Page 1

USER INSTRUCTIONAL BROCHURE
BTE, BTE P
Page 2

Congratulations on your digital hearing instruments.
They represent some of the most advanced technology
currently available in hearing care. Carefully follow
these instructions when using and maintaining them.
These instructions will help you get the most out
of the instruments and ensure their continued high
performance.
Contents
View of BTE Instrument 5
View of BTE Instrument with Corda thin sound tube 7
On/Off 9
Inserting your hearing instruments 11
Inserting hearing instruments into your
ear with a Corda thin sound tube 13
Warnings for hearing instruments with
Corda thin sound tube 15
Push-button 17
Telecoil 19
Volume Control (optional) 21
Battery Replacement 23
DAI (Direct Audio Input) 25
FM 26
Important notice
Please familiarize yourself with the entire
contents of this booklet before using your hearing
instruments. It contains instructions and important information about the use and handling of
your hearing instruments and batteries.
Daily care of your hearing instruments 28
Using your hearing instruments 31
Common problems and their solutions 36
International Warranty 38
Service 38
Warning/caution Yellow pages
Page 3
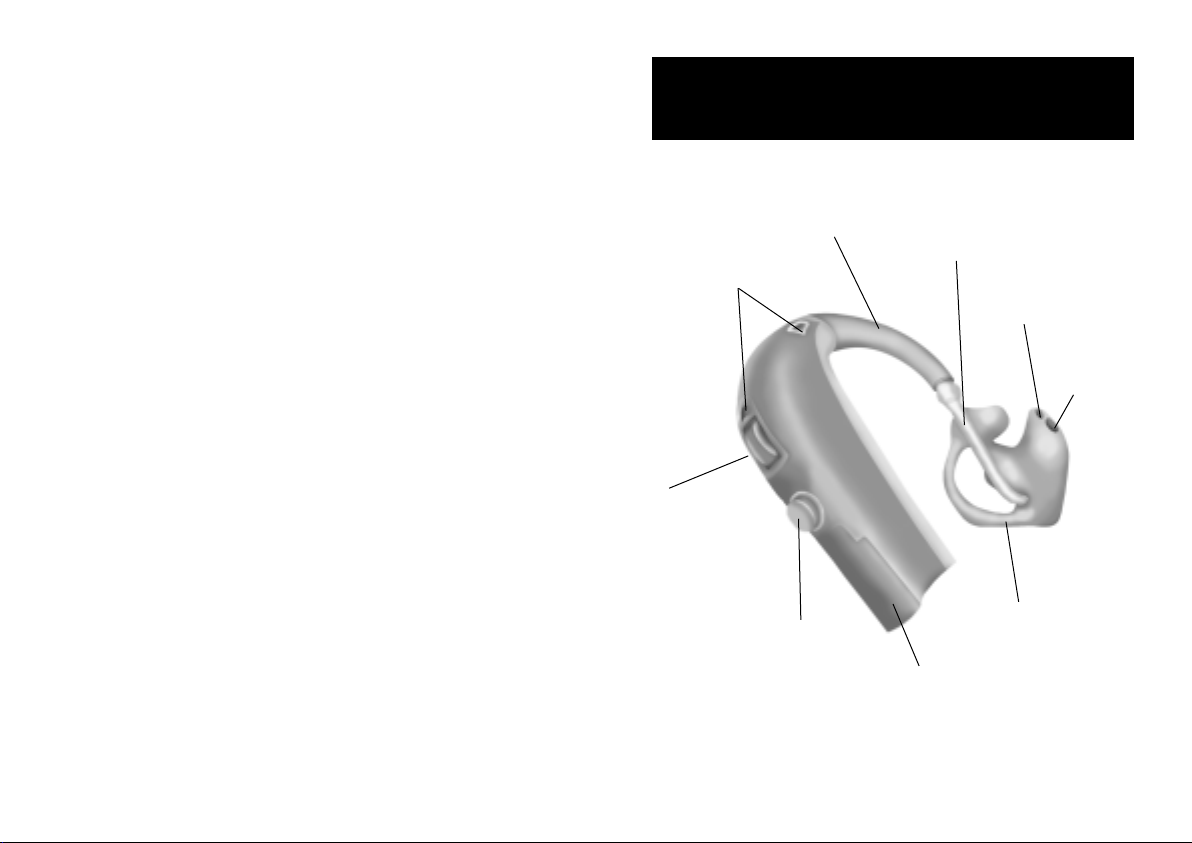
BTE
Microphone
openings
Volume
control
(Optional)
Push-button
Battery size: 13
Sound hook
Plastic tube
Sound outlet
Ventilation
opening
Earmold
Battery
door
5
Page 4
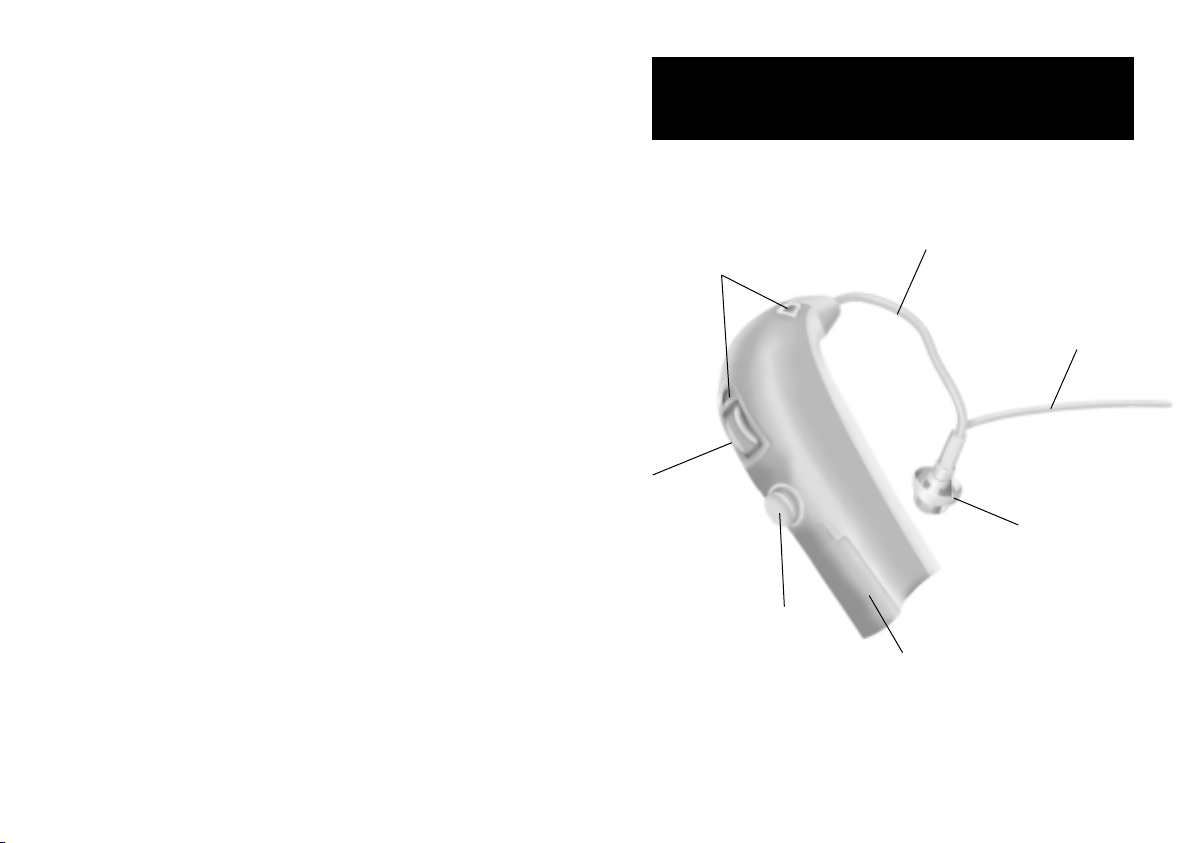
Behind-the-ear instruments with
Corda thin sound tube
Microphone
openings
Volume
control
(Optional)
Push-button
Battery size: 13
Thin sound tube
Ear grip
Dome
Battery
door
7
Page 5

Turning your instruments
ON and OFF
Turn on your hearing instru ment by closing the
battery door completely.
When the battery door is closed
you will hear three beeps followed by a short series of beeps.
This indicates that the battery is
working.
Turn off your hearing instrument
by opening the battery door
slightly until a click is felt.
If you have dexterity problems
an alternative way of turning
off the hearing instrument is to
place the base of the hearing
instrument on a flat surface,
gently press and drag the
instrument as illustrated below.
The battery door will slightly
open (turning off the hearing
instrument).
On
Off
To preserve the battery, make sure your hearing instrument is switched off when you are not wearing it.
9
Page 6

Standby
A long push on the button (min. 3 seconds) will set
the instrument in standby mode. To reactivate the
instrument, push the button again.
Use the standby function if you need to silence the
instrument while you have the instrument on.
Inserting your hearing instruments
• Hold the earmold as
shown.
• Gently pull down your
earlobe and press the
earmold in the direction
of the ear canal.
• Place the tip of the earmold
in your ear canal, twisting
slightly, making sure that
the top part of the earmold
(A) is pushed behind and
under the fold (B) of your
ear.
• With the earmold
positioned correctly in
your ear, place the hearing
instrument behind your ear
by lifting its lower part and
sliding it over the top of
your ear.
B
A
10
11
Page 7

Inserting hearing instruments
into your ear with a
Corda thin sound tube
A. Place the hearing instrument
behind your ear.
B. Hold the bend of the tube
between your thumb and index
finger. The dome should be
pointing towards the ear canal
opening. Gently push the dome
into your ear canal until the
sound tube sits close against
the side of your head.
C. Position the flexible ear grip into
the indentation above your ear
lobe using your index finger.
Look in a mirror. If the sound tube
is sticking out from your ear, the
dome has not been placed correctly
or deeply enough in the ear canal.
If the ear grip is visibly sticking
out from your ear it has not been
positioned correctly. To remove the
instrument from your ear, pull the
bend of the tube.
13
Page 8

Cleaning the Corda thin tube
To remove ear wax or debris from the
thin tube:
• Click the tube off the instrument by
lifting the thin tube up and away at the
thicker neck of the tube, at the junction
of the hearing aid and the tube.
Warnings about using hearing
instruments with Corda thin
sound tube
• Only use parts designed for Oticon hearing aids
• The cleaning tools should only be used for cleaning the tubing when it is detached from the hearing
instrument and not on the ear.
• Insert the cleaning tool in the tube all
the way through. It may be easier to
insert the cleaning tool starting at the
larger opening at the neck.
• Remove the cleaning tool and click on
the tube to the hearing instrument.
• Your hearing care professional can
advise you how often to clean the
tube. If the tube becomes
hardened, yellow, or cracked,
consult your hearing care
professional to obtain
replacement tubes and/or
domes.
14
• The dome must be properly attached to the sound
tube before inserting it in your ear. Failure to follow
the instructions could result in injury.
• If the dome is not correctly attached and falls off in
the ear, please see your hearing care professional or
seek medical consultation.
• The tube should never be used without a dome
attached.
• Do not use hearing aids in ears with excessive
ear wax accumulation or infection.
• Proper preventive care and maintenance will go
a long way toward ensuring reliability and safe
performance. Clean your sound tube on a regular
basis.
• Do not share your hearing aids or any of the parts
with others.
• Ensure your hands are clean when handling the
hearing instrument and its parts.
15
Page 9
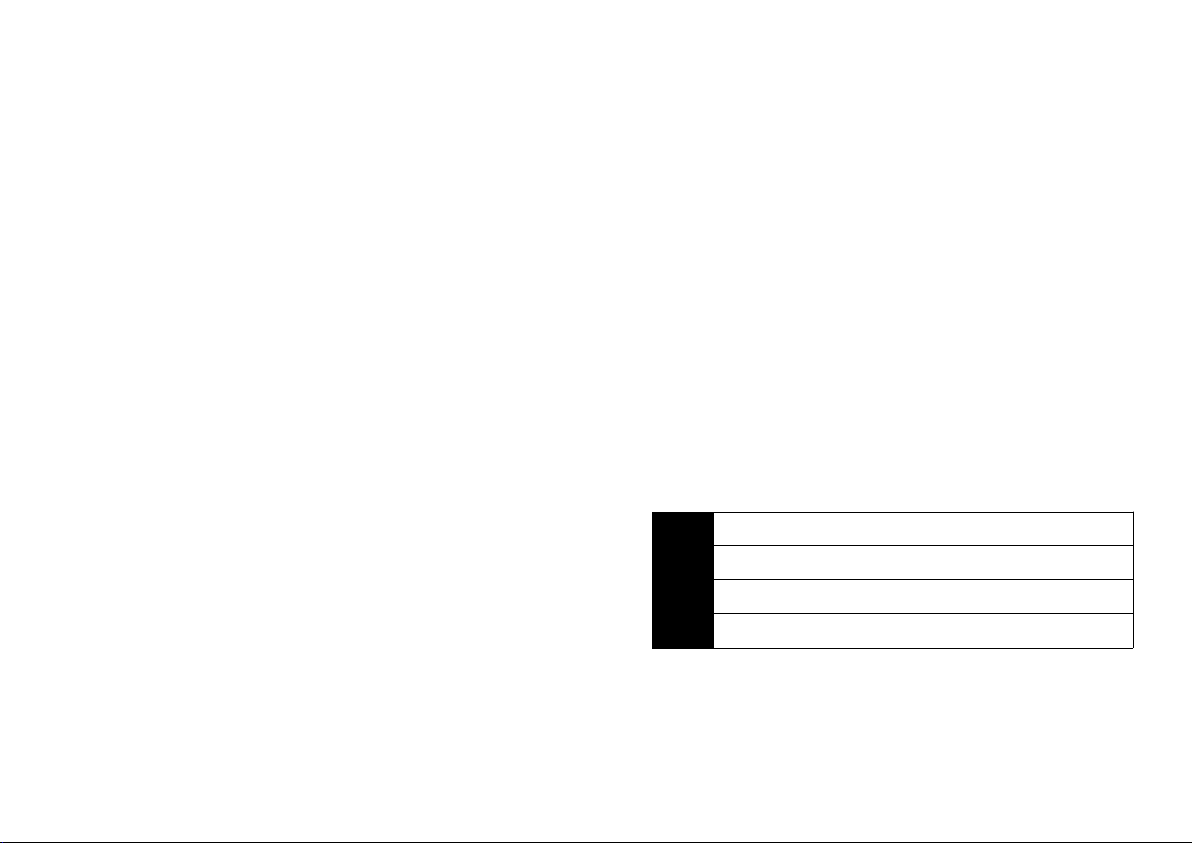
Push-button
Your hearing instruments have a push-button for
switching between different programs.
• When you switch between different programs, your
hearing instruments will beep.
• Press the button for several seconds to activate the
program switch. When switching between programs, press and hold the button until you hear the
beeps. The number of beeps will indicate which
program you are using.
Your hearing instrument can have up to three
programs in Tego and up to four programs in Tego
Pro.
One beep, when you switch to program 1
e
Two beeps, when you switch to program 2
ee
Three beeps, when you switch to program 3
eee
Four beeps, when you switch to program 4
eeee
17
Page 10

Below you can read the description of the programs
available in your hearing instrument.
Program 1
Program 2
Program 3
Program 4
Telecoil
The telecoil is meant for telephone conversations
and for induction loop systems in e.g. theatres,
churches or lecture rooms. To use the telecoil in your
hearing aid, the telephone must be hearing aid compatible.
The telecoil is activated by the push-button. When
activated you will hear a certain number of beeps.
See previous page for where the telecoil program is
placed.
18
19
Page 11

Optional – Volume Control
The Volume Control allows you to adjust the volume
in specific listening situations to the level you feel
comfortable with.
• Use your fingertip to turn the control.
• Rotating the control upwards gives more volume.
• Rotating the control downwards gives less volume.
• The preferred volume control level is indicated
with a beep. This level has been programmed
according to your preferences. Consult your Hearing
Care Professional if you find this level too loud or
too weak in most situations.
Note!
If you find that you have to
adjust the volume of sound
too often, your initial amplification setting may need to be
adjusted by your Hearing Care
Professional.
21
Volume Control
Page 12

Warning
Hearing instruments and batteries can be dangerous if
swallowed or improperly used. Such actions can result in
severe injury, permanent hearing loss or even be fatal.
You should fully familiarize yourself with the following general
warnings and the full contents of this booklet before using your
hearing instrument.
• Hearing instruments should be used only as directed and
adjusted by your trained Hearing Specialist. Misuse can result
in sudden and permanent hearing loss.
• Hearing instruments, their parts and batteries are not toys
and should be kept out of reach of anyone who might
swallow these items or otherwise cause themselves injury.
• Never change the battery of the hearing instrument in front
of infants, small children and people with learning difficulties.
• Discard batteries carefully in a place where they cannot be
reached by infants, small children or people with learning
difficulties.
• Never put your hearing instrument or batteries in your
mouth for any reason, as they are slippery and could be
swallowed.
• Never allow others to wear your hearing instrument, as it
could be misused and permanently damage another’s hearing.
• Hearing instruments may stop functioning, for instance if
the battery goes dead. You should be aware of this possibility, in particular when you are in traffic or otherwise
depend on warning sounds.
If a battery or hearing instrument is swallowed, see a doctor immediately and call the National Poison Center,
collect (202) 625-3333.
Page 13

Warning to hearing instrument dispensers
A hearing instrument dispenser should advise a prospective
hearing instrument user to consult immediately with a licensed
physician (preferably an ear specialist) before dispensing a hearing instrument. If the hearing instrument dispenser determines
through inquiry, actual observation, or review of any other
available information concerning the prospective user, that the
prospective user has any of the following conditions:
(i) Visible congenital or traumatic deformity of the ear.
(ii) History of active drainage from the ear within the previous
90 days.
(iii) History of sudden or rapidly progressive hearing loss with-
in the previous 90 days.
(iv) Acute or chronic dizziness.
(v) Unilateral hearing loss of sudden or recent onset within
the previous 90 days.
(vi) Audiometric air-bone gap equal to or greater than 15 deci-
bels at 500 Hertz (Hz), 1,000 Hz, and 2,000 Hz.
(vii) Visible evidence of significant cerumen accumulation or a
foreign body in the ear canal.
(viii) Pain or discomfort in the ear.
Special care should be exercised in selecting and fitting a hearing instrument whose maximum sound pressure capability
exceeds 132 dB SPL as there may be risk of impairing the
remaining hearing of the hearing instrument user.
Important notice for prospective hearing
instrument users
Good health practice requires that a person with a hearing loss
have a medical evaluation by a licensed physician (preferably a
physician who specializes in diseases of the ear) before purchasing a hearing instrument. Licensed physicians who specialize in
diseases of the ear are often referred to as Otolaryngologists,
Otologists or Otorhinolaryngologists. The purpose of medical
evaluation is to ensure that all medically treatable conditions
that may affect hearing are identified and treated before the
hearing instrument is purchased.
Following the medical evaluation, the physician will give you a
written statement that states that your hearing loss has been
medically evaluated and that you may be considered a candidate for a hearing instrument.
The physician will refer you to an audiologist or a hearing instrument dispenser, as appropriate, for a hearing instrument evaluation.
The audiologist or hearing instrument dispenser will conduct a
hearing instrument evaluation to assess your ability to hear with
and without a hearing instrument. The hearing instrument evaluation will enable the audiologist or dispenser to select and fit a
hearing instrument to your individual needs. If you have reservations about your ability to adapt to amplification, you should
inquire about the availability of a trial, rental or purchase-option
program. Many hearing instrument dispensers now offer programs
that permit you to wear a hearing instrument for a period of time
for a nominal fee, after which you may decide if you want to purchase the hearing instrument.
Federal law limits the sale of hearing instruments to those individuals who have obtained a medical evaluation from
a licensed physician.
Federal law permits a fully informed adult to sign a waiver statement declining the medical evaluation for religious or personal
beliefs that preclude consultation with a physician. The exercise
of such a waiver is not in your best health interest and its use is
strongly discouraged.
A hearing aid is only part of hearing rehabilitation and may
need to be supplemented by auditory training and lip reading.
Page 14

Possible side effects
The hearing aid or earmold is a custom-made product. If you are
experiencing discomfort, see your audiologist or hearing instrument dispenser immediately for modification of the hearing
instrument or earmold at the point of irritation.A hearing instrument or earmold may cause an accelerated accumulation of
cerumen (earwax). Also in rare cases, the otherwise non-allergenic material may cause a discharge from the ear, allergic reaction, or any other unusual condition. Please seek immediate
consultation with a physician if these conditions occur.
Children with hearing loss
In addition to seeing a physician for medical evaluation, a child
with a hearing loss should be directed to an audiologist for
evaluation and rehabilitation, since hearing loss may cause
problems in language development, educational and social
growth of a child. An audiologist is qualified by training and
experience to assist in the evaluation and rehabilitation of a
child with a hearing loss.
If the user is an infant, small child or person of mental incapacity, it is recommended that the hearing instrument be modified
with a tamper-resistant battery compartment.
Warning to hearing instrument dispenser and user
Special care should be excercised in selecting, fitting and
using a hearing instrument where maximum sound pressure
capability exceeds 132 dB SPL (IEC 711) as there may be risk of
impairing the remaining hearing of the hearing instrument user.
Page 15

Changing batteries
A worn-out battery should be removed immediately.
When battery power is low, you will hear a series of
short beeps. This indicates that it is time to change
the battery. It is not an indication of malfunction. To
replace the battery, follow these instructions:
• Open the battery drawer by pushing back the raised
edge and remove the old battery. To remove the old
battery, gently push with a pen.
• Remove the sticky label from the + side of the new
battery.
• Insert the new battery (size 13) so that its + sign
faces the + sign printed on the inside of the battery
drawer.
Any moisture on the battery surface should be wiped
off before use. When you change batteries, it may take
a couple of minutes before the new battery works with
full effect.
To remove the
battery – gently
push with a pen
23
Page 16

Disposal:
• Check with your Hearing Care Professional about
arrangements for battery disposal. There may be
a system for disposing of them.
• Never try to charge non-rechargeable batteries.
• Never dispose of batteries with household waste.
They cause environmental pollution.
• Never dispose of batteries by burning them. There
is a risk that they will explode and cause serious
injury.
Tamper-resistant battery door (optional)
This is strongly recommended for infants, small
children, and persons of diminished mental capacity.
Instructions: To open the
battery compartment,
simply insert the end of a
ballpoint pen or something
similar into the small recess
and apply pressure in the
direction of the arrow.
Important: Do not force the battery door beyond
its fully open position. Insert the battery correctly.
Excessive strain can deform the battery door, which
will reduce its tamper resistant effectiveness.
Off
DAI (Direct Audio Input)
If your hearing instrument is connected by means of
a DAI shoe with an external sound source, like a
walkman, discman or hand mic, the signals of these
devices will be directly transferred to your hearing
instrument.
It is necessary to remove the DAI shoe first before you
are able to turn your hearing instrument off.
Connecting DAI to Hearing Instrument
Start by clicking the DAI shoe onto the instrument.
Then insert the DAI cord into the shoe.
IMPORTANT: If you are using
DAI in connection with A/C
equipment that is plugged into
an electrical outlet (i.e., TV,
computer), the DAI cord should
be disconnected from the
hearing aid during an electrical
(lightning) storm.
When the DAI shoe is connected, the instrument will
automatically switch to a combination of a DAI program and the microphone. If you would like the DAI
program alone, you can switch to the next program by
using the push button.
DAI-shoe
24
25
Page 17
The two new programs will automatically place
themselves after the standard programs, which your
Hearing Care Professional has stored in your hearing
instrument.
Program DAI + Microphone
Program DAI
To release the shoe from the hearing instrument, click
the grey button and pull back.
Safety requirements regarding
Direct Audio Input (DAI)
The safety of hearing instruments with DAI (Direct
Audio Input) is determined by the externalsignal
source. When the DAI is connected to equipment
which plugs into a wall outlet, this equipment must
comply with IEC-60065, IEC-60601 or equivalent
safety standards.
FM
An FM receiver enables the hearing instrument to
receive signals directly from an external wireless FM
transmitter.
Connecting the FM
To use an FM receiver start by clicking the FM shoe
onto the instrument. Then attach the FM receiver to
the base of the FM shoe via the connector. When
the FM receiver is connected, the instrument will
automatically switch to a program that receives signals from the microphone in combination with an
external wireless FM transmitter. If you would like to
receive input from the FM transmitter alone, you can
switch to the next program by using the push-button.
The two new programs will automatically place
themselves after the standard programs, which
your Hearing Care Professional has given you.
Program FM + Microphone
Program FM
To release the shoe from the
hearing instrument, click the
grey button and pull back.
26
27
Page 18

Daily care of your hearing
instruments
When handling a hearing instrument, hold it over a
soft surface to avoid damage if dropped.
Before retiring for the evening:
• Make sure that there is no ear wax in any of the
earmold openings since it may reduce the hearing
instruments’ efficiency.
• Rinse with water.
• Dry the earmold.
• Any water drops inside
the earmold or tubing
should be blown out. A
special device for this
purpose (an earmold blower) is
available from your Hearing Care Professional.
• Open the battery compartments to allow air to
circulate.
Cleaning your earmolds
The earmolds should be washed regularly:
• Disconnect the earmold and tubing
from the hearing instrument.
• Wash the earmold in lukewarm water
using a mild soap. Do not use
strong detergents.
The hearing instruments
themselves must never be
washed!
28
• Make sure the earmold and tubing are completely
dry before they are reconnected to the hearing
instruments as shown in the drawing.
Left Right
Replacing the tubing
The tubing in the earmould
should be replaced when
it becomes yellow or stiff.
Consult your Hearing Care
Professional about this.
29
Page 19

Avoiding heat, humidity and chemicals
Your hearing instruments must never be exposed to
extreme heat e.g. left inside a parked car in the sun
or dried in microwave ovens. They must never be
exposed to a lot of moisture e.g. steam baths,
showers or heavy rain. If your hearing aid will not be
used for an extended period of time, be sure to remove
the battery and store the hearing aid in an area that
will not be exposed to extreme heat or moisture.
Using your hearing instruments
It takes time to adjust to a new hearing instrument.
How long this adjustment takes differs from person to
person. It will depend on a number of factors, such as
whether you have had hearing instruments before and
the degree of your hearing loss.
Seven easy steps to better hearing
If your hearing instruments have been exposed to
moisture or very humid conditions it may affect their
performance. Using an anti-humidity or drying kit can
help to avoid these problems and may even extend the
life of your hearing instruments. Consult your hearing
care professional for further advice. Wipe the batteries
thoroughly if moisture is present.
The chemicals in cosmetics, hairspray, hair dye,
perfume, aftershave-lotion, suntan lotion and insect
repellant can discolor and even damage your hearing
instruments. You should always remove your hearing
instruments before applying such products and allow
time for the product to dry before reinserting your
hearing instruments. If you use lotion be sure to
wipe your hands dry before inserting your hearing
instruments.
30
1. In the quiet of your home
Try to acclimate yourself to all the new sounds you
are able to hear, including background sounds. Listen
to the many background sounds and try to identify
each sound. Keep in mind that some sounds will
sound different. You may have to learn to identify them again. Note that in time you will become
acclimated to the sounds in your environment – if not
please contact your hearing care professional.
If using the hearing instruments causes you to feel
fatigued, remove them. Initially, you may need to wear
the hearing instruments for shorter periods of time.
You will gradually be able to increase the amount of
time you wear your hearing instruments. Eventually,
you will be able to wear your hearing instruments
comfortably all day long.
31
Page 20

2. Conversation with another person
Sit with someone else in a quiet room. Face each other
so you can read facial expressions easily. You might
experience new speech sounds which can seem a little
disturbing in the beginning. However, after the brain
has adapted to the new speech sounds, you may hear
speech clearer.
3. Listen to radio or TV
When listening to the TV or the radio, start out by
listening to news commentators since they usually
speak clearly, then try other programs.
If you find it difficult to listen to TV or radio, contact
your Hearing Professional for advice about assistive
listening devices. If your hearing instrument has a
telecoil program, you may benefit from using it with
an induction loop system.
4. In group conversations
Group situations are usually accompanied by a greater
degree of background noise. Therefore, making it a
more difficult listening situation. In difficult listening
situations, focus your attention on the person you
want to hear. If you miss a word, ask the speaker to
repeat it.
5. Telecoil use in church, theatre, or cinema
An increasing number of churches, theatres and
public buildings have installed induction loop
systems. These systems send out wireless sound to be
received by the telecoil in your hearing instruments.
Typically, the facility will post a sign indicating that
an induction loop system is available for use by its
patrons. Contact your Hearing Care Professional for
additional information.
6. Using the telephone
When using the telephone tilt the receiver edge lightly
on your cheek-bone in order to let the sound flow
directly into the hearing instrument’s microphone
opening. This way, the hearing aid will not whistle
and you ensure the best conditions to understand
the conversation. When you have the receiver in
this position, remember to speak directly into the
microphone on the telephone in order to ensure good
understanding at the opposite “end of the line”.
If your hearing aid has
a telecoil (and your
telephone is hearing aid
compatible) you can switch
into the telecoil program
in order to further improve
the sound reception.
32
33
Page 21

Remember that the telecoil in hearing aids may pick
up disturbing signals from electronic devices, such
as a fax machines, computers, televisions or similar.
Make sure that the hearing aid has a distance of
2 - 3 meters to such devices when using the telecoil
program.
Use your hearing instruments all day long
The best way to ensure better hearing is to practice
listening with your hearing instruments until you
are able to wear them comfortably all day. Generally,
infrequent use of the hearing instrument does not
provide you with the full benefit of amplification.
7. Wireless and mobile phones
Your hearing instruments are designed to comply
with the most stringent Standards of International
Electromagnetic Compatibility. However not all
mobile phones are hearing instrument compatible. Use
the microphone position unless you have a special
loop for your mobile phone. The varying degree of
disturbance can be due to the nature of your particular
mobile phone.
34
Your hearing instruments will not restore normal
hearing. Hearing instruments will not prevent
or improve hearing impairment resulting from a
physiological condition. Hearing instruments will
help you to make better use of your residual hearing.
If you have two hearing instruments always wear both.
The most important benefits of wearing two
hearing instruments are:
• Improved ability to localize sounds in the listening
environment.
• Improved speech understanding in the presence of
background noise.
• Improved sound recognition and comfort.
35
Page 22
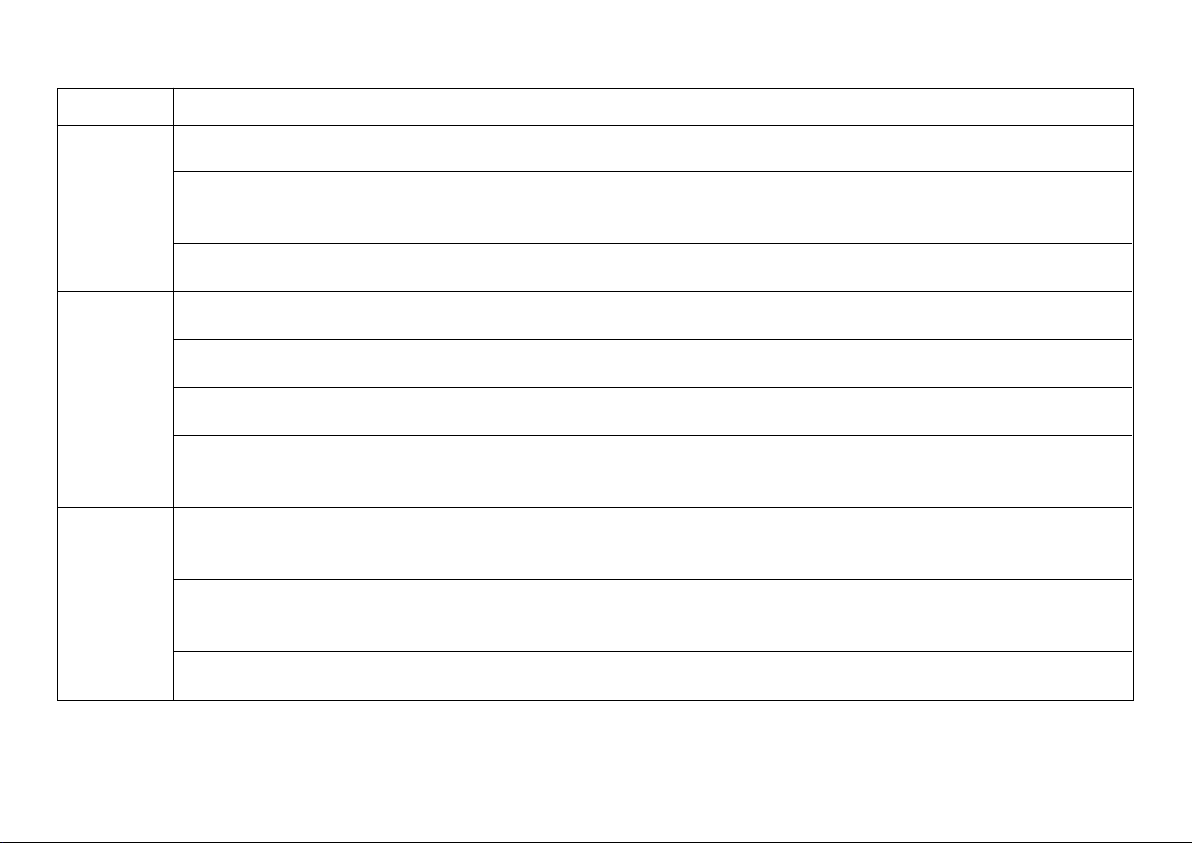
Common problems and their solutions
Effect
Cause
Solution
Whistling
Ear wax accumulated in ear canal
or
squealing
noise
No sound
Whirring
noise or
Hearing instrument inserted
improperly
Split or damaged tubing
Clogged earmold
Clogged microphone opening
Exhausted battery
Dirty or corroded battery
contacts
Dirty or corroded battery
contacts
beeping
Dirty or corroded battery
Exhausted battery
If none of the above solutions solves the problem,
ask your Hearing Care Professional for assistance.
Have ear canal examined by your doctor
Reinsert earmold (pg. 11)
Replace tubing
Clean earmold (pg. 28)
Clean microphone opening with a brush
Replace battery (pg. 23)
Open and close the battery door
several times or replace battery (pg. 23)
Open and close the battery door
several times or replace battery (pg. 23)
Clean battery surfaces with dry cloth
or replace battery (pg. 23)
Replace battery (pg. 23)
36
37
Page 23

International Warranty
Oticon hearing instruments are covered by a limited
warranty issued by the manufacturer for a period
of 12 months from the date of delivery. The limited
warranty covers manufacturing and material defects in
the hearing instrument itself, it does not cover accessories such as batteries, tubing, ear molds, ear wax
filters, etc.
Problems arising from improper handling or care, accidents, repairs made by an unauthorized party, exposure to corrosive conditions, physical changes in your
ear, damage due to foreign objects entering the device,
or incorrect adjustments are NOT covered by the limited warranty and may void it.
The above warranty does not affect any legal rights
that you might have under applicable national
legis lation governing sale of consumer goods. Your
Hearing Care Professional may have issued a warranty
that goes beyond the clauses of this limited warranty.
Please consult him/her for further information.
Oticon Warranty Certificate
Name of Owner:
Dispenser:
Dispenser Address:
Dispenser Phone:
Purchase date:
Warranty period: Month:
Model left: Serial no.:
Model right: Serial no.:
Battery size:
If you need service
Take your hearing instrument to your Hearing Care
Professional, who may be able to determine and repair
minor problems in their office. We strongly recommend that you contact your local hearing care provider for service to your hearing aids. However, if this
is not possible, contact Oticon Inc. for help locating a
hearing care professional in your area or, in some circumstances the hearing aid can be sent to Oticon Inc.
Oticon, Inc.
29 Schoolhouse Rd.
Somerset, NJ 08873
www.oticonus.com
39
Page 24

906 65 811 00 / 07.07 Printed in Denmark
 Loading...
Loading...