NSC DS96176CN Datasheet
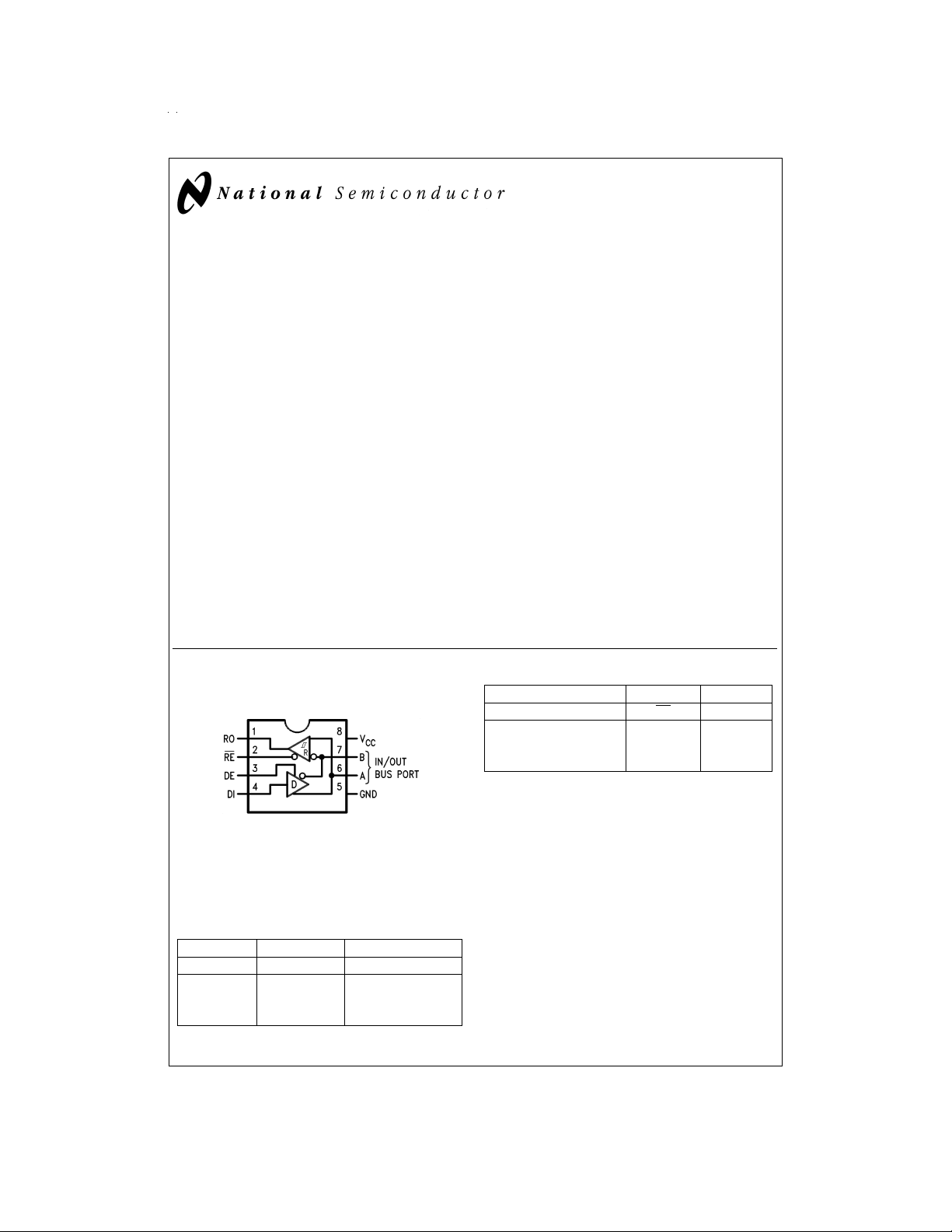
DS96176
RS-485/RS-422 Differential Bus Transceiver
General Description
The DS96176 Differential Bus Transceiverisamonolithicintegrated circuit designed for bidirectional data communication on balanced multipoint bus transmission lines. The
transceiver meets EIA Standard RS-485 as well as
RS-422A.
The DS96176combinesa TRI-STATE
and a differential input line receiver, both of which operate
from a single 5.0V power supply. The driver and receiver
have an active Enable that can be externally connected to
function as a direction control. The driver differential outputs
and the receiver differential inputs are internally connected
to form differential input/output (I/O) bus ports that are designed to offer minimum loading to the bus whenever the
driver is disabled or when V
wide positive and negative common mode voltage ranges,
making the device suitable for multipoint applications in
noisy environments.
The driver is designed to handle loads up to 60 mAof sink or
source current. The driver features positive and negative
current-limiting and thermal shutdown for protection from line
fault conditions. Thermal shutdown is designed to occur at
junction temperature of approximately 160˚C. The receiver
features a typical input impedance of 15 kΩ, an input sensi-
±
tivity of
200 mV, and a typical input hysteresis of 50 mV.
®
differential line driver
=
0V. These ports feature
CC
The DS96176 can be used in transmission line applications
employing the DS96172 and the DS96174 quad differential
line drivers and the DS96173 and DS96175 quad differential
line receivers.
Features
n Bidirectional transceiver
n Meets EIA Standard RS-422A and RS-485
n Designed for multipoint transmission
n TRI-STATE driver and receiver enables
n Individual driver and receiver enables
n Wide positive and negative input/output bus voltage
ranges
n Driver output capability
n Thermal shutdown protection
n Driver positive and Negative current-limiting
n High impedance receiver input
n Receiver input sensitivity of
n Receiver input hysteresis of 50 mV typical
n Operates from single 5.0V supply
n Low power requirements
±
60 mA Maximum
±
200 mV
DS96176 RS-485/RS-422 Differential Bus Transceiver
May 1998
Connection Diagram
8–Lead DIP
DS009630-1
Top View
Order Number DS96176CN
See NS Package Number N08E
Receiver
Differential Inputs Enable Output
A-B RE
V
≥ 0.2V L H
ID
V
≤ −0.2V L L
ID
XHZ
=
H
High Level
L=Low Level
X=Immaterial
Z=High Impedance (off)
R
Function Table
Driver
Input Enable Outputs
DI DE A B
HHHL
LHLH
XLZZ
TRI-STATE®is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
© 1998 National Semiconductor Corporation DS009630 www.national.com

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 2)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Storage Temperature Range
Molded DIP −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature
Molded DIP (soldering, 10
sec.) 265˚C
Maximum Power Dissipation (Note 1) at 25˚C
Molded Package 930 mW
Supply Voltage 7.0V
Differential Input Voltage +15V/−10V
Enable Input Voltage 5.5V
Recommended Operating
Conditions
Supply Voltage (V
) 4.75 5.0 5.25 V
CC
Voltage at Any Bus Terminal
(Separately or Common Mode) −7.0 12 V
Differential Input Voltage (V
Output Current HIGH (I
)
OH
Driver −60 mA
Receiver −400 µA
Output Current LOW (I
)
OL
Driver 60 mA
Receiver 16 mA
Operating Temperature (T
Note 1: Derate molded DIP package 7.5 mW/˚C above 25˚C.
) 0 25 70 ˚C
A
Min Typ Max Units
)
ID
±
12 V
Electrical Characteristics (Notes 3, 4)
Over recommended temperature, common mode input voltage, and supply voltage ranges, unless otherwise specified
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
DRIVER SECTION
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
V
IC
|V
| Differential Output Voltage I
OD1
|V
| Differential Output Voltage R
OD2
∆|V
OD2
V
OC
∆|V
| Change in Magnitude of
OC
I
O
I
IH
I
IL
I
OS
I
CC
RECEIVER SECTION
V
TH
V
TL
V
T+−VT−
V
IH
V
IL
V
IC
Input Voltage HIGH 2.0 V
Input Voltage LOW 0.8 V
Output Voltage HIGH I
Output Voltage LOW I
Input Clamp Voltage I
| Change in Magnitude of R
Differential Output Voltage (Note 5) V
Common Mode Output Voltage (Note 6) R
=
−20 mA 3.1 V
OH
=
20 mA 0.85 V
OL
=
−18 mA −1.5 V
I
=
0 mA 6.0 V
O
=
L
=
R
L
=
L
=
CM
=
R
L
=
L
Figure 1
100Ω,
Figure 1
54Ω,
54Ω
Figure 1
0V
Figure 1
100Ω
54Ω or 100Ω,
and
Figure 2
and
Figure 2
Figure 1
2.0 2.25 V
1.5 2.0
Common Mode Output Voltage (Note 5)
Output Current (Note 5) Output Disabled V
(Includes Receiver I
Input Current HIGH V
Input Current LOW V
Short Circuit Output Current V
(Note 10) V
)V
I
=
2.4V 20 µA
I
=
0.4V −100 µA
I
=
−7.0V −250
O
=
0V −150 mA
O
=
V
V
O
CC
=
V
12V 250
O
=
12V 1.0 mA
O
=
−7.0V −0.8
O
Supply Current No Load Outputs Enabled 35 mA
Outputs Disabled 40
Differential Input High V
=
O
2.7V, I
=
−0.4 mA 0.2 V
O
Threshold Voltage
Differential Input Low V
=
O
0.5V, I
=
8.0 mA −0.2 V
O
Threshold Voltage (Note 7)
Hysteresis (Note 8) V
=
0V 50 mV
CM
Enable Input Voltage HIGH 2.0 V
Enable Input Voltage LOW 0.8 V
Enable Input Clamp Voltage I
=
−18 mA −1.5 V
I
±
0.2 V
3.0 V
±
0.2 V
150
www.national.com 2
Electrical Characteristics (Notes 3, 4) (Continued)
Over recommended temperature, common mode input voltage, and supply voltage ranges, unless otherwise specified
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
RECEIVER SECTION
V
OH
Output Voltage HIGH V
ID
=
200 mV, I
=
−400 µA, 2.7 V
OH
Figure 3
V
OL
Output Voltage LOW V
=
−200 mV, I
ID
Figure 3
I
OZ
I
I
I
IH
I
IL
R
I
I
OS
I
CC
High Impedance State Output V
Line Input Current (Note 9) Other Input
Enable Input Current HIGH V
Enable Input Current LOW V
Input Resistance 12 kΩ
Short Circuit Output Current (Note 10) −15 −85 mA
Supply Current (Total Package) No Load Outputs Enabled 40 mA
=
0.45V to 2.4V
O
=
0V
=
2.7V 20 µA
IH
=
0.4V −100 µA
IL
=
8,0 mA 0.45 V
OL
=
I
16 mA 0.50
OL
=
V
12V 1.0
I
=
V
−7.0V 0.8
I
±
20 µA
Outputs Disabled
Driver Switching Characteristics
=
V
CC
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
t
DD
t
TD
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
PZH
t
PZL
t
PHZ
t
PLZ
=
5V, T
25˚C
A
Differential Output Delay Time R
Differential Output Transition Time R
Propagation Delay Time, R
Low-to-High Level Output
Propagation Delay Time, R
High-to-Low Level Output
Output Enable Time to High Level R
Output Enable Time to Low Level R
Output Disable Time from High Level R
Output Disable Time from Low Level R
=
Figure 4
60Ω,
L
=
Figure 4
60Ω,
L
=
Figure 5
27Ω,
L
=
Figure 5
27Ω,
L
=
Figure 6
110Ω,
L
=
Figure 7
110Ω,
L
=
Figure 6
110Ω,
L
=
Figure 7
110Ω,
L
15 25 ns
15 25 ns
12 20 ns
12 20 ns
25 35 ns
25 35 ns
20 25 ns
29 35 ns
mA
Receiver Switching Characteristics
=
V
CC
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
PZH
t
PZL
t
PHZ
t
PLZ
Note 2: “Absolute Maximum Ratings” are those values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. They are not meant to imply that the devices
should be operated at these limits. The tables of “Electrical Characteristics” provide conditions for actual operation.
Note 3: Unless otherwise specified min/max limits apply across the 0˚C to +70˚C range for the DS96176. All typicals are given for V
Note 4: Allcurrents into the device pins are positive; all currents out of the device pins are negative. All voltages are referenced to ground unless otherwise specified.
Note 5: ∆|V
Note 6: In EIA Standards RS-422A and RS-485, V
Note 7: The algebraic convention, where the less positive (more negative) limit is designated minimum, is used in this data sheet for common mode input voltage
and threshold voltage levels only.
Note 8: Hysteresis is the difference between the positive-going input threshold voltage V
=
5.0V, T
25˚C
A
Propagation Delay Time, V
Low-to-High Level Output C
=
0V to 3.0V 16 25 ns
ID
=
L
15 pF,
Figure 8
Propagation Delay Time, 16 25 ns
High-to-Low Level Output
Output Enable Time to High Level C
=
L
15 pF,
Figure 9
15 22 ns
Output Enable Time to Low Level 15 22 ns
Output Disable Time from High Level C
L
=
5.0 pF,
Figure 9
14 30 ns
Output Disable Time from Low Level 24 40 ns
=
5V and T
CC
| and ∆|VOC| are the changes in magnitude of VODand VOC, respectively, that occur when the input is changed from a high level to a low level.
OD
, which is the average of the two output voltages with respect to ground, is called output offset voltage, VOS.
OC
, and the negative-going input threshold voltage, VT−.
T+
=
25˚C.
A
www.national.com3
Receiver Switching Characteristics (Continued)
Note 9: Refer to EIA Standard RS-485 for exact conditions.
Note 10: Only one output at a time should be shorted.
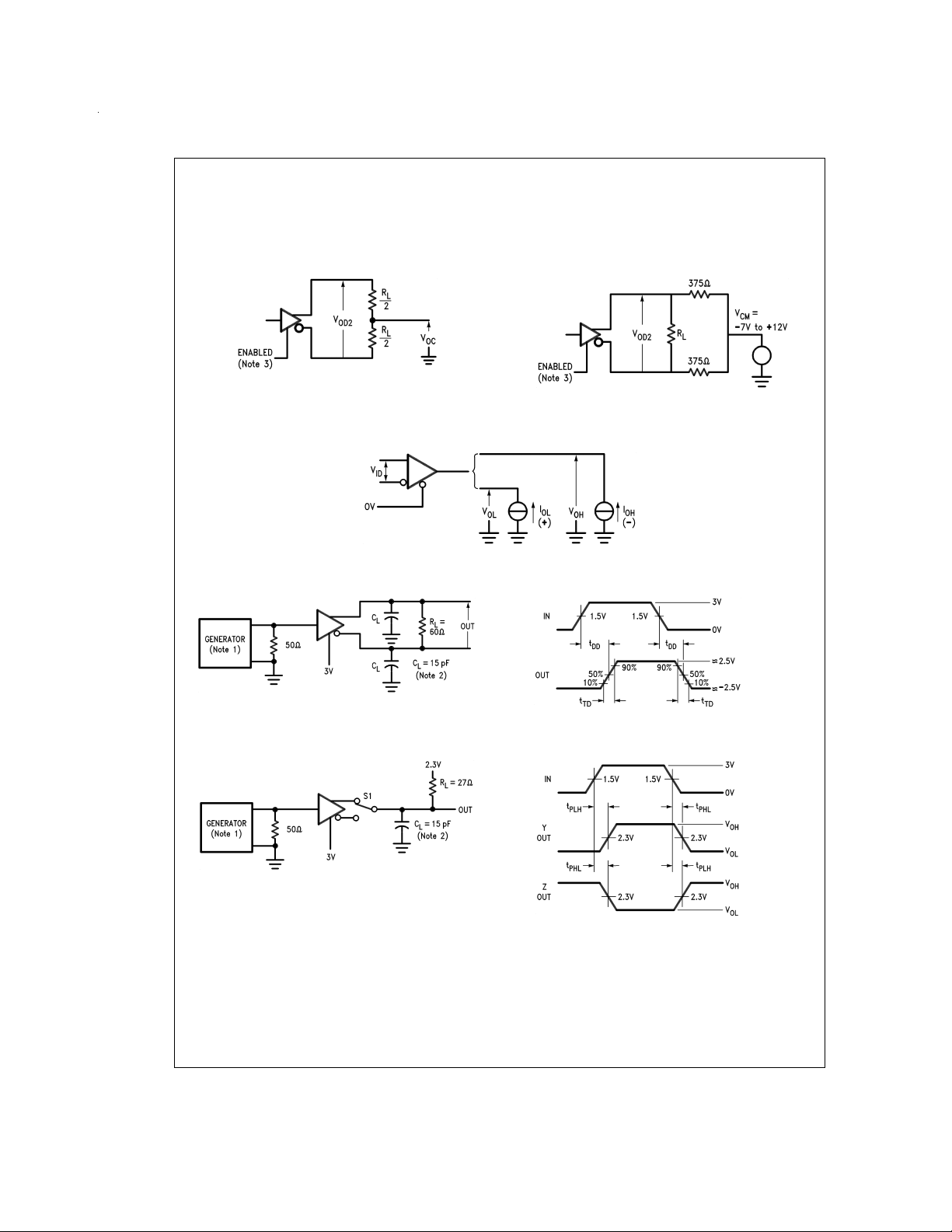
Parameter Measurement Information
DS009630-2
FIGURE 1. Driver VODand V
OC
FIGURE 3. Receiver VOHand V
DS009630-3
FIGURE 2. Driver VODwith Varying
Common Mode Voltage
DS009630-4
OL
DS009630-5
FIGURE 4. Driver Differential Output Delay and Transition Times
DS009630-7
FIGURE 5. Driver Propagation Times
www.national.com 4
DS009630-6
DS009630-8
 Loading...
Loading...