NSC LMC1992N, LMC1992CCV, LMC1992CCN Datasheet
TL/H/10789
LMC1992 Digitally-Controlled Stereo Tone and
Volume Circuit with Four-Channel Input Selector
December 1994
LMC1992 Digitally-Controlled Stereo Tone and Volume
Circuit with Four-Channel Input-Selector
General Description
The LMC1992 is a monolithic integrated circuit that provides
four stereo inputs, bass and treble tone controls, and volume, balance, and front-rear fader controls. These functions
are digitally controlled through a three-wire communication
interface. All of the LMC1992s functions are achieved with
only three external capacitors per channel. It is designed for
line level input signals (300 mV
b
2V) and has a maximum
gain of 0 dB.
The internal design is optimized for external capacitors having values of 0.1 mF or less. This allows the use of chip
capacitors for coupling and tone control functions.
Low noise and distortion result from using analog switches
and thin-film silicon-chromium resistor networks in the signal path.
Volume and fader are at minimum and tone controls are flat
when supply voltage is first applied.
Additional tone control can be achieved using the LMC835
stereo 7-band graphic equalizer connected to the
LMC1992’s select-out/select-in external processor loop.
Features
Y
Low noise and distortion
Y
Four stereo inputs
Y
40 volume levels including mute
Y
20 fader levels
Y
All attenuators havea2dBofattenuation per step
Y
Front/back fade control
Y
External processor loop
Y
Only three external components per channel
Y
Serial programmable: standard MICROWIRE
TM
interface
Y
Single supply operation: 6V to 12V supply voltage
Y
Protection address (similar to DS8906)
Y
DC-coupled inputs
Y
Single supply operation
Applications
Y
Automotive audio systems
Y
Sound reinforcement systems
Y
Home entertainmentÐstereo television and music reproduction systems
Y
Electronic music (MIDI)
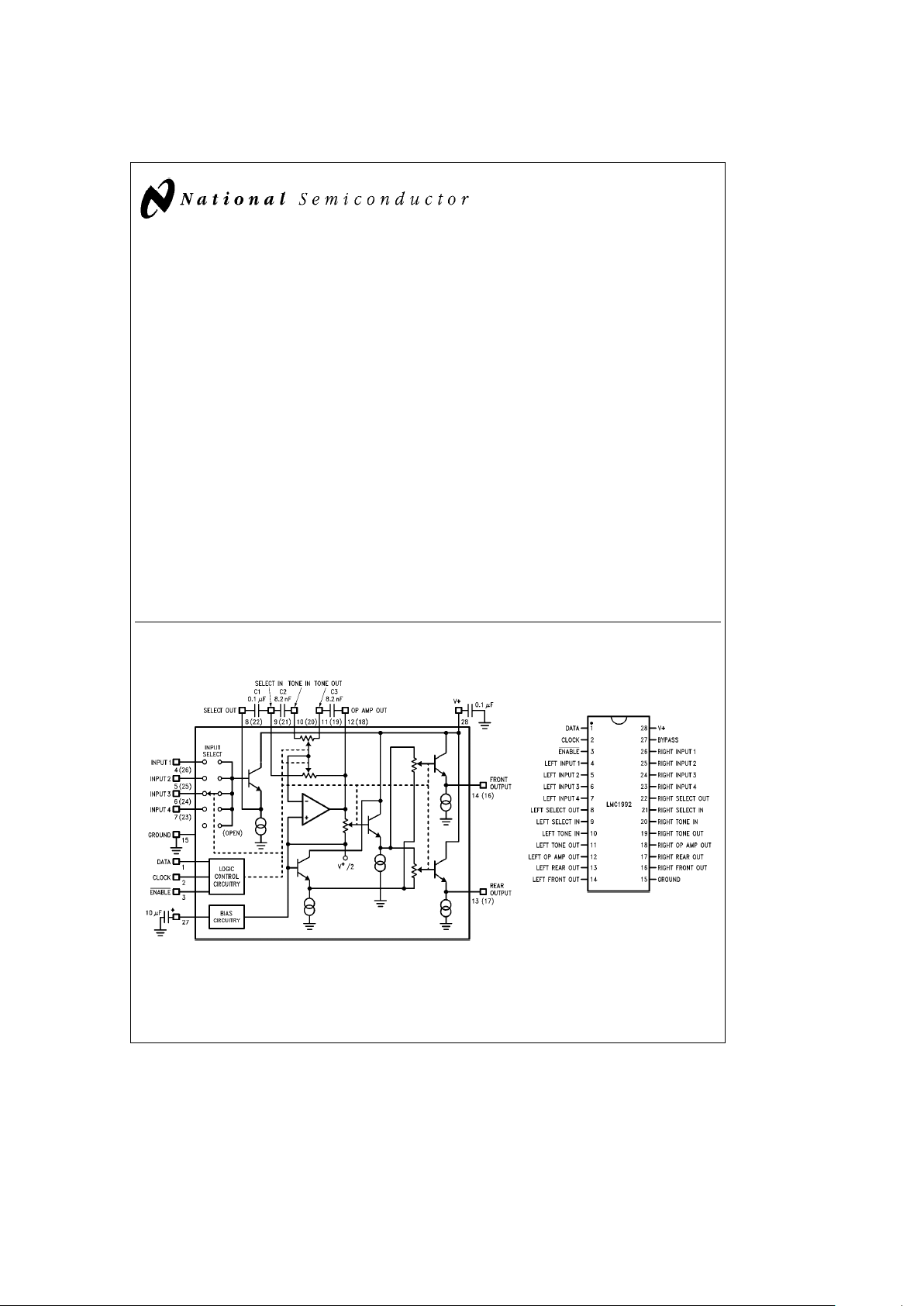
Block and Connection Diagrams
TL/H/10789– 1
Left channel shown. Pin numbers in parentheses are for the right channel.
TL/H/10789– 2
Order Number LMC1992CCN
See NS Package Number N28B
DNRÉis a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
COPS
TM
and MICROWIRETMare trademarks of National Semiconductor Corporation.
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M75/Printed in U. S. A.
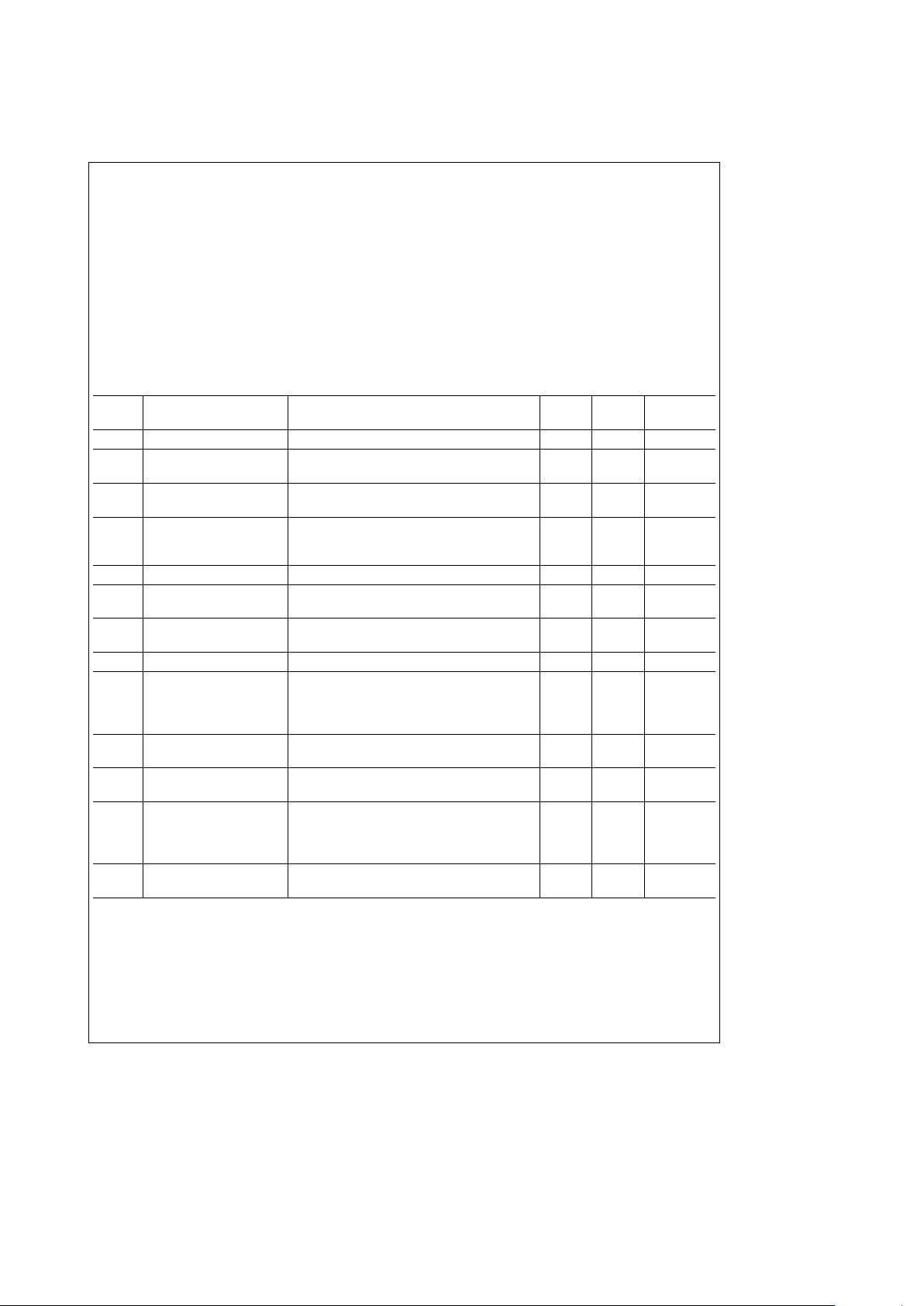
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes 1 and 2)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
a
b
GND) 15V
Voltage at Any Pin GNDb0.2V to V
a
a
0.2V
Input Current at Any Pin (Note 3) 5 mA
Package Input Current (Note 3) 20 mA
Power Dissipation (Note 4) 500 mW
Junction Temperature 125
§
C
Storage Temperature
b
65§Ctoa150§C
Lead Temperature
N Package, Soldering, 10 sec.
a
260§C
ESD Susceptibility (Note 5) 2000V
Pins 9, 10, 11, 19, 20, 21 850V
Operating Ratings (Notes 1 and 2)
Temperature Range T
MIN
s
T
A
s
T
MAX
LMC1992CCN 0§CsT
A
s
70§C
Supply Voltage Range (V
a
b
Vb) 6Vto12V
Electrical Characteristics The following specifications apply for V
a
e
8V, f
IN
e
1 kHz, input signal applied to
channel 1, volume
e
0 dB, basse0 dB, treblee0 dB, and faderse0 dB unless otherwise specified. All limits T
A
e
T
J
e
25§C.
Symbol Parameter Conditions
Typical Limit Units
(Note 6) (Note 7) (Limit)
I
S
Supply Current 27.0 mA (max)
V
IN
Input Voltage Clipping Level (1.0% THD),
2.3 2.0 V
rms
(min)
Select Out (Pins 8, 22)
V
OUT
Output Voltage Clipping Level (1.0% THD),
1.2 0.65 V
rms
(min)
Outputs (Pins 13, 14, 16, 17)
THD Total Harmonic Distortion All Four Channels
Volume Attenuator at 0 dB, Input Level 0.3 V
rms
0.15 0.3 % (max)
Volume Attenuator at
b
20 dB, Input Level 0.6 V
rms
0.03 0.1 % (max)
E
nOUT
Output Noise All Four Channels CCIR/ARM Filter, R
S
e
0X 6.5 30.0 mV
rms
(max)
E
nOUT
Output Noise All Four Channels CCIR/ARM Filter, R
S
e
0X
5.0 20.0 mV
rms
(max)
Volume Attenuatoreb80 dB
R
OUT
DC Output Impedance Pins 8, 22 100 150 X (max)
Pins 13, 14, 16, 17 80 120 X (max)
R
IN
DC Input Impedance Pins 4, 5, 6, 7, 23, 24, 25, 26 2 MX
Volume Attenuator Range Pins 16, 17; Volume Attenuation at
0101110100X (0 dB); (Absolute Gain)
b
1.0
b
1.5 dB (max)
01011000000 (80 dB); (Relative to Attenuation at
80.0 75.0 dB (min)
the 0 dB setting)
Volume Step Size All Volume Attenuation Settings from 01011001010 2.0 0.7 dB (min)
(60 dB) to 0101110100X (0 dB) (Note 9) 4.3 dB (max)
Channel-to-Channel Volume Fader Attenuation from 1XXX000000
g
0.5
g
1.0 dB (max)
Tracking Error (40 dB) to 1XXX1010X (0 dB)
Fader Attenuation Range Pins 16, 17; Fader Attenuation at
011XXX1010X (0 dB); (Absolute Gain)b1.0
b
1.5 dB (max)
011XXX00000 (40 dB); (Relative to Attenuation at
40 38.0 dB (min)
the 0 dB setting)
Fader Step Size All Fader Attenuation Settings from 011XXX00000 2.0 1.0 dB (min)
(40 dB) to 011XXX1010X (0 dB) (Note 10) 4.5 dB (max)
2
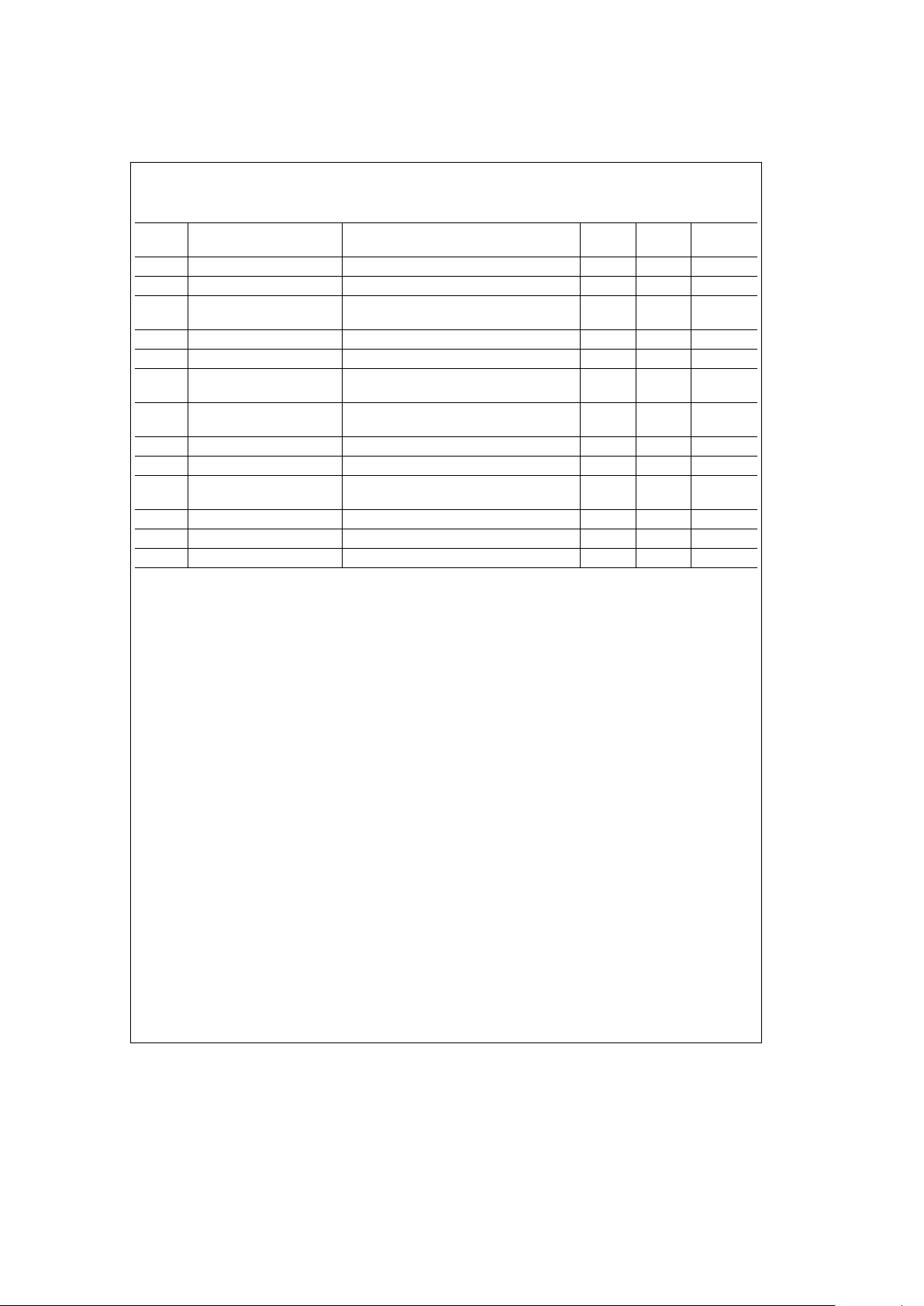
Electrical Characteristics The following specifications apply for V
a
e
8V, f
IN
e
1 kHz, input signal applied to
channel 1, volume
e
0 dB, basse0 dB, treblee0 dB, and faderse0 dB unless otherwise specified. All limits T
A
e
T
J
e
25§C. (Continued)
Symbol Parameter Conditions
Typical Limit Units
(Note 6) (Note 7) (Limit)
Bass Gain Range f
IN
e
100 Hz, Pins 14, 16
g
12
g
10.0 dB (min)
Bass Tracking Error f
IN
e
100 Hz, Pins 14, 16
g
0.1
g
1.0 dB (max)
Bass Step Size f
IN
e
100 Hz, Pins 14, 16 2.0 1.0 dB (min)
(Relative to Previous Level) 3.0 dB (max)
Treble Gain Range f
IN
e
10 kHz, Pins 14, 16
g
12
g
10.0 dB (min)
Treble Tracking Error f
IN
e
10 kHz, Pins 14, 16
g
0.1
g
1.0 dB (max)
Treble Step Size f
IN
e
10 kHz, Pins 14, 16 2.0 1.0 dB (min)
(Relative to Previous Level) 3.0 dB (max)
Frequency Response
b
3 dB 450 kHz
b
0.3 dB (Relative to Signal Amplitude at 1 kHz) 20 kHz (min)
Channel Separation V
IN
e
1.0 V
rms
97 70 dB (min)
Input-Input Isolation V
IN
e
1.0 V
rms
(Note 8) 90 70 dB (min)
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio V
a
e
8VDC; 100 mV
P-P
,
40 31 dB (min)
100 Hz Sinewave Applied to Pin 28
f
CLK
Clock Frequency 1.0 0.5 MHz (max)
V
IN(1)
Logic ‘‘1’’ Input Voltage 1.3 2.0 V (min)
V
IN(0)
Logic ‘‘0’’ Input Voltage 0.4 0.8 V (max)
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is
functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The guaranteed
specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics may degrade when the device is not operated under the listed test
conditions.
Note 2: All voltages are specified with respect to ground.
Note 3: When the input voltage (V
IN
) at any pin exceeds the power supply voltages (V
IN
k
Vbor V
IN
l
Va) the absolute value of the current at that pin should be
limited to 5 mA or less. The 20 mA package input current limits the number of pins that can exceed the power supply voltages with 5 mA current limit to four.
Note 4: The maximum power dissipation must be de-rated at elevated temperatures and is dictated by T
JMAX
, wJA, and the ambient temperature TA. The maximum
allowable power dissipation is PD
e
(T
JMAX
b
TA)/iJAor the number given in the Absolute Maximum Ratings, whichever is lower. For the LMC1992CCN, T
JMAX
e
125§C, and the typical junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, when board mounted, is 67§C/W.
Note 5: Human body model; 100 pF discharged through a 1.5 kX resistor.
Note 6: Typicals are at T
J
e
25§C and represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 7: Limits are guaranteed to National’s AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
Note 8: The Input-Input Isolation is tested by driving one input and measuring the front outputs when the undriven inputs are selected.
Note 9: The Volume Step Size is defined as the change in attenuation between any two adjacent volume attenuation settings. The nominal Volume Step Size is
2 dB.
Note 10: The Fader Step Size is defined as the change in attenuation between any two adjacent fader attenuation settings. The nominal Volume Step Size is 2 dB.
3
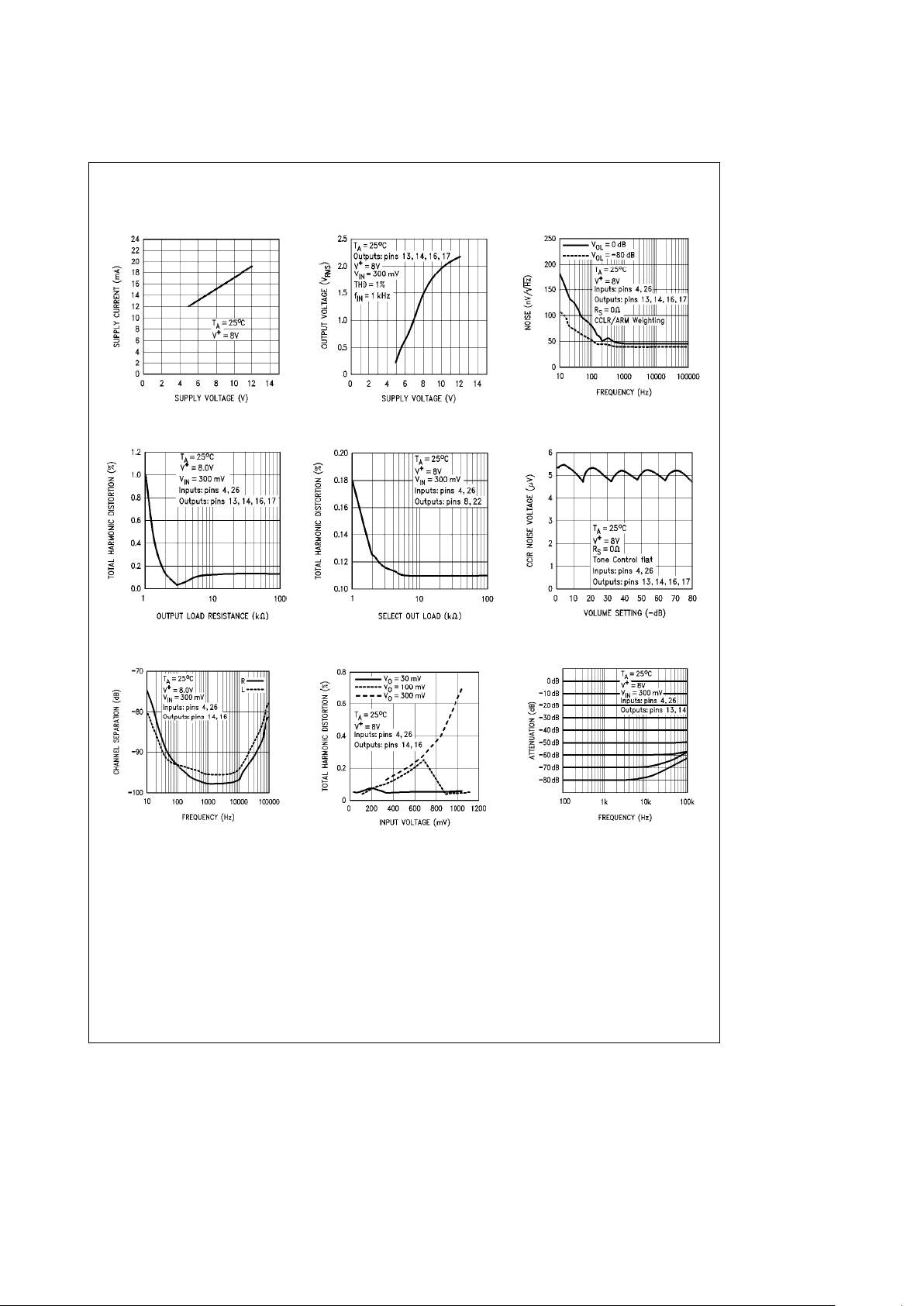
Typical Performance Characteristics
Supply Voltage
Quiescent Current vs
Supply Voltage
Maximum Output Swing vs
vs Frequency
Output Noise Voltage
TL/H/10789– 3 TL/H/10789– 4
TL/H/10789– 5
vs Output AC Load
Total Harmonic Distortion
vs Select Out AC Load
Total Harmonic Distortion
vs Volume Setting
CCIR Output Noise Voltage
TL/H/10789– 6 TL/H/10789– 7
TL/H/10789– 8
vs Frequency
Channel Separation
vs Input Voltage
Total Harmonic Distortion
Attenuation vs Frequency
TL/H/10789– 9
TL/H/10789– 10
TL/H/10789– 11
4
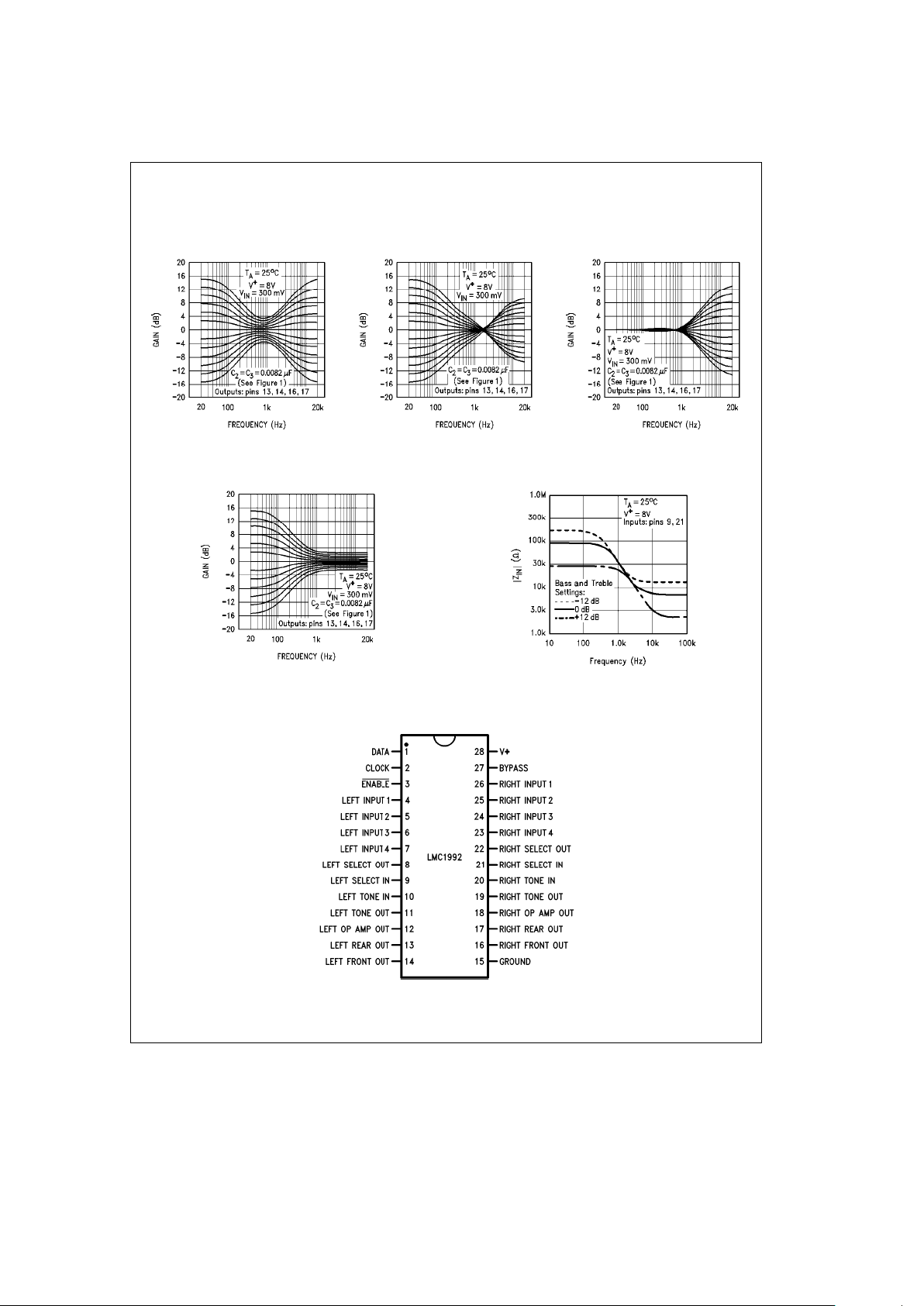
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Treble Control Settings
with Equal Bass and
Tone Control Response
Treble Control Settings
with Reciprocal Bass and
Tone Control Response
Response
Treble Tone Control
TL/H/10789– 12 TL/H/10789– 13 TL/H/10789– 14
Response
Bass Tone Control
vs Frequency
Select In Impedance
TL/H/10789– 15
TL/H/10789– 16
Connection Diagram
TL/H/10789– 17
5
 Loading...
Loading...