Page 1
Cat. No. I528-E1-1
USER’S MANUAL
FIRST DRAFT!
SYSDRIVE 3G3JV
Compact Simplified Inverter
Page 2
Thank you for choosing this SYSDRIVE 3G3JV
-series product. Proper use
and handling of the product will ensure proper product performance, will
lengthen product life, and may prevent possible accidents.
Please read this manual thoroughly and handle and operate the product
with care.
NOTICE
1. This
2. Although care has been given in documenting the product, please contact
3. The product contains potentially dangerous parts under the cover. Do not
4. We recommend that you add the following precautions to any instruction
5. Specifications
manual describes the functions of the product and relations with other
products. You should assume that anything not described in this manual is
not possible.
OMRON representative if you have
your
manual.
attempt
injury
assemble the product.
manuals
S Precautions on the dangers of high-voltage equipment.
S Precautions
been
prove product performance.
to open the cover under any circumstances. Doing so
or death and may damage the product. Never attempt to repair or dis
you prepare for the system into which the product is being installed.
on touching the terminals of the
turned of
f. (These
and functions may be changed without notice in order to im
terminals are live even with the power turned of
any suggestions on improving this
may result in
product even after power has
f.)
-
-
Items to Check Before Unpacking
Check
the following items before removing the product from the package:
S Has
the correct product been delivered (i.e., the correct model number and
specifications)?
S Has the product been damaged in shipping?
S Are any screws or bolts loose?
Page 3
Overview
1-1 Function
1-2 Nomenclature
1
Chapter 1
Page 4
3 p ase 00 C
C osed,
S g e p ase 00 C
C osed,
C ect es
Overview Chapter 1
1-1 Function
The compact simple SYSDRIVE 3G3JV-Series Inverter ensures greater
ease of use than any conventional model.
The 3G3JV Inverter meets EC Directives and UL/cUL standard requirements for worldwide use.
H SYSDRIVE 3G3JV Inverter Models
•The following 3- and single-phase 200-VAC-class 3G3JV models are available.
Rated voltage Protective
structure
3-phase 200 VAC Closed,
wall-mounting type
(conforming to IP20)
Single-phase 200 VAC Closed,
wall-mounting type
(conforming to IP20)
Maximum applied
motor capacity
0.1 (0.1) kW 3G3JV-A2001
0.2 (0.25) kW 3G3JV-A2002
0.4 (0.55) kW 3G3JV-A2004
0.75 (1.1) kW 3G3JV-A2007
1.5 (1.5) kW 3G3JV-A2015
2.2 (2.2) kW 3G3JV-A2022
0.1 (0.1) kW 3G3JV-AB001
0.2 (0.25) kW 3G3JV-AB002
0.4 (0.55) kW 3G3JV-AB004
0.75 (1.1) kW 3G3JV-AB007
1.5 (1.5) kW 3G3JV-AB015
Model
Note The figures in parentheses indicate capacities for motors used outside Japan.
H International Standards (EC Directives and UL/cUL
Standards)
The 3G3JV Inverter meets the EC Directives and UL/cUL standard requirements for
worldwide use.
EC Directives
UL/cUL UL508C
1-2
Classification Applicable standard
EMC directive EN50081-2 and EN5008-2
Low-voltage directive prEN50178
Page 5
Overview Chapter 1
H Versatile Easy-to-use Functions
•Incorporates
•Easy to initialize and operate with the FREQ adjuster on the Digital Operator.
•Ease
can
•Optional
face cards.
of maintenance. The cooling fan is easily replaceable. The life of the cooling fan
be prolonged by turning on the cooling fan only when the Inverter is in operation.
the
functions and operability ensured by the conventional 3G3EV Series.
RS232 (3G3JV
-PSI232J)
and RS422/485 MODBUS (3G3JV
-PSI485J) inter
H Suppression of Harmonics
Connects to DC reactors, thus suppressing harmonics more effectively than conventional AC reactors.
Further
of the DC and AC reactors.
improvement in the suppression of harmonics is possible with the combined use
-
1-3
Page 6
Overview Chapter 1
1-2 Nomenclature
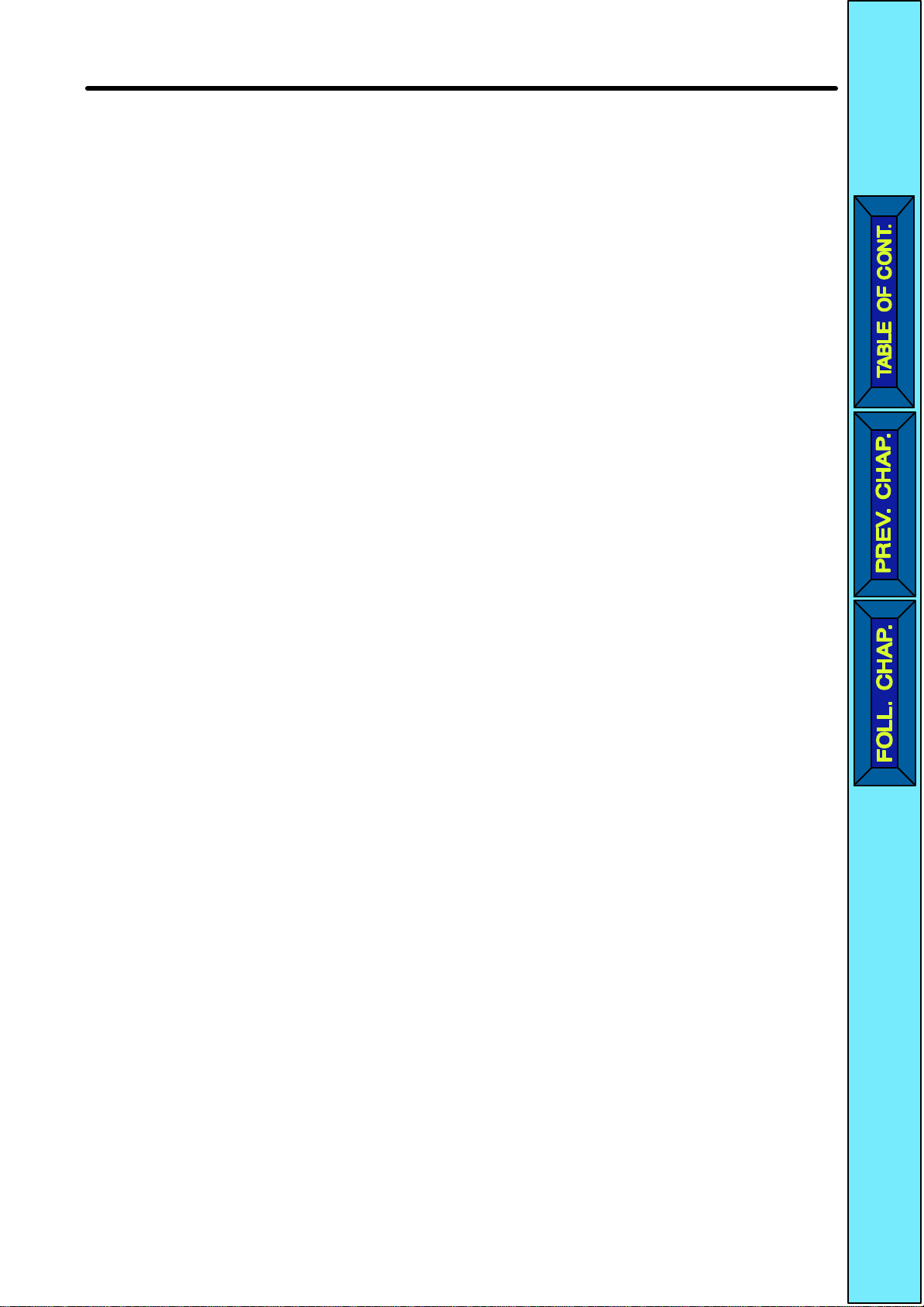
H Panel
Top protection cover
Mounting holes
Terminal
block
(Two)
Digital Operator
ALARM display
RUN indicator
Terminal
block
U-shaped
cutouts
(Two)
Note 1. The
front cover functions as a terminal cover
be removed.
Note 2. Instead
outs located diagonally.
3G3JV-A2001 (0.1 kW), 3G3JV-A2002 (0.25 kW), 3G3JV-A2004 (0.55 kW),
and 3G3JV-A2007 (1.1 kW)
3G3JV-AB001 (0.1 kW), 3G3JV-AB002 (0.25 kW), and 3G3JV-AB004
(0.55 kW)
of mounting holes, each of
Optional cover
Front cover
Front cover
mounting screw
Bottom
protection cover
. The Digital Operator Unit cannot
the following models has two U-shaped cut
-
1-4
Page 7
Overview Chapter 1
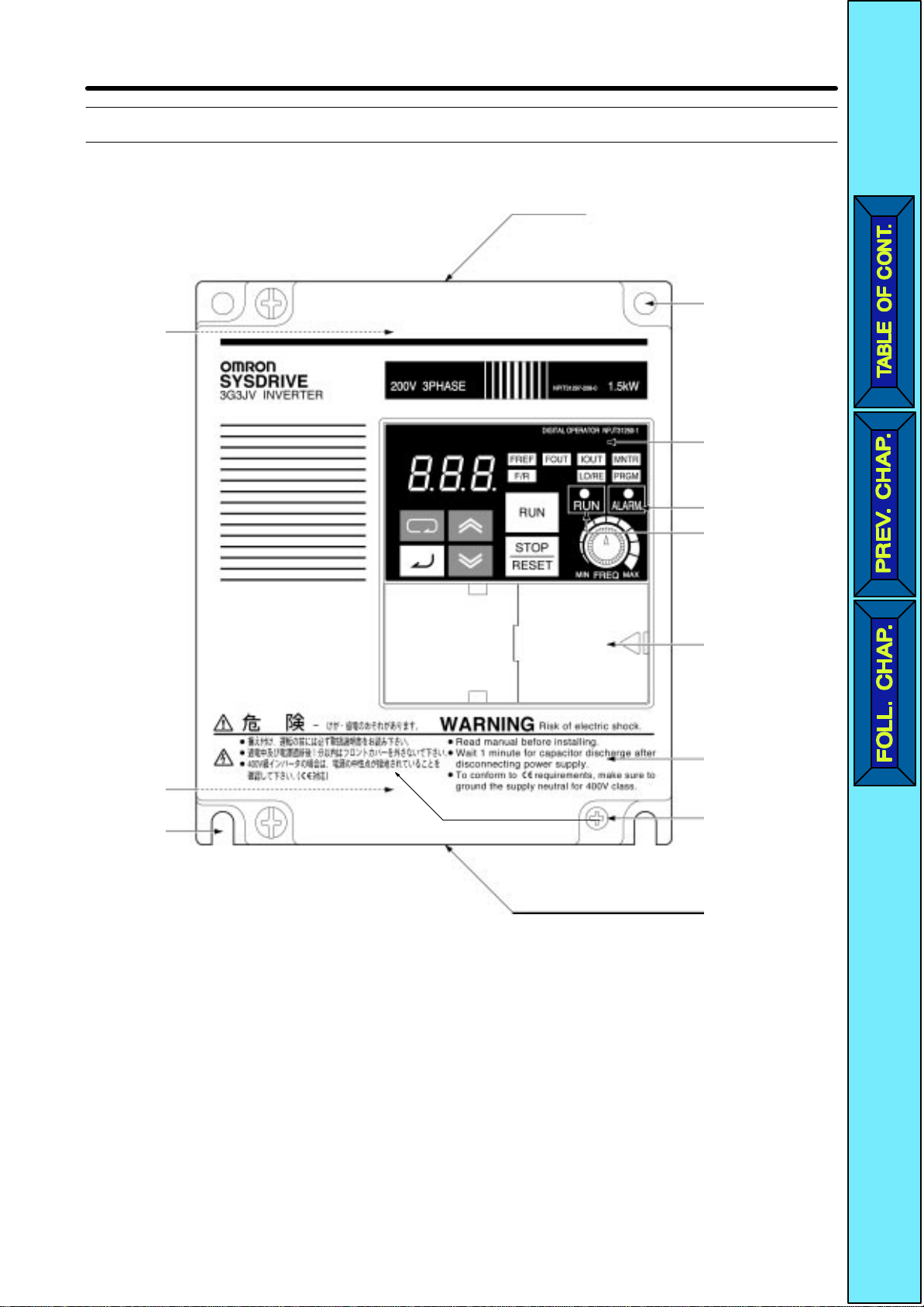
H Digital Operator
Indicators
Data display
(Setting/Monitor
item indicators)
Keys
Appearance Name Function
Data display Displays relevant data items, such as frequency
reference, output frequency, and parameter set
values.
FREQ adjuster Sets the frequency reference within a range
between 0 Hz and the maximum frequency.
FREF indicator The frequency reference can be monitored or set
while this indicator is lit.
FOUT indicator The output frequency of the Inverter can be
monitored while this indicator is lit.
IOUT indicator The output current of the Inverter can be
monitored while this indicator is lit.
MNTR indicator The values set in U01 through U10 are
monitored while this indicator is lit.
F/R indicator The direction of rotation can be selected while
this indicator is lit when operating the Inverter
with the RUN Key.
LO/RE indicator The operation of the Inverter through the Digital
Operator or according to the set parameters is
selectable while this indicator is lit.
FREQ adjuster
Note This status of this indicator can be only
monitored
Any RUN command input is ignored while
this indicator is lit.
PRGM indicator The parameters in n01 through n79 can be set or
monitored while this indicator is lit.
Note While the Inverter is in operation, the pa-
rameters can be only monitored and only
some parameters can be changed. Any
RUN command input is ignored while this
indicator is lit.
while the Inverter
is in operation.
1-5
Page 8
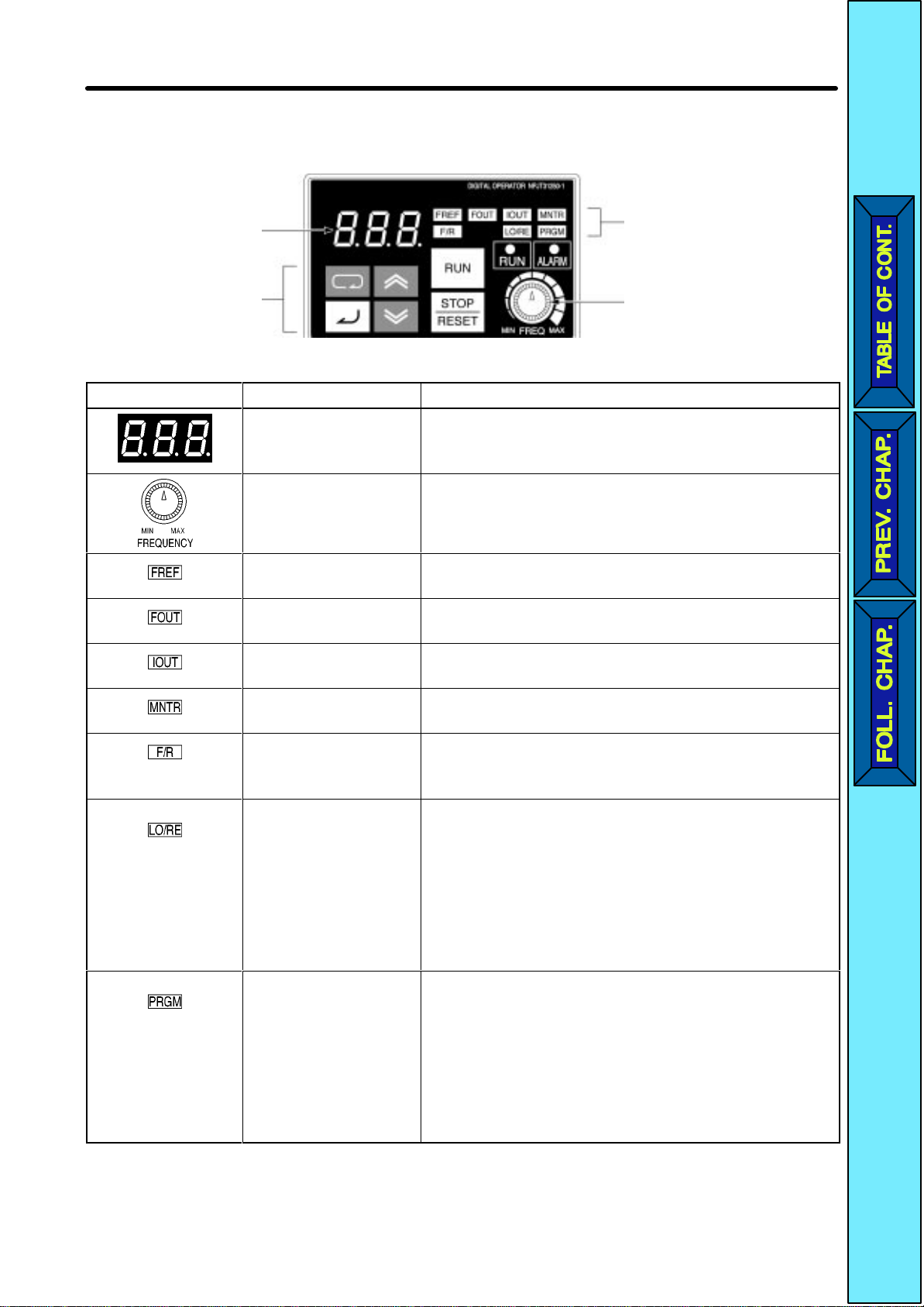
Overview Chapter 1
Appearance FunctionName
Mode Key Switches the setting and monitor item indicators
in sequence.
Parameter being set will be canceled if this key is
pressed before entering the setting.
Increment Key Increases multi-function monitor numbers,
parameter numbers, and parameter set values.
Decrement Key Decreases multi-function monitor numbers,
parameter numbers, and parameter set values.
Enter Key Enters multi-function monitor numbers,
parameter numbers, and internal data values
after they are set or changed.
RUN Key Starts the Inverter running when the 3G3FV is in
operation with the Digital Operator.
STOP/RESET Key Stops the Inverter unless parameter n06 is not
set to disable the STOP Key.
1-6
Page 9

Design
2-1 Installation
2-2 Wiring
2
Chapter 2
Page 10

ated o tage
ode 3G3J
eg t( g)
3 p ase 00 C
S g e p ase 00 C
Design Chapter 2
2-1 Installation
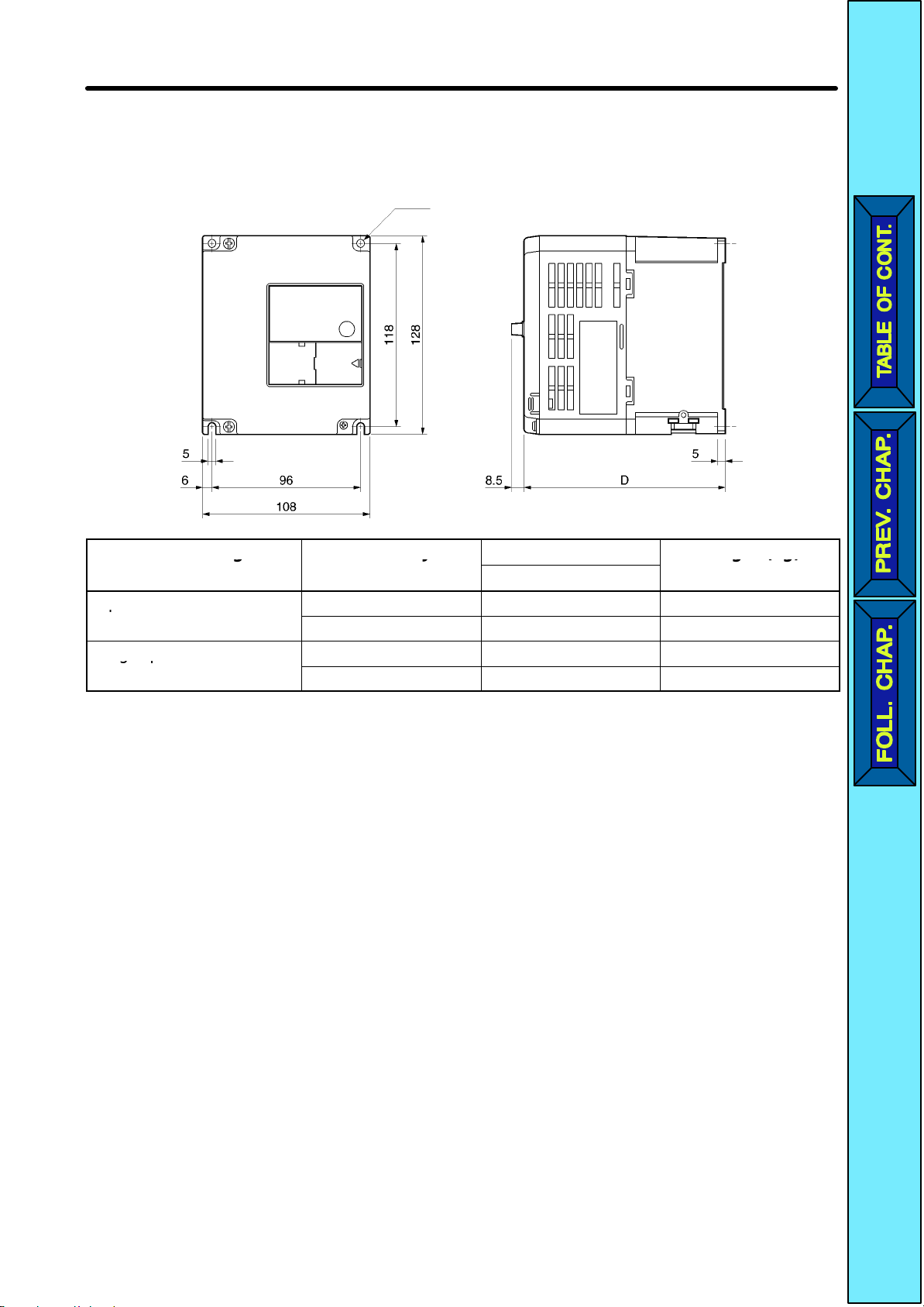
2-1-1 Dimensions
D 3G3JV-A2001 to 3G3JV-A2007 (0.1 to 0.75 kW) 3-phase 200-VAC Input
3G3JV-AB001 to 3G3JV-AB004 (0.1 to 0.4 kW) Single-phase 200-VAC
Input
Rated voltage Model 3G3JV-
3-phase 200 VAC
Single-phase 200 VAC
A2001 70 Approx. 0.5
A2002 70 Approx. 0.5
A2004 102 Approx. 0.8
A2007 122 Approx. 0.9
AB001 70 Approx. 0.5
AB002 70 Approx. 0.5
AB004 112 Approx. 0.9
Dimensions (mm)
D
Weight (kg)
2-2
Page 11
ated o tage
ode 3G3J
eg t( g)
3 p ase 00 C
S g e p ase 00 C
Design Chapter 2
D 3G3JV-A2015 to 3G3JV-A2022 (1.5 to 2.2 kW) 3-phase 200-VAC Input
3G3JV-AB007 to 3G3JV-AB015 (0.75 to 1.5 kW) Single-phase 200-VAC
Input
Two, 5-dia. holes
Rated voltage Model 3G3JV-
3-phase 200 VAC
Single-phase 200 VAC
A2015 129 Approx. 1.3
A2022 154 Approx. 1.5
AB007 129 Approx. 1.5
AB015 154 Approx. 1.5
Dimensions (mm)
D
Weight (kg)
2-3
Page 12

Design Chapter 2
2-1-2 Installation Conditions
Caution Be
!
sure to install the product in the correct direction and provide spe
cified
clearances between the Inverter and control panel
or with oth
er devices. Not doing so may result in fire or malfunction.
Caution Do not allow foreign objects to enter inside the product. Doing so
!
may result in fire or malfunction.
Caution Do
!
not apply any strong impact. Doing so
may result in damage to
the product or malfunction.
Caution Provide an appropriate stopping device on the machine side to
!
secure
safety
. (A holding brake is not a stopping
device for securing
safety.) Not doing so may result in injury.
Caution Provide an external emergency stopping device that allows an
!
instantaneous stop of operation and power interruption. Not doing
so may result in injury.
-
-
2-4
Page 13
Design Chapter 2
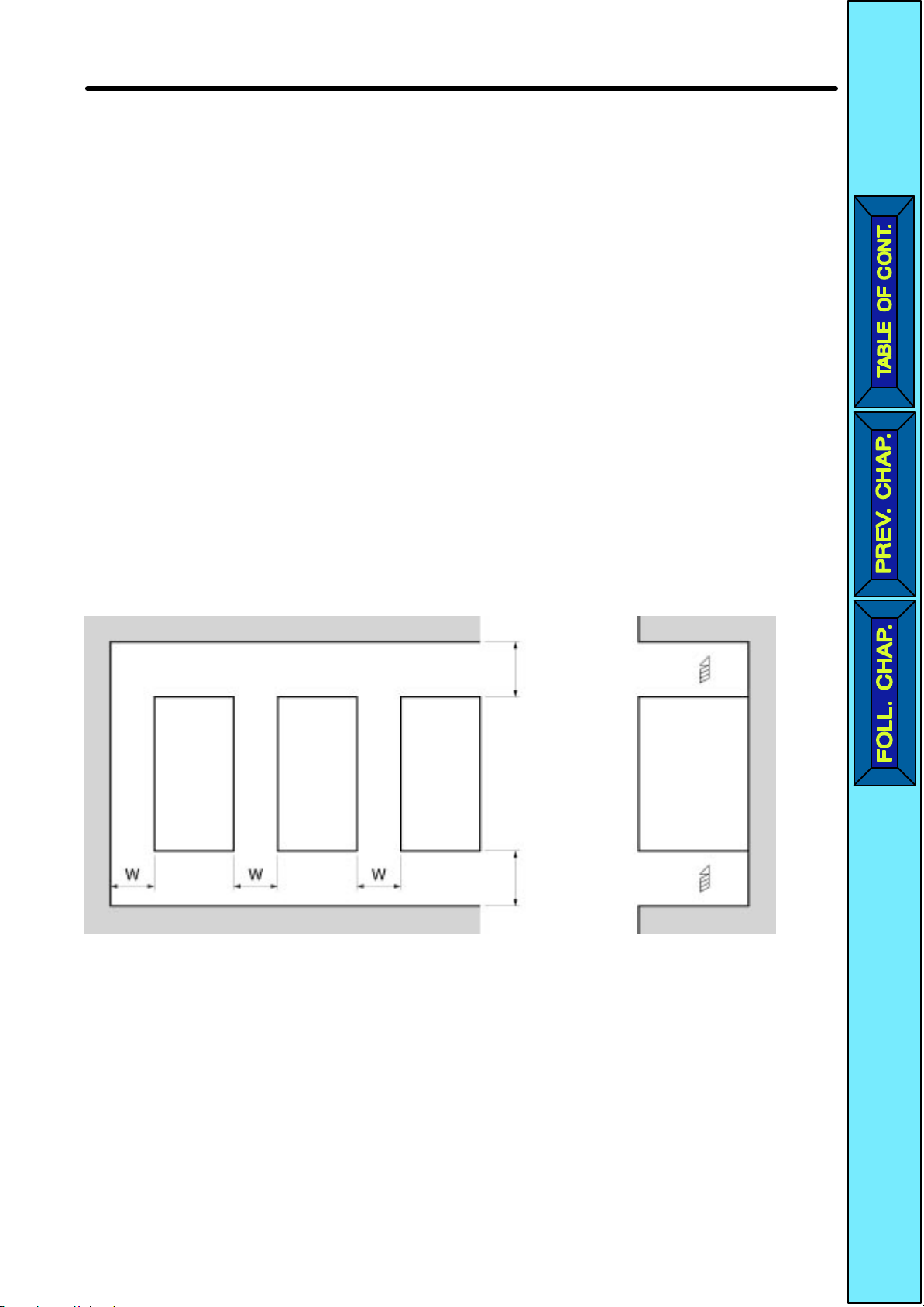
H Installation Direction and Dimensions
•Install the Inverter under the following conditions.
Ambient temperature for operation (panel-mounting): –10°C to 50°C
Humidity: 90% or less (no condensation)
•Install
in a totally enclosed panel that is completely protected from floating dust.
•When
der, oil, water, or other foreign matter does not get into the Inverter.
•Do not install the Inverter on inflammable material such as wood.
the Inverter in a clean location free from oil mist and dust. Alternatively
installing or operating the Inverter
, always take special care so that metal pow
, install it
H Direction
•Install the Inverter on a vertical surface so that the characters on the nameplate are
oriented
upward.
H Dimensions
•When
heat dissipation from the Inverter.
installing the Inverter
W = 30 mm min.
, always provide the following clearances to allow normal
100 mm min. Air
-
Inverter
SideInverter Inverter
100 mm min. Air
2-5
Page 14
Design Chapter 2
H Ambient Temperature Control
•To
enhance operation reliability
from extreme temperature changes.
the Inverter is installed in an enclosed environment such as a box, use a cooling fan
•If
or air conditioner to maintain the internal air temperature below 50°C.
life of the built-in electrolytic capacitors of the Inverter is prolonged by maintaining
The
the internal air temperature as low as possible.
surface temperature of the Inverter may rise approximately 30°C higher than the
•The
ambient
far as possible if the equipment and wires are easily influenced by heat.
temperature. Be sure to keep away equipment and wires from the Inverter as
H Protecting Inverter from Foreign Matter during Installation
•Place a cover over the Inverter during installation to shield it from metal power pro-
duced by drilling.
Upon
ventilation will be affected, causing the Inverter to overheat.
completion of installation, always remove the cover from the Inverter
, the Inverter should be installed in an environment
. Otherwise,
free
2-6
Page 15
Design Chapter 2
2-2 Wiring
WARNING Wiring must be performed only after confirming that the power
!
supply has been turned OFF. Not doing so may result in electrical
shock.
WARNING Wiring must be performed by authorized personnel. Not doing so
!
may result in electrical shock or fire.
WARNING Be sure to confirm operation only after wiring the emergency stop
!
circuit. Not doing so may result in injury.
WARNING Always
!
connect the ground terminals
to a ground of 100 Ω or less for
the 200-VAC class, or 10 Ω or less for the 400-VAC class. Not
connecting to a proper ground may result in electrical shock.
Caution Install external breakers and take other safety measures against
!
short-circuiting in external wiring. Not doing so may result in fire.
Caution Confirm
!
that the rated input voltage of the Inverter is the same as the
AC power supply voltage. An incorrect power supply may result in
fire, injury, or malfunction.
Caution Connect
!
the Braking Resistor and Braking Resistor Unit as specified
in the manual. Not doing so may result in fire.
Caution Be
!
sure to
wire correctly and securely
. Not doing so may result in in
jury or damage to the product.
-
Caution Be
!
Caution Do
!
sure to firmly tighten the screws on the terminal block. Not
so may result in fire, injury, or damage to the product.
not connect an AC power to the U, V
, or W output. Doing so may
result in damage to the product or malfunction.
doing
2-7
Page 16
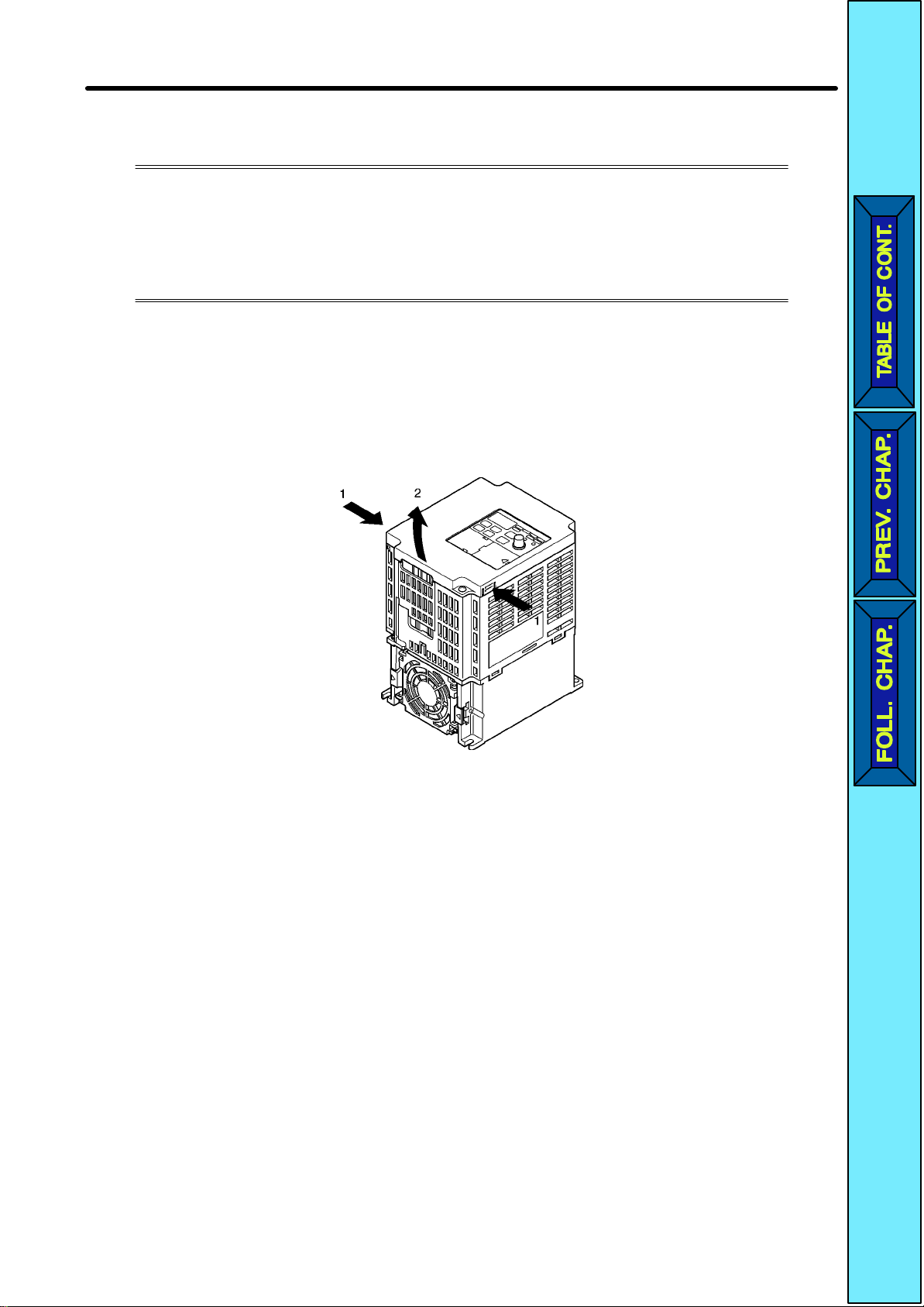
Design Chapter 2
2-2-1 Removing and Mounting the Covers
It
is necessary to remove the front cover
er, and the bottom protection cover from the Inverter to wire the terminal
block.
Follow the instructions below to remove the covers from the Inverter.
To mount the covers, take the opposite steps.
H Removing the Front Cover
•Loosen the front cover mounting screws with a screwdriver.
, optional cover
, top protection cov
-
•Press
tom
lowing illustration.
the left and right sides of the front cover in the arrow 1 directions and lift the bot
of the cover in the arrow 2 direction to
remove the front cover as shown in the fol
-
-
2-8
Page 17

Design Chapter 2
H Removing the Top and Bottom Protection Covers and
Optional Cover
D Removing the Top and Bottom Protection Covers
•After
D Removing the Optional Cover
•After
removing the front cover
directions.
removing the front cover
position A as a fulcrum.
, pull the top and bottom protection covers in the arrow
, lift the optional cover
Position A
in the arrow 2 direction based on
1
Note The
moved.
front cover functions as a terminal cover
. The Digital Operator cannot be re
2-9
-
Page 18
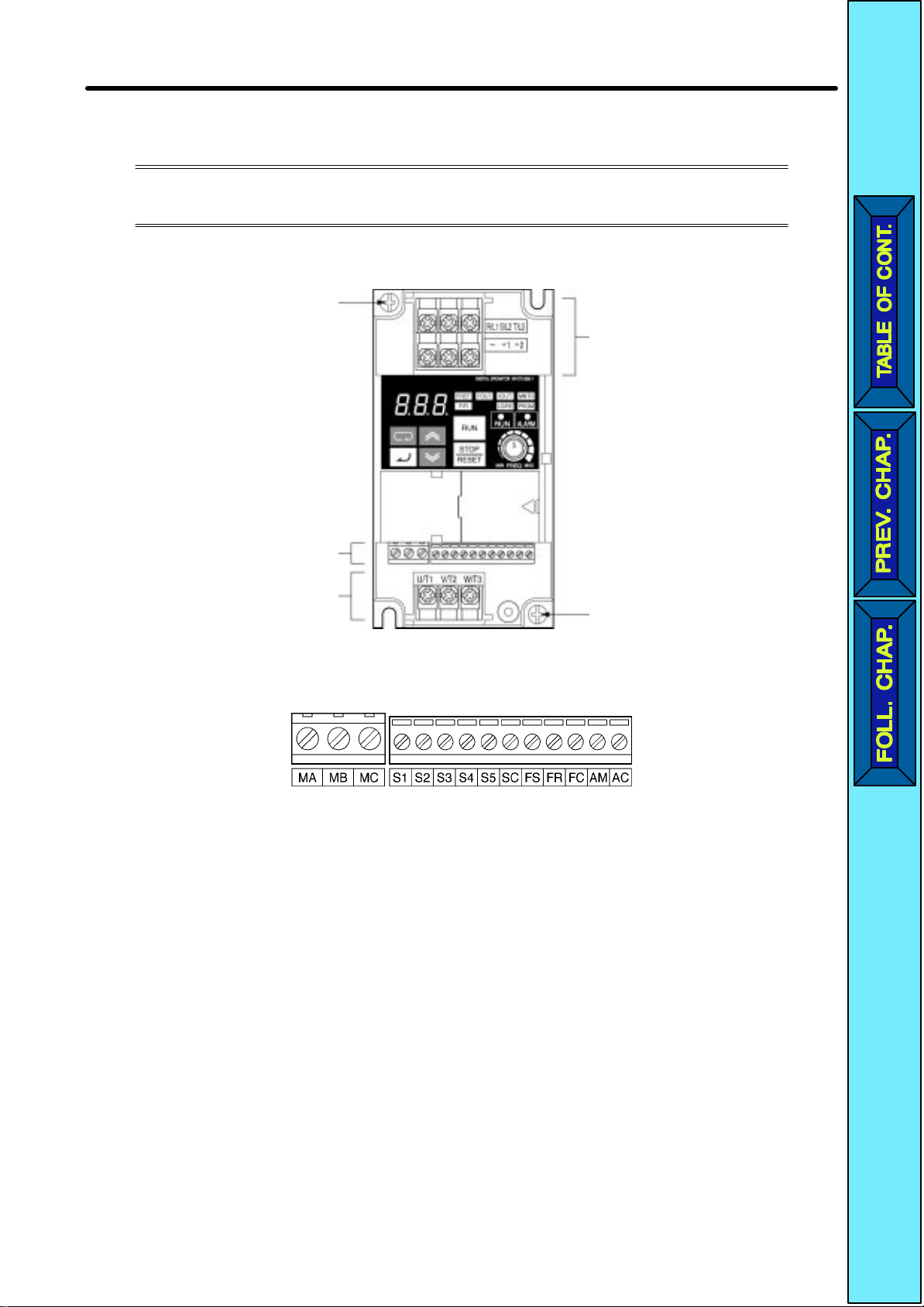
Design Chapter 2
2-2-2 Terminal Block
Before wiring the terminal block, be sure to remove the front cover, top
protection cover, and the bottom protection cover.
H Position
Control circuit terminals
Main circuit output terminals
of T
erminal Block
Ground terminal
H Arrangement of Control Circuit Terminals
Main circuit input terminals
Ground terminal
2-10
Page 19
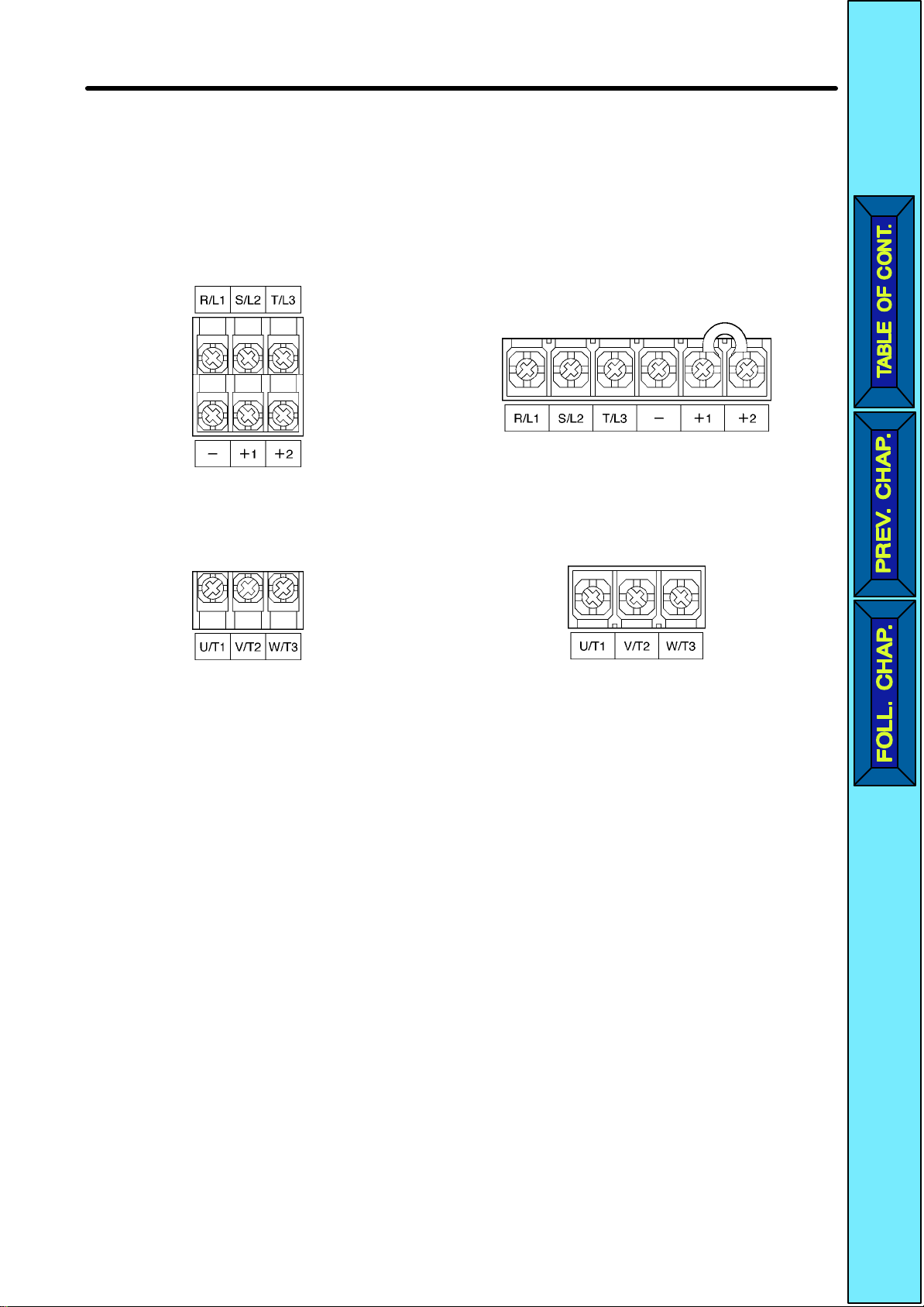
Design Chapter 2
H Arrangement of Main Circuit Terminals
D 3G3JV-A2001 to 3G3JV-A2007
3G3JV-AB001 to 3G3JV-AB004
Main Circuit Input Terminals
(Upper Side)
Main Circuit Output Terminals
(Lower Side)
D 3G3JV-A2015 to 3G3JV-A2022
3G3JV-AB007 to 3G3JV-AB015
Main Circuit Input Terminals
(Upper Side)
Main Circuit Output Terminals
(Lower Side)
2-11
Page 20
(T
iti
)
Design Chapter 2
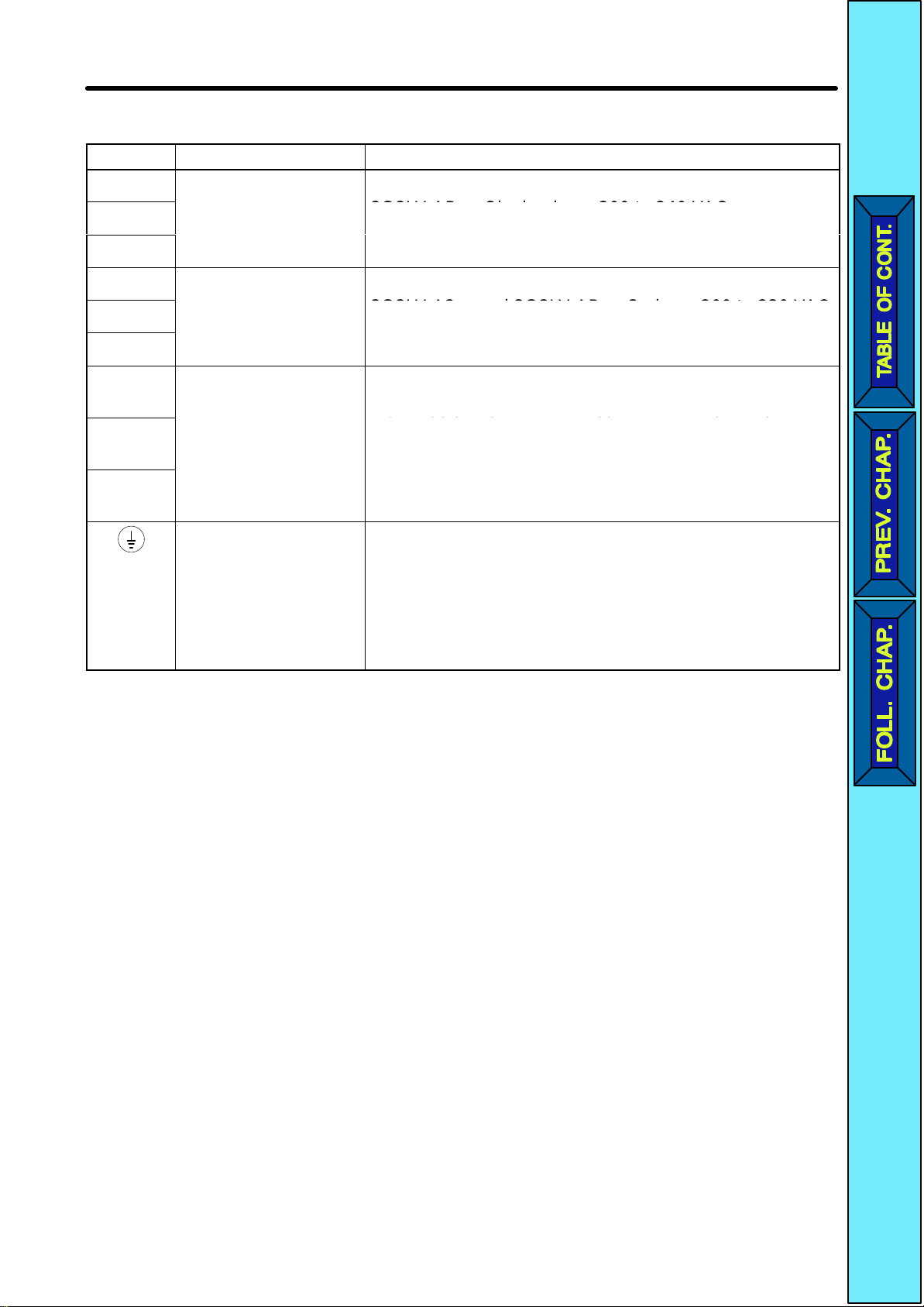
H Main Circuit Terminals
Symbol Name Description
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
+1
+2
–
Power supply input
terminals
Motor output
terminals
Connection terminals
+1 and +2:
DC reactor
connection terminals
+1 and –:
DC power supply
input terminals
Ground terminal Be sure to ground the terminal under the following
–
3G3JV-A2j: 3-phase 200 to 230 VAC
3G3JV-ABj: Single-phase 200 to 240 VAC
Note Connect single-phase input to terminals R/L1
and S/L2.
3-phase power supply output for driving motors.
3G3JV-A2j and 3G3JV-ABj: 3-phase 200 to 230 VAC
Note The maximum output voltage corresponds to the
power supply input voltage of the Inverter.
Connect the DC reactor for suppressing harmonics to
terminals +1 and +2.
When driving the Inverter with DC power, input the DC
power to terminals +1 and –.
erminal +1 is a pos
conditions.
ve terminal.
3G3JV-A2j: Ground at a resistance of 100 Ω or less.
3G3JV-ABj: Ground at a resistance of 100 Ω or less.
Note Be sure to connect the ground terminal directly
to the motor frame ground.
2-12
Page 21
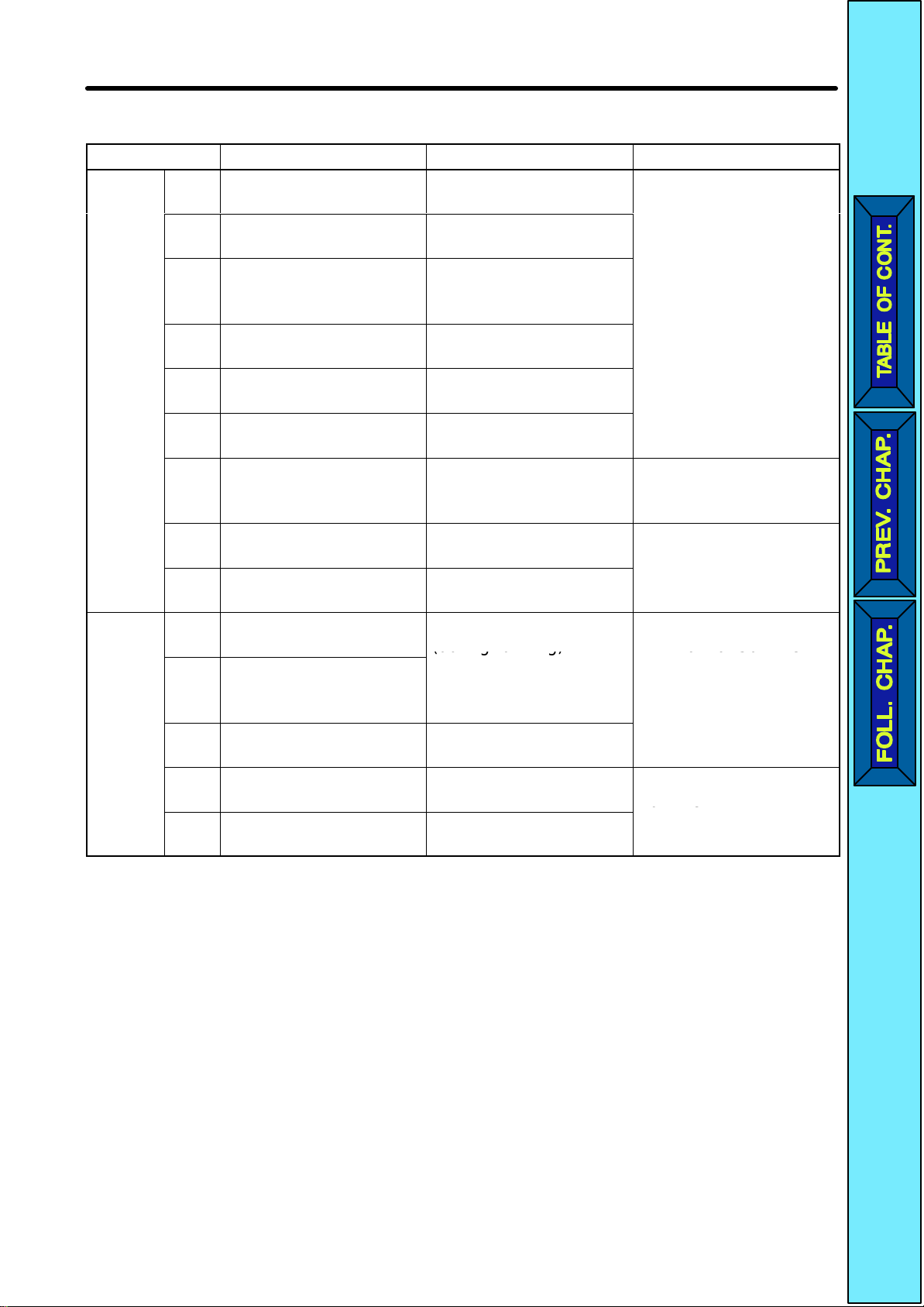
8 mA at 24 VDC
(during running)
1 A max. at 30 VDC
10 VDC
Design Chapter 2
H Control Circuit Terminals
Symbol Name Function Signal level
Input
Output
S1 Forward/Stop Forward at ON. Stops
at OFF.
S2 Multi-function input 1
(S2)
S3 Multi-function input 2
(S3)
S4 Multi-function input 3
(S4)
S5 Multi-function input 4
(S5)
SC Sequence input com-
mon
FS Frequency reference
power supply
FR Frequency reference
input
FC Frequency reference
common
MA Multi-function contact
output (Normally open)
MB Multi-function contact
output (Normally
closed)
MC Multi-function contact
output common
AM Analog monitor output Set by parameter n44
AC Analog monitor output
common
Set by parameter n36
(Reverse/Stop)
Set by parameter n37
(External fault: Normally open)
Set by parameter n38
(Fault reset)
Set by parameter n39
(Multi-step reference 1)
Common for S1
through S5
DC power supply for
frequency reference
use
Input terminal for frequency reference use
Common for frequency
reference use
Set by parameter n40
(during running)
Common for MA and
MB use
(Output frequency)
Common for AM use
Photocoupler
8 mA at 24 VDC
20 mA at 12 VDC
0 to 10 VDC (20 kΩ)
Relay output
1 A max. at 30 VDC
1 A max. at 250 VAC
2 mA max. at 0 to
10 VDC
Note Functions in parentheses are default settings.
2-13
Page 22
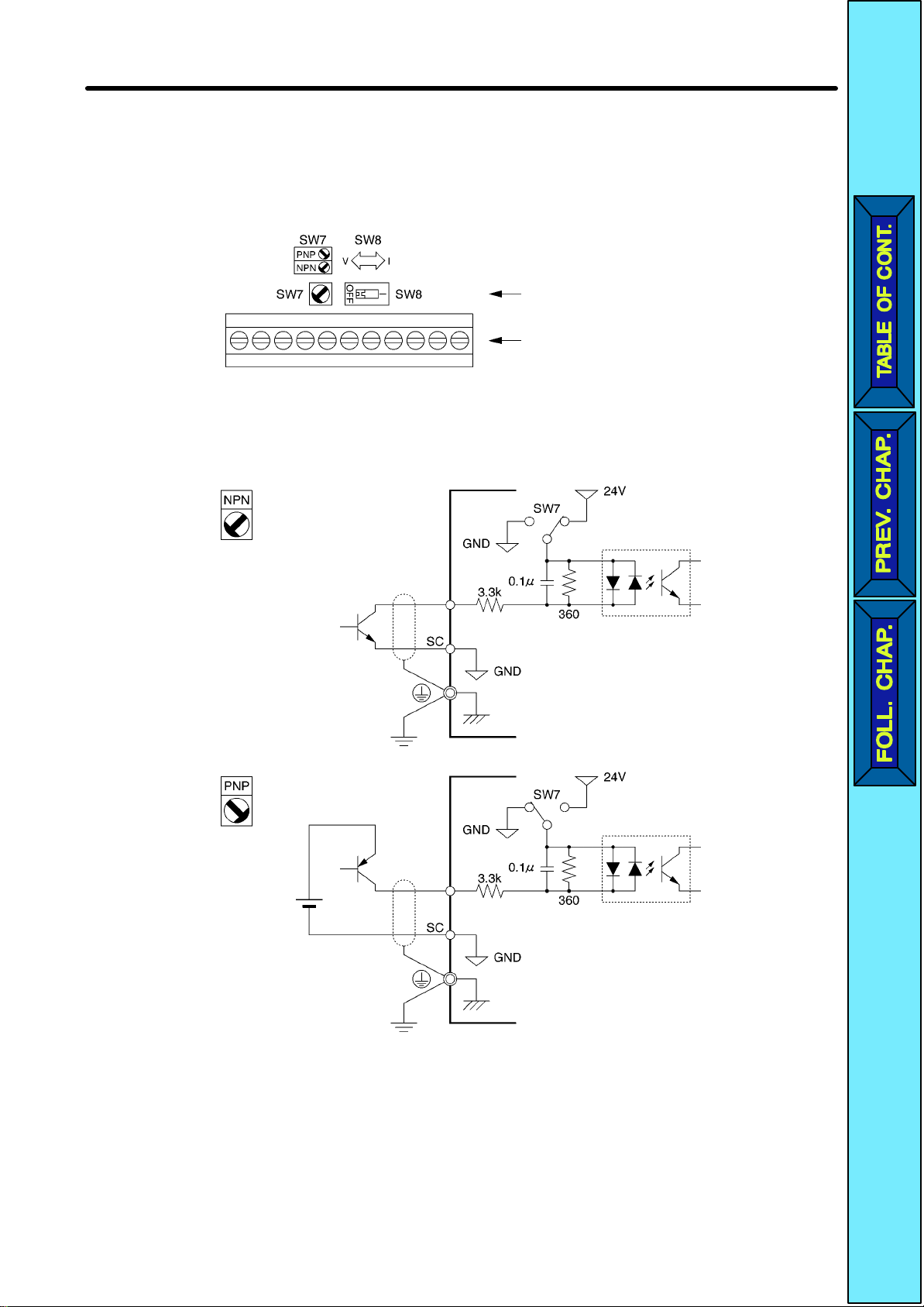
Design Chapter 2
H Selecting Input Method
•Switches
SW7 and SW8, both of which are located above the control circuit terminals,
are used for input method selection.
Remove the front cover and optional cover to use these switches.
Selector
Control circuit
terminal block
D Selecting Sequence Input Method
•By using SW7, NPN or PNP input can be selected as shown below.
S1 to 5
2-14
S1 to 5
24 VDC
Page 23
Design Chapter 2
D Selecting Frequency Reference Input Method
•By using SW8, frequency reference voltage or current input can be selected.
Parameter
input method.
settings are required together with the selection of the frequency reference
Frequency reference input
method
SW8 setting Frequency reference
selection (parameter n03)
Voltage input V (OFF) Set value 2
Current input I (ON) Set value 3 or 4
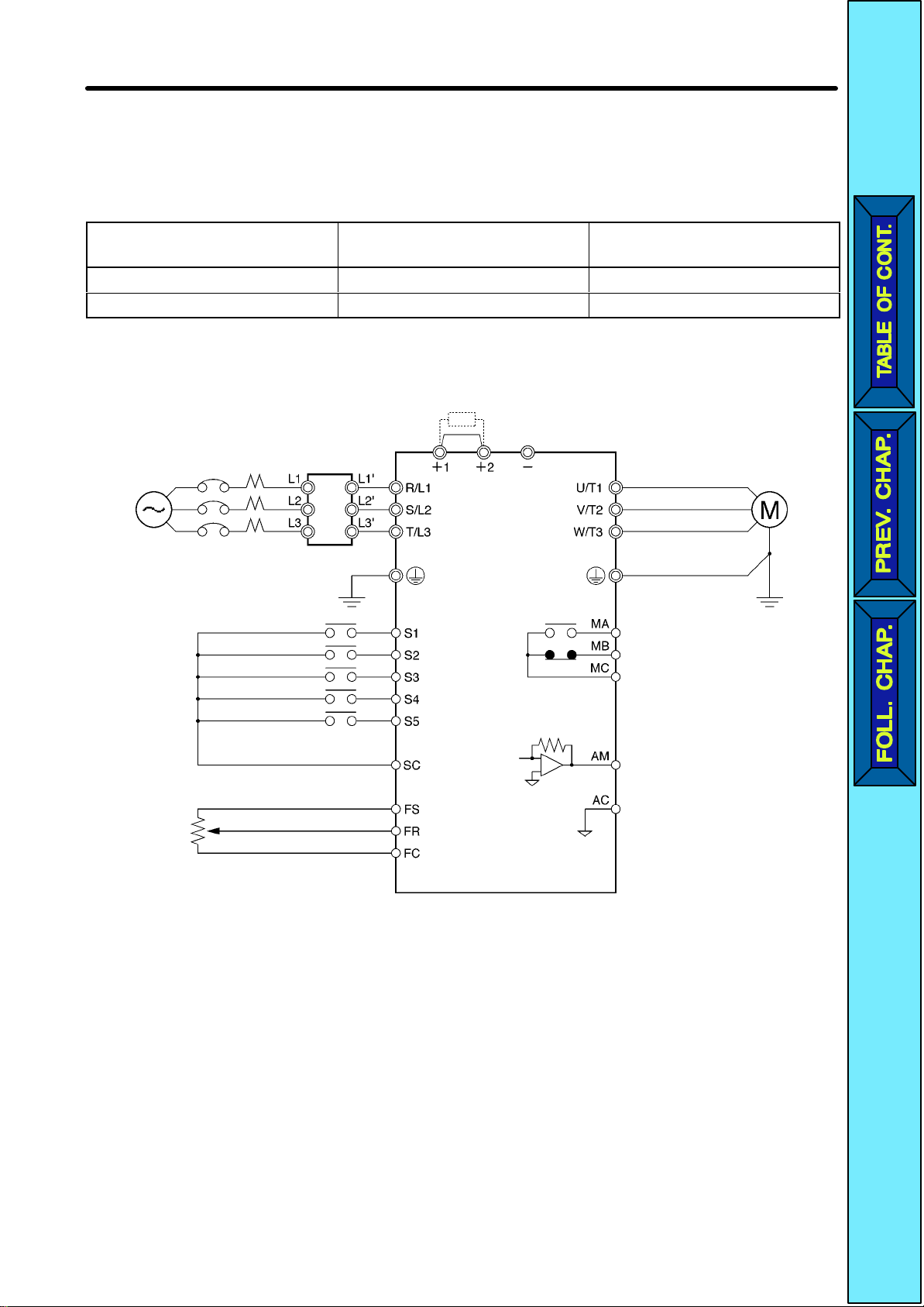
2-2-3 Standard Connections
DC reactor
(optional)
Noise Filter
3-phase 200 VAC
Single-phase 200 VAC
(see note 1)
Forward/Stop
Multi-function
Multi-function input 2 (S3)
Multi-function input 3 (S4)
Multi-function input 4 (S5)
input 1 (S2)
Multi-function contact output
NO
NC
Common
Sequence input common
Frequency reference power
supply 20 mA at +12 V
FREQ
adjuster
Frequency reference input
Frequency reference common
Note 1. Connect
Note 2. The
braking resistor cannot be connected because no braking transistor is
corporated.
single-phase 200 V
AC to
Analog monitor output
Analog monitor output common
terminals R/L1 and S/L2 of the 3G3JV
-ABj.
in
2-15
-
Page 24
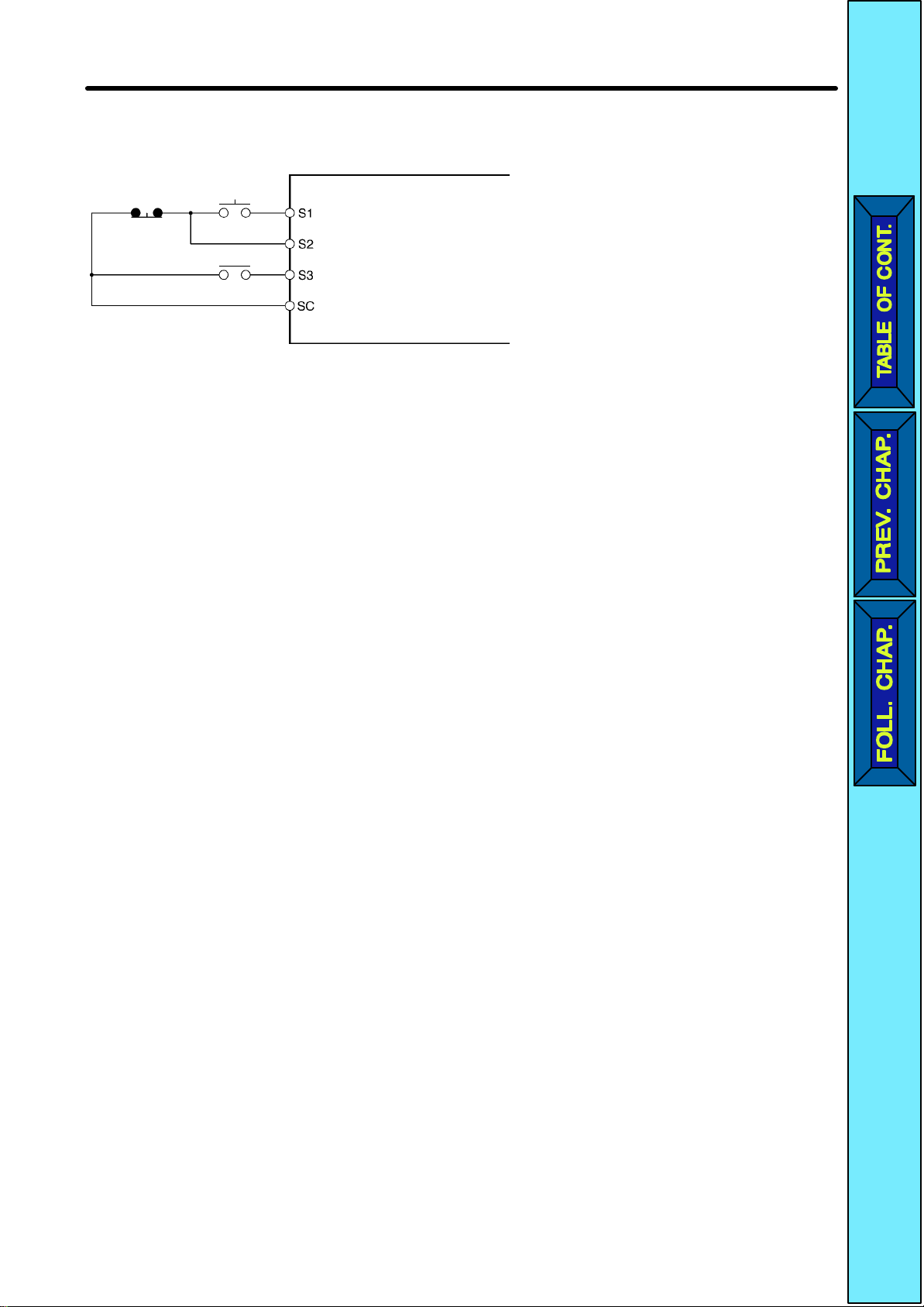
Design Chapter 2
D Example of 3-wire Sequence Connections
Stop
switch
(NC)
RUN
switch
(NO)
Direction switch
RUN input (Operates with the stop switch and RUN switch closed.)
Stop input (Stops with the stop switch opened.)
Forward/Stop reference (Forward with the direction switch opened
and reverse with the direction switch closed.)
Sequence input common
Note Set parameter n37 for 3-wire sequence input.
2-16
Page 25
Design Chapter 2
2-2-4 Wiring around the Main Circuit
H Wire
Size, T
erminal Screw, Screw T
ightening T
orque, and
Molded-case Circuit Breaker Capacities
•For the main circuit and ground, always use 600-V polyvinyl chloride
(PVC) cables.
any cable is long and may cause voltage drops, increase the wire size according to
•If
the cable length.
D 3-phase 200-VAC Model
Model
3G3JV-
A2001
A2002
Terminal symbol Termi-
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
Screw
nal
screw
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 0.75 to 2 2 5
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 0.75 to 2 2 5
tighten-
ing
torque
(NSm)
Wire
size
(mm
2
)
Recom-
mended
wire
size
2
(mm
)
Molded-
case
circuit
breaker
capac-
ity (A)
A2004
A2007
A2015
A2022
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 0.75 to 2 2 5
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 0.75 to 2 2 10
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 2 to 5.5 2 20
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 2 to 5.5 3.5 20
2-17
Page 26
Design Chapter 2
D Single-phase 200-VAC Model
Model
3G3JV-
AB001
AB002
AB004
AB007
AB015
Terminal symbol Termi-
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, –, +1,
+2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3
Terminal
nal
screw
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 0.75 to 2 2 5
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 0.75 to 2 2 5
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 0.75 to 2 2 10
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 2 to 5.5
M3.5 0.8 to 1.0 2 to 5.5
torque
(NSm)
Wire
size
(mm
2
)
Recom-
mended
wire
size
2
(mm
3.5
2
5.5
2
breaker
)
20
20
Circuit
capac-
ity (A)
2-18
Page 27
Design Chapter 2
H Wiring on the Input Side of the Main Circuit
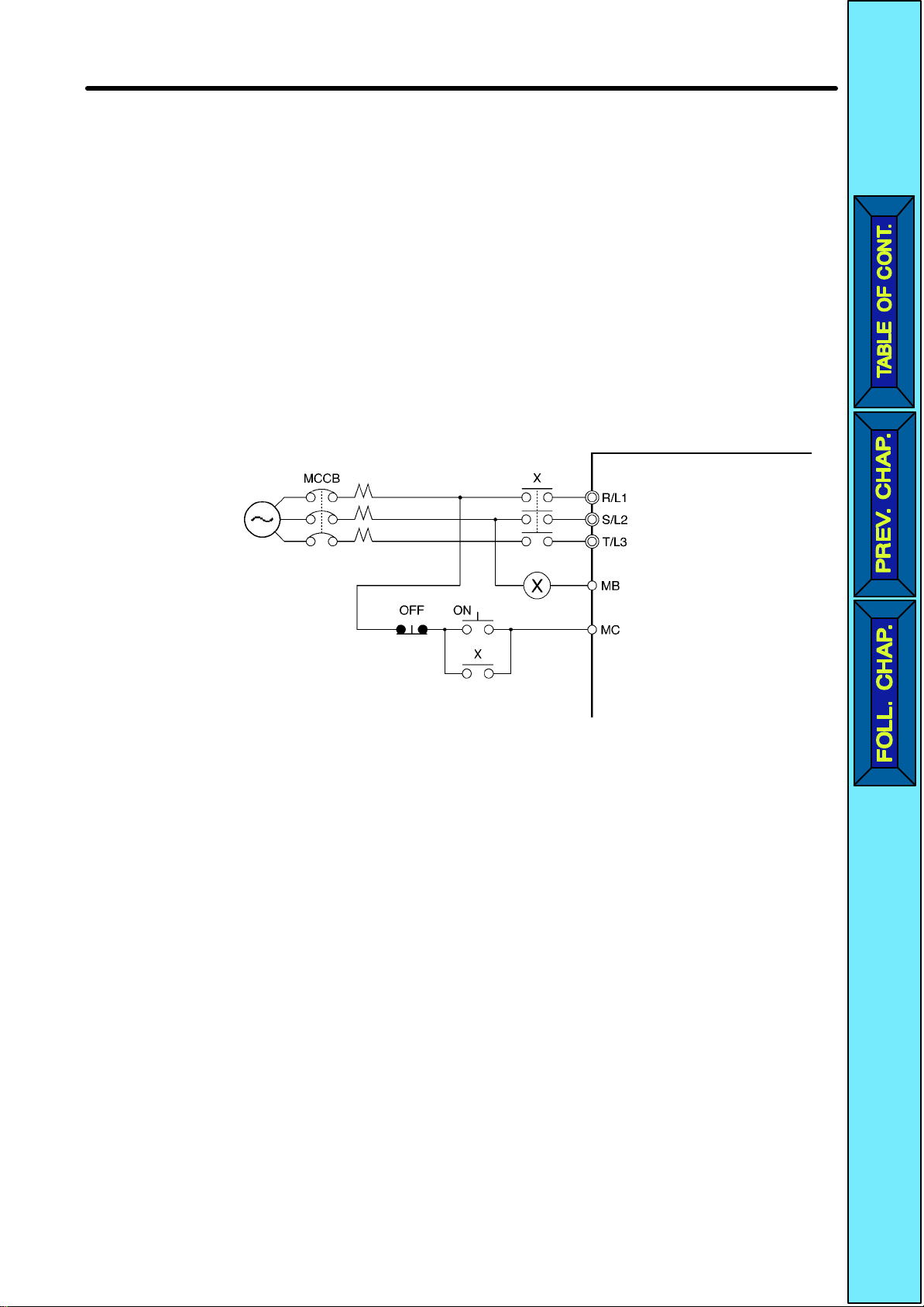
D Installing a Molded-case Circuit Breaker
Always
molded case circuit breaker (MCCB) suitable to the Inverter.
•Choose an MCCB with a capacity of 1.5 to 2 times the Inverter’s rated current.
•For the MCCB’s time characteristics, be sure to consider the Inverter’s overload
protection (one minute at 150% of the rated output current).
•If
a
the following diagram.
connect the power input terminals (R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3) and power supply via a
the MCCB is to be used in common among multiple Inverters, or other devices, set up
sequence such that the power supply will be turned of
Power
supply
3-phase/Singlephase 200 VAC
f by a fault output, as shown in
Inverter
Fault output
(NC)
D Installing a Ground Fault Interrupter
Inverter
ated.
general, a leakage current of approximately 100 mA will occur for each Inverter (when
In
the power cable is 1 m) and approximately 5 mA for each additional meter of power
cable.
Therefore,
which
mans and excludes high-frequency leakage current.
outputs use high-speed switching, so high-frequency leakage
current is gener
at the power supply input area, use a special-purpose breaker for Inverters,
detects only the
leakage current in the frequency range that is hazardous to hu
-
-
2-19
Page 28
Design Chapter 2
•For
the special-purpose breaker for Inverters, choose a ground fault interrupter with a
sensitivity amperage of at least 10 mA per Inverter.
•When
tivity
more.
using a
amperage of 200 mA or more per Inverter and with an operating time of 0.1 s or
general leakage breaker
, choose a ground fault interrupter with a sensi
D Installing a Magnetic Contactor
If
the power supply of the main circuit is to be shut of
netic contactor can be used instead of a molded-case circuit breaker.
When
load
stop.
•A
•When
a magnetic contactor is installed on the primary side of the main circuit to stop a
forcibly, however
load can be started and stopped by opening and
the primary side. Frequently opening and closing the magnetic contactor, however,
may cause the Inverter to break down.
the Inverter is operated with
performed after recovery from a power interruption.
, the regenerative braking does not work and the load coasts to a
the Digital Operator
f because of the sequence, a mag
closing the magnetic contactor on
, automatic operation cannot be
D Connecting Input Power Supply to the Terminal Block
Input
power supply can be connected
phase
and R/L3).
sequence of input power supply is irrelevant to the phase sequence (R/L1, S/L2,
to any terminal on the terminal block because the
-
-
D Installing an AC Reactor
If
the
Inverter is connected to a large-capacity power transformer (660 kW or more) or
the
phase advance capacitor is switched, an excessive peak current may flow
the input power circuit, causing the converter unit to break down.
To prevent this, install an optional AC reactor on the input side of the Inverter.
This also improves the power factor on the power supply side.
D Installing a Surge Absorber
Always
inductive
solenoid, and magnetic brakes.
2-20
use a surge absorber or diode for the inductive loads near the Inverter
loads
include magnetic contactors, electromagnetic relays, solenoid valves,
through
. These
Page 29
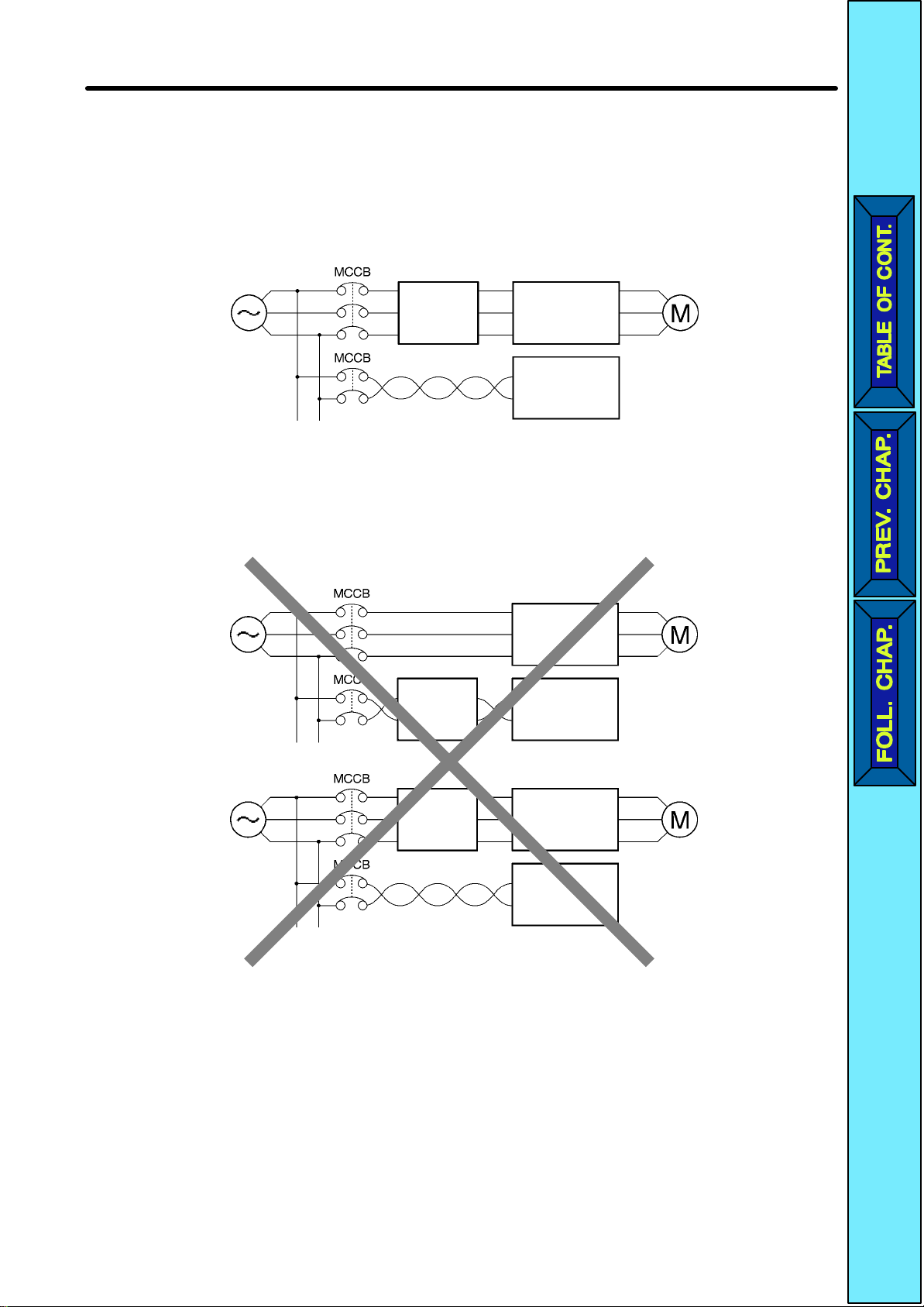
Design Chapter 2
D Installing a Noise Filter on the Power Supply Side
Install
verter.
Wiring Example 1
a Noise Filter to eliminate noise transmitted between the power line and the In
-
Power
supply
3G3IV-PHF
Noise
Filter
3G3JV
SYSDRIVE
Programmable
Controller
Other controllers
Note Use a special-purpose Noise Filter for the SYSDRIVE 3G3JV.
Wiring Example 2
Power
supply
Generalpurpose
noise
filter
3G3JV
SYSDRIVE
Programmable
Controller
Note
Power
supply
Generalpurpose
noise
filter
Do not use any general-purpose noise filter
Other controllers
3G3JV
SYSDRIVE
Programmable
Controller
Other controllers
. No general-purpose
effectively suppress noise generated from the Inverter.
noise filter can
2-21
Page 30
Design Chapter 2
H Wiring on the Output Side of the Main Circuit
D Connecting the Terminal Block to the Load
Connect output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3 to motor lead wires U, V, and W.
Check
the
forward command.
that the motor rotates forward with the forward command. Switch over any two
output terminals to each
other and reconnect if the motor rotates in reverse with the
of
D Never Connect a Power Supply to Output Terminals
Never connect a power supply to output terminals U/T1, V/T2, or W/T3.
If
voltage is applied to the output terminals, the internal circuit of the Inverter will be
aged.
dam
-
D Never Short or Ground Output Terminals
If
the output terminals are touched with bare hands or the output wires come into contact
with
the Inverter casing, an electric shock or
ardous.
Also, be careful not to short the output wires.
grounding will occur
. This is extremely haz
-
D Do not Use a Phase Advancing Capacitor or Noise Filter
Never connect a phase advance capacitor or LC/RC Noise Filter to the output circuit.
Doing so will result in damage to the Inverter or cause other parts to burn.
D Do not Use an Electromagnetic Switch of Magnetic Contactor
Do not connect an electromagnetic switch of magnetic contactor to the output circuit.
If
a load is connected to the Inverter during running, an inrush current will actuate
overcurrent protective circuit in the Inverter.
the
D Installing a Thermal Relay
The Inverter has an electronic thermal protection function to protect the motor from
overheating.
polar
motor
motor and set n33 to 2 (no thermal protection).
this case, program the sequence so that the magnetic contactor on the input side of
In
the main circuit is turned off by the contact of the thermal relay.
If, however
is used, always install a thermal relay (THR) between the Inverter and the
, more than one motor is operated with one inverter
or a multi-
2-22
Page 31

Design Chapter 2
D Installing a Noise Filter on the Output Side
Connect
tion noise.
a Noise Filter to the output side of the Inverter to reduce radio noise and
induc
-
Power
supply
Signal line
Induction Noise: Electromagnetic
3G3JV
SYSDRIVE
induction generates noise
3G3IV-PLF
Noise
Filter
Induction noise Radio noise
Controller
AM radio
on the signal line, caus
ing the controller to malfunction.
Radio Noise: Electromagnetic waves from the Inverter and cables cause the
broadcasting radio receiver to make noise.
D Countermeasures against Induction Noise
As
described previously
ing generated on the output side. Alternatively, cables can be routed through a
grounded
metal pipe to prevent induction noise. Keeping the metal
away from the signal line considerably reduces induction noise.
, a Noise Filter can be used to prevent induction noise from be
pipe at least 30 cm
-
-
Power supply
3G3JV
SYSDRIVE
Signal line
Metal pipe
30 cm min.
Controller
2-23
Page 32

Design Chapter 2
D Countermeasures against Radio Interference
Radio
duce
Inverter in a totally enclosed steel box.
The cable between the Inverter and the motor should be as short as possible.
noise is generated from the Inverter as well as the input and output lines. T
o re
radio noise, install Noise Filters on both input and output sides, and also install the
Steel box
-
Power supply
Noise
Filter
3G3JV
SYSDRIVE
Noise
Filter
Metal pipe
D Cable Length between Inverter and Motor
If
the cable between
rent
will increase, causing the Inverter output current to increase as well. This may af
peripheral devices.
prevent
To
this, adjust the carrier frequency (set in n46) as shown in the table below
details, refer to the parameter settings.
Cable length 50 m max. 100 m max. More than 100 m
Carrier frequency 15 kHz max. 10 kHz max. 5 kHz max.
the Inverter and the motor is long, the high-frequency leakage cur
-
fect
. For
2-24
Page 33

Design Chapter 2
H Ground Wiring
•Always
or less.
•Do
tools.
Always use a
•
ment and minimize the length of the ground wire.
Leakage current flows through the Inverter. Therefore, if the distance between the
ground
nal of the Inverter will become unstable.
•When using more than one Inverter, be careful not to loop the ground wire.
use the
not share the ground wire
electrode and the ground terminal
ground terminal of the 200-V Inverter with a ground resistance of 100
with other devices such as welding machines or power
ground
wire that complies with technical standards on electrical equip
is too long, the potential on the ground termi
Ω
-
-
2-25
Page 34

Design Chapter 2
H Countermeasures against Harmonics
With
the continuing development of electronics, the
ics from industrial machines has been causing problems recently.
The
Ministry of International T
in
September 1994 for the suppression of harmonics from electrical house
hold
appliances and electrical equipment in
rade and Industry provided some guidelines
Japan. Since then, the prob
lem has been drawing considerable attention.
Refer
to the following information for the definition of
monic currents with voltages) and countermeasures against the generation of harmonics from the Inverter.
D Harmonics
Definition
Harmonics consist of electric power produced from AC power and alternating at frequencies that are integral multiples of the frequency of the AC power.
generation of harmon
harmonics (i.e., har
-
-
-
-
The
following frequencies are harmonics of a 60- or 50-Hz commercial power supply
Second harmonic:
Third harmonic:
120 (100) Hz
180 (150) Hz
Second harmonic (120 Hz)
Basic frequency (60 Hz)
Third harmonic (180 Hz)
Problems Caused by Harmonics Generation
The
waveform of the commercial power supply will be distorted if the commercial power
supply
will malfunction or generate excessive heat.
contains excessive harmonics. Machines with such a commercial power supply
Basic frequency (60 Hz) Third harmonic (180 Hz)
.
2-26
Distorted current wave
form
Page 35

Design Chapter 2
D Causes of Harmonics Generation
•Usually, electric
supply into DC power.
Such
AC power
tween DC and AC.
Obtaining DC from AC Using Rectifiers and Capacitors
DC
voltage is obtained by converting AC voltage into a pulsating one-side voltage with
rectifiers
and smoothing the pulsating one-side voltage with capacitors. Such AC cur
rent, however, contains harmonics.
Inverter
The Inverter as well as normal electric machines has an input current containing harmonics
comparatively
er is higher than that of any other electric machine.
because the Inverter
machines have built-in circuitry that converts commercial AC power
, however
, contains
harmonics due to the dif
ference in current flow be
converts AC into DC. The output current of the Inverter is
high. Therefore, the ratio of harmonics in the output current of the Invert
-
-
-
A current flows into the
capacitors. The current
is different from the
voltage in waveform.
Voltage
Time
Rectified
Voltage
Time
Smoothed
Voltage
Time
Current
Time
2-27
Page 36

Design Chapter 2
D Countermeasures with Reactors against Harmonics Generation
DC/AC Reactors
The
DC reactor and
and greatly.
AC reactor suppress harmonics and currents that change suddenly
DC reactor suppresses harmonics better than the AC reactor
The
. The DC reactor used
with the AC reactor suppresses harmonics more effectively.
input power factor of the Inverter is improved by
The
suppressing the harmonics of the
input current of the Inverter.
Connection
Connect
the
power supply to the Inverter and making sure that the charge indicator of the Inverter
turns off.
Do not touch the internal circuitry of the Inverter in operation, otherwise an electric
shock or burn injury may occur.
the DC reactor to the internal DC power supply of the Inverter after shutting of
Wiring Method
[With
DC Reactor]
DC reactor
(optional)
f
Power supply
3-phase 200 VAC
or single-phase
200 VAC
[With DC and AC Reactors]
Power supply
3-phase 200 VAC
or single-phase
200 VAC
DC reactor
(optional)
AC reactor
(optional)
SYSDRIVE
3G3JV
SYSDRIVE
3G3JV
2-28
Page 37

aocs
o yet y e e s e ded cab e
Design Chapter 2
Reactor Effects
Harmonics
as shown in the following table.
are ef
fectively suppressed when the DC reactor is used with the AC reactor
Harmonics
suppression
method
No reactor 65 41 8.5 7.7 4.3 3.1 2.6 1.8
AC reactor 38 14.5 7.4 3.4 3.2 1.9 1.7 1.3
DC reactor 30 13 8.4 5 4.7 3.2 3.0 2.2
DC and AC
reactors
5th
har-
monic
28 9.1 7.2 4.1 3.2 2.4 1.6 1.4
7th
har-
monic
Harmonic generation rate (%)
11th
har-
monic
13th
har-
monic
17th
har-
monic
monic
19th
har-
23rd
har-
monic
2-2-5 Wiring Control Circuit Terminals
A control signal line must be 50 m maximum and separated from power
lines.
The
frequency reference must be input into the
twisted-pair wires.
H Wiring Sequence I/O Terminals
Inverter through shielded,
25th
har-
monic
Wire
the sequence input terminals (S1 to S5 and SC) and multi-function contact output
terminals (MA, MB, and MC) as described below.
D Wires Used
Wire type Wire size Wire to be used
Single wire 0.5 to 1.25 mm
Stranded wire 0.5 to 0.75 mm
2
2
Polyethylene-shielded cable
2-29
Page 38

Design Chapter 2
D Solderless Terminals for Control Circuit Terminals
The use of solderless terminals for the control circuit terminals is recommended because solderless terminals are easy to connect securely.
Note When using the following solderless terminal, make sure that the wire size is
0.5 mm
2
.
1.0 dia.
Model: Phoenix Contact’s A1 0.5-8 WH
2.6 dia.
(Size: mm)
D Wiring Method
1. Loosen the terminal screws with a thin-slotted screwdriver.
2. Insert the wires from underneath the terminal block
3. Tighten the terminal screws firmly to a torque of 0.5 NSm.
Note 1. Always
power cables.
Note 2. Do
not solder the wires to the control
tact well with the control circuit terminals if the wires are soldered.
Note 3. The
end of each wire connected to the control circuit terminals must be stripped
for approximately 5.5 mm.
separate the control
Thin-slotted screwdriver
signal line from the main circuit cables and other
circuit terminals. The wires may not con
Control circuit
terminal block
-
Strip the end for 5.5 mm
if no solderless terminal
is used.
Wires
2-30
Solderless
terminal or wire
without soldering
Note Applying a torque of greater
than 0.5 NSm may damage the
terminal block. If the tightening
torque is insufficient, however,
wires may be disconnected.
Page 39

o yet y e e s e ded cab e
Design Chapter 2
H Wiring Frequency Reference Input Terminals
Wire
the frequency reference input terminals FR and FC as described below for execut
frequency references with
ing
ternal power supply.
D Wires Used
Use
shielded, twisted-pair wires for wiring in order to prevent the Inverter from malfunc
tioning due to noise.
Wire type Wire size Wire to be used
Single wire 0.5 to 1.25 mm
Stranded wire 0.5 to 0.75 mm
D Solderless Terminals for Frequency Reference Input Terminals
The use of solderless terminals for the frequency reference input terminals is recommended because solderless terminals are easy to connect securely.
the D/A Unit for digital-to-analog data conversion or ex
2
2
Polyethylene-shielded cable
for measurement use
-
-
-
Note Make
sure
that the wire size is 0.5 mm2 when using the following solderless termi
nal.
1.0 dia.
Model: Phoenix Contact’s A1 0.5-8 WH
2.6 dia. (Size: mm)
D Wiring Method
•The
wiring method of the frequency reference input terminals is the
control circuit terminals.
•Always
cables.
separate the control signal line from the main
circuit cables and other power
-
same as that of the
•Connect
the shield to the ground terminal of the
the load.
•Cover
the shield with tape so that the shield will
wires or machines.
Inverter
. Do not connect the shield to
not come into contact with other signal
2-31
Page 40

Design Chapter 2
2-2-6 Conforming to EC Directive
The following description provides the wiring method of the Inverter to
meet
DC Directive requirements. If the following requirements
tisfied, the whole equipment incorporating the Inverter will need further
confirmation.
H Standard Connection
D Main Circuit Terminals
are not sa
-
Line breakers
Noise Filter
3-phase 200 VAC or
single-phase 200 VAC
D Control Circuit Terminals
Forward/Stop
Multi-function input 1 (S2)
Multi-function input 2 (S3)
Multi-function input 3 (S4)
Multi-function input 4 (S5)
Sequence
input common
Clamp core
Multi-function
NO
NC
Common
Analog-monitor output
contact output
Frequency reference power
supply at +12 V
FREQ
adjuster
Frequency reference input
Frequency reference common
Note I/O signals can be connected to a single shielded cable.
2-32
Analog monitor output common
Page 41

Design Chapter 2
D Wiring the Power Supply
Make sure that the Inverter and Noise Filter are grounded together.
•Always
connect the power input terminals (R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3) and power supply via
a dedicated Noise Filter.
•Reduce the length of the ground wire as much as possible.
•Locate
the Noise Filter as close as possible to the Inverter
. Make sure that the cable
length between the Noise Filter and the Inverter does not exceed 40 cm.
•The following Noise Filters are available (all footprint type).
3-phase 200-VAC Noise Filter
Inverter 3-phase 200-VAC Noise Filter
Model 3G3JV- Model 3G3JV- Rated current (A)
A2001/A2002/A2004/A2007 PFI2010-E 10
A2015/A2022 PFI2020-E 20
Single-phase 200-VAC Noise Filter
Inverter Single-phase 200-V Noise Filter
Model 3G3JV- Model 3G3JV- Rated current (A)
AB001/AB002/AB004 PFI1010-E 10
AB007/AB015 PFI1020-E 20
D Connecting a Motor to the Inverter
•When
•Reduce
er
and the motor does not exceed 20 cm.
ter) close to the output terminals of the Inverter.
Clamp Filter 2CAT3035-1330 TDK
connecting a motor to the Inverter
the length of
the cable as short as possible and ground the shield on the Invert
, be sure to use a cable with a braided shield.
side as well as the motor side. Make sure that the cable length between the Inverter
Furthermore, connect a clamp core (Clamp Fil
Product Model Manufacturer
D Wiring a Control Cable
•Be sure to connect a cable with a braided shield to the control circuit terminals.
•Ground the shield on the Inverter side only.
-
-
2-33
Page 42

30
30
Design Chapter 2
D Grounding the Shield
In
order to
connected to the ground plate as shown below.
ground the shield securely
, it is recommended that a cable clamp be directly
Ground plate
Shield
Cable clamp
Cable
H LVD Conformance
•Always connect the Inverter and power supply via a molded case circuit breaker
(MCCB)
from short-circuiting.
•Use one MCCB per Inverter.
•Select a suitable MCCB from the following table.
suitable to the Inverter for protecting the Inverter from damage that may result
200-V Models
Inverter MCCB (Mitsubishi Electric)
Model 3G3JV- Type Rated current (A)
A2001
A2002
A2004 5
A2007 10
A2015 20
A2022 20
AB001
AB002
AB004 10
AB007 20
AB015 20
The frequency reference power supply (FS) of the Inverter is of basic insulation
construction.
When connecting the Inverter to peripheral devices, be sure to increase
the degree of insulation.
NF30
NF30
5
5
5
5
2-34
Page 43

Preparing for
Operation and
Monitoring
3-1 Nomenclature
3-2 Outline of Operation
3
Chapter 3
Page 44

Preparing for Operation and Monitoring Chapter 3
3-1 Nomenclature
Data display
Keys
Appearance Name Function
Data display Displays relevant data items, such as frequency
reference, output frequency, and parameter set
values.
FREQ adjuster Sets the frequency reference within a range
between 0 Hz and the maximum frequency.
FREF indicator The frequency reference can be monitored or set
while this indicator is lit.
FOUT indicator The output frequency of the Inverter can be
monitored while this indicator is lit.
IOUT indicator The output current of the Inverter can be
monitored while this indicator is lit.
MNTR indicator The values set in U01 through U10 are
monitored while this indicator is lit.
F/R indicator The direction of rotation can be selected while
this indicator is lit, when operating the Inverter
with the RUN Key.
LO/RE indicator The operation of the Inverter through the Digital
Operator or according to the parameters set is
selectable while this indicator is lit.
Indicators
Setting/Monitor item indicators
FREQ adjuster
3-2
Note This status of this indicator can be only
monitored
Any RUN command input is ignored while
this indicator is lit.
PRGM indicator The parameters in n01 through n79 can be set or
monitored while this indicator is lit.
Note While
rameters
some
while the Inverter
is in operation.
the Inverter is in operation, the pa
can be only
monitored and only
parameters can be changed. The
RUN command input is ignored while
this indicator is lit.
-
Page 45

Preparing for Operation and Monitoring Chapter 3
Appearance FunctionName
Mode Key Switches the setting and monitor item indicators
in sequence.
Parameter setting being made is canceled if this
key is pressed before entering the setting.
Increment Key Increases multi-function monitor numbers,
parameter numbers, and parameter set values.
Decrement Key Decreases multi-function monitor numbers,
parameter numbers, and parameter set values.
Enter Key Enters multi-function monitor numbers,
parameter numbers, and internal data values
after they are set or changed.
RUN Key Starts the Inverter running when the 3G3FV is in
operation with the Digital Operator.
STOP/RESET
Key
Stops the Inverter unless n06 is not set to
disable the STOP Key.
3-3
Page 46

Preparing for Operation and Monitoring Chapter 3
3-2 Outline of Operation
H Selecting Indicators
Whenever
the Mode Key is pressed, an indicator is lit in sequence begin
ning with the FREF indicator. The data display indicates the item corresponding to the indicator selected.
The
FOUT or
Inverter
cator
is turned of
will be lit by turning the Inverter on again if the Inverter is turned of
IOUT indicator will be lit by turning the Inverter on again if the
f while the FOUT or IOUT indicator is lit. The FREF indi
while an indicator other than the FOUR or IOUT indicator is lit.
Power On
FREF (Frequency Reference)
Monitors and sets the frequency reference.
FOUT (Output Frequency)
Monitors the output frequency.
Note This
IOUT (Output Current)
Monitors the output current.
Note This
indicator will be lit by turning the Inverter on
if the Inverter is turned off while this indicator is lit.
indicator will be lit by turning the Inverter on again
if the Inverter is turned off while this indicator is lit.
again
-
f
3-4
MNTR (Multi-function Monitor)
Monitors the values set in U01 through U10.
F/R (Forward/Reverse Rotation)
Selects the direction of rotation.
LO/RE (Local/Remote)
Selects the operation of the Inverter through the Digital
Operator or according to the parameters.
PRGM (Parameter Setting)
Monitors or sets the values in n01 through n79.
The FREF indicator is lit again.
Page 47

Preparing for Operation and Monitoring Chapter 3
H Example of Frequency Reference Settings
Key
sequence
Note 1.
The Enter Key need not be pressed when performing the setting for
frequency
Indicator Display
example
Power On
Note If the FREF indicator has not been lit,
press
FREF indicator is lit.
Use the Increment or Decrement Key to set
the frequency reference.
The data display will flash while the
frequency reference is set. (see note 1)
Press the Enter Key so that the set value will
be entered and the data display will be lit.
(see note 1)
Explanation
the Mode Key repeatedly until the
reference will change when the set value is changed with the Incre
ment or Decrement Key while the data display is continuously lit.
Note 2. The frequency reference can be set in either of the following cases.
n03
S Parameter
for frequency reference selection is set to 1 (i.e., frequency refer
ence 1 is enabled) and the Inverter is in remote mode.
n08.
The
-
-
S Parameter
n07 for frequency selection in local mode is set to 1 (i.e., the Digital
Operator is enabled) and the Inverter is in local mode.
S Frequency references 2 through 8 are input for multi-step speed operation.
Note 3. The frequency reference can be changed, even during operation.
3-5
Page 48

Preparing for Operation and Monitoring Chapter 3
H Example of Multi-function Display
Key
sequence
Indicator Display Explanation
Power On
Press the Mode Key repeatedly until the
MNTR indicator is lit.
U01 will be displayed.
Use the Increment or Decrement Key to
select the monitor item to be displayed.
Press the Enter Key so that the data of the
selected monitor item will be displayed.
The monitor number display will appear again
by pressing the Mode Key.
3-6
Page 49

U06
put te a
U0
Output te a
U09
o og ( ost
Preparing for Operation and Monitoring Chapter 3
D Status Monitor
Item Display Display
Function
unit
U01 Frequency
Hz Monitors the frequency reference. (Same as FREF)
reference
U02 Output
Hz Monitors the output frequency. (Same as FOUT)
frequency
U03 Output current A Monitors the output current. (Same as IOUT)
U04 Output voltage V Monitors the internal output voltage reference value
of the Inverter.
U05 DC bus voltage V Monitors the DC voltage of the internal main circuit of
the Inverter.
U06 Input terminal
---
Shows the ON/OFF status of inputs.
status
: Input ON : No input
Terminal S1: Forward/Stop
Terminal S2: Multi-function input 1 (S2)
Terminal S3: Multi-function input 2 (S3)
Terminal S4: Multi-function input 3 (S4)
Terminal S5: Multi-function input 4 (S5)
U07 Output terminal ---
Not
used
Shows the ON/OFF status of outputs.
status
Not
used
U09 Error log (most
---
Displays the latest error.
recent one)
Error
U10 Software No. --- OMRON use only.
: Closed : Open
Terminal MA: Multi-function
contact output
3-7
Page 50

Preparing for Operation and Monitoring Chapter 3
H Example of Forward/Reverse Selection Settings
Key
sequence
Indicator Display
example
Explanation
Press the Mode Key repeatedly until the F/R
indicator is lit.
The present setting will be displayed.
For: Forward; rEv: Reverse
Use the Increment or Decrement Key to
change the direction of motor rotation. The
direction of motor rotation selected will be
enabled when the display changes after the
key is pressed.
Note The direction of motor rotation can be changed, even during operation.
H Example of Local/Remote Selection Settings
Key
sequence
Note 1. Local
Indicator Display
example
Press the Mode Key repeatedly until the
LO/RE indicator is lit.
The present setting will be displayed.
rE: Remote; Lo: Local
Use the Increment or Decrement Key to set
the Inverter to local or remote mode. The
selection will be enabled when the display
changes after the key is pressed.
Explanation
or remote selection is possible only when the Inverter is not in operation.
The present setting can be monitored when the Inverter is in operation.
Note 2. Local or remote settings in multi-function input terminals can be changed
through the multi-function input terminals only.
Note 3. Any RUN command input will be ignored while the LO/RE indicator is lit.
3-8
Page 51

Preparing for Operation and Monitoring Chapter 3
H Example of Parameter Settings
Cancels set data.
In approximately 1 s.
Key
sequence
In
approximately
1 s.
Indicator Display
example
Note 1. To cancel the set value, press
will be displayed.
Explanation
Power On
Press the Mode Key repeatedly until the
PRGM indicator is lit.
Use the Increment or Decrement Key to set
the parameter number.
Press the Enter Key.
The data of the selected parameter number
will be displayed.
Use the Increment or Decrement Key to set
the data. At that time the display will flash.
Press the Enter Key so that the set value will
be entered and the data display will be lit.
(see note 1)
The parameter number will be displayed.
the Mode Key instead. The parameter number
Note 2. There
Refer
the
data display will not change
are parameters that cannot be changed while
the Inverter is in operation.
to the list of parameters. When attempting to change such parameters,
by pressing the Increment or Decrement Key
3-9
.
Page 52

Preparing for Operation and Monitoring Chapter 3
3-10
Page 53

Chapter 4
Test Run
4-1 Procedure for Test Run
4-2 Operation Example
4
Page 54

Test Run Chapter
4
WARNING Turn
!
ON the input power supply only after mounting the front
cover
terminal covers, bottom cover, Operator, and optional items. Not
doing so may result in electrical shock.
WARNING Do not remove the front cover, terminal covers, bottom cover,
!
Operator, or optional items while the power is being supplied. Not
doing so may result in electrical shock.
WARNING Do
!
not operate the Operator or switches with wet hands. Doing so
may result in electrical shock.
WARNING Do not touch the inside of the Inverter. Doing so may result in
!
electrical shock.
WARNING Do
!
not come close to the machine when using the error retry function
because
the machine may
abruptly start when stopped by an alarm.
Doing so may result in injury.
,
WARNING Do not come close to the machine immediately after resetting
!
momentary power interruption to avoid an unexpected restart (if
operation
after
momentary
is set to be continued in the
power interruption is reset). Doing so may result in
processing selection function
injury.
WARNING Provide
!
on
the Operator is valid only when function settings are performed.
a separate emergency stop switch because the STOP Key
Not doing so may result in injury.
WARNING Be
!
sure
confirm that the RUN signal is turned OFF before turning ON
the power supply, resetting the alarm, or switching the
LOCAL/REMOTE
selector
. Doing
so while the RUN signal is turned
ON may result in injury.
Caution Be
!
sure to confirm permissible ranges of motors and machines be
fore operation because the Inverter speed can be easily changed
low to high. Not doing so may result in damage to the product.
from
-
Caution Provide a separate holding brake when necessary. Not doing so
!
may result in injury.
4-2
Page 55

Test Run Chapter
4
Caution Do
!
Caution Do
!
not perform a signal check during operation. Doing so may result
in injury or damage to the product.
not carelessly change settings. Doing so may result in injury or
damage to the product.
4-3
Page 56

Test Run Chapter
4-1 Procedure for Test Run
1. Installation and Mounting
4
Install
that the installation conditions are met.
2. Wiring and Connection
Connect to the power supply and peripheral devices. Refer to page 2-7. Select
peripheral devices which meet the specifications and wire correctly.
3. Power Connection
Carry
Always
Make
Ensure
Set the motor to no-load status (i.e., not connected to the mechanical system).
the Inverter according to the installation conditions. Refer to page
out the following pre-connection checks before turning on the power supply
ensure that a power supply to the correct voltage is used and that the power
input terminals (R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3) are wired correctly.
3G3JV-A2: 3-phase 200 to 230 VAC
3G3JV-AB: Single-phase 200 to 240 VAC (Wire R/L1 and S/L2)
sure that the motor output terminals (U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3) are connected to
the motor correctly.
that the control circuit terminals and the control device are wired correctly
Make sure that all control terminals are turned off.
2-2. Ensure
.
.
Having conducted the above checks, connect the power supply.
4. Check the Display Status
Check to be sure that there are no faults in the Inverter.
If the display at the time the power is connected is normal, it will read as follows:
RUN indicator: Flashes
ALARM indicator: Off
Setting/Monitor indicators: FREF, FOUT, or IOUT is lit.
Data display: Displays the corresponding data of the indicator that is lit.
When a fault has occurred, the details of the fault will be displayed. In that case,
refer to
5. Initializing Parameters
Initialize the parameters.
Set n01 to 8 for initialization in 2-wire sequence.
6. Setting Parameters
Set the parameters required for a test run.
Set
loading.
Chapter
the rated motor current in order to prevent the motor from burning due to over
7 Maintenance Operations
and take necessary remedies.
-
4-4
Page 57

Test Run Chapter
7. No-load Operation
Start the no-load motor using the Digital Operator.
Set the frequency reference using the Digital Operator and start the motor using
key sequences.
8. Actual Load Operation
Connect the mechanical system and operate using the Digital Operator.
4
When
system to the motor and operate using the Digital Operator.
9. Operation
Basic Operation:
Operation
page 5-1.
Advanced Operation:
Operation that uses PID control or other functions. Refer to page 6-1.
For operation within standard parameters, refer to
Refer
ous
torque detection, torque compensation, and slip compensation.
there are no dif
based on the basic settings required to start and stop the Inverter
to
Chapter
advanced functions, such as stall prevention, carrier frequency setting,
ficulties using the
5 Basic
Operation
no-load operation, connect the mechanical
Chapter
and
Chapter
6 Advanced Operation
. Refer to
5 Basic Operation
for the vari
over
.
-
-
4-5
Page 58

Test Run Chapter
4-2 Operation Example
1 Power Connection
Checkpoints before Connecting the Power Supply
4
•Check
nals (R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3) are connected to the motor correctly.
•Make
motor correctly.
•Ensure that the control circuit terminals and the control device are wired correctly.
Make sure that all control terminals are turned off.
•Set the motor to no-load status (i.e., not connected to the mechanical system).
that the power supply is of the correct voltage and that the motor output termi
3G3JV-A2: Three-phase 200 to 230 VAC
3G3JV-AB: Single-phase 200 to 240 VAC (Wire R/L1 and S/L2)
sure that the motor output terminals (U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3) are connected to the
Connecting the Power Supply
•After conducting the above checks, connect the power supply.
2 Check the Display Status
•If the display is normal when the power is connected, it will read as follows:
-
Normal
RUN indicator: Flashes
ALARM indicator: Off
Setting/Monitor indicators: FREF, FOUT, or IOUT is lit.
Data display: Displays the corresponding data for the indicator that is lit.
•When
Chapter 7
4-6
a fault has occurred, the details of the fault will be displayed. In that
Maintenance
Fault
RUN indicator: Flashes
ALARM indicator: Lit (fault detection) or flashes (alarm detection)
Setting/Monitor indicators: FREF, FOUT, or IOUT is lit.
Data display: The fault code, such as UV1, is displayed. The display will differ de-
pending on the type of fault.
Operations
and take necessary action.
case, refer to
Page 59

Test Run Chapter
3 Initializing Parameters
•Initialize the parameters using the following procedure.
•To initialize the parameters, set n01 to 8.
4
Key sequence Indicator Display
example
In approximately
1 s.
Power On
Press the Mode Key repeatedly until the
PRGM indicator is lit.
Press the Enter Key. The data of n01 will be
displayed.
Use the Increment or Decrement Key to set
n01 to 8. The display will flash.
Press the Enter Key so that the set value will
be entered and the data display will be lit.
The parameter number will be displayed.
Explanation
4 Setting the Motor Current Parameter
•Set
the motor current parameter in n32 in order to prevent the motor from burning
to overloading.
due
Setting the Rated Motor Current
•Check
•This
(OL1).
burning.
Setting
range
Note 1. The standard rated current of the maximum applicable motor is the default
Note 2. Motor overload detection (OL1) is disabled by setting the parameter to 0.0.
the rated current on the motor nameplate and set the motor current parameter
parameter is used
for the electronic thermal function for motor overload detection
By setting the correct parameter, the overloaded motor will be protected from
n32 Rated Motor Current Changes during
operation
0.0% to 120% (A) of rated
output current of the Inverter
Unit of
setting
0.1 A Default setting (see
rated motor current.
No
note 1)
.
4-7
Page 60

Test Run Chapter
4
Key sequence Indicator Display
example
In approximately
1 s.
5 No-load Operation
•Start
the no-load motor (i.e., not connected to the mechanical system) using the Digital
Operator.
Explanation
Displays the parameter number.
Use the Increment or Decrement Key until n32
is displayed.
Press the Enter Key. The data of n32 will be
displayed.
Use the Increment or Decrement Key to set
the rated motor current. The display will flash.
Press the Enter Key so that the set value will
be entered and the data display will be lit.
The parameter number will be displayed.
Note
Before operating the Digital Operator
, check that the FREQ adjuster is set to MIN.
Forward/Reverse Rotation with the Digital Operator
Key
sequence
Indicator Display
example
Explanation
Monitors the frequency reference.
Press the RUN Key. The RUN Indicator will be lit.
Turn the FREQ adjuster clockwise slowly.
The monitored frequency reference will be
displayed.
The motor will start rotating in the forward direction
according to the frequency reference.
Press the MODE Key to turn on the F/R indicator.
“For” will be displayed.
Use the Increment or Decrement Key to change the
direction of motor rotation. The direction of motor
rotation selected will be enabled when the display is
changed after the Key is pressed.
4-8
Page 61

Test Run Chapter
4
•After
•Check that no faults have occurred in the Inverter during operation.
changing the frequency reference or the rotation direction, check that there is no
vibration or abnormal sound from the motor.
Stopping the Motor
•On completion of operating the motor in the no-load state in the forward or reverse
direction, press the STOP/RESET Key. The motor will stop.
6 Actual Load Operation
•After
Note Before
checking the operation with the motor in
system and operate with an actual load.
operating the Digital Operator
no-load status, connect the mechanical
, check that the FREQ adjuster is set to MIN.
Connecting the System
•After
confirming that the motor has stopped completely
tem.
, connect the mechanical sys
-
sure to tighten all the screws when fixing the motor axis in
•Be
the mechanical system.
Operation Using the Digital Operator
•In
case a fault occurs during operation, make sure the Stop Key on the Digital Operator
is easily accessible.
•Use the Digital Operator in the same way as no-load operation.
•First set the frequency reference to a low speed of one tenth the normal operating
speed.
Checking the Operating Status
•Having
ing smoothly at slow speed, increase the frequency reference.
•After
vibration
function monitor U03) to ensure that the output current is not becoming excessive.
checked that the operating direction is correct and that the machine is operat
changing the frequency reference or the rotation direction, check that there is no
or abnormal sound from the motor
. Check the monitor display (IOUT or multi-
-
4-9
Page 62

Test Run Chapter
4
4-10
Page 63

5
Chapter 5
Basic Operation
5-1 Initial Settings
5-2 V/f Control
5-3 Setting the Local/Remote Mode
5-4 Selecting the Operation Command
5-5 Setting the Frequency Reference
5-6 Setting the Acceleration/Deceleration
Time
5-7 Selecting the Reverse Rotation-prohibit
5-8 Selecting the Interruption Mode
5-9 Multi-function I/O
5-10 Analog Monitor Output
Page 64

Basic Operation Chapter
This section explains the basic settings required to operate and stop the
Inverter.
The
settings of parameters described here will be suf
verter operations.
First,
make these basic settings, then skip to the explanations
functions, even when your application requires
cial
as
stall
prevention, carrier frequency setting, overtorque detection, torque
compensation, slip compensation. Refer to
.
tion
Chapter 6 Advanced Opera-
ficient for simple In
of those spe
special functions, such
-
-
5-1 Initial Settings
•The following initial settings are required.
Parameter Write-prohibit Selection/Parameter Initialization (n01): Set n01 to 1 so
that n01 through n79 can be set or displayed.
5
Rated
the parameter.
Motor Current (n32): Check the rated current on the motor nameplate and set
H Setting the Parameter Write-prohibit Selection/Parameter
Initialization (n01)
•Set n01 to 1 so that n01 through n79 can be set or displayed.
n01 Parameter Write-prohibit Selection/Parameter
Initialization
Setting
range
Note This parameter makes it possible to write-prohibit parameters, change the pa-
0, 1, 6, 8, 9 Unit of
setting
rameter set or displayed range, or initialize all parameters to default values.
1 Default setting 1
Set Values
Value Description
0 Only n01 can be displayed and set. The n02 through n79 parameters can be
displayed only.
1 The n01 through n79 parameters can be displayed and set.
6 Only the error log memory is cleared.
8 Enables the initialization of all parameters in 2-wire sequence so that the
parameters will return to default values.
9 Enables the initialization of all parameters in 3-wire sequence.
Changes during
operation
No
5-2
Page 65

Basic Operation Chapter
5
H Setting the Rated Motor Current (n32)
Set
the rated motor
loading.
Check the rated current on the motor nameplate and set the parameter.
parameter is used for the electronic thermal function for motor overload detection
This
(OL1). By setting the correct parameter, the overloaded motor will be protected from
burning.
current (n32) in order to prevent the motor from burning due to over
-
n32 Rated Motor Current Changes during
operation
Setting
range
Note 1. The standard rated current of the maximum applicable motor is the default
Note 2. Motor overload detection (OL1) is disabled by setting the parameter to 0.0.
0.0% to 120% (A) of rated
output current of Inverter
rated motor current.
Unit of
setting
0.1 A Default setting (see
No
note 1)
5-3
Page 66

Basic Operation Chapter
5
5-2 V/f Control
H Setting the V/f Patterns (n09 to n15)
•Set the V/f pattern so that the motor output torque is adjusted to the required load
torque.
3G3JV incorporates an automatic torque boost function. Therefore, a maximum of
• The
150%
system
teristic changes are required.
torque can be output at 3 Hz without changing
in trial
operation and leave the default settings as they are if no torque charac
the default settings. Check the
-
n09 Maximum Frequency (FMAX) Changes during
operation
Setting
range
n10 Maximum Voltage (VMAX) Changes during
Setting
range
n11 Maximum Voltage Frequency (FA) Changes during
Setting
range
n12 Middle Output Frequency (FB) Changes during
Setting
range
n13 Middle Output Frequency Voltage (VC) Changes during
Setting
range
50.0 to 400 (Hz) Unit of
setting
1 to 255 (V) Unit of
setting
0.2 to 400 (Hz) Unit of
setting
0.1 to 399 (Hz) Unit of
setting
1 to 255 (V) Unit of
setting
0.1 Hz
(see note)
1 V Default settings 200
0.1 Hz
(see note)
0.1 Hz
(see note)
1 V Default setting 12
Default setting 60.0
operation
operation
Default setting 60.0
operation
Default setting 1.5
operation
No
No
No
No
No
n14 Minimum Output Frequency (FMIN) Changes during
operation
Setting
range
n15 Minimum Output Frequency Voltage (VMIN) Changes during
Setting
range
5-4
0.1 to 10.0 (Hz) Unit of
setting
1 to 50 (V) Unit of
setting
0.1 Hz Default setting 1.5
operation
1 V Default setting 12
No
No
Page 67

Basic Operation Chapter
5
Note Values
will be
set in 0.1-Hz increments if the frequency is less than 100 Hz and
1-Hz increments if the frequency is 100 Hz or greater.
Output
voltage (V)
•
The vertical-axis load or the load with high viscous friction may require high torque at
Note 1. Set the parameters so that
the
satisfied.
n14 x n12 < n11 x n09
Note 2. The
nored if parameters n14 and
n12 are the same in value.
Frequency (Hz)
following
value set in n13 will be ig
condition will be
-
low speed. If the torque is insufficient at low speed, increase the voltage in the lowspeed
range by 1 V
, provided that no overload (OL1
or OL2) is detected. If an overload
is detected, decrease the set values or consider the use of an Inverter model with a
higher capacity.
required torque of fan or pump control increases in proportion to the square of the
•The
speed. By setting a quadratic V/f pattern to increase the voltage in the low-speed
range, the power consumption of the system will increase.
5-5
Page 68

Basic Operation Chapter
5-3 Setting the Local/Remote Mode
The 3G3JV operates in local or remote mode. The following description
provides information on these modes and how to select them.
H Basic Concept
Operation mode Basic concept Description
Local The Inverter in a system
operates independently in
this mode so that the
Inverter can be checked
independently.
Remote The Inverter in a system
operates according to the
control signal of the host
controller.
Operation Command
Starts with the RUN Key of the Digital
Operator and stops with the
STOP/RESET Key.
Frequency Reference
Set with the Digital Operator or the FREQ
adjuster.
Set with frequency reference selection in
local mode in n07.
Operation Command
Selectable from two types and set in n02.
Frequency Reference
Selectable from five types and set in n03.
5
H Local/Remote Selection Methods
•The
following two selection methods are
mode.
S Select the mode with the LO/RE Key of the Digital Operator.
any one of multi-function inputs 1 through 4 (n36 through n39) to 17
S Set
Inverter to local mode with control input turned ON.
Note If
the above setting is made, mode selection with multi-function input will be
sible, but not with the Digital Operator.
available to set the Inverter to local or remote
to set the
pos
-
5-6
Page 69

Basic Operation Chapter
5
5-4 Selecting the Operation Command
The following description provides information on how to input operation
commands
the Inverter.
Two types of command input
them according to the application.
H Selecting the Operation Mode (n02)
•Select the method of operation mode input to start or stop the Inverter.
•The following method is enabled in remote mode only. The command can be input
through key sequences on the Digital Operator.
to start or stop the Inverter or change the direction of rotation of
methods are available. Select either one of
n02 Operation Command Selection Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0, 1 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
No
Set Values
Value Description
0 The RUN and STOP/RESET Keys of the Digital Operator are enabled.
1 Multi-function input in 2- or 3-wire sequence through the control circuit
terminals is enabled.
H Selecting the STOP/RESET Key Function (n06)
•When
Digital
enabled in local mode regardless of the setting in n02.
Setting
range
parameter n02 is set to 1, set whether or not to use the ST
Operator to stop the Inverter in remote mode. The ST
n06 STOP Key Function Selection Changes during
operation
0, 1 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
OP/RESET Key of the
OP/RESET Key is always
No
Set Values
Value Description
0 The STOP/RESET Key of the Digital Operator is enabled.
1 The STOP/RESET Key of the Digital Operator is disabled. This setting is
available only when the Digital Operator is selected for operation command
input.
5-7
Page 70

Basic Operation Chapter
5-5 Setting the Frequency Reference
5-5-1 Selecting the Frequency Reference
The
following description provides information on how to set the frequency
reference in the Inverter. Select the method according to the operation
mode.
Remote mode:Select
Local mode: Select
H Selecting the Frequency Reference (n03) in Remote Mode
•Select the input method of frequency references in remote mode.
and set one out of
and set one out of two frequency
five frequency references in n03.
references in n07.
5
•Five
frequency references are available in remote mode. Select one of them according
to the application.
n03 Frequency Reference Selection Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0 to 4 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
No
Set Values
Value Description
0 The FREQ adjuster of the Digital Operator is enabled. (see note 1)
1 Frequency reference 1 (n21) is enabled.
2 The frequency reference control terminal (for 0- to 10-V input) is enabled.
(see note 2)
3 The frequency reference control terminal (for 4- to 20-mA current input) is
enabled. (see note 3)
4 The frequency reference control terminal (for 0- to 20-mA current input) is
enabled. (see note 3)
Note 1. The
maximum frequency (FMAX) is set when the FREQ adjuster is set to
MAX.
Note 2. The maximum frequency (FMAX) is set with 10 V input.
Note 3. The
frequency reference set in n03 works as frequency reference 1 when the Inverter
•The
is
in multi-step speed operation. The set values in n22 through n28 for frequency refer
ences 2 through 8 are enabled.
5-8
maximum frequency (FMAX) is set with 20 mA input, provided that SW8 on
the control PCB is switched from V to I.
-
Page 71

Basic Operation Chapter
H Selecting the Frequency Reference (n07) in Local Mode
•Select the input method of frequency references in local mode.
5
•Two
frequency references are available in local mode. Select one of them according to
the application.
n07 Frequency Reference Selection in Local
Mode
Setting
range
0, 1 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
Changes during
operation
No
Set Values
Value Description
0 The FREQ adjuster of the Digital Operator is enabled. (see note 1)
1 Key sequences on the Digital Operator are enabled. (see note 2)
Note 1. The
Note 2. The
maximum frequency (FMAX) is set when the FREQ adjuster is set to
frequency reference can be set with key sequences while the FREF indica
tor
is lit or with the set value in n21 for frequency reference 1. In either case, the
value is set in n21.
5-5-2 Upper and Lower Frequency Reference Limits
MAX.
-
Regardless
of the methods of operation mode and
frequency reference in
put, the upper and lower frequency reference limits can be set.
H Setting the Upper and Lower Frequency Reference Limits
(n30 and n31)
•Set
the upper and lower frequency reference limits as percentage based on the maxi
mum frequency as 100%.
n30 Upper Frequency Reference Limit Changes during
operation
Setting
range
n31 Lower Frequency Reference Limit Changes during
Setting
range
Note If
0% to 110%
(Max. frequency = 100%)
0% to 110%
(Max. frequency = 100%)
n31 is set to a value
er
will have no output when a frequency reference less than the minimum output
less than the minimum output frequency (FMIN), the Invert
Unit of
setting
Unit of
setting
1% Default setting 100
operation
1% Default setting 0
frequency input is ON.
No
No
-
-
-
5-9
Page 72

Basic Operation Chapter
5
5-5-3 Adjusting the Analog Input
Input characteristic adjustments may be necessary for analog frequency
references
bias, and filter time parameter adjustments.
H FR Terminal Adjustments for Frequency Reference Input
D Gain and Bias Settings (n41 and n42)
•Set
the input characteristics of analog frequency references in n41 (for the frequency
reference gain) and n42 (for the frequency reference bias).
•Set the frequency of maximum analog input (10 V or 20 mA) in n41 as percentage
based on the maximum frequency as 100%.
•Set
the frequency of minimum analog input (0 V
based on the maximum frequency as 100%.
to be input. At that time, use the following parameters for gain,
, 0 mA, or 4 mA) in n42 as percentage
n41 Frequency Reference Gain Changes during
operation
Setting
range
n42 Frequency Reference Bias Changes during
Setting
range
0% to 255%
(Max. frequency = 100%)
–99% to 99%
(Max. frequency = 100%)
Unit of
setting
Unit of
setting
1% Default setting 100
operation
1% Default setting 0
D Filter Time Constant Settings (n43)
•The
digital filter with a first-order lag can be set for
input.
•This
setting is ideal if the analog input signal changes rapidly or the signal is subject to
noise interference.
•The larger the set value is, the slower the response speed will be.
n43 Analog Frequency Reference Filter Time Changes during
Setting
range
0.00 to 2.00 (s) Unit of
setting
analog frequency references to be
operation
0.01 s Default setting 0.10
Yes
Yes
No
5-10
Page 73

Basic Operation Chapter
5-5-4 Setting Frequency References through Key
Sequences
The following description provides information on parameters related to
frequency
tor
H Setting Frequency References 1 through 8 and the Inching
Frequency Command (n21 through n28 and n29)
A
total of nine frequency references (frequency references 1 through 8) and an inching
frequency command can be set together in the Inverter.
D Setting Frequency References 1 through 8 (n21 through n28)
reference settings through key sequences on
the Digital Opera
-
5
n21 Frequency Reference 1 Changes during
operation
Setting
range
n22 Frequency Reference 2 Changes during
Setting
range
n23 Frequency Reference 3 Changes during
Setting
range
n24 Frequency Reference 4 Changes during
Setting
range
n25 Frequency Reference 5 Changes during
Setting
range
0.0 to max. frequency Unit of
setting
0.0 to max. frequency Unit of
setting
0.0 to max. frequency Unit of
setting
0.0 to max. frequency Unit of
setting
0.0 to max. frequency Unit of
setting
0.01 Hz
(see note 1)
0.01 Hz
(see note 1)
0.01 Hz
(see note 1)
0.01 Hz
(see note 1)
0.01 Hz
(see note 1)
Default setting 6.0
operation
Default setting 0.0
operation
Default setting 0.0
operation
Default setting 0.0
operation
Default setting 0.0
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
n26 Frequency Reference 6 Changes during
operation
Setting
range
n27 Frequency Reference 7 Changes during
Setting
range
0.0 to max. frequency Unit of
setting
0.0 to max. frequency Unit of
setting
0.01 Hz
(see note 1)
0.01 Hz
(see note 1)
Default setting 0.0
operation
Default setting 0.0
Yes
Yes
5-11
Page 74

Basic Operation Chapter
5
n28 Frequency Reference 8 Changes during
operation
Setting
range
Note 1. Values
0.0 to max. frequency Unit of
setting
0.01 Hz
(see note 1)
will be set in 0.1-Hz increments if the frequency is
Default setting 0.0
less than 100 Hz and
Yes
1-Hz increments if the frequency is 100 Hz or over.
Note 2. Frequency reference 1 is enabled with n03 for frequency reference selection
set to 1.
Note 3. Frequency
erences 1, 2, and 3 in
lowing
references 2 through 8 are enabled by setting multi-step speed ref
n36
through n39 for multi-function input. Refer to the fol
table for the relationship between
multi-step speed references 1 through
3 and frequency references 1 through 8.
Frequency reference Multi-step speed
reference 1
(Set value: 6)
Frequency reference 1 OFF OFF OFF
Frequency reference 2 ON OFF OFF
Frequency reference 3 OFF ON OFF
Frequency reference 4 ON ON OFF
Frequency reference 5 OFF OFF ON
Frequency reference 6 ON OFF ON
Frequency reference 7 OFF ON ON
Frequency reference 8 ON ON ON
Multi-step speed
reference 2
(Set value: 7)
Multi-step speed
reference 3
(Set value: 8)
-
-
No
multi-step speed reference 3 settings will be required if only frequency references 1
through
4 are used, for example. Any multi-step speed reference not set is regarded as
turned-OFF input.
D Setting the Inching Frequency Command (n29)
•The
inching frequency command must be set as multi-function input in order to use
inching frequency command.
n29 Inching Frequency Command Changes during
operation
Setting
range
Note 1. The
0.0 to max. frequency Unit of
setting
0.01 Hz
(see note 1)
Default setting 6.0
value will be set in 0.1-Hz increments if the frequency is less than 100 Hz
and 1-Hz increments if the frequency is 100 Hz or over.
5-12
Yes
the
Page 75

Basic Operation Chapter
5
Note 2. In order to use the inching frequency command, one of the n36 through n39
parameters
for multi-function input
must be set to 10 as an inching frequency
command. Parameter n29 is selectable by turning on the multi-function input
set with the inching frequency command. The inching frequency command
takes
precedence over the
multi-step speed reference (i.e., when the inching
frequency command is ON, all multi-step speed reference input will be ignored).
H Setting the Frequency Reference with the FREF Indicator Lit
•The
frequency reference can be set
lit in the following cases.
while the FREF indicator of the Digital Operator is
S Parameter
n03 for frequency reference selection is set to 1, which enables frequen
cy reference 1, and the Inverter is in remote mode.
S Parameter
n07 for frequency selection in local mode is set to 1, which enables key
sequences on the Digital Operator, and the Inverter is in local mode.
S Frequency references 2 through 8 are set with multi-step speed reference input.
•The frequency reference can be changed, even during operation.
•When the frequency reference is changed while the FREF indicator is lit, the corre-
sponding
has
been selected with
parameter is changed simultaneously
multi-function input (a multi-step speed reference), the set val
. For example, if
frequency reference 2
ue in n22 (for frequency reference 2) will be changed simultaneously when the frequency reference is changed while the FREF indicator is lit.
•Take
the following default steps, for example, to change the frequency reference with
the FREF indicator lit.
-
-
Key
sequence
Indicator Display
example
Explanation
Power On
Note If
Use the Increment or Decrement Key to set the
frequency reference.
The data display will flash while the frequency
reference is set.
Press the Enter Key so that the set value will be
entered and the data display will be lit.
the FREF indicator has not been lit, press the
Mode Key repeatedly until the FREF indicator
is lit.
5-13
Page 76

Basic Operation Chapter
D Setting the Key Sequential Frequency (n08)
•The
Enter Key need not be pressed when changing the setting in n08. In that case, the
frequency
Decrement Key while the data display is continuously lit.
reference will change when the set value is changed with the Increment or
5
n08 Key Sequential Frequency Setting Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0, 1 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
No
Set Values
Value Description
0 Enter Key enabled (The set value is entered with the Enter Key pressed.)
1 Enter Key disabled (The set value set is entered immediately.)
5-14
Page 77

Basic Operation Chapter
5-6 Setting the Acceleration/Deceleration Time
The following description provides information on parameters related to
acceleration and deceleration time settings.
Trapezoidal
ing the S-shape characteristic function for acceleration and deceleration
can reduce shock to the machinery when stopping or starting.
H Setting the Acceleration/Deceleration Time (n16 through n19)
•Two acceleration times and two deceleration times can be set.
and S-shape acceleration and deceleration are available. Us
-
5
acceleration time is
•The
the time required to go from 0% to 100% of the maximum fre
quency and the deceleration time is the time required to go from 100% to 0% of the
maximum
frequency
. The actual acceleration or deceleration time is obtained from the
following formula.
Acceleration/Deceleration time = (Acceleration/Deceleration time set value)
(Frequency reference value) ÷ (Max. frequency)
×
Acceleration
deceleration
time 2 and deceleration time 2 are enabled by setting 1
1 for acceleration/
time selection in any of the n36 through n39 parameters for multi-function
input.
Deceleration time 2 is also enabled by emergency-stop settings 19, 20, 21, and 22 in
of the n36, n37, n38, and n39 parameters for multi-function input with n04 for inter
any
ruption mode selection set to 0 (i.e., deceleration stop).
n16 Acceleration time 1 Changes during
operation
Setting
range
n17 Deceleration Time 1 Changes during
Setting
range
0.0 to 999 (s) Unit of
setting
0.0 to 999 (s) Unit of
setting
0.1 s
(see note)
0.1 s
(see note)
Default setting 10.0
operation
Default setting 10.0
Yes
Yes
-
-
n18 Acceleration Time 2 Changes during
operation
Setting
range
n19 Deceleration Time 2 Changes during
Unit of
setting
Note Values
0.0 to 999 (s) Unit of
setting
0.0 to 999 (s) Unit of
setting
will be
set in 0.1-Hz increments if the frequency is less than 100 Hz and
0.1 s
(see note)
0.1 s
(see note)
Default setting 10.0
operation
Default setting 10.0
1-Hz increments if the frequency is 100 Hz or over.
Yes
Yes
5-15
Page 78

Basic Operation Chapter
5
H S-shape Acceleration/Deceleration Characteristic (n20)
•Trapezoidal and S-shape acceleration and deceleration are available. Using the Sshape characteristic function for acceleration and deceleration can reduce shock to
the machinery when stopping or starting.
•Any
one of three S-shape acceleration/deceleration times
lectable.
(0.2, 0.5, and 1.0 s) is se
-
n20 S-shape Acceleration/Deceleration
Characteristic
Setting
range
0 to 3 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
Changes during
operation
Set Values
Value Description
0 No S-shape acceleration/deceleration characteristic (Trapezoidal
acceleration/deceleration)
1 S-shape acceleration/deceleration characteristic time is 0.2 s
2 S-shape acceleration/deceleration characteristic time is 0.5 s
3 S-shape acceleration/deceleration characteristic time is 1.0 s
Note When
eration and deceleration times will be lengthened according
beginning and end of acceleration/deceleration.
the S-shape acceleration/deceleration characteristic time is set, the accel
to the S-shape at the
No
-
5-16
Page 79

Basic Operation Chapter
5-7 Selecting the Reverse Rotation-prohibit
This
parameter is used to specify whether to enable or disable the
rotation
Digital
The
systems that prohibit the reverse rotation of the Inverter.
command sent to the Inverter from
Operator
parameter should be set to “not accept” when the Inverter is applied to
.
the control circuit terminals or
H Selecting the Reverse Rotation-prohibit (n05)
reverse
5
n05 Reverse Rotation-prohibit Selection Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0, 1 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
Set Values
Value Description
0 Accept
1 Not accept
No
5-17
Page 80

Basic Operation Chapter
5-8 Selecting the Interruption Mode
This parameter is used to specify the interruption mode when the STOP
command is input.
The
Inverter either decelerates or coasts
ruption mode selection.
H Selecting the Interruption Mode (n04)
to a stop according to the inter
-
5
n04 Interruption Mode Selection Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0, 1 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
Set Values
Value Description
0 Frequency deceleration stop (see note)
1 Free running
Note The
Inverter will decelerate to stop according to the setting in n17 for deceleration
time
1 if any of the n36 through
11
for acceleration/deceleration time selection. If any one of the n36 through n39
multi-function
the
Inverter will decelerate to stop according to the selected setting of decelera
tion time when the STOP command is input.
input parameters is
n39 parameters for multi-function input is not set to
set to acceleration/deceleration time selection,
No
-
5-18
Page 81

Basic Operation Chapter
5-9 Multi-function I/O
5-9-1 Multi-function Input
The 3G3JV incorporates four multi-function input terminals (S2 through
Inputs into these terminals have a variety of functions according to the
S5).
application.
H Multi-function Input (n36 through n39)
5
n36 Multi-function Input 1 (S2) Changes during
operation
Setting
range
n37 Multi-function Input 2 (S3) Changes during
Setting
range
n38 Multi-function Input 3 (S4) Changes during
Setting
range
n39 Multi-function Input 4 (S5) Changes during
Setting
range
2 to 8, 10 to 22
(see note)
0, 2 to 8, 10 to 22
(see note)
2 to 8, 10 to 22
(see note)
2 to 8, 10 to 22, 34
(see note)
Unit of
setting
Unit of
setting
Unit of
setting
Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 2
operation
1 Default setting 5
operation
1 Default setting 3
operation
1 Default setting 6
Note Do not set values outside the above setting ranges.
No
No
No
No
5-19
Page 82

references
Basic Operation Chapter
Set Values
Value Function Description
5
0 Forward/Reverse
rotation command
2 Reverse/Stop Reverse rotation command (2-wire sequence)
3 External fault (NO) ON: External fault (FPj detection: j is a terminal
4 External fault (NC) OFF: External fault (EFj detection: j is a terminal
5 Fault reset ON: Fault reset (disabled while RUN command is input)
6 Multi-step speed
reference 1
7 Multi-step speed
reference 2
8 Multi-step speed
reference 3
3-wire sequence (to be set in n37 only)
By setting n37 to 0, the set value in n36 is ignored and
the following setting are forcibly made.
S1: RUN input (RUN when ON)
S2: STOP input (STOP when OFF)
S3: Forward/Reverse rotation command
(OFF: Forward; ON: Reverse)
number)
number)
Signals to select frequency references 2 through 8.
Note Refer to
through Key Sequences
tween
references.
Note Any
as turned-OFF input.
5-5-4 Setting the Frequency References
for the relationship be-
multi-step speed references and
.
multi-step speed reference not set is regarded
frequency
10 Inching frequency
command
11 Acceleration/Decel-
eration time selection
12 External base block
command (NO)
13 External base block
command (NC)
14 Search command
(Searching starts
from maximum
frequency)
15 Search command
(Searching starts
from preset
frequency)
16 Acceleration/Decel-
eration-prohibit command
ON: Inching frequency command (taking precedence
over the multi-step speed reference)
ON: Acceleration time 2 and deceleration time 2 are
selected.
ON: Output shut off (while motor coasting to a stop and
“bb” flashing)
OFF: Output shut off (with motor free running and “bb”
flashing)
ON: Speed search (Searching starts from n09)
ON: Speed search
ON: Acceleration/Deceleration is on hold (running at
parameter frequency)
5-20
Page 83

input turned ON.
Note NO: Emergency stop with the contact closed
Basic Operation Chapter
Value DescriptionFunction
17 Local or remote
selection
19 Emergency stop fault
(NO)
20 Emergency stop
alarm (NO)
21 Emergency stop fault
(NC)
22 Emergency stop
alarm (NC)
ON: Local mode (operated with the Digital Operator)
Note After
this setting is made, mode selection with
the
Digital Operator is not possible.
The Inverter stops according to the setting in n04 for
interruption mode selection with the emergency stop
input turned ON.
n04 set to 0: Decelerates to stop at deceleration time
2 set in n19. n04 set to 1: Coasts to a stop.
Note NO: Emer
enc
sto
with the contact closed.
.
NC: Emergency stop with the contact opened.
Note Fault:
Fault output is ON and reset with RESET in
put. Alarm output is ON (no reset required).
Note “STP” is displayed (lit with fault input ON and
flashes with alarm input ON)
5
-
34 Up or down
command
Up or down command (set in n39 only)
By setting n39 to 34, the set value in n38 is ignored and
the following settings are forcibly made.
S4: Up command S5: Down command
Note It
Note For
is impossible to set the up or down command and
multi-step speed references 1
up and down
fer to
6-7-7 UP/DOWN Command Frequency
Memory (n62)
command functions in detail, re
.
through 3 together
H Operation in 2-wire Sequence (Set Value: 2)
•The
Inverter operates in 2-wire sequence by setting a multi-function input parameter to
2 (reverse/stop).
•The following diagram shows a wiring example of the terminals in 2-wire sequence.
.
-
Forward-rotation
switch
Reverse-rotation
switch
Forward/Stop (Forward rotation with the forward-rotation switch
closed and reverse-rotation switch opened)
Reverse/Stop (Reverse rotation with the reverse-rotation switch
closed and forward-rotation switch opened)
Sequence input common
j
: 2 to 5
5-21
Page 84

Basic Operation Chapter
H Operation in 3-wire Sequence (n37 = 0)
•The
Inverter operates in 3-wire sequence by setting n37 for multi-function input 2 to 0.
5
•Only
n37 can be set to 0 (3-wire sequence). By making this setting, the set value in n36
is ignored and the following settings are forcibly made.
S1: RUN input (RUN when ON)
S2: STOP input (STOP when OFF)
S3: Forward/Reverse rotation command (OFF: Forward; ON: Reverse)
•The following diagram shows a wiring example of the terminals in 3-wire sequence.
Stop switch
(NC)
Operation
switch (NO)
Direction switch
RUN input (RUN with the STOP switch and RUN switch closed)
STOP input (with the STOP switch opened)
Forward/Reverse
switch opened and reverse rotation with the direction switch closed)
Sequence input common
rotation command (Forward rotation with the direction
5-9-2 Multi-function Output
The
3G3JV incorporates
Output
from these terminals has a
plication.
H Selecting the Multi-function Output (n40)
n40 Multi-function Output (MA/MB and MC) Changes during
Setting
range
Note Do not set values outside the above setting ranges.
0 to 7, 10 to 17
(see note)
two multi-function output terminals (MA and MB).
variety of functions according to the ap
operation
Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 1
-
No
5-22
Page 85

60)
Basic Operation Chapter
Set Values
Value Function Description
0 Fault output ON: Fault output (with protective function working)
1 Operation in progress ON: Operation in progress (with RUN command input or
inverter output)
2 Frequency detection ON: Frequency detection (with frequency reference
coinciding with output frequency)
3 Idling ON: Idling (at less than min. output frequency)
4 Frequency detection 1 ON: Output frequency y frequency detection level (n58)
5 Frequency detection 2 ON: Output frequency x frequency detection level (n58)
6 Overtorque being
monitored
(NO-contact output)
Output if any of the following parameter conditions is
satisfied.
•Overtorque detection function selection (n59)
5
7 Overtorque being
monitored
(NC-contact output)
10 Alarm output ON: Alarm being detected (Nonfatal error being
11 Base block in
progress
12 RUN mode ON: Local mode (with the Digital Operator)
13 Inverter ready ON: Inverter ready to operate (with no fault detected)
14 Fault retry ON: Fault retry (Inverter resetting with fault retry (n48)
15 UV in progress ON: Undervoltage being monitored (main circuit
16 Rotating in reverse
direction
17 Speed search in
progress
•Overtorque detection level (n
•Overtorque detection time (n61)
Note NO contact: ON with overtorque being detected;
NC contact: OFF with overtorque being detected
detected)
ON: Base block in progress (in operation with output
shutoff)
not set to 0)
undervoltage UV1 detected)
ON: Rotating in reverse direction
ON: Speed search in progress
5-23
Page 86

Basic Operation Chapter
5-10 Analog Monitor Output
The 3G3JV incorporates analog monitor output terminals AM and AC.
These terminals have analog monitor values of output frequency or current.
H Setting the Analog Monitor Output (n44 and n45)
•The output frequency or current as a monitored item is set in n44.
•The analog output characteristics are set as an analog monitor output gain in n45.
5
n44 Analog Monitor Output Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0, 1 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
Set Values
Value Description
0 Output frequency (Reference: 10 V at max. frequency)
1 Output current (Reference: 10 V with rated output current)
n45 Analog Monitor Output Gain Changes during
operation
Set range 0.00 to 2.00 Unit of
setting
Note 1. Set the multiplication ratio based on the set value in n44.
example, if an output of 5 V is desired at maximum frequency (with n44 set
For
to 0), set n45 to 0.50.
Note 2. The
maximum output voltage of the analog monitor output terminals are 10 V
0.01 Default setting 1.00
No
Yes
.
5-24
Page 87

6
Chapter 6
Advanced Operation
6-1 Setting the Carrier Frequency
6-2 DC Injection Braking Function
6-3 Stall Prevention Function
6-4 Overtorque Detection Function
6-5 Torque Compensation Function
6-6 Slip Compensation Function
6-7 Other Functions
Page 88

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
This
chapter provides information on the use of advanced functions of the
Inverter for operation.
Refer
to this chapter to use the various advanced functions, such as stall
prevention, carrier frequency setting, overtorque detection, torque compensation, and slip compensation.
6-1 Setting the Carrier Frequency
The
carrier frequency of the 3G3JV can be fixed or varied in proportion to
the output frequency.
n46 Carrier Frequency Selection Changes during
operation
Setting
range
1 to 4, 7 to 9 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting (see note)
No
Note The default setting varies with the capacity of the Inverter model.
Set Values
Value Description
1 2.5 kHz
2 5.0 kHz
3 7.5 kHz
4 10.0 kHz
7 2.5 kHz (12×): 12 times as high as output frequency (between 1.0 and 2.5 kHz)
8 2.5 kHz (24×): 24 times as high as output frequency (between 1.0 and 2.5 kHz)
9 2.5 kHz (36×): 36 times as high as output frequency (between 1.0 and 2.5 kHz)
•The default setting does not need any changes in normal operation.
•Change the default setting in the following cases.
The wiring distance between the Inverter and motor is long:
Set the Inverter to a lower carrier frequency.
Reference carrier frequency: 10 kHz at a maximum wiring distance of 100 m
and
5 kHz at a wiring distance exceeding 100
Excessive speed or torque dispersion at low speed:
Set the carrier frequency to a lower value.
6-2
m.
Page 89

3 p ase
S g e p ase
Advanced Operation Chapter 6
Note The
carrier frequency changes as shown in the following graph with 7 through 9
set in n46.
Carrier Frequency (n46: 7 through 9)
Carrier
Frequency
Output frequency
83.3 Hz (Set value: 7)
41.6 Hz (Set value: 8)
27.7 Hz (Set value: 9)
208.3 Hz (Set value: 7)
104.1 Hz (Set value: 8)
69.4 Hz (Set value: 9)
•The Inverter cannot maintain rated output current with the carrier frequency set to a
value higher than the default one.
The following table shows the default value and a decrease in the output current of
each Inverter model.
Be sure to use the Inverter so that there will be no decrease in rated output current.
Voltage Model
3-phase
200 V
Single-phase
200 V
A2001 4 (10 kHz) 0.8 ← ←
A2002 4 (10 kHz) 1.6 ← ←
A2004 4 (10 kHz) 3.0 ← ←
A2007 4 (10 kHz) 5.0 ← ←
A2015 3 (7.5 kHz) 8.0 ← 7.0
A2022 3 (7.5 kHz) 11.0 ← 10.0
AB001 4 (10 kHz) 0.8 ← ←
AB002 4 (10 kHz) 1.6 ← ←
AB004 4 (10 kHz) 3.0 ← ←
AB007 4 (10 kHz) 5.0 ← ←
AB015 3 (7.5 kHz) 8.0 ← 7.0
3G3JV-
Default
setting
Rated
output
current (A)
Set to 3
Reduced
rated output
current (A)
Set to 4
Reduced
rated output
current (A)
6-3
Page 90

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
n75 Low Carrier Frequency at Low Speed Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0, 1 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
No
Set Values
Value Description
0 Low carrier frequency at low speed disabled.
1 Low carrier frequency at low speed enabled.
•Normally set n75 to 0.
•When
the
load
the output frequency is 5 Hz or higher and the output current rate is 1
carrier frequency will be automatically reduced to 2.5 kHz with n75 set to 1. If the
is heavy at low speed, the Inverter will withstand higher overcurrent by suppres
sing the heat radiation of the Inverter caused by the carrier frequency.
•This function is enabled with 2, 3, or 4 set in n46 for carrier frequency.
10% or less,
-
6-4
Page 91

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
6-2 DC Injection Braking Function
The DC injection braking function applies DC on the induction motor for
braking control.
Startup DC Injection Braking:
This
braking is used for stopping and starting the motor rotating by inertia
with no regenerative processing.
DC Injection Braking to Stop:
Adjust the stop DC injection braking time if the motor rotating does not
decelerate
By
increasing the DC injection braking time or DC injection braking current,
the time required for stopping the motor is reduced.
to a stop in normal operation due to inertia from a heavy load.
n52 DC Injection Braking Current Changes during
operation
Setting
range
n53 DC Injection Braking-to-stop Time Changes during
Setting
range
n54 Startup DC Injection Braking Time Changes during
Setting
range
•
Set the DC injection braking current as percentage based on the rated current of the
0 to 100 (%) Unit of
setting
0.0 to 25.5 (s) Unit of
setting
0.0 to 25.5 (s) Unit of
setting
1% Default setting 50
operation
0.1 s Default setting 0.5
operation
0.1 s Default setting 0.0
No
No
No
Inverter as 100%.
•After
the startup DC injection braking time
is set, the Inverter starts up at minimum fre
quency on completion of the startup DC injection braking control of the Inverter.
•After
the speed is reduced, the Inverter is switched to
DC injection braking at minimum
output frequency.
-
DC Injection Braking Control
Output
frequency
Minimum
output
frequency
(n14)
n54
Startup DC injection
braking time
Time
n53
DC injection
braking-to-stop time
6-5
Page 92

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
6-3 Stall Prevention Function
A
stall will occur if the motor cannot keep up with the rotating magnetic
on
the motor stator side when a large load is applied to the motor or a sud
den acceleration/deceleration is performed.
In
the 3G3JV
, stall prevention functions can be set independently for
erating, running, and decelerating conditions.
field
accel
-
-
n55 Stall Prevention Level during
Deceleration
Setting
range
0, 1 Unit of
1 Default setting 0
setting
Changes during
operation
No
Set Values
Value Description
0 Stall prevention during deceleration
1 No stall prevention during deceleration
•If
1 is set, the motor will be decelerated according to the set deceleration time. If
deceleration time is too short, the main circuit may result in overvoltage.
•If 0 is set, the deceleration time will be automatically lengthened to prevent overvoltage.
Stall Prevention during Deceleration with n55 Set to 0
Output
frequency
Deceleration time is controlled
to prevent overvoltage.
the
6-6
Time
Deceleration time (Set value)
Page 93

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
n56 Stall Prevention Level during
Acceleration
Setting
range
30 to 200 (%) Unit of
1% Set Values 170
setting
Changes during
operation
No
Set Values
•This
•Set the parameter as percentage based on the rated Inverter current as 100%.
•The default setting does not need any changes in normal operation.
•Decrease
function is used to stop accelerating
current
accelerates
value so that the Inverter will continue operating without stalling. The Inverter
the load while the output current is
the set value if the capacity of the motor is smaller than
the load if the output current exceeds the set
the same as or less than the set value.
that of the Inverter or
the motor stalls with the default value.
The
set value is normally 2 or 3 times higher than the rated current of the motor
current as percentage based on the rated inverter current as 100%.
Stall Prevention during Acceleration
Output
current
n56 (stall prevention level
during acceleration)
. Set this
Output
frequency
Time
The output frequency is controlled
so that the Inverter will not stall.
Time
6-7
Page 94

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
n57 Stall Prevention during Operation Changes during
operation
Setting
range
30 to 200 (%) Unit of
setting
1% Default setting 160
No
Set Values
•This
•The
•Set the parameter as percentage based on the rated Inverter current as 100%.
•The default setting does not need any changes in normal operation.
•Decrease
function will decrease the output frequency
current
operating
value by a minimum of approximately 100 ms so that the Inverter will continue
without
stalling. The Inverter will increase the output frequency to return to
if the output current exceeds the set
the set frequency reference level when the output current is less than the set value.
Inverter accelerates or decelerates the output frequency according
acceleration or deceleration time. (Acceleration
time 1: n16, n17 or acceleration time
to the preset
2: n18, n19)
the set value if the capacity of the motor is smaller than
that of the Inverter or
the motor stalls with the default value.
The
set value is normally 2 or 3 times higher than the rated current of the motor
. Set this
current in percentage based on the rated Inverter current as 100%.
Stall Prevention during Acceleration
Output
current
Output
frequency
n57 (Stall prevention
level during acceleration)
Time
The output frequency is controlled
so that the Inverter will not stall.
Time
6-8
Page 95

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
6-4 Overtorque Detection Function
When
an excessive load is applied to the equipment, the Inverter
detects
the overtorque condition through an increase in the output current.
n59 Overtorque Detection Function Selection Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0 to 4 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
No
Set Values
Value Description
0 Inverter does not monitor overtorque.
1 Inverter monitors overtorque only when speed is matched. It continues
operation (issues warning) even after overtorque is detected.
2 Inverter monitors overtorque only when speed is matched. It discontinues
operation (through protective function) when overtorque is detected.
3 Inverter always monitors overtorque during operation. It continues operation
(issues warning) even after overtorque is detected.
4 Inverter always monitors overtorque during operation. It discontinues
operation (through protective function) when overtorque is detected.
•Set
n60 for overtorque detection level and n61 for overtorque detection time to enable
the
overtorque detection function. The Inverter will detect overtorque when the
the
same as or higher than the detection level is output for the preset detection time.
•
Set n40 for multi-function output to either of the following so that external overtorque
current
detection output will be ON.
Set Value: 6 for overtorque detection (NO)
Set Value: 7 for overtorque detection (NC)
Overtorque Detection
Output
current
Overtorque
detection (NO)
Note Overtorque
imately 5% of the Inverter rated current.
Overtorque detection time
detection will be canceled if the output current decreases from the detection level by approx
See note.
n60 (Overtorque
detection level)
Time
n61
Time
-
6-9
Page 96

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
n60 Overtorque Detection Level Changes during
operation
Setting
range
30 to 200 (%) Unit of
setting
1% Default setting 160
No
Set Values
•Set the parameter as percentage based on the rated Inverter current as 100%.
n61 Overtorque Detection Time Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0.1 to 10.0 (s) Unit of
setting
0.1 s Default setting 0.1
No
Set Values
•Set the overtorque detection time.
•The Inverter will detect overtorque when the current the same as or higher than the
detection level is output for the preset detection time.
6-10
Page 97

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
6-5 Torque Compensation Function
This function increases the output torque of the Inverter by detecting an
increase in the motor load.
n63 Torque Compensation Gain Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0.0 to 2.5 Unit of
setting
0.1 Default setting 1.0
Yes
Set Values
•The default setting does not need any changes in normal operation.
•Change the default setting in the following cases.
The wiring distance between the Inverter and motor is long:
Set the gain to a larger value.
The capacity of
the Inverter:
Set the gain to a larger value.
The motor vibrates:
Set the gain to a smaller value.
•The torque compensation gain must be adjusted so that the output current at low
speed will not exceed 50% of the rated output current of the Inverter, otherwise the
Inverter may be damaged.
the motor is lower than the maximum applicable motor capacity of
6-11
Page 98

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
6-6 Slip Compensation Function
The slip compensation function calculates the motor torque according to
the output current, and sets gain to compensate for output frequency.
This function is used to improve speed accuracy when operating with a
load.
n64 Rated Motor Slip Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0.0 to 20.0 (Hz) Unit of
setting
0.1 Hz Default setting (see note)
Note The default setting varies with the capacity of the Inverter model.
Set Values
•Set the rated slip value of the motor in use.
•This parameter is used as a slip compensation constant.
•Calculate
tor nameplate by using the following formula.
Rated slit value (Hz) y Rated frequency (Hz) –
n65 Motor Current with No Load Changes during
Setting
range
the rated motor slip value from the rated frequency (Hz) and rpm on the
Rated rpm Number of poles
120
operation
0 to 99 (%) Unit of
setting
1% Default setting (see note)
Yes
No
mo
-
Note The default setting varies with the capacity of the Inverter model.
Set Values
•Set
the motor current with
100%.
•Contact the motor manufacturer for the motor current with no load.
•This parameter is used as a slip compensation constant.
6-12
no load in percentage based on the rated motor current as
Page 99

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
n66 Slip Compensation Gain Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0.0 to 2.5 Unit of
setting
0.1 Default setting 0.0
Note This parameter is disabled with the value set to 0.0.
Set Values
•Set
the parameter to 1.0
first and check the operation of the Inverter
gain with 0.1-gain increments or decrements.
If the speed is lower than the target value, increase the set value.
If the speed is higher than the target value, decrease the set value.
n67 Slip Compensation Parameter Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0.0 to 25.5 (s) Unit of
setting
0.1 s Default setting 2.0
Set Values
•This
parameter is used for the response adjustment of the slip compensation function.
Yes
(see note)
. Then fine-tune the
No
•The default setting does not need any changes in normal operation.
•Change the default setting in the following cases.
The motor vibrates: Set the value to a larger value.
The motor response is low: Set the value to a smaller value.
6-13
Page 100

Advanced Operation Chapter 6
6-7 Other Functions
The
following description provides information on the other functions and
parameter settings of the Inverter.
6-7-1 Motor Protection Characteristics (n33 and n34)
•This parameter setting is for motor overload detection (OL1).
n33 Motor Protection Characteristic Selection Changes during
operation
Setting
range
0 to 2 Unit of
setting
1 Default setting 0
Set Values
Value Description
0 Protection characteristics for general-purpose induction motors
1 Protection characteristics for Inverter-dedicated motors
2 No protection
•This
•Set the parameter according to the motor.
•If
parameter is used to set the electric thermal characteristics of the motor to be con
nected.
a single Inverter is connected to more than one motor
protection.
n34 Motor Protection Time Changes during
Setting
range
The parameter is also disabled by setting n32 for rated motor current to 0.0.
1 to 60 (min) Unit of
setting
1 min Default setting 8
, set the parameter to 2 for no
operation
No
-
No
6-14
 Loading...
Loading...