Page 1

ForceWare Graphics Drivers
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide
Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
August 22, 2005
Page 2

NVIDIA ForceWare Graphics Drivers Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide v2.1
Published by
NVIDIA Corporation
2701 San Tomas Expressway
Santa Clara, CA 95050
Notice
ALL NVIDIA DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS, REFERENCE BOARDS, FILES, DRAWINGS, DIAGNOSTICS,
LISTS, AND OTHER DOCUMENTS (TOGETHER AND SEPARATELY, “MATERIALS”) ARE BEING
PROVIDED “AS IS.” NVIDIA MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR
OTHERWISE WITH RESPECT TO THE MATERIALS, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE.
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, NVIDIA Corporation assumes no
responsibility for the consequences of use of such information or for any infringement of patents or other rights of
third parties that may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent
rights of NVIDIA Corporation. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject to change without notice.
This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. NVIDIA Corporation products are not
authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of
NVIDIA Corporation.
Tradem arks
NVIDIA, the NVIDIA logo, 3DFX, 3DFX INTERACTIVE, the 3dfx Logo, STB, STB Systems and Design, the STB
Logo, the StarBox Logo, NVIDIA nForce, GeForce, NVIDIA Quadro, NVDVD, NVIDIA Personal Cinema,
NVIDIA Soundstorm, Vanta, TNT2, TNT, RIVA, RIVA TNT, VOODOO, VOODOO GRAPHICS, WAVEBAY,
Accuview Antialiasing, the Audio & Nth Superscript Design Logo, CineFX, the Communications & Nth Superscript
Design Logo, Detonator, Digital Vibrance Control, DualNet, FlowFX, ForceWare, GIGADUDE, Glide, GOFORCE,
the Graphics & Nth Superscript Design Logo, Intellisample, M-BUFFER, nfiniteFX, NV, NVChess, nView,
NVKeystone, NVOptimizer, NVPinball, NVRotate, NVSensor, NVSync, the Platform & Nth Superscript Design
Logo, PowerMizer, Quincunx Antialiasing, Sceneshare, See What You've Been Missing, StreamThru, SuperStability,
T-BUFFER, The Way It's Meant to be Played Logo, TwinBank, TwinView and the Video & Nth Superscript Design
Logo are registered trademarks or trademarks of NVIDIA Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Other company and product names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of the respective owners with which
they are associated.
Intel, Indeo, and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT,
Direct3D, DirectDraw, and DirectX are trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. OpenGL is a
registered trademark of Silicon Graphics Inc.
Other company and product names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of the respective owners with which
they are associated.
Copyright
© 2004.2005 by NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 3

Driver Utilities Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide Version
Table of Contents
1.About NVIDIA Graphics to SDI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2.NVIDIA Graphics-to-SDI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Feature Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Basic Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Hardware Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Software Setup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Recommended Operating Practices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
How to Set Up the SDI Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Basic SDI Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Advanced Adjustments. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Synchronizing the SDI Output to an External Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Genlock Versus Frame Lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Supported Synchronization Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Synchronization Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Viewing System Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
4.API Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
The Property Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
API Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Function Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Function Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
NVIDIA Corporation i
Page 4

NVIDIA Drivers Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 5

HAPTER 1
About NVIDIA Graphics to SDI
C
C HAPTER
A
BOUT
Serial Digital Interface (SDI) is a digital, uncompressed high quality video format used for
film and video post production and broadcast applications. The Quadro FX 4000 SDI
graphics card converts composited video and graphics to uncompressed 8-bit or 10-bit
SDI output.
NVIDIA G
RAPHICS TO
SDI
About This Document
This manual explains the graphics-to-SDI functionality of the NVIDIA Quadro FX 4000
SDI graphics card and software, described in the following sections:
• “NVIDIA Graphics-to-SDI” on page 3 lists the supported SDI features and explains the
basic operation in a broadcast environment.
• “Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel” on page 11 describes how to use the Display
Properties control panel to set up and start the SDI output.
• “API Control” on page 23 gives an overview of API control of the SDI functions.
For instructions on installing the graphics card and drivers, refer to the documentation
that accompanies your Quadro FX 4000 SDI graphics card.
Other Documents
For details on using the NVIDIA Display Properties control panel, see the ForceWare
Release XX Graphics Drivers User’s Guide.
System Requirements
•Windows® 2000 or Windows® XP.
• Quadro FX 4000 SDI Graphics Card
• NVIDIA Forceware Graphics Driver for Windows, version 62.42 or later.
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 1
Page 6

HAPTER 1
C
About NVIDIA Graphics to SDI
Revision History
Revision Date Description
1.0 8/6/04 Initial Release.
2.0 12/16/04 Added more HD modes under “Supported SDI Signal Formats”
2.1 8/22/05 Removed reference to Direct3D API support from “Using the
on page 4.
SDI APIs” on page 8.
2 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 7

HAPTER 2
NVIDIA Graphics-to-SDI
C
C HAPTER
This chapter provides an overview of the NVIDIA graphics-to-SDI functionality,
described in the following sections:
• “Feature Overview” on page 3 lists the hardware connections, supported SDI formats,
and additional SDI support features of the Quadro FX 4000 SDI graphics card.
• “Basic Operation” on page 5 describes the hardware connections and summarizes the
software setup.
• “Recommended Operating Practices” on page 9 describes some basic operating
practices that NVIDIA recommends to ensure the best performance.
Feature Overview
Output Connections
• Two BNC connections that can be configured for fill + key dual-link SDI outputs, or for
single-link SDI outputs
• One DVI video monitoring output
NVIDIA G
RAPHICS-TO
-SDI
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 3
Page 8

HAPTER 2
C
NVIDIA Graphics-to-SDI
Supported SDI Signal Formats
• Standard Defintion (SD) Modes
• 487i @ 59.95 Hz (SMPTE259) NTSC
• 576i @ 50.00 Hz (SMPTE259) PAL
• High Definition (HD) Modes
• 720p @ 23.97 Hz, 24.00 Hz, 25.00 Hz, 29.97 Hz, 30.00 Hz, and 50.00 Hz
• 720p @ 59.94Hz, 60.00 Hz (SMPTE296)
• 1035i @ 59.94 Hz, 60.00 Hz (SMPTE260)
• 1080i @ 50.00 Hz (SMPTE295)
• 1080i @ 50.00 Hz, 59.94 Hz, 60.00 Hz (SMPTE274)
• 1080PsF @ 24.00 Hz, 23.976 Hz
• 1080PsF @ 25.00 Hz, 29.97 Hz, 30 Hz (SMPTE274)
• 1080p @ 23.976 Hz, 24.00 Hz, 25.00 Hz, 29.97 Hz, 30.00 Hz (SMPTE274)
1
2
Supported SDI Color Formats
• RGB 4:4:4
• YCrCb 4:2:2 or 4:4:4
• RGBA 4:4:4:4
• YCrCbA 4:2:2:4
Desktop Region Adjustment Capability
Lets you define a portion of the desktop to convert to SDI output.
Genlock and Frame Lock Capability
Lets you synchronize the SDI output to an external digital or analog sync source.
1. The 720p modes in this bullet entry are available with firmware revision 6 or later.
2. The 1080PsF modes in this bullet entry are available with firmware revision 6 or later.
4 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 9
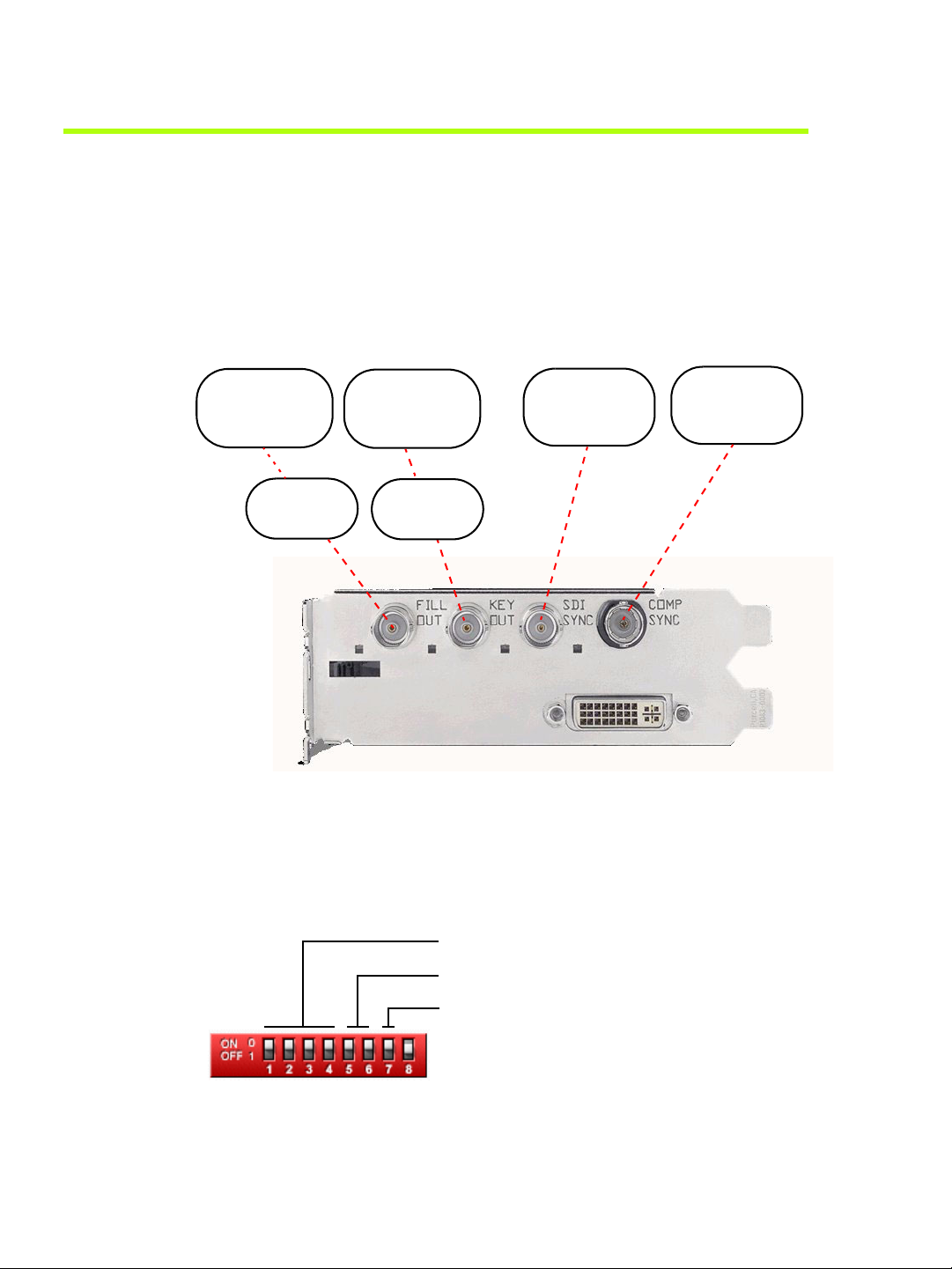
Basic Operation
Hardware Setup
Understanding the Connectors
Figure 2.1 shows the available SDI and external sync connectors on the Quadro FX 4000
SDI graphics card.
HAPTER 2
NVIDIA Graphics-to-SDI
C
Fill portion
of a dual link
SDI output
Figure 2.1
Single link
SDI output
SDI Connectors
Key portion
of a dual link
SDI output
- or -
Single link
SDI output
Understanding the OnBoard DIP Switch
The Quadro FX 4000 SDI graphics card has an onboard dip switch that determines the
default SDI operating mode. Subsequent software changes override these settings.
(1-4) Output Video Format (See Table 2.1)
SDI
Genlock
Sync Signal
Composite
Genlock
Sync Signal
(5-6) Sync Source (See Table 2.2)
(7) Auto Switch (See Table 2.3)
Figure 2.2
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 5
Onboard DIP Switch Positions
Page 10

HAPTER 2
C
NVIDIA Graphics-to-SDI
Table 2.1
Switch
Position
1234
0000
1000
0100
1100
0010
1010
0110
1110
0001
1001
0101
1101
0011
1011
0111
1111
Output Video Format Switch Settings
Video Format
Reserved
SMPTE 259 NTSC, 1440x487, 30/1.001 Hz, Interlace
SMPTE 259 PAL, 1440x576, 25 Hz, Interlace
SMPTE 260, 1920x1035, 30 Hz, Interlace
SMPTE 260, 1920x1035, 30/1.001 Hz, Interlace
SMPTE 295, 1920x1080, 25 Hz, Interlace
SMPTE 274, 1920x1080, 30 Hz, Interlace
SMPTE 274, 1920x1080, 30/1.001 Hz, Interlace
SMPTE 274, 1920x1080, 25 Hz, Interlace
SMPTE 274, 1920x1080, 30 Hz, Progressive
SMPTE 274, 1920x1080, 30/1.001 Hz, Progressive
SMPTE 274, 1920x1080, 25 Hz, Progressive
SMPTE 274, 1920x1080, 24 Hz, Progressive
SMPTE 274, 1920x1080, 24/1.001 Hz, Progressive
SMPTE 296, 1280x720, 60 Hz, Progressive
SMPTE 296, 1280x720, 60/1.001 Hz, Progressive
Table 2.2
Sync Source Switch Settings
Switch
Position
56
00
10
01
11
Table 2.3
Sync Source
Internal (free running)
Synchronize to SDI sync source
Synchronize to Composite sync source
Reserved
Auto Switch Settings
Switch
Position
7
0
1
6 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
Auto Switch Setting
Do not auto switch
Automatically switch to the new video format based on the
source sync.
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 11

Connecting the SDI Video Output
Refer to Figure 2.1.
• 4:4:4/4:2:2:4/4:4:4:4 dual-link signals are sent to the Fill Out and Key Out BNC
connectors (fill + key signals are sent to the corresponding BNC connectors).
• 4:2:2 single-link signals are sent to the Fill Out BNC connector only.
In application control mode, using the APIs, an additional 4:2:2 signal can be sent to the
Key Out BNC connector.
Connecting to an External Sync Source
• You can genlock the output to an external digital or analog sync source.
NVIDIA Genlock supports the following two external synchronization signal types:
• SDI
• Composite, which can be one of
Composite Bi-level (NTSC or PAL sources use bi-level composite signals.)
HAPTER 2
NVIDIA Graphics-to-SDI
C
Composite Tri-level (HDTV sources commonly use tri-level composite signals.)
• To use an external sync source, connect the sync signal to the appropriate BNC
connector as indicated in Figure 2.1.
You can connect to both types of sync sources at the same time. The software gives
precedence to the SDI signal, but you can use the control panel to choose which signal
to use (see “Synchronizing the SDI Output to an External Source” on page 19.)
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 7
Page 12

HAPTER 2
C
NVIDIA Graphics-to-SDI
Software Setup
The NVIDIA SDI software lets you specify the
•SDI signal format
• Color formats
• Synchronization method
• Gamma correction
Graphics-to-SDI functionality can be set up and controlled in two basic ways—using the
NVIDIA control panel or using the NVIDIA SDI API.
Using the SDI APIs
The SDI application programming interface allows OpenGL applications to have full and
exclusive control of the SDI output. This is also known as extended mode.
When the SDI output is under application control, you can use the NVIDIA Graphics to
SDI property page to view the SDI hardware status.
• See the chapter “API Control” on page 23 for a description of the graphics-to-video-out
API calls.
• Also, refer to the document
instructions on using the API.
Using the Control Panel
When the SDI output is not being controlled by an application, you can use the NVIDIA
Graphics to SDI property page to
• Specify the SDI signal format, output format, and then enable the SDI output.
• Configure the external synchronization signal if needed.
This is also known as transparent mode. In this mode, the SDI software work on top of
existing applications, and the active workstation desktop or full screen application
display is automatically forwarded to the SDI video outputs.
See the chapter “Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel” on page 11 for detailed
instructions on using the Graphics to SDI property page.
Programming the NVIDA Quadro FX 4000 SDI for
8 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 13

Recommended Operating Practices
This section provides some basic operating practices to follow in order to obtain the best
SDI performance for your application.
Initial On-Air Broadcast
When starting a live broadcast of SDI video, follow the sequence below to ensure proper
allocation of system resources and to prevent visual disturbances in the on air broadcast.
1 Set up the SDI format settings and start the SDI output
2 Start the application to be broadcast
3 Verify the video quality
4 Close the Graphics to SDI control panel
HAPTER 2
NVIDIA Graphics-to-SDI
C
5 Go on air
To avoid visual disturbances while broadcasting live, DO NOT
• Start or stop the graphics or video application
• Turn on or off the SDI output
• Make changes to the SDI signal format
Changing Applications
To avoid visual disturbances while switching applications, observe the following
sequence:
1 Stop the live broadcast (go off air)
2 Stop the application
3 Start the new application
4 Verify video quality
5 Resume the live broadcast
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 9
Page 14

HAPTER 2
C
NVIDIA Graphics-to-SDI
Changing Video Formats
When changing any of the SDI settings, visual disturbances might occur as the video
resets to the new settings. To prevent such disturbances from being visible to the public or
from being recorded, observe the following sequence when making changes to any SDI
setting:
1 Stop the live broadcast (go off air)
2 Change video format or SDI settings
3 Verify video quality
4 Resume the live broadcast
When Using the Control Panel
NVIDIA recommends the following
• Set the desktop to the same or higher resolution than the SDI output for better image
quality.
• Close all background applications—such as virus scan, backup, and archiving
applications—before starting the SDI output and going on air.
• Close the Display Properties panel before going on air.
• When running multiple OpenGL applications, tearing may occur if the applications are
not synchronized.
In general, NVIDIA does not recommend running multiple OpenGL applications when
starting the SDI output or when going live.
Running Multiple OpenGL Applications
To maximize the system resources and bandwidth available for converting graphics to
SDI output, NVIDIA recommends broadcasting only one OpenGL application at a time.
10 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 15

HAPTER 3
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
C HAPTER
U
SING THE
This chapter explains how to set up the NVIDIA Quadro FX 4000 SDI graphics card using
the NVIDIA Graphics to SDI properties page—also known as transparent mode. It
contains the following sections:
G
RAPHICS TO
SDI C
ONTROL
C
P
ANEL
• “How to Set Up the SDI Output” on page 12 provides step-by-step instructions for
using the control panel to set up the SDI output.
• “Synchronizing the SDI Output to an External Source” on page 19 explains in more
detail the genlock and frame lock features.
• “Viewing System Information” on page 22
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 11
Page 16

HAPTER 3
C
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
How to Set Up the SDI Output
Basic SDI Setup
To ensure proper operation, NVIDIA recommends the following -
• Set the desktop resolution to be the same or larger than the SDI output for better image quality
• Stop background applications—such as virus scan, backup and archiving applications—prior
to starting SDI output and going on air.
• Close the control panel before going on air.
• When running multiple OpenGL applications, synchronize them, otherwise tearing may occur.
Step 1: Enable the Graphics to SDI Property Page
1 Open the NVIDIA Graphics to SDI property page.
a Open the Windows Display Properties control panel, click Settings>Advanced, and
then click the Quadro FX 4000 tab to open the NVIDIA graphics card display
properties page.
b Click the Graphics to SDI tree item from the slide-out tray.
Figure 3.1
2 In the Output Options group box, click Yes for Send Output to SDI.
12 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
Graphics to SDI Page
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 17

Step 2: Choose a Synchronization Method
Click the Sync Option arrow and then click the method you want to use to synchronize
the SDI output:
• Internal: The SDI output will be synchronized with the timing chosen from the SDI
signal format list.
• Genlock: The SDI output will be synchronized with the external sync signal.
• Frame Lock: The SDI output will be synchronized with the timing chosen from the SDI
signal format list.
This list is limited to timings that can be synchronized with the detected external sync
signal.
For more information regarding genlock and frame lock, see the section “Synchronizing
the SDI Output to an External Source” on page 19.
Step 3: Specify the SDI Signal Format
HAPTER 3
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
C
The SDI signal format controls the video resolution, field rate, and SMPTE signalling
standard for the outgoing video stream. Your options for this setting depend on which
Sync option you chose in the previous step.
Internal
If you chose internal synchronization, then click the SDI signal format arrow and click
the signal format you want to use.
Genlock
If you chose genlock synchronization, the sync source controls the SDI signal format. The
list box will be grayed out, preventing you from choosing another format.
Frame Lock
If you chose frame lock synchronization, only those modes that are compatible with the
detected sync signal will appear in the SDI signal format list.
Click the SDI signal format arrow and then click the signal format you want to use.
Step 4: Specify the SDI Output Format
The SDI output format controls the color model, data packing, and alpha or z components
in the outgoing video stream.
Click the SDI output format arrow and then click the color format you want to use.
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 13
Page 18

HAPTER 3
C
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
Step 5: Apply and Verify the Changes
Click OK or Apply to put the new settings into effect.
The Graphics to SDI property page banner indicates the status of the SDI output as well as
the external synchronization signals. Figure 3.2 shows the correlation between the
indicators on the banner and the actual connectors.
Quadro FX 4000 SDI
Connectors
Graphics to SDI
Property Page
Banner
Figure 3.2
Connection Status Indicators
The activity of the LED graphics indicates the signal status as follows:
• Vid. 1 Out or Vid. 2 Out
Status Meaning
Off (gray)
Blinking Green
Blinking Yellow
SDI output is not in use
SDI output is active and is in HD mode.
SDI output is active and is in SD mode.
• SDI Sync
Status Meaning
Off (gray)
Blinking Green
Blinking Yellow
Steady Yellow
SDI synchronization signal is not present or not detected.
SDI synchronization signal is detected in HD mode.
SDI synchronization signal is detected in SD mode.
SDI synchronization error has occurred.
• COMP Sync
Status Meaning
Off (gray)
Blinking Green
Composite synchronization signal is not present or not
detected.
Composite synchronization signal is detected.
14 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 19

More About the External Sync Signal
When the software detects the external sync signal, the sync format information appears
in the Genlock format text box.
This section describes other situations that might come up when attempting to sync to an
external sugnal.
Switching External Sync Signals
If you have both SDI and composite sync signals connected, the software automatically
chooses the SDI signal.
If you want to switch to the composite signal, click the arrow in the Genlock format
group box and then click COMP Sync.
Manually Detecting the Signal
• If the software loses the external sync signal or does not detect it automatically,
click the signal detect button to force detection of the sync signal.
HAPTER 3
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
C
• For composite signals, the software automatically detects the signal type that is being
used—either bi-level or tri-level.
If the software is unable to detect the signal type, click the Genlock format list box
arrow and then click the COMP option corresponding to your sync source.
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 15
Page 20

HAPTER 3
C
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
Advanced Adjustments
This section describes the following additional settings that you can control using the
Graphics to SDI page:
• “Adjusting the Desktop Area” on page 16
• “Applying Gamma Correction” on page 18
Adjusting the Desktop Area
By default, the entire desktop is converted to SDI output. If the desktop is smaller than the
size of the SDI output, it will be scaled to fit. If the desktop is larger than the SDI output, it
will be cropped to fit.
Instead of using the entire desktop, you can specify a region of the desktop to convert to
SDI output as follows:
1 In the Desktop group box, click Change Desktop region.
The display property page minimizes and the SDI Output dialog box appears.
Superimposed over the desktop is a rectangular outline that shows the region that will
be used for SDI output.
Figure 3.3
16 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
Desktop Region Adjustment
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 21

HAPTER 3
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
C
2 Click the Select Region to use option.
3 Adjust the region size.
• Click and drag within the rectangular outline to adjust the position on the desktop.
• Click and drag the appropriate corner or side grab handles to resize.
• You can also adjust the region by specifying the X, Y, Width, and Height values in
the SDI Output dialog box. Either enter pixel values directly into the corresponding
text boxes or click the up and down arrows by the appropriate box.
Note: The X and Y values indicate the pixel distance of the upper left corner of the
output box from the upper left corner of the desktop.
4 Click OK when finished.
The desktop graphic image shows a thumbnail preview of the desktop region that you
have set up for SDI output.
5 Click OK or Apply to put the settings into effect.
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 17
Page 22

HAPTER 3
C
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
Applying Gamma Correction
To specify the gamma correction to use for the source stream:
1 In the Desktop group box, click Adjust Gamma Correction.
The SDI Color Settings dialog box appears.
2 Specify the RGB Gamma values using one or more of the following methods:.
• Click and drag the slider for the appropriate R, G, or B setting
• Specify the R, G, or B gamma value by entering a value in the text box or using the
up and down arrows.
• Click and drag the handle in the graphic.
• To keep all gamma channels at the same value while you adjust them
simultaneously, click the Lock all channels option.
3 Click OK when finished.
18 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 23

Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
Synchronizing the SDI Output to an External Source
You can synchronize the SDI output with other equipment in a broadcast or post
production environment.
Genlock Versus Frame Lock
The Graphics to SDI page provides two methods for synchronizing the SDI output to a
common sync source—Genlock and Frame lock.
Using Genlock
Genlock synchronizes the pixel scanning of the SDI output to an external synchronization
source.
When using genlock, the SDI refresh rate is determined by the sync source, so any refresh
rates that you may have chosen in the SDI signal format list do not apply.
HAPTER 3
C
Using Frame Lock
Frame lock synchronizes the frame rate of the SDI output to an external synchronization
source.
When using frame lock, only modes that are valid for the frame rate of the sync source
can be used for the SDI output. The valid modes will appear in the SDI signal format list.
Supported Synchronization Signals
NVIDIA Genlock supports the following external synchronization signal types:
•SDI
• Composite Bi-level (NTSC or PAL sources use bi-level composite signals.)
• Composite Tri-level (HDTV sources commonly use tri-level composite signals.)
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 19
Page 24

HAPTER 3
C
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
Synchronization Instructions
Basic Setup Summary
The following are the basic steps to synchronize the SDI output.
1 Connect the external sync source to the appropriate BNC connector on the graphics
card.
See “Hardware Setup” on page 5 for instructions on connecting the external sync signal
to the graphics card.
2 Configure the sync source.
Use the NVIDIA Graphics to SDI property page to configure the SDI output
synchronization.
Figure 3.4
a Choose either genlock or frame lock synchronizing modes.
b If using frame lock, choose an SDI signal format to synchronize with the sync source.
See “Basic SDI Setup” on page 12 for more detailed instructions on setting up the sync
source.
3 Add a sync delay, if needed.
See “Adding a Delay to the Signal” on page 21 for instructions on how to introduce a
delay to the SDI output.
20 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
Graphics to SDI Page—Configuring an External Sync Source
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 25

Adding a Delay to the Signal
You can introduce a slight delay in genlocked or frame locked SDI output. For example, if
delivery of video from other equipment is delayed because of greater cable length, you
can introduce a delay in the SDI output from this card so that both deliveries are in sync.
To introduce a synchronization delay:
1 Click Advanced Options from the Graphics to SDI page.
The SDI Advanced Options window appears.
HAPTER 3
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
C
Figure 3.5
SDI Advanced Options Window
2 Click the Synchronization Delay tab.
Figure 3.6
Synchronization Delay Page
3 Introduce delays in the HSYNC and VSYNC signals as needed by clicking the
appropriate up and down arrows.
You can also enter values directly into the text boxes.
4 Click OK or Apply when finished.
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 21
Page 26

HAPTER 3
C
Using the Graphics to SDI Control Panel
Viewing System Information
To view information about the graphics card and the installed driver software, click
Advanced Options from the Graphics to SDI page.
The General tab shows the graphics card model, firmware version, driver version and
current SDI resolution.‘
Figure 3.7
SDI Advanced Options—General tab
22 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 27

HAPTER 4
C
API Control
C HAPTER
API C
The SDI application programming interface allows OpenGL or Direct3D applications to
have full and exclusive control of the SDI output. This method of controlling the SDI
output is also known as extended mode.
This chapter gives a brief introduction to this method of implementing graphics to SDI,
and includes the following sections:
• “The Property Page” on page 24
• “API Description” on page 25
Refer to the document
using the API.
Programming the NVIDA Quadro FX 4000 SDI for instructions on
ONTROL
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 23
Page 28
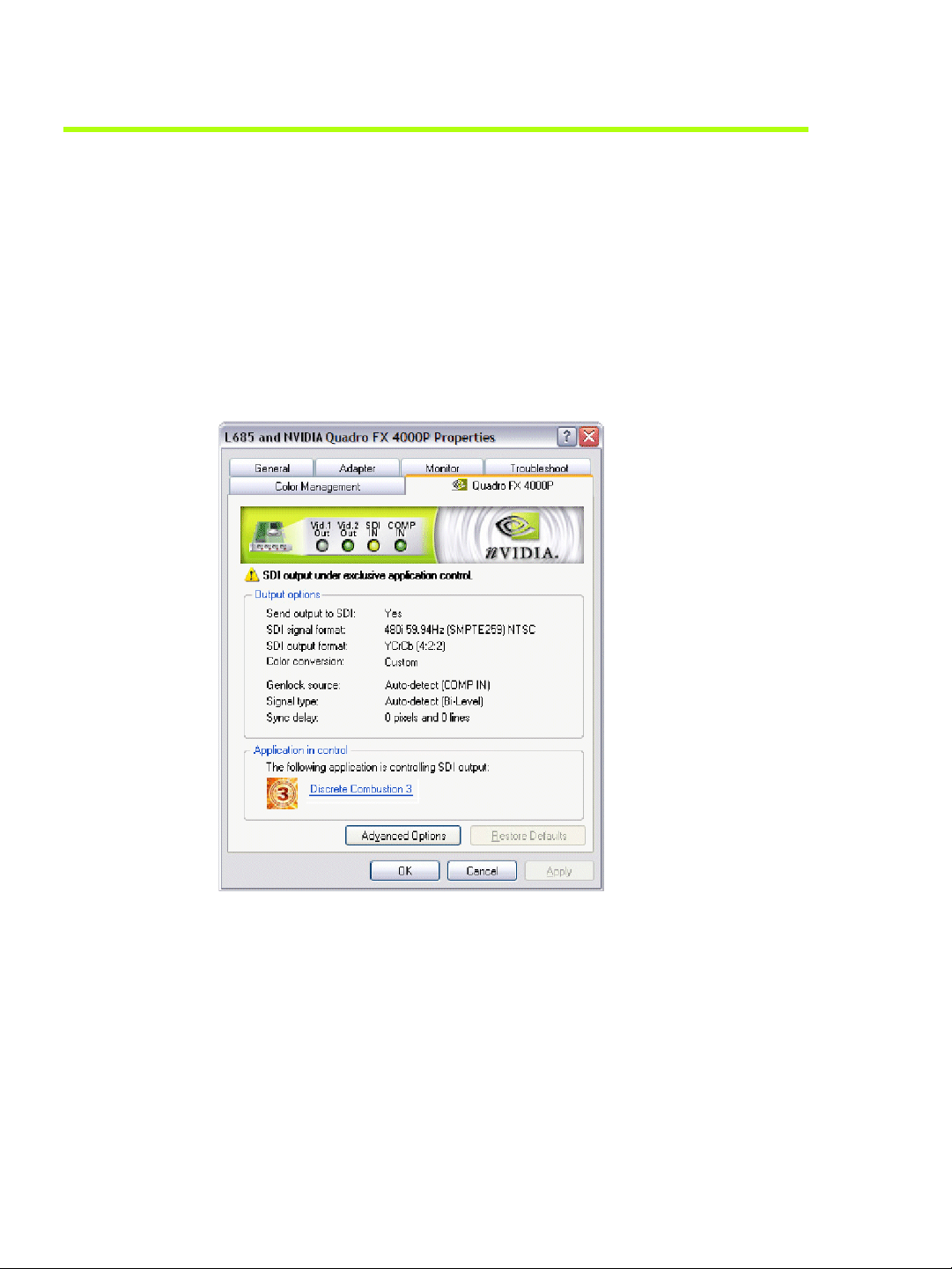
HAPTER 4
C
API Control
The Property Page
When the SDI output is under application control, you can use the NVIDIA Graphics to
SDI property page to view the SDI hardware status.
To view the SDI status using the NVIDIA Graphics to SDI property page
1 Open the Windows Display Properties control panel, click Settings>Advanced, and
then click the Quadro FX 4000 tab to open the NVIDIA graphics card display properties
page.
2 Click the Graphics to SDI tree item from the slide-out tray.
Figure 4.1
24 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
Graphics to SDI Page—Application Control
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 29

API Description
Function Index
Call Description
NvGvoCaps()
NvGvoOpen()
NvGvoClose()
NvGvoDesktopOpen()
NvGvoDesktopClose()
NvGvoStatus()
NvGvoSyncFormatDetect()
NvGvoConfigGet()
NvGvoConfigSet()
NvGvoIsRunning()
NvGvoStart()
NvGvoStop()
NvGvoEnumSignalFormats()
NvGvoIsFrameLockModeCompatible()
NvGvoEnumDataFormats()
HAPTER 4
C
API Control
Determine the graphics-to-video capabilities of
the graphics card.
Open the graphics card for graphics-to-video
operations using the OpenGL application
interface.
Close the graphics card for graphics-to-video
operations using the OpenGL application
interface.
Open the graphics cards for graphics-to-vVideo
operations using the Desktop transparent
mode interface.
Close the graphics cards for graphics-to-video
operations using the Desktop transparent
mode interface.
Get the graphics-to-video status.
Detect the video format of the iincoming sync
signal.
Get the current graphics-to-video
configuration.
Set the graphics-to-video configuration.
Determine if there is an SDI out video stream.
Start the SDI out video stream.
Stop the SDI out video stream.
Enumerate the supported SDI signal formats.
Verify whether a mode is compatible with
frame lock mode.
Enumerate the supported SDI data formats.
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 25
Page 30

HAPTER 4
C
API Control
Function Description
NvGvoCaps()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoCaps
// Description: Determine graphics adapter Graphics to Video capabilities.
// Parameters: nAdapterNumber - Graphics adapter number
// nReserved - Reserved (must be set to zero)
// pAdapterCaps - Pointer to receive capabilities
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
// NV_NOTSUPPORTED - Graphics to Video not supported
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoCaps(UINT nAdapterNumber IN,
UINT nReserved IN,
NVGVOCAPS* pAdapterCaps OUT);
NvGvoOpen()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoOpen
// Description: Open graphics adapter for Graphics to Video operations
// using the OpenGL application interface. Read operations
// are permitted in this mode by multiple clients, but Write
// operations are application exclusive.
// Parameters: nAdapterNumber - Graphics adapter number
// nReserved - Reserved (must be set to zero)
// dwClass - Class interface (NVGVOCLASS_* value)
// dwAccessRights - Access rights (NVGVO_O_* mask)
// phGvoHandle - Pointer to receive handle
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
// NV_ACCESSDENIED - Access denied for requested access
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoOpen(UINT nAdapterNumber IN,
UINT nReserved IN,
DWORD dwClass IN,
DWORD dwAccessRights IN,
NVGVOHANDLE* phGvoHandle OUT);
26 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 31

NvGvoClose()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoClose
// Description: Closes graphics adapter for Graphics to Video operations
// using the OpenGL application interface. Closing an
// OpenGL handle releases the device.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoClose(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN);
NvGvoDesktopOpen()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoDesktopOpen
// Description: Open graphics adapter for Graphics to Video operations
// using the Desktop transparent mode interface. Read
// operations are permitted in this mode by multiple clients,
// but write operations are application exclusive.
// Parameters: nAdapterNumber - Graphics adapter number
// nReserved - Reserved (must be set to zero)
// dwClass - Class interface (NVGVOCLASS_* value)
// dwAccessRights - Access rights (NVGVO_O_* mask)
// phGvoHandle - Pointer to receive handle
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
// NV_ACCESSDENIED - Access denied for requested access
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoDesktopOpen(UINT nAdapterNumber IN,
UINT nReserved IN,
DWORD dwClass IN,
DWORD dwAccessRights IN,
NVGVOHANDLE* phGvoHandle OUT);
HAPTER 4
C
API Control
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 27
Page 32

HAPTER 4
C
API Control
NvGvoDesktopClose()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoDesktopClose
// Description: Closes graphics adapter for Graphics to Video operations
// using the Desktop transparent mode interface.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// bGvoRelease - TRUE to release device when handle closes
// FALSE to remain in desktop mode when handle
// closes (other clients can open using
// NvGvoDesktopOpen and release using
// NvGvoDesktopClose)
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoDesktopClose(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN,
BOOL bRelease IN);
NvGvoStatus()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoStatus
// Description: Get Graphics to Video status.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoStatus(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN,
NVGVOSTATUS* pStatus OUT);
NvGvoSyncFormatDetect()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoSyncFormatDetect
// Description: Detects Graphics to Video incoming sync video format.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// pdwWait - Pointer to receive milliseconds to wait
// before NvGvoStatus will return detected
// syncFormat.
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoSyncFormatDetect(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN,
DWORD* pdwWait OUT);
28 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 33

NvGvoConfigGet()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoConfigGet
// Description: Get Graphics to Video configuration.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// pConfig - Pointer to Graphics to Video configuration
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoConfigGet(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN,
NVGVOCONFIG* pConfig OUT);
NvGvoConfigSet()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoConfigSet
// Description: Set Graphics to Video configuration.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// pConfig - Pointer to Graphics to Video config
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
// NV_ACCESSDENIED - Access denied (no write access)
// NV_RUNNING - Requested settings require NvGvoStop
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoConfigSet(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN,
const NVGVOCONFIG* pConfig IN);
HAPTER 4
C
API Control
NvGvoIsRunning()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoIsRunning
// Description: Determine if Graphics to Video output is running.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// Returns: NV_RUNNING - Graphics-to-Video is running
// NV_NOTRUNNING - Graphics-to-Video is not running
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoIsRunning(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN);
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 29
Page 34

HAPTER 4
C
API Control
NvGvoStart()
NvGvoStop()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoStart
// Description: Start Graphics to Video output.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
// NV_ACCESSDENIED - Access denied (no write access)
// NV_RUNNING - Graphics to Video already running
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoStart(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN);
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoStop
// Description: Stop Graphics to Video output.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
// NV_ACCESSDENIED - Access denied (no write access)
// NV_NOTRUNNING - Graphics to Video not running
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoStop(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN);
30 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
Page 35

NvGvoEnumSignalFormats()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoEnumSignalFormats
// Description: Enumerate signal formats supported by Graphics to Video.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// nEnumIndex - Enumeration index
// bByEnum - TRUE nEnumIndex is NVSIGNALFORMAT_*
// FALSE nEnumIndex is 0..n-1
// pSignalFormatDetail - Pointer to receive detail or NULL
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
// NV_NOMORE - No more signal formats to enumerate
// NV_NOTSUPPORTED - Unsupported NVSIGNALFORMAT_ enumeration
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoEnumSignalFormats(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN,
int nEnumIndex IN,
BOOL bByEnum IN,
NVGVOSIGNALFORMATDETAIL*
pSignalFormatDetail OUT);
HAPTER 4
C
API Control
NvGvoIsFrameLockModeCompatible()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoIsFrameLockModeCompatible
// Description: Checks whether modes are compatible in framelock mode
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// nSrcEnumIndex - Source Enumeration index
// nDestEnumIndex - Destination Enumeration index
//
// pbCompatible - Pointer to receive compatability
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
// NV_NOTSUPPORTED - Unsupported NVSIGNALFORMAT_ enumeration
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoIsFrameLockModeCompatible(NVGVOHANDLE
hGvoHandle IN,
int
nSrcEnumIndex IN,
int
nDestEnumIndex IN,
BOOL*
pbCompatible OUT);
NVIDIA Corporation
Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide – Version 2.1 31
Page 36

HAPTER 4
C
API Control
NvGvoEnumDataFormats()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function: NvGvoEnumDataFormats
// Description: Enumerate data formats supported by Graphics to Video.
// Parameters: hGvoHandle - Handle to graphics adapter
// nEnumIndex - Enumeration index
// bByEnum - TRUE nEnumIndex is NVDATAFORMAT_*
// FALSE nEnumIndex is 0..n-1
// pDataFormatDetail - Pointer to receive detail or NULL
// Returns: NV_OK - Success
// NV_NOMORE - No more data formats to enumerate
// NV_NOTSUPPORTED - Unsupported NVDATAFORMAT_ enumeration
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
NVRESULT NVAPIENTRY NvGvoEnumDataFormats(NVGVOHANDLE hGvoHandle IN,
int nEnumIndex IN,
BOOL bByEnum IN,
NVGVODATAFORMATDETAIL* pDataFormatDetail
OUT);
32 Quadro FX 4000 SDI User’s Guide– Version 2.1
NVIDIA Corporation
 Loading...
Loading...