................................................................................................................................... 33
Offset ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 35
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 1
Page 4

Table of Contents
Multiple-Inverter Installations (Stacking) .................................................................................................................................. 36
Parallel Stacking (Dual-Stack and Larger) ............................................................................................................................................. 37
Three-Phase Stacking (Three Inverters) ................................................................................................................................................ 38
Power Save ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Auxiliary Terminals ............................................................................................................................................................................. 43
System Display-Based Functions ................................................................................................................................. 47
Advanced Generator Start (AGS) .................................................................................................................................................. 47
Grid Functions ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 47
High Battery Transfer (HBX) ...................................................................................................................................................................... 47
Grid Use Time ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 48
Load Grid Transfer ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 48
Metering .................................................................................................... 49
MATE3 Screens ................................................................................................................................................................... 49
Inverter Screens ................................................................................................................................................................................... 49
Battery Screen ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 50
Troubleshooting ......................................................................................... 51
Basic Troubleshooting ..................................................................................................................................................... 51
Module Select ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 56
Error Messages ................................................................................................................................................................... 57
Warning Messages ............................................................................................................................................................ 58
Temperature Events .......................................................................................................................................................................... 59
Disconnect Messages ...................................................................................................................................................... 60
Sell Status ............................................................................................................................................................................. 61
Specifications ............................................................................................. 63
Electrical Specifications ................................................................................................................................................... 63
Mechanical Specifications .............................................................................................................................................. 64
Environmental Specifications ....................................................................................................................................... 64
Temperature Derating ...................................................................................................................................................................... 65
Certifications ....................................................................................................................................................................... 65
Compliance.......................................................................................................................................................................... 66
Firmware Revision ............................................................................................................................................................. 67
Default Settings and Ranges ......................................................................................................................................... 67
Definitions ............................................................................................................................................................................ 70
Index ......................................................................................................... 71
2 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 5

Table of Contents
List of Tables
Table 1 Summary of Input Modes .......................................................................................................... 21
Table 2 Charge Currents for Radian Models ....................................................................................... 27
Table 3 Offset Interaction with AC Source .......................................................................................... 35
Table 4 Changing Master Power Save Levels (GS7048E)................................................................ 42
Table 5 Aux Mode Functions ................................................................................................................... 46
Table 6 Troubleshooting ........................................................................................................................... 51
Table 7 Error Troubleshooting ................................................................................................................ 57
Table 8 Warning Troubleshooting ......................................................................................................... 58
Table 9 Temperature Events .................................................................................................................... 59
Table 10 Disconnect Troubleshooting .................................................................................................... 60
Table 11 Sell Status Messages .................................................................................................................... 61
Table 12 Electrical Specifications for Radian Models ......................................................................... 63
Table 13 Mechanical Specifications for Radian Models .................................................................... 64
Table 14 Environmental Specifications for Radian Models .............................................................. 64
Table 15 AS4777.3 Acceptance Settings ................................................................................................ 66
Table 16 Radian Inverter Settings ............................................................................................................. 67
Table 17 Terms and Definitions ................................................................................................................. 70
List of Figures
Figure 1 Radian Series Inverter/Charger .................................................................................................. 7
Figure 2 MATE3 System Display and Controller .................................................................................... 8
Figure 3 AC Test Points ................................................................................................................................ 10
Figure 4 Charging Stages Over Time ...................................................................................................... 28
Figure 5 Charging Stages Over Time (24/7) .......................................................................................... 28
Figure 6 Repeated Charging Cycles ........................................................................................................ 32
Figure 7 OutBack HUB4 and MATE3 ........................................................................................................ 36
Figure 8 Example of Parallel Stacking Arrangement (Three Inverters)........................................ 37
Figure 9 Example of Three-Phase Stacking (Three Inverters) ......................................................... 38
Figure 10 Example of Three-Phase Stacking (Nine Inverters) ........................................................... 38
Figure 11 Power Save Levels and Loads................................................................................................... 39
Figure 12 GS3548E Power Save Priority ................................................................................................... 40
Figure 13 GS7048E Power Save Priority ................................................................................................... 41
Figure 14 Home Screen .................................................................................................................................. 49
Figure 15 Inverter Screens ............................................................................................................................ 49
Figure 16 Battery Screen ............................................................................................................................... 50
Figure 17 AC Test Points ................................................................................................................................ 51
Figure 18 Temperature Derating ................................................................................................................ 65
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 3
Page 6

Table of Contents
This page intentionally left blank.
4 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 7
Introduction
WARNING: Hazard to Human Life
CAUTION: Hazard to Equipment
This type of notation indicates that the hazard may cause damage to the equipment.
IMPORTANT:
recommendations in such a notation could result in voiding the equipment warranty.
MORE INFORMATION
Inverter/Charger Installation Manual. Another common reference is the system display manual.
WARNING: Limitations on Use
equipment or devices.
WARNING: Reduced Protection
internal safety protection may be impaired.
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
Technologies or its authorized agents.
Audience
This manual provides instructions for setup and operation of the product. It does not cover
installation. The manual is intended to be used by anyone required to operate the Radian Series
Inverter/Charger. Operators must be familiar with all the safety regulations pertaining to operating
power equipment of this type as required by local code. Operators are advised to have basic electrical
knowledge and a complete understanding of this equipment’s features and functions. Do not use this
product unless it has been installed by a qualified installer in accordance with the Radian Series
Inverter/Charger Installation Manual.
Symbols Used
This type of notation indicates that the hazard could be harmful to human life.
This type of notation indicates that the information provided is important to the
installation, operation and/or maintenance of the equipment. Failure to follow the
When this symbol appears next to text, it means that more information is available in other
manuals relating to the subject. The most common reference is to the Radian Series
General Safety
This equipment is NOT intended for use with life support equipment or other medical
If this product is used in a manner not specified by GS product literature, the product’s
Only use components or accessories recommended or sold by OutBack Power
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 5
Page 8

Introduction
Welcome to OutBack Power Technologies
IMPORTANT:
Display and Controller.
Thank you for purchasing the OutBack Radian Series Inverter/Charger. It is designed to offer a
complete power conversion system between batteries and AC power. As part of an OutBack
Grid/Hybrid™ system, it can provide off-grid power, grid backup power, or grid-interactive service
which sells excess renewable energy back to the utility.
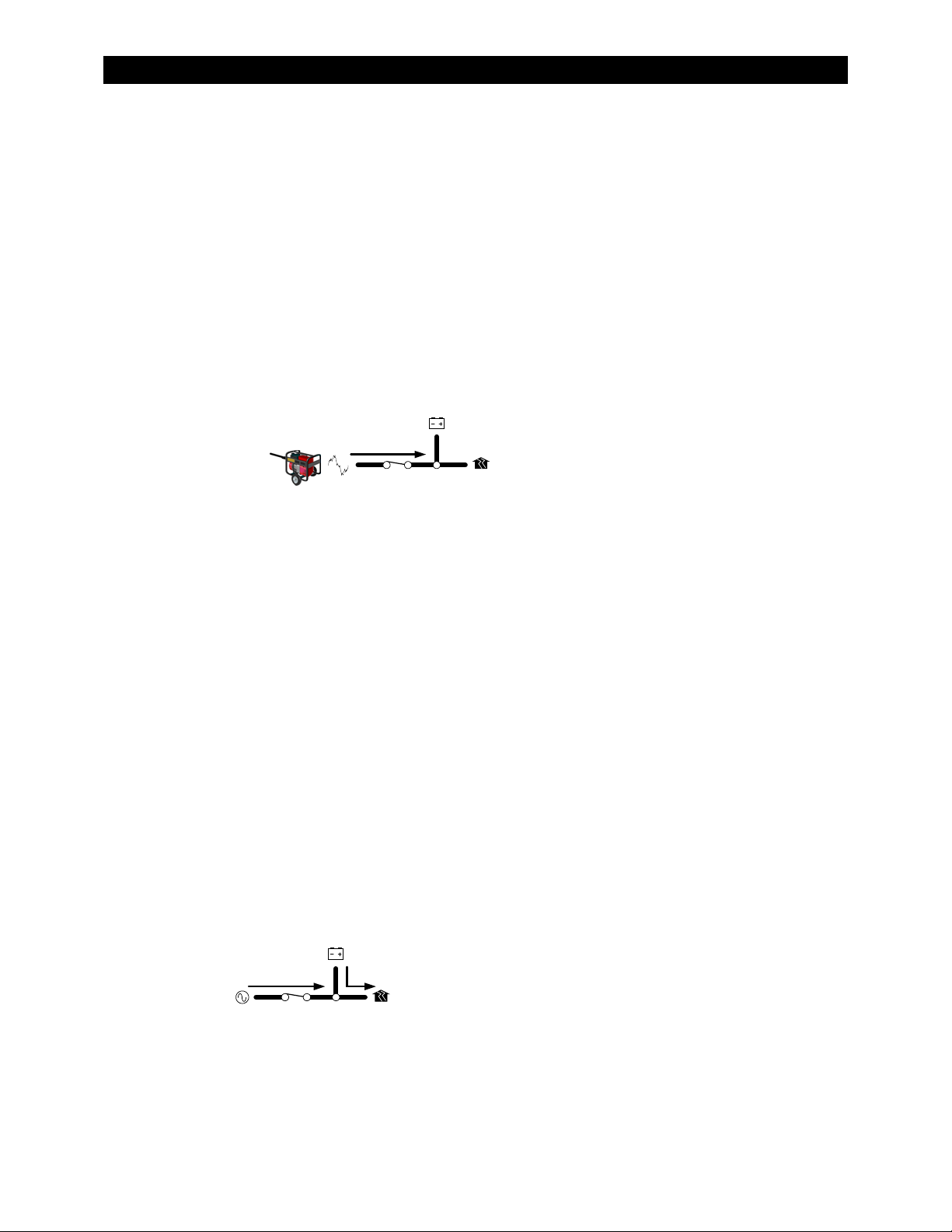
Inverter Functions
Battery-to-AC inverting which delivers power to run backup loads and other functions
∼ Provides single-phase output
∼ Adjustable range of output voltage
∼ Settable nominal output frequency
AC-to-battery charging (OutBack systems are battery-based)
∼ Accepts a wide variety of AC sources
∼ Requires single-phase input
Uses battery energy stored from renewable resources
∼ Can utilize stored energy from many sources (PV arrays, wind turbines, etc.)
∼ OutBack FLEXmax charge controllers will optimize PV power production as part of a Grid/Hybrid system
Dual AC inputs allow direct connection to utility grid and AC generator
Rapid transfer between AC source and inverter output with minimal delay time
Uses MATE3 System Display and Controller (sold separately) for user settings as part of a Grid/Hybrid system
Stackable in parallel configuration up to ten inverters
Stackable in three-phase configuration with up to nine inverters (using HUB10.3 Communications Manager)
Field-upgradeable firmware
Seven selectable input modes for different applications
∼ Generator
∼ Support
∼ Grid Tied
∼ UPS
∼ Backup
∼ Mini Grid
∼ Grid Zero
The Radian Series Inverter/Charger is not intended for use with the OutBack MATE or
MATE2 System Display and Controller. It is only compatible with the MATE3 System
6 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 9

Introduction
Figure 1 Radian Series Inverter/Charger
GS7048E
7000 watts (7 kW) continuous power at 48 Vdc
16.3 kVA peak surge capacity
Modular internal design allows low idle consumption and high efficiency at high or low power operation
GS3548E
3500 watts (3.5 kW) continuous power at 48 Vdc
8.2 kVA peak surge capacity
Certified by ETL to IEC 62109-1
: This product has a settable AC output range. In this book, many references to the output refer
NOTE
to the entire range. However, some references are made to 230 Vac or 50 Hz output. These are
intended as examples only.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 7
Page 10

Introduction
Inverter Controls
IMPORTANT:
The Radian inverter has no external controls. It can operate normally without an external control or
interface. Basic modes and settings are pre-programmed at the factory. (See page 67 for default
settings.) However, certain external devices can be used to operate or program the Radian.
On/Off Switch
The inverter can be equipped with a switch to turn it on and off. This switch is not sold as an inverter
accessory; a common toggle switch can be used. It is wired to the
(See the Radian Series Inverter/Charger Installation Manual for more information on wiring the switch.)
This switch controls the inverting function only; it does not control the charger or any other function.
Switch INV
MATE3 System Display and Controller
The Radian inverter has no display or LED indicators. It is not possible to monitor its status or
operating mode without a metering device. The MATE3 System Display and Controller (sold
separately) is designed to accommodate programming and monitoring of a Grid/Hybrid power
system. The MATE3 provides the means to adjust the factory default settings to correctly match the
installation where needed. It provides the means to monitor system performance and troubleshoot
fault or shutdown conditions. It also has data logging and interface functions using the Internet.
auxiliary terminals.
Once settings are modified using a MATE3, the MATE3 can be removed from the installation. The
settings are stored in the nonvolatile memory of the Radian inverter. However, it is highly
recommended to include a MATE3 as part of the system. This provides the means to monitor system
performance and respond quickly should it be necessary to correct a fault or shutdown condition.
The MATE3’s Configuration Wizard is capable of automatically configuring inverters to a series of
preset values. This is often more efficient than attempting to manually program each setting in each
inverter. Affected fields include system type, battery charging, and AC source configuration.
NOTE:
Model GS7048E can only be used with MATE3 firmware revision 002.010.xxx or higher.
Model GS3548E can only be used with MATE3 firmware revision 002.017.xxx or higher.
Some functions are not based in the inverter, but are part of the MATE3 system
display’s firmware. They will not function if the system display is removed.
These functions are listed beginning on page 46.
8 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Figure 2 MATE3 System Display and Controller
Page 11
Commissioning
WARNING: Shock Hazard and Equipment Damage
carry hazardous voltages. Use appropriate care to avoid the risk of electric shock or equipment damage.
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
This damage is not covered by the warranty.
IMPORTANT:
correct AC operation. The default setting is 50 Hz, but this can be changed to 60 Hz.
Functional Test
It is necessary to remove the inverter cover to perform these tests. The components are close together and
Pre-startup Procedures
1. Ensure all DC and AC overcurrent devices are opened, disconnected, or turned off.
2. Double-check all wiring connections.
3. Confirm that the total load does not exceed the inverter’s wattage. (See page 22.)
4. Inspect the work area to ensure tools or debris have not been left inside.
5. Using a digital voltmeter (DVM) or standard voltmeter, verify battery voltage. Confirm the
voltage is correct for the inverter model. Confirm the polarity.
6. Connect the MATE3 system display, if present.
Incorrect battery polarity will damage the inverter. Excessive battery voltage also may damage the inverter.
Prior to programming (see Startup), verify the operating frequency of the AC source. This is necessary for
Startup
It is highly recommended that all applicable steps be performed in the following order. However, if
steps are inapplicable, they can be omitted.
If the results of any step do not match the description, see the Troubleshooting section on page 50.
To start a single-inverter system:
1. Close the main DC circuit breakers (or connect the fuses) from the battery bank to the inverter.
Confirm that the system display is operational, if present.
2. If a system display is present, perform all programming for all functions.
These functions may include AC input modes, AC output voltage, input current limits, battery
charging, generator starting, and others.
AC input modes are described beginning on page 13 and are summarized on page 21. The
inverter’s individual operations are described beginning on page 22.
3. Turn on the inverter using the MATE3 or external switch. The Radian’s default condition is Off.
Do not turn on any AC circuit breakers at this time.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 9
Page 12

Commissioning
Metal pads are located at these
locations. In commissioning,
AC voltages can be measured at
this series of test points.
Figure 3 AC Test Points
4. Using a DVM or voltmeter, verify 230 Vac (or appropriate voltage) between the “L” and “N” OUT
terminals. (See Figure 3 for AC test points.) The inverter is working correctly if the AC output reads
within 10% of 230 Vac or the programmed output voltage.
5. Proceed past the items below to Step 6 on the next page.
To start a multiple-inverter (stacked) system:
1. Close the main DC circuit breakers (or connect the fuses) from the battery bank to the inverter.
Repeat for every inverter present.
2. With the system display, perform any programming for stacking and all other functions.
These functions may also include AC input modes, AC output voltage, input current limits, battery
charging, generator starting, and others.
When stacking in parallel, all slave inverters will observe the programming settings for the master. They
do not need to be programmed individually.
When stacking in three-phase configuration, all subphase masters will observe the AC input mode and
many of the settings used by the master inverter. However, they need to be individually programmed
as appropriate for AC output voltage and frequency. They also need to be programmed for AC input
voltage and frequency (for both AC inputs). All slaves will observe the programming settings for the
master or for their individual subphase master. They do not need to be programmed individually.
AC input modes are described beginning on page 13 and are summarized on page 21. The
inverter’s individual operations are described beginning on page 22. Stacking is described
beginning on page 36. The MATE3 Configuration Wizard may be used to assist programming.
3. Turn on the master inverter using the system display (or external switch, if one has been installed).
The Radian’s default condition is Off. Do not turn on any AC circuit breakers at this time.
4. Using a DVM or voltmeter, verify 230 Vac (or appropriate voltage) between the master “L” and “N”
OUT terminals. (See Figure 3 for AC test points.)
The inverter is working correctly if the AC output reads within 10% of 230 Vac or the programmed
output voltage.
10 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
If subphase masters are used in three-phase configuration, perform this test on each subphase master.
If necessary, confirm appropriate voltages from one inverter to the next.
Page 13

Commissioning
5. Using the system display, temporarily bring each slave out of Silent mode by raising the Power
Save Level of the master. (See page 39.)
As each slave is activated, it will click and create an audible hum.
Confirm that the system display shows no fault messages. Confirm that the output voltages are still
correct. Individual slave voltage readings are not necessary since all slave inverters are in parallel.
When this test is finished, return the master to its previous settings.
After output testing is completed, perform the following steps:
6. Close the AC output circuit breakers. If AC bypass switches are present, place them in the normal
(non-bypass) position. Do not connect an AC input source or close any AC input circuits.
7. Use a DVM to verify correct voltage at the AC load panel.
8. Connect a small AC load and test for proper functionality.
9. Close the AC input circuit breakers and connect an AC source.
Using a DVM on the correct input, check the “L” and “N” input terminals for 230 Vac (or appropriate
voltage from the AC source.)
If a system display is present, confirm that the inverter accepts the AC source as appropriate for its
programming. (Some modes or functions may restrict connection with the source. If one of these
modes has been selected for the system, it may not connect.) Check the system display indicators for
correct performance.
NOTE: If any Phase B or Phase C inverters are wired to the wrong AC source phases, the inverters
will not connect to the AC source and will display a Phase Loss warning. See page 58.
10. If the charger is activated, the inverter will perform a battery charging cycle after powering up.
This can take several hours. If restarted after a temporary shutdown, the inverter may skip most or
all of the charging cycle. Confirm that it is charging as appropriate by using the system display.
11. Test other functions which have been enabled, such as generator start, selling, or search mode.
12. Compare the DVM’s readings with the system display meter readings. If necessary, the system
display’s readings can be calibrated to match the DVM more accurately. Calibrated settings
include AC input voltage for the Grid and Gen inputs, AC output voltage, and battery voltage.
Powering Down
If steps are inapplicable, they can be omitted. However, it is highly recommended that all applicable
steps be performed in the following order. These steps will completely isolate the inverter.
To remove power from the system:
1. Turn off all load circuits and AC input sources.
2. Turn off all renewable energy circuits.
3. Turn each inverter OFF using the MATE3 system display or external switch.
4. Turn off the main DC overcurrent devices for each inverter.
Adding New Devices
When adding new devices to the system, first turn off the system according to the preceding
instructions. After adding new devices, perform another functional test, including programming.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 11
Page 14
Commissioning
Each requires about 5 minutes.
NOTES:
Firmware Updates
IMPORTANT:
All inverters will shut down during firmware updates. If loads need to be run while
updating the firmware, bypass the inverter with a maintenance bypass switch.
Communication cables must remain connected and DC power must remain on.
Interrupted communication will cause the update to fail and the inverter(s) may not
work afterward. Inverters automatically update one at a time beginning with Port 1.
Updates to the Radian’s internal programming are periodically available at the OutBack website
www.outbackpower.com. If multiple inverters are used in a system, all units must be upgraded at the
same time. All units must be upgraded to the same firmware revision.
If multiple stacked Radian inverters are used with different firmware revisions, any inverter with a
revision different from the master will not function. (See the stacking section on page 36.) The MATE3
will display the following message:
An inverter firmware mismatch has been detected. Inverters X, Y, Z
www.outbackpower.com for current inverter firmware.
1
are disabled. Visit
1 The port designations for the mismatched inverters are listed here.
12 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 15

Operation
AC IN
DC
TRANSFER
These items represent the input from the AC
source, the output to the AC loads, DC functions
(inverting, charging, etc
Arrows on each symbol represent power flow.
Inverter Functionality
The inverter is capable of being used for many applications. Some of the inverter’s operations occur
automatically. Others are conditional or must be enabled manually before they will operate.
Most of the inverter’s individual operations and functions can be programmed using the system
display. This allows customization or fine tuning of the inverter’s performance.
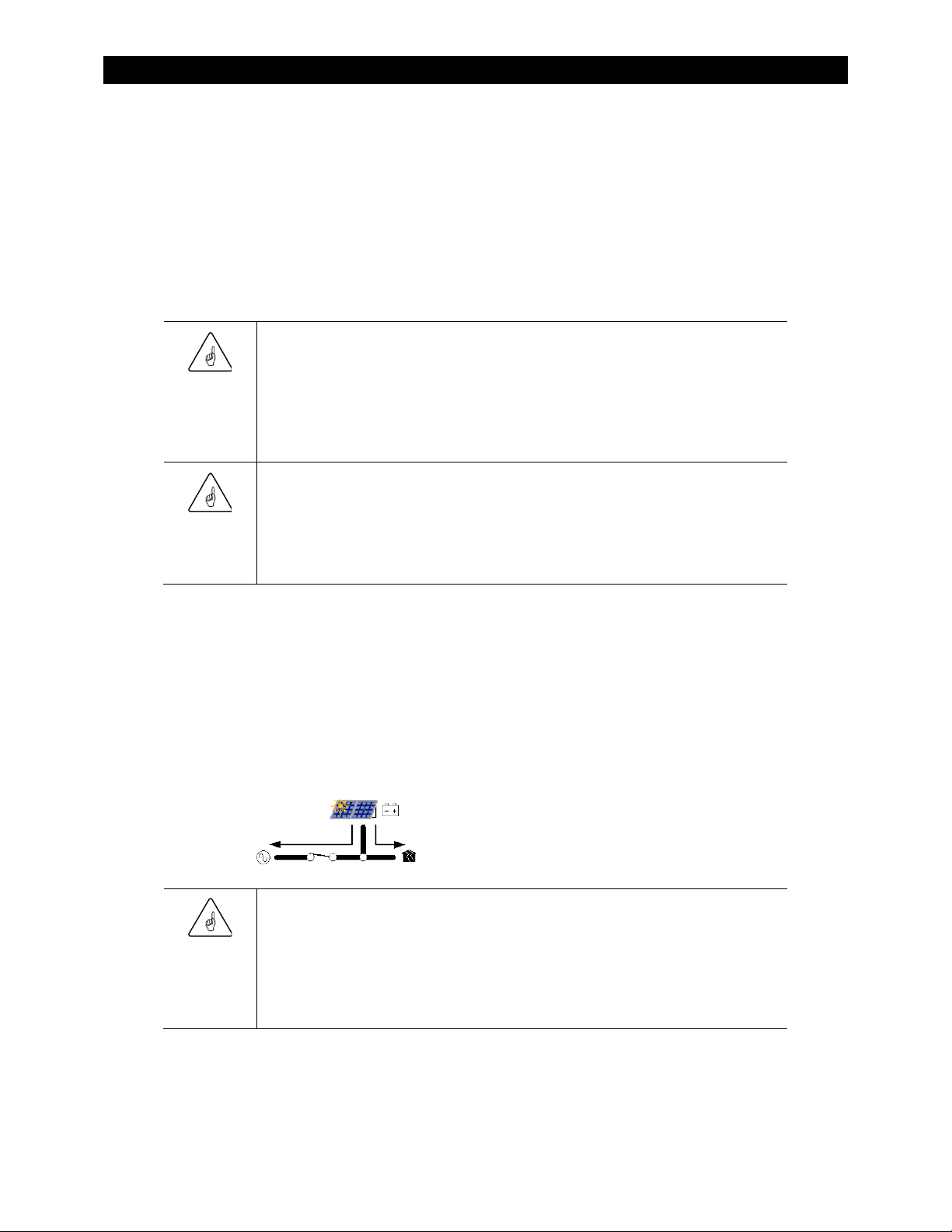
The Radian inverter has two sets of input connections, which are labeled
AC sources can be connected during inverter installation.
Before operating the inverter:
The operator needs to define the application and decide which functions will be needed. The Radian
inverter is programmed with seven AC input modes. Each mode has certain advantages which make it
ideal for a particular application. Some modes contain functions unique to that mode.
The modes are described in detail following this section. To help decide which mode will be used, the
basic points of each mode are compared in Table 1 on page 21.
Apart from the input modes, Radian inverters possess a set of common functions or operations. These
operations are described in detail beginning on page 22. Most of these items operate the same
regardless of which input mode is selected; however, this is not always true. The exceptions are noted
where appropriate.
NOTE:
which input is used. It does not have independent charger settings on each input.
Each distinct mode, function, or operation is accompanied by a symbol representing the inverter and
that operation:
The Radian’s battery charger uses the same programming and settable limits regardless of
and
Grid
), and the transfer relay.
. Two different
Gen
The symbols may have other features depending on the operation.
Description of AC Input Modes
These modes control aspects of how the inverter interacts with AC input sources. Each mode is
intended to optimize the inverter for a particular application. The names of the modes are
Support, Grid Tied, UPS, Backup, Mini Grid
compared in Table 1.
Both of the Radian’s inputs,
The
The
NOTE:
because of inverter requirements. Each input can accept any AC source as long as it meets the
requirements of the Radian inverter and the selected input mode. If necessary, the
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 13
input can be set in the
Grid
input can be set in the
Gen
The input terminals are labeled for grid and generator due to common conventions, not
Grid
, and
Grid Zero
and
Grid AC Input Mode and Limits
Gen AC Input Mode and Limits
, can be programmed for separate modes.
Gen
. The modes are summarized and
menu.
menu.
Generator
terminals can
Gen
,
Page 16
Operation
accept grid power. The opposite is also true. However, if using the
generator must use the
terminals. See page 43 (
Gen
Gen Alert
) and page 47 (
Gen Alert
or
AGS
functions, the
AGS
).)
When multiple inverters are stacked together in parallel, the master inverter’s input mode is imposed
on all slaves. The slave settings are not changed; they retain any mode that was previously
programmed. However, the slave will ignore its own input mode and use that of the master. This also
applies to any parameters in the mode menu (
Voltage Limit, Connect Delay
, and so on).
If inverters are stacked using subphase masters, the subphase masters will observe the AC input mode
and many of the settings used by the master inverter. However, they need to be individually
programmed as appropriate for AC output voltage and frequency. They also need to be programmed
for AC input voltage and frequency (for both AC inputs).
See the stacking section on page 36 for explanation of both parallel and subphase master
(three-phase) stacking.
The following pages compare the various aspects of each input mode.
Generator
The
Generator
mode allows the use of a wide range of AC sources, including generators with a rough
or imperfect AC waveform. In other modes, a “noisy” or irregular waveform may not be accepted by
the inverter. (Self-excited induction generators may require this mode when used with the Radian.)
Generator
allows these waveforms to be accepted. The charging algorithm of this mode is designed
to work well with AC generators regardless of power quality or regulation mechanism. The generator
must still comply with the inverter’s nominal input specifications. (See page 24.)
BENEFITS:
The Radian inverter will charge the batteries from the generator even when the generator is undersized, of
low quality, or has other problems. See page 26 for recommended parameters for sizing a generator.
In cases where utility grid power is unstable or unreliable,
accept the power.
A programmable delay time is available which will allow a generator to stabilize before connection. In the
MATE3, this menu item is
the
NOTES
Any AC fluctuations that are accepted by the inverter will be transferred to the output. The loads will be
exposed to these fluctuations. It may not be advisable to install sensitive loads under these conditions.
The name of
mode. The use of this mode does not require the use of the
Conversely, the Radian is not required to be placed in this mode just because a generator is installed.
Connect Delay
Gen AC Input Mode and Limits
:
Generator
mode does not mean that the Radian requires a generator input when using this
Generator
. It is available in both the
menus, depending on which input is being programmed.
Gen
mode may allow the Radian inverter to
Grid AC Input Mode and Limits
input; either input can be used.
and
Support
The
Support
amount of current available from the source is limited due to size, wiring, or other reasons. If large
loads need to be run, the Radian inverter augments (supports) the AC source. The inverter uses
battery power and additional sources to ensure that the loads receive the power they demand.
In the MATE3 system display, the
14 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
mode is intended for systems that use the utility grid or a generator. In some cases the
Grid Input AC Limit
dictates the maximum AC draw for the
Grid
Page 17
Operation
input. The
IMPORTANT:
of power, load use should be planned accordingly.
IMPORTANT:
common with generators smaller than the wattage of the inverter.
IMPORTANT:
check with the utility company and obtain their permission before using this mode.
Gen Input AC Limit
sets the maximum draw for the Gen input. The Support function takes
effect if the AC demand on either input exceeds the
AC Limit
setting.
BENEFITS
Large inverter loads can be powered while staying connected to the AC input, even if the input is limited.
The added battery power prevents overload of the input source, but the batteries are not in constant use.
The Radian inverter will offset the loads with excess renewable energy if it is available from the batteries.
See page 35 for more information.
NOTES
:
:
The inverter will draw energy from the batteries when the loads exceed the
appropriate
batteries may discharge to the Low Battery Cut-Out point. The inverter will
shut down with a Low Battery error. (See pages 22 and 57
AC Limit
. With sustained loads and no other DC source, the
.) To prevent the loss
A “noisy” or irregular AC source may prevent
The inverter will transfer the power, but will not support the source, charge the
batteries, or interact with the current in any other way. This problem is more
A programmable delay time is available which will allow an AC source to stabilize before connection. In the
MATE3, this menu item is
the
Gen AC Input Mode and Limits
Connect Delay
. It is available in both the
menus, depending on which input is being programmed.
Support
from working normally.
Grid AC Input Mode and Limits
and
Grid Tied
The
to using power from the utility grid for charging and loads, the inverter can also convert excess battery
power and sell it to the utility grid. Excess battery power usually comes from renewable energy
sources, such as PV arrays, hydroelectric turbines, and wind turbines.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 15
Because the inverter limits the current draw from the AC source, it will reduce the charge rate as necessary
to support the loads. If the loads equal the appropriate
If the AC loads
reverse. It will take power
The
Support
exceed
function is not available in any other input mode.
the
AC Limit
from
setting, the Support function is activated by operating the charger in
the batteries and use it to support the incoming AC current.
AC Limit
setting, the charge rate will be zero.
Selling power to the utility company requires the authorization of the local
electric jurisdiction. How the utility company accommodates this will depend
on their policies on the issue. Some may pay for power sold; others may issue
credit. Some policies may prohibit the use of this mode altogether. Please
Grid Tied
mode allows the Radian inverter to become grid-interactive. This means that in addition
Page 18

Operation
The grid-interactive function is integrally tied with Offset operation and with the battery charger. See
pages 35 and 27 for more information on these items.
BENEFITS
:
Excess power is returned to the utility grid.
The inverter will offset the loads with excess renewable energy if it is available from the batteries.
If the excess energy is greater than the AC demand (the load size), the excess will be sold to the utility grid.
Due to varying requirements in different locations around the world, the grid-interactive settings are
adjustable. These adjustments are made in the
∼ This menu is only available to operators with installer-level access. There are firm rules concerning the
acceptable voltage range, frequency range, clearance time during power loss, and reconnect delay
when exporting power to the utility. Generally it is expected that the end user cannot alter the settings.
∼ The installer password must be changed from the default in order to get access to these settings. Once
this password has been changed, the settings can only be accessed by using the installer password. See
pages 67 and 69 for more information.
∼ The inverter’s operating frequency can be changed between 50 and 60 Hz using the Grid Interface
Protection menu. This setting changes the inverter’s input acceptance parameters, as well as its output.
See Table 16 beginning on page 67 for the locations of all menu items in the MATE3 menus.
NOTES
:
The inverter has a delay before selling will begin. This delay has a default setting of one minute. During this
time, the inverter will not connect to the utility grid. This setting is adjustable in the
menu. Upon initial connection to the utility grid, the inverter may be required to perform a battery charging
cycle. This may delay the operation of the grid-interactive function.
Grid Interface Protection
menu.
Grid Interface Protection
The grid-interactive function only operates when excess DC (renewable) power is available.
The grid-interactive function is not available in any of the other input modes.
When power is returned to the utility grid, it may be possible to reverse the utility meter. However, this
depends on other loads in the system. Loads on the main panel (not on the inverter’s output) may consume
power as fast as it is sold. The meter would not run backwards, even if the system display showed the
inverter selling power. The result of selling would be to reduce AC power consumption, not reverse it.
The amount of power an inverter can sell is not equal to its specified output wattage. The
Current
Protection
∼ The amount of power that is sold is controlled by the utility grid voltage. The wattage sold is
∼ This recommendation is specifically for the inverter’s grid-interactive function. In some cases, the
The grid-interactive function can only operate while the utility grid power is stable and within specific limits.
∼ In Grid Tied mode, the inverter will operate in accordance with the Grid Interface Protection settings.
can be decreased if it is necessary to limit the power sold. This item is available in the
menu.
determined by this voltage multiplied by the current. For example, if the inverter sells 30 amps and the
voltage is 231 Vac, the inverter will sell 6.93 kVA. If the voltage is 242 Vac, the inverter will sell 7.26 kVA.
Additionally, output will vary with inverter temperature, battery type, and other conditions.
source may be sized larger to account for environmental conditions or the presence of DC loads. This
depends on individual site requirements.
The default settings and ranges are listed in Table 16
If the AC voltage or frequency vary outside the Grid Interface Protection limits, the inverter will
disconnect from the utility grid to prevent selling under unacceptable conditions. These limits override
the AC source acceptance limits described on page 24, which are used in other input modes.
, which begins on page 67.
Maximum Sell
Grid Interface
16 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 19
Operation
∼ If the inverter stops selling or disconnects due to Grid Interface Protection, the MATE3 will show the
Failure
reason. Sell Status messages are listed on page 61. Disconnect messages are listed on page 60. Often
these messages will be the same.
∼ Due to varying requirements in different locations around the world, the grid-interactive settings are
adjustable. However, this is only available to operators with installer-level access. There are firm rules
concerning the acceptable voltage range, frequency range, clearance time during power loss, and
reconnect delay when exporting power back to the utility. Generally it is expected that the settings
cannot be altered by the end user. For this reason, it is necessary to change the installer password from
the default in order to get access to these settings. Once this password has been changed, the settings
can only be accessed by using the installer password. See pages 67 and 69 for more information.
Before operating in Grid Tied mode, contact the utility company that provides power to the installation.
They can provide information regarding the rules that must be followed in order to export power back
to the utility. The items below are the selectable options for Grid Interface Protection. It may be
necessary to provide these options to the utility company to make certain their standards are met.
The utility may simply name a standard to be followed, as with AS 4777.3 for Australia. It may be
necessary to look up the requirements for a local standard and program them accordingly.
STAGE 1 Voltage (basic settings)
Over Voltage Clearance Time (seconds)
Over Voltage Trip (AC Voltage)
Under Voltage Clearance Time (seconds)
Under Voltage Trip (AC Voltage)
STAGE 2 Voltage (if required by utility)
Over Voltage Clearance Time (seconds)
Over Voltage Trip (AC Voltage)
Under Voltage Clearance Time (seconds)
Under Voltage Trip (AC Voltage)
See Table 16 on page 67 for the default settings and ranges.
Frequency Trip
Over Frequency Clearance Time (seconds)
Over Frequency Trip (Hertz)
Under Frequency Clearance Time (seconds)
Under Frequency Trip (Hertz)
The
NOTE:
dependent on the inverter’s operating frequency,
which must be set correctly. See pages 9 and 69.
Mains Loss
Clearance Time (seconds)
Reconnect Delay (seconds)
Frequency Trip
settings are
UPS
In
times. If the utility grid becomes unstable or is interrupted, the Radian can transfer to inverting in
minimal time. This allows the system to support sensitive AC loads without interruption.
mode, the Radian’s parameters have been optimized to reduce the response and transfer
UPS
BENEFITS
Constant power is provided to the loads with virtually no drop in voltage or current.
NOTES
Due to the need for the Radian inverter to react quickly to AC source fluctuations, it must remain fully active
:
:
at all times. The inverter requires a continuous consumption of 42 watts.
For this reason, the Search function does not operate in this mode. (See page 23.)
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 17
Page 20
Operation
Failure
Backup
The
Backup
mode is intended for systems that have utility grid available as the primary AC source.
This source will pass through the Radian inverter’s transfer circuit and will power the loads unless
utility power is lost. If utility grid power is lost, then the Radian inverter will supply energy to the loads
from the battery bank. When the utility power returns, it will be used to power the loads again.
BENEFITS
This mode will continuously maintain the batteries in a fully-charged state, unlike the
does not have the overhead consumption of the
Mini Grid
In
Mini Grid
:
mode. It
UPS
Support
mode.
mode, the Radian inverter automatically rejects an AC source and runs solely from battery
(and renewable) energy. The inverter only connects to the AC source (usually the utility grid) when
the batteries run too low.
The Radian inverter runs on battery-supplied power for as long as the batteries can be sustained. It is
expected that the batteries will also be charged from renewable sources such as PV. When the
batteries become depleted, the system reconnects to the utility grid to operate the loads.
The inverter will reconnect to the utility grid if the battery voltage decreases to the
set point and remains there for the
time period. These items are shown in Table 16 on page 67.
Delay
Connect to Grid
While connected to the utility grid, the inverter’s charger can be set either on or off. If the charger is
turned on, the inverter will proceed through a full charging cycle. Upon reaching float stage, the
inverter will disconnect from the grid.
If the inverter is connected to the utility grid and the charger is turned off, another DC source such as
renewable energy should be present to charge the batteries. The inverter will observe the batteries as
if it was performing the charge. When the batteries reach the required voltages and charging times to
achieve float stage, the inverter will disconnect from the grid. This means that the regulator for the
renewable source must be set to the same settings as the Radian (or higher). Check the settings of
both devices as needed.
See page 27 for more information on the battery charging cycle.
BENEFITS
Mini Grid
possible if certain conditions are met. See the Notes below.
NOTES
The Radian inverter will offset the loads with excess renewable energy if it is available from the batteries.
See page 35 for more information on Offset operation. However, the Offset function is inapplicable when
the Radian disconnects from an AC source. The renewable energy supports the inverting function instead.
This mode has similar priorities to the high-battery transfer (
display. However, it is not compatible with
Grid
:
mode allows a system to minimize or eliminate dependence on the utility grid. This is only
:
) function used by the MATE3 system
HBX
and cannot be used at the same time. When using
HBX
mode, the system display should disable
to prevent conflicts.
HBX
Mini
18 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 21
Operation
Mini Grid
system display. These functions do not have similar priorities to
inverter’s connection and disconnection with the grid.
When deciding whether to use
∼ Mini Grid logic is based in the Radian inverter and can function in the absence of the MATE3. HBX logic
∼ Mini Grid can use utility grid power to fully recharge the batteries every time it reconnects to the
∼ HBX set points have a wide range of settings. Mini Grid uses settings intended to protect the batteries
∼ HBX works more efficiently with a larger renewable source, but there is no specification for renewable
∼ HBX can be combined with the settings of any other input mode (Generator, UPS, etc.). The Mini Grid
∼ See page 47 for more information on HBX, Grid Use Time, and Load Grid Transfer.
mode is also incompatible with the
Mini Grid
is based in the MATE3 and cannot function unless the MATE3 is installed and operating.
grid. HBX can only do so under specific circumstances.
from excessive discharge; however, most of its settings are automatic and do not allow customization.
size. Mini Grid cannot work properly unless the source is larger than the size of the loads. If this
condition is not met, Mini Grid will not disconnect the inverter from the utility grid.
input mode is limited to its own settings and does not have access to certain functions of other modes.
Grid Use Time
mode or
HBX
and
Load Grid Transfer
Mini Grid
Mini Grid
, the user should consider the aspects of each.
should not be used with these functions.
or
HBX
functions of the MATE3
, but they do control the
Grid Zero
In
Grid Zero
mode, the Radian inverter runs primarily from battery (and renewable) energy while
remaining connected to an AC source. The inverter only draws on the AC source (usually the utility
grid) when no other energy is available. Using the DC sources, the inverter attempts to decrease the
use of the AC source to zero.
In the MATE3 system display, the selectable options are
batteries exceed the
DoD Volts
the battery voltage decreases to the
setting, the Radian will send power from the batteries to the loads. As
DoD Volts
setting, the inverter will reduce the rate of flow toward
DoD Volts
and
DoD Amps
. Any time the
zero. It will maintain the batteries at this setting.
The Radian inverter can manage large quantities of power. To prevent damage to the batteries from
rapid discharge, the rate of discharge can be limited using the
DoD Amps
setting. This item should be
set lower than the amperage provided by the renewable source.
When
DoD Volts
the loads. However, it will also leave less of a battery reserve in the event of a grid failure.
When
DoD Volts
reserve. However, not as much renewable energy will be sent to the loads.
is set low, this mode allows more renewable energy to be delivered from the batteries to
is set high, the batteries will not be discharged as deeply and will retain more of a backup
The renewable energy source needs to exceed the size of the loads after accounting for all possible
losses. The renewable source is also required to charge the batteries after this mode discharges them.
The inverter’s battery charger does not function in
Grid Zero
mode.
BENEFITS
Grid Zero
possible if certain conditions are met. See the Notes section.
This mode puts battery and renewable energy to the most effective use without selling power to the utility
grid and without dependence on the grid.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 19
:
mode allows a system to minimize or eliminate dependence on the utility grid. This is only
Page 22

Operation
The inverter remains connected to the utility grid in case the grid is needed. If large loads require the use of
grid power, no transfer is necessary to support the loads.
NOTES
:
If the renewable energy source is not greater than the size of the inverter loads, this mode will not work well
over time. The renewable source must be capable of charging the batteries as well as running the loads.
This occurs when renewable energy production exceeds the
The inverter will offset the loads with excess renewable energy if it is available from the batteries. See
page 35 for more information on Offset operation. However, the behavior of Offset in Grid Zero mode is
different because it uses the
The inverter’s battery charger cannot be used in this mode. However, the menu settings and timer
operations are not changed when this mode is selected.
The battery should be discharged whenever possible in the attempt to “zero” the grid usage. If the
setting is limited or loads are not present, the batteries will be unable to accept much renewable
Amps
recharging the next time it is available. The renewable energy will be wasted, leaving the system
dependent on the utility grid more than necessary.
DoD Volts
exclusively.
DoD Amps
setting.
DoD
20 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 23
Operation
Table 1 Summary of Input Modes
Mode
Summary
Benefits
Cautions
Intended
Charger
devices
AC source
response time
reacts accordingly
Generator
Support
GridTied
UPS
Accepts power
from an
irregular or
low-quality
AC source
Adds battery
power to
augment an
AC source that
has limited
output
Inverter sells
excess power
(renewable)
to utility
In grid failure,
unit switches
to batteries
with fastest
possible
Can use AC that may be
unusable in other modes
Can charge even with a
poor generator or
low-quality AC source
Can use battery power
in conjunction with
AC source
Offset operation sends
excess DC to loads
Bidirectional input
Can reduce utility bills
and still provide backup
Offset operation sends
excess DC to loads
Any additional Offset
excess is sold to the grid
Quick backup for
sensitive devices during
grid outage
Will pass irregular or
low-quality power to
the output; could
damage sensitive loads
Offset unavailable
Drains batteries during
support; intended for
intermittent use only
May not function with
low-quality AC source
Requires utility
approval
Other approvals may be
required depending on
electrical codes
Has exact requirements
for accepting AC input
Requires renewable
energy source
Uses higher idle power
than other modes
Search function
unavailable
Offset unavailable
Source:
Generator
Loads:
Nonsensitive
Source:
Grid or
Generator
Loads:
Can be
larger than
Source:
Grid
Loads:
Any type
Source:
Grid
Loads:
PC, audio,
video, etc.
Performs three-stage
charge and goes
silent as specified by
settings.
Performs three-stage
charge and goes
silent as specified by
user settings.
Performs three-stage
charge and goes
silent as specified by
user settings.
Performs three-stage
charge and goes
silent as specified by
user settings.
Backup
In grid failure,
unit switches
batteries to
support loads;
this is the
default mode
Mini Grid
Stays off grid
most of the
time; only uses
grid when
batteries low
Grid Zero
On-grid but
actual grid use
is “zeroed out”
with battery
and renewable
power; does
not sell or
charge
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 21
Simple use compared to
other modes; often
used with generators for
this reason
Less idle power than
Does not drain battery as
in
Support
Can minimize/eliminate
dependence on grid
Offset operation sends
excess DC to loads (but
only when on grid)
Can minimize/eliminate
dependence on grid
Offset operation sends
excess DC to loads at
adjustable rate
Remains on-grid to avoid
transfer problems
UPS
Has none of the special
functions described in
other modes, including
Offset
Will not work properly
unless renewable
source is above a
certain size
Conflicts with related
modes in MATE3
Discharges batteries
while remaining on grid
Will not work properly
unless renewable
source is above a
certain size
Battery charger
inoperative
Source:
Grid or
Generator
Loads:
Any type
Source:
Grid
Loads:
Any type
Source:
Grid
Loads:
Any type
Performs three-stage
charge and goes
silent as specified by
user settings.
Performs three-stage
charge on reconnect;
if charger is disabled,
inverter emulates
charge cycle from
external source and
Charger inoperative;
batteries must be
charged using an
external (renewable)
energy source
Page 24
Operation
Description of Inverter Operations
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
the batteries and the inverter, but not in place of the batteries.
V
V
The items in this section are operations common to all Radian inverters. These are used in most or all
of the input modes described in the preceding section.
Some of the items in this section are functions which can be manually selected, enabled, or
customized. Other items are general topics or applications for the inverter. These items may not have
their own menus, but their activity can still be influenced or optimized by changing certain settings.
Any of these items may need to be adjusted so that the inverter is best matched to a particular
application. The operator should review these items to see which are applicable.
All items described as settable or adjustable have set points which can be accessed using the
system display. The default settings and ranges of adjustment are listed in Table 16 beginning on
page 67 of this manual.
Inverting
This is the Radian inverter’s primary task. The inverter converts DC voltage from batteries into AC
voltage that is usable by AC appliances. It will continue to do this as long as the batteries have
sufficient energy. The batteries can be supplied or recharged from other sources, such as solar, wind,
or hydroelectric power.
The inverter’s design uses transformers and high-frequency H-Bridge FET modules to achieve the
required high-wattage output. In the GS7048E, the dual design allows half the inverter to shut down
for lower idle consumption when not in use.
The Radian can deliver the rated wattage continuously at 25°C. The maximum output is derated at
temperatures exceeding 25°C. See pages 63 and 65 for these wattages.
Measure the total load wattage so that it does not exceed the Radian’s capacity. The Radian cannot
maintain its AC voltage under an excessive load. It will shut down with a
DC and AC Voltages
The Radian inverter requires batteries to operate
that are consistent enough for the inverter to operate reliably.
Do not substitute other DC sources in place of the batteries. High or irregular
The following items will affect the inverter’s operation. These are only used when the inverter is
generating AC power on its own.
Low Battery Cut-Out
DC voltage drops below a specified level for 5 minutes, the inverter will stop functioning. The MATE3 will
give a
Low Battery V
on the MATE3 system display.
voltages may damage the inverter. It is normal to use other DC sources with
: This function prevents the inverter from draining the batteries completely. When the
error. This is one of the error messages described on page 57. It appears as an event
. Other sources may not maintain DC voltages
Low Output Voltage
error.
This function is intended to protect both the batteries and the inverter’s output. (Continuing to invert on a
low DC voltage may produce a distorted waveform.) This item is adjustable.
22 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 25

Operation
IMPORTANT:
should be made at the same time. (See AC Source Acceptance on page 24.)
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
inverter’s output frequency matches the installation.
Hz
Low Battery Cut-In
point for 10 minutes, the error will clear and the inverter will resume functioning. This item is adjustable.
∼ Connecting an AC source for the Radian to charge the batteries will also clear a low battery error.
Output Voltage
to be used for different nominal (single-phase) voltages such as 220 Vac, 230 Vac, and 240 Vac.
: The recovery point from Low Battery Cut-Out. When the DC voltage rises above this
: The AC output voltage can be adjusted. Along with small changes, this allows the inverter
The output voltage can adjusted to a different nominal value for a particular region.
Making this change will not affect the default input voltage range accepted by the
inverter from an AC source. The input range must be adjusted manually. These changes
The inverter is also controlled by a high battery cut-out limit. If the DC voltage rises above this limit, the
inverter will immediately stop functioning and give a
described on page 57. The shutdown occurs to protect the inverter from damage due excessive DC voltage.
It appears as an event on the MATE3 system display.
∼ For the Radian inverter, the high battery cut-out voltage is 68 volts. It cannot be changed.
∼ If the voltage drops below this point, the inverter automatically recovers.
High Battery V
error. This is one of the error messages
AC Frequency
Setting the inverter’s output frequency to deliver 50 Hz to 60-Hz loads, or setting it to
deliver 60 Hz to 50-Hz loads, could damage sensitive devices. Make certain the
The inverter’s output can operate at a frequency of either 50 or 60 hertz. This output frequency (and
the AC acceptance frequency) can be changed with the
Operating Frequency
menu item. This
requires high-level access. Due to the possibility of damage, access to this setting was restricted by
placing it in the
Grid Interface Protection
menu.
The installer password must be changed from the default in order to get access to this menu. Once
this password has been changed, the
Grid Interface Protection
menu can only be accessed by using
the installer password. This password can be changed in the system display.
See page 17 for more information on the
on page 67, for the location of the
Search
Operating Frequency
Grid Interface Protection
menu item.
menu. See Table 16, which begins
An automated search circuit is available to minimize the power draw when no loads are present.
When enabled, the inverter does not always deliver full output. The output is reduced to brief pulses
with a delay between them. These pulses are sent down the output lines to see if a resistance is
present. Basically, the pulses “search” for a load. If a load is detected on the output, the inverter’s
output increases to full voltage so that it can power the load. When the load is turned off, the inverter
“goes to sleep” and begins searching again.
The sensitivity of Search mode is in increments of approximately 0.1 Aac. The default is 6 increments,
or about 0.6 Aac. A load which draws this amount or greater will “wake up” the inverter.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 23
Page 26

Operation
NOTE:
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
damage is not covered by warranty. Use protective devices of appropriate size.
A
A
A
Due to load characteristics, these increments are only approximate and may not function
exactly as listed.
The pulse duration and the delay both have a time period that is measured in AC cycles. These two
items and the load detection threshold are adjustable.
Search mode may not be useful in larger systems with loads that require continuous power (e.g., clocks,
answering machines, fax machines). Search mode may cause nuisance shutdowns, or it may sleep so rarely
that there is no benefit.
Some devices may not be easily detected by Search mode.
Search is inoperative if the
input mode is in use. See page 17 for more information on this mode.
UPS
Input
When the Radian inverter input terminals are connected to a stable AC source, the inverter will
synchronize itself with that source and use it as the primary source of AC power. Its transfer relay will
engage, linking the AC source directly with the inverter’s output. It can also use the source to charge
batteries. (See Battery Charging on page 27.)
Two sets of AC input terminals are available. Both inputs are identical and can be used for any AC source.
However, for easy reference, the first input has been labeled
labeled
∼ Each input has a separate set of input criteria and input modes.
∼ The criteria, modes, and other programming for each input contain identical content.
The independent inputs are intended to simplify the connection to multiple AC sources; however, the
inverter can only use one input at a time. If both inputs are powered, the default setting is for the inverter to
accept the
using
Seven input modes are available which affect the Radian inverter’s interactions with AC input sources.
The
Grid Tied
battery power to assist a smaller AC source. See page 21 for descriptions of these and other input modes.
The loads powered by the inverter
(for a generator). These designations are also used in the menus of the MATE3 system display.
GEN
input. This can be changed. In the MATE3 system display, these priorities are selected
GRID
Input Priority
mode allows the Radian to sell power using the input connection. The
in the
AC Input and Current Limit
must not
exceed the size of the inverter’s transfer relay.
menu.
(for the utility grid). The second input is
GRID
Support
mode can use
Current draw in excess of the transfer relay rating can damage the transfer relay. This
AC Current Settings
The AC current settings,
Grid Input AC Limit
that the inverter draws from the source(s). When using either of the Radian’s AC inputs, the
appropriate setting limits the input. Adjust these settings to match the input circuit breakers.
The adjustment is meant to protect a generator or source that cannot supply enough current for both
charging and loads. If the combined charging and loads exceed the setting, the inverter will reduce its
charge rate and give priority to the loads. If the loads exceed this number on their own, the charge rate will
be reduced to zero.
The Radian’s battery charger and grid-interactive function have individual settings. However, the
settings can also limit the charging or selling current.
Limit
The
Support
24 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
input mode allows the Radian to support the AC source with battery power. See page 14.
and
Gen Input AC Limit
, control the amount of current
AC
Page 27

Operation
The AC input current is used to power both loads and battery charging. The combined amount should not
IMPORTANT:
exceed the size of the AC overcurrent device or AC source. These devices should be sized appropriately
during planning and installation of the inverter system.
If multiple parallel inverters are installed with an AC source of limited amperage, the total combined
amperage settings for all units must be less than the AC input circuit. The Configuration Wizard in the
MATE3 can perform this calculation. However, the inverters do not perform this calculation. If the MATE3 or
the Configuration Wizard are not used, divide the input size by the number of inverters and assign an equal
part of the amperage to each port.
AC Source Acceptance
The input source must meet the following specifications to be accepted. This is true in all modes
except
Voltage (both inputs): 208 to 252 Vac (default)
Frequency (both inputs): If output frequency is set to 50 Hz (default), the input range of acceptance is 45 to
See Table 16 on page 67 for the available selections for these items.
Grid Tied
55 Hz. If the output frequency is set to 60 Hz, the input acceptance range is 55 to 65 Hz.
(see
NOTES
on page 26):
When these conditions are met, the inverter will close its transfer relay and accept the input source.
This occurs after a delay which is specified below. If the conditions are not met, the inverter will not
accept the source. If it was previously accepted and then rejected, the inverter will open the relay and
return to inverting power from the batteries. This occurs after a specified transfer delay, which is an
adjustable menu item.
The Radian’s output voltage can adjusted to a different nominal value for a particular
region. (See page 23.) If this occurs, the source acceptance range should be adjusted to
match this nominal value or the inverter may not accept the new source normally.
The voltage limits can be adjusted to allow (or exclude) a source with weak or irregular voltages. These
items are adjustable in the appropriate menu of the MATE3 (
Input Mode and Limits
changing the range of allowed voltages.
Each of the AC inputs has a settable
input source to stabilize before connection.
∼ The default setting for the Grid input is 0.2 minutes (12 seconds).
∼ The default setting for the Gen input is 0.5 minutes (30 seconds).
These items are adjustable in the appropriate menu of the MATE3 (Grid AC Input Mode and Limits or Gen
AC Input Mode and Limits).
). The settings are titled
Connect Delay
Voltage Limit Lower
. This is intended as a warmup period which allows an
Grid AC Input Mode and Limits
and
. There can be side effects to
Upper
or
Gen AC
NOTES:
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 25
The
Grid Tied
settings instead. (See page 17 for more information.) The inverter may not accept AC power if it meets the
settings noted here but does not meet the
AC Acceptance is controlled separately between the Radian inverter’s two inputs. An AC source that is
unacceptable on one input may be acceptable on the other if the input mode or settings are different.
Certain input modes such as
conditions are met. (See page 18.)
Several items external to the inverter may prevent the inverter from accepting AC power even if electrical
conditions are met. Some examples are the
input mode does not use these acceptance limits and uses the
settings.
Mini Grid
Grid Interface Protection
may prevent the inverter from accepting AC power even if electrical
High Battery Transfer, Grid Usage Time
Grid Interface Protection
, or
Load Grid Transfer
Page 28
Operation
functions, all of which are operated by the MATE3 system display. (See page 47.) Another example is the
CAUTION: Equipment Damage
damage is not covered by warranty. Use protective devices of appropriate size.
MATE3’s
AC INPUT
hot key menu, which can order all inverters to disconnect when set to
Drop
.
Generator Input
A generator should be sized to provide enough power for all inverters, both for loads and for battery
charging. The generator’s voltage and frequency must match the inverter’s acceptance settings.
It is usually recommended that the generator be sized at twice the wattage of the inverter system.
Many generators may not be able to maintain AC voltage or frequency for long periods of time if they
are loaded more than 80% of rated capacity.
The generator is required to have a stable output before its power is accepted by the inverter. Some
generators with less stable or uneven outputs may not be accepted. The use of the
mode may assist with this problem.
Transfer
The inverter uses a transfer relay to alternate between the states of inverting and of accepting an AC
source. Until the relay energizes, the output terminals are electrically isolated from the input that is in
use. When it closes, the input and output terminals become electrically common. (The terminals for
the unused input remain isolated during this time.) When the relay changes states, the physical
transfer delay is approximately 25 milliseconds.
The relay contacts are limited to 50 amps per phase or leg. The continuous loads on that output
should never exceed this number. When connected to an AC source, the Radian inverter cannot limit
the load current. An overload condition is possible.
Generator
input
Current draw in excess of the transfer relay rating can damage the transfer relay. This
The inverter does not filter or clean up the power from the AC source. The voltage and power quality
received by the output loads is the same as that of the source. If the voltage or quality do not meet
the inverter’s input requirements, it will disconnect and return to the inverting mode.
NOTES
If the charging function is turned off, the inverter will transfer power from the source but will not use it
to charge. If the inverting function is turned off, the inverter will transfer (“pass through”) the source
power when connected, but will not invert when the source is removed.
In a stacked system, slaves are ordered to transfer at the same time as the master. If a slave does not
sense an AC source at the same time as the master, it will continue inverting, and will experience a
Phase Loss
:
To ensure a smoother transition, it may be advisable to raise the inverter’s lower acceptance limit.
The default setting is 208 Vac. A higher setting will cause the inverter to transfer sooner in the event of a
quality problem.
If the AC source meets the inverter’s requirements but is irregular, any fluctuations will be transferred to the
loads. If the loads are sensitive, it may be necessary to improve the quality of the AC source.
The
Generator
so than other modes. This should be considered before using this mode with sensitive loads. (See page 13.)
input mode is intended to accept irregular or unfiltered AC sources and is more likely to do
warning (see page 58). This appears as an Event on the MATE3 system display.
26 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 29

Operation
Battery Charging
IMPORTANT:
undercharged or overcharged.
IMPORTANT:
Table 2 Charge Currents for Radian Models
Model
Maximum DC Output (sent to battery)
Maximum AC Input (used from source)
Battery charger settings need to be correct for a given battery type. Always
follow battery manufacturer recommendations. Making incorrect settings, or
leaving them at factory default settings, may cause the batteries to be
Charge Current
Batteries or battery banks usually have a recommended limit on the maximum current used for
charging. Often this is calculated as a percentage or fraction of the battery capacity, represented by
“C”. For example, C/5 would be a DC amperage figure that is 1/5 of the total amp-hours of the bank.
Any chargers must be set so that the peak charge current does not exceed the recommended
maximum. If multiple chargers are present (including other chargers besides the Radian), this
calculation must accommodate the total combined current. The Radian’s charger may need to be set
at less than maximum. The system display can be used to change charger settings.
Although the recommended current is generally represented in DC amperes, the
AC Limit
To convert the recommended DC current into a usable AC figure, divide the DC figure by
4 and round up. The result can be used as a charger setting for the Radian inverter.
Examples:
setting is measured in AC amperes, which are not measured on the same scale.
1) Battery bank consists of 8 x L16 FLA batteries in series. Recommended
maximum charge current is 75 Adc.
75 ÷ 4 = 18.75 or 19 Aac.
2) Battery bank consists of 12 x OutBack EnergyCell 200RE VRLA batteries in
series/parallel. Recommended maximum charge current is 90 Adc.
90 ÷ 4 = 22.5 or 23 Aac.
Charger
The maximum DC charge rate for Radian models is specified in Table 12 on page 63. The actual
Charger AC Limit
setting is available in the
display. See Table 16 on page 67. These numbers are also summarized in Table 2 below. If multiple
Radian inverters are installed, divide the total current by the number of inverters and program each
with the resulting number.
GS7048E 100 Adc 30 Aac
GS3548E 50 Adc 15 Aac
Charge Cycle
The inverter uses a “three-stage” battery charging process which is designed around batteries using
lead-acid chemistry. The three stages are Bulk, Absorption, and Float. These stages follow a series of
steps, which are shown on graphs and described in text (see page 28). On the graphs, the transitions
between steps are marked with vertical dotted lines. A circle indicates that the inverter has begun
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 27
AC Input and Current Limit
menu of the MATE3 system
Page 30

Operation
charging to a new voltage setting. A square indicates that the inverter has reached the setting (a
Absorption
Float
Bulk
(c.c.)
Silent
Float Timer (c .v.)
Silent
Float
Float Timer
Re-Float
No
Float
Silent
Float
(c.v.)
Float
Absorption (c.v.)
c.c. = Constant-Current Stage; charger can deliver up to inverter’s maximum (or maximum setting)
c.v. = Constant-Voltage Stage; charger delivers the current needed to maintain voltage; usually tapers
Voltage
Time
Bulk
(c.c.)
Float (c.v.)
Absorption (c.v.)
No Charge
Time
Absorption
Float
No
Voltage
c.c. = Constant-Current Stage; can deliver up to the inverter’s limit
c.v. = Constant
horizontal dotted line). A triangle indicates that the inverter has stopped charging and is no longer
using the previous set point. (The charging may have stopped for any of several reasons.) The battery
voltage must drop to one of several low set points before the inverter resumes charging.
Specialized Charging
Lithium-ion, sodium-sulfur, and similar advanced battery technologies may require charger settings
that are very different from the inverter’s defaults or the three-stage cycle in general. The Charging
Steps section describes the individual selections and behavior. All charger settings are adjustable.
The selection range for each step allows very different priorities from the defaults. For example, the
Float voltage could be set higher than the Absorption voltage, or a step could be completely skipped..
Charging Graphs
Figure 4 shows the progression of steps of the default three-stage charging cycle.
Set Point
Set Point
Set Point
Charging
(c.c.)
(c.c.)
(c.c.)
Timer
Figure 4 Charging Stages Over Time
Figure 5 shows the charge cycle used by the inverter when the
Float Time
This setting eliminates the Silent and Float Timer steps. The charger remains in Float continuously.
The Float stage lasts until the AC source is removed.
Set Point
Set Point
menu item is set to
24/7
.
Charge
-Voltage Stage; delivers only the current needed to maintain voltage; usually tapers
Figure 5 Charging Stages Over Time (24/7)
28 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
(Source removed)
Page 31

Operation
Charging Steps
The following items describe the operation and intended use for each individual charging step as
shown in the graphs. Note that some charging cycles may not follow this exact sequence. These
include cycles which were previously interrupted, and also customized charging. Each step describes
how to defeat or customize the step if specialized charging is required.
See page 31 for a description of multiple cycles when the charger is restarted after completion.
This page also describes multiple cycles when the charger is restarted after being interrupted.
For multiple inverters:
The charging of parallel stacked inverters is synchronized by the master inverter. The charger settings
of slave or subphase masters are ignored. Slaves or subphase masters use the master inverter settings.
No Charging
If the inverter is not charging, any of the following conditions may apply:
The unit is not connected to a qualified AC source. If a generator is present, it may not be running.
The unit is connected to an AC source but is in a mode or step (such as Silent) that does not use the charger.
The unit is connected to an AC source but the charger has been turned off.
Bulk Stage
This is the first stage in the three-stage charge cycle. It is a constant-current stage which drives the
battery voltage up. This stage typically leaves the batteries at 75% to 90% of their capacity,
depending on the battery type, the exact charger setting, and other conditions.
Voltage Used:
The initial DC current may be as high as the charger’s maximum current, depending on conditions.
It will begin at a high level, but will drop slightly as the voltage rises. This is not a decrease in charging;
the charger delivers constant power in Bulk stage. It can be viewed as a wattage “tradeoff”; the
increase in voltage results in a decrease in current for a constant wattage.
To skip this step:
through the normal three-stage cycle, but at a single voltage. Setting
the charger to skip both the Bulk and Absorption stages and proceed directly to Float. This may not
be desired if the intent is to include the Bulk stage but skip Absorption.
Absorb Voltage
Setting
setting. The default setting is 57.6 Vdc.
Absorb Voltage
equal to
Float Voltage
will cause the charger to proceed
Absorb Time
to zero will cause
Absorption Stage
This is the second stage of charging. It is a constant-voltage stage. Current varies as needed to
maintain the voltage, but will typically decrease to a very low number over time. This “tops off the
tank”, leaving the batteries at essentially 100% of capacity.
Voltage Used:
page 35.) For the three-stage cycle to proceed normally, this setting should be kept higher than the
Float Voltage
Time limit:
until it reaches zero. The time remaining can be viewed in the system display.
The Absorption timer does not reset to zero when AC power is disconnected or reconnected. It only
resets to zero if it runs out, or if an external STOP BULK command is sent; otherwise it retains any
remaining time.
Absorb Voltage
and
Re-Bulk Voltage
Absorb Time
setting. This setting is also used by Offset when in this stage. (See
settings.
setting. This timer counts down from the inception of the Absorption stage
The
Absorb Time
The duration of Absorption is equal to the amount of time the
battery voltage (up to the maximum Absorption limit). The counter adds more time to the Absorption
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 29
setting is not a required minimum period for Absorption. It is only a maximum limit.
Re-Bulk Voltage
setting exceeds the
Page 32

Operation
period whenever the battery voltage decreases below this setting. (See page 31 for more information
on how the timer works.)
To skip this step:
minimal time in Absorption once the Bulk stage is complete. Setting
the charger to skip both the Bulk and Absorption stages and proceed directly to Float. This may not
be desired if the intent is to skip Absorption but retain the Bulk stage.
Setting
Absorb Time
to a very short duration will cause the charger to spend
Absorb Time
to zero will cause
Silent
This is not a charging stage, but a quiescent period between stages. The inverter remains on the AC
source, but the charger is inactive. It enters this condition upon completing a timed stage such as
Absorption, Float, or Equalize.
In Silent, the batteries are not in significant use by the inverter, but they are also not being charged.
The battery voltage will naturally decrease when not maintained by another means such as a
renewable source.
The term “Silent” is also used in an unrelated context regarding Power Save levels. See page 39.
Voltage Used:
charger becomes active again. The default set point is 50.0 Vdc.
To skip this step:
that it does not proceed through the Silent, Bulk, Absorption, or Float timer steps.
Re-Float Voltage
Setting
setting. When the battery voltage decreases to this point, the
Float Time
to
will cause the charger remain in Float continuously so
24/7
Float Stage
This is the third stage of charging. It is sometimes known as maintenance charging. Float stage is
initially a constant-current stage. The initial DC current may be as high as the charger’s maximum
current, depending on conditions. This current is only sustained until the charger reaches the
Voltage
setting, after which the charger switches to constant-voltage operation.
Float
Float stage balances the batteries’ tendency to self-discharge (as well as balancing the draw of any
other DC loads). It maintains the batteries at 100% of capacity.
Voltage Used:
Offset when in this stage. (See page 35.) For the charger to work normally, this setting needs to be
higher than the
Time limit:
bulk and absorption stages, the charger will not enter Float and will go directly to Silent instead. See
Float Timer.
To skip this step:
total bulk and absorption times. Decreasing the
enter Silent as soon as the absorption stage is complete. The inverter will perform neither the
constant-current nor the constant-voltage portions of Float.
Setting
the normal three-stage cycle, but at a single voltage.
Float Voltage
Float Voltage
Re-Float Voltage
This can vary. If the duration of the
As noted, the charger will not enter Float if the
equal to the
setting. The default set point is 54.4 Vdc. This setting is also used by
setting.
Float Time
Float Time
Absorb Voltage
level will cause the charger to proceed through
setting is less than the total time of the
Float Time
setting to zero will cause the inverter to
setting is less than the
Float Timer
This is not a separate stage of charging. In Figure 4 on page 28, it is marked as a separate step to note
when the charger switches from constant-current to constant-voltage charging. When this occurs,
the current varies as needed to maintain the
: The Float timer begins running any time the battery voltage exceeds the
NOTE
point. This usually means that it begins running during the Bulk stage, once the battery voltage rises
Float Voltage
, but typically drops to a low number.
Float Voltage
set
30 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 33

Operation
above that level. Often the timer will expire before the bulk and absorption stages are complete. If
this happens, the charger will not enter Float but will go directly to Silent. The charger only spends
time in Float stage if the timer is still running.
Time limit:
is not still in progress.) The Float timer is reset to its maximum amount whenever the batteries
decrease to the
To skip this step:
that the Float timer no longer applies. (The charger also skips Bulk, Absorption, and Silent.) However,
the charger can initiate a single three-stage charge if the criteria are met, after which it will return to
continuous Float again.
Float Time
Re-Float Voltage
setting. The charger will go Silent once the timer has expired (if another stage
to 24/7 will cause the charger remain in Float continuously so
Setting
setting.
Float Time
Silent
Following the expiration of the Float timer, the unit enters (or re-enters) the Silent stage. The unit
remains connected to the AC source, but the charger is inactive.
The unit will continue cycling between Float and Silent for as long as the AC source is present.
New Charging Cycle
If the AC source is lost or disconnected, the unit will return to inverting mode if enabled. The battery
voltage will begin to decrease due to loads or natural loss. When the AC source is restored, the
inverter will return to the charging cycle.
Re-Bulk
If the battery voltage decreases due to discharge, the inverter will restart the cycle as soon as the AC
source is available, beginning at Bulk stage.
Voltage Used:
If the batteries do not decrease to the Re-Bulk point, the charger will not enter the Bulk stage and will
return to its previous stage.
Re-Bulk Voltage
setting. The default set point is 49.6 Vdc.
Absorption Timer
Time limit:
setting is not a required minimum period for Absorption. It is only a maximum limit. The duration of
Absorption is equal to the amount of time the battery voltage was less than the
setting, up to the maximum limit.
If the Absorption timer expired on the previous cycle, it is not reset afterward and retains a “remaining
run time” of zero. Whenever the battery voltage decreases to Re-Bulk or lower, the Absorption timer
will begin gaining time. For as long as the batteries remain below this voltage, the Absorption timer
will gain an equal amount of time. This controls the duration of the Absorption stage. The intent was
to avoid a “blind” cycle that operates regardless of conditions. The charger avoids maintaining the
batteries at high voltages for excessive or unnecessary time.
The Absorption timer continues this operation even if the charger is still on. For example, if the
charger is in Float stage and there is a significant battery drain, the charger may not be able to
maintain the batteries at the Float voltage. Once the batteries fall below the Re-Bulk point, the
Absorption timer will begin accumulating time. (However, the accumulation will be minor, as this will
also cause the charger to re-enter the Bulk stage.)
Absorb Time
setting. The charger will not necessarily run through its full duration, as this
Re-Bulk Voltage
The remaining charging steps will proceed as described on the previous pages.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 31
Page 34

Operation
Voltage
Bulk
Absorption
Float
Re-Float
Re-Bulk
Set Point
Time
Absorption
(c.v.)
Absorption
(c.v.)
Absorption (c.v.)
AC Loss
Float
AC Loss
Bulk
Silent
Silent
Float
(c.v.)
Float
Float
Timer
Silent
Silent
AC Loss
Timer
Timer
accumulates
Timer
runs
Timer
runs
Timer runs
Cycle 4
Cycle 1
Cycle 3
Cycle 2
Set Point
(c.c.)
Set Point
Timer
Set Point
(c.c.)
(c.c.)
(c.c.)
accumulates
Figure 6 Repeated Charging Cycles
Example of Multiple Cycles
In Figure 6 (Cycle 1), the charger initially completes Absorption. When the Absorption timer expires, the
charger goes Silent until battery voltage decreases to the
Re-Float
maximum. The charger enters Float and proceeds until it is interrupted by a loss of AC power.
Cycle 2 begins when the AC source is restored. During the AC loss, the battery voltage did not decrease to
the
Re-Float
setting, so
Float Time
retains the remainder of the previous cycle. The charger returns to Float
and completes the stage when its timer expires. It then goes Silent.
During the Silent period, AC is lost again. The battery voltage decreases until it reaches the Re-Bulk set
point. This causes the charger to prepare a new three-stage cycle from the beginning, but it cannot do so
until the AC source is restored.
In Cycle 1,
Absorb Time
Whenever the battery voltage decreases to
had expired. It was not reset afterward and retained a “remaining run time” of zero.
Re-Bulk
or lower, the Absorption timer will begin accumulating
run time. The first set of arrows below the graph show the length of time accumulated on the Absorption
timer at the end of Cycle 2.
Cycle 3 begins when the AC source is restored again. The charger begins a new cycle by entering Bulk stage.
When it enters Absorption, the amount of time spent in this stage is equal to the amount of time
accumulated at the end of Cycle 2. (The space between the first and second set of arrows is the same.)
Absorption ends when the timer expires.
This means that the length of Absorption may be shorter than the
AC loss, the batteries may not be used enough to require a total recharge.
In this example, the duration was also longer than the
Float Time
running near the beginning of Cycle 3 (when the batteries exceeded the
has also expired. The charger does not enter Float and goes Silent.
Time
During the Silent period, AC is lost again. The battery voltage decreases until it reaches the
point, prompting a new charge cycle. The Absorption timer accumulates run time while the batteries are
below this set point.
The first set of barred arrows below the graph show the length of time accumulated on the Absorption
timer. Note that the timer stops accumulating well before the beginning of Cycle 4 when the AC source is
restored. The accumulation of the Absorption timer cannot exceed the
When Cycle 4 begins, the charger proceeds through the Bulk stage and then the Absorption stage. (The
space between the first and second set of barred arrows is the same.) The duration of Absorption is equal
to
Absorb Time
, which is the maximum time allowed. At the end of Cycle 4, the
the charger goes Silent.
32 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
setting. The Float timer is reset to its
Absorb Time
setting. During intermittent
setting. Because the Float timer began
Float Voltage
Absorb Time
setting), the
setting.
Float Time
Float
Re-Bulk
set
has expired, so
Page 35

Operation
Equalization
CAUTION: Battery Damage
Equalization is a controlled overcharge that is part of regular battery maintenance. Equalization
brings the batteries to a much higher voltage than usual and maintains this high voltage for a period
of time. This has the result of removing inert compounds from the battery plates, and reducing
stratification in the electrolyte.
Equalization follows the same pattern as standard three-stage charging, as shown in the figures on
page 28. However, instead of the Absorption voltage and time set points, it is controlled by the
Equalize Voltage
and
Equalize Time
settings in the MATE3.
The Radian inverter can perform Offset when equalizing. (See page 35.)
Equalize Voltage
is also the
reference voltage for Offset during equalization.
This process must be started manually using the system display. The inverter cannot be programmed
for automatic battery equalization. This is a safety measure.
Equalization is normally performed only on flooded lead-acid batteries. The schedule for equalization
varies with battery use and type, but it is usually performed every few months. If performed correctly,
this process can extend battery life by a considerable amount.
Equalization is not normally performed on nickel-technology batteries or any sort of sealed battery.
Do not equalize OutBack EnergyCell batteries of any model.
Do not equalize any sealed battery types (VRLA, AGM, Gel, or other) unless
approved by the manufacturer. Some batteries may suffer severe damage
from equalization.
Contact the battery manufacturer for recommendations on equalization
voltage, duration, schedule, and/or advisability. Always follow
manufacturer recommendations for equalization.
Battery Temperature Compensation
Battery performance will change when the temperature varies above or below room temperature
(77°F or 25°C). Temperature compensation is a process that adjusts battery charging to correct for
these changes.
When a battery is cooler than room temperature, its internal resistance goes up and the voltage
changes more quickly. This makes it easier for the charger to reach its voltage set points. However,
while accomplishing this process, it will not deliver all the current that the battery requires. As a result,
the battery will tend to be undercharged.
Conversely, when a battery is warmer than room temperature, its internal resistance goes down and
the voltage changes more slowly. This makes it harder for the charger to reach its voltage set points.
It will continue to deliver energy as time passes until the charging set points are reached. However,
this tends to be far more than the battery requires, meaning it will tend to be overcharged.
The Radian inverter, when equipped with the Remote Temperature Sensor (RTS) will compensate for
changes in temperature. The RTS is attached to a single battery near the center of the bank, to achieve
a representative temperature. The Radian inverter has a designated port for installing the RTS.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 33
Page 36

Operation
If installed in a multiple-inverter system, only a single RTS is necessary. It must be plugged into the
master inverter and will automatically control the charging of all slaves and all charge controllers.
When charging, an inverter system with an RTS will increase or decrease the charge voltage by 5 mV
per degree Celsius per battery cell. This setting affects the
points. The
Equalization
In a 48 Vdc system (24 cells, 2 volts each), this means 0.12 volts per degree Celsius above or below 25°C.
Maximum compensation is ± 2.4 Vdc.
EXAMPLES:
A 48 Vdc system with batteries at 15°C will compensate its charging to 1.2 Vdc
A 48 Vdc system with batteries at 40°C will compensate its charging to 1.8 Vdc
Sell Voltage
set points are not compensated in OutBack charge controllers.
and
Re-Float Voltage
set points are not temperature compensated. The
Absorption, Float
, and
Equalization
than the set points.
higher
than the set points.
lower
set
Slope
Some batteries require different amounts of compensation. The OutBack FLEXmax Extreme charge
controller has an adjustable rate of compensation (“slope”) and is not limited to 5 mV. The FLEXmax
Extreme can be networked with the Radian with the HUB Communications Manager. If this is done,
the Radian can import the slope setting from the FLEXmax Extreme charge controller.
:
NOTE
Temperature compensation only applies to the battery charging function. Other set points in the
inverter, such as the AUX functions, are not compensated for temperature.
34 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 37

Operation
Table 3 Offset Interaction with AC Source
Mode
Excess DC ≥ loads
Excess DC < loads
Generator
N/A; Offset operation does not function
Support
Grid Tied
Sells excess to AC source (grid); remains connected
Offsets load use with whatever power is available
UPS
N/A; Offset operation does not function
Backup
N/A; Offset operation does not function
Mini Grid
Offsets load use with whatever power is available; inapplicable if disconnected from utility grid
Grid Zero
Offsets load use, but only according to the
DoD Volts
setting
Offset
This operation is designed to use excess battery energy to power the loads when an AC source is
present. This allows the system to take advantage of renewable energy sources, in effect “offsetting”
dependence on the AC source.
A renewable energy source will raise the battery voltage as it charges the batteries. When the voltage
exceeds a designated reference voltage, the Radian inverter begins drawing power from the batteries
(discharging them) and using that power to offset usage of the AC source. The batteries are kept at
equilibrium and are maintained at the reference voltage.
The Radian inverter uses excess DC energy for offset under the following rules:
If the load demand is higher than the exported power, the inverter’s use of the AC source is reduced. The
exported amount of power has “offset” the same amount of demand on the AC source. (This is sometimes
known as “selling to the loads”.)
If the excess DC energy (and exported power) is equal or greater than the load demand, and the Radian is in
the
Grid Tied
of the
input mode, the inverter will sell the additional power to the utility grid. This is the key priority
Grid Tied
mode.
The Radian inverter uses several set points as reference voltages for the Offset operation, particularly
the battery charger settings.
The charger settings
are all used as reference voltages. Normally the charger regulates to these set points by adding power to
the batteries. Offsetting does the opposite; it uses the same set points but regulates the voltage by
removing power from the batteries.
If none of the battery charger’s timers are active, the Offset voltage is
This is true in any input mode where Offset is used, not just the
The
Grid Zero
Absorb Voltage, Float Voltage
mode only uses a single reference voltage for Offset, the
, and
Equalize Voltage
Sell Voltage
Grid Tied
(as shown in the system display)
in the
Grid-Tie Sell
input mode.
DoD Volts
setting.
menu.
NOTES
Offset operation is not available in the Generator, UPS, and Backup input modes.
Offset operation is available in the Support, Grid Tied, and Grid Zero modes.
Offset operation is available in the Mini Grid mode. However, it may not be used often since the Mini Grid
The Grid-Tie Enable menu item must be set to Y (yes) for Offset to work. This is true even if the inverter is
:
priority is to avoid grid use.
not used in a grid-tied mode or application.
Offsets load use, but also uses DC and batteries to support the AC source based on
Support
mode settings
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 35
Page 38

Operation
Multiple-Inverter Installations (Stacking)
IMPORTANT:
revision different from the master will not function. The MATE3 will display
Additional Ports
Port 1
MATE Port
HUB4
MATE3
Multiple inverters in a single system can support larger loads than a single inverter can handle.
Installing inverters in this configuration is called “stacking”. Stacking inverters does not refer to
physically placing one on top of another. It refers to how they are wired within the system and
then programmed to coordinate activity. Stacking allows all units to work together as one system.
The GS7048E and GS3548E models can stack up to ten units in parallel for increased capacity. For
three-phase output, up to nine models can be stacked, three per phase.
Stacking requires an OutBack HUB Communications Manager, as well as a MATE3 system display.
There are usually other specialized stacking instructions during installation.
A system of four or fewer units may use the HUB4.
Systems of up to ten units require the HUB10 or HUB10.3.
All interconnections between the products are made using CAT5 non-crossover cable. (See the Radian
Series Inverter/Charger Installation Manual for more stacking instructions.)
Each inverter needs to be assigned a status — “master” or “slave”. The master is the primary and most
heavily used unit. Slave inverters provide assistance when the loads are more than the master can
handle alone. In addition, in a three-phase system, “subphase masters” allow control of outputs that
the master inverter cannot monitor.
Programming involves using the MATE3 to assign a status and stacking value to the inverter on each
port. See the MATE3 and HUB manuals for programming instructions.
Figure 7 OutBack HUB4 and MATE3
The Radian GS7048E can be stacked with the Radian GS3548E in either a
parallel or a three-phase configuration.
The master inverter must always be connected to port 1 on the HUB.
36 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Connecting it elsewhere, or connecting a slave to port 1, will result in
backfeed or output voltage errors which will shut the system down
immediately.
All stacked Radian inverters must have the same firmware revision. If
inverters are stacked with different firmware revisions, any unit with a
Page 39

Operation
the following message:
An inverter firmware mismatch has been detected. Inverters X, Y, Z 2 are disabled.
21 kVA
7 kVA
7 kVA
7 kVA
Visit www.outbackpower.com for current inverter firmware.
Installing multiple inverters without stacking them (or stacking them
incorrectly) will result in similar errors and shutdown.
Although stacking allows greater capacity, the loads, wiring, and
overcurrent
devices must still be sized appropriately. Additional terminations or bus
bars may be required. Overloading may cause circuit breakers to open or
inverters to shut down.
Parallel Stacking (Dual-Stack and Larger)
In parallel stacking, two or more inverters are stacked to create a single, common AC output.
All inverters share a common input (AC source) and run loads on a common output bus. The master inverter
provides the primary output. The slaves are connected to the same output and assist the master.
The slave outputs are controlled directly by the master and cannot operate independently.
Slave inverters can go into Power Save mode when not in use. The master will activate individual slaves
based on load demand. This reduces idle power consumption and improves system efficiency.
Up to ten inverters may be installed in a parallel arrangement.
Figure 8 Example of Parallel Stacking Arrangement (Three Inverters)
230 Vac
230 Vac
230 Vac
230 Vac
2 The port designations for the mismatched inverters are listed here.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 37
Page 40

Operation
Three-Phase Stacking (Three Inverters)
21 kVA
7 kVA 230 Vac
7 kVA
7 kVA 230 Vac
7 kVA 230 Vac
7 kVA
7 kVA
21 kVA
7 kVA 230 Vac (x3)
21 kVA
230 Vac
7 kVA 230 Vac (x3)
7 kVA 230 Vac (x3)
21 kVA
63 kVA
Vac
In three-phase stacking, inverters are stacked to create three AC outputs in a wye configuration.
The three outputs operate independently of each other. Each can run in independent Search mode if
desired, although this does not normally occur when three-phase loads are connected.
Each output is 120° out of phase from the others. Any two outputs produce 400 Vac between them. (This
voltage is nominal and may vary with output settings.) The outputs can be used to power three-phase loads
when all inverters work together.
Only three inverters, one per phase, may be installed in a three-phase arrangement when using the HUB4 or
HUB10 products. Up to nine inverters, three per phase, may be stacked when using the HUB10.3.
230 Vac
230 Vac
230 Vac
230/400 Vac
Figure 9 Example of Three-Phase Stacking (Three Inverters)
230 Vac
230/400
230 Vac
Figure 10 Example of Three-Phase Stacking (Nine Inverters)
38 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 41
Operation
Power Save
IMPORTANT:
Figure 13 for differences.
IMPORTANT:
MATE3 owner’s manual.)
Master
Slave 1
Slave 3
Slave 2
Off
Off
Off
On
Off
Off
On
On
Off
On
On
On
On
On
On
Minimal load
Increasing load
High load
On
Maximum load
Each inverter consumes approximately 30 watts of idle power while it remains on, even if it is not
actively inverting or charging. The Power Save function allows the option to put part of a parallel
system into a quiescent state known as Silent mode. This mode minimizes the idle consumption.
The inverters will come on again when the loads require power. (The term “Silent” is also used in an
unrelated context during battery charging. See page 30.)
When the load increases by approximately 2.5 kW, the master inverter activates one or more additional
modules for assistance. When the load decreases to a lesser wattage (as detected by the master), the
modules deactivate and return to Silent mode. Additional load increments of approximately 2.5 kW will
activate additional modules.
The first module in the master does not enter Silent mode. It remains active unless specifically turned off.
The order in which additional modules activate (or return to Silent mode) is controlled by programming in
the MATE3. The inverters are given a “rank”, or level number. Lower rank numbers activate when lesser
loads are applied. Higher ranks only activate when the load increases to a high level.
Power Save functionality is different between Radian models. The Radian
GS3548E contains only one 4kW module. Activating one module is the same
as activating the full inverter. The GS7048E contains two modules and
operates differently. Do not confuse the behavior of each. See Figure 12 and
Figure 11 Power Save Levels and Loads
The actual watt and ampere thresholds for activating each model are depicted on the following pages.
It is highly recommended to use the MATE3 Configuration Wizard to set up this
function. It is essential to set the slave Power Save Levels in sequential order.
Failure to set them up correctly will cause erratic system performance. The
Configuration Wizard automatically programs the correct priorities. (See the
To set these items manually without the Configuration Wizard:
In the MATE3 system display, the
assign inverter ranks. The screen reads
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 39
Power Save Ranking
Master Power Save Level
screen uses
or
Power Save Level
selections to
Slave Power Save Level
,
Page 42

Operation
depending on the inverter’s stacking designation.
IMPORTANT:
continuously active.
IMPORTANT:
long-term system problems.
Minimal Load On Off Off Off
Master
Slave 1
Slave 3
Slave 2
Master Power Save
= 0
Slave Power Save
Slave Power Save
Slave Power Save
Master Power Save Level
appears on an inverter which is set as master (the default setting). In a stacked
system, this selection should only appear on the inverter using Port 1 of the communications manager.
The range of rank numbers is 0 to 31. The default value is 0. The master is normally left at this value.
This heading also appears on an inverter which is set as the B phase or C phase master. The range of rank
numbers is 0 to 31. The default value is 0.
Slave Power Save Level
appears on an inverter which is set as slave. The range of rank numbers is 1 to 31.
(The default value for all ports is 1.)
The ranks are prioritized so that lower-numbered ranks turn on sooner and higher ranks turn on later.
The lowest-ranked unit will not go silent and will remain on unless ordered otherwise. The lowest-ranked
unit is expected to be the master. The priorities are the same across both screens; thus, if P01 (master) is set
at 0 and P02 (slave) is set at 1, the slave will turn on later. Since the
item is the only one that goes to
Master
0, it is easy to ensure that all other units besides the master go silent.
Set the master rank at 0 and arrange the slave ranks in order (1, 2, 3, 4, etc.). Another
order may defeat the purpose of Power Save mode. Leaving the master at 0 makes 4
kW of power available from the master; the other inverters should not be active. If a
slave is ranked lower (prioritized higher) than the master, that slave will not go silent.
Disregard this rule if the installation requires some of the slaves to be
NOTE:
Do not give slave inverters the same rank numbers. If, for example, multiple slaves
were all ranked at 1, they would all come on at the same time. Once they came on, the
divided load would cause the master to detect a minimal load on its output, so it
would shut off all the slaves, at which point the master would read a high load again.
This could quickly escalate into a rapid on/off cycling of inverters and could cause
Figure 12 shows a system of four GS3548E inverters (the master and three slaves) in a parallel system
with a common load bus. The labels at the top indicate the ranking of each unit. The notations at the
bottom show how the units are activated in sequence as loads of approximately 2.5 kW are applied.
= 1
approx. 2.5 kW (12 Aac) On On Off Off
approx. 5 kW (24 Aac) On On On Off
approx. 7 to 8 kW (36 Aac) On On On On
= 2
Figure 12 GS3548E Power Save Priority
The last line indicates that loads of approximately 7 to 8 kW are present on the system, causing all four
inverters to be activated.
40 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
= 3
Page 43

Operation
Additional Notes for the Radian GS7048E:
On
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
On
On
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
Module 1 Module 2
Module 1 Module 2
Module 1 Module 2
Module 1 Module 2
On
On
On
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
On
On
On
On
Off
Off
Off
Off
Minimal load
approx. 5 kW
approx. 2.5 kW
approx. 7 to 8 kW
Master
Master Power Save
Slave 1
Slave Power Save
Slave 2
Slave Power Save
Slave 3
Slave Power Save
The GS7048A has two modules. The modules are controlled individually. The Power Save function
will activate one module at a time, making an additional 3.5 kW of power available for every load
increase of approximately 2.5 kW.
Figure 13 shows a system of four GS7048E inverters (the master and three slaves) in a parallel system
with a common load bus. The labels at the top indicate the ranking of each unit. The notations at the
bottom show how the units are activated in sequence as loads of approximately 2.5 kW are applied.
The first line shows little load and only the first module in Master is activated.
The second line shows load beginning to be applied. The second module in Master is activated.
The third line shows increasing load. The first module in Slave 1 is activated.
The fourth line shows even higher load. Slave 1 is completely activated.
In general, roughly 5 kW of loads are applied to fully activate an additional slave inverter.
In the example shown in Figure 13, an 8-kW load has been applied, fully activating the first slave.
In this example, loads of approximately 17 to 18 kW would be needed to turn on all inverters.
= 0
= 1
= 2
= 3
Figure 13 GS7048E Power Save Priority
Forcing Specific Slaves to be Active:
It is possible to raise the priority of a slave and force it to activate. This is done by setting the master
rank higher than that slave. However, the
level.
level settings apply to the whole inverter.
Slave
Master Power Save Level
Master
scale is not the same as the
Slave
level settings are applied per module.
This means that increasing the master by one rank will only turn on one additional module. To
completely turn on a slave inverter, the master must be increased two ranks. See the next page.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 41
Page 44
Operation
In Table 4, instead of loads, the number on the far left of each line shows the master increased by one
Table 4 Changing Master Power Save Levels (GS7048E)
rank. (This example is otherwise the same as Figure 13.)
The last line of the table shows the master increased to 3, which is the same as the rank of the highest
slave. However, this only activates the first of the three slaves. The master would need to be set to
rank 7 to activate all slaves.
Master Slave 1 Slave 2 Slave 3
Power
Save
Module1 Module
0
1
2
3
2
On Off
On On
On On
On On
Power
Save
1
1
1
1
Module
3
Off Off
Off Off
On Off
On On
Module
4
Power
Save
2
2
2
2
Module
5
Off Off
Off Off
Off Off
Off Off
Module
6
Power
Save
3
3
3
3
Module
7
Off Off
Off Off
Off Off
Off Off
Module
8
42 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 45

Operation
Auxiliary Terminals
The Radian inverter has two sets of terminals which can respond to different criteria and control many
operations. The 12V AUX terminals provide a 12 Vdc output that can deliver up to 0.7 Adc to control
external loads. The RELAY AUX terminals are “dry” relay contacts rated up to 10 amps (at 250 Vac or 30
Vdc). Each set of terminals has its own set of programmed criteria. Each has identical options
available. (When the options described below refer generically to the “AUX output”, it can mean
either set of terminals.)
Each AUX output has three states: continuous
to be activated using the automatic auxiliary functions. (All functions are defaulted to
, continuous On, and
Off
, which allows that output
Auto
.) These
Off
items are based in the Radian and accessed using the system display. The system display and other
devices also have programming, such as AGS, that can control the AUX outputs. To avoid conflicts,
the output should be turned
when the AGS function is active. (See page 47.)
Off
For the Radian automatic functions, typical applications include signaling a generator to start, sending
a fault alarm signal, or running a small fan to ventilate the batteries. When considering these
applications, plan for both connection requirements and programming with the system display.
The AUX terminals have a series of set points which are used by various functions. Both sets of
terminals have the same options available, but they are programmed independently. Not all set
points are used by all functions. Each AUX mode description below will detail the set points that are
used for that function.
∼ Low DC voltage settings
∼ High DC voltage settings
∼ On delay settings, in increments of 0.1 minutes
∼ Off delay settings, in increments of 0.1 minutes
These settings are not temperature compensated. Compensation is only used for inverter battery charging.
There are nine functions, each geared toward a different application. (The 12V AUX and RELAY AUX
outputs are defaulted to different selections.) These functions are summarized in Table 5 on page 46.
Load Shed
battery periods to conserve remaining battery power.
can perform load management. It is intended to turn off designated loads during low
When battery voltage rises above a settable high voltage level, the AUX output is activated after a
settable delay. The AUX output is used to energize a larger external relay (normally open) which is
connected to non-vital loads. The AUX output will be deactivated once the battery voltage falls below a
low voltage setting for a settable delay period.
∼ Load Shed will also turn off when the inverter enters a high-temperature condition or when the AC
output voltage drops below a specific AC voltage for more than 3 seconds. This voltage limit is 30 volts
below the setting of the inverter’s output voltage. For the Radian’s default output voltage of 230 Vac,
the limit is 200 Vac. (See page 69.) The limit is not otherwise settable.
∼ Load Shed will also turn off if the input current exceeds the Input AC Limit setting while the inverter is
using an AC source.
∼ Settable parameters include:
• Low and high DC voltage
• On and off delay
Gen Alert
functionality. (The generator recharges batteries using the inverter’s battery charger.)
∼ Either set of AUC terminals may be used to start the generator by closing the appropriate circuit. The
is used as a controller for an AC generator with a remote start feature, although it has limited
specific choice of RELAY AUX or 12V AUX may depend on the generator’s starting circuitry. Different
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 43
Page 46

Operation
examples are illustrated in the Radian Series Inverter/Charger Installation Manual.
IMPORTANT:
working correctly when using the
GRID
terminals.
∼ The AUX output will activate to start the generator when the battery voltage falls to a low set point for a
settable delay. The AUX output is deactivated, shutting off the generator, once the battery voltage rises
to a high voltage setting for a settable delay period.
∼ Settable parameters include:
• Low and high DC voltage
• On and off delay
∼ Gen Alert control logic is located in the inverter. It has the advantage of functioning when the system
display is removed. However, it may not completely charge the batteries and does not have all the
advantages of the Advanced Generator Start (AGS) function that is found in the system display. For
many users, the AGS function may prove more useful than Gen Alert. Gen Alert, however, could be
used as a literal “Generator Alert”, a signal to the user to manually start a generator.
NOTE: Gen Alert is the default selection for the RELAY AUX settings.
44 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
When using
terminals. If the input priority is set to
automatically controlled generator will shut down. This prevents an automatic generator from
activates the AUX output when the inverter shuts down due to an error condition (see page 57). It can
Fault
Gen Alert
(or AGS), the generator must be connected to the inverter’s
GRID
and the
terminals are energized, an
GRID
GEN
activate a light or alarm to show that the inverter has failed. With the appropriate devices, it could send an
alarm signal through a radio, pager, or telephone dialer.
∼ This function does not have settable parameters.
Vent Fan
activates the AUX output in response to a high DC (battery) voltage set point. It can run a small
fan to ventilate the battery compartment to eliminate gases that result from battery charging. (This is
illustrated in the Radian Series Inverter/Charger Installation Manual.) When the voltage falls below this set
point for a settable delay period, the AUX output turns off.
∼ Settable parameters include:
• High DC voltage
• Off delay
NOTE: Vent Fan
Cool Fan
activates the AUX output when the inverter reaches a high internal temperature. It is intended to
is the default selection for the 12V AUX settings.
trigger a small external fan for additional cooling. See the Warning Troubleshooting table on page 58 for a
description of the fan criteria.
∼ This function does not have settable parameters.
DC Divert
activates the AUX output to divert (or “dump”) excess renewable energy to a DC load, such as a
resistor, a heater, or a fuel cell. This prevents overcharging of the batteries. This function can serve as rough
charge regulation for an external charging source.
When battery voltage rises above a settable high voltage level, the AUX output is activated after a
∼
settable delay. The AUX output controls a larger, external relay. When energized, the relay allows
current to flow from the batteries to a dedicated DC load. (This is illustrated in the Radian Series
Inverter/Charger Installation Manual.) The resistor or load must be sized to dissipate all of the energy
from the renewable source if necessary. Diversion will turn off following a delay when a low DC voltage
setting is reached.
∼ Settable parameters include:
• Low and high DC voltage
• On and off delay
Page 47

Operation
GT Limits
parameters for the grid-interactive function (see page 15). It can activate a light or alarm to show that the
grid-interactive function has shut down and that there may be problems with the grid. The AUX output will
cycle on and off if grid parameters are met and the reconnection timer is counting down.
∼ This function does not have settable parameters other than those of the Grid Interface Protection
Source Status
or alarm to show that the utility grid is present or that a generator has started. Alternately, it could be used
to show that the source has disconnected.
∼ This function does not have settable parameters.
activates the AUX output as an alert that the utility grid does not meet Grid Interface Protection
menu (see Table 16 beginning on page 67).
activates the AUX output whenever the inverter accepts an AC source. It can activate a light
AC Divert
AC device powered by the inverter itself. This prevents overcharging of the batteries. This function can
serve as rough charge regulation for an external charging source.
∼ When battery voltage rises above a settable high voltage level, the AUX output is activated after a
∼ The AUX output will automatically turn on to run the loads if the inverter accepts an AC source.
∼ Settable parameters include:
∼ During variable conditions, the AUX output is triggered no more than once per minute (if voltage
∼ AC Divert should not be used as the sole source of battery regulation. If the inverter shuts down or fails,
activates the AUX output to divert (or “dump”) excess renewable energy to an AC load, usually an
settable delay. The AUX output controls a larger relay, which allows current to flow from the batteries
to a dedicated AC load when energized. Diversion is usually used to regulate battery charging. The AC
device is usually wired to the output or load panel and must be left on. It must be sized to dissipate all
of the energy from the renewable source if necessary. Diversion will turn off following a delay when a
low DC voltage setting is reached.
• Low and high DC voltage
• On and off delay
conditions are still met). This prevents rapid nuisance cycling of the AC load in the event of rapidly
changing conditions.
the batteries could suffer severe damage. This function should be supported by an external regulator.
• If the inverter shuts down due to overload, the AUX output will also shut down. If the inverter load
exceeds 30 Aac, the AUX output will turn off to prevent an overload condition.
• If either the FETs or the capacitors (see page 58) become too hot, the AUX will turn off due to
diminished inverter wattage capacity.
Note that even if every function in the menu is set to
, the AUX output may still be triggered by an
Off
external function such as AGS (see page 47).
The AUX functions are summarized in Table 5 on the next page.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 45
Page 48

Operation
Table 5 Aux Mode Functions
Triggers
Start
Stop
Load
Operates designated loads
High Vdc
Low Vdc
Low & high Vdc
Gen Alert
Starts generator to charge
Low Vdc
High Vdc
Low & high Vdc
Fault
Signals that the Radian shut
down due to error
Error present
Error cleared
Vent Fan
Runs fan to vent batteries
High Vdc
Below high Vdc
High Vdc
Cool Fan
Runs fan to cool Radian
Internal sensor > 60°C
Internal sensor < 49°C
DC Divert
Turns on DC dump load to
High Vdc
Low Vdc
Low & high Vdc
GT Limits
Signals disconnect of grid-tied
GIP parameters not
GIP parameters met
Source
Signals that the Radian
AC source accepted
AC source
AC Divert
Turns on AC dump load to
High Vdc
Low Vdc
Low & high Vdc
NOTES:
Name Purpose
Shed
Status
normally; turns off loads in
severe conditions
batteries
while charging
prevent overcharging
Radian due to AC conditions
accepted an AC source
prevent overcharging
met
AC source accepted
High temp
Low output Vac
High input Aac
disconnected
High output load
High temp
Settable
Points
On & Off delay
On & Off delay
None
Off delay
None
On & Off delay
None
None
On & Off delay
46 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 49
Operation
System Display-Based Functions
IMPORTANT:
setting it to
OFF
. This will avoid programming conflicts.
IMPORTANT:
generator from working correctly when using the
GRID
terminals.
A system display such as the OutBack MATE3 can provide functions not available in the inverter.
These functions are briefly described to provide a better idea of overall system capabilities.
The system display must be present for these functions to operate. If a function is set up (or already in
operation) but the system display is removed, the function will not operate.
Advanced Generator Start (AGS)
As noted under the
Gen Alert
simply starts and stops the generator based on battery voltage. For more advanced control,
Gen Alert
function (see Table 5), the system is capable of starting a generator.
the inverter system can use the Advanced Generator Start (AGS) function, which runs through the
entire three-stage charging cycle. It can start according to battery voltage, inverter load, time of day,
and other criteria. AGS has a quiet time application which restricts the generator from starting at
inconvenient times. Additional applications are also available.
This function is higher-priority than
activate the 12V AUX or RELAY AUX even if the inverter has disabled them. When AGS is
in use,
Gen Alert
When using AGS (or
terminals. If the input priority is set to
automatically controlled generator will shut down. This prevents an automatic
and other AUX functions should be disabled on that AUX output by
Gen Alert
Gen Alert
), the generator must be connected to the inverter’s
or any other inverter function. It can
GRID
and the
terminals are energized, an
GRID
GEN
Grid Functions
The following functions affect the transfer of the Radian inverter to and from an AC source (usually the
utility grid). These functions are based in the system display because they are system-wide. They
affect the transfer of all inverters on the system.
High Battery Transfer (HBX)
In HBX mode, the system is connected to the utility grid. However, it will use battery power as the first
priority. The utility grid is locked out until needed.
The system runs on battery-supplied power for as long as the batteries can be sustained. It is
expected that the system will be supplied by renewable sources such as PV power. When the
batteries become depleted, the system reconnects to the utility grid to operate the loads.
The batteries may be recharged during this time using the renewable source. When the batteries are
recharged to a high enough voltage, the system transfers back to the batteries as the primary source
(hence the name High Battery Transfer).
NOTE:
renewable source for charging batteries. Renewable charging is the motivator for returning to battery
(and renewable) operation. Use of the inverter’s charger interferes with this priority. It also may not
charge effectively.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 47
The inverter’s charger should be off. High Battery Transfer mode is intended to use only the
Page 50

Operation
This mode has similar priorities to the
NOTES:
Either mode may achieve similar results, but they are not identical. See page 18 for the advantages
and disadvantages of each mode.
Mini Grid
input mode contained within the Radian inverter.
Grid Use Time
The inverter system is capable of connecting to, or disconnecting from, the utility grid based on time
of day. It can also be programmed to connect at different times on weekdays and on weekends.
Load Grid Transfer
The inverter system is capable of connecting to, or disconnecting from, the utility grid based on load
size. This avoids undesirable battery discharge from excessive loads. It can also be programmed to
connect to the grid when the batteries reach a low voltage due to excessive discharge.
48 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 51
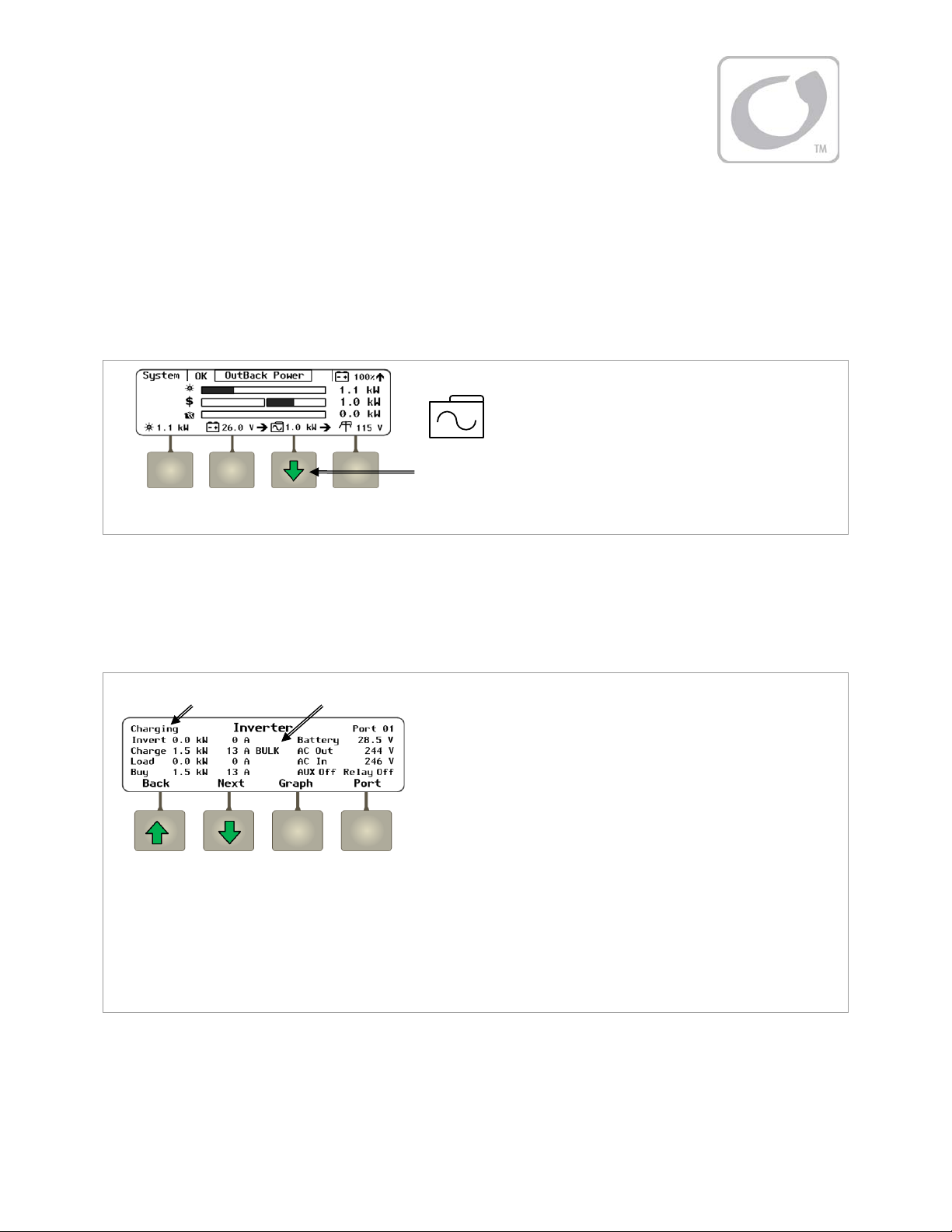
Metering
Inverter Soft Key
Inverter Mode
Charge Mode
Inverter Modes:
Charge Modes (see page
MATE3 Screens
The MATE3 system display can monitor the GS inverter and other networked OutBack devices.
From the MATE3 Home screen, the Inverter “soft” key accesses the screens for monitoring the inverter.
(See the MATE3 owner’s manual for more information.)
Figure 14 Home Screen
Inverter Screens
The Inverter soft key opens a series of screens showing the inverter operating mode, battery voltage,
and status of several AC operations. The
inverters, if present.
Screen items:
The upper left corner is the Inverter Mode (see above). When
specifies the stage.
Invert
grid-interactive system it may be sold back to the utility grid.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 49
<Port>
soft key will select other networked OutBack
Inverting (see page 22)
Searching (see page 23)
Support (see page 14)
Sell (see page 15)
Charging (see Bulk on page 29)
Charger Off (see pages 26 and 30)
Float (see page 30)
EQ (see page 30)
Silent (see page 30)
PassThru (see page 26)
Error (see page 57)
Off
Figure 15 Inverter Screens
Charging
displays the kilowatts and AC amperage generated by the inverter. It may go to loads, or in a
BULK
FLOAT
EQ
is indicated, the Charge Mode
27:
Page 52

Metering
NOTE:
An arrow will appear to the right of
indicate that the charger is in that stage. The arrow will not appear if
the charger is in the Bulk stage, or if it is inactive.
Charge
line also shows the present charging stage.
Load
as
Buy
This is usually a total of
Battery
AC Out
usually the same as
AC In
erratic or inaccurate upon first connection until the inverter synchronizes with the input source.
AUX
status of the inverter’s Auxiliary relay contacts. (See page 41.)
A diode symbol may appear to the left of the screen name to indicate “diode charging” mode. This is a
mode that allows fine control of charging, selling, and load support. It does not visibly affect operation.
displays the kilowatts and AC amperage consumed for the inverter to charge the battery bank. This
displays kilowatts and AC amperage consumed by devices on the inverter’s output. It can be the same
.
Invert
displays the kilowatts and AC amperage brought into the inverter’s input for both charging and loads.
Load
.
displays the current
Relay
.
and
Charge
displays the uncompensated battery voltage.
displays the AC voltage measured at the inverter’s output. If an AC source is present, this reading is
AC In
displays the AC voltage measured at the inverter’s input from an AC source. This number may be
displays the current status of the inverter’s Auxiliary (AUX) 12-volt output.
The
<Graph>
MATE3 screen.
soft key brings up a series of screens which plot various types of data over time on the
Battery Screen
From the
Inverter
settings, and battery voltage and temperature information.
Screen items:
Actual
Absorb
Float
Equalize
Temp Comp
Temperature Sensor (RTS). If no RTS is present,
Batt Temp
port 1 on the HUB. If other ports are selected, or if no RTS is present, the characters ### will be displayed.
Re-Float
voltage used for the inverter to return from Silent mode to the float stage. (See page 30.)
Sell RE
when the charger is otherwise inactive. (See pages 15 and 35.)
displays the uncompensated battery voltage.
displays the charger’s Float voltage setting. (See page 30.)
voltage is the target voltage used by the inverter for both the Offset and grid-interactive functions
screen, the
<Next>
soft key brings up a screen showing charger status, charger
The charger settings cannot be adjusted on this screen.
Absorb, Float
, or
Equalize
Figure 16 Battery Screen
displays the charger’s Absorption voltage setting. (See page 29.)
displays the charger’s Equalization voltage setting. (See page 30.)
displays the corrected battery voltage using temperature readings from the Remote
Temp Comp
displays the battery temperature in degrees Celsius, as measured by the RTS. It is only valid for
displays the Re-Float setting which was programmed into the inverter’s charger. This is the
and
Actual
will read the same. (See page 33.)
to
The
<Warn>
50 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
and
<Error>
keys bring up screens with various fault information. See the next section.
Page 53
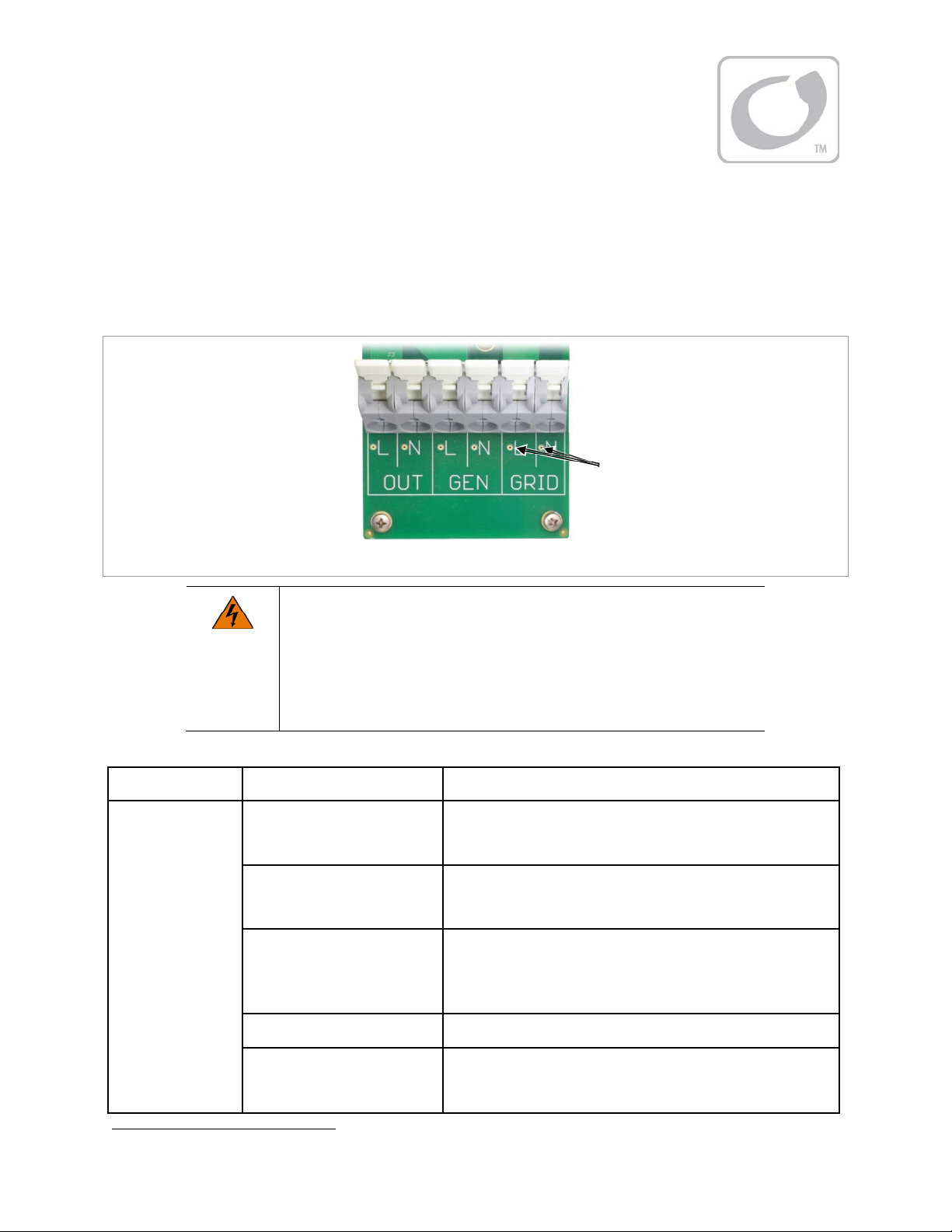
Troubleshooting
WARNING: Shock Hazard
. See page 57.
Table 6 Troubleshooting
Symptom
Possible Cause
Possible Remedy
No DC voltage.
Use a DC voltmeter to check the voltage directly on the DC
inverter could be damaged. Contact OutBack Technical Support.3
Jumper J3 missing.
See the Installation Manual for the location of J3. Confirm the
Installation Manual instructions to install an external switch.
Inverter set to
Off
.
MATE3 system display only: Set to On with the
INVERTER
hot key.
Inverter set to
Search
(Search
MATE3 system display only: If constant power is required, set to On
INVERTER
no action is required.)
Metal pads are located at
this series of test points.
Basic Troubleshooting
Table 6 is organized in order of common symptoms, with a series of possible causes. Each cause also
shows possible troubleshooting remedies, including system display checks where appropriate.
these locations.
In troubleshooting, AC
voltages can be measured at
Figure 17 AC Test Points
No AC output
(will not invert).
During an error shutdown, the inverter’s output terminals are not live.
However, if the inverter recovers from a shutdown, the terminals will
become live without notice. Several error shutdowns can be recovered
automatically, including
Temperature
Unit defaulted off
(No MATE3 present; initial
install; J3 confirmed present).
Low Battery V, High Battery V
terminals. If not present, the problem is external. If present, the
jumper is present. If missing, replace the jumper. Or follow the
The Radian inverter is given an initial Off command in the factory.
With DC present, use narrow pliers to remove jumper J3 from its
pins. Once removed, install it again. This is the equivalent of
“jiggling the switch.”
, and
Over
mode).
3 See inside front cover of this manual.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 51
with the
hot key. (If this setting was intentional, then
Page 54
Troubleshooting
Table 6 Troubleshooting
Symptom
Possible Cause
Possible Remedy
One or more
system).
Unit is slave and is in Power
MATE3 system display only: Check Power Save levels in
AC INPUT
AC INPUT
AC INPUT
to AC on the second input. This is true even if the first input is not
inverters will not
invert while others
do (in multi-inverter
Save mode.
No AC input. Check the AC voltage on the inverter’s input test points. (See
AC source does not meet
requirements.
AC source meets requirements
but is “noisy” or irregular.
Inverter was manually set to
disconnect from AC.
Grid use function has
disconnected from AC.
the
Inverter Stacking
inverter comes on at the appropriate levels. (If this setting was
intentional, then no action is required.)
page 51.) If not present, the problem is external. If present, the
inverter could be damaged. Contact OutBack Technical Support.
MATE3 system display only: Check the
(using the
reason for disconnection. If the unit never originally connected,
check the
Home screen). Confirm source voltage and frequency.
MATE3 system display only: The
irregular AC power. Select that mode for that input.
MATE3 system display only: Change the AC Input Control setting
from
was intentional, then no action is required.)
MATE3 system display only: If activated prematurely, check both
the MATE3’s
in the
action is required.)
Drop
System
Warning
to
Grid Use Time
menu and test with loads. Determine if the
Last AC Disconnect
hot key and the
menu (using the Inverter soft key from the
Generator
with the
Use
settings and the MATE3 clock settings
menu. (If this setting was intentional, then no
selection) for the
Discon
input mode can accept
hot key. (If this setting
screen
4
Will not connect to
the AC source.
High Battery Transfer
(
) mode has disconnected
HBX
from AC.
Mini Grid
disconnected from AC.
Conflicting programming. MATE3 system display only: Check to see if more than one of the
Grid Tied
disconnected from AC.
For only the B or C inverters on
a three-phase system: Power is
unacceptable on that phase.
Conflicting AC sources. Priority
input is interfering with
secondary input.
input mode has
mode has
MATE3 system display only: Check the
to see if
settings of
action is required.)
MATE3 system display only: Check the
menu to see if
check the settings of
intentional, then no action is required.)
following are enabled:
conflicting priorities and only one can be used at a time.
AC source does not meet requirements; see related entry under
“Will not sell power to the utility grid” (next page).
Check the source voltage and frequency. If the AC source voltage
or frequency cannot be maintained on the B or C phases, the
inverters on those phases will return to inverting. This ensures
that a three-phase output is maintained to the loads. If the source
becomes acceptable, the inverters will connect to it again.
If AC is present on the priority input, the inverter will not connect
connected for other reasons (programming, low power quality).
mode is in use. If activated prematurely, check the
HBX
mode. (If this setting was intentional, then no
HBX
Inverter
Mini Grid
mode is in use. If activated prematurely,
Mini Grid
mode. (If this setting was
Mini Grid
, HBX, Grid Use Time. These have
hot key screen
part of the
Settings
4 See inside front cove r of this manual.
52 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 55

Troubleshooting
Table 6 Troubleshooting
Symptom
Possible Cause
Possible Remedy
Charge complete or nearly
Check the DC voltage and charging stage using the MATE3, if
CHARGER
.)
Incorrect input mode.
Generator, UPS
Backup
setting. Other reference voltages are not used.
AC source voltage is driven high
When the inverter senses a rise in grid voltage while selling, it
Low charge rate.
Will not charge.
Unusual voltage on
AC hot input line.
complete.
MATE3’s DC meter reads
significantly higher than actual
battery voltage.
High output loads. If total loads and charge exceed the AC input setting, charge rate
High temperature. The inverter will reduce the current rate for charging and other
No AC input. See “Will not connect to AC” category.
Charger set to
Grid Zero
Inverter has not synchronized
with input source.
mode in use. MATE3 system display only: The charger is inoperative in
. MATE3 system display only: Check the
Off
present. Confirm with DC voltmeter.
Check the DC voltage on the inverter’s DC terminals. If different
from the MATE3 reading, the inverter could be damaged.
Otherwise, check the DC voltage on batteries with a voltmeter. If
different from the reading on the inverter, this could be a DC
connection problem.
decreases to give priority to the loads. Turn off some of the
output loads and test the charge rate again.
activities if the internal temperature exceeds a certain level.
Check temperature readings and allow the inverter to cool if
necessary. (See page 59.) External cooling may also be applied.
Charger Mode
the
intentional, then no action is required.)
mode. (If this setting was intentional, then no action is required.)
MATE3 system display only: The
Inverter soft key may be erratic or inaccurate after initial
connection until the inverter has synchronized with the AC
source. This may require a short time.
hot key and set to On or
reading accessed by the
AC In
Auto
screen with
. (If this setting was
Grid Zero
Unusual voltage on
hot or neutral output
line.
Inverter does not
perform the Offset
function when
expected.
Reduced power sold
to the utility grid.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 53
System neutral and ground may
not be bonded.
Specific mode only offsets
under particular conditions.
when the inverter sells large
amounts of power.
High temperature. The inverter will reduce the current rate for selling and other
Test “L” and “N” OUT test points with AC voltmeter. (See page 51
These measurements should give full voltage. Test neutral and
ground connections. This measurement should read zero volts.
Any other result means neutral and ground are not bonded
correctly. (If bonding is not required or prohibited by national or
local codes, then no action may be required.)
Offset does not function in
Support
This may appear as Offset without reaching the reference voltage.
Grid Zero
reduces the sell current, to avoid forcing the voltage to
unacceptable levels. Check AC input voltage while selling. The
inverter may be operating correctly.
activities if the internal temperature exceeds a certain level.
Check temperature readings and allow the inverter to cool if
necessary. (See page 59.) External cooling may also be applied.
mode will perform the Support function based on load.
mode will perform Offset based on the
, and
modes.
DoD Volts
Page 56
Troubleshooting
Table 6 Troubleshooting
Symptom
Possible Cause
Possible Remedy
Grid-tied function has been
Grid-Tie Enable
Home screen’s soft keys. The inverter may be operating correctly.
turned down to accommodate a problematic AC source. To make
INVERTER
oversized, the unit will falter or crash when switching to batteries.
Will not sell power to
the utility grid.
MATE3 system display only: Check the
manually disabled.
Grid Tied
the appropriate input.
AC source does not meet
requirements; this item is
usually accompanied by
disconnecting from the
utility grid when in
mode.
The inverter has other criteria
besides the AC source which
must be met, such as the
qualifying time.
The inverter will perform the
Offset function before
attempting to sell.
Erratic AC source voltage. Check AC voltage on the inverter’s input test points. (See
mode not in use on
Grid Tied
the
Grid-Tie Sell
MATE3 system display only: Check the
menu to see if
selected for the correct Radian input terminals.
Verify grid voltage and frequency. Determine if they are within
the inverter’s approved limits. If not, the inverter is operating
correctly. Contact the utility company if necessary.
MATE3 system display only: The program limits are found in the
inverter’s
mode beginning on page 15 for more information on this menu.
MATE3 system display only: Check
Depending on the conditions which need to be met, the delay
may be temporary,
Output loads can consume all excess renewable power if they are
large enough. (The Offset function “sells to the loads.” Turn off
some output loads and observe the sell operation.
page 51.) If not consistent, the problem is external.
MATE3 system display only: AC source voltage may have dipped or
hovered at a low enough point to crash a sensitive load before
the inverter could take over. This can happen if the inverter’s
AC Input Voltage Limits
menu. Confirm it is set to Y.
Grid Tied
Grid Interface Protection
mode is in use. Confirm that it has been
or
Gen AC Input Voltage Limits
Inverter
menu. See the
Sell Status
screen using the
part of the
setting in
Grid Tied
Settings
Grid
were
Loads drop out or
crash during transfer.
the inverter respond sooner, raise the lower limit setting in the
appropriate menu. (If this setting was intentional, then no action
is required.)
Inverter set to
mode).
Loads sensitive to inverter’s
transfer time.
use on the appropriate input.
Loads too large. The unit can transfer more power than it can invert. If loads are
Undersized battery cables. Battery cables smaller than recommended will cause a significant
Search
mode not in
UPS
(Search
The unit will take a moment to come out of Search mode after
transferring.
MATE3 system display only: If constant power is required, set
to ON with the
intentional, then no action is required.)
MATE3 system display only: Most of the inverter’s input modes
feature a small but noticeable response time during transfer.
Certain loads (such as highly sensitive computers) may not
respond well. The
Select this mode for the appropriate input. (See page 17.)
Reduce the size of the loads.
voltage drop when switching to batteries, acting like either an
overload or a low-battery condition. Size all cables correctly.
UPS
hot key. (If this setting was
input mode has a faster response time.
54 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 57
Troubleshooting
Table 6 Troubleshooting
Symptom
Possible Cause
Possible Remedy
Inverter’s output has been
match its own voltage.
Disconnect the wires from the inverter’s AC input or AC output
remain isolated from each other.
Low AC input voltage. Can be
by faulty input connection.
Test AC hot and neutral input test points with an AC voltmeter.
A generator is connected to the
The inverter is not intended to sell power to a generator. The
input with a different mode selected.
Unit reads AC input,
Internal transfer relay may be
Disconnect AC input wires and turn inverter on. Test the AC input
both.
Inverter hums loudly.
Inverter output is being
Disconnect AC output wires. Turn the inverter off and then on. If
connected to the output.
Inverter has been incorrectly
Check HUB ports and make certain the master inverter is plugged
Stacking
menu. Only one master is allowed per system.
AUX output is not connected.
Test the generator or device to confirm functionality. Test the
circuit may be damaged. Contact OutBack Technical Support.5
Wrong AUX terminals have
MATE3 system display only: Confirm that the AUX menu that was
Relay
menu programs the RELAY AUX terminals.
Wrong AUX terminals are in use.
If generator or external device requires 12 Vdc, confirm the 12V
do not provide voltage.
Inverter clicks
repeatedly. AC
output voltage rises
or drops to unusual
levels with every
click.
even though no
source is present.
System display may
show messages for
high battery voltage,
low battery voltage,
or backfeed error.
connected to its input. Voltage
shifts are the result of trying to
caused by weak AC source, or
input terminals while the unit is
in the
Grid Tied
damaged. May be
accompanied by
error and shutdown.
False reading due to noise. Electrical noise can cause false readings on the metering circuits
supplied with an external AC
source that is out of phase.
stacked with another unit on
the same output. All units
come defaulted as master.
input mode.
AC Relay Fault
terminals, or both. If the problem immediately disappears, it is an
external wiring issue. The inverter’s AC IN and AC OUT must
(See page 51.) If low or fluctuating, this is an external problem.
selling activity will drive the generator voltage up to the
disconnection point. It will then reconnect to the generator and
try again. Change input modes, or move the generator to an
and neutral test points with an AC voltmeter. (See page 51.) If
voltage appears there, the transfer relay may be jammed. Contact
OutBack Technical Support.5 This problem is not common. If this
occurs, it will likely occur on only the Grid or Gen input — not
when no voltage is present. The readings are usually less than
30 Vac. If this is the case, no action is required.
the problem clears, reconnect the AC output wires. If the
problem recurs when reconnected, an external AC source is
into port 1.
MATE3 system display only: Check stacking settings in the
Inverter
Generator, external
fan, etc. fails to start
when signal is
provided by AUX
output.
5 See inside front cover of this manual.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 55
been programmed.
appropriate AUX terminals with a DVM. (If the RELAY AUX
terminals are in use, test for continuity. If the 12V AUX terminals
are in use, test for 12 Vdc.) If the proper results are present when
the menu indicates the function is On (and the device still does
not work), then there is an external connection problem. If the
proper results are not present with the function
programmed matches the terminals that are in use. The
menu programs the 12V AUX terminals. The
Output
AUX terminals have been connected. The RELAY AUX terminals
, the AUX
On
Auxiliary
Auxiliary
Page 58

Troubleshooting
Table 6 Troubleshooting
Symptom
Possible Cause
Possible Remedy
AGS
Check both inputs for a second AC source (utility grid). If the
MATE3 system display is not
present.
AGS
programming is located in the MATE3 and cannot function if
the MATE3 is removed.
Other AUX functions are in
Gen Alert
or another AUX function may try to start or stop the
functions are disabled.
AGS
or
Gen Alert
The inverter’s
GRID
input is in
If the input priority is set to
GRID
and the
GRID
terminals are
controlling a generator.
inverter detects an acceptable AC source, it will not allow
This is true even if it is internally disconnected from the source
(due to
generator using the wrong criteria. Make sure all other AUX
energized, an automatically controlled generator will shut down.
This could indicate that the generator has been wired to the
input, or it could indicate that another AC source is active on
the
The
automatically controlling a generator.
Either the
mode,
HBX
input while the generator is using the
GRID
input must be the only terminals in use when
GEN
GRID
Mini Grid
or
GEN
mode, or similar programming).
input can be used when manually
GEN
AGS
input.
.
GRID
Advanced
Generator Start
(
) fails to
AGS
activate when
conditions are met
(or starts when
conditions are not
met).
functions start the
generator, but the
inverter does not
accept the power
and shuts off the
generator again.
MATE3 system display only:
function does not work if
another valid input is present.
operation.
use and the input priority is set
.
to
GRID
Module Select
The GS7048E uses two high-frequency H-Bridge FET modules. The dual design allows half the inverter
to shut down for lower idle consumption. Normally this is automatically selected. If one module fails
or if troubleshooting is otherwise needed, the module selection can be performed manually. The
GS7048E can be directed to use a single, specified module (left or right), or it can be directed to turn
on both modules continuously. This procedure should only be performed if directed by OutBack
Technical Support (see inside the front cover of this manual).
Although the GS3548E has only a single module, this command is still available. The default setting is
, which is the location of the module. Do not change this setting in the GS3548E.
Left
The Module Select menu options are displayed as part of Table 16, which begins on page 67.
56 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 59

Troubleshooting
Error Messages
Table 7 Error Troubleshooting
Message
Causes
Possible Remedy
Inverter’s AC regulation cannot be maintained
Check loads and measure current draw.
Inverter exceeded its maximum surge current
Check the loads and wiring. This issue is
as opposed to a poorly-sized load.
Usually indicates another AC power source (out
Disconnect the AC OUT wires from the
present, shut it off.
Stacking Error
DC voltage is below low battery cut-out set
DC voltage exceeded acceptable level. See
Check the charging source. This problem is
removed.
Inverter has exceeded its maximum allowed
Allow the inverter to remain off to reduce the
Comm Fault
The inverter has suffered an internal
communication failure.
Loose DC Neg
Loose DC connection on left (L) or right (R)
Tighten all DC connections between inverter
AC Relay Fault
AC transfer relay damaged.
An error is caused by a critical fault. In most cases when this occurs, the unit will shut down. The
MATE3 system display will show an event and a specific error message. This screen is viewed using
the MATE3 Home screen’s soft keys. (See the MATE3 manual for more instructions.) One or more
messages will display Y (yes). If a message says N (no), it is not the cause of the error.
NOTE:
The Radian series has no external indicators and requires a system display to identify an error.
Some errors will reset automatically when the cause is resolved. These are noted.
It is possible to clear an error by resetting the inverter. The inverter must be turned off, and then on,
to reset it. Other possible steps are shown below. Each should be followed by resetting the inverter.
Low Output Voltage
AC Output Shorted
AC Output Backfeed
Low Battery V
under high load conditions.
due to severe overload.
of phase with the inverter) was connected to
the unit’s AC output.
Programming problem among stacked units.
(Often occurs if there is no master.)
Can also occur if
6
point, usually due to battery discharge.
This error can be triggered by other causes. It
can appear along with
Output Shorted
AC Output Backfeed
Low Output Voltage, AC
, or
AC Output Backfeed
occurs.
errors.
Remove loads as necessary.
usually the result of a wiring problem (a short),
inverter. Check the wires (not the inverter)
with an AC voltmeter. If an AC source is
Check stacking programming and designation
of master. (See page 34.)
Check for output backfeed from an external
source. Disconnect output if necessary.
If this error accompanies other errors, treat
those conditions as appropriate.
If it occurs by itself: Recharge the batteries.
The error will clear automatically if an AC
source is connected and the charger turns on.
6
High Battery V
Over Temperature
Terminals (L or R)
page 22.
6
operating temperature. See page 59.
internal power module.
6 This error will clear automatically when the cause of the error is resolved. The inverter will begin functioning again when this occurs.
7 See inside front cover of this manual.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 57
usually the result of external charging. The
error clears automatically if conditions are
temperature, or add external cooling.
Contact OutBack Technical Support.7
and battery. If error is not resolved, contact
OutBack Technical Support.7
Contact OutBack Technical Support.
7
Page 60

Troubleshooting
Table 8 Warning Troubleshooting
Message
Definition
Possible Remedy
AC Freq Too High
The AC source is above the upper acceptable
frequency limit and prevents connection.
Check the AC source. If it is a generator, reduce its
speed.
AC Freq Too Low
The AC source is below the lower acceptable
Check the AC source. If it is a generator, increase
Voltage Too High
The AC source is above the upper acceptable
Check the AC source. The inverter’s acceptance
problematic AC source, but it will not fix it.
Voltage Too Low
The AC source is below the lower acceptable
Check the AC source. Check the AC wiring. The
Adjusting the range may accommodate a
problematic AC source, but it will not fix it.
Input Amps > Max
AC loads are drawing more current from the AC
Check the loads. Oversized loads can open circuit
load, as opposed to a wiring problem.
Temp Sensor Bad
An internal inverter temperature sensor may be
In the MATE3, the three readings are
Celsius. See next page.
Phase Loss
A slave was ordered to transfer to an AC source
Check the AC voltage on the inverter input
Support.8
Warning Messages
A warning message is caused by a non-critical fault. When this occurs, the unit will not shut down, but
the MATE3 system display will show an event and a specific warning message. This screen is viewed
using the MATE3 Home screen’s soft keys. (See the MATE3 manual for more instructions.) One or
more messages will display Y (yes). If a message says N (no), it is not the cause of the warning.
NOTE:
The Radian series has no external indicators and requires the MATE3 system display to identify
a warning.
Some warnings can become errors if left unattended. Frequency and voltage warnings are meant to
warn of a problematic AC source. Often the inverter will disconnect from the source. This will occur if
the condition lasts longer than the inverter’s transfer delay settings. If the inverter disconnects, the
warning will display as long as the source is present, accompanied by a disconnect message. (See
page 60.)
Warning screens can only display warnings; they cannot clear them. The way to correct the fault may
be obvious from the message.
frequency limit and prevents connection.
voltage limit and prevents connection.
voltage limit and prevents connection.
source than allowed by the input setting.
malfunctioning. One of the three internal
sensor meters may give an unusual reading.
by the master, but the AC source is the wrong
phase or no AC source is present.
its speed.
range is adjustable.
Adjusting the range may accommodate a
NOTE:
inverter’s acceptance range is adjustable.
NOTE:
breakers. If they exceed the inverter’s transfer
relay size, the relay can be damaged.
This issue is usually the result of a poorly-sized
labeled
Capacitors
terminals. If AC voltage is not present, problem
is external. If AC voltage is present, the unit may
be damaged. Contact OutBack Technical
Transformer, Output FETs,
. These values are given in degrees
and
8 See inside front cover of this manual.
58 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 61

Troubleshooting
Table 8 Warning Troubleshooting
Message
Definition
Possible Remedy
Fan Failure
The inverter’s internal cooling fan is not
Turn the battery disconnect off, and then on, to
step. (The next step will depend on the results of
system can continue to operate if the
Transformer
D
isplays the ambient temperature around the
In the MATE3, these values are given in degrees
Output FETs
Temps
Displays the temperature of the FETs (Field
Capacitors
(in
Temps
menu)
Displays the temperature of the inverter’s
Table 9 Temperature Events
Temperature Reading
Transformer
Output FETs
Capacitors
Over Temperature
error
>125°C
>80°C
>80°C
Reduced charging or selling
=120°C
=80°C
=80°C
Fan turns on
>60°C
>60°C
>60°C
Fan turns off
<49°C
<49°C
<49°C
(in
(in
Temps
menu)
menu)
operating properly. Lack of cooling may result
in derated inverter output wattage.
inverter’s transformer.
Effect Transistors) and heat sink.
ripple capacitors.
determine if the fan self-tests. After this test,
contact OutBack Technical Support for the next
the test.)
The
NOTE:
inverter can be run at reasonable levels. External
cooling may also be applied.
Celsius.
If any reading does not seem to reflect the
inverter’s temperature or conditions, contact
OutBack Technical Support.9
Temperature Events
The temperature sensor readings shown in Table 8 are used to limit the inverter operation in high
temperatures. Table 9 shows the effects on the inverter and the temperature used by each sensor to
cause the effect.
Effect
9 See inside front cover of this manual.
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 59
Page 62

Troubleshooting
Disconnect Messages
AC
INPUT
Table 10 Disconnect Troubleshooting
Message
Definition
Possible Remedy
Frequency Too High
The AC source has exceeded acceptable
frequency levels.
Check AC source. If it is a generator, reduce speed.
Frequency Too Low
The AC source has dropped below
acceptable frequency levels.
Check AC source. If it is a generator, increase speed.
Voltage > Maximum
The AC source has exceeded acceptable
Check AC source. The inverter’s acceptance range is
problematic AC source, but it will not fix it.
Voltage < Minimum
The AC source has dropped below
Check AC source. The inverter’s acceptance range is
problematic AC source, but it will not fix it.
Backfeed
Usually indicates that another AC power
Disconnect the AC OUT wires. Check the wires (not
Check input source and wiring. This can be caused by
a source with phase problems
Phase Lock
The unit cannot remain in phase with an
Check AC source. This can be caused by a generator
the
Generator
input mode. (See page 13.)
Island Detect
The grid seems to be present but normal
Check all input disconnects or circuit breakers for an
open circuit. Check for any other inverters installed in
Generator
Disconnect messages explain why the inverter has disconnected from an AC source after previously
being connected. The unit returns to inverting mode if turned on. This screen is viewed using the
hot key on the MATE3. One or more messages will display Y (yes). If a message says N (no), it
is not the cause of the disconnection. The MATE3 system display may generate a concurrent event
and warning message following the disconnection. (See page
warning will be blank, but the cause of the last disconnection will remain.
58.) If the AC source is removed, the
Disconnect messages only display the reason for the disconnection; they cannot correct it. It is usually
the result of external conditions, not an inverter fault. If the condition is corrected, the inverter will
reconnect. A few settings can be changed to accommodate problems with the AC source.
The reasons shown in the Sell Status menu for ceasing to sell power (see next page) may be the same
as disconnect messages. If the Grid Interface Protection settings are exceeded (see page 12), the
inverter will disconnect from the utility grid.
Table 10 shows the primary seven reasons for disconnection. An eighth field may be visible, but it can
feature several different messages which vary with conditions. A list of these messages and their
definitions is featured on the OutBack website at www.outbackpower.com.
voltage levels.
acceptable voltage levels.
source (out of phase with the inverter) was
connected to the AC output.
Can also occur if an out-of-phase AC source
is connected to the AC input.
erratic AC source.
grid conditions are not detected. This can
occur if the Radian’s input is powered by
another inverter instead of the grid. It may
60 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
be the result of an open main disconnect.
adjustable.
Adjusting the range may accommodate a
NOTE:
adjustable.
Adjusting the range may accommodate a
NOTE:
the inverter) with an AC voltmeter. If an AC source is
present, shut it off. (This is more often accompanied
by an
AC Output Backfeed
with a poorly regulated output. Some generators
perform this way when low on fuel. If necessary, use
the system and disable them.
This may (rarely) occur with a generator. If necessary,
use the
input mode. (See page 13.)
error.)
Page 63

Troubleshooting
Sell Status
Table 11 Sell Status Messages
Sell Status
Definition
Selling Disabled
The
Grid-Tie Enable
command has been set to N (no).
Qualifying Grid
All utility grid conditions are acceptable. The inverter is
that time, the inverter may be ready to sell.
Frequency Too Low
The utility grid’s AC frequency is below the acceptable
range for selling.
Frequency Too High
The utility grid’s AC frequency is above the acceptable
range for selling.
Voltage Too Low
The utility grid’s AC voltage is below the acceptable
range for selling.
Voltage Too High
The utility grid’s AC voltage is above the acceptable
range for selling.
Battery < Target
The battery voltage is below the target voltage for that
to sell.
Sell Status messages describe conditions relating to the inverter’s grid-interactive mode. This screen is
viewed using the MATE3 Home screen’s soft keys. (See the MATE3 manual for more instructions.) One
or more messages will display Y (yes). If a message says N (no), it is not the cause of the disconnection.
If the inverter has stopped selling or charging unexpectedly, this screen may identify the reason. More
often these messages are used by a normally functioning inverter to identify external conditions that
are preventing selling or charging. (If nothing has stopped, the messages will indicate that as well.)
The acceptable limits for AC source voltage and frequency are controlled by the Grid Interface
Protection settings, which are shown on page 69. If the AC source exceeds these limits, the inverter
will stop selling and display the appropriate code. (At the same time it will disconnect from the utility
grid, with an appropriate message in Table 10 as shown on page 60.) After the source returns to the
acceptable range, the screen will begin its reconnection timer (with a default setting of five minutes).
When the timer expires, the inverter will reconnect to the utility grid and begin selling power again.
If the AC source is unstable, it may become unacceptable before the timer expires. This may cause the
timer to continually reset. It is possible for brief fluctuations to occur that are too fast to be seen on a
DVM. If this happens, the appropriate message will still appear on the system display for a short time
to help troubleshoot the problem.
Additionally, undersized wires or bad connections can result in local voltage problems. If a
Too Low
or
Voltage Too High
message is accompanied by voltage changes that do not appear at the
main utility connection, check the wiring.
running a timed test during which it confirms the grid
quality. The timer is shown on the screen. At the end of
Voltage
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 61
stage (Float, Selling, etc.). No excess energy is available
Page 64

Troubleshooting
NOTES:
62 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 65
Specifications
Specification
GS7048E
GS3548E
Electrical Specifications
: Items qualified with “default” can be manually changed using the system display.
NOTE
Table 12 Electrical Specifications for Radian Models
Continuous Output Power at 25°C 7000 VA 3500 VA
Continuous AC Output Current at 25°C 30.4 Aac 15.2 Aac
AC Output Voltage (nominal) 230 Vac 230 Vac
AC Output Frequency (default) 50 Hz 50 Hz
AC Output Type Single-phase Single-phase
AC Waveform True Sinewave True Sinewave
Efficiency (typical) 92% 92%
Total Harmonic Distortion (maximum) < 5% < 5%
Harmonic Distortion (maximum single voltage) < 2% < 2%
AC Output Voltage Regulation ± 2% ± 2%
Appliance Protective Class (IEC) Class I Class I
Power Factor –1 to 1 –1 to 1
Inrush Current None None
AC Maximum Output Current (1 ms peak) 100 Aac 50 Aac
AC Maximum Output Current (100 ms RMS) 70.7 Aac 35.35 Aac
AC Overload Capability (100 ms surge) 16.3 kVA 8.15 kVA
AC Overload Capability (5 second) 11.5 kVA 5.75 kVA
AC Overload Capability (30 minute) 7.9 kVA 3.95 kVA
AC Maximum Output Fault Current and Duration 109 Aac for 0.364 seconds 54.5 Aac for 0.364 seconds
Power Consumption (idle) – Invert mode, no load 34 watts 34 watts
Power Consumption (idle) – Search mode 10 watts 10 watts
Power Consumption – Off 4 watts 4 watts
AC Input Voltage Range 170 to 290 Vac 170 to 290 Vac
AC Input Frequency Range (default) 45 to 55 Hz 45 to 55 Hz
AC Input Current (maximum continuous) 50 Aac 50 Aac
Grid-Interactive Voltage Range (default) 208 to 252 Vac 208 to 252 Vac
Grid-Interactive Frequency Range (default) 47 to 51 Hz 47 to 51 Hz
DC Input Voltage (nominal) 48 Vdc 48 Vdc
DC Input Voltage Range 40 to 64 Vdc 40 to 64 Vdc
DC Maximum Input Voltage 68 Vdc 68 Vdc
DC Input Power (continuous) 7.634 kVA 3.817 kVA
DC Input Maximum Current (continuous full power) 175 Adc 87.5 Adc
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 63
Page 66

Specifications
Table 12 Electrical Specifications for Radian Models
Specification
GS7048E
GS3548E
Specification
GS7048E
GS3548E
71.1 x 40.6 x 22.2 cm
(28 x 16 x 8.75")
71.1 x 40.6 x 22.2 cm
(28 x 16 x 8.75")
36.8 x 53.3 x 87.6 cm
(14.5 x 21 x 34.5")
36.8 x 53.3 x 87.6 cm
(14.5 x 21 x 34.5")
RJ11 (batt temp) and
RJ45 (remote)
RJ11 (batt temp) and
RJ45 (remote)
Specification
Value
Rated Temperature Range (meets component specifications; however, please note
that the inverter output wattage is derated above 25°C)
Operational Temperature Range (functions, but does not necessarily meet all
component specifications)
DC Input Maximum Current (surge) 406.5 Adc 203.3 Adc
DC Input Maximum Current (short-circuit) 8975 Adc 4488 Adc
Battery Charger Maximum AC Input 30 Aac at 230 Vac 15 Aac at 230 Vac
Battery Charger Maximum DC Output 100 Adc 50 adc
DC Output Voltage Range (charging) 44 to 68 Vdc 44 to 68 Vdc
Auxiliary Output 0.7 Adc at 12 Vdc 0.7 Adc at 12 Vdc
Auxiliary Relay 10 A at 250 Vac or 30 Vdc 10 A at 250 Vac or 30 Vdc
Mechanical Specifications
Table 13 Mechanical Specifications for Radian Models
Inverter Dimensions (H x W x D)
Shipping Dimensions (H x W x L)
Inverter Weight 56.8 kg (125 lb) 37.2 kg (82 lb)
Shipping Weight 63.5 kg (140 lb) 42.6 kg (94 lb)
Accessory Ports
Non-volatile Memory Yes Yes
Neutral-Ground Bond Switching No No
Chassis Type Vented Vented
Environmental Specifications
Table 14 Environmental Specifications for Radian Models
–20°C to 50°C ( –4°F to 122°F)
–40°C to 60°C (–40°F to 140°F)
Storage Temperature Range –40°C to 60°C (–40°F to 140°F)
IP (Ingress Protection) Rating of Enclosure IP20
Environmental Category Indoor unconditioned
Wet Locations Classification Wet locations: No
Relative Humidity Rating 93%
Pollution Degree Classification PD 2
Maximum Altitude Rating 2000 m (6561’)
Overvoltage Category (AC Input) 3
Overvoltage Category (DC Input) 1
64 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 67

Specifications
Temperature Derating
10°C
40°C
50°C
25°C
8000
6000
4000
2000
0
0
Output
5250
7000
20°C
30°C
All Radian inverters can deliver their full rated wattage at temperatures up to 25°C (77°F). The Radian
maximum wattage is rated less in higher temperatures. Above 25°C, the GS7048E is derated by a
factor of 70 VA for every increase of 1°C. The GS3548E is derated by 35 VA per 1°C.
Figure 18 is a graph of wattage over temperature, showing the decrease in rated wattage with
increased temperature. The graph ends at 50°C (122°F) because the Radian inverter is not rated for
operation above that temperature.
Watts
50°F
68°F
77°F
86°F
104°F
Figure 18 Temperature Derating
Certifications
The Radian GS3548E is certified by ETL to the following standards:
IEC 62109-1:2010 — Safety of Power Converters for use in Photovoltaic Systems (2010)
IEC 62477-1:2012 — Safety Requirements for Power Electronic Converter Systems and Equipment
EN 61000-6-1 — EMC Standard: Immunity for Residential, Commercial, and Light-Industrial Environments
EN 61000-6-3 — EMC Standard: Emissions for Residential, Commercial, and Light-Industrial Environments
EN 61000-3-3 — EMC Standard: Limitation of Voltage Changes, Voltage Fluctuations, and Flicker in Public
Low-Voltage Supply Systems
AS4777.2 and AS4777.3 — Grid Connection of Energy Systems via Inverters
AS/NZS 3100 — General Requirements for Electrical Equipment
The Radian GS7048E is certified by ETL to the following standards:
IEC 62477-1:2012 — Safety Requirements for Power Electronic Converter Systems and Equipment
EN 61000-6-1 — EMC Standard: Immunity for Residential, Commercial, and Light-Industrial Environments
EN 61000-6-3 — EMC Standard: Emissions for Residential, Commercial, and Light-Industrial Environments
EN 61000-3-3 — EMC Standard: Limitation of Voltage Changes, Voltage Fluctuations, and Flicker in Public
Low-Voltage Supply Systems
AS4777.2 and AS4777.3 — Grid Connection of Energy Systems via Inverters
AS/NZS 3100 — General Requirements for Electrical Equipment
122°F
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 65
Page 68
Specifications
Compliance
Table 15 AS4777.3 Acceptance Settings
RoHS: per directive 2011/65/EU
These inverter/charger models have grid-interactive functions. All models are
tested to comply with certain limits for acceptable output voltage ranges,
acceptable output frequency, total harmonic distortion (THD) and anti-islanding performance when
the inverter exports power to a utility source. The OutBack inverter/charger models listed in this
document are validated through compliance testing. The following specifications refer to exporting
power to a simulated utility source of less than 1% voltage total harmonic distortion (THD).
The THD of the root mean square (RMS) current is less than 5%.
The output of the Radian inverter exceeds the minimum power factor of 0.85 with a typical power factor of
0.96 or better.
The reconnection delay has a default setting of 1 minute. The grid-interactive default settings are
shown in the
Grid Interface Protection Menu
portion of Table 16 on page 69.
The
Grid Interface Protection
settings are adjustable. However, this is only available to operators with
installer-level access. The reason for this limitation is that there are firm rules concerning the
acceptable voltage range, frequency range, clearance time during power loss, and reconnect delay
when exporting power back to the utility. The rules differ in different locations around the world,
although generally it is expected that the settings cannot be altered by the end user. For this reason,
the installer password must be changed from the default to get access to these settings.
See the
Grid Tied
function on page 15 for more information.
To meet the standard AS4777.3 for installations in Australia, the acceptance settings shall not exceed
the following. The factory default settings meet these requirements.
Minimum
Voltage
200 Vac 270 Vac 45 Hz 55 Hz
Maximum
Voltage
Minimum
Frequency
Maximum
Frequency
66 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 69
Specifications
INVERTER
CHARGER
AC Input
Sensitivity (see page 23 for increments)
Pulse Spacing
60 AC Cycles
4 AC Cycles
120 AC Cycles
Voltage Limit Lower
Upper
Firmware Revision
This manual applies to inverter models GS7048E and GS3548E with Revision 001.005.xxx or higher.
Updates to the Radian’s firmware are periodically available. These can be downloaded from the
OutBack website www.outbackpower.com. See page 12.
Default Settings and Ranges
NOTE:
defaults. These items are noted with the letter “X” in the Item column.
Certain items, particularly those in the Auxiliary menus, share common set points. If one of these
items is changed in a mode menu, the change will appear in other menus that use the same set point
Certain menus are only visible when the installer password is used, particularly the Grid Interface
Protection menu. These menus are bordered in the table with a double line of this style:
Search
Some items are retained at the present setting even when the inverter is reset to factory
Table 16 Radian Inverter Settings
Field Item Default Minimum Maximum
Hot Key Inverter Mode Off On, Off, or Search
Hot Key Charger Control On On or Off
Hot Key AC Input Mode Use Drop or Use
10 0 250
Pulse Length
8 AC Cycles 4 AC Cycles 20 AC Cycles
AC Input and
Current Limit
Grid AC Input
Mode and Limits
Gen AC Input
Mode and Limits
Input Priority Grid Grid or Gen
Grid Input AC Limit
Gen Input AC Limit
Charger AC Limit
Input Mode Grid Tied
(Voltage Limit) Upper
Transfer Delay
Connect Delay
When Mini Grid
mode is selected:
When Grid Zero
mode is selected:
Input Mode Generator
Voltage Limit Lower
(Voltage Limit)
Transfer Delay
Connect Delay
If Mini Grid mode
is selected:
If Grid Zero mode
is selected:
Connect to Grid
(Connect) Delay
DoD Volts
DoD
Amps
Connect to Grid
(Connect) Delay
DoD Volts
DoD
Amps
GS7048E 30 Aac 0 Aac 30 Aac
GS3548E 15 Aac 0 Aac 15 Aac
GS7048E 5 Aac 1 Aac 30 Aac
GS3548E
GS7048E 5 Aac 1 Aac 30 Aac
GS3548E 5 Aac 1 Aac 15 Aac
50 Aac 5 Aac 55 Aac
50 Aac 5 Aac 55 Aac
Generator, Support, Grid Tied, UPS, Backup,
Mini Grid, Grid Zero
208 Vac 170 Vac 230 Vac
252 Vac 232 Vac 290 Vac
1 second 0.12 seconds 4.0 seconds
0.2 minutes 0.2 minutes 25.0 minutes
48.0 Vdc 44.0 Vdc 64.0 Vdc
10 minutes 2 minutes 200 minutes
48.0 Vdc 44.0 Vdc 64.0 Vdc
5 Aac 1 Aac 15 Aac
Generator, Support, Grid Tied, UPS, Backup,
Mini Grid, Grid Zero
208 Vac 170 Vac 230 Vac
252 Vac 232 Vac 290 Vac
1 second 0.12 seconds 4.0 seconds
0.5 minutes 0.2 minutes 25.0 minutes
48.0 Vdc 44.0 Vdc 64.0 Vdc
10 minutes 2 minutes 200 minutes
48.0 Vdc 44.0 Vdc 64.0 Vdc
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 67
Page 70

Specifications
Table 16 Radian Inverter Settings
Output Voltage
X
230 Vac
200 Vac
260 Vac
Cut-In Voltage
Absorb Voltage
57.6 Vdc
44.0 Vdc
64.0 Vdc
(Absorb) Time
1.0 hours
0.0 hours
24.0 hours
Float Voltage
(Float) Time
1.0 hours
0.0 hours
24/7
Re-Bulk Voltage
49.6 Vdc
44.0 Vdc
64.0 Vdc
Equalize Voltage
58.4 Vdc
44.0 Vdc
68.0 Vdc
(Equalize) Time
1.0 hours
0.0 hours
24.0 hours
Aux Control
Auto
Off, Auto or On
Load Shed, Gen Alert, Fault, Vent Fan, Cool Fan,
DC Divert, GT Limits, Source Status, AC Divert
(Load Shed) ON: Batt >
56.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
72.0 Vdc
(Load Shed ON) Delay
0.5 minutes
0.1 minutes
25 minutes
Delay
(Gen Alert) ON: Batt <
44.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
56.0 Vdc
(Gen Alert ON) Delay
OFF: Batt >
56.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
72.0 Vdc
ON: Batt >
(Vent Fan) Off Delay
0.5 minutes
0.1 minutes
25 minutes
(DC Divert) ON: Batt >
56.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
72.0 Vdc
Delay
0.5 minutes
0.1 minutes
25 minutes
(DC Divert) OFF: Batt <
44.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
56.0 Vdc
Delay
(AC Divert) ON: Batt >
56.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
72.0 Vdc
(AC Divert ON) Delay
0.5 minutes
0.1 minutes
25 minutes
(AC Divert) OFF: Batt <
44.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
56.0 Vdc
Aux Control
Auto
Off, Auto or On
Load Shed, Gen Alert, Fault, Vent Fan, Cool Fan,
DC Divert, GT Limits, Source Status, AC Divert
ON: Batt >
(Load Shed ON) Delay
0.5 minutes
0.1 minutes
25.0 minutes
(Load Shed OFF) Delay
0.5 minutes
0.1 minutes
25.0 minutes
(Gen Alert) ON: Batt <
44.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
56.0 Vdc
Delay
0.5 minutes
0.1 minutes
25.0 minutes
(Gen Alert) OFF: Batt >
56.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
72.0 Vdc
(Gen Alert OFF) Delay
(Vent Fan) ON: Batt >
56.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
72.0 Vdc
(Vent Fan) Off Delay
0.5 minutes
0.1 minutes
25.0 minutes
ON: Batt >
(DC Divert) OFF: Batt <
(DC Divert OFF) Delay
0.5 minutes
0.1 minutes
25.0 minutes
(AC Divert) ON: Batt >
56.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
72.0 Vdc
Delay
(AC Divert) OFF: Batt <
44.0 Vdc
40.0 Vdc
56.0 Vdc
Field Item Default Minimum Maximum
AC Output
Low Battery
Battery Charger
Battery Equalize
Auxiliary Output
AC Coupled Mode
Cut-Out Voltage
Re-Float Voltage 54.4 Vdc 44.0 Vdc 64.0 Vdc
Aux Mode Vent Fan
(Load Shed) OFF: Batt <
(Load Shed OFF)
(Gen Alert)
(Gen Alert OFF) Delay 0.5 minutes 0.1 minutes 25 minutes
(Vent Fan)
42.0 Vdc 36.0 Vdc 48.0 Vdc
50.0 Vdc 40.0 Vdc 56.0 Vdc
54.4 Vdc 44.0 Vdc 64.0 Vdc
44.0 Vdc 40.0 Vdc 56.0 Vdc
0.5 minutes 0.1 minutes 25 minutes
0.5 minutes 0.1 minutes 25 minutes
56.0 Vdc 40.0 Vdc 72.0 Vdc
This selection is inoperative
Auxiliary
Relay
(DC Divert ON)
(DC Divert OFF)
(AC Divert OFF) Delay
Aux Mode Gen Alert
(Load Shed)
(Load Shed) OFF: Batt <
(Gen Alert ON)
(DC Divert)
(DC Divert ON) Delay
(AC Divert ON)
0.5 minutes 0.1 minutes 25 minutes
0.5 minutes 0.1 minutes 25 minutes
56.0 Vdc 40.0 Vdc 72.0 Vdc
44.0 Vdc 40.0 Vdc 56.0 Vdc
0.5 minutes 0.1 minutes 25.0 minutes
56.0 Vdc 40.0 Vdc 72.0 Vdc
0.5 minutes 0.1 minutes 25.0 minutes
44.0 Vdc 40.0 Vdc 56.0 Vdc
0.5 minutes 0.1 minutes 25.0 minutes
(AC Divert OFF) Delay
68 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
0.5 minutes 0.1 minutes 25.0 minutes
Page 71

Specifications
Table 16 Radian Inverter Settings
Auto
Auto, Left, Right, Both
Grid Interface Protection Menu
GS3548E
15 Aac
5 Aac
15 Aac
Field Item Default Minimum Maximum
Inverter Stacking
Power Save
Ranking
Grid-Tie Sell
Module Control
Calibrate
Operating Frequency
Stage 1 Voltage Trip
Stage 2 Voltage Trip
Frequency Trip
Mains Loss
Sell Current Limit
Stack Mode Master Master, Slave, B Phase Master, C Phase Master
Mode = Master: Master Power Save Level
Mode = Slave: Slave Power Save Level
Mode = B Phase Master Master Power Save Level
Mode = C Phase Master: Master Power Save Level
Grid-Tie Enable Y Y or N
Sell Voltage
Module Control
Grid AC Input Voltage X
Gen AC Input Voltage X
Output Voltage X
Battery Voltage X
Operating Frequency X
Over Voltage Clearance Time X
Over Voltage Trip X
Under Voltage Clearance Time X
Under Voltage Trip X
Over Voltage Clearance Time X
Over Voltage Trip X
Under Voltage Clearance Time X
Under Voltage Trip X
Over Frequency
Clearance Time
Over
Frequency
Trip
Under Frequency
Clearance Time
Under
Frequency
Trip
Clearance Time X
Reconnect Delay X
Maximum
Sell Current
50-Hz system
60-Hz system 61.0 Hz 60.1 Hz 65.0 Hz
50-Hz system
60-Hz system 57.0 Hz 55.0 Hz 59.9 Hz
GS7048E
GS3548E
GS7048E
X
X
X
X
X
0 0 31
1 1 31
0 0 31
0 0 31
52.0 Vdc 44.0 Vdc 64.0 Vdc
Left Auto, Left, Right, Both
0 Vac –7 Vac 7 Vac
0 Vac –7 Vac 7 Vac
0 Vac –7 Vac 7 Vac
0.0 Vdc –0.8 Vdc 0.8 Vdc
50 Hz 50 Hz, 60 Hz
1.5 seconds 0.12 seconds 4.0 seconds
252 Vac 240 Vac 300 Vac
1.5 seconds 0.12 seconds 4.0 seconds
208 Vac 160 Vac 240 Vac
0.2 seconds 0.12 seconds 4.0 seconds
264 Vac 240 Vac 300 Vac
0.2 seconds 0.12 seconds 4.0 seconds
196 Vac 160 Vac 240 Vac
0.2 seconds 0.12 seconds 5.0 seconds
51.0 Hz 50.1 Hz 55.0 Hz
0.2 seconds 0.12 seconds 5.0 seconds
47.0 Hz 45.0 Hz 49.9 Hz
2.0 seconds 1.0 seconds 5.0 seconds
300 seconds 2 seconds 302 seconds
30 Aac 5 Aac 30 Aac
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 69
Page 72
Specifications
Definitions
Table 17 Terms and Definitions
Term
Definition
12V AUX
Auxiliary connection that supplies 12 Vdc to control external devices
AC
Alternating Current; refers to voltage produced by the inverter, utility grid, or generator
AGS
Advanced Generator Start
DC
Direct Current; refers to voltage produced by the batteries or renewable source
DVM
Digital Voltmeter
GND
Ground; a permanent conductive connection to earth for safety reasons; also known as
Chassis Ground, Protective Earth, PE, Grounding Electrode Conductor, and GEC
Grid/Hybrid™
System technology which optimizes both grid-interactive and off-grid options
Grid-interactive,
grid-intertie, grid-tie
Utility grid power is available for use and the inverter is a model capable of returning
(selling) electricity back to the utility grid
HBX
High Battery Transfer; a function of the remote system display
IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission; an international standards organization
LBCO
Low Battery Cut-Out; set point at which the inverter shuts down due to low voltage
NEU
AC Neutral; also known as Common
Off-grid
Utility grid power
is not
available for use
PV
Photovoltaic
RELAY AUX
Auxiliary connection that uses switch (relay) contacts to control external devices
RTS
Remote Temperature Sensor; accessory that measures battery temperature for charging
System display
Remote interface device (such as the MATE3), used for monitoring, programming and
communicating with the inverter; also called “remote system display”
Three-phase, 3-phase
A type of utility electrical system with three “hot” lines, each 120° out of phase;
respect to each other equaling the line voltage multiplied by 1.732
Utility grid
The electrical service and infrastructure supported by the electrical or utility company;
also called “mains”, “utility service”, or “grid”
The following is a list of initials, terms, and definitions used in conjunction with this product.
Neutral-to-ground
bonding
A mechanical connection between the AC neutral (Common) bus and the ground (PE)
bus; this bond makes the AC neutral safe to handle
each carries the nominal line voltage with respect to neutral; each carries voltage with
70 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Page 73

1
12V AUX ................................................................................. 43
A
Absorption Stage ................................................................ 29
AC Input ................................................................................. 24
AC Source Acceptance ..................................................... 25
AC Test Points ............................................................... 10, 51
Adding New Devices ......................................................... 11
AGS ........................................................................................... 47
Audience ................................................................................... 5
AUX ................................................................................... 43, 70
AUX Functions
Cool Fan ........................................................................... 44
Diversion Control ................................................... 44, 45
Fault ................................................................................... 44
GenAlert .................................................................... 44, 47
GT Limits .......................................................................... 45
LoadShed ......................................................................... 43
Source Status .................................................................. 45
Summary Table.............................................................. 46
Vent Fan ........................................................................... 44
B
Backup .................................................................................... 18
Battery Charging ................................................................. 27
Current .............................................................................. 27
Graphs ........................................................................ 28, 32
Steps .................................................................................. 28
Battery Charging Graph ................................................... 32
Index
Silent .................................................................................. 30
Steps ............................................................................ 29, 31
Commissioning ...................................................................... 9
Cool Fan .................................................................................. 44
D
Default Settings ................................................................... 67
Definitions ............................................................................. 70
Design ..................................................................................... 22
Disconnect ............................................................................. 60
Diversion Control ......................................................... 44, 45
DVM ..................................................................................... 9, 11
E
Equalization........................................................................... 33
Errors ........................................................................................ 57
F
Features .................................................................................... 6
Firmware ......................................................................... 12, 67
Float Stage ............................................................................. 30
Functional Test....................................................................... 9
Functions .................................................................................. 6
AC Input Limit ................................................................. 24
AC Transfer ...................................................................... 26
Inverting ........................................................................... 22
LBCO ................................................................................... 22
Offset .................................................................................. 35
Search ................................................................................ 23
G
C
Caution Symbol ...................................................................... 5
Charging
Absorption Stage .......................................................... 29
Current .............................................................................. 27
Float Stage ...................................................................... 30
Float Timer ...................................................................... 30
New Bulk .......................................................................... 32
None .................................................................................. 29
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 71
GenAlert........................................................................... 44, 47
Generator ........................................................................ 14, 38
Sizing.................................................................................. 26
Generator Acceptance ...................................................... 25
Grid Acceptance .................................................................. 25
Grid Interface Protection ............................. 17, 25, 66, 69
Grid Tied ................................................................................. 15
Grid Use Time ................................................................ 18, 48
Grid Zero................................................................................. 19
Grid-Interactive ............................................................. 15, 70
Page 74

Index
GT Limits ................................................................................ 45
H
High Battery Cut-Out ........................................................ 22
High Battery Transfer (HBX) ..................................... 18, 47
I
IEC ............................................................................................. 70
Important Symbol ................................................................. 5
Input Modes ....................................................... 6, 13, 24, 35
Summary Table.............................................................. 21
Input Priorities ..................................................................... 24
Inverting ................................................................................. 22
L
LBCO (Low Battery Cut-Out)........................................... 22
Levels, Power Save ............................................................. 39
Load Grid Transfer ....................................................... 18, 48
LoadShed ............................................................................... 43
Low Battery Cut-In ............................................................. 22
M
MATE or MATE2 ...................................................................... 6
MATE3 ..................................................................... 6, 8, 49, 51
Mini Grid.......................................................................... 18, 47
Modes ........................................................................................ 6
Backup .............................................................................. 18
Generator ......................................................................... 14
Grid Tied ........................................................................... 15
Grid Zero .......................................................................... 19
Mini Grid .................................................................... 18, 47
Summary Table.............................................................. 21
Support ............................................................................. 14
UPS ..................................................................................... 17
Module Select ...................................................................... 56
Modules .................................................................................. 39
O
Offset ....................................................................................... 35
Output
Frequency ........................................................................ 23
Voltage .............................................................................. 23
P
R
Regulatory ............................................................................. 65
Relay AUX ............................................................................... 43
Remote System Display .................................................... 70
Remote Temperature Sensor (RTS) ....................... 33, 70
S
Safety ......................................................................................... 5
Search ...................................................................................... 23
Sell Status ............................................................................... 61
Settings ................................................................................... 67
Silent
Charging ........................................................................... 30
Power Save ...................................................................... 39
Source Status ........................................................................ 45
Specifications
Electrical............................................................................ 63
Environmental ................................................................ 64
Mechanical ....................................................................... 64
Regulatory........................................................................ 65
Stacking .................................................................................. 36
Parallel ............................................................................... 37
Three-Phase..................................................................... 38
Startup ....................................................................................... 9
Support ................................................................................... 14
Switch ........................................................................................ 8
Symbols Used ......................................................................... 5
System Display ................................................ 38, 49, 51, 70
T
Temperature .................................................... 58, 59, 64, 65
Temperature Compensation .......................................... 33
Terms and Definitions ....................................................... 70
Test ............................................................................................. 9
Test Points ...................................................................... 10, 51
Three-Phase Stacking ........................................................ 38
Timers
Absorption ....................................................................... 29
Equalize ............................................................................. 33
Float .................................................................................... 31
Transfer Relay ................................................................ 24, 26
Troubleshooting .................................................................. 51
Disconnect Messages .................................................. 60
Error Messages ............................................................... 57
Sell Status Messages .................................................... 61
Warning Messages ........................................................ 58
Parallel Stacking .................................................................. 37
Power Save ............................................................................ 39
Powering Down .................................................................. 11
72 900-0145-01-01 Rev A
U
Updating Firmware ..................................................... 12, 67
UPS............................................................................................ 17
Utility Grid ....................................................................... 38, 70
Page 75

Index
V
W
Vent Fan Control ................................................................. 44
Warning Symbol .................................................................... 5
Warnings ................................................................................ 58
Website ............................................................................ 12, 67
900-0145-01-01 Rev A 73
Page 76

Masters of the Off-Grid.™ First Choice for the New Grid.
Corporate Headquarters
+1.360.435.6030
European Office
+49.9122.79889.0
17825 – 59th Avenue N.E.
Suite B
Arlington, WA 98223 USA
900-0145-01-01 Rev A
Hansastrasse 8
D-91126
Schwabach, Germany
 Loading...
Loading...