Page 1

MLIB User's Guide
ARM® Cortex® M4
Document Number: CM4MLIBUG
Rev. 5, 12/2020
Page 2

MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
2 NXP Semiconductors
Page 3

Contents
Section number Title Page
Chapter 1
Library
1.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................................... 7
1.2 Library integration into project (MCUXpresso IDE) ....................................................................................................9
1.3 Library integration into project (Kinetis Design Studio) .............................................................................................. 19
1.4 Library integration into project (Keil µVision) ............................................................................................................. 25
1.5 Library integration into project (IAR Embedded Workbench) ..................................................................................... 35
Chapter 2
Algorithms in detail
2.1 MLIB_Abs......................................................................................................................................................................45
2.2 MLIB_AbsSat.................................................................................................................................................................46
2.3 MLIB_Add..................................................................................................................................................................... 47
2.4 MLIB_AddSat................................................................................................................................................................ 49
2.5 MLIB_Add4................................................................................................................................................................... 50
2.6 MLIB_Add4Sat.............................................................................................................................................................. 51
2.7 MLIB_Clb...................................................................................................................................................................... 53
2.8 MLIB_Conv................................................................................................................................................................... 54
2.9 MLIB_Div...................................................................................................................................................................... 55
2.10 MLIB_DivSat.................................................................................................................................................................57
2.11 MLIB_Div1Q................................................................................................................................................................. 58
2.12 MLIB_Div1QSat............................................................................................................................................................ 60
2.13 MLIB_Log2....................................................................................................................................................................62
2.14 MLIB_Mac.....................................................................................................................................................................63
2.15 MLIB_MacSat................................................................................................................................................................64
2.16 MLIB_MacRnd.............................................................................................................................................................. 66
2.17 MLIB_MacRndSat......................................................................................................................................................... 68
2.18 MLIB_Mac4...................................................................................................................................................................69
2.19 MLIB_Mac4Sat..............................................................................................................................................................71
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 3
Page 4

Section number Title Page
2.20 MLIB_Mac4Rnd............................................................................................................................................................ 72
2.21 MLIB_Mac4RndSat....................................................................................................................................................... 74
2.22 MLIB_Mnac...................................................................................................................................................................75
2.23 MLIB_MnacSat..............................................................................................................................................................77
2.24 MLIB_MnacRnd............................................................................................................................................................ 78
2.25 MLIB_MnacRndSat....................................................................................................................................................... 80
2.26 MLIB_Msu.....................................................................................................................................................................81
2.27 MLIB_MsuSat................................................................................................................................................................83
2.28 MLIB_MsuRnd.............................................................................................................................................................. 84
2.29 MLIB_MsuRndSat......................................................................................................................................................... 86
2.30 MLIB_Msu4...................................................................................................................................................................87
2.31 MLIB_Msu4Sat..............................................................................................................................................................89
2.32 MLIB_Msu4Rnd............................................................................................................................................................ 90
2.33 MLIB_Msu4RndSat....................................................................................................................................................... 92
2.34 MLIB_Mul..................................................................................................................................................................... 93
2.35 MLIB_MulSat................................................................................................................................................................ 95
2.36 MLIB_MulNeg...............................................................................................................................................................96
2.37 MLIB_MulNegSat..........................................................................................................................................................98
2.38 MLIB_MulRnd...............................................................................................................................................................99
2.39 MLIB_MulRndSat..........................................................................................................................................................101
2.40 MLIB_MulNegRnd........................................................................................................................................................ 103
2.41 MLIB_MulNegRndSat...................................................................................................................................................105
2.42 MLIB_Neg..................................................................................................................................................................... 106
2.43 MLIB_NegSat................................................................................................................................................................ 107
2.44 MLIB_Rcp......................................................................................................................................................................108
2.45 MLIB_Rcp1Q.................................................................................................................................................................110
2.46 MLIB_Rnd..................................................................................................................................................................... 111
2.47 MLIB_RndSat................................................................................................................................................................ 112
2.48 MLIB_Sat.......................................................................................................................................................................113
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
4 NXP Semiconductors
Page 5

Section number Title Page
2.49 MLIB_Sh1L................................................................................................................................................................... 114
2.50 MLIB_Sh1LSat.............................................................................................................................................................. 115
2.51 MLIB_Sh1R................................................................................................................................................................... 117
2.52 MLIB_ShL..................................................................................................................................................................... 118
2.53 MLIB_ShLSat................................................................................................................................................................ 119
2.54 MLIB_ShR..................................................................................................................................................................... 120
2.55 MLIB_ShLBi..................................................................................................................................................................122
2.56 MLIB_ShLBiSat.............................................................................................................................................................123
2.57 MLIB_ShRBi................................................................................................................................................................. 124
2.58 MLIB_ShRBiSat............................................................................................................................................................ 126
2.59 MLIB_Sign.....................................................................................................................................................................127
2.60 MLIB_Sub......................................................................................................................................................................128
2.61 MLIB_SubSat.................................................................................................................................................................130
2.62 MLIB_Sub4....................................................................................................................................................................131
2.63 MLIB_Sub4Sat...............................................................................................................................................................133
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 5
Page 6

MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
6 NXP Semiconductors
Page 7

Chapter 1
Library
1.1 Introduction
1.1.1 Overview
This user's guide describes the Math Library (MLIB) for the family of ARM Cortex
M4ARM Cortex M33ARM Cortex M33F core-based microcontrollers. This library
contains optimized functions.
1.1.2
Data types
MLIB supports several data types: (un)signed integer, fractional, and accumulator. The
integer data types are useful for general-purpose computation; they are familiar to the
MPU and MCU programmers. The fractional data types enable powerful numeric and
digital-signal-processing algorithms to be implemented. The accumulator data type is a
combination of both; that means it has the integer and fractional portions.
The following list shows the integer types defined in the libraries:
• Unsigned 16-bit integer —<0 ; 65535> with the minimum resolution of 1
• Signed 16-bit integer —<-32768 ; 32767> with the minimum resolution of 1
• Unsigned 32-bit integer —<0 ; 4294967295> with the minimum resolution of 1
• Signed 32-bit integer —<-2147483648 ; 2147483647> with the minimum resolution
of 1
The following list shows the fractional types defined in the libraries:
• Fixed-point 16-bit fractional —<-1 ; 1 - 2
• Fixed-point 32-bit fractional —<-1 ; 1 - 2
-15
> with the minimum resolution of 2
-31
> with the minimum resolution of 2
-15
-31
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 7
Page 8
Introduction
The following list shows the accumulator types defined in the libraries:
• Fixed-point 16-bit accumulator —<-256.0 ; 256.0 - 2-7> with the minimum
resolution of 2
• Fixed-point 32-bit accumulator —<-65536.0 ; 65536.0 - 2
resolution of 2
-7
-15
-15
> with the minimum
1.1.3 API definition
MLIB uses the types mentioned in the previous section. To enable simple usage of the
algorithms, their names use set prefixes and postfixes to distinguish the functions'
versions. See the following example:
f32Result = MLIB_Mac_F32lss(f32Accum, f16Mult1, f16Mult2);
where the function is compiled from four parts:
• MLIB—this is the library prefix
• Mac—the function name—Multiply-Accumulate
• F32—the function output type
• lss—the types of the function inputs; if all the inputs have the same type as the
output, the inputs are not marked
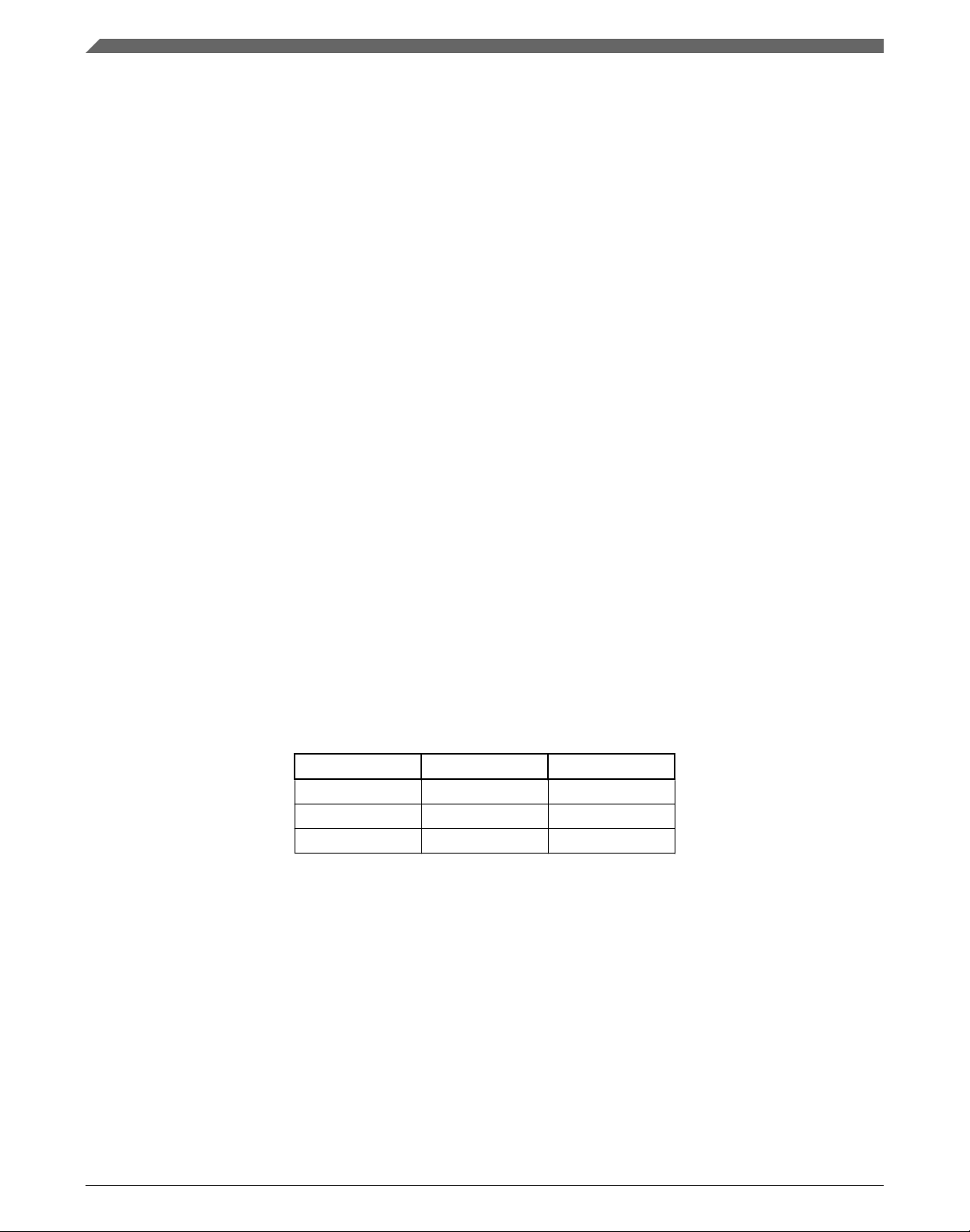
The input and output types are described in the following table:
Table 1-1. Input/output types
Type Output Input
frac16_t F16 s
frac32_t F32 l
acc32_t A32 a
1.1.4 Supported compilers
MLIB for the ARM Cortex M4ARM Cortex M33ARM Cortex M33F core is written in C
language or assembly language with C-callable interface depending on the specific
function. The library is built and tested using the following compilers:
• MCUXpresso IDE
• IAR Embedded Workbench
• Keil µVision
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
8 NXP Semiconductors
Page 9

Chapter 1 Library
For the MCUXpresso IDE, the library is delivered in the mlib.a file.
For the Kinetis Design Studio, the library is delivered in the mlib.a file.
For the IAR Embedded Workbench, the library is delivered in the mlib.a file.
For the Keil µVision, the library is delivered in the mlib.lib file.
The interfaces to the algorithms included in this library are combined into a single public
interface include file, mlib.h. This is done to lower the number of files required to be
included in your application.
1.1.5
MLIB for the ARM Cortex M4ARM Cortex M33ARM Cortex M33F core is written in C
language or assembly language with C-callable interface depending on the specific
function. Some functions from this library are inline type, which are compiled together
with project using this library. The optimization level for inline function is usually
defined by the specific compiler setting. It can cause an issue especially when high
optimization level is set. Therefore the optimization level for all inline assembly written
functions is defined by compiler pragmas using macros. The configuration header file
RTCESL_cfg.h is located in: specific library folder\MLIB\Include. The optimization level
can be changed by modifying the macro value for specific compiler. In case of any
change the library functionality is not guaranteed.
Similarly as optimization level the PowerQuad DSP Coprocessor and Accelerator support
can be disable or enable if it has not been done by defined symbol RTCESL_PQ_ON or
RTCESL_PQ_OFF in project setting described in the PowerQuad DSP Coprocessor and
Accelerator support cheaper for specific compiler.
Library configuration
1.1.6
1. The equations describing the algorithms are symbolic. If there is positive 1, the
2. The library functions that round the result (the API contains Rnd) round to nearest
1.2
NXP Semiconductors 9
Special issues
number is the closest number to 1 that the resolution of the used fractional type
allows. If there are maximum or minimum values mentioned, check the range
allowed by the type of the particular function version.
(half up).
Library integration into project (MCUXpresso IDE)
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
Page 10
Library integration into project (MCUXpresso IDE)
This section provides a step-by-step guide on how to quickly and easily include MLIB
into any MCUXpresso SDK example or demo application projects using MCUXpresso
IDE. This example uses the default installation path (C:\NXP\RTCESL
\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_MCUX). If you have a different installation path, use
that path instead.
1.2.1 PowerQuad DSP Coprocessor and Accelerator support
Some LPC platforms (LPC55S6x) contain a hardware accelerator dedicated to common
calculations in DSP applications. This section shows how to turn the PowerQuad (PQ)
support for a function on and off.
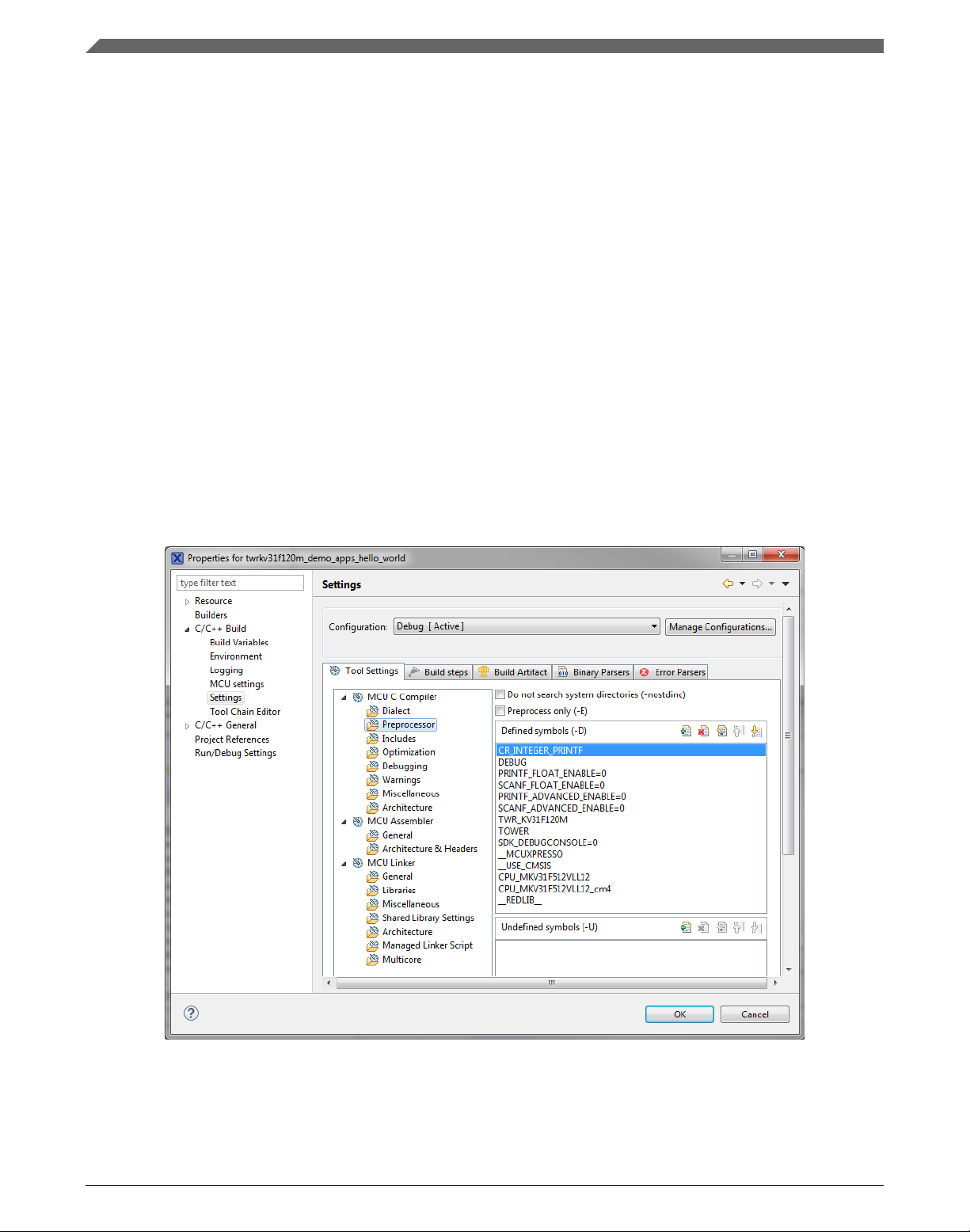
1. In the MCUXpresso SDK project name node or in the left-hand part, click Properties
or select Project > Properties from the menu. A project properties dialog appears.
2. Expand the C/C++ Build node and select Settings. See .
3. On the right-hand side, under the MCU C Compiler node, click the Preprocessor
node. See .
Figure 1-1. Defined symbols
4. In the right-hand part of the dialog, click the Add... icon located next to the Defined
symbols (-D) title.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
10 NXP Semiconductors
Page 11
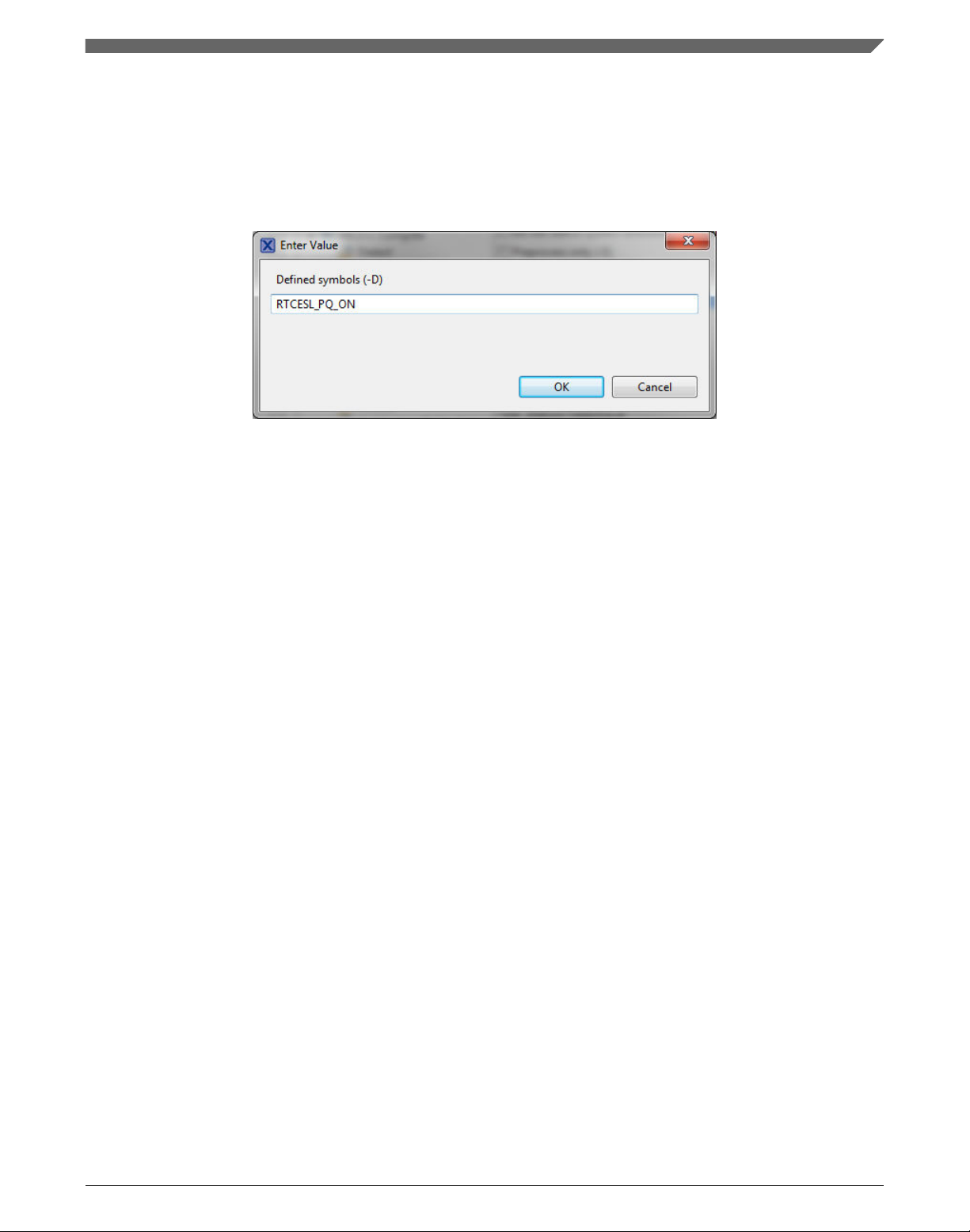
5. In the dialog that appears (see ), type the following:
• RTCESL_PQ_ON—to turn the PowerQuad support on
• RTCESL_PQ_OFF—to turn the PowerQuad support off
If neither of these two defines is defined, the hardware division and square root
support is turned off by default.
Figure 1-2. Symbol definition
6. Click OK in the dialog.
7. Click OK in the main dialog.
8. Ensure the PowerQuad moduel to be clocked by calling function
RTCESL_PQ_Init(); prior to the first function using PQ module calling.
Chapter 1 Library
See the device reference manual to verify whether the device contains the PowerQuad
DSP Coprocessor and Accelerator support.
1.2.2
Library path variable
To make the library integration easier, create a variable that holds the information about
the library path.
1. Right-click the MCUXpresso SDK project name node in the left-hand part and click
Properties, or select Project > Properties from the menu. A project properties dialog
appears.
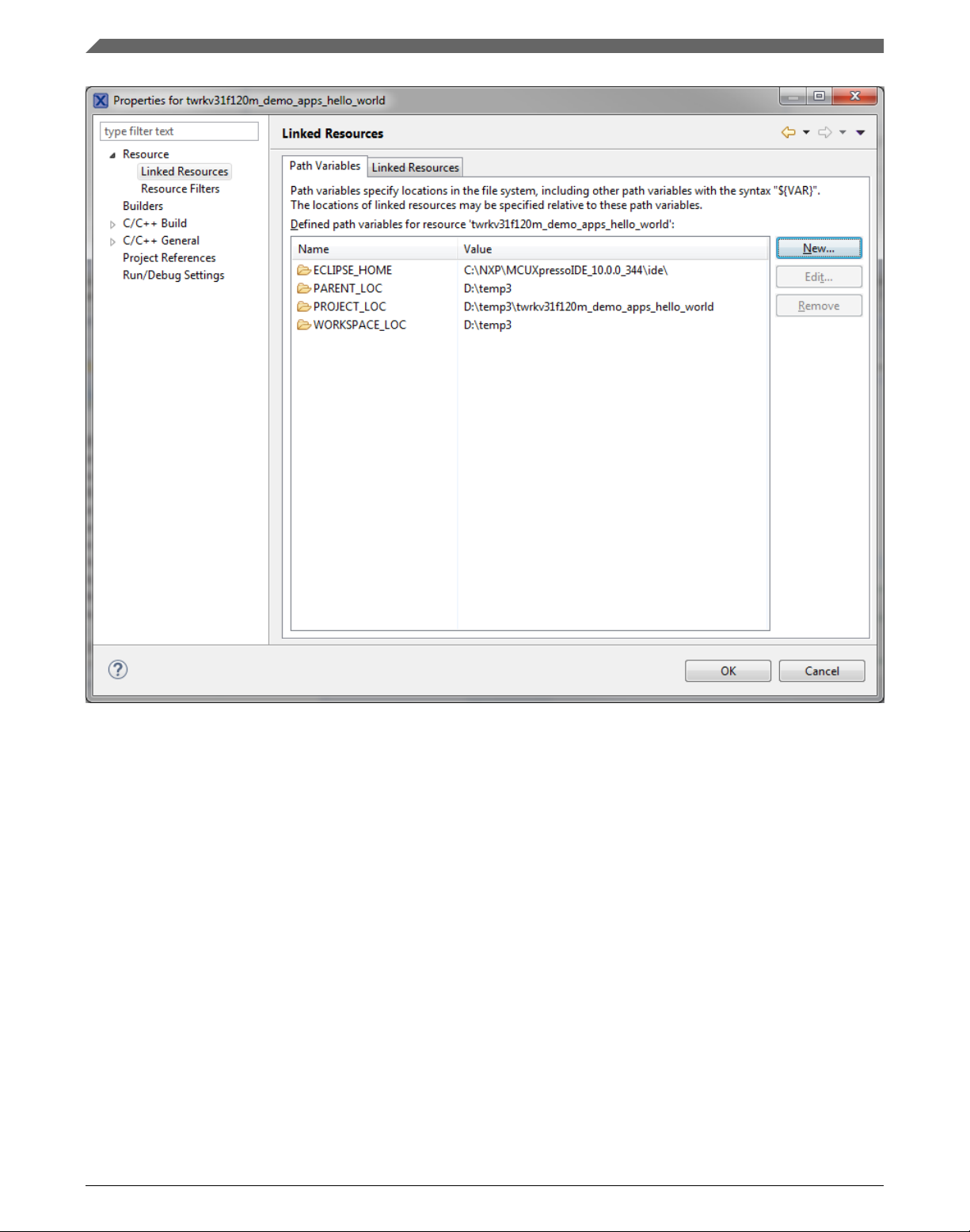
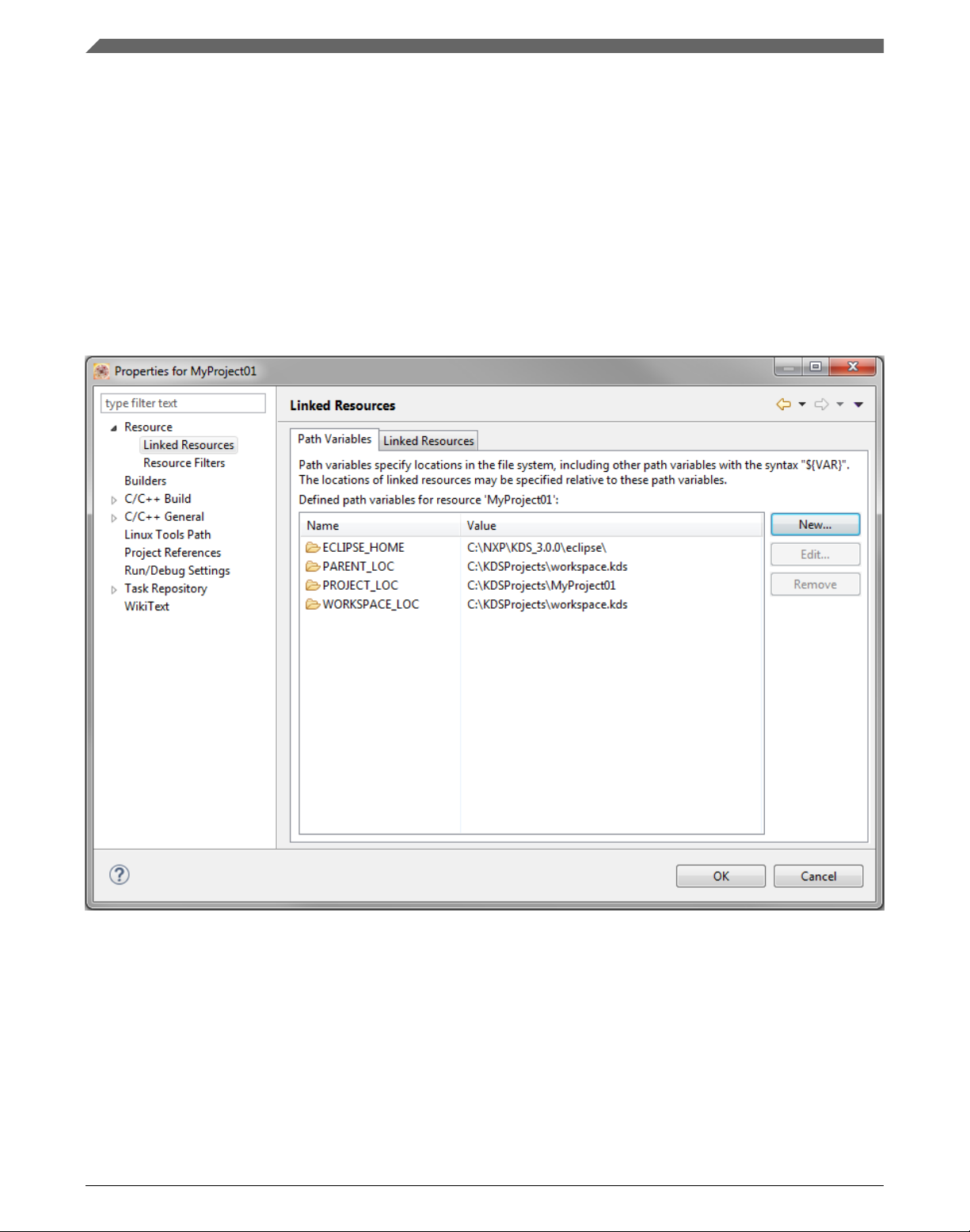
2. Expand the Resource node and click Linked Resources. See Figure 1-3.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 11
Page 12
Library integration into project (MCUXpresso IDE)
Figure 1-3. Project properties
3. Click the New… button in the right-hand side.
4. In the dialog that appears (see Figure 1-4), type this variable name into the Name
box: RTCESL_LOC.
5. Select the library parent folder by clicking Folder…, or just type the following path
into the Location box: C:\NXP\RTCESL\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_MCUX.
Click OK.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
12 NXP Semiconductors
Page 13

Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-4. New variable
6. Create such variable for the environment. Expand the C/C++ Build node and click
Environment.
7. Click the Add… button in the right-hand side.
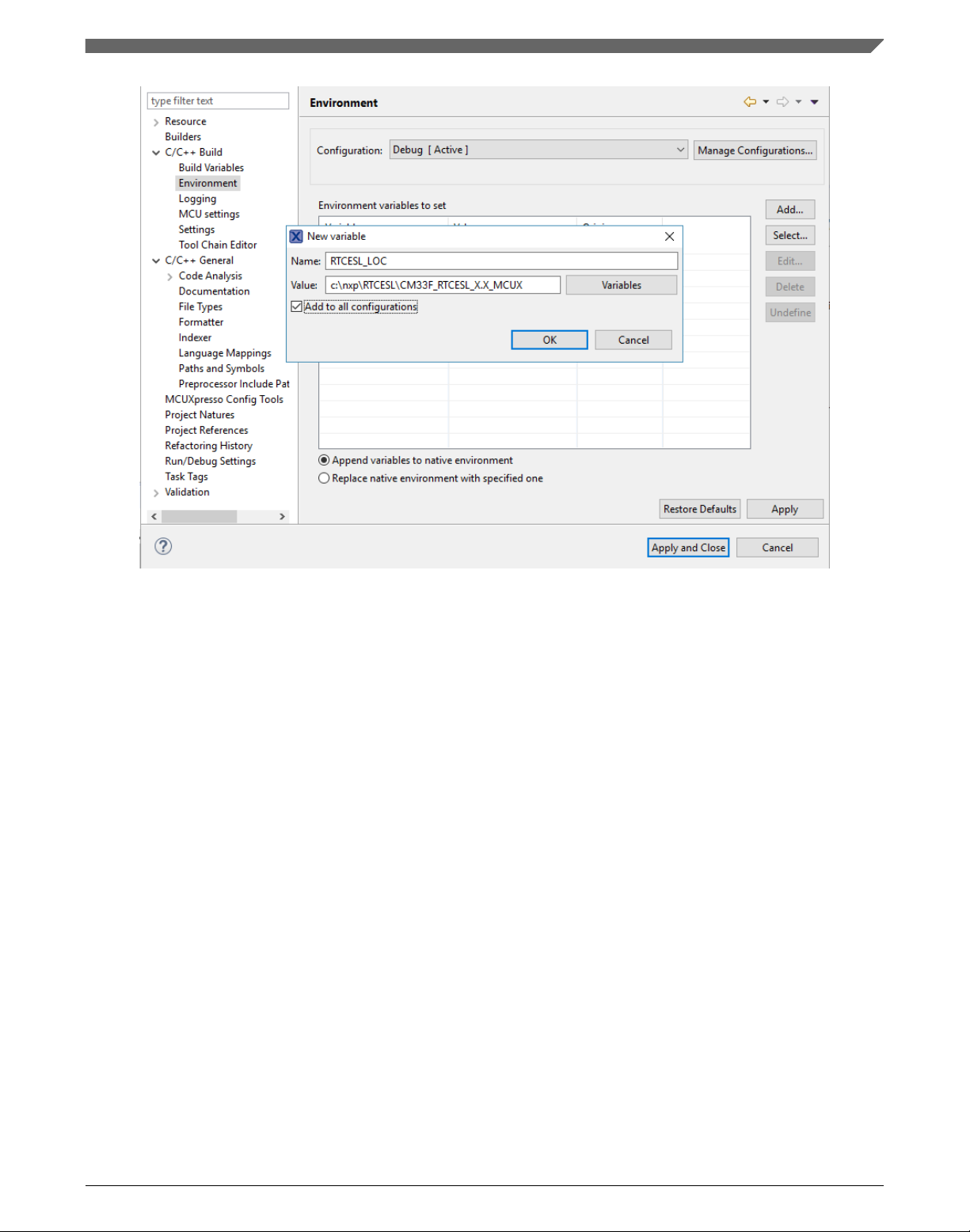
8. In the dialog that appears (see Figure 1-5), type this variable name into the Name
box: RTCESL_LOC.
9. Type the library parent folder path into the Value box: C:\NXP\RTCESL
\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_MCUX.
10. Tick the Add to all configurations box to use this variable in all configurations. See
Figure 1-5.
11. Click OK.
12. In the previous dialog, click OK.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 13
Page 14

Library integration into project (MCUXpresso IDE)
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
14 NXP Semiconductors
Page 15
Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-5. Environment variable
1.2.3
Library folder addition
To use the library, add it into the Project tree dialog.
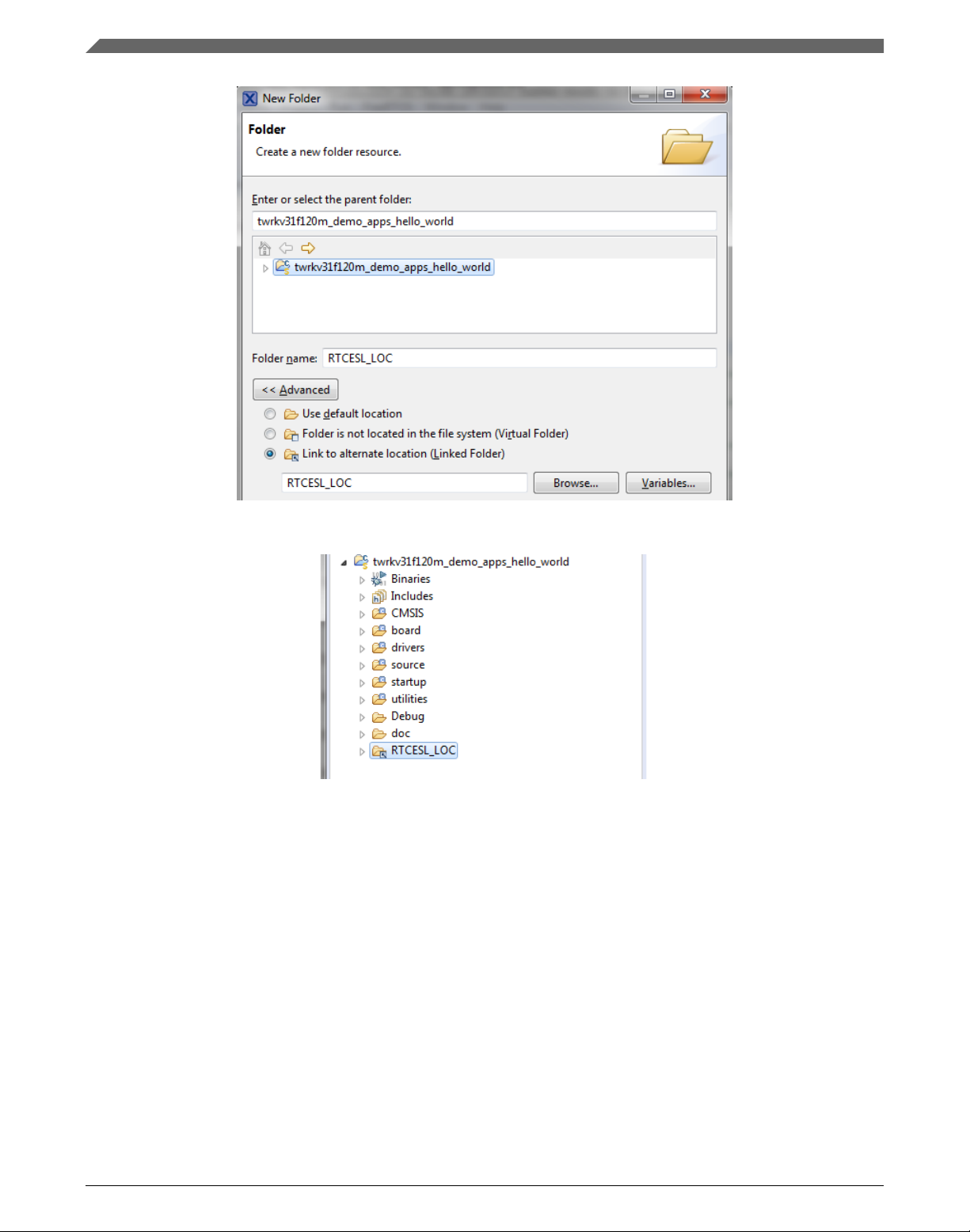
1. Right-click the MCUXpresso SDK project name node in the left-hand part and click
New > Folder, or select File > New > Folder from the menu. A dialog appears.
2. Click Advanced to show the advanced options.
3. To link the library source, select the Link to alternate location (Linked Folder)
option.
4. Click Variables..., select the RTCESL_LOC variable in the dialog, click OK, and/or
type the variable name into the box. See Figure 1-6.
5. Click Finish, and the library folder is linked in the project. See Figure 1-7.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 15
Page 16
Library integration into project (MCUXpresso IDE)
Figure 1-6. Folder link
Figure 1-7. Projects libraries paths
1.2.4
Library path setup
1. Right-click the MCUXpresso SDK project name node in the left-hand part and click
Properties, or select Project > Properties from the menu. The project properties
dialog appears.
2. Expand the C/C++ General node, and click Paths and Symbols.
3. In the right-hand dialog, select the Library Paths tab. See Figure 1-9.
4. Click the Add… button on the right, and a dialog appears.
5. Look for the RTCESL_LOC variable by clicking Variables…, and then finish the
path in the box by adding the following (see Figure 1-8): ${RTCESL_LOC}\MLIB.
6. Click OK, you will see the path added into the list. See Figure 1-9.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
16 NXP Semiconductors
Page 17
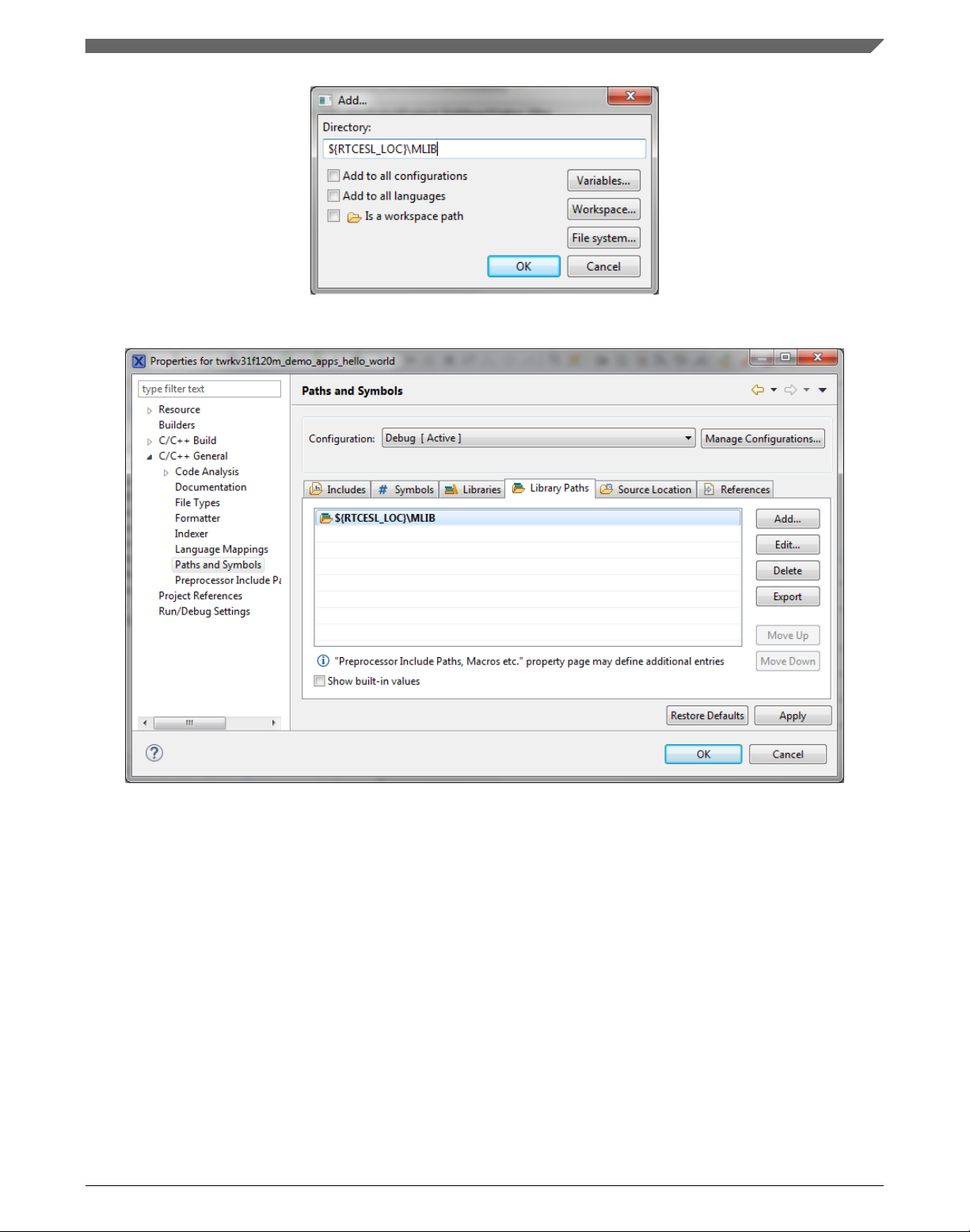
Figure 1-8. Library path inclusion
Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-9. Library paths
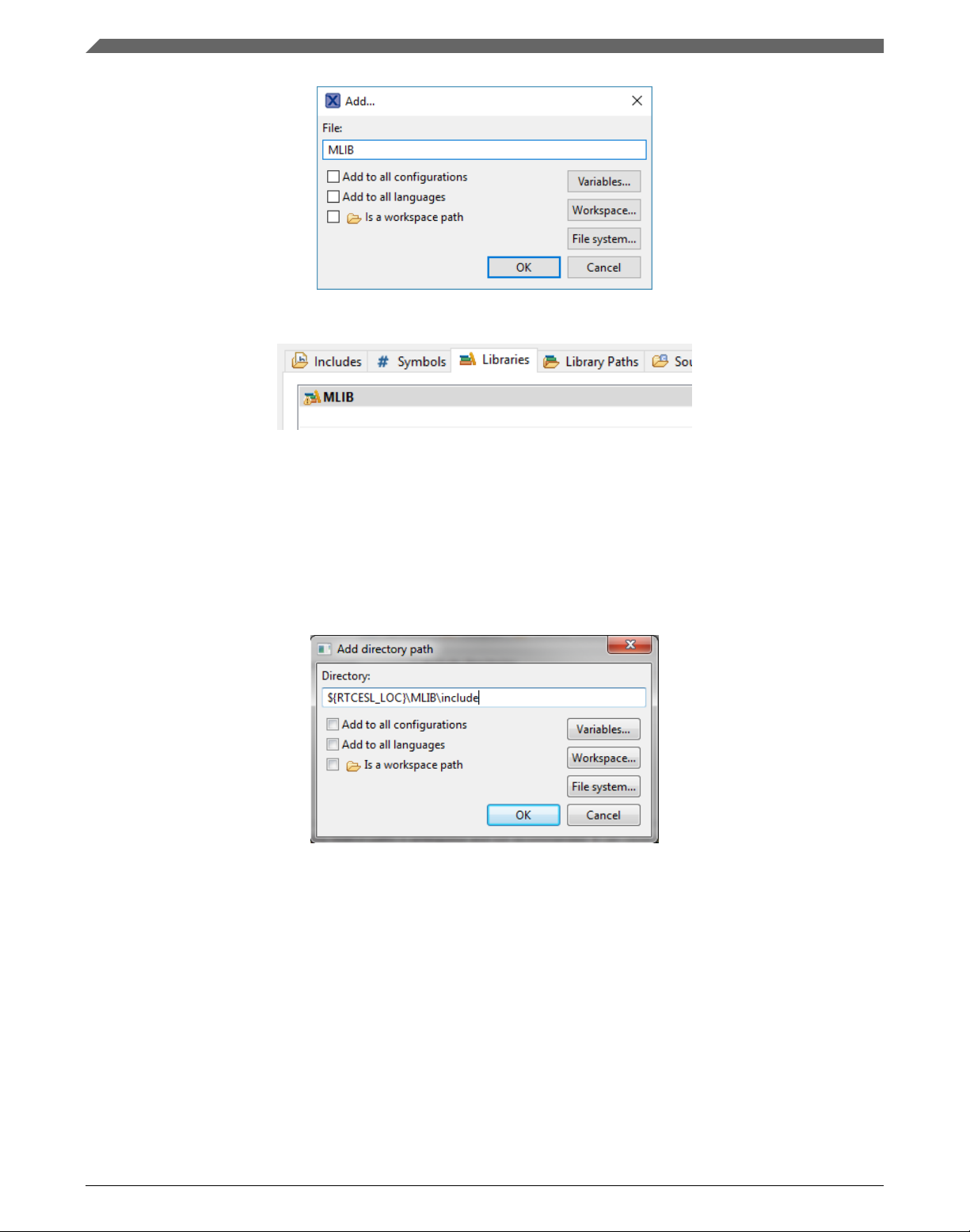
7. After adding the library path, add the library file. Click the Libraries tab. See Figure
1-11.
8. Click the Add… button on the right, and a dialog appears.
9. Type the following into the File text box (see Figure 1-10): :mlib.a
10. Click OK, and you will see the library added in the list. See Figure 1-11.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 17
Page 18
Library integration into project (MCUXpresso IDE)
Figure 1-10. Library file inclusion
Figure 1-11. Libraries
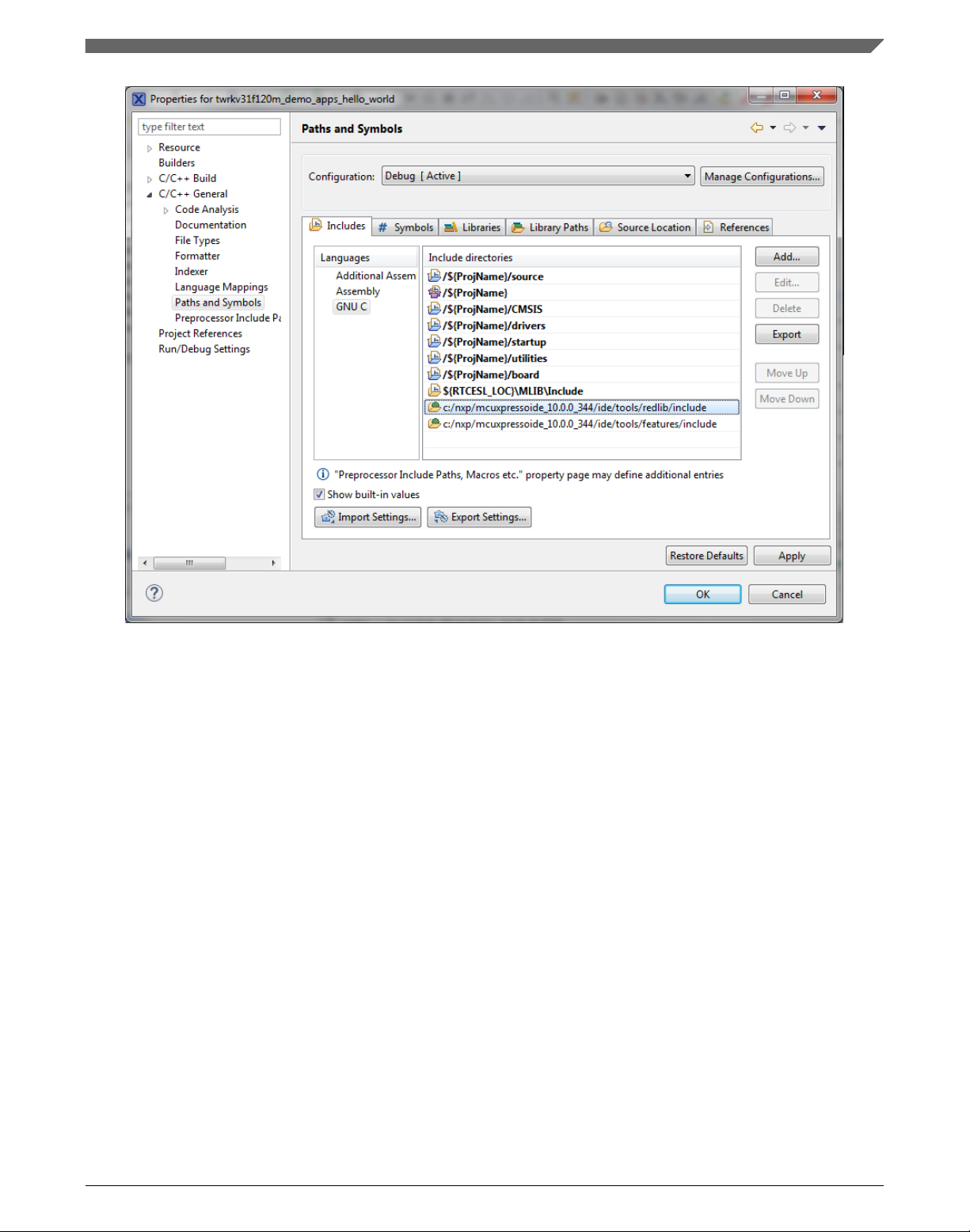
11. In the right-hand dialog, select the Includes tab, and click GNU C in the Languages
list. See Figure 1-13.
12. Click the Add… button on the right, and a dialog appears. See Figure 1-12.
13. Look for the RTCESL_LOC variable by clicking Variables…, and then finish the
path in the box to be: ${RTCESL_LOC}\MLIB\Include
14. Click OK, and you will see the path added in the list. See Figure 1-13. Click OK.
Figure 1-12. Library include path addition
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
18 NXP Semiconductors
Page 19
Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-13. Compiler setting
Type the #include syntax into the code where you want to call the library functions. In
the left-hand dialog, open the required .c file. After the file opens, include the following
line into the #include section:
#include "mlib_FP.h"
When you click the Build icon (hammer), the project is compiled without errors.
1.3
Library integration into project (Kinetis Design Studio)
This section provides a step-by-step guide on how to quickly and easily include MLIB
into an empty project or any MCUXpresso SDK example or demo application projects
using Kinetis Design Studio. This example uses the default installation path (C:\NXP
\RTCESL\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_KDS). If you have a different installation
path, use that path instead. If you want to use an existing MCUXpresso SDK project (for
example the hello_world project) see Library path variable. If not, continue with the next
section.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 19
Page 20
Library integration into project (Kinetis Design Studio)
1.3.1 Library path variable
To make the library integration easier, create a variable that will hold the information
about the library path.
1. Right-click the MyProject01 or MCUXpresso SDK project name node in the lefthand part and click Properties, or select Project > Properties from the menu. A
project properties dialog appears.
2. Expand the Resource node and click Linked Resources. See Figure 1-14.
Figure 1-14. Project properties
3. Click the New… button in the right-hand side.
4. In the dialog that appears (see Figure 1-15), type this variable name into the Name
box: RTCESL_LOC.
5. Select the library parent folder by clicking Folder…, or just type the following path
into the Location box: C:\NXP\RTCESL\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_KDS.
Click OK.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
20 NXP Semiconductors
Page 21

Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-15. New variable
6. Create such variable for the environment. Expand the C/C++ Build node and click
Environment.
7. Click the Add… button in the right-hand side.
8. In the dialog that appears (see Figure 1-16), type this variable name into the Name
box: RTCESL_LOC.
9. Type the library parent folder path into the Value box: C:\NXP\RTCESL
\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_KDS.
10. Tick the Add to all configurations box to use this variable in all configurations. See
Figure 1-16.
11. Click OK.
12. In the previous dialog, click OK.
Figure 1-16. Environment variable
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 21
Page 22
Library integration into project (Kinetis Design Studio)
1.3.2 Library folder addition
To use the library, add it into the Project tree dialog.
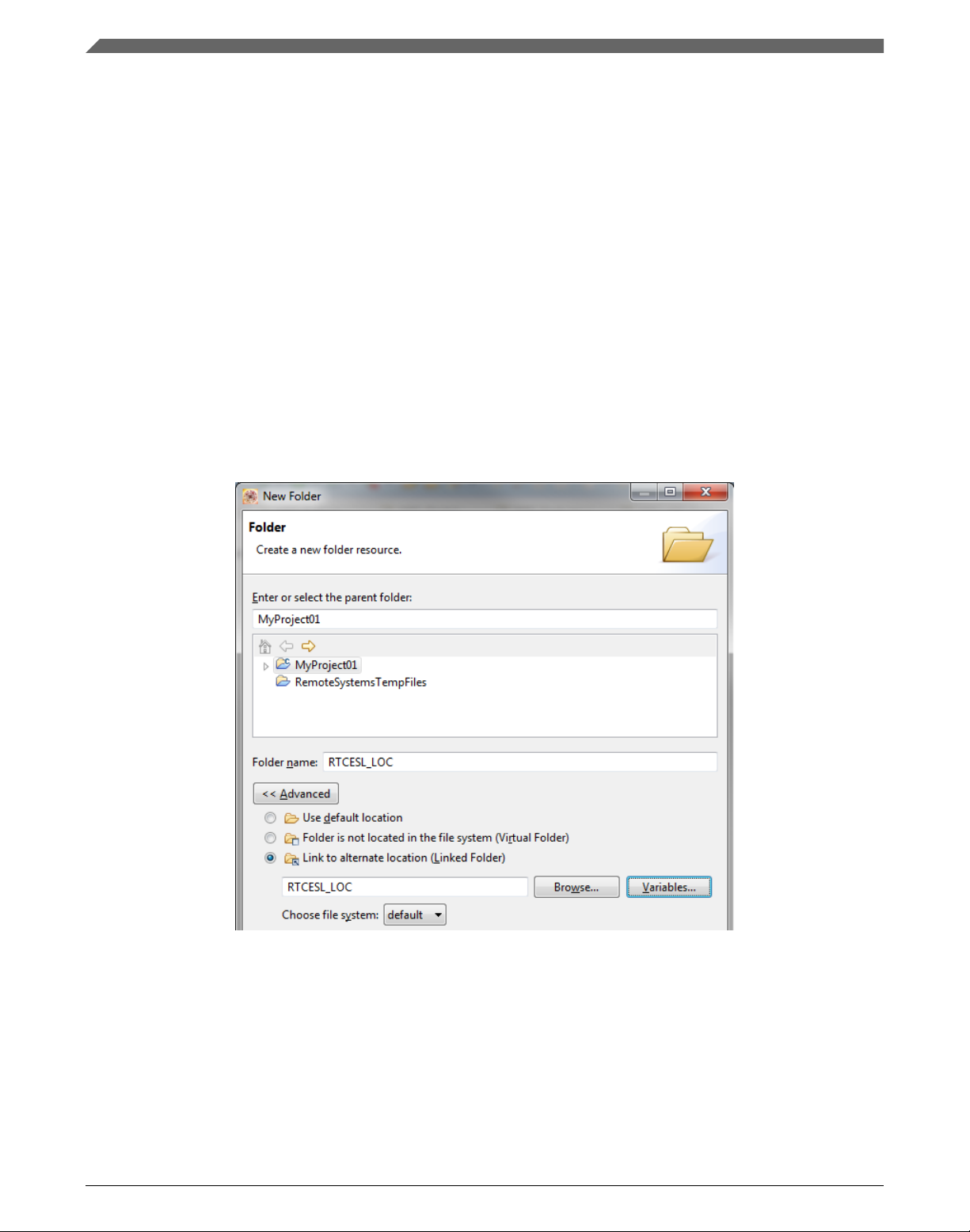
1. Right-click the MyProject01 or MCUXpresso SDK project name node in the lefthand part and click New > Folder, or select File > New > Folder from the menu. A
dialog appears.
2. Click Advanced to show the advanced options.
3. To link the library source, select the option Link to alternate location (Linked
Folder).
4. Click Variables..., select the RTCESL_LOC variable in the dialog, click OK, and/or
type the variable name into the box. See Figure 1-17.
5. Click Finish, and you will see the library folder linked in the project. See Figure
1-18.
Figure 1-17. Folder link
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
22 NXP Semiconductors
Page 23
Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-18. Projects libraries paths
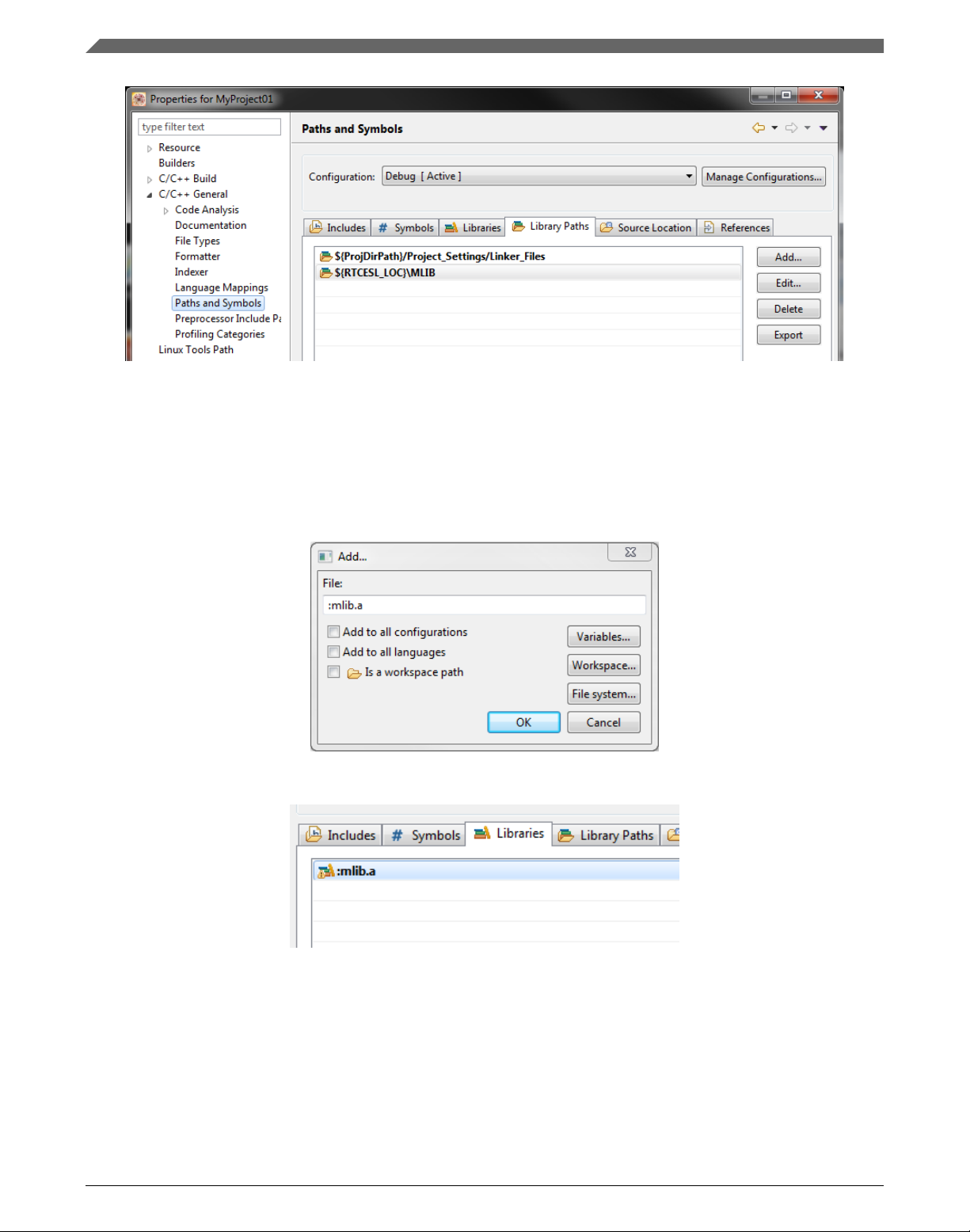
1.3.3 Library path setup
1. Right-click the MyProject01 or MCUXpresso SDK project name node in the lefthand part and click Properties, or select Project > Properties from the menu. A
project properties dialog appears.
2. Expand the C/C++ General node, and click Paths and Symbols.
3. In the right-hand dialog, select the Library Paths tab. See Figure 1-20.
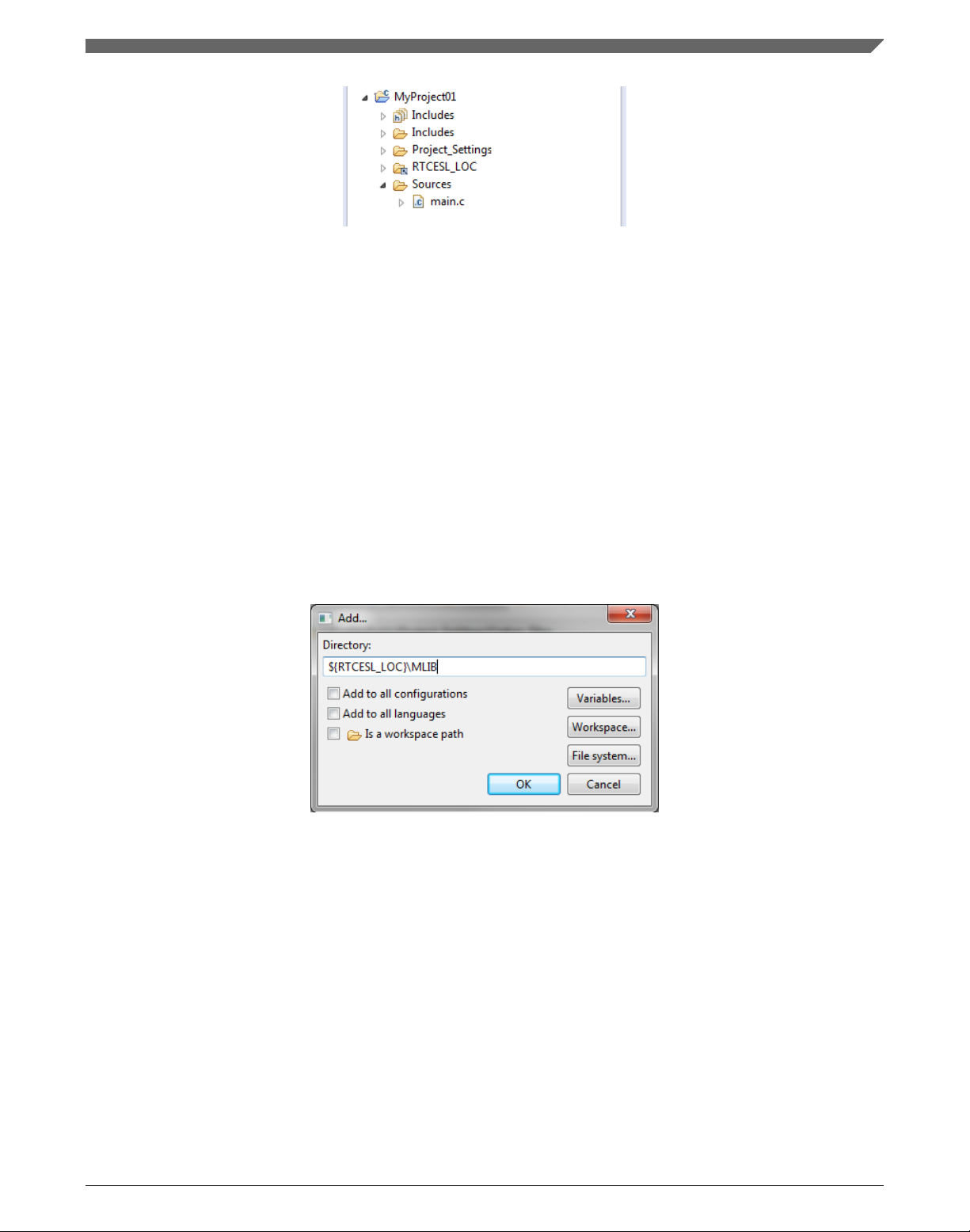
4. Click the Add… button on the right, and a dialog appears.
5. Look for the RTCESL_LOC variable by clicking Variables…, and then finish the
path in the box by adding the following (see Figure 1-19): ${RTCESL_LOC}\MLIB.
6. Click OK, and the path will be visible in the list. See Figure 1-20.
Figure 1-19. Library path inclusion
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 23
Page 24
Library integration into project (Kinetis Design Studio)
Figure 1-20. Library paths
7. After adding the library path, add the library file. Click the Libraries tab. See Figure
1-22.
8. Click the Add… button on the right, and a dialog appears.
9. Type the following into the File text box (see Figure 1-21): :mlib.a
10. Click OK, and you will see the library added in the list. See Figure 1-22.
Figure 1-21. Library file inclusion
Figure 1-22. Libraries
11. In the right-hand dialog, select the Includes tab, and click GNU C in the Languages
list. See Figure 1-24.
12. Click the Add… button on the right, and a dialog appears. See Figure 1-23.
13. Look for the RTCESL_LOC variable by clicking Variables…, and then finish the
path in the box to be: ${RTCESL_LOC}\MLIB\Include
14. Click OK, and you will see the path added in the list. See Figure 1-24. Click OK.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
24 NXP Semiconductors
Page 25
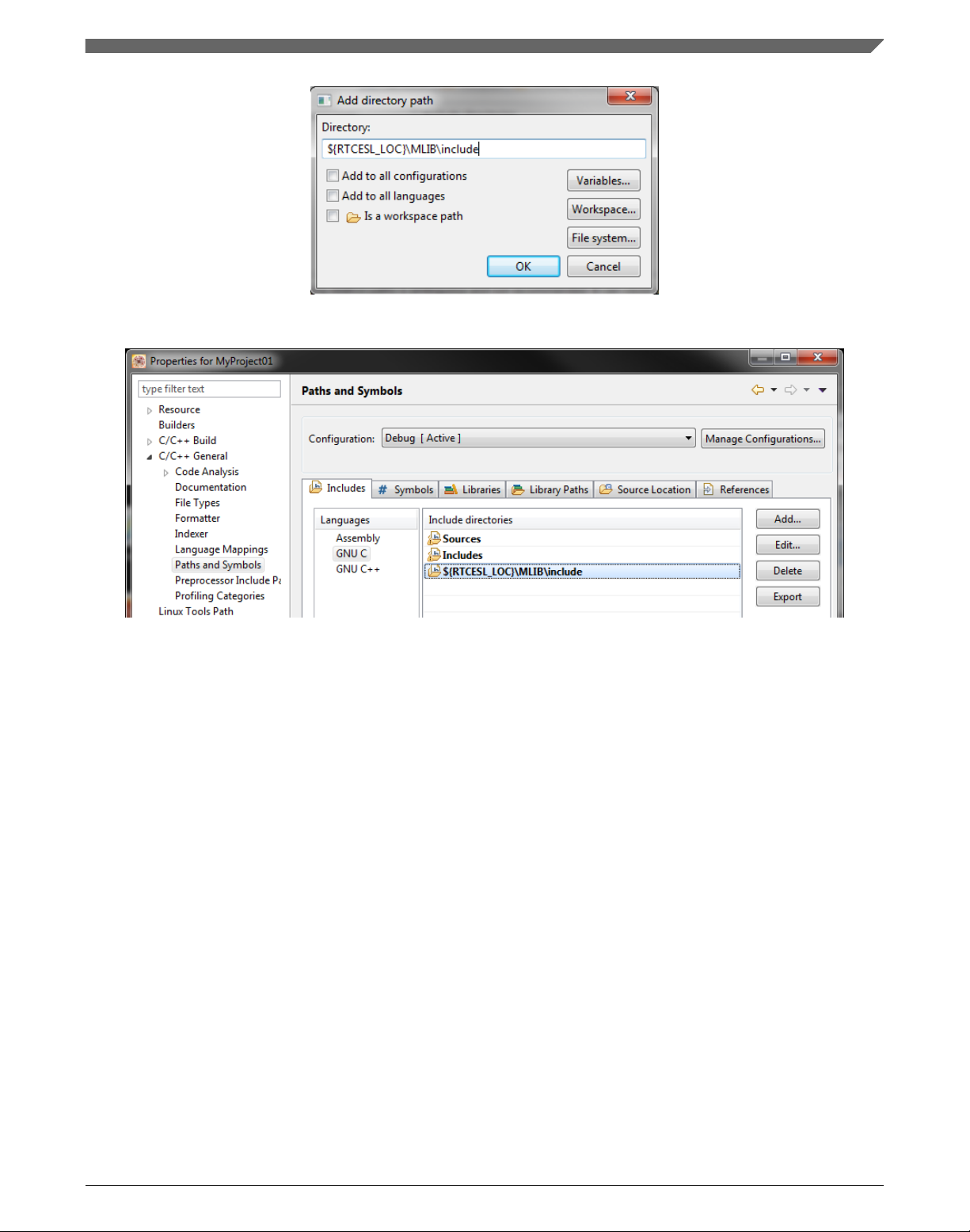
Figure 1-23. Library include path addition
Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-24. Compiler setting
Type the #include syntax into the code. Include the library into the main.c file. In the lefthand dialog, open the Sources folder of the project, and double-click the main.c file.
After the main.c file opens up, include the following line in the #include section:
#include "mlib.h"
When you click the Build icon (hammer), the project will be compiled without errors.
1.4
Library integration into project (Keil µVision)
This section provides a step-by-step guide on how to quickly and easily include MLIB
into an empty project or any MCUXpresso SDK example or demo application projects
using Keil µVision. This example uses the default installation path (C:\NXP\RTCESL
\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_KEIL). If you have a different installation path, use
that path instead. If any MCUXpresso SDK project is intended to use (for example
hello_world project) go to Linking the files into the project chapter otherwise read next
chapter.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 25
Page 26

Library integration into project (Keil µVision)
1.4.1 NXP pack installation for new project (without MCUXpresso
SDK)
This example uses the NXP MKV46F256xxx15LPC55s69 part, and the default
installation path (C:\NXP\RTCESL\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_KEIL) is
supposed. If the compiler has never been used to create any NXP MCU-based projects
before, check whether the NXP MCU pack for the particular device is installed. Follow
these steps:
1. Launch Keil µVision.
2. In the main menu, go to Project > Manage > Pack Installer….
3. In the left-hand dialog (under the Devices tab), expand the All Devices > Freescale
(NXP) node.
4. Look for a line called "KVxx Series" and click it.
5. In the right-hand dialog (under the Packs tab), expand the Device Specific node.
6. Look for a node called "Keil::Kinetis_KVxx_DFP." If there are the Install or Update
options, click the button to install/update the package. See Figure 1-25.
7. When installed, the button has the "Up to date" title. Now close the Pack Installer.
Figure 1-25. Pack Installer
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
26 NXP Semiconductors
Page 27
Chapter 1 Library
1.4.2 New project (without MCUXpresso SDK)
To start working on an application, create a new project. If the project already exists and
is opened, skip to the next section. Follow these steps to create a new project:
1. Launch Keil µVision.
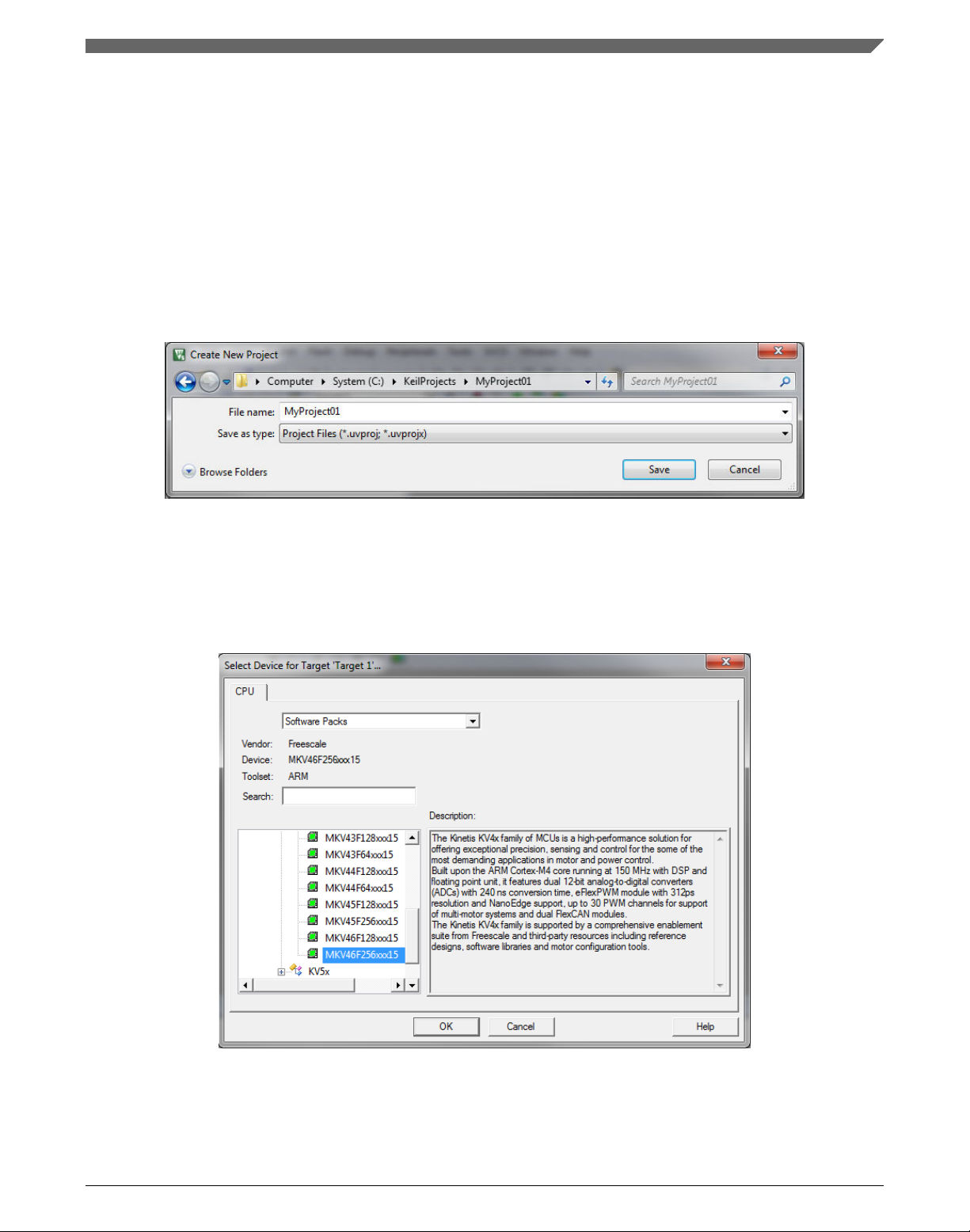
2. In the main menu, select Project > New µVision Project…, and the Create New
Project dialog appears.
3. Navigate to the folder where you want to create the project, for example C:
\KeilProjects\MyProject01. Type the name of the project, for example MyProject01.
Click Save. See Figure 1-26.
Figure 1-26. Create New Project dialog
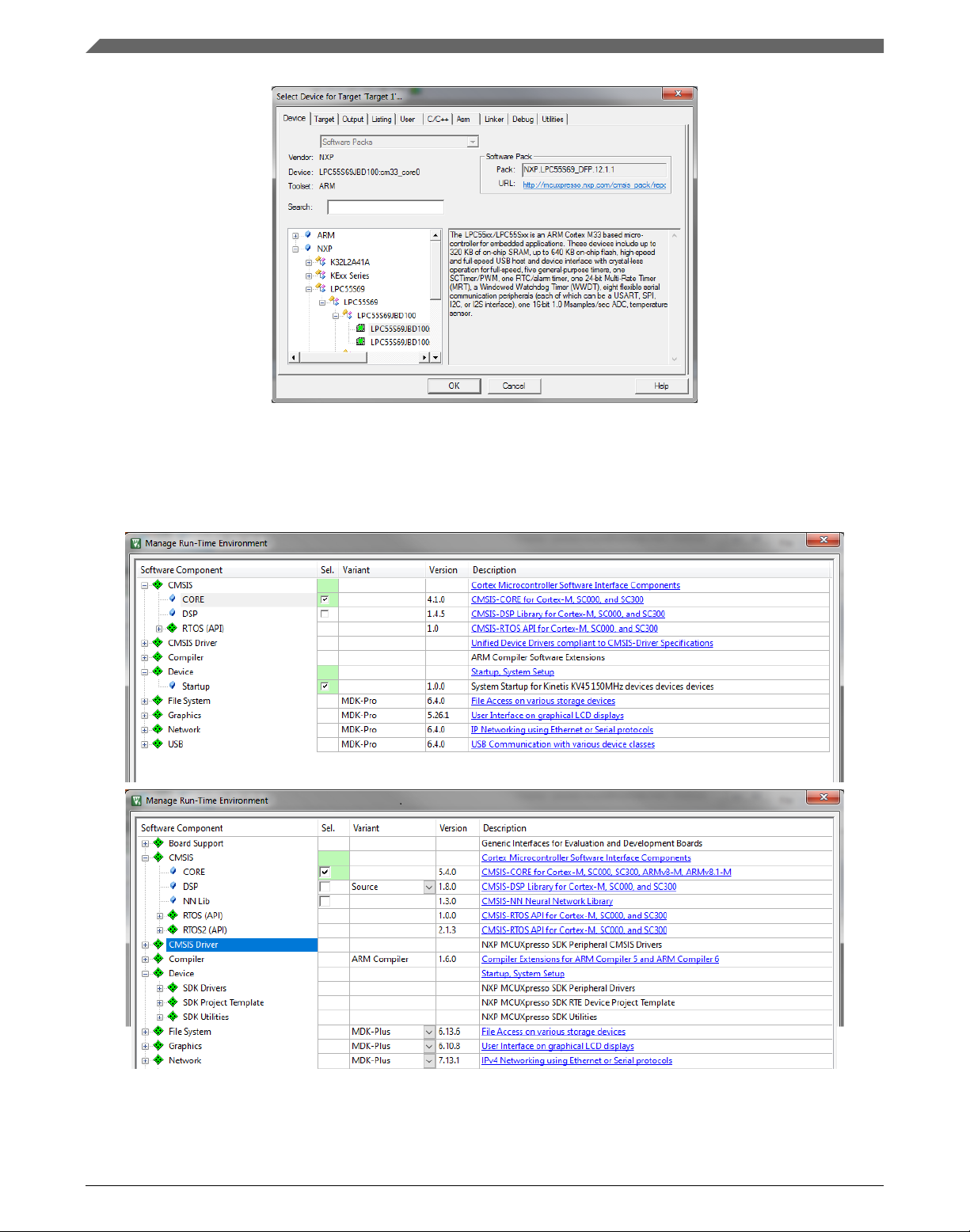
4. In the next dialog, select the Software Packs in the very first box.
5. Type 'kv4' into the Search box, so that the device list is reduced to the KV4x devices.
6. Expand the KV4x node.
7. Click the MKV46F256xxx15LPC55s69 node, and then click OK. See Figure 1-27.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 27
Page 28
Library integration into project (Keil µVision)
Figure 1-27. Select Device dialog
8. In the next dialog, expand the Device node, and tick the box next to the Startup node.
See Figure 1-28.
9. Expand the CMSIS node, and tick the box next to the CORE node.
Figure 1-28. Manage Run-Time Environment dialog
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
28 NXP Semiconductors
Page 29
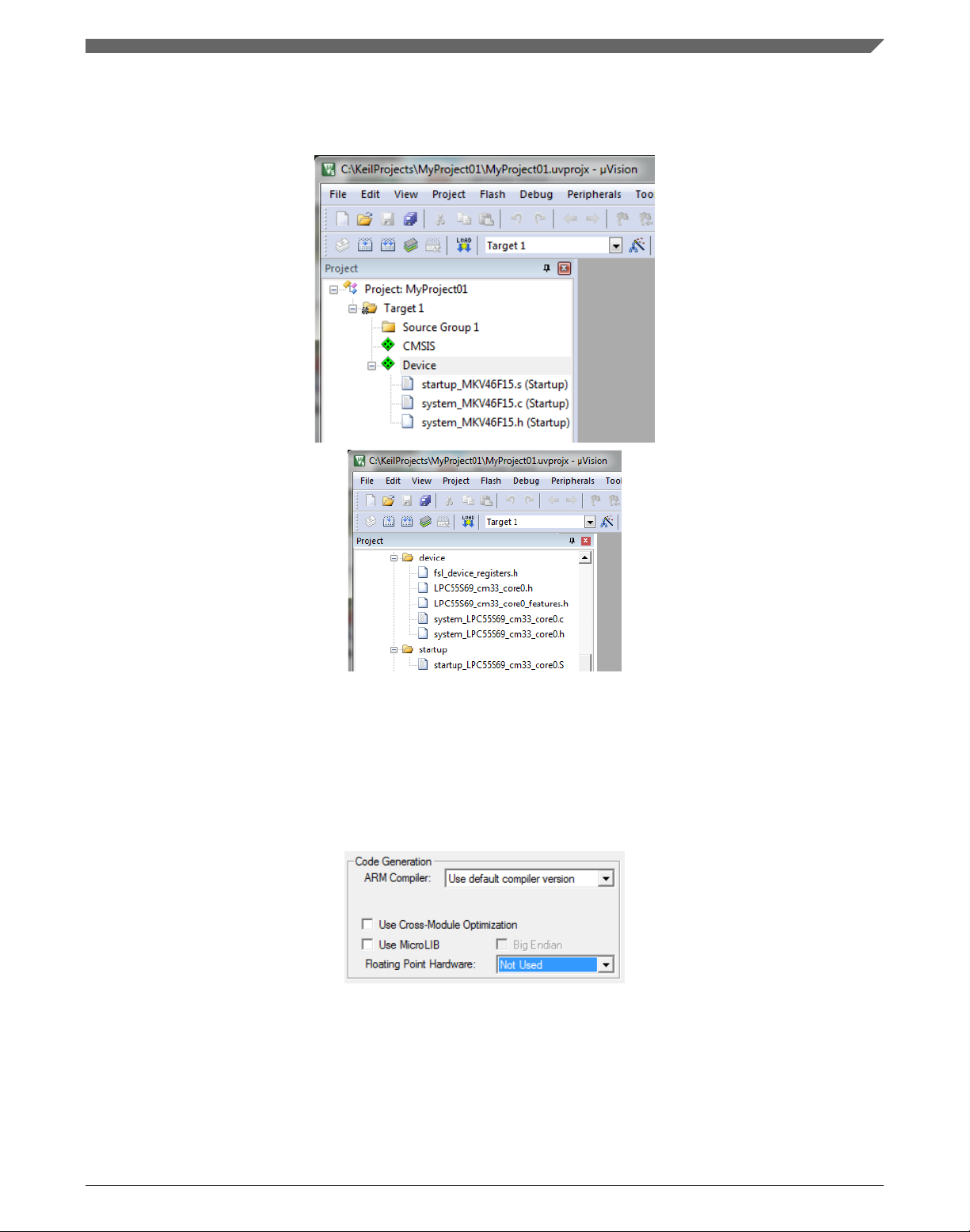
Chapter 1 Library
10. Click OK, and a new project is created. The new project is now visible in the lefthand part of Keil µVision. See Figure 1-29.
Figure 1-29. Project
11. In the main menu, go to Project > Options for Target 'Target1'…, and a dialog
appears.
12. Select the Target tab.
13. Select Not UsedUse Single Precision in the Floating Point Hardware option. See
Figure 1-29.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 29
Page 30
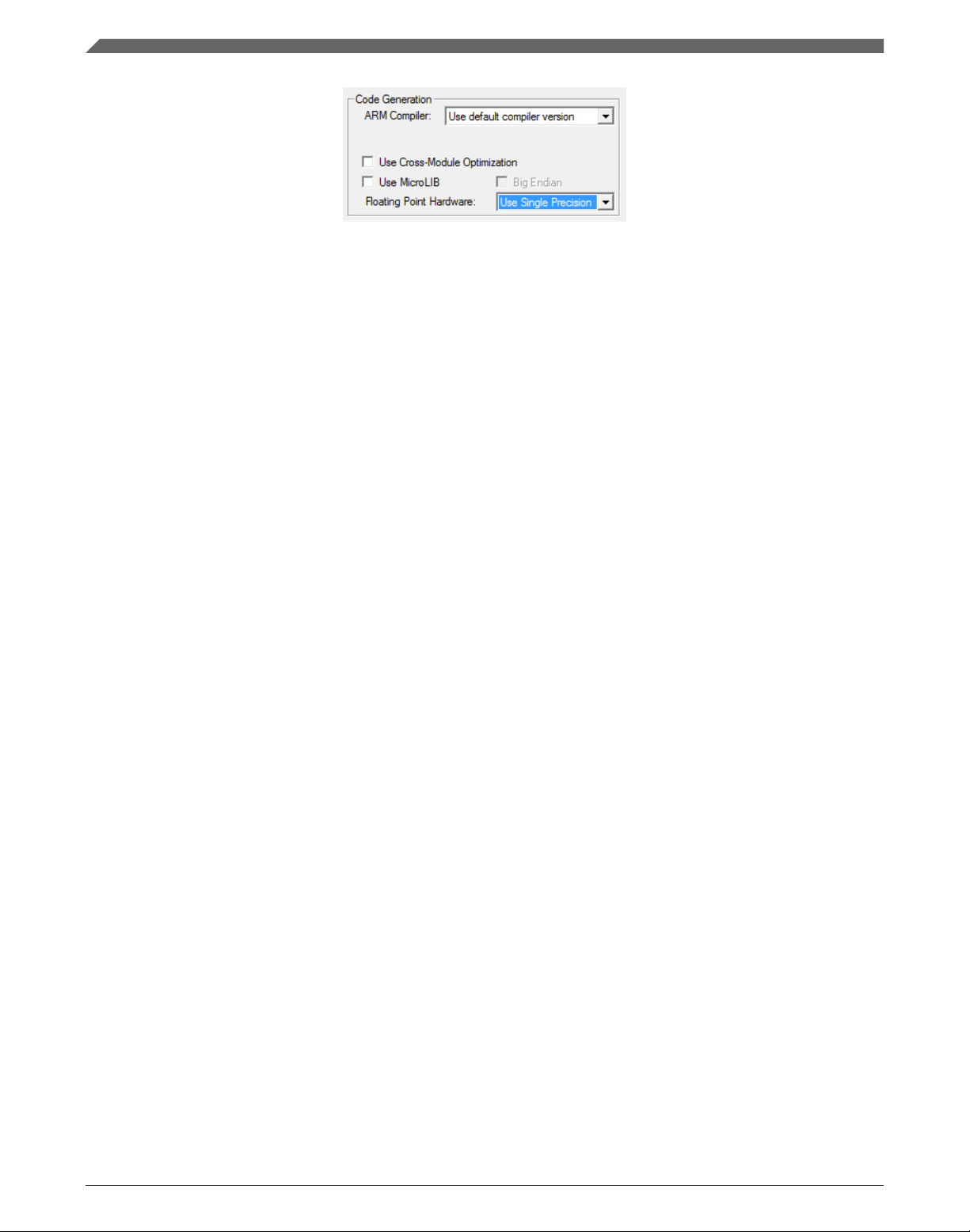
Library integration into project (Keil µVision)
Figure 1-30. FPU
1.4.3 PowerQuad DSP Coprocessor and Accelerator support
Some LPC platforms (LPC55S6x) contain a hardware accelerator dedicated to common
calculations in DSP applications. This section shows how to turn the PowerQuad (PQ)
support for a function on and off.
1. In the main menu, go to Project > Options for Target 'Target1'…, and a dialog
appears.
2. Select the C/C++ tab. See Figure 1-31.
3. In the Include Preprocessor Symbols text box, type the following:
• RTCESL_PQ_ON—to turn the hardware division and square root support on.
• RTCESL_PQ_OFF—to turn the hardware division and square root support off.
If neither of these two defines is defined, the hardware division and square root
support is turned off by default.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
30 NXP Semiconductors
Page 31

Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-31. Preprocessor symbols
4. Click OK in the main dialog.
5. Ensure the PowerQuad moduel to be clocked by calling function
RTCESL_PQ_Init(); prior to the first function using PQ module calling.
See the device reference manual to verify whether the device contains the PowerQuad
DSP Coprocessor and Accelerator support.
1.4.4
Linking the files into the project
To include the library files in the project, create groups and add them.
1. Right-click the Target 1 node in the left-hand part of the Project tree, and select Add
Group… from the menu. A new group with the name New Group is added.
2. Click the newly created group, and press F2 to rename it to RTCESL.
3. Right-click the RTCESL node, and select Add Existing Files to Group 'RTCESL'…
from the menu.
4. Navigate into the library installation folder C:\NXP\RTCESL
\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_KEIL\MLIB\Include, and select the mlib_FP.h
file. If the file does not appear, set the Files of type filter to Text file. Click Add. See
Figure 1-32.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 31
Page 32

Library integration into project (Keil µVision)
Figure 1-32. Adding .h files dialog
5. Navigate to the parent folder C:\NXP\RTCESL
\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_KEIL\MLIB, and select the mlib.lib file. If the
file does not appear, set the Files of type filter to Library file. Click Add. See Figure
1-33.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
32 NXP Semiconductors
Page 33

Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-33. Adding .lib files dialog
6. Now, all necessary files are in the project tree; see Figure 1-34. Click Close.
Figure 1-34. Project workspace
1.4.5
Library path setup
The following steps show the inclusion of all dependent modules.
1. In the main menu, go to Project > Options for Target 'Target1'…, and a dialog
appears.
2. Select the C/C++ tab. See Figure 1-35.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 33
Page 34

Library integration into project (Keil µVision)
3. In the Include Paths text box, type the following path (if there are more paths, they
must be separated by ';') or add it by clicking the … button next to the text box:
• "C:\NXP\RTCESL\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_KEIL\MLIB\Include"
4. Click OK.
5. Click OK in the main dialog.
Figure 1-35. Library path addition
Type the #include syntax into the code. Include the library into a source file. In the new
project, it is necessary to create a source file:
1. Right-click the Source Group 1 node, and Add New Item to Group 'Source Group
1'… from the menu.
2.
Select the C File (.c) option, and type a name of the file into the Name box, for
example 'main.c'. See Figure 1-36.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
34 NXP Semiconductors
Page 35

Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-36. Adding new source file dialog
3. Click Add, and a new source file is created and opened up.
4. In the opened source file, include the following line into the #include section, and
create a main function:
#include "mlib_FP.h"
int main(void)
{
while(1);
}
When you click the Build (F7) icon, the project will be compiled without errors.
1.5
Library integration into project (IAR Embedded Workbench)
This section provides a step-by-step guide on how to quickly and easily include the
MLIB into an empty project or any MCUXpresso SDK example or demo application
projects using IAR Embedded Workbench. This example uses the default installation
path (C:\NXP\RTCESL\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_IAR). If you have a different
installation path, use that path instead. If any MCUXpresso SDK project is intended to
use (for example hello_world project) go to Linking the files into the project chapter
otherwise read next chapter.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 35
Page 36

Library integration into project (IAR Embedded Workbench)
1.5.1 New project (without MCUXpresso SDK)
This example uses the NXP MKV46F256xxx15LPC55S69 part, and the default
installation path (C:\NXP\RTCESL\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_IAR) is supposed.
To start working on an application, create a new project. If the project already exists and
is opened, skip to the next section. Perform these steps to create a new project:
1. Launch IAR Embedded Workbench.
2. In the main menu, select Project > Create New Project… so that the "Create New
Project" dialog appears. See Figure 1-37.
Figure 1-37. Create New Project dialog
3. Expand the C node in the tree, and select the "main" node. Click OK.
4. Navigate to the folder where you want to create the project, for example, C:
\IARProjects\MyProject01. Type the name of the project, for example, MyProject01.
Click Save, and a new project is created. The new project is now visible in the lefthand part of IAR Embedded Workbench. See Figure 1-38.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
36 NXP Semiconductors
Page 37

Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-38. New project
5. In the main menu, go to Project > Options…, and a dialog appears.
6. In the Target tab, select the Device option, and click the button next to the dialog to
select the MCU. In this example, select NXP > KV4x > NXP MKV46F256xxx15.
Select None in the FPU option.> LPC55S69 > NXP LPC55S69_core0. Select
NoneVFPv5 single precision in the FPU option.The DSP instructions group is
required please check the DSP Extensions checkbox if not checked. Click OK. See
Figure 1-39.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 37
Page 38

Library integration into project (IAR Embedded Workbench)
Figure 1-39. Options dialog
1.5.2
PowerQuad DSP Coprocessor and Accelerator support
Some LPC platforms (LPC55S6x) contain a hardware accelerator dedicated to common
calculations in DSP applications. Only functions runing faster through the PowerQuad
module than the core itself are supported and targeted to be calculated by the PowerQuad
module. This section shows how to turn the PowerQuad (PQ) support for a function on
and off.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
38 NXP Semiconductors
Page 39

Chapter 1 Library
1. In the main menu, go to Project > Options…, and a dialog appears.
2. In the left-hand column, select C/C++ Compiler.
3. In the right-hand part of the dialog, click the Preprocessor tab (it can be hidden in the
right-hand side; use the arrow icons for navigation).
4. In the text box (at the Defined symbols: (one per line)), type the following (See
Figure 1-40):
• RTCESL_PQ_ON—to turn the PowerQuad support on.
• RTCESL_PQ_OFF—to turn the PowerQuad support off.
If neither of these two defines is defined, the hardware division and square root
support is turned off by default.
Figure 1-40. Defined symbols
5. Click OK in the main dialog.
6. Ensure the PowerQuad moduel to be clocked by calling function
RTCESL_PQ_Init(); prior to the first function using PQ module calling.
See the device reference manual to verify whether the device contains the PowerQuad
DSP Coprocessor and Accelerator support.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 39
Page 40

Library integration into project (IAR Embedded Workbench)
1.5.3 Library path variable
To make the library integration easier, create a variable that will hold the information
about the library path.
1. In the main menu, go to Tools > Configure Custom Argument Variables…, and a
dialog appears.
2. Click the New Group button, and another dialog appears. In this dialog, type the
name of the group PATH, and click OK. See Figure 1-41.
Figure 1-41. New Group
3. Click on the newly created group, and click the Add Variable button. A dialog
appears.
4. Type this name: RTCESL_LOC
5. To set up the value, look for the library by clicking the '…' button, or just type the
installation path into the box: C:\NXP\RTCESL
\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_IAR. Click OK.
6. In the main dialog, click OK. See Figure 1-42.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
40 NXP Semiconductors
Page 41

Chapter 1 Library
Figure 1-42. New variable
1.5.4
Linking the files into the project
To include the library files into the project, create groups and add them.
1. Go to the main menu Project > Add Group…
2. Type RTCESL, and click OK.
3. Click on the newly created node RTCESL, go to Project > Add Group…, and create
a MLIB subgroup.
4. Click on the newly created node MLIB, and go to the main menu Project > Add
Files… See Figure 1-44.
5. Navigate into the library installation folder C:\NXP\RTCESL
\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_IAR\MLIB\Include, and select the mlib.h file. (If
the file does not appear, set the file-type filter to Source Files.) Click Open. See
Figure 1-43.
6. Navigate into the library installation folder C:\NXP\RTCESL
\CM4CM33CM33F_RTCESL_4.6_IAR\MLIB, and select the mlib.a file. If the file
does not appear, set the file-type filter to Library / Object files. Click Open.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 41
Page 42

Library integration into project (IAR Embedded Workbench)
Figure 1-43. Add Files dialog
7. Now you will see the files added in the workspace. See Figure 1-44.
Figure 1-44. Project workspace
1.5.5
Library path setup
1. In the main menu, go to Project > Options…, and a dialog appears.
2. In the left-hand column, select C/C++ Compiler.
3. In the right-hand part of the dialog, click on the Preprocessor tab (it can be hidden in
the right; use the arrow icons for navigation).
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
42 NXP Semiconductors
Page 43

Chapter 1 Library
4. In the text box (at the Additional include directories title), type the following folder
(using the created variable):
• $RTCESL_LOC$\MLIB\Include
5. Click OK in the main dialog. See Figure 1-45.
Figure 1-45. Library path adition
Type the #include syntax into the code. Include the library included into the main.c file.
In the workspace tree, double-click the main.c file. After the main.c file opens up, include
the following line into the #include section:
#include "mlib_FP.h"
When you click the Make icon, the project will be compiled without errors.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 43
Page 44

Library integration into project (IAR Embedded Workbench)
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
44 NXP Semiconductors
Page 45

Chapter 2
Algorithms in detail
2.1 MLIB_Abs
The
MLIB_Abs functions return the absolute value of the input. The function does not
saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 1. Algorithm formula
2.1.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_Abs function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-1. Function versions
Function name Input type Result type Description
MLIB_Abs_F16 frac16_t frac16_t Absolute value of a 16-bit fractional value. The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
MLIB_Abs_F32 frac32_t frac32_t Absolute value of a 32-bit fractional value. The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
2.1.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Abs functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Abs_F16(frac16_t f16Val)
frac32_t MLIB_Abs_F32(frac32_t f32Val)
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 45
Page 46

MLIB_AbsSat
2.1.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_Abs function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Result;
static frac32_t f32Val;
void main(void)
{
f32Val = FRAC32(-0.354); /* f32Val = -0.354 */
/* f32Result = |f32Val| */
f32Result = MLIB_Abs_F32(f32Val);
}
2.2
MLIB_AbsSat
The MLIB_AbsSat functions return the absolute value of the input. The function
saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 2. Algorithm formula
2.2.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <0 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_AbsSat function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-2. Function versions
Function name Input type Result type Description
MLIB_AbsSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t Absolute value of a 16-bit fractional value. The output is within the
range <0 ; 1).
MLIB_AbsSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t Absolute value of a 32-bit fractional value. The output is within the
range <0 ; 1).
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
46 NXP Semiconductors
Page 47

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
2.2.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_AbsSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_AbsSat_F16(frac16_t f16Val)
frac32_t MLIB_AbsSat_F32(frac32_t f32Val)
2.2.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_AbsSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac16_t f16Val, f16Result;
void main(void)
{
f16Val = FRAC16(-0.835); /* f16Val = -0.835 */
/* f16Result = sat(|f16Val|) */
f16Result = MLIB_AbsSat_F16(f16Val);
}
2.3
MLIB_Add
The MLIB_Add functions return the sum of two addends. The function does not saturate
the output. See the following equation:
Equation 3. Algorithm formula
2.3.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 47
Page 48

MLIB_Add
• Accumulator output with fractional inputs - the output is the accumulator type, where
the result can be out of the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the fractional values only.
• Accumulator output with mixed inputs - the output is the accumulator type, where
the result can be out of the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the accumulator and
fractional values. The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_Add function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-3. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Addend 1 Addend 2
MLIB_Add_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Addition of two 16-bit fractional addends. The output is
MLIB_Add_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Addition of two 32-bit fractional addends. The output is
MLIB_Add_A32ss frac16_t frac16_t acc32_t Addition of two 16-bit fractional addends; the result is a 32-
MLIB_Add_A32as acc32_t frac16_t acc32_t A 16-bit fractional addend is added to a 32-bit accumulator.
type
within the range <-1 ; 1).
within the range <-1 ; 1).
bit accumulator. The output may be out of the range <-1 ; 1).
The output may be out of the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.3.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Add functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Add_F16(frac16_t f16Add1, frac16_t f16Add2)
frac32_t MLIB_Add_F32(frac32_t f32Add1, frac32_t f32Add2)
acc32_t MLIB_Add_A32ss(frac16_t f16Add1, frac16_t f16Add2)
acc32_t MLIB_Add_A32as(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Add)
2.3.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Add function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static acc32_t a32Result;
static frac16_t f16Add1, f16Add2;
void main(void)
{
f16Add1 = FRAC16(-0.8); /* f16Add1 = -0.8 */
f16Add2 = FRAC16(-0.5); /* f16Add2 = -0.5 */
/* a32Result = f16Add1 + f16Add2 */
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
48 NXP Semiconductors
Page 49

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
a32Result = MLIB_Add_A32ss(f16Add1, f16Add2);
}
2.4 MLIB_AddSat
The MLIB_AddSat functions return the sum of two addends. The function saturates the
output. See the following equation:
Equation 4. Algorithm formula
2.4.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_AddSat function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-4. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Addend 1 Addend 2
MLIB_AddSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Addition of two 16-bit fractional addends. The output is
MLIB_AddSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Addition of two 32-bit fractional addends. The output is
type
within the range <-1 ; 1).
within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.4.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_AddSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Add_F16(frac16_t f16Add1, frac16_t f16Add2)
frac32_t MLIB_Add_F32(frac32_t f32Add1, frac32_t f32Add2)
2.4.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_AddSat function is shown in the following example:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 49
Page 50

MLIB_Add4
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Add1, f32Add2, f32Result;
void main(void)
{
f32Add1 = FRAC32(-0.8); /* f32Add1 = -0.8 */
f32Add2 = FRAC32(-0.5); /* f32Add2 = -0.5 */
/* f32Result = sat(f32Add1 + f32Add2) */
f32Result = MLIB_AddSat_F32(f32Add1, f32Add2);
}
2.5 MLIB_Add4
The MLIB_Add4 functions return the sum of four addends. The function does not
saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 5. Algorithm formula
2.5.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_Add4 function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-5. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Add. 1 Add. 2 Add. 3 Add. 4
MLIB_Add4_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Addition of four 16-bit fractional addends.
MLIB_Add4_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Addition of four 32-bit fractional addends.
type
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.5.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Add4 functions have the following declarations:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
50 NXP Semiconductors
Page 51

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
frac16_t MLIB_Add4_F16(frac16_t f16Add1, frac16_t f16Add2, frac16_t f16Add3, frac16_t
f16Add4)
frac32_t MLIB_Add4_F32(frac32_t f32Add1, frac32_t f32Add2, frac32_t f32Add3, frac32_t
f32Add4)
2.5.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_Add4 function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Result;
static frac32_t f32Add1, f32Add2, f32Add3, f32Add4;
void main(void)
{
f32Add1 = FRAC32(-0.3); /* f32Add1 = -0.3 */
f32Add2 = FRAC32(0.5); /* f32Add2 = 0.5 */
f32Add3 = FRAC32(-0.2); /* f32Add3 = -0.2 */
f32Add4 = FRAC32(-0.4); /* f32Add4 = -0.4 */
/* f32Result = f32Add1 + f32Add2 + f32Add3 + f32Add4 */
f32Result = MLIB_Add4_F32(f32Add1, f32Add2, f32Add3, f32Add4);
}
2.6
MLIB_Add4Sat
The MLIB_Add4Sat functions return the sum of four addends. The function saturates the
output. See the following equation:
Equation 6. Algorithm formula
2.6.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 51
Page 52

MLIB_Add4Sat
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_Add4Sat function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-6. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Add. 1 Add. 2 Add. 3 Add. 4
MLIB_Add4Sat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Addition of four 16-bit fractional addends.
MLIB_Add4Sat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Addition of four 32-bit fractional addends.
type
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.6.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Add4Sat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Add4Sat_F16(frac16_t f16Add1, frac16_t f16Add2, frac16_t f16Add3, frac16_t
f16Add4)
frac32_t MLIB_Add4Sat_F32(frac32_t f32Add1, frac32_t f32Add2, frac32_t f32Add3, frac32_t
f32Add4)
2.6.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Add4Sat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac16_t f16Result, f16Add1, f16Add2, f16Add3, f16Add4;
void main(void)
{
f16Add1 = FRAC16(-0.7); /* f16Add1 = -0.7 */
f16Add2 = FRAC16(0.9); /* f16Add2 = 0.9 */
f16Add3 = FRAC16(0.4); /* f16Add3 = 0.4 */
f16Add4 = FRAC16(0.7); /* f16Add4 = 0.7 */
/* f16Result = sat(f16Add1 + f16Add2 + f16Add3 + f16Add4) */
f16Result = MLIB_Add4Sat_F16(f16Add1, f16Add2, f16Add3, f16Add4);
}
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
52 NXP Semiconductors
Page 53

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
2.7 MLIB_Clb
The MLIB_Clb functions return the number of leading bits of the input. If the input is 0,
it returns the size of the type minus one.
2.7.1 Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Integer output with fractional input - the output is the unsigned integer value when
the input is fractional; the result is greater than or equal to 0.
The available versions of the MLIB_Clb function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-7. Function versions
Function name Input type Result type Description
MLIB_Clb_U16s frac16_t uint16_t Counts the leading bits of a 16-bit fractional value. The output is within
the range <0 ; 15>.
MLIB_Clb_U16l frac32_t uint16_t Counts the leading bits of a 32-bit fractional value. The output is within
the range <0 ; 31>.
2.7.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Clb functions have the following declarations:
uint16_t MLIB_Clb_U16s(frac16_t f16Val)
uint16_t MLIB_Clb_U16l(frac32_t f32Val)
2.7.3
The use of the MLIB_Clb function is shown in the following example:
Function use
#include "mlib.h"
static uint16_t u16Result;
static frac32_t f32Val;
void main(void)
{
f32Val = FRAC32(0.00000452); /* f32Val = 0.00000452 */
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 53
Page 54

MLIB_Conv
/* u16Result = clb(f32Val) */
u16Result = MLIB_Clb_U16l(f32Val);
}
2.8 MLIB_Conv
The MLIB_Conv functions return the input value, converted to the output type.
2.8.1 Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1).
The available versions of the MLIB_Conv function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-8. Function versions
Function name Input type Result type Description
MLIB_Conv_F16l frac32_t frac16_t Conversion of a 32-bit fractional value to a 16-bit fractional value. The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
MLIB_Conv_F32s frac16_t frac32_t Conversion of a 16-bit fractional value to a 32-bit fractional value. The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
2.8.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Conv functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Conv_F16l(frac32_t f32Val)
frac32_t MLIB_Conv_F32s(frac16_t f16Val)
2.8.3
The use of the MLIB_Conv function is shown in the following examples:
Function use
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Result;
static frac16_t f16Val;
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
54 NXP Semiconductors
Page 55

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
void main(void)
{
f16Val = FRAC16(-0.354); /* f16Val = -0.354 */
/* f32Result = (frac32_t)f16Val << 16 */
f32Result = MLIB_Conv_F32s(f16Val);
}
2.9 MLIB_Div
The
MLIB_Div functions return the fractional division of the numerator and
denominator. The function does not saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 7. Algorithm formula
2.9.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The function is only defined for: |nominator| < |
denominator|. The function returns undefined results out of this condition.
• Accumulator output - the output is the accumulator type, where the result may be out
of the range <-1 ; 1).
The available versions of the MLIB_Div function are shown in the following table:
Table 2-9. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Num. Denom.
MLIB_Div_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Division of a 16-bit fractional numerator and denominator. The
MLIB_Div_F16ls frac32_t frac16_t frac16_t Division of a 32-bit fractional numerator by a 16-bit fractional
MLIB_Div_F16ll frac32_t frac32_t frac16_t Division of a 32-bit fractional numerator and denominator; the
MLIB_Div_F32ls frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t Division of a 32-bit fractional numerator by a 16-bit fractional
type
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
denominator; the output is a 16-bit fractional result. The output is
within the range <-1 ; 1).
output is a 16-bit fractional result. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
denominator; the output is a 32-bit fractional result. The output is
within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
Table continues on the next page...
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 55
Page 56

MLIB_Div
Table 2-9. Function versions (continued)
Function name Input type Result
Num. Denom.
MLIB_Div_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Division of a 32-bit fractional numerator and denominator. The
MLIB_Div_A32ss frac16_t frac16_t acc32_t Division of a 16-bit fractional numerator and denominator; the
MLIB_Div_A32ls frac32_t frac16_t acc32_t Division of a 32-bit fractional numerator by a 16-bit fractional
MLIB_Div_A32ll frac32_t frac32_t acc32_t Division of a 32-bit fractional numerator and denominator; the
MLIB_Div_A32as acc32_t frac16_t acc32_t Division of a 32-bit accumulator numerator by a 16-bit fractional
type
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
output is a 32-bit accumulator result. The output may be out of the
range <-1 ; 1).
denominator; the output is a 32-bit accumulator result. The output
may be out of the range <-1 ; 1).
output is a 32-bit accumulator result. The output may be out of the
range <-1 ; 1).
denominator; the output is a 32-bit accumulator result. The output
may be out of the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.9.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Div functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Div_F16(frac16_t f16Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac16_t MLIB_Div_F16ls(frac32_t f32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac16_t MLIB_Div_F16ll(frac32_t f32Num, frac32_t f32Denom)
frac32_t MLIB_Div_F32ls(frac32_t f32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac32_t MLIB_Div_F32(frac32_t f32Num, frac32_t f32Denom)
acc32_t MLIB_Div_A32ss(frac16_t f16Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
acc32_t MLIB_Div_A32ls(frac32_t f32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
acc32_t MLIB_Div_A32ll(frac32_t f32Num, frac32_t f32Denom)
acc32_t MLIB_Div_A32as(acc32_t a32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
2.9.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Div function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Num, f32Result;
static frac16_t f16Denom;
void main(void)
{
f32Num = FRAC32(0.2); /* f32Num = 0.2 */
f16Denom = FRAC16(-0.495); /* f16Denom = -0.495 */
/* f32Result = f32Num / f16Denom */
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
56 NXP Semiconductors
Page 57

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
f32Result = MLIB_Div_F32ls(f32Num, f16Denom);
}
2.10 MLIB_DivSat
The MLIB_DivSat functions return the fractional division of the numerator and
denominator. The function saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 8. Algorithm formula
2.10.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
• Accumulator output - the output is the accumulator type, where the result may be out
of the range <-1 ; 1).
The available versions of the MLIB_DivSat function are shown in the following table:
Table 2-10. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Num. Denom.
MLIB_DivSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Division of a 16-bit fractional numerator and denominator. The
MLIB_DivSat_F16ls frac32_t frac16_t frac16_t Division of a 32-bit fractional numerator by a 16-bit fractional
MLIB_DivSat_F16ll frac32_t frac32_t frac16_t Division of a 32-bit fractional numerator and denominator; the
MLIB_DivSat_F32ls frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t Division of a 32-bit fractional numerator by a 16-bit fractional
MLIB_DivSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Division of a 32-bit fractional numerator and denominator. The
MLIB_DivSat_A32as acc32_t frac16_t acc32_t Division of a 32-bit accumulator numerator by a 16-bit fractional
type
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
denominator; the output is a 16-bit fractional result. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
output is a 16-bit fractional result. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
denominator; the output is a 32-bit fractional result. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
denominator; the output is a 32-bit accumulator result. The
output may be out of the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 57
Page 58

MLIB_Div1Q
2.10.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_DivSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_DivSat_F16(frac16_t f16Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac16_t MLIB_DivSat_F16ls(frac32_t f32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac16_t MLIB_DivSat_F16ll(frac32_t f32Num, frac32_t f32Denom)
frac32_t MLIB_DivSat_F32ls(frac32_t f32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac32_t MLIB_DivSat_F32(frac32_t f32Num, frac32_t f32Denom)
acc32_t MLIB_DivSat_A32as(acc32_t a32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
2.10.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_DivSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Num, f32Denom, f32Result;
void main(void)
{
f32Num = FRAC32(0.4); /* f32Num = 0.4 */
f32Denom = FRAC32(-0.02); /* f32Denom = -0.02 */
/* f32Result = f32Num / f32Denom */
f32Result = MLIB_DivSat_F32(f32Num, f32Denom);
}
2.11
MLIB_Div1Q
The MLIB_Div1Q functions return the single-quadrant fractional division of the
numerator and denominator. The numerator and denominator must be non-negative
numbers, otherwise the function returns undefined results. The function does not saturate
the output. See the following equation:
Equation 9. Algorithm formula
2.11.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
58 NXP Semiconductors
Page 59

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <0 ; 1). The function is only defined for: nominator < denominator,
and both are non-negative. The function returns undefined results out of this
condition.
• Accumulator output - the output is the accumulator type, where the result is greater
than or equal to 0.
The available versions of the MLIB_Div1Q function are shown in the following table:
Table 2-11. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Num. Denom.
MLIB_Div1Q_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Division of a non-negative 16-bit fractional numerator and
MLIB_Div1Q_F16ls frac32_t frac16_t frac16_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit fractional numerator by a non-
MLIB_Div1Q_F16ll frac32_t frac32_t frac16_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit fractional numerator and
MLIB_Div1Q_F32ls frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit fractional numerator by a non-
MLIB_Div1Q_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit fractional numerator and
MLIB_Div1Q_A32ss frac16_t frac16_t acc32_t Division of a non-negative 16-bit fractional numerator and
MLIB_Div1Q_A32ls frac32_t frac16_t acc32_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit fractional numerator by a non-
MLIB_Div1Q_A32ll frac32_t frac32_t acc32_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit fractional numerator and
MLIB_Div1Q_A32as acc32_t frac16_t acc32_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit accumulator numerator by a
type
denominator. The output is within the range <0 ; 1).
negative 16-bit fractional denominator; the output is a nonnegative 16-bit fractional result. The output is within the range
<0 ; 1).
denominator; the output is a non-negative 16-bit fractional
result. The output is within the range <0 ; 1).
negative 16-bit fractional denominator; the output is a nonnegative 32-bit fractional result. The output is within the range
<0 ; 1).
denominator. The output is within the range <0 ; 1).
denominator; the output is a non-negative 32-bit accumulator
result. The output is greater than or equal to 0.
negative 16-bit fractional denominator; the output is a nonnegative 32-bit accumulator result. The output is greater than or
equal to 0.
denominator; the output is a non-negative 32-bit accumulator
result. The output is greater than or equal to 0.
non-negative 16-bit fractional denominator; the output is a 32-bit
accumulator result. The output is greater than or equal to 0.
Description
2.11.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Div1Q functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Div1Q_F16(frac16_t f16Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac16_t MLIB_Div1Q_F16ls(frac32_t f32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac16_t MLIB_Div1Q_F16ll(frac32_t f32Num, frac32_t f32Denom)
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 59
Page 60

MLIB_Div1QSat
frac32_t MLIB_Div1Q_F32ls(frac32_t f32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac32_t MLIB_Div1Q_F32(frac32_t f32Num, frac32_t f32Denom)
acc32_t MLIB_Div1Q_A32ss(frac16_t f16Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
acc32_t MLIB_Div1Q_A32ls(frac32_t f32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
acc32_t MLIB_Div1Q_A32ll(frac32_t f32Num, frac32_t f32Denom)
acc32_t MLIB_Div1Q_A32as(acc32_t a32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
2.11.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_Div1Q function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Num, f32Denom, f32Result;
void main(void)
{
f32Num = FRAC32(0.2); /* f32Num = 0.2 */
f32Denom = FRAC32(0.865); /* f32Denom = 0.865 */
/* f32Result = f32Num / f32Denom */
f32Result = MLIB_Div1Q_F32(f32Num, f32Denom);
}
2.12
MLIB_Div1QSat
The MLIB_Div1QSat functions return the fractional division of the numerator and
denominator. The numerator and denominator must be non-negative numbers. The
function saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 10. Algorithm formula
2.12.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <0 ; 1). The result may saturate.
• Accumulator output - the output is the accumulator type, where the result is greater
than or equal to 0.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
60 NXP Semiconductors
Page 61

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
The available versions of the MLIB_Div1QSat function are shown in the following table:
Table 2-12. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Num. Denom.
MLIB_Div1QSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Division of a non-negative 16-bit fractional numerator and
MLIB_Div1QSat_F16ls frac32_t frac16_t frac16_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit fractional numerator by a
MLIB_Div1QSat_F16ll frac32_t frac32_t frac16_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit fractional numerator and
MLIB_Div1QSat_F32ls frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit fractional numerator by a
MLIB_Div1QSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit fractional numerator and
MLIB_Div1QSat_A32as acc32_t frac16_t acc32_t Division of a non-negative 32-bit accumulator numerator by
type
denominator. The output is within the range <0 ; 1).
non-negative 16-bit fractional denominator; the output is a
non-negative 16-bit fractional result. The output is within the
range <0 ; 1).
denominator; the output is a non-negative 16-bit fractional
result. The output is within the range <0 ; 1).
non-negative 16-bit fractional denominator; the output is a
non-negative 32-bit fractional result. The output is within the
range <0 ; 1).
denominator. The output is within the range <0 ; 1).
a non-negative 16-bit fractional denominator; the output is a
32-bit accumulator result. The output is greater than or
equal to 0.
Description
2.12.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Div1QSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Div1QSat_F16(frac16_t f16Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac16_t MLIB_Div1QSat_F16ls(frac32_t f32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac16_t MLIB_Div1QSat_F16ll(frac32_t f32Num, frac32_t f32Denom)
frac32_t MLIB_Div1QSat_F32ls(frac32_t f32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
frac32_t MLIB_Div1QSat_F32(frac32_t f32Num, frac32_t f32Denom)
acc32_t MLIB_Div1QSat_A32as(acc32_t a32Num, frac16_t f16Denom)
2.12.3
The use of the MLIB_Div1QSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Num, f32Result;
static frac16_t f16Denom;
void main(void)
{
f32Num = FRAC32(0.02); /* f32Num = 0.02 */
Function use
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 61
Page 62

MLIB_Log2
f16Denom = FRAC16(0.4); /* f16Denom = 0.4 */
/* f32Result = f32Num / f16Denom */
f32Result = MLIB_Div1QSat_F32ls(f32Num, f16Denom);
}
2.13 MLIB_Log2
The MLIB_Log2 functions return the binary logarithm of the input. See the following
equation:
Equation 11. Algorithm formula
2.13.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Unsigned integer output - the output is the unsigned integer result.
The available versions of the MLIB_Log2 function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-13. Function versions
Function name Input type Result type Description
MLIB_Log2_U16 uint16_t uint16_t Binary logarithm of a 16-bit unsigned integer value. The output is
greater than or equal to 0.
2.13.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Log2 functions have the following declarations:
uint16_t MLIB_Log2_U16(uint16_t u16Val)
2.13.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Log2 function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
62 NXP Semiconductors
Page 63

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
static uint16_t u16Result, u16Val;
void main(void)
{
u16Val = 5; /* u16Val = 5 */
/* u16Result = log2(u16Val) */
u16Result = MLIB_Log2_U16(u16Val);
}
2.14 MLIB_Mac
The MLIB_Mac functions return the sum of the input accumulator, and the fractional
product of two multiplicands. The function does not saturate the output. See the
following equation:
Equation 12. Algorithm formula
2.14.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
• Accumulator output with mixed inputs - the output is the accumulator type, where
the result can be out of the range <-1 ; 1). The accumulator is the accumulator type,
the multiplicands are the fractional types. The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_Mac function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-14. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Mac_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The upper 16-bit portion [16..31] of the fractional
MLIB_Mac_F32lss frac32_t frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
MLIB_Mac_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The upper 32-bit portion [32..63] of the fractional
type
product (of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands) is
added to a 16-bit fractional accumulator. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
multiplicands) is added to a 32-bit fractional
accumulator. The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
product (of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands) is
added to a 32-bit fractional accumulator. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
Table continues on the next page...
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 63
Page 64

MLIB_MacSat
Table 2-14. Function versions (continued)
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Mac_A32ass acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t acc32_t The upper 16-bit portion [16..31] of the fractional
type
product (of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands) is
added to a 32-bit accumulator. The output may be
out of the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.14.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Mac functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Mac_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Mac_F32lss(frac32_t f32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Mac_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
acc32_t MLIB_Mac_A32ass(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
2.14.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Mac function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Accum, f32Result;
static frac16_t f16Mult1, f16Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f32Accum = FRAC32(0.3); /* f32Accum = 0.3 */
f16Mult1 = FRAC16(0.1); /* f16Mult1 = 0.1 */
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.2); /* f16Mult2 = -0.2 */
/* f32Result = f32Accum + f16Mult1 * f16Mult2 */
f32Result = MLIB_Mac_F32lss(f32Accum, f16Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
2.15
MLIB_MacSat
The MLIB_MacSat functions return the sum of the input accumulator and the fractional
product of two multiplicands. The function saturates the output. See the following
equation:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
64 NXP Semiconductors
Page 65

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
Equation 13. Algorithm formula
2.15.1 Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_MacSat function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-15. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MacSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The upper 16-bit portion [16..31] of the fractional
MLIB_MacSat_F32lss frac32_t frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional product (of two 16-bit
MLIB_MacSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The upper 32-bit portion [32..63] of the fractional
type
product (of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands) is
added to a 16-bit fractional accumulator. The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
fractional multiplicands) is added to a 32-bit
fractional accumulator. The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
product (of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands) is
added to a 32-bit fractional accumulator. The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.15.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MacSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_MacSat_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MacSat_F32lss(frac32_t f32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MacSat_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
2.15.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_MacSat function is shown in the following example:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 65
Page 66

MLIB_MacRnd
#include "mlib.h"
static frac16_t f16Mult1, f16Mult2;
static frac32_t f32Accum, f32Result;
void main(void)
{
f32Accum = FRAC32(-0.7); /* f32Accum = -0.7 */
f16Mult1 = FRAC16(-1.0); /* f16Mult1 = -1.0 */
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(0.8); /* f16Mult2 = 0.8 */
/* f32Result = sat(f32Accum + f16Mult1 * f16Mult2) */
f32Result = MLIB_MacSat_F32lss(f32Accum, f16Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
2.16 MLIB_MacRnd
The
MLIB_MacRnd functions return the sum of the input accumulator and the rounded
fractional product of two multiplicands. The round method is the round to nearest. The
function does not saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 14. Algorithm formula
2.16.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
• Accumulator output with mixed inputs - the output is the accumulator type where the
result can be out of the range <-1 ; 1). The accumulator is the accumulator type, the
multiplicands are the fractional types. The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_MacRnd function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-16. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MacRnd_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
type
multiplicands), rounded to the upper 16 bits, is
added to a 16-bit fractional accumulator. The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
Table continues on the next page...
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
66 NXP Semiconductors
Page 67

Table 2-16. Function versions (continued)
Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MacRnd_F32lls frac32_t frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t The fractional product (of a 32-bit and 16-bit
MLIB_MacRnd_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The fractional product (of two 32-bit fractional
MLIB_MacRnd_A32ass acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t acc32_t The fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
type
fractional multiplicand), rounded to the upper 32
bits [16..48], is added to a 32-bit fractional
accumulator. The output is within the range <-1 ;
1).
multiplicands), rounded to the upper 32 bits
[32..63], is added to a 32-bit fractional
accumulator. The output is within the range <-1 ;
1).
multiplicands), rounded to the upper 16 bits
[16..31], is added to a 32-bit accumulator. The
output may be out of the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.16.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MacRnd functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_MacRnd_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MacRnd_F32lls(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MacRnd_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
acc32_t MLIB_MacRnd_A32ass(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
2.16.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_MacRnd function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac16_t f16Accum, f16Mult1, f16Mult2, f16Result;
void main(void)
{
f16Accum = FRAC16(0.3); /* f16Accum = 0.3 */
f16Mult1 = FRAC16(0.1); /* f16Mult1 = 0.1 */
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.2); /* f16Mult2 = -0.2 */
/* f16Result = round(f16Accum + f16Mult1 * f16Mult2) */
f16Result = MLIB_MacRnd_F16(f16Accum, f16Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 67
Page 68

MLIB_MacRndSat
2.17 MLIB_MacRndSat
The MLIB_MacRndSat functions return the sum of the input accumulator and the
rounded fractional product of two multiplicands. The round method is the round to
nearest. The function saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 15. Algorithm formula
2.17.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_MacRndSat function are shown in the following
table.
Table 2-17. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MacRndSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
MLIB_MacRndSat_F32lls frac32_t frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t The fractional product (of a 32-bit and 16-bit
MLIB_MacRndSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The fractional product (of two 32-bit fractional
type
multiplicands), rounded to the upper 16 bits,
is added to a 16-bit fractional accumulator.
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
fractional multiplicands), rounded to the upper
32 bits [16..48], is added to a 32-bit fractional
accumulator. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
multiplicands), rounded to the upper 32 bits
[32..63], is added to a 32-bit fractional
accumulator. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
Description
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
68 NXP Semiconductors
Page 69

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
2.17.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MacRndSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_MacRndSat_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MacRndSat_F32lls(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MacRndSat_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
2.17.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_MacRndSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Accum, f32Mult1, f32Mult2, f32Result;
void main(void)
{
f32Accum = FRAC32(-0.7); /* f32Accum = -0.7 */
f32Mult1 = FRAC32(-1.0); /* f32Mult1 = -1.0 */
f32Mult2 = FRAC32(0.8); /* f32Mult2 = 0.8 */
/* f32Result = sat(round(f32Accum + f32Mult1 * f32Mult2)) */
f32Result = MLIB_MacRndSat_F32(f32Accum, f32Mult1, f32Mult2);
}
2.18
MLIB_Mac4
The MLIB_Mac4 functions return the sum of two products of two pairs of multiplicands.
The function does not saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 16. Algorithm formula
2.18.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 69
Page 70

MLIB_Mac4
The available versions of the MLIB_Mac4 function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-18. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Product 1 Product 2
Mult. 1 Mult. 2 Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Mac4_F32ssss frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t Addition of two 32-bit fractional
type
products (of two 16-bit fractional
multiplicands). The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.18.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Mac4 functions have the following declarations:
frac32_t MLIB_Mac4_F32ssss(frac16_t f16Add1Mult1, frac16_t f16Add1Mult2, frac16_t
f16Add2Mult1, frac16_t f16Add2Mult2)
2.18.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Mac4 function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Result;
static frac16_t f16Add1Mult1, f16Add1Mult2, f16Add2Mult1, f16Add2Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f16Add1Mult1 = FRAC16(0.2); /* f16Add1Mult1 = 0.2 */
f16Add1Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.7); /* f16Add1Mult2 = -0.7 */
f16Add2Mult1 = FRAC16(0.3); /* f16Add2Mult1 = 0.3 */
f16Add2Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.25); /* f16Add2Mult2 = -0.25 */
/* f32Result = f16Add1Mult1 * f16Add1Mult2 + f16Add2Mult1 * f16Add2Mult2*/
f32Result = MLIB_Mac4_F32ssss(f16Add1Mult1, f16Add1Mult2, f16Add2Mult1, f16Add2Mult2);
}
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
70 NXP Semiconductors
Page 71

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
2.19 MLIB_Mac4Sat
The MLIB_Mac4Sat functions return the sum of two products of two pairs of
multiplicands. The function saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 17. Algorithm formula
2.19.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_Mac4Sat function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-19. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Product 1 Product 2
Mult. 1 Mult. 2 Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Mac4Sat_F32ssss frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t Addition of two 32-bit fractional
type
products (of two 16-bit fractional
multiplicands). The output is within
the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.19.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Mac4Sat functions have the following declarations:
frac32_t MLIB_Mac4Sat_F32ssss(frac16_t f16Add1Mult1, frac16_t f16Add1Mult2, frac16_t
f16Add2Mult1, frac16_t f16Add2Mult2)
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 71
Page 72

MLIB_Mac4Rnd
2.19.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_Mac4Sat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Result;
static frac16_t f16Add1Mult1, f16Add1Mult2, f16Add2Mult1, f16Add2Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f16Add1Mult1 = FRAC16(-1.0); /* f16Add1Mult1 = -1.0 */
f16Add1Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.9); /* f16Add1Mult2 = -0.9 */
f16Add2Mult1 = FRAC16(0.8); /* f16Add2Mult1 = 0.8 */
f16Add2Mult2 = FRAC16(0.7); /* f16Add2Mult2 = 0.7 */
/* f32Result = sat(f16Add1Mult1 * f16Add1Mult2 + f16Add2Mult1 * f16Add2Mult2) */
f32Result = MLIB_Mac4Sat_F32ssss(f16Add1Mult1, f16Add1Mult2, f16Add2Mult1, f16Add2Mult2);
}
2.20
MLIB_Mac4Rnd
The MLIB_Mac4Rnd functions return the rounded sum of two products of two pairs of
multiplicands. The round method is the round to nearest. The function does not saturate
the output. See the following equation:
Equation 18. Algorithm formula
2.20.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
72 NXP Semiconductors
Page 73

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
The available versions of the MLIB_Mac4Rnd function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-20. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Product 1 Product 2
Mult. 1 Mult. 2 Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Mac4Rnd_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Addition of two 16-bit fractional products
MLIB_Mac4Rnd_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Addition of two 32-bit fractional products
type
(of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands),
rounded to the upper 16 bits. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
(of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands),
rounded to the upper 32 bits. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.20.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Mac4Rnd functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Mac4Rnd_F16(frac16_t f16Add1Mult1, frac16_t f16Add1Mult2, frac16_t
f16Add2Mult1, frac16_t f16Add2Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Mac4Rnd_F32(frac32_t f32Add1Mult1, frac32_t f32Add1Mult2, frac32_t
f32Add2Mult1, frac32_t f32Add2Mult2)
2.20.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Mac4Rnd function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac16_t f16Result, f16Add1Mult1, f16Add1Mult2, f16Add2Mult1, f16Add2Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f16Add1Mult1 = FRAC16(0.256); /* f16Add1Mult1 = 0.256 */
f16Add1Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.724); /* f16Add1Mult2 = -0.724 */
f16Add2Mult1 = FRAC16(0.365); /* f16Add2Mult1 = 0.365 */
f16Add2Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.25); /* f16Add2Mult2 = -0.25 */
/* f16Result = round(f16Add1Mult1 * f16Add1Mult2 + f16Add2Mult1 * f16Add2Mult2) */
f16Result = MLIB_Mac4Rnd_F16(f16Add1Mult1, f16Add1Mult2, f16Add2Mult1, f16Add2Mult2);
}
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 73
Page 74

MLIB_Mac4RndSat
2.21 MLIB_Mac4RndSat
The MLIB_Mac4RndSat functions return the rounded sum of two products of two pairs
of multiplicands. The round method is the round to nearest. The function saturates the
output. See the following equation:
Equation 19. Algorithm formula
2.21.1
Available versions
The function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_Mac4RndSat function are shown in the following
table.
Table 2-21. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Product 1 Product 2
Mult. 1 Mult. 2 Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Mac4RndSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Addition of two 16-bit fractional
MLIB_Mac4RndSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Addition of two 32-bit fractional
type
products (of two 16-bit fractional
multiplicands), rounded to the upper
16 bits. The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
products (of two 32-bit fractional
multiplicands), rounded to the upper
32 bits. The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.21.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Mac4RndSat functions have the following declarations:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
74 NXP Semiconductors
Page 75

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
frac16_t MLIB_Mac4RndSat_F16(frac16_t f16Add1Mult1, frac16_t f16Add1Mult2, frac16_t
f16Add2Mult1, frac16_t f16Add2Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Mac4RndSat_F32(frac32_t f32Add1Mult1, frac32_t f32Add1Mult2, frac32_t
f32Add2Mult1, frac32_t f32Add2Mult2)
2.21.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_Mac4RndSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Result, f32Add1Mult1, f32Add1Mult2, f32Add2Mult1, f32Add2Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f32Add1Mult1 = FRAC32(-1.0); /* f32Add1Mult1 = -1.0 */
f32Add1Mult2 = FRAC32(-0.9); /* f32Add1Mult2 = -0.9 */
f32Add2Mult1 = FRAC32(0.8); /* f32Add2Mult1 = 0.8 */
f32Add2Mult2 = FRAC32(0.7); /* f32Add2Mult2 = 0.7 */
/* f32Result = sat(round(f32Add1Mult1 * f32Add1Mult2 + f32Add2Mult1 * f32Add2Mult2))*/
f32Result = MLIB_Mac4RndSat_F32(f32Add1Mult1, f32Add1Mult2, f32Add2Mult1, f32Add2Mult2);
}
2.22
MLIB_Mnac
The MLIB_Mnac functions return the product of two multiplicands minus the input
accumulator. The function does not saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 20. Algorithm formula
2.22.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
• Accumulator output with mixed inputs - the output is the accumulator type, where
the result can be out of the range <-1 ; 1). The accumulator is the accumulator type,
the multiplicands are the fractional types. The result may overflow.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 75
Page 76

MLIB_Mnac
The available versions of the MLIB_Mnac function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-22. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Mnac_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The 16-bit fractional accumulator is subtracted from
MLIB_Mnac_F32lss frac32_t frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional accumulator is subtracted from
MLIB_Mnac_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional accumulator is subtracted from
MLIB_Mnac_A32ass acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t acc32_t The 32-bit accumulator is subtracted from the upper
type
the upper 16-bit portion [16..31] of the fractional
product (of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands). The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
the 32-bit fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
multiplicands). The output is within the range <-1 ;
1).
the upper 32-bit portion [32..63] of the fractional
product (of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands). The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
16-bit portion [16..31] of the fractional product (of two
16-bit fractional multiplicands). The output may be
out of the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.22.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Mnac functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Mnac_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Mnac_F32lss(frac32_t f32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Mnac_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
acc32_t MLIB_Mnac_A32ass(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
2.22.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Mnac function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Accum, f32Result;
static frac16_t f16Mult1, f16Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f32Accum = FRAC32(0.3); /* f32Accum = 0.3 */
f16Mult1 = FRAC16(0.1); /* f16Mult1 = 0.1 */
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.2); /* f16Mult2 = -0.2 */
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
76 NXP Semiconductors
Page 77

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
/* f32Result = f16Mult1 * f16Mult2 - f32Accum */
f32Result = MLIB_Mnac_F32lss(f32Accum, f16Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
2.23 MLIB_MnacSat
The MLIB_MnacSat functions return the product of two multiplicands minus the input
accumulator. The function saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 21. Algorithm formula
2.23.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_MnacSat function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-23. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MnacSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The 16-bit fractional accumulator is subtracted from
MLIB_MnacSat_F32lss frac32_t frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional accumulator is subtracted from
MLIB_MnacSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional accumulator is subtracted from
type
the upper 16-bit portion [16..31] of the fractional
product (of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands). The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
the 32-bit fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
multiplicands). The output is within the range <-1 ;
1).
the upper 32-bit portion [32..63] of the fractional
product (of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands). The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.23.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MnacSat functions have the following declarations:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 77
Page 78

MLIB_MnacRnd
frac16_t MLIB_MnacSat_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MnacSat_F32lss(frac32_t f32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MnacSat_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
2.23.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_MnacSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Accum, f32Result;
static frac16_t f16Mult1, f16Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f32Accum = FRAC32(0.3); /* f32Accum = 0.3 */
f16Mult1 = FRAC16(0.1); /* f16Mult1 = 0.1 */
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.2); /* f16Mult2 = -0.2 */
/* f32Result = f16Mult1 * f16Mult2 - f32Accum */
f32Result = MLIB_MnacSat_F32lss(f32Accum, f16Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
2.24
MLIB_MnacRnd
The MLIB_MnacRnd functions return the rounded product of two multiplicands minus
the input accumulator. The round method is the round to nearest. The function does not
saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 22. Algorithm formula
2.24.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
• Accumulator output with mixed inputs - the output is the accumulator type, where
the result can be out of the range <-1 ; 1). The accumulator is the accumulator type,
the multiplicands are the fractional types. The result may overflow.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
78 NXP Semiconductors
Page 79

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
The available versions of the MLIB_MnacRnd function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-24. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MnacRnd_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The 16-bit fractional accumulator is
MLIB_MnacRnd_F32lls frac32_t frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional accumulator is
MLIB_MnacRnd_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional accumulator is
MLIB_MnacRnd_A32ass acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t acc32_t The 32-bit accumulator is subtracted from
type
subtracted from the fractional product (of two
16-bit fractional multiplicands) rounded to the
upper 16 bits. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
subtracted from the fractional product (of a
32-bit and a 16-bit fractional multiplicand)
rounded to the upper 32 bits [16..48]. The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
subtracted from the fractional product (of two
32-bit fractional multiplicands) rounded to the
upper 32 bits [32..63]. The output is within
the range <-1 ; 1).
the fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
multiplicands) rounded to the upper 16-bits
[16..31]. The output may be out of the range
<-1 ; 1).
Description
2.24.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MnacRnd functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_MnacRnd_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MnacRnd_F32lls(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MnacRnd_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
acc32_t MLIB_MnacRnd_A32ass(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
2.24.3
The use of the MLIB_MnacRnd function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Accum, f32Result, f32Mult1;
static frac16_t f16Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f32Accum = FRAC32(0.3); /* f32Accum = 0.3 */
f32Mult1 = FRAC32(0.4); /* f32Mult1 = 0.4 */
Function use
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 79
Page 80

MLIB_MnacRndSat
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.2); /* f16Mult2 = -0.2 */
/* f32Result = round(f32Mult1 * f16Mult2 - f32Accum) */
f32Result = MLIB_MnacRnd_F32lls(f32Accum, f32Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
2.25 MLIB_MnacRndSat
The MLIB_MnacRndSat functions return the rounded product of two multiplicands
minus the input accumulator. The round method is the round to nearest. The function
saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 23. Algorithm formula
2.25.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_MnacRndSat function are shown in the following
table.
Table 2-25. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MnacRndSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The 16-bit fractional accumulator is
MLIB_MnacRndSat_F32lls frac32_t frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional accumulator is
MLIB_MnacRndSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional accumulator is
type
subtracted from the fractional product (of
two 16-bit fractional multiplicands)
rounded to the upper 16 bits. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
subtracted from the fractional product (of
a 32-bit and a 16-bit fractional
multiplicand) rounded to the upper 32 bits
[16..48]. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
subtracted from the fractional product (of
two 32-bit fractional multiplicands)
rounded to the upper 32 bits [32..63]. The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
80 NXP Semiconductors
Page 81

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
2.25.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MnacRndSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_MnacRnd_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MnacRnd_F32lls(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MnacRnd_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
2.25.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_MnacRndSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Accum, f32Result, f32Mult1;
static frac16_t f16Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f32Accum = FRAC32(0.3); /* f32Accum = 0.3 */
f32Mult1 = FRAC32(0.4); /* f32Mult1 = 0.4 */
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.2); /* f16Mult2 = -0.2 */
/* f32Result = round(f32Mult1 * f16Mult2 - f32Accum) */
f32Result = MLIB_MnacRndSat_F32lls(f32Accum, f32Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
2.26
MLIB_Msu
The MLIB_Msu functions return the fractional product of two multiplicands subtracted
from the input accumulator. The function does not saturate the output. See the following
equation:
Equation 24. Algorithm formula
2.26.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 81
Page 82

MLIB_Msu
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
• Accumulator output with mixed inputs - the output is the accumulator type, where
the result can be out of the range <-1 ; 1). The accumulator is the accumulator type,
the multiplicands are the fractional types. The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_Msu function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-26. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Msu_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The upper 16-bit portion [16..31] of the fractional
MLIB_Msu_F32lss frac32_t frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
MLIB_Msu_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The upper 32-bit portion [32..63] of the fractional
MLIB_Msu_A32ass acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t acc32_t The upper 16-bit portion [16..31] of the fractional
type
product (of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands) is
subtracted from a 16-bit fractional accumulator. The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
multiplicands) is subracted from a 32-bit fractional
accumulator. The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
product (of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands) is
subtracted from a 32-bit fractional accumulator. The
output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
product (of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands) is
subtracted from a 32-bit accumulator. The output
may be out of the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.26.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Msu functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Msu_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Msu_F32lss(frac32_t f32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Msu_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
acc32_t MLIB_Msu_A32ass(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
2.26.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Msu function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static acc32_t a32Accum, a32Result;
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
82 NXP Semiconductors
Page 83

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
static frac16_t f16Mult1, f16Mult2;
void main(void)
{
a32Accum = ACC32(2.3); /* a32Accum = 2.3 */
f16Mult1 = FRAC16(0.1); /* f16Mult1 = 0.1 */
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.2); /* f16Mult2 = -0.2 */
/* a32Result = a32Accum - f16Mult1 * f16Mult2 */
a32Result = MLIB_Msu_A32ass(a32Accum, f16Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
2.27 MLIB_MsuSat
The MLIB_MsuSat functions return the fractional product of two multiplicands
subtracted from the input accumulator. The function saturates the output. See the
following equation:
Equation 25. Algorithm formula
2.27.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_MsuSat function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-27. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MsuSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The upper 16-bit portion [16..31] of the fractional
MLIB_MsuSat_F32lss frac32_t frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t The 32-bit fractional product (of two 16-bit
MLIB_MsuSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The upper 32-bit portion [32..63] of the fractional
type
product (of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands) is
subtracted from a 16-bit fractional accumulator.
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
fractional multiplicands) is subtracted from a 32-bit
fractional accumulator. The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
product (of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands) is
subracted from a 32-bit fractional accumulator.
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 83
Page 84

MLIB_MsuRnd
2.27.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MsuSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_MsuSat_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MsuSat_F32lss(frac32_t f32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MsuSat_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
2.27.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_MsuSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Accum, f32Mult1, f32Mult2, f32Result;
void main(void)
{
f32Accum = FRAC32(0.9); /* f32Accum = 0.9 */
f32Mult1 = FRAC32(-1.0); /* f32Mult1 = -1.0 */
f32Mult2 = FRAC32(0.2); /* f32Mult2 = 0.2 */
/* f32Result = sat(f32Accum - f32Mult1 * f32Mult2) */
f32Result = MLIB_MsuSat_F32(f32Accum, f32Mult1, f32Mult2);
}
2.28
MLIB_MsuRnd
The MLIB_MsuRnd functions return the rounded fractional product of two multiplicands
subtracted from the input accumulator. The round method is the round to nearest. The
function does not saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 26. Algorithm formula
2.28.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
84 NXP Semiconductors
Page 85

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
• Accumulator output with mixed inputs - the output is the accumulator type, where
the result can be out of the range <-1 ; 1). The accumulator is the accumulator type,
the multiplicands are the fractional types. The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_MsuRnd function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-28. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MsuRnd_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
MLIB_MsuRnd_F32lls frac32_t frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t The fractional product (of a 32-bit and 16-bit
MLIB_MsuRnd_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The fractional product (of two 32-bit fractional
MLIB_MsuRnd_A32ass acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t acc32_t The fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
type
multiplicands), rounded to the upper 16 bits, is
subtracted from a 16-bit fractional accumulator.
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
fractional multiplicands), rounded to the upper
32 bits [16..48], is subtracted from a 32-bit
fractional accumulator. The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
multiplicands), rounded to the upper 32 bits
[32..63], is subtracted from a 32-bit fractional
accumulator. The output is within the range <-1 ;
1).
multiplicands), rounded to the upper 16 bits
[16..31], is subtracted from a 32-bit accumulator.
The output may be out of the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.28.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MsuRnd functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_MsuRnd_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MsuRnd_F32lls(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MsuRnd_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
acc32_t MLIB_MsuRnd_A32ass(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
2.28.3
The use of the MLIB_MsuRnd function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
NXP Semiconductors 85
Function use
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
Page 86

MLIB_MsuRndSat
static frac16_t f16Accum, f16Mult1, f16Mult2, f16Result;
void main(void)
{
f16Accum = FRAC16(0.3); /* f16Accum = 0.3 */
f16Mult1 = FRAC16(0.1); /* f16Mult1 = 0.1 */
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.2); /* f16Mult2 = -0.2 */
/* f16Result = round(f16Accum - f16Mult1 * f16Mult2) */
f16Result = MLIB_MsuRnd_F16(f16Accum, f16Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
2.29 MLIB_MsuRndSat
The MLIB_MsuRndSat functions return the rounded fractional product of two
multiplicands subtracted from the input accumulator. The round method is the round to
nearest. The function saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 27. Algorithm formula
2.29.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_MsuRndSat function are shown in the following
table.
Table 2-29. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MsuRndSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t The fractional product (of two 16-bit fractional
MLIB_MsuRndSat_F32lls frac32_t frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t The fractional product (of a 32-bit and 16-bit
type
multiplicands), rounded to the upper 16 bits,
is subtracted from a 16-bit fractional
accumulator. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
fractional multiplicands), rounded to the upper
32 bits [16..48], is subtracted from a 32-bit
fractional accumulator. The output is within
the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
Table continues on the next page...
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
86 NXP Semiconductors
Page 87

Table 2-29. Function versions (continued)
Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
Function name Input type Result
Accum. Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MsuRndSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t The fractional product (of two 32-bit fractional
type
multiplicands), rounded to the upper 32 bits
[32..63], is subtracted from a 32-bit fractional
accumulator. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
Description
2.29.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MsuRndSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_MsuRndSat_F16(frac16_t f16Accum, frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MsuRndSat_F32lls(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MsuRndSat_F32(frac32_t f32Accum, frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
2.29.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_MsuRndSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Accum, f32Mult1, f32Mult2, f32Result;
void main(void)
{
f32Accum = FRAC32(0.3); /* f32Accum = 0.3 */
f32Mult1 = FRAC32(0.1); /* f32Mult1 = 0.1 */
f32Mult2 = FRAC32(-0.2); /* f32Mult2 = -0.2 */
/* f32Result = sat(round(f32Accum - f32Mult1 * f32Mult2)) */
f32Result = MLIB_MsuRndSat_F32(f32Accum, f32Mult1, f32Mult2);
}
2.30
MLIB_Msu4
The MLIB_Msu4 functions return the subtraction of the products of two multiplicands.
The function does not saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 28. Algorithm formula
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 87
Page 88

MLIB_Msu4
2.30.1 Available versions
The function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_Msu4 function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-30. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Minuend product Subtrahend product
Mult. 1 Mult. 2 Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Msu4_F32ssss frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t Subtraction of two 32-bit
type
fractional products (of two 16-bit
fractional multiplicands). The
output is within the range <-1 ;
1).
Description
2.30.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Msu4 functions have the following declarations:
frac32_t MLIB_Msu4_F32ssss(frac16_t f16MinMult1, frac16_t f16MinMult2, frac16_t f16SubMult1,
frac16_t f16SubMult2)
2.30.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Msu4 function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Result;
static frac16_t f16MinMult1, f16MinMult2, f16SubMult1, f16SubMult2;
void main(void)
{
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
88 NXP Semiconductors
Page 89

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
f16MinMult1 = FRAC16(0.2); /* f16MinMult1 = 0.2 */
f16MinMult2 = FRAC16(-0.7); /* f16MinMult2 = -0.7 */
f16SubMult1 = FRAC16(0.3); /* f16SubMult1 = 0.3 */
f16SubMult2 = FRAC16(-0.25); /* f16SubMult2 = -0.25 */
/* f32Result = f16MinMult1 * f16MinMult2 - f16SubMult1 * f16SubMult2 */
f32Result = MLIB_Msu4_F32ssss(f16MinMult1, f16MinMult2, f16SubMult1, f16SubMult2);
}
2.31 MLIB_Msu4Sat
The
MLIB_Msu4Sat functions return the subtraction of the products of two
multiplicands. The function saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 29. Algorithm formula
2.31.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_Msu4Sat function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-31. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Minuend product Subtrahend product
Mult. 1 Mult. 2 Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Msu4Sat_F32ssss frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t Subtraction of two 32-bit
type
fractional products (of two
16-bit fractional
multiplicands). The output is
within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.31.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Msu4Sat functions have the following declarations:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 89
Page 90

MLIB_Msu4Rnd
frac32_t MLIB_Msu4Sat_F32ssss(frac16_t f16MinMult1, frac16_t f16MinMult2, frac16_t
f16SubMult1, frac16_t f16SubMult2)
2.31.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_Msu4Sat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Result;
static frac16_t f16MinMult1, f16MinMult2, f16SubMult1, f16SubMult2;
void main(void)
{
f16MinMult1 = FRAC16(0.8); /* f16MinMult1 = 0.8 */
f16MinMult2 = FRAC16(-0.9); /* f16MinMult2 = -0.9 */
f16SubMult1 = FRAC16(0.7); /* f16SubMult1 = 0.7 */
f16SubMult2 = FRAC16(0.9); /* f16SubMult2 = 0.9 */
/* f32Result = sat(f16MinMult1 * f16MinMult2 - f16SubMult1 * f16SubMult2) */
f32Result = MLIB_Msu4Sat_F32ssss(f16MinMult1, f16MinMult2, f16SubMult1, f16SubMult2);
}
2.32
MLIB_Msu4Rnd
The MLIB_Msu4Rnd functions return the rounded subtraction of two products of two
pairs of multiplicands. The round method is the round to nearest. The function does not
saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 30. Algorithm formula
2.32.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
90 NXP Semiconductors
Page 91

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
The available versions of the MLIB_Msu4Rnd function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-32. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Minuend product Subtrahend product
Mult. 1 Mult. 2 Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Msu4Rnd_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Subtraction of two 16-bit
MLIB_Msu4Rnd_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Subtraction of two 32-bit
type
fractional products (of two 16-bit
fractional multiplicands), rounded
to the upper 16 bits. The output is
within the range <-1 ; 1).
fractional products (of two 32-bit
fractional multiplicands), rounded
to the upper 32 bits. The output is
within the range <-1 ; 1).
Description
2.32.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Msu4Rnd functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Msu4Rnd_F16(frac16_t f16MinMult1, frac16_t f16MinMult2, frac16_t f16SubMult1,
frac16_t f16SubMult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Msu4Rnd_F32(frac32_t f32MinMult1, frac32_t f32MinMult2, frac32_t f32SubMult1,
frac32_t f32SubMult2)
2.32.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Msu4Rnd function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac16_t f16Result, f16MinMult1, f16MinMult2, f16SubMult1, f16SubMult2;
void main(void)
{
f16MinMult1 = FRAC16(0.256); /* f16MinMult1 = 0.256 */
f16MinMult2 = FRAC16(-0.724); /* f16MinMult2 = -0.724*/
f16SubMult1 = FRAC16(0.365); /* f16SubMult1 = 0.365 */
f16SubMult2 = FRAC16(-0.25); /* f16SubMult2 = -0.25 */
/* f32Result = round(f16MinMult1 * f16MinMult2 - f16SubMult1 * f16SubMult2) */
f16Result = MLIB_Msu4Rnd_F16(f16MinMult1, f16MinMult2, f16SubMult1, f16SubMult2);
}
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 91
Page 92

MLIB_Msu4RndSat
2.33 MLIB_Msu4RndSat
The MLIB_Msu4RndSat functions return the rounded subtraction of two products of two
pairs of multiplicands. The round method is the round to nearest. The function saturates
the output. See the following equation:
Equation 31. Algorithm formula
2.33.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output - the output is the fractional portion of the result; the result is
within the range <-1 ; 1). The result may saturate.
The available versions of the MLIB_Msu4RndSat function are shown in the following
table.
Table 2-33. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Minuend product Subtrahend product
Mult. 1 Mult. 2 Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Msu4RndSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Subtraction of two 16-bit
MLIB_Msu4RndSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Subtraction of two 32-bit
type
fractional products (of two 16bit fractional multiplicands),
rounded to the upper 16 bits.
The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
fractional products (of two 32bit fractional multiplicands),
rounded to the upper 32 bits.
The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
Description
2.33.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Msu4RndSat functions have the following declarations:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
92 NXP Semiconductors
Page 93

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
frac16_t MLIB_Msu4RndSat_F16(frac16_t f16MinMult1, frac16_t f16MinMult2, frac16_t
f16SubMult1, frac16_t f16SubMult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Msu4RndSat_F32(frac32_t f32MinMult1, frac32_t f32MinMult2, frac32_t
f32SubMult1, frac32_t f32SubMult2)
2.33.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_Msu4RndSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac16_t f16Result, f16MinMult1, f16MinMult2, f16SubMult1, f16SubMult2;
void main(void)
{
f16MinMult1 = FRAC16(0.8); /* f16MinMult1 = 0.8 */
f16MinMult2 = FRAC16(-0.9); /* f16MinMult2 = -0.9 */
f16SubMult1 = FRAC16(0.7); /* f16SubMult1 = 0.7 */
f16SubMult2 = FRAC16(0.9); /* f16SubMult2 = 0.9 */
/* f16Result = sat(round(f16MinMult1 * f16MinMult2 - f16SubMult1 * f16SubMult2)) */
f16Result = MLIB_Msu4RndSat_F16(f16MinMult1, f16MinMult2, f16SubMult1, f16SubMult2);
}
2.34
MLIB_Mul
The MLIB_Mul functions return the product of two multiplicands. The function does not
saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 32. Algorithm formula
2.34.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output with fractional inputs - the output is the fractional portion of the
result; the result is within the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the fractional values only.
The result may overflow.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 93
Page 94

MLIB_Mul
• Fractional output with mixed inputs - the output is the fractional portion of the result;
the result is within the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the accumulator and fractional
values. The result may overflow.
• Accumulator output - the output is the accumulator type where the result can be out
of the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_Mul function are shown in the following table:
Table 2-34. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_Mul_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Product of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands; the output are the
MLIB_Mul_F16as acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t Product of a 32-bit accumulator and a 16-bit fractional multiplicand;
MLIB_Mul_F32ss frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t Product of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands; the result is a 32-bit
MLIB_Mul_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Product of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands; the output are the
MLIB_Mul_A32 acc32_t acc32_t acc32_t Product of two 32-bit accumulator multiplicands; the output is a 32-
type
upper 16 bits of the results [16..31]. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
the output is a 16-bit fractional portion, which has the upper 16 bits
of the fractional value of the result [16..31]. The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
fractional value. The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
upper 32 bits of the results [16..31]. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
bit accumulator, which has the upper mid bits of the result [16..47].
The output is within the range <-65536.0 ; 65536.0).
Description
2.34.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_Mul functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_Mul_F16(frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac16_t MLIB_Mul_F16as(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult)
frac32_t MLIB_Mul_F32ss(frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_Mul_F32(frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
acc32_t MLIB_Mul_A32(acc32_t a32Mult1, acc32_t a32Mult1)
2.34.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_Mul function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
94 NXP Semiconductors
Page 95

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
static frac32_t f32Result;
static frac16_t f16Mult1, f16Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f16Mult1 = FRAC16(0.4); /* f16Mult1 = 0.4 */
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.2); /* f16Mult2 = -0.2 */
/* f32Result = f16Mult1 * f16Mult2 */
f32Result = MLIB_Mul_F32ss(f16Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
2.35 MLIB_MulSat
The MLIB_MulSat functions return the product of two multiplicands. The function
saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 33. Algorithm formula
2.35.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output with fractional inputs - the output is the fractional portion of the
result; the result is within the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the fractional values only.
The result may saturate.
• Fractional output with mixed inputs - the output is the fractional portion of the result;
the result is within the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the accumulator and fractional
values. The result may saturate.
• Accumulator output - the output is the accumulator type where the result can be out
of the range <-1;1). The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_MulSat function are shown in the following table:
Table 2-35. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MulSat_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Product of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands; the output is the
type
upper 16 bits of the results [16..31]. The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
Description
Table continues on the next page...
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 95
Page 96

MLIB_MulNeg
Table 2-35. Function versions (continued)
Function name Input type Result
Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MulSat_F16as acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t Product of a 32-bit accumulator and a 16-bit fractional
MLIB_MulSat_F32ss frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t Product of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands; the result is a 32-
MLIB_MulSat_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Product of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands; the output are the
MLIB_MulSat_A32 acc32_t acc32_t acc32_t Product of two 32-bit accumulator multiplicands; the output is a
type
multiplicand; the output is a 16-bit fractional value, which has
the upper 16 bits of the fractional portion of the result [16..31].
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
bit fractional value. The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
upper 32 bits of the results [16..31]. The output is within the
range <-1 ; 1).
32-bit accumulator, which has the mid bits of the result [16..47].
The output is within the range <-65536.0 ; 65536.0).
Description
2.35.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MulSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_MulSat_F16(frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac16_t MLIB_MulSat_F16as(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult)
frac32_t MLIB_MulSat_F32ss(frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MulSat_F32(frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
acc32_t MLIB_MulSat_A32(acc32_t a32Mult1, acc32_t a32Mult1)
2.35.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_MulSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static acc32_t a32Accum;
static frac16_t f16Mult, f16Result;
void main(void)
{
a32Accum = ACC32(-5.5); /* a32Accum = -5.5 */
f16Mult = FRAC16(0.3); /* f16Mult = 0.3 */
/* f16Result = sat(a32Accum * f16Mult) */
f16Result = MLIB_MulSat_F16as(a32Accum, f16Mult);
}
2.36
96 NXP Semiconductors
MLIB_MulNeg
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
Page 97

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
The MLIB_MulNeg functions return the negative product of two multiplicands. The
function does not saturate the output. See the following equation:
Equation 34. Algorithm formula
2.36.1 Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output with fractional inputs - the output is the fractional portion of the
result; the result is within the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the fractional values only.
• Fractional output with mixed inputs - the output is the fractional portion of the result;
the result is within the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the accumulator and fractional
values. The result may overflow.
• Accumulator output - the output is the accumulator type where the result can be out
of the range <-1;1). The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_MulNeg function are shown in the following table.
Table 2-36. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MuNegl_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Negative product of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands; the
MLIB_MulNeg_F16as acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t Negative product of a 32-bit accumulator and a 16-bit fractional
MLIB_MulNeg_F32ss frac16_t frac16_t frac32_t Negative product of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands; the
MLIB_MulNeg_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Negative product of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands; the
MLIB_MulNeg_A32 acc32_t acc32_t acc32_t Product of two 32-bit accumulator multiplicands; the output is a
type
output are the upper 16 bits of the results [16..31]. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
multiplicand; the output is a 16-bit fractional value, which has
the upper 16 bits of the fractional portion of the result [16..31].
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
result is a 32-bit fractional value. The output is within the range
<-1 ; 1).
output are the upper 32 bits of the results [16..31]. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
32-bit accumulator, which has the mid bits of the result
[16..47]. The output is within the range <-65536.0 ; 65536.0).
Description
2.36.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MulNeg functions have the following declarations:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 97
Page 98

MLIB_MulNegSat
frac16_t MLIB_MulNeg_F16(frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac16_t MLIB_MulNeg_F16as(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult)
frac32_t MLIB_MulNeg_F32ss(frac16_t f16Mult1, frac16_t f16Mult2)
frac32_t MLIB_MulNeg_F32(frac32_t f32Mult1, frac32_t f32Mult2)
acc32_t MLIB_MulNeg_A32(acc32_t a32Mult1, acc32_t a32Mult1)
2.36.3 Function use
The use of the MLIB_MulNeg function is shown in the following examples:
Fixed-point version:
#include "mlib.h"
static frac32_t f32Result;
static frac16_t f16Mult1, f16Mult2;
void main(void)
{
f16Mult1 = FRAC16(0.5); /* f16Mult1 = 0.5 */
f16Mult2 = FRAC16(-0.3); /* f16Mult2 = -0.3 */
/* f32Result = f16Mult1 * (-f16Mult2) */
f32Result = MLIB_MulNeg_F32ss(f16Mult1, f16Mult2);
}
2.37
MLIB_MulNegSat
The MLIB_MulNegSat functions return the negative product of two multiplicands. The
function saturates the output. See the following equation:
Equation 35. Algorithm formula
2.37.1
Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output with mixed inputs - the output is the fractional portion of the result;
the result is within the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the accumulator and fractional
values. The result may saturate.
• Accumulator output - the output is the accumulator type where the result can be out
of the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
98 NXP Semiconductors
Page 99

Chapter 2 Algorithms in detail
The available versions of the MLIB_MulNegSat function are shown in the following
table:
Table 2-37. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MulNegSat_F16as acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t Negative product of a 32-bit accumulator and a 16-bit fractional
MLIB_MulNegSat_A32 acc32_t acc32_t acc32_t Negative product of two 32-bit accumulator multiplicands; the
type
multiplicand; the output is a 16-bit fractional value, which has
the upper 16 bits of the fractional portion of the result [16..31].
The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
output is a 32-bit accumulator, which has the middle bits of the
result [16..47]. The output is within the range <-65536.0 ;
65536.0).
Description
2.37.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MulNegSat functions have the following declarations:
frac16_t MLIB_MulNegSat_F16as(acc32_t a32Accum, frac16_t f16Mult)
acc32_t MLIB_MulNegSat_A32(acc32_t a32Mult1, acc32_t a32Mult2)
2.37.3
Function use
The use of the MLIB_MulNegSat function is shown in the following example:
#include "mlib.h"
static acc32_t a32M1, a32M2, a32Result;
void main(void)
{
a32M1 = ACC32(1.5); /* a32M1 = 1.5 */
a32M2 = ACC32(4.1); /* a32M2 = 4.1 */
/* f16Result = sat(-a32M1 * f32M2) */
a32Result = MLIB_MulNegSat_A32(a32M1, a32M2);
}
2.38
MLIB_MulRnd
The MLIB_MulRnd functions return the rounded product of two multiplicands. The
round method is the round to nearest. The function does not saturate the output. See the
following equation:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
NXP Semiconductors 99
Page 100

MLIB_MulRnd
Equation 36. Algorithm formula
2.38.1 Available versions
This function is available in the following versions:
• Fractional output with fractional inputs - the output is the fractional portion of the
result; the result is within the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the fractional values only.
The result may overflow.
• Fractional output with mixed inputs - the output is the fractional portion of the result;
the result is within the range <-1 ; 1). The inputs are the accumulator and fractional
values. The result may overflow.
• Accumulator output - the output is the accumulator type where the result can be out
of the range <-1 ; 1). The result may overflow.
The available versions of the MLIB_MulRnd function are shown in the following table:
Table 2-38. Function versions
Function name Input type Result
Mult. 1 Mult. 2
MLIB_MulRnd_F16 frac16_t frac16_t frac16_t Product of two 16-bit fractional multiplicands; the output is
MLIB_MulRnd_F16as acc32_t frac16_t frac16_t Product of a 32-bit accumulator and a 16-bit fractional
MLIB_MulRnd_F32ls frac32_t frac16_t frac32_t Product of a 32-bit and a 16-bit fractional multiplicand; the
MLIB_MulRnd_F32 frac32_t frac32_t frac32_t Product of two 32-bit fractional multiplicands; the output is
MLIB_MulRnd_A32 acc32_t acc32_t acc32_t Product of two 32-bit accumulator multiplicands; the output is
type
rounded to the upper 16 bits of the results [16..31]. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
multiplicand; the output is a 16-bit fractional value, which is
rounded to the upper 16 bits of the fractional portion of the
result [16..31]. The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
output is rounded to the upper 32 bits of the fractional portion
of the result [16..47]. The output is within the range <-1 ; 1).
rounded to the upper 32 bits of the results [16..31]. The output
is within the range <-1 ; 1).
rounded to the middle bits of the result [16..47]. The output is
within the range <-65536.0 ; 65536.0).
Description
2.38.2 Declaration
The available MLIB_MulRnd functions have the following declarations:
MLIB User's Guide, Rev. 5, 12/2020
100 NXP Semiconductors
 Loading...
Loading...