Page 1

User Guide
NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI
Motherboard
NVIDIA Corporation
October, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 2

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
NVIDIA Corporation
ii October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 3

nForce 780i SLI Motherboard
Table of Contents
Before You Begin…................................................................................................ix
Parts NOT in the Kit.............................................................................................ix
Intentions of the Kit..............................................................................................x
NVIDIA nForce 780i Motherboard...........................................................................1
Motherboard Specifications..................................................................................1
Unpacking and Parts Descriptions.........................................................................3
Unpacking............................................................................................................3
Equipment............................................................................................................3
NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI Motherboard...................................................................4
Hardware Installation...............................................................................................7
Safety Instructions................................................................................................7
Preparing the Motherboard...................................................................................8
Installing the CPU.............................................................................................8
Installing the CPU Fan......................................................................................9
Installing Memory DIMMs.................................................................................9
Installing the Motherboard..................................................................................10
Installing the I/O Shield...................................................................................10
Securing the Motherboard into the Chassis....................................................11
Connecting Cables and Setting Switches...........................................................11
Power Connections........................................................................................12
24-pin ATX Power (PWR1)..........................................................................13
8-pin ATX 12V Power (PWR2).....................................................................14
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 iii
Page 4

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Connecting IDE Hard Disk Drives....................................................................14
Connecting Serial ATA Cables........................................................................16
Connecting Internal Headers...........................................................................17
Front Panel Header.....................................................................................17
IEEE 1394a.................................................................................................18
USB Headers..............................................................................................19
Audio..............................................................................................................20
Fan Connections.............................................................................................21
COM1.............................................................................................................22
FDD Connector...............................................................................................23
Expansion Slots..............................................................................................23
PCI Slots.....................................................................................................23
PCI Express x1 Slot....................................................................................24
PCI Express x16 Slots.................................................................................24
Jumper Settings.................................................................................................25
Clear CMOS Jumper: CLR_CMOS..................................................................25
Configuring the BIOS.............................................................................................27
Enter BIOS Setup...............................................................................................28
Main Menu.........................................................................................................28
Standard CMOS Features Menu.........................................................................31
Date and Time................................................................................................32
IDE Channel and SATA Channel.....................................................................32
Drive A............................................................................................................34
Halt On...........................................................................................................34
Memory..........................................................................................................35
Advanced BIOS Features...................................................................................36
Removable Device Priority..............................................................................37
Hard Disk Boot Priority...................................................................................37
NVIDIA Corporation
iv October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 5

nForce 780i SLI Motherboard
Network Boot Priority......................................................................................37
CPU Internal Cache........................................................................................37
Quick Power On Self Test...............................................................................38
First/Second/Third Boot Device......................................................................38
Boot Other Device..........................................................................................38
Boot Up NumLock Status...............................................................................38
Security Option...............................................................................................39
APIC Mode.....................................................................................................39
MPS Version Control For OS..........................................................................39
Full Screen LOGO Show.................................................................................39
Advanced Chipset Features................................................................................40
System Clocks................................................................................................41
Frequency Settings.....................................................................................42
HT Multiplier...............................................................................................43
Spread Spectrum........................................................................................43
FSB & Memory Config....................................................................................44
CPU Configuration..........................................................................................48
System Voltages.............................................................................................50
NVMEM Memory Test.....................................................................................52
Load Timing/Voltage Set.................................................................................52
Save Timing/Voltage Set.................................................................................53
System BIOS Cacheable.................................................................................53
HPET Function................................................................................................53
NVIDIA GPU Ex...............................................................................................53
Integrated Peripherals Menu...............................................................................54
IDE Function Setup.........................................................................................55
RAID Config....................................................................................................56
USB Config.....................................................................................................56
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 v
Page 6

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
MAC Config....................................................................................................57
IEEE1394 controller........................................................................................57
HD Audio........................................................................................................57
IDE HDD Block Mode.....................................................................................57
Onboard FDC Controller.................................................................................57
Onboard Serial Port 1.....................................................................................58
Power Management Setup Menu........................................................................58
ACPI Function.................................................................................................59
ACPI Suspend Type........................................................................................59
Soft-Off by PBNT............................................................................................59
WOL(PME#) From Soft-Off..............................................................................59
Power On by Alarm.........................................................................................59
POWER ON Function......................................................................................60
PnP/PCI Configuration Menu..............................................................................61
Init Display First..............................................................................................62
Reset Configuration Data................................................................................62
Resources Controlled By................................................................................62
IRQ Resources...............................................................................................63
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop..................................................................................63
Maximum Payload Size...................................................................................63
System Monitor Menu........................................................................................64
Dynamic Fan Control......................................................................................65
Installing Drivers and Software.............................................................................67
Windows XP Drivers Install.................................................................................68
Using the NVIDIA Software...................................................................................69
NVIDIA Performance Group of NVIDIA Control Panel..........................................70
Device Settings...............................................................................................71
Current Hardware Settings..........................................................................72
NVIDIA Corporation
vi October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 7

nForce 780i SLI Motherboard
Dynamic BIOS Access....................................................................................78
View System Information................................................................................79
Profile Policies................................................................................................80
Manage Your System BIOS............................................................................81
NVIDIA System Monitor......................................................................................82
Appendix A. POST Codes for Tritium Platform.....................................................87
Appendix B. Configuring an SLI Configuration.....................................................97
SLI Connector....................................................................................................97
ForceWare Driver................................................................................................98
Enabling 3-Way SLI......................................................................................100
Verifying 3-way SLI is Active.............................................................................102
Index....................................................................................................................103
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 vii
Page 8

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
List of Figures
Figure 1. NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI Motherboard Layout.......................................5
Figure 2. Chassis Backpanel Connectors...........................................................6
Figure 3. Power Supply Connectors.................................................................12
Figure 4. PWR1 Motherboard Connector.........................................................13
Figure 5. BIOS CMOS Setup Utility Main Menu................................................29
Figure 6. Standard CMOS Features Menu........................................................31
Figure 7. Advanced BIOS Features Menu.........................................................36
Figure 8. Advanced Chipset Features...............................................................40
Figure 9. System Clocks Menu.........................................................................41
Figure 10. FSB & Memory Config Menu.............................................................44
Figure 11. CPU Configuration Menu...................................................................48
Figure 12. System Voltages Menu......................................................................50
Figure 13. Integrated Peripherals Menu..............................................................54
Figure 14. Power Management Setup Menu.......................................................58
Figure 15. PnP/PCI Configuration Menu.............................................................61
Figure 16. System Monitor Menu.......................................................................64
Figure 31. 3-way NVIDIA SLI connector (600-10732-0000-000).........................98
Figure 18. Windows Vista Device Manager.........................................................99
Figure 19. NVIDIA Control Panel, Set SLI Configuration...................................100
Figure 20. SLI Visual Indicators Operating in 3DMark2006...............................101
NVIDIA Corporation
viii October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 9

Parts NOT in the Kit
This kit contains all the hardware necessary to install and connect your new
NVIDIA® nForce® 780i SLI motherboard. However, it does not contain the
following items that must be purchased separately to make the motherboard
functional.
q Intel microprocessor:
Intel Core 2 Extreme, Intel Core 2 Quad, Intel Core 2 Duo Pentium EE,
Pentium D, Pentium
q Cooling fan for the microprocessor
q System memory support:
Supports dual channel DDR2 533/667/800, and up to 1200 MHz SLI-Ready
Memory. Supports up to 8 GBs DDR2 memory.
q Graphics Card
This motherboard supports 3-way SLI with three x16 PCI Express slots.
q Power Supply
The power supply requirement is dependent upon the power and the number
of the GPUs you install. If you are going to SLI two graphics cards, you are
going to require more power. As a rule, for one GPU you need a minimum of
a 300 W power supply. If you have two GPUs in an SLI configuration, you
will need a minimum of a 500 W power supply. If you have three GPUs in an
SLI configuration, you will need a minimum of a 1000 W power supply. To
calculate the power you are going to require for your specific configuration,
go to www.slizone.com.
nForce 780i SLI Motherboard
Before You Begin…
These instructions tell you how to install each of the parts listed so you can
have a functioning motherboard. As you go through the installation
instructions, we are assuming you have purchased the necessary parts.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 ix
Page 10

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Intentions of the Kit
This kit provides you with the motherboard and all connecting cables necessary
to install the motherboard into a PC cabinet. If you are building a PC, you will
use most of the cables provided in the kit. If however, you are replacing a
motherboard, you will not need many of the cables.
When replacing a motherboard in a PC cabinet, you will need to reinstall an
operating system even though the current drives have an operating system.
NVIDIA Corporation
x October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 11

NVIDIA nForce 780i
Thank you for buying the NVIDIA NFORCE 780i SLI Motherboard. This
motherboard offers the tools and performance PC users’ demand. When
combined with two or three SLI-Ready NVIDIA GeForce graphics cards, you
get innovative NVIDIA SLI Technology for enhanced system performance.
Motherboard Specifications
q Size
ATX form factor of 12 inch x 9.6 inch
q Microprocessor support
Intel Core 2 Extreme, Intel Core 2 Quad, Intel Core 2 Duo, Pentium EE,
Pentium D, Pentium
q Operating systems:
Supports Windows XP 32bit/64bit and Windows Vista 32bit/64bit
q Contains NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI MCP and SPP
q System Memory support
Supports dual channel JEDEC DDR2-800 and SLI-Ready memory up to
1200 MHz. Supports up to 8 GBs DDR2 memories.
q Ten USB 2.0 Ports
Ø Supports hot plug
Ø Ten USB 2.0 ports (six rear panel ports, four onboard USB headers)
Ø Supports wake-up from S1 and S3 mode
Ø Supports USB 2.0 protocol up to 480 Mbps transmission rate
Motherboard
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597x-001_v01 1
Page 12

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
q Onboard Serial ATA II
Ø 300MBps data transfer rate
Ø Six Serial ATA II connectors
Ø NVIDIA MediaShield RAID with support for RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID
0+1, RAID 5, and JBOD
Ø Supports hot plug and NCQ (Native Command Queuing )
q Onboard LAN
Ø Dual LAN interface built-in onboard
Ø Supports 10/100/1000 Mbit/sec Ethernet
q Onboard 1394
Ø Support hot plug
Ø Two 1394a ports (one rear panel port, one onboard header) with rate of
transmission at 400 Mbps
q Onboard Audio
Ø Azalia High-Definition audio
Ø Supports 8-channel audio
Ø Supports S/PDIF output
Ø Supports Jack-Sensing function
q Triple PCI Express x16 Support
Ø 2 x16 PCI Express 2.0
Ø 1 x16 PCI Express 1.0
Ø Supports 4 GB/sec (8 GB/sec concurrent) bandwidth
Ø Low power consumption and power management features
q Green Function
Ø Supports ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface)
Ø Supports S0 (normal), S1 (power on suspend), S3 (suspend to RAM), S4
(Suspend to disk - depends on OS), and S5 (soft - off)
q Expansion Slots
Ø Two PCI slots
Ø One PCI Express x1 slot
Ø Three PCI Express x16 Graphics slots
NVIDIA Corporation
2 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 13
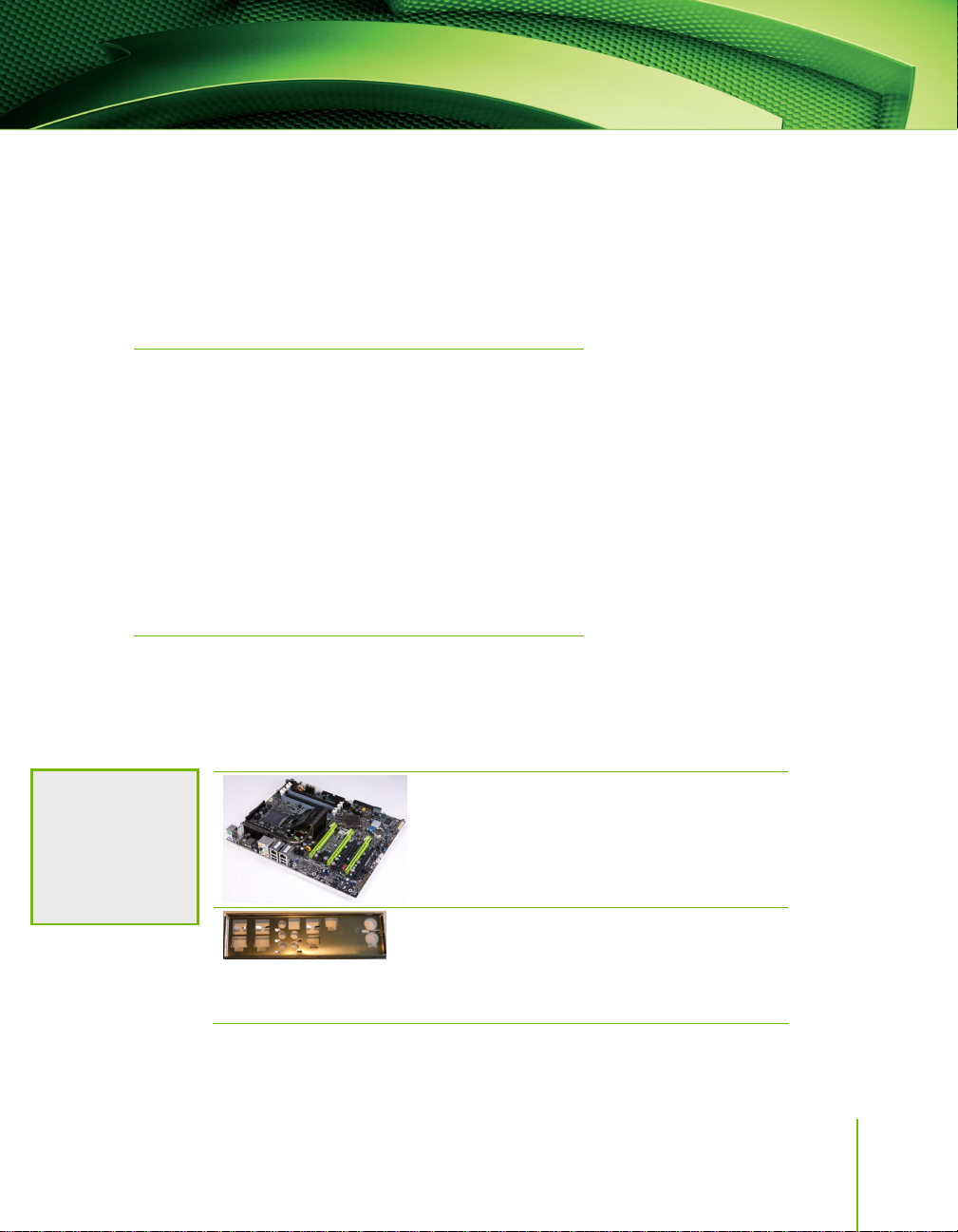
Unpacking
The NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI motherboard comes with all the necessary cables
for adding a motherboard to a new chassis. If you are replacing a motherboard,
you may not need many of these cables.
Be sure to inspect each piece of equipment shipped in the packing box. If
anything is missing or damaged, contact your reseller.
All parts shipped in this kit are RoHS-compliant (lead-free) parts.
Unpacking and
Parts Descriptions
Equipment
The following equipment is included in the NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI
motherboard box.
Note to Partners:
Revise this list with
the equipment you
are shipping in the
kit.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597x-001_v01 3
NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI Motherboard
This PCI Express motherboard contains the
NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI SPP and MCP and is
SLI-ready.
I/O Shield
Installs in the chassis to block radio
frequency transmissions, protect internet
components from dust and foreign objects
and aids in proper airflow within the chassis.
Page 14

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
IDE-ATA 133 HDD Cable
Floppy Cable
Used to attach a floppy drive to the
motherboard.
2-Port SATA Power Cable (Qty Three)
1394 Cable
Provides two additional 1394 ports to either
the front or back panels of the chassis.
USB 2.0 4-Port Cable
Provides four additional USB ports to either
the front or back panels of the chassis.
SATA Signal Cable (Qty Six)
Used to support the Serial ATA protocol and
each one connects a single drive to the
motherboard
Comm2 Bracket Cable
NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI
Motherboard
The NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI motherboard with the NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI
SPP and MCP processors is a PCI Express, SLI-ready motherboard. Figure 1
shows the motherboard and Figures 2 shows the back panel connectors.
NVIDIA Corporation
4 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 15
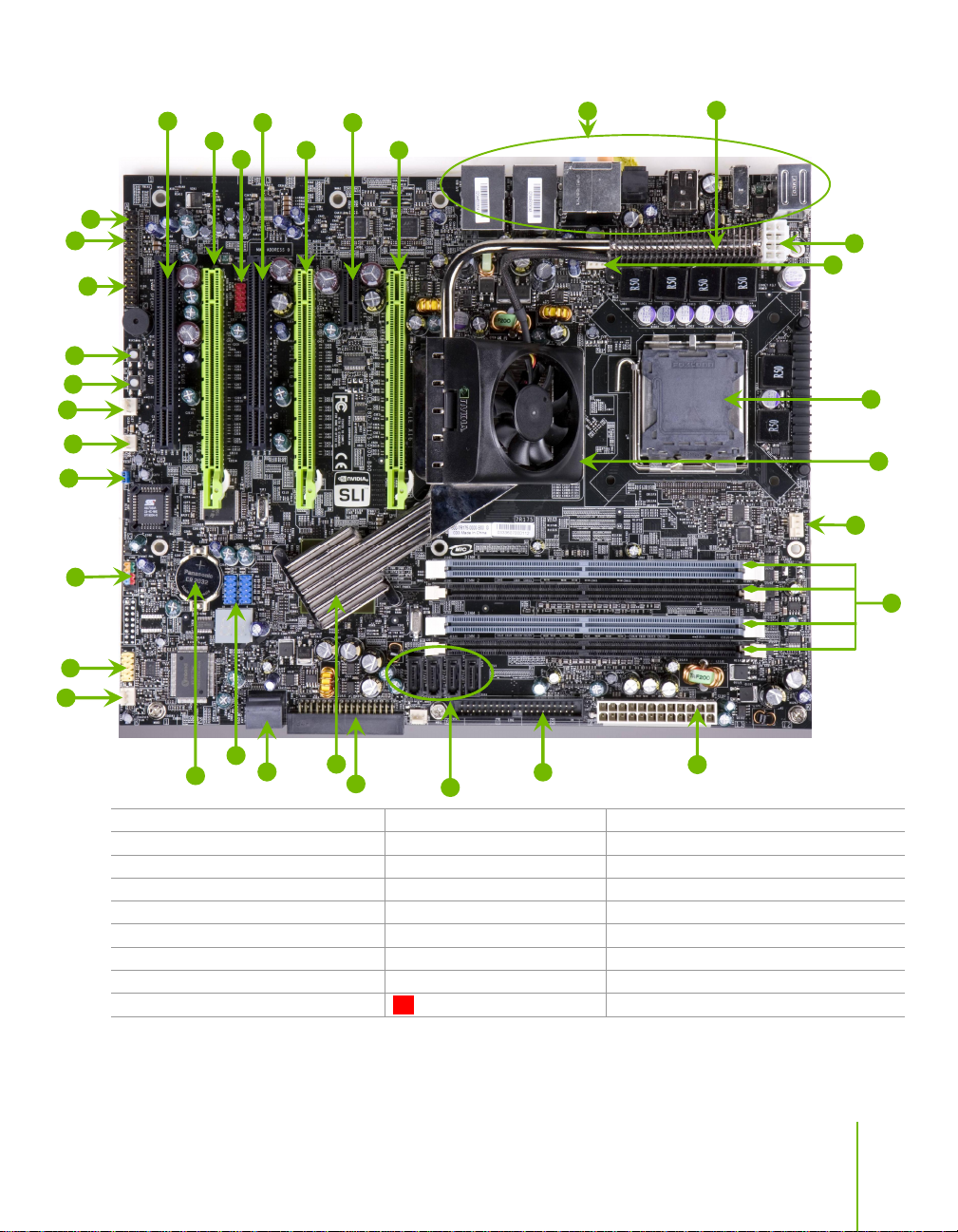
nForce 780i SLI Motherboard
4
5
10 8 9 7
6
13
14 15
16 22 23
22 25
23 28
11
12
20
23
24
17 13 13
27
19
21
18
29
2
3
1. CPU Socket 11. USB headers 21. SPDIF connector
2. NVIDIA SPP with Active fan 12. Motherboard battery 22. PCI slots
3. CPU fan connector 13. Fan connector 23. PCI Express x16 slots (SLI)
4. DDR DIMM Slots 0 - 3 14. Serial connector 24. 1394a connector
5. 24-pin ATX Power Connector 15. Front panel connector 25. PCI Express x1 slot
6. IDE Connector 16. Jumper 26. Backpanel connectors (Figure 2)
7. Serial-ATA (SATA) connectors 17. Power button 27. Heat dissipater
8. FDD connector 18. Reset Button 28. 8-pin ATX_12V power connector
9. NVIDIA MCP (passive heat sink) 19. Azalia HD Audio Header 29 MCP/SPP fan connector
10. Serial-ATA (SATA) connectors 20. FP Audio connector
Figure 1. NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI Motherboard Layout
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 5
Page 16
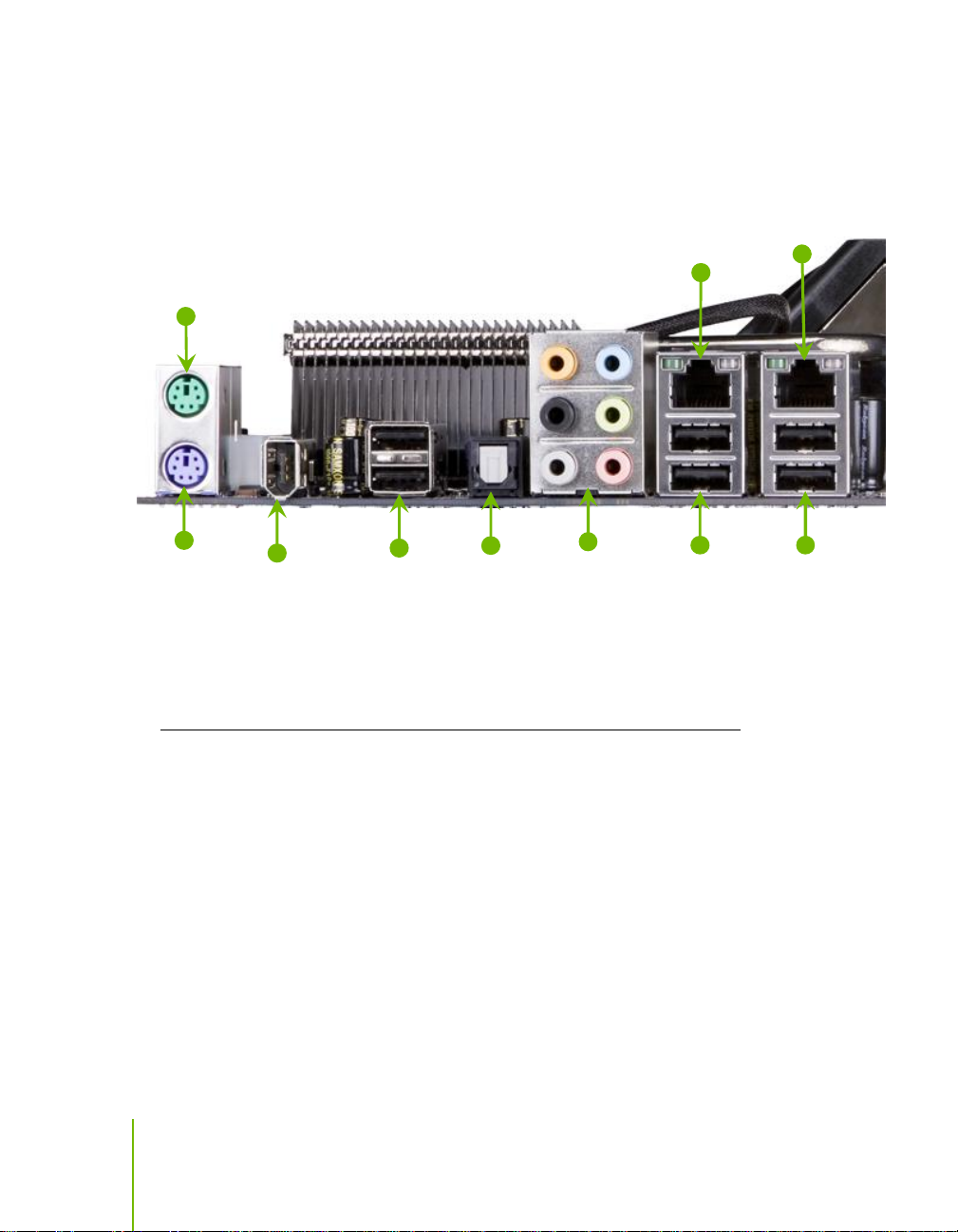
780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
1 2 5
6 7 4
3
4
7
4
1. PS/2 Mouse Port
2. PS/2 Keyboard Port
3. 1394a (Firewire) Port
4. USB 2.0 ports (SIX)
5. SPDIF output
6. Port 2-Channel 4-Channel 6-Channel/8-Channel
Blue Line-In Line-In Line-In
Green Line-Out Front Speaker Out Front Speaker Out
Pink Mic In Mic In Mic In
Orange Center/Subwoofer
Black Rear Speaker Out Rear Speaker Out
Grey
7. Lan Port with LEDs to indicate status.
• Yellow/Light Up/Blink = 10 Mbps/Link/Activity
• Yellow and Green/Light Up/Blink = 100 Mbps/link/Activity
• Green/Light Up/Blink = 1000 Mbps/Link/Activity
Figure 2. Chassis Backpanel Connectors
NVIDIA Corporation
6 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 17

This section will guide you through the installation of the motherboard. The
topics covered in this section are:
q Preparing the motherboard
Ø Installing the CPU
Ø Installing the CPU fan
Ø Installing the memory
q Installing the motherboard
q Connecting cables and setting switches
Safety Instructions
Hardware Installation
To reduce the risk of fire, electric shock, and injury, always follow basic
safety precautions.
Remember to remove power from your computer by disconnecting the
AC main source before removing or installing any equipment from/to the
computer chassis.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597x-001_v01 7
Page 18
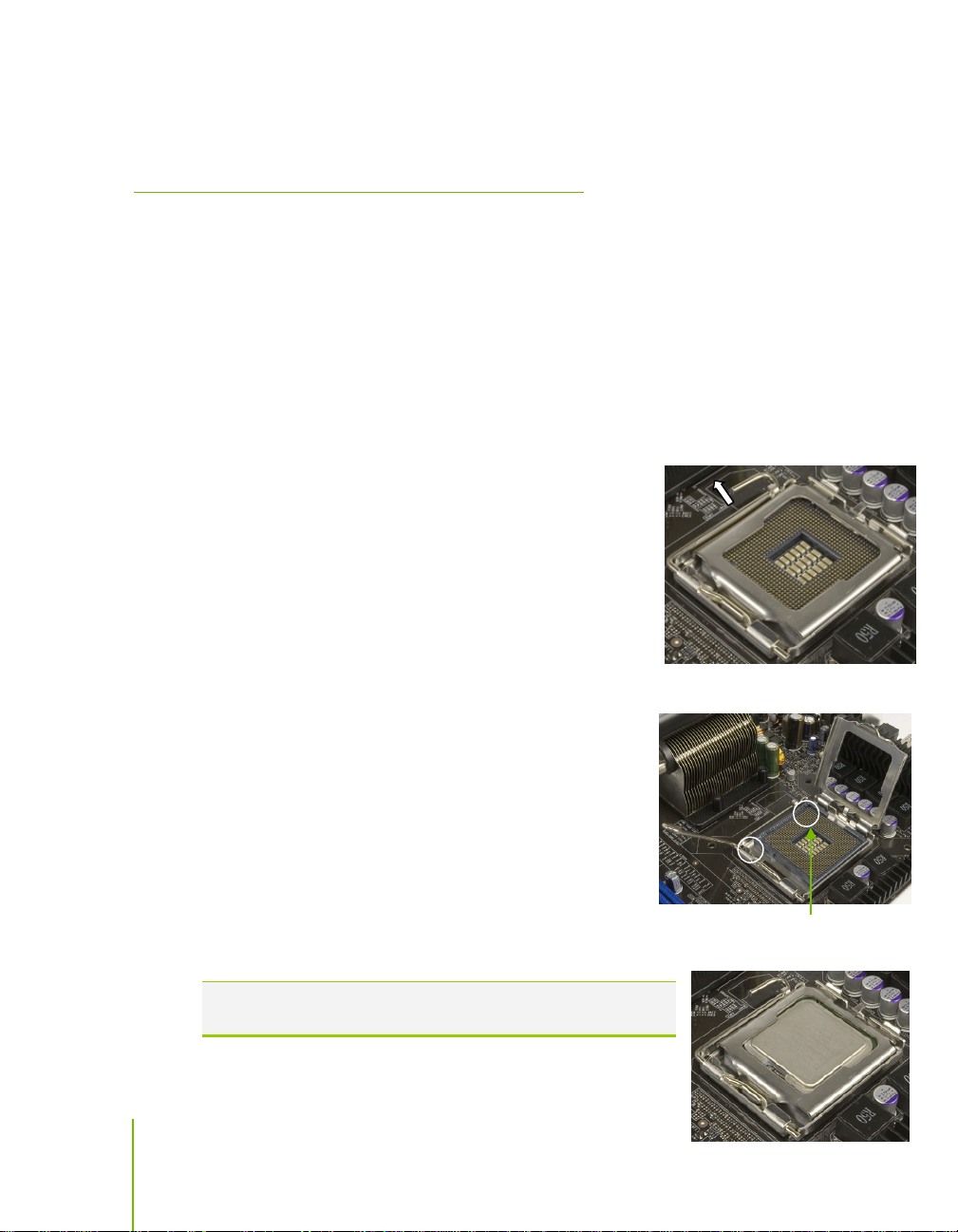
780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
notches on the CPU
Preparing the Motherboard
The motherboard shipped in the box does not contain a CPU or memory. You
need to purchase these to complete this installation.
Installing the CPU
Be very careful when handling the CPU. Make sure not to bend or break any
pins on the back. Hold the processor only by the edges and do not touch the
bottom of the processor.
Use the following procedure to install the CPU onto
the motherboard.
1. Unhook the socket lever by pushing down and
away from the socket.
2. Lift the load plate. There is a protective socket
cover on the load plate to protect the socket when
there is no CPU installed.
NVIDIA Corporation
8 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
3. Remove the protective socket cover from the load plate.
4. Remove the processor from its protective cover,
making sure you hold it only by the edges.
It is a good idea to save the cover so that
whenever you remove the CPU, you have a safe
place to store it.
5. Align the notches in the processor with the
notches on the socket.
6. Lower the processor straight down into the socket
with out tilting or sliding it into the socket
Note: Make sure the CPU is fully seated and level in the
socket.
Align notches with
Page 19

Hardware Installation
Card-edge
7. Close the load plate over the CPU and press down while you close and
engage the socket lever.
Installing the CPU Fan
There are many different fan types that can be used with this motherboard.
Follow the instruction that came with you fan assembly. Be sure that the fan
orientation is correct for your chassis type and your fan assembly.
Installing Memory DIMMs
Your new motherboard has four 1.8V 240-pin slots for DDR2 memory. These
slots support 256 Mb, 512 Mb and 1 Gb DDR2 technologies for x8 and x16
devices. They also support dual channel DDR2 memory technology up to
10.7GB/s. There must be at least one memory bank populated to ensure
normal operation. Use the following the recommendations for installing
memory. (See Figure 1 on page 5 for the location of the memory slots.)
q One DIMM: Install into slot 0. You can install the DIMM into any slot,
however, slot 0 is preferred.
q Two DIMMs: Install into either slots 0 and 1 or 2 and 3. The idea is to not
have the DIMMs in adjacent slots.
q Four DIMMS: Install into slots 0, 1, 2, and 3.
DIMM Slot 0
DIMM Slot 2
DIMM Slot 1
DIMM Slot 3
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 9
Page 20
780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Use the following procedure to install memory DIMMs. Note that there is only
one gap near the center of the DIMM slot. This slot matches the slot on the
memory DIMM to ensure the component is installed properly.
1. Unlock a DIMM slot by pressing the module clips outward.
2. Align the memory module to the DIMM slot, and insert the module
vertically into the DIMM slot. The plastic clips at both sides of the DIMM
slot automatically lock the DIMM into the connector.
Installing the Motherboard
The sequence of installing the motherboard into the chassis depends on the
chassis you are using and if you are replacing an existing motherboard or
working with an empty chassis. Determine if it would be easier to make all the
connections prior to this step or to secure the motherboard and then make all
the connections. It is normally easier to secure the motherboard first.
Use the following procedure to install the I/O shield and secure the
motherboard into the chassis.
Note: Be sure that the CPU fan assembly has enough clearance for the chassis
covers to lock into place and for the expansion cards. Also make sure the
CPU Fan assembly is aligned with the vents on the covers.
Installing the I/O Shield
The motherboard kit comes with an I/O shield that is used to block radio
frequency transmissions, protects internal components from dust and foreign
objects, and promotes correct airflow within the chassis.
Before installing the motherboard, install the I/O shield from the inside of the
chassis. Press the I/O shield into place and make sure it fits securely. If the
I/O shield does not fit into the chassis, you would need to obtain the proper
size from the chassis supplier.
NVIDIA Corporation
10 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 21

Hardware Installation
Securing the Motherboard into the Chassis
Most computer chassis have a base with mounting studs or spacers to allow the
mother board to be secured to the chassis and help to prevent short circuits. If
there are studs that do not align with a mounting hole on the motherboard, it is
recommended that you remove that stud to prevent the possibility of a short
circuit. In most cases, it is recommended to secure the motherboard using a
minimum of nine (9) spacers.
1. Carefully place the motherboard onto the studs/spacers located inside the
chassis.
2. Align the mounting holes with the studs/spacers.
3. Align the connectors to the I/O shield.
4. Ensure that the fan assembly is aligned with the chassis vents according to
the fan assembly instruction.
5. Secure the motherboard with a minimum of eight-to-ten screws.
Connecting Cables and
Setting Switches
This section takes you through all the connections and switch settings necessary
on the motherboard. This will include:
q Power Connections
Ø 24-pin ATX power (PWR1)
Ø 8-pin ATX 12V power (PWR2)
q Internal Headers
Ø Front panel
Ø IEEE 1394a
Ø USB Headers
Ø Audio
Ø Speaker
Ø COM
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 11
Page 22
780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
q FDD
q IDE
q Serial ATA II
q Chassis Fans
q Rear panel USB 2.0 Adapter
q Expansion slots
q CMOS jumper settings
See Figure 1 on page 5 to locate the connectors and jumpers referenced in the
following procedure.
Power Connections
To support 3-way SLI, this motherboard has the following specific power
supply requirements:
q Minimum 1000 W peak power
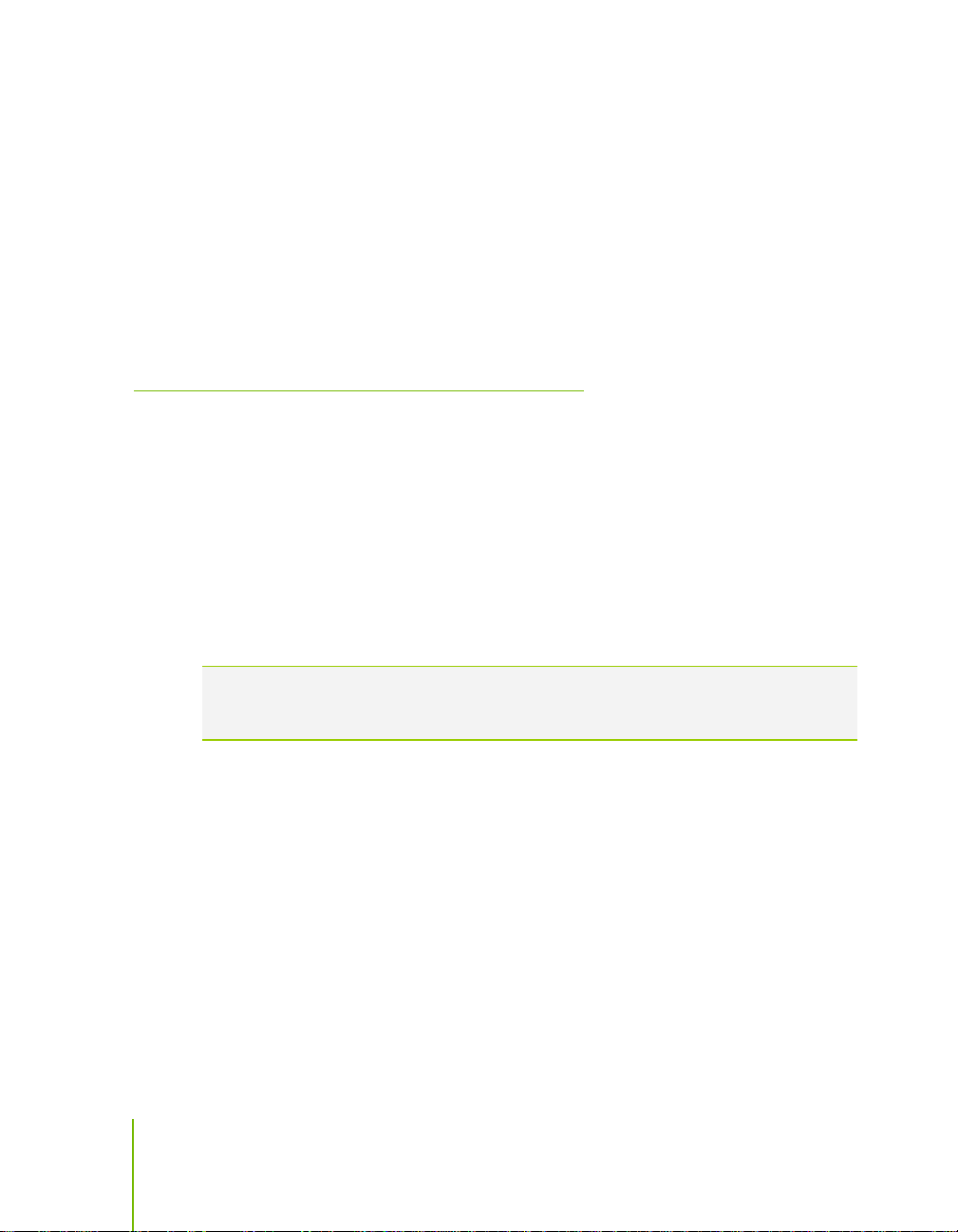
q Six PCI-E power connectors configured in either of the following
configurations (see Figure 3):
Ø Four 6-pin (3x2) and two 8-pin (4x2) PCI-E power connectors
or
Ø Six 6-pin (3x2) PCI-E power connectors
8-pin (4x2) PCT-E Connector 6-pin (3x2) PCI-E connector
Figure 3. Power Supply Connectors
NVIDIA Corporation
12 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 23

Hardware Installation
Make sure you have enough power to cover all the expansion cards you will be
installing. To determine what you power requirements are for your specific
configuration or a certified power supply vendor, refer to www.slizone.com.
24-pin ATX Power (PWR1)
PWR1 is the main power supply connector located along the edge of the board
next to the DIMM slots. Make sure that the power supply cable and pins are
properly aligned with the connector on the motherboard. Firmly plug the power
supply cable into the connector and make sure it is secure.
PWR1 connector
Plug power cable from system
power supply to PWR1
Card edge
Figure 4. PWR1 Motherboard Connector
Table 1. PWR1 Pin Assignments
Connector Pin Signal Pin Signal
24 13
12 1
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 13
1 +3.3V 13 +3.3V
2 +3.3V 14 -12V
3 GND 15 GND
4 +5V 16 PS_ON
5 GND 17 GND
6 +5V 18 GND
7 GND 19 GND
8 PWROK 20 RSVD
9 +5V_AUX 21 +5V
10 +12V 22 +5V
11 +12V 23 +5V
Page 24

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Connector Pin Signal Pin Signal
8-pin ATX 12V Power (PWR2)
PWR2, the 8-pin ATX 12V power connection, is used to provide power to the
CPU. Align the pins to the connector and press firmly until seated.
Backpanel connector
12 +3.3V 24 GND
5
1
12V
8 4
Connecting IDE Hard Disk Drives
The IDE connector supports Ultra ATA 133/100/66 IDE hard disk drives.
1. Connect the blue connector (the cable end with a single connector) to the
motherboard.
2. Connect the black connector (the cable with the two closely spaced black
and gray connectors) to the Ultra ATA master device.
3. Connect the gray connector to a slave device.
GND
If you install two hard disk drives, you must configure the second drive as a
slave device by setting its jumper accordingly. Refer to the hard disk
documentation for the jumper settings.
NVIDIA Corporation
14 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 25
Hardware Installation
Note: If an ATA-66/100 disk drive and a disk drive using any other IDE transfer
protocol are attached to the same cable, the maximum transfer rate between
the drives may be reduced to that of the slowest drive.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 15
Page 26
780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
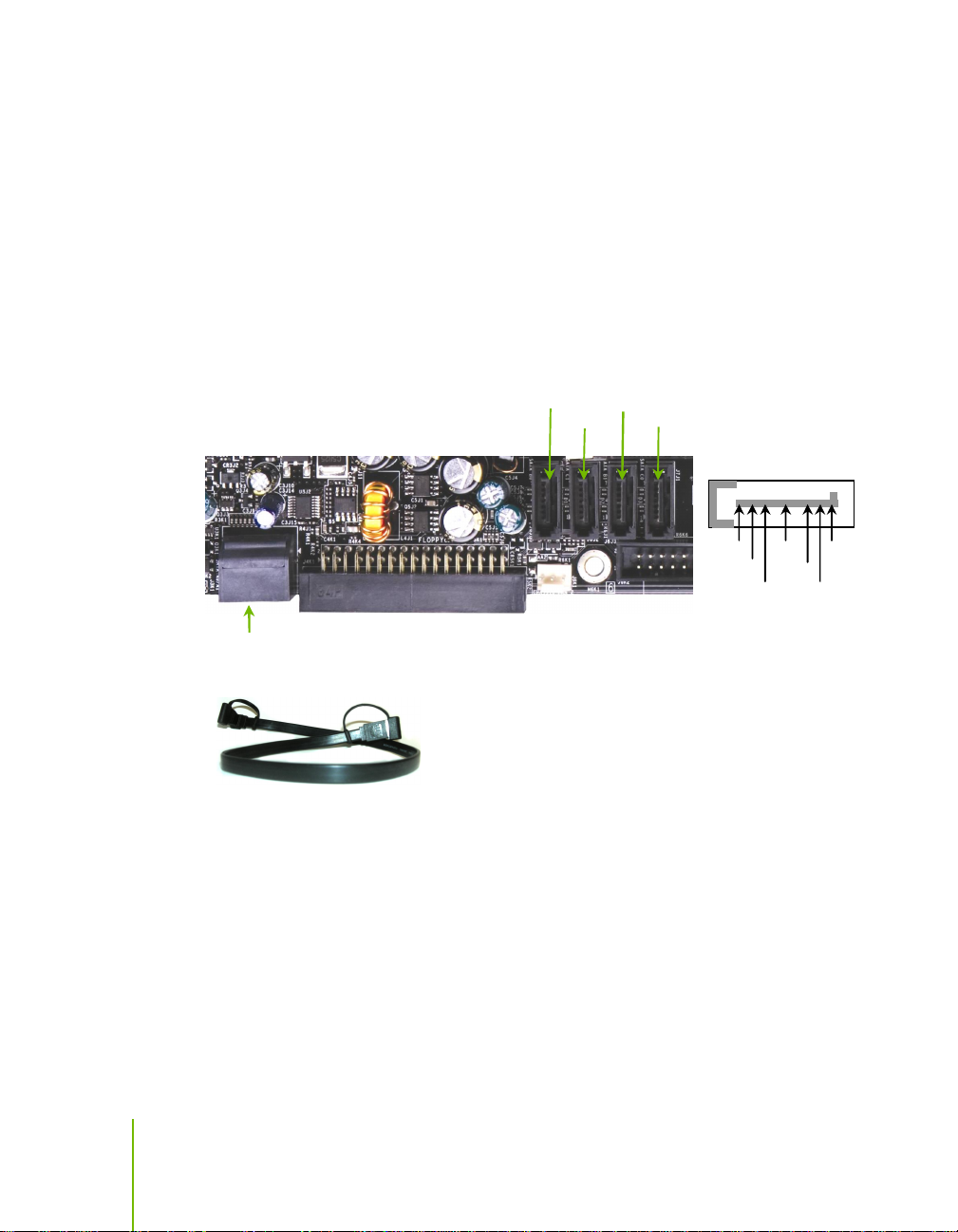
Connecting Serial ATA Cables
The Serial ATA II connector is used to connect the Serial ATA II device to the
motherboard. These connectors support the thin Serial ATA II cables for
primary storage devices. The current Serial ATA II interface allows up to
300MB/s data transfer rate.
There are six serial ATA connectors on the motherboard that support RAID 0,
RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 0+1 and JBOD configurations.
SATA 1 (bottom)
SATA 2 (top)
Connect the locking cable end to the motherboard connector.
Connect the end without the lock to the drive.
SATA 3 SATA 4
SATA 6 SATA 5
GND GND GND
TX+ RX+
TX- TX-
NVIDIA Corporation
16 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 27

Hardware Installation
Connecting Internal Headers
Front Panel Header
The front panel header on this motherboard is one connector used
to connect the following four cables
(see Table 2 for pin definitions):
q PWRLED
Attach the front panel power LED
cable to these two pins of the connector.
The Power LED indicates the system’s
status. When the system is in S0 status,
the LED is on. When the system is in S1,
S3, S4, S5 status, the LED is off.
Note: Some chassis do not have all four cables. Be sure to match the name on the
connectors to the corresponding pins.
PWRSW
-
PWRLED
+
910
RESET
HD_LED
+
12
No ConnectBlank
q PWRSW
Attach the power button cable from the case to these two pins. Pressing the
power button on the front panel turns the system on and off rather than
using the power supply button.
q HD_LED
Attach the hard disk drive indicator LED cable to these two pins. The HDD
indicator LED indicates the activity status of the hard disks.
q RESET
Attach the Reset switch cable from the front panel of the case to these two
pins. The system restarts when the RESET switch is pressed.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 17
Page 28

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Table 2. Front Panel Header Pins
Pin Signal In/Out Description
1 HD_PWR Out Hard disk LED pull-up to +5V HD_LED
3 HDA# Out Hard disk active LED
2 HDR_BLNK_GRN Out Front panel green light PWRLED
4 HDR_BLNK_YEL Out Front panel yellow light
5 GND Ground RESET
7 FP_RESET# In Reset switch
6 SWITCH_ON# In Power switch PWRSW
8 GND Ground
No Connect 9 No Connect
Empty 10 Empty
IEEE 1394a
Partner
Update this
section with
the type of
bracket you
are going to
ship with your
kit.
The IEEE 1394 expansion cable bracket is provided in the box but if you do
not require the additional external connections, you do not need to install it.
1. Secure the bracket to either the front or rear panel of your chassis (not all
chassis are equipped with the front panel option).
2. Connect the two ends of the cables to the IEEE 2394 connectors on the
motherboard.
Table 3. IEEE 1394a Connector Pins
Connector
IEEE 1394a Connector
10
8
6
4
2
9
7
5
3
1
Pin Signal
1 TPA+
2 TPA3 GND
4 GND
5 TPB+
6 TPB7 +12V
8 +12V
9 Empty
10 GND
NVIDIA Corporation
18 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 29
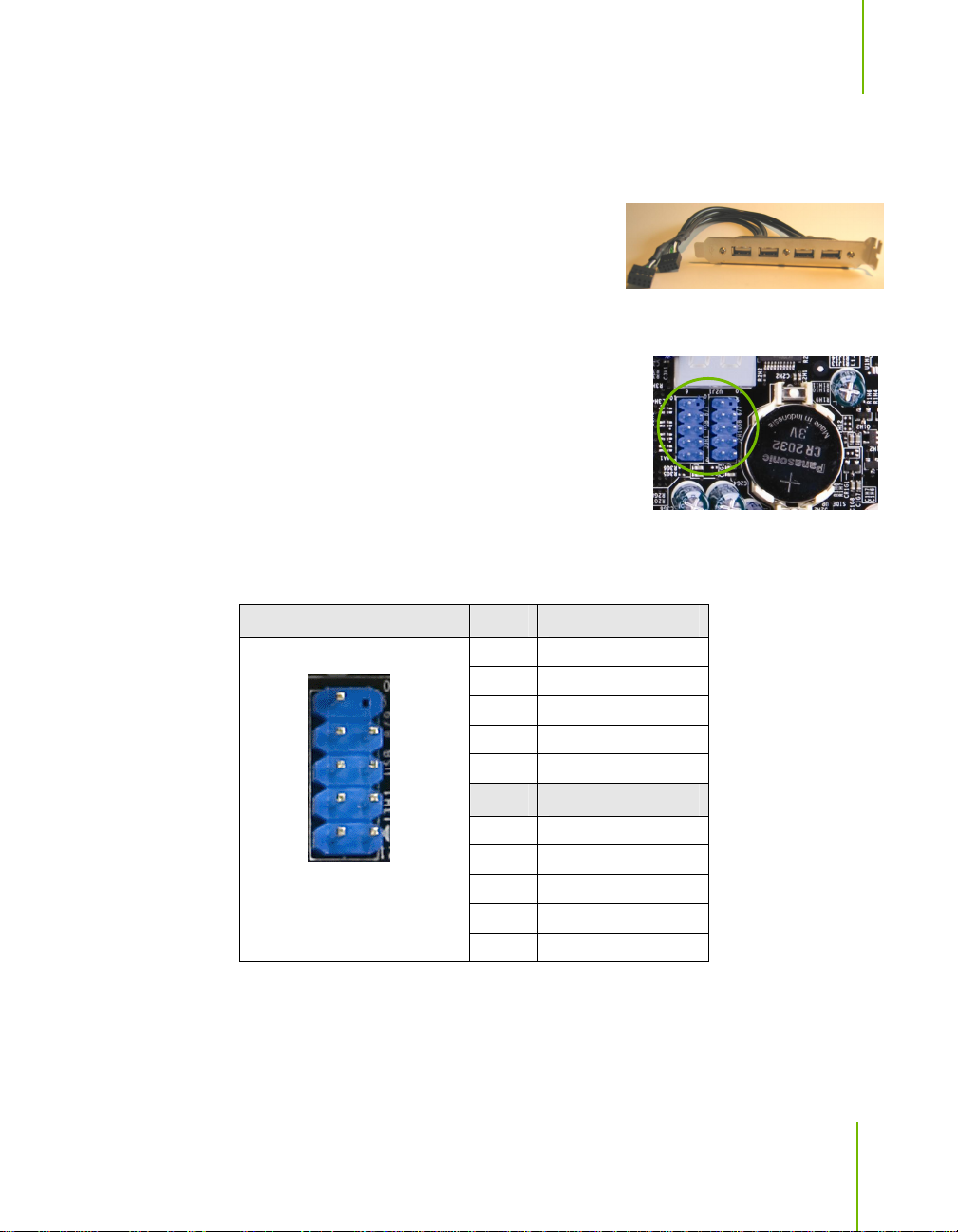
Hardware Installation
USB Headers
This motherboard contains six (6) USB 2.0 ports
that are exposed on the rear panel of the chassis
(Figure 2). The motherboard also contains two
10-pin internal header connectors onboard that
can be used to connect an optional external bracket containing four (4) more
USB 2.0 ports.
1. Secure the bracket to either the front or rear
panel of your chassis (not all chassis are
equipped with the front panel option).
2. Connect the two ends of the cables to the USB
2.0 headers on the motherboard.
Table 4. USB 2.0 Header Pins
Connector Pin Signal
USB 2.0 Header Connector
10
8
6
4
2
9
7
5
3
1
1 5V_DUAL
3 D5 D+
7 GND
9 Empty
Pin Signal
2 5V_DUAL
4 D6 D+
8 GND
10 No Connect
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 19
Page 30

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Audio
The audio connector supports HD audio standard and provides two kinds of
audio output choices: the Front Audio, the Rear Audio. The front Audio
supports re-tasking function.
Table 5. Front Audio Connector
Connector
Front Audio Connector
1
3
5
7
9
2
4
6
8
10
Pin Signal
1 PORT1_L
2 AUD_GND
3 PORT1_R
4 PRECENCE_J
5 PORT2_R
6 SENSE1_RETURN
7 SENSE_SEND
8 Empty
9 PORT2_L
10 SENSE2_RETURN
NVIDIA Corporation
20 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 31

Hardware Installation
Note that the CPU fan cable
4
3
2
Fan Connections
There are five fan connections on the motherboard. The fan speed can be
detected and viewed in the PC Health Status section of the CMOS Setup. The
fans are automatically turned off after the system enters S3, S4 and S5 mode.
can be either a 3-pin or a
4-pin connector. Connect a
3-pin connector to pins 1,
2, and 3 on the
motherboard connector.
CPU Fan Connector
GND SENSE
PWR CONTROL
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 21
Fan Connector
3 2
GND
+12V
SENSE
nForce 780i SLI SPP/MCP fan connector.
Install the fan over the nForce 780i SLI SPP to
draw heat from the MCP. The fans plug into a 3pin connector.
Page 32

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
There are four more fan connectors on the motherboard. For this installation,
these will not be used.
Auxiliary fan connector
Auxiliary fan
connector
Fan Connector
3 2
GND
+12V
SENSE
Auxiliary fan
connector
System fan
connector
COM1
The motherboard kit provides an additional serial COM header for your
machine. Connect one side of a switching cable to the header and then attach
the serial COM device to the other side of the cable.
NVIDIA Corporation
22 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 33

Hardware Installation
2
FDD Connector
The motherboard supports a standard 360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44m, and a 2.88M
floppy disk drive (FDD).
Expansion Slots
The NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI motherboard contains six expansion slots, four
PCI Express slots and two PCI slots. For a full list of PCI Express x16 graphics
card supported by this motherboard, go to www.nvidia.com/estore.
1
2
1
3
2
1 – PCI slots
2 – PCIe x16 slots
(3-Way SLI)
3 – PCIe x1 slot
PCI Slots
The two PCI slots support many expansion cards such as a LAN card, USB
card, SCSI card and other cards that comply with PCI specifications. When
installing a card into the PCI slot, be sure that it is fully seated. Secure the card’s
metal bracket to the chassis back panel with the screw used to hold the blank
cover.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 23
Page 34

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
PCI Express x1 Slot
There is one PCI Express x1 slot that is designed to accommodate less
bandwidth-intensive cards, such as a modem or LAN card. The x1 slot provides
250 MB/sec bandwidth.
PCI Express x16 Slots
These three PCI Express x16 slots are reserved for graphics or video cards. The
bandwidth of the x16 slot is up to 4GB/sec (8GB/sec concurrent). The design
of this motherboard supports three PCI-Express graphics cards using
NVIDIA’s SLI technology with multiple displays.
When installing a PCI Express x16 card, be sure the retention clip snaps and
locks the card into place. If the card is not seated properly, it could cause a
short across the pins. Secure the card’s metal bracket to the chassis back panel
with the screw used to hold the blank cover.
To configure for SLI, follow the instructions that come with the SLI kit (the kit
is purchased separately from the motherboard).
NVIDIA Corporation
24 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 35

Hardware Installation
Jumper Settings
The motherboard contains a 3-pin BIOS configuration jumper that enables all
board configurations to be done in the BIOS Setup program.
The silk screen on the motherboard shows a ∆ next to pin 1.
Clear CMOS Jumper: CLR_CMOS
The motherboard uses the CMOS RAM to store all the set parameters. The
CMOS can be cleared by removing the CMOS jumper.
Use the following procedure to clear CMOS:
1. Turn off the AC power supply and connect pins 1 and 2 together using the
jumper cap.
2. Return the jumper setting to normal (pins 2 and 3 together with the jumper
cap).
3. Turn the AC power supply back on.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 25
Page 36

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
This page is blank.
NVIDIA Corporation
26 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 37

Configuring the BIOS
This section discusses how to change the system settings through the BIOS
Setup menus. Detailed descriptions of the BIOS parameters are also provided.
This section includes the following information:
q Enter BIOS Setup
q Main Menu
q Standard CMOS Features
q Advanced BIOS Features
q Advanced Chipset Features
q Integrated Peripherals
q Power Management Setup
q PnP/PCI Configurations
q System Monitor
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597x-001_v01 27
Page 38

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Enter BIOS Setup
The BIOS is the communication bridge between hardware and software.
Correctly setting the BIOS parameters is critical to maintain optimal system
performance.
Use the following procedure to verify/change BIOS settings.
1. Power on the computer.
2. Press the Del key when the following message briefly displays at the bottom
of the screen during the Power On Self Test (POST).
Press F1 to continue, DEL to enter Setup.
Pressing Del takes you to the Phoenix-Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility.
Note: It is strongly recommended that you do not change the default BIOS settings.
Changing some settings could damage your computer.
Main Menu
The main menu allows you to select from the list of setup functions and two
exit choices. Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the
options or press Enter to display the associated submenu. Use the #$ arrow
keys to position the selector in the option you choose. To go back to the
previous menu, press Esc.
Note: Note that on the BIOS screens all data in white is for information only, data in
yellow is changeable, data in blue is non-changeable, and data in a
red box is highlighted for selection.
NVIDIA Corporation
28 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 39

Configuring the BIOS
F10 : Save & Exit Setup
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
} Standard CMOS Features
} Advanced BIOS Features
} Advanced Chipset Features
} Integrated Peripherals
} Power Management Setup
} PnP/PCI Configurations
Esc : Quit
Time, Date, Hard Disk Type..,
SLI-Ready memory - Disabled
} System Monitor
Load Defaults
Set Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
#$"! : Select Item
Figure 5. BIOS CMOS Setup Utility Main Menu
q Standard CMOS Features
Use this menu to set up the basic system configuration.
q Advanced BIOS Features
Use this menu to set up the advanced system features and boot sequence.
q Advanced Chipset Features
Use this menu to optimize system performance and configure clocks,
voltages, memory timings, and more.
q Integrated Peripherals
Use this menu to set up onboard peripherals such as IDE, RAID, USB, LAN,
and MAC control.
q Power Management Setup
Use this menu to configure power management, power on, and sleep features.
q PnP/PCI Configurations
Use this menu to modify the system’s Plug-and-Play and PCI configurations.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 29
Page 40

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
q System Monitor
Use this menu to monitor the real-time system status of your PC, including
temperature, voltages, and fan speed.
The following items on the CMOS Setup Utility main menu are commands
rather than submenus:
q Load Defaults
Load default system settings.
q Set Password
Use this command to set, change, and disable the password used to access the
BIOS menu.
q Save & Exit Setup
Use this command to save settings to CMOS and exit setup.
q Exit Without Saving
Use this command to abandon all setting changes and exit setup.
SLI-Ready Memory is a status indicator displayed at the bottom of the BIOS
screen. The three status indicators are:
q Enabled: SLI-Ready memory is detected and enabled.
q Disabled: SLI-Ready memory is detected but disabled.
q Not Detected: SLI-Ready memory is not detected.
NVIDIA Corporation
30 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 41

Configuring the BIOS
F5: Previous Values F7:Defaults
Standard CMOS Features
Menu
The Standard CMOS Features menu is used to configure the standard CMOS
information, such as the date, time, HDD model, and so on. Use the Page Up
and Page Down keys to scroll through the options or press Enter to display the
sub-menu. Use the #$ arrow keys to position the selector in the option you
choose. To go back to the previous menu, press Esc.
The information shown in Item Help corresponds to the option highlighted.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Date (mm:dd:yy) Sat, Jul 01 2006
Time (hh:mm:ss) 12 : 48: 23
} IDE Channel (.) Master [None]
} IDE Channel (.) Slave [None]
} SATA Channel 1 Master [None]
} SATA Channel 2 Master [None]
} SATA Channel 3 Master [None]
} SATA Channel 4 Master [None]
} SATA Channel 5 Master [None]
} SATA Channel 6 Master [None]
Drive A [1.44, 3.5 in.]
Halt On [All , But Keyboard]
Base Memory 640K
Extended Memory 1047552K
Total Memory 1048576K
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
Standard CMOS Features
Item Help
Main Level }
Change the day, month,
year and century
Figure 6. Standard CMOS Features Menu
Note: Note that all data in white is for information only, data in yellow is changeable,
data in blue is non-changeable, and data in a red box is highlighted for
selection.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 31
Page 42

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Date and Time
Using the arrow keys, position the cursor over the month, day, and year. Use
the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through dates and times. Note that
the weekday (Sun through Sat) cannot be changed. This field changes to
correspond to the date you enter. Note that the hour value is shown in a
24-hour clock format. Time is represented as hour : minute : second.
Date (mm:dd:yy) Sat, Jul 01 2006
Time (hh:mm:ss) 14 : 48: 43
IDE Channel and SATA Channel
Use these functions to detect and configure the individual IDE and SATA
channels. Select a channel and press Enter to display the IDE/SATA sub-menu.
} IDE Channel (.) Master [None]
} IDE Channel (.) Slave [None]
} SATA Channel 1 Master [None]
} SATA Channel 2 Master [None]
} SATA Channel 3 Master [None]
} SATA Channel 4 Master [None]
} SATA Channel 5 Master [None]
} SATA Channel 6 Master [None]
IDE Auto-Detect [Press Enter]
Extended IDE Drive [None}
Access Mode Auto
Capacity 0 MB
Cylinder 0
Head 0
Precomp 0
Landing Zone 0
Sector 0
Press ENTER to display
SATA Channel sub-
Press ENTER to display
IDE Channel sub-menu
IDE HDD Auto-Detect [Press Enter]
IDE Channel 0 Slave [Manual}
Access Mode [CHS]
Capacity 0 MB
Cylinder [ 0]
Head [ 0]
Precomp [ 0]
Landing Zone [ 0]
Sector [ 0]
NVIDIA Corporation
32 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 43

Configuring the BIOS
Press Enter to auto-detect IDE and SATA channels in the system. Once the
channel is detected, the values for Capacity, Cylinder, Heads, Precomp, Landing
Zone, and Sector are automatically filled in.
q None
There is no HDD installed or set.
q Auto
The system can auto-detect the hard disk when booting up.
q Manual
When you set the channel to [Manual] and change Access Mode to [CHS],
you can then enter the number of cylinders, heads, Precomp, landing zone,
and sector. You can manually enter the values or you can press Enter to
display a window that tells you the min and max values.
IDE HDD Auto-Detect [Press Enter]
IDE Channel 0 Slave [Manual}
Access Mode [CHS]
Capacity 0 MB
Cylinder .....0
Head [ 0]
Precomp [ 0]
Landing Zone [ 0]
Sector [ 0]
The BIOS supports the following HDD
Access Modes:
Ø CHS
For HDD less than 528 MB.
Ø LBA
For HDD greater than 528 MB and
Press ENTER to display sub-
menu
Cylinder
Min= 0
Max=65535
Key in a DEC number :
#$
:Move ENTER:Accept ESC:Abort
supporting LBA (Logical Block
Addressing).
Ø Large
For HDD greater than 528 MB but not supporting LBA.
Ø Auto
Recommended mode.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 33
Page 44

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Halt On
[All , But Keyboard]
Press ENTER to di
splay sub
-
menu
Drive A
The Drive A option allows you to select the kind of FDD to install.
Options are:
Drive A [1.44, 3.5 in.]
q None
q 360K, 5.25 in.
q 1.2M, 5.25 in.
q 720K, 3.5 in.
q 1.44M, 3.5 in.
q 2.88M, 3.5 in.
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll
through the options or press Enter to display
the sub-menu. Use the #$ arrow keys to
position the selector in the option you choose. Press Enter to accept the
changes and return to the Standard CMOS Features menu.
Drive A
None ..... [ ]
360K, 5.25 in. ..... [ ]
1.2M, 5.25 in. ..... [ ]
720K, 3.5 in. ..... [ ]
1.44M, 3.5 in. ..... [ ]
2.88M, 3.5 in. ..... [ ]
#$
:Move ENTER:Accept ESC:Abort
NVIDIA Corporation
34 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Halt On
Halt On determines whether or not the computer stops if an error is detected
during power on. Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the
options or press Enter to display the Halt On sub-menu. Use the #$ arrow keys
to position the selector in the option you choose. Press Enter to accept the
changes and return to the Standard CMOS Features menu.
Drive A [1.44, 3.5 in.]
Halt On [All , But Keyboard]
q All Errors
Whenever the BIOS detects a nonfatal
error, the system stops and prompts you.
q No Errors
System boot does not stop for any detected
errors.
Halt On
All Errors ..... [ ]
No Errors ..... [ ]
All , But Keyboard ..... [
All , But Diskette ..... [ ]
All , But Disk/Key ..... [ ]
#$
:Move ENTER:Accept ESC:Abort
]
Page 45

Configuring the BIOS
q All, But Keyboard
System boot does not stop for keyboard errors, but does stop for all other
errors.
q All, But Diskette
The system boot does not stop for a diskette error but will stop for all other
errors.
q All, But Disk/Key
The system boot does not stop for a keyboard or disk error, but will stop for
all other errors.
Memory
These settings are display-only values that are determined by the BIOS POST
(Power-On Self Test).
q Base Memory
BIOS POST determines the
amount of base (or conventional) memory installed in the system.
q Extended Memory
BIOS determines how much extended memory is present during the POST.
q Total Memory
This value represents the total memory of the system.
Base Memory 640K
Extended Memory 1047552K
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 35
Page 46

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
F5: Previous Values F7:Defaults
Advanced BIOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Access the Advanced BIOS Features menu from the CMOS Utility Setup
screen. Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the options or
press Enter to display the sub-menu. Use the #$ arrow keys to position the
selector in the option you choose. To go back to the previous menu, press Esc.
Note: The options that have associated sub-menus are designated by a }, which
precedes the option. Press Enter to display the sub-menus.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
} Removable Device Priority [Press Enter]
} Hard Disk Boot Priority [Press Enter]
} Network Boot Priority [Press Enter]
CPU Internal Cache [Enabled]
Quick Power On Self Test [Enabled]
First Boot Device [Removable]
Second Boot Device [CDROM]
Third Boot Device [Hard Disk]
Boot Other Device [Enabled]
Boot Up NumLock Status [On]
Security Option [Setup]
APIC Mode [Enabled]
MPS Version Control For OS [1.4]
Full Screen LOGO Show [Disabled]
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
Item Help
Main Level }
Select Removable Boot
Device Priority
Figure 7. Advanced BIOS Features Menu
Note: Note that all data in white is for information only, data in yellow is changeable,
data in blue is non-changeable, and data in a red box is highlighted for
selection.
NVIDIA Corporation
36 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 47

Configuring the BIOS
1.
Floppy Disks
2. Network 1 : <description of network>
2. Bootable Add
-
in Cards
the priority of the device within
Removable Device Priority
Use this option to select the priority for removable device startup. Press Enter
to see the list of removable devices in your system. Use the #$ arrow keys to go
to the various devices. Then use the + or – keys to move the device priority up
or down in the list. To go back to the previous menu, press Esc.
Hard Disk Boot Priority
Use this option to select the priority for HDD startup. Press Enter to see the
list of bootable devices in your system. Use the #$ arrow keys to go to the
various devices. Then use the + or – keys to move the device priority up or
down in the list. To go back to the previous menu, press Esc.
1. Ch0. : ST3802110A
Network Boot Priority
Use this option to select the priority for network startup. Select Network Boot
Priority and press Enter to view available networks. Use the #$ arrow keys
to go to the various devices. Then use the + or – keys to move the device
priority up or down in the list. To go back to the previous menu, press Esc.
1. Network 0 : <description of network>
CPU Internal Cache
Use this option to enable or disable the CPU internal cache. Use the Page Up
and Page Down keys to scroll through the options or press Enter to display the
options in a sub-menu. Use the #$ arrow keys to position the selector in the
option you choose.
Use the + and – keys to move
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 37
Page 48

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Quick Power On Self Test
Enabling this option allows the system to skip certain test while booting, which
reduces the time needed to boot the system. Use the Page Up and Page Down
keys to toggle between Enable and Disable.
First/Second/Third Boot Device
Use this option to set the priority sequence of the devices booted at power on.
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the options or press
Enter to display the sub-menu. Use the #$ arrow keys to position the selector
in the option you choose.
First Boot Device
Removable ..... [
Hard Disk ..... [ ]
CDROM ..... [ ]
Network ..... [ ]
Disabled ..... [ ]
#$
:Move ENTER:Accept ESC:Abort
]
Boot Other Device
With the option set to Enable, the system boots from some other device if the
first/second/third boot devices fail.
Boot Up NumLock Status
This option allows you to select the power-on state of NumLock. Select On to
activate the keyboard NumLock when the system is started. Select Off to disable
the NumLock key.
NVIDIA Corporation
38 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 49

Configuring the BIOS
Security Option
The Security Options allows you to require a password every time the system
boots or only when you enter setup. Select Setup to require a password to gain
access to the CMOS Setup screen. Select System to require a password to
access the CMOS Setup screen and when the system boots.
APIC Mode
Use this function to enable or disable the Advanced Programmable Interrupt
Controller (APIC). If you disable this option, you also disable the MPS Version
Control for OS option.
MPS Version Control For OS
Use this function to select the Multi-Processor Specification (MPS) version that
BIOS passes to the operating system. Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to
scroll through the options.
Full Screen LOGO Show
This option allows you to enable or disable the display of the full-screen logo
when the system boots. Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to toggle
between Enable and Disable
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 39
Page 50

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
F5: Previous Values F7:Defaults
Advanced Chipset Features
Advanced Chipset Features
Select Advanced Chipset Features from the CMOS Setup Utility menu and
press Enter to display the functions of the Advanced Chipset Functions menu.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
} System Clocks [Press Enter]
} FSB & Memory Config [Press Enter]
} CPU Configuration [Press Enter]
} System Voltages [Press Enter]
NVMEM memory test [Disable]
Load timing/voltage set [Press Enter]
Save timing/voltage set [Press Enter]
System BIOS Cacheable [Disabled]
HPET Function [Enable]
NVIDIA GPY Ex [Enable]
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
Figure 8. Advanced Chipset Features
Item Help
Main Level }
Voltage control
NVIDIA Corporation
40 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 51

Configuring the BIOS
F5: Previous Values F7:Defaults
System Clocks
Select System Clocks from the Advanced Chipset Features menu and press
Enter to display the System Clocks menu. From this menu, you are able to
specify frequency settings, HT multipliers, and Spread Spectrum settings. Note
that in Figure 9, all of the options are listed. On the actual BIOS screen, you will
need to scroll down to see all the options.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Parameters Settings Current Val•e
**Frequency Settings**
CPU Freq, MHz 2933.3 2933.3
FSB Reference Clock, MHz 1066.7 1066.7
CPU Multiplier [11 X] 11X
PCIe x16_1, MHz [Auto] 100
PCIe x16_3, MHz [Auto] 100
PCIe x16_2, MHz [Auto] 100
SPP<->MCP Ref Clock, MHz [Auto] 100
**HT Multiplier**
nForce SPP --> nForce MCP [5 x]
nForce SPP <-- nForce MCP [5 x]
**Spread Spectrum**
CPU Spread Spectrum [UP Spread]
HT Spread Spectrum Disabled
PCIe Spread Spectrum(SPP) [Auto]
PCIe Spread Spectrum(MCP) Disabled
SATA Spread Spectrum Disabled
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
System Clocks
Figure 9. System Clocks Menu
Item Help
Main Level }
CPU frequency
multiplier.
CPU core clock
= FSB Ref Clock/4 *
CPU Multiplier
‚
Note: Note that all data in white is for information only, data in yellow is changeable,
data in blue is non-changeable, and data in a red box is highlighted for
selection.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 41
Page 52

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Frequency Settings
q CPU Freq, MHz
This value is set by the CPU Multiplier (value cannot be changed by the user).
q FSB Reference Clock. MHz
This value is set by the system (value cannot be changed by the user). To
change the SLI-Ready memory, FSB memory, and memory timing, go to the
FSB & Memory screen.
q CPU Multiplier
This value changes the CPU Frequency value depending on the value you
choose. Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the options.
The options are from 6 X through 60 X.
q PCIe x16_1, MHz
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the frequency
options for the PCI Express Bus, Slot 1 (the black slot closest to the CPU).
Note that as you go higher in value, PCIe Spread Spectrum(SPP) is
disabled and cannot be changed from this status.
q PCIe x16_3, MHz
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the frequency
options for the PCI Express Bus, Slot 3 (the blue slot in the middle).
q PCIe x16_2, MHz
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the frequency
options for the PCI Express Bus, Slot 3 (the black slot farthest from the
CPU).
q SPP<
—
>MCP Ref Clock, MHz
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the frequency
options for the reference clock between the SPP chip and the MCP chip.
NVIDIA Corporation
42 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 53

Configuring the BIOS
HT Multiplier
q nForce SPP
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the HT multiplier
options and set the link speed from the SPP chip to the MCP chip. Values are
[1 x] through [5 x].
q nForce MCP <
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the HT multiplier
options and set the link speed from the MCP chip to the SPP chip. Values are
[1 x] through [5 x].
— —
> nForce MCP
— —
nForce SPP
Spread Spectrum
q CPU Spread Spectrum
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the Spread Spectrum
options for the CPU. Option values are [Disabled], [UP Spread], and
[Center Spread].
q HT Spread Spectrum
Disabled
q PCIe Spread Spectrum (SPP)
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the Spread Spectrum
options for the SPP PCIe. Option values are [Disabled], [UP Spread], and
[Center Spread]. This option reverts to Disabled and cannot be changed
when the value for PCIe x16_1 exceeds 100MHz.
q PCIe Spread Spectrum(MCP)
Disabled
q SATA Spread Spectrum
Disabled
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 43
Page 54

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
F5: Previous Values F7:Defaults
stability
FSB & Memory Config
Select FSB & Memory Config from the Advanced Chipset Features menu and
press Enter to display the FSB & Memory Config menu. This menu provides
the means to set SLI-Ready memory, FSB memory, and memory timing.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
FSB & Memory Config
Parameters Settings Current Value
SLI-Ready Memory [Disabled] Disabled
CPU Freq, MHz 2933.3 2933.3
CPU Multiplier 11X 11X
FSB – Memory Clock Mode [Auto]
x FSB (QDR), MHz Auto 1066.7
Actual FSB (QDR), MHz 1066.7
x MEM (DDR), MHz Auto 800.6
Actual MEM (DDR), MHz 800.0
} Memory Timing Setting [Press Enter]
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
Item Help
Main Level }}
“CPUOC MAX” realizes
the complete optimized
memory settings when
SLI-Ready memory is
installed
Optimized memory
settings by allowing
X% CPU overclocking
CPU overclocking may
require manual
overvolting of the CPU
to improve system
Figure 10. FSB & Memory Config Menu
q SLI-Ready Memory
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the SLI-Ready
Memory options. The options are:
Ø Disabled
Ø CPUOC 0%
Ø CPUOC 1%
Ø CPUOC 2%
Ø CPUOC 3%
NVIDIA Corporation
44 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 55

Configuring the BIOS
Ø CPUOC 4%
Ø CPUOC 5%
Ø CPUOC MAX
When you select one of the CPUOC x% options, the FSB - Memory
Clock Mode is set to Unlinked and cannot be changed until SLIReady Memory is set to Disable.
q FSB and Memory Clock Mode
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the FSB and
Memory Clock Mode options. The options are:
Ø Auto
This is the optimal setting since it sets the FSB and memory speeds
automatically.
Ø Linked
When Link is selected, FSB (QDR), MHz is changed to editable and
the FSB speed can be entered manually. As the FSB speed is changed,
CPU Freq, MHz changes proportionally.
CPU Freq, MHz 2933.3 2933.3
CPU Multiplier 11X 11X
FSB – Memory Clock Mode [Linked]
FSB (QDR), MHz [1067] 1066.7
Actual FSB (QDR), MHz 1066.7
x MEM (DDR), MHz Auto 800.6
Actual MEM (DDR), MHz 800.0
Ø Unlinked
When Unlink is selected, FSB (QDR), MHz and MEM (DDR), MHz
are changed to editable and the FSB and memory speeds can be entered
manually. As the FSB speed is changed, CPU Freq, MHz changes
proportionally.
FSB – Memory Clock Mode [Linked]
FSB (QDR), MHz [1067] 1066.7
Actual FSB (QDR), MHz 1066.7
MEM (DDR), MHz [1067] 800.6
Actual MEM (DDR), MHz 800.0
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 45
Page 56

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
F5: Previous Values F7:Defaults
q FSB (QDR), MHz
Use the + or – keys to scroll through new values for the CPU FSB frequency
or type in a new value. Note that the Actual FSB (QDR) reflects the actual
frequency that takes effect on a reboot.
q MEM (DDR), MHz
Use the + or – keys to scroll through new values for the memory frequency
or type in a new value. Note that the Actual MEM (DDR) reflects the actual
frequency that takes effect when the system reboots.
q Memory Timing Setting
Press Enter to display the Memory Timing Setting menu. Use this menu to
set optimal timings or to manually enter timings.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Memory Timing Setting
Parameters Settings Current Value
Memory Timing Setting [Optimal]
x tCL (CAS Latency) Auto(5) 5
x tRDC Auto(7) 5
x tRP Auto(7) 5
x tRAS Auto(23) 18
x Command Per Clock (CDM) Auto(2T) 1T
** Advanced Memory Settings **
x tRRD Auto(4) 3
x tRC Auto(28) 22
x tWR Auto(7) 5
x tWTR Auto(10) 9
x tREF Auto 6.1uS
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help[
Item Help
Main Level }}
Select [Expert] to
enter timings manually
Ø Optimal
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to select Optimal. Optimal
prohibits you from manually setting any timing. All timing is set for
optimal performance.
NVIDIA Corporation
46 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 57

Configuring the BIOS
tREF [Auto]
6.1uS
Ø Expert
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to select Expert. When Expert is
selected, all timing categories are enabled for manual input. Note that you
should set the value to Optimal to use the manufacturers’ recommended
values.
Parameters Settings Current Value
Memory Timing Setting [Expert]
tCL (CAS Latency) [Auto(5)] 5
tRDC [Auto(7)] 5
tRP [Auto(7)] 5
tRAS [Auto(23)] 18
Command Per Clock (CDM) [Auto(2T)] 1T
** Advanced Memory Settings **
tRRD [Auto(4)] 3
tRC [Auto(28)] 22
tWR [Auto(7)] 5
tWTR [Auto(10)] 9
w tCL: CAS# latency (options are 1 through 6).
w tRDC: RAS#-to-CAS# Delay for Read/Write commands to the
same bank (options are 1 through 7).
w tRP: Row Precharge time. This is the Precharge-to-Active or Auto-
to-Refresh of the same bank (options are 1 through 7).
w tRAS: This is the minimum RAS# active time (options are 1 through
31).
w Command Per Clock: This is the command timing setting on a per
clock unit basis (options are 1T and 2T).
w tRRD: RAS#-to-RAS# delay of different banks (options are 1
through 15).
w tRC: RAS#-to-RAS# or auto refresh time of the same bank (options
are 1 through 31).
w tWR: The Write recovery time (options are 2 through 7).
w tWTR: This is the minimum write-to-read delay with the same chip
selected (options are 1 through 10).
w tREF: This is the DRAM refresh rate (options are Auto, 7.8uS, and
3.9uS).
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 47
Page 58

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
F5: Previous Values F7:Defaults
CPU Configuration
Select CPU Configuration from the Advanced Chipset Features menu and
press Enter to display the CPU Configuration menu.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
CPU Configuration
Limit CPUID MaxVal [Disabled]
x Intel SpeedStep Disabled
CPU Thermal Control [Disabled]
C1E Enhanced Halt State [Enabled]
Execute Disable Bit [Enabled]
Virtualization Technology [Enabled]
CPU Core 0 Enabled
CPU Core 1 [Enabled]
x CPU Core 2 Disabled
x CPU Core 3 Disabled
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
Item Help
Main Level }}
Set linit CPUID MaxVal
to 3, should be
“Disabled” for WinXP
Figure 11. CPU Configuration Menu
q Limit CPUID MaxVal
Use this function to enable the set limit of the CPUID MaxVal to 3. Set to
Disable for Win XP.
q CPU Thermal Control
Use this function to enable or disable TM1 and TM2 support. Options are:
Ø Disable
Disable support for TM1 and TM2.
Ø TM1 Only
The CPU is thermally throttled by cutting active processor clock cycles.
NVIDIA Corporation
48 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 59

Configuring the BIOS
Ø TM2 Only
Thermal throttling is achieved by reducing the CPU multiplier and CPU
core voltage.
Ø TM1 & TM2
Enables support for both TM1 and TM2.
q C1E Enhanced Halt State
Enabled, this function reduces the CPU power consumption when the CPU
is idle. Idle occurs when the operating system issues a halt instruction.
q Execute Disable Bit
When this function is disabled, it forces the XD feature flag to always return
to zero (0).
q Virtualization Technology
When this function is enabled, it allows a VMM to utilize the additional
hardware capabilities provided by Intel Virtualization Technology.
q CPU Core 1
This function allows you to enable or disable CPU Core.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 49
Page 60

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
F5: Previous Values F7:Defaults
System Voltages
Select System Voltages from the Advanced Chipset Features menu and press
Enter to display the System Voltages menu.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
System Voltages
Parameters Settings Current Value
CPU Core [Auto] 1.28
CPU FSB [Auto] 1.2V
Memory [Auto] 1.85V
nForce SPP [Auto] 1.30V
nForce MCP [Auto] 1.50V
HT nForce SPP <-> MCP [Auto] 1.20V
nForce MCP Auxiliary [Auto] 1.50V
GTLVREF Lane 0 [Auto] +00mv
GTLVREF Lane 1 [Auto] +00mv
GTLVREF Lane 2 [Auto] +00mv
GTLVREF Lane 3 [Auto] +00mv
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
Item Help
Main Level }}
Voltage level for CPU
Core (CPU VID)
Figure 12. System Voltages Menu
q CPU Core
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the voltages or select
[Auto] to automatically set the voltage level for the CPU Core.
q CPU FSB
Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through the voltages or select
[Auto] to automatically set the voltage level for the CPU FSB.
q Memory
This function defines the voltage level for the DRAM. Use the Page Up and
Page Down keys to select a voltage or select [Auto] to automatically set the
voltage.
NVIDIA Corporation
50 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 61

Configuring the BIOS
q nForce SPP
This function defines the core voltage level for the NVIDIA nForce SPP
chip. Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to select a voltage (1.20V, 1.30V,
1.40V, 1.50V) or select [Auto]to automatically set the voltage.
q nForce MCP
This function defines the core voltage level for the NVIDIA nForce MCP
chip. Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to select a voltage or select
[Auto]to automatically set the voltage.
q HT nForce SPP <-> MCP
This function defines the voltage level for the NVIDIA HT nForce SPP <->
MCP Link. Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to select a voltage or select
[Auto]to automatically set the voltage.
q nForce MCP Auxiliary
This function defines the core voltage level for the NVIDIA nForce MCP
Auxiliary voltage. Use the Page Up and Page Down keys to select a voltage or
select [Auto]to automatically set the voltage.
q GTLVREF Lane 0
This function defines the voltage level for GTLVREF Lane 0. Use the Page
Up and Page Down keys to select a voltage or select [Auto]to automatically
set the voltage.
q GTLVREF Lane 1
This function defines the voltage level for GTLVREF Lane 1. Use the Page
Up and Page Down keys to select a voltage or select [Auto]to automatically
set the voltage.
q GTLVREF Lane 2
This function defines the voltage level for GTLVREF Lane 2. Use the Page
Up and Page Down keys to select a voltage or select [Auto]to automatically
set the voltage.
q GTLVREF Lane 3
This function defines the voltage level for GTLVREF Lane 3. Use the Page
Up and Page Down keys to select a voltage or select [Auto]to automatically
set the voltage.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 51
Page 62

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
NVMEM Memory Test
This function defines whether you run the NVIDIA memory testing module
during POST. The options are Fast, Medium, Slow, and Disable.
Load Timing/Voltage Set
This function loads the system voltages and timing settings that were defined in
the System Voltages menu. You can set up to four profile settings using the
Save timing/voltage set function.
There are four profile options that can be loaded. The default setting is Auto
for all settings. Press Enter to see the options.
Load timing/voltage set
Press Enter to Exit ..... [
Select Profile 1 ..... [ ]
Select Profile 2 ..... [ ]
Select Profile 3 ..... [ ]
#$
:Move ENTER:Accept ESC:Abort
]
NVIDIA Corporation
52 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 63

Configuring the BIOS
Save Timing/Voltage Set
This function saves the system voltages and timing settings that were defined in
the System Voltages menu. There are four profile options that can be loaded.
The default setting is Auto for all settings. Press Enter to see the options.
Save timing/voltage set
Press Enter to Exit ..... [
Select Profile 1 ..... [ ]
Select Profile 2 ..... [ ]
Select Profile 3 ..... [ ]
#$
:Move ENTER:Accept ESC:Abort
]
System BIOS Cacheable
This function allows you to enable or disable caching the system BIOS.
HPET Function
This function allows you to enable or disable the High Precision Even Timer
(HPET). When Enabled, HPET is used as the timing hardware for multimedia
and other time-sensitive application. When HPET is Disabled, the APIC
timer is used.
NVIDIA GPU Ex
To enable or disable this function you need to have the NVIDIA®
ForceWare® graphics driver with NVIDIA EX support. When enabled, the
system uses the optimized NVIDIA EX graphics driver.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 53
Page 64

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Integrated Peripherals
Integrated Peripherals
Menu
Select Integrated Peripherals from the CMOS Setup Utility menu and
press Enter to display the Integrated Peripherals menu.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
} IDE Function Setup [Press Enter]
} RAID Config [Press Enter]
} USB Config [Press Enter]
} MAC Config [Press Enter]
IEEE1394 controller [Auto]
HD Audio [Auto]
IDE HDD Block Mode [Enabled]
Onboard FDC Controller [Enabled]
Onboard Serial Port 1 [3FB/IRQ4]
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
Figure 13. Integrated Peripherals Menu
Item Help
Main Level }
NVIDIA Corporation
54 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 65

Configuring the BIOS
IDE Function Setup
Press Enter to display the IDE Function Setup menu.
OnChip IDE Channel0 [Enabled]
Primary Master PIO [Auto]
Primary Slave PIO [Auto]
Primary Master UDMA [Auto]
Primary Slave UDMA [Auto]
IDE DMA transfer access [Enabled]
Serial-ATA Controller [All Enabled]
IDE Prefetch Mode [Enabled]
q OnChip IDE Channel0
Use this function to enable
or disable the onchip IDE
Channel0. When disabled,
the Primary Master/Slave
functions are changed to
Auto and cannot be
changed.
q Primary Master/Slave PIO
When OnChip IDE Channel0 is set to [Enabled], you can select a
mode for the primary Master and Slave PIO. Select from Auto, or Mode 1
through Mode 4.
q Primary Master/Slave UDMA
When OnChip IDE Channel0 is set to [Enabled], you can disable the
primary Master and Slave UDMA or set it to [Auto].
q IDE DMA transfer access
Use this function to enable or disable IDE DMA transfer access.
q Serial-ATA Controller
This function allows you to enable specific SATA controllers, enable all
controllers, or disable all controllers. The options available are [SATA-0],
[SATA-0+1], [Enable All], and [Disabled].
q IDE Prefetch Mode
Use this function to enable or disable the IDE Prefetch mode.
OnChip IDE Channel0 [Disabled]
x Primary Master PIO Auto
x Primary Slave PIO Auto
x Primary Master UDMA Auto
x Primary Slave UDMA Auto
IDE DMA transfer access [Enabled]
Serial-ATA Controller [All Enabled]
IDE Prefetch Mode [Enabled]
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 55
Page 66

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
RAID Config
Press Enter to display the RAID Config menu.
RAID Enable [Enabled]
SATA 0 Primary RAID [Disabled]
SATA 0 Secondary RAID [Disabled]
SATA 1 Primary RAID [Disabled]
SATA 1 Secondary RAID [Disabled]
SATA 2 Primary RAID [Disabled]
SATA 2 Secondary RAID [Disabled]
q RAID Enable
Use this function to enable or
disable RAID. When RAID is set
to [Disabled], all SATA
functions are changed to
Disabled and cannot be changed.
q SATA x Primary/Secondary
When RAID Enable is set to [Enabled], you can enable or disable the
various SATA functions.
RAID Enable [Disabled]
x SATA 0 Primary RAID Disabled
x SATA 0 Secondary RAID Disabled
x SATA 1 Primary RAID Disabled
x SATA 1 Secondary RAID Disabled
x SATA 2 Primary RAID Disabled
x SATA 2 Secondary RAID Disabled
USB Config
Press Enter to display the USB Config menu.
OnChip USB [Enabled]
USB Keyboard Support [Disabled]
USB Mouse Support [Disabled]
q OnChip USB
Use this function to enable specific versions of the USB or disable the onchip
USB. When the onchip USB is set to [Disabled], the keyboard and mouse
support functions are set to Enabled and cannot be changed. Versions that
can be selected are
[V1.1+V2.0] or [V1.1].
q USB Keyboard/Mouse
Support
Use these function to enable or disable the onchip WSB support of the
keyboard and/or mouse.
NVIDIA Corporation
56 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
OnChip USB [Disabled]
x USB Keyboard Support Enabled
x USB Mouse Support Enabled
Page 67

Configuring the BIOS
MAC1 LAN
[Disabled
]
MAC Config
Press Enter to display the MAC Config menu.
MAC0 LAN [Enabled]
q MACx LAN
Use these functions to set the MAC0 and/or MAC1 LANs to Auto or
disable their functions.
IEEE1394 controller
This function on the Integrated Peripherals menu allows you to enable or
disable the IEEE1394 (Firewire) interface.
HD Audio
This function on the Integrated Peripherals menu allows you to enable or
disable the hard disk audio function.
IDE HDD Block Mode
Using this function on the Integrated Peripherals menu allows your IDE hard
drive needs to support block mode. Select [Enabled] to automatically detect
the optimal number of block read/writes per sector the drive can support.
Select [Disabled] if your drive does not support block mode.
Onboard FDC Controller
This function on the Integrated Peripherals menu allows you to enable or
disable the onboard FDC controller function.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 57
Page 68

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Power Management Setup
Onboard Serial Port 1
This function on the Integrated Peripherals menu allows you to select the
onboard serial port 1 function. Options are [3F8/IRQ4], [2E8/IRQ3],
[3E8/IRQ4], [Auto], and [Disabled].
Power Management Setup
Menu
Select Power Management Setup from the CMOS Setup Utility menu and
press Enter to display the Power Management Setup menu.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
ACPI function [Enabled]
APCI Suspend Type [S1&S3]
Soft-Off by PBTN [Instant-Off]
WOL(PME#) From Soft-Off [Disabled]
Power-on by Alarm [Disabled]
x Day of Month Alarm 0
x Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm 0 : 0 : 0
POWER ON Function [BUTTON ONLY]
x KB Power ON Password Enter
x Hot Key Power On Ctrl-F1
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
Main Level }
Figure 14. Power Management Setup Menu
Item Help
NVIDIA Corporation
58 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 69

Configuring the BIOS
ACPI Function
This function on the Power Management Setup menu allows you to enable or
disable the ACPI function.
ACPI Suspend Type
This function on the Power Management Setup menu allows you to select an
ACPI Suspend Type. Types to select from are [S1&S3], [S1(POS)], and
[S3(STR)].
Soft-Off by PBNT
This function on the Power Management Setup menu allows you to set SoftOff by PBNT to [Instant-Off] or [Delay 4 Sec].
WOL(PME#) From Soft-Off
This function on the Power Management Setup menu allows you to enable or
disable WOL(PMW#) from soft-off.
Power On by Alarm
This function on the Power Management Setup menu allows you to enable or
disable the Power-on by alarm function. Set to [Disable] to prevent poweron by alarm. When set to [Enable], you can manually put in the day of the
month and the time of the alarm.
Power-on by Alarm [Disabled]
Day of Month Alarm [ 0]
Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm [0 : 0 : 0]
To enter a day or time, use the Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through
numbers or enter the number using the keyboard number or the + and – keys.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 59
Page 70

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
x
Hot Key Power On
Ctrl
-F1
POWER ON Function
This function on the Power Management Setup menu allows you to define the
power-on function. Options for this function are:
q BUTTON ONLY
q Keyboard 98
q Password
When [Password] is selected, the KB Power ON Password function is
enabled so that you must enter a password.
POWER ON Function [Password]
KB Power ON Password [Enter]
q Hot Key Power On
When [Hot Key] is selected, the Hot key Power On function is
enabled so that you must select a keyboard key as the hot key. To select a hot
key use Ctrl+F1 though Ctrl+F12
POWER ON Function [Hot key]
x KB Power ON Password Enter
Hot Key Power On [Ctrl-F1]
q Mouse Left
q Mouse Right
q Any Key
NVIDIA Corporation
60 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 71

Configuring the BIOS
PnP/PCI Configuration
PnP/PCI Configuration
Menu
Select PnP/PCI Configuration from the CMOS Setup Utility menu and press
Enter to display the PnP/PCI Configuration menu.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Init Display First [PCI Slot]
Reset Configuration Data [Disabled]
Resources Controlled By [Auto(ESCD)]
x IRQ Resources Press Enter
** PCI Express relative items **
Maximum Payload Size [4096]
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
Figure 15. PnP/PCI Configuration Menu
Item Help
Main Level }
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 61
Page 72

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
IRQ Resources
[Press Enter]
Init Display First
This function on the PnP/PCI Configuration menu allows you to define if the
initial display is in the PCI slot or in the PCI Express slot. Options are
[PCI Slot] and [PCIEx].
Reset Configuration Data
This function on the PnP/PCI Configuration menu allows you to enable or
disable the resetting of Extended System Configuration Data (ESCD) when you
exit Setup. Set this to [Enabled] if you have installed a new add-on and the
system reconfiguration has caused a serious conflict that prevents the OS from
booting. The default setting is [Disabled].
Resources Controlled By
This function on the PnP/PCI Configuration menu allows you to define if the
BIOS can automatically configure all the boot and plug-and-play compatible
devices or if you can manually select IRQ, DMA, and memory base address
fields. Select [Auto(ESCD)] if you want the BIOS to automatically populate
these fields. If you select [Manual] so you can assign the resources, IRQ
Resources is enabled for input.
NVIDIA Corporation
62 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Resources Controlled By [Auto(ESCD)]
x IRQ Resources Press Enter
Resources Controlled By [Manual)]
Page 73

Configuring the BIOS
IRQ Resources
To enable this field for input, set Resources Controlled By to
[Manual]. With this field enabled, press Enter to see options.
IRQ-5 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-9 assigned to [Reserved]
IRQ-10 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-11 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-14 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-15 assigned to [PCI Device]
Use Legacy ISA for devices compliant with the original PC AT Bus
specification. Use PCI/ISA PnP for devices compliant with the plug-and-play
standard, whether designed for PCI or ISA Bus architecture.
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
This function on the PnP/PCI Configuration menu allows you to enable or
disable the Palette Snoop function.
Maximum Payload Size
This function on the PnP/PCI Configuration menu allows you to set the
maximum TLP payload size (in bytes) for the PCI Express devices. Use the
Page Up and Page Down keys to scroll through sizes or enter the number using
the keyboard numbers or use the + and – keys to go up and down the list of
sizes.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 63
Page 74

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
System Monitor
System Monitor Menu
Select System Monitor from the CMOS Setup Utility menu and press Enter to
display the System Monitor menu.
Phoenix – AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
} Dynamic Fan Control [Press Enter]
CPU 47ºC/ 117ºF
CPU Core 1.28V
CPU FSB 1.19V
Memory 1.81V
+3.3V 3.16V
+3.3V Dual 3/16V
+12V 11.92V
+5V 4.99V
+Vbat 3.00V
CPU Fan Speed 4272 RPM
Aux Fan Speed 4891 RPM
nForce Fan Speed 0 RPM
Chassis Fan Speed 0 RPM
Chassis Fan2 Speed 0 RPM
#$"!
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
Item Help
Main Level }
Figure 16. System Monitor Menu
All of the values shown in Blue are dynamic and change as the speed and
voltages of the various components change with system usage.
NVIDIA Corporation
64 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 75

Configuring the BIOS
Dynamic Fan Control
Press Enter to display the Dynamic Fan Control menu.
CPU Fan Speed Control [SmartFan]
If temp > 70ºC, Set Fan Speed 100%
If temp < 30ºC, Set Fan Speed 0%
x Manual Fan Speed, % 100
AUX Fan Speed Control, % [100]
nForce Fan Speed Control, % [100]
Chassis Fan Speed Control, % [100]
Use this menu to control the speed of the various fans on the motherboard. Set
CPU fan speed to [SmartFan] when you want the speed of the fans
automatically controlled based on temperature. To set the fan speed to a
constant rate, select [Manual] and then enter the speed from 0% to 100%.
Set the desired speed for the Aux, nForce, and Chassis fans from 0% to 100%.
The system defaults to 100%.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 65
Page 76

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
This page is blank.
NVIDIA Corporation
66 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 77

Installing Drivers and
Software
Note: It is important to remember that before installing the driver CD that is shipped
in the kit, you need to load your operating system. The motherboard supports
Windows XP 32bit and 64bit and is Vista-capable.
The kit comes with a CD that contains utility drivers and additional NVIDIA
software.
The CD that has been shipped with your NVIDIA motherboard contains the
following software and drivers:
q NVIDIA nForce drivers
q RealTek Audio drivers
q Microsoft DirectX 9.0C
q NVIDIA Control Panel
q Adobe Acrobat Reader
q NVIDIA MediaShield RAID Manager
q NVIDIA Networking (FirstPacket)
q Norton Internet Security
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597x-001_v01 67
Page 78

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Windows XP Drivers Install
Note: When installing the graphics drivers, the resolution defaults to the lowest
setting (typically 800 x 600), making your display very large. Adjust
accordingly.
3. Insert the NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI installation CD for the graphics
drivers included in the kit.
Note: If you have multiple graphics cards installed, you will be asked multiple times
for all events once the drivers are installed.
4. Run setup.exe.
Depending on your system setup, the install disk may automatically run the
install setp.exe. If it does not run, go to My Computer and click on the CD
to open.
Partner
Update this section with your setup.exe process.
NVIDIA Corporation
68 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 79

Using the
NVIDIA Software
Built upon the foundation of NVIDIA’s core motherboard and GPU
technologies, NVIDIA System Monitor and Performance Server software
utilities bring consolidated reporting and control to the desktop in seamless
fashion. Traditionally, users have been forced to endure a sequence of trial and
error attempts within the BIOS in order to customize the operation and
performance of the system to their needs. As settings are attempted, the user
must start and restart Windows several times. Fortunately, NVIDIA’s new
System Monitor and Performance Group utilities bring the same rich
functionality found in the BIOS to the user’s desktop. From a single convenient
interface, the user can adjust settings to minimize noise, optimize performance,
and maximize system stability. In addition, a wealth of system information is
readily available in a lush 3D presentation which is customizable to suit the user.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597x-001_v01 69
Page 80

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
NVIDIA Performance Group
of NVIDIA Control Panel
You can start the NVIDIA Performance Group several ways:
q Double-click the NVIDIA Performance Group icon on the desktop
q Right-click on the desktop and select NVIDIA Control Panel
q From the Windows Control Panel, double-click the NVIDIA Control Panel
NVIDIA Performance Server menus are located under the Performance group
in the left column.
Note All changes made within NVIDIA Performance Group are dynamically applied,
and will only remain active for the current Windows session. You can save
these settings as a profile by using the Profile menu item.
CAUTION: Increasing the voltage or the clock speed of a component may void its
warranty due to exceeding recommended specifications. NVIDIA and the board
manufacturer are not responsible for damage that may occur when component
tolerances are exceeded.
Historically, NVIDIA’s Control Panel has contained a wealth of settings and
adjustments for NVIDIA GPU’s. In similar fashion, the new NVIDIA
Performance Group applies the same depth of control to the rest of the
components within a system. Without ever leaving Windows or entering the
BIOS, users can optimize and adjust nearly every system component.
NVIDIA Corporation
70 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 81

Using NVIDIA Software
Device Settings
Device Settings has two tabs, Current Hardware Settings and Hardware
Profiles. Under the Current Hardware Settings tab there are settings for the
CPU, Motherboard, Memory, and GPU.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 71
Page 82

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Current Hardware Settings
CPU
This option deals with CPU parameters and information. Here, the user has the
ability to dynamically change FSB speeds, CPU Voltages, and CPU fan speeds.
At all times, real-time values for CPU frequency and appropriate CPU multiplier
are reported.
CAUTION: Increasing the voltage or the clock speed of a component may void its
warranty due to exceeding recommended specifications. NVIDIA and the board
manufacturer are not responsible for damage that may occur when component
tolerances are exceeded.
NVIDIA Corporation
72 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 83

Using NVIDIA Software
Motherboard
The Motherboard option showcases a wide variety of motherboard and system-wide
options and settings. The controls located in the Adjust Motherboard Timings screen
allow the bus speeds to be adjusted manually to increase performance for gaming, or
lower performance to conserve power and create a quieter user environment. The
number to the right of the slider is the new bus speed that will be applied. Adjustments
can be made by using the mouse to drag the slider. All changes will take effect
immediately after selecting Apply; however, these setting will only remain active for the
current Windows session. This will allow a user to safely return to Windows in the event
of a crash, without any possibility of boot issues since the changes are not made directly
to the BIOS settings.
Note: All changes on Adjust Motherboard Settings are dynamically made when you
apply them, and only remain active for the current Windows session. You can
save these settings as a profile for use later by using the Profile menu item. If
a setting does not allow a change, it probably requires a reboot and should
be changed in the BIOS or from the Dynamic BIOS Access page (if
available).
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 73
Page 84

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Memory
Memory is one of the most critical components in terms of determining overall
system stability and overclocking success, a wealth of information and options
for memory modules is available. Both timings and voltage are dynamically
adjustable, with real-time values for memory frequency, FSB frequency, and
more being viewable to help dictate which settings are most appropriate.
q Row Address Strobe
Adjusts the minimum RAS active time. This is the amount of time between a
row being activated by Precharge and deactivated. A row cannot be
deactivated until tRAS has completed. The lower this value, the faster the
performance. However, if it is set too low it can cause data corruption by
deactivating the row to soon. Adjustable from 1 to 63.
NVIDIA Corporation
74 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 85

Using NVIDIA Software
q Write Recovery Time
Memory timing that determines the delay between a write command and a
Precharge command is set to the same bank of memory. Adjustable from 1 to
15.
q W to R Termination Turnaround
The Write-to-Read time is the number of clock cycles between the last write
data pair and the subsequent READ command to the same physical block.
Adjustable from 1 to 15.
q RAS to CAS access
The RAS-to-CAS access (tRCD) is the amount of time in cycles for issuing an
active command and the read/write commands. Adjustable from 1 to 15.
q RAS to RAS Delay
The RAS-to-RAS delay (tRRD) is the is the amount of cycles it takes to
activate the next bank of memory (this is the opposite of tRAS). The lower
the timing the better the system performance. However, this scenario can
cause instability. Adjustable from 1 to 15.
q Refresh Rate
This value is filled in by the system and can not be changed by the user.
q Memory bank switch
The row Precharge time (tRP) is the minimum time between active
commands and the read/writes of the next bank on the memory module.
Adjustable from 1 to 15.
q R to W Turnaround
The Read-to-Write turnaround (tRWT) is a the amount of cycles for the
command to be executed when a Write command is received. Adjustable
from 1 to 15.
q R to R Timing
the Read-to-Read time (tRDRD) is the number of clock cycles between the
last read and the subsequent READ command to the same physical bank.
Adjustable from 1 to 15.
q Row Cycle Time
The Row Cycle Time is the minimum time in cycles it take a row to complete
a full cycle. This can be determined by tRC=tRAS+tRP. If this value is set
too short, it can cause corruption of data. If this value is set too high, it causes
a loss in performance but an increase in stability. Adjustable from 1 to 63
cycles
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 75
Page 86

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
q W to R Command Delay
The Write-to-Read (tWRD) command delay is the amount of cycles required
between a valid write command and the next read command. A lower cycle
time results in better performance but is can instability. Adjustable from 0 to
6 cycles.
q W to W Timing
The Write-to-Write (tWRWR) timing is the number of clock cycles between
the last write and the subsequent Write command to the same physical bank.
Adjustable from 2 to 15 cycles.
q CAS Latency
The CAS Latency (tCL) is the time (in number of clock cycles) that elapses
after the memory controller sends a request to read a memory location and
before the data is sent to the module's output pins. The value shown cannot
be changed.
q Clock Drive Strength
This value is filled in by the system and can not be changed by the user.
q Command Per Clock
The Command Per Clock (tCPC) sets the Command Rate for the memory
controller. The value shown cannot be changed
q Async Latency
This value is filled in by the system and can not be changed by the user.
NVIDIA Corporation
76 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 87

Using NVIDIA Software
GPU
The graphics processing unit (GPU) located on your video card(s) can be
adjusted using Device Setting interface. You can override the shipped clock
frequencies of your GPU and GPU memory, and you can set the GPU fan
speed. Increasing the clock speeds will increase your GPU performance but may
necessitate improved cooling to maintain the same level of reliability.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 77
Page 88

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Dynamic BIOS Access
The Dynamic BIOS Access page allows you to change your system BIOS settings.
The changes do not go into effect until after you reboot your system. Since these
changes are made to actual BIOS settings in the CMOS, the settings remain active until
you change them again or restore the CMOS to the default settings.
Click the Available BIOS Pages list arrow and select the BIOS page that you want to
edit. The BIOS page chosen determines which items on the page are available for
changing. To edit an item, select the corresponding list arrow and then select one of the
values from the list. When finished making your changes, click the OK or Apply.
Note This feature is available only with BIOS support from the motherboard
manufacturer. Available screen and features will vary between different makes
and models of motherboards.
NVIDIA Corporation
78 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 89

Using NVIDIA Software
View System Information
The View System Information menu is a high-level view where all the critical values
of the system are consolidated and presented within a single view. At a glance, the user
can clearly see the current status of their components and receives a clear depiction of
overall system performance.
Within the View System
Information section, the
user can also double-click
values for both memory
modules and processors to
receive even more-detailed
information regarding those
components.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 79
Page 90

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Profile Policies
Easily one of the most powerful aspects of NVIDIA Performance Server is the
ability to create custom profiles and rules. Essentially, NVIDIA Performance
Server allows the user to offer a custom set of settings and alerts which can be
tailored from a global setting all the way to something as granular as a particular
game. In short, you can effortlessly customize your system to run as silent as
possible when performing less-demanding tasks such as browsing the web.
When loading a game however, system settings adjust to extract the highest
possible performance from every system component and ensure you have the
ultimate gaming experience with your current hardware.
NVIDIA Corporation
80 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 91

Using NVIDIA Software
Manage Your System BIOS
Thanks to the power and flexibility of NVIDIA’s Performance Server software,
users can even backup or update their system BIOS from within Windows. In
addition to displaying a complete collection of information regarding the
current BIOS version being used, the user also has the option of saving a
backup version of the BIOS being used. This is especially useful when updating
the current BIOS because you have a known good BIOS to revert to should the
other version have issues with system stability or performance.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 81
Page 92

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
NVIDIA System Monitor
You can open the NVIDIA System Monitor several ways:
q Double-click the NVIDIA System Monitor icon on the desktop
q Click Start, then click All ProgramsÚNVIDIA CorporationÚNVIDIA
System Monitor.
The NVIDIA System Monitor is a unique 3D presentation of core component
values. For every supported device, a wide range of information ranging from
temperature, frequency, and voltage are reported. Given the fact that the
NVIDIA System Monitor is based around an OpenGL foundation, there is
nearly zero performance overhead associated with running the utility.
Users can effortlessly navigate through NVIDIA System Monitor by selecting a
particular component in order to view that hardware’s appropriate information.
The selected component comes to the foreground and all supported
information is presented. Should the user prefer an overhead view of the
components in the system, they can utilize the mouse-wheel to control the angle
of the display.
NVIDIA Corporation
82 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 93

Using NVIDIA Software
In this example, we can see that the motherboard is selected. As a result, a wide
array of related settings and status information is displayed in real-time. In
addition to fan speeds and temperatures, we also find critical voltage values for
core components. By moving the slider on the bottom of the screen, the user
also can control the translucency of the screen allowing them to view the
desktop if desired.
Specific information fields
that the user wants to
always have on display can
be selected by doubleclicking the appropriate
information box. The box
will be moved to the top
of the screen where it will
remain regardless of which
component is selected
from that point on.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 83
Page 94

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
By pressing Ctrl+Alt+C or by clicking the arrow icon in the top-right of the
screen, the user can switch modes and bring all selected component fields to the
desktop. From here, the component fields can be oriented and moved anywhere
on the desktop. Furthermore, component fields can be removed from this view
by clicking the small button in the top right of the icon’s box.
By clicking on the Global Settings image in the bottom left of the screen, the user can
customize the way nV Monitor looks and behaves. The first series of options the user
is presented with deals with the application’s appearance. The user can control
everything from temperature units to overall translucency of the application, and can
manipulate a number of other settings to tailor the program to one’s liking.
NVIDIA Corporation
84 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 95

Using NVIDIA Software
The second series of options the user can alter deals with Event Logging. Here, one can
easily select which system components to track and can specify the name of the
resulting output file. All fields within the application will be logged and written to this
file to aid in troubleshooting issues and tracking overall system behavior.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 85
Page 96

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
The final series of options the user can change handles the specific hotkeys used to
control various application actions. In this screen, the user simply enters their desired
hotkey configuration and they are able to control every aspect of functionality for nV
Monitor according to their own personal preferences.
NVIDIA Corporation
86 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 97

Appendix A.
POST Codes for Tritium Platform
This section provides the Award POST Codes (Table 6) and the NVMM POST
Codes (Table 7) for Tritium platforms during system boot up.
Table 6. Award POST Code
Award POST Codes
Co
Name Description
de
01 Reserved
02 Jumps to E000
segment
03 Early SuperIO Init Early Initialized the super IO
04 Reserved
05 Blank video Reset Video controller
06 Reserved
07 Init KBC Keyboard controller init
08 KB test Test the Keyboard
09 Reserved
0A Mouse Init Initialized the mouse
0B Reserved
0C Reserved
0D Reserved
0E CheckSum Check Check the integrity of the ROM,BIOS and message
0F Reserved
10 Autodetect
EEPROM
Execution of POST routines in E000
Check Flash type and copy flash write/erase routines
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597x-001_v01 87
Page 98

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Award POST Codes
Co
Name Description
de
11 Reserved
12 Test CMOS Test and Reset CMOS
13 Reserved
14 Load Chipset Load Chipset Defaults
15 Reserved
16 Init Clock Initialize onboard clock generator
17 Reserved
18 Init CPU CPU ID and initialize L1/L2 cache
19 Reserved
1A Reserved
1B Setup Interrupt
Vector Table
1C CMOS Battery
Check
1D Early PM Early PM initialization
1E Reserved
1F Re-initial KB Load keyboard matrix
20 Reserved
21 HPM init Init Heuristic Power Management (HPM)
22 Reserved
23 Program chipset Early Programming of chipset registers
24 Init PNP Init PNP
25 Shadow VBIOS Shadow system/video BIOS
26 Clock Gen Init onboard clock generator and sensor
27 Setup BDA Setup BIOS DATA AREA (BDA)
28 Reserved
29 CPU Speed detect Chipset programming and CPU Speed detect
2A Reserved
Initialize first 120 interrupt vectors with
SPURIOUS_INT_HDLR and initialize INT 00h-1Fh
according to INT_TBL
Test CMOS and check Battery Fail
NVIDIA Corporation
88 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
Page 99

Post Codes
Award POST Codes
Co
Name Description
de
2B Init video Initialize Video
2C Reserved
2D Video memory
test
2E Reserved
2F Reserved
30 Reserved
31 Reserved
32 Reserved
33 Early keyboard
reset
34 Reserved
35 Test DMA
Controller 0
36 Reserved
37 Test DMA
Controller 1
38 Reserved
39 Test DMA Page
Registers
3A Reserved
3B Reserved
3C Test Timer Test 8254 Timer 0 Counter 2.
3D Reserved
3E Test 8259-1 Mask Verify 8259 Channel 1 masked interrupts by
3F Reserved
40 Test 8259-2 Mask Verify 8259 Channel 2 masked interrupts by
41 Reserved
Test Video Memory and display Logos
Early Keyboard Reset
Test DMA channel 0
Test DMA channel 1
Test DMA Page Registers
alternately turning off and on the interrupt lines.
alternately turning off and on the interrupt lines.
NVIDIA Corporation
October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01 89
Page 100

780i 3-Way SLI Motherboard
Award POST Codes
Co
Name Description
de
42 Reserved
43 Test Stuck
Interrupt
44 Reserved
45 Reinit serial port Reinitialize Preboot agent serial port
46 Reserved
47 EISA Test If EISA non-volatile memory checksum is good,
48 Reserved
49 Size Memory Size base memory from 256K to 640K and extended
4A Reserved
4B Reserved
4C Reserved
4D Reserved
4E Init APIC Initialize APIC and set MTRR
4F Reserved
50 USB init Initialize USB controller
51 Reserved
52 Memory Test Test all memory of memory above 1MB using Virtual
53 Reserved
54 Reserved
55 CPU display Detect CPU speed and display CPU vendor specific
56 Reserved
57 PnP Init Display PnP logo and PnP early init
58 Reserved
Turn off interrupts then verify no 8259's interrupt
mask register is on. Test 8259 Force an interrupt and
verify the interrupt occurred.
execute EISA initialization. If not, execute ISA tests
and clear EISA mode flag.
memory above 1MB.
8086 mode, page mode and clear the memory
version string and turn on all necessary CPU features
NVIDIA Corporation
90 October 17, 2007 | DU-03597-001_v01
 Loading...
Loading...