Page 1

Freescale Semiconductor SLK0101UG
User Guide Rev. 0, 9/2006
Application Module Student Learning Kit Users
Guide featuring the Freescale MC9S12C32
For use with the following part numbers:
CSM-12C32
APS12C32SLK
PBS12C32SLK
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2006. All rights reserved.
_______________________________________________________________________
Page 2

CONTENTS
CAUTIONARY NOTES ..............................................................................................................4
FEATURES................................................................................................................................5
REFERENCES...........................................................................................................................6
INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................7
GETTING STARTED..................................................................................................................7
OPERATION..............................................................................................................................7
POWER................................................................................................................................. 8
PWR.................................................................................................................................. 8
CONNECTOR J1............................................................................................................... 8
PWR_SEL JUMPER.......................................................................................................... 8
RESET SWITCH ................................................................................................................... 9
LOW-VOLTAGE DETECT..................................................................................................... 9
TIMING.................................................................................................................................. 9
COMMUNICATIONS............................................................................................................. 9
COM CONNECTOR........................................................................................................ 10
CONNECTOR J1............................................................................................................. 11
USER OPTIONS ................................................................................................................. 11
SWITCHES ..................................................................................................................... 11
LED’S............................................................................................................................... 12
DEVELOPMENT SUPPORT....................................................................................................12
ASCII MONITOR OPERATION........................................................................................... 12
ASCII MONITOR MEMORY MAP ................................................................................... 12
MONITOR COMMANDS................................................................................................. 13
INTERRUPT SUPPORT.................................................................................................. 13
INTERRUPT VECTOR TABLE........................................................................................ 14
SERIAL MONITOR OPERATION........................................................................................ 15
SERIAL MONITOR MEMORY MAP................................................................................ 15
BDM_PORT HEADER......................................................................................................... 16
2 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 3
FIGURES
Figure 1: PWR_SEL ...................................................................................................................8
Figure 2: COM Connector.........................................................................................................10
Figure 3: MCU_PORT Connector.............................................................................................11
Figure 4: BDM_PORT...............................................................................................................16
TABLES
Table 1: Serial COM Signals ....................................................................................................10
Table 2: User Option Jumper Settings......................................................................................11
Table 4: Monitor Commands ....................................................................................................13
Table 5: Monitor Memory Map..................................................................................................12
Table 6: MON12 Interrupt Vector Table....................................................................................14
Table 7: Serial Monitor Memory Map........................................................................................15
REVISION
August 25, 2006 A Initial release
Freescale Semiconductor 3
Page 4

Cautionary Notes
♦ Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) prevention measures should be used when handling this
product. ESD damage is not a warranty repair item.
♦ Axiom Manufacturing does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of
any product or circuit described herein; neither does it convey any license under patent
rights or the rights of others.
♦ EMC Information on the APS12C32SLK module:
a) This product as shipped from the factory with associated power supplies and cables, has
been verified to meet with requirements of CE and the FCC as a CLASS B product.
b) This product is designed and intended for use as a development platform for hardware or
software in an educational or professional laboratory.
c) In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference in which case the
user may be required to take adequate prevention measures.
d) Attaching additional wiring to this product or modifying the products operation from the
factory default as shipped may effect its performance and cause interference with nearby
electronic equipment. If such interference is detected, suitable mitigating measures should
be taken.
TERMINOLOGY
This module uses option selection jumpers and cut-traces to setup default configuration.
Terminology for application of the option jumpers is as follows:
Jumper – a plastic shunt that connects 2 terminals electrically
Jumper on, in, or installed - jumper is installed such that 2 pins are connected together
Jumper off, out, or idle - jumper is installed on 1 pin only. It is recommended that
jumpers be idled by installing on 1 pin so they will not be lost.
Cut-Trace – a circuit trace connection between component pads. The circuit trace may
be cut using a razor knife to break the default connection. To reconnect the circuit,
simply install a suitably sized 0-ohm resistor or attach a wire across the pads.
4 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 5
FEATURES
The APS12C32SLK is an educational application module for the Freescale Semiconductor
MC9S12C32 microcontroller. Application module SLK’s include components for out-of-box
operation and are preprogrammed with a serial monitor to make application development quick
and easy. A background DEBUG port is provided for development tool use and is compatible
with HCS12 BDM interface cables and software. The 40-pin connector allows the
APS12C32SLK module to be connected to an expanded evaluation environment such as the
Microcontroller Project Board Student Learning Kit (PBMCUSLK) or user’s custom PCB.
Features:
♦ MC9S12C32 MCU, 48 QFP
♦ 32K Byte Flash EEPROM
♦ 2K Bytes RAM
♦ 31 I/O lines
♦ Timer/PWM
♦ SCI and SPI Communications Ports
♦ Key Wake-up Port
♦ BDM DEBUG Port
♦ CAN 2.0 Module
♦ Analog Comparator
♦ 8 MHz Internal Bus Operation Default
♦ 25 MHz Bus Operation using internal PLL
♦ +3.3VDC to +5VDC operation
♦ Power Input Selection Jumper
♦ On-board, regulated +5V power supply
♦ Optional power input/output from Connector J1
♦ 16 MHz Ceramic Resonator
♦ RS-232 Serial Port w/ DB9 Connector
♦ 8-Ch, 10-bit, Analog Comparator with full rail-to-r ail operation and
external trigger capability
♦ 8-Channel, 16-bit Timer with Input Capture, Output Compare, and
PWM capabilities
♦ User Components Provided
♦ 3 Push Button Switches: 2 User, RESET
♦ 3 LED Indicators: 2 User, VDD
♦ Jumpers
♦ Disable User Components
♦ Power Select
♦ Connectors
♦ 40 pin connector provides access to most MCU I/O signals
♦ 2.0mm Barrel Connector Power Input
♦ DEBUG BDM Connector
♦ DB9 Communications Connector
♦ Supplied with DB9 Serial Cable, Documentation (CD), Manual, and Wall plug type power supply.
Specifications:
Module Size 2.2” x 1.6”
Power Input: +9VDC @ 200 mA typical, +6 to +16VDC range
Freescale Semiconductor 5
Page 6

References
Reference documents are provided on the support CD in Acrobat Reader format. More
information can be found in the Application Notes section of the Freescale Web site.
APS12C32SLKSCHEM.pdf APS12C32SLK Application Module Schematic
APS12C32SLKUG.pdf APS12C32SLK User Guide
9S12C32DGV1.pdf MC9S12C32 Device User Guide
9S12C32_ZIP.zip Zip file containing Device Block User Guides
APS12C32SLKQSUG.pdf Quick Start Guide for use with stand-alone module
APS12C32SLKSW.zip CodeWarrior project for use with
APS12C32SLK_QSUG
AN2548.pdf Serial Monitor Program for HCS12 MCU’s
The following reference documents are for using the application module in conjunction with the
Freescale Microcontroller Project Board Student Learning Kit:
PBS12C32SLKQSUG.pdf Quick Start Guide for application module use with
PBMCUSLK
PBS12C32SLKSW.zip CodeWarrior project for use with
PBS12C32SLK_QSUG
Visit www.freescale.com\universityprogram for current product information, reference materials
and updates.
6 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 7

INTRODUCTION
Before using this module, the user should be familiar with the hardware and software operation
of the target MCU. Refer to the MC9S12C32 User Manual and MC9S12C32 Reference
Manual for details on MCU operation. The module’s purpose is to promote the features of the
MC9S12C32 and to assist the user in quickly developing an application in a known working
environment. Users should be familiar with memory mapping, memory types, and embedded
software design for quick, successful, application development.
The APS12C32SLK Educational Module is a fully assembled, fully functional module
supporting Freescale MC9S12C32 microcontroller. The module comes with a serial cable,
power supply, and an embedded monitor for stand-alone operation. Support software for this
module is provided for Windows 95/98/NT/2000/XP operating systems.
Application development may be performed by using the embedded monitor, or any
compatible BDM cable with supporting host software. The embedded monitor provides an
effective, low cost, debug method. Note that when a BDM cable is used for debugging, the
BDM pod should be powered from an external supply.
GETTING STARTED
Please refer to the APS12C32SLK Quick Start Users Guide to quickly setup the stand-alone
application module or PBS12C32SLK Quick Start Users Guide to get started with the
microcontroller project board (PBMCUSLK).
Operation
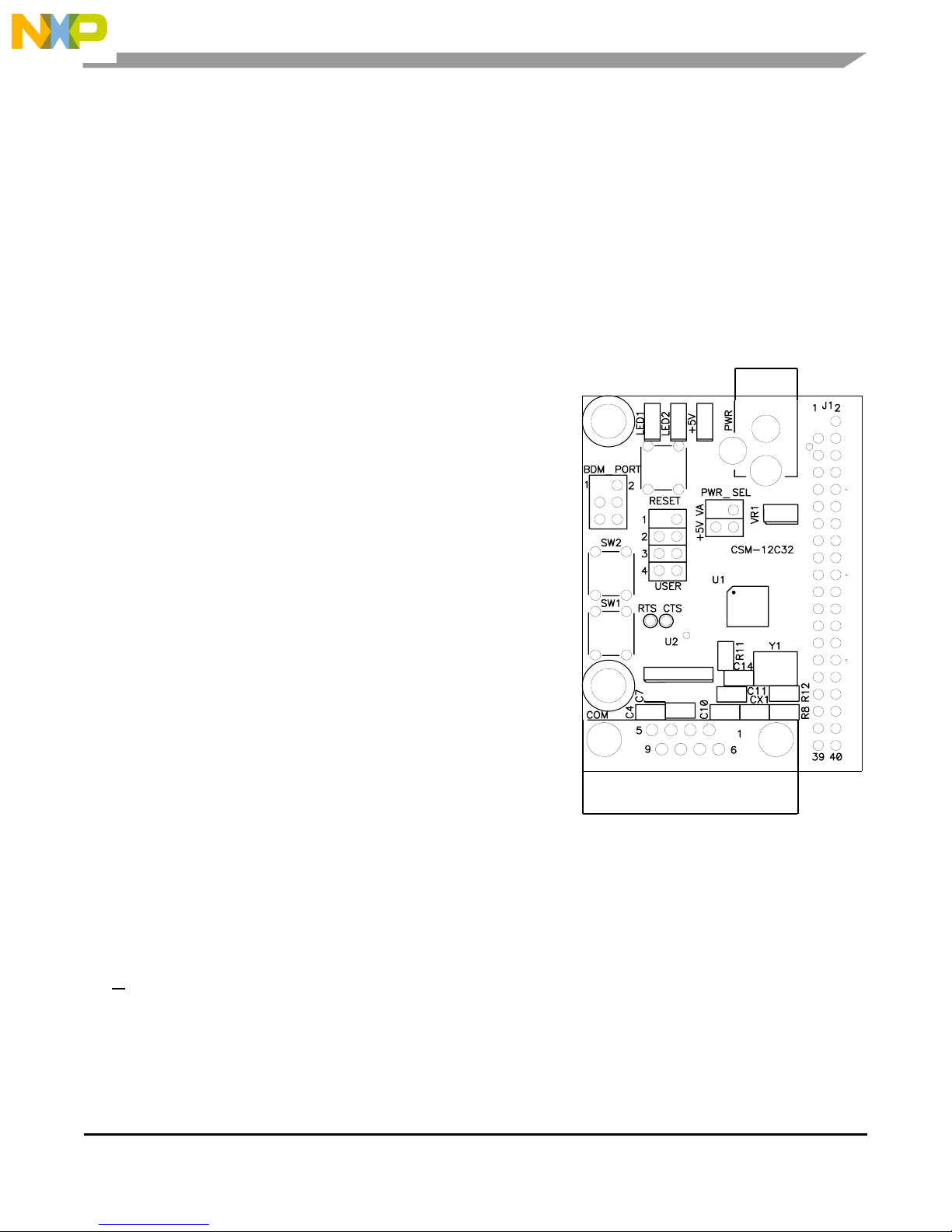
The APS12C32SLK module provides input and output features designed to assist embedded
application development. Access to the MCU port signals is available through module
connector J1. This connector may also be used to input power to the module or to output
power to attached modules. RS-232 communications signals may also be input through
connector J1. Care must be exercised when using the J1 to power the module, as only
regulated voltage in the range of +3.3V to +5V should be supplied to this connection. The onboard regulator provides a fixed +5V voltage to the module.
Five user option jumpers and 3 cut-traces control module operation. Enabling a user option
requires installing a jumper across the associated header pins. Removing the jumper disables
the associated option. An option enabled by a cut-trace can be disabled by removing the
circuit trace between the cut-trace component pads. Use a sharp knife to cut the embedded
circuit trace. Be careful not to damage adjacent circuitry. To re-enable the option, simply
install a 1206 sized 0-ohm resistor or piece of wire across the cut-trace component pads.
Freescale Semiconductor 7
Page 8

Power
Power is supplied to the module through a 2.0mm barrel connector at location PWR for standalone operation. The module may also be powered through connector J1 when connected to
the PBMCUSLK. Power may be sourced off-module through connector J1 to external circuitry.
Power routing on the module is determined by the PWR_SEL jumper.
PWR
The PWR connector accepts a 2.1mm, center-positive, barrel plug that allows the module to be
powered from a wall-plug transformer or from a desktop power supply. Input voltage should be
limited to between +7V and +20V. Input voltage of +9VDC is typical. This input supplies the
on-board +5V regulator that powers the module.
Connector J1
Power may be supplied to the module through the pins J1-1 and J1-2. Use of this option
requires a regulated voltage input limited to the range of +3.3VDC to +5VDC. This input is
connected directly to the module power and ground planes. Care should be exercised not to
over-drive this input. Use of connector J1 to supply +3.3V to the module requires disabling the
voltage supervisor (LV1) by opening cut-trace CT-1. See the Low-Voltage Detect section
below. To re-enable the low-voltage supervisor, install a 1206 sized 0-ohm resistor at CT1.
Connector J1 may also be used to source +5V power from the on-board regulator to external
modules attached to connector J1. The PWR_SEL option header determines how power is
routed to the module.
PWR_SEL Jumper
The PWR_SEL jumper is a 4-position option header that configures power routing on the
APS12C32SLK module. The module may be powered by an external transformer connected
to the PWR connector or through connector J1. The module may also source power to
auxiliary modules connected to the connector J1. Damage may occur if the J1 power input
pins are over-driven. Refer to the Figure 1 to determine correct PWR_SEL jumper setting.
Figure 1: PWR_SEL
1
2
1
2
1
2
8 Freescale Semiconductor
Source power input from barrel connector PWR.
Source power input from connector J1.
Source power from barrel connector PWR and supply power to external
circuitry connected to J1.
Page 9

Reset Switch
The RESET switch provides an asynchronous reset input to the MCU. Pressing the RESET
switch produces a low-voltage level on the RESET input to the MCU. The low-voltage
supervisor (LV1) holds the RESET line low for approximately 150 ms after the pushbutton is
released.
Low-Voltage Detect
A DS1813 (LV1) provides POR, low-voltage detect, and pushbutton reset services for the
module. At power-on, LV1 holds the MCU in reset for 150 ms after VCC reaches approximately
4.35V. During normal operation, LV1 asserts RESET when VCC falls below 4.35V and holds
RESET true for 150 ms after VCC returns to normal. The push-button operation is described
in the paragraph above. Use of connector J1 to supply +3.3V to the module requires disabling
LV1.
LV1 may be disabled by opening the cut-trace CT1. Simply remove the circuit trace between
the cut-trace pads to open the circuit. To restore the circuit functionality, install a 1206 size, 0ohm, resistor or a short piece of wire across the cut-trace pads.
Timing
A ceramic resonator (Y1) provides a 16.0 MHz base operating frequency to the MCU. This
supports a default 8.0 MHz internal operating frequency. Higher frequencies are possible
using the embedded PLL. The resonator output is routed to the MCU only and is not available
at the MCU Port connector (J1). The MCU ECLK output is available to the user at connector
J1 if enabled.
Communications
The APS12C32SLK module provides a single RS-232 communications port. An RS-232
transceiver (U2) provides RS-232 signal level to TTL/CMOS logic level translation. RS232
signals TXD and RXD are routed between the transceiver and the MCU. These signals are
also routed to connector J1. RS-232 communication signals input on J1 must be TTL/CMOS
logic levels; no translation support is provided through this path. The transceiver output may
also be driven off-module if the signals are suitably buffered. As added development support,
hardware flow control signals RTS and CTS are available on the logic side of U2. These
signals are routed to vias located near the transceiver (U2). RTS has been biased properly to
support 2-wire RS-232 communications.
Freescale Semiconductor 9
Page 10

Use of the J1 connector to input RS-232 signals requires disabling the on-board RS-232
transceiver. Otherwise, signal corruption may occur. Disabling the on-board transceiver is
accomplished by opening cut-traces CT1, and CT2. Simply remove the circuit trace between
the cut-trace pads to open the circuit. To restore the circuit functionality, install a 1206 size, 0ohm, resistor or a short piece of wire across the cut-trace pads.
Table 1: Serial COM Signals
COM Signal MCU Port Connector Disable
TXD PS1/TXD J1-5 CT5
RXD PS0/RXD J1-7 CT4
COM Connector
A standard 9-pin D- Sub connector provides external connections for the COM port. The COM
port is configured as a DCE device. Component U2 provides RS-232 translation services.
The figure below shows the DB9 connector.
Figure 2: COM Connector
TXD
RXD
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
RTS
CTS
NC
Female DB9 connector that interfaces to the DCE serial port via an
RS232 transceiver. It provides simple 2-wire asynchronous serial
communications without flow control. A straight-through serial cable may
be connected to a DTE device such a PC
Pins 1, 4, and 6 are connected together.
10 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 11

Connector J1
Connector J1 provides access to APS12C32SLK I/O port signals.
Figure 3: MCU_PORT Connector
V
GND
PS1/TXD
PS0/RXD
PP5/KWP5
PE0/XIRQ*
PT0/PW0/IOC0
PT1/PW1/IOC1
PM4/MOSI
PM2/MISO
PM5/SCK
PM3/SS*
PE4/ELCK
PE7/XCLKS
PAD02/AN02
PAD03/AN03
PAD04/AN04
PAD05/AN05
PAD06/AN06
PAD07/AN07
1 2
x
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
PE1/IRQ* Default Signal Assignments
RESET* MCU PORT Signal Disable
MODC/BKGD
NC PS1/TXD COM1 TXD CT-5
NC PS0/RXD COM1 RXD CT-4
NC PE1/IRQ* SW1 User1
NC PP5/KWP5 SW2 User2
NC PA0 LED1 User3
PAD00/AN00 PB4 LED2 User4
PAD01/AN01
PB4
PA0
PM1/TXCAN
PM0/RXCAN
PT2/PW2/IOC2
PT3/PW3/IOC3
PT4/PW04/IOC4
PT5/IOC5
PT6/IOC6
PT7/IOC7
Note: Default signal assignment should be
disabled to use the signal at connector J1
User Options
User options include 2 LED’s, and 2 pushbutton switches. Each user option may be enabled
individually using the USER option header. When the appropriate USER option jumper is
installed, the associated user option is enabled. Removing a jumper disables the associated
user option.
Table 2: User Option Jumper Settings
Jumper On Off MCU Signal
User 1 Enable SW1 Disable SW1 PE0/XIRQ*
User 2 Enable SW2 Disable SW2 PP5 /KWP5
User 3 Enable LED1 Disable LED1 PA0
User 4 Enable LED2 Disable LED2 PB4
Switches
Two push button switches provide momentary, active low, input to the MCU for user
applications. Pressing a switch provides a momentary low logic level input tot the MCU. SW1
and SW2 provide input to MCUI/O ports PE0 and PP5 respectively.
Freescale Semiconductor
11
Page 12

LED’s
Two LED’s provide active-low, visual output for user applications. A low voltage level driven
out on the appropriate MCU port causes the LED to light. MCU ports PA0 and PB4 drive
LED1 and LED2 respectively.
Development Support
The APS12C32SLK ships from the factory with a serial monitor installed in FLASH. An ASCII
monitor is also installed to provide quick and easy debug access to the user. The text monitor
is available out of RESET. The serial monitor is available by pressing and holding SW1 as the
module exits RESET. In the discussion below, the terms text and ASCII are used
interchangeably.
ASCII Monitor Operation
The debug monitor provides a simple application development platform for developing
application code. The debug monitor allows the user to quickly and easily develop and debug
RAM based application code.
The debug monitor is accessible through the COM port using an ASCII terminal program such
as HyperTerminal or AxIDE. The terminal should be configured for 9600, 8, N, 1 with no flowcontrol. The monitor relocates the hardware interrupt vector table from 0xFF8A:0xFFFF to
0X0F8A:0x0FFF(see Table 3 below). The vectors remain in the same order as the default
hardware table. The Reset vector is reserved; user should use autostart to start applications
from reset.
ASCII Monitor Memory Map
Table 3: Monitor Memory Map
$0000 $03FF
Reserved
$0800 $0DFF
$0E00 $0F8B
$0F8A $0FFF
Reserved
$8000 $BFFF
$C000 $FFFF
Registers 1K bytes
Internal RAM. 1.5K bytes
Monitor Reserved
Relocated Interrupt Vector Table
User Program Memory 16K bytes
Protected Monitor Space 16K bytes
512 bytes
12 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 13

Monitor Commands
Table 4: Monitor Commands
BF <StartAddress> <EndAddress> [<data>] Block Fill memory range with data
BR [<Address>] Set/Display user breakpoints
CALL [<Address>] Call user subroutine at <Address>
GO [<Address>] Begin/continue execution of user code
HELP Display the Mon12 command summary
LOAD [P] Load S-Records into memory, P = Paged S2
MD <StartAddress> [<EndAddress>] Memory Display Bytes
MM <Address> Modify Memory Bytes (8 bit values)
MW <Address> Modify memory Words (16 bit values)
MOVE <StartAddress> <EndAddress>
<DestAddress>
RD Display all CPU registers
OFFSET – [arg] Offset for download
Proceed Continue program execution
RM Modify CPU Register Contents
STOPAT <Address> Trace until address
T [<count>] Trace <count> instructions
Move a block of memory
NOTE: Items in Italics are not implemented at this time.
Interrupt Support
All interrupt services under are provided through the relocated vector table, see Table 5 below.
Each location in the table is initialized to a value of $0000 to cause the trap of an unscheduled
interrupt. Any nonzero value will allow the interrupt to proceed to the user's service routine
that should be located at the address indicated. The interrupt service delay is +21 cycles over
the standard interrupt service.
To use vectors specified in the table, the user must insert the address of the interrupt service
routine during software initialization into the ram interrupt table. For an example, for the IRQ
vector, the following is performed:
Example: IRQ Service routine label = IRQ_SRV
Ram Vector Table address is defined in table below, IRQ vector definition:
VIRQ EQU $0FF2 ; define ram table vector location
Place IRQ service routine address in the table:
MOVW #IRQ_SRV,VIRQ
This vector initialization will remain in effect until a RESET is invoked.
Freescale Semiconductor
13
Page 14

Interrupt Vector Table
Table 5: MON12 Interrupt Vector Table
Ram Interrupt Vector
Address
MCU Interrupt Vector
Address
TRAP code Vector
Source
0F8A FF8A 02 LVI
0F8C FF8C 04 PWME
0F8E FF8E 06 PTPI
0F90 FF90 08 C4TX
0F92 FF92 0A C4RX
0F94 FF94 0C C4ERR
0F96 FF96 0E C4WU
0F98 FF98 10 C3TX
0F9A FF9A 12 C3RX
0F9C FF9C 14 C3ERR
0F9E FF9E 16 C3WU
0FA0 FFA0 18 C2TX
0FA2 FFA2 1A C2RX
0FA4 FFA4 1C C2ERR
0FA6 FFA6 1E C2WU
0FA8 FFA8 20 C1TX
0FAA FFAA 22 C1RX
0FAC FFAC 24 C1ERR
0FAE FFAE 26 C1WU
0FB0 FFB0 28 C0TX
0FB2 FFB2 2A C0RX
0FB4 FFB4 2C C0ERR
0FB6 FFB6 2E C0WU
0FB8 FFB8 30 FEPRG
0FBA FFBA 32 EEPRG
0FBC FFBC 34 SPI2
0FBE FFBE 36 SPI1
0FC0 FFC0 38 I2C
0FC2 FFC2 3A BDLC
0FC4 FFC4 3C CRGC
0FC6 FFC6 3E CRGL
0FC8 FFC8 40 PACBO
0FCA FFCA 42 MCNT
0FCC FFCC 44 PTHI
0FCE FFCE 46 PTJI
0FD0 FFD0 48 ADC1
0FD2 FFD2 4A ADC0
0FD4 FFD4 4C SCI1
0FD6 FFD6 4E SCI0
0FD8 FFD8 50 SPI0
0FDA FFDA 52 PACAI
0FDC FFDC 54 PACAO
0FDE FFDE 56 TOF
0FE0 FFE0 58 TC7
0FE2 FFE2 5A TC6
14 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 15

Ram Interrupt Vector
Address
0FE6 FFE6 5E TC4
0FE8 FFE8 60 TC3
0FEA FFEA 62 TC2
0FEC FFEC 64 TC1
0FEE FFEE 66 TC0
0FF0 FFF0 68 RTI
0FF2 FFF2 6A IRQ
0FF4 FFF4 6C XIRQ
0FF6 FFF6 6E SWI
0FF8 FFF8 70 TRAP
0FFA FFFA 72 COP
0FFC FFFC 74 CLM
0FFE FFFE 76 RESERVED
MCU Interrupt Vector
Address
TRAP code Vector
Source
Serial Monitor Operation
A serial binary monitor is loaded in the MCU internal flash memory. Press and hold SW1 while
pressing the RESET button or applying power. This section provides a brief description of this
serial monitor operation. Refer to application note AN2548 for complete details on the serial
monitor operation. This application note may be found on the Support CD received with the
module or from the Freescale web site.
Serial Monitor Memory Map
Table 6: Serial Monitor Memory Map
0x0000 –
0x03FF
Reserved
0x3800 –
0x3FFF
0x8000 –
0xBFFF
0xC000 –
0xF77F
0xF780 –
0xF7FF
0xF800 –
0xFFFF
NOTE: Although the monitor does not support external memory, the user can enable external
memory accesses in the unfilled areas of the memory map.
The 2K-byte serial monitor program provides an RS-232 serial interface to a host PC. Serial
data rate is 115.2K bps. The monitor is compatible with Metrowerks CodeWarrior
Registers 1K bytes
Internal RAM
(Relocated)
Reserved
Fixed Flash EEPROM Block 1
(visible at RESET)
Fixed Flash EEPROM Block 2
User Vectors (Relocated)
User Reset Vector F7FE:F7FF
Vectors (Protected)
2K bytes
16K bytes
13.8K bytes
2.12K bytes
Freescale Semiconductor
15
Page 16

Development Studio and other serial monitor interface IDE’s. The serial monitor is not
compatible with ASCII interface programs such as HyperTerm or AxIDE. The monitor supports
23 primitive commands to control the target MCU. To allow a user to specify the address of
each interrupt service routine, this monitor redirects interrupt vectors to an unprotected portion
of FLASH.
To boot to the serial monitor, the user simply pressed and holds SW1 while pressing the
RESET switch or applying power. The status of SW1 is read only during the rising edge of
RESET. To load user application on start-up, the user is responsible for programming the
pseudo-reset vector (0xF7FE:0xF7FF). Pressing SW1 after the MCU exits reset will not
access the serial monitor. After exiting reset, pressing SW1 has effect as defined in the user
application.
BDM_PORT Header
BDM access is gained through the BDM_PORT header. This is a 6-pin header that allows
connection of a compatible HCS12 BDM cable. Refer to the documentation for the specific
BDM cable used for details on its use. The figure below shows the pin-out for the DEBUG
header.
Figure 4: BDM_PORT
MODC/BKGD
1 2
3 4
5 6
GND
RESET*
VDD
See the HC12 Reference Manual for complete
DEBUG documentation
16 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 17

f
A
How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
E-mail:
support@freescale.com
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Information Center, CH370
1300 N. Alma School Road
Chandler, Arizona 85224
+1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130
support@freescale.com
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
support@freescale.com
:
Japan
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku,
Tokyo 153-0064, Japan
0120 191014 or +81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 2666 8080
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
1-800-441-2447 or 303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSeminconductor@hibbertgroup.com
Design and/or Manufacturing services for this
product provided by:
Axiom Manufacturing
2813 Industrial Lane
Garland, Tx. 75041
Phone: 972-926-9303
Web: www.axman.com
Email: sales@axman.com
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and
software implementers to use Freescale Semiconductor products. There are
no express or implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or
fabricate any integrated circuits or integrated circuits based on the
information in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further
notice to any products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty,
representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any
particular purpose, nor does Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability
arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically
disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or
incidental damages. “Typical” parameters that may be provided in Freescale
Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different
applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating
parameters, including “Typicals”, must be validated for each customer
application by customer’s technical experts. Freescale Semiconductor does
not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others.
Freescale Semiconductor products are not designed, intended, or authorized
for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the
body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any
other application in which the failure of the Freescale Semiconductor product
could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should
Buyer purchase or use Freescale Semiconductor products for any such
unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold
Freescale Semiconductor and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates,
and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses,
and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim o
personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized
use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale Semiconductor was negligent
regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale
Semiconductor, Inc.
ll other product or service names are the property of their respective
owners.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2006. All rights reserved.
SLK0101UG
Rev. 0
09/2006
 Loading...
Loading...