Omron CP1H-X40DR-A, CP1H-X40DT-D, CP1H-X40DT1-D, CP1H-XA40DR-A, CP1H-XA40DT-D Brochure
...
Advanced Industrial Automation
» A n a l o gu e I /O bu il t- i n
» Fl e xi b le co m mu n ic a ti o ns
»
4 axe s p ul se I/O
CP1H
T h e A l l - i n - O n e Co n t r o l l e r

With 4 high-speed encoder inputs up to 1 MHz (single phase)
and 4 pulse outputs up to 1 MHz (line driver), CP1H CPUs are
ideal for positioning and speed control.
Their optional 4 analogue inputs and 2 analogue outputs plus
advanced PID control with auto-tuning also make them ideal
for continuous control applications.
The All-in-One Controller
Combining the processing power and data capacity
of the CJ1M series and the built-in digital I/O
functionality of the CPM2A series in a compact PLC
outline, the CP1H CPU series sets new standards.
Advanced Industrial Automation
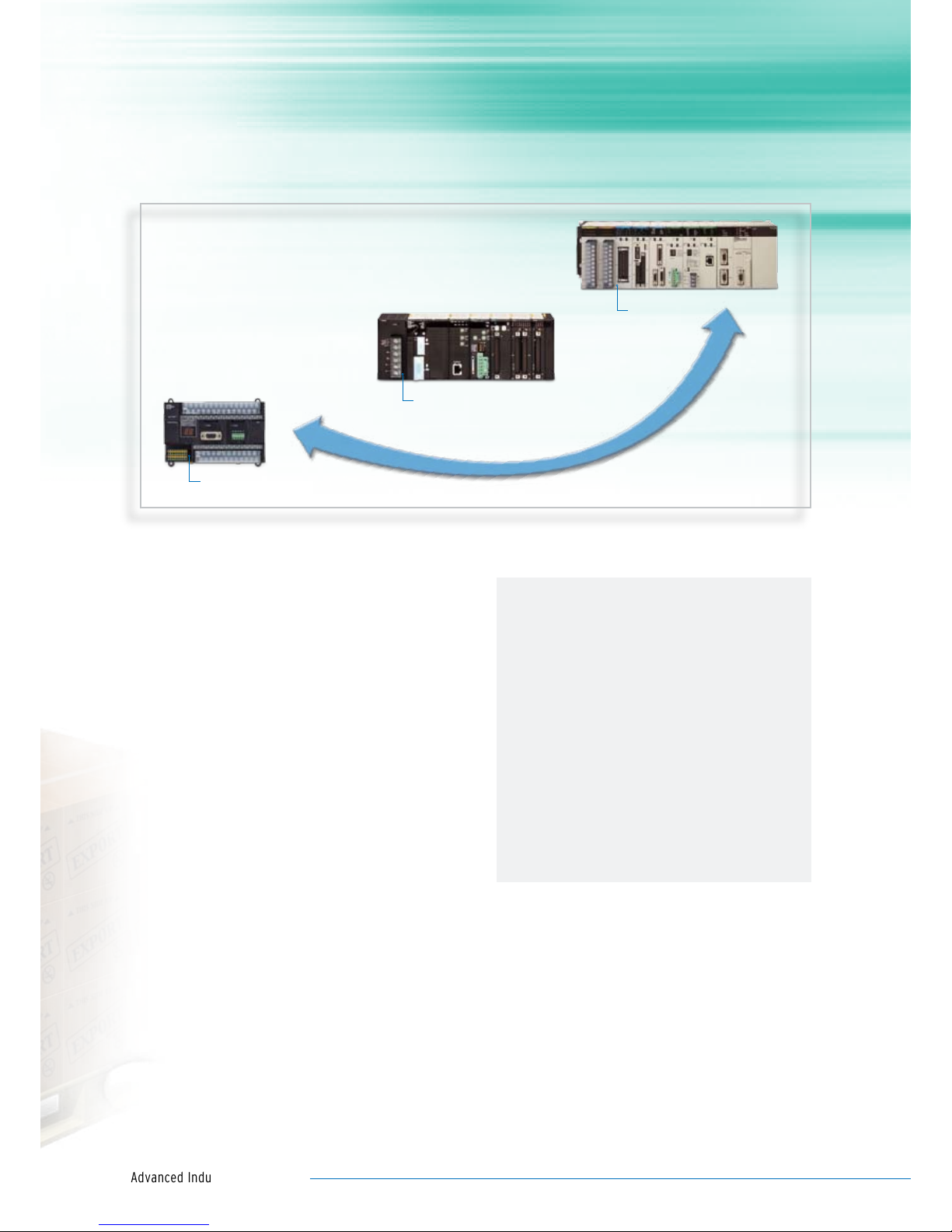
Rack PLCs
CS series
Modular PLCs
CJ series
Omron’s PLC Lineup
What’s more, expandable with CPM1A I/O units (up to 320 I/O
points) and up to two CJ1 Special I/O units or CPU bus units,
CP1H CPUs offer a wide range of communication interfaces and
advanced I/O units.
Equipped with a USB interface as standard for programming
and monitoring, the new CPUs allow up to two serial ports
to be plugged in for communication with HMI or field devices.
And, of course, they provide ‘Smart Platform’ communication
routing over multiple network layers.
Using CX-One, programs can be created that enable the user
to build, configure and program networks, PLCs, HMIs, motion-
control systems, drives, temperature controllers and sensors.
The CP1H CPU series has the same architecture as the CS/CJ
PLC series, which means programs are compatible for memory
allocations and instructions and also support Function Blocks
and Structured Text.
Compact PLCs
CP series
Features at a glance
• 4 high-speed encoder inputs and 4 fast pulse outputs
• AC or DC supply, 24 digital inputs and 16 digital outputs
(transistor or relay)
• CJ1M-compatible instruction set and execution speed
• Expandable with intelligent CJ1 I/O and
communication units
• Analogue I/O built-in (optional), RS232C and
RS-422A/485 serial ports (plug-in option boards)
Small-scale control
Large-scale control
Same programming method
Same instruction set
including FB/ST.

4
Four-axes Counter Function (Single-phase or Differential Phases)
CP1H-X(A) CPU Units: Four axes, single-phase at 100 kHz or differential phases at 50 kHz
CP1H-Y CPU Units: Two axes, single-phase at 1 MHz or differential phases at 500 kHz plus two axes,
single-phase at 100 kHz or differential phases at 50 kHz
Eight Interrupt Inputs
Eight inputs can be used as:
• 50 μs pulse catch inputs
• interrupt inputs
• simple counter inputs (< 5 kHz)
Program execution speed
Interrupt inputs
Quick-response
inputs
Counter inputs
8 normal inputs
High-speed counter/encoder input
General purpose
motors
Inverters
Rotary encoders
High speed counter
CP1H RS-485
Fast I/O requires fast response, the CJ1M core provides
class-leading program execution speed.
CP1H
CPM2A
CPM1A
LD instruction
MOV instruction
μs 0.1
μs
0.3
0.64 μs
7.8 μs
1.72 μs
16.3 μs
Advanced Industrial Automation
5
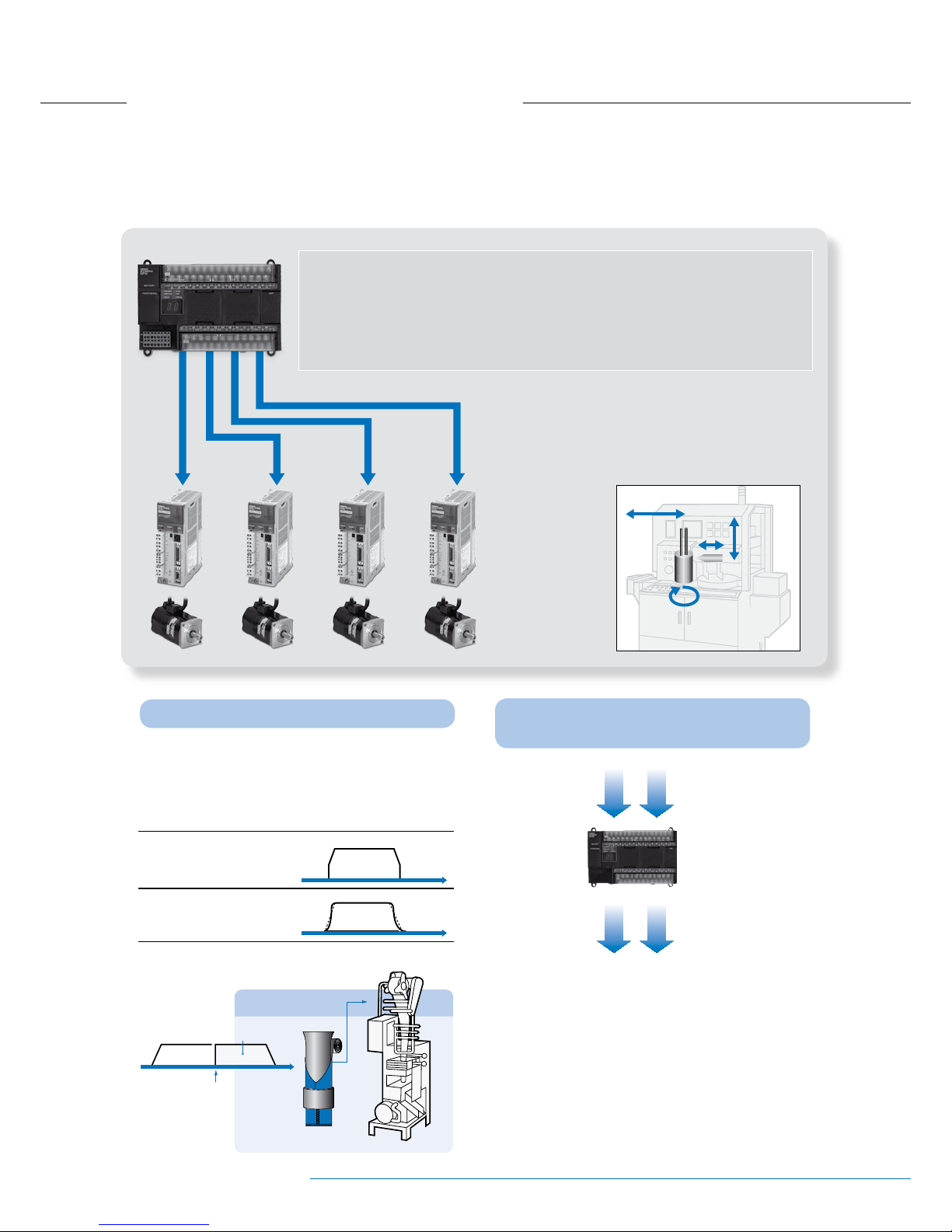
Pulse Output Function for Up to Four Axes.
CP1H-X(A) CPU Units: Two axes at 100 kHz and two axes at 30 kHz
CP1H-Y CPU Units: Two axes at 1 MHz and two axes at 30 kHz
Two 1-MHz high-speed
counter line-driver
inputs (special pulse
input terminals)
Example: Four-axes Control in Electronic
Component Manufacturing Equipment
Capacitor removal
Rotation
(final positioning)
Processing
positioning
Processing
depth
Easy engineering with standard functions
Easily achieved with special positioning
instruction (PLS2).
1MHz High-speed Pulse Output
(CP1H-Y CPU Units: To be released soon.)
Two 1-MHz high-speed
counter line-driver
outputs (special pulse
output terminals)
Two high-speed counter normal
inputs (100 kHz)
CP1H-Y CPU Unit
Two 30-kHz normal pulse outputs
CP1H-Y CPU Units offer built-in 1-MHz line-driver I/O.
• Line-driver outputs: Two each for CW and CCW.
• Line-driver inputs: Two each for phases A, B, and Z.
CP1H-Y CPU Units also have 20 normal I/O points (12 inputs
and 8 outputs), and can provide 100-kHz high-speed counter
inputs for two axes and 30-kHz pulse outputs for two axes.
PLS2 executed
Speed control
(ACC instruction)
Stop after output of
set number of pulses
Feed Control for
Packing Material
4 Pulse outputs for
precise positioning
CP1H
Pulse outputs
Servo Drivers
Servomotors
• Single-instruction Origin Search Function
• Positioning with Trapezoidal Acceleration and
Deceleration (PLS2 Instruction)
Target speed control
Acceleration
Start frequency
Deceleration
Specified number
of travel pulses
S-curve
acceleration
S-curve
deceleration
Interrupt Feeding (ACC and PLS2 Instructions)
S-curve acceleration/deceleration can be used
to reduce vibration in high-speed positioning.
6
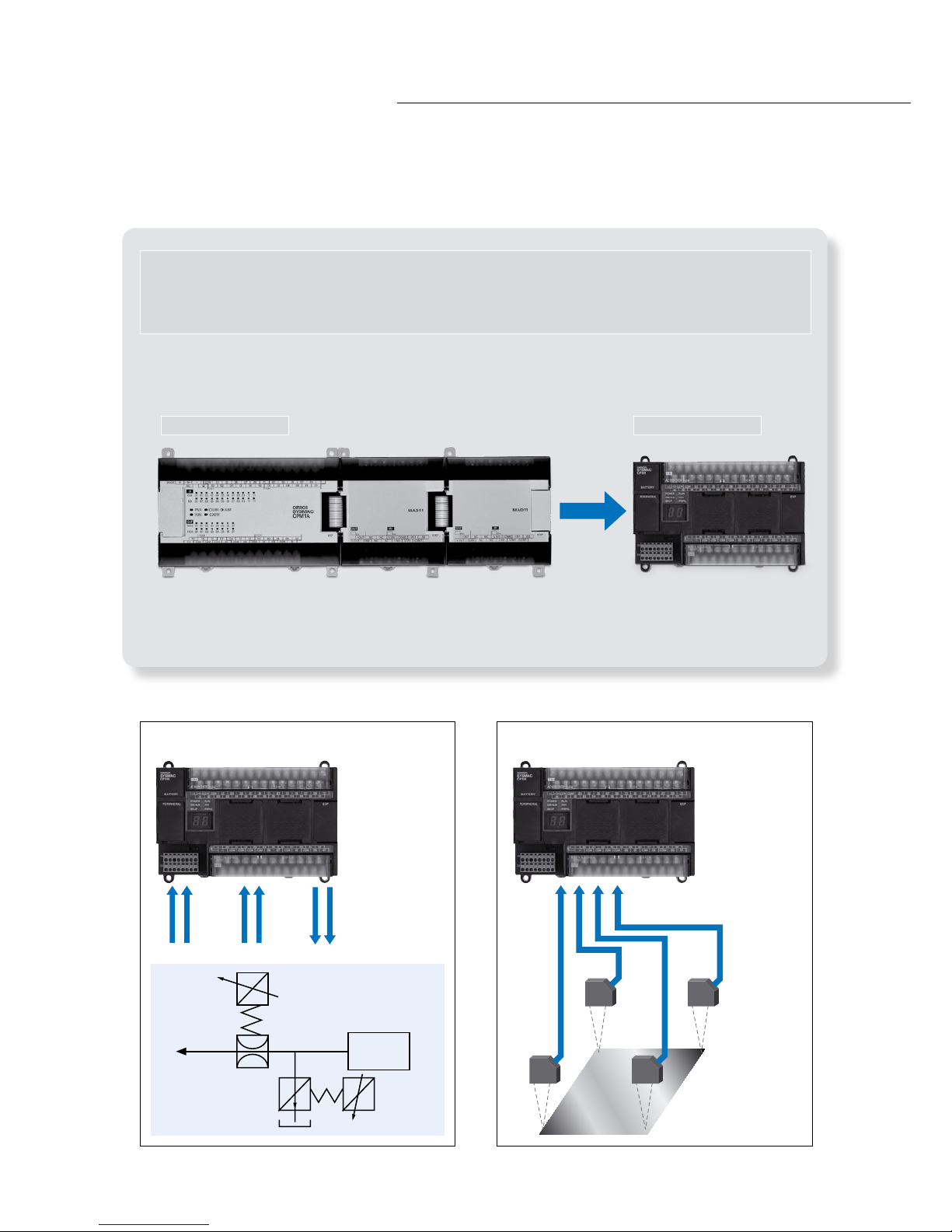
• Oil Pressure Control
Pressure Position Control valves
• Inspection Devices
Analogue I/O
Analogue Control without Using Expansion Units
CP1H-XA CPU Units have four analogue inputs and two analogue outputs built in.
CP1H-XA
CPM2A CPU Unit with Two CPM1A-MAD11 Analogue I/O Units
(2 Analogue Inputs and 1 Analogue Output)
Previously CP1H
Pressure
actuator
Pressure
pump
Flow control valve
Pressure
control
valve
Displacement
sensors
Inspection for warping
and twisting
 Loading...
Loading...