
OKI Semiconductor
ML7037-003
Dual Echo Canceler & Noise Canceler with Dual Codec for Hands-Free
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ML7037-003 is an IC device developed for portable, handsfree communication with built-in line echo
canceler, acoustic echo canceler, and transmission signal noise canceler. Built-in to the voice signal interface is a
PCM CODEC for the analog interface on the acoustic-side, and another PCM CODEC for the analog interface on
the line-side. On the line-side, in addition to the analog interface, there is also a -law PCM/16-bit linear digital
interface.
Equipped with gain and mute controls for data transmission and reception, a -law PCM/16-bit linear digital
interface for memo recording and message output, and transfer clock and sync clock generators for digital
communication, this device is ideally suited for a handsfree system.
FEATURES
• Single 3.3 V Power Supply Operation (3.0 to 3.6 V) [with built-in regulator to generate internal power supply]
• Built-in 2-channel (line and acoustic) echo canceler
Echo attenuation : 35 dB (typ.) for white noise
Cancelable echo delay time :
Single echo canceler mode (only an acoustic echo canceler is enabled)
Tacoud= 64 ms (max)
Dual echo canceler mode (both of an acoustic and line echo cancelers are enabled)
Tacoud = 64 ms Tlined = 20 ms
• Built-in transmission signal noise canceler
Noise attenuation : 13 dB (typ.) for white noise
• Built-in 2-channel CODEC’s
• Analog input gain amp’s (Acoustic side = 2 stages; Line-side = 1 stage)
• Analog output configuration : Push-pull drive (can drive a 2.0 k load)
• Receive-side ALC (Auto Level Controler)
• Programmable Gain/Mute
• A slope filter on transmit side
• 16 GPI’s and 8 GPO’s
• Speech digital interface coding formats : µ-law PCM (G.711 [64kbps]), 16-bit linear (2's complement)
• Speech digital interface sync formats : Long-frame-sync, short-frame-sync
• PCM shift clocks (BCLK)
Clock slave mode : 64kHz to 2.048MHz (µ-law PCM) / 128kHz to 2.048MHz (16bit Linear PCM)
Clock master mode : 64kHz (µ-law PCM) / 128kHz (16bit Linear PCM)
• Master clock frequency : 12.288 MHz (crystal unit the ML7037’s built-in driving circuit for a crystal unit or a
crystal oscillator)
• Transmission signal equalizer
• Package : 64-pin plastic TQFP (TQFP64-P-1010-0.50-K) (ML7037-003TB)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* This is a digest version of the ML7037-003 datasheet. Ask an OKI sales for a full version before you start actual designing
Not for Publication
activities.
PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
Issue Date: May. 21, 2007
1/41
PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
SYNCSEL
SYNCSEL
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
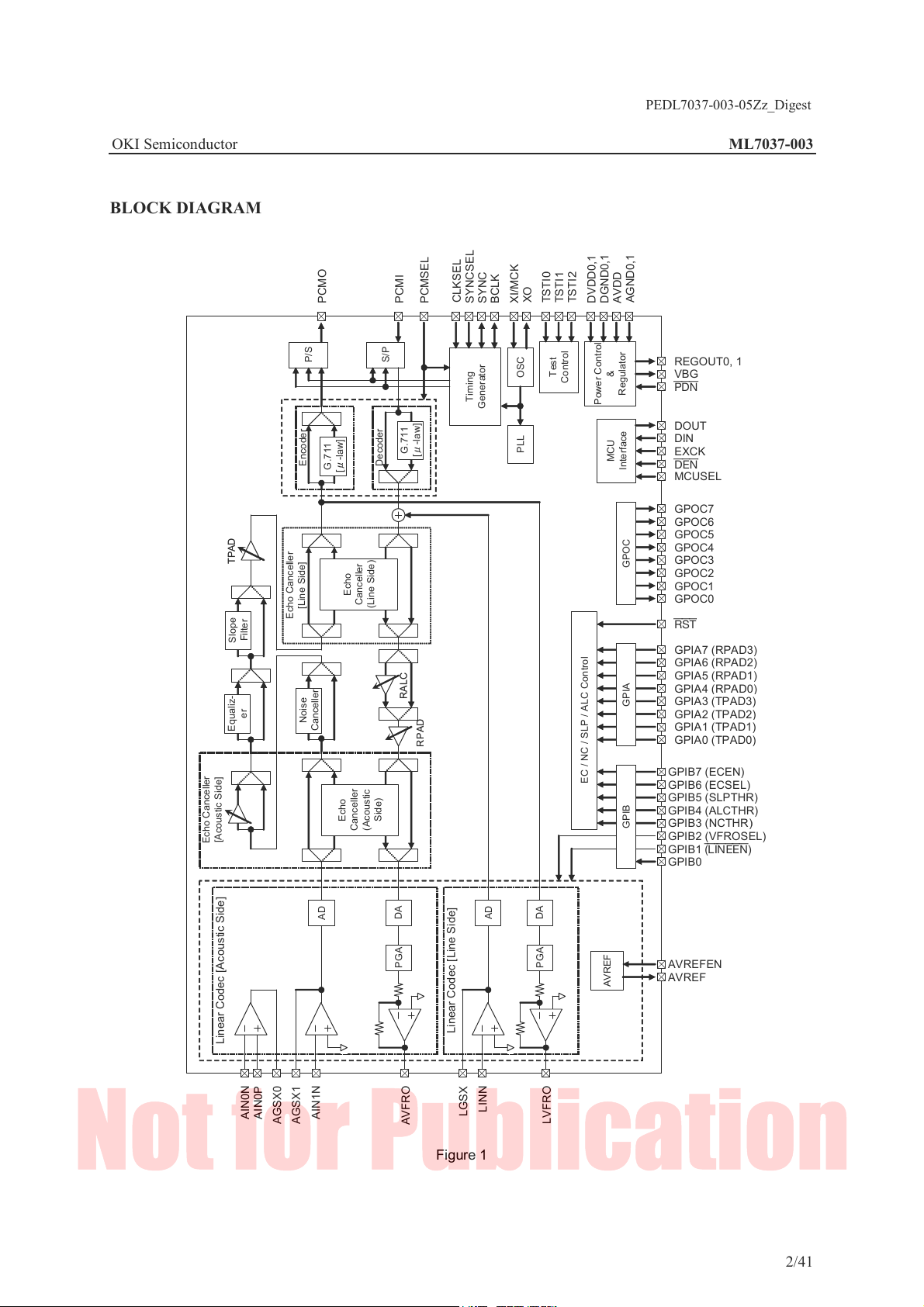
BLOCK DIAGRAM
CLKSEL
PCMO
PCMO
PCMI
PCMI
CLKSEL
PCMSEL
PCMSEL
XO
TSTI0
TSTI1
TSTI2
XO
TSTI0
TSTI1
SYNC
BCLK
XI/MCK
SYNC
BCLK
XI/MCK
TSTI2
P/S
P/S
S/P
S/P
Timing
Timing
Generator
Generator
Test
Test
OSC
OSC
Control
Control
G.711
G.711
Encoder
Encoder
G.711
G.711
Decoder
Decoder
[μ-law]
[μ-law]
[μ-law]
[μ-law]
PLL
PLL
TPAD
TPAD
Echo
Echo
Canceller
Canceller
(Line Side)
[Line Side]
[Line Side]
Echo Canceller
Echo Canceller
Filter
Filter
Slope
Slope
(Line Side)
RALC
RALC
er
er
Equaliz-
Equaliz-
Noise
Noise
Canceller
Canceller
RPAD
RPAD
Echo
Echo
Side)
Side)
(Acoustic
(Acoustic
Canceller
[Acoustic Side]
[Acoustic Side]
Echo Canceller
Echo Canceller
Canceller
DA
AD
AD
DA
AD
AD
DA
DA
PGA
PGA
PGA
PGA
Linear Codec [Line Side]
Linear Codec [Acoustic Side]
Linear Codec [Acoustic Side]
Linear Codec [Line Side]
LINN
LINN
LGSX
AIN0P
AIN0P
AIN0N
AIN0N
AIN1N
AIN1N
AGSX1
AGSX1
AGSX0
AGSX0
AVFRO
AVFRO
LGSX
LVFRO
LVFRO
Not for Publication
Figure 1
AGND0,1
AGND0,1
DVDD0,1
DGND0,1
DVDD0,1
DGND0,1
AVDD
AVDD
REGOUT0, 1
&
&
Regulator
Regulator
Power Control
Power Control
MCU
MCU
Interface
Interface
EC / NC / SLP / ALC Control
EC / NC / SLP / ALC Control
AVREF
AVREF
REGOUT0, 1
VBG
VBG
PDN
PDN
DOUT
DOUT
DIN
DIN
EXCK
EXCK
DEN
DEN
MCUSEL
MCUSEL
GPOC7
GPOC7
GPOC6
GPOC6
GPOC5
GPOC5
GPOC4
GPOC4
GPOC3
GPOC3
GPOC2
GPOC2
GPOC1
GPOC1
GPOC0
GPOC0
RST
RST
GPIA7 (RPAD3)
GPIA7 (RPAD3)
GPIA6 (RPAD2)
GPIA6 (RPAD2)
GPIA5 (RPAD1)
GPIA5 (RPAD1)
GPIA4 (RPAD0)
GPIA4 (RPAD0)
GPIA3 (TPAD3)
GPIA3 (TPAD3)
GPIAGPIB GPOC
GPIAGPIB GPOC
GPIA2 (TPAD2)
GPIA2 (TPAD2)
GPIA1 (TPAD1)
GPIA1 (TPAD1)
GPIA0 (TPAD0)
GPIA0 (TPAD0)
GPIB7 (ECEN)
GPIB7 (ECEN)
GPIB6 (ECSEL)
GPIB6 (ECSEL)
GPIB5 (SLPTHR)
GPIB5 (SLPTHR)
GPIB4 (ALCTHR)
GPIB4 (ALCTHR)
GPIB3 (NCTHR)
GPIB3 (NCTHR)
GPIB2 (VFROSEL)
GPIB2 (VFROSEL)
GPIB1 (LINEEN)
GPIB1 (LINEEN)
GPIB0
GPIB0
AVREFEN
AVREFEN
AVREF
AVREF
2/41
PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
DE N
GPOC 0
GPOC 1
GPOC 2
GPOC 3
GPOC 4
GPOC 5
GPOC 6
GPOC 7
CLKSEL
RST
PD N
XO
MCK/XI
TST I1
TST I2
PCMO
PCMI
SYNC
BCLK
SYNCSEL
GPIB7 (ECEN)
GPIB6 (ECSEL)
GPIB5 (SLPTHR)
GPIB4 (ALCTHR )
GPIB3 (NCTH R)
GPIB2 (VFROSEL)
GPIB1 (
GPIB0
DVDD1
REGOUT1
DGND1
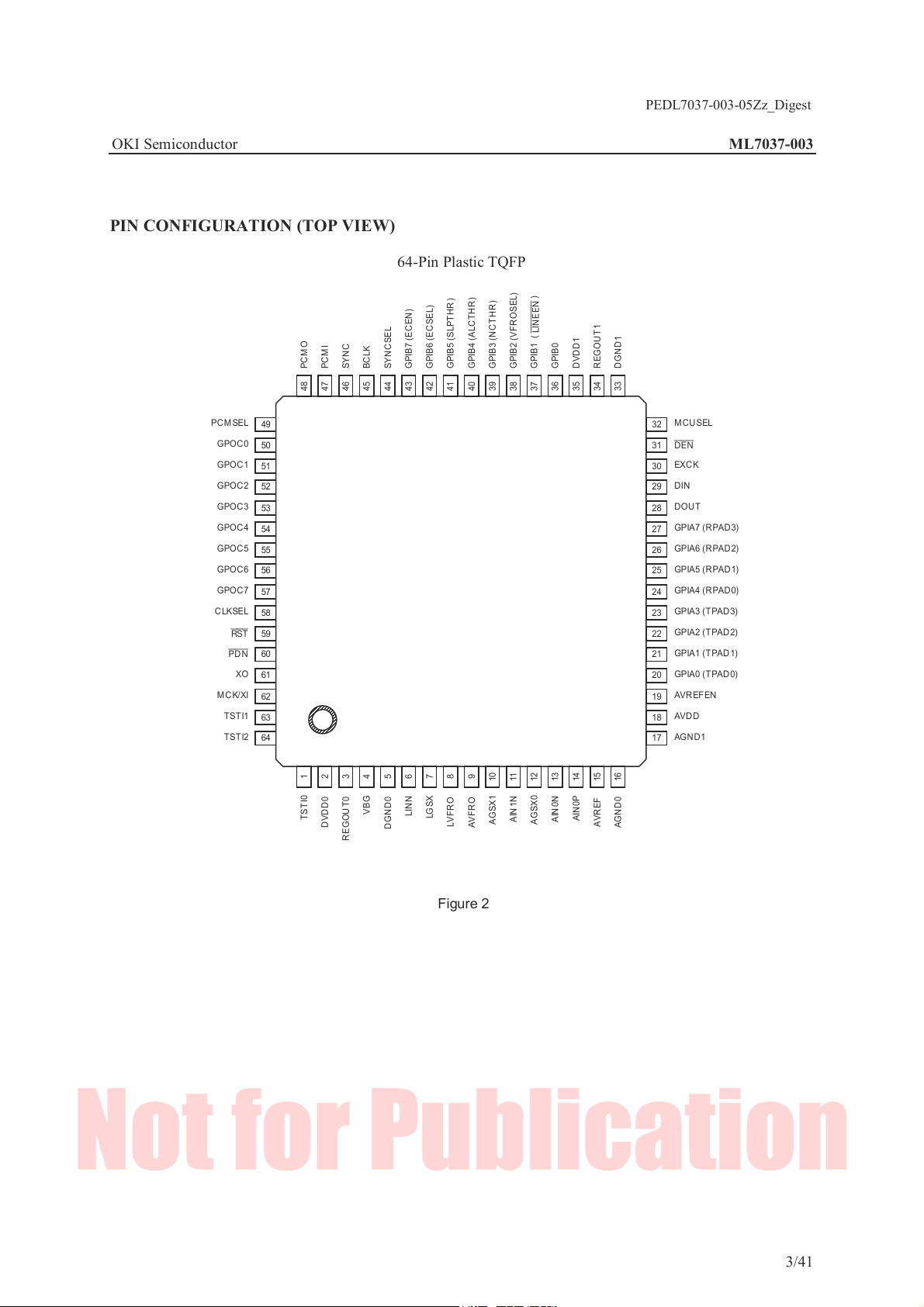
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
64-Pin Plastic TQFP
)
LINEEN
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
PCMSEL
MCU SEL
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
VBG
LINN
TST I0
DVDD 0
REGOUT0
LGSX
DG ND0
LVFRO
AIN1N
AGSX1
AVFRO
AIN0P
AIN0N
AGSX0
AVREF
32
31
EXCK
30
DIN
29
DOU T
28
GPIA7 (R PAD 3)
27
GPIA6 (R PAD 2)
26
GPIA5 (R PAD 1)
25
GPIA4 (R PAD 0)
24
GPIA3 (T PAD 3)
23
GPIA2 (T PAD 2)
22
GPIA1 (T PAD 1)
21
GPIA0 (T PAD 0)
20
AVREF EN
19
AVDD
18
AGND1
17
16
AGND0
Figure 2
Not for Publication
3/41
PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
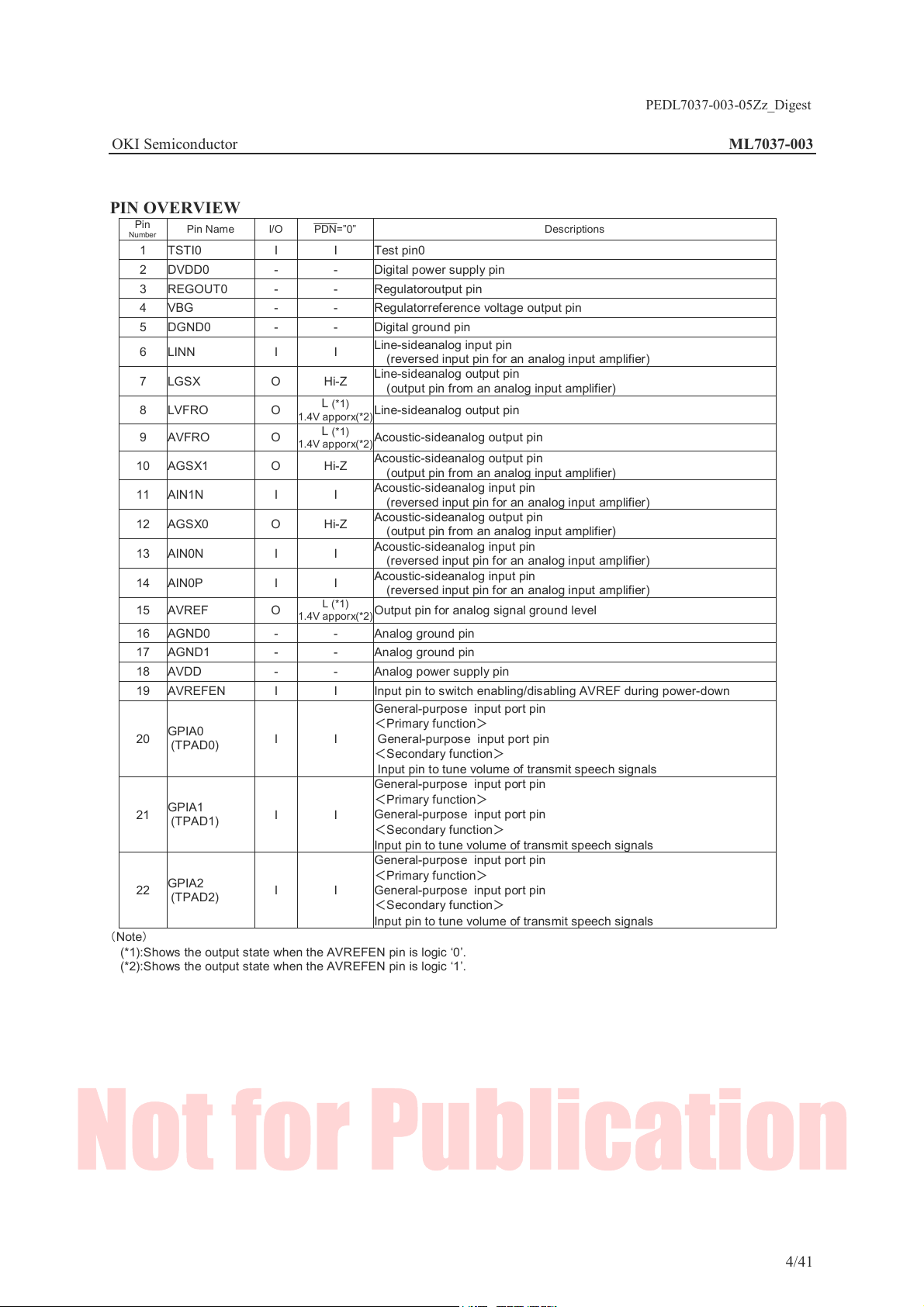
PIN OVERVIEW
Pin
Number
1 TSTI0 I I Test pin0
2 DVDD0 - - Digital power supply pin
3 REGOUT0 - - Regulatoroutput pin
4 VBG - - Regulatorreference voltage output pin
5 DGND0 - - Digital ground pin
6 LINN I I
7 LGSX O Hi-Z
8 LVFRO O
9 AVFRO O
10 AGSX1 O Hi-Z
11 AIN1N I I
12 AGSX0 O Hi-Z
13 AIN0N I I
14 AIN0P I I
15 AVREF O
16 AGND0 - - Analog ground pin
17 AGND1 - - Analog ground pin
18 AVDD - - Analog power supply pin
19 AVREFEN I I Input pin to switch enabling/dis abling AVREF during power-down
20
21
22
(Note)
(*1):Shows the output state when the AVREFEN pin is logic ‘0’.
(*2):Shows the output state when the AVREFEN pin is logic ‘1’.
Pin Name I/O
GPIA0
(TPAD0)
GPIA1
(TPAD1)
GPIA2
(TPAD2)
PDN=”0”
L (*1)
1.4V apporx(*2)
L (*1)
1.4V apporx(*2)
L (*1)
1.4V apporx(*2)
I I
I I
I I
Descriptions
Line-sideanalog input pin
(reversed input pin for an analog input amplifier)
Line-sideanalog output pin
(output pin from an analog input amplifier)
Line-sideanalog output pin
Acoustic-sideanalog output pin
Acoustic-sideanalog output pin
(output pin from an analog input amplifier)
Acoustic-sideanalog input pin
(reversed input pin f or an analog input amplifier)
Acoustic-sideanalog output pin
(output pin from an analog input amplifier)
Acoustic-sideanalog input pin
(reversed input pin f or an analog input amplifier)
Acoustic-sideanalog input pin
(reversed input pin f or an analog input amplifier)
Output pin for analog signal ground level
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to tune volume of transmit speech signals
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to tune volume of transmit speech signals
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to tune volume of transmit speech signals
Not for Publication
4/41
PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
DEN
side analog
rmal mode and through
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
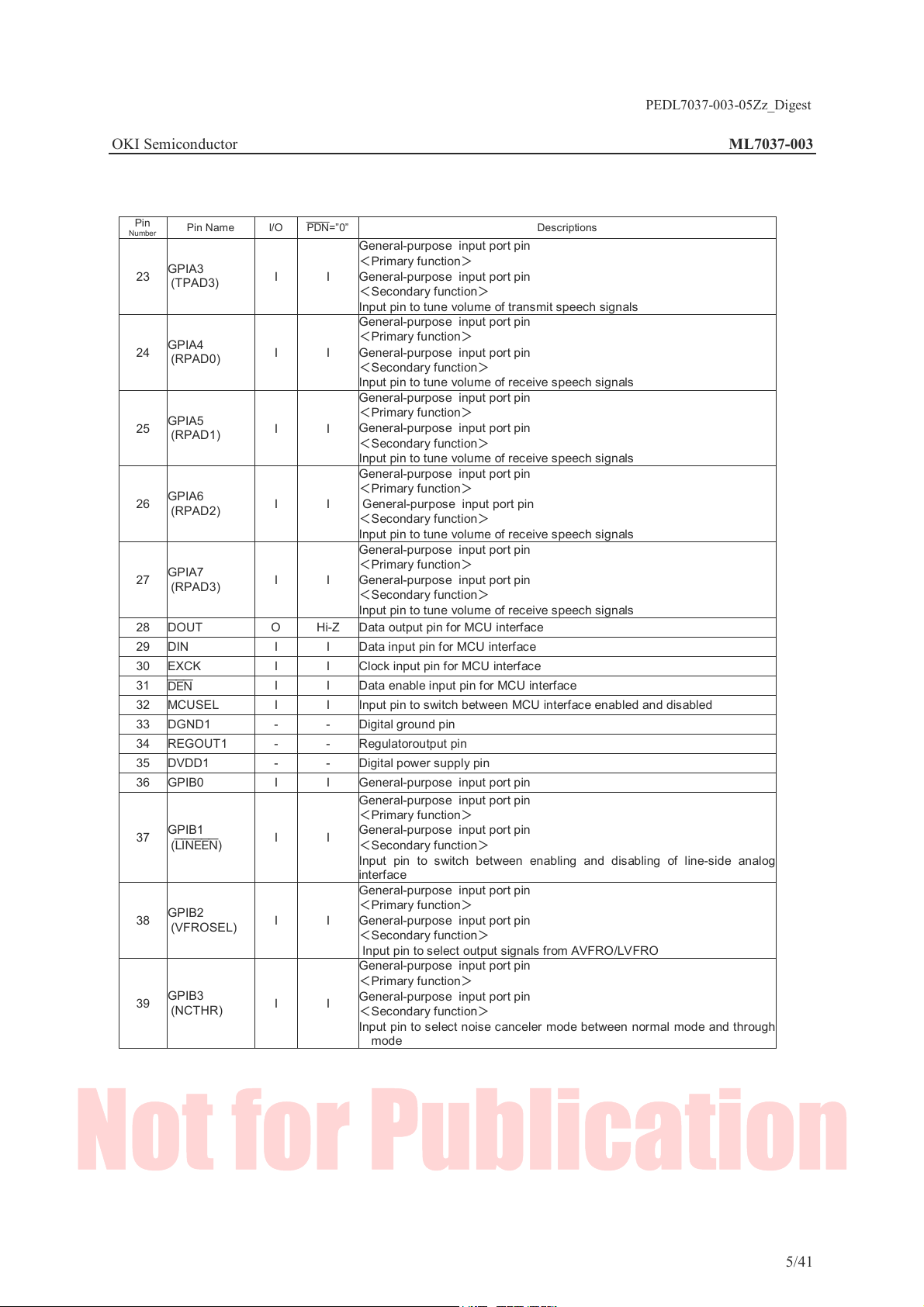
Pin
Number
23
24
25
26
27
28 DOUT O Hi-Z Data output pin for MCU interface
29 DIN I I Data input pin for MCU interface
30 EXCK I I Clock input pin for MCU interface
31
32 MCUSEL I I Input pin to switch between MCU interface enabled and disabled
33 DGND1 - - Digital ground pin
34 REGOUT1 - - Regulatoroutput pin
35 DVDD1 - - Digital power supply pin
36 GPIB0 I I General-purpose input port pin
37
38
39
Pin Name I/O
GPIA3
(TPAD3)
GPIA4
(RPAD0)
GPIA5
(RPAD1)
GPIA6
(RPAD2)
GPIA7
(RPAD3)
GPIB1
(
LINEEN)
GPIB2
(VFROSE L)
GPIB3
(NCTHR)
PDN=”0”
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
I I
I I
I I
I I
I I
I I Data enable input pin for MCU interface
I I
I I
I I
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to tune volume of transmit speech signals
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to tune volume of receive speech signals
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to tune volume of receive speech signals
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to tune volume of receive speech signals
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to tune volume of receive speech signals
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to switc h between enabling and disabling of line-
interface
General-purpos e input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to select output signals from AVFRO/LVFRO
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to select noise canceler mode between no
mode
Descriptions
Not for Publication
5/41
PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
Input pin to select echo canceler mode between single echo canceler mode
)
)
)
)
6bit
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
Pin
Number
40
41
42
43
44 SYNCSEL I I Input pin to select between long frame sync and short frame sync
45 BCLK I/O
46 SYNC I/O
47 PCMI I I line-side PCM data input pin
48 PCMO O Hi-Z line-side PCMdata output pin
49 PCMSEL I I
50 GPOC0 O L General-purpose output port pin
51 GPOC1 O L General-purpose output port pin
52 GPOC2 O L General-purpose output port pin
53 GPOC3 O L General-purpose output port pin
Pin Name I/O
GPIB4
(ALCTHR)
GPIB5
(SLPTHR)
GPIB6
(ECSEL)
GPIB7
(ECEN)
PDN=”0”
I I
I I
I I
I I
Descriptions
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to select ALC mode between normal mode and through mode
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to select slope filter mode between normal mode and through mode
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
and dual echo canceler mode
General-purpose input port pin
<Primary function>
General-purpose input port pin
<Secondary function>
Input pin to switch between disabling and enabling echo canceler
L (*1
Shift clock input pin for PCM interface
I (*2
L (*1
Sync clock input pin for PCM interface
I (*2
Input pin to select speech digital interface coding format between 1
Linear PCM and -law PCM
(Note)
(*1):Shows the output state when the CLKSEL-pin is logic ‘0’.
(*2):Shows the output state when the CLKSEL-pin is logic ‘1’.
Not for Publication
6/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
Input pin to select between clock slave mode and clock master mode for
RST
PDN
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
Pin
Number
54 GPOC4 O L General-purpose output port pin
55 GPOC5 O L General-purpose output port pin
56 GPOC6 O L General-purpose output port pin
57 GPOC7 O L General-purpose output port pin
58 CLKSEL I I
59
60
61 XO O H Ouput pin to connect a crystal unit for master clock
62 MCK/XI I I
63 TSTI1 I I Test pin1
64 TSTI2 I I Test pin2
Pin Name I/O
PDN=”0”
PCM interface
I I Reset pin
I I Power-down pin
Input pin to connect a crystal unit for master clock
Master clock input pin
Descriptions
Not for Publication
7/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
Buffer Amp
F
Gain= (R2/R 1) x ( R4/R 3)
1.3Vpp
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
PIN FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
AIN0N, AIN0P, AGSX0, AIN1N, AGSX1
These are the acoustic analog input and level tuning pins. The AIN0N pin and the AIN1N pin are connected to the
inverting input of the internal amp (AMP2、AMP1), and the AIN0P pin is connected to the non-inverting input of
the internal amp (AMP2). The AGSX0 pin and the AGSX1 pin are connected to the internal amp (AMP2、AMP1).
For the way to tune the level, refer to Figure 3 Analog Interface.
During power-down mode (
pin go to a high impedance state.
(Note) When the acoustic side LSI-internal amplifier (AMP2) is not used, connect the AIN0P pin and the
AVREF pin and short the AIN0N pin and the AGSX0 pin.
(Note) Please refer to the application circuit example when the acoustic side LSI-internal amplifier (AMP2) is
used as a single-end input.
VAGSX1,0 ≦ 1.3Vp p
10k ≦ R2 ≦ 510k
10k ≦ R4 ≦ 510k
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’), the AGSX0 pin and the AGSX1
R4
C2
R3
AGSX1
AIN1N
AGSX0
Gain-Max(AMP1)≦5 times (+13.97dB)
(AMP1)
A/D
C1
C1
10
C3
≦
VAVFRO
C4
Gain=R6/R5
10k ≦ R6 ≦ 510k
VLGSX ≦ 1.3Vpp
C4
VLVFRO ≦ 1.3Vpp
R2
R1
R1
R2
R5
R6
0.1F
AIN0N
AIN0P
AVREF
AVFRO
LGSX
LINN
LVFRO
(AMP2)
Gain-Max(AMP2)≦10 times(+20dB)
(AMP4)
(AMP3)
Gain-Max(AMP3)≦10 times(+20dB)
(AMP5)
AVREF
D/APGA
A/D
D/APGA
Figure 3 Analog Interface
Not for Publication
8/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
LINN, LGSX
These are the line analog input and level tuning pins. The LINN pin is connected to the inverting input of the
internal amp (AMP3) and the LGSX pin is connected to the output of the amp (AMP3). For level tuning, refer to
Figure 3 Analog Interface.
During power-down mode (
impedance state.
(Note) When the line side analog interface is not used, set the secondary function of the GPIB1 pin (
logic ‘1’ or set the
AVFRO, LVFRO
These are analog output pins respectively for acoustic-side and line-side. The AVFRO is connected to the output of
the internal amp (AMP4), and the LVFRO is connected to the output of the internal amp (AMP5).
The output state of the AVFRO pin and the LVFRO pin can be selected between speech signal output and the
AVREF level output (1.4V approx.) by the VFROSEL pin or by the AVFROSEL-bit [CR16-B1] and the
LVFROSEL-bit [CR16-B0]. When the concerned pin or the concerned bit is logic ‘1’, the AVFRO and/or the
LVFRO pin outputs speech signals; when the concerned pin and the concerned bit is logic ‘0’, the AVFRO pin
and/or the LVFRO pin outputs the AVREF level (1.4V approx.).
During power-down mode (
AVREFEN-bit [CR16-B7] are logic ‘0’, the AVFRO pin and the LVFRO pin go to a high impedance state; and, if
the AVREFEN pin or the AVREFEN-bit [CR16-B7] are logic ‘1’, the pins output 1.4V approx..
(Note) If the AVREFEN pin and the AVREFEN-bit [CR16-B7] are logic ‘0’, pop noises may occur on release
and execution of power-down. If the AVREFEN pin and the AVREFEN-bit [CR16-B7] need to be logic
‘0’ and still the pop noises have to be eliminated, it has to be fixed outside of this LSI.
To avoid the pop noises, set the AVREFEN pin or the AVREFEN-bit [CR16-B7] to logic ‘1’ and let the
AVREF and the analog output amps alive. Furthermore, the power-down should be released and executed
having the output state of the AVFRO pin and the LVFRO pin the AVREF level.
In concrete, the power-down should be released while keeping the VFROSEL pin and by the
AVFROSEL-bit [CR16-B1] and the LVFROSEL-bit [CR16-B0] to logic ‘0’, and then change the
VFROSEL pin or the AVFROSEL-bit [CR16-B1] and the LVFROSEL-bit [CR16-B0] to logic ‘1’.
And, the VFROSEL pin and the AVFROSEL-bit [CR16-B1] and the LVFROSEL-bit [CR16-B0] should
be changed to logic ‘0’ before the power-down execution.
Please note that the power supply current during the power-down would be I
the specification under the DC Characteristics to come in a later section.) if the AVREFEN pin or the
AVREFEN-bit [CR16-B7] are logic ‘1’.
AVREF
This is the output pin for the analog signal ground level. The output voltage is approximately 1.4 V.
Insert a 10 µF bypass capacitor (a tantalum capacitor [recommendation] or an aluminum electrolytic capacitor) and
a 0.1 µF capacitor (laminating ceramic type) in parallel between this pin and the AGND0 pin.
During power-down mode (
AVREFEN-bit [CR16-B7] to be logic ‘0’, the AVREF pin outputs 0.0V.
During power-down mode (
AVREFEN-bit [CR16-B7] to be logic ‘1’, the AVREF pin outputs 1.4V approx..
(Note) If you make use of the AVREF pin output externally in your system, it must be via a buffer amp.
AVREFEN
This is to select disabling and enabling the AVREF output during power-down mode (
SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’).
When this is logic ‘0’, the AVREF pin is disabled (power-down state).
When this is logic ‘1’, the AVREF pin is enabled, and the outputs of the AVREF, the AVFRO and the LVFRO
become 1.4V approx..
This pin control is valid only during power-down.
Not for Publication
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’), the LGSX pin goes to a high
LINEEN) to
LINEEN-bit [CR0-B5] to ‘1’, and short the LINN pin and the LGSX pin.
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’), if the AVREFEN pin and the
compliant (Please refer to
SS2
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’) with the AVREFEN pin and the
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’) with the AVREFEN pin or the
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or
9/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
C2
Floating
12.288MHz
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
GPIB1 (
This is a general-purpose input port pin.
This also works as a power-down control over the line-side analog interface as the secondary function.
When this pin is logic ‘0’, the line-side analog interface is enabled; and, when this pin is logic ‘1’, the line-side
analog interface is powered-down (excluding the LVFRO output amp).
During power-down, the LVFRO outputs 1.4V approx..
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘1’, this pin is automatically assigned with its secondary function.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘0’, this pin’s function assignment follows the state of GPFB1-bit [GPCR1-B1].
(Note) The change of the input state to this pin is detected at the rising edge of the SYNC clock so that the change
(Note) In an application where the line-side codec is never enabled, the LINN pin and the LGSX pin must be
(Note) The change of the enabled/disabled state of the line-side codec must be made during power-down state
GPIB2 (VFROSEL)
This is a general-purpose input port pin.
This also works as the output state control over the AVFRO pin and the LVFRO pin as the secondary function.
When this pin is logic ‘0’, they output the AVREF level (1.4V apporx.); and, when this pin is logic ‘1’, they output
speech signals.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘1’, this pin is automatically assigned with its secondary function.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘0’, this pin’s function assignment follows the state of GPFB2-bit [GPCR1-B2].
(Note) When, during a call, the output state is changed or the reset is made, minor noises could happen due to an
(Note) The power-down execution and its release are recommended to be made when the AVFRO pin and the
(Note) When this pin is not used, set this pin to logic ‘0’.
MCK/X1, XO
These are pins to connect a crystal unit, and the former is used as the master clock input pin as well. The clock
frequency is 12.288 MHz.
During power-down mode (
crystal unit is stopped.
After the release of the power-down, the connected crystal unit starts being oscillated, but the master clocks start
being utilized within this LSI only after the steady oscillation waiting time (28ms approx.).
Refer to Figure 4 for an example application with an external clock and that with a crystal unit.
LINEEN)
of the input state to this pin less than 250 s may not be reflected as the LSI behavior.
shorted.
(
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’) or during initial mode.
interruption at an arbitrary point in a sequence of PCM codes so that this output state selection and the
reset are recommended to be made before a call as long as it is application-wise allowed.
LVFRO pin are selected to output the AVREF level.
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’), oscillation of the connected
MCK/XI XO
MCK/XI
C1
X'tal
XO
R
X’tal
(12.288MHz)
HC-49/U-S 1M 10pF 10pF
R C1 C2
ex) External Clock ex) Crystal Unit
Figure 4 Examples of external clock and crystal unit as a master clock
(Note) When a crystal unit is used, connect the unit and a feedback resistor of 1M (R) between the MCK/XI
and the XO. The appropriate values of capacitors (C1, C2) to be connected between the MCK/XI and
GND and between the XO and GND are influenced by load capacitance of a crystal unit and PCB patterns
so that they are recommended to be determined by asking a crystal unit vendor for a matching test.
Not for Publication
10/41
PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
SYNC
This is the 8 kHz sync clcok I/O pin for PCM interface. When the internal clock mode is selected by the CLKSEL
pin = logic ‘0’, this pin outputs 8kHz sync clocks synchronizing with the BCLK. When the external clock mode is
selected by the CLKSEL pin = logic ‘1’, input 8kHz clocks to this pin in synchronization with the BCLK.
When the SYNCSEL pin is logic ‘0’, this pin outputs/expects to have sync clocks in a long frame sync timing;
whereas, when the SYNCSEL pin is logic ‘1’, this pin outputs/expects to have sync clocks in a short frame sync
timing.
BCLK
This is the shift clock I/O pin for PCM interface. When the internal clock mode is selected by the CLKSEL pin =
logic ‘0’, this pin outputs 64kHz in µ-law PCM mode or 128kHz in 16-bit linear PCM mode. When the external
clock mode is selected by the CLKSEL pin = logic ‘1’, input shift clocks to this pin in synchronization with the
SYNC. The input frequency must be between 64 kHz and 2048 kHz in µ-law PCM mode and 128 kHz and 2048
kHz in 16-bit linear PCM mode.
CLKSEL
This pin selects internal or external clock modes for PCM interface.
A logic ‘0’ selects the internal clock mode where the SYNC pin and the BCLK pin output clocks so that this LSI
could works as a clock master device in your system.
A logic ‘1’ selects the external clock mode where this LSI needs the SYNC and the BCLK externally so that this
LSI could works as a clock slave device in your system.
If PCM digital interface is not used, set this pin to a logic ‘0’ to select internal clock mode.
(Note) The change of the input state of this pin must be made during power-down state (
SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’) or during initial mode.
SYNCSEL
This is the frame sync timing selection pin for PCM interface.
A logic “0” selects long frame sync timing, and a logic “1” selects short frame sync timing.
Refer Figure 5 to Figure8 for the timing.
(Note) The change of the input state of this pin must be made during power-down state (
SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’) or during initial mode.
PCMSEL
This is the coding format selection pin for PCM interface for the PCMO-pin output and the PCMI-pin input signal.
A logic ‘0’ selects 16-bit linear PCM (2’s complement) coding format, and a logic ‘1’ selects µ-law PCM coding
format.
The full scale table for both formats are shown below;
16bit Linear PCM (2’s complement) Full Scale Table
Level MSB
+ Full Scale 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
+1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
- Full Scale 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-law PCM Full Scale Table
Level MSB
+ Full Scale 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
+0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
-0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
- Full Scale 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
(Note) If PCM interface is not used, set this pin to a logic ‘0’.
(Note) The change of the input state of this pin must be made during power-down state (
Not for Publication
SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’) or during initial mode.
LSB
LSB
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or
11/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
PCMI
This is the receive PCM data input pin on the line-side. This input data is shifted at the falling edge of the BCLK.
The PCM coding format can be selected between 16-bit linear PCM (2’s complement) coding format and µ-law
PCM coding format with the PCMSEL pin or the PCMSEL-bit [CR0-B4].
The PCM frame sync timing can be selected between a long frame sync and a short frame sync with the SYNCSEL
pin.
Refer Figure 5 to Figure8 for the timing.
(Note) If this pin is not used, set this pin to a logic ‘0’.
(Note) The change of the input state of this pin must be made during power-down state (
SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’) or during initial mode.
PCMO
This is the receive PCM data output pin on the line-side. This output data is shifted at the rising edge of the BCLK.
During power-down mode (
PCM data bits are not being output, this pin goes to a high impedance state.
The PCM coding format can be selected between 16-bit linear PCM (2’s complement) coding format and -law
PCM coding format with the PCMSEL pin or the PCMSEL-bit [CR0-B4].
The PCM frame sync timing can be selected between a long frame sync and a short frame sync with the SYNCSEL
pin.
Refer Figure 5 to Figure8 for the timing.
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’) and initial mode or while effective
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or
Not for Publication
12/41
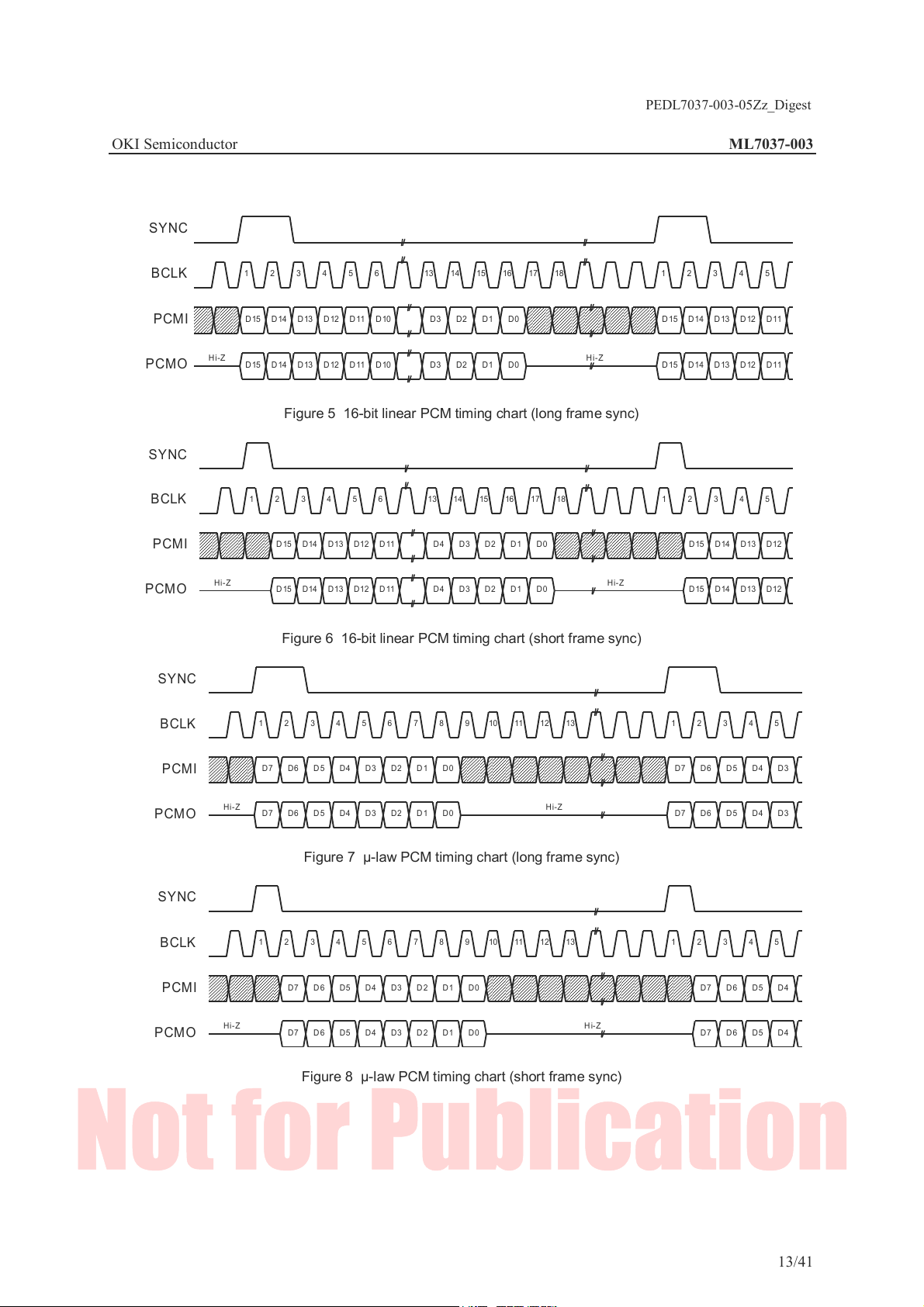
PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
BCLK
PCMI
BCLK
BCLK
BCLK
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
SYNC
1 2 3 4 5 6 13 14 15 16 17 18 1 2 3 4 5
D10
D10
PCMO
D15 D14 D 13 D12 D 11 D3 D 2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D 13 D12 D 11
Hi -Z Hi -Z
D15 D14 D 13 D12 D 11 D3 D 2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D 13 D12 D 11
Figure 5 16-bit linear PCM timing chart (long frame sync)
SYNC
1 2 3 4 5 6 13 14 15 16 17 18 1 2 3 4 5
PCMI
PCMO
Hi -Z Hi -Z
D15 D14 D13 D12 D 11 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D13 D12D4
D15 D14 D13 D12 D 11 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D13 D12D4
Figure 6 16-bit linear PCM timing chart (short frame sync)
SYNC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 513
PCMI
D7 D6 D5 D 3 D2 D 0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3D 1D4
Hi -Z Hi -Z
PCMO
D7 D6 D5 D 3 D2 D 0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3D 1D4
Figure 7 µ-law PCM timing chart (long frame sync)
SYNC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 513
PCMI
PCMO
Hi-Z Hi-Z
D7 D6 D5 D3 D2 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4D1D4
D7 D6 D5 D3 D2 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4D1D4
Figure 8 µ-law PCM timing chart (short frame sync)
Not for Publication
13/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
GPIB3 (NCTHR)
This is a general-purpose input port pin.
This also works as a through-mode control pin over the noise canceller as the secondary function.
A logic ‘0’ enables the noise canceller, and a logic ‘1’ disables the noise canceller and the speech data by-passes
the noise canceller.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘1’, this pin is automatically assigned with its secondary function.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘0’, this pin’s function assignment follows the state of GPFB3-bit [GPCR1-B3].
(Note) The change of the input state to this pin is detected at the rising edge of the SYNC clock so that the change
of the input state to this pin less than 250 s may not be reflected as the LSI behavior.
(Note) For 24ms approx. after the state change from a noise canceller enabling mode to a through-mode, the
speech signals may not be ordinarily processed and be got mute or attenuated. The state change, if needed,
is recommended to be made before a call.
(Note) If this pin is not used, set this pin to a logic ‘0’.
GPIB4 (ALCTHR)
This is a general-purpose input port pin.
This also works as a through-mode control pin over the automatic level controller (ALC) as the secondary
function.
A logic ‘0’ enables the ALC, and a logic ‘1’ disables the ALC and the speech data by-passes the ALC.
The ALC is a function to mainly aim to absorb the difference in speech volume with handsets to connect to a
hands-free. For the functional details, please refer to descriptions under the RALCTHR-bit [CR2-B4].
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘1’, this pin is automatically assigned with its secondary function.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘0’, this pin’s function assignment follows the state of GPFB4-bit [GPCR1-B4].
(Note) The change of the input state to this pin is detected at the rising edge of the SYNC clock so that the change
of the input state to this pin less than 250 s may not be reflected as the LSI behavior.
(Note) If this pin is not used, set this pin to a logic ‘0’.
GPIB5 (SLPTHR)
This is a general-purpose input port pin.
This also works as a through-mode control pin over the slope filter as the secondary function.
A logic ‘0’ enables the slope filter, and a logic ‘1’ disables the slope filter and the speech data by-passes the slope
filter.
The slope filter has frequency characteristics to suppress low frequency range and gain high frequency range so
that it helps to relax near-end ambient noises usually dominant in low frequency range and to emphasize speech
consonants mostly dominant in high frequency range. For the functional details, please refer to the slope filter
characteristics under Reference Data.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘1’, this pin is automatically assigned with its secondary function.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘0’, this pin’s function assignment follows the state of GPFB5-bit [GPCR1-B5].
(Note) The change of the input state to this pin is detected at the rising edge of the SYNC clock so that the change
of the input state to this pin less than 250 s may not be reflected as the LSI behavior.
(Note) If this pin is not used, set this pin to a logic ‘0’.
GPIB6 (ECSEL)
This is a general-purpose input port pin.
This also works as an echo canceller selection as the secondary function.
A logic ‘0’ selects single echo canceller mode (enables only acoustic echo canceller), and a logic ‘1’ selects dual
echo canceller mode (enables both of acoustic and line echo cancellers).
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘1’, this pin is automatically assigned with its secondary function.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘0’, this pin’s function assignment follows the state of GPFB6-bit [GPCR1-B6].
(Note) The change of the input state to this pin is detected at the rising edge of the SYNC clock so that the change
of the input state to this pin less than 250 s may not be reflected as the LSI behavior.
(Note) The single echo canceller mode should be selected in an environment where no line echoes exist.
(Note) The change of the input state of this pin must be made during power-down state (
Not for Publication
(Note) If this pin is not used, set this pin to a logic ‘0’.
SPDN-bit [CR0-B7] = ‘1’) or during initial mode.
PDN pin = logic ‘0’ or
14/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
GPIB7 (ECEN)
This is a general-purpose input port pin.
This also works as an enabling/disabling selection for echo cancellers as the secondary function.
A logic ‘0’ disables echo cancellers and their auxiliary functions (ATTrA/ATTrL, ASIPAD/LPAL,
ASOPAD/LSOPAD, ATTsA/ATTrA, Center Clip), and a logic ‘1’ enables them.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘1’, this pin is automatically assigned with its secondary function.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘0’, this pin’s function assignment follows the state of GPFB7-bit [GPCR1-B7].
(Note) The change of the input state to this pin is detected at the rising edge of the SYNC clock so that the change
of the input state to this pin less than 250 s may not be reflected as the LSI behavior.
(Note) If this pin is not used, set this pin to a logic ‘0’.
GPIA0 (TPAD0), GPIA1 (TPAD1), GPIA2 (TPAD2), GPIA3 (TPAD3)
These are general-purpose input port pins.
These also work as transmit-side volume control as the secondary function.
For the setting, please refer to Table 1.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘1’, these pins are automatically assigned with their secondary function.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘0’, these pins’ function assignment follows the state of GPFA3-0-bits
[GPCR0-B3,2,1,0].
(Note) The change of the input state these pins is detected at the rising edge of the SYNC clock so that the change
of the input state to this pin less than 250 s may not be reflected as the LSI behavior.
(Note) If these pins are not used, set them to a logic ‘0’.
GPIA4(RPAD0), GPIA5(RPAD1), GPIA6(RPAD2), GPIA7(RPAD3)
These are general-purpose input port pins.
These also work as receive-side volume control as the secondary function.
For the setting, please refer to Table 1.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘1’, these pins are automatically assigned with their secondary function.
When the MCUSEL pin is logic ‘0’, these pins’ function assignment follows the state of GPFA7-4-bits
[GPCR0-B7,6,5,4].
(Note) The change of the input state to these pins is detected at the rising edge of the SYNC clock so that the
change of the input state to this pin less than 250 s may not be reflected as the LSI behavior.
(Note) If these pins are not used, set them to a logic ‘0’.
Table 1 Receive-/Transmit-Side Volume Control
GPIA7
(RPAD3)
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 +21dB
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 +18dB
0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 +15dB
0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 +12dB
0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 +9dB
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 +6dB
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 +3dB
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0dB
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 -3dB
1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 -6dB
1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 -9dB
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 -12dB
1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 -15dB
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 -18dB
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 -21dB
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 MUTE
GPIA6
(RPAD2)
GPIA5
(RPAD1)
GPIA4
(RPAD0)
GPIA3
(TPAD3)
GPIA2
(TPAD2)
GPIA1
(TPAD1)
GPIA0
(TPAD0)
Level
Not for Publication
15/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
MCUSEL
This pin selects whether the microcontroller interface is used or unused.
When the microcontroller interface is used, set this pin to a logic ‘0’.
When the microcontroller interface is not used, set this pin to a logic “1”.
A logic ‘1’ with this pin automatically determines general-purpose input port pins to work as their secondary
functions.
This pin is OR’ed with OPE_STAT-bit [CR0-B0].
Refer to NOTE ON USE.
DEN, EXCK, DIN, DOUT
These are serial control ports for the microcontroller interface.
This LSI has 32 bytes control registers, and the data read and write between the registers and the microcontroller
are made via these pins.
The
DEN pin is a data read/write enabling signal input pin, the EXCK pin is a clock signal input pin for data
shifting, the DIN pin is an address and data input pin, the DOUT pin is a data output pin. If the mirrocontroller
interface is not used, set the
pin to logic ‘1’.
Figure 9-12 shows the input/output timing.
DEN pin to a logic “1”, the EXCK pin and DIN pins to a logic “0”, and the MCUSEL
Not for Publication
16/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
DEN
DOUT
DEN
DOUT
DEN
DOUT
DEN
DOUT
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
EXCK
DIN
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4
W A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 W A6 A5 A4
Hi- Z
Figure 9 MCU Interface Input/Output Timing (Data Write with 8-bit MCU)
EXCK
DIN
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4
W A6 A5 A4 A3 A 2 A1 A0 B7 B6 B5 B 4 B3 B2 B1 B0 W A6 A5 A4
Hi -Z
Figure 10 MCU Interface Input/Output Timing (Data Write with 16-bit MCU)
EXCK
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4
DIN
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B 1 B0
R A6 A5 A4R A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A 1 A0
Hi -ZHi -Z
Figure 11 MCU Interface Input/Output Timing (Data Read with 8-bit MCU)
EXCK
DIN
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4
R A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
R A6 A5 A4
Hi-ZH i-Z
Figure 12 MCU Interface Input/Output Timing (Data Read with 16-bit MCU)
Not for Publication
17/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
GPIB0
This is a general-purpose input port pin.
(Note) If this pin is not used, set this pin to a logic ‘0’.
GPOC0, GPOC1, GPOC2, GPOC3, GPOC4, GPOC5, GPOC6, GPOC7
These are general-purpose output port pins.
(Note) If these pins are not used, leave these pins floating.
DVDD0, DVDD1, AVDD
These are power supply pins. The DVDD0 and the DVDD1 are connected to digital circuits and the AVDD is
connected to analog circuits in this LSI via the built-in regulator.
Connect them common in the shortest distance, and insert a 10 µF bypass capacitor (a tantalum capacitor
[recommendation] or an aluminum electrolytic capacitor) and a 0.1 µF capacitor (laminating ceramic type) in
parallel between these pins and the DGND0, 1 pins and the AGND0, 1 pins respectively.
DGND0, DGND1, AGND0, AGND1
These are ground pins. The DGND0 pin and the DGND1 pin are connected to the ground of digital circuits in this
LSI. The AGND0 pin and the AGND1 pin are connected to the ground of analog circuits in this LSI. Connect them
common in the shortest distance
REGOUT0, REGOUT 1
These are the built-in regulator output pins (2.6V approx.).
Insert a 10 µF capacitor (a tantalum capacitor [recommendation] or an aluminum electrolytic capacitor) and a 0.1
µF capacitor (laminating ceramic type) in parallel between the REGOUT0 pin and the DGND0 pin.
Insert a 0.1 µF capacitor (laminating ceramic type) in parallel between the REGOUT1 pin and the DGND1 pin.
VBG
This is an output pin for a reference voltage of the built-in regulator (1.2V approx.).
Insert a 150 pF (approx.) laminating ceramic capacitor between the this pin and the DGND0.
PDN
This is the power-down reset control input pin.
A logic ‘0’ executes the power-down reset.
When a logic ‘1’ is input to this pin, this LSI is in a normal operation.
This execution also initializes all of this LSI including the control registers, the internal data memories, the filter
coefficients of the echo cancellers and those of the noise cancellers.
(Note) The negative logic of this pin is ORed with the SPDN-bit [CR0-B7].
(Note) To avoid unstable operations, right after the power-up, execute the power-down rest with this pin (not
with the SPDN-bit [CR0-B7]). The master clock input to the XI pin and the REGOUT output higher than
90% of the normal state are prerequisite to secure the power-down reset.
(Note) When an ORed logic of the AVREFEN pin and the AVREFEN-bit [CR16-B7] are logic ‘1’, the AVREF
and analog output amps keep powered up even during the power-down state.
RST
This is an input pin to initialize the filter coefficients of the echo cancellers and the noise canceller and the ALC
acquired gain.
A logic ‘0’ executes the initialization. For a normal operation, give this pin a logic ‘1’.
During the reset state, no speech signals are output. Control registers are preserved.
Execute the initialization in cases where the echo path changes (due to line switching during a telephone
conversation, etc.), or for another call.
(Note) The negative logic of this pin is ORed with the RST-bit [CR0-B6].
(Note) The change of the input state to these pins is detected at the rising edge of the SYNC clock so that the
change of the input state to this pin less than 250 s may not be reflected as the LSI behavior.
(Note) The execution of this reset during a call may cause minor noises due to interruption at an arbitrary point in
Not for Publication
a sequence of PCM codes so that an execution of the reset is recommended to be made in a silent state.
18/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
TSTI0, TSTI1, TSTI2
These are LSI manufacturer’s test input pins. Set these pins to a logic “0”.
Not for Publication
19/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Parameter Symbol
Analog power supply voltage AVDD — –0.3 to +4.6 V
Digital power supply voltage DVDD — –0.3 to +4.6 V
V
Analog pins –0.3 to AVDD+0.3 V
Input voltage
Short-circuit output current IOS — –20 to +20 mA
Power dissipation PD Ta = 85 °C, per package
Storage Temperature T
AIN
V
Digital pins –0.3 to DVDD+0.3 V
DIN
— –65 to +150 °C
STG
Condition Rating Unit
350 mW
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITION (1)
Parameter Symbol
Analog power supply voltage (*1) AVDD AVDD 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
Digital power supply voltage (*1) DVDD DVDD0, DVDD1 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
Operating temperature Ta — -40 — 85 °C
V
MCK/XI
IH1
High-level input voltage
V
Normal digital pins
IH2
V
MCK/XI 0.0 —
IL1
Low-level input voltage
V
Normal digital pins
IL2
Digital input rise time tIR Digital pins - 2 20 ns
Digital input fall time tIF Digital pins - 2 20 ns
Master clock frequency f
Master Clock Duty Ratio d
Note
*1 Turn on and off the analog power supply and digital power supply simultaneously, or turn on digital power supply
prior to analog power supply and turn off analog power supply prior to digital power supply.
MCK/XI
MCK
MCK/XI 40 50 60 %
MCK
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
DVDD x
0.75
DVDD x
0.75
0.0 —
12.2867712
(-0.01%)
—
—
12.288
DVDD +
0.3
DVDD +
0.3
DVDD x
0.19
DVDD x
0.19
12.2892288
(+0.01%)
V
V
V
V
MHz
Not for Publication
20/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITION (2)
Parameter Symbol Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
f
BCLK1
Bit clock frequency
f
BCLK2
Bit clock duty ratio d
Synchronous Signal Frequency f
Synchronous Signal Width fWS SYNC (*1) 1BCLK — 100 µs
Setting Time
Digital output load resistance CDL Digital pins — — 50 pF
Bypass capacitor for AVREF C
Bypass capacitor for VBG C
Bypass capacitor for REGOUT
Note
*1 In external clock mode (CLKSEL = logic “1’)
BCLK (*1) 40 50 60 %
BCLK
SYNC (*1)
SYNC
tBS BCLK to SYNC (*1) 100 — — ns Transmit/Receive Sync Signal
t
SYNC to BCLK (*1) 100 — —- ns
SB
AVREF - AGND0 — 10+0.1 — µF
AVREF
VBG-DGND0 — 150 — pF
VBG
C
C
REGOUT0-DGND0 — 10+0.1
REGOUT1
REGOUT1-DGND1 — 0.1 — µF
REGOUT2
BCLK (*1)
µ-law PCM
BCLK (*1)
16bit Linear PCM
64 —- 2048 kHz
128 — 2048 KHz
7.992
(-0.1%)
8.0
8.008
(+0.1%)
— µF
kHz
Not for Publication
21/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DC Characteristics
DVDD0,1=3.00V to 3.60V, AVDD=3.00V to 3.60V, DGND0,1=0.0V, AGND0,1=0.0V, T a=-40°C to +85°C (otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol
I
SS1
I
SS2
Power supply current
I
DD1
V
V
I
I
V
V
I
IH1
I
IL1
OZH
OZL
OH1
OH2
OL1
OL2
Digital input pin input leak
current
Digital I/O pin input leak current
High-level output voltage
Low-level output voltage
Input capacitance CIN Input pins, I/O pins — 6.0 — pF
PDN=”0”, AVREFEN=”0”,
PDN
AVDD=DVDD0,1=3.30V,
VIN=DVDD — 0.02 10 µA
VIN=0.0V -10 -0.02 — µA
VIN=DVDD — 0.02 10 µA
VIN=0.0V -10 -0.02 — µA
Analog Interface
DVDD0,1=3.00V to 3.60V, AVDD=3.00V to 3.60V, DGND0,1=0.0V, AGND0,1=0.0V, Ta=-40°C to +85°C (otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol
Input resistance RIN Analog input pins (*2) 10 — —
Output load resistance
Output load capacitance CL Analog output pins (*3) — — 50 pF
Offset voltage VOF Analog output pins (*3) -40 — 40 mV
Output voltage level (*1) VO
Note
*1 -7.7dBm(600)=0dBm0, +3dBm0=1.3Vpp
*2 Analog input pins (AIN0P, AIN0N, AIN1N, LINN)
*3 Analog output pins (AGSX0, AGSX1, LGSX, AVFRO, LVFRO)
RL1 AGSX0, AGSX1, LGSX 10 — —
R
AVFRO, LVFRO 2 — —
L2
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Stand-by state (1)
— 100 500 µA
AVDD=DVDD0,1=3.30V
Stand-by state (2)
=”0”, AVREFEN=”1”,
AVDD=DVDD0,1=3.30V
Operating state
MCK/XI, XO 12.288MHz
crystal connected
Inpu signal : none
T
=25°C
a
Digital output pins
Digital I/O pins
I
=4.0mA
OH
XO pin
I
=0.5mA
OH
Digital output pins
Digital I/O pins
I
=-4.0mA
OL
XO pin
I
=-0.5mA
OL
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
LVFRO, AVFRO
RL=10k, Input=+3dBm0
— 3.5 7.0 mA
— 50 60 mA
0.78 x
DVDD
0.78 x
DVDD
— — 0.4 V
— — 0.4 V
1.158 1.3 1.458 V
— — V
— — V
M
k
k
PP
Not for Publication
22/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
Operation
PDN
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
PDN, XO, AVREF Timing
DVDD0,1=3.00V to 3.60V, AVDD=3.00V to 3.60V, DGND0,1=0.0V, AGND0,1=0.0V, T a=-40°C to +85°C (otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol
AVDD supply start delay time t
DVDD supply cease delay time t
Power-down reset start latency t
Power-dwon reset signal pulse
width
Power-down reset release latency t
Oscillation activation time t
AVDD 0 — — ns
AVDDS
DVDD0,1 0 — — ns
DVDDE
— — 100 ns
RSTS
t
1.0 — — µs
RSTW
RSTE
crystal unit (*1) — — 28 ms
SXO
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
PDN
— — 250 ms
Note
*1 Crystal unit (HC-49/U-S), R=1M, C1=C2=10pF
Timing Chart (
PDN, XO, AVREF timing)
DVDD0,1
AVDD
REGOUT0,1
AVREF
Internal
XO
t
AVDDS
>=90%
Power-ON ( AVDD)
Power-ON (DVDD1,0)
t
t
RSTS
RSTW
t
SXO
t
RSTE
Power
down
Figure 13
Initial
mode
Normal Operation
PDN, XO, AVREF Timing
t
DVDDE
t
RSTS
Power
down
Power-OFF (AVDD)
Power-OFF (DVDD1,0)
VDD
0V
VDD
0V
REGOUT
0V
50% VDD
AVREF
0V
50% VDD
Not for Publication
23/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
Co ntrol inpu t pi ns/
ports (*1)
DEN
EXCK
DOUT
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
Digital Interface (Pin control, general port timing)
DVDD0,1=3.00V to 3.60V, AVDD=3.00V to 3.60V, DGND0,1=0.0V, AGND0,1=0.0V, Ta=-40°C to +85°C (otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol
Pin control latency (Low to High) t
Pin control pulse width t
Pin control latency (High to Low) t
General purpose output port
output delay time
General output port hold time t
— — 250 µs
PARD
250 — — µs
PARW
PARH
t
— — 100 ns
GPOD
GPOH
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
*1
— — 250 µs
*2
— — 100 ns
Note
*1 GPIA7-4 (RPAD3-0), GPIA3-0 (TPAD3-0), GPIB7 (ECEN), GPIB6 (ECSEL), GPIB5 (SLPTHR), GPIB4
(ALCTHR), GPIB3 (NCTHR), GPIB2 (VFROSEL), GPIB1 (
LINEEN), GPIB0, RST, PCMSEL, CLKSEL
*2 GPOC7-0
Timing Chart (Pin Control, General Ports)
General purpose input
Internal process
(Contr ol pi n state r eflection)
t
PA RD
t
PA RW
In ter n al Pr oce ss
t
PA RH
General output ports
DIN
(*2)
Addres s Data
W
Hi-Z
t
GPOD
Addres s
R
Data
Gen eal Pu rpose Outpu t P or t Pin s
Address Data
W
Hi-Z
Figure 14 Control Input Pin and General Purpose Output Port Pin Timing
t
GPOH
Not for Publication
24/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
BCLK
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
PCM Interface
DVDD0,1=3.00V to 3.60V, AVDD=3.00V to 3.60V, DGND0,1=0.0V, AGND0,1=0.0V, Ta=-40°C to +85°C (otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol
Bit clock frequency
Bit clock duty ratio d
Sync signal frequency f
f
µ-law PCM mode (*1, *2, *3) 63.36 64 64.64 kHz
BCLK1
f
BCLK2
BCLK
SYNC
16bit Linear PCM mode
(*1, *2, *3)
(*1, *2, *3) 40 50 60 %
(*1, *2, *3) 7.92 8.0 8.08 kHz
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
126.72
128 129.28 kHz
µ-law PCM mode (*1, *2, *3)
d
SYNC1
Long frame sync mode
(*1, *2, *3)
24.85 25 25.15 %
16bit Linear PCM mode
d
Sync signal duty ratio
SYNC2
d
SYNC3
Long frame sync mode
(*1, *2, *3)
µ-law PCM mode (*1, *2, *3)
Short frame sync mode
(*1, *2, *3)
12.35 12.5 12.65 %
12.35 12.5 12.65 %
16bit Linear PCM mode
d
Transmit/Receive Sync
signal timing
SYNC4
tSB
t
BS
Short frame sync mode
(*1, *2, *3)
SYNC to BCLK
(*3)
BCLK to SYNC
(*3)
6.10 6.25 6.40 %
100 — — ns
100 — — ns
Input setup time tDS — 100 — — ns
Input hold time tDH — 100 — — ns
t
CDL=50pF — — 100 ns
Digital output delay time
Digital output hold time
SDX
t
CDL=50pF — — 100 ns
XD1
t
CDL=50pF — — 100 ns
XD2
t
CDL=50pF — — 100 ns
XD3
Note
*1 C
=20pF
DL
*2 MCK/XI=12.288MHz
*3 In internal clock mode (CLKSEL = logic “0’)
Timing Chart (PCM Interface)
SYNC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 16 17 18
tSBt
BS
t
WS
tDSt
DH
50% VDD
50% VDD
PCMI
(-law PCM)
PCMI
(16bit Linear PCM )
MSB
MSB
LSB
LSB
50% VDD
50% VDD
Figure 15 PCM Input Timing (Long Frame Sync)
Not for Publication
25/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
BCLK
BCLK
BCLK
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
SYNC
PCMI
(-law PCM)
PCMI
(16bit Linear PCM )
SYNC
PCMO
(-law PCM)
PCMO
(16bit Linear PCM )
SYNC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 7 1 8 19
tSBt
BS
t
WS
t
DS
MSB
MSB
t
DH
LSB
LSB
Figure 16 PCM Input Timing (Short Frame Sync)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 16 17 1810
tSBt
BS
t
WS
t
t
XD1tXD2
SDX
t
SDX
Hi-Z Hi-Z
Hi-Z
MSB
MSB
LSB
t
XD3
t
XD3
Hi-Z
LSB
Figure 17 PCM Output Timing (Long Frame Sync)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 17 18 1 910
tSBt
BS
t
WS
50% VDD
50% VDD
50% VDD
50% VDD
50% VDD
50% VDD
50% VDD
50% VDD
50% VD D
50% VD D
PCMO
Hi-Z Hi-Z
(-law PCM)
PCMO
Hi-Z
(16bit Linear PCM )
t
t
XD1tXD2
SDX
MSB
MSB
LSB
t
XD3
50% VD D
t
XD 3
Hi-Z
LSB
50% VD D
Figure 18 PCM Output Timing (Short Frame Sync)
Not for Publication
26/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
DEN
EXCK
DOUT
DE N
EXCK
DOUT
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
Microcontroller Interface (Serial Interface)
DVDD0,1=3.00V to 3.60V, AVDD=3.00V to 3.60V, DGND0,1=0.0V, AGND0,1=0.0V, Ta=-40°C to +85°C (otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
tM1 20 — — ns
tM2 20 — — ns
tM3 50 — — ns
tM4 100 — — ns
tM5 50 — — ns
Digital input/output timing
tM6 50 — — ns
C
DL
=50pF
tM7 — — 30 ns
tM8 0 — — ns
tM9 50 — — ns
t
— — 30 ns
M10
EXCK clock frequency f
t
M11
— — — 10 MHz
EXCK
100 — — ns
Timing Chart (Microcontroller Serial Interface)
t
M11
50% VDD
DIN
t
M1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
tM2t
M3
A6 A5 A 4 A3 A 2 A1 A 0 B7 B6 B5 B 4 B3 B2 B1 B0
t
tM5t
M4
M6
t
M9
50% VDD
50% VDD
Hi-Z
0V
Figure 19 Write Timing
t
M11
50% VDD
DIN
t
M1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 1 5 16
tM2t
M3
A6 A 5 A 4 A 3 A 2 A1 A 0
Hi -Z Hi -Z
t
tM5t
M4
M6
t
M7
t
M8
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B 1 B0
t
M9
50% VDD
50% VDD
t
M10
50% VDD
Figure 20 Read Timing
Not for Publication
27/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
Microcontroller Interface (Serial Interface)
DVDD0,1=3.00V to 3.60V, AVDD=3.00V to 3.60V, DGND0,1=0.0V, AGND0,1=0.0V, Ta=-40°C to +85°C (otherwise specified)
Condition
Parameter Symbol
LossT1 0 to 60 25 — — dB
LossT2 300 to 3000
Transmit frequency
response
Receive frequency
response
Transmit signal to
distortion ratio
Receive signal to
distortion ratio
Transmit gain tracking
Receive gain tracking
Idle channel noise
Absolute signal level
(*4)
Note
*1 Echo cancellers, Noise canceller, slope filter, ALC = off
Programmable gain = 0dB
*2 Analog and digital gain = 1
*3 with a psophometric filter
*4 0.32Vrms = 0dBm0 = -7.7dBm (600)
*5 Input signals = Idle pattern
LossT3 1020 Reference —
LossT4 3300 -0.15 — 0.8 dB
LossT5 3400 0 — 0.8 dB
LossT6 3968.75
LossR1 0 to 3000 -0.15 — 0.2 dB
LossR2 1020 Reference —
LossR3 3300 -0.15 — 0.8 dB
LossR4 3400 -0.15 — 0.8 dB
LossR5 3968.75
SDT1 +3 35 — — dB
SDT2 0 35 — — dB
SDT3 -30 35 — — dB
SDT4 -40 28
SDT5
SDR1 +3 35 — — dB
SDR2 0 35 — — dB
SDR3 -30 35 — — dB
SDR4 -40 28 — — dB
SDR5
GTT1 +3 -0.2 — 0.2 dB
GTT2 -10 Reference —
GTT3 -40 -0.2 — 0.2 dB
GTT4 -50 -0.5 — 0.5 dB
GTT5
GTR1 +3 -0.2 — 0.2 dB
GTR2 -10 Reference —
GTR3 -40 -0.2 — 0.2 dB
GTR4 -50 -0.5 — 0.5 dB
GTR5
N
IDL
N
IDL
AVT 0 0.285 0.32 0.359 Vrms
AVR
Frequency
(Hz)
1020
1020
1020
1020
T — — — — -68 dBm0p
R — —
1020
Level
(dBm0)
-45
-45
-55
-55
Others
0 *1, *2
0 *1, *2
*1, *2, *3
*1, *2, *3
*1, *2, *3
*1, *2, *3
*1, *2, *3
*5
0
*1, *2
Min. Typ. Max. Unit
-0.15 — 0.25 dB
13 — - dB
13 — — dB
— —
23 — — dB
23 — — dB
-1.2 — 1.2 dB
-1.2 — 1.2 dB
— — -72 dBm0p
0.285
0.32 0.359 Vrms
dB
AC Characteristics (Programmable Gain Characteristics)
DVDD0,1=3.00V to 3.60V, AVDD=3.00V to 3.60V, DGND0,1=0.0V, AGND0,1=0.0V, Ta=-40°C to +85°C (otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol
G
against a set gain (*1) -1.0 — +1.0 dB
Transmit/Receive gain
accuracy
Note *1 TPAD, RPAD
*2 Acoustic-side PGA’s(Programmable Gain Amp’s), Line-side PGA
AC1
G
against an adjacent gain step
AC2
(*2)
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
-1.0 — +1.0 dB
Not for Publication
28/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
LVFR O
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
Noise Canceller Characteristics
DVDD0,1=3.00V to 3.60V, AVDD=3.00V to 3.60V, DGND0,1=0.0V, AGND0,1=0.0V, Ta=-40°C to +85°C (otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
with white noise
Noise attenuation N
for voice band
RES
noise attenuation setting =
— 13 — dB
default
[ Measurement System Block Diagram ]
White Noise Generator
L.P.F
5kHz
Analog
Power suppl y voltag e : 3.30V
CO DEC Input Gain = 1
COD EC Output Gain = 1
ML7037
NC
AnalogAIN
Level Meter
Figure 21 Measurements (Noise Attenuation)
Echo Canceller Characteristics
DVDD0,1=3.00V to 3.60V, AVDD=3.00V to 3.60V, DGND0,1=0.0V, AGND0,1=0.0V, T a=-40°C to +85°C (otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Acoustic-side, Line-side *3
Echo attenuation E
(Analog interface or 16bit Linear
RES
PCM mode)
— 35 — dB
Line-side (µ-law PCM mode) — 30 — dB
Cancellable echo delay time
T
ACOUD
T
Acoustic-side — — 100 ms
Line-side *3 — — 20 ms
LINED
Note *3 Only in dual echo canceller mode
[ Measurement System Block Diagram ]
White Noise Generator
L.P.F.
5kHz
Level Meter
Analog Anal og
Anal og
ML7037
Rin Rout
Line or Acoustic
Ech o Canceller
Sout S in
Power supply voltag e : 3.30V
CO DEC Input Gain = 1
COD EC Output Gain = 1
Anal og
Delay
Echo Delay T ime
A TT
E.R .L
( Echo R eturn Los s)
Figure 22 Measurements (Echo Attenuation)
Not for Publication
29/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Control Register
The control register map and the general-purpose port control register map are shown as Table 2 and Table3
respectively.
Table 2-1 Control Register Map
Register
Name
CR10 0Ah READY
CR11 0Bh LTHR LECEN LHLD # LCLP LSLC LATT #
CR12 0Ch ATHR AECEN AHLD # ACLP ASLC AATT #
CR13 0Dh ASOPAD1 ASOPAD0 ASIPAD1 ASIPAD0 LSOPAD1 LSOPAD0 LSIPAD1 LSIPAD0
CR14 0Eh SLPTHR
Address
CR0 00h SPDN RST
/E /E I/ I/ I/ I/ I/ I/
CR1 01h DMWR
I/E - - - - - - -
CR2 02h # # #
- - - I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
CR3 03h # # # # TPAD3 TPAD2 TPAD1 TPAD0
- - - - I/E I/E I/E I/E
CR4 04h # # # APGA4 APGA3 APGA2 APGA1 APGA0
- - - I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
CR5 05h # # # LPGA4 LPGA3 LPGA2 LPGA1 LPGA0
- - - I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
CR6 06h A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8
I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
CR7 07h A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
CR8 08h D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
CR9 09h D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
- - - - - - - -
I/E I/E I/E - I/E I/ I/E -
I/E I/E I/E - I/E I/ I/E -
I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
I/E - - - I/E - - -
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
LINEEN
# # # # # # #
# # # # # # #
# # # NCTHR
PCMSEL
RALCTHR
Data
CLKEN
RPAD3 RPAD2 RPAD1 RPAD0
PCMEN ECSEL
# # #
OPE_STAT
(MCUSEL)
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
Not for Publication
30/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
Register
Name
CR15 0Fh $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR16 10h
CR17 11h # # # # # #
CR18 12h # # # # # #
CR19 13h $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR20 14h # # # # EQL_EN EQL_2 EQL_1 EQL_0
CR21 15h $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR22 16h $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR23 17h $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR24 18h $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR25 19h $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR26 1Ah $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR27 1Bh $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR28 1Ch $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR29 1Dh $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR30 1Eh $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
CR31 1Fh $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
Address
- - - - - - - -
I/E - - - - - I/E I/E
- - - - - - I/E I/E
- - - - - - I/E I/E
- - - - - - - -
- - - - I/E I/E I/E I/E
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
AVREFE
N
Table 2-2 Control Register Map
Data
# # # # #
AVFROS
EL
AATTMO
DE1
LATTMO
DE1
LVFROS
AATTMO
LATTMO
EL
DE0
DE0
R/W
/
R/W
R/W
R/W
/
R/W
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
Not for Publication
31/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
Table 3 General-Purpose Port Control Register Map
Register
Name
GPCR0 20h GPFA7 GPFA6 GPFA5 GPFA4 GPFA3 GPFA2 GPFA1 GPFA0
GPCR1 21h GPFB7 GPFB6 GPFB5 GPFB4 GPFB3 GPFB2 GPFB1
GPCR2 22h $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
GPCR3 23h GPDA7 GPDA6 GPDA5 GPDA4 GPDA3 GPDA2 GPDA1 GPDA0
GPCR4 24h GPDB7 GPDB6 GPDB5 GPDB4 GPDB3 GPDB2 GPDB1 GPDB0
GPCR5 25h GPDC7 GPDC6 GPDC5 GPDC4 GPDC3 GPDC2 GPDC1 GPDC0
GPCR6 26h $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
GPCR7 27h $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
GPCR8 28h $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
Address
I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E -
- - - - - - - -
I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E I/E
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Data
R/W
R/W
#
R/W
/
R/W
R/W
R/W
/
/
/
Symbols for register name
# : Reserved bits
$ : Don’t read nor write
Symbols to show when it can be altered (When to alter)
I/E : both in the initial mode and in normal operation
I/ : only in the initial mode
/E : only in normal operation
- : Don’t change
Symbols to show Read or Write
R/W : Both for Read and Write
R/ : Read only
/W : Write only
/ : Both read and write prohibited
(Note) The change of control registers (including the control registers for general-purpose ports) is detected with
SYNC signals (8kHz) so that the change of the control registers less than 250 ms may not be reflected as
the LSI behavior.
(Note) When you write a control register in any other mode than the initial mode, SYNC signals (8kHz) must be
supplied unless the ML7037-003 is in the internal clock mode (the CLKSEL pin = logic 0’).
(Note) Refer to descriptions under Internal Data Memory Access for a way to set CR6, CR7, CR8 and CR9.
Not for Publication
32/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
(
Read
)
Memory Access
(Read)
(Read)
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
MICRO CONTROLLER INTERFACE
A way to use the micro controller interface is shown herebelow;
Start
Power Supply ON
REGOUT (90% or higher)
pin = logic '0'
PDN
pin = logic '1'
PDN
CR10-B7="1"
Yes
Internal Data
No
Set CR's (excl . CR0)
No
Yes
CR6 (Upper Address Write)
CR7 (Lower Address Write)
CR8 (Upper Data Write)
CR9 (LowerData Write)
CR1-B7="1" (Write)
CR1 -B7="0"
Anoth er Int ernal Da ta
Memory Setting?
Wait for 250ms (approx.) or
Yes
No
longer
* CR1-B7 is automatically cleared
after a completion of a writ e.
No
Yes
Internal Data Memory
Acc ess
Initial Mode
Set CR0
CR10-B7="0"
Yes
Starts Operation
No
Figure 25 Micro Controller Interface Flow Chart
Not for Publication
33/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
INTERNAL DATA MEMORY ACCESS
The ML7037-003 has an area called the internal data memories (16-bit wide address and 16-bit wide data), and
operates reading variables such as coefficients and thresholds retained therein. By alternating the data in the given
memory addresses, the default state could be customized.
How to Write into the Internal Data Memory
The CR6 (A15-A8) and the CR7 (A7-A0) are registers to specify the address of the internal data memory to alter.
The CR8 (D15-D8) and the CR9 (D7-D0) are registers to store the data to write into the internal data memory to
alter.
When the MCUSEL pin is given a logic ‘0’, the ML7037-003 automatically transits into the initial mode 250ms
(approx.) after a release of power-down reset by the
[CR10-B7] turns to be a logic ‘1’ which shows the ML7037-003 has got ready for the control register access.
During this initial mode, specify both the 16-bit wide address by the CR6-CR7 and the 16-bit wide data by the
CR8-CR9 first, and then write a logic ‘1’ into the DMWR-bit [CR1-B7], which executes alternation of the internal
data memory in the given address. After the internal data memory alternation, the DMWR-bit [CR1-B7]
automatically is cleared to be a logic ‘0’. The flow of this internal data memory access is shown in Figure 26.
When more than an internal data memory, repeat the procedure above. A change of the OPE_STAT-bit [CR0-B0]
to a logic ‘1’ let the ML7037-003 out of the initial mode, and it starts normal operation.
Start
PDN pin or the SPDN-bit [CR0-B7], and the READY-bit
CR6 (Upper Address W rite)
CR7 (Lower Address W rite)
CR8 (Upper Data Write)
CR9 (LowerData Write)
CR1-B7="1" (Write)
CR1- B7=" 0"
(Read)
Yes
Another Internal Data
Memory Setting?
No
End
Figure 26 Internal Data Memory Access Flow Chart
* CR1-B7 is automatically cleared
after a completion of a write.
No
Yes
Not for Publication
34/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
Control register value to set when
Micro Control Interface Enable/Disable
Down
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
PIN CONTROL AND CONTROL REGISTERS
Some of functions and states with the ML7037-003 could be determined either by input state of certain pins (their
secondary functions, if the pins are general-purpose input port pins) and/or the control registers. In such cases, the
functions and states are determined by ORed logics between them. Hence, when a function or a state is determined
(called as “State Control”) by the concerned pin input, it is required to be careful with the concerned register
setting; and visa versa.
Table 13 shows such pins and the relevant control registers.
All the values to be set in the relevant control registers are the initial values set on a release of power-down reset by
the
PDN pin or the SPDN-bit [CR0-B7].
Function
Power-down reset logic ‘1’
Reset logic ‘1’
PCM Coding Format Selection logic ‘0’ PCMSEL logic ‘0’ PCMSEL
Selection
Transmit-Side Volume Control logic ‘0’
Receive-Side Volume Control logic ‘0’
Line-Side Analog Interface Power-
Control
Analog Output Selection logic ‘0’
Noise Canceller Through Mode Selection logic ‘0’
Receive-Side ALC Through Mode Selection
Slope Filter Through Mode Selection logic ‘0’
Echo Canceller Mode Selection Register logic ‘0’
Acoustic Echo Canceller Enable Control logic ‘0’
*1 : A name in (bracket) shows the pin name when the secondary function is assigned.
Pin input to make when State Control
is made by the control register
logic ‘0’ MCUSEL logic ‘0’ OPE_STAT
logic ‘0’
logic ‘0’
Pin
PDN
RST
GPIA[3-0]
(TPAD[3-0]) *1
GPIA[4-7]
(RPAD[3-0]) *1
GPIB1
(LINEEN) *1
GPIB2
(VFROSEL) *1
GPIB3
(NCTHR) *1
GPIB4
(ALCTHR) *1
GPIB5
(SLPTHR) *1
GPIB6
(ECSEL) *1
GPIB7
(ECEN) *1
State Control is made by the pin
Table 13 Relevant Input Pins And Control Registers
Control
logic ‘0’ SPDN
logic ‘0’ RST
logic ‘0’ TPAD[3-0]
logic ‘0’ RPAD[3-0]
logic ‘0’
logic ‘0’
logic ‘0’ NCTHR
logic ‘0’ RALCT HR
logic ‘0’ SLPTHR
logic ‘0’ ECSEL
logic ‘0’
Register
LINEEN
AVFROSEL
LVFROSEL
LECEN
AECEN
Not for Publication
35/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
DEN
EXCK
PDN
SYNC
AVREFEN
CLKSEL
RST
DOUT
General-purpose input ports - A
Line-side
Line-side
Acoustic-side
Acoustic-side
Acoustic-side
General-purpose input ports - B
output port - C
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
APPLICATION CIRCUIT (1)
analog input sign als
analog outputsign als
analog outputsign als
analog input sign als
analog input sign als
Power-down
1.0μF
1.0μF
1.0μF
1.0μF
1.0μF
+3.3V
+3.3V
Buffer amp
10μF 0.1μF
0.1μF10μF
0.1μF
10μF
10pF
1.0MΩ
10pF
10kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
10μF
1.0μF
0.1μF
10kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
0.1μF10μF
150pF
0.1μF
12.288MHz
LGSX
LINN
LVFRO
AVFRO
AGSX1
AIN1N
AGSX0
AIN0N
AIN0P
AVDD
AVREF
AGND0
AGND1
DVDD0
REGOUT0
VBG
DGND0
DVDD1
REGOUT1
DGND1
MCK/XI
XO
ML7037
BCLK
PCMI
PCMO
GPIA0
GPIA1
GPIA2
GPIA3
GPIA4
GPIA5
GPIA6
GPIA7
GPIB0
GPIB1
GPIB2
GPIB3
GPIB4
GPIB5
GPIB6
GPIB7
GPOC[7:0]
DIN
MCUSEL
PCMSEL
SYNCSEL
TSTI2
TSTI1
TSTI0
(NC)
(NC)
(NC)
8
※ NC : No Connection
General-purpose
MCU interface
(Conditions)
Speech signal interface on line-side : Analog
Speech signal input on acoustic side : Differential
PCM coding format : 16bit Linear PCM
PCM frame sync timing : Long frame sync
PCM clock mode : Internal clock mode (Clock master)
MCU interface : used
Figure 27
Not for Publication
36/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
DEN
EXCK
PDN
SYNC
AVREFEN
RST
DOUT
Power-down
Reset
)
GPIB3 (NCTHR)
analog input signals
Analog output selection
AVREF/Analog amps power-down control
analog output signals
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
APPLICATION CIRCUIT (2)
LGSX
Acoustic-side
1.0μF
Acoustic-side
1.0μF
10kΩ
10kΩ
(NC)
10kΩ
1.0μF
10kΩ
LINN
LVFRO
AVFRO
AGSX1
AIN1N
AGSX0
AIN0N
AIN0P
GPIB2 (VFROSEL)
BCLK
PCMI
PCMO
GPIA0 (TPAD0)
GPIA1 (TPAD1)
GPIA2 (TPAD2)
GPIA3 (TPAD3)
GPIA4 (RPAD0)
GPIA5 (RPAD1)
GPIA6 (RPAD2)
GPIA7 (RPAD3)
GPIB0
GPIB1 (LINEEN
10kΩ
ML7037
BCLK input (64k Hz~
8kHz Sync signal input
Line-side PCM input
Line-side PCM output
Transmit-side volume control
Receive-side volume control
+3.3V
+3.3V
10μF 0.1μF
0.1μF10μF
0.1μF
10μF
10pF
1.0MΩ
10pF
10μF
0.1μF
0.1μF10μF
150pF
0.1μF
12.288MHz
AVDD
AVREF
AGND0
AGND1
DVDD0
REGOUT0
VBG
DGND0
DVDD1
REGOUT1
DGND1
MCK/XI
XO
GPIB4 (ALCTHR)
GPIB5 (SLPTHR)
GPIB6 (ECSEL)
GPIB7 (ECEN)
GPOC[7:0]
DIN
CLKSEL
MCUSEL
PCMSEL
SYNCSEL
TSTI2
TSTI1
TSTI0
10kΩ
8
(NC)
10kΩ
(NC)
10kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
※ NC : No Connection
+3.3V
(Conditions)
Speech signal interface on line-side : Digital (PCM)
Speech signal input on acoustic side : Single
PCM coding format : µ-law PCM
PCM frame sync timing : Short frame sync
PCM clock mode : External clock mode (Clock slave)
MCU interface : used
Figure 28
Not for Publication
37/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
NOTE ON USE
1. Use a stabilized power supply with a low level of noises (especially spike noises and pulse noises of high
frequencies) in order to prevent this device from malfunction or degradation in characteristics.
2. Place bypass-capacitors with a good high frequency characteristics for the power supply near the pins of this
device in order to assure its electrical characteristics.
3. Place bypass-capacitors with a good high frequency characteristics for the analog signal ground (AVREF
pin) near the pins of this device in order to assure its electrical characteristics.
4. Place bypass-capacitors with a good high frequency characteristics for the regulator’s reference voltage
output (VBG pin) and for the regulator outputs (REGOUT0,1 pins) near the pins of this device in order to
assure its electrical characteristics.
5. Connect the AGND0, AGND1, DGND0 and DGND 2 to the system ground at a shortest distance and in a low
impedance state.
6. Turn on and off the analog power supply and digital power supply simultaneously, or turn on digital power
supply prior to analog power supply and turn off analog power supply prior to digital power supply.
7. After turning on the power, be sure to reset the device with the
supplied.
8. Set a system level diagram so that a value of the Echo Return Loss (E.R.L. = [Power of echo-originating
signals at RoutA/RoutL] – [Power of echo signals at SinA/SinL]) is negative and the ASLC function is
recommended to be enabled. When the E.R.L. cannot be negative all the time, the GLPAD function is
recommended to be enabled with the ASLC function disabled. Refer to a reference data for the E.R.L level vs.
echo attenuation of an echo canceller.
9. The input level should be –10 to –20 dBm0. Refer to a reference data for Rin input level vs. echo attenuation.
10. Application-level volume control on use is recommended to be made outside of the echo path such as by the
RALC, the RPAD and the TPAD (not between the RoutA and the SinA in the single echo canceller mode; or
not between the RoutA and the SinA nor not between the RoutL and the SinL).
in Dual Echo Canceler mode : to be controlled with the TPAD, the RPAD, and/or the RALC.
in Signal Echo Canceler mode : to be controlled with the TPAD, the RPAD, the RALC, and/or with the
analog input (LINN) that is set at less than 1.3 VPP.
11. Turn off an echo canceller in an environment where no echoes exist.
12. When the echo path is changed (such as when resuming telephone communication), reset the device either
with the
PDN pin, the SPDN bit [CR0-B7], the RST pin or the RST bit [CR0-B6].
PDN pin while the master clocks are being
13. The Pin Control Mode (the MCUSEL-pin = logic ‘1’) which defines behaviors of this LSI by logic ‘0’ / ‘1’ to
concerned input pins has less flexibility in comparison with the External MCU Mode (the MCUSEL-pin =
logic ‘0’) which defines behaviors of this LSI through control register setting due to its limitation of the
available pin count. Therefore, basically, this LSI is recommended to use in the External MCU Mode.
Not for Publication
38/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
(Unit : mm)
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The surface mount type packages are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity
absorbed in storage.
Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki’s responsible sales person for the product
name, package name, pin number, package code, and desired mounting conditions (reflow method,
temperature and times).
Not for Publication
39/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
REVISION HISTORY
Document
No.
PEDL7037-003-01Zz
_Digest
PEDL7037-003-02Zz
_Digest
PEDL7037-003-03Zz
_Digest
PEDL7037-003-04Zz
_Digest
PEDL7037-003-05Zz
_Digest
Date
Oct. 13, 2006 – – First edition
Nov. 29, 2006 18 18
Dec. 11, 2006 24 24
Feb. 19, 2007
May. 21, 2007
Previous
Page
Current
Edition
23 23
24 24
39 39 Update of Package Dimensions
Edition
As what is initialized by the
acquired gain is added.
Correction of REGOUT0, 1 output level after
DVDD0, 1 stop to be fed in Figure 13
Correction of REGOUT0, 1 output level after
DVDD0, 1 stop to be fed in Figure 13
Recovery of Figure 14 which was falsely
corrected by PEDL7037-003-03Zz_Digest
Description
RST-pin, ALC
Not for Publication
40/41

PEDL7037-003-05Zz_Digest
OKI Semiconductor ML7037-003
NOTICE
1. The information contained herein can change without notice owing to product and/or technical improvements.
2. The outline of action and examples for application circuits described herein have been chosen as an
3. When designing your product, please use our product below the specified maximum ratings and within the
4. Oki assumes no responsibility or liability whatsoever for any failure or unusual or unexpected operation
5. Neither indemnity against nor license of a third party’s industrial and intellectual property right, etc. is
6. The products listed in this document are intended for use in general electronics equipment for commercial
Such applications include, but are not limited to, traffic and automotive equipment, safety devices, aerospace
7. Certain products in this document may need government approval before they can be exported to particular
8. No part of the contents contained herein may be reprinted or reproduced without our prior permission.
Before using the product, please make sure that the information being referred to is up-to-date.
explanation for the standard action and performance of the product. When planning to use the product, please
ensure that the external conditions are reflected in the actual circuit, assembly, and program designs.
specified operating ranges including, but not limited to, operating voltage, power dissipation, and operating
temperature.
resulting from misuse, neglect, improper installation, repair, alteration or accident, improper handling, or
unusual physical or electrical stress including, but not limited to, exposure to parameters beyond the specified
maximum ratings or operation outside the specified operating range.
granted by us in connection with the use of the product and/or the information and drawings contained herein.
No responsibility is assumed by us for any infringement of a third party’s right which may result from the use
thereof.
applications (e.g., office automation, communication equipment, measurement equipment, consumer
electronics, etc.). These products are not authorized for use in any system or application that requires special
or enhanced quality and reliability characteristics nor in any system or application where the failure of such
system or application may result in the loss or damage of property, or death or injury to humans.
equipment, nuclear power control, medical equipment, and life-support systems.
countries. The purchaser assumes the responsibility of determining the legality of export of these products
and will take appropriate and necessary steps at their own expense for these.
Copyright 2007 Oki Electric Industry Co., Ltd.
Not for Publication
41/41
 Loading...
Loading...