Page 1
OPERATION MANUAL
PROFIBUS-DP Gateway
to Host Link/Compoway-F
PRT1-SCU11
Cat. No. W01E-EN-02
Page 2

PRT1-SCU11
PROFIBUS DP Gateway
Operation Manual
Revised September 19, 2005
Page 3

iv
Page 4

v
Notice:
OMRON products are manufactured for use by a trained operator and only for the purposes described
in this manual.
The following conventions are used to classify and explain the precautions in this manual. Always
heed the information provided with them.
!DANGER
Indicates information that, if not heeded, is likely to result in serious injury or loss of life.
!WARNING
Indicates information that, if not heeded, could possibly result in serious injury or loss of
life.
!Caution
Indicates information that, if not heeded, could possibly result in minor or relatively serious
injury, damage to the product or faulty operation.
OMRON Product References
All OMRON products are capitalized in this manual. The first letter of the word
Unit
is also capitalized
when it refers to an OMRON product, regardless of whether it appears in the proper name of the product.
The abbreviation
Ch
appears in some displays and on some OMRON products. It often means
word
and is abbreviated as Wd in the documentation.
The abbreviation
PLC
means Programmable Logic Controller.
Visual Aids
The following headings appear in the left column of the manual to help you locate different types of
information.
Note Indicates information of particular interest for efficient and convenient opera-
tion of the product.
1, 2, 3...Indicates various lists such as procedures, checklists etc.
Page 5

vi
Trademarks and Copyrights
PROFIBUS, PROFIBUS FMS, PROFIBUS DP, and PROFIBUS PA are trademarks of PROFIBUS
International.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Explorer and ActiveX are
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other product names and company names in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies.
The copyright of the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway belongs to OMRON Corporation.
OMRON, 2005
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form, o
r
by any means, mechanical, electronic, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission o
f
OMRON.
No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein. Moreover, because OMRON is con-
stantly striving to improve its high-quality products, the information contained in this manual is subject to change without
notice. Every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this manual. Nevertheless, OMRON assumes no responsibility
for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for damages resulting from the use of the information contained in
this publication.
Page 6

vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
About this Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
1 Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
2 General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
3 Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
4 Operating Environment Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
5 Application Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xiii
6 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
SECTION 1
Features and Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1-1 Overview of PROFIBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-2 PROFIBUS DP Network configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-3 PROFIBUS DP Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1-4 Basic Operating Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SECTION 2
Installation and Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2-1 Unit Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2-2 Installing the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2-3 Wiring the RS-422A / RS-485 Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2-4 Initial Setup Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2-5 Setting up a PROFIBUS Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2-6 Configuring the PROFIBUS DP network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
SECTION 3
Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3-1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-2 PROFIBUS Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-3 Compoway-F Communication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3-4 K-Format Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3-5 Host Link Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3-6 Memobus Communication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3-7 PROFIBUS Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3-8 Auxiliary RS-232C interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Page 7

viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 4
Troubleshooting and Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
4-1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4-2 Troubleshooting Using LED Indicators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4-3 Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
4-4 Replacing the Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Appendices
A Memory Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
B Function Block Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Page 8
ix
About this Manual
This manual describes the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway, how to install it and how and operate the Unit. The Unit version number on the side case of the housing indicates supported functionality. If no version number is shown, the version number is 1.0. The following table lists the functions
supported per version number.
Unit version 2.0 includes the same functions as Unit version 1.0, in addition to new protocols supported. Unit version 2.0 will eventually replace Unit version 1.0.
Note This manual describes the features and functions of Unit version 2.0.
Please read this manual carefully so that you understand the information provided before installing or
using the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway. Start with the precautions in the following section.
They describe the operating environment and application safety measures which must be observed
prior to and when using the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway.
The sections of this manual are as follows:
Section 1
introduces the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway.
Section 2
describes the installation and setup of the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway.
Section 3
describes operational aspects of the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway.
Section 4
provides procedures for troubleshooting the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway.
The
Appendices
contain information supplementary to the information in the main body of the man-
ual. They are referred to in the various sections as required.
Unit name Unit Version Protocols supported
PRT1-SCU11 1.0 Compoway-F
Host Link
2.0 Compoway-F
Host Link
K-Format protocol
Memobus
Manual Products Contents Cat. No.
CS/CJ Series PROFIBUS DP
Master Units
Operation Manual
SYSMAC CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 Describes the Installation and Opera-
tion of the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP Master Units and CX-Profibus
Configurator.
W409-E2-
@
E5GN Temperature Controller
User manual
E5GN Temperature Controller Describes the Installation and Opera-
tion of the E5GN Temperature Controller.
H101-E1-
@
E5EN Temperature Controller
User manual
E5EN Temperature Controller Describes the Installation and Opera-
tion of the E5EN Temperature Controller.
H111-E1-
@
E5AN Temperature Controller
User manual
E5AN Temperature Controller Describes the Installation and Opera-
tion of the E5AN Temperature Controller.
H112-E1-
@
E5CN Temperature Controller
User manual
E5CN Temperature Controller Describes the Installation and Opera-
tion of the E5CN Digital Temperature
Controller.
H129-E1-
@
Page 9
x
E5@N Communication Functions User manual
E5AN/E5EN/E5CN/E5GN Temperature Controllers
Describes the Compoway-F Communication Functions for the E5AN/E5EN/
E5CN/E5GN Temperature Controllers.
H102-E1-
@
H130-E1-
@
E5ZN Temperature Controller
User manual
E5ZN Temperature Controller Describes the Installation and Opera-
tion of the E5ZN Temperature Controller.
H113-E1-
@
E5AR/E5ER Digital Controller
Users Manual
E5AR/E5ER Digital Controller Describes the Installation and Opera-
tion of the E5AR/E5ER Digital Controllers.
Z182-E1-
@
E5@K Communication Functions User manual
E5AK/E5EK Process Controllers Describes the Installation and Opera-
tion of the E5AK/E5EK Intelligent Digital Controller.
H083-E1-
@
H085-E1-
@
R88A-MCW151-E / R88AMCW151-DRT-E Motion Control Option Board Operation
Manual
R88A-MCW151-E / R88AMCW151-DRT-E Motion Control
Option Board
Describes the Installation and Operation of the R88A-MCW151-E / R88AMCW151-DRT-E Motion Control
Option Board.
I203-E2-
@
VARISPEED F7
Vector Control Frequency
Inverter User’s Manual
OMRON-Yaskawa VARISPEED
F7 Inverter
Describes the Installation and Operation of the OMRON-Yaskawa
VARISPEED F7 Inverter.
YEG-TOES616-55.1OY
Manual Products Contents Cat. No.
!WARNING
Failure to read and understand the information provided in this manual may result in personal injury or death, damage to the product, or product failure. Please read each section
in its entirety and be sure you understand the information provided in the section and
related sections before attempting any of the procedures or operations given.
Page 10

xi
PRECAUTIONS
This section provides general precautions for using the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway modules, Programmable
Controllers and related devices.
The information contained in this section is important for the safe and reliable operation of the PRT1-SCU11
PROFIBUS DP Gateway. You must read this section and understand the information contained before attempting
to set up or operate a PROFIBUS DP Gateway system.
1 Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
2 General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
3 Safety Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
4 Operating Environment Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
5 Application Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
6 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
6-1 Applicable Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
6-2 Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
6-3 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Page 11

xii
Intended Audience
1
1 Intended Audience
This manual is intended for the following personnel, who must also have a
knowledge of electrical systems (an electrical engineer or the equivalent).
• Personnel in charge of installing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of designing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of managing FA systems and facilities.
2 General Precautions
The user must operate the product according to the performance specifications described in the operation manuals.
Before using the product under conditions which are not described in the
manual or applying the product to nuclear control systems, railroad systems,
aviation systems, vehicles, combustion systems, medical equipment, amusement machines, safety equipment, and other systems, machines, and equipment that may have a serious influence on lives and property if used
improperly, consult your OMRON representative.
Make sure that the ratings and performance characteristics of the product are
sufficient for the systems, machines, and equipment, and be sure to provide
the systems, machines, and equipment with double safety mechanisms.
This manual provides information for programming and operating OMRON
PROFIBUS DP Gateway. Be sure to read this manual before attempting to
use the Unit and keep this manual close at hand for reference during operation.
!WARNING
It is extremely important that the Unit is used for its specified purpose and
under the specified conditions, especially in applications that can directly or
indirectly affect human life. You must consult your OMRON representative
before using it in a system in the above-mentioned applications.
3 Safety Precautions
!WARNING
Do not attempt to take any Unit apart while the power is being supplied. Doing
so may result in electric shock.
!WARNING
Never touch any of the terminals while power is being supplied. Doing so may
result in serious electrical shock or electrocution.
!WARNING
Do not attempt to disassemble, repair, or modify any of the Units. Any attempt
to do so may result in malfunction, fire, or electric shock.
Page 12

xiii
Operating Environment Precautions
4
4 Operating Environment Precautions
!Caution
Do not operate the Unit in the following places:
• Locations subject to direct sunlight.
• Locations subject to temperatures or humidities outside the range specified in the specifications.
• Locations subject to condensation as the result of severe changes in temperature.
• Locations subject to corrosive or flammable gases.
• Locations subject to dust (especially iron dust) or salt.
• Locations subject to exposure to water, oil, or chemicals.
• Locations subject to shock or vibration.
Provide proper shielding when installing in the following locations:
• Locations subject to static electricity or other sources of noise.
• Locations subject to strong electromagnetic fields.
• Locations subject to possible exposure to radiation.
• Locations near to power supply lines.
!Caution
The operating environment of the PROFIBUS DP Gateway can have a large
effect on the longevity and reliability of the system. Unsuitable operating environments can lead to malfunction, failure and other unforeseeable problems
with the system. Ensure that the operating environment is within the specified
conditions at installation time and remains that way during the life of the system. Follow all installation instructions and precautions provided in the operation manuals.
5 Application Precautions
Observe the following precautions when using the PROFIBUS DP Gateway.
!WARNING
Failure to abide by the following precautions could lead to serious or possibly
fatal injury. Always heed these precautions.
• Always connect to a class-3 ground (100
Ω or less) when installing the
Units.
!Caution
Failure to abide by the following precautions could lead to faulty operation of
the Unit or the system or could damage the Unit or Temperature Controllers
and R88A-MCW151-E. Always heed these precautions.
• Install double safety mechanisms to ensure safety against incorrect signals that may be produced by broken signal lines or momentary power
interruptions.
• When adding a new device to the network, make sure that the baud rate
is the same as other nodes.
Page 13

xiv
Application Precautions
5
• When adding a new Host Link or Compoway-F node to the network, make
sure that the PROFIBUS DP Gateway is powered down, to prevent unexpected results when starting up the new node.
• Use specified communications cables.
• Do not extend connection distances beyond the ranges given in the specifications.
• Always turn OFF the power supply to the personal computer, Slaves, and
Communications Units before attempting any of the following.
• Mounting or dismounting the PROFIBUS DP Gateway, Power Supply
Units, I/O Units, CPU Units, or any other Units.
• Assembling a Unit.
• Setting DIP-switches or rotary switches.
• Connecting or wiring the cables.
• Connecting or disconnecting connectors.
• Be sure that all the mounting screws, terminal screws, Unit mounting
screws, and cable connector screws are tightened to the torque specified
in the relevant manuals. Incorrect tightening torque may result in malfunction.
• Leave the label attached to the Unit when wiring. Removing the label may
result in malfunction if foreign matter enters the Unit.
• Remove the label after the completion of wiring to ensure proper heat dissipation. Leaving the label attached may result in malfunction.
• Always use the power supply voltage specified in this manual.
• Double-check all the wiring and connection of terminal blocks and connectors before mounting the Units.
• Use crimp terminals for wiring. Do not connect bare stranded wires
directly to terminals.
• Observe the following precautions when wiring the communications
cable.
• Separate the communications cables from the power lines or high-tension lines.
• Do not bend the communications cables.
• Do not pull on the communications cables.
• Do not place heavy objects on top of the communications cables.
• Be sure to wire communications cable inside ducts.
• Use appropriate communications cables.
• Take appropriate measures to ensure that the specified power with the
rated voltage and frequency is supplied in places where the power supply
is unstable. An incorrect power supply may result in malfunction.
• Install external breakers and take other safety measures against short-circuits in external wiring. Insufficient safety measures against short-circuits
may result in burning.
• Double-check all the wiring and switch settings before turning ON the
power supply.
• When transporting or storing the product, cover the PCB’s with electrically
conductive materials to prevent LSI’s and IC’s from being damaged by
static electricity, and also keep the product within the specified storage
temperature range.
Page 14

xv
Conformance to EC Directives
6
• When transporting the Unit, use special packing boxes and protect it from
being exposed to excessive vibration or impacts during transportation.
• Do not attempt to disassemble, repair, or modify any Units.
6 Conformance to EC Directives
6-1 Applicable Directives
•EMC Directives
• Low voltage directive
6-2 Concepts
OMRON units complying with EC Directives also conform to related product
standards making them easier to incorporate in other units or machines. The
actual products have been checked for conformity to product standards.
Whether the products conform to the standards in the system used by the
customer, however, must be checked by the customer.
Product related performance of OMRON units complying with EC Directives
will vary depending on the configuration, wiring, and other conditions of the
equipment or control panel in which OMRON devices are installed. The customer must, therefore, perform final checks to confirm that units and the overall system conforms to product standards.
A Declaration of Conformity for the PROFIBUS DP Gateway can be
requested at your nearest OMRON representative.
6-3 Conformance to EC Directives
PROFIBUS units should be installed as follows, for the complete configuration
to meet the EC directives:
1,2,3...
1. The units are designed for installation inside control panels. All units must
be installed within control panels.
2. Use reinforced insulation or double insulation for the DC power supplies
used for the communications power supply, internal circuit power supply,
and the I/O power supplies.
3. The PROFIBUS DP Gateway product meets the generic emission standard. However as EMC performance can vary in the final installation, additional measures may be required to meet the standards. It should
therefore be verified that the overall machine or device also meets the relevant standards. You must therefore confirm that EC directives are met for
the overall machine or device, particularly for the radiated emission requirement (10 m).
Page 15

Page 16

1
SECTION 1
Features and Specifications
This section provides an introductory overview of PROFIBUS, its functions and how to setup and configure a network. It
also addresses the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateways and the Configurator, their features and specifications.
1-1 Overview of PROFIBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-1-1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-1-2 PROFIBUS Communication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-1-3 Device Types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1-1-4 Bus Access Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1-1-5 Diagnostic functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1-1-6 Protection mechanisms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1-1-7 Network Operation Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-2 PROFIBUS DP Network configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-3 PROFIBUS DP Gateway. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1-3-1 PROFIBUS DP Gateway Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1-3-2 Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1-4 Basic Operating Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
1-4-1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
1-4-2 Procedures Prior to Starting Communications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Page 17

2
Overview of PROFIBUS
Section 1-1
1-1 Overview of PROFIBUS
1-1-1 Introduction
Standard EN50170 PROFIBUS (PROcess FIeldBUS) is an open fieldbus standard for a wide
range of applications in manufacturing, processing and building automation.
The Standard, EN 50170 (the Euronorm for field communications), to which
PROFIBUS adheres, guarantees vendor independence and transparency of
operation. It enables devices of various manufacturers to intercommunicate
without having to make any special interface adaptations.
The PROFIBUS family comprises three mutually compatible versions:
PROFIBUS FMS, PROFIBUS DP and PROFIBUS PA.
PROFIBUS FMS FMS means Fieldbus Message Specification. This version is the general-pur-
pose solution for high-level extensive and complex communication tasks.
Powerful services open up a wide range of applications and provide great
flexibility.
PROFIBUS DP DP means Decentralized Periphery. PROFIBUS DP is optimized for high
speed and low-cost interfacing. It is specially designed for communication
between automation control systems and distributed I/O at the device level.
PROFIBUS PA PA means Process Automation. It permits sensors and actuators to be con-
nected to one common bus even in areas where intrinsically safe products are
required. It also permits data and power to be supplied over the bus using
2-wire technology according the international standard IEC 1158-2.
Uniform Bus Access
Protocol
PROFIBUS DP and PROFIBUS FMS use the same transmission technology
and uniform bus access protocol. Consequently, both versions can be operated simultaneously on the same bus. FMS field devices, however, cannot be
controlled by DP masters and vice versa.
!Caution
It is not possible to exchange one of these family members by another family
member. This will cause faulty operation.
The rest of this section describes the PROFIBUS DP Protocol architecture.
1-1-2 PROFIBUS Communication Protocol
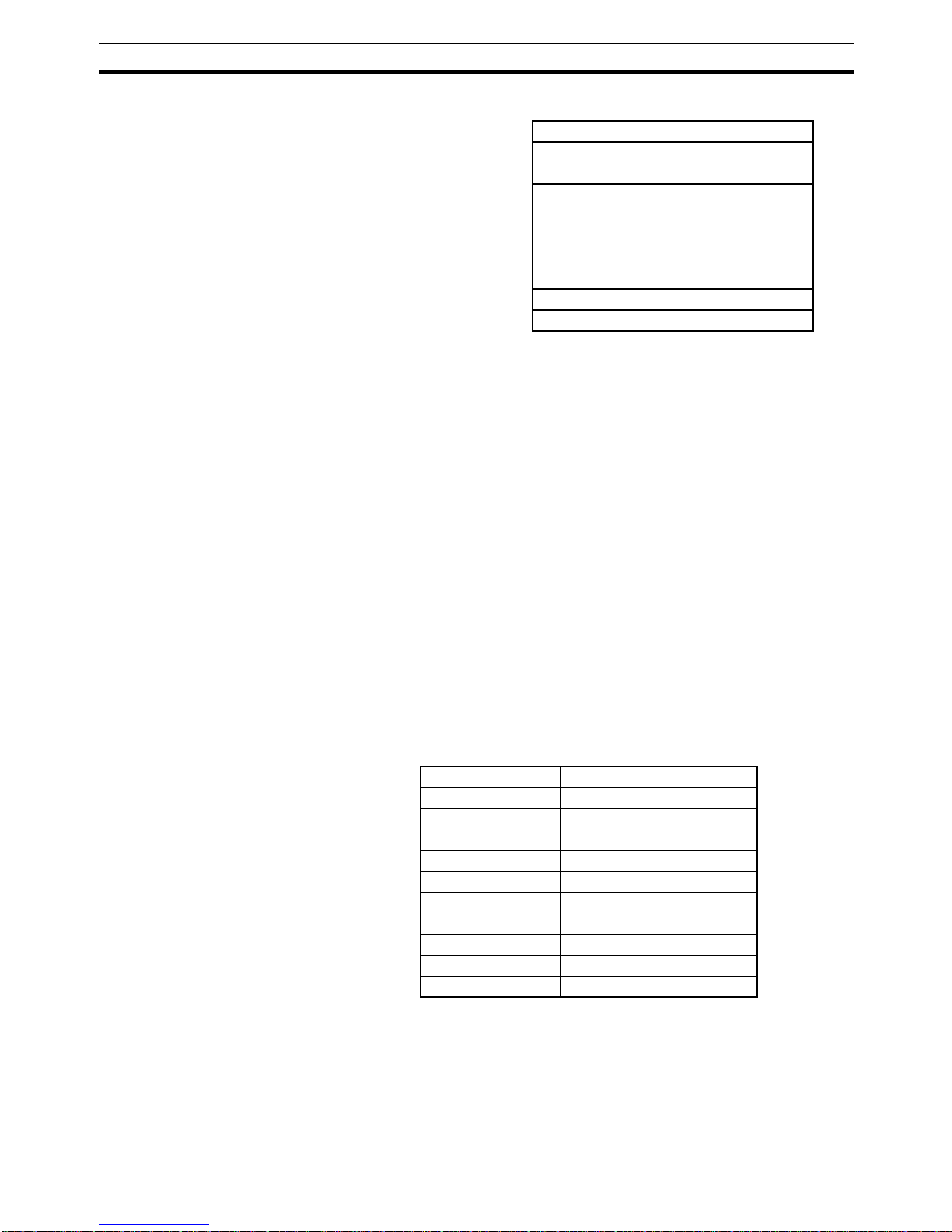
OSI reference model
ISO-7498
In general, the PROFIBUS communication protocol is based on the Open
System Interconnection (OSI) reference model in accordance with the international standard ISO-7498 (see the following illustration). The model defines
7 layers of communication functions, three of which - layers 1, 2, and 7 - are
used in PROFIBUS.
• Layer 1, the Physical Layer of this model, defines the physical transmission characteristics.
• Layer 2, the Data Link Layer of this model, defines the bus access protocol. This protocol also includes data security and the handling of transmission protocols and telegrams.
• Layer 7, the Application Layer of this model, defines the application functions. This Layer is only applicable to PROFIBUS FMS.
Page 18
3
Overview of PROFIBUS
Section 1-1
OSI Layer 1, 2 and User
Interface
PROFIBUS DP uses layers 1 and 2, and the user interface. Layers 3 to 7 are
not defined for PROFIBUS DP. The user interface Layer defines the interface
functions for specific application areas, i.e. the PROFIBUS DP basic functions
and communication profiles.This streamlined architecture ensures fast and
efficient data transmission. The application functions which are available to
the user, as well as the system and device behaviour of the various PROFIBUS DP device types, are specified in the user interface.
OSI Layer 1: Transmission
Medium
RS-485 transmission technology or fibre optics are available for transmission.
RS-485 transmission is the most frequently used transmission technology. Its
application area includes all areas in which high transmission speed and simple inexpensive installation are required. PROFIBUS modules are interconnected by single twisted-pair shielded copper wires.
RS-485 Technology The RS-485 transmission technology is very easy to handle. Installation of the
twisted pair cable does not require expert knowledge. The bus structure permits addition and removal of devices or step-by-step commissioning of the
system without influencing the other devices. Later expansions have no effect
on devices which are already in operation.
RS-485 Transmission
Speed
Transmission speeds between 9.6 kbit/s and 12 Mbit/s can be selected as
shown in the table below. One unique transmission speed must selected for
all devices on the bus (master and slave devices) when the system is commissioned
Cable length The maximum cable length values depend on the transmission speed and are
based on type-A cable (see
Bus Cable Connector
on page 34). The length
can be increased by the use of repeaters.However, it is not recommended to
use more than three repeaters in series in a PROFIBUS network.
DP-Profiles
User Interface Layer DP Basic Functions
(7) Application Layer
(6) Presentation Layer
(5) Session Layer NOT DEFINED
(4) Transport Layer
(3) Network Layer
(2) Data Link Layer Fieldbus Data Link (FDL)
(1) Physical Layer RS-485 / Fibre Optics
Baud rate (kbit/s) Distance / segment (m)
9.6 1200
19.2 1200
45.45 1200
93.75 1200
187.5 1000
500 400
1500 200
3000 100
6000 100
12000 100
Page 19

4
Overview of PROFIBUS
Section 1-1
1-1-3 Device Types
PROFIBUS distinguishes between master devices and slave devices.
Master Devices Master devices determine the data communication on the bus. A Master can
send messages without an external request, as long as it holds the bus
access right (the token). Masters are also referred to as active devices in the
PROFIBUS standard.
There are two types of master devices:
Class 1 Master (DPM1) A PROFIBUS DP Class 1 Master (DPM1) device is a central controller, which
exchanges information with the decentralized devices (i.e. DP slaves) within a
specified message cycle.
Class 2 Master (DPM2) PROFIBUS DP class 2 Master (DPM2) devices are programmers, configura-
tion devices or operator panels. They are used during commissioning, for configuration of the DP system, or for operation and monitoring purposes.
Slave Devices Slave devices are peripheral devices. Typical slave devices include input/out-
put devices, valves, drives, and measuring transmitters. They do not have bus
access rights and they can only acknowledge received messages or send
messages to the master when requested to do so. Slave devices are also
called passive devices. The PRT1-SCU11 is a slave device.
Device Profile To enable the exchange of devices from different vendors, the user data has
to have the same format. The PROFIBUS DP protocol does not define the format of user data, it is only responsible for the transmission of this data. The
format of user data may be defined in so called profiles. Profiles can reduce
engineering costs since the meaning of application-related parameters is
specified precisely. Profiles have been defined for specific areas like drive
technology, encoders, and for sensors / actuators.
1-1-4 Bus Access Protocol
OSI Layer 2: Bus Access
Protocol
The PROFIBUS bus access protocol is implemented by OSI layer 2. This protocol also includes data security and the handling of the transmission protocols and messages.
Medium Access Control The Medium Access Control (MAC) specifies the procedures which determine
when a device is permitted to transmit data. A token passing procedure is
used to handle the bus access between master devices, and a polling procedure is used to handle the communication between a master device and its
assigned slave device(s).
Token Passing The token passing procedure guarantees that the bus access right (the token)
is assigned to each master within a precisely defined time frame. The token
message, a special message for passing access rights from one master to the
next master, must be passed around the logical token ring - once to each
master - within a specified target rotation time. Each master executes this procedure automatically.
Polling Procedure The polling or master-slave procedure permits the master, currently in pos-
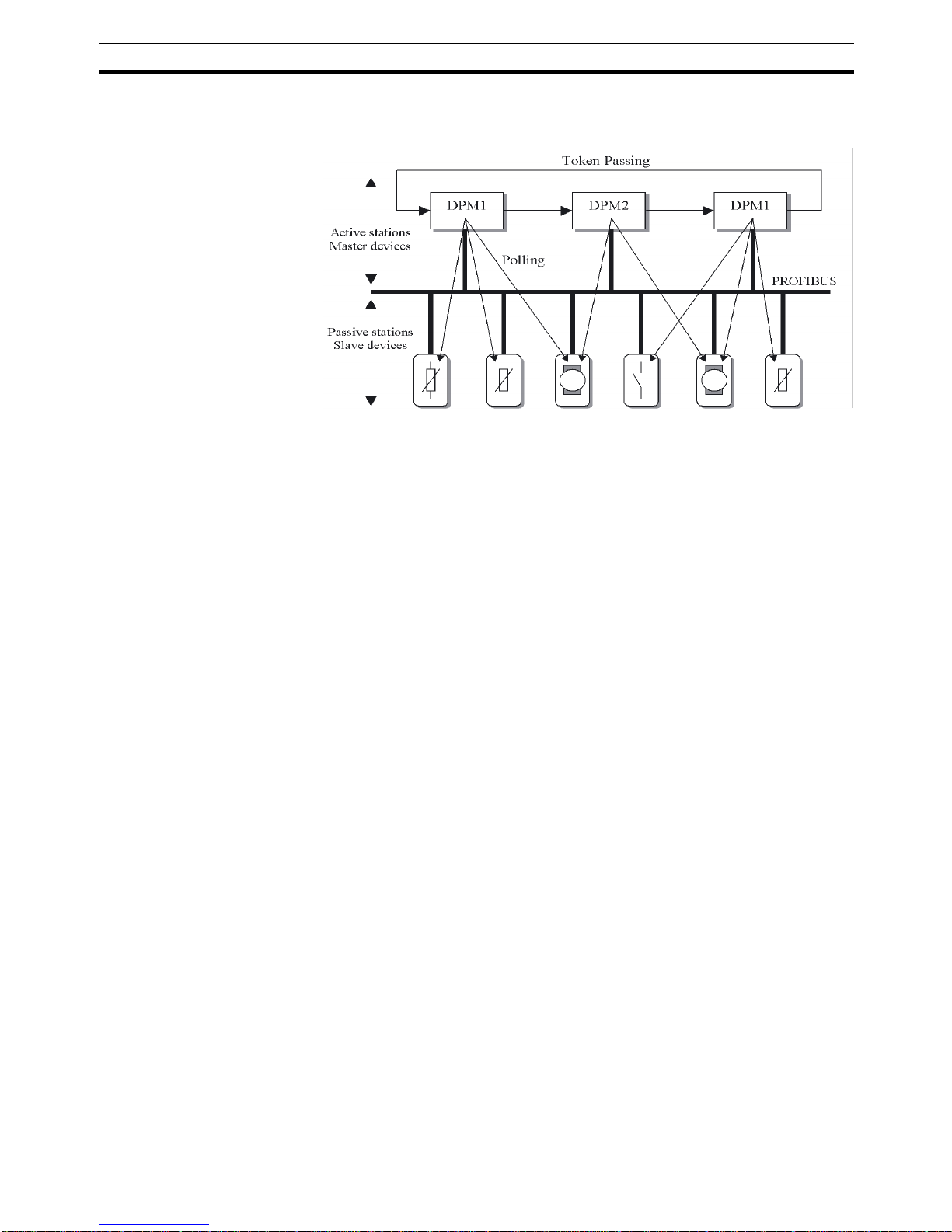
session of the token, to access its assigned slaves. The figure below shows a
possible configuration The configuration shows three active devices (masters)
and six passive devices (slaves).
The three masters form a logical token ring. When an active device receives
the token message, it can perform its master role for a certain period of time.
During this time it can communicate with all assigned slave devices in a master-slave communication relationship, and a DPM2 master can take the initia-
Page 20
5
Overview of PROFIBUS
Section 1-1
tive to communicate with DPM1 master devices in a master-master
communication relationship.
Multi-peer Communication In addition to logical peer-to-peer data transmission, PROFIBUS DP provides
multi-peer communication (broadcast and multicast).
Broadcast
Communication
In the case of broadcast communication a master device sends an unacknowledged message to all other devices (masters and slaves).
Multicast Communication In the case of multicast communication a master device sends an un-
acknowledged message to a predetermined group of devices (masters and
slaves).
1-1-5 Diagnostic functions
Extensive Diagnostics Extensive diagnostic functions defined in PROFIBUS DP enable the fast loca-
tion of error at slave devices. Diagnostic messages are transmitted over the
bus and collected at the master. Three levels of diagnostic messages are
defined:
Device Related
Diagnostics
• Messages concerning the general operational status of the whole device,
e.g. over temperature, low voltage.
Module Related
Diagnostics
• Messages indicating that an error is present in a specific I/O range of a
device, e.g. an 8-bit output module.
Channel Related
Diagnostics
• Messages indicating an error at a given input or output, e.g. short circuit
on Output 5.
1-1-6 Protection mechanisms
Monitoring Time PROFIBUS DP provides effective protection functions against parameteriza-
tion errors or failure of the transmission equipment. Time monitoring is provided both at the master and the slave devices. The monitoring interval is
specified when the system is configured.
Monitoring at the Master The PROFIBUS DP Master monitors data transmission of the slaves with the
Data-Control-Timer. A separate control timer is used for each slave. This
timer expires if response data is not correctly transmitted by the slave within
the monitoring interval. The user is informed when this happens. If the automatic error reaction (Auto-CLEAR) has been enabled, the PROFIBUS DP
Page 21

6
PROFIBUS DP Network configuration
Section 1-2
master exits its OPERATE state, switches the outputs of all assigned slaves
to the fail-safe status and changes to the CLEAR state.
Monitoring at the Slave Slave devices use a watchdog to detect failures of the master or the bus. If
data communication with the master does not occur within the set watchdog
time interval, a slave automatically switches its outputs to the fail-safe mode.
Also, access protection is provided for the inputs and outputs of the slaves
operating in multi-master systems. Only authorized masters can access their
slaves.
1-1-7 Network Operation Modes
PROFIBUS DP distinguishes four different network operation modes:
OFF-LINE Communication with all PROFIBUS DP participants (masters and slaves) is
stopped. The Master ceases to access the PROFIBUS network.
STOP Communication between the master and its slaves is stopped. Only communi-
cation between the master and other masters is still possible.
CLEAR The master tries to set parameters, check the configuration, and perform data
exchange with its associated slaves. Data exchange involves reading the
inputs of the PROFIBUS DP slaves and writing zeros to the outputs of the
slaves.
OPERATE The master exchanges data with its assigned slaves, inputs are read and out-
puts are written. Also, the master cyclically sends its local status to all its
assigned PROFIBUS DP slaves (using a broadcast message).
Auto-CLEAR
Fail-safe State
If an error occurs during the data exchange phase of the master, the ‘AutoCLEAR’ function determines the subsequent actions. If this function has been
disabled, the master remains in the OPERATE mode. If the function has been
enabled, the master automatically changes the network to the CLEAR mode,
in which the outputs of the assigned PROFIBUS DP slaves are switched to
zero, i.e. the ‘fail-safe’ state. The master continues to read the inputs of the
slaves.
1-2 PROFIBUS DP Network configuration
In order to operate a PROFIBUS network, each master in the network needs
to be configured. This process of PROFIBUS Master configuration involves:
• setting up the network topology, i.e. assigning the slave devices with
which the master will be exchanging data,
• defining the parameterization data, which the master will send to each of
the slave devices, before process data exchange can commence
• defining the configuration data, i.e. defining the process data, which will
be exchanged,
• setting up the bus parameters, which define the baud rate and the bus
timing parameters.
• downloading the configuration setup to the master device.
Configuration Technology The configuration process is usually facilitated by a special Computer based
program, often referred to as a Configurator. The Configurator requires special configuration files, defining the configuration options for each device,
which is to participate in data exchange. The files must be provided by the
manufacturer of the device.
Page 22

7
PROFIBUS DP Network configuration
Section 1-2
Two types of configuration technology exist:
• Configuration technology based on FDT/DTM technology
• Configuration technology based on GSD-files
FDT/DTM Concept The FDT/DTM concept specifies the interfaces between the engineering sys-
tems called Field Device Tools (FDT), and the device-specific software components called Device Type Managers (DTM).
The FDT/DTM concept separates the device dependent functionality (which is
in the DTM) from the application. It provides separate interfaces for device
configuration, monitoring and maintenance solutions, which before largely
depended on the manufacturer of the application. Because of this concept,
FDT/DTM technology is not limited to PROFIBUS applications. In concept,
any type of network can be configured and accessed, provided the appropriate DTM’s are available.
CX-Profibus is an example of a FDT container application. It is described in
detail in the following sections.
GSD file Technology The older and most commonly used configuration technology is the based on
GSD files (General Slave Data file). A GSD file is a text file, containing the
characteristic features and configuration options of a device. The device data
base file of each device is loaded in the configurator and downloaded to the
master device.
GSD files are usually supplied with a unit, or can be downloaded from the
Internet, either from the manufacturer's site, or from the GSD library of the
PROFIBUS Nutzer Organisation at http://www.profibus.com.
GSD File Language The language used in the GSD file is indicated by the last letter of the file
extension, *.GS?:
Default = GSD
English = GSE
German = GSG
Italian = GSI
Portuguese = GSP
Spanish = GSS
The GSD files are prepared individually by the vendor for each type of device,
according to a fixed format. Some parameters are mandatory, some have a
default value and some are optional. The device data base file is divided into
three parts:
General Section • General specifications
This section contains the vendor name, the device name, hardware- and software release versions, device type and identification number, protocol specification and supported baud rates.
DP-master Section • DP master-related specifications
This section contains all parameters which only apply to DP master devices
(e.g. maximum memory size for the master parameter set, maximum number
of entries in the list of active devices, or the maximum number of slaves the
master can handle).
DP-slave Section • DP slave-related specifications
This section contains all specification related to slaves (e.g. minimum time
between two slave poll cycles, specification of the inputs and outputs, and
consistency of the I/O data).
Page 23
8
PROFIBUS DP Gateway
Section 1-3
1-3 PROFIBUS DP Gateway
1-3-1 PROFIBUS DP Gateway Features
PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS
DP Gateway
The PRT1-SCU11 is a standalone product, providing an interface between a
PROFIBUS DP Master device and the following OMRON units.
In addition to this functionality, an auxiliary RS-232C interface is provided on
the Unit, to provide a direct connection to a Personal Computer. This direct
connection links the Personal Computer directly to Compoway-F / K-Format /
Memobus protocol, thus bypassing the PROFIBUS DP connection.
Note The PRT1-SCU11 supports only one of the possible protocols at a time. This
means that for example a mix of Compoway-F and Host Link devices is not
supported.
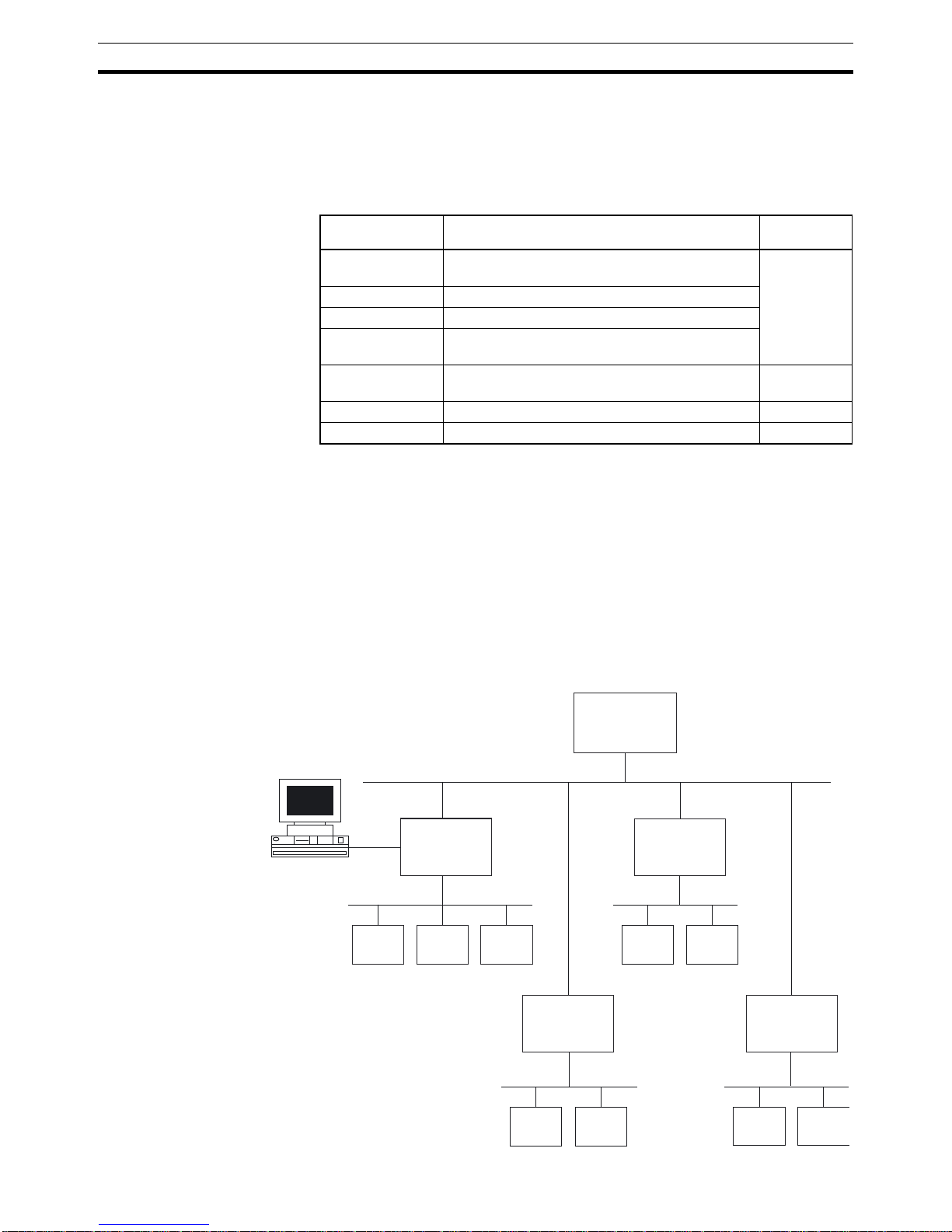
Typical application setup A typical application setup for the PRT1-SCU11 is shown in the figure below.
The PRT1-SCU11 Unit interfaces between PROFIBUS DP and Host Link,
Compoway-F, Memobus and the K-Format protocol.
Unit Description Protocol
supported
E5AN / E5CN /
E5EN / E5GN
OMRON single channel Temperature controllers. Compoway-F
E5ZN OMRON 2-channel Temperature controllers.
E5AR / E5ER OMRON 4-channel Temperature controllers.
E5__ / K3__ /
H8GN
OMRON instruments, supporting OMRON’s RS485 based Compoway-F protocol.
E5AK / E5EK OMRON Intelligent Digital Controllers K-Format
protocol
R88A-MCW151-E Option board for W-series servo drives. Host Link
F7 Inverter OMRON-Yaskawa Varispeed F7 Inverter. Memobus
PROFIBUS-DP
Master
PROFIBUS DP network
IBM PS/2
Compoway-F network
(e.g.) E5ZN
PRT1-SCU11
PROFIBUS DP
Gateway
(e.g.) E5_N
(e.g.) E5ER
Host Link network
R88AMCW151
R88AMCW151
Memobus network
F7 Inverter
F7 Inverter
K-Format network
E5EK
E5AK
PRT1-SCU11
PROFIBUS DP
Gateway
PRT1-SCU11
PROFIBUS DP
Gateway
PRT1-SCU11
PROFIBUS DP
Gateway
Page 24

9
PROFIBUS DP Gateway
Section 1-3
The PRT1-SCU11 is present on the PROFIBUS DP network as a slave unit.
The interface of the PRT1-SCU11 is controlled by a Master unit on the network. This Master unit can be any PROFIBUS DP class 1 or class 2 master
Compoway-F Compoway-F is the OMRON proprietary serial communication bus system,
based on RS-485, to communicate with a range of OMRON Temperature
Controllers.
K-Format The K-Format protocol is the OMRON proprietary serial communication bus
system, based on either RS-422A or RS-485, to communicate with OMRON’s
E5AK/E5EK Intelligent Digital Controllers.
Host Link Host Link is the OMRON proprietary serial communication bus system, based
on RS-422A, to communicate with the OMRON/Yaskawa R88A-MCW151-E
option board for W-series servo drives.
Memobus The Memobus protocol is the Omron-Yaskawa variation of the Modbus RTU
Protocol used to communicate over either RS-422A or RS-485 with OmronYaskawa F7 Inverters.
IBM compatible Personal
Computer
An IBM compatible Personal Computer is connected to the PRT1-SCU11
PROFIBUS DP Gateway via a RS-232C serial communication to the auxiliary
port. Application programs running on the Personal Computer can communicate through the auxiliary port with Compoway-F, K-Format and Memobus
components, thus bypassing the PROFIBUS DP interface. The Host Link protocol is not supported by the Auxiliary port.
I/O Data The data exchanged over PROFIBUS DP are word sized, and represent
either fixed length communication blocks or Free Communication blocks. The
PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway limits the total number of input words
to 100 words, and the total number of output words to 100 words.
Fixed Communication
Blocks
Fixed Communication Blocks are I/O modules with predefined parameter content. These modules are to be used to send output and control data to a
device and read status from a device. These I/O modules are defined in the
PRT1-SCU11 and cannot be changed by the user. They are the most commonly used and straight forward way to exchange data between a Master and
one or more of the devices attached to the PRT1-SCU11.
In general there are at least two Fixed Communication Blocks defined for
each device type or group of devices attached to a PRT1-SCU11. One block
is always available for limited I/O data, e.g. setpoint and process value, and
one block is available for extended I/O data transfer.
Free Communication
Blocks
Free Communications Blocks, are predefined I/O modules, which allow the
user to send any read, write or operate instruction to any attached Compoway-F, K-Format or Memobus device without unit interference. The information in the Free Communication Block is used by the PRT1-SCU11 to
assemble the correct message format.
Three types of Free Communication Blocks are defined, the types are Operate, Read and Write.
• Operate: Execution of a special operation command, which is defined in a
controller.
• Write: Execution of a write data command to any parameter defined in a
controller.
• Read: Execution of a read data command of any parameter defined in a
controller.
Page 25
10
PROFIBUS DP Gateway
Section 1-3
PROFIBUS I/O Data
Exchange
The PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway supports cyclic Master - Slave
communications, i.e. data exchange mode. In data exchange mode the
PRT1-SCU11:
• retrieves all data from the attached units (e.g. Compoway-F) according to
the PROFIBUS configuration and stores this data in the PROFIBUS input
buffer. All input data is obtained before the data is sent to the PROFIBUS
Master as input data.
• writes all data from the PROFIBUS outputs to the attached units according to the PROFIBUS configuration, using the proper protocol. Only if the
data received from the Master differs from the current value in the units,
the new output data is sent.
• sends special operation commands.
• sends command data from Free Communication Blocks to the addressed
unit, and returns the command response to the Master as PROFIBUS
input data.
Troubleshooting
Functions
The PRT1-SCU11 is provided with a variety of troubleshooting functions for
prompt recovery in case of errors:
• Extensive self-diagnostic function at startup.
• Diagnostics information is sent to the PROFIBUS Master unit in case:
• One or more units attached to the PRT1-SCU11 has a communication
error.
• The PRT1-SCU11 has a system error.
• Diagnostics flags, indicating if units attached to the PRT1-SCU11 are
functioning correctly. For Host Link there is a communication active bit
that indicates to the Host Link Unit if the received PROFIBUS data is
valid.
1-3-2 Specifications
General Specifications The PRT1-SCU11 is a Gateway between PROFIBUS DP and a range of
OMRON devices, supporting OMRON proprietary protocols. The Unit version
number on the side case of the housing indicates supported protocols. If no
version number is shown, the version number is 1.0. The following table lists
the protocols supported per version number.
PROFIBUS DP Gateway
Model
Note 1. Unit version 2.0 includes the same functions as Unit version 1.0, in addition
to new protocols supported, and it is backward compatible with Unit version 1.0. Unit version 2.0 will eventually replace Unit version 1.0.
2. This manual describes all features and functions of Unit version 2.0.
Model name Unit Version Protocol supported
PRT1-SCU11 1.0 Compoway-F
Host Link
2.0 Compoway-F
Host Link
K-Format
Memobus
Page 26
11
PROFIBUS DP Gateway
Section 1-3
PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway Specifications
Item Specification (Unit version 2.0)
Installation
Model PRT1-SCU11
Mounting position DIN rail mounted
Power supply 24 Vdc +10% -15% (20.4 to 26.4 Vdc)
Current consumption 85 mA (max), 75 mA typical at 24 Vdc
Dimensions (W x H x D) 40 x 90 x 65 mm
Weight 130g
Environment
Ambient temperatures Operating temperature: 0 to 55°C
Storage temperature: –20 to 75°C
Ambient operating humidity 10% to 90% (with no condensation)
Vibration resistance Conforms to IEC60068-2-6, test Fc.
10 to 55Hz, 0.25-mm amplitude, 55 to 300Hz, acceleration: 29.4 m/s
2
in X, Y, and Z directions for 120 minutes each.
(Total time: 12 linear sweeps x 10 minutes / sweep = 120 minutes)
Shock resistance Conforms to IEC60068-2-27, test Ea.
196 m/s
2
three times each in X, Y, and Z directions
Dielectric strength 600 VAC (between isolated circuits)
Conformance to EMC and Electrical
safety standards
EN61000-6-2: 2001
EN61000-6-4: 2001/CISPR11
EN61131-2: 2003, IDT
Front case
Settings, rotary switches 2 Slave address rotary switches, range: 0 ~ 99 (Decimal)
Settings DIP-switches 4 DIP-switches on the front of the Unit:
• Switch 1, Switch 2: Baud rate setting RS-422A / RS-485 communication interface.
• Switch 3: not used.
• Switch 4: auxiliary
RS-232C interface function selector.
Indicators 6 LED’s, indicating Unit status and PROFIBUS status:
Unit status: RUN (Green LED)
ERR (Red LED)
RS-422A/RS-485 protocol: FCOM (Green LED)
FERR (Red LED)
PROFIBUS status: COMM (Green LED)
BF (Red LED)
PROFIBUS Connector 9-pin sub-D female connector (#4/40 UNC thread).
I/O units + data
Number of GSD I/O Units 15.
Number of GSD I/O modules 18, maximum number of modules represent 15 units and 1 read, 1 write
and 1 operation Free Communication Block.
Total sum of all modules must not exceed 18 modules, this includes a
maximum of 15 physical units.
Number of I/O data supported by slave
Unit
Up to 100 words input and 100 words output maximum.
Number of diagnostics data supported
by slave Unit
Up to 7 bytes of diagnostics max. per attached unit.
Diagnostic data is collected at the attached unit, and is part of the
PROFIBUS input/output message.
Extended diagnostics supported by the
slave Unit
The Unit reports system errors and communication errors in a PROFIBUS extended diagnostic message, this message has a length of 7
bytes. After detection of a system error, the data exchange is stopped.
Page 27
12
PROFIBUS DP Gateway
Section 1-3
Protocol Specifications
Item Specification
Protocol port physical layer
Media types • RS-422A, galvanically isolated.
• RS-485, galvanically isolated.
Selection for RS-485 is made with Physical layer switch 1 (see
2-1-3
Switch Settings
).
ON: RS-485
OFF: RS-422A
termination resistor Internal 220 Ohm resistor between receiver lines.
Use of resistor can be enabled or disabled, using Physical layer switch
2 (see
2-1-3 Switch Settings
).
ON: Termination resistor enabled.
OFF: Termination resistor disabled.
Connector 5-pin Phoenix connector
Baud rates supported • 9.6 kbit/s
• 19.2 kbit/s
• 38.4 kbit/s
Selection via DIP-switches 1 and 2. (See
2-1-3 Switch Settings
).
Protocol types supported via this port • Compoway-F
• Host Link
•K-Format
• Memobus
Device address range
1 ~ 15, set through the slot number of the PROFIBUS module configu-
ration. Number 0 (zero) is reserved.
Auxiliary port
Media type RS-232C, located behind cover marked “Peripheral”
Use the CS1W-CN226 connection cable for connecting the PRT1SCU11 with Thermotools
Baud rates supported Baud rate used on Auxiliary port is the same as the baud rate used on
the main protocol port.
Selection via DIP-switches 1 and 2. (See
2-1-3 Switch Settings
).
Protocol types supported via this port • Compoway-F
•K-Format
• Memobus
PROFIBUS DP interface
Applicable standards EN50170, Volume 2
Protocol type supported PROFIBUS DP
PROFIBUS Unit type PROFIBUS DP slave
PROFIBUS Media type RS-485, galvanically isolated
PROFIBUS Connector 9-pin sub-D female connector (#4/40 UNC thread)
Termination according to EN50170 provided by the cable connector
Unit device address range
0 ~ 99, set through rotary switches
Remote setting not supported.
Baud rates supported (Auto-detect) • 9.6 kbit/s
• 19.2 kbit/s
• 45.45 kbit/s
• 93.75 kbit/s
• 187 kbit/s
• 500 kbit/s
• 1.5 Mbit/s
•3 Mbit/s
•6 Mbit/s
• 12 Mbit/s
Page 28
13
PROFIBUS DP Gateway
Section 1-3
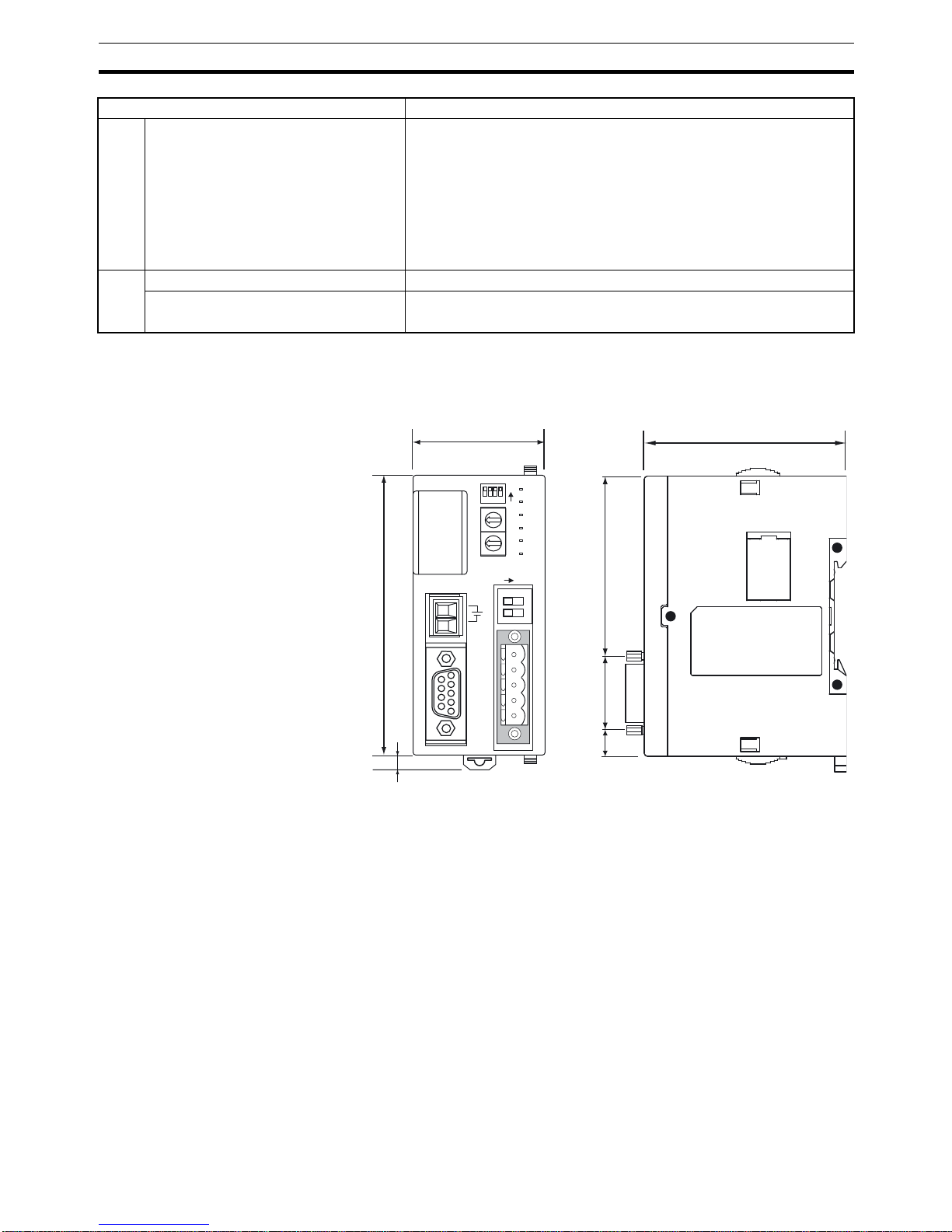
External Dimensions
PROFIBUS services
PROFIBUS services supported • Set_Prm
• Chk_Cfg
• Get_Cfg
• Slave_Diag
• Data_Exchange
• RD_Inp
• RD_Outp
• Global_Control - Sync / Unsync Freeze / Unfreeze/ Clear
I/O Data
Number of I/O data supported Up to 100 words input and 100 words output max.
Number of diagnostics data supported 6 Bytes basic, and 9 bytes extended.
Item Specification
PERIPHERAL
PRT1-SCU11
ON
NODE
ADDRESS
RUN
ERR
COMM
BF
FCOM
FERR
x10
x1
24 Vdc
BUS
ON
1
2
40
90
65
25
57
8
Units: mm
0
23
4
5
6
78
9
1
0
23
4
5
6789
1
1234
R-
R+
S-
S+
FG
5
Page 29
14
Basic Operating Procedure
Section 1-4
1-4 Basic Operating Procedure
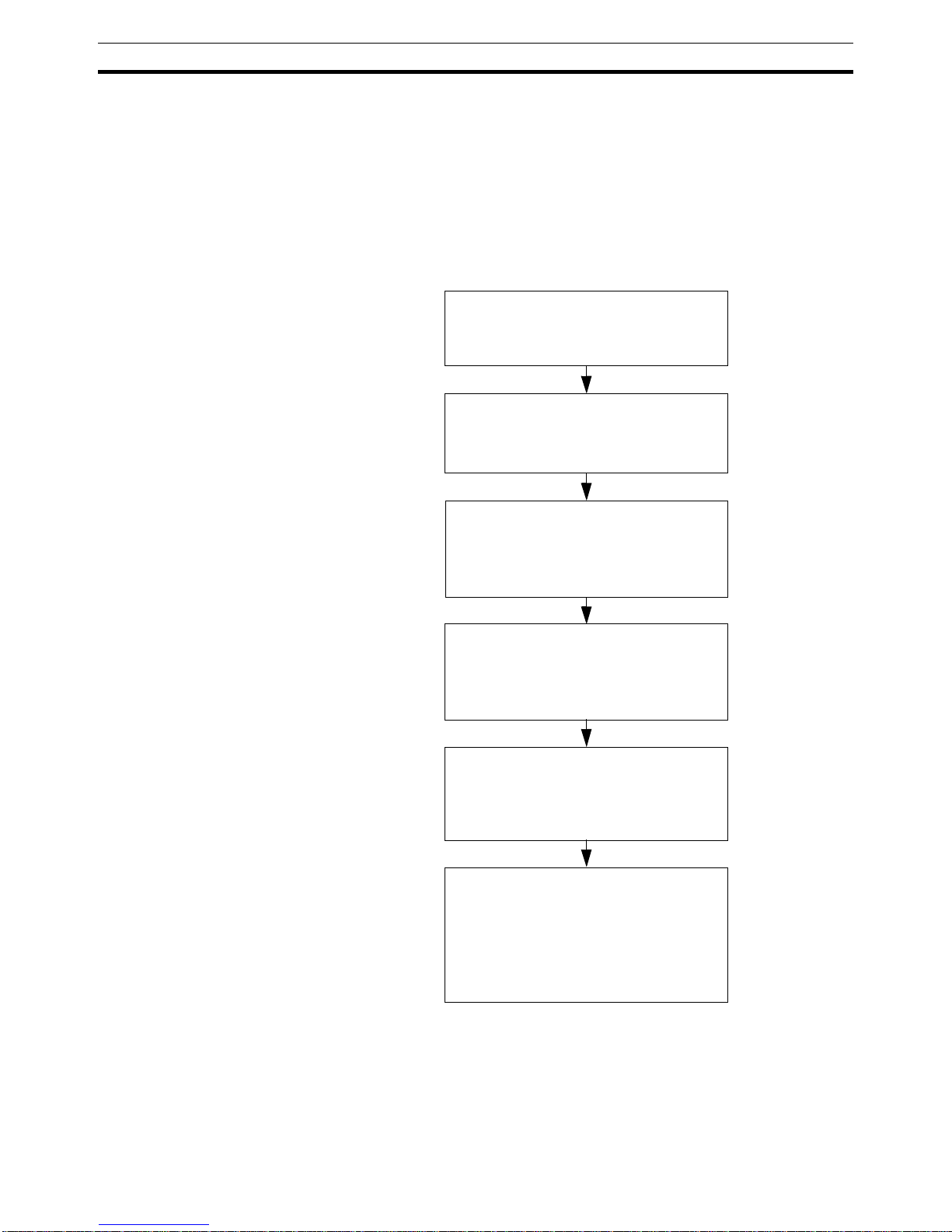
1-4-1 Overview
The following diagram provides an overview of the installation procedures.
For experienced installation engineers, this may provide sufficient information. For others, cross-references are made to various sections of this manual
where more explicit information is given. When reading this manual online,
the flow chart entries provide links to the sections containing detailed information.
Mount the PRT1-SCU11 on a DIN-rail,
and wire the Unit.
(See section
2-2-2 Mounting the PRT1-
SCU11
)
Select a Device address using the two
rotary switches on the front of the
PRT1-SCU11
(See section
2-1-3 Switch Settings
)
Select a baud rate to be used on the
RS-422A/RS-485 protocol network.
Disable the auxiliary RS-232C port on
the front.
(See section
2-1-3 Switch Settings
)
Connect the I/O Modules Units to the
RS-422A/RS-485 network, and connect
the PRT1-SCU11 to the PROFIBUS
network (See section
2-3 Wiring the
RS-422A / RS-485 Devices
)
Power up the PRT1-SCU11.
Configure the PROFIBUS Master,
using the Master Configuration tool
(See section
2-6 Configuring the
PROFIBUS DP network
).
The PRT1-SCU11 starts exchanging
I/O data between the RS-422A/RS-485
devices and the PROFIBUS Master.
Status is confirmed by the FCOM and
COMM LED indicators.
(See section
2-1-2 LED Indicators
).
Page 30

15
Basic Operating Procedure
Section 1-4
1-4-2 Procedures Prior to Starting Communications
Use the following procedure to configure the Unit using CX-Profibus:
1,2,3...
1. Wire the network, to connect the PRT1-SCU11 to the RS-422A / RS-485
devices.
2. Turn ON the PLC power supply and the power supply of the PRT1-SCU11.
3. In CX-Profibus, create a network and define the parameters and I/O configurations for the PRT1-SCU11 settings and the allocated modules. Determine the baud rate and the bus parameter setup,
see section
2-6
Configuring the PROFIBUS DP network
.
4. Download the network configuration to the PROFIBUS DP master. After
downloading the configuration, CX-Profibus will restart the PROFIBUS DP
master automatically.
5. After restarting the PRT1-SCU11 it will automatically start communication.
Page 31

Page 32

17
SECTION 2
Installation and Wiring
This section describes the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway and identifies its controls and indicators. It contains the
procedures for installing the PROFIBUS DP Gateway and setting up the PROFIBUS network.
2-1 Unit Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2-1-1 Nomenclature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2-1-2 LED Indicators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2-1-3 Switch Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2-1-4 PROFIBUS Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
2-1-5 RS-422A / RS-485 Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2-2 Installing the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2-2-1 Handling Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2-2-2 Mounting the PRT1-SCU11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2-2-3 Wiring the Power Terminals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2-3 Wiring the RS-422A / RS-485 Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2-3-1 Precautions When Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2-3-2 2-Wire and 4-Wire Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2-3-3 Connection for E5_N Compoway-F Communications . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2-3-4 Connection for E5ZN Compoway-F Communications . . . . . . . . . . . 25
2-3-5 Connection for E5AR/E5ER Compoway-F Communications . . . . . 26
2-3-6 Connection for R88A-MCW151-E Host Link Communications . . . 27
2-3-7 Connection for E5AK/E5EK K-Format Communication . . . . . . . . . 28
2-3-8 Connection for F7 Inverter Memobus Communication. . . . . . . . . . . 29
2-4 Initial Setup Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2-4-1 Selecting a Node Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2-5 Setting up a PROFIBUS Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2-5-1 Network Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2-5-2 Bus Termination. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2-5-3 PROFIBUS Cable Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2-5-4 Shielding Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2-6 Configuring the PROFIBUS DP network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2-6-1 Configuring the Slave Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2-6-2 Defining the I/O Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2-6-3 Setting Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Page 33

18
Unit Components
Section 2-1
2-1 Unit Components
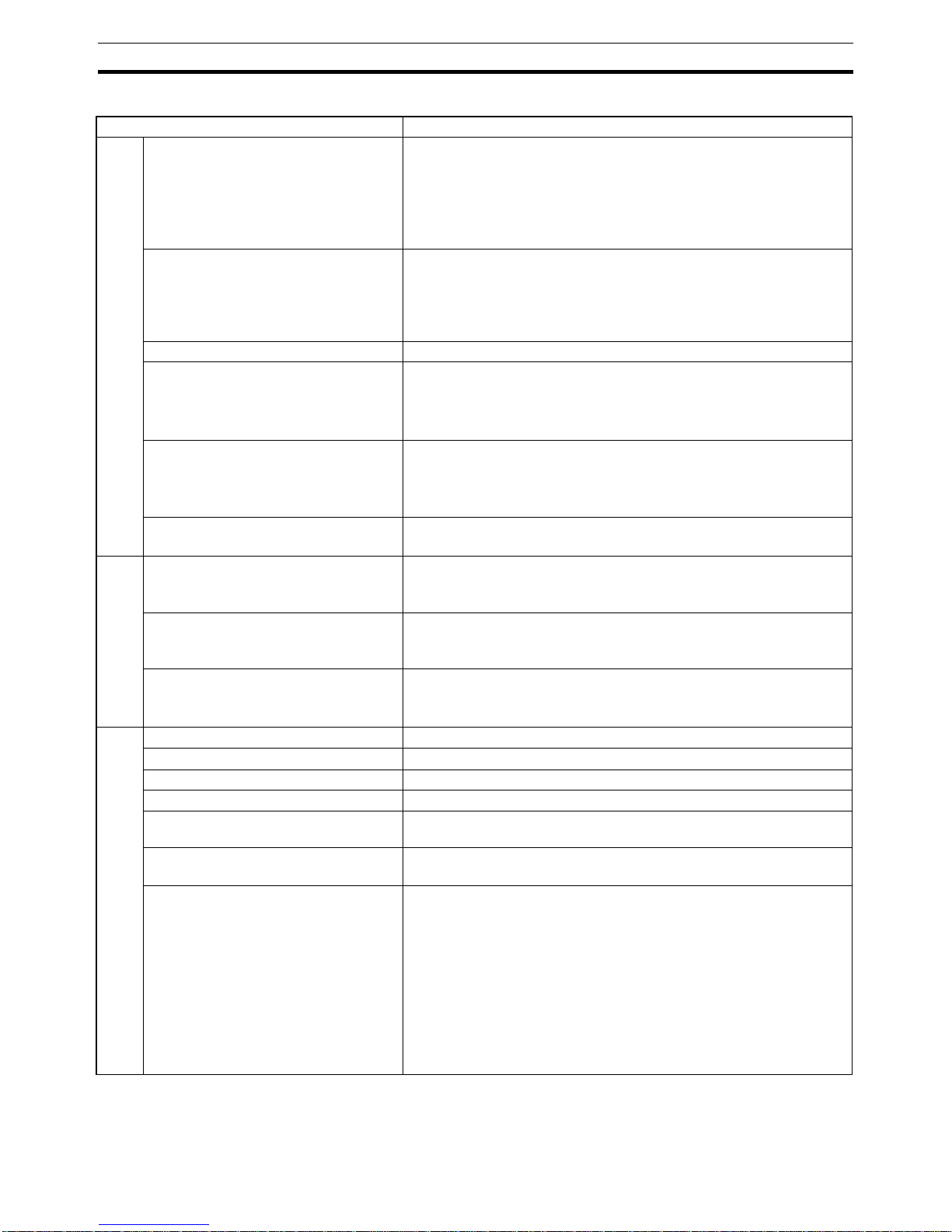
2-1-1 Nomenclature
The illustration below shows the DIP-switches, physical layer switches, auxiliary RS-232C port (behind cover), the status LED indicators, the unit number
selector switch, and a 9-pin female sub-D connector on the front side of the
PRT1-SCU11. Each of these components is explained in the following sections.
2-1-2 LED Indicators
The PRT1-SCU11 has six colored (red and green) LED’s to indicate the operational mode, and status of the Unit, the status of the PROFIBUS interface
and the status of the RS-422A / RS-485 interface.
PERIPHERAL
PRT1-SCU11
ON
NODE
ADDRESS
RUN
ERR
COMM
BF
FCOM
FERR
x10
x1
24 Vdc
BUS
ON
1
2
0
23
4
5
6
78
9
1
0
23
4
5
6789
1
1234
R-
R+
S-
S+
FG
DIP switches
Unit LED indicators
RS-422A / RS485
connector
PROFIBUS address
rotary switches
Power supply input
PROFIBUS
connector
Peripheral port
(behind cover)
RS-422A / RS485 switch
Termination switch
PERIPHERAL
PRT1-SCU11
ON
NODE
ADDRESS
RUN
ERR
COMM
BF
FCOM
FERR
x10
x1
0
23
4
5
6
78
9
1
0
23
4
5
6789
1
1234
Unit LED indicators
Page 34

19
Unit Components
Section 2-1
Indicator Specifications
2-1-3 Switch Settings
Node address Two rotary switches on the front of the PRT1-SCU11, marked Address x10
and x1, are provided to set the PROFIBUS DP device address of the Unit. The
address can be set in the range of 00 through 99. The device address on the
Unit must be the same as the address used in the master’s configuration.
The device address is used to identify individual slave devices on the PROFIBUS DP network. The device address must be unique for each unit. Selecting
a non-unique address for a unit will prevent the PROFIBUS DP network from
starting or operating correctly.
In order to set the device address, perform the following steps.
1,2,3...
1. Turn OFF the power supply before setting the device address.
2. Set the switch to the (new) device address. Use a small screwdriver to
make the setting, taking care not to damage the rotary switch. The node
address is factory-set to 0.
3. Turn ON the power again.
Indicator Color Status Description
RUN Green Not lit • Startup test failed, Unit not operational.
• Operation stopped due to a fatal error.
• Power is off.
Lit Initialization successful, Unit is in normal operation.
ERR
(unit error)
Red Not lit The PRT1-SCU11 is in normal operation (RUN LED is lit).
Flashing The Unit was not able to initialize normally due to a fatal error during
system startup.
Lit Fatal error during operation occurred.
FCOM
(RS-422A / RS-485
communication)
Green Not lit No communication with any devices attached to the RS-422A / RS-485
network. This may be caused by:
• a communication failure (broken wire).
• a non initialized PROFIBUS DP interface.
• the PRT1-SCU11 is not able to exchange data with all configured
devices.
Flashing Communication with the RS-422A / RS-485 network is performed
through the auxiliary port. The PROFIBUS DP interface is bypassed.
Lit RS-422A / RS-485 communication active, no errors.
FERR
(RS-422A / RS-485
communication)
Green Not lit No RS-422A / RS-485 network errors present. The PRT1-SCU11 is
exchanging data with all configured devices.
Lit A failure occurred in the RS-422A / RS-485 network communication.
COMM
(PROFIBUS communica-
tion)
Green Not lit The PRT1-SCU11 is not in Data_Exchange with the PROFIBUS DP
master.
Flashing Auxiliary port ready, PROFIBUS DP interface is not active.
Lit The PRT1-SCU11 is in Data_Exchange with the PROFIBUS DP mas-
ter.
BF
(PROFIBUS Bus fail)
Green Not lit No PROFIBUS DP communication errors, Set_Prm and Chk_Cfg mes-
sages have been accepted. Data_Exchange in progress.
Flashing Either the Set_Prm or the Chk_Cfg message has been rejected by the
PRT1-SCU11. The Unit is not in Data Exchange with the PROFIBUS
DP master.
Lit All communication with the PROFIBUS DP master is lost. The PRT1-
SCU11 is awaiting a new Set_Prm message.
ADDRES
S
x 10
x 1
0
23
4
5
6789
1
0
23
4
5
6789
1
Page 35

20
Unit Components
Section 2-1
Note Always turn OFF the power to the Unit before changing the device address
setting. The Unit only reads the address setting during the initialization following a power-up, i.e. any changes after power up will have no effect.
Baud rate setting In order to select the baud rate used for communication over the RS-422A/
RS-485 network, two DIP-switches are available. Baud rate switches are part
of the DIP-switch bank of 4 switches on the front-case of the Unit. Switch 1
and 2 are used to select the baud rate to be used for communication over the
RS-422A / RS-485 network. The possible combinations are summarized
below.
Note The two DIP-switches for the baud rate are only read during power-up/restart
of the PRT1-SCU11. Changing them during operation has no effect.
Communication Format
Selection
DIP-Switch 3 allows the user to select the communication protocol on the RS422A / RS-485 network, to be either Memobus or one of the other protocols.
Note The communication format selection must be set prior to power-up. Changes
made during operation have no effect.
Auxiliary Port Selection DIP-Switch 4 allows the user to enable or disable the use of the RS-232C
Port, behind the cover next to the DIP-switches.
Note DIP-Switch 4 can be changed during operation. The selected mode is
reflected through the LED Indicators.
DIP-
Switch 1
DIP-
Switch 2
Baud rate
(bits/sec.)
OFF OFF 9600 (default)
OFF ON 19200
ON OFF 38400
ON ON Reserved for future use
PRT1-SCU11
ON
RUN
ERR
COMM
BF
FCOM
x10
x1
0
23
4
5
6
78
9
1
23
4
1
1234
DIP switches
DIP-
Switch 3
Description
OFF Communication protocol on RS-422A / RS-485 is
• Compoway-F
• Host Link
•K-Format
Note Selection of the protocol is made through I/O module selection in
the PROFIBUS Master configuration.
Note The communication format used is 7 data bits, 2 stop bits, 1 even
parity bit.
ON Communication protocol on RS-422A / RS-485 is Memobus.
Note The communication format used is 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, 1 even
parity bit.
DIP-
Switch 4
Description
OFF PROFIBUS to Compoway-F and Host Link is active. The RS-232C Auxil-
iary Port is inactive.
Communication from PROFIBUS is rerouted to the RS-485/RS-422A
communication port.
ON PROFIBUS to Compoway-F and Host Link is inactive. The RS-232C Aux-
iliary Port is active.
Communication from the Auxiliary Port is rerouted to the RS-485/RS-
422A communication port.
Page 36

21
Unit Components
Section 2-1
Peripheral setting For the physical layer settings on the RS-422A / RS-485 network port, two
switches are provided on the front-case of the Unit, located close to the RS422A / RS-485 network connector.
Switch 1 defines whether to use RS-422A or RS-485 as the physical layer on
the RS-422A / RS-485 network.
Switch 2 enables or disables the termination resistor on the RS-422A / RS485 receiver channel.
The two switches are independent of the selected protocol. They can be
changed during operation and take effect immediately.
Note 1. It is recommended to switch the power off before changing switches.
2. If the wrong combination is selected for this PRT1-SCU11 (e.g. Host Link
and RS-485 or Compoway-F and RS-422A), the communication between
the PRT1-SCU11 and the connected devices may not work. The Unit has
no direct way of detecting this, apart from a possible time-out.
2-1-4 PROFIBUS Connector
The PROFIBUS connector on the font of the Unit is a 9-pin female sub-D connector, as recommended by the PROFIBUS standard EN50170.
The signal RTS (TTL signal) is for the direction control of repeaters, which do
not have a self-controlling capability.
Switch 1 Description
OFF RS-422A
ON RS-485
Switch 2 Description
OFF 220 Ohm Termination resistor disabled.
ON 220 Ohm Termination resistor enabled.
PERIPHERAL
NODE
24 Vdc
ON
1
2
Termination switch
RS-422A / RS485 switch
ADDRESS
Pin No. Signal Description
1 Shield Shield/protective ground
2-3 B-line Receive/Transmit data - plus (B wire)
4 RTS Control signal for repeaters (direction control) (TTL)
5 DGND Data ground (reference potential for VP)
6 VP Supply voltage of the terminator resistance (5 Vdc)
7-8 A-line Receive/Transmit data - minus (A wire)
9--
5
9
1
6
Page 37

22
Unit Components
Section 2-1
The signals DGND and VP are used to power the bus terminator located in
the cable connector.
Note 1. The orientation of the sub-D connector allows the use of PROFIBUS con-
nectors with a 90° angle cable outlet, e.g ERNI, Delconec and Phoenix.
2. The 9-pin sub-D connector uses #4/40 UNC thread for mechanical fixation
of the cable connector. Make sure that if non-standard PROFIBUS connectors are used, the same thread is used on the cable connector.
3. PROFIBUS DP Baud rate setting is accomplished through automatic detection, all the defined PROFIBUS DP baud rate values are supported.
2-1-5 RS-422A / RS-485 Connector
The RS-422A / RS-485 port is a dedicated RS-422A / RS-485 compliant interface, which is galvanically isolated. The PRT1-SCU11 has a switch on the
front case, allowing the user to select either the RS-422A or the RS-485 physical layer. The Unit also provides a switch to turn a 220 Ohm termination resistor ON or OFF The termination resistor is placed inside the Unit and between
the two receiver lines of either RS-422A or RS-485.
Note In case Switch 1 is set to ON and RS-485 is selected, the A and B lines are
doubled on the S-/S+ connector pins, i.e. the signal on R- is the same signal
as on S- and the signal on R+ is the same signal as on S+.
Address setting The communication through the RS-422A / RS-485 interface does not require
a separate address setting feature. All connected devices must have
addresses selected in the range of 1 through 15. The address set on the
device must match the slot number of the selected PROFIBUS I/O-module.
Free Communication Blocks carry their own address as part of the message
itself.
The default communication format used on the RS-422A / RS-485 interface
depends on whether Memobus or one of the other protocols will be used, i.e.
it depends on the setting of DIP-switch 3. The table below lists the default
communication settings used.
Pin No. Description
RS-422A (Switch1 OFF) RS-485 (Switch 1 ON)
R- RD- Receiver line A line Transmit/Receive line
R+ RD+ Receiver line B line Transmit/Receive line
FG Frame Ground Frame Ground
S- SD- Transmission line A line Transmit/Receive line
S+ SD+ Transmission line B line Transmit/Receive line
S+
S-
FG
R+
R-
Format Memobus
(DIP-Switch 3 ON)
Compoway-F / Host Link / K-Format
(DIP-switch 3 OFF)
Data length 8 bits 7 bits
Stop bit length 1 bits 2 bits
Error detection 1 bit, even parity 1 bit, even parity
Page 38

23
Installing the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway
Section 2-2
2-2 Installing the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP Gateway
2-2-1 Handling Precautions
When installing the PROFIBUS DP Gateway, observe the following handling
precautions
• Always turn OFF the power supply to the Unit before mounting or dismounting the Unit or connecting or disconnecting cables.
• Provide separate conduits or ducts for the I/O lines to prevent noise from
high-tension lines or power lines.
• Prevent foreign matters to enter the Unit when wiring. Failure to do so,
may result in malfunction if foreign matter enters the Unit.
2-2-2 Mounting the PRT1-SCU11
The PRT1-SCU11 can be mounted directly on a DIN-rail.
Mounting Procedure Mount the PRT1-SCU11 to the DIN-rail using the following procedure.
!Caution
Always turn OFF the power supply to the Unit before mounting or dismounting
the Unit or connecting or disconnecting cables.
1,2,3...
1. Pull the hook down on the bottom.
2. Latch the top hook onto the track
3. Push the Unit until the hook locks onto the track.
4. Push the hook back up to lock the Unit in place.
2-2-3 Wiring the Power Terminals
• Supply power to the Unit using the 2 pin power connector provided with
the Unit.
• When wiring the power, observe the required polarity. Failure to do so can
damage the Unit.
• Use a Phillips screw driver to tighten the connector screw, using a torque
value between 0.25 and 0.3 N·m.
4) Lock
1) Pull down.
2) Insert
onto track.
3) Push in on
the Unit.
Page 39

24
Wiring the RS-422A / RS-485 Devices
Section 2-3
2-3 Wiring the RS-422A / RS-485 Devices
2-3-1 Precautions When Wiring
• Always switch off the power to the Unit and to the RS-422A / RS-854
devices, before wiring.
• Make sure that no foreign objects enter the Unit when wiring. Failure to do
so, may damage the Unit when power is applied.
• Use a Phillips screw driver to secure the network connector to the Unit
after setting up the RS-422A / RS-485 network. Tighten the screws to a
torque of 0.25 to 0.3 Nm.
2-3-2 2-Wire and 4-Wire Connections
The transmission circuits for 2-wire and 4-wire connections are different, as
shown in the following diagram.
Note 1. Use a 2-wire transmission circuit to connect E5_N, E5ZN and E5_R Tem-
perature Controllers to the PRT1-SCU11. Use a 4-wire transmission circuit
to connect the R88A-MCW151-E Motion Control option Board to the
PRT1-SCU11. Use the same transmission circuit (2-wire or 4-wire) for all
nodes.
2. Do not use 4-wire connections when the 2/4-wire switch on the PRT1SCU11 is set to 2-wire.
3. Do not intermix Temperature Controllers, R88A-MCW151-E devices and
F7-Inverter devices on one and the same transmission circuit.
4. In case the PRT1-SCU11 is on one of the ends of the transmission network, switch on the Termination Resistor - by setting Switch 2 to ON.
2-3-3 Connection for E5_N Compoway-F Communications
The E5AN / E5CN / E5EN / E5GN Temperature Controllers all use Compoway-F communications over 2-wire RS-485.
• The RS-485 connection can be either one-to-one or one-to-N. Up to 15
E5_N units can be connected in a one-to-N system.
• The total cable length is 500 m max.
• Use a shielded twisted-pair cable with wires of a thickness of AWG24
(0.205 mm
2
) to AWG14 (2.081 mm2)
Example of 4-Wire
Connections
Example of 2-Wire
Connections
2/4-wire switch
PRT1-SCU11
2/4-wire switch
PRT1-SCU11
Not connected
R88AMCW151-E
E5ZNE5_N
R88AMCW151-E
Page 40

25
Wiring the RS-422A / RS-485 Devices
Section 2-3
The figure below shows the connection between one PRT1-SCU11 and 1 to
15 E5_N Temperature Controller units. Refer to the E5AN / E5CN / E5EN and
E5GN User Manuals for more information on Wiring.
This way of communication also allows the use of other stand-alone Compoway-F instruments, for example a K3GN Digital Panel Meter.
Note The E5AN / E5CN / E5EN and E5GN support baud rates of 9.6 and 19.2
kbits/sec. Ensure that the PRT1-SCU11 baud rate setting (DIP-switch 1 and
2) is set to the correct setting.
2-3-4 Connection for E5ZN Compoway-F Communications
The E5ZN Temperature Controllers use Compoway-F communications over 2wire RS-485. Multiple E5ZN units can be connected together, using one RS485 Terminal. The RS-485 connection is extended through the E5ZN sockets.
However, these units all have unique RS-485 addresses.
The RS-485 connection can be either one-to-one or one-to-N. Up to 15 E5ZN
units can be connected in a one-to-N system.
The figure below shows the connection between one PRT1-SCU11 and 1 to
15 E5ZN Temperature Controller units. Refer to the E5ZN User Manuals for
more information on Wiring.
Note The E5ZN supports baud rates of 9.6, 19.2 and 38.4 kbits/sec. Ensure that
the PRT1-SCU11 baud rate setting (DIP-switch 1 and 2) is set to the correct
setting.
FG
R-
R+
RS-485 RS-485
S- / R−
S+ / R+
12
11
220 Ω
(1/2 W)
6
5
Pin No.
Description
PRT1-SCU11 E5_N side
Shield
Shield
Terminator
Use a 220 Ω (1/2 W)
terminator.
AN/EN/CN GN
RS-485
S- / R−
S+ / R+
12
11
6
5
Pin No.
Description
E5_N side
AN/EN/CN GN
End Node
Page 41

26
Wiring the RS-422A / RS-485 Devices
Section 2-3
2-3-5 Connection for E5AR/E5ER Compoway-F Communications
The E5AR/E5ER Temperature Controllers all use Compoway-F communications over 2-wire RS-485.
• The RS-485 connection can be either one-to-one or one-to-N. Up to 15
Temperature Controller units can be connected in a one-to-N system.
• The total cable length is 500 m max.
The figure below shows the connection between one PRT1-SCU11 and 1 to
15 E5AR/E5ER Temperature Controller Units. Refer to the E5AR/E5ER User
Manuals for more information on Wiring.
Note The E5AR/E5ER supports baud rates of 9.6, 19.2 and 38.4 kbits/sec. Ensure
that the PRT1-SCU11 baud rate setting (DIP-switch 1 and 2) is set to the correct setting.
E5ZN
(No.0,1,2)
E5ZN
(No.3,4,5)
(B)
(A)
24
23
(B)
(A)
24
23
E5ZN
(No.13,14,15)
(B)
(A)
24
23
Terminator
220 Ω (1/2 W)
Terminator
220 Ω (1/2 W)
FG
R-
R+
RS-485
PRT1-SCU11
Shield
FG
R-
R+
RS-485 RS-485
R-
R+
1
2
220 Ω
(1/2 W)
1
2
Pin No.
Description
PRT1-SCU11 E5ER / E5AR side
Shield
Shield
Terminator
Use a 220 Ω (1/2 W)
terminator.
E5ER E5AR
RS-485
R-
R+
2
1
2
1
Pin No.
Description
E5ER / E5AR side
E5ER E5AR
End Node
Page 42

27
Wiring the RS-422A / RS-485 Devices
Section 2-3
2-3-6 Connection for R88A-MCW151-E Host Link Communications
The R88A-MCW151-E uses Host link communications over 4-wire RS-422A.
The figure below shows the connection between one PRT1-SCU11 and 1 to
15 R88A-MCW151-E units.
Note 1. If the PRT1-SCU11 is connected on one end of the transmission circuit,
the termination resistor must be enabled on the Unit, by setting Switch 2 to
ON.
2. The R88A-MCW151-E connected at one end of the transmission circuit,
must also have its termination resistor enabled, by setting Pin 3 of DIPswitch SW2 to ON.
3. The R88A-MCW151-E supports baud rates of 9.6, 19.2 and 38.4 kbits/sec.
Ensure that the PRT1-SCU11 baud rate setting (DIP-switch 1 and 2) is set
to the correct setting.
PRT1-SCU11
RS422A
Interface
Signal Pin
R- 1
R+ 2
FG 3
S- 4
S+ 5
R88A-MCW151-E unit
Pin Signal RS-
422A
Interface
1 RD2 RD+
3FG
4SD5SD+
R88A-MCW151-E unit
Pin Signal RS-
422A
Interface
1 RD2 RD+
3FG
4SD5SD+
RS-422A Port
Connector
Phoenix Connector
RS-422A Port
Connector
Switch SW1: OFF
Switch SW2: ON
DIP switch SW2
Pin 1 OFF
Pin 2 OFF
Pin 3 OFF
DIP switch SW2
Pin 1 OFF
Pin 2 OFF
Pin 3 ON
Page 43

28
Wiring the RS-422A / RS-485 Devices
Section 2-3
2-3-7 Connection for E5AK/E5EK K-Format Communication
The E5AK/E5EK Intelligent Digital Controllers use the K-Format communications over either 4-wire RS-422A or 2-wire RS-485. Both are supported,
through dedicated communication option units. Refer to the E5AK/E5EK User
Manuals for more information on these dedicated communication units.
RS-422A Connection to
E5AK/E5EK
The RS-422A connection can be either one-to-one or one-to-N. Up to 15
E5AK/E5EK units can be connected in a one-to-N system.
The figure below shows the connection between one PRT1-SCU11 and 1 to
15 E5AK/E5EK Intelligent Digital Controller units. The table below shows the
pin numbers used on the E5AK and E5EK units for connection of communication signals. Refer to the E5AK/E5EK User Manuals for more information on
Wiring.
RS-485 Connection to
E5AK/E5EK
The E5AK/E5EK Intelligent Digital Controllers can also communicate over
RS-485, using the dedicated communication option for RS-485. Refer to the
E5AK/E5EK User Manuals for more information on the RS-485 dedicated
communication unit.
The RS-485 connection can be either one-to-one or one-to-N. Up to 15 E5AK/
E5EK units can be connected in a one-to-N system.
The figure below shows the connection between one PRT1-SCU11 and 1 to
15 E5AK/E5EK Intelligent Digital Controller units. Refer to the E5AK/E5EK
User Manuals for more information on Wiring
RR+
FG
S-
RS-422
S+
PRT1-SCU11
RS-422 Interface
SDB
SDA
RDB
RS-422
RDA
SDB
SDA
RDB
RS-422
RDA
Terminator
220 Ω, 1/2W
E5AK / E5EK (1)
(See table below)
E5AK / E5EK (15)
(See table below)
RS-422A Signal E5AK Pin number E5EK Pin number
SDB (Transmission line) 31 21
SDA (Transmission line) 32 22
RDB (Receiver line) 20 20
RDA (Receiver line) 19 19
Page 44

29
Wiring the RS-422A / RS-485 Devices
Section 2-3
Note The E5AK/E5EK supports baud rates of 9.6, and 19.2 kbits/sec. Ensure that
the PRT1-SCU11 baud rate setting (DIP-switch 1 and 2) is set correctly.
2-3-8 Connection for F7 Inverter Memobus Communication
The F7 Inverter use the Memobus communications over either 4-wire RS422A or 2-wire RS-485.
RS-422A Connection to F7
Inverter
The RS-422A connection can be either one-to-one or one-to-N. Up to 15 F7
Inverter units can be connected in a one-to-N system.
The figure below shows the connection between one PRT1-SCU11 and 1 to
15 F7 Inverter units. Refer to the F7 Inverter User Manual for more information
on Wiring.
R-
R+
FG
S-
RS-485
S+
PRT1-SCU11
RS-485 Interface
A (2)
B (2)
A (1)
RS-485
B (1)
E5AK / E5EK (1)
(See table below)
A (2)
B (2)
A (1)
RS-485
B (1)
E5AK / E5EK (15)
(See table below)
Terminator
220 Ω, 1/2W
RS-485 Signal E5AK Pin number E5EK Pin number
A (2) 32 22
B (2) 31 21
A (1) 19 19
B (1) 20 20
R-
R+
FG
S-
RS-422
S+
PRT1-SCU11
RS-422 Interface
RS-422
SS+
RR+
RS-422
Terminator
220 Ω, 1/2W
F7 Inverter (1)
F7 Inverter (15)
SS+
RR+
Page 45

30
Initial Setup Procedure
Section 2-4
RS-485 Connection to F7
Inverter
The F7 Inverter can also communicate over RS-485. The RS-485 connection
can be either one-to-one or one-to-N. Up to 15 F7 Inverter units can be connected in a one-to-N system.
The figure below shows the connection between one PRT1-SCU11 and 1 to
15 F7 Inverter units. Refer to the F7 Inverter User Manuals for more information on Wiring.
2-4 Initial Setup Procedure
After mounting the PRT1-SCU11, the following Initial Setup Procedure must
be applied to allow the Unit to start up properly and to be configured for operation.
• A unique PROFIBUS node address must be selected, before the unit’s
power supply is turned on, see section
2-4-1 Selecting a Node Address
.
• Select the required baud rate to be used on the RS-422A / RS-485 network, using DIP-switches 1 and 2. Select the protocol to be used, i.e.
Memobus or one of the other protocols, using DIP-switch 3. Disable the
Auxiliary port, using DIP-switch 4.
• Select the required physical layer, either RS-422A or RS-485, using
switch number 1, directly over the RS-422A / RS-485 connector.
• Setup the PROFIBUS network, see section
2-5 Setting up a PROFIBUS
Network
, configure the PROFIBUS Master unit using the master configuration tool on the Personal Computer, and download the configuration to
the master unit.
• Refer to the manuals of the connected devices, on how to set up the
devices.
2-4-1 Selecting a Node Address
1,2,3...
1. Make sure that the power supply is turned OFF before setting the node address.
2. Set the switch to the desired node address, using a small screwdriver, and
taking care not to damage the rotary switch. The default node address is
0. Make sure that the node address is unique on the PROFIBUS DP network, i.e. there must be no other unit with the same node address.
3. Turn ON the power supply of the Unit.
R-
R+
FG
S-
RS-485
S+
PRT1-SCU11
RS-485 Interface
SS+
R-
RS-485
R+
F7 Inverter (1)
S-
S+
R-
RS-485
R+
F7 Inverter (15)
Page 46

31
Setting up a PROFIBUS Network
Section 2-5
2-5 Setting up a PROFIBUS Network
2-5-1 Network Structure
Communication Medium The PROFIBUS standard defines the use of EIA RS-485 as the main commu-
nication transport medium. The PRT1-SCU11 is designed to interface directly
to this type of medium. This section will discuss the setup of networks based
on this medium.
Note The other communication medium specified for PROFIBUS is optical fibre.
The PRT1-SCU11 does not provide a direct interface to this type of medium.
However, by using third party couplers an interface between EIA RS-485 and
optical fibre networks can be made.
Linear Bus Topology PROFIBUS DP defines the use of the Linear Bus Network Topology. The Bus
must be terminated at both ends, and must not contain network branches.
The total cable length of the bus depends on the cable and the selected baud
rate. Also, RS-485 specifies a maximum of up to 32 devices - master and
slave devices - per line segment. If more than 32 devices are to be connected,
or if the total length of the segment must be extended beyond its maximum,
repeaters must be used to link the separate segments.
Note Repeaters are devices which connect two segments. They do not have a
device address of their own, but they do count in the total number of devices
in a segment.
Repeaters A maximum of up to three repeaters between two devices in a network can be
used, i.e. a network can consist of up to 4 segments. The maximum number
of PROFIBUS devices in such a network is then 122. The figure below shows
an example of a two-segment network.
Tree Topology The use of repeaters allows the extension of three or more Linear Bus seg-
ments into a Tree topology. In a tree topology more than three repeaters are
allowed, provided that there are no more than three repeaters between any
Station 2 Station 3 Station 31
Repeater
Station 63 Station 33 Station 32
Termination
Termination
Termination
Termination
OMRON
SYSMAC CS1G
PROGRAMMABLE
CONTROLLER
Station 1
Page 47

32
Setting up a PROFIBUS Network
Section 2-5
two devices in the network. The following figure presents an example of a network with more than three segments and repeaters.
Cable Type The PROFIBUS standard EN 50170 specifies Type A shielded, twisted- pair
cable as the recommended cable type for use in an RS-485 based PROFIBUS network. This cable type has the following characteristics:
Note The PROFIBUS standard EN 50170 also specifies a Type B cable with slightly
different cable characteristics. This Type B cable is no longer recommended
for use.
Maximum PROFIBUS
Cable Length
The transmission speed defines the maximum advised cable distance or
cable segment in metres before the use of a repeater is recommended. The
cable lengths specified in the following table are based on PROFIBUS type A
cable.
Segment 1
Max. 31 stations
Segment 2
Max. 31 stations
M / S
M / S
M / S
M / S
Segment 3
Max. 28 stations
Segment 4
Max. 31 stations
Segment 5
Max. 30 stations
Segment 6
Max. 31 stations
M / S
R
R
R
R
M / S
R
Master or slave station
Repeater
Termination
Max. total number of stations = 126
M / S
R
Characteristic Value
Impedance 135 - 165 ohms
Capacitance per unit length < 30 pF/m
Loop resistance 110 ohms/km
Core diameter 0.64 mm
Core cross section
0.34 mm
2
Baud rate
(kbit/s)
Distance/segment
(m)
Baud rate
(kbit/s)
Distance/segment
(m)
9.6 1200 500 400
19.2 1200 1500 200
45.45 1200 3000 100
93.75 1200 6000 100
187.5 1000 12000 100
Page 48

33
Setting up a PROFIBUS Network
Section 2-5
Note If the network must be extended beyond the range of the advised cable
length, the use of a fibre optic segment to cross the larger distance should be
considered.
Stub Lines Passive Stub lines (branches from the main line) should be avoided for data
transmission speeds of more than 500 kbit/s. Except at end devices with termination, it is recommended to always use plug connectors that permit two
data cables to be connected directly to the plug. This method allows the bus
connector to be plugged and unplugged at all times without interrupting data
communication between other devices.
2-5-2 Bus Termination
Termination Resistors In order to minimize cable reflections and ensure a defined signal level on the
data lines, the data transfer cable must be terminated at both ends with a terminating resistor combination. The bus termination diagram is shown on the
left.
The bus terminator connects the two data lines via a 220 ohm resistor which,
in turn, is connected to VP 5Vdc and DGND via two 390 ohm resistors. Powering the terminator resistor via VP 5V and DGND ensures a defined idle
state potential on the data lines.
To ensure the correct functioning up to the highest baud rate, the bus cable
must be terminated at both its ends.
A missing bus termination can cause errors during data transfer. Problems
can also arise if too many bus terminators are fitted, since each bus terminator represents an electrical load and reduces the signal levels and thus the
signal-to-noise ratio. Too many or missing bus terminators can also cause
intermittent data transfer errors, particularly if the bus segment is operated
close to the specified limits for maximum numbers of devices, maximum bus
segment length and maximum data transfer rate.
Inductors In addition to the bus termination, additional precautions must be taken to
ensure proper operation at high baud rates, i.e. baud rates of 500 kbit/s and
higher. Due to the capacitive load of the device and the resulting cable reflections, bus connectors must be provided with built-in series inductors, of 110
mH each, as shown in the figure on the left.
Installing the inductors applies to all devices on the network, and not only to
the devices at both ends of the bus cable.
390 Ohm
390 Ohm
220 Ohm
VP
B-Line
A-Line
DGND
Networ
k
B-Line
A
-Line
110 mH
110 mH
Network
Page 49

34
Setting up a PROFIBUS Network
Section 2-5
2-5-3 PROFIBUS Cable Connector
Bus Cable Connector The plug connector to be used on the PRT1-SCU11 is a 9-pin male sub-D
type, preferably encased in metal and having a facility to connect the shield of
the cable to the case or to pin 1. The cable should be connected to the receive
/ transmit lines, pin 3 (B-line) and pin 8 (A-line).
The use of special PROFIBUS DP cable connectors, which are available from
several manufacturers, is highly recommended. Various models are widely
available, with or without the bus termination and inductors built-in. If provided
in the connector, the Bus termination can often be enabled or disabled
through a switch on the connector.
The special PROFIBUS DP cable connectors often provide a convenient way
of connecting the cables. The figure on the left, provides an example of such a
bus cable connector.
A standard 9-pin sub-D plug can only be used if the PRT1-SCU11 is not at the
start or the end of a bus segment, or on a stub line at a baud rate of 500 kbit/
s or less.
The two PROFIBUS data lines are designated A and B. There are no regulations on which cable core color should be connected to which of the two data
terminals on each PROFIBUS device; the sole requirement is to ensure that
the same core color is connected to the same terminal (A or B) for all devices
throughout the entire system (across all devices and bus segments). The
PROFIBUS Organization recommends the following rule for data line color
codes: PROFIBUS cables in general will use the colors red and green for the
data lines, with the following assignment:
Data cable wire A - green
Data cable wire B - red
This rule applies to both the incoming and the outgoing data lines.
2-5-4 Shielding Precautions
Cable Shield Connection To ensure electro-magnetic compatibility (EMC), the shield of the cable should
be connected to the metal case of the plug connector.
When entering the control cabinet in which the PRT1-SCU11 Unit is installed,
the bus cable shield should be brought into physical contact with a grounding
rail using a grounding clamp or similar device. The cable shield should continue in the cabinet right up to the PROFIBUS device.
Ensure that the Unit and the control cabinet in which it is mounted have the
same ground potential by providing a large-area metallic contact to ground,
e.g. galvanized steel to ensure a good electrical connection. Grounding rails
should not be attached to painted surfaces.
For further information regarding PROFIBUS network installation, please refer
to “Installation Guideline for PROFIBUS DP/FMS” (PNO Order No. 2.112),
which is available at every regional PROFIBUS Organization. The information
covers:
• Commissioning of PROFIBUS equipment.
• Testing the PROFIBUS cable and bus connectors.
• Determining loop resistance.
• Testing for correct bus termination.
• Determining the segment length and cable route.
• Other test methods.
• Example of an equipment report in the PROFIBUS guideline.
To next
station
From
previous
station
Ground Rail
Outside cabinet
Inside cabinet
Page 50

35
Configuring the PROFIBUS DP network
Section 2-6
2-6 Configuring the PROFIBUS DP network
Defining the Configuration After making the physical connections of the network, the PROFIBUS Master
unit has to be configured using the PROFIBUS Master’s configuration tool.
OMRON provides a Personal Computer based configuration program, called
CX-Profibus (only required for OMRON masters), as well as the required
DTM’s for this purpose. It must be used to:
• Install new GSD-file
• Define the master(s).
• Assign slaves to their respective master(s).
• Assign slaves to groups for broadcast/multicast messages.
• Enter bus parameters, e.g. baud rate, target rotation time etc.
• Enable / Disable watchdog.
• Adjust watchdog settings
Refer to CS/CJ Series PROFIBUS DP Master Units Operation Manual
(W409-E2-
@
) for more information on CX-Profibus.
Downloading the
Configuration
The configuration must be downloaded to the Master unit after configuring it
at the Personal Computer. This can be accomplished by either connecting the
serial COM port of the Personal Computer to the CS1/CJ1 PLC with a serial
interface cable, or use an Ethernet connection between the Personal Computer and the CS1/CJ1 PLC via an Ethernet unit.
2-6-1 Configuring the Slave Devices
After adding each of the slave DTM’s to the network, configurations have to be
selected for each of them. Setting up a configuration involves
• Selecting the proper I/O modules
I/O Modules represent either a fixed number of setpoint and process
parameters for each connected RS-422A / RS-485 device or a fixed size
I/O slot which can be used to send user defined protocol data. One type
of I/O slot needs to be selected for each connected RS-422A / RS-485
device.
• Setting up the device parameters
Depending on the I/O module, device settings can be made, which will be
transferred to the RS-422A / RS-485 device through the PRT1-SCU11.
The PRT1-SCU11 itself will validate the settings and reject the data in
case of faulty parameters.
• Selecting the group assignment, which defines the group of slave devices
each slave belongs to and to allow sending Global-Control commands to
this particular group.
All these settings will be downloaded to the Master unit, which will send the
data to the individual slave devices over the PROFIBUS network.
Note The available I/O Modules are discussed in
SECTION 3 Operation
.
Page 51

36
Configuring the PROFIBUS DP network
Section 2-6
2-6-2 Defining the I/O Configuration
Opening the DTM
Configuration User
Interface
In order to define the I/O configuration, the DTM Configuration User Interface
must be opened. The next example uses CX-Profibus to define, edit and
download an I/O configuration.
The figure below, shows the DTM User Interface for the PRT1-SCU11 PROFIBUS DP slave device. The DTM Configuration User Interface displays two
lists.
• The Available Modules list, which contains the I/O modules the user can
select.
• The Configured Modules list, which contains all the I/O modules selected
by the user.
Adding/Inserting I/O
Modules
To select the I/O modules, perform one of the following procedures.
• Select the I/O module that needs to be added in the Available Modules
list, and double-click it with the left mouse button. If more than one module must be added, repeat this step for the other modules.
• Select the I/O module that needs to be added in the Available Modules
list, and press either the Insert or Append button.
Note 1. When pressing the Insert button, the selected I/O module will be inserted
above the selected module in the Configured Modules list.
2. The selected I/O modules are sent to the slave device, in the same sequence as selected in the user interface. The sequence determines the
target Temperature Controller / R88A-MCW151-E for the I/O data. For example, the I/O data of the first selected Fixed Communication Block will be
sent to the first temperature Controller
3. A mandatory I/O module sequence is sometimes indicated in the GSD file,
by using non-PROFIBUS standard GSD file keywords (i.e. only interpreted
Page 52

37
Configuring the PROFIBUS DP network
Section 2-6
by a specific configurator). The Generic Slave DTM does not check such
keywords. In this case, refer to the manual of the specific device for details.
4. Also in this window are the maximum values, which can be set, and the totals of I/O data that actually have been set. If - while selecting I/O modules
- one of the maximum values is exceeded, a warning message will be displayed.
Removing I/O Modules To remove I/O modules from the Configured Modules list, perform one of the
following procedures.
• Select the I/O module that needs to be removed from the Configured
Modules list, and double-click it with the left mouse button. If more than
one module must be added, repeat this step for the other modules.
• Select the I/O module that needs to be removed from the Configured
Modules list, and press the Remove button.
Example For the PRT1-SCU11, the I/O modules for two E5ZN devices, and two E5_N
devices have been selected, see figure above. The E5ZN devices have Compoway-F addresses 1 and 2, the E5_N devices have Compoway-F addresses
3 and 5. Address 4 is not used in this example.
Watchdog Settings Apart from the I/O module selection, the Configuration tab also contains the
settings for two other parameters.
1. Enable Watchdog Control
This parameter will enable/disable the monitoring of the Master-Slave
communication in the slave device. If enabled, the slave will stop I/O data
exchange with the Master, if the Master has not sent any request message
to the slave, within the configured Watchdog time. Furthermore, the slave
will
• switch its outputs to a known state.
• signal its change of state in a diagnostics message, the next time the
Master addresses the slave.
• request re-parameterization from the Master, before resuming I/O data
exchange.
If disabled, the slave will remain in data exchange, even if the Master is not
communicating, thus maintaining its outputs in the latest known state,
based on the last I/O data exchange message.
2. Watchdog Interval
This value is the watchdog time-out related to the Master-Slave communication time out.
Note Enabling the Watchdog Control is highly recommended for safe operation of
the network.
!Caution
In the current version of CX-Profibus, the watchdog value for each of the slave
devices is overruled by the value determined by the Master DTM. Therefore,
changing the value in the Generic Slave DTM has no effect.
Page 53

38
Configuring the PROFIBUS DP network
Section 2-6
2-6-3 Setting Parameters
The parameters are sent by the Master unit to the slave device prior to establishing I/O data exchange. The slave device will reject incorrect parameters
and not establish I/O data exchange, unless the parameters are changed.
In general there will be two types of parameters.
• Common Parameters
The PRT1-SCU11 defines one Common parameter, which applies to the
unit itself. This parameter - Fail Safe support - defines whether or not the
unit will accept empty output messages or messages containing all zeros
in case the PROFIBUS DP Master switches to Clear mode. Clear mode is
often the indication of a failure on the network.
• Module Parameters
Modular Parameters are parameters which are associated with the I/O
modules selected. In the case of the PRT1-SCU11 these parameters
define behaviour with respect to the devices attached to the PRT1SCU11. They are discussed in the next section.
Example The Parameter tab of the PRT1-SCU11 is shown in the figure below. It lists
the parameters for the selected temperature controller the E5ZN-Extended 2
Channel 11WI/3WO. The parameter captions are listed in the left column and
the options can be set in the right column. In order to change settings, doubleclick the required parameter row with the left mouse button. Depending on the
parameter type, either a drop-down list will become available for selection or a
value can be entered.
Page 54

39
SECTION 3
Operation
This section describes how to operate the PRT1-SCU11 in a network. It will discuss setting up a network, configuring all
the connected devices and starting the network. Furthermore, it provides information the I/O data exchange performance
and it also provides information on how to monitor a network, using the unit and monitoring the status of the Temperature
Controller by using CX-Thermo (not shipped with the PRT1-SCU11).
3-1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-2 PROFIBUS Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-3 Compoway-F Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3-3-1 Fixed Communication Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3-3-2 Special Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
3-3-3 Compoway-F Parameter Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-3-4 Free Communication Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-4 K-Format Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3-4-1 Fixed Communication Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3-4-2 Operation Execute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3-4-3 K-Format Parameter Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3-4-4 Free Communication Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3-5 Host Link Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3-6 Memobus Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3-6-1 Fixed / Flexible Communication Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3-6-2 Memobus Parameter Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
3-7 PROFIBUS Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3-8 Auxiliary RS-232C interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Page 55

40
Introduction
Section 3-1
3-1 Introduction
This section discusses the operational aspects of using the PRT1-SCU11 and
the configuration software. The section has been setup, to follow the general
process flow of setting up and configuring a network, downloading the configuration, and operating the PROFIBUS network, the Compoway-F, K-Format,
Host Link or Memobus network.
The PROFIBUS Master can communicate with the PRT1-SCU11 using fixed
communication block and/or Free Communication blocks.
In case Error messages are displayed, while using CX-Profibus, refer to the
appropriate manual for more information on errors.
Note 1. The maximum number of devices is 15.
2. The maximum of modules is 18. This number consists of 15 fixed communication blocks, 1 write, 1 read and 1 operation Free Communication block.
3-2 PROFIBUS Communication
As mentioned in the previous section there are two ways of PROFIBUS communication. Communication with fixed communication blocks and Free Communication blocks.
Fixed Communication
Blocks
Fixed communication blocks are pre-defined blocks of data to be read/written
from/to a device. Fixed communication blocks can not be changed. The most
common data can be read/written using fixed communication blocks.
Example For an E5ZN connected to the PRT1-SCU11 a 2-channel basic fixed I/O block
defines the data transfer of 1 Setpoint Value for each channel and 1 Process
Value for each channel between the PROFIBUS Master unit and the E5ZN
through the PRT1-SCU11.
Free Communication
Blocks
Free communication blocks are sent directly to the device connected to the
PRT1-SCU11. The PRT1-SCU11 does not interfere with the data contents of
the block. This allows Free Communication blocks to be used to access data
in a device which can not be accessed through fixed communication blocks.
Free Communication Blocks can be used for Compoway-F and the K-Format
protocol.
Flexible Communication
Blocks
Flexible communication blocks are defined for the Memobus protocol and are
a mix between the fixed blocks and the Free Communication blocks. The flexible communication blocks will contain 3 input words and 3 output words, for
each of which a target register in the Varispeed F7 Inverter can be defined.
Maximum PRT1-SCU11
PROFIBUS DP I/O Size
The maximum amount of PROFIBUS data the PRT1-SCU11 can handle is
100 words input data and 100 words100 output data. If more capacity is
needed an extra PRT1-SCU11 is required to access additional devices.
Note As per PROFIBUS DP definition the I/O data words are sent in Big Endian for-
mat, i.e. the high byte is sent first.
Page 56

41
Compoway-F Communication
Section 3-3
3-3 Compoway-F Communication
3-3-1 Fixed Communication Blocks
Fixed communication blocks are pre-defined blocks, which define specific
groups of I/O data words. Each device has at least one Fixed communication
block for specific status and control words. In the next table an overview of all
devices and their communication blocks is listed. In addition to the Input and
Output words, a number of I/O modules also provide Special Operations
words, which can be used to change the control status of a Temperature Con-
troller, for example from STOP to RUN.
Compoway-F
Device
type
Module name Output words Input words Total
output
words
Tota l
input
words
Number of
channels
- Empty slot (No device) - - 0 0 N/A
E5_R E5_R-Basic 1 channel SV channel 1 PV-channel 1 1 1 1
E5_R-Basic 2 channels SV channel 1
SV channel 2
PV channel 1
PV channel 2
22 2
E5_R-Basic 4 channels SV channel 1
SV channel 2
SV channel 3
SV channel 4
PV channel 1
PV channel 2
PV channel 3
PV channel 4
44 4
E5_R-Extended 1 channel SV channel 1
Special operation
(See Note)
PV channel 1
MV1 channel 1
MV2 channel 1
Status high word channel 1
Status low word channel 1
Operation execute
26 1
E5_R-Extended 2 channel SV channel 1
SV channel 2
Special operation
(See Note)
PV channel 1
MV1 channel 1
MV2 channel 1
Status high word channel 1
Status low word channel 1
PV channel 2
MV1 channel 2
MV2 channel 2
Status high word channel 2
Status low word channel 2
Operation execute
311 2
E5_R-Extended 4 channels
SV channel 1
SV channel 2
SV channel 3
SV channel 4
Special operation
(See Note)
PV channel 1
MV1 channel 1
MV2 channel 1
Status high word channel 1
Status low word channel 1
PV channel 2
MV1 channel 2
MV2 channel 2
Status high word channel 2
Status low word channel 2
PV channel 3
MV1 channel 3
MV2 channel 3
Status high word channel 3
Status low word channel 3
PV channel 4
MV1 channel 4
MV2 channel 4
Status high word channel 4
Status low word channel 4
Operation execute
521 4
Page 57

42
Compoway-F Communication
Section 3-3
Note The Special operation word is explained in the section below.
3-3-2 Special Operation
Command Word The Special Operation word format is shown in the figure below. It contains
the Command Code, and the Channel Number. The Command Code specifies the action to be performed, the Channel Number specifies channel to
which the action will apply. Both the Command Code and Channel Number
coding are listed in the table below.
Since the Command Word will be part of the cyclic data exchange, a mechanism in the PRT1-SCU11 is used to send this word to the targeted device only
when needed. The PRT1-SCU11 will transfer the command word to the target
device up on a change of one or more of the bits in the contents of the Command Word.
Response Word Once the command has been sent, the response from the device is placed in
the PROFIBUS input Operation Execute word. The format of the response is
shown in the figure below. the Operation Execute word contains the Command Code, the Channel Number as well as an Error Code bit. If the Error bit
(bit 4) is set, an error has occurred in the communication with the targeted
device.
E5ZN E5ZN-Basic 2 channels SV channel 1
SV channel 2
PV channel 1
PV channel 2
22 2
E5ZN-Extended 2 channels
SV channel 1
SV channel 2
Special operation
(See Note)
PV channel 1
MV1 channel 1
MV2 channel 1
Status high word channel
Status low word channel
PV channel 2
MV1 channel 2
MV2 channel 2
Status high word channel 2
Status low word channel 2
Operation execute
311 2
E5_N E5_N-Basic 1 channel SV channel 1 SV channel 1 1 1 1
E5_N-Extended 1 channel SV channel 1
Special operation
(See Note)
PV channel 1
MV1 channel 1
MV2 channel 1
Status high word channel 1
Status low word channel 1
Operation execute
26 1
Compoway-F
Device
type
Module name Output words Input words Total
output
words
Tota l
input
words
Number of
channels
1514131211109876543210
Command Code
Channel Number
Special Operation Word
Page 58

43
Compoway-F Communication
Section 3-3
An overview of all the Command Codes, Channel Numbers and Error Codes
is given in the table below.
Handshaking In order to prevent an overflow of commands being sent to one or more
devices, the user must implement a simple handshaking mechanism in the
PROFIBUS DP Master unit.
• When no command is to be sent to a device, set the Special Operation
Word in the PROFIBUS DP Master to 0. The PRT1-SCU11 will respond
by setting the Operation Execute word to 0.
• When a command must be sent to a device, set the Command Code and
the Channel Number. For another Special Operation command to be
sent, the user must first wait for the Operation Execute word to change to
a non-zero value, indicating the completion of the first Special operation
command.
1514131211109876543210
Command Code
Channel Number
Error
Operation Execute Word
Bit group
name
Binary
Value
Value description
Command
code
0000 Clear command
0001 Run
0010 Stop
0011 AT Cancel
0100 AT Execute
0101 Auto
0110 Manual
0111-1111 Reserved
Channel
numbers
000 Channel 1
001 Channel 2
010 Channel 3
011 Channel 4
100-110 Not supported
111 All channels
Error code,
one bit
0No error
1Error
• Not supported command number
• Not supported channel number
• Command execution failed
• Communication with Temperature Controller fails
Page 59

44
Compoway-F Communication
Section 3-3
3-3-3 Compoway-F Parameter Settings
For the Fixed Communication blocks the user can define behaviour of the
PRT1-SCU11 on the Compoway-F communication in case the PROFIBUS
communication fails.
PROFIBUS
Communication Fails
In case the PROFIBUS communication fails, there are two options for the
PRT1-SCU11 to handle this, as defined by the a user.
• The PRT1-SCU11 can send a stop command to one or more of the
devices, causing the control cycle to stop.
• The Temperature Controller can Hold the last received Setpoint Value.
This behavior can be selected in CX-Profibus when configuring the PROFIBUS DP Master unit, see the example in the figure below.
This setting can be defined for every individual Temperature Controller and
will be sent to the PRT1-SCU11 as part of the PROFIBUS DP Set_Prm message.
3-3-4 Free Communication Blocks
With Free Communication blocks it is possible to read data, write data or send
an operation instruction directly from or to any parameter in a Compoway-F
device. With Free Communication blocks, however, the commands have to be
assembled by the PROFIBUS Master system. The user also has to provide a
simple handshaking mechanism to prevent too many commands being sent.
The PRT1-SCU11 uses the contents of the Free Communication block to
assemble a Compoway-F mini-FINS command, which is sent to the device.
The Free Communications blocks can be selected as I/O modules from the
GSD file. Three Free Communication blocks are defined for Compoway-F and
can be used to configure the PRT1-SCU11.
1. Read for reading one parameter defined in the device.
2. Write for writing one parameter defined in the device.
3. Operation for executing any operation defined in device.
Note The Free Communication blocks do not require the user to make parameter
settings.
Page 60

45
Compoway-F Communication
Section 3-3
In the next table an overview is presented on how the Free Communication
blocks are composed for several different device types.
A Free Communication block always contains a device address (one word
with a value in the range between 0000 (hex) and 0063(hex)) and a mini FINS
command. The length of the mini FINS command depends on the command
type (operation, write or read) to be executed.
Operation Mini FINS
Command
The Operation mini FINS command type consists of a command code MRC/
SRC, followed by an instruction code, the value of this instruction code is command type dependent. The operation of a mini FINS command is defined as
follows.
The response of this command for a correct executing of the command is
defined as:
Refer to the operation manual of the targeted Compoway-F device for more
commands and detailed information.
Example To stop control on channel 1 of the E5_R, with address 05, the contents of the
Fee Communication block must be set to 0005 3005 0101 (hex), or
• Device address: 0005 (hex)
• Command code: 3005 (hex)
• Instruction code: 0101 (hex).
Assuming there is no error, the response is four bytes: 3005 0000 (hex).
Read Mini FINS Command The Read mini FINS command consists of
• A device address number.
• A command code MRC/SRC.
• A variable area type, indicating the area within the device, from where the
parameter must be read.
• A Read start address within the specified area.
• A Bit position within the parameter to be read.
• The Number of bits/bytes to read from the parameter area/location.
This format is shown below.
Compoway-F
Device
type
Module name Output words Input words Total
output
words
Total
input
words
E5_N,
E5ZN,
E5_R
Free comms Read
4 WI / 5 WO
Device address (1 word)
Command data (4 words)
Response code (2 words)
Read data (2 words)
54
Free comms Write
2 WI / 7 WO
Device address (1 word)
Command data (4 words)
Write data (2 words)
Response code (2 words) 7 2
Free comms Operation
2 WI / 3 WO
Device address (1 word)
Command data (2 words)
Response code (2 words) 3 2
Device address Command code
MRC/SRC
Instruction code &
related information
2 bytes 2 bytes 2 bytes
Command code
MRC/SRC
Response
code
2 bytes 2 bytes
Page 61

46
Compoway-F Communication
Section 3-3
The response of this command for a correct executing of the command is
defined as:
Refer to the operation manual of the Compoway-F device for more detail
regarding the read mini FINS command.
Note 1. The actual data to be written to the device consists of one double word. If
a CS1/CJ1 PLC is used to assemble the Write command, de data will be
swapped before sending it over PROFIBUS, due to the communication formats of both Compoway-F and PROFIBUS. The PLC program must swap
these words before the data can be transmitted.
2. For CX-Programmer 5.0 or higher OMRON provides function blocks to implement the assembly of the Free Communication Read command. When
processing the response this function block will perform the word swapping
automatically. Refer to
Appendix B Function Block Programming
for more
details.
Example Reading the internal setpoint from an E5ZN (device 2), channel 1 (start
address 2, 1 element to read) is done with the command:
0002 0101 C1 0002 00 0001(hex).
The response is (no error occurred): 0101 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000(hex).
Write Mini FINS Command The Write mini FINS command consists of
• A device address number.
• A command code MRC/SRC.
• A variable area type, indicating the area within the device, to where the
parameter must be written.
• A Read start address within the specified area.
• A Bit position within the parameter to be read.
• The Number of bits/bytes to read from the parameter area/location.
• The data to be written.
This format is shown below.
The response of this command for a correct executing of the command is
defined as:
Device
address
Command
code
MRC/SRC
Variable
type
Read start
address
Bit position Number of
elements
2 bytes 2 bytes 1 byte 2 bytes 1 byte 2 bytes
Command code
MRC/SRC
Response
code
Data
2 bytes 2 bytes 4 bytes
Device
address
Command
code
MRC/SRC
Variable
type
Write
start
address
Bit
position
Number
of
elements
Element1
2 bytes 2 bytes 1 byte 2 bytes 1 byte 2 bytes 4 bytes
Command code
MRC/SRC
Response
code
2 bytes 2 bytes
Page 62

47
Compoway-F Communication
Section 3-3
1. Refer to the operation manual of the Compoway-F device for more detail
regarding the read mini FINS command.
The actual data written to the Temperature Controller consists of one double word. Due to the communication formats of both Compoway-F and
PROFIBUS, de data will end up as two swapped words in a CS1/CJ1 PLC,
when the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21PROFIBUS Master is used. The PLC program must swap these words before the data can be sued.
2. For CX-Programmer 5.0 or higher OMRON provides function blocks to implement the assembly of the Free Communication Write command. When
processing the response this function block will perform the word swapping
automatically. Refer to
Appendix B Function Block Programming
for more
details.
Example Writing the lower limit of the setpoint an E5ZN (device 2), channel 1 is done
with the command: 0002 0102 C1 0003 00 0001 0000 0005(hex).
The response is (no error occurred): 0102 0000(hex).
Free Communication
Blocks
A write or operation command will be sent to the device when the command is
changed from zero’s to the correct data. When the command data is set to
zero, the response data will also be cleared. The read type command blocks
are sent every Compoway-F cycle.
Broadcast Broadcasting can be used for operations and writes. If the device address is
set to 00FF(hex), a broadcast is sent to all devices using XX broadcast. The
response code will be filled with a response to indicate that the command has
been sent to the devices.
Note It is recommended to restrict the Free Communication blocks to the end of the
I/O configuration. Placing a Free Communication block in the middle of other
modules is allowed, but it will influence the device number of other modules.
The device number is affected due to the fact that the slot number is a representation of the device number.
Example Configuring 2 x E5ZN basic modules and a Free Communication write block:
If there is no device for a device address between two existing consecutive
device addresses, the empty slot module must be used. The slot number represents the device address.
Note The PROFIBUS Configuration for this slave is limited to 100 words input and
100 words output.
Slot
number
Recommended Not recommended
Module Device
number
Module Device
number
1 E5ZN Basic 1 E5ZN Basic 1
2 E5ZN Basic 2 Free communication write
block
--
3 Free communication write
block
-- E5ZN Basic 3
Page 63

48
K-Format Communication
Section 3-4
3-4 K-Format Communication
3-4-1 Fixed Communication Blocks
The K-Format protocol supports Fixed Communication blocks to allow easy
configuration for a number of I/O parameters, supported by the E5AK / E5EK
intelligent Digital Controllers. In the next table an overview of the Fixed Communication blocks is listed.
Note The Special operation word is explained in the section below.
3-4-2 Operation Execute
The Operation Execute word can be used to Start or Stop a control cycle in
the E5AK / E5EK Controller. The command options are shown below.
Note Other values for Operation Execute are not supported.
3-4-3 K-Format Parameter Settings
For the Fixed Communication blocks the user can define behaviour of the
PRT1-SCU11 on the K-Format communication in case the PROFIBUS communication fails.
PROFIBUS
Communication Fails
In case the PROFIBUS communication fails, there are two options for the
PRT1-SCU11 to handle this, as defined by the a user.
• The PRT1-SCU11 can send a stop command to the device, causing the
control cycle to stop.
• The E5AK / E5EK can Hold the last received Setpoint Value.
K-Format
Device
type
Module name Output words Input words Total
output
words
Tot al
input
words
Number of
channels
- Empty slot (No device) - - 0 0 N/A
E5AK/
E5EK
E5_K-Basic 5WI/2WO SV channel 1
Operation Execute
(See Note)
PV channel 1
SV channel 1
Status A group
Status B group
Special Operation
25 1
E5_K-Extended 5WI/4WO SV channel 1
Alarm value 1
Alarm Value 2
Operation Execute
(See Note)
PV channel 1
SV channel 1
Status A group
Status B group
Special Operation
45 1
Command Value
(See Note)
Description
Run 0000 Start Control cycle.
Stop 0001 Stop Control Cycle.
Page 64

49
K-Format Communication
Section 3-4
This behavior can be selected in CX-Profibus when configuring the PROFIBUS DP Master unit, see the example in the figure below.
This setting can be defined for every individual Temperature Controller and
will be sent to the PRT1-SCU11 as part of the PROFIBUS DP Set_Prm message.
3-4-4 Free Communication Blocks
For the K-Format protocol one Free Communication Block is available, which
has however, a different format as compared to the Free Communication
Block for Compoway-F. The one Free Communication block allows implementation of Read, Write and special Operation type of commands.
Free Communication
Block Format
The Free Communication block reserves 3 words of input data and 3 words of
output data. The output format is shown below.
The table below lists the message parameters.
The input format is shown below.
Device
address
Reserved Command
type
Parameter Number/
Command code
Data
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte 1 byte 2 byte
Message parameter Description
Device address The address number of the target device.
Reserved A reserved byte, which will be ignored by the PRT1-SCU11
Command type A command type code
1 = Read command
2 = Write command
3 = Special command
4 ~ FF = Invalid command
Parameter Number /
Command Code
Refer to the E5AK / E5EK Operation Manual.
In case the Command type is set to 1 or 2, use the Parameter
number to specify the parameter to be read or written.
In case the Command type is set to 3, use the Command
code to define the Special Operation.
Data Data to be written. The PRT1-SCU11 will ignore this part in
case of a Read command or a special operation command.
Page 65

50
Host Link Communication
Section 3-5
The table below lists the message parameters.
3-5 Host Link Communication
In the following table the fixed communication blocks for Host Link communication are listed.
The required data on VR-memory address can be programmed in the R88AMCW151-E. For more detailed information refer to the R88A-MCW151-E
Operation Manual.
The status of the PROFIBUS communication can be checked by the R88AMCW151-E through the R88A-MCW151-E status word (see figure below).
This word is sent by the PRT1-SCU11 to the R88A-MCW151-E.In case
PROFIBUS communication fails, the first bit of the status word will be set to
Device
address
End code Command
type
Parameter Number/
Command code
Data
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte 1 byte 2 byte
Message
parameters
Description
Device address The address number of the target device.
End code Indicates failure or success of the command transmission.
If the End code is not equal to 0, the data part must be considered invalid.
Command type A command type code
1 = Read command
2 = Write command
3 = Special command
4 ~ FF = Invalid command
This is the same as sent to the device via the output data.
Parameter Number /
Command Code
Refer to the E5AK / E5EK Operation Manual.
In case the Command type is set to 1 or 2, use the Parameter
number to specify the parameter to be read or written.
In case the Command type is set to 3, use the Command
code to define the Special Operation.
Data Data read from or written to the E5AK / E5EK Controller.
Host Link
Device type Module name Output words Input words Total
output
words
Tota l
input
words
- Empty slot (No device) - - 0 0
R88A-MCW151-E “MCW151 Host Link 5 IW/5 OW” VR(5) (Status word)
VR(6) - VR(10)
VR(0) - VR(4) 5 5
“MCW151 Host Link 10 IW /10 OW” VR(10) (Status word)
VR(11) - VR(20)
VR(0) - VR(9) 10 10
“MCW151 Host Link 15 IW / 15 OW” VR(15) (Status word)
VR(16) - VR(30)
VR(0) - VR(14) 15 15
Page 66

51
Memobus Communication
Section 3-6
OFF. If the PROFIBUS communication is active the same bit will be set to ON,
regardless the number of I/O communication words.
3-6 Memobus Communication
3-6-1 Fixed / Flexible Communication Blocks
The Memobus protocol supports Fixed Communication blocks to allow easy
configuration for a number of I/O parameters, supported by the E5AK / E5EK
intelligent Digital Controllers. In the next table an overview of the Communication blocks is listed.
Note 1. The addresses of these registers are fixed in the PROFIBUS parameter
message. They can not be changed by the user.
2. The user can define each of the addresses of the registers in the Input and
Output area. This must be done upon configuring the PROFIBUS DP Master unit, see section
2-6 Configuring the PROFIBUS DP network
.
76543210
PROFIBUS Communication Active
R88A-MCW151-E Status Word
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Memobus
Device type Module name Output words Input words Total
output
words
Total
input
words
- Empty slot (No device) - - 0 0
F7 Inverter Memobus Fixed 3WI/3WO
(Fixed)
Command Register
Frequency Register
Voltage Register
(See Note 1)
Status Register
Frequency Register
Voltage Register
(See Note 1)
33
Memobus 3WI/3WO
(Flexible)
Register 1
Register 2
Register 3
(See Note 2)
Register 1
Register 2
Register 3
(See Note)
33
Page 67

52
Memobus Communication
Section 3-6
3-6-2 Memobus Parameter Settings
During configuration of the PROFIBUS Master unit the user must set a number of parameters, depending on the selected Communication block. De figure below shows the selection options for a Fixed Communication Block.
The parameter options are listed in the table below.
Parameter name Range
(Hex)
Description
Fixed Comm. Block
Device Address 00 ~ 1F Defines the Memobus address of the device to exchange the I/O
data of this module with.
Read Status Register 0020 Address of the status register (Fixed).
Read Frequency Register 0023 Address of the Actual Frequency register (Fixed).
Read Voltage Register 0025 Address of the Actual Voltage register (Fixed).
Write Command Register 0001 Address of the Command register (Fixed).
Write Frequency Register 0002 Address of the Required Frequency register (Fixed).
Write Voltage Register 0003 Address of the Required Voltage register (Fixed).
Flexible Comm. Block
Device Address 00 ~ 1F Defines the Memobus address of the device to exchange the I/O
data of this module with.
Read Register Address One 0000 ~ FFFF Address of first register to read from.
Read Register Address Two 0000 ~ FFFF Address of second register to read from.
Read Register Address Three 0000 ~ FFFF Address of third register to read from
Write Register Address One 0000 ~ FFFF Address of first register to write to.
Write Register Address Two 0000 ~ FFFF Address of second register to write to.
Write Register Address Three 0000 ~ FFFF Address of third register to write to.
Page 68

53
PROFIBUS Diagnostics
Section 3-7
3-7 PROFIBUS Diagnostics
The PRT1-SCU11 provides extended diagnostics over PROFIBUS to notify
the PROFIBUS DP Master of the Unit’s status and the status of the RS-422A/
RS-485 communication. These extended diagnostics are sent to the Master
unit via a PROFIBUS Diagnostics message. These messages are only sent
up on occurrence of the error or status event.
A PROFIBUS Diagnostics message will contain 6 standard diagnostics bytes,
followed by the Extended diagnostics bytes, in case any extended diagnostics
data is available. The extended diagnostics bytes as produced by the PRT1SCU11 are shown below.
Note 1. Byte 1 in the figure above represents the 7th byte in a diagnostics mes-
sage. The first 6 bytes (not shown here) are standard diagnostics.
2. If a bit flag in byte 2 to 5 is ON, the corresponding device on the RS-422A/
RS-485 network is not responding or it has reported a communication error.
Byte 1
7654 3210
Block length (Bytes)
Including Header byte
Fixed to 00
Byte 2
76543 210
Device 01 Comm. error
Device 02 Comm. error
Device 03 Comm. error
Device 04 Comm. error
Device 05 Comm. error
Device 06 Comm. error
Device 07 Comm. error
Device 08 Comm. error
76543 210
Device 09 ~ 16 Comm. error
Byte 3
Byte 4
76543 210
Device 17 ~ 24 Comm. error
Byte 5
76543 210
Device 25 ~ 31 Comm. error
Byte 6, Byte 7
76543 210
Reserved
76543 210
Reserved
Byte 8, Byte 9
Page 69

54
Auxiliary RS-232C interface
Section 3-8
3-8 Auxiliary RS-232C interface
The PRT1-SCU11 provides an RS-232C interface, behind a cover lid on the
front of the Unit. This interface allows a user to connected an IBM compatible
computer with a serial port and send and receive data to a Compoway-F, or KFormat device using the software package CX-Thermo.
Equally, when Memobus has been selected as the protocol, the RS-232C
interface can be used to transfer commands from CX-Drive and the Varispeed
F7 Inverter.
Using CX-Thermo Before using CX-Thermo DIP-switch 4 must be set on, a group of four DIP-
switches is located on the front of the PRT1-SCU11 Unit.
Note CX-Thermo is not shipped with the PRT1-SCU11.
!WARNING
When DIP-switch 4 is switched on, the PRT1-SCU11 will stop the data
exchange with the PROFIBUS Master. The PROFIBUS DP interface will stay
inactive until switch 4 is switch off.
When DIP-switch 4 is set on:
• The diagnostics indicates Slave Not_Ready.
• FERR LED is switched off.
• COMM LED starts flashing.
• FCOM start flashing.
• BF LED is switched off.
To connect with the PRT1-SCU11 use an auxiliary RS-232C compatible interface on an IBM compatible computer and a standard Omron RS-232C PLC
cable e.g. (CS1W-CN226).
Note The interface connection is not galvanically isolated.
The baud rate settings are the same as used for the Compoway-F interface,
as set through the associated DIP-switches.
Page 70

55
Auxiliary RS-232C interface
Section 3-8
To connect with the unit use the second button in the menu, starting from the
left, see figure below.
When connected with CX-Thermo you can configure the required Temperature Controller. For detailed information please use the ThermoTool online
help and read the manual of the used Temperature Controller.
Note Make sure that the baud rate settings in CX-Thermo is the same as selected
on the PRT1-SCU11 with DIP-switch 1 and 2. It is required to use the following communication format:
• Data length: 7 bits
• Stop bit length: 2 bits
• Parity: even
Page 71

Page 72

57
SECTION 4
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
This section describes the troubleshooting procedures and maintenance operations needed to keep the PROFIBUS network
optimally working.
4-1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4-2 Troubleshooting Using LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4-2-1 Unit Led Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4-2-2 RS-422A / RS-485 Communication LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4-2-3 PROFIBUS LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
4-3 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
4-3-1 Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
4-3-2 Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
4-4 Replacing the Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
4-4-1 Replacement Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Page 73

58
Overview
Section 4-1
4-1 Overview
The PRT1-SCU11 has several LED indicators, allowing the user to troubleshoot and check the operation.
These LED indicators are:
• RUN, indicates normal operation.
• ERR, fatal error.
• FCOM, RS-422A / RS-485 communication.
• FERR, communication error on RS-422A / RS-485.
• COMM, communication with PROFIBUS Master.
• BF, all communication with the PROFIBUS Master has lost or configuration/parameter error occurs.
The LED’s can be categorized into 3 categories.
1. Unit LED indicators.
2. RS-422A / RS-485 Communication LED indicators.
3. PROFIBUS communication LED indicators.
4-2 Troubleshooting Using LED Indicators
4-2-1 Unit Led Indicators
The Unit LED’s indicate the status of the PRT1-SCU11. These are the two
highest LED’s. In the next table there is an overview of all possible LED states
of the two Unit LED’s. A description of the error and a possible solution to
solve the error.
4-2-2 RS-422A / RS-485 Communication LED Indicators
The Unit LED indicators show the status of the communication with Compoway-F, Host Link, K-Format or Memobus over RS-422A / RS-485. These are
the two LED’s in the middle. In the next table an overview of all possible LED
states of the two LED indicators, a description of the error and a possible
solutions to solve the error are presented.
Unit LED’s
RUN ERR Description Solution
Lit Not lit Normal operation -
Not lit Not lit • Initialization fails.
• No power connected to the Unit.
• Restart the module by switching the power off and
on, if the problem remains replace the Unit.
• Switch power to the Unit.
Not lit Blinks Initialization error during startup. Restart the module by switching the power off and on,
if the problem remains replace the Unit.
Not lit Lit Fatal error. Restart the module by switching the power off and on,
if the problem remains replace the Unit.
Page 74

59
Troubleshooting Using LED Indicators
Section 4-2
4-2-3 PROFIBUS LED Indicators
The Unit LED indicators show the status of the communication with PROFIBUS. These are the two lowest LED’s. In the next table an overview of all possible LED states of the two PROFIBUS LED indicators, a description of the
error and a possible solutions to solve the error are presented.
RS-422A / RS-485 LED’s
FCOM FERR Description Solution
Not lit Not lit • No communication over RS-422A /
RS-485. Probably a broken wire.
• Unit has not initialized.
• Not all devices configured in the PRT1SCU11 are communicating.
• No power connected to the Unit.
• No PROFIBUS communication. Unit
has not been initialized with a configuration and cannot proceed with RS422A/ RS-485 communication.
• Check all cables and connections.
• Switch the Unit off and on, make sure the network
configuration has been downloaded.
• Check Compoway-F, Host Link, K-Format or
Memobus addresses, baud rate settings. If baud
rate settings are changed a restart must performed
• Switch power to the Unit. The hardware does not
correspond with the configured network in the software.
Lit Not lit Communication with RS-422A / RS-485
devices fails, the Unit is unable to establish communication with all devices.
-
Blinks Not lit Communication by auxiliary port selected. • End your ThemoTools session and switch DIP-
switch 4 to off. Switch to the old baud rate settings
if these ware changed, when baut rate settings are
changed a restart must performed.
Not lit Lit No communication with RS-422A / RS-
485 network.
• Check Compoway-F, Host Link, K-Format or
Memobus addresses, baud rate settings, when
baut rate settings are changed a restart must performed.
• Check all cables and connections.
PROFIBUS LED
COMM BF Description Solution
Not lit Not lit No power connected to the Unit Switch power to the Unit
Not lit Lit No communication with PROFIBUS Mas-
ter
• Check if the PROFIBUS Master is running
• Check all PROFIBUS cables and connections, termination resistor.
Not lit Blinks The wrong module selected in the network
configuration
• The hardware does not correspond with the configured network in the software,
• Check also the PROFIBUS addresses of the Unit
Blinks Not lit Compoway-F, K-Format or Memobus
communication through the auxiliary port
• End your ThemoTools / CX-Drive session and
switch DIP-switch 4 to off. Switch to the old baud
rate settings if these ware changed, when baut rate
settings are changed a restart must performed
Lit Not lit Communication in progress -
Page 75

60
Maintenance
Section 4-3
4-3 Maintenance
This section describes the routine cleaning and inspection recommended as
regular maintenance.
4-3-1 Cleaning
Clean the PRT1-SCU11 regularly as described below in order to keep it in an
optimum operating condition.
• Regularly wipe the Unit with a dry, soft cloth.
• If a spot cannot be removed with a dry cloth, dampen the cloth with a neutral cleaner, wring out the cloth and wipe the Unit.
!Caution
Never use volatile solvents such as paint thinner, benzine or chemical wipes.
These substances could damage the surface of the Unit.
4-3-2 Inspection
Be sure to inspect the system periodically to keep it in optimum operating condition. In general, inspect the system once or twice a year, but more frequently if the system is used in high temperature or high humidity
environments or dirty/dusty conditions.
Inspection Equipment Prepare the following equipment before inspecting the system.
Required Equipment
Phillips type screwdriver, multimeter, alcohol, and a clean cloth.
Optional Test Equipment
Depending on system conditions, a synchroscope, oscilloscope, thermometer
or hygrometer (to measure humidity) might be needed.
Inspection Procedure Check the items in the following table and correct any that are below stan-
dard.
Item Standard Equipment
Environmental
conditions
Ambient temperature 0° C to 55° C Thermometer
Ambient humidity 10% to 90% Hygrometer
Dust/dirt accumulation None ---
Installation Are the units installed securely? No looseness ---
Are the communications connectors fully inserted?
No looseness ---
Are the external wiring screws
tight?
No looseness ---
Are the connecting cables undamaged?
No damage ---
Page 76

61
Replacing the Unit
Section 4-4
4-4 Replacing the Unit
4-4-1 Replacement Precautions
The PRT1-SCU11 is a network device. If the Unit is damaged, it will effect the
entire Network, so always ensure repairs are undertaken immediately. It is
recommended to have a spare PRT1-SCU11 on hand so that repairs may be
conducted quickly.
Replacement Precautions Observe the following precautions when replacing the Unit.
• Always turn OFF the power before replacing the Unit.
• Ensure that the new Unit is not faulty.
• If a poor connection is suspected of causing the malfunction, clean the
connectors using a clean, soft cloth and industrial-grade alcohol. Remove
any lint or threads left from the cloth, and remount the Unit.
• When returning a faulty unit for repair, always attach a detailed fault
report to the unit and return it to the nearest OMRON dealer.
Note 1. In order to prevent faulty operation be sure to turn off the power to all mas-
ter and slave devices before replacing the Unit.
2. When replacing the Unit, do not reconnect it to the Network before carrying
out the procedures listed below.
Page 77

Page 78

63
Appendix A
Memory Mapping
A-1 Memory Mapping for Compoway-F Devices
The table below lists the Mapping of individual parameters in the Basic and Extended on to the applicable Temperature Controller variable areas.
The table below lists the command codes used by the PRT1-SCU11 to translate the Special Operation Commands to mini FINS messages.
Note Each type of command lists two possible channel addressing methods: the first row specifies commands
for individual channels, the second row the command for all channels.
Parameter Read/
Write
MRC/
SRC
E5_N E5ZN E5_R
Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3 Channel 4
Basic block
SV W 0102 C1:0003 C1:0003 C1:0103 C1:0003 C1:0103 C1:0203 C1:0303
PV R 0101 C0:0000 C0:0000 C0:0100 C0:0000 C0:0100 C0:0200 C0:0300
Extended block
SV W 0102 C1:0003 C1:0003 C1:0103 C1:0003 C1:0103 C1:0203 C1:0303
Special
Operation
Command
W See table below
PV R 0101 C0:0000 C0:0000 C0:0100 C0:0000 C0:0100 C0:0200 C0:0300
Status R 0101 C0:0001 C0:0001 C0:0101 C0:0001 C0:0101 C0:0201 C0:0301
MV1 R 0101 C0:0004 C0:0004 C0:0104 C0:0004 C0:0104 C0:0204 C0:0304
MV2 R 0101 C0:0005 C0:0005 C0:0105 C0:0005 C0:0105 C0:0205 C0:0305
Special
Operation
Executed
R See table below
Parameter
(See Note)
MRC/
SRC
Cmd
Code
E5_N E5ZN E5_R
Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3 Channel 4
Special Operation
Run / Stop 3005 01 00 / 01 00 / 01 10 / 11 00 / 01 10 / 11 20 / 21 30 / 31
3005 01 NA F0 / F1 F0 / F1
AT Cancel/
Execute
3005 03 00 / 01 00 / 01 10 / 11 01 and 0A
Refer to E5AR/E5ER Digital Controller Users
Manual (Z182-E1-
@
)
for details
3005 03 NA F0 / F1
Auto/
Manual
3005 09 NA 00 / 01 10 / 11 00 / 01 10 / 11 20 / 21 30 / 31
3005 09 NA F0 / F1 F0 / F1
Page 79

64
Memory Mapping Appendix A
A-2 Parameter / Command Mapping for K-Format Devices
The table below lists the Mapping of individual parameters in the Basic and Extended blocks on to the E5AK/
E5EK Intelligent Digital Controller. Refer to the E5AK and E5EK Operation Manuals (H083-E1-
@,
H085-E1-@)
for more information
.
Parameter Read/
Write
Parameter
Number
Remarks
Basic
Setpoint W 01
Special operation W -- Special Command is used to initiate Run or Stop.
• 0000 = Run
• 0001 = Stop
PV monitor R 00
SP monitor R 01
Status A group R -- Special Command is used to read Status A/Status B.
• 0000 = Status group A
• 0001 = Status group B
Status B group R
Operation Execute R -- Response to Special Operation is returned.
Extended block
Setpoint W 01
Special operation W -- Special Command is used to initiate Run or Stop.
• 0000 = Run
• 0001 = Stop
Alarm Value 1 W 02
Alarm Value 2 W 03
PV monitor R 00
SP monitor R 01
Status A group R -- Special Command is used to read Status A/Status B.
• 0000 = Status group A
• 0001 = Status group B
Status B group R
Operation Execute R -- Response to Special Operation is returned.
Page 80

65
Memory Mapping Appendix A
A-3 Parameter / Command Mapping for Memobus Devices
The table below lists the Mapping of individual parameters in the Fixed and Flexible I/O blocks on to the OYMC
Varispeed F7 Inverter. Refer to the F7 Inverter’s Operation Manual (YEG-TOE-S616-55.1-OY) for more information
.
Note Being able to write to the voltage register, a special firmware version - VSF108981 - for the Varispeed F7
Inverter is required. Contact your supplier on how to obtain this firmware upgrade.
Parameter Read/
Write
Register Number
(Hex)
Remarks
Fixed block
Command register W 0001
Frequency register W 0002
Voltage register W 0003 See Note
Status register R 0020
Frequency register R 0023
Voltage register R 0025
Flexible block
Write register 1 W 0000 ~ FFFF The registers to read/write can be selected by the user
when setting up the PROFIBUS I/O configuration.
An invalid register address selection (i.e. non-existent or
read-only) will result in a Memobus error.
Write register 2 W 0000 ~ FFFF
Write register 3 W 0000 ~ FFFF
Read register 1 R 0000 ~ FFFF
Read register 2 R 0000 ~ FFFF
Read register 3 R 0000 ~ FFFF
Page 81

Page 82

67
Appendix B
Function Block Programming
B-1 Introduction
In order to facilitate the data transfer to and from Temperature Controllers from a CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS DP Master via the PRT1-SCU11, OMRON provides a number of PLC Function Blocks. These function
blocks can be used in the CS1/CJ1 PLC program to assemble the output data or extract the input data from the
CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master I/O data areas. This appendix describes these function blocks.
Note Function Blocks are only supported by CX-Programmer version 5.0 and higher.
B-2 Basic / Extended Function Blocks
A total of 10 function blocks are provided for the basic and extended I/O configuration blocks for the E5_N,
E5ZN and E5_R Temperature controllers. The table below lists the specifics of these function blocks.
Item Description
Basic function Writes the SV/Operation command and reads the PV/MV/Status/Operation Executed word.
Symbol
Note Only the function block for a 4 channel E5_R is shown. The other function blocks are limited
versions of this one.
Start Word
Profibus output data
Start Word
Profibus input data
SV Channel 1
SV Channel 2
SV Channel 3
SV Channel 4
Operation Command word
PV Channel 1
MV1 Channel 1
MV2 Channel 1
Status High Word Channel 1
Status Low Word Channel 1
PV Channel 2
MV1 Channel 2
MV2 Channel 2
Status High Word Channel 2
Status Low Word Channel 2
PV Channel 3
MV1 Channel 3
MV2 Channel 3
Status High Word Channel 3
Status Low Word Channel 3
PV Channel 4
MV1 Channel 4
MV2 Channel 4
Status High Word Channel 4
Status Low Word Channel 4
Special Operation Executed
Word
Start Trigger
(BOOL)
EN
(BOOL)
ENO
(UINT)
StratWordOutput
(WORD )
PV_CH1
(UINT)
StartWordInput
(WORD )
MV1_CH1
(WORD)
SV_CH1
(WORD )
MV2_CH1
(WORD)
SV_CH2
(WORD )
Status_HW_CH1
(WORD)
SV_CH3
(WORD )
Status_LW_CH1
(WORD)
SV_CH4
(WORD )
PV_CH2
(WORD)
Oper_Cmmnd
(WORD )
MV1_CH2
(WORD)
MV2_CH2
(WORD)
Status_HW_CH2
(WORD)
Status_LW_CH2
(WORD)
PV_CH3
(WORD)
MV1_CH3
(WORD)
MV2_CH3
(WORD)
Status_HW_CH3
(WORD)
Status_LW_CH3
(WORD)
PV_CH4
(WORD)
MV1_CH4
(WORD)
MV2_CH4
(WORD)
Status_HW_CH4
Status_LW_CH4
Operation_Exec
Page 83

File name PRT1_SCU11_E5_N_Basic_1CH.cxf
PRT1_SCU11_E5_N_Extended_1CH.cxf
PRT1_SCU11_E5_R_Basic_1CH.cxf
PRT1_SCU11_E5_R_Basic_2CH.cxf
PRT1_SCU11_E5_R_Basic_4CH.cxf
PRT1_SCU11_E5_R_Extended_1CH.cxf
PRT1_SCU11_E5_R_Extended_2CH.cxf
PRT1_SCU11_E5_R_Extended_4CH.cxf
PRT1_SCU11_E5ZN_Basic_2CH.cxf
PRT1_SCU11_E5ZN_Extended_2CH.cxf
Function description • Writes SV/Operation command to the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master I/O addresses
allocated to the targeted Temperature Controller.
• Reads PV/MV/Status/Operation Executed words from the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master I/O addresses allocated to the targeted Temperature Controller.
EN Input condition Connect EN to an OR between an upwardly differentiated condition for the start trigger and the
BUSY output from the Function Block.
Restrictions on Input
variables
• Always use an upwardly differentiated condition for the EN.
• If the Input variables are out of range, the ENO flag will turn OFF and the Function Block will not
be processed.
Application example
Note Only the function block for a 4 channel E5_R is shown. The other function blocks are limited
versions of this one.
Item Description
Start Word Profibus output data
&3300
Start Word Profibus input data
&3200
SV Channel 1
&100
SV Channel 2
#75
SV Channel 3
125
SV Channel 4
126
Operation Command word
#0062
PV Channel 1
1000
MV1 Channel 1
1001
MV2 Channel 1
1002
Status High Word Channel 1
1003
Status Low Word Channel 1
1004
PV Channel 2
1005
MV1 Channel 2
1006
MV2 Channel 2
1007
Status High Word Channel 2
1008
Status Low Word Channel 2
1009
PV Channel 3
1010
MV1 Channel 3
1011
MV2 Channel 3
1012
Status High Word Channel 3
1013
Status Low Word Channel 3
1014
PV Channel 4
1015
MV1 Channel 4
1016
MV2 Channel 4
1017
Status High Word Channel 4
1018
Status Low Word Channel 4
1019
Special Operation Executed Word
1020
Start Trigger
(BOOL)
EN
(BOOL)
ENO
(UINT)
StratWordOutput
(WORD )
PV_CH1
(UINT)
StartWordInput
(WORD )
MV1_CH1
(WORD)
SV_CH1
(WORD )
MV2_CH1
(WORD)
SV_CH2
(WORD )
Status_HW_CH1
(WORD)
SV_CH3
(WORD )
Status_LW_CH1
(WORD)
SV_CH4
(WORD )
PV_CH2
(WORD)
Oper_Cmmnd
(WORD )
MV1_CH2
(WORD)
MV2_CH2
(WORD)
Status_HW_CH2
(WORD)
Status_LW_CH2
(WORD)
PV_CH3
(WORD)
MV1_CH3
(WORD)
MV2_CH3
(WORD)
Status_HW_CH3
(WORD)
Status_LW_CH3
(WORD)
PV_CH4
(WORD)
MV1_CH4
(WORD)
MV2_CH4
(WORD)
Status_HW_CH4
Status_LW_CH4
Operation_Exec
Page 84

69
Function Block Programming Appendix B
The table below lists the Input and Output variables for the basic / extended function blocks.
Note The table lists all possible variables for the maximum size function block, i.e. the Extended block for the
E5_R. For other basic / extended function blocks subsets of variables apply.
Name Variable name Data
type
Default Range Description
Input variables
EN EN BOOL 1 (ON): Function block started
0 (OFF): Function block not started
Start Word
PROFIBUS Output data
StartWordOutput UINT 3000 Start Word of PROFIBUS Output data in
PROFIBUS Master Output data area.
Start Word
PROFIBUS Input
data
StartWordInput UINT 3010 Start Word of PROFIBUS Input data in PROFI-
BUS Master Input data area.
SV values SV_CH1 WORD 0 SV Channel 1
SV_CH2 WORD 0 SV Channel 2
SV_CH3 WORD 0 SV Channel 3
SV_CH4 WORD 0 SV Channel 4
Operation Command
Oper_Cmmnd WORD 0 Special Operation Executed word
Output variables
ENO ENO BOOL 1 (ON): Function block processed normally
0 (OFF): Function block not processed or
ended in an error
Process variables PV_CH1 WORD PV Channel 1
MV1_CH1 WORD MV1 Channel 1
MV2_CH1 WORD MV2 Channel 1
Status_HW_CH1 WORD Status High Word Channel 1
Status_LW_CH1 WORD Status Low Word Channel 1
PV_CH2 WORD PV Channel 2
MV1_CH2 WORD MV1 Channel 2
MV2_CH2 WORD MV2 Channel 2
Status_HW_CH2 WORD Status High Word Channel 2
Status_LW_CH2 WORD Status Low Word Channel 2
PV_CH3 WORD PV Channel 3
MV1_CH3 WORD MV1 Channel 3
MV2_CH3 WORD MV2 Channel 3
Status_HW_CH3 WORD Status High Word Channel 3
Status_LW_CH3 WORD Status Low Word Channel 3
PV_CH4 WORD PV Channel 4
MV1_CH4 WORD MV1 Channel 4
MV2_CH4 WORD MV2 Channel 4
Status_HW_CH4 WORD Status High Word Channel 4
Status_LW_CH4 WORD Status Low Word Channel 4
Operation_Exec WORD 0 Special Operation Executed word
Page 85

70
Function Block Programming Appendix B
B-3 Operate Function Block
The Operate Function Block facilitates the transmission of aN OPERATE command to a specific temperature
Controller (refer to section
3-3-4 Free Communication Blocks
). The table below lists the specifics of this func-
tion block.
Item Description
Basic function Sends an Operation command to a specified Temperature Controller via PROFIBUS.
Symbol
File name PRT1_SCU11_Operate.cxf
Function description Sends an operation command to the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master I/O addresses allo-
cated to the targeted Temperature Controller, specified by the Unit No. The command is specified
by the command code and related information.
Precautions
EN Input condition Connect EN to an OR between an upwardly differentiated condition for the start trigger and the
BUSY output from the Function Block.
Restrictions on Input
variables
• Always use an upwardly differentiated condition for the EN.
• If the Input variables are out of range, the ENO flag will turn OFF and the Function Block will not
be processed.
Restrictions on Output variables
• This function block requires multiple cycles to process. Always connect an OR including the
BUSY output variable to the EN input variable to ensure that the function block is processed to
completion (see Symbol)
• Do not turn the BUSY output variable ON or OFF outside the function block.
Application example
Start Word
Profibus output data
Start Word
Profibus input data
Unit No of TC
Command Code
Related information to the
operation command
Response code from TC
Busy flag
Start Trigger
(BOOL)
EN
(BOOL)
ENO
(UINT)
StratWordOutput
(WORD)
ResponseCode
(UINT)
StartWordInput
(BOOL)
Busy
(UINT)
UnitNo
(UINT)
CommandCode
(UINT)
RelatedInformation
Busy Flag
Timechart
Start Trigger
ON
OFF
Busy Flag (BUSY)
ON
OFF
FB execution completed.
A
t normal end: Sending data has been completed.
Start Word Profibus output data
&3200
Start Word Profibus input data
&3300
Unit No of TC
&1
Command Code
#01
Related information to the operation command
#10
Response code from TC
Channel 2
Busy flag
Bit B
Bit A
(BOOL)
EN
(BOOL)
ENO
(UINT)
StratWordOutput
(WORD )
ResponseCode
(UINT)
StartWordInput
(BOOL)
Busy
(UINT)
UnitNo
(UINT)
CommandCode
(UINT)
RelatedInformation
Bit B
Page 86

71
Function Block Programming Appendix B
The table below lists the Input and Output variables for the Operate function block.
B-4 Read Function Block
The Read Function Block facilitates the transmission of a READ command to a specific temperature Controller
(refer to section
3-3-4 Free Communication Blocks
). The table below lists the specifics of this function block.
Name Variable name Data
type
Default Range Description
Input variables
EN EN BOOL 1 (ON): Function block started.
0 (OFF): Function block not started.
Start Word
PROFIBUS Output data
StartWordOutput UINT 3000 Start Word of PROFIBUS Output data in
PROFIBUS Master Output data area.
Start Word
PROFIBUS Input
data
StartWordInput UINT 3010 Start Word of PROFIBUS Input data in PROFI-
BUS Master Input data area.
Unit No of device UnitNo UINT 0 #0 - #63
(0-99)
Unit number of device.
Command code CommandCode UINT 0 Variable type in device.
Information
related to the
operation command
RelatedInformation UINT 0 Specify the Write Start address.
Output variables
ENO ENO BOOL 1 (ON): Function block processed normally
0 (OFF): Function block not processed or
ended in an error.
Result of execution of the command
ResponseCode WORD Outputs the error code when execution ended
in an error in the communications command
level. Refer to section
3-3-4 Free Communica-
tion Blocks
for more information.
Busy flag BUSY BOOL Automatically turns OFF when processing is
completed.
Item Description
Basic function Reads data from a Temperature Controller’s variable area.
Symbol
File name PRT1_SCU11_Read_Data.cxf
Function description Sends a Read Data command to the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master I/O addresses allo-
cated to the targeted Temperature Controller, specified by the Unit No. The data to be read is specified by the Variable Type and the Read Start Address.
Start Word
Profibus output data
Start Word
Profibus input data
Unit No of TC
Variable Type
Read Start address from TC
Response code from TC
Data read from TC
Busy flag
Start Trigger
(BOOL)
EN
(BOOL)
ENO
(UINT)
StratWordOutput
(WORD)
ResponseCode
(UINT)
StartWordInput
(DWORD)
DataRead
(UINT)
UnitNo
(BOOL)
Busy
(UINT)
VarType
(UINT)
ReadStartAddress
Busy Flag
Page 87

72
Function Block Programming Appendix B
The table below lists the Input and Output variables for the Read function block.
Precautions
EN Input condition Connect EN to an OR between an upwardly differentiated condition for the start trigger and the
BUSY output from the Function Block.
Restrictions on Input
variables
• Always use an upwardly differentiated condition for the EN.
• If the Input variables are out of range, the ENO flag will turn OFF and the Function Block will not
be processed.
Restrictions on Output variables
• This function block requires multiple cycles to process. Always connect an OR including the
BUSY output variable to the EN input variable to ensure that the function block is processed to
completion (see Symbol)
• Do not turn the BUSY output variable ON or OFF outside the function block.
Application example
Name Variable name Data
type
Default Range Description
Input variables
EN EN BOOL 1 (ON): Function block started.
0 (OFF): Function block not started.
Start Word
PROFIBUS Output data
StartWordOutput UINT 3000 Start Word of PROFIBUS Output data in
PROFIBUS Master Output data area.
Start Word
PROFIBUS Input
data
StartWordInput UINT 3010 Start Word of PROFIBUS Input data in
PROFIBUS Master Input data area.
Unit No of device UnitNo UINT 0 #0 - #63
(0-99)
Unit number of device.
Variable Type VarType UINT 0 Variable type in device.
Read Start
address from
device
ReadStartAddress UINT 0 Specify the Read Start address.
Item Description
Timechart
Start Trigger
ON
OFF
Busy Flag (BUSY)
ON
OFF
FB execution completed.
A
t normal end: Sending data has been completed.
Start Word Profibus output data
&3200
Start Word Profibus input data
&3300
Unit No of TC
&1
Variable Type
#C0
Read Start address from TC
#0100
Response code from TC
Channel 2
Data read from TC
Channel 2
Busy flag
Bit B
it A
(BOOL)
EN
(BOOL)
ENO
(UINT)
StratWordOutput
(WORD)
ResponseCode
(UINT)
StartWordInput
(DWORD)
DataRead
(UINT)
UnitNo
(BOOL)
Busy
(UINT)
VarType
(UINT)
ReadStartAddress
it B
Page 88

73
Function Block Programming Appendix B
Note The function block ensures that Double Word sized data read from the Temperature Controller is cor-
rectly formatted, to match the DWORD data type as defined in the PLC.
B-5 Write Function Block
The Write Function Block facilitates the transmission of a WRITE command to a specific temperature Controller (refer to section
3-3-4 Free Communication Blocks
). The table below lists the specifics of this function block.
Output variables
ENO ENO BOOL 1 (ON): Function block processed normally.
0 (OFF): Function block not processed or
ended in an error.
Result of execution of the command
ResponseCode WORD Outputs the error code when execution ended
in an error in the communications command
level. Refer to section
3-3-4 Free Communica-
tion Blocks
for more information.
Data read from
the device
DataRead DWORD Data read from the device.
(See Note)
Busy flag BUSY BOOL Automatically turns OFF when processing is
completed.
Item Description
Basic function Writes data to a Temperature Controller’s variable area.
Symbol
File name PRT1_SCU11_Write_Data.cxf
Function description Sends a Write Data command to the CS1/CJ1W-PRM21 PROFIBUS Master I/O addresses allo-
cated to the targeted Temperature Controller, specified by the Unit No. The data to be written and
the location to write is to are specified by the DataWrite and the WordStartAddress variables.
Precautions
EN Input condition Connect EN to an OR between an upwardly differentiated condition for the start trigger and the
BUSY output from the Function Block.
Restrictions on Input
variables
• Always use an upwardly differentiated condition for the EN.
• If the Input variables are out of range, the ENO flag will turn OFF and the Function Block will not
be processed.
Name Variable name Data
type
Default Range Description
Start Word
Profibus output data
Start Word
Profibus input data
Unit No of TC
Variable Type
Write Start address from TC
Data to be written
Response code from TC
Busy flag
Start Trigger
(BOOL)
EN
(BOOL)
ENO
(UINT)
StratWordOutput
(WORD)
ResponseCode
(UINT)
StartWordInput
(BOOL)
Busy
(UINT)
UnitNo
(UINT)
VarType
(UINT)
WriteStartAddress
(DWORD)
Busy Flag
Timechart
Start Trigger
ON
OFF
Busy Flag (BUSY)
ON
OFF
FB execution completed.
A
t normal end: Sending data has been completed.
Page 89

74
Function Block Programming Appendix B
The table below lists the Input and Output variables for the Write function block.
Note The function block ensures that Double Word sized data written to the Temperature Controller is cor-
rectly formatted.
Restrictions on Output variables
• This function block requires multiple cycles to process. Always connect an OR including the
BUSY output variable to the EN input variable to ensure that the function block is processed to
completion (see Symbol)
• Do not turn the BUSY output variable ON or OFF outside the function block.
Application example
Response data is copied to channel 2 after Busy flag is OFF.
Name Variable name Data
type
Default Range Description
Input variables
EN EN BOOL 1 (ON): Function block started.
0 (OFF): Function block not started.
Start Word
PROFIBUS Output data
StartWordOutput UINT 3000 Start Word of PROFIBUS Output data in
PROFIBUS Master Output data area.
Start Word
PROFIBUS Input
data
StartWordInput UINT 3010 Start Word of PROFIBUS Input data in
PROFIBUS Master Input data area.
Unit No of device UnitNo UINT 0 #0 - #63
(0-99)
Unit number of device.
Variable Type VarType UINT 0 Variable type in device.
Write Start
address from
device
WriteStartAddress UINT 0 Start address of variable to which the data
must be written.
Data to be written DataWrite DWORD 0 Specify the data to be written.
Output variables
ENO ENO BOOL 1 (ON): Function block processed normally
0 (OFF): Function block not processed or
ended in an error.
Result of execution of the command
ResponseCode WORD Outputs the error code when execution ended
in an error in the communications command
level. Refer to section
3-3-4 Free Communica-
tion Blocks
for more information.
Busy flag BUSY BOOL Automatically turns OFF when processing is
completed.
Item Description
Start Word Profibus output data
&3200
Start Word Profibus input data
&3300
Unit No of TC
&1
Variable Type
#C1
Read Start address from TC
#0104
Data to be written
&99
Response code from TC
Channel 2
Busy flag
Bit B
it A
(BOOL)
EN
(BOOL)
ENO
(UINT)
StratWordOutput
(WORD)
ResponseCode
(UINT)
StartWordInput
(BOOL)
Busy
(UINT)
UnitNo
(UINT)
VarType
(UINT)
WriteStartAddress
(DWORD)
DataWrite
it B
Page 90

Index
Numbers
110 mH Inductor, 33
220 ohm resistor
, 33
2-wire
, 24
3-3-1 Using CX-Thermo
, 54
4-wire
, 24, 27
A
About
Manual
, ix
A-line
, 21
Auto-CLEAR
, 6
Auxiliary RS-323 interface
, 54
B
Basic Operating Procedure, 14
Baud rate
, 12, 20, 22, 32, 54
BF
, 19, 54, 58, 59
B-line
, 21
Broadcast
, 5, 47
Bus Access Protocol
, 2
Bus fail
, 19
Bus Termination
, 33
Bus termination
, 33
C
Cable, 32, 34
Cable Length
, 32
Cable length
, 3
Cable shield connection
, 34
Channel numbers
, 43
Chk_Cfg
, 19
Class 1
, 4
Class 1 Master
, 4
Class 2
, 4
Class 2 Master
, 4
Cleaning
, 60
CLEAR
, 5, 6
COMM
, 19, 54, 58, 59
Command code
, 43
Command word
, 42
Common parameters
, 38
Communication
Broadcast
, 5
Multicast
, 5
Multi-peer
, 5
Communication fails
, 44, 48
Communication format
, 22
Communication Medium
, 31
Compoway-F
, 9
Configuration
, 6, 35
Connector
, 12, 21, 34
Bus cable connector
, 34
DGND
, 22
RTS
, 21
VP
, 22
CX-Profibus
, 35, 36, 40, 44, 49
CX-Thermo
, 54, 55
D
Data length, 55
Data_Exchange
, 19
Declaration of Confirmity
, xv
Device profile
, 4
Diagnostic
, 5, 13
Digital Panel Meter
, 25
Dimensions
, 13
DIN-rail
, 23
DIP-switch
, 20
DIP-switches
, 18
Download configuration
, 35
DTM Configuration
, 36
E
E5AK/E5EK
Connection
, 28
Wiring
, 28
RS-422
, 28
E5AR
, 8, 26
E5ER
, 26
E5ZN
, 8, 25
Electro-magnetic compatibility
, 34
EMC directive
, xv
EN50170
, 2, 21
Environment
, 11
ERR
, 19, 58
Error code
, 43
Extensive Diagnostics
, 5
External Dimensions
, 13
Page 91

76
Index
F
F7 Inverter
Connection
, 29
Wiring
, 29
RS-422
, 29
RS-485
, 30
Fail-safe
, 6
FCOM
, 19, 54, 58, 59
FDT/DTM
FDT Container application
, 7
FDT/DTM Concept
, 7
FERR
, 19, 54, 58, 59
Fixed communication block
, 40, 41, 48, 51
Fixed communication blocks
, 40
Flexible communication blocks
, 40
Free communication block
, 40
Free Communication Blocks
, 9
Free communication blocks
, 40, 44
Front case
, 11
G-H
Galvanically isolated, 54
Gateway
Compoway-F
, 9
Configuration
, 10
Free Communication Blocks
, 9
I/O Data
, 9
setup
, 8
Special operations
, 9
Troubleshooting
, 10
unit
, 8
Generic slave DTM
Configuring
, 35
I/O Configuration
Appending
, 36
Inserting
, 36
Ground
, 34
GSD File
DTM
, 8
GSD file
, 7, 36
DP-master
, 7
DP-slave
, 7
General Section
, 7
Language
, 7
GSD File Language
, 7
GSD-file
, 7, 35
Host Link
, 9, 10, 50
I
I/O configuration, 36
I/O Data
, 9
I/O data
, 11, 13
I/O module
, 35
IEC 1158-2
, 2
Inductor
, 33
Inspection
, 60
Inspection Equipment
, 60
Inspection Procedure
, 60
Installation
, 11, 14
ISO-7498
, 2
K
K3GN Digital Panel Meter, 25
K-Format
Fixed Communication blocks
, 48
Free Communication blocks
, 49
Operation Execute
, 48
Parameters
, 48
Wiring
RS-422A
, 28
RS-485
, 28
L-M
LED, 18, 58
BF
, 19, 54, 58, 59
COMM
, 19, 54, 58, 59
ERR
, 19, 58
FCOM
, 19, 54, 58, 59
FERR
, 19, 54, 58, 59
RUN
, 19, 58
LED Indicators
Specifications
, 19
LED indicators
, 18, 58
Low voltage directive
, xv
MAC
, 4
Maintenance
, 60
Cleaning
, 60
Inspection
, 60
Manual
About
, ix
Revision history
, 79
Master
, 4
Master Devices
, 4
Maximum amount of data
, 40
Maximum number of devices
, 40
Maximum number of modules
, 40
MCW151
, 8, 9, 27
Memobus
Fixed Communication blocks
, 51
Flexible Communication blocks
, 51
Page 92

Index
77
Parameters, 52
Wiring
RS-422A
, 29
RS-485
, 30
Module parameters
, 38
Monitoring
Interval
, 5
Master
, 5
Slave
, 6
Mounting
, 23
Mounting Procedure
, 23
MRC/SRC
, 45
Multicast
, 5
Multi-peer
, 5
N
Network operation modes
Auto-CLEAR
, 6
CLEAR
, 6
Fail-safe State
, 6
OFF-LINE
, 6
OPERATE
, 6
STOP
, 6
Network structure
, 31
Linear bus topology
, 31
Repeater
, 31
Tree topology
, 31
Node address
, 19, 30
Noise
, 23
Not_Ready
, 54
O-P
OFF-LINE, 6
OMRON
Copyright notice
, vi
OPERATE
, 6
Operation
, 45
Operation mini FINS command
, 45
OSI
ISO-7498
, 2
Layer 1
, 2, 3
Layer 2
, 2, 4
Layer 3
, 3
Layer 7
, 2
Medium Access Control
, 4
OSI Layer 1, 2 and User Interface
, 3
Polling Procedure
, 4
Token Passing
, 4
OSI reference model
, 2
Parameters
, 38
Common
, 38
Module
, 38
Parity
, 55
Pheripheral setting
, 21
Polling Procedure
, 4
Precautions
, 23
Application
, xiii
General
, xii
Operating Environment
, xiii
Safety
, xii
PROFIBUS
, 2
Diagnostics
, 53
PROFIBUS-DP
, 2
PROFIBUS-FMS
, 2
PROFIBUS-PA
, 2
R
R88A-MCW151-E, 8, 9, 27
Read
, 45
Read mini FINS command
, 45
Receiver line
, 22
Repeater
, 3
Replacement
, 61
Response word
, 42
Rotary switch
, 19
RS-232C
, 9, 12, 18, 54
RS-422
, 9, 22
RS-422A
, 27
RS-485
, 3, 9, 22, 24, 25, 31
Cable Type
, 32
RUN
, 19, 58
S
Safety Precautions, xii
Sending Free Communication
, 47
Services
, 13
Set_Prm
, 19
Shielding
, 34
shock resistance
, 11
Slave
, 4
Slave Devices
, 4
Special Operation
, 42
Special operations
, 9, 41
Specifications
, 10
Status word
, 50
STOP
, 6
Stop bit
, 55
Stub Lines
, 33
Page 93

78
Index
T
Temperature Controller, 26
Temperature Controllers
, 24
Termination resister
, 12
Termination Resistor
, 33
Token Passing
, 4
Trademarks
, vi
Transmission Speed
, 3
Transmission speed
, 3
Troubleshooting
, 10
U
Unit replacement, 61
Precautions
, 61
Using CX-Thermo
, 54
V-W
vibration resistance, 11
Watchdog
, 37
Wire A
, 34
Wire B
, 34
Wiring
, 34
Write
, 45, 46
Write mini FINS command
, 46
Page 94

79
Revision History
A manual revision code appears as a suffix to the catalog number on the front cover of the manual.
The following table outlines the changes made to the manual during each revision. The page numbers of a revision refer to the previous version.
Revision Code Date Revised Content
01 November 22, 2004 Initial version.
02 September 19, 2005 Changed manual title.
Corrected PROFIBUS DP naming to comply with PROFIBUS standards.
Changed unit name reference to Host Link / Compoway-F to RS-422A/RS-485.
Changed unit naming to more consistent name.
Page ix: Added Unit version table.
Page ix: Added E5_K and F7 Inverter manuals to table.
Page 6: Removed bullets from list.
Page 9: Added E5AK/E5EK and F7 Inverter to table.
Page 9: Added text below table on Auxiliary port connection t o other protocols.
Page 9: Added note on multiple protocol use.
Page 9: Added a branches for Memobus and K-Format protocol to image.
Page 9: Added description for Memobus and K-Format protocols.
Page 10: Removed sentence on Special Operation.
Page 10: Added paragraph on Fixed Communication blocks.
Page 10: Added descriptions on Memobus and K-Format protocol.
Page 11: Added text and version table to Specifications section.
Page 11: Changed ‘modules’ to ‘units’
Page 11: Changed I/O words to bytes.
Page 12: Reformatted specification table, added new protocols.
Page 14: Improved flow chart.
Page 19: Reformatted table.
Page 19: Improved text of section 2-1-3.
Page 20: Added paragraph on dip-switch 3.
Page 20: Reformatted information on switches in to tables and notes.
Page 21: Changed title of section 2-1-5.
Page 21: Reformatted table on switches, to include switch dependencies.
Page 21: Added Note to RS-422A/RS-485 table.
Page 22: Renamed sections 2-2 and 2-2-2.
Page 22: Reformatted communication formats in to table.
Page 23: Added note on baud rates to end of section 2-3-3.
Page 24: Added note on baud rates to end of section 2-3-4.
Page 25: Renamed E5ZN terminals in figure.
Page 25: Added note on baud rates to end of section 2-3-5.
Page 26: Added section 2-3-7 and 2-3-8.
Page 32: Added reference to CS1/CJ1 PROFIBUS Master manual.
Page 32: Improved text of section 2-6-1.
Page 35: Removed Note after example.
Revision code
Cat. No. W01E-EN-01
Page 95

02 September 19, 2005 Page 38: Added paragraph on Flexible communication blocks.
Page 38: Reformatted paragraph on PROFIBUS I/O size.
Page 40: Improved text and figures of section 3-3-2.
Page 41: Inserted new section 3-3-1.
Page 42: Improved text, reformatted table.
Page 43: Improved text on mini-FINS commands.
Page 44: Changed section 3-3-4 to 3-8, inserted new section 3-4.
Page 47: Inserted new sections 3-6 and 3-7.
Page 50, Renamed section 4.2.2.
Page 55: Added Appendices A2 and A3.
Removed Abbreviations section.
Revision Code Date Revised Content
 Loading...
Loading...