Page 1

Cat. No. I558-E1-02
USER’S MANUAL
SYSDRIVE JX
SERIES
Compact Simplified Inverters
Page 2

Page 3

Introduction
Thank you for choosing the general-purpose Inverter 3G3JX. This User's Manual (hereinafter called
"this manual") describes the parameter setting methods required for installation/wiring and
operation of the 3G3JX model, as well as troubleshooting and inspection methods.
z This manual should be delivered to the actual end user of the product.
z After reading this manual, keep it handy for future reference.
z This manual describes the specifications and functions of the product as well as the relations
between them. You should assume that anything not described in this manual is not possible with
the product.
z Intended readers
This manual is intended for:
Those with knowledge of electrical systems (qualified electrical engineers or the equivalent), and
also in charge of:
• Introducing the control equipment
• Designing the control system
• Installing and/or connecting the control equipment
• Field management
Introduction
1
Page 4

Read and Understand This Manual
Read and Understand This Manual
Please read and understand this manual before using the product. Please consult your OMRON representative
if you have any questions or comments.
Warranty and Limitations of Liability
WARRANTY
OMRON's exclusive warranty is that the products are free from defects in materials and workmanship for a
period of one year (or other period if specified) from date of sale by OMRON.
OMRON MAKES NO WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING
NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE OF THE
PRODUCTS. ANY BUYER OR USER ACKNOWLEDGES THAT THE BUYER OR USER ALONE HAS
DETERMINED THAT THE PRODUCTS WILL SUITABLY MEET THE REQUIREMENTS OF THEIR
INTENDED USE. OMRON DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
LIMITATIONS OF LIABILITY
OMRON SHALL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES, LOSS OF PROFITS OR COMMERCIAL LOSS IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE
PRODUCTS, WHETHER SUCH CLAIM IS BASED ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, NEGLIGENCE, OR
STRICT LIABILITY.
In no event shall the responsibility of OMRON for any act exceed the individual price of the product on
which liability is asserted.
IN NO EVENT SHALL OMRON BE RESPONSIBLE FOR WARRANTY, REPAIR, OR OTHER CLAIMS
REGARDING THE PRODUCTS UNLESS OMRON'S ANALYSIS CONFIRMS THAT THE PRODUCTS
WERE PROPERLY HANDLED, STORED, INSTALLED, AND MAINTAINED AND NOT SUBJECT TO
CONTAMINATION, ABUSE, MISUSE, OR INAPPROPRIATE MODIFICATION OR REPAIR.
2
Page 5

Read and Understand This Manual
Application Considerations
SUITABILITY FOR USE
OMRON shall not be responsible for conformity with any standards, codes, or regulations that apply to
the combination of products in the customer's application or use of the products.
At the customer's request, OMRON will provide applicable third party certification documents identifying
ratings and limitations of use that apply to the products. This information by itself is not sufficient for a
complete determination of the suitability of the products in combination with the end product, machine,
system, or other application or use.
The following are some examples of applications for which particular attention must be given. This is not
intended to be an exhaustive list of all possible uses of the products, nor is it intended to imply that the
uses listed may be suitable for the products:
• Outdoor use, uses involving potential chemical contamination or electrical interference, or conditions
or uses not described in this manual.
• Nuclear energy control systems, combustion systems, railroad systems, aviation systems, medical
equipment, amusement machines, vehicles, safety equipment, and installations subject to separate
industry or government regulations.
• Systems, machines, and equipment that could present a risk to life or property.
Please know and observe all prohibitions of use applicable to the products.
NEVER USE THE PRODUCTS FOR AN APPLICATION INVOLVING SERIOUS RISK TO LIFE OR
PROPERTY WITHOUT ENSURING THAT THE SYSTEM AS A WHOLE HAS BEEN DESIGNED TO
ADDRESS THE RISKS, AND THAT THE OMRON PRODUCTS ARE PROPERLY RATED AND
INSTALLED FOR THE INTENDED USE WITHIN THE OVERALL EQUIPMENT OR SYSTEM.
PROGRAMMABLE PRODUCTS
OMRON shall not be responsible for the user's programming of a programmable product, or any
consequence thereof.
3
Page 6

Read and Understand This Manual
Disclaimers
CHANGE IN SPECIFICATIONS
Product specifications and accessories may be changed at any time based on improvements and other
reasons.
It is our practice to change model numbers when published ratings or features are changed, or when
significant construction changes are made. However, some specifications of the products may be
changed without any notice. When in doubt, special model numbers may be assigned to fix or establish
key specifications for your application on your request. Please consult with your OMRON representative
at any time to confirm actual specifications of purchased products.
DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHTS
Dimensions and weights are nominal and are not to be used for manufacturing purposes, even when
tolerances are shown.
PERFORMANCE DATA
Performance data given in this manual is provided as a guide for the user in determining suitability and
does not constitute a warranty. It may represent the result of OMRON's test conditions, and the users
must correlate it to actual application requirements. Actual performance is subject to the OMRON
Warranty and Limitations of Liability.
ERRORS AND OMISSIONS
The information in this manual has been carefully checked and is believed to be accurate; however, no
responsibility is assumed for clerical, typographical, or proofreading errors, or omissions.
4
Page 7
Safety Precautions
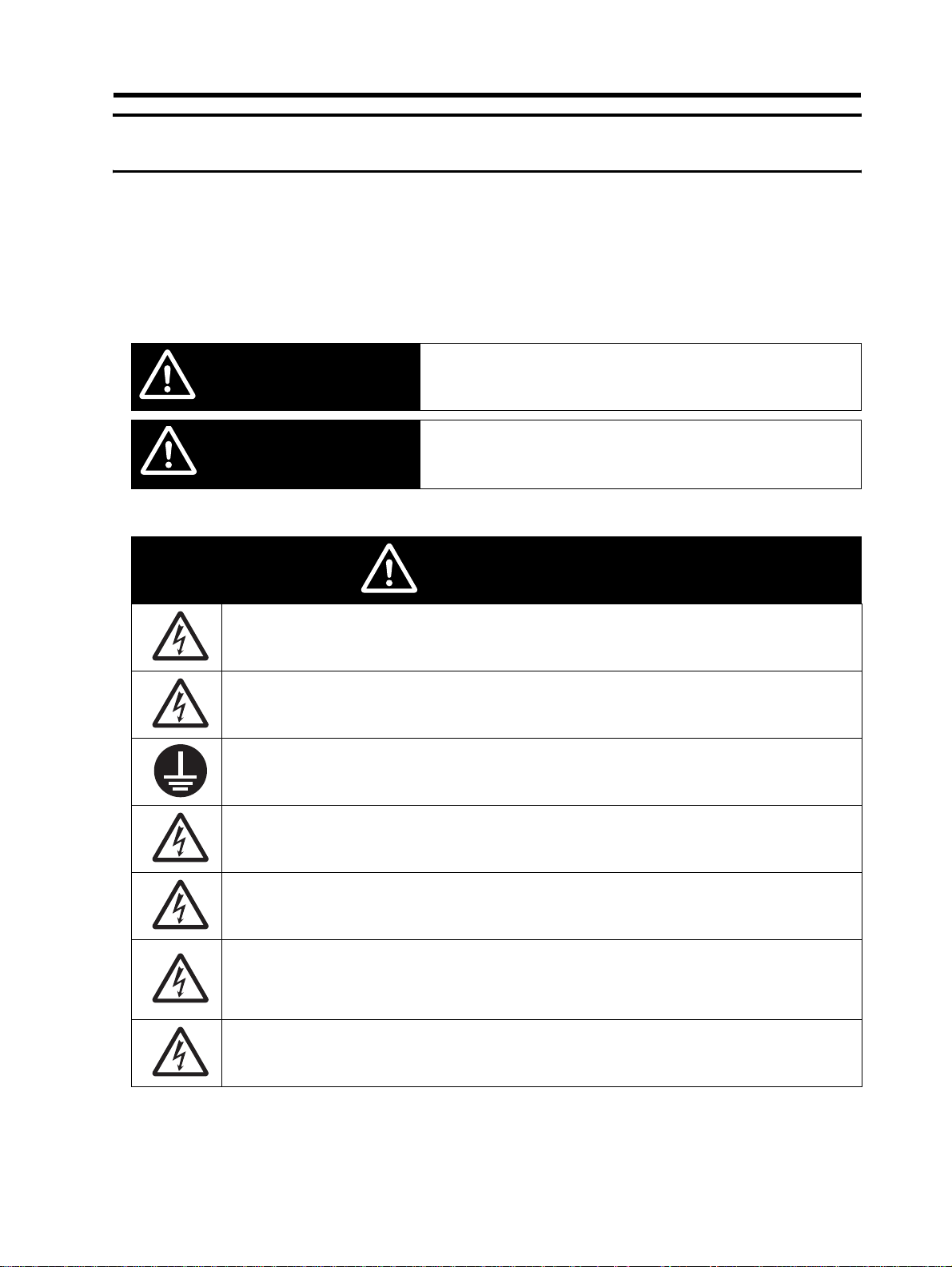
Safety Precautions
Indications and Meanings of Safety Information
In this user's manual, the following precautions and signal words are used to provide information to ensure the
safe use of the 3G3JX Inverter.
The information provided here is vital to safety. Strictly observe the precautions provided.
Meanings of Signal Words
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
WARNING
CAUTION
Alert Symbols in This Document
is likely to result in serious injury or may result in death. Additionally
there may be severe property damage.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
may result in minor or moderate injury or in property damage.
WARNING
Turn off the power supply and implement wiring correctly. Not doing so may result in a serious injury
due to an electric shock.
Wiring work must be carried out only by qualified personnel. Not doing so may result in a serious
injury due to an electric shock.
Be sure to ground the unit. Not doing so may result in a serious injury due to an electric shock or
fire.
(200-V class: type-D grounding, 400-V class: type-C grounding)
Do not remove the front cover during the power supply and 5 minutes after the power shutoff. Doing
so may result in a serious injury due to an electric shock.
Do not operate the Digital Operator or switches with wet hands. Doing so may result in a serious
injury due to an electric shock.
Inspection of the Inverter must be conducted after the power supply has been turned off. Not doing
so may result in a serious injury due to an electric shock.
The main power supply is not necessarily shut off even if the emergency shutoff function is
activated.
Do not change wiring, mode change switches (S7, S8), optional devices or replace cooli ng fans
while the input power is being supplied.
Doing so may result in a serious injury due to an electric shock.
5
Page 8

Safety Precautions
Do not connect resistors to the terminals (+1, P/+2, N/-) directly.
Doing so might result in a small-scale fire, heat generation or damage to the unit.
Install a stop motion device to ensure safety. Not doing so might result in a minor injury. (A holding
brake is not a stop motion device designed to ensure safety.)
Be sure to use a specified type of braking resistor/regenerative braking unit. In case of a braking
resistor, install a thermal relay that monitors the temperature of the resistor. Not doing so might
result in a moderate burn due to the heat generated in the braking resistor/regenerative braking
unit. Configure a sequence that enables the Inverter power to turn off when unusual overheating is
detected in the braking resistor/regenerative braking unit.
The Inverter has high voltage parts inside which, if short-circuited, might cause damage to itself or
other property. Place covers on the openings or take other precautions to make sure that no metal
objects such as cutting bits or lead wire scraps go inside when installing and wiring.
Do not touch the Inverter fins, braking resistors and the motor, which become too hot during the
power supply and for some time after the power shutoff. Doing so may result in a burn.
CAUTION
Take safety precautions such as setting up a molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB) that matches
the Inverter capacity on the power supply side. Not doing so might result in damage to property due
to the short circuit of the load.
Do not dismantle, repair or modify the product.
Doing so may result in an injury.
6
Page 9

Precautions for Safe Use
Precautions for Safe Use
Installation and Storage
Do not store or use the product in the following places.
•Locations subject to direct sunlight.
•Locations subject to ambient temperature exceeding the specifications.
•Locations subject to relative humidity exceeding the specifications.
•Locations subject to condensation due to severe temperature fluctuations.
•Locations subject to corrosive or flammable gases.
•Locations subject to exposure to combustibles.
•Locations subject to dust (especially iron dust) or salt.
•Locations subject to exposure to water, oil, or chemicals.
•Locations subject to shock or vibration.
Transporting, Installation, and Wiring
•Do not drop or apply a strong impact on the product. Doing so may result in damaged parts or malfunction.
•Do not hold by the front cover, but hold by the fins during transportation.
•Do not connect an AC power supply voltage to the control input/output terminals. Doing so may result in
damage to the product.
•Be sure to tighten the screws on the terminal block securely.
Wiring work must be done after installing the unit body.
•Do not connect any load other than a three-phase inductive motor to the U, V, and W output terminals.
•Take sufficient shielding measures when using the product in the following locations. Not doing so may
result in damage to the product.
Locations subject to static electricity or other forms of noise.
Locations subject to strong magnetic fields.
Locations close to power lines.
Operation and Adjustment
•Be sure to confirm the permissible range of motors and machines before operation because the Inverter
speed can be changed easily from low to high.
•Provide a separate holding brake if necessary.
Maintenance and Inspection
•Be sure to confirm safety before conducting maintenance, inspection or parts replacement.
7
Page 10

Precautions for Correct Use
Precautions for Correct Use
Installation
•Mount the product vertically on a wall or on a DIN track (optional) with the product's longer sides upright.
The material of the wall has to be nonflammable such as a metal plate.
Main Circuit Power Supply
•Confirm that the rated input voltage of the Inverter is the same as AC power supply voltage.
Error Retry Function
•Do not come close to the machine when using the error retry function because the machine may abruptly
start when stopped by an alarm.
•Be sure to confirm the RUN signal is turned off before resetting the alarm because the machine may
abruptly start.
Non-Stop Function at Momentary Power Interruption
•Do not come close to the machine when selecting restart in the non-stop function at momentary power
interruption selection (b050) because the machine may abruptly start after the power is turned on.
Operation Stop Command
•Provide a separate emergency stop switch because the STOP key on the Digital Operator is valid only when
function settings are performed.
•When checking a signal during the power supply and the voltage is erroneously applied to the control input
terminals, the motor may start abruptly. Be sure to confirm safety before checking a signal.
Product Disposal
•Comply with the local ordinance and regulations when disposing of the product.
8
Page 11
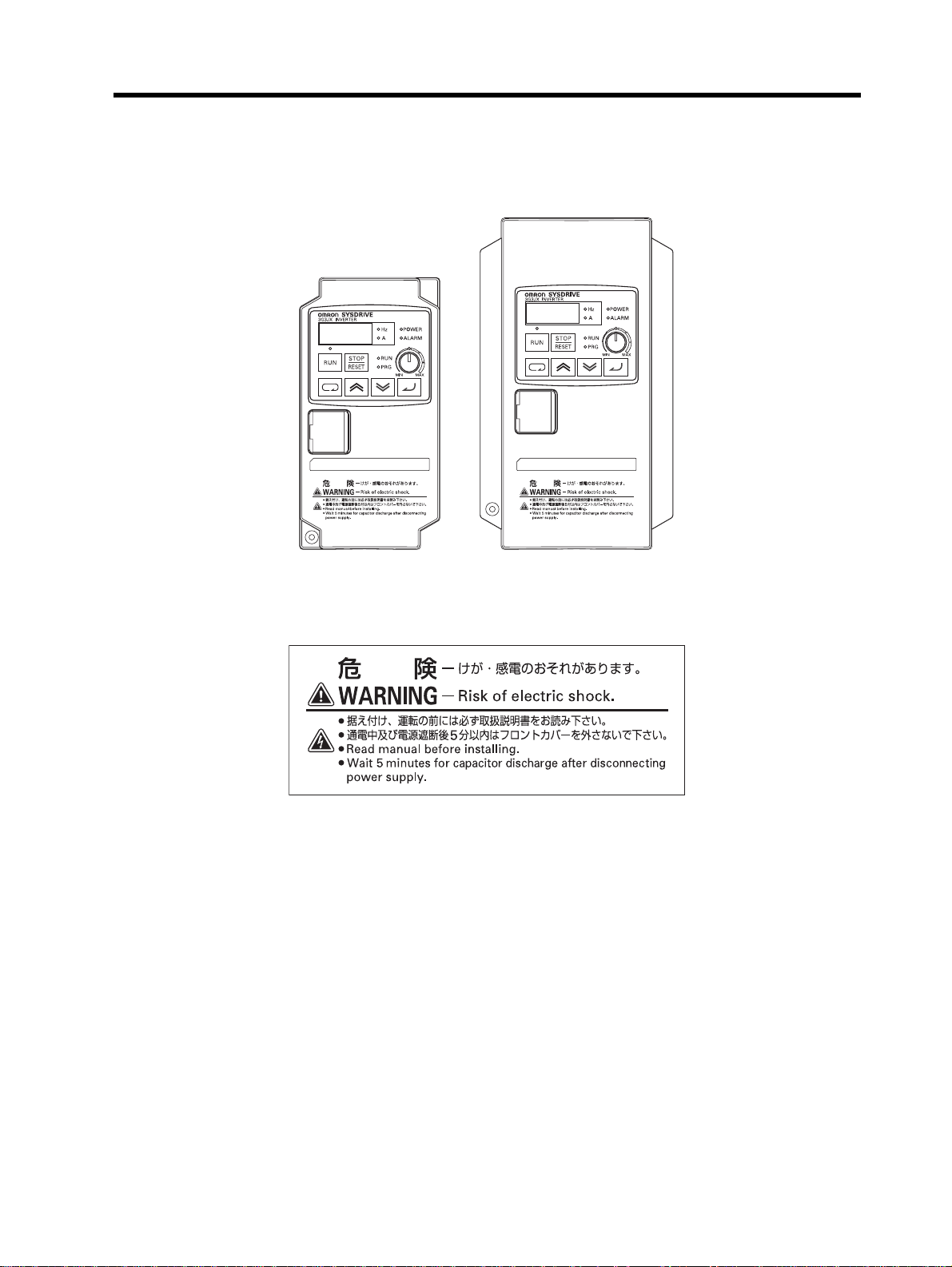
Warning Labels
Warning labels are located on the Inverter as shown in the following illustration.
Be sure to follow the instructions.
Precautions for Correct Use
Warning Description
9
Page 12

Checking Before Unpacking
Checking Before Unpacking
Checking the Product
On delivery, be sure to check that the delivered product is the Inverter 3G3JX model that you
ordered.
Should you find any problems with the product, immediately contact your nearest local sales
representative or OMRON sales office.
zChecking the Nameplate
Inverter model
Input specifications
Output specifications
zChecking the Model
3G3JX-A2002
Maximum applicable motor capacity
0.2 kW
002
0.4 kW
004
0.75 kW
007
1.5 kW
015
2.2 kW
022
3.7 kW
037
5.5 kW
055
7.5 kW
075
Voltage class
3-phase 200 V AC (200-V class)
2
1/3-phase 200 V AC (200-V class)
E
3-phase 400 V AC (400-V class)
4
Enclosure rating
Panel-mounting (IP10 min.) or closed
A
wall-mounting models
Checking the Accessories
Note that this manual is the only accessory included with the 3G3JX model.
Mounting screws and other necessary parts must be provided by the user.
10
Page 13
Revision History
Revision History
A manual revision code appears as a suffix to the catalog number located at the
lower left of the front and back covers.
Cat. No.
Revision code Revision date Changes and revision pages
01 December 2007 First printing
02 April 2008
I558-E1-02
Revision code
New Inverters with different capacities added (3G3JX-
A2055/-A2075/-A4055/-A4075)
New functions added for with 5.5-/7.5-kW Inverters
Manual descriptions improved and/or corrected
Page10, Page 1-1, Page 1-2, Page 2-2, Page 2-8, Page 213, Page 2-14, Page 2-15, Page 2-16, Pages 4-77 to 4104, Page 7-1, Page 7-2, Page 7-6, Page 7-18, Page 7-20,
Page 7-26, Page 7-27, Page 7-30
11
Page 14
About This Manual
About This Manual
This User's Manual is compiled chapter by chapter for user's convenience as follows.
Understanding the following configuration ensures more effective use of the product.
Chapter 1 Overview Describes features and names of parts.
Provides external dimensions, installation dimensions, peripheral device
Chapter 2 Design
Chapter 3 Operation
Chapter 4 Functions Describes the functions of the Inverter.
Chapter 5
Chapter 6
Maintenance
Operations
Inspection and
Maintenance
design/selection instructions, and other information necessary for
design.
Describes names of parts, the Inverter's operations, including how to use
the keys on the Digital Operator, and the monitor function.
Describes the causes and their countermeasures if the Inverter fails,
including the solutions to possible troubles (troubleshooting).
Describes items for periodic inspection and/or maintenance for the
Inverter.
Overview
Chapter 7 Specifications
Appendix
Provides Inverter specifications, as well as the specifications and
dimensions of peripheral devices.
Describes the summarized parameter settings as a reference for users
who have used this Inverter and understood the functions.
12
Page 15

Contents
Introduction..............................................................................................1
Read and Understand This Manual.........................................................2
Safety Precautions ..................................................................................5
Precautions for Safe Use.........................................................................7
Precautions for Correct Use....................................................................8
Checking Before Unpacking....................................................................10
Revision History.......................................................................................11
About This Manual...................................................................................12
Chapter 1 Overview
1-1 Functions.................................................................................................1-1
1-2 Appearance and Names of Parts.............................................................1-3
Chapter 2 Design
2-1 Installation................................................................................................2-1
2-2 Wiring.......................................................................................................2-6
Chapter 3 Operation
3-1 Test Run Procedure.................................................................................3-3
3-2 Test Run Operation .................................................................................3-4
3-3 Part Names and Descriptions of the Digital Operator..............................3-9
3-4 Operation Procedure (Example: Factory Default)....................................3-11
3-5 Keys.........................................................................................................3-17
3-6 Parameter Transition................................................. .... ..... .... .... .... .... .....3-18
3-7 Parameter List ..... .... .... .... .... ..... .... .... .... .... ...............................................3-20
Chapter 4 Functions
4-1 Monitor Mode...........................................................................................4-1
4-2 Function Mode.........................................................................................4-5
Chapter 5 Maintenance Operations
5-1 Special Display List................... .... .... .... .... ..... .... .... .... .... ..... .... .... .... .... .....5-1
5-2 Troubleshooting.......................................................................................5-5
Chapter 6 Inspection and Maintenance
6-1 Inspection and Maintenance....................................................................6-1
6-2 Storage....................................................................................................6-7
Chapter 7 Specifications
7-1 Standard Specification List............................................ ..... .... .................7-1
7-2 Measurement Method of Output Voltage.................................................7-5
13
Page 16

Contents
7-3 Connection Example............................................................................... 7-6
7-4 Dimensional Drawing .............................................................................. 7-8
7-5 Options.................................................................................................... 7-14
Appendix
Appendix-1 Parameter List ................................................................................ App-1
Appendix-2 Product Life Curve.......................................................................... App-17
Index
14
Page 17

Chapter 1
Overview
1-1 Functions.......................................................... 1-1
1-2 Appearance and Names of Parts.................... 1-3
Page 18
1-1 Functions
1Overview
1
1-1 Functions
3G3JX Inverter Models
Overview
Rated voltage Enclosure rating Max. applicable motor capacity Model
0.2 kW 3G3JX-A2002
0.4 kW 3G3JX-A2004
0.75 kW 3G3JX-A2007
3-phase 200 V AC
IP20
(Complies with
JEM1030)
3-phase 400 V AC
1.5 kW 3G3JX-A2015
2.2 kW 3G3JX-A2022
3.7 kW 3G3JX-A2037
5.5 kW 3G3JX-A2055
7.5 kW 3G3JX-A2075
0.4 kW 3G3JX-A4004
0.75 kW 3G3JX-A4007
1.5 kW 3G3JX-A4015
2.2 kW 3G3JX-A4022
3.7 kW 3G3JX-A4037
5.5 kW 3G3JX-A4055
7.5 kW 3G3JX-A4075
0.2 kW 3G3JX-AE002
0.4 kW 3G3JX-AE004
1/3-phase 200 V AC
0.75 kW 3G3JX-AE007
1.5 kW 3G3JX-AE015
2.2 kW 3G3JX-AE022
International Standards Models (EC Directives and UL/cUL Standards)
The 3G3JX Inverter meets the EC Directives and UL/cUL standard requirements for worldwide use.
Classification Applicable standard
EC Directives
UL/cUL Standards UL508C
EMC Directive EN61800-3: 2004
Low-voltage Directive EN61800-5-1: 2003
1-1
Page 19

1-1 Functions
Compact Simplified Inverter for Customer's Environment and Application Demands
Simple Wiring and Easy Installation
The main circuit adopts upper/lower wiring as with a conductor. In addition, the side-by-side
mounting of the Inverters and the built-in zero-phase reactor contribute to space saving in control
panel.
Wide Ranging Capacity and Power Supply
In spite of its compact size, the 3G3JX Inverter provides a wide ranging capacity from 0.2 to 7.5 kW.
Moreover, the three-phase 200 V, three-phase 400 V, and single/three-phase 200 V common types
are made to meet the power supply specifications for use outside Japan.
PID Function
The PID function is featured for the easier control of the fan and pump. It helps to control airflow and
pressure.
Emergency Shutoff Function
Switching the dedicated switch (S8) changes from the multi-function input (input 3) to the
emergency shutoff input. You can directly turn off a motor control power module without operating
the software.
Compliance With All Standards
The 3G3JX Series has achieved compliance with CE and UL/cUL.
1
Overview
The RoHS Directive
The standard model meets the requirements of the RoHS Directive.
Noise and Harmonics Suppression Option
The three-phase models incorporate a zero-phase reactor (radio noise filter) as a standard
specification.
For the single/three-phase common type, optional suppression is available.
When the optional DC reactor is added, the 3G3JX Series will also meet the requirements specified
by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism of Japan.
Handles a Variety of I/O Signals
The 3G3JX Series can handle a variety of I/O signals for wide-ranging applications.
•Analog voltage input: 0 to 10 V
•Analog current input: 4 to 20 mA
1-2
Page 20
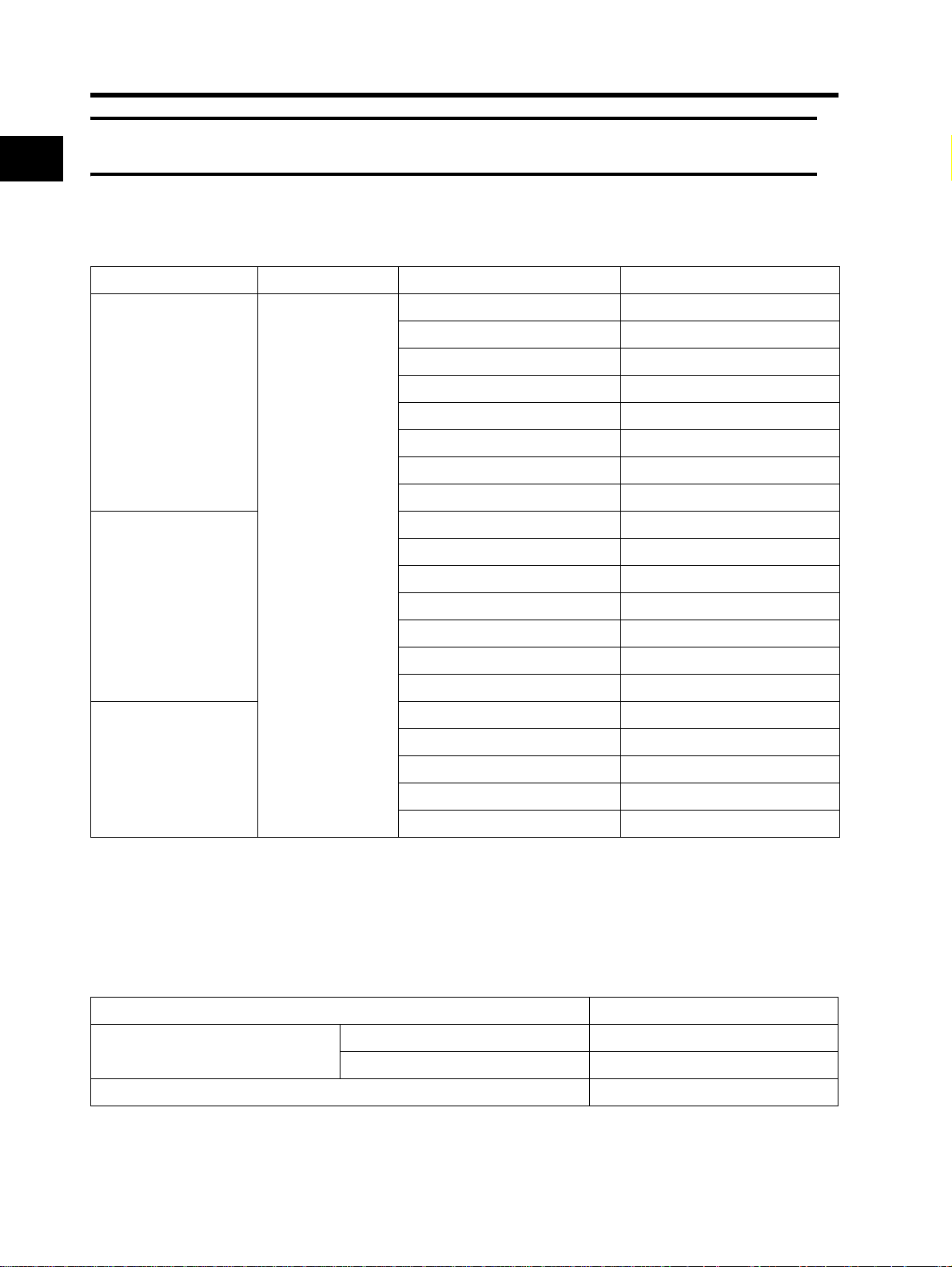
1-2 Appearance and Names of Parts
r
1
1-2 Appearance and Names of Parts
Overview
Top cover
Fin
Digital Operator
Front cover
Bottom cover
•The size of the fin varies with the motor capacity.
•There are two sizes depending on the motor capacity, but the fundamental structure is the same.
•Remove the front cover when connecting the power supply, the motor, and the control signal.
FREQ (FREQUENCY) adjuste
Main housing
Connection to RJ45 Jack
Connect the communications cable after opening the cover of the communications connector.
Remove the front cover to switch communications. Refer to "Removing the Front Cover" (page 2-
6) for instructions on how to remove the front cover.
Communications connector
8k8k8k8
(with cover)
1-3
*The cover of the communications connector is removable. Remove the front cover to attach it.
Page 21
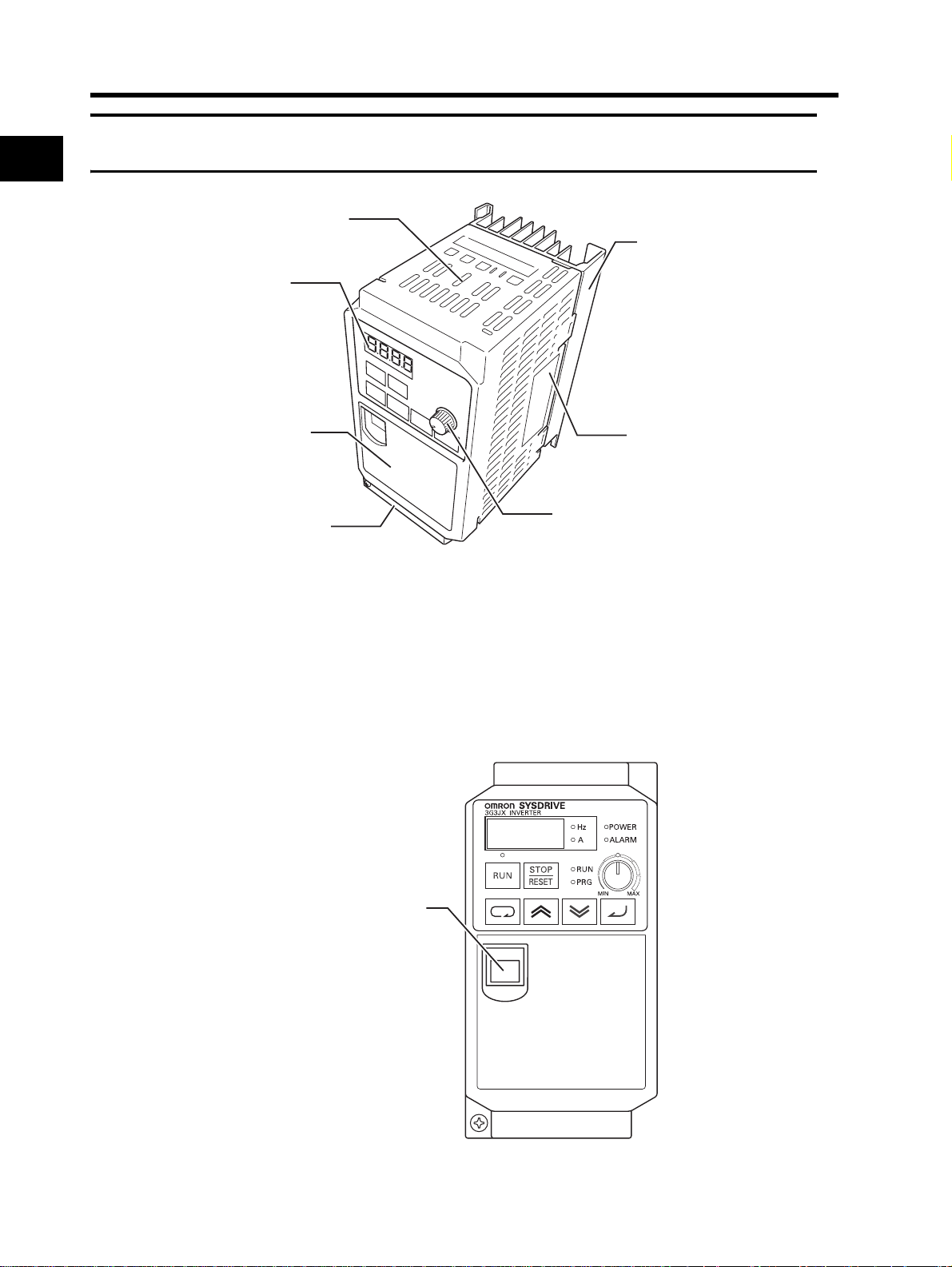
Names of Parts Inside the Front Cover
1-2 Appearance and Names of Parts
Main circuit terminal block
(input side)
8k8k8k8
Communications connector
Relay output terminal block
Control circuit terminal block
Main circuit terminal block
(output side)
S7: OPE/485 communications selector (Default = OPE side)
S8: Emergency shutoff function selector (Default = OFF)
OPE
Do not touch these!
(ELECTRICAL HAZARD:
For factory maintenance only)
S7 S8
485
ON
OFF
1
Overview
(Caution)
Do not switch the emergency shutoff function selector (S8) without reason as the allocation of the
multi-function input terminals may change.
For details, refer to "Emergency Shutoff Input Function" (page 4-45).
1-4
Page 22

1-2 Appearance and Names of Parts
1
Overview
1-5
Page 23

Chapter 2
Design
2-1 Installation........................................................2-1
2-2 Wiring................................................................ 2-6
Page 24
2
Design
2-1 Installation
2Design
2-1 Installation
WARNING
Turn off the power supply and implement wiring correctly. Not doing so may result in a serious injury
due to an electric shock.
Wiring work must be carried out only by qualified personnel. Not doing so may result in a serious
injury due to an electric shock.
Be sure to ground the unit. Not doing so may result in a serious injury due to an electric shock or fire.
(200-V class: type-D grounding, 400-V class: type-C grounding)
CAUTION
Do not connect resistors to the terminals (+1, P/+2, N/-) directly.
Doing so might result in a small-scale fire, heat generation or damage to the unit.
Install a stop motion device to ensure safety. Not doing so might result in a minor injury. (A holding
brake is not a stop motion device designed to ensure safety.)
Be sure to use a specified type of braking resistor/regenerative braking unit. In case of a braking
resistor, install a thermal relay that monitors the temperature of the resistor. Not doing so might result
in a moderate burn due to the heat generated in the braking resistor/regenerative braking unit.
Configure a sequence that enables the Inverter p ower to turn off when unusual overheating is
detected in the braking resistor/regenerative braking unit.
The Inverter has high voltage parts inside which, if short-circuited, might cause damage to itself or
other property. Place covers on the openings or take other precautions to make sure that no metal
objects such as cutting bits or lead wire scraps go inside when installing and wiring.
Safety Information
Installation and Storage
Do not store or use the product in the following places.
•Locations subject to direct sunlight.
•Locations subject to ambient temperature exceeding the specifications.
•Locations subject to relative humidity exceeding the specifications.
•Locations subject to condensation due to severe temperature fluctuations.
•Locations subject to corrosive or flammable gases.
•Locations subject to exposure to combustibles.
•Locations subject to dust (especially iron dust) or salts.
•Locations subject to exposure to water, oil, or chemicals.
•Locations subject to shock or vibration.
2-1
Page 25
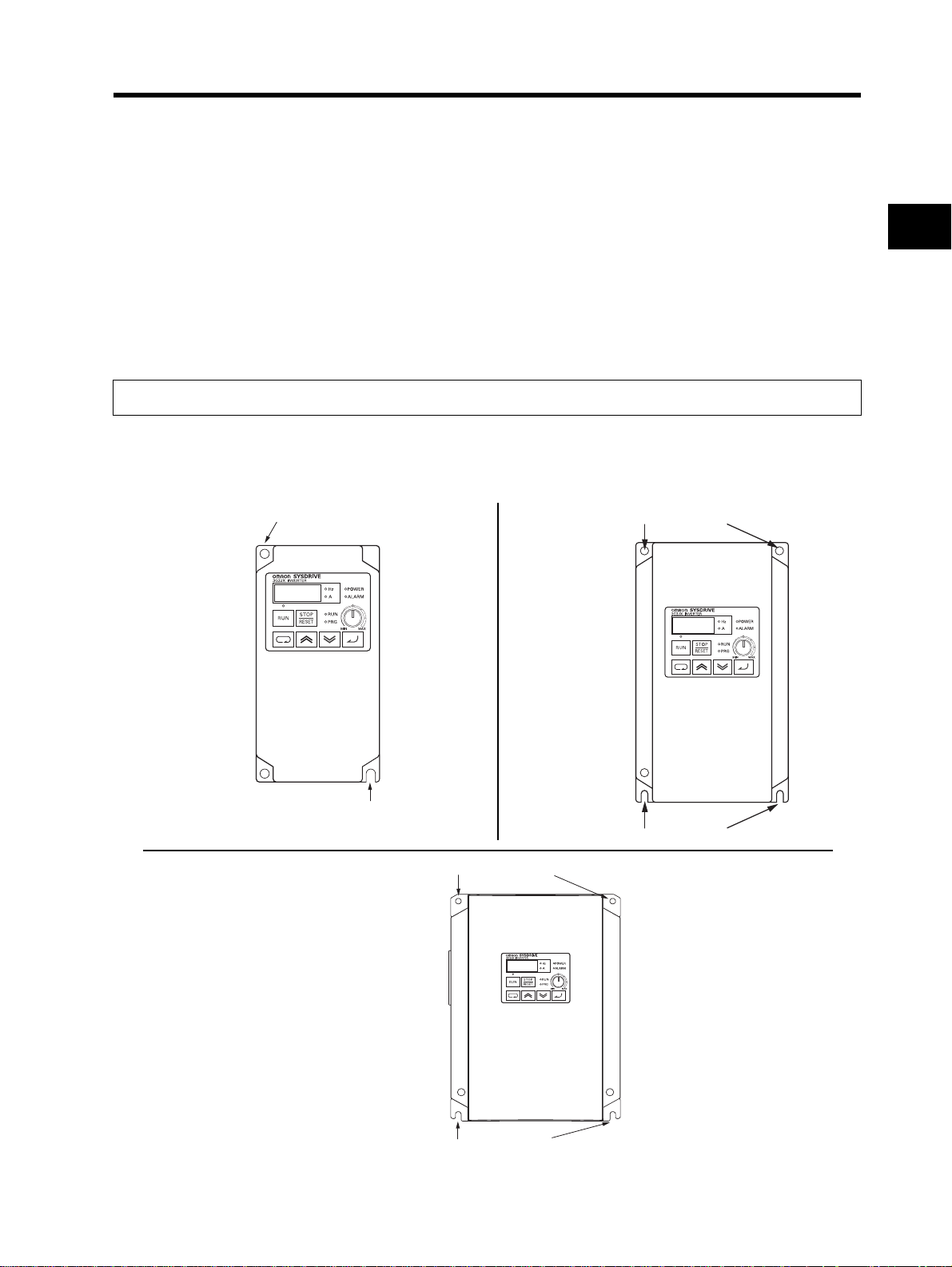
2-1 Installation
w
w
Transporting, Installation, and Wiring
•Do not drop or apply strong impact on the product. Doing so may result in damaged parts or malfunction.
•Do not hold by the front cover, but hold by the fins during transportation.
•Do not connect an AC power supply voltage to the control input/output terminals. Doing so may result in
damage to the product.
•Be sure to tighten the screws on the terminal block securely.
Wiring work must be done after installing the unit body.
•Do not connect any load other than a three-phase inductive motor to the U, V, and W output terminals.
•Take sufficient shielding measures when using the product in the following locations. Not doing so may
result in damage to the product.
Locations subject to static electricity or other forms of noise.
Locations subject to strong magnetic fields.
Locations close to power lines.
Precautions for Use
Installation
•Install the Inverter vertically on the wall or DIN tracks (optional).
Install the Inverter on a nonflammable wall surface material, like metal.
2
Design
Model
3G3JX-A2002
A2004
A2007
AE002
AE004
Screw size for
installation: M5
Position for installing a screw
Position for installing a scre
Model
3G3JX-A2055
-A2075
-A4055
-A4075
Model
3G3JX-A2015
A2022
A2037
A4004
A4007
A4015
A4022
A4037
AE007
AE015
AE022
Screw size for
installation: M5
Position for installing a scre
Positions for installing screws
Positions for installing screws
Screw size for
installation: M6
Position for installing a screw
2-2
Page 26
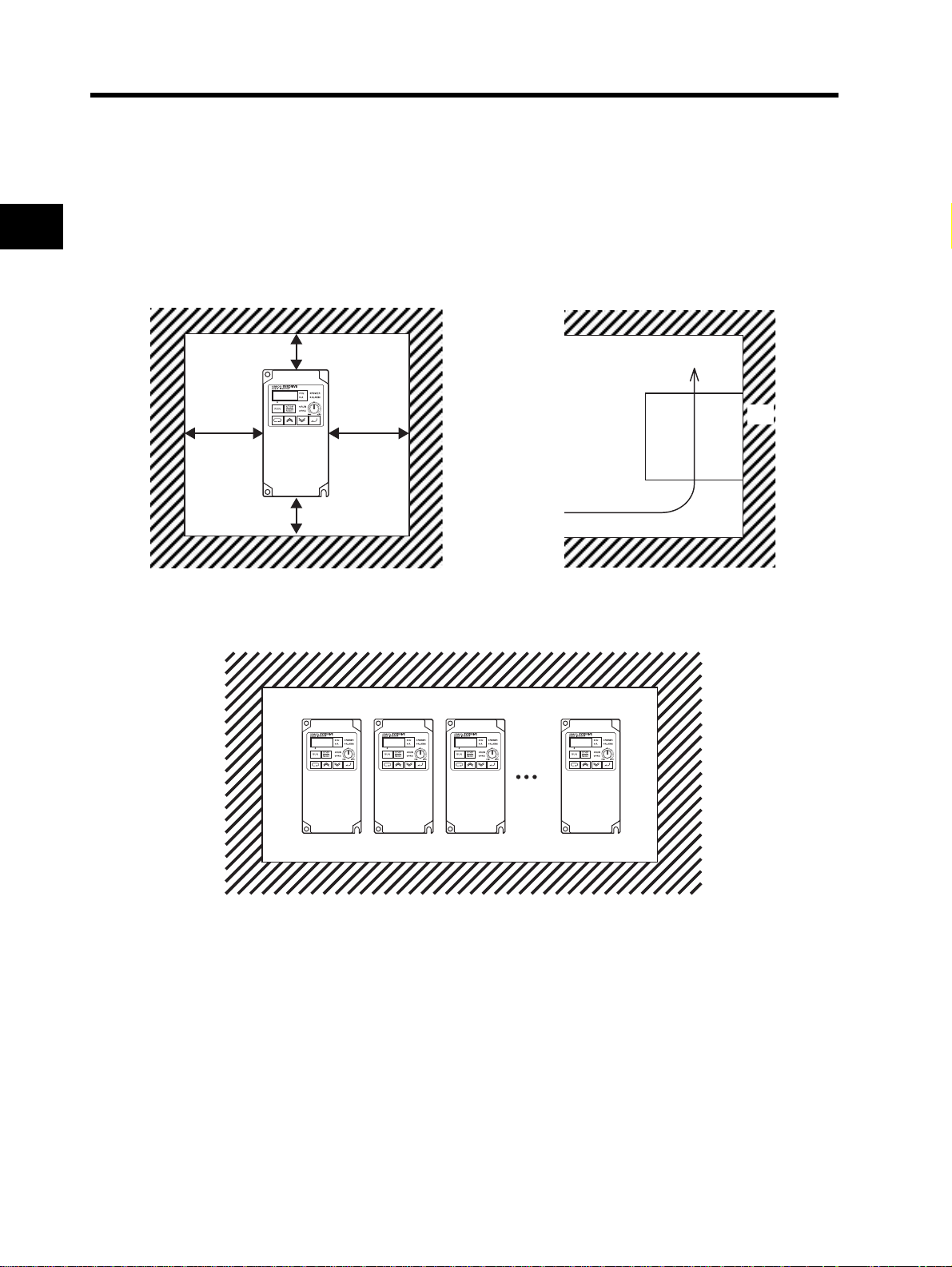
2-1 Installation
Main Circuit Power Supply
•Confirm that the rated input voltage of the Inverter matches the AC power supply voltage.
Installation Environment
2
•Increased ambient temperatures will shorten the life of the Inverter.
•Keep the Inverter away from heating elements (such as a braking resistor, DC reactor, etc.).
If the Inverter is installed in a control panel, keep the ambient temperature within the range of the
specifications, taking dimensions and ventilation into consideration.
Design
10 cm min.
5 cm min. 5 cm min.
10 cm min.
•You can install multiple 3G3JX Inverters side by side in the control panel (side-by-side installation). Again,
keep the ambient temperature within the specified range (40°C or below).
Airflow
Wall
•If the ambient temperature is from 40°C through to 50°C, the carrier frequency should be reduced and the
Inverter capacity should be increased.
2-3
Page 27
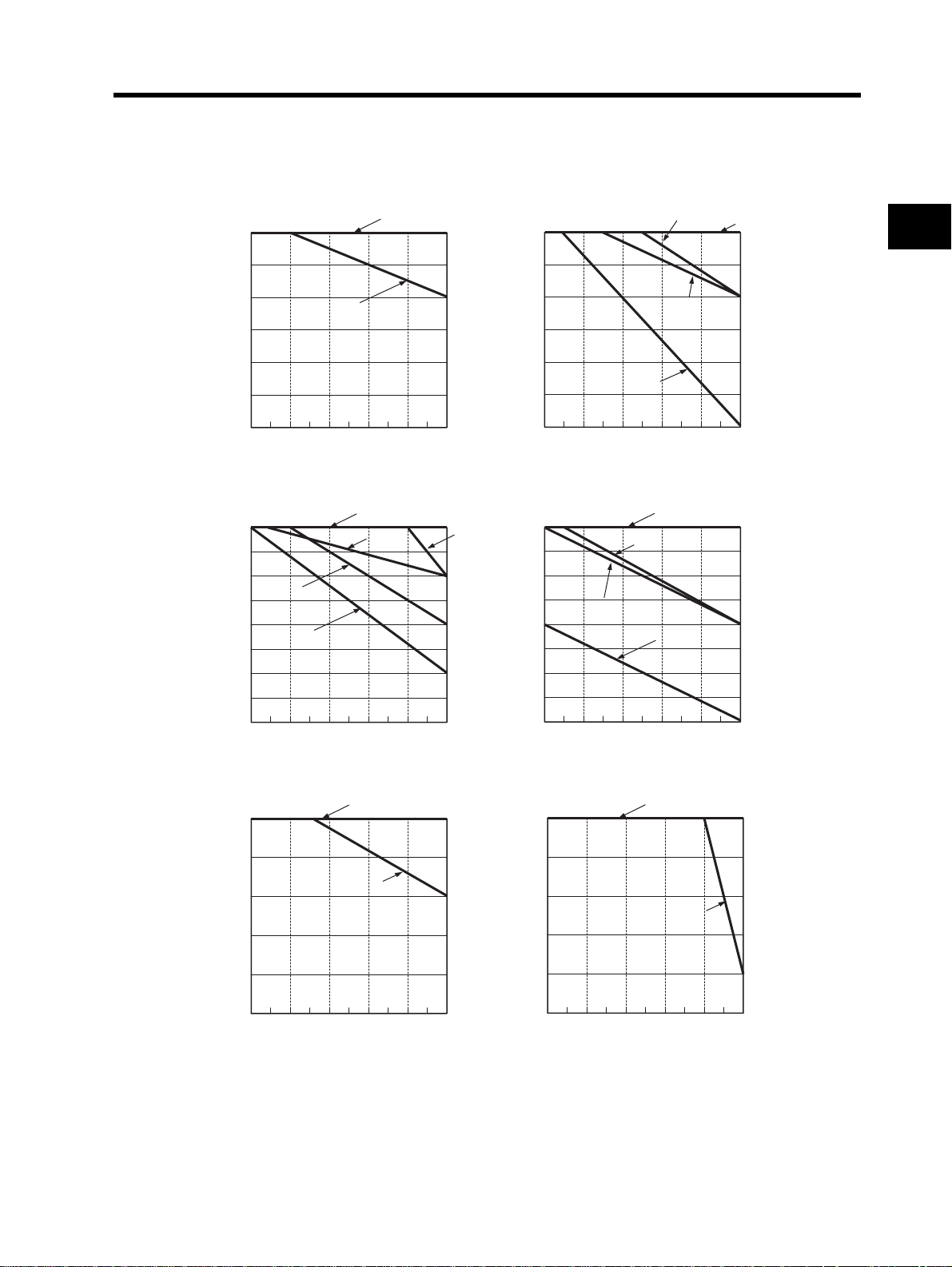
2-1 Installation
•To raise the carrier frequency, reduce the output current (or derate the rated current) as shown in the graph
below.
(1) Side-By-Side installation (ambient temperature:40°C)
0.4 to 2.2kW
5.5/kW
100%
200-V Class
0.2 to 2.2 · 5.5/7.5kW
400-V Class
100%
2
95%
90%
85%
80%
75%
Output current (Rated current %)
70%
2
3.7 kW
4 6 8 10 12
Carrier frequency [kHz]
(2) Ambient temperature 50°C
200-V Class
100%
95%
90%
0.75kW
85%
80%
75%
70%
65%
Output current (Rated current %)
60%
3.7kW
2
4 6 8 10 12
Carrier frequency [kHz] Carrier frequency [kHz]
0.2/0.4/2.2/5.5kW
7.5kW
1.5kW
95%
90%
85%
80%
75%
Output current (Rated current %)
70%
100%
95%
90%
85%
80%
75%
70%
65%
Output current (Rated current %)
60%
4 6 8 10 12
2
400-V Class
4 6 8 10 12
2
3.7kW
Carrier frequency [kHz]
5.5kW
0.4 to 1.5/7.5kW
2.2kW
3.7kW
7.5kW
Design
(3) Ambient temperature 40°C
200-V Class
100%
95%
90%
85%
80%
Output current (Rated current %)
75%
2
4 6 8 10 12
Carrier frequency [kHz] Carrier frequency [kHz]
0.2 to 2.2 · 5.5/7.5kW
3.7kW
400-V Class
100%
95%
90%
85%
80%
Output current (Rated current %)
75%
2
4 6 8 10 12
0.4 to 2.2 · 5.5/7.5kW
3.7kW
2-4
Page 28
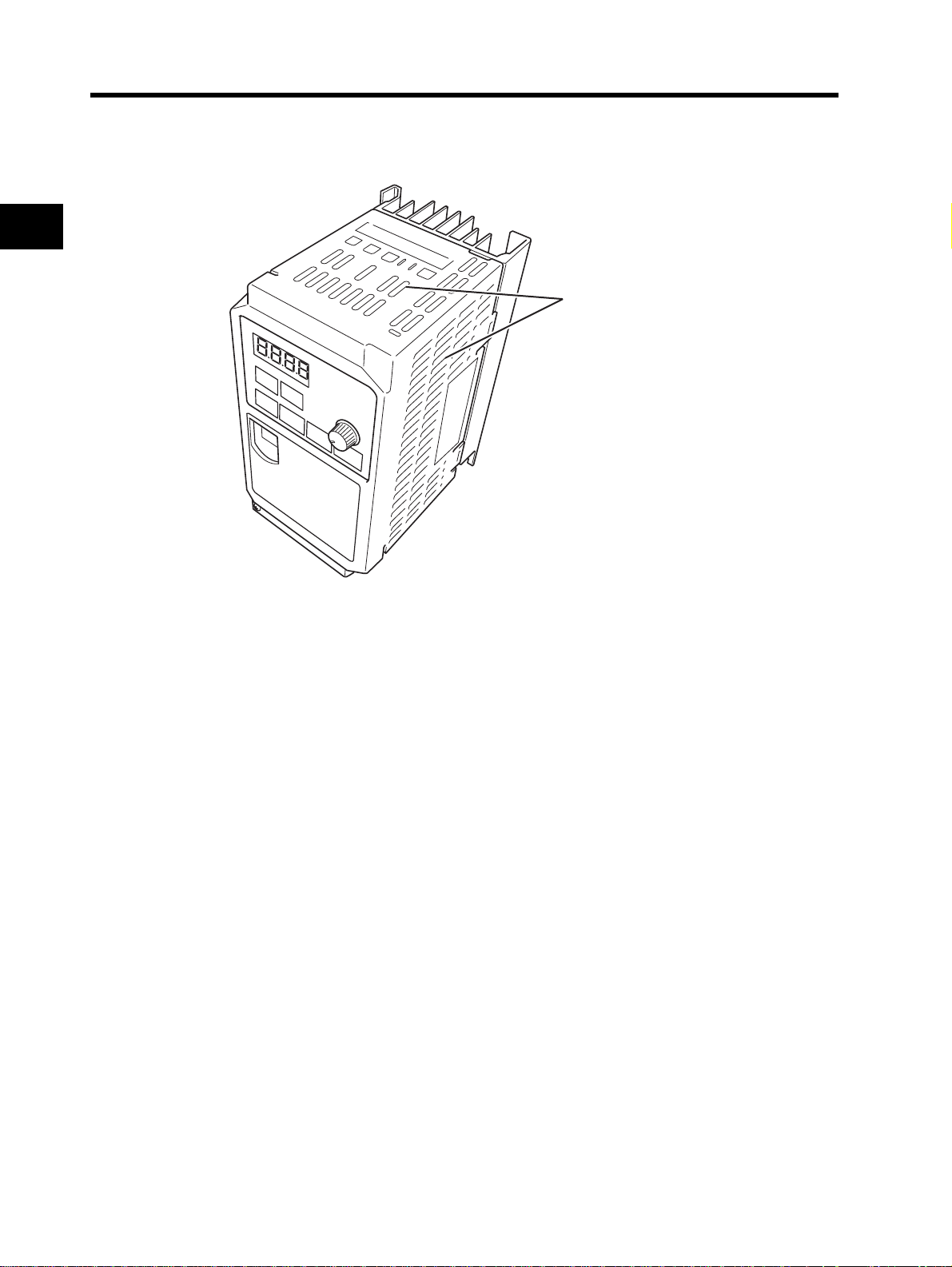
2
Design
2-1 Installation
•Before installing the Inverter, place a cover over all the ventilation openings to shield them from foreign
objects.
After completing the installation process, be sure to remove the covers from the Inverter before operation.
Ventilation openings
(Both sides and top)
2-5
Page 29
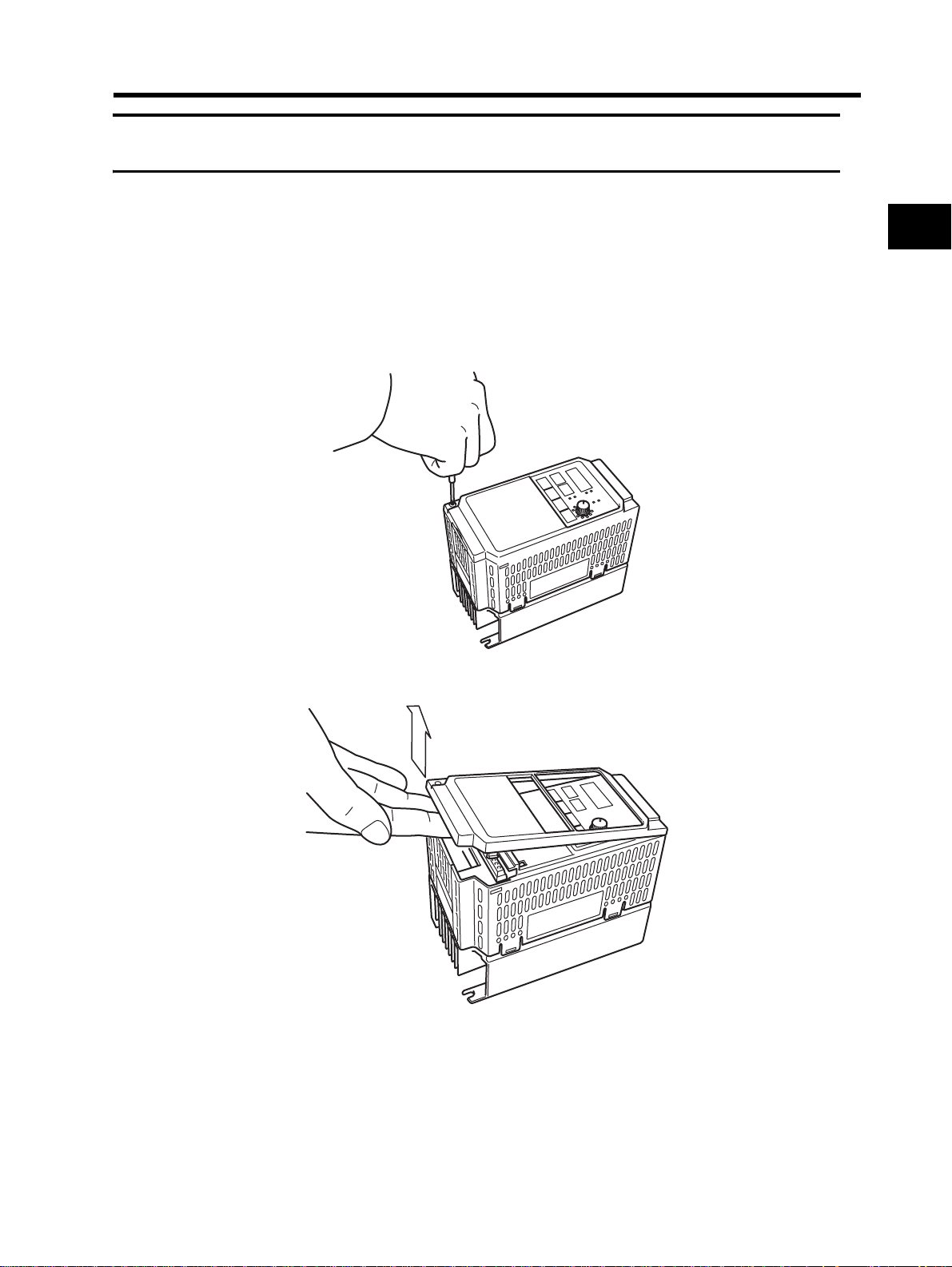
2-2 Wiring
2-2 Wiring
Removing and Mounting the Front Cover
Removing the Front Cover
Loosen the mounting screw at the lower left of the front cover. Lift the bottom of the front cover to
remove while holding the body.
1. Loosen the front cover mounting screw.
2. Lift the bottom of the front cover to remove.
2
Design
2-6
Page 30
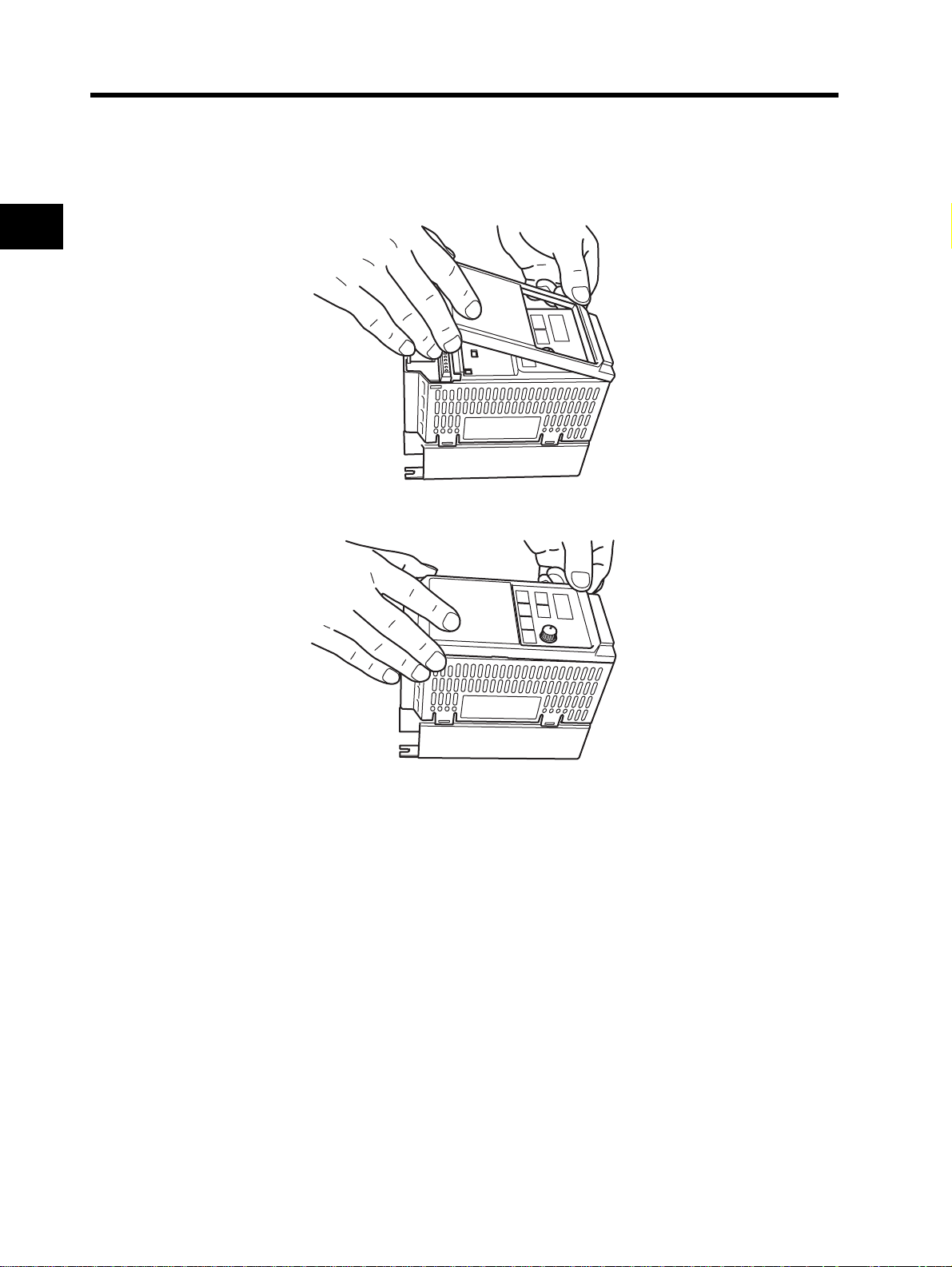
2
Design
2-2 Wiring
Mounting the Front Cover
Hang the upper side of the front cover on the hooks, and push down both sides of the cover
simultaneously until it clicks into place.
1. Hang the upper side on the hooks. (Two hooks)
2. Push down the cover until it clicks into place. (Both sides)
2-7
Page 31

Standard Connection Diagram
2-2 Wiring
3-phase 200 V AC
1/3-phase 200 V AC *2
3-phase 400 V AC
Multi-function input 1
Multi-function input 2
Multi-function input 3
Multi-function input 4
Multi-function input 5
Sequence input common
Frequency reference power supply
Frequency
reference
(1 to 2 kΩ)
DC reactor
(optional)
R/L1 (L1) *1
S/L2 (L2)
T/L3 (N/L3)
P24
PSC
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
SC
FS
Frequency reference input (voltage)
Frequency reference common
Frequency reference input (current)
FV
FC
FI
+1 P/+2 N/-
Regenerative
braking unit
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
MB
Relay output *3
MA
MC
Common
P1PCMulti-function output
Multi-function output common
AM Analog monitor output
2
M
Design
*1. The items in parentheses indicate terminal symbols for 3G3JX-AE.
*2. Connect a single-phase 200-V AC input to terminals L1 and N/L3.
*3. By factory default, MA is set to NC contact, and MB to NO contact in the
relay output (MA, MB) contact selection (C036).
2-8
Page 32

2-2 Wiring
Wiring to the Power Supply and Motor
2
Design
(Example) 3G3JX-A2004
Main circuit terminal block (input side)
Main circuit terminal block (output side)
Power supply
Ground
(Example) 3G3JX-A2037
Main circuit terminal block (input side)
Main circuit terminal block (output side)
Power supply
Ground
R/L1S/L2 T/L3
N/- P/+2 +1
U/T1 V/T2 W/T3
Motor
earth
Motor
•Do not connect the power supply other than to R/L1, S/L2, or T/L3.
•Do not remove the short-circuit bar between P/+2 and +1, except when a DC reactor is connected.
Note 1: Install an earth leakage breaker on the power supply input side.
(Select an earth leakage breaker having a larger high-frequency sensed current and avoid
unnecessary operation.)
If the wiring between the Inverter and the motor is too long (longer than 10 m), the thermal
relay may malfunction due to harmonics. Install an AC reactor on the Inverter output side,
or use a current sensor instead of the thermal relay.
Motor
earth
R/L1S/L2T/L3
U/T1V/T2
W/T3
Motor
N/- P/+2 +1
2-9
Page 33

2-2 Wiring
Note 2: Connect securely to the ground as specified (type-D grounding for 200-V class, and
type-C grounding for 400-V class). Do not share the grounding electrode with other strong
electrical devices.
Example of incorrect grounding Example of correct grounding
Inverter
Inverter
Inverter
Inverter
Ground bolt
Inverter
Inverter
Wiring the Control Circuit Terminals and Relay Terminals
Relay
output
MB MA MC
Analog
monitor
output
Frequency
reference
input
Multi-function input
Multi-function
output
2
Design
AM
FS FV FI FC S5 S4 S3 S2 S1 SC
PSC P24
PC
P1
Short-circuit bar
2-10
Page 34

2
Design
2-2 Wiring
Wiring Example of the Control Circuit Terminal Block (Sink Logic)
At sink logic (NPN) : External power supply input
At source logic (PNP) : Power supply output
Note: By factory default, the input logic of the multi-function input terminal circuit is
set to the sink logic.
Reverse rotation RUN command
Forward rotation RUN command
AM
Frequency meter
FS FV FI FC S5 S4 S3 S2 S1 SC
Variable resistor
frequency reference
(1 to 2 k)
Input common
Reset input
Multi-step speed reference 2
Multi-step speed reference 1
External power supply
terminal for input signal
PSC P24
Short-circuit bar
(at sink logic
[when internal
power supply is
used])
Frequency arrival signal
(27 V DC 50 mA max.)
PC P1
RY
Note 1: When connecting a relay to the multi-function output terminal, install a surge-absorbing
diode in parallel with the relay. The output circuit can break down due to surge voltage when
the relay is switched on/off.
Note 2: Remove the short-circuit bar when the external power supply is used.
Note 3: For the signal line, use a twisted shield wire and apply the shield coating as illustrated
below. Keep the length to 20 m or less.
Perform insulating treatment.
Ground connection is not required.
Connect to the ground terminal of the Inverter.
Note 4: Keep the wiring away from the power cable of the main circuit and from the wiring on the
relay control circuit. (More than 10 cm apart)
2-11
Page 35

Selecting the Sequence Input Method (Sink/Source Logic)
C
Logic Selection Method for the Multi-function Input Terminals
When the internal power supply is used, you can switch the logic by rearranging the short-circuit bar
on the control circuit terminal block. The default setting is sink logic.
2-2 Wiring
2
Sink logicSource logic
<Sink Logic>
S1 SC PSC P24 PC
Short-circuit bar
<Source Logic>
S1 SC PSC P24
Short-circuit bar
PC
Note 1: Remove the short-circuit bar when the external power supply is used.
Inside the Inverter
When interface power supply is used
+V
Short-circuit
bar
COM
Output unit etc.
P24
PSC
SC
S1
S5
Inverter
24 V DC
When external power supply is used
+V
COM
Output unit etc.
DC24V
P24
PSC
SC
S1
S5
Inverter
Design
24 V D
COM
0V
Output unit etc.
Short-circuit
bar
P24
PSC
SC
S1
S5
Inverter
24 V DC
\
COM
24 V DC
0V
Output unit etc.
P24
PSC
SC
S1
S5
Inverter
24 V DC
2-12
Page 36

2-2 Wiring
Wiring the Main Circuit Terminals
Connecting the Main Circuit Terminals
2
Design
Motor output
(kW)
Applicable Inverter model
0.2 3G3JX-A2002 1.25 mm
3G3JX-A2004
0.4
3G3JX-A4004 3 A
3G3JX-A2007 2.0 mm
0.75
3G3JX-A4007 1.25 mm
3G3JX-A2015 2.0 mm
1.5
3G3JX-A4015 2.0 mm
3G3JX-A2022 2.0 mm
2.2
3G3JX-A4022 2.0 mm
3G3JX-A2037 3.5 mm
3.7
3G3JX-A4037 2.0 mm
3G3JX-A2055 5.5 mm
5.5
3G3JX-A4055 3.5 mm
3G3JX-A2075 8.0 mm
7.5
3G3JX-A4075 3.5 mm
0.2 3G3JX-AE002 2.0 mm
0.4 3G3JX-AE004 2.0 mm
0.75 3G3JX-AE007 2.0 mm
1.5 3G3JX-AE015 5.5 mm
2.2 3G3JX-AE022 5.5 mm
Wiring Applicable device
Power cable
2
1.25 mm
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
Earth leakage breaker
(ELB)
5 A 10 A
5 A
10 A 15 A
5 A 6 A
15 A 15 A
10 A 10 A
20 A 20 A
10 A 10 A
30 A 30 A
15 A 15 A
50 A 40 A
30 A 20 A
60 A 50 A
30 A 25 A
5A 14 A
5 A ⎯
10 A ⎯
15 A ⎯
20A ⎯
Fuse size
(class J)
Rated 600 V
10 A
•For the main circuit terminals, always use insulated electrical wires with a rated voltage of 600 V and a rated
temperature of 80°C or higher.
•Use the crimp-type terminal with an insulating sleeve to connect to the terminals.
•Up to two wires can be connected to one terminal.
•To prevent possible voltage drops, increase the wire size in accordance with the cable length.
2
•To connect the 100-V or 200-V model to the relay output terminal block, use a wire of 0.75 mm
•To connect seven wires or more to the control circuit terminal block, use a shield line of 0.5 mm
.
2
or less.
•Strip the signal line by 5 to 6 mm, and connect the exposed wire. (In the case of stranded wires, make sure that
the wires are not unraveled.)
•Make sure that the maximum outside coating diameter of the signal line is 2.0 mm or less (except for the alarm
signal line). (For the mark tube mounted cable and multi-core cable, keep both the mark tube and the sheathstripped length 40 mm or more from the connecting end. A thick line may prevent proper closing of the cover of
the terminal block.)
•To meet UL standards, always insert a UL-standard fuse (J type) on the power supply side.
•Use a ground wire with a larger diameter than that of the power cable shown above.
2-13
Page 37

2-2 Wiring
k
Choose the sensitivity current of the earth leakage breaker (ELB), depending on the total distance (L) between
the Inverter and the power supply, and the Inverter and the motor.
L
100 m max. 30
300 m max. 100
800 m max. 200
Sensitivity
current (mA)
Guide of leakage current: If a CV wire is used and routed through a metal pipe,
Due to the higher specific inductive capacity of the H-IV wire, the leakage current
increases about eight times. Use a wire with a sensitivity current one-level higher.
The leakage current mentioned here is the effective value of the fundamental
wave, and high-frequency currents are excluded.
Terminal Arrangement
Main circuit terminal block Model (3G3JX-) Screw size W (mm)
Upper side of the body
R/L1 S/L2 T/L3
Lower side of the body
N/- P/+2 +1
U/T1 V/T2
W/T3
the leakage current is 30 mA/km.
A2002 to A2007
AE002 to AE004
(*1)
M3.5 7.1
2
Design
7.1
Main Circuit
Terminal Bloc
Upper side of the body
A2015 to A2037
R/L1 S/L2 T/L3
Lower side of the body
U/T1 V/T2 W/T3 N/- P/+2 +1
*1. For 3G3JX-AE, R/L1 corresponds to L1, S/L2 to L2, and T/L3 to N/L3.
Connect a single-phase 200-V AC input to terminals L1 and N/L3.
Relay Output
Terminal Block
MB MA MC
AM FS FV FI FC S5
A4004 to A4037
AE007 to AE022
(*1)
A2055 to A2075
A4055 to A4075
Control Circuit Terminal Block
S4 S3 S2 S1 SC PSC P24 PC P1
M4 9.2
M5 13
9.2 or 13
Main Circuit
Terminal Block
2-14
Page 38

2-2 Wiring
2
Design
Model
(3G3JX-)
Main circuit M3.5 7.1 M4 9.2 M5 13
Control circuit M2 ⎯ M2 ⎯ M2 ⎯
Relay M2.5 ⎯ M2.5 ⎯ M2.5 ⎯
Ground M4 ⎯ M4 ⎯ M5 13
A2002 to A2007
AE002 to AE004
Screw size W (mm) Screw size W (mm) Screw size W (mm)
A2015 to A2037
A4004 to A4037
AE007 to AE022
A2055 to A2075
A4055 to A4075
Screw Tightening Torque
Screw Tightening torque
M2 0.2 N•m (max. 0.25 N•m)
M2.5 0.5 N•m (max. 0.6N•m)
M3.5 0.8 N•m (max. 0.9 N•m)
M4 1.2 N•m (max. 1.3 N•m)
M5 3.0 N•m (max. 3.3 N•m)
Explanation of the Main Circuit Terminal Connection
Terminal
symbol
R/L1, S/L2,
T/L3 *
U/T1,
V/T2, W/T3
+1,
P/+2
P/+2, N/-
* For 3G3JX-AE's terminal symbols, R/L1 corresponds to L1, S/L2 to L2, and T/L3 to N/L3.
Connect a single-phase 200-V AC input to terminals L1 and N/L3.
Terminal name Function Connection example
Main power supply
input terminal
Inverter output
terminal
External DC reactor
terminal
Regenerative
braking unit
connection terminal
Ground terminal
Connect the input power supply.
Connect to the motor.
Normally connected by the short-circuit
bar. Remove the short-circuit bar
between +1 and P/+2 when a DC reactor
is connected.
Connect optional regenerative braking
units.
(If a braking torque is required)
Ground (Connect to ground to prevent
electric shock and reduce noise.)
ELB
Power supply
Do not remove the short-circuit bar
between +1 and P/+2 when a DC
reactor is not connected.
Motor
2-15
Page 39

Main Circuit Connection Diagram
)
2-2 Wiring
Regenerative braking unit
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3 *
Inverter
3G3JX
Power supply
Molded case
circuit-breaker
(MCCB)
MC
AC reactor
noise filter
Fuse
* For 3G3JX-AE's terminal symbols, R/L1 corresponds to L1, S/L2 to L2, and T/L3 to N/L3.
Wiring the Main Circuit Terminals (Input Side)
Installing a Molded-case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
•Always connect the Inverter and power supply via a molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB) to protect
the Inverter from damage that may result from short-circuiting.
•Always connect the power input terminals (R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3) and power supply via an MCCB,
according to the Inverter capacity.
•Install one MCCB per Inverter.
•Choose an appropriate MCCB capacity according to the fuse size on page 2-13.
•When choosing MCCB's time characteristics, be sure to consider the Inverter's overload protection
(1 minute at 150% of the rated output current).
•By programming the sequence as illustrated below, you can turn off the power via the relay outputs
(MA, MB, and MC) for the 3G3JX Series.
P/+2 N/-
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
M
2
Design
Molded-case
Power supply
circuit breaker
(MCCB)
MC
OFF
ON
X1
X1
X1
X2
X2
DC (24 V) relay
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3 *
MA
MC
Inverter
3G3JX
(30 V DC, 50 mA max.
* For 3G3JX-AE's terminal symbols, R/L1 corresponds to L1, S/L2 to L2, and T/L3 to N/L3.
Installing a Ground Fault Interrupter
•The Inverter's output uses high-speed switching, and so generates high-frequency current
leakage. (Generally, if the power cable is 1 m, the leakage current is approx. 100 mA per Inverter,
and approx. 5 mA is added per additional meter of the power cable.)
•At the power supply input part, install a special-purpose ground fault interrupter for Inverters that
excludes high-frequency leakage current and detects only the leakage current within a frequency
range that is hazardous to humans. (Choose a ground fault interrupter with a sensitivity current of
at least 10 mA per Inverter.)
•Alternatively, use a general ground fault interrupter with a sensitivity current of 200 mA or more per
Inverter, and with an operating time of 0.1 s or more.
2-16
Page 40

2-2 Wiring
Installing a Magnetic Contactor (MC)
•If the power supply of the main circuit is shut off due to sequencing, a magnetic contactor (MC) can
be used. (When forcibly stopping the load with an MC on the primary side of the main circuit,
however, the regenerative braking does not work and the load coasts to a stop (free run).)
•Frequently opening and closing the magnetic contactor (MC) to start and stop a load may cause
2
Connection Sequence to the Terminal Block
the Inverter to break down. To extend the life of the Inverter's internal electrolytic capacitor, limit
the frequency to no more than once every 30 minutes.
•Input power supply can be connected to any terminal because the phase sequence of the input
power supply is irrelevant to that of the terminal block (R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3).
Design
Installing an AC Reactor
•If the Inverter is connected to a large-capacity power transformer (660 kVA or more) or the phase
advance capacitor is in use, a large peak current may flow through the input power circuit, causing
the converter unit to break down.
•Install an optional AC reactor on the input side of the Inverter. An AC reactor will also improve the
power factor of the power input side.
Installing a Surge Absorber
•Always use a surge absorber or diode when magnetic contactors (MC), electromagnetic relays,
solenoid valves, solenoid, and magnetic brakes are used.
Connecting a Regenerative Braking Unit
When running a load with a large inertia or a vertical axis, regenerative energy will return to the
Inverter.
If overvoltage in the main circuit is generated during deceleration, this indicates that the
regenerative energy exceeds the capacity of the Inverter. In this case, use a regenerative braking
unit.
Select a regenerative braking unit referring to the allowable operation cycle of the regenerative
braking unit specifications regardless of the Inverter capacity.
When using a braking resistor with the resistor of a regenerative braking unit removed, refer to the
connectable resistance of the regenerative braking unit and the allowable braking frequency of the
braking resistor in making a selection.
Refer to “ 7-5 Options” (page 7-14 to 16) for further information when making a selection.
2-17
Page 41

2-2 Wiring
r
•When using a regenerative braking unit, be sure to include a sequence whereby the power supply
for the Inverter will be turned off in the event of abnormal overheating. Not doing so may result in
fire.
For a regenerative braking unit: Use the error contact output (MA, MB).
Molded-case
Power supply
XB
circuit breaker
(MCCB)
OFF ON
MC
Magnetic contactor
MC
(MC)
R/L1 (L1) *
S/L2 (L2)
T/L3 (N/L3)
N/- P/+2 +1
Inverter
3G3JX
2
Design
MC
SA
MC
SA
NP
AL1
AL2
PRB R1R2
Regenerative braking unit
DCL
DC reacto
* The items in parentheses indicate terminal symbols for 3G3JX-AE.
<Braking Resistors and Braking Resistor Units for the Inverter>
Name Model Specifications
3G3AX-RBU21
For general use (with built-in resistor)
3/1-phase
Regenerative
braking unit
3G3AX-RBU22
3G3AX-RBU41
200 V
3-phase
400 V
For heavy instantaneous regenerative power
(with built-in resistor)
For general use (with built-in resistor)
Installing a Noise Filter on the Input Side
•The Inverter's output uses high-speed switching, so noise may be transmitted from the Inverter to
the power line, affecting peripheral devices.
•It is recommended that a noise filter be installed on the input side to minimize noise transmission.
(Installing a noise filter on the input side can also reduce the noise from the power line to the
Inverter.)
<Recommended Input Noise Filters for the Inverter>
General EMC-conforming
3G3AX-NFI 3G3AX-EFI
2-18
Page 42

2-2 Wiring
Molded-case
circuit breaker
Power supply
2
(MCCB)
Molded-case
circuit breaker
(MCCB)
Input noise
filter for
Inverter *
Inverter
3G3JX
Other device
M
Design
Wiring the Main Circuit Terminals (Output Side)
* Use a noise filter designed for Inverters. A general-purpose noise filter will be less effective and
may not reduce noise.
Connect the Terminal Block to the Load
•Connect motor output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3 to motor lead wires U, V, and W.
•Check that the motor rotates forward with the forward command. Switch over any two of the output
terminals (U/T1, V/T2, W/T3) and reconnect if the motor rotates in reverse to the forward
command.
Never Connect a Power Supply to the Output Terminals
•If voltage is applied to the output terminals, the internal circuit of the Inverter will be damaged.
Never connect a power supply to output terminals U/T1, V/T2, or W/T3.
2-19
Page 43

Never Short-circuit or Ground the Output Terminals
•Never touch the output terminals by hand.
•If the output wires come into contact with metal materials, an electric shock or ground fault will
occur. This is extremely hazardous. Be careful not to short-circuit the output wires.
2-2 Wiring
Do Not Use a Phase Advance Capacitor or Noise Filter
•Doing so may result in damage to the Inverter or cause the parts to burn. Never connect a phase
advance capacitor or LC/RC noise filter to the output circuit.
Do Not Use an Electromagnetic Switch
•If a load is connected to the Inverter during running, an inrush current will actuate the overcurrent
protective circuit in the Inverter. Do not connect an electromagnetic switch or magnetic contactor
(MC) to the output circuit.
Install a Noise Filter on the Output Side
Connect a noise filter to the output side of the Inverter to reduce induction and radio noise.
Power
supply
Molded-case circuit breaker
(MCCB)
Inverter
3G3JX
Signal line
Noise filter
3G3AX-NFO
Induction noise
M
Radio noise
AM radioController
2
Design
Induction noise: Electromagnetic induction can generate noise on the signal line, causing the
controller to malfunction.
Radio noise: Electromagnetic waves from the Inverter and I/O cables can cause the radio receiver
to generate noise.
Countermeasures Against Induction Noise
To reduce induction noise from the output side, the following method is also effective.
•Run the cables collectively through the mounted metal pipe. Keeping the metal pipe at least 30 cm
away from the signal line reduces induction noise.
Power
supply
Molded-case circuit breaker
(MCCB)
Inverter
3G3JX
M
30 cm min.
Signal line
Controller
2-20
Page 44

2
Design
2-2 Wiring
Cable Length Between Inverter and Motor
Use a cable of 50 m or less between the Inverter and the motor. If the cable length is increased, the
stray capacitance between the Inverter outputs and the ground is increased proportionally. An
increase in stray capacitance causes high-frequency leakage current to increase, affecting the
current detector in the Inverter's output unit and peripheral devices. If your system configuration
requires a cable length of 50 m or more, perform the following:
•Wire in metallic ducts.
•Use separate cables for each phase.
•Set the Inverter to a lower carrier frequency (b083).
Do Not Use Single-phase Motors
•A single-phase motor uses the capacitor start method or split-phase start method to determine its
rotation direction at startup, and thus is not suitable for the variable speed control via the Inverter.
Do not use single-phase motors.
* If a capacitor start motor is used, the capacitor may be damaged by a sudden electric charge and
discharge caused by Inverter output. If a split-phase start motor is used, the startup coil may burn
because the centrifugal switch does not operate.
2-21
Page 45

Specifications of the Control Circuit Terminals
2-2 Wiring
Input signal
Monitor
signal
Frequency
reference
input
Terminal
symbol
PSC
S1
S2 Reverse/Stop
S3 Fault reset
S4
S5
SC Input signal common ⎯
AM
FS Frequency reference power supply ⎯
FV Voltage frequency reference signal ⎯
FI Current frequency reference signal ⎯
Terminal name and function Default setting Specifications
External power supply terminal for input
signal (input).......................At sink logic
Internal power supply output terminal for
input signal (output)......At source logic
Multi-function input terminals S1 to S5
Select 5 functions among the 31
functions and allocate them to from
terminals S1 to S5.
The terminal allocation is changed
automatically when the emergency
shutoff function is used. Refer to
"Emergency Shutoff Input Function"
(page 4-45).
Analog frequency monitor/
Analog output current monitor
Forward/Stop
Emergency stop
fault
Multi-step speed
reference 1
Analog
frequency
monitor
⎯
24 V DC ±10%
30 mA max.
24 V DC ±10%
100 mA max.
Contact input
Close: ON (Start)
Open: OFF (Stop)
Minimum ON time:
12 ms min.
10 V DC
10 mA max.
0 to 10 V DC
Input impedance 10 kΩ
When installing variable
resistors at FS, FV, and FC
(1 to 2 kΩ)
4 to 20 mA DC
Input impedance 250 Ω
2
Design
Output signal
Relay output
signal
FC Frequency reference common ⎯
Multi-function output terminal
P1
PC Output signal common ⎯
MA
MB
MC
Select the status of the Inverter and
allocate it to terminal P1.
MB MA MC
Under normal operation : MA-MC Closed
Under abnormal operation or power
shutdown : MA-M
(Default)
C Open
Frequency
arrival signal at
a constant
speed
Contact ratings
250 V AC 2.0 A (resistance load) 100 V AC min.
30 V DC 3.0 A (resistance load) 5 V DC
27 V DC
50 mA max.
0.2 A (inductive load) 10 mA
0.6 A (inductive load) 100 mA
2-22
Page 46

2-2 Wiring
Ω
(
)
Functions and Connections of the Control Circuit Terminals
2
Design
Terminal
function
Contact
input
(for
switching
function)
Power
supply
External
analog
frequency
reference
Monitor
output
Terminal
symbol
Terminal name Function and connecting method Wire size
Select functions and allocate them to terminals S1 to S5.
S1
S2
S3
S4
Multi-function
input
(The figure below illustrates the wiring of the sink logic.)
S5
P24 Internal 24 V DC 24 V DC output
SC Input common Input signal common
If the multi-function input is set as the sink logic, the PSC
terminal acts as an external power supply input terminal.
If the multi-function input terminal is set as the source logic,
the PSC terminal acts as an internal power supply output
PSC
Input power
supply
terminal.
Frequency
FS
reference power
• External voltage directive is 0 to 9.8 V.
(Nominal input: 10 V)
supply output
FS FV FI FC
Variable resistor
(1/2 W min.)
1 to 2 kΩ
FS
FV
FI
Frequency
reference Input
(Voltage
directive)
Frequency
reference Input
(Current
directive)
Frequency
FC
reference
common
4 to 19.6 mA DC
Nominal input: 20 mA
• Choose from frequency or output current.
Output terminal specifications
AM
Multi-function
analog output
0 to 10 V DC full-scale
1 mA max.
SC S5 S4 S3 S2 S1
*1
FC
FI
FV
-
+
FS
FV
FC
FI
+
-
0 to 9.8 V DC
(Nominal input: 10 V)
Input impedance 10
AM
SC
Shield wire
of 0.14 to
0.75 mm
2
Recomme
nded wire
size:
0.75 mm
2
Output terminal specifications
Open collector output
27 V DC max.
50 mA max.
Open
Collector
Output
Relay
output
P1
PC
MA
MB
MC
Multi-function
*2
output
Multi-function
output common
Relay output
Relay output
common
P1
PC
RY
Select the status of the Inverter and allocate it to terminal P1.
Selection of functions is the same as the multi-function
*3 *4
output.
*1. Simultaneous input of current and voltage is not possible. Do not connect the signal lines simultaneously.
*2.
By factory default, multi-function output P1 is set to NO contact. To switch to NC contact, change the C031
setting.
2-23
Page 47

*3. Below are the contact specifications of the relay output.
2-2 Wiring
Output
terminal
MA-MC
MB-MC
By factory default, the relay output (MA, MB) contact selection (C036) is set at NC contact between MA-MC, and
*4.
NO contact between MB-MC.
Contact
capacity
Max.
Min.
Max.
Min.
Resistance load Inductive load
250 V AC 2.5 A
30V DC 3 A
100 V AC 10 mA
5 V DC 100 mA
250 V AC 1 A
30 V DC 1 A
100 V AC 10 mA
5 V DC 100 mA
250 V AC 0.2 A
30 V DC 0.7 A
250 V AC 0.2 A
30 V DC 0.2 A
Mode Selector
RS-485 Communication/Operator Selector (S7)
Select the mode according to the option connected to the communications connector.
When using the 3G3AX-OP01 supplied with the Inverter, it is available regardless of the switch
condition.
Symbol Name Status Description
S7
RS-485 communication/
operator selector
485 RS485 ModBus communication
OPE [Default] Digital Operator (Option: 3G3AX-OP1)
2
Design
Emergency shutoff selector (S8)
Use this selector to enable the emergency shutoff input function.
Symbol Name Status Description
ON Emergency shutoff input enabled
OFF
[Default]
Normal
S8
Emergency
shutoff
selector
*1 The multi-function input terminal 3 is switched to a terminal for emergency shutoff input, and the allocation of
other multi-function input terminals is also changed automatically. Do not set to ON immoderately. For details,
refer to "Emergency Shutoff Input Function" (page 4-45).
*1
2-24
Page 48

2
Design
2-2 Wiring
Conforming to EC Directives
Conforming Standards
•EMC directive EN 61800-3
•Low-voltage directive EN 61800-5-1
Concept of Conformity
EMC Directive
OMRON products are the electrical devices incorporated and used in various machines or
manufacturing equipment. For this reason, we make efforts to conform our products to their related
EMC standards so that the machines or equipment which have incorporated our products should
easily conform to the EMC standards. The 3G3JX models have conformed to the EMC directive EN
61800-3 by following the installation and wiring method as shown below. Your machines or
equipment, however, vary in type, and in addition, EMC performance depends on the configuration,
wiring, or location of the devices or control panels which incorporate the EC directive conforming
products. This in turn does not allow us to confirm the condition and the conformity in which our
products are used. Therefore, we appreciate confirmation of the final EMC conformity for the whole
machine or equipment on your own.
Wiring the Power Supply
•Be sure to connect the power input terminals (R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3) and power supply via an EMC
conforming dedicated noise filter 3G3AX-EFI.
•Keep the ground cable as short as possible.
•Keep the cable between the Inverter and the noise filter as short as possible.
Connecting a Motor to the Inverter
•When connecting a motor to the Inverter, be sure to use shielded braided cables.
•Keep the cables as short as possible.
Low-voltage Directive
The 3G3JX models have conformed to the EMC directive EN61800-5-1 by performing the machine
installation and wiring as shown below.
•The 3G3JX models are an open type device. Be sure to install it inside the control panel.
•The power supply and voltage (SELV) with reinforced or double insulation should be used for
wiring to the control circuit terminals.
•To satisfy requirements of the LVD (low-voltage) directive, the Inverter must be protected with a
molded case circuit breaker (MCCB) in case a short-circuiting accident occurs. Be sure to install a
molded case circuit breaker (MCCB) on the power supply side of the Inverter.
•Use one molded case circuit breaker (MCCB) per Inverter.
•Use the crimp-type terminal with an insulation sleeve to connect to the main circuit terminals.
•When not using the braking resistor or braking resistor unit, connect the crimp-type terminal with
an insulation sleeve to the braking resistor connection terminals (P/+2, N/-).
2-25
Page 49

Chapter 3
Operation
3-1 Test Run Procedure......................................... 3-3
3-2 Test Run Operation.......................................... 3-4
3-3 Part Names and Descriptions of the Digital
Operator............................................................ 3-9
3-4 Operation Procedure (Example: Factory Default)
...........................................................................3-11
3-5 Keys................................................................... 3-17
3-6 Parameter Transition ....................................... 3-18
3-7 Parameter List..................................................3-20
Page 50

3Operation
WARNING
Do not remove the front cover during the power supply and 5 minutes after the power shutoff.
Doing so may result in a serious injury due to an electric shock.
3
Operation
Do not operate the Digital Operator or switches with wet hands. Doing so may result in a serious
injury due to an electric shock.
Inspection of the Inverter must be conducted after the power supply has been turned off. Not doing
so may result in a serious injury due to an electric shock.
The main power supply is not necessarily shut off even if the emergency shutoff function is activated.
Do not change wiring, mode change switches (S7, S8), optional devices or replace cooling fans while
the input power is being supplied.
Doing so may result in a serious injury due to an electric shock.
CAUTION
Do not touch the Inverter fins, braking resistors and the motor, which become too hot during the
power supply and for some time after the power sh utoff. Doing so may result in a burn.
Take safety precautions such as setting up a molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB) that matches the
Inverter capacity on the power supply side. Not doing so might result in damage to property due to
the short circuit of the load.
Safety Information
Operation and Adjustment
•Be sure to confirm the permissible range of motors and machines before operation because the Inverter
speed can be changed easily from low to high.
•Provide a separate holding brake if necessary.
Precautions for Use
Error Retry Function
•Do not come close to the machine when using the error retry function because the machine may abruptly
start when stopped by an alarm.
•Be sure to confirm the RUN signal is turned off before resetting the alarm because the machine may
abruptly start.
Non-Stop Function at Momentary Power Interruption
•Do not come close to the machine when selecting restart in the non-stop function at momentary power
interruption selection (b050) because the machine may abruptly start after the power is turned on.
3-1
Page 51

Operation Stop Command
•Provide a separate emergency stop switch because the STOP key on the Digital Operator is valid only when
function settings are performed.
•When checking a signal during the power supply and the voltage is erroneously applied to the control input
terminals, the motor may start abruptly. Be sure to confirm safety before checking a signal.
3
Operation
3-2
Page 52

3-1 Test Run Procedure
3-1 Test Run Procedure
Item Description Reference page
Installation and Mounting
3
Wiring and Connection Connect to the power supply and peripheral devices. 2-6
Operation
Display Status Check Make sure that th ere are no faults in the Inverter.
Install the Inverter according to the installation conditions. 2-1
•Make sure that the installation conditions are met.
•Select peripheral devices that meet the specifications, and wire correctly.
Power On Check the following before turning on the power.
•Make sure that an appropriate power supply voltage is supplied and that the power input
terminals (R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3) are wired correctly.
3G3JX-A2: 3-phase 200 to 240 V AC
3G3JX-AE: 1/3-phase 200 to 240 V AC
(Connect to L1 and N/L3 for 1 phase)
3G3JX-A4: 3-phase 380 to 480 V AC
•Make sure that the motor output terminals (U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3) are connected to the
motor correctly.
•Make sure that the control circuit terminals and the control device are wired correctly
and that all control terminals are turned off.
•Set the motor to no-load status (i.e., not connected to the mechanical system).
•After checking the above, turn on the power.
•When the power is turned on normally, the display shows:
RUN LED indicator : ON ALARM LED indicator : OFF
POWER LED indicator : ON RUN command LED indicator : ON
Volume LED indicator : ON Data LED indicator (frequency) : ON
Data display : Displays the set value in d001.
•If an error occurs, the error code is displayed on the data display. In this case, refer to
"Chapter 5 Maintenance Operations" and make the necessary changes to remedy.
Parameter Initialization Initialize the parameters.
•Set parameter No. b084 to "02", and press the key while holding down the and
keys simultaneously.
Parameter Settings Set the parameters requi red for a test run.
•Set the motor capacity selection (H003) and the motor pole number selection (H004).
No-load Operation Start the no-load motor via the Digital Operator.
•Use the FREQ adjuster on the Digital Operator to rotate the motor.
Actual Load Operation Connect the mechanical system and operate via the Digital Operator.
•If there is no problem with the no-load operation, connect the mechanical system to the
motor and operate via the Digital Operator.
Operation Refer to "Chapter 4 Functions", and set the necessary parameters.
3-3
Page 53

3-2 Test Run Operation
Power On
Checkpoints Before Turning On the Power
•Make sure that an appropriate power supply voltage is supplied and that the power input terminals
(R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3) are wired correctly.
3G3JX-A2: 3-phase 200 to 240 V AC
3G3JX-AE: 1/3-phase 200 to 240 V AC (Connect to L1 and N/L3 for 1 phase)
3G3JX-A4: 3-phase 380 to 480 V AC
•Make sure that the motor output terminals (U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3) are connected to the motor
correctly.
•Make sure that the control circuit terminals and the control device are wired correctly and that all
control terminals are turned off.
•Set the motor to no-load status (i.e., not connected to the mechanical system).
3-2 Test Run Operation
3
Operation
Power On
•After checking the above, turn on the power.
Display Status Check
•When the power is turned on normally, the display shows:
[Normal] RUN LED indicator (during RUN) : ON ALARM LED indicator : OFF
POWER LED indicator : ON RUN command LED indicator : ON
Volume LED indicator : ON Data LED indicator (frequency) : ON
Data display : Displays the set value in d001
•If an error occurs, refer to "Chapter 5 Maintenance Operations" and make the necessary changes
to remedy.
[Fault] RUN LED indicator (during RUN) : ON ALARM LED indicator : ON
POWER LED indicator : ON RUN command LED indicator : ON
Volume LED indicator : ON Data LED indicator (frequency) : ON
Data display : An error code, such as "E-01", is displayed.
(The display varies depending on the type of error.)
3-4
Page 54

3-2 Test Run Operation
Parameter Initialization
3
Operation
•Initialize the parameters using the following procedure.
•To initialize the parameters, set parameter b084 to "02".
Key sequence Display example Description
Power On
k0.0
Press the Mode key once, and then press the Decrement key three
bk-k-k-
bk0k0k1
times to display "b---".
Press the Mode key.
"b001" is displayed.
Use the Increment or Decrement key to display "b084".
bk0k8k4
Press the Mode key. The set value in "b084" is displayed.
0k0
Use the Increment or Decrement key to display "02".
0k2
Press the Enter key. The set value is entered and "b084" is displayed.
bk0k8k4
Press the STOP/RESET key while holding down the Mode and
Decrement keys simultaneously.
When the display blinks, release the STOP/RESET key first, and then
the Mode and Decrement keys.
Displays initialization.
=k.k0k0
(In 1 s) The parameter number is displayed again in approximately 1 s.
dk0k0k1
3-5
Page 55

3-2 Test Run Operation
Setting the Motor Capacity Selection (H003) and Motor Pole Number Selection
(H004)
Parameter
No.
H003 1165h
H004 1166h
Key sequence Display example Description
Register
No.
Name Description Setting range
200-V class
0.2/0.4/0.75/
Motor
capacity
selection
Motor pole
number
selection
Sets the capacity of the
motor connected to the
Inverter.
Sets the pole number of
the motor connected to
the Inverter.
Press the Mode key twice to display the mode selection.
1.5/2.2/3.7/
5.5/7.5
400-V class
0.4/0.75/1.5/
2.2/3.7/5.5/7.5
2/4/6/8 Pole 4 No
bk-k-k-
Use the Increment or Decrement key to display "H---".
hk-k-k-
Unit of
setting
kW
Default
setting
Varies
with the
capacity.
Interrupt
during
RUN
No
3
Operation
Press the Mode key. "H003" is displayed.
hk0k0k3
Press the Mode key. The set value in "H003" is displayed.
0.2k0
Use the Increment or Decrement key to set the rated motor capacity.
0.4k0
Press the Enter key. The set value is entered.
0.4k0
(In approx. 1 s) The parameter number is displayed again.
hk0k0k3
3-6
Page 56

3-2 Test Run Operation
No-load Operation
Forward/Reverse Rotation via the Digital Operator
3
Operation
•Start the no-load motor (i.e., not connected to the mechanical system) using the Digital Operator.
*Before operating the Digital Operator, check that the FREQ adjuster is set to "MIN."
*Make sure that the LED indicator above the FREQ adjuster and the RUN command LED indicator
are lit.
Key sequence Display example Description
Press and hold the Mode key for 3 seconds or more to display "d001",
and then press again.
0.0
0.0
1k0.0k0
(Monitors the frequency reference.)
Press the RUN key.
The RUN command LED indicator is lit.
Turn the FREQ adjuster slowly.
The monitor value of the frequency reference is displayed.
The motor starts rotating forward in accordance with the frequency
reference.
•By turning the FREQ adjuster, make sure that there is no vibration or abnormal sound from the
motor.
•Make sure that no errors have occurred in the Inverter during operation.
•Switch between forward and reverse with the operator rotation direction selection (F004).
Stopping the Motor
•After completing the no-load operation, press the STOP/RESET key. The motor will stop.
Actual Load Operation
•After checking the operation with the motor in the no-load status, connect the mechanical system
and operate with an actual load.
*Before operating the Digital Operator, check that the FREQ adjuster is set to "MIN."
Connecting the Mechanical System
•After confirming that the motor has stopped completely, connect the mechanical system.
•Be sure to tighten all the screws when fixing in the motor axis.
Operation via the Digital Operator
•Because a possible error may occur during operation, make sure that the STOP/RESET key on
the Digital Operator is easily accessible.
•Use the Digital Operator to operate the Inverter the same way as in no-load operation.
3-7
Page 57

Checking the Operating Status
•After making sure that the operating direction is correct and that the Inverter is operating smoothly
at a slow speed, increase the frequency reference.
•By changing the frequency reference or the rotation direction, make sure that there is no vibration
or abnormal sound from the motor.
Make sure that the output current (output current monitor [d002]) is not excessive.
3-2 Test Run Operation
3
Operation
3-8
Page 58

3-3 Part Names and Descriptions of the Digital Operator
r
3-3 Part Names and Descriptions of the
Digital Operator
3
Operation
8k8k8k8
Data display
RUN command LED indicator
Operation keys
Name Description
POWER LED indicator Lit when the power is supplied to the control circuit.
ALARM LED indicator Lit when an Inverter error occurs.
RUN (during RUN) LED
indicator
PROGRAM LED
indicator
Data display
FREQ adjuste
Lit when the Inverter is running.
Lit when the set value of each function is indicated on the data
display.
Blinks during warning (when the set value is incorrect).
Displays relevant data, such as frequency reference, output current,
and set values.
3-9
Data display LED
indicator
Volume LED indicator Lit when the frequency reference source is set to the FREQ adjuster.
FREQ adjuster
RUN command LED
indicator
RUN key
STOP/RESET key
Mode key
Lit according to the indication on the data display.
Hz: Frequency A: Current
Sets a frequency. Available only when the frequency reference
source is set to the FREQ adjuster. (Check that the Volume LED
indicator is lit.)
Lit when the RUN command is set to the Digital Operator.
(The RUN key on the Digital Operator is available for operation.)
Activates the Inverter. Available only when operation via the Digital
Operator is selected.
(Check that the RUN command LED indicator is lit.)
Decelerates and stops the Inverter. Functions as a reset key if an
Inverter error occurs.
Switches between: the monitor mode (d), the basic function
mode (F), and the extended function mode (A, b,
C, H).
Page 59

3-3 Part Names and Descriptions of the Digital Operator
Name Description
Enter key
Increment key
Decrement key
Enters the set value.
(To change the set value, be sure to press the Enter key.)
Changes the mode.
Also, increases the set value of each function.
Changes the mode.
Also, decreases the set value of each function .
3
Operation
3-10
Page 60

3-4 Operation Procedure (Example: Factory Default)
3-4 Operation Procedure
(Example: Factory Default)
Displaying the Monitor Mode, Basic Function Mode, and Extended
3
Function Mode
Power On
1. The data of the set monitor is displayed. (Default is "0.0")
Operation
0.0
Press
2. The code of the monitor mode is displayed (as "d001").
•Press the Mode key once to return from the code
dk0k0k1
Press Press
("d002" is displayed.)
display of the monitor mode to the monitor
display.
dk0k0k2
3-11
Press Press
(13 times)(13 times)
(Continued to the next page)
Page 61

3-4 Operation Procedure (Example: Factory Default)
3. The code of the basic function mode is displayed (as "F001").
fk0k0k1
Press Press
(4 times)(4 times)
4. The extended function mode is displayed (as "A---").
•Extended function mode
ak-k-k-
Press Press
(4 times)(4 times)
5. The code of the monitor mode is displayed (as "d001").
Displays in order of A ⇔ b ⇔ C ⇔ H.
•Returns to step 2.
dk0k0k1
3
Operation
3-12
Page 62

3-4 Operation Procedure (Example: Factory Default)
Setting Functions
•Switch the method of the RUN command. (Digital Operator → Control terminal block)
•To switch the method of the RUN command from the Digital Operator (factory default) to the control
terminal block, you need to change the frequency reference selection (A001) from the Digital
Operator (02) to the terminal (01).
3
Operation
1. Display the extended function mode (as "A---").
•To display "A---", follow the indication method
ak-k-k-
Press
2. The code of the extended function mode is displayed (as "A001").
described in "Displaying the Monitor Mode,
Basic Function Mode, and Extended Function
Mode" (page 3-11).
•By default, the RUN command LED indicator will
light up as the RUN command selection is set to
the Digital Operator.
ak0k0k1
Press
("A002" is displayed.)
3-13
ak0k0k2
Press
3. The setting of the extended function mode is displayed (setting in "A002").
•"02 (Digital Operator)" (default setting) is
0k2
Press
(Continued to the next page)
displayed in the RUN command selection
(A002).
•The PROGRAM (PRG) LED indicator lights up
while the extended function mode setting is
displayed.
Page 63

3-4 Operation Procedure (Example: Factory Default)
(Change the A002 setting.)
0k1
•Change the RUN command selection to the
terminal "01".
Press
4. The code of the monitor mode is displayed (as "A002").
•Press the Enter key to fix the changed setting
ak0k0k2
Press
(3 times)
5. The extended function mode is displayed (as "A---").
ak-k-k-
data.
•The RUN command selection is changed to the
terminal, and the RUN command LED indicator
will go off.
•You can now change to another extended
function code.
•You can now move to another extended function
mode, the monitor mode, and the basic function
mode.
3
Operation
Setting Function Codes
•You can enter codes for the monitor mode, basic function mode, and extended function mode
directly, as well as through the scrolling method.
•Below is an example where code d001 of the monitor mode is changed to extended function A029.
1. Display the code of the monitor mode (as "d001").
dk0k0k1
Press and simultaneously
(Continued to the next page)
3-14
Page 64

3-4 Operation Procedure (Example: Factory Default)
2. Change the function code.
•You can change the 4th digit when "d" blinks.
dk0k0k1
3
Operation
Press
(2 times)
("A001" is displayed.)
•"A" blinks.
•Press the Enter key to fix the blinking digit.
ak0k0k1
Press
("A" is entered.)
3. Change the 3rd digit of the function code.
•"0" of the 3rd digit blinks.
•Press the Enter key to fix "0" of the 3rd digit as
ak0k0k1
you need not change it.
•Press the Mode key to start "A" blinking again.
3-15
Press
("0" is entered.)
4. Change the 2nd digit of the function code.
•"0" of the 2nd digit blinks.
ak0k0k1
Press
(2 times)
(Continued to the next page)
•Press the Mode key to start "0" of the 3rd digit
blinking again.
Page 65

("A021" is displayed.)
ak0k2k1
3-4 Operation Procedure (Example: Factory Default)
•"2" of the 2nd digit blinks.
Press
5. Change the 1st digit of the function code.
•"1" of the 1st digit blinks.
ak0k2k1
Press or
(2 times)(8 times)
("A029" is displayed.)
•Press the Mode key to start "2" of the 2nd digit
blinking again.
•"9" of the 1st digit blinks.
ak0k2k9
Press
("9" is entered.)
6. The function code selection is complete.
3
Operation
ak0k2k9
"A029" selection completed.
(Supplemental Information)
•If you enter a parameter number that is not included in the parameter list, the display
returns to the parameter previously displayed.
•Press the Enter key to shift the digit to the right, and the Mode key to shift to the left.
•Press the Mode key to change the data for
A029.
3-16
Page 66

3-5 Keys
3-5 Keys
Name Description
Switches between the command setting and the data setting, and between the
extended function mode and the basic function mode.
3
With this key, you can always change the display as follows.
[Supplemental Information]
To jump to "d001" from any function mode, hold down the Mode key for 3
seconds.
Operation
Mode key
fk0k0k1 fk0k0k1
k5k8.1
or
5k8.0
5k7.9
Note: Always press the Enter key to store any changed data.
Increment key
Changes the set values, parameters, and commands.
Decrement key
RUN key Starts the operation. Forward/Reverse rotation depends on the "F004" setting.
STOP/RESET key Stops the operation. Functions as a reset key if an error occurs.
3-17
Enter key
Enters and stores changed data.
Do not press the Enter key if you don't want to store any changes, for example, if
you have changed the data inadvertently.
Page 67

3-6 Parameter Transition
*4
dk0k0k1 0.0
*4
3-6 Parameter Transition
*4
dk0k8k3
*4
fk0k0k1
*5
fk0k0k4
ak-k-k-
bk-k-k-
Press the key
*5
ak0k0k1
*5
ak0k0k2
3
Operation
ak0k0k1
*3
*1
0k0k0k0
*2
0k0k0k1 9k9k9k9
*1
0k0k0k0
*2
ck-k-k-
*5
hk-k-k-
*1. Data is not stored by pressing the Mode key.
*2. Press the Enter key to store the data.
*3. When you press the Mode key after you return to the parameter number display without storing data in the
extended function mode, the mode selection function is selected.
*4. When you press the Enter key with d*** or F001 displayed, the monitor value is stored as the initial display
that appears when the power is turned on.
*5. When you press the Enter key, the first digit of each parameter setting is stored as the initial display that
appears when the power is turned on.
(Example: , etc.)
fk0k0k2 ak-k-k-
,
ak0k0k3
0k0k0k1 9k9k9k9
3-18
Page 68

3-6 Parameter Transition
* To display a specific monitor when the power is turned on, press the Enter key with that monitor displayed. If a
parameter for an extended function code is stored after pressing the Enter key, however, that code (A---, b---,
C---, d---, or H---) appears at the next power-on. To prevent this, always press the Enter key again with the
desired monitor displayed after storing a parameter.
3
Operation
3-19
Page 69

3-7 Parameter List
Monitor Mode (d) / Basic Function Mode (F)
3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
No.
d001
d002 Output current monitor 0.0 to 999.9 ⎯⎯A4-1
d003
d004
d005
d006
d007
d013 Output voltage monitor 0. to 600. ⎯⎯V4-3
Output frequency
monitor
Rotation direction
monitor
PID feedback value
monitor
Multi-function input
monitor
Multi-function output
monitor
Output frequency
monitor
(after conversion)
Name
0.0 to 400.0 ⎯⎯Hz 4-1
F: Forward
o: Stop
r: Reverse
0.00 to 99.99
100.0 to 999.9
1000. to 9999.
(Enabled when the PID function is selected)
0.00 to 99.99
100.0 to 999.9
1000. to 9999.
1000 to 3996 (10000 to 39960)
(Output frequency × Conversion factor of
b086)
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
ON
OFF
S5 S4 S3 S2 S1
ON
OFF
MA P1
Example)
Terminal
S4, S2: ON
Terminal
S5, S3, S1: OFF
Example)
Terminal P1: ON
Terminal MA: OFF
Default
setting
⎯⎯⎯4-1
⎯⎯⎯4-1
⎯⎯⎯4-2
⎯⎯⎯4-2
⎯⎯⎯4-2
Changes
during
operation
Unit Page
3
Operation
0. to 9999.
d016 Total RUN Time
d017
d018
d080
d081 Fault monitor 1 (Latest)
d083 Fault monitor 3
d102 DC voltage monitor 0.0 to 999.9 ⎯⎯V4-4
Power ON time
monitor
Fin temperature
monitor
Fault frequency
monitor
1000 to 9999
⎡100 to ⎡999[h]
0. to 9999.
1000 to 9999
⎡100 to ⎡999[h]
0.0 to 200.0 °C4-3
0. to 9999. ⎯⎯⎯4-3
Error code (condition of occurrence) →
Output frequency [Hz] → Output current [A]
→ Internal DC voltage [V] → RUN time [h] →
ON time [h]
⎯⎯h4-3
⎯⎯h4-3
⎯⎯ 4-4d082 Fault monitor 2
3-20
Page 70

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
d104
F001
3
F002 Acceleration time 1
F202
F003 Deceleration time 1
Operation
F203
F004
* 2nd control is displayed when SET(08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
No.
Electronic thermal
monitor
Output frequency
setting/monitor
*2nd acceleration
time 1
*2nd deceleration
time 1
Operator rotation
direction selection
Name
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
0.0 to 100.0 ⎯⎯%4-4
Starting frequency to 1st or 2nd max.
frequency
0.01 to 99.99
100.0 to 999.9
1000. to 3000.
0.01 to 99.99
100.0 to 999.9
1000. to 3000.
0.01 to 99.99
100.0 to 999.9
1000. to 3000.
0.01 to 99.99
100.0 to 999.9
1000. to 3000.
00: Forward
01: Reverse
Default
setting
⎯ Yes Hz 4-5
10.0 Yes s 4-5
10.0 Yes s 4-5
10.0 Yes s 4-5
10.0 Yes s 4-5
00 No ⎯ 4-6
Changes
during
operation
Unit Page
Extended function mode
Parameter
No.
A001
A201
A002
A202
Basic setting
A003 Base frequency 30. to Max. frequency [A004] 60.
A203
A004
A204
Function name
Frequency
reference
selection
*2nd frequency
reference
selection
RUN command
selection
*2nd RUN
command
selection
*2nd base
frequency
Maximum
frequency
*2nd maximum
frequency
00: Digital Operator (FREQ adjuster)
01: Terminal
02: Digital Operator (F001)
03: ModBus communication
10: Frequency operation result
01: Terminal
02: Digital Operator
03: ModBus communication
30. to Max. frequency [A204] 60.
30. to 400.
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
Default
setting
Changes
during
operation
00 No ⎯ 4-7
00 No ⎯ 4-7
02 No ⎯ 4-7
02 No ⎯ 4-7
No Hz 4-8
60.
No Hz 4-9
60.
Unit Page
3-21
Page 71

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
No.
A005 FV/FI selection
A011 FV start frequency 0.0 to Max. frequency 0.0 No Hz 4-10
A012 FV end frequency 0 .0 to Max. frequency 0.0 No Hz 4-10
A013 FV start ratio 0. to 100. 0. No % 4-10
Analog input
A014 FV end ratio 0. to 100. 100. No % 4-10
A015 FV start selection
A016 FV, FI sampling 1. to 17. 8. No ⎯ 4-11
A020
A220
Multi-step speed, Jogging
Function name
Multi-step speed
reference 0
*2nd multi-step
speed reference 0
02: Switches between FV/FREQ adjuster via
terminal AT
03: Switches between FI/FREQ adjuster via
terminal AT
04: FV input only
05: FI input only
00: External start frequency (A011 set value)
01: 0 Hz
0.0/Starting frequency to Max. frequency 6.0 Yes Hz 4-11
0.0/Starting frequency to 2nd max. frequency 6.0 Yes Hz 4-11
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
Default
setting
Changes
during
operation
02 No ⎯ 4-9
01 No ⎯ 4-10
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
Unit Page
3
Operation
3-22
Page 72

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
3
Operation
Multi-step speed, Jogging
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
No.
A021
A022
A023
A024
A025
A026
A027
A028
A029
A030
A031
A032
A033
A034
A035
A038 Jogging frequency 0.00/Starting frequency to 9.99 6.00 Yes Hz
A039
Function name
Multi-step speed
reference 1
Multi-step speed
reference 2
Multi-step speed
reference 3
Multi-step speed
reference 4
Multi-step speed
reference 5
Multi-step speed
reference 6
Multi-step speed
reference 7
Multi-step speed
reference 8
Multi-step speed
reference 9
Multi-step speed
reference 10
Multi-step speed
reference 11
Multi-step speed
reference 12
Multi-step speed
reference 13
Multi-step speed
reference 14
Multi-step speed
reference 15
Jogging stop
selection
0.0/Starting frequency to Max. frequency
00: Free-run stop
01: Deceleration stop
02: DC injection braking stop
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
Default
setting
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
Changes
during
operation
Yes Hz 4-11
00 No ⎯
Unit Page
4-12
4-49
4-12
4-49
3-23
Page 73

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
No.
A041
A241
A042
A242
A043
A243
A044
Characteristics, Torque boost
A244
A045
A245
A051
A052
A053
A054
Function name
Torque boost
selection
*2nd torque boost
selection
Manual torque
boost voltage
*2nd manual
torque boost
voltage
Manual torque
boost frequency
*2nd manual
torque boost
frequency
V/f characteristics
selection
*2nd V/f
characteristics
selection
Output voltage
gain
*2nd output
voltage gain
DC injection
braking selection
DC injection
braking frequency
DC injection
braking delay time
DC injection
braking power
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
00: Manual torque boost only
01: Automatic (simple) torque boost
0.0 to 20.0
0.0 to 50.0
00: Constant torque characteristics (VC)
01: Reduced torque characteristics (VP 1.7th
power)
06: Special reduced torque characteristics
(Special VP)
20. to 100.
00: Disabled
01: Enabled
02: Frequency control [A052 set value]
0.0 to 60.0 0.5 No Hz 4-15
0.0 to 5.0 0.0 No s 4-15
0. to 100. 50 No % 4-15
Default
setting
5.0
0.0
2.5
0.0
100.
100. 4-12
Changes
during
operation
00
No - 4-12
00
Yes % 4-12
Yes % 4-12
00
No - 4-12
00
Yes %
00 No ⎯ 4-15
Unit Page
4-12
4-76
3
Operation
DC injection braking
A055
A056
DC injection
braking time
DC injection
braking method
selection
0.0 to 60.0 0.5 No s 4-15
00: Edge operation
01: Level operation
01 No ⎯ 4-15
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
3-24
Page 74

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
3
Upper/Lower limit, Jump
Operation
PID control
AVR
No.
A061
A261
A062
A262
A063 Jump frequency 1
A064
A065 Jump frequency 2 0.0
A066
A067 Jump frequency 3 0.0
A068
A071 PID selection
A072 PID P gain 0.2 to 5.0 1.0 Yes ⎯ 4-20
A073 PID I gain 0.0 to 150.0 1.0 Yes s 4-20
A074 PID D gain 0.00 to 100.0 0.0 Yes s 4-20
A075 PID scale 0.01 to 99.99 1.00 No
A076
A077
A078
A081 AVR selection
A082
Function name
Frequency upper
limit
*2nd frequency
upper limit
Frequency lower
limit
*2nd frequency
lower limit
Jump frequency
width 1
Jump frequency
width 2
Jump frequency
width 3
PID feedback
selection
Reverse PID
function
PID output limit
function
AVR voltage
selection
0.0/Frequency lower limit to Max. frequency 0.0
0.0/Frequency lower limit to 2nd Max.
frequency
0.0/Starting frequency to Frequency upper
limit
0.0/Starting frequency to 2nd freque ncy upper
limit
Jump frequency: 0.0 to 400.0
Jump frequency width: 0.0 to 10.0
00: Disabled
01: Enabled
00: FI
01: FV
02: RS485 communication
10: Operation function output
00: OFF (Deviation = Target value - Feedback
value)
01: ON (Deviation = Feedback value - Target
value)
0.00 to 100.0 0.0 No % 4-20
00: Always ON
01: Always OFF
02: OFF during deceleration
200-V class: 200/215/220/230/240
400-V class: 380/400/415/440/460/480
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
Default
setting
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
200/
400
Changes
during
operation
No Hz 4-19
No Hz 4-19
No Hz 4-19
00 No ⎯ 4-20
00 No ⎯ 4-20
00 No ⎯ 4-20
02 No ⎯ 4-23
No V 4-23
Unit Page
Time
4-20
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
3-25
Page 75

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
No.
A085
A086
A092
A292
A093
A293
A094
A294
A095
RUN mode, Acceleration/Deceleration functions
A295
A096
A296
A097
A098
Function name
RUN mode
selection
Energy-saving
response/
accuracy
adjustment
Acceleration time
2
*2nd acceleration
time 2
Deceleration
time 2
*2nd deceleration
time 2
2-step
acceleration/
deceleration
selection
*2nd 2-step
acceleration/
deceleration
selection
2-step
acceleration
frequency
*2nd 2-step
acceleration
frequency
2-step
deceleration
frequency
*2nd 2-step
deceleration
frequency
Acceleration
pattern selection
Deceleration
pattern selection
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
00: Normal operation
01: Energy-saving operation
0 to 100 50 No % 4-23
0.01 to 99.99
100.0 to 999.9
1000. to 3000.
0.01 to 99.99
100.0 to 999.9
1000. to 3000.
00: Switched via multi-function input 09 (2CH)
01: Switched by setting
0.0 to 400.0
0.0 to 400.0
00: Line
01: S-shape curve
00: Line
01: S-shape curve
Default
setting
15.00
15.00
15.00
15.00
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
Changes
during
operation
00 No - 4-23
Yes s 4-24
Yes s 4-24
00
No ⎯ 4-24
00
No Hz 4-24
No Hz 4-24
00 No ⎯ 4-25
00 No ⎯ 4-25
Unit Page
3
Operation
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
3-26
Page 76

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
3
External frequency adjustment
Operation
Operation frequency
No.
A101 FI start frequency 0.0 to 400.0 0.0 No Hz
A102 FI end frequency 0.0 to 400.0 0.0 No Hz
A103 FI start ratio 0. to 100. 0. No %
A104 FI end ratio 0. to 100. 100. No %
A105 FI start selection
A141
A142
A143 Operator selection
Function name
Operation
frequency input A
setting
Operation
frequency input B
setting
00: Use FI start frequency [A101]
01: 0 Hz start
00: Digital Operator (F001)
01: Digital Operator (FREQ adjuster)
02: Input FV
03: Input FI
04: RS485 communication
00: Addition (A + B)
01: Subtraction (A - B)
02: Multiplication (A × B)
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
Default
setting
Changes
during
operation
01 No ⎯
01 No ⎯ 4-26
02 No ⎯ 4-26
00 No ⎯ 4-26
Unit Page
4-10
4-25
4-10
4-25
4-10
4-25
4-10
4-25
4-10
4-25
A145
A146
Frequency addition
A151 VR start frequency 0.0 to 400.0 0.0 No Hz
A152 VR end frequency 0.0 to 400.0 0.0 No Hz
A153 VR start ratio 0. to 100. 0. No %
VR adjustment
A154 VR end ratio 0. to 100. 100. No %
A155 VR start selection
Frequency
addition amount
Frequency
addition direction
0.0 to 400.0 0.0 Yes Hz 4-26
00: Adds A145 value to output frequency
01: Subtract A145 value from output
frequency
00: Use VR start frequency [A151]
01: 0 Hz start
00 No ⎯ 4-26
01 No ⎯
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
4-10
4-27
4-10
4-27
4-10
4-27
4-10
4-27
4-10
4-27
3-27
Page 77

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
No.
b001 Retry selection
b002
b003 Retry wait time 0.3 to 100.0 1.0 No s
b004
b005
Restart during momentary power interruption
b011
Function name
Allowable
momentary power
interruption time
Momentary power
interruption/
undervoltage trip
during stop
selection
Momentary power
interruption retry
time selection
Starting frequency
at frequency pullin restart
00: Alarm
01: 0 Hz start
02: Frequency matching start
03: Trip after frequency matching deceleration
stop
0.3 to 25.0 1.0 No s 4-27
00: Disabled
01: Enabled
00: 16 times
01: No limit
00: Frequency at interruption
01: Max. frequency
02: Set frequency
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
Default
setting
Changes
during
operation
00 No ⎯ 4-27
00 No ⎯ 4-28
00 No ⎯ 4-28
00 No ⎯ 4-28
Unit Page
4-27
4-53
3
Operation
b012
b212
b013
Electronic thermal
b213
Electronic thermal
level
*2nd electronic
thermal level
Electronic thermal
characteristics
selection
*2nd electronic
thermal
characteristics
selection
0.2 × Rated current to 1.0 × Rated current
00: Reduced torque characteristics 1
01: Constant torque characteristics
02: Reduced torque characteristics 2
Rated
current
Rated
current
00
00
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
No A 4-29
No ⎯ 4-29
3-28
Page 78

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
3
Overload limit
Operation
Frequency pull-in
Lock
No.
b021
b221
b022
b222
b023
b223
b028
b228
b029
b030
b031 Soft lock selection
Function name
Overload limit
selection
*2nd overload limit
selection
Overload limit
level
*2nd overload limit
level
Overload limit
parameter
*2nd overload limit
parameter
Overload limit
source selection
*2nd overload limit
source selection
Deceleration rate
constant at
frequency pull-in
restart
Frequency pull-in
restart level
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
00: Disabled
01: Enabled in acceleration/constant speed
operation
02: Enabled in constant speed operation
0..1 × Rated current to 1.5 × Rated current
0.1 to 3000.0
00: b022, b222 set values
01: Input terminal FV
0.1 to 3000.0 0.5 No s 4-28
0.2 × Rated current to 2.0 × Rated current
00: Data other than b031 cannot be changed
when terminal SFT is ON.
01: Data other than b031 and the specified
frequency parameter cannot be changed
when terminal SFT is ON.
02: Data other than b031 cannot be changed.
03: Data other than b031 and the specified
frequency parameter cannot be changed.
10: Data other than parameters changeable
during operation cannot be changed.
Default
setting
1.5 ×
Rated
current
1.5 ×
Rated
current
1.0
1.0
Rated
current
Changes
during
operation
01
No ⎯ 4-31
01
No A 4-31
No s 4-31
00
No ⎯ 4-31
00
No A 4-28
01 No ⎯
Unit Page
4-33
4-56
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
3-29
Page 79

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
No.
b050
b051
b052
b053
Non-stop function at momentary power interruption
b054
b055
b056
Others
b080 AM adjustment
b082 Starting frequency 0.5 to 9.9 1.5 No Hz 4-36
b083 Carrier frequency 2.0 to 12.0 3.0 No kHz
b084
b085
Initialization
Function name
Selection of nonstop function at
momentary power
interruption
Starting voltage of
non-stop function
at momentary
power interruption
Stop deceleration
level of non-stop
function at
momentary power
interruption
Deceleration time
of non-stop
function at
momentary power
interruption
Deceleration
starting width of
non-stop function
at momentary
power interruption
Overvoltage
protection
proportional gain
during
deceleration
Overvoltage
protection integral
time during
deceleration
Initialization
selection
Initialization
parameter
selection
00: Disabled
01: Enabled (Stop)
02: Enabled (Restart)
0.0 to 1000. 0.0 No V 4-33
0.0 to 1000. 0.0 No V 4-33
0.01 to 99.99
100.0 to 999.9
1000 to 3000
0.0 to 10.0 0.0 No Hz 4-33
0.2 to 5.0 0.2 Yes ⎯ 4-35
0.0 to 150.0 0.2 Yes s 4-35
0. to 255.
(Shared with C086 for AM offset adjustment)
00: Clears the trip monitor
01: Initializes data
02: Clears the trip monitor and initializes data
00
* Do not change.
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
Default
setting
1.0 No s 4-33
100. Yes ⎯
Changes
during
operation
00 No 4-33
00 No ⎯ 4-38
00 No ⎯ 4-38
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
Unit Page
3
Operation
4-35
4-75
4-36
4-76
3-30
Page 80

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
3
Operation
Others
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
No.
b086
b087
b088
b089
b091 Stop selection
b092 Cooling fan control
b130
b131
b133
b134
b140
b150
b15
Function name
Frequency
conversion
coefficient
STOP key
selection
Free-run stop
selection
Monitor display
selection
Overvoltage LAD
stop function
Overvoltage LAD
stop function level
setting
Overvoltage
protection function
selection during
deceleration
Overvoltage
protection level
setting during
deceleration
Overcurrent
suppression
function
Automatic carrier
reduction
R
eady function
1
selection
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
0.1 to 99.9 1.0 Yes ⎯ 4-39
00: Enabled
01: Disabled
00: 0 Hz start
01: Frequency pull-in restart
01: Output frequency monitor
02: Output current monitor
03: Rotation direction monitor
04: PID feedback value monitor
05: Multi-function input monitor
06: Multi-function output monitor
07: Frequency conversion monitor
00: Deceleration → Stop
01: Free-run stop
00: Always ON
01: ON during RUN
02: Depends on the fin temperature
00: Disabled
01: Enabled
200-V class: 330. to 395.
400-V class: 660. to 790.
00: Disabled
01: Enabled
200-V class: 330. to 395.
400-V class: 660. to 790.
00: Disabled
01: Enabled
00: Disabled
01: Enabled
00: Disabled
01: Enabled
Default
setting
380/
760
380/
760
Changes
during
operation
00 No ⎯ 4-39
00 No ⎯
01 Yes ⎯ 4-40
00 No ⎯ 4-39
01 No ⎯ 4-40
00 No ⎯ 4-41
Yes V 4-41
00 No ⎯ 4-35
No V 4-35
01 No ⎯ 4-42
00 No ⎯
00 No ⎯ 4-42
Unit Page
4-39
4-53
4-42
3-31
Page 81

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
No.
C001
C201
C002
C202
C003
C203
C004
C204
C005
Multi-function input terminals
C205
C011
C012
C013
C014
C015
Function name
Multi-function
input 1 selection
*2nd multi-function
input 1 selection
Multi-function
input 2 selection
*2nd multi-function
input 2 selection
Multi-function
input 3 selection
*2nd multi-function
input 3 selection
Multi-function
input 4 selection
*2nd multi-function
input 4 selection
Multi-function
input 5 selection
*2nd multi-function
input 5 selection
Multi-function
input 1 operation
selection
Multi-function
input 2 operation
selection
Multi-function
input 3 operation
selection
Multi-function
input 4 operation
selection
Multi-function
input 5 operation
selection
00: FW (forward)
01: RV (reverse)
02: CF1 (multi-step speed setting binary 1)
03: CF2 (multi-step speed setting binary 2)
04: CF3 (multi-step speed setting binary 3)
05: CF4 (multi-step speed setting binary 4)
06: JG (jogging)
07: DB (external DC injection braking)
08: SET (2nd control)
09: 2CH (2-step acceleration/deceleration)
11: FRS (free-run stop)
12: EXT (external trip)
13: USP (USP function)
15: SFT (soft lock)
16: AT (analog input switching)
18: RS (reset)
19: PTC (thermistor input)
20: STA (3-wire start)
21: STP (3-wire stop)
22: F/R (3-wire forward/reverse)
23: PID (PID enabled/disabled)
24: PIDC (PID integral reset)
27: UP (UP/DWN function accelerated)
28: DWN (UP/DWN function decelerated)
29: UDC (UP/DWN function data clear)
31: OPE (forced operator)
50: ADD (frequency addition)
51: F-TM (forced terminal block)
52: RDY (ready function)
53: SP-SET (special 2nd function)
64: EMR (emergency shutoff
255: No function
*1. The EMR is set forcibly with switch S8, not
with parameters.
00: NO
01: NC
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
*1
)
Default
setting
00
00
01
01
18
18
12
12
02
02
00
00
00
00
00
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
Changes
during
operation
No ⎯ 4-43
No ⎯ 4-44
Unit Page
3
Operation
3-32
Page 82

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
3
Operation
Multi-function output setting
No.
C021
C026
C028 AM selection
C031
C036
C038
C039
C041
C241
C042
Function name
Multi-function
output terminal P1
selection
Relay output (MA,
MB) function
selection
Multi-function
output terminal P1
contact selection
Relay output (MA,
MB) contact
selection
Light load signal
output mode
Light load
detection level
Overload warning
level
*2nd overload
warning level
Arrival frequency
during
acceleration
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
00: RUN (signal during RUN)
01: FA1 (constant speed arrival signal)
02: FA2 (over set frequency arrival signal)
03: OL (overload warning)
04: OD (excessive PID deviation)
05: AL (alarm output)
06: Dc (disconnection detection)
07: FBV (PID FB status output)
08: NDc (network error)
09: LOG(logic operation output)
10: ODc (Do not use.)
43: LOC (light load detection signal)
00: Output frequency
01: Output current
00: NO contact at MA; NC contact at MB
01: NC contact at MA; NO contact at MB
00: Enabled during acceleration/deceleration/
constant speed
01: Enabled only during constant speed
0.0 to 2.0 × Rated current (0.0 setting:
Function disable)
0.0: Does not operate
0.1 × Rated current to 2.0 × Rated current
0.0 to 400.0 0.0 No Hz 4-64
Default
setting
Rated
current
Rated
current
Rated
current
Changes
during
operation
00
No ⎯ 4-62
05
00 No ⎯
00
No ⎯ 4-71
01
01 No ⎯ 4-70
No ⎯ 4-70
No A
Unit Page
4-35
4-75
4-31
4-65
Arrival frequency
C043
C044
Level output status setting
C052 PID FB upper limit
C053 PID FB lower limit 0.0
during
deceleration
PID deviation
excessive level
0.0 to 400.0 0.0 No Hz 4-64
0.0 to 100.0 3.0 No %
0.0 to 100.0
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
3-33
4-20
4-65
100
No % 4-20
Page 83

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
No.
C070
C071
C072
C074
C075
C076
Communication function adjustment
C077
Function name
Operator/ModBus
selection
Communication
speed selection
(Baud rate
selection)
Communication
station No.
selection
Communication
parity selection
Communication
stop bit selection
Communication
error selection
Communication
error timeout
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
02: Digital Operator
03: ModBus
04: 4800 bps
05: 9600 bps
06: 19200 bps
1. to 32. 1. No ⎯
00: No parity
01: Even
02: Odd
1: 1-bit
2: 2-bit
00: Trip
01: Trip after deceleration stop
02: Ignore
03: Free run
04: Deceleration stop
0.00 to 99.99 0.00 No s
Default
setting
Changes
during
operation
02 No ⎯
04 No ⎯
00 No ⎯
1No⎯
02 No ⎯
Unit Page
4-79
3
Operation
4-79
C078
C081 FV adjustment 0.0 to 200.0 100.0 Yes % 4-74
C082 FI adjustment 0.0 to 200.0 100.0 Yes % 4-74
Various adjustment
Communication
wait time
0. to 1000. 0. No ms
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
3-34
Page 84

3-7 Parameter List
Parameter
3
Operation
Others
No.
C086
C091 Not used
C101 UP/DWN selection
C102 Reset selection
C141
C142
Function name
AM offset
adjustment
Logic operation
function A input
Logic operation
function B input
Monitor or data range
(Digital Operator)
0.0 to 10.0 0.0 Yes V
Use "00".
*Do not change.
00: Do not store the frequency data
01: Store the frequency data
00: Trip reset at power-on
01: Trip reset when the power is OFF
02: Enabled only during trip (Reset when the
power is ON.)
00: RUN (signal during RUN)
01: FA1 (constant speed arrival signal)
02: FA2 (over set frequency arrival signal)
03: OL (overload warning)
04: OD (excessive PID deviation)
05: AL (alarm output)
06: Dc (disconnection detected)
07: FBV (PID FB status output)
08: NDc (network error)
10: ODc (
43: LOC (light load detection signal)
Do not use.
)
Default
setting
Changes
during
operation
00 ⎯⎯⎯
00 No ⎯ 4-60
00 No ⎯ 4-57
00 No ⎯ 4-69
01 No ⎯ 4-69
Unit Page
4-35
4-75
Control parameter
C143
C144
C145
C148
C149
H003
H203
H004
H204
H006
H206
Logic operator
selection
Output terminal P1
ON delay
Output terminal P1
OFF delay
Relay output ON
delay
Relay output OFF
delay
Motor capacity
selection
*2nd motor
capacity selection
Motor pole number
selection
*2nd motor pole
number selection
Stabilization
parameter
*2nd stabilization
parameter
00: AND
01: OR
02: XOR
0.0 to 100.0 0.0 No s 4-70
0.0 to 100.0 0.0 No s 4-70
0.0 to 100.0 0.0 No s 4-70
0.0 to 100.0 0.0 No s 4-70
200-V class
0.2/0.4/0.75/1.5/2.2/3.7/5.5/7.5
400-V class
0.4/0.75/1.5/2.2/3.7/5.5/7.5
2
4
6
8
0. to 255.
00 No ⎯ 4-69
Factory
default
No kW 4-76
Factory
default
4
No Pole 4-76
4
100 Yes %
4-76
4-76
100 Yes %
* 2nd control is displayed when SET (08) is allocated to one of from C001 to C005.
3-35
Page 85

Chapter 4
Functions
4-1 Monitor Mode.................................................... 4-1
4-2 Function Mode.................................................. 4-5
Page 86

4-1 Monitor Mode
4Functions
4-1 Monitor Mode
Output Frequency Monitor [d001]
4
Output Current Monitor [d002]
Functions
Displays the output frequency of the Inverter.
The monitor LED indicator "Hz" lights up while d001 is displayed.
(Display)
0.0 to 400.0: Displays in increments of 0.1 Hz.
Displays the output current value of the Inverter.
The monitor LED indicator "A" lights up while d002 is displayed.
(Display)
0.0 to 999.9: Displays in increments of 0.1 A.
Rotation Direction Monitor [d003]
Displays whether the Inverter output is in forward/reverse/stop status. The RUN LED indicator lights
up during forward/reverse rotation.
(Display)
F: Forward
o: Stop
r: Reverse
PID Feedback Value Monitor [d004]
Displays a feedback value converted by [A075] (PID scale) when the PID selection is enabled
([A071] = 01).
"Monitor display" = "PID feedback value (%)" × "PID scale"
(Setting)
A071: 01 (PID enabled)
A075: 0.01 to 99.99 (Can be set in increments of 0.01.)
(Display)
0.00 to 99.99 : Displays in increments of 0.01.
100.0 to 999.9 : Displays in increments of 0.1.
1000 to 9999 : Displays in increments of 1.
[A075]
4-1
Page 87

Multi-function Input Monitor [d005]
Displays the input status of the multi-function input terminals.
C011 to C015 (contact selection) are excluded.
(Example) Multi-function input terminals S4, S2 : ON
Multi-function input terminals S5, S3, S1 : OFF
ON
OFF
4-1 Monitor Mode
Display
: ON
: OFF
S1S2S3S4S5
(OFF) (ON) (OFF) (ON)(OFF)
Multi-function input monitor
Multi-function Output Monitor [d006]
Displays the output status of the multi-function output terminals and relay output terminals.
C031 and C036 (contact selection) are excluded.
This monitor indicates the signal status of the functions (C021 and C026) allocated to each multifunction output terminal.
(Example) Multi-function output terminal P1 : ON
Relay output terminal MA : OFF
Display
ON
OFF
P1MA
(OFF) (ON)
Multi-function output monitor
: ON
: OFF
Output Frequency Monitor (After Conversion) [d007]
4
Functions
Displays a conversion value obtained by multiplying the Inverter output frequency by the coefficient
set in [b086].
Displayed value = "Output frequency [d001]" × "Frequency conversion coefficient [b086]"
(Display) [d007]
0.00 to 99.99 : Displays in increments of 0.01.
100.0 to 999.9 : Displays in increments of 0.1.
1000. to 9999. : Displays in increments of 1.
1000 to 3996 : Displays in increments of 10.
(Setting range) [b086]
0.1 to 99.9: Can be set in increments of 0.1.
(Example)
When the output frequency [d001] = 50.0 Hz, and
the frequency conversion coefficient [b086] = 1.1,
the monitor [d007] displays "55.0" through 50.0 × 1.1 = 55.0.
4-2
Page 88

4-1 Monitor Mode
Output Voltage Monitor [d013]
Displays the output voltage value (Vac) of the Inverter.
The monitor LED indicator "V" lights up.
(Display)
0. to 600.: Displays in increments of 1 V.
Total RUN Time [d016]
Displays the Inverter RUN time.
4
(Display)
0. to 9999. : Displays in increments of 1 hour.
1000 to 9999 : Displays in increments of 10 hours.
⎡100 to ⎡999 : Displays in increments of 1000 hours.
Power ON Time Monitor [d017]
Functions
Fin Temperature Monitor [d018]
Fault Frequency Monitor [d080]
Displays the total power supply time of the Inverter.
(Display)
0. to 9999. : Displays in increments of 1 hour.
1000 to 9999 : Displays in increments of 10 hours.
⎡100 to ⎡999 : Displays in increments of 1000 hours.
Displays the fin temperature.
(Display)
0. to 200. : Displays in increments of 1 °C.
Displays the number of times the Inverter has tripped.
(Display)
0. to 9999. : Displays in increments of 1 time.
1000 to 6553 : Displays in increments of 10 times.
4-3
Page 89

Fault Monitors 1[d081], 2[d082], 3[d083]
Displays the details of the last three trips.
The most recent trip is displayed on trip monitor 1.
4-1 Monitor Mode
(Display)
•Factor (E01 to E60)
•Output frequency at the time of tripping (Hz)
•Output current at the time of tripping (A)
•Internal DC voltage at the time of tripping (V)
•Total RUN time before the trip (hr)
•Total power supply time before the trip (hr)
*1. Refer to "Error Code List" (page 5-1) and "Trip Monitor Display" (page 5-4).
(Trip Monitor Display Sequence)
(1)Trip factor
*1
*2
(2)Trip frequency (3)Trip current (4)Trip P-N voltage (5)Total RUN time (6)Power ON time
dk0k8k1 ekLk0k7 6k0.0 4.0 3k9k8. 1k5. 1k8.
*2. Displays if there has been no trip.
_k_k_k_
4
Functions
DC Voltage Monitor [d102]
Displays the main circuit DC voltage of the Inverter.
(Display)
0.0 to 999.9 : Displays in increments of 0.1 V.
Electronic Thermal Monitor [d104]
Displays the count integration value of the electronic thermal. An overload trip occurs if it reaches
100% (E05).
(Display)
0.0 to 100.0 : Displays in increments of 0.1%.
4-4
Page 90

4-2 Function Mode
4-2 Function Mode
<Group F: Basic Function Parameter>
Output Frequency Setting/Monitor
4
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
Functions
F001
•Set the Inverter output frequency.
•With the frequency reference set to the Digital Operator ([A001] = 02), you can set the output
frequency in F001. For other methods, refer to the [A001] section in "Frequency Reference
Selection" (page 4-7).
•If a frequency is set in [F001], the same value is automatically set in multi-step speed reference 0
[A020]. To set the 2nd multi-step speed reference, use [A220], or use [F001] with the SET terminal
turned on.
To set by using the SET terminal, allocate 08 (SET) to the desired multi-function input.
Output frequency
setting/monitor
Multi-step speed
reference 0
*
A220
Related functions A001, A201, C001 to C005
* To switch to the 2nd multi-step speed, allocate 08 (SET) to the multi-function input terminal and then turn it on.
2nd multi-step
speed reference 0
0.0/Starting frequency to Max.
frequency
6.0 HzA020
Acceleration/Deceleration Time
Set an acceleration/deceleration time for the motor. For a slow transition, set a large value, and for
a fast transition, set a small one.
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
F002 Acceleration time 1
*
F202 2 nd acceleration time 1
F003 Decelera tion time 1
*
F203 2nd deceleration time 1
Related functions A004, A204, C001 to C005
0.01 to 3000 10.0 s
* To switch to 2nd acceleration/deceleration time 1, allocate 08 (SET) to the multi-function input terminal and then
turn it on.
4-5
Page 91

4-2 Function Mode
e
•The set time here indicates the acceleration/deceleration time between 0 Hz and the maximum
frequency.
Output frequency
Max. frequency
A004/A204
Output frequency set valu
Actual
acceleration
time
F002/F202
Actual
deceleration
time
F003/F203
Even if a short acceleration/deceleration time is set, the actual time cannot be shorter than the
minimum acceleration/deceleration time that is determined by the mechanical inertia moment and
the motor torque. If you set a time shorter than the minimum time, an overcurrent/overvoltage trip
may occur.
Acceleration Time TS
(
T
=
S
9.55
Deceleration Time T
(
T
=
B
9.55
NJJ
+)×
×
+)×
×
MML
()
TT
–
LS
NJJ
MML
()
TT
+
LB
L :Inertia moment of the load converted to the motor shaft [kg·m
J
M :Inertia moment of the motor [kg·m
J
N
M :Motor rotation speed [r/min]
T
S :Max. acceleration torque with the Inverter driving [N·m]
T
B
B :Max. deceleration torque with the Inverter driving [N·m]
L :Required driving torque [N·m]
T
For short-time deceleration, use the regenerative braking unit (optional).
Digital Operator Rotation Direction Selection
4
Functions
2
]
2
]
Select the direction of motor rotation applied to the RUN command via the Digital Operator.
This is disabled at terminals.
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
F004
Operator rotation
direction selection
00: Forward
01: Reverse
00 ⎯
4-6
Page 92

4-2 Function Mode
<Group A: Standard Function Parameter>
Frequency Reference Selection
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
4
* To switch to the 2nd frequency reference, allocate 08 (SET) to the multi-function input terminal and then turn it
on.
Functions
Select the method of the frequency reference.
A001
*
A201
Related functions A005, A141 to A143, A145, A146
Frequency reference
selection
2nd frequency
reference selection
Data Frequency reference source
00 FREQ adjuster
01 Voltage or current directive from the terminal.
02 F001 value set via the Digital Operator.
03 ModBus communication
10 Result of the frequency operation function
00: Digital Operator (FREQ adjuster)
01: Terminal
02: Digital Operator (F001)
03: ModBus communication
10: Frequency operation result
00 ⎯
RUN Command Selection
Select the method of the RUN/STOP command.
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
A002
*
A202
Related functions F004, A005, C001 to C005
* To switch to the 2nd RUN command, allocate 08 (SET) to the multi-function input terminal and then turn it on.
Data RUN command source
RUN command
selection
2nd RUN command
selection
Turn ON/OFF the FW and RV allocated to the terminal.
01
02 Use the STOP/RESET key on the Digital Operator.
03 Use the ModBus communication.
The STOP command is activated if both Forward/Reverse commands are input
simultaneously.
01: Terminal
02: Digital Operator
03: ModBus communication
02 ⎯
4-7
Page 93

4-2 Function Mode
A
)
Base Frequency
Base Frequency and Motor Voltage
Match the Inverter output (frequency/voltage) to the motor rating. Be careful, especially if you set a
base frequency at below 50 Hz. Otherwise, the motor may burn out.
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
A003 Base frequency 30 to max. frequency [A004]
*
A203
2nd base
frequency
30 to max. frequency [A204]
60.0 Hz
Related functions A004, A204, A081, A082
* To switch to the 2nd base frequency, allocate 08 (SET) to the multi-function input terminal and then turn it on.
Output voltage
VR voltage
selection
(A082)
Base frequency
(A003/A203)
Output
frequency (Hz
•If you apply a base frequency of over 60 Hz, a special motor is required. This may require the
Inverter to increase its capacity to accommodate a different applicable motor.
•Select the motor voltage according to the motor specifications. If the voltage exceeds the specified
level, the motor may burn out.
•The Inverter cannot output voltage beyond that of the incoming voltage.
Maximum Frequency
Set the maximum value of the output frequency.
4
Functions
•The value set here will be the maximum value (e.g.,10 V in the range from 0 to 10 V) of the external
analog input (frequency reference).
•The maximum Inverter output voltage from base to maximum frequencies is the voltage set at AVR
voltage selection A082.
•The Inverter cannot output voltage beyond that of the incoming voltage.
Output voltage
AVR voltage
selection
(100%)
(A082)
Base frequency
(A003/A203)
Maximum frequency
(A004/A204)
4-8
Page 94

4-2 Function Mode
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
A004 Maximum frequency
*
A204
Related functions A003, A203, A081, A082
* To switch to the 2nd max. frequency, allocate 08 (SET) to the multi-function input terminal and then turn it on.
2nd maximum
frequency
30 to 400 60.0 Hz
Analog Input (FV, FI)
4
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
Functions
AT terminal input status OFF ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF ON
Analog input enabled FV-FC VR FI-FC VR FV-FC FI-FC
The Inverter has two types of analog input terminals.
FV-FC terminal: 0 to 10 V (voltage input)
FI-FC terminal: 4 to 20 mA (current input)
Simultaneous inputs are not acceptable. Do not connect the signal lines for inputs FV and FI
simultaneously.
02: Switches between FV/FREQ adjuster
via terminal AT
A005 FV/FI selection
Related functions A011 to A016, A101 to A105, A151 to A155, C001 to C005, C081, C082
This function is enabled with the frequency reference set to the terminal block (A001 or A201 = 01).
The settings are as follows. (VR: FREQ adjuster)
A005 set value02030405
If AT is not allocated to any of the multi-function input, this means the AT input = OFF in the above
table.
03: Switches between FI/FREQ adjuster
via terminal AT
04: FV input only
05: FI input only
02 ⎯
4-9
Page 95

4-2 Function Mode
A
A
External Frequency (Voltage/Current) Adjustment
External Analog Input (Frequency Reference)
FV-FC terminal: 0 to 10 V (voltage input)
FI-FC terminal: 4 to 20 mA (current input)
Also set an output frequency for the FREQ adjuster on the Digital Operator.
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
A011
A101
A151
A012
A102
A152
A013
A103
A153
A014
A104
A154
A015
A105
A155
FV/FI/VR start frequency
0.00 to 400.0
(Set start/end frequency.)
FV/FI/VR end frequency
FV/FI/VR start ratio
0. to 100.
(Set a start/end ratio relative to an
external frequency reference of
FV/FI/VR end ratio 100.
FV/FI/VR start selection
between 0 to 10 V and 4 to 20 mA.)
00: Start frequency (A011 set value)
01: 0 Hz
0.0 Hz
0.
01 ⎯
4
Functions
%
Related functions A005, A016, AT input
•To input voltage ranging from 0 to 5 V on the FV-FC terminal, set A014 to 50%.
(Example 1) A015/A105 = 00
Max. frequency
012/A102/A152
011/A101/A151
0
A013/A103
/A153
(0 V/4 mA/VR min.)
A014/A104
/A154
Frequency reference
100%
(10 V/20 mA/VR max.)
(Example 2) A015/A105 = 01
Max. frequency
A012/A102/A152
A011/A101/A151
0
A013/A103
/A153
(0 V/4 mA/VR min.)
A014/A104
/A154
(10 V/20 mA/VR max.)
Frequency reference
100%
4-10
Page 96

4-2 Function Mode
FV, FI Sampling
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
4
Multi-step Speed Operation Function
Functions
Set the built-in filter applied to frequency setting signals via external voltage/current input.
A016 FV, FI sampling 1. to 17. 8. Time
Related functions A011 to A016, C001 to C005
•Helps remove noise in the frequency setting circuit.
•Set a larger data value if stable operation cannot be secured because of noise.
Note that the larger the data value is, the slower the response time.
•In case of setting "17", it indicates the setting of 16 moving average calculation disregarding the
voltage fluctuation equivalent to 0.1 Hz. Though the frequency becomes less likely to fluctuate, the
resolution for analog input decreases. This setting is not suitable for equipment that requires rapid
response.
Set different RUN speeds by using codes and switch the set speed via the terminal.
For details on the operation and settings, refer to "Multi-step Speed Operation Function" (page 4-
47).
Parameter No. Function name Data Default se tting Unit
A020
A220
A021
A022
A023
A024
A025
A026
A027
A028 to A035
Multi-step speed
reference 0
*
2nd multi-step speed
reference 0
Multi-step speed
reference 1
Multi-step speed
reference 2
Multi-step speed
reference 3
Multi-step speed
reference 4
Multi-step speed
reference 5
Multi-step speed
reference 6
Multi-step speed
reference 7
Multi-step speed
references 8 to 15
0.0/Starting frequency to Max.
frequency [A004]
6.0
Hz
0.0
Related functions F001, C001 to C005, CF1 to CF4 inputs
* To switch to the 2nd multi-step speed reference 0, allocate 08 (SET) to the multi-function input terminal and then
turn it on.
4-11
Page 97

4-2 Function Mode
Jogging Operation Function
The motor rotates while the input is turned ON.
For details on the operation and settings, refer to "Jogging Operation" (page 4-48).
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
A038 Jogging frequency 0.00/Starting frequency to 9.99 6.00
00: Free-run stop
A039 Jogging stop selection
Related functions C001 to C005, JG input
01: Deceleration stop
02: DC injection braking stop
00
Hz
•The Inverter runs at the speed set in A038 while the JG terminal allocated to one of the multifunction input terminals is turned on. Stop selection is also available in A039.
Relation Between Torque Boost and V/f Characteristics
Determine the relation of output voltage against output frequency.
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
A041 Torque boost selection
*
A241 2nd torque boost selection
A042 Manual torque boost voltage
*
A242 2nd manual torque boost voltage 0.0
A043 Manual torque boost frequency
*
A243
2nd manual torque boost
frequency
00: Manual torque boost
01: Automatic (simple) torque boost
0.0 to 20.0
(Ratio to the value of AVR voltage
selection A082)
0.0 to 50.0
(Ratio to base frequency)
00 ⎯
5.0
2.5
0.0
4
Functions
%
%
A044 V/f characteristics selection
*
A244 2nd V/f characteristics selection
A045 Output voltage gain
A245 2nd output voltage gain
Related functions A082, H003/H203, H004/H204
00: Constant torque characteristics
(VC)
01: Reduced torque characteristics
(VP 1.7th power)
06: Special reduced torque
characteristics (Special VP)
20. to 100. 100. %
00 ⎯
* To switch to the 2nd control, allocate 08 (SET) to the multi-function input terminal and then turn it on.
4-12
Page 98

4-2 Function Mode
Control Method (V/f Characteristics)
4
Functions
Constant Torque Characteristics (VC)
•Ouput voltage is proportional to output frequency.
While proportional from 0 Hz to base frequency, the output voltage is constant from base to
maximum frequencies regardless of the frequency.
Output
voltage
(100%)
Output
frequency (Hz)
0
Base frequency
(A003/A203)
Max. frequency
(A004/A204)
Reduced Torque Characteristics (VP 1.7th power)
•Suitable for a fan or pump that does not require large torque in a low speed range.
These provide high efficiency, reduced noise and vibration, owing to reduced output voltage in a
low speed range.
Output
voltage
(100%)
0
Base frequency
(A003/A203)
VP (1.7th
power of VP)
Max. frequency
(A004/A204)
Output
frequency (Hz)
Special Reduced Torque Characteristics (Special VP)
•Suitable for a fan or pump that requires torque in a low speed range. These have VC
characteristics only for low deceleration in reduced torque characteristics.
Output
voltage
(100%)
VC
0
10% of base
frequency
ab c
Period a: Provides constant torque characteristics (VC) within a range from 0 Hz to 10% of the base
frequency.
(Example) If the base frequency is 60 Hz, the Inverter provides constant torque
characteristics within a range from 0 to 6 Hz.
Period b:Provides reduced torque characteristics within a range from 10% to 100% of the base
frequency.
The Inverter outputs voltage based on a curve of the 1.7th power of the frequency.
Period c: Provides constant voltage within a range from the base frequency to the maximum
frequency.
VP
(1.7th power)
Base frequency
(A003/A203)
Output
frequency (Hz)
Max. frequency
(A004/A204)
4-13
Page 99

Torque Boost
This function helps compensate for insufficient motor torque in a low speed range.
•Compensates for the voltage drop caused by the primary resistance of the motor or by wiring to
suppress torque reduction in a low speed range.
•To select the simple torque boost in the torque boost selection (A041/A241), set the motor capacity
selection (H003/H203) and motor pole number selection (H004/H204) according to your motor.
Manual Torque Boost [A042/A242, A043/A243]
•Adds the voltage set in A042/A242 and A043/A243 to the V/f characteristics, and outputs the
resulting voltage. The addition value is set in percentage terms based on the AVR voltage selection
(A082) as 100%.
•The manual torque boost frequency (A043/A243) is set in percentage terms based on the base
frequency as 100%.
4-2 Function Mode
4
Output
voltage (100%)
Manual torque
boost voltage
(A042/A242)
•If you raise the set value of the manual torque boost, be careful about motor overexcitation.
Otherwise, the motor may burn out.
•Should such a situation occur, lower the set value of A042/A242.
Simple Torque Boost [A041/A241]
•If simple torque boost is selected in the torque boost selection (A041/A241: 01), it operates to
adjust the output voltage depending on the load level.
•To select simple torque boost in the torque boost selection (A041/A241), set the motor capacity
selection (H003/H203) and motor pole number selection (H004/H204) correctly according to your
motor.
•You may avoid a possible overcurrent trip during deceleration by always setting the AVR selection
to ON (A081: 00).
•Sufficient characteristics may not be obtained if you select two or more lower rank motor size than
specified.
Output Voltage Gain
0
Manual torque boost
frequency (A043/A243)
Base frequency
(A003/A203)
Output frequency (Hz)
Functions
V/f characteristics
(Example: VC)
Max. frequency
(A004/A204)
•Changes the Inverter output voltage in percentage terms based on the AVR voltage selection
[A082] as 100%.
•The Inverter cannot output voltage beyond that of the incoming voltage.
Motor voltage
selection
(A082)
A045
Base frequency
(A003/A203)
When A045 = 100
Max. frequency
(A004/A204)
4-14
Page 100

4-2 Function Mode
DC Injection Braking (DB)
This function securely stops the motor rotation during deceleration.
Parameter No. Function name Data Default setting Unit
00: Disabled
A051
A052
4
A053
DC injection braking
selection
DC injection braking
frequency
DC injection braking
delay time
01: Enabled
02: DB when output frequency
< A052
0.0 to 60.0 0.5 Hz
0.0 to 5.0 0.0 s
00 ⎯
Functions
A054
A055 DC injection braking time 0.0 to 60.0 0.5 s
A056
DC injection braking
power
DC injection braking
method selection
Related functions C001 to C005
•Two methods are available for DC injection braking: One is the external method via the multifunction input (external DC injection braking); the other is the internal method performed
automatically to stop the motor (internal DC injection braking).
•Below are operation types:
Edge operation: DB operates during the specified time period from the DB signal input.
Level operation: DB operates while a signal is being input.
Frequency control mode: DB operates when the frequency reaches the specified level during
operation.
•If DC injection braking operates at a high motor speed, an overcurrent trip (E01 to E04) or overload
trip (E05) may occur. For internal DC injection braking, the following adjustment may help you
avoid such a situation:
Lower the DC injection braking frequency (A052).
Increase the DC injection braking delay time (A053)
For external DC injection braking via the multi-function input, use the external DC injection braking
terminal (along with deceleration stop).
0. to 100. 50 %
00: Edge operation
01: Level operation
01 ⎯
External DC Injection Braking (A051 = 00)
•Allocate 07 (DB) to the desired multi-function input. DC injection braking can be applied by turning
on/off the DB terminal, regardless of the DC injection braking selection (A051).
•Set the DC injection braking power in A054.
•If the DC injection braking delay time (A053) is set, the Inverter output will be shut off during the
specified time period and the motor goes into free-run status. After the set time elapses, DC
injection braking starts.
•Set the DC injection braking time (A055) via the Digital Operator or the DB terminal while taking
into account motor heat generation. Long continuous use of DB may cause the motor to burn out.
•Perform each setting according to your system after selecting the level or edge operation in A056.
4-15
 Loading...
Loading...