NSC MM58167BVX, MM58167BV, MM58167BN-T, MM58167BN, MM58167MWC Datasheet
TL/F/11070
MM58167B Microprocessor Real Time Clock
October 1990
MM58167B
Microprocessor Real Time Clock
General Description
The MM58167B is a low threshold metal gate CMOS circuit
that functions as a real time clock in bus oriented microprocessor systems. The device includes an addressable real
time counter, 56 bits of RAM, and two interrupt outputs. A
POWER DOWN
input allows the chip to be disabled from
the rest of the system for standby low power operation. The
time base is a 32.768 kHz crystal oscillator.
Features
Y
Microprocessor compatible (8-bit data bus)
Y
Milliseconds through month counters
Y
56 bits of RAM with comparator to compare the real
time counter to the RAM data
Y
2 INTERRUPT OUTPUTS with 8 possible interrupt
signals
Y
POWER DOWN input that disables all inputs and outputs except for one of the interrupts
Y
Status bit to indicate rollover during a read
Y
32.768 kHz crystal oscillator
Y
Four-year calendar (no leap year)
Y
24-hour clock
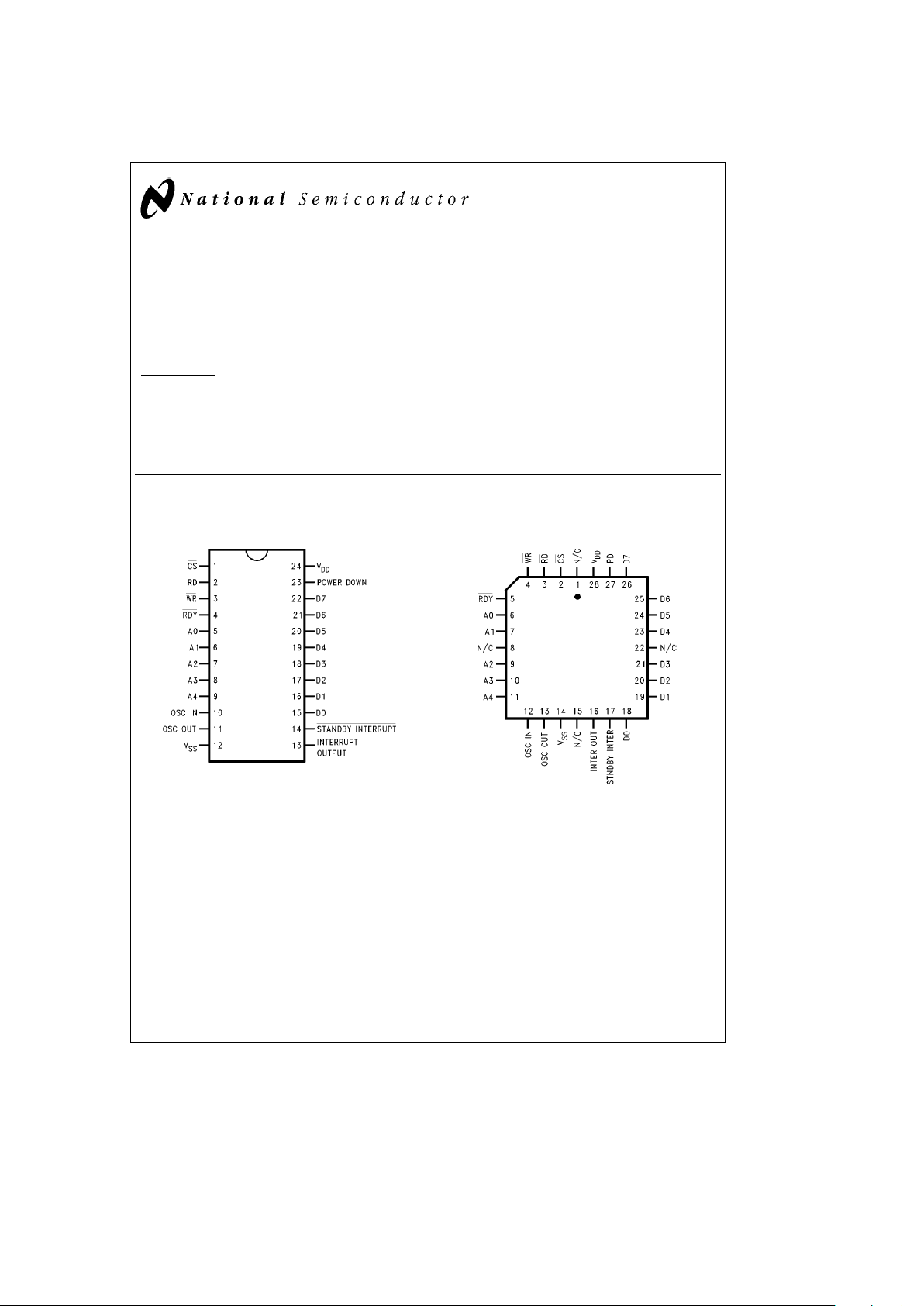
Connection Diagrams
Dual-In-Line Package
TL/F/11070– 1
Top View
Order Number MM58167BN
See NS Package Number N24A
PCC Package
TL/F/11070– 2
Top View
Order Number MM58167BV
See NS Package Number V28A
TRI-STATEÉis a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M105/Printed in U. S. A.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
Voltage at All Pins V
SS
b
0.3V to V
DD
a
0.3V
Operating Temperature 0§Cto70§C
Storage Temperature
b
65§Ctoa150§C
V
DD
b
V
SS
6.0V
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.) 300§C
Electrical Characteristics V
SS
e
0V, 0§CsT
A
s
70§C
Parameter Conditions Min Max Units
Supply Voltage
V
DD
Outputs Enabled 4.5 5.5 V
V
DD
POWER DOWN Mode 2.2 5.5 V
Supply Current
I
DD
, Dynamic Outputs TRI-STATE
É
f
IN
e
32.768 kHz, V
DD
e
5.5V
20 mA
V
IH
t
V
DD
b
0.3V
V
IL
s
V
SS
a
0.3V
IDD, Dynamic Outputs TRI-STATE
f
IN
e
32.768 kHz, V
DD
e
5.5V 5 mA
V
IH
e
2.0V, V
IL
e
0.8V
Input Voltage
Logical Low 0.0 0.8 V
Logical high 2.0 V
DD
V
Input Leakage Current V
SS
s
V
IN
s
V
DD
b
11mA
Output Impedance I/O and INTERRUPT OUT
Logical Low V
DD
e
4.5V, I
OL
e
1.6 mA 0.4 V
Logical High V
DD
e
4.5V, I
OH
eb
400 mA 2.4 V
I
OH
eb
10 mA 0.8 V
DD
V
TRI-STATE V
SS
s
V
OUT
s
V
DD
b
11mA
Output Impedance RDY and STANDBY INTERRUPT
(Open Drain Devices)
Logical Low, Sink V
DD
e
4.5V, I
OL
e
1.6 mA 0.4 V
Logical High, Leakage V
OUT
s
V
DD
10 mA
2
Functional Description
Real Time Counter
The real time counter is divided into 4-bit digits with 2 digits
being accessed during any read or write cycle. Each digit
represents a BCD number and is defined in Table I. Any
unused bits are held at a logical zero during a read and
ignored during a write. An unused bit is any bit not necessary to provide a full BCD number. For example tens of
hours cannot legally exceed the number 2, thus only 2 bits
are necessary to define the tens of hours. The other 2 bits in
the tens of hours digit are unused. The unused bits are designated in Table I as dashes.
The addressable portion of the counter is from milliseconds
to months. The counter itself is a ripple counter. The ripple
delay is less than 60 ms above 4.5V and 300 ms at 2.2V.
RAM
56 bits of RAM are contained on-chip. These can be used
for any necessary power down storage or as an alarm latch
for comparison to the real time counter. The data in the
RAM can be compared to the real time counter on a digit
basis. The only digits that are not compared are the unit ten
thousandths of seconds and tens of days of the week
(these are unused in the real time counter). If the two most
significant bits of any RAM digit are ones, then this RAM
location will always compare. The rule of thumb for an
‘‘alarm’’ interrupt is: All nibbles of higher order than specified are set to C hex (always compare). All nibbles lower
than specified are set to ‘‘zero’’. As an example, if an alarm
is to occur everyday at 10:15 a.m., configure the bits in RAM
as shown in Table II.
The RAM is formatted the same as the real time counter, 4
bits per digit, 14 digits, however there are no unused bits.
The unused bits in the real time counter will compare only to
zeros in the RAM.
An address map is shown in Table III.
Interrupts and Comparator
There are two interrupt outputs. The first is the INTERRUPT
OUTPUT (a true high signal). This output can be programmed to provide 8 different output signals. They are:
10 Hz, once per second, once per minute, once per hour,
once a day, once a week, once a month, and when a RAM/
real time counter comparison occurs. To enable the output
a one is written into the interrupt control register at the bit
location corresponding to the desired output frequency (
Fig-
ure 1
). Once one or more bits have been set in the interrupt
control register, the corresponding counter’s rollover to its
reset state will clock the interrupt status register and cause
the interrupt output to go high. To reset the interrupt and to
identify which frequency caused the interrupt, the interrupt
status register is read. Reading this register places the contents of the status register on the data bus. The interrupting
frequency will be identified by a one in the respective bit
position. Removing the read will reset the interrupt.
The second interrupt is the STANDBY
INTERRUPT (open
drain output, active low). This interrupt occurs when enabled
and when a RAM/real time counter comparison occurs. The
STANDBY
INTERRUPT is enabled by writing a one on the
D0 line at address 16
H
or disabled by writing a zero on the
D0 line. This interrupt is not triggered by the edge of the
compare signal, but rather by the level. Thus if the compare
is enabled when the STANDBY
INTERRUPT is enabled, the
interrupt will turn on immediately.
TABLE I. Real Time Counter Format
Units
Max
Tens
Max
Counter Addressed
D0 D1 D2 D3
BCD
D4 D5 D6 D7
BCD
Code Code
Milliseconds (00H) Ð Ð Ð Ð 0 D4 D5 D6 D7 9
Hundredths and Tenths Sec (01
H
) D0 D1 D2 D3 9 D4 D5 D6 D7 9
Seconds (02
H
) D0 D1 D2 D3 9 D4 D5 D6 Ð 5
Minutes (03
H
) D0 D1 D2 D3 9 D4 D5 D6 Ð 5
Hours (04H) D0 D1 D2 D3 9 D4 D5 Ð Ð 2
Day of the Week (05
H
)D0D1D2Ð7ÐÐÐÐ0
Day of the Month (06
H
) D0 D1 D2 D3 9 D4 D5 Ð Ð 3
Month (07
H
)D0D1D2D3 9 D4 Ð Ð Ð 1
(Ð) indicates unused bits
3
 Loading...
Loading...