NSC LMX2372MDC, LMX2372SLB Datasheet
LMX2370/LMX2371/LMX2372
PLLatinum
™
Dual Frequency Synthesizer for RF
Personal Communications
LMX2370 2.5 GHz/1.2 GHz
LMX2371 2.0 GHz/1.2 GHz
LMX2372 1.2 GHz/1.2 GHz
General Description
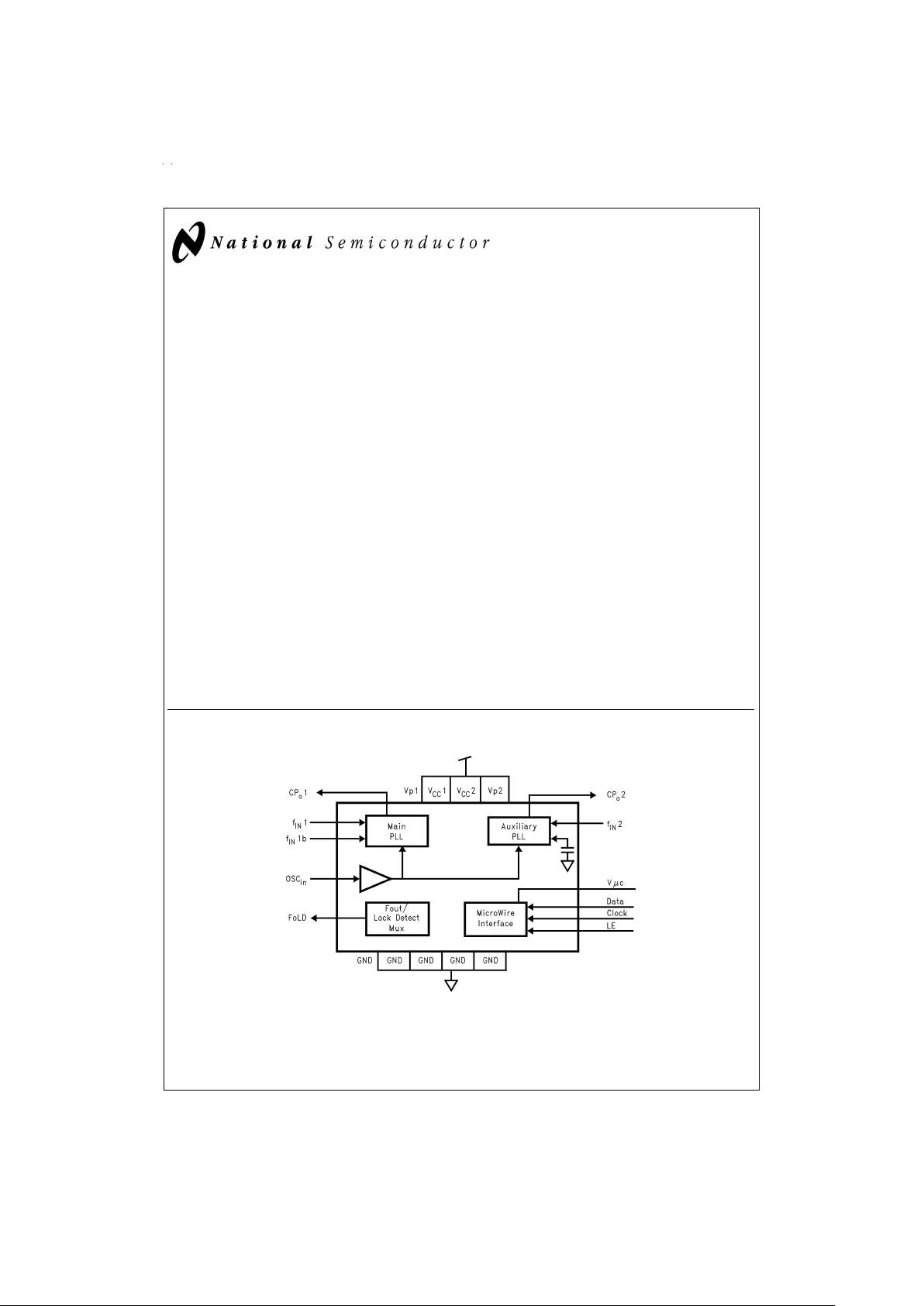
The LMX237X family of monolithic, integrated dual frequency synthesizers, including prescalers, is designed to be
used as a first and second local oscillator for dual mode or
dual conversion transceivers. It is fabricated using National’s
0.5u ABiCV silicon BiCMOS process. The LMX237X contains two dual modulus prescalers. A 32/33 or a 16/17
prescaler can be selected for the 2.5 GHz and 2.0 GHz RF
synthesizers with the 16/17 prescaler rated for input frequencies below 1.2 GHz. A 16/17 or an 8/9 prescaler can be selected for the 1.2 GHz RF synthesizers with the 8/9 prescaler
rated for input frequencies below 550 MHz. Using a digital
phase locked loop technique, the LMX237X can generate
very stable, low noise control signals for UHF and VHF voltage controlled oscillators (VCO’s). Serial data is transferred
into the LMX237X via a 1.8V three wire interface (Data, Enable, Clock) compatible with low voltage baseband processors. Supply voltage can range from 2.7V to 5.5V. The
LMX237X family features very low current consumption typically: LMX2370 - 6.0 mA
@
3V, LMX2371 - 5.0 mA@3V,
LMX2372 - 4.0 mA
@
3V.
The LMX237X are available in a 24-pad chip scale (CSP) or
a 20-pin TSSOP surface mount plastic package.
Features
n 2.7V–5.5V operation
n Ultra low current consumption
n Low phase detector noise floor
n Low voltage MICROWIRE
™
interface (1.8V up to VCC)
n Low prescaler values
32/33
@
fIN≤ 2.5 GHz
16/17
@
fIN≤ 1.2 GHz
8/9
@
fIN≤ 550 MHz
n Selectable charge pump current levels
n Selectable FastLock
™
mode
n Enhanced ESD protection
n Small 24 pad chip scale package (3.5 x 4.5 x 1.0 mm)
Applications
n Portable wireless communications (PCS/PCN, cordless)
n Dual mode cellular telephone systems
n Spread spectrum communication systems (CDMA)
n Cable TV tuners (CATV)
Functional Block Diagram
FastLock™, PLLatinum™and MICROWIRE™are trademarks of National Semiconductor Corporation.
TRI-STATE
®
is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
DS101026-1
PRELIMINARY
March 1999
LMX2370/LMX2371/LMX2372 PLLatinum Dual Frequency Synthesizer for RF Personal
Communications
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS101026 www.national.com
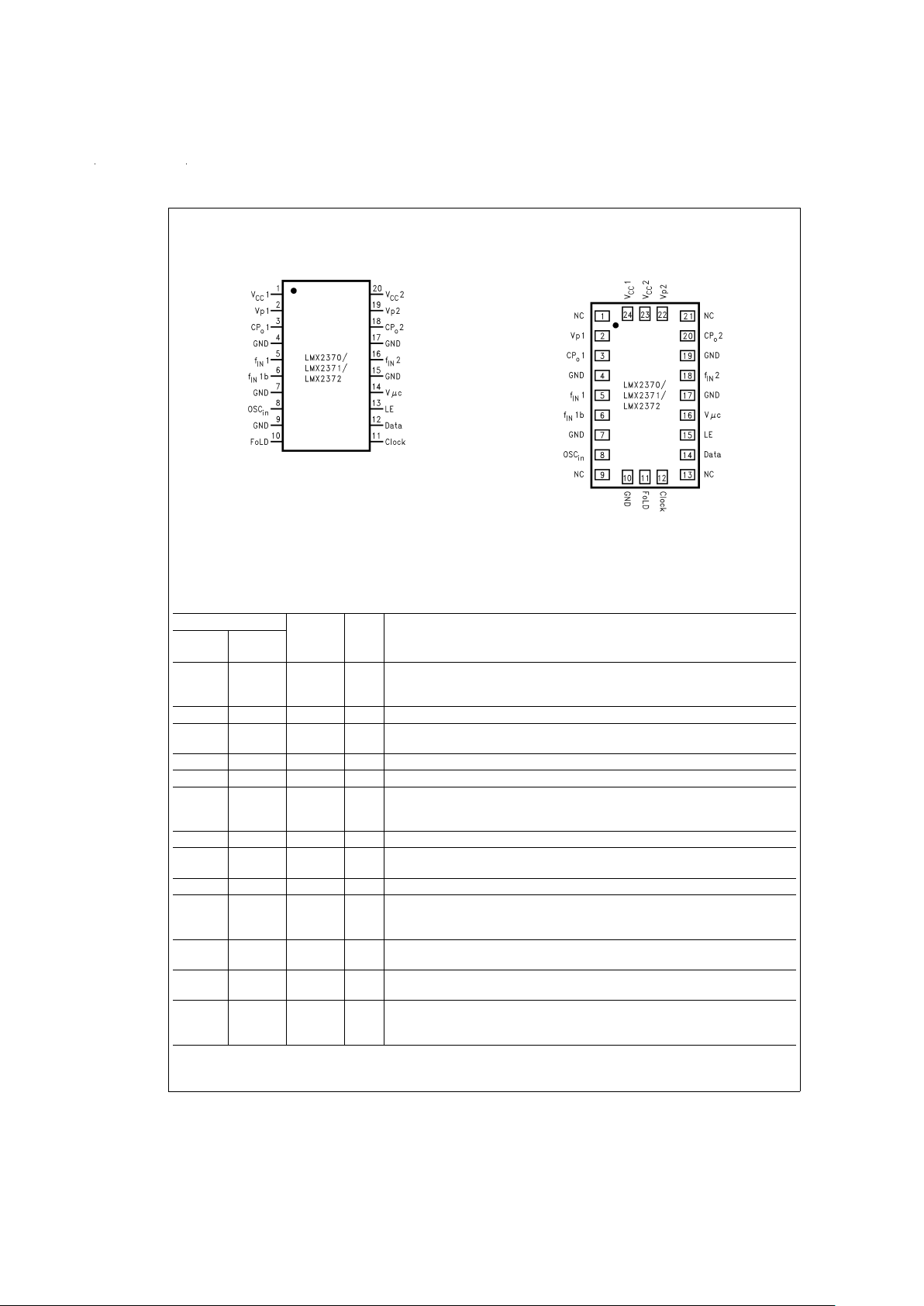
Connection Diagrams
Pin Descriptions
Pin No.
Pin
Name
I/O Description
24-Pin
CSP
20-Pin
TSSOP
24 1 V
CC
1 — Power supply voltage input for RF analog and RF digital circuits. Input may range
from 2.7V to 5.5V. V
CC
1 must equal VCC2. Bypass capacitors should be placed as
close as possible to this pin and be connected directly to the ground plane.
2 2 Vp1 — Power supply for Main charge pump. Must be ≥ V
CC
.
33CP
o
1 O Internal Main charge pump output. For connection to a loop filter for driving the
input of an external VCO.
4 4 GND — Ground for Main digital circuitry.
55f
IN
1 I Main prescaler input. Small signal input from the VCO.
66f
IN
1b I Main prescaler complementary input. For single ended operation, a bypass
capacitor should be placed as close as possible to this pin and be connected
directly to the ground plane.
7 7 GND — Ground for Main analog circuitry.
8 8 OSC
in
I Oscillator input. The input has a VCC/2 input threshold and can be driven from an
external CMOS or TTL logic gate.
10 9 GND — Ground for Aux digital, MICROWIRE, FoLD, and oscillator circuits.
11 10 Fo/LD O Multiplexed output of the Main/Aux programmable or reference dividers,
Main/Auxiliary lock detect signals and Fastlock mode. CMOS output
(see
Programmable Modes in the Datasheet).
12 11 Clock I High impedance CMOS Clock input. Data for the various counters is clocked in on
the rising edge, into the 22-bit shift register.
14 12 Data I Binary serial data input. Data entered MSB first. The last two bits are the control
bits. High impedance CMOS input.
15 13 LE I Load enable. High impedance CMOS input. When LE goes HIGH, data stored in
the shift registers is loaded into one of the 4 appropriate latches (control bit
dependent).
TSSOP 20-Pin Package
DS101026-2
Top View
Order Number LMX2370TM, LMX2370TMX,
LMX2371TM, LMX2371TMX,
LMX2372TM or LMX2372TMX
See NS Package Number MTC20
CSP 24-Pin Package
DS101026-3
Top View
Order Number LMX2370SLBX,
LMX2371SLBX or LMX2372SLBX
See NS Package Number SLB24A
www.national.com 2
Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pin No.
Pin
Name
I/O Description
24-Pin
CSP
20-Pin
TSSOP
16 14 Vµc — Power supply for MICROWIRE circuitry. Must be ≤ V
CC
. Typically connected to
same supply level as µprocessor or baseband controller to enable programming at
low voltages.
17 15 GND — Ground for Aux analog circuitry.
18 16 f
IN
2 I Auxiliary prescaler input. Small signal input from the VCO.
19 17 GND — Ground for Aux digital, MICROWIRE, FoLD, and oscillator.
20 18 CP
o
2 O Aux internal charge pump output. For connection to a loop filter for driving the
input of an external VCO.
22 19 Vp2 — Power supply for Aux charge pump. Must be ≥ V
CC
.
23 20 V
CC
2 — Power supply voltage input for Aux analog, Aux digital, FoLD, and oscillator
circuits. Input may range from 2.7V to 5.5V. V
CC
2 must equal VCC1. Bypass
capacitors should be placed as close as possible to this pin and be connected
directly to the ground plane.
1, 9,
13, 21
— NC — No Connect
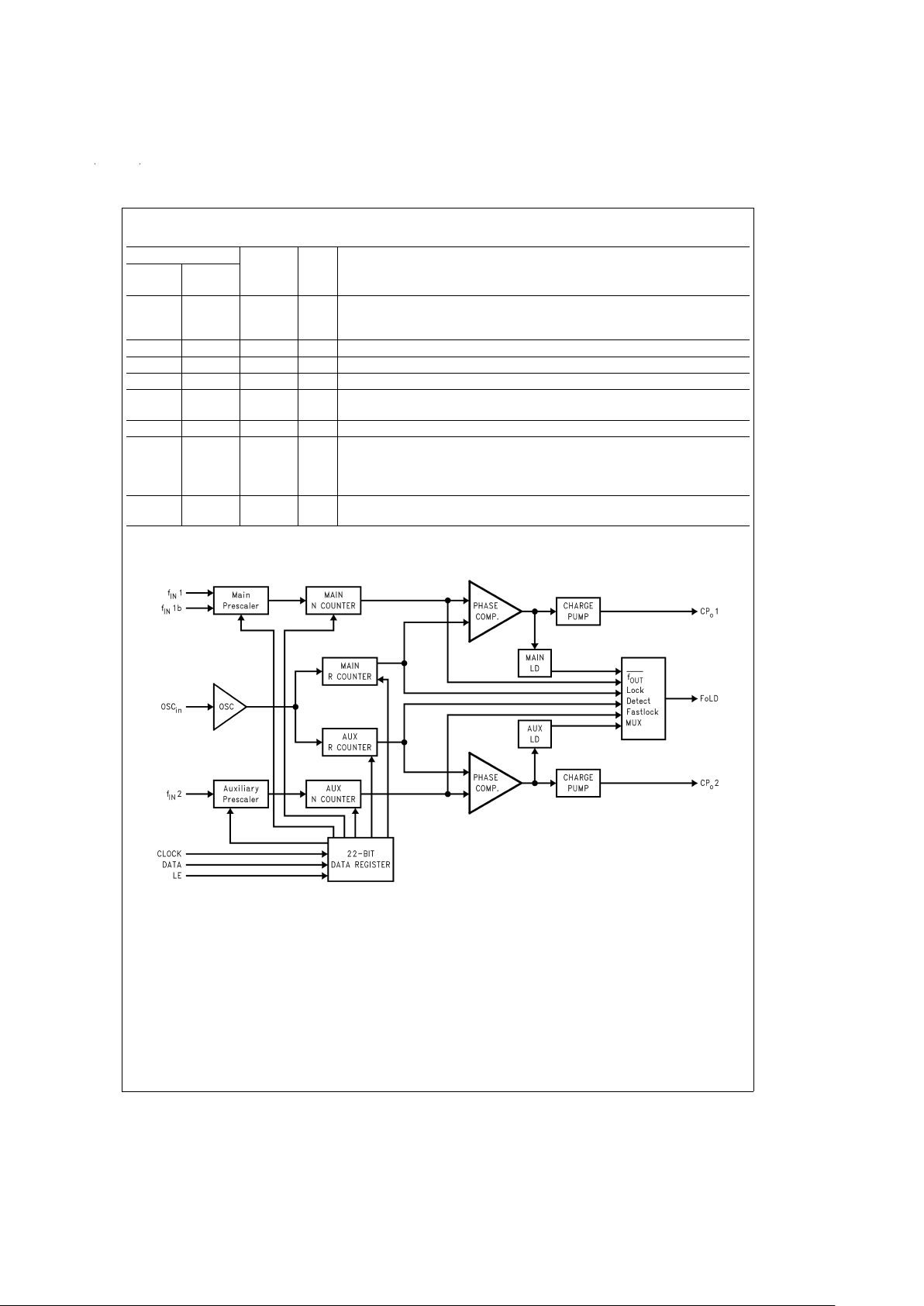
Block Diagram
DS101026-4
www.national.com3
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes 1, 2)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Power Supply Voltage
V
CC
1 −0.3V to 6.5V
V
CC
2 −0.3V to 6.5V
Vp1 −0.3V to 6.5V
Vp2 −0.3V to 6.5V
Vµc −0.3V to 6.5V
Voltage on any pin with
GND=0V (V
I
) −0.3V to VCC+0.3V
Storage Temperature Range (T
S
) −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature (solder, 4 sec.) (T
L
) +260˚C
ESD - Human Body Model (Note 2) TBD
Recommended Operating
Conditions
(Note 3)
Power Supply Voltage
V
CC
1 2.7V to 5.5V
V
CC
2 2.7V to 5.5V
V
CC
1–VCC2 −0.2V to 0.2V
Vp1 V
CC
to 5.5V
Vp2 V
CC
to 5.5V
Vµc 1.72V to V
CC
Operating Temperature (TA) −40˚C to +85˚C
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to
the device may occur.Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is intended to be functional, but do not guarantee specific performance
limits. For guaranteed specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical
Characteristics. The guaranteed specifications apply only for the test conditions listed.
Note 2: This device is a high performance RF integrated circuit and is ESD
sensitive. Handling and assembly of this device should only be done at ESD
free workstations.
Note 3: V
CC
is defined as V
CC
=
V
CC
1=VCC2.
Electrical Characteristics (V
CC
=Vp=
Vµc=3.0V; −40˚C
<
T
A
<
85˚C except as specified).
GENERAL Value
Unit
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max
I
CC
Power Supply
Current
LMX2370 Main=On, Aux=On 6 8.5 mA
LMX2371 Main=On, Aux=On 5 7.5 mA
LMX2372 Main=On, Aux=On 4 6.0 mA
LMX2370
/71/72
Aux Only
2 3.25 mA
I
CC-PWDN
Power Down Current EN_Main, EN_Aux=01550µA
f
IN
1 Main PLL
Operating
Frequency
LMX2370 P=32/33 1.2 2.5 GHz
P = 16/17 45 1200 MHz
LMX2371 P = 32/33 1.2 2.0 GHz
P = 16/17 45 1200 MHz
LMX2372 P = 16/17 45 1200 MHz
P = 8/9 45 550 MHz
f
IN
2 Auxiliary PLL Operating
Frequency
P = 16/17 45 1200 MHz
P = 8/9 45 550 MHz
Zf
IN
Main Main PLL Input Impedance RF On, f
IN
=
1800 MHz TBD Ω
RF Off, f
IN
=
1800 MHz TBD Ω
Zf
IN
Aux Aux Input Impedance f
IN
=
120 MHz TBD Ω
fφ Phase Detector Frequency 10 MHz
Pf
IN
1, PfIN2 RF Input Sensitivity 2.7 ≤ VCC≤ 3.6V −15 0 dBm
3.6 ≤ V
CC
≤ 5.5V −10 0 dBm
OSCILLATOR INPUT Value
Unit
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max
OSC
in
Reference Oscillator Input
Operating Frequency
2 50 MHz
Z
IN
OSC OSC Input Impedance OSC On, Freq = 10 MHz TBD kΩ
OSC Off, Freq = 10 MHz TBD kΩ
V
OSC
Oscillator Input Sensitivity OSC
in
0.5 V
CC
V
PP
I
IH
OSCinInput Current VIH=VCC= 5.5V 100 µA
I
IL
OSCinInput Current VIL=0,VCC= 5.5V −100 µA
www.national.com 4

Electrical Characteristics (V
CC
=Vp=
Vµc=3.0V; −40˚C
<
T
A
<
85˚C except as specified). (Continued)
CHARGE PUMP Value
Unit
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max
ICP
o-source
Main and Auxiliary Charge
Pump Output Current (Note 4)
VCP
o
=
Vp/2, ICP
o
_4X=0 1.0 mA
ICP
o-sink
VCP
o
=
Vp/2, ICP
o
_4X=0 −1.0 mA
ICP
o-source
VCP
o
=
Vp/2, ICP
o
_4X=1 4.0 mA
ICP
o-sink
VCP
o
=
Vp/2, ICP
o
_4X=1 −4.0 mA
ICP
o-TRI
Charge Pump TRI-STATE
®
Current
0.5 ≤ VCP
o
≤ Vp − 0.5,
−40˚C
<
T
A
<
85˚C
−2.5 0.1 2.5 nA
ICP
o-sink
vs
ICP
o-source
CP Sink vs Source Mismatch VCP
o
=
Vp/2, T
A
=
25˚C
310
%
ICP
o
vs
VCP
o
CP Current vs Voltage 0.5 ≤ VCPo≤ Vp − 0.5, T
A
=
25˚C
815
%
ICP
o
vs TACP Current vs Temperature VCP
o
=
Vp/2, −40˚C
<
T
A
<
85˚C 8
%
DIGITAL INTERFACE (DATA, CLOCK, LE) Value
Unit
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max
V
IH
High-Level Input Voltage Vµc=1.72V to 5.5V 0.8 Vµc V
V
IL
Low-Level Input Voltage Vµc=1.72V to 5.5V 0.2 Vµc V
I
IH
High-Level Input Current V
IH
=
Vµc=5.5V −1.0 1.0 µA
I
IL
Low-Level Input Current V
IL
=
0, Vµc=5.5V −1.0 1.0 µA
V
OL
Low-Level Output Current I
OL
=
1.0 mA, V
EXT
=
1.8V (Note
5)
0.1 0.4 V
MICROWIRE TIMING Value
Unit
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max
t
CS
Data to Clock Setup Time See Data Input Timing 50 ns
t
CH
Data to Clock Hold Time See Data Input Timing 20 ns
t
CWH
Clock Pulse Width High See Data Input Timing 50 ns
t
CWL
Clock Pulse Width Low See Data Input Timing 50 ns
t
ES
Clock to Load Enable Setup
Time
See Data Input Timing
50 ns
t
EW
Load Enable Pulse Width See Data Input Timing 50 ns
Note 4: Main and Auxiliary Charge Pump magnitude are controlled by Main_ICPo_4X and Aux_ICPo_4X bits respectively.
Note 5: Lock Detect open drain output only pulled up to V
EXT
. Typically V
EXT
=
V
CC
.
1.0 Functional Description
The basic phase-lock-loop (PLL) configuration consists of a high-stability crystal reference oscillator, a frequency synthesizer
such as the National Semiconductor LMX2370/2371/2372, a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), and a passive loop filter.The frequency synthesizer includes a phase detector, a current mode charge pump, as well as programmable reference [R] and feedback [N] frequency dividers. The VCO frequency is established by dividing the crystal reference signal down via the R-counter to
obtain a comparison reference frequency. This reference signal (
f
R
) is then presented to the input of a phase/frequency detector
and compared with the feedback signal (
f
N
), which is obtained by dividing the VCO frequency down by way of the N-counter.The
phase/frequency detector’s current source output pumps charge into the loop filter, which then integrates into the VCO’s control
voltage. The function of the phase/frequency comparator is to adjust the control voltage presented to the VCO until the feedback
signal frequency and phase match that of the reference signal. When this “Phase-Locked” condition exists, the VCO frequency
will be N times that of the comparison frequency, where N is the integer divide ratio.
1.1 REFERENCE OSCILLATOR INPUT
The reference oscillator frequency for the Main and Auxiliary PLLs is provided from the external reference through the OSC
in
pin.
OSC
in
can operate up to 50 MHz with input sensitivity of 0.5 VPP. The OSCinpin drives both the Main R-counter and the Auxiliary
R-counter.The input has a V
CC
/2 input threshold that can be driven from an external CMOS or TTL logic gate. Typically,the OSC
in
is connected to the output of a crystal oscillator.
1.2 REFERENCE DIVIDERS (R-COUNTERS)
The Main and Auxiliary R-counters are both clocked through the oscillator block in common. The maximum frequency is 50 MHz.
Both R-counters are CMOS design and 15-bit in length with programmable divider ratio from 2 to 32,767.
www.national.com5
 Loading...
Loading...