OKI MSM6947RS, MSM6927RS, MSM6927GS-2K, MSM6947GS-K, MSM6927GS-K Datasheet

E2A0011-16-X1
¡ Semiconductor MSM6927/6947
¡ Semiconductor
This version: Jan. 1998
Previous version: Nov. 1996
MSM6927/6947
1200 bps Single Chip FSK MODEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MSM6927 and the MSM6947 are OKI's 1200 bps single chip modem series which transmit
and receive serial, binary data over a switched telephone network using frequency shift
keying(FSK).
The MSM6927 is compatible with ITU-T V.23 series data sets, while the MSM6947 is compatible
with Bell 202 series data sets.
These devices provide all the necessary modulation, demodulation, and filtering required to
implement a serial, asynchronous communication link.
OKI's single chip modem series is designed for users who are not telecommunication experts and
are easy to use cost effective alternative to standard discrete modem design.
CMOS LSI technology provides the advantages of small size, low power, and increased
reliability.
The design of the integrated circuit assures compatibility with a broad base of installed low speed
modems and acoustic couplers. Applications include interactive terminals, desk top computers,
point of sale equipment, and credit verification systems.
FEATURES
• Compatible with ITU-T V.23 (MSM6927)
• Compatible with BELL 202 (MSM6947)
• CMOS silicon gate process
• Switched capacitor and advanced CMOS analog technology
• Data rate from 0 to 1200 bps
• Half duplex (2-Wire)
• Receive squelch delay
• Selectable built-in timers and external delay timers possible
• All filtering, modulation, demodulation, and DTE interface on chip
• Crystal controlled oscillator on chip
• TTL compatible digital interface
• Low power dissipation: 90 mW Typ.
• Package options:
28-pin plastic DIP (DIP28-P-600–2.54) (Product name: MSM6927RS)
(Product name: MSM6947RS)
44-pin plastic QFP (QFP44-P-910-0.80–K) (Product name: MSM6927GS-K)
(Product name: MSM6947GS-K)
(QFP44-P-910-0.80–2K) (Product name: MSM6927GS-2K)
1/31
¡ Semiconductor MSM6927/6947
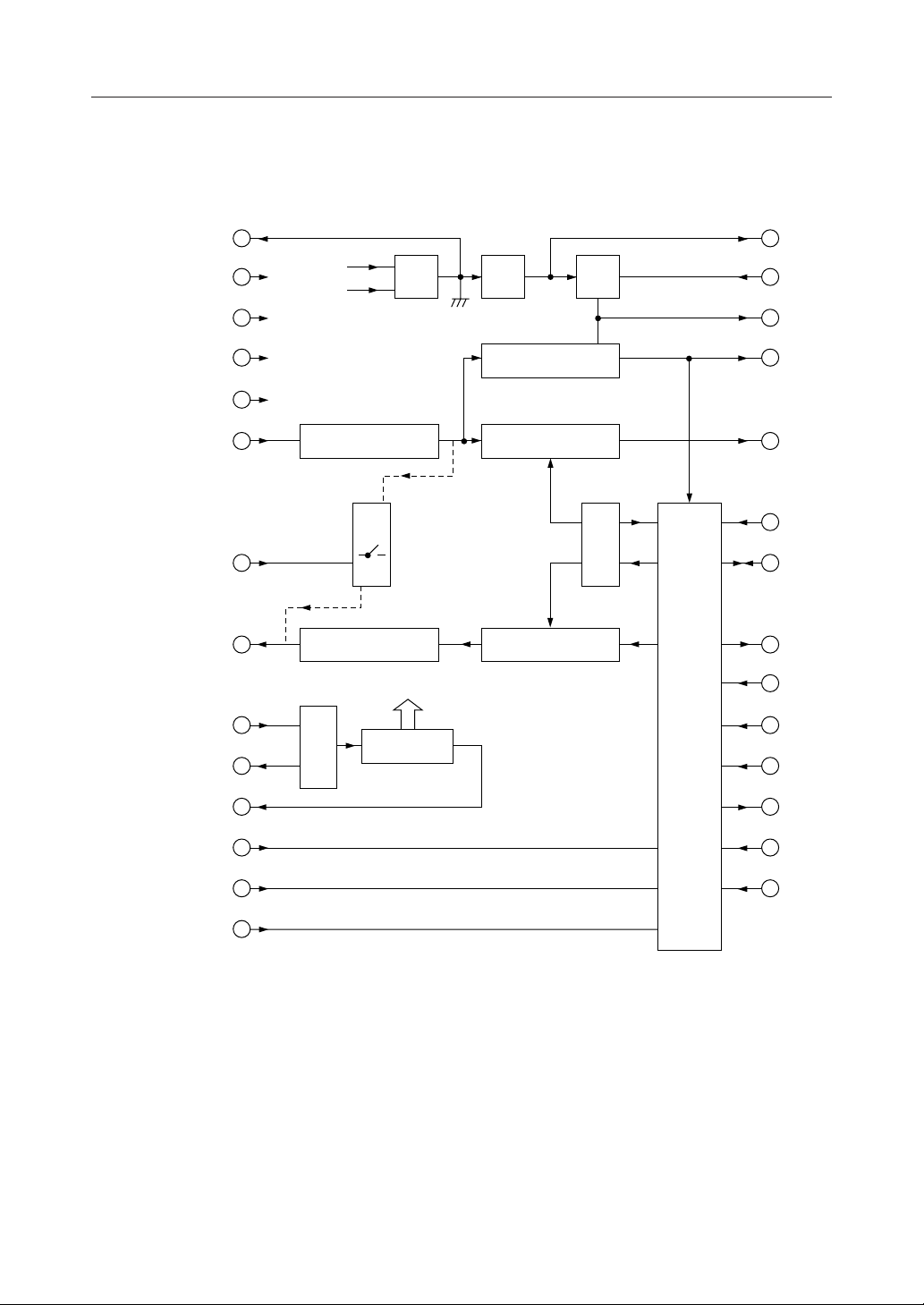
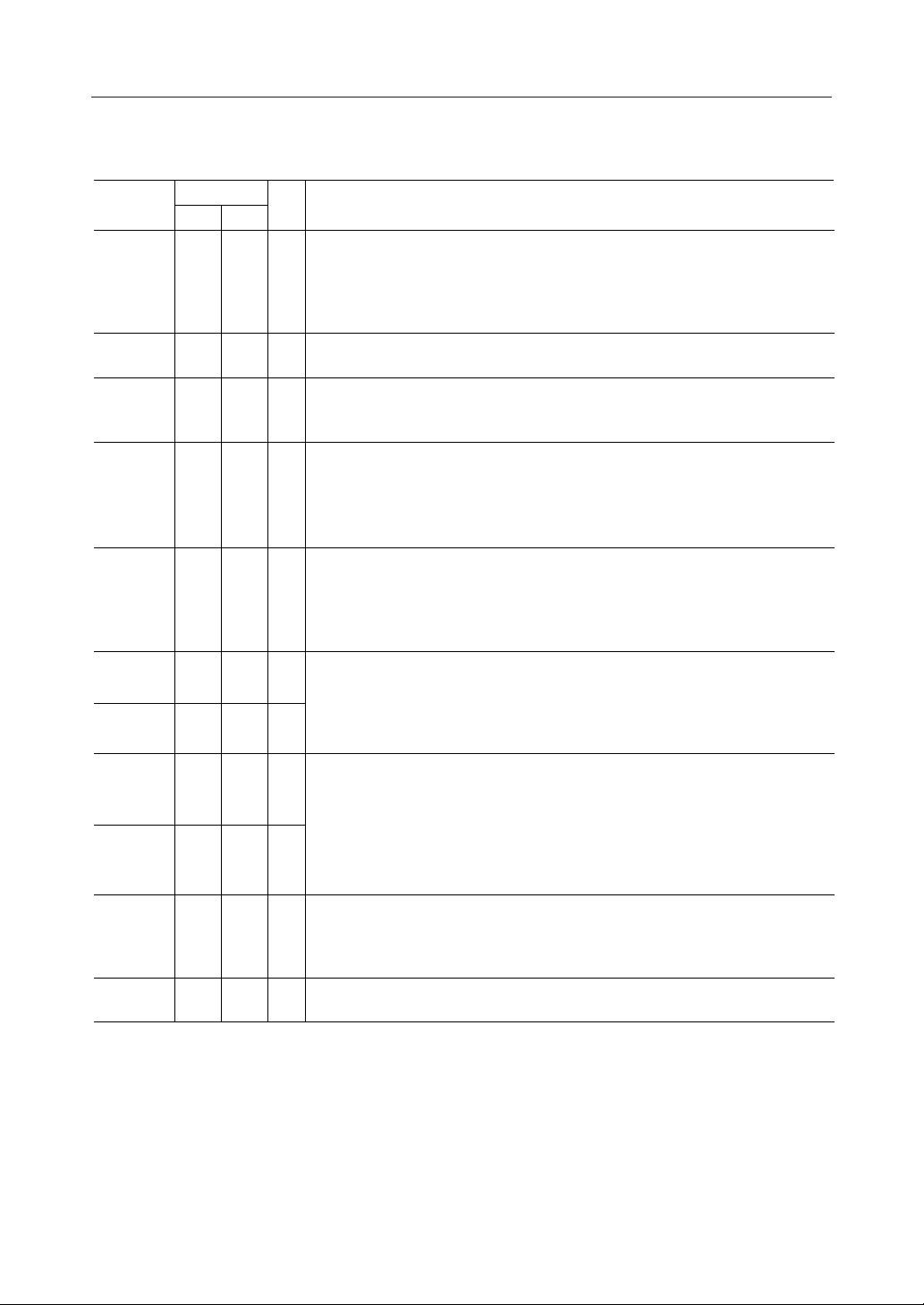
BLOCK DIAGRAM
SG1
V
V
AG
DG
AIN
FT
AO
X1
X2
CLK
SG2
V
A
D
A
AG
SG1 SG2 V
SW
Carrier Detect
DemodulatorReceive Filter
REF
Cont.
CDR2
CDR1
CD1
RD1
RD2
ROM
CD2
DTE
ModulatorTransmit Filter
Inter-
RD
face
XD
RS1
OSC
Clock Gen.
Loop
Test
RS2
CS
TS1(MSM6927RS)/
TS (MSM6947RS)
TS2(MSM6927RS)/
ATE(MSM6947RS)
SQ
CC
Delay
LT
2/31
¡ Semiconductor MSM6927/6947
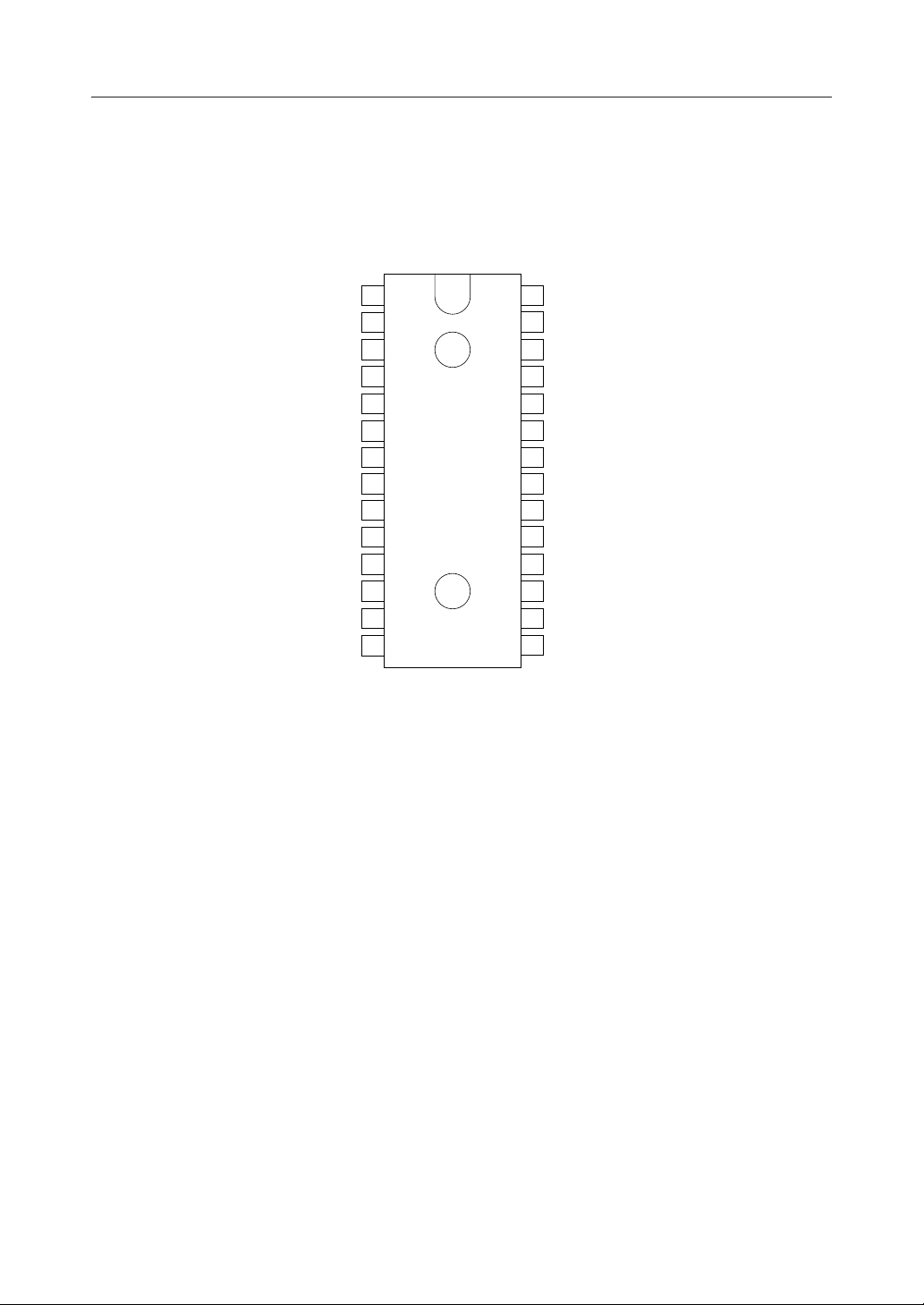
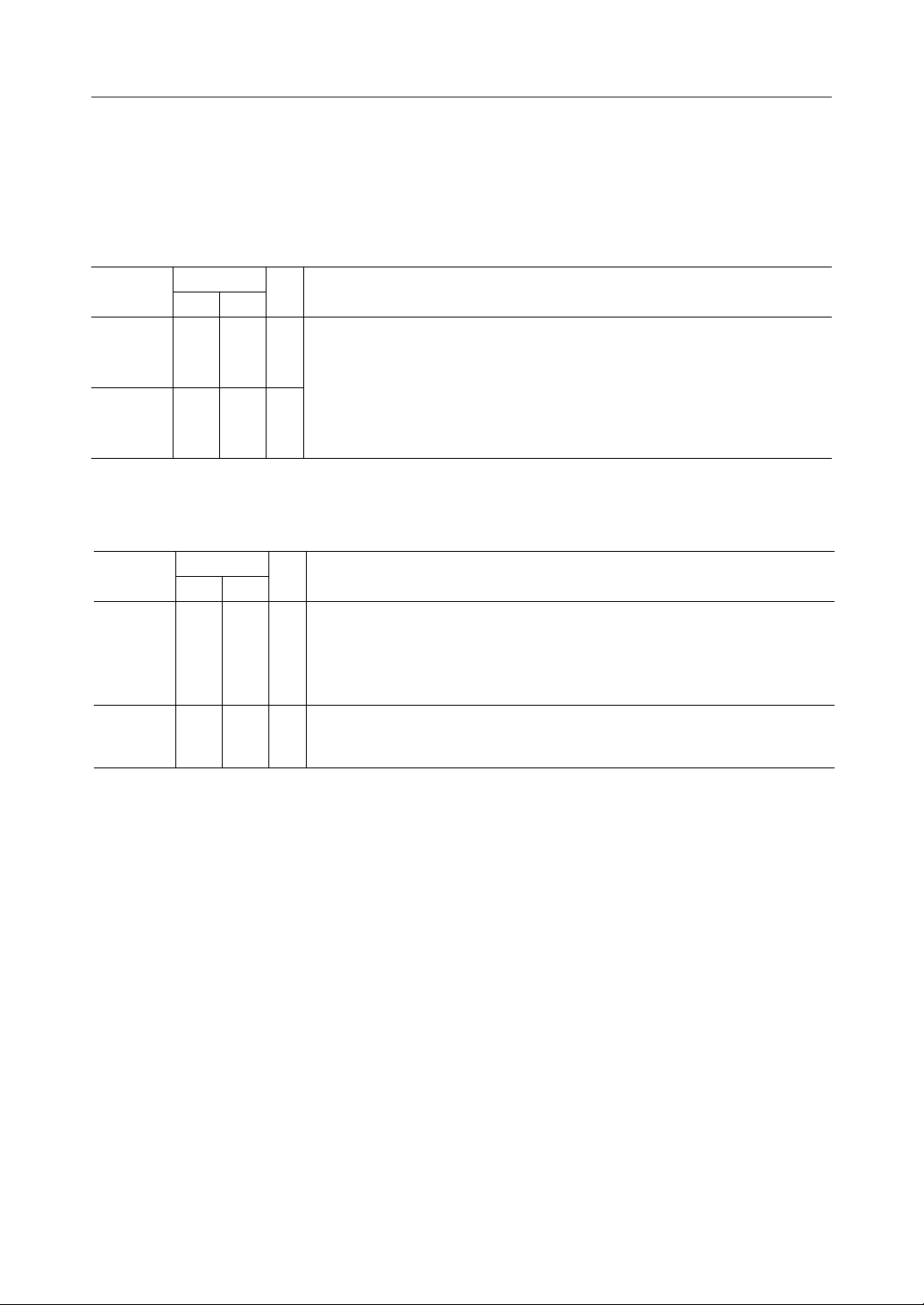
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
TS2 (MSM6927RS)
X1 1
X2 2
CLK 3
LT 4
CC 5
CS 6
RS1 7
RS2 8
XD 9
RD 10
CD1 11
CD2 12
RD1 13
RD2 14
28
ATE (MSM6947RS)
TS1 (MSM6927RS)
27
TS (MSM6947RS)
26
V
D
AO25
24
V
A
FT23
SQ22
AIN21
20
SG1
AG19
SG218
CDR217
CDR116
DG15
28-Pin Plastic DIP
Note: All pin descriptions except No. 27 pin and No. 28 pin are same for both MSM6927RS and
MSM6947RS.
3/31
¡ Semiconductor MSM6927/6947
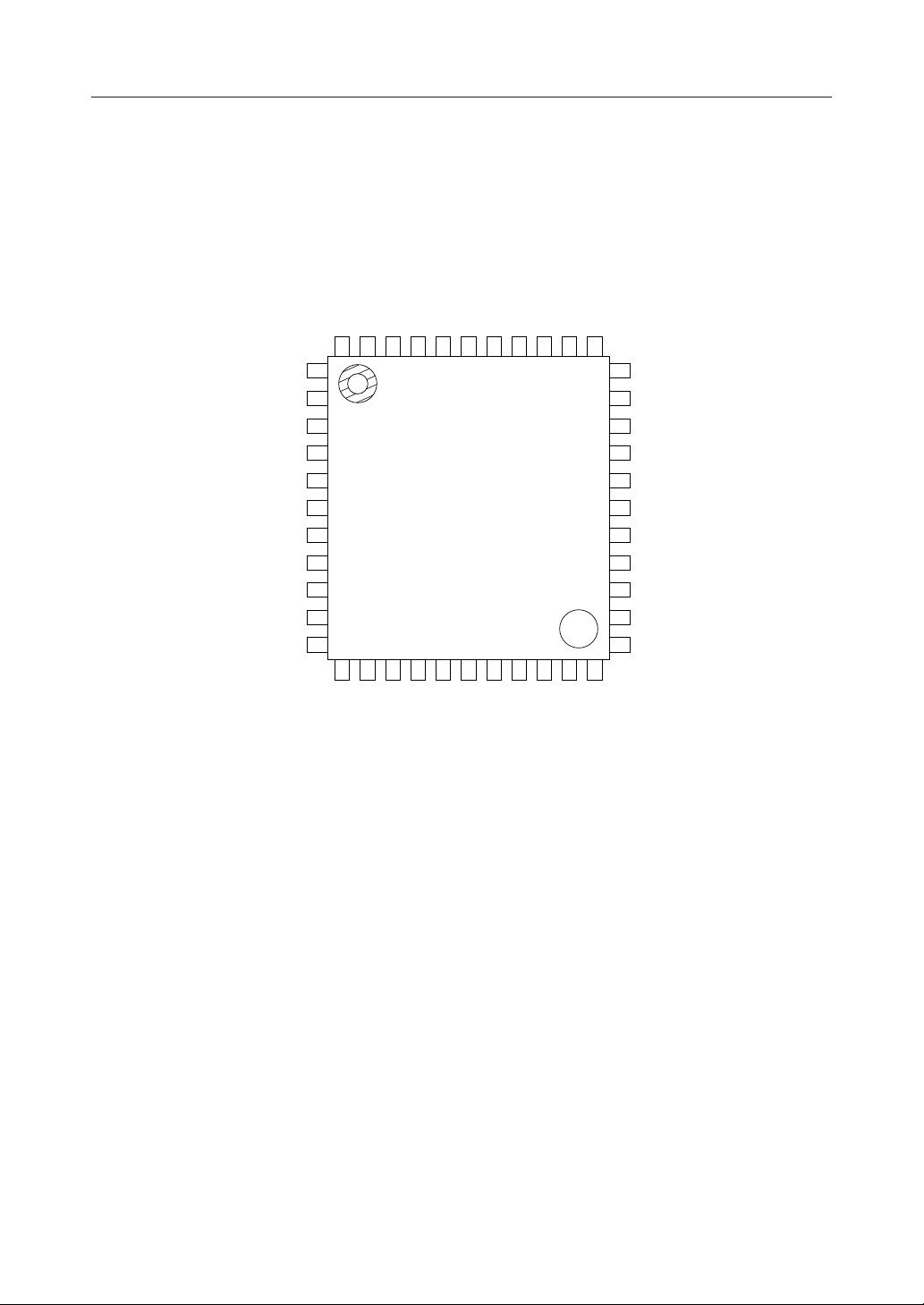
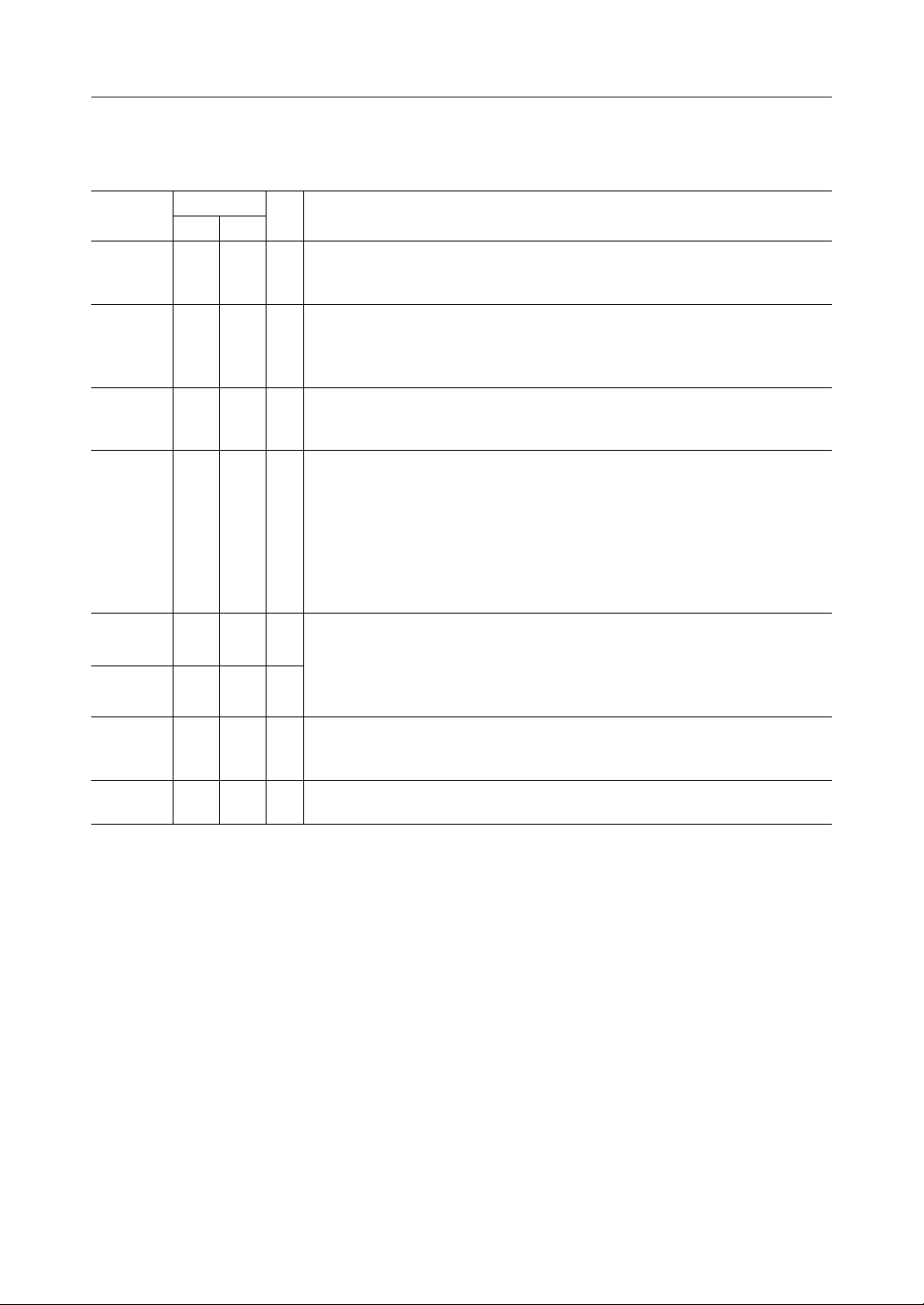
*
NC
CC
CS
RS1
NC
NC
NC
RS2
XD
RD
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
CLK
LT
444342
121314
CD1
CD2
41
15
40
16
A
V
39
17
*
A
V
X2X1NC
RD1NCRD2
44-Pin Plastic QFP
ATE (MSM6947GS-K)
TS2 (MSM6927GS-K)
38
18
NC
D
TS1 (MSM6927GS-K)
TS (MSM6947GS-K)
NC
37
36
V
35
AO
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
DG
CDR1
CDR2
SG2
V
A
FT
SQ
NC
NC
NC
NC
AIN
NC
SG1
AG
Notes: All pin description except No. 36 pin and No. 28 pin are same for both MSM6927GS-K
and MSM6947GS-K.
*: Both No. 17 pin and No. 39 pin are set to be at VA level by setting No. 33 pin at V
level.
NC: No connect pin
4/31
A
¡ Semiconductor MSM6927/6947
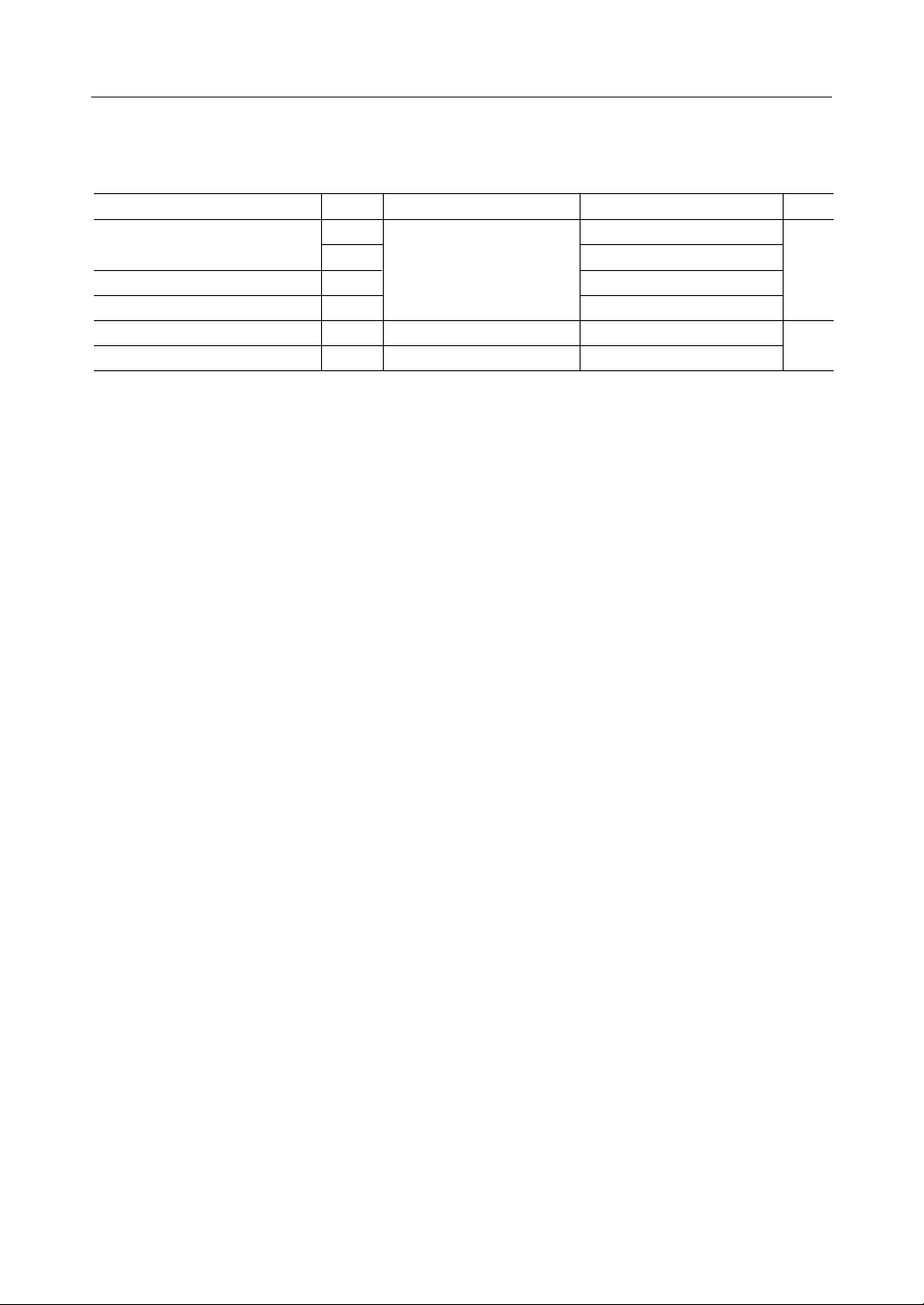
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Power
Name
DG 15 19 — Ground reference of VD (digital ground)
AG
V
A
V
D
Pin No.
RS GS-K
19 23 — Ground reference of VA (digital ground)
24 33 — Supply voltage (+12 V nominal)
26 35 — Supply voltage (+5 V nominal)
I/O
Clocks
Name
X1 141
X2 2 42 —
CLK
Pin No.
RS GS-K
343O873.9 Hz clock output. This clock is used to implement external delay circuits etc.
I/O
Master clock timing is provided by either a series resonant crystal (3.579545 MHz
—
±0.01%) connected across X1 and X2, or by an external TTL/CMOS clock driving
X2 with AC coupling. In this latter case, X1 is left unconnected.
See Fig. 10.
Description
Description
5/31
¡ Semiconductor MSM6927/6947
Control
Name
Pin No.
RS GS-K
I/O
LT 444I
CC 52I
RS2 88I
CD1 11 12 O
CD2 12 13 I/O
RD1 13 14 O
RD2 14 16 I
CDR1 16 20 O
CDR2 17 21 I
SQ 22 31 I
FT 23 32 I
Description
Digital loop back test. During digital "High", any data sent on the X
pin will appear
D
on the RD pin, and any data sent on the RS1 pin will immediately appear on the
CS pin. Any data demodulated from the received carrier on the A
pin will be the
IN
modulated data to implement the transmitted carrier. In this case, sending the
transmitted carrier to the phone line depends on the CC, but never on RS1.
During digital loop back test, the data on this pin becomes a control signal for sending
the transmitted carrier to the phone line in place of RS1.
When an external circuit gives the RS/CS delay time which is not within the device
as required, this pin should be connected to the external circuit output.
See Fig. 11-1 or Fig. 11-2 for MSM6927, MSM6947 respectively.
The fast carrier detection output. This pin is internally connected to the input of
the built-in carrier detect delay circuit. When an external delay circuit provides
the delay time which is not within the device as required, the CD1 should be
connected to the external circuit input. See Fig. 11-1 or Fig. 11-2 for MSM6927,
MSM6947 respectively.
When an external circuit gives the carrier detect delay time which is not within
the device as required, this pin becomes the input pin for the external circuit
output signal. In other cases (when using the delay time within the device, the
data on the TS1 (TS) or TS2 is not digital "High"), this pin becomes the Carrier
detect signal output.
The RD1 data is demodulated data from the received carrier and the RD2 is the
input of the following logic circuits referred to in Fig. 12-1and Fig. 12-2. for MSM6927
and MSM6947, respectively Usually, the RD1 data is input directly to RD2. In some
cases, as input data to RD2, the data that is controlled by NCU (Network control
unit) etc. may be required in stead of the RD1 data.
These two pins are the output (CRD1) and inverting input (CDR2) of the buffer
operational amplifier of which the noninverting input is connected to the built-in
voltage reference, stabilized to variations in the supply voltage and temperature.
See Fig. 13. An adequate carrier-detect level can be set by selecting the ratio of
to R9. Therefore, the loss in the received carrier level by phone-line
R
8
transformer can be compensated by adjusting the ratio of R
to R9. R8 + R9
8
should be greater than 50 kW.
When the data rate is 1200 bps and in half duplex mode on two-wire facilities,
the delay function called as receiver-squelch is required. In case of four wire
facilities, this function is not usually required.
When a digital "High" is input to the SQ pin, this function is omitted.
This pin may be used for device tests only. During digital "High", the A
pin will
O
be connected to receiving filter output instead of transmitting filter output.
6/31
¡ Semiconductor MSM6927/6947
Both MSM6927RS (or GS-K) and MSM6947RS (or GS-K) have 28 (or 44) pins. The pin descriptions
for these 28 (or 44) pins are same except those for No. 27 (or No. 36) pin and No. 28 (or No. 38).
The pin descriptions for No. 27 (or No. 36) pin and No. 28 (or No. 38) pin are described as follows.
MSM6927
Name
TS1 27 36 I
TS2 28 38 I
Pin No.
RS GS-K
MSM6947
Name
TS 27 36 I
ATE 28 38 I
Pin No.
RS GS-K
I/O
RS/CS delay and carrier detect delay options referred to chapter about timing
characteristics are selected by TS1 and TS2 inputs. Be careful that each delay
can not be individually selected. If another delay time than the ones within the
device are required as an option, input a digital "High" to the TS1 and TS2 pin
and implement the external delay circuits to obtain the desired delay
characteristics. In this case, the CD2 pin becomes not only the input for the
external circuit output signal, but also the Carrier detect output. See Fig. 11-1.
I/O
When a digital "Low" is input to the TS pin, the built-in RS/CS, carrier detect and
receiver-squelch delay are provided. If another delay time is required, it can be
implemented by inputting a digital "High" to this pin and incorporates the external
delay circuits. In this case, the CD2 pin becomes not only the input for the
external circuit output signal, but also the Carrier detect output. See Fig. 11-2.
Answer tone enable input. When a digital "Low" is input to this pin and the RS1
pin is in the digital "Low" level, the Answer Tone (to 2025 Hz) is sent over the
phone line via the A
O
pin.
Description
Description
7/31
¡ Semiconductor MSM6927/6947
Input/Output
Name
Pin No.
RS GS-K
I/O
CS 63O
RS1 74I
XD 99I
RD 10 10 O
SG2 18 22 O
SG1 20 24 O
A
IN
A
O
21 26 I
25 34 O
Description
Clear to send signal output. The digital "High" level indicates the "OFF" state and
digital "Low" indicates the "ON" state. This output goes "Low" at the end of a delay
(RS/CS delay) initiated when RS1 (Request to send) goes "Low".
Request to send signal input. The digital "High" level indicates the "OFF" state.
The digital "Low" level indicates the "ON" state and instructs the modem to enter
the transmit mode. This input must remain "Low" for the duration of data
transmission. "High" turns the transmitter off.
This is digital data to be modulated and transmitted via A
. Digital "High" will be
O
transmitted as "Mark". Digital "Low" will be transmitted as "Space". No signal
appears at A
Digital data demodulated from A
unless RS1 is "Low".
O
is serially available at this output. Digital
IN
"High" indicates "Mark" and digital "Low" indicates "Space". For example, under
the following condition, this output is forced to be "Mark" state because the data
may be invalid.
• When CD2 (Carrier detect) is in the "OFF" state.
• When SQ is in digital "Low" (two-wire facilities) and RS1 is in the "ON" state.
• During the receive data squelch delay at half duplex operation on two wire
facilities.
The SG1 and ST2 are built-in analog signal grounds. SG2 is used only for
Carrier detect function. The DC voltage of SG1 is approximately 6 V, so the
analog line interface must be implemented by AC coupling. See Fig. 9. To make
impedance lower and ensure the device performance, it is necessary to put
bypass capacitors on SG1 and SG2 in close physical proximity to the device.
This is the input for the analog signal from the phone line. The modem extracts
the information in this modulated carrier and converts it into a serial data stream
for presentation at RD output.
This analog output is the modulated carrier to be conditioned and sent over the
phone line.
8/31
¡ Semiconductor MSM6927/6947
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Parameter
Power Supply Voltage
Analog Input Voltage
Digital Input Voltage
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
*1*2CDR2, A
IN
*1
*2
*3
Symbol
V
A
V
D
V
IA
V
ID
T
op
T
STG
Condition
Ta = 25°C
With respect
to AG or DG
X1, LT, CC, RS1, RS2, XD, CD2, RD2, SQ, FT, TS1 (TS), TS2 (ATE)
*3 CD2 is I/O terminal
Rating
Unit
–0.3 to 15
–0.3 to 7
–0.3 to VA + 0.3
–0.3 to V
—
—
+ 0.3
D
0 to +70
–55 to 150
V
°C
9/31
¡ Semiconductor MSM6927/6947
pp
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter UnitMax.Typ.Min.Symbol Condition
13.212.010.8VA With respect to AG
Power Supply Voltage
Operating Temperature 70—0T
op
—
CRYSTAL —3.579545———
R
1
R
2
R
3
R
4
R
5
R
6
R
7
R
8
R
9
C0, C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
C
5
C
6
lication circuits using above conditions are provided in Fig. 8.
A
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Transformer
impedance = 600 W
—
5.255.004.75VD With respect to DG
V
—0—AG, DG —
°C
MHz
—600—
W
—51—
—51—
—51—
—51—
—51—
kW
—51—
—33—
—51—
—0.047—
—2.2—
——22
——0.01
mF—
—10—
—10—
10/31
 Loading...
Loading...