Page 1

Low Voltage Switch Gear
Appendix
Precautions
■ Notice
Use under rated condition, otherwise contactors will not only cause
malfunction, but also cause a fire or damage the contactor.
Life period of contactor depends on the operating application. Please
check the electrical life under real application in advance.
If you continue to use malfunctioning contactor, a fire or breakdown
may occur.
Do not miss-wire or miss-charge the power supply, otherwise the
contactor does not work correctly.
Do not operate in places with explosive or flammable gas, otherwise
a fire or explosion may occur by arc or heating from contactor.
Make sure to use the circuit well considered about safety, in case
there is any possibility to cause secondary disaster by contact trouble (welding, faulty contact).
Do not supply short-circuit current to electromagnetic switch (contactor with thermal relay). Doing so may result failure in heater of thermal relay. Please use short-circuit protection like fuse or protective
circuit breaker.
Do not use a contactor or thermal relay which has been dropped or
dismantled. Doing so may cause malfunction or a fire.
Make sure to shut off power supply to contactors before wiring or
replacing.
Do not operate the actuator of a contactor manually. Doing so may
cause contact welding by chattering or burn out by arc.
Unless otherwise stated in the catalogue,
modifications, especially those of stated values,
sizes and weights are subject to alternation.
Diagrams and tables are subject to alternation and
not to be regarded as binding drawings.
■ Correct use
General use
Unexpected malfunction may occur in real application. Please carry
out as many tests as possible.
Ratings in this catalogue measured under the condition according to
IEC unless otherwise specified. In cases of check by real application,
please carry out the test under the same condition as expected in the
actual application.
Selection
Coil specification
Please select suitable coil to circuit design, otherwise malfunction
may occur or coil may have a burn out by overvoltage etc.
Type
Please check contact ratings, switching capacity, thermal characteristics etc. when selecting product type.
Thermal relay
Motor current differs by supplier, type, number of poles, frequency.
Please confirm operational current level.
Coil surge suppressor
Coil surge suppressor type should be selected by contactor type,
auxiliary relay type and applied voltage. Make sure to use defined
each contactor.
In case of installing coil surge suppressor, please check the actual
circuit because the release time will be delayed.
Electrical life expectancy
Electrical life expectancy tests in this catalogue are based on IEC.
Circuit design
Supplied voltage waveform for input
Make sure to apply and remove the voltage instantly. Do not use
under the condition that the coil voltage waveform increases or
decreases gradually.
In case of DC contactor use (input voltage
ripple)
Please use DC contactor input voltage with a ripple ratio less than
5%. Excessive ripple (pulsating current) may cause contact welding.
Fluctuation of input voltage
Make sure to supply sufficient voltage to actuate contactors properly.
Continuous supply of insufficient voltage results in excessive heating
and may cause burn out of coil.
Maximum applied voltage
Do not supply the voltage over the maximum rated voltage, otherwise
burn out or insulation failure may occur.
The temperature inside control panel has much influence to the coil
temperature, so make sure not to exceed the specified value in the
catalogue.
Basically rated voltage should be supplied to coil. To supply higher
voltage than rated would result in shorter electrical life, even if it is
lower than the maximum rated voltage.
Reverse
Make sure to use reversible contactors for reverse operation.
Make sure to use interlock device in reverse operation by two contactors, otherwise short circuit current may burn out or give damage to
contactors and motors.
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 81
Page 2

Installation
Operation ambience
Mounting
Make sure to use specified wire size, mounting screw size, mounting
screw number, and DIN rail size.
Tightening Screw
Tighten each screw securely by specified tightening torque. Loose
tightening may cause a fire by excessive heating.
Combination
Please use only OMRON product combinations in case of thermal
relay, timer block and auxiliary contact block etc.
Wrong-combinations may result in damage to contactors.
Mounting direction
Some products have a defined specific mounting direction. Please
refer to datasheet before use.
Dust
Dust on the surface of the contacts could result in contact malfunctioning. Take countermeasure in excessive dusty surrounding.
Temperature, humidity
Use contactors within the temperature and humidity conditions specified in datasheet. To use or store contactor in excessive temperature
or humidity may result in malfunction of contact by organic film composed by sulfication and oxidation on the surface of the contacts.
Use contactors within the temperature and humidity conditions specified in the datasheet, to prevent contactors from insulation resistance failure by condensation or insulation resistance deterioration
by tracking.
Gas
NH3, H2S, SO2, CI2, Si and NO2 have bad effects on a contactor.
With these gases, a corrosive metal film ist generated on the surface
of the contacts and could result in contact malfunctioning. Use a contactor in low humidity and no corrosive gas surroundings.
Oil
Do not use a contactor in places where oil is sprayed onto the contactor. It will cause cracks on polymer parts.
Shock and vibration
Do not use a contactor in places where there is excessive shock or
vibration. It may cause malfunctioning.
Storage
Store contactors in a place with no direct sunshine or ultraviolet rays.
It will cause crack on polymer parts.
When contactors are to be stored for a long time, they must be stored
with care. Though it generally depends where contactors are stored,
deterioration of contacts may occur after long storage. Please check
the characteristics before use after long time storage.
82 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
Page 3
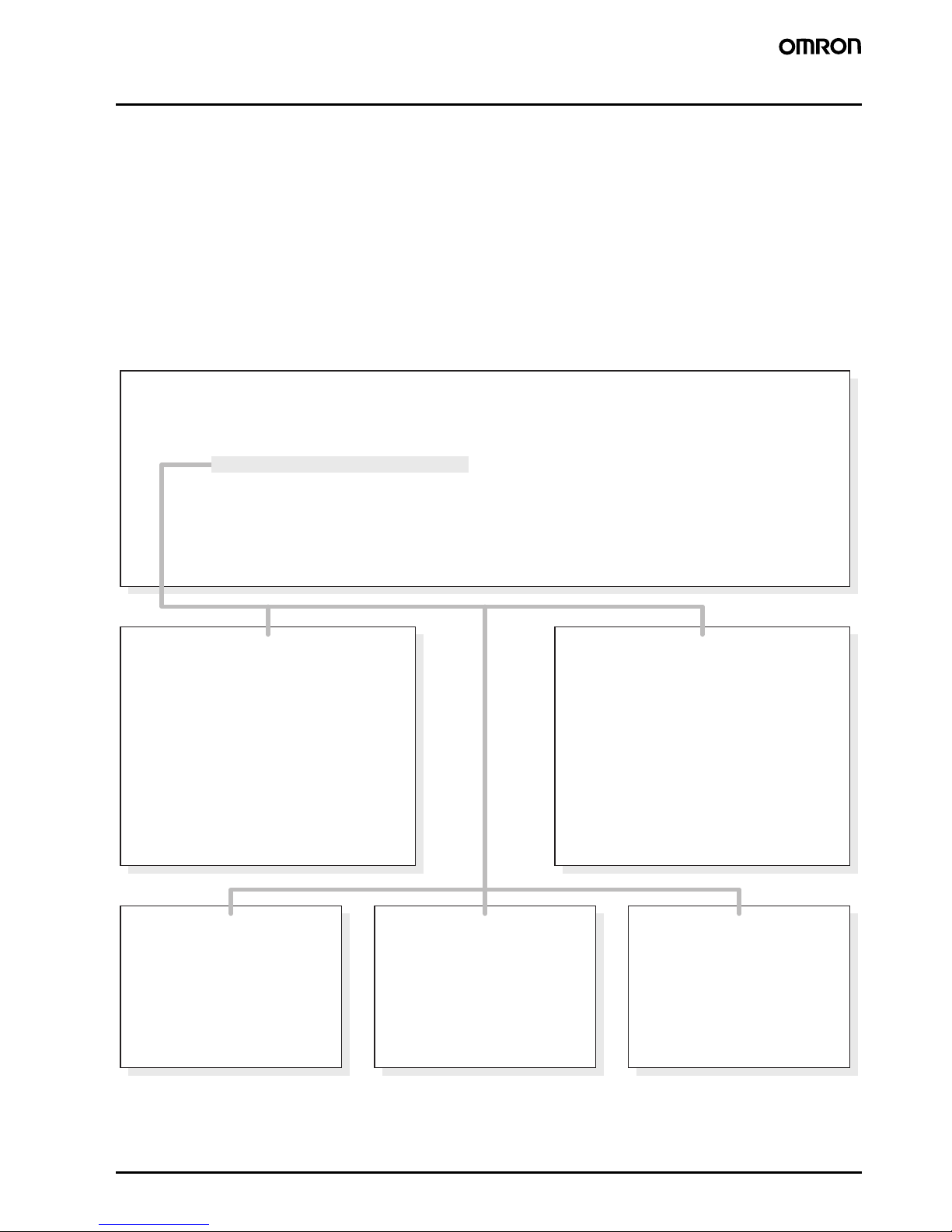
European Standards
■ IEC 947, EN 60947
European Standards for Low-Voltage Switchgear
For Europe and most other industrial countries of the world, the new
IEC 947 and EN 60 947 specifications for low-voltage switchgear
have unified the regulations which previously varied from nation to
nation.
This required the introduction of new terms, and new test methods
and utilization categories. The new specifications are aimed
primarily at manufacturers. However, the user also will come across
new technical terms and data in the manufacturers’ catalogues
and on the devices themselves which are important for the selection
and application of the devices. The present paper deals with the currently published specifications. Further specifications and
supplements are in preparation.
IEC 947
IEC 947-1 General rules
IEC 947-2 Circuit-breakers
IEC 947-3 Switches, disconnectors, switch-disconnectors and fuse-combination units
IEC 947-4-1 Connectors and motor-starters
IEC 947-5-1 Control circuit devices and switching elements
IEC 947-6-1 Multiple function equipment, Automatic transfer switching equipment
IEC 947-6-2 Multiple function equipment, Control and protective switching devices (or equipment)
(CPS)
IEC 947-7-1 Ancillary equipment
Since 1993, all low-voltage switchgear purchased in Europe had to
satisfy the EN 60 947 European Standard. Installations in existence
prior to 1993 are not affected by the standard and need not to be
refitted with new devices. Devices constructed and tested to the IEC
standards and EN standards can be used worldwide, with the exception of the USA and Canada. In these countries UL and CSA specifications continue to apply. Switchgear which conforms to IEC 947
and EN 60 947 and which has, in addition, UL- and CSA approvals,
in the meantime has entered the market. Such ‘world market’ devices
offer the advantage that they can be used throughout the world,
including the USA and Canada.
Conditions for compliance with
Type "1" coordination
(Extract from IEC 947-4-1)
- The contactor or the starter must not endanger
personnel or equipment in the event of a short
circuit
- The contactor or the starter does not need to be
suitable for continued operation without repair and
replacement of parts
- Damage to the contactor and the overload relay is
permissible
Rated conditional
short-circuit current l
- The rated conditional short-circuit
current l
indicates the max. short-
q
circuit breaking capacity of the starter
q
Rated operation current l
- The rated operational current le for
the starter is the current when the
starter is in the On position
Conditions for compliance with
Type "2" coordination
(Extract from IEC 947-4-1)
- The contactor or the starter must not endanger
personnel or equipment in the event of a short
circuit
- The contactor or the starter must be suitable for
further use
- No damage may occur to the overload relay or
other parts, with the exception of welding of the
contactor or starter contacts, provided they can
be separated easily without any significant
deformation (e.g. using a screwdriver)
e
Rated uninterrupted current l
(to IEC 947-1)
- The rated uninterrupted current lu of
a unit is a current, specified by the
manufacturer, which the unit can
carry without interruption
u
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 83
Page 4
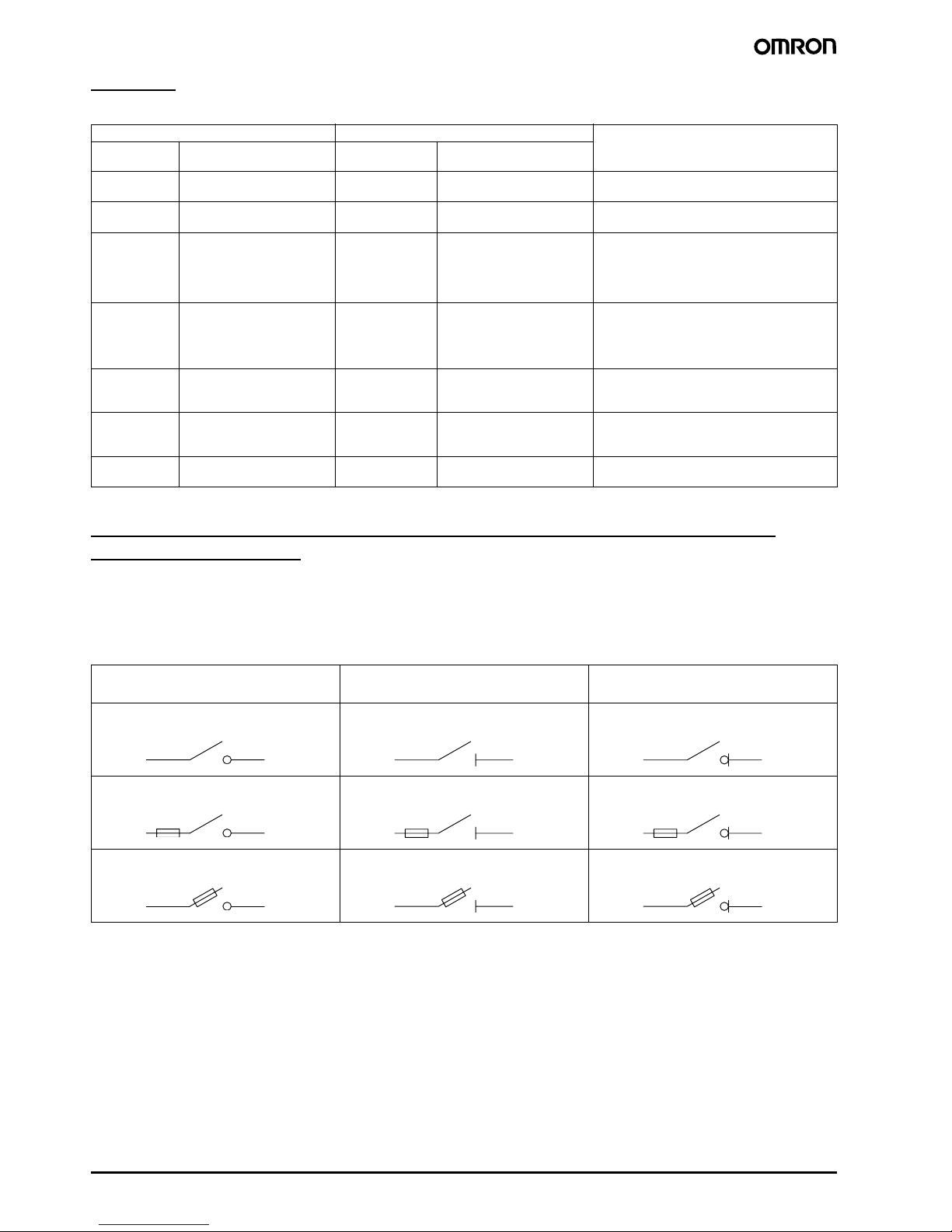
Overview
The following table shows in summarized form both the previous and the new IEC, EN and DIN VDE standards.
Previous specification New specification
EN 60947
DIN VDE
- - 947-1 60947-1
157 0660, Part 101 947-2 60947-2
406 0660, Part 107 947-3 60947-3
158
292-1
292-2
292-3
337 0660 Part 200 to Part 205 947-5-1 60947-5-1
- - 947-6-1 60947-6-1
- 0611 Part 1 and 2 947-7-1 60947-7-1
0660, Part 102
0660, Part 104
0660, Part 106
0660, Part 301
947-4-1 60947-4-1
0660, Part 100
0660, Part 101
0660, Part 107
0660, Part 102
0660, Part 200
0660, Part 114
0611, Part 1
ContentIEC DIN VDE IEC
Low-voltage switchgear,
General rules
Low-voltage switchgear,
Circuit-breakers
Low-voltage switchgear,
Switches,
Disconnectors,
Switch-disconnectors,
Fuse-combination units
Low-voltage switchgear,
Control circuit devices and switching elements
Low-voltage switchgear,
Multiple-function equipment,
Automatic transfer switching equipment
Low-voltage switchgear,
Multiple-function equipment,
Control and protective switching devices (CPS)
Low-voltage switchgear,
Ancillary equipment (e.g. terminal blocks)
Switches, disconnectors, switch-disconnectors and fuse combination units
(IEC 947-3, EN 60947-3)
These devices must now be labelled with the product function designated by the manufacturer. This means placing clearly visible symbols on the
device itself.
Devices with an isolating function are subject to special safety requirements. They must for example have greater creepage distances and clearances across the opened contacts than is necessary for other devices.
Device functions and corresponding symbols
Making/breaking Isolating
Switch Disconnector Switch-disconnector
Switch-fuse Disconnector-fuse Switch-disconnector-fuse
Fuse-switch Fuse-disconnector Fuse switch-disconnector
Making/breaking
+ isolating
OMRON equipment is designed for the world’s markets
It is manufactured and tested in accordance with national and international specifications, the most important of which are listed below:
IEC 947-..., EN 60947: Low-voltage switch gear and control gear
IEC 664: Insulation co-ordination including clearances and creepage distances for equipment
IEC364: Electrical installations of buildings
IEC 204-..., EN 60204-...: Electrical equipment of industrial machines
DIN VDE 0105: Operation of electrical power installations
IEC 536: Protection against electric shock
84 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
Page 5
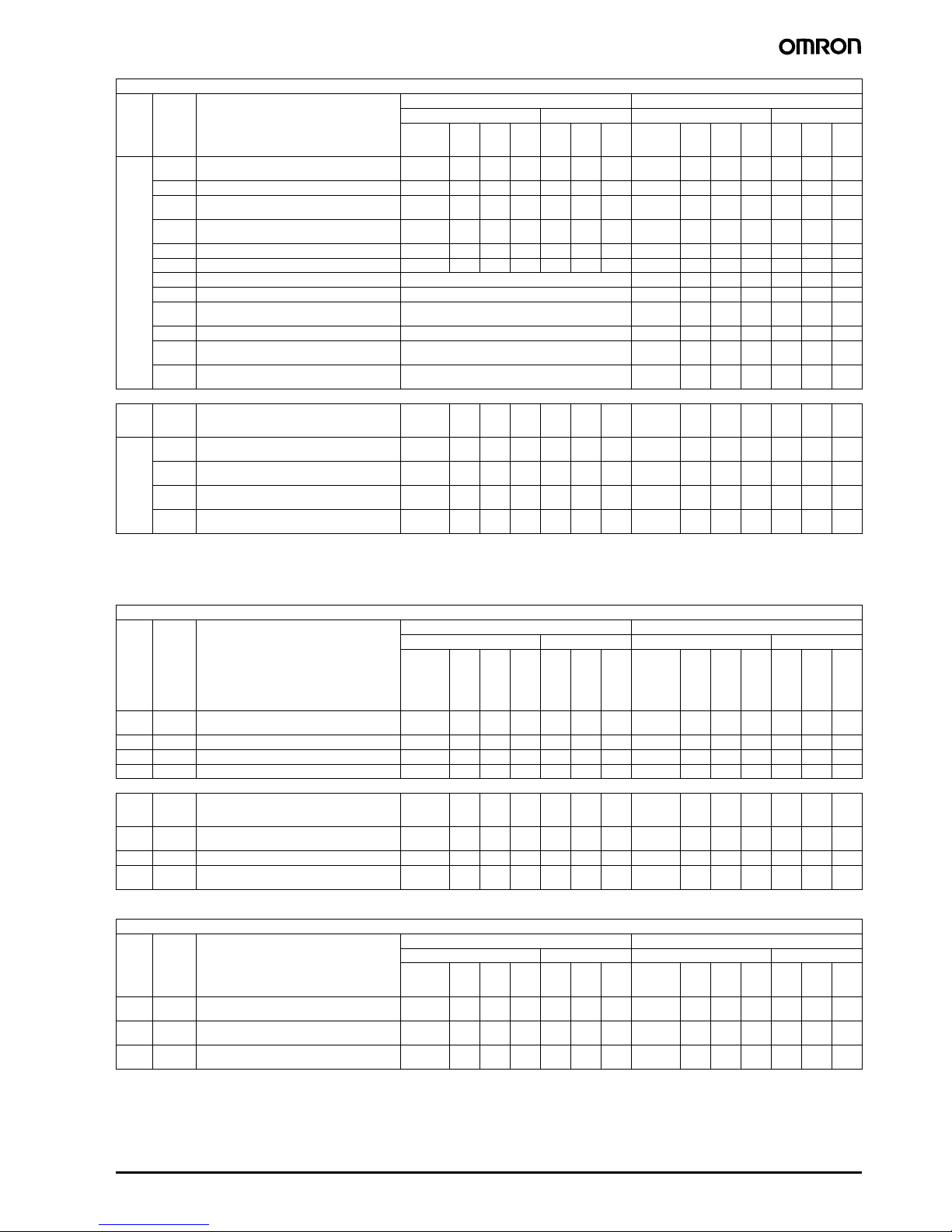
Utilization categories for contactors to IEC 947-4-1 and EN 60947
Verification of electrical endurance Verification of rated making and breaking ca pacities
Make Break Make Break
I
A
I
e
U
-
-
I
e
cos ϕIc-
U
e
U
r
-
U
I
e
e
cos ϕ
I
A
I
e
U
-
-
I
e
cos ϕ
U
e
All values 1 1 0.95 1 1 0.95 All values 1.5 1.05 0.8 1.5 1.05 0.8
Type of
current
Typical examples of application
I = current made, I
Utilization
Ie = rated operational current
category
U = voltage before make
Ue = rated operational voltage
Ur = reco very volt age
Non-inductive or slightly inductive loads, resistance
AC-1
furnaces
= current broken
c
AC-2 Slip-ring motors: star ting, switching off All values 2.5 1 0.65 2.5 1 0.6 5 All values 4 1 .05 0.6 5 4 1.05 0.65
Squirrel-cage motors: star ting, switching off motors
AC-3
during running
4
AC-4 Squirrel-cage motors: starting, plugging, inching
AC-5A Switching of electric discharge lamp controls - - - - - - - - 3.0 1.05 0.45 3.0 1.05 0.45
AC-5B Switching of incandescent lamps - - - - - - - - 1.5
AC
3
AC-6A
Switching of transformers As given by the manufacturer - - - - - - -
Ie ≤ 17
Ie > 176611
Ie ≤ 17
Ie > 176611
0.65
0.3511
0.65
0.356611
0.17
0.17
0.65
0.35
0.65
0.35
Ie ≤ 100
Ie > 1001010
Ie ≤ 100
Ie > 1001212
1.05
0.45
1.05
0.3588
1.05
0.45
1.05
0.351010
2
1.052)1.521.052)
AC-6B3Switching of capacitor banks As given by the manufacturer - - - - - - -
Slightly inductive loads in household appliances and
AC-7A
similar applications
AC-7B Motor-loads for household applications As given by the manufacturer - 8.0 1.05
Hermetic refrigerant compressor motor control with
DC
AC-8A
manual resetting of overload releases
Hermetic refrigerant compressor motor control with
AC-8B
automatic resetting of overload releases
Non-inductive or slightly inductive loads, resistance
DC-1
furnaces
Shunt motors: starting, plugging, inching, dynamic
DC-3
braking
Series motors: starting, plugging, inching, dynamic
DC-5
braking
5
5
DC-6 Switching of incandescent lamps - - - - - - - -
Note 1: cos ϕ = 0.45 for Ie ≤ 100 A; cos ϕ = 0.35 for Ie > 100 A.
2: The tests are to be carried out with an incandescent light load.
3: The test data are to be derived from the test values for AC-3 or AC-4 according to
Table VIIb, EN 60947-4-1.
As given by the manufacturer - 1.5 1.05 0.8 1.5 1.05 0.8
1
)8.01.051)
As given by the manufacturer - 6.0 1.051)6.01.051)
As given by the manufacturer - 6.0 1.051)6.01.051)
I
U
I
e
I
A
e
L/RmsIc
U
e
U
L/RmsI
r
-
-
I
U
e
e
A
I
U
e
I
e
L/RmsI
U
e
All values 1 1 1 1 1 1 All values 1.5 1.05 1 1.5 1.05 1
All values 2.5 1 2 2.5 1 2 All values 4 1.05 2.5 4 1.05 2.5
All values 2.5 1 7.5 2.5 1 7.5 All values 4 1.05 15 4 1.05 15
1.5
2
)
4: AC-3 category may be used for occasional inching (jogging) or plugging for limited
time periods such as machine set-up; during such limited time periods the numb er
of such operations should not exceed five per minute or more than ten in a ten
minute period.
5: A hermetic refr igerant compressor motor is a combination consisting of a compres-
sor and a motor, both of which are enclosed in the same housing, with no external
shaft or shaft seals, the motor operating in the refrigerant.
1.05
2
)
Utilization categories for control switches to IEC 947-5-1 and EN 60947
Normal conditions of use Abormal conditions of use
Make Brea k Make Break
I
U
-
-
I
U
e
e
cos ϕ
I
U
c
r
-
-
I
e
cos ϕ
U
e
I
U
-
-
I
e
cos ϕ
U
e
110.9110.9 - - - - - -
Type of
Utilization
current
category
AC AC-12
Typical examples of application
I = current made, Ic = current broken
= rated operational current
I
e
Ue = rated operational voltage
Ur = reco very volt age
U = voltage before make
t
= time in ms to reach 95 % of the steady-state
0.95
current
P = Ue x Ie = rated power consumption in watts
Control of resistive and solid state loads as in optocoupler input circuits
AC-13 Control of solid state loads with transformer isolation 2 1 0.65 1 1 0.65 10 1.1 0.65 1.1 1.1 0.65
AC-14 Control of small electromagnetic loads (≤ 72 VA) 6 1 0.3 1 1 0.3 6 1.1 0.7 6 1.1 0.7
AC-15 Control of electromagnetic loads (> 72 VA) 10 1 0.3 1 1 0.3 10 1.1 0.3 10 1.1 0.3
I
U
c
r
I
e
c
I
e
1.5
2
)
I
c
I
e
-
U
1.05
1.05
1.05
1.05
U
-
U
1.05
U
U
cos ϕ
e
0.45
0.35
0.45
0.35
L/R
r
ms
e
2
)
r
cos ϕ
e
DC DC-12
Control of resistive and solid state loads as in optocoupler input circuits
DC-13 Control of electromagnets 1 1 6xP1)1 1 6xP1)1.11.16xP
Control of electromagnetic loads having economy
DC-14
resistors in circuits
Note 1: The value “6 x P” results from an empirical relationship which is found to represent most DC magnetic loads to an upper limit of P = 50 W, viz 6 x P = 300 ms. Loads having power
consumption greater than 50 W are assumed to consist of smaller loads in parallel. Therefore, 300 ms is to be an upper limit, irrespective of the power consumption value.
Utilization categories for switches, disconnectors, switch-disconnectors, and fuse combination units to IEC 947-3 and EN 60947
Typical applications
Type of
current
AC
I = current made, Ic = current broken
Utilization
Ie = rated operational current
category
U = voltage before make
Ue = rated operational voltage
Ur = reco very volt age
AC-20
Connecting and disconnecting under no-load condi-
2
A(B)
tions
AC-21
Switching of resistive loads, including moderate
2
A(B)
overloads
AC-22
Switching of mixed resistive and inductive loads, in-
2
A(B)
cluding moderate overloads
I
U
-
-
I
U
e
e
I
U
c
t
0.95
r
-
-
t
I
e
0.95
U
e
I
U
-
-
I
U
e
e
I
U
c
t
0.95
r
-
-
t
I
e
0.95
U
e
111 ms111 ms - - -- - -
1
)1.1 1.1 6xP1)
10 1 15 ms 1 1 15 ms 10 1.1 15 ms 10 1.1 15 ms
Verification of electrical endurance Verification of switching capacity
Make Brea k Make Break
I
A
I
e
U
-
-
I
U
e
e
cos ϕ
I
U
c
r
-
-
I
U
e
e
cos ϕ
I
A
I
e
U
-
-
I
U
e
e
cos ϕ
I
U
c
r
-
-
I
e
cos ϕ
U
e
All values1)1)1)1)1)1) All values1)1.051)1)1.051)
All values 1 1 0.95 1 1 0.95 All values 1.5 1.05 0.95 1.5 1.05 0.95
All values 1 1 0.8 1 1 0.8 All values 3 1.05 0.65 3 1.05 0.65
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 85
Page 6
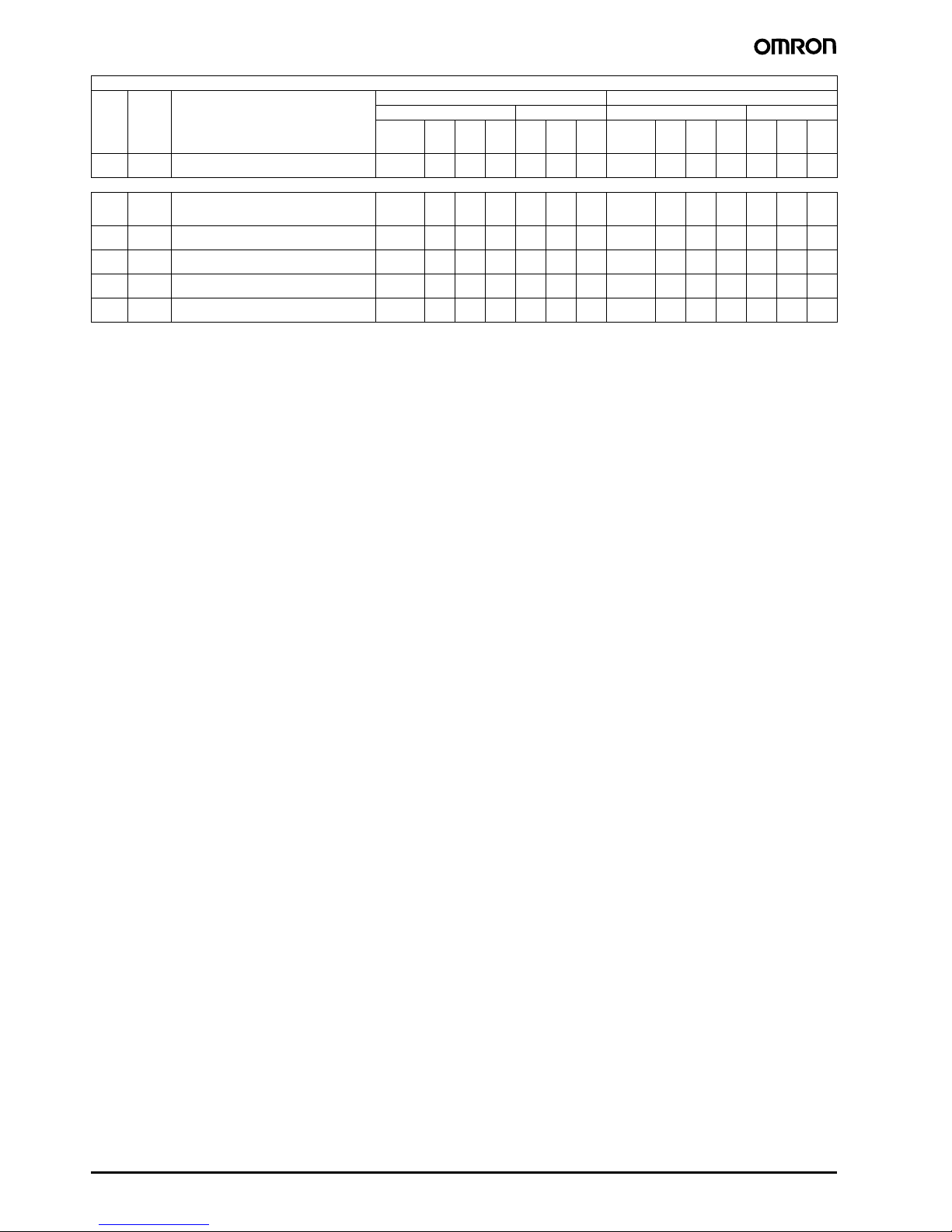
Utilization categories for switches, disconnectors, switch-disconnectors, and fuse combination units to IEC 947-3 and EN 60947
Verification of electrical endurance Verification of switching capacity
Make Break Make Break
I
I
e
A
U
-
-
I
e
cos ϕ
U
e
U
I
c
r
-
-
I
e
cos ϕ
U
e
All values 1 1 0.65 1 1 0.65
Type of
current
Typical applications
I = current made, I
Utilization
Ie = rated operational current
category
U = voltage before make
Ue = rated operational voltage
Ur = recovery voltage
AC-23
Switching of motor loads or other highly inductive
2
A(B)
loads
= current broken
c
I
e
A
Ie ≤ 100
Ie > 1001010
I
U
-
U
1.05
1.05
cos ϕ
e
0.45
0.3588
I
e
U
I
c
r
-
U
1.05
1.05
cos ϕ
e
0.45
0.35
I
e
I
DC-20
DC
Note 1: If the switching device has a making and/or breaking capacity, the figures for the current and the power factor (time constants) must be stated by the manufacturer.
2: A: frequent operation, B: infrequent operation.
Connecting and disconnecting under no-load condi-
2
A(B)
tions
Switching of resistive loads, including moderate
DC-21
2
overloads
A(B)
DC-22
Switching of mixed resistive and inductive loads, in-
2
A(B)
cluding moderate overloads (e.g. shunt motors)
DC-23
Switching of highly inductive loads (e.g. series mo-
2
A(B)
tors)
A
All values1)1)1)1)1)1)All values1)1.051)1)1.051)
All values111111All values1.51.0511.51.051
All values112112All values41.052.541.052.5
All values 1 1 7.5 1 1 7.5 All values 4 1.05 15 4 1.05 15
Protection against electrical shock, to IEC 536
IEC 536 covers the setting up of electrical apparatus, and its
arrangement in electrical installations with rated voltages up to 1000
VAC and 1500 VDC, with regard to protection against direct contact
I
U
e
I
e
L/RmsI
U
e
U
c
I
e
L/RmsI
r
U
e
A
I
U
e
I
e
L/RmsI
U
e
Damp heat, constant, to IEC 68 Part 2-3
In this test, the effects of a constant high level of humidity
(93 +2/-3%) and a constant temperature (40 ±2)°C over a prescribed
duration, are observed.
where operating elements such as push-buttons and switches are
located in the vicinity of live parts.
“Finger-proofing” relates only to the operating device, and only in the
normal direction of operation. A clearance of at least 30 mm radius
from the centre point of the device to any live parts, must be ensured.
The IP 20 degree of protection is superior to “finger-proofing” in that
it embodies protection against contact with electrical apparatus in
Damp heat, cyclic, to IEC 68 Part 2 - 30, Test Db
This test is used to assess the suitability of electrical products for
operation and storage at high relative humidity levels, in conjunction
with cyclic temperature fluctuation. A test cycle consists of 12 hours
at 40 ±2°C, with relative humidity of 93 ±3%, and 12 hours at
25 ±3°C, with the relative humidity of at least 95%.
any direction. Devices which are “finger-proof” and of IP 00 degree of
protection can be provided with further protection against contact in
the form of shrouding, if so desired.
Ambient temperature
Ambient temperature is the temperature of the room (e.g. factory bay
or switchgear room), in which the open or enclosed device is
installed, a prerequisite being that this temperature is not significantly
influenced by the heat losses from the device.
U
c
I
e
L/R
r
U
ms
e
86 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
Page 7

Glossary of standard terms
This Glossary offers brief expIanations of some of the standard
terms used in this catalogue. However, it must not be regarded as a
substitute for the actual text of the standard, especially where the
new terms used in IEC 947 are concerned.
Rated conditional short-circuit current I
(IEC 947-1; 2.5.29/IEV 441-17-20)
The prospective current which a switching device, e.g. a circuitbreaker, protected by a short-circuit protective device such as a
motor-protective circuit-breaker, can carry for the duration of the protective device tripping time.
q
Mininum command time
Minimum duration for a trip-initiating factor (controI puIse, short circuit) to effect the corresponding reaction, e.g. the short-circuit duration necessary to initiate tripping.
Rated breaking capacity
(IEC 947-1; 4.3.5.3)
The r.m.s. value of current which a switching device is capable of
breaking according to its utiIization category. The rated breaking
capacity is stated by reference to the rated operational voltage and
the rated operational current.
The equipment must be capable of breaking any value of current up
to and incIuding its rated breaking capacity stated.
Rated actuating voltage Uc
(rated control circuit voltage)
(IEC 947-1; 4.5.1)
The voltage which is applied to the actuating make contact in a control circuit. Due to the presence in the controI circuit of transformers
or resistors, this voltage may differ from the rated control supply voltage.
Rated service short-circuit breaking capacity I
(IEC 947-2; 4.3.5.2.2)
The prospective short-circuit current which, depending on the rated
operationaI voltage, a circuit-breaker is capable of breaking repeatedly (test cycle: O - CO - CO; previousIy P-2). After interrupting this
current vaIue, the circuit-breaker must be capable, despite its own
thermal level having increased, of continuing to carry and disconnect
in the event of overIoading, the rated uninterrupted current.
Rating or rated power
(IEC 947-1; 4.3.2.3)
The rated operational power which an equipment is capable of
switching at the associated rated operational voItage in accordance
with the utilization category.
For example:
motor contactor utilization category AC-3: 37 kW at 400 V.
Rated operational voltage U
(IEC 947-1; 4.3.1.1)
The voItage to which the characteristics of an equipment are
referred. The rated operational current must not in any case exceed
the rated insulation voltage.
e
Rated operational current Ie
(IEC 947-1; 4.3.2.3)
The current which an equipment is capabIe of carrying taking into
account the rated operational current, duration of operation, utilization category and ambient temperature.
Reference is therefore made aIongside each such term to the reIevant section of the standard, e.g. IEC 947-1 in addition, IEV numbers
are given to enable you to find foreign language equivalents in the
International EIectrotechnicaI Vocabulary
(IEG 50), if required.
Rated uninterrupted current I
(IEC 947-1; 4.3.2.4)
The vaIue of current which an equipment can carry in uninterrupted
duty (i.e. for weeks, months or years).
u
Rated making capacity
(IEC 947-1; 4.3.5.2)
The vaIue of current which an equipment is capabIe of switching On
in accordance with the utilization category and at the rated operational voltage.
Rated frequency
(IEC 847-1; 4,3.3)
The frequency for which an equipment is designed and to which the
other characteristic vaIues are referred.
Rated ultimate short-circuit breaking
capacity I
(IEC 947-2; 4.3.5.2.1)
The maximum prospective fault current which a circuit-breaker is
capable of interrupting
(test cycIe: O - CO; previously P-1)
Rated insulation voltage U
(IEG 947-1; 4.3.1 .2)
The voltage to which insulation tests and creepage distances of an
equipment are referred. The maximum operationaI voltage must not
in any case exceed the rated insulation voltage.
cs
Rated short-circuit breaking capacity Icn
(IEC 947-1; 4.3.6.3)
The maximum value of current which an equipment is capable of
switching Off at rated operational voItage and rated frequency, and
without sustaining damage. It is expressed as r.m.s. value.
cu
i
Motor rating
(IEC 947-1; 4.3.2.3)
Power output of a motor at the associated operational voltage.
Rated control supply voltage Us
(IEC 947-1; 4.5.1)
The voltage applied to the input terminals of the control circuit of an
equipment. Due to the presence of transformers or resistors in the
control circuit, this may differ from the rated actuating (control circuit)
voltage.
Rated impulse withstand voltage U
(IEC 947-1; 4.3.1 .3)
Measures the stability of the internal clearances of an equipment
against overvoltage peaks. The utilization of suitable switchgear can
ensure that overvoltages are prevented from transferring from the
mains to deenergized system sections within it.
Rated current I
(of a circuit-breaker)
(IEC 947-2; 4.3.2.3)
For circuit-breakers, this current value is equal to the uninterrupted
current and the conventional free air thermaI current.
n
imp
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 87
Page 8

Protection against direct contact
Design measures incorporated into equipment in order to prevent
direct contact, i.e. without tools, with live parts of a system (finger
proof, back-of-hand proof).
Control circuit reliability
Measures the probability of switching states arising during the
lifespan of a contact, which would be interpreted as faults by downstream electronic controllers (PLCs). Control circuit reliability is
expressed in values based on tests using standard limit values for
signal inputs.
Damp heat, constant
This test subjects the equipment to an ambient temperature of 40°C
at a constant humidity of 93%. At set intervals during the test, the
electrical and mechanical function of the equipment are examined.
Damp heat, cyclic
This test subjects the equipment to cyclically changing climatic conditions: a cycle applies 40°C ambient temperature at 93% relative
humidity for 12 hours, followed by 12 hours of 25°C at 95% relative
humidity. At set intervals during the test, the electrical and mechanical function of the equipment are examined.
Finger proof
An equipment whose live parts cannot be touched by the operator
during actuation is termed finger proof. This also affects operator
activity on neighbouring switching devices. The finger proof area of a
push-actuated operating medium is a circular area of at least 30 mm
radius around the actuating element, and vertical to the direction of
actuation.
Within this circular area, touch-critical parts must be located at not
less than 80 mm depth under the actuating level.
Utilization category
(IEC 947-1; 2.1 .18/IEV 441-17-19)
A combination of specified requirements relating to the condition in
which the switching device or the fuse fulfills its purpose, selected to
represent a characteristic group of practical applications. The speci-
fied requirements may concern, e.g. the values of making capacities,
breaking capacities and other characteristic values, data concerning
associated circuits, and the relevant conditions of use and behaviour.
(IEC 947-2; 4.4)
For circuit-breakers, the utilization category denotes whether the
equipment is designed for selectivity using time delay (category B) or
not (category A).
Back-of-hand proof
An equipment whose live parts cannot be touched by a sphere of
50 mm diameter, is regarded as back-of-hand proof.
Altitude
The density of air decreases with increasing altitude, and this
reduces its insulating capacity as well as its heat transfer capability.
The rated operational voltage and current of switching devices, con-
ductors and motors as well as the tripping behaviour of thermal over-
load relays are affected by this.
Upon request, OMRON ELECTRONICS will supply information as to
the suitability or otherwise of switchgear for operation at altitudes
above the 2000 m limit specified by the standard.
Conventional free air thermal current
(IEC 947-1; 4.3.2.1)
The maximum value of current which an equipment is capable of car-
rying for a minimum of eight hours without thermal overloading. As a
rule, it corresponds to the maximum operational current.
Creepage path
(IEC 947-1; 2.5.51/IEV 151-03-37)
The shortest distance along the surface of the insulating material
between two conductive parts. The creepage distance is determined
by the rated insulation voltage, the pollution degree and the creep-
age current resistance of the material used.
Clearance
(IEC 947-1; 2.5.46/IEV 441-17-31)
The distance between two conductive parts along a string stretched
the shortest way between these conductive parts. The clearance in
air is determined by the rated impulse withstand voltage, overvoltage
category and pollution degree.
88 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
Page 9

Emergency-stop switching device
Switching device within an emergency-stop circuit which is intended
to prevent danger to persons, damage to machinery or working
materials.
Opening delay
(IEV 441-17-36)
The interval of time between the specified instant of initiation of the
opening operation and the instant when the arcing contacts have
separated in all poles. The opening time is the sum of the tripping
time and the inherent delay of the contacts.
Closing delay
The interval of time between the instant of command and the first
make operation of the contacts of the first pole to close. The closing
delay is made up of the response delay and the closing time.
Shock resistance
The capacity of an equipment to withstand pulse-like motions without
changing its operating status or sustaining damage. No contact lifting
must take place on devices in the On position, the main contacts
must not knock against each other in the Off position. A safety switch
must not trip, and control circuit switches must not change their
switching status.
Overvoltage category
(IEC 947-1; 2.5.60)
Conventional number for prospective overvoltages at the point of
installation, as might be caused for example by the effect of lightning
or switching processes. The overvoltage category applicable to
industrial switchgear is III. The applicability of switchgear according
to the overvoltage categories is defined as follows:
Overvoltage category IV:
Use allowed directly at the termination point of the installation
(directly affected by any lightning), e.g. at an overhead line connection point.
Overvoltage category III:
Operating media with special requirements as to the serviceability for
connection in fixed installations, which are protected by overvoltage
diversion measures, e.g. circuit-breakers in low-voltage distribution
systems or in control systems for industrial use.
Overvoltage category II:
Power consumers for connection to fixed installations, e. g. household appliances, electrical tools.
Overvoltage category I:
Operating media for connection to circuits containing overvoltage
protection schemes, e.g. electronic devices.
Safe isolation
(IEC 536, DIN VDE 0106 Part 101)
Isolation of circuits not carrying dangerous voltages (e.g. protective
extra-low voltage) from circuits in which dangerous voltages flow.
Such isolation is achieved by means of reinforced or double insulation which reliably prevents voltage transfer from one circuit to
another. This might otherwise take place between main circuits and
control circuits in switching devices or between transformer primary
and secondary. ”Safe isolation” is a priority requirement for safety circuits and functional low-voltage circuits.
Isolating function
(IEC 947-1; 2.1.19)
Equipments are deemed to possess this isolating function provided
their switching contacts when in the open position, achieve the separation distance prescribed for the isolation of electrical circuits, and
their creepage paths and clearance distances are of the required
size. The power supply to the entire installation or a section of the
installation can thus be cut off for safety reasons, e.g. during maintenance.
Tamper proof
An emergency-stop switching device is regarded as tamper proof
provided it cannot be reset without tools or via a prescribed procedure, after tripping has taken place. The device latches in the tripped
position. Accidental or deliberate manipulation (inching) is thus ruled
out.
Ambient temperature, open
(IEV 441-11-13)
Room temperature for example of the workshop or switch room in
which the switching device is located.
Ambient temperature, enclosed
(IEV 441-11-13)
Temperature at which the switching device is capable of being operated within a closed housing. For this purpose, it must be taken into
account that the heat losses of the device will add to the internal temperature rise within the enclosure.
Losses
(IEV 151-03-18)
The difference between the input power and the output power of a
device. The main type of loss in electrical power distribution switchgear and operating media is current heat loss.
Pollution degree
(IEC 947-1; 6./1.3.2)
Conventional number for the prospective quantities of conductive
dust and humidity which can lead to a reduction in the control circuit
reliability of a device. The pollution degree is described by the following influencing factors:
Pollution degree 1:
No pollution or only dry, non-conductive pollution occurs. The pollution does not affect the control circuit reliability.
Pollution degree 2:
Usually, only non-conductive pollution. However, transient conductivity through condensation is to be expected.
Pollution degree 3: (switchgear for industrial use)
Conductive pollution or dry, non-conductive pollution which is rendered conductive through condensation.
Pollution degree 4:
The pollution leads to long-term conductivity, e.g. pollution by conductive dust, rain or snow.
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 89
Page 10

Coordination type
Status of a switchgear combination (motor starter) during and after
testing at rated conditional current:
Coordination Type “1“:
- No risk to persons or installations
- No requirement for immediate readiness for renewed operation
- Damage to the starter is permissible
Coordination type “2“:
- No risk to persons or installations
- Starter is capable of renewed operation
- No damage to the starter with the exception of a slight welding of
the contacts, provided they can be separated without significant
deformation.
Positive opening operation
(IEC 947-1; 2.4.11/IEV 441-16-12)
This opening operation is designed to ensure that auxiliary contacts
of a switching device are always in the respective positions corresponding to the open or closed position of the main contacts. The
contacts of a contactor are interlocked opposing contacts, pro-
Symbols used in Technical Data and Formulae
DF Duty factor
Rated short-circuit breaking capacity
I
cn
Rated service short-circuit breaking capacity
I
cs
Rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity
I
cu
Rated operational current
I
e
Transformer initial short-circuit current AC
I”
sc
Rated current
I
n
Rated transformer current
I
NT
Rated conditional short-circuit current
I
q
Set value of overcurrent release
I
r
Response value of non-delayed short-circuit release
I
rm
vided they are mechanically linked in such a way as to ensure that
normally open and normally closed contacts can never be closed
simultaneously.
This arrangement must also ensure that minimum contact separation
of 0.5 mm is maintained over the entire lifespan of the device, even
during a fault, e.g. the welding of one contact.
The relevant German Trade Association requires the use of contac-
tors with interlocked opposing contacts for control systems on power
presses in the metal processing industry.
Positive/enforced
operation/actuation
This describes an arrangement where a link between the actuator
and the switching element ensures that the force exerted on the actu-
ator is transferred directly, i.e. without the intervention of sprung
parts, onto the switching element.
Positive opening
(IEC 947-1; 2.4.10/IEV 441-16-11)
An opening operation which ensures that the main contacts of a
mechanical switching device have attained the open position when
the actuator is in the Off-position.
I
Conventional free air thermal current
th
Conventional thermal current of enclosed devices
I
the
Rated uninterrupted current
I
u
Transformer rating
S
NT
Rated actuating voltage
U
c
Rated operational voltage
U
e
Rated insulation voltage
U
i
Rated impulse withstand voltage
U
imp
Transformer short-circuit voltage
u
k
Rated control voltage
U
s
90 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
Page 11

Additional ordering information for contactors
CE-Marking
The manufacturer has to sign his products with the CE-Marking. With
the CE-Marking the manufacturer confirms the accordance with the
different EEC Directives. The CE-Marking is absolutely necessary to
sell the products in the EEC.
Test Authorities, Registration Mark, Approvals
OMRON Low voltage switchgear is built and tested to national and
international specifications. All devices suit all important specifications without any test obligation, like VDE, BS and also relative to
IEC Recommendations and to European Standards like IEC 947 and
EN 60947.
It is for this reason OMRON Low voltage switchgear is used all over
the world. In order to provide special versions, limitations to the max.
voltages, currents and power ratings or special markings are sometimes necessary.
Country Canada USA Switzer-
State deputy or private
examination
(state admitted)
Label marking of examination boards
CSA UL UL SEV DEMKO NEMKO SEMKO SETI SEP SKTC EZU MEEI
*1
land
Denmark
Attached you find the EEC Directives concerning our products.
Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC)
EMC Directive (89/336/EEC)
Declarations of Conformity art. no. D586.. on request.
OMRON Low voltage switchgear is also suitable for applications in
marine environments.
They are classified in "Lloyd`s Register of Shipping" and in the "Maritime Register of Shipping" (GUS). The "American Bureau of Shipping" does not claim a general approval for single components, the
complete electrical equipment on board has to be approved. The
devices should have UL- and CSA-approvals. Further information for
Guide-No. and File-No. (CSA, UL) you will find on page 95.
For approved values see technical data of the devices.
Norway Sweden Finland Poland Slowa-
kia
State deputy
Czech Hun-
garia
Duty of approvals All switchgear or R
Approval of
switchgear
commendable
Specification UL is authorised for approvals
acc. to Canadian Standards
*1 CSA-approvals are replaced by UL-approvals valid for USA and Canada. From 1. 1. 2000 switchgear will be marked with the combined ap-
proval. UL-mark or only.
No approval since 1.1.1994
Our devices are according to the harmonised
European Standards e.g. EN 60947 (IEC 947,
VDE 0660) and can be used generally
Marking with approbation label is no longer
necessary
Explanations for choice and supply of low voltage switchgears in Canada and USA
Marking of auxiliary contacts
At several devices in UL-data are two voltages for auxiliary contacts
mentioned (e. g.: 600 volts at same potential, 150 volts at different
potentials). That means, if the voltage is higher than 150 volts, the control voltage applied to input terminals must be at the same potential
Marking of
auxiliary
contacts
according to
CSA and UL
Heavy Duty
(HD or HVY DTY)
Standard Duty
(SD or STD DTY)
Max. rated values per pole Contact
VoltageVCurrent Cont.
MakeABreak
A
AC 120 60 6 10 A150
AC 240 30 3 10 A300
AC 480 15 1,5 10 A600
AC 600 12 1,2 10 A600
DC 125 2,2 2,2 10 N150
DC 250 1,1 1,1 10 N300
DC 600 0,4 0,4 10 N600
AC 120 30 3 5 B150
AC 240 15 1,5 5 B300
AC 480 7,5 0,75 5 B600
AC 600 6 0,6 5 B600
DC 125 1,1 1,1 5 P150
DC 250 0,55 0,55 5 P300
DC 600 0,2 0,2 5 P600
Current
A
Rating
Code
Designation
Low voltage switchgear for auxiliary circuits (e. g. contactor relays,
control units, auxiliary contacts in general) usually approved for
"Heavy Duty" or "Standard Duty" UL and besides these marked with
the admissible max. voltage or with short codes (see table).
Marking of
auxiliary
contacts
according to
CSA and UL
- AC 120 15 1,5 2,5 C150
- AC 120 3,6 0,6 1 D150
- AC 120 1,8 0,3 0,5 E150
Max. rated values per pole Contact
VoltageVCurrent Cont.
MakeABreak
A
AC 240 7,5 0,75 2,5 C300
AC 480 3,75 0,375 2,5 C600
AC 600 3 0,3 2,5 C600
DC 125 0,55 0,55 2,5 Q150
DC 250 0,27 0,27 2,5 Q300
DC 600 0,1 0,1 2,5 Q600
AC 240 1,8 0,3 1 D300
DC 125 0,22 0,22 1 R150
DC 250 0,11 0,11 1 R300
Current
A
Rating
Code
Designation
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 91
Page 12
Discernment at UL-Standards
Recognized Component Industrial Control Equipment Listed Industrial Control Equipment
UL issues yellow "Guide cards" with Guide- and File-No. UL issues white "Guide cards" with Guide- and File-No.
Devices have permission to be marked with on the label Devices have to be marked with the "UL-Listing Mark"
Devices as components approved for "factory wiring":
devices for employment in control panels, when they are selected,
mounted and wired according to the charging conditions by skilled worker.
Valid UL-Standards:
UL 508„Standard for Industrial Control Equipment“
(partly limited)
Are devices approved as "Listed Equipment" the approval is also valid for using as "Recognized Component" R.
Devices approved for "field wiring",
a) devices for employment in control panels, when they are mounted
and wired by skilled worker.
b) devices for retail in USA
Valid UL-Standards:
UL 508„Standard for Industrial Control Equipment“
(unlimited)
UL 486"Standard for Wire Connectors and Soldering Lugs"
Approvals
Country
Typ e
Mini Contactors J7KNA and Accessories
J7KNA-AR..(D) o--o---o
J7KNA-09..(D) o--o---o
J7KNA-12..(D) o--o----
J73KN-A..., J73KN-AM o--o---o
Contactors Series J7KN
J7KN(G)-10...(D) o--o---o
J7KN(G)-14...(D) o--o---o
J7KN(G)-18...(D) o--o---o
J7KN(G)-22...(D) o--o---o
J7KN(G)-24...(D) o--o---o
J7KN(G)-32...(D) o--o---o
J7KN(G)-40...(D) o--o---o
J7KN-50...(D) o--o---o
J7KN-62...(D) o--o---o
J7KN-74...(D) o--o---o
J7KN-85...(D) o--o---o
J7KN-110...(D) o--o---o
J7KN-151... o--o----
J7KN-176... o--o----
J7KN-200... ---o----
Accessories
J73KN-B... o--o---o
J73KN-C... o--o---o
J74KN-B-PT... o--o----
J74KN-A-VG... o--o----
J74KN-B-VG ---o----
J74KN-C... o--o----
J74KN-D... o--o----
Thermal Overload Relays
J7TKN-A... o--o---o
J7TKN-B... o--o---o
J7TKN-C... o--o---o
J7TKN-D... o--o---o
J7TKN-E... o--o---o
J7TKN-F... ---o----
o In Standard version approved x In Test - Not provided for test until now
USA, Canada Switzerland Europe Register of Shipping CENELEC
UL SEV
Great Britain
LRS
GUS
MRS
Italy
RINA
CB-Certificates
92 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
Page 13
Permissible ratings of devices approved for North America
Circuit breakers of J7MN series are approved for USA and Canada. According to UL 508 and C22.2 No.14 they can also be used with a load feeder
contactor. These Circuit breakers can be used as „Manual Motor Starter“ for „Group Fusing“ or for „Group Installation“ or as „Manual Motor Controller Suitable for Tap Conductor Protection in Group Installations“ or as „Self Protected Combination Motor Controller“ (Type E).
Circuit breakers J7MN as „Manual Motor Starter“
If used as „Manual Motor Starter“ the circuit breaker is always operated in combination with a short circuit
device. For use with approbated fuses or circuit breakers according to UL489 or CSA22.2 No. 5 only. The
size are selected according to National Electrical Code (UL), or Canadian Electrical Code (CSA).
Circuit breaker J7MN12 J7MN25 J7MN50 J7MN100
NEMA Size 00
FLA max. 12 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
V 1-phas. 3-phas. 1-phas. 3-phas. 1-phas. 3-phas. 1-phas. 3-phas.
110/120 1/2 – 2 – 3 – 10 –
200 11/2 3 3 71/2 71/2 15 20 30
220/240 2 3 5 71/2 10 20 20 40
440/480 – 71/2 – 15 – 40 – 75
550/600 – 10 – 20 – 50 – 100
Circuit breakers J7MN as „Manual Motor Controller Suitable for Tap Conductor Protection in Group
Installations“
For UL only, not for CSA. If used as „Manual Motor Controller Suitable for Tap Conductor Protection in
Group Installations“ the circuit breaker is always operated in combination with a short circuit device. For
use with approbated fuses or circuit breakers according to UL489 only. The size are selected according
to National Electrical Code.
Circuit breaker J7MN12 J7MN25 J7MN50 J7MN100
NEMA Size 00
FLA max. 12 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
V 1-phas. 3-phas. 1-phas. 3-phas. 1-phas. 3-phas. 1-phas. 3-phas.
110/120 1/3 – 2 – 3 – 10 –
200 3/4 2 3 71/2 71/2 15 20 30
220/240 1 2 3 71/2 10 20 20 40
440/480 – 5 – 15 – 40 – 75
550/600 – – – 10 – 50 – 75
Circuit breakers J7MN as „Combination Motor Controller Type E“
As of UL 16. 07. 2001, UL508 demands a line-side 1 air and 2 creepage distance for „Combination Motor Controller Type E“ Therefor circuitbreakers
J7MN-25 and J7MN-100 are approved to UL 508 in combination with the terminal blocks listed below. The basic unit of circuit-breakers J7MN-25
conforms with the required air/creepage distances. According to CSA these terminal blocks can be omitted when the device is used as „Combination Motor Controller Type E“.
Circuit breaker J7MN12 J7MN25 + J74MN-TB25 J7MN50 J7MN100 + J74MN-TB100
NEMA Size 00
FLA max. 12 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
V 1-phas. 3-phas. 1-phas. 3-phas. 1-phas. 3-phas.
110/120 – 2 – 3 – 10 –
200 – 3 71/2 71/2 15 20 30
220/240 – 3 71/2 10 20 20 40
440/480 – – 15 – 40 – 75
550/600 – – 10 – 50 – 75
NEMA Size 1
FLA max. 25 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
NEMA Size 1
FLA max. 25 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
NEMA Size 1
FLA max. 25 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
NEMA Size 2
FLA max. 50 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
NEMA Size 2
FLA max. 50 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
NEMA Size 2
FLA max. 50 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
NEMA Size 3
FLA max. 100 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
NEMA Size 3
FLA max. 100 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
NEMA Size 3
FLA max. 100 A, 600 V
hp-rating max.
Inlet according
upstream
short circuit
protection device
Inlet according
outlet
short circuit
protection device
Ratings of auxiliary switches and alarm switches Lateral auxiliary switch with 1NO + 1 NC
Max. rated voltage to NEMA AC V 600 240
uninterupted current A 10 2,5
Breaking capacity AC A600 C300
DC Q300 R300
J73MN11S
Transversal auxiliary switch with 1NO +
1NC
J73MN11F
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 93
Page 14

Permissible ratings of devices approved for North America
Ratings Icu complies with „short
circuit breaking breaking capacity“
Circuit breaker
Ty p e
J7MN-12 0,11... 3,2 65 50 65 50 30 10 65 65 - - - - - - -
J7MN-25
(+J74MN-TB25)
J7MN-50 25 65 50 65 50 25 25 65 65 25 65 50 65 50 25 25
J7MN-100
(+J74MN-TB100)
hp-rating = Power rating in in horse power (maximum motor rating)
FLA = Full Load Amps / Motor full load current
Icu complies with „short circuit breaking capacity“ to UL
Rated
current
IN
A
4 65506550301065 65 - - - - - - 5 65506550301065 65 - - - - - - 6,3 65506550301065 65 - - - - - - 8 65506550301065 65 - - - - - - 10 505010-----------12 505010-----------0,11 ... 3,2 65 50 65 50 30 30 65 65 30 65 50 65 30 50 30
4 65506550303065 65 30 655065305030
5 65506550303065 65 30 655065305030
6,3 65506550303065 65 30 655065305030
8 65506550303065 65 30 655065305030
10 65 50 65 50 30 30 65 65 30 65 50 65 30 50 30
12,5 65506550303065 65 30 655065305030
16 65 50 65 50 30 30 65 65 - 65 50 65 30 - 20 65 50 65 50 30 30 65 65 - 65 50 65 30 - 22 65 50 65 50 30 30 65 65 - 65 50 65 30 - 25 655065503030---------
32 65 50 65 50 25 25 65 65 25 65 50 65 50 25 25
40 65 50 65 50 25 25 65 65 25 65 50 65 50 25 25
45 65 50 65 50 25 25 65 65 25 65 50 65 50 25 25
50 65 50 65 50 25 25 65 65 25 65 50 65 50 25 25
50 65 50 65 50 30 30 65 65 30 65 50 65 30 50 30
63 65 50 65 50 30 30 65 65 30 65 50 65 30 50 30
75 65 50 65 50 30 30 65 65 30 65 50 65 30 50 30
90 65 50 65 50 30 30 65 65 - 65 50 65 30 - 100(99) 65 50 65 50 30 30 65 65 - 65 50 65 30 - -
Manual Motor Starter Manual Motor Controller
up to AC
240 V
ULkACSAkAULkACSAkAULkACSAkAUL
up to AC
480 V
up to AC
600 V
Suitable for Tap
Conductor Protection in
Group Installations
up to AC
240 V
kA
up to AC
480 V
UL
kA
up to AC
240 V
UL
kA
Combination Motor Controller Type E
up to AC
240 V
ULkACSAkAULkACSAkAULkACSA
up to AC
480 V
up to AC
600 V
kA
Approvals
Country USA Canada USA Canada Europe
MANUAL MOTOR
CONTROLLER
UL UL UL UL
Typ e
J7MN-12oo--o
J7MN-25ooo
J7MN-50ooooo
J7MN-100ooo
J73MN-11F o o - - o
J73MN-N o o - - o
J73MN-S o o - - o
J73MN-T-11S o o - - o
J73MN-Lo---o
J74MN-TB25 o o - - o
J74MN-TB100 o o - - o
*1 in use with J74MN-TB25
*2 un use with J74MN-TB100
o In standard version approved
- Not provided for test till now
COMBINATION
MOTOR
CONTROLLER
*1
*2
94 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
and R-Guide- and File-No.
These data are important for UL-inspecting
Devices Guide-No. File-No.
Canada USA
Circuit Breakers J7MN
as Manual Motor Controller
*1
o
*2
o
o
o
Circuit Breakers J7MN
as Combination Motor Controller
J74MN busbar system NLRV7 NLRV E129916
J74MN accessories NKCR7 NKCR E66273
NLRV7 NLRV E129916
NKJH7 NKJH E197641
Page 15
and R-Guide- and File-No.
These data are important for UL-inspecting
Devices Guide-No.
Kanada USA Kanada USA
Contactors NLDX7 NLDX NLDX8 NLDX2
Accessories NKCR7 NKCR NKCR8 NKCR2
Thermal Overload Relays NKCR7 NKCR - Circuit Breakers J7MN
as Manual Motor Controller
Circuit Breakers J7MN
as Combination Motor Controller
J7MN Bus Bar Assemblies NLRV7 NLRV - J7MN Accessories NKCR7 NKCR - -
NLRV7 NLRV - -
NKJH7 NKJH - -
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 95
Page 16

■ Technical information
Degree of protection acc. to EN60947
Protection ratings are prefixed by the internationally agreed letters IP
followed by two digits.
st
1
digit: Pertains to solid objects
nd
2
digit: Pertains to water.
st
Short description Definition
1
digit
1 Protected against
solid objects greater than 50 mm
2L Protected against
solid objects greater than 12,5 mm
and against contact
by standard test
finger
3 Protected against
solid objects greater than 2,5 mm
4 Protected against
solid objects greater than 1 mm
5 Dust protected Prevents ingress of dust in quantities
6 Dust tight Prevents ingress of dust.
Excludes solid objects exceeding
50 mm in diameter and protects against
contact with live and moving parts by a
large body surface such as a hand (but
not against deliberate access).
Excludes solid objects exceeding
12,5 mm in diameter and protects
against contact with live and moving
parts by a standard test finger or similar
objects not exceeding 80 mm in length.
Excludes solid objects exceeding
2,5 mm in diameter or thickness.
Excludes solid objects exceeding 1 mm
in diameter or thickness.
and locations that would interfere with
the intended operation of the equipment.
2nd
Short description Definition
digit
1 Protected against-
dripping water
2 Protected against
dripping water
when tilted up to
15°
3 Protected against
spraying water
4 Protected against
splashing water
5 Protected against
water jets
6 Protected against
heavy seas
7 Protected against
the effects of immersion
8 Protected against
submersion
Dripping water (vertically falling drops)
shall have no harmful effect.
Vertically dripping water shall have no
harmful effect when the enclosure is tilted at any angle up to 15° from its normal position.
Water falling as a spray at an angle up
to 60° from the vertical shall have no
harmful effect.
Water splashed against the enclosure
from any direction shall have no harmful effect.
Water protected by a nozzle against the
enclosure from any direction shall have
no harmful effect.
Water from heavy seas or water projected in powerful jets shall not enter
the enclosure in harmful quanties.
Ingress of water in a harmful quantity
shall not be possible when the enclosure is immersed in water under standard conditions of pressure and time.
No ingress of water.
Terminal markings acc. to EN50011
Auxiliary contacts of AC contactors and contacts of contactor relays
and thermal overload relays are particularly marked. The terminal
markings of normally-open contacts are printed as positive figures,
they of normally-closed contacts as negative figures.
This gives a clear indication of the function of the contacts.
The figure below illustrates the determination of terminal markings
for contactors with auxiliary contact blocks.
Sequence number
Function number
The complete terminal marking according
to EN 50011 and EN 50012 results from the
sequence numbers on the contactor relay
or ac contactor (2., 3.) and the function
numbers on the auxiliary contact blocks
(e. g. .1, .2, or .3, .4).
Resistance to climatic conditions acc. to IEC 68
Open-type devices are climate-resistant in the constant climate
according to IEC 68-2-3 (this is a climate with an ambient temperature of 40°C and an atmospheric humidity of 90 to 95%).
Enclosed devices are climate-resistant in an alternating climate
according to IEC 68-2-30 (this is a moist alternating climate with a
24-hour cycle between climates with an ambient temperature of
25°C, and an atmospheric humidity of 95 to 100% and an ambient
temperature of 40°C, and an atmospheric humidity of 90 to 96% in
the presence of condensation during rises in temperature).
Data are valid up to an altitude of 2000m above sea level.
Short circuit protection
Back up fuses should be used to protect contactors and starters
against short circuits. For starters the device with the smaller admissible fuse at the main and at the control circuit (contactor or thermal
overload) determines the fuse size.
After a short circuit devices have to be checked for correct operation.
Disconnect power before proceeding with any work on the equipment!
96 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
Page 17

Mounting positions of contactors
J7KNA-AR... and J7KNA-12... J7KN-10 to J7KN-74, J7KN-85 to J7KN-110 J7KN-151... to J7KN-200
Terminal screws
Devices Kind of connection
Typ e
Mini Contactors
All conductors
J7KN-AR...; J7KNA-09...;
J7KNA-12...
Contactors
Main conductor
J7KN-10... to J7KN-22... M3,5 J7KN-24... to J7KN-40... - M5
J7KN-50... to J7KN-74... - M6
J7KN-85..., J7KN-110... - M8
Auxiliary conductor
J7KN-10... to J7KN-22... M3,5 J7KN-85... to J7KN-110 M3,5 -
Screw with
washer
M3,5 -
Screw with
clamp box
Devices Kind of connection
Type
Coil conductor
J7KN-10... to J7KN-110... M3,5 -
Accessories
J73KNA(M)... M3,5 J73KN-B, J73KN-C M3,5 -
Thermal Overload Relays
Main conductor
J7TKN-A M4 J7TKN-B M3,5 J7TKN-C M5 J7TKN-D - M6
Auxiliary conductor
All devices M3,5 -
Screw with
washer
Screw with
clamp box
Terminal screws in relation to screwdriver sizes and tightening torques
Terminal screws Pozidriv Screw driver Tightening torque
Version Size Nm lb. inch
Screw with Pozidriv and slot M3 Pz 1 Size 1 0,6 - 1,2 5 - 11
M3,5 Pz 2 Size 2, 3 0,8 - 1,4 7 - 12
M4 Pz 2 Size 3, 4 1,2 - 1,8 11 - 16
M5 Pz 2 Size 3, 4, 5 2,5 - 3 22 - 26
M6 Pz 3 Size 4, 5 3,5 - 4,5 31 - 40
Screw or
nut with hexagonal-head
M8 - - 6 - 10 53 - 88
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 97
Page 18

General technical information
■ Current carrying capacities of PVC insulated 600/1000 Volt cables
with copper or aluminium conductors.
In accordance with the 16th edition of the “Wiring Regulations for Electrical Installations“.
Basic assumptions: Ambient temperature of 30°C.
Circuit of protected by a OMRON circuit-breaker to IEC 947-2, or a fuse to BS 88 or BS 1361.
Figures must be adjusted by the correction factors for ambient temperature and/or cable grouping as detailed in the IEE regs.
Conductor
size In conduit or trunking (enclosed)
Single-phase Three-phase Single-phase Three-phase Single-phase Three-phase
mm²
Single core, PVC insulated cable non-armoured, copper or aluminium conductors.
1.0
1.5
2.5
4.0
6.0
10.0
16.0
25.0
35.0
50.0
70.0
95.0
120.0
150.0
185.0
240.0
300.0
400.0
500.0
630.0
Twin and multi-core PVC insulated cable, non-armoured, copper or aluminium conductors.
1.0
1.5
2.5
4.0
6.0
10.0
16.0
25.0
35.0
50.0
70.0
95.0
120.0
150.0
185.0
240.0
300.0
400.0
Cu [A] Al [A] Cu [A] Al [A] Cu [A] Al [A] Cu [A] Al [A] Cu [A] Al [A] Cu [A] Al [A]
13.5 - 12.0 - 15.5 - 14.0 - ----
17.5 - 15.5 - 20.0 - 18.0 - ----
24.0 - 21.0 - 27.0 - 25.0 - ----
32.0 - 28.0 - 37.0 - 33.0 - ----
41.0 - 36.0 - 47.0 - 43.0 - ----
57.0 - 50.0 - 65.0 - 59.0 - ----
76.0 - 68.0 - 87.0 - 79.0 - ----
101.0 - 89.0 - 114.0 - 104.0 - 126.0 - 112.0 -
125.0 - 110.0 - 141.0 - 129.0 - 156.0 - 141.0 -
151.0 118.0 134.0 104.0 182.0 134.0 167.0 123.0 191.0 144.0 172.0 132.0
192.0 150.0 171.0 133.0 234.0 172.0 214.0 156.0 246.0 185.0 223.0 169.0
232.0 181.0 207.0 161.0 284.0 210.0 261.0 194.0 300.0 225.0 273.0 206.0
296.0 210.0 239.0 186.0 330.0 245.0 303.0 226.0 349.0 261.0 318.0 240.0
300.0 234.0 262.0 204.0 381.0 283.0 349.0 261.0 404.0 301.0 369.0 277.0
341.0 266.0 296.0 230.0 436.0 324.0 400.0 299.0 463.0 344.0 424.0 317.0
400.0 312.0 346.0 269.0 515.0 384.0 472.0 354.0 549.0 407.0 504.0 375.0
458.0 358.0 394.0 306.0 594.0 444.0 545.0 410.0 635.0 469.0 584.0 435.0
546.0 - 467.0 - 694.0 - 634.0 - 732.0 - 679.0 -
626.0 - 533.0 - 792.0 - 723.0 - 835.0 - 778.0 -
720.0 - 611.0 - 904.0 - 826.0 - 953.0 - 892.0 -
11.0 - 11.5 - 15.0 - 13.5 - 17.0 - 14.5 -
14.0 - 15.0 - 19.5 - 17.5 - 22.0 - 18.5 -
18.5 - 20.0 - 27.0 - 24.0 - 30.0 - 25.0 -
25.0 - 27.0 - 36.0 - 32.0 - 40.0 - 34.0 -
32.0 - 34.0 - 46.0 - 41.0 - 51.0 - 43.0 -
43.0 - 46.0 - 63.0 - 57.0 - 70.0 - 60.0 -
57.0 54.0 62.0 48.0 85.0 66.0 76.0 59.0 94.0 73.0 80.0 61.0
75.0 71.0 80.0 62.0 112.0 83.0 96.0 73.0 119.0 89.0 101.0 78.0
92.0 86.0 99.0 77.0 138.0 103.0 119.0 90.0 148.0 111.0 126.0 96.0
110.0 104.0 118.0 92.0 168.0 125.0 144.0 110.0 180.0 135.0 153.0 117.0
139.0 131.0 149.0 116.0 213.0 160.0 184.0 140.0 232.0 173.0 196.0 150.0
167.0 157.0 179.0 139.0 258.0 195.0 261.0 170.0 282.0 210.0 238.0 183.0
192.0 - 206.0 160.0 299.0 245.0 259.0 197.0 328.0 - 276.0 212.0
219.0 - 225.0 184.0 344.0 283.0 299.0 227.0 379.0 - 319.0 245.0
248.0 - 255.0 210.0 392.0 324.0 341.0 259.0 434.0 - 364.0 280.0
291.0 - 297.0 248.0 461.0 384.0 403.0 305.0 514.0 - 430.0 330.0
334.0 - 339.0 258.0 530.0 444.0 464.0 351.0 593.0 - 497.0 381.0
--402.0 - 634.0 - 557.0 - 715.0 - 597.0 -
Clipped to surface or cable tray,
bunched, embedded in plaster
(unenclosed)
Fixed to vertical surface of wall or open
cable trench with 20 mm separation
between cables and wall
98 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
Page 19

■ Overall diameter of cables (Copper)
The dimensions are based on BS specification or the average values as given by the manufacturers.
The overall diameters given are for cables of 600/1000 V grade.
Number and nominal
area of cables (mm
1 x 1.0 - 4.5 2 x 1.0 - 1 x 1.5 - 4.9 2 x 1.5 11.7 7.2
1 x 2.5 - 5.8 2 x 2.5 13.1 8.6
1 x 4.0 - 6.8 2 x 4.0 15.1 10.7
1 x 6.0 - 7.4 2 x 6.0 16.5 12.0
1 x 10.0 - 8.8 2 x 10.0 20.1 14.9
1 x 16.0 - 10.5 2 x 16.0 21.9 17.2
1 x 25.0 - 12.5 2 x 25.0 23.0 18.4
1 x 35.0 - 13.5 2 x 35.0 24.9 20.1
1 x 50.0 19.1 15.1 2 x 50.0 27.8 22.8
1 x 70.0 21.1 16.9 2 x 70.0 30.4 25.5
1 x 95.0 23.4 19.4 2 x 95.0 35.5 29.3
1 x 120.0 26.3 21.0 2 x 120.0 38.0 31.8
1 x 150.0 28.3 23.2 2 x 150.0 41.3 35.1
1 x 185.0 30.8 25.8 2 x 185.0 46.4 39.1
1 x 240.0 34.1 29.0 2 x 240.0 51.2 43.9
1 x 300.0 37.0 32.1 2 x 300.0 56.4 48.7
1 x 400.0 42.0 35.8 2 x 400.0 61.9 54.2
1 x 500.0 45.6 39.6 --1 x 630.0 49.7 43.8 ---
Approx. overall diameter in mm
2
)
PVC/SWA PVC PVC/SWA PVC
Number and nominal
area of cables (mm2)
Approx. overall diameter in mm
Number and nominal
area of cables (mm2)
3 x 1.0 - - 4 x 1.0 - -
3 x 1.5 12.3 7.6 4 x 1.5 13.0 8.3
3 x 2.5 13.6 9.1 4 x 2.5 14.5 10.0
3 x 4.0 15.8 11.5 4 x 4.0 17.8 12.6
3 x 6.0 18.0 12.8 4 x 6.0 19.2 14.2
3 x 10.0 21.2 15.8 4 x 10.0 22.8 17.7
3 x 16.0 23.1 19.7 4 x 16.0 26.3 20.6
3 x 25.0 25.0 20.4 4 x 25.0 27.8 22.9
3 x 35.0 27.3 22.4 4 x 35.0 30.5 25.4
3 x 50.0 30.5 25.5 4 x 50.0 35.4 29.2
3 x 70.0 35.0 28.7 4 x 70.0 39.2 33.0
3 x 95.0 39.3 33.3 4 x 95.0 44.3 38.3
3 x 120.0 42.2 36.3 4 x 120.0 49.3 41.8
3 x 150.0 47.5 40.0 4 x 150.0 53.6 46.3
3 x 185.0 51.9 44.6 4 x 185.0 59.0 61.3
3 x 240.0 57.8 50.1 4 x 240.0 65.7 58.0
3 x 300.0 63.2 55.6 4 x 300.0 72.0 64.6
3 x 400.0 69.6 62.2 4 x 400.0 81.3 72.0
Approx. overall diameter in mm
PVC/SWA PVC PVC/SWA PVC
Number and nominal
area of cables (mm2)
Approx. overall diameter in mm
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 99
Page 20

■ Conversion table
To convert Multiply by
Inches to millimeters (mm) 25.4
Millimeters to inches (In.) 0.03937
Feet to meters (m) 0.3048
meters to feet (ft) 3.2808
Yards to meters (m) 0.9144
meters to yards (yd) 1.0936
Miles to kilometers (km) 1.6093
Kilometers to miles (mil.) 0.6214
Square inches to square millimeters (mm
Square millimeters to square inches (inch
Square yards to square meters (m
Square meters to square yards (yd
Cubic inches to cubic centimeters (cm
Cubic centimeters to cubic inches (inch
Pounds to kilogrammes (kg) 0.4536
Kilogrammes to pounds (lb) 2.2046
Tons (2,240 lb) to kilogrammes (kg) 1,016.05
Kilogrammes to tons (240 lb) 0.0009842
Ounces (avoirdpois) to grammes (g) 28.3495
Grammes to ounces 0.0353
Gallons to litres (l) 4.561
Litres to gallons 0.220
Force N (newtons) to lbft
1 N = 1 kg (mass) accelerated at 1 metre/sec.
1 Nm = 1 J (joule) to calorie 0.239
Horse-power to kilowatts (kW) 0.7458
Kilowatts to horse-power (h.p.)
1 W (watt) = 1J/s
Atmospheres to lb per square inch (lb/inch
1 bar = 1 kg/cm
2
= 735.6 mm Hg = 14.2 lb/inch
2
)
2
)
2
)
2
)
3
)
3
)
645.16
0.00155
0.8361
1.196
16.387
0.06102
0.225
1.3408
2
)
2
14.68
Conversion table for:
Centigrade/Fahrenheit
BP-212
200
190
180
170
160
150
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
FP-
30
20
10
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
10
200
˚C˚F
Conversion table for mm²/AWG cable sizes
2
mm
0.75 18
1.0 17
1.5 16
2.5 13
4.0 12
6.0 10
10.0 8
AWG
100 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
Page 21

■
Rated currents of 3-phase motors (approx. figures for squirrel-cage motors)
Minimum fuse size for protection of 3-phase motors
The maximum size is determined by the requirements of the switchgear or overload relay.
The rated motor currents are for standard 1500 r.p.m. 3-phase enclosed ventilated and totally enclosed fan-cooled motors.
D.O.L. starting: Maximum starting current 6 x rated motor current. Maximum starting time 5 s.
Y/D starting: Maximum starting current 2 x rated motor current. Maximum starting time 15 s.
Rated fuse currents for Y/D starting are also valid for 3-phase motors with slip-ring motors.
For higher rated currents, starting currents and/or longer starting times, larger fuses are required.
Table is valid for “slow” and/or “gL” fuses (DIN VDE 0636).
For NH fuses with aM characteristics, fuses = rated current is selected.
Motor rating
kW cos ϕη %AAAAAAAA, BSA, BS
0.06 0.7 58 0.37 2.0 - 0.21 2.0 - 0.21 2.0 2
0.09 0.7 60 0.54 2.0 - 0.31 2.0 - 0.30 2.0 2
0.12 0.7 60 0.72 4.0 2 0.41 2.0 - 0.40 2.0 2
0.18 0.7 62 1.04 4.0 2 0.6 2.0 - 0.58 2.0 2
0.25 0.7 62 1.4 4.0 2 0.8 4.0 2 0.8 4.0 2
0.37 0.72 66 2.0 6.0 4 1.1 4.0 2 1.1 4.0 2
0.55 0.75 69 2.7 10.0 4 1.5 4.0 2 1.5 6.0 4
0.75 0.79 74 3.2 10.0 4 1.9 6.0 4 1.8 6.0 4
1.1 0.81 74 4.6 10.0 6 2.6 6.0 4 2.6 10.0 6
1.5 0.81 74 6.3 16.0 10 3.6 6.0 4 3.5 16.0 10
2.2 0.81 78 8.7 20.0 10 5.0 10.0 6 4.8 16.0 10
3.0 0.82 80 11.5 25.0 16 6.6 16.0 10 6.4 20.0 16
4.0 0.82 83 14.8 32.0 16 8.5 20.0 10 8.2 20.0 16
5.5 0.82 86 19.6 32.0 25 11.3 25.0 16 10.9 25.0 20
7.5 0.82 87 26.4 50.0 32 15.2 32.0 16 14.6 35.0 25
11.0 0.84 87 38.0 80.0 40 21.7 40.0 25 20.9 50.0 32
15.0 0.84 88 51.0 100.0 63 29.3 63.0 32 28.2 80.0 40
18.5 0.84 88 63.0 125.0 80 36.0 63.0 40 35.0 80.0 50
22.0 0.84 92 71.0 125.0 80 41.0 80.0 50 40.0 80.0 50
30.0 0.85 92 96.0 200.0 100 55.0 100.0 63 53.0 100.0 80
37.0 0.86 92 117.0 200.0 125 68.0 125.0 80 65.0 125.0 80
45.0 0.86 93 141.0 250.0 160 81.0 160.0 100 78.0 125.0 80
55.0 0.86 93 173.0 250.0 200 99.0 200.0 125 96.0 160.0 100
75.0 0.86 94 233.0 315.0 250 134.0 200.0 160 129.0 250.0 160
90.0 0.86 94 279.0 400.0 315 161.0 250.0 200 155.0 250.0 160
110.0 0.86 94 342.0 500.0 400 196.0 315.0 200 189.0 315.0 200
132.0 0.87 95 401.0 630.0 500 231.0 400.0 250 222.0 355.0 250
160.0 0.87 95 486.0 630.0 630 279.0 400.0 315 269.0 355.0 315
200.0 0.87 95 607.0 800.0 630 349.0 500.0 400 337.0 450.0 355
250.0 0.87 95 ---437.0 630.0 500 421.0 500.0 450
315.0 0.87 96 ---544.0 800.0 630 525.0 630.0 560
400.0 0.88 96 ---683.0 1000.0 800 ---
450.0 0.88 96 ---769.0 1000.0 800 ---
500.0 0.88 97 ---------
560.0 0.88 97 ---------
630.0 0.88 97 ---------
Set overload relay in the phase lead to 0.58 x rated motor current.
230 V400 V415 V
Rated
motor
current
Fuse
starting
D.O.L. Y/∆
Rated
motor
current
Fuse
starting
D.O.L. Y/∆
Rated
motor
current
Fuse
starting
D.O.L. Y/∆
Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix 101
Page 22

Minimum fuse size for protection of 3-phase motors
The maximum size is determined by the requirements of the switchgear or overload relay.
The rated motor currents are for standard 1500 r.p.m. 3-phase enclosed ventilated and totally enclosed fan-cooled motors.
D.O.L. starting: Maximum starting current 6 x rated motor current. Maximum starting time 5 s.
Y/D starting: Maximum starting current 2 x rated motor current. Maximum starting time 15 s.
Rated fuse currents for Y/D starting are also valid for 3-phase motors with slip-ring motors.
For higher rated currents, starting currents and/or longer starting times, larger fuses are required.
Table is valid for “slow” and/or “gL” fuses (DIN VDE 0636).
For NH fuses with aM characteristics, fuses = rated current is selected.
Motor rating
kW cos ϕη %AAAAAA
0.06 0.7 58 0.17 2.0 - 0.12 2.0 -
0.09 0.7 60 0.25 2.0 - 0.18 2.0 -
0.12 0.7 60 0.33 2.0 - 0.24 2.0 -
0.18 0.7 62 0.48 2.0 - 0.35 2.0 -
0.25 0.7 62 0.70 2.0 - 0.50 2.0 -
0.37 0.72 66 0.90 2.0 2 0.70 2.0 -
0.55 0.75 69 1.20 4.0 2 0.90 4.0 2
0.75 0.79 74 1.50 4.0 2 1.10 4.0 2
1.1 0.81 74 2.1 6.0 4 1.5 4.0 2
1.5 0.81 74 2.9 6.0 4 2.1 6.0 4
2.2 0.81 78 4.0 10.0 4 2.9 10.0 4
3.0 0.82 80 5.3 16.0 6 3.8 10.0 4
4.0 0.82 83 6.8 16.0 10 4.9 16.0 6
5.5 0.82 86 9.0 20.0 16 6.5 16.0 10
7.5 0.82 87 12.1 25.0 16 8.8 20.0 10
11.0 0.84 87 17.4 32.0 20 12.6 25.0 16
15.0 0.84 88 23.4 50.0 25 17.0 32.0 20
18.5 0.84 88 28.9 50.0 32 20.9 32.0 25
22.0 0.84 92 33.0 63.0 32 23.8 50.0 25
30.0 0.85 92 44.0 80.0 50 32.0 63.0 32
37.0 0.86 92 54.0 100.0 63 39.0 80.0 50
45.0 0.86 93 65.0 125.0 80 47.0 80.0 63
55.0 0.86 93 79.0 160.0 80 58.0 100.0 63
75.0 0.86 94 107.0 200.0 125 78.0 160.0 100
90.0 0.86 94 129.0 200.0 160 93.0 160.0 100
110.0 0.86 94 157.0 250.0 160 114.0 200.0 125
132.0 0.87 95 184.0 250.0 200 134.0 250.0 160
160.0 0.87 95 224.0 315.0 250 162.0 250.0 200
200.0 0.87 95 279.0 400.0 315 202.0 315.0 250
250.0 0.87 95 349.0 500.0 400 253.0 400.0 315
315.0 0.87 96 436.0 630.0 500 316.0 500.0 400
400.0 0.88 96 547.0 800.0 630 396.0 630.0 400
450.0 0.88 96 615.0 800.0 630 446.0 630.0 630
500.0 0.88 97 ---491.0 630.0 630
560.0 0.88 97 ---550.0 800.0 630
630.0 0.88 97 ---618.0 800.0 630
Set overload relay in the phase lead to 0.58 x rated motor current.
500 V 600 V
Rated
motor
current
Fuse
starting
D.O .L. Y /∆
Rated
motor
current
Fuse
starting
D.O.L. Y /∆
ALL DIMENSIONS SHOWN ARE IN MILLIMETERS.
Cat. No. J09E-EN-01A
In the interest of product improvement, specifications are subject to change without notice.
102 Low Voltage Switch Gear Appendix
 Loading...
Loading...