NSC DS90LV048ATMX, DS90LV048ATMTCX, DS90LV048ATMTC, DS90LV048ATM Datasheet
DS90LV048A
3V LVDS Quad CMOS Differential Line Receiver
General Description
The DS90LV048Ais a quad CMOS flow-through differential
line receiver designed for applications requiring ultra low
power dissipation and high data rates. The device is designed to support data rates in excess of 400 Mbps (200
MHz) utilizing Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS)
technology.
The DS90LV048A accepts low voltage (350 mV typical) differential input signals and translates them to 3V CMOS output levels. The receiver supports a TRI-STATE
®
function that
may be used to multiplex outputs. The receiver also supports
open, shorted and terminated (100Ω) input fail-safe. The receiver output will be HIGH for all fail-safe conditions. The
DS90LV048Ahasaflow-through pinout for easy PCB layout.
The EN and EN
*
inputs are ANDed together and control the
TRI-STATE outputs. The enables are common to all four receivers. The DS90LV048Aand companion LVDS line driver
(eg. DS90LV047A) provide a new alternative to high power
PECL/ECL devices for high speed point-to-point interface
applications.
Features
n
>
400 Mbps (200 MHz) switching rates
n Flow-through pinout simplifies PCB layout
n 150 ps channel-to-channel skew (typical)
n 100 ps differential skew (typical)
n 2.7 ns maximum propagation delay
n 3.3V power supply design
n High impedance LVDS inputs on power down
n Low Power design (40mW 3.3V static)
n Interoperable with existing 5V LVDS drivers
n Accepts small swing (350 mV typical) differential signal
levels
n Supports open, short and terminated input fail-safe
n Conforms to ANSI/TIA/EIA-644 Standard
n Industrial temperature operating range (-40˚C to +85˚C)
n Available in SOIC and TSSOP package
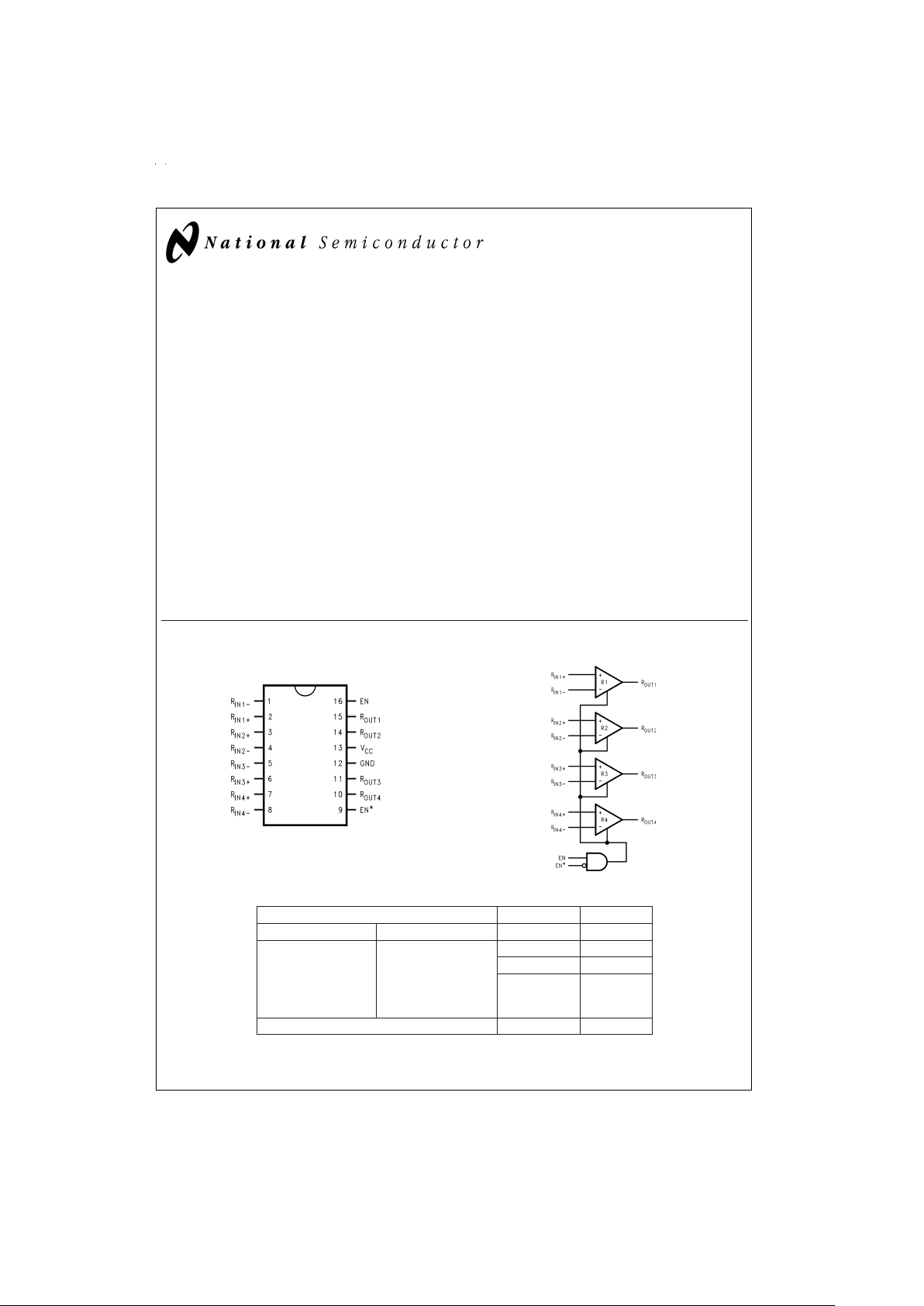
Connection Diagram Functional Diagram
ENABLES INPUTS OUTPUT
EN EN* R
IN+−RIN−
R
OUT
H L or Open VID≥ 0.1V H
V
ID
≤ −0.1V L
Full Fail-safe
OPEN/SHORT
or Terminated
H
All other combinations of ENABLE inputs X Z
TRI-STATE®is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
Dual-in-Line
DS100888-1
Order Number DS90LV048ATM, DS90LV048ATMTC
See NS Package Number M16A, MTC16
DS100888-2
July 1999
DS90LV048A 3V LVDS Quad CMOS Differential Line Receiver
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS100888 www.national.com

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
CC
) −0.3V to +4V
Input Voltage (R
IN+,RIN−
) −0.3V to 3.9V
Enable Input Voltage (EN, EN*) −0.3V to (V
CC
+ 0.3V)
Output Voltage (R
OUT
) −0.3V to (VCC+ 0.3V)
Maximum Package Power Dissipation +25˚C
M Package 1025 mW
MTC Package 866 mW
Derate M Package 8.2 mW/˚C above +25˚C
Derate MTC Package 6.9 mW/˚C above +25˚C
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature Range Soldering
(4 sec.) +260˚C
Maximum Junction Temperature +150˚C
ESD Rating (Note 10)
(HBM, 1.5 kΩ, 100 pF) ≥ 10 kV
(EIAJ, 0 Ω, 200 pF) ≥ 1200 V
Recommended Operating
Conditions
Min Typ Max Units
Supply Voltage (V
CC
) +3.0 +3.3 +3.6 V
Receiver Input Voltage GND +3.0 V
Operating Free Air
Temperature (T
A
) −40 25 +85 ˚C
Electrical Characteristics
Over Supply Voltage and Operating Temperature ranges, unless otherwise specified. (Notes 2, 3)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Pin Min Typ Max Units
V
TH
Differential Input High Threshold VCM= +1.2V, 0.05V, 2.95V (Note 13) R
IN+
, +100 mV
V
TL
Differential Input Low Threshold R
IN−
−100 mV
VCMR Common-Mode Voltage Range VID=200mV pk to pk (Note 5) 0.1 2.3 V
I
IN
Input Current VIN= +2.8V VCC= 3.6V or 0V −10
±
5 +10 µA
V
IN
= 0V −10
±
1 +10 µA
V
IN
= +3.6V VCC= 0V -20
±
1 +20 µA
V
OH
Output High Voltage IOH= −0.4 mA, VID= +200 mV R
OUT
2.7 3.3 V
I
OH
= −0.4 mA, Input terminated 2.7 3.3 V
I
OH
= −0.4 mA, Input shorted 2.7 3.3 V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage IOL= 2 mA, VID= −200 mV 0.05 0.25 V
I
OS
Output Short Circuit Current Enabled, V
OUT
= 0V (Note 11) −15 −47 −100 mA
I
OZ
Output TRI-STATE Current Disabled, V
OUT
=0VorV
CC
−10
±
1 +10 µA
V
IH
Input High Voltage EN,
EN*
2.0 V
CC
V
V
IL
Input Low Voltage GND 0.8 V
I
I
Input Current VIN=0VorVCC, Other Input = VCCor
GND
−10
±
5 +10 µA
V
CL
Input Clamp Voltage ICL= −18 mA −1.5 −0.8 V
I
CC
No Load Supply Current
Receivers Enabled
EN=VCC, Inputs Open V
CC
915mA
I
CCZ
No Load Supply Current EN = GND, Inputs Open 1 5 mA
Receivers Disabled
Switching Characteristics
Over Supply Voltage and Operating Temperature ranges, unless otherwise specified. (Notes 3, 4, 7, 8)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
t
PHLD
Differential Propagation Delay High to Low CL= 15 pF 1.2 2.0 2.7 ns
t
PLHD
Differential Propagation Delay Low to High VID= 200 mV 1.2 1.9 2.7 ns
t
SKD1
Differential Pulse Skew |t
PHLD−tPLHD
| (Note 6) (
Figure 1
and
Figure 2
) 0 0.1 0.4 ns
t
SKD2
Differential Channel-to-Channel Skew; same device
(Note 7)
0 0.15 0.5 ns
t
SKD3
Differential Part to Part Skew (Note 8) 1.0 ns
t
SKD4
Differential Part to Part Skew (Note 9) 1.5 ns
t
TLH
Rise Time 0.5 1.0 ns
t
THL
Fall Time 0.35 1.0 ns
www.national.com 2
Switching Characteristics (Continued)
Over Supply Voltage and Operating Temperature ranges, unless otherwise specified. (Notes 3, 4, 7, 8)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
t
PHZ
Disable Time High to Z RL=2kΩ 814ns
t
PLZ
Disable Time Low to Z CL=15pF 8 14 ns
t
PZH
Enable Time Z to High (
Figure 3
and
Figure 4
) 9 14 ns
t
PZL
Enable Time Z to Low 914ns
f
MAX
Maximum Operating Frequency (Note 14) All Channels Switching 200 250 MHz
Note 1: “Absolute Maximum Ratings” are those values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. They are not meant to imply that the devices
should be operated at these limits. The table of “Electrical Characteristics” specifies conditions of device operation.
Note 2: Currentintodevice pins is defined as positive. Currentoutofdevicepins is defined as negative.Allvoltagesarereferenced to ground unless otherwise specified.
Note 3: All typicals are given for: V
CC
= +3.3V, TA= +25˚C.
Note 4: Generator waveform for all tests unless otherwise specified:f=1MHz, Z
O
=50Ω,trand tf(0%to 100%) ≤ 3 ns for RIN.
Note 5: TheVCMRrangeisreducedforlargerVID.Example:ifVID=400mV,theVCMRis0.2Vto2.2V. The fail-safe condition with inputs shorted is not supported
over the common-mode range of 0V to 2.4V,but is supported only with inputs shorted and no external common-mode voltage applied. A VID up to V
CC
− 0V may be
applied to the R
IN+/RIN−
inputs with the Common-Mode voltage set to VCC/2. Propagation delay and Differential Pulse skew decrease when VID is increased from
200mV to 400mV. Skew specifications apply for 200mV ≤ VID ≤ 800mV over the common-mode range .
Note 6: t
SKD1
is the magnitude difference in differential propagation delay time between the positive going edge and the negative going edge of the same channel
Note 7: t
SKD2
, Channel-to-Channel Skew is defined as the difference between the propagation delay of one channel and that of the others on the same chip with
any event on the inputs.
Note 8: t
SKD3
, part to part skew, is the differential channel-to-channel skew of any event between devices. This specification applies to devices at the same VCC,
and within 5˚C of each other within the operating temperature range.
Note 9: t
SKD4
, part to part skew, is the differential channel-to-channel skew of any event between devices. This specification applies to devices over recommended
operating temperature and voltage ranges, and across process distribution. t
SKD4
is defined as |Max−Min| differential propagation delay.
Note 10: ESD Rating:HBM (1.5 kΩ, 100 pF) ≥ 10kV
EIAJ (0Ω, 200 pF) ≥ 1200V
Note 11: Output short circuit current (I
OS
) is specified as magnitude only, minus sign indicates direction only. Only one output should be shorted at a time, do not
exceed maximum junction temperature specification.
Note 12: C
L
includes probe and jig capacitance.
Note 13: V
CC
is always higher than R
IN+
and R
IN−
voltage. R
IN−
and R
IN+
are allowed to have a voltage range −0.2V to VCC− VID/2. However, to be compliant with
AC specifications, the common voltage range is 0.1V to 2.3V
Note 14: f
MAX
generator input conditions: t
r
=
t
f
<
1ns(0%to 100%), 50%duty cycle, differential (1.05V to 1.35V peak to peak). Output criteria: 60/40%duty cycle,
V
OL
(max 0.4V), VOH(min 2.7V), Load=15 pF (stray plus probes).
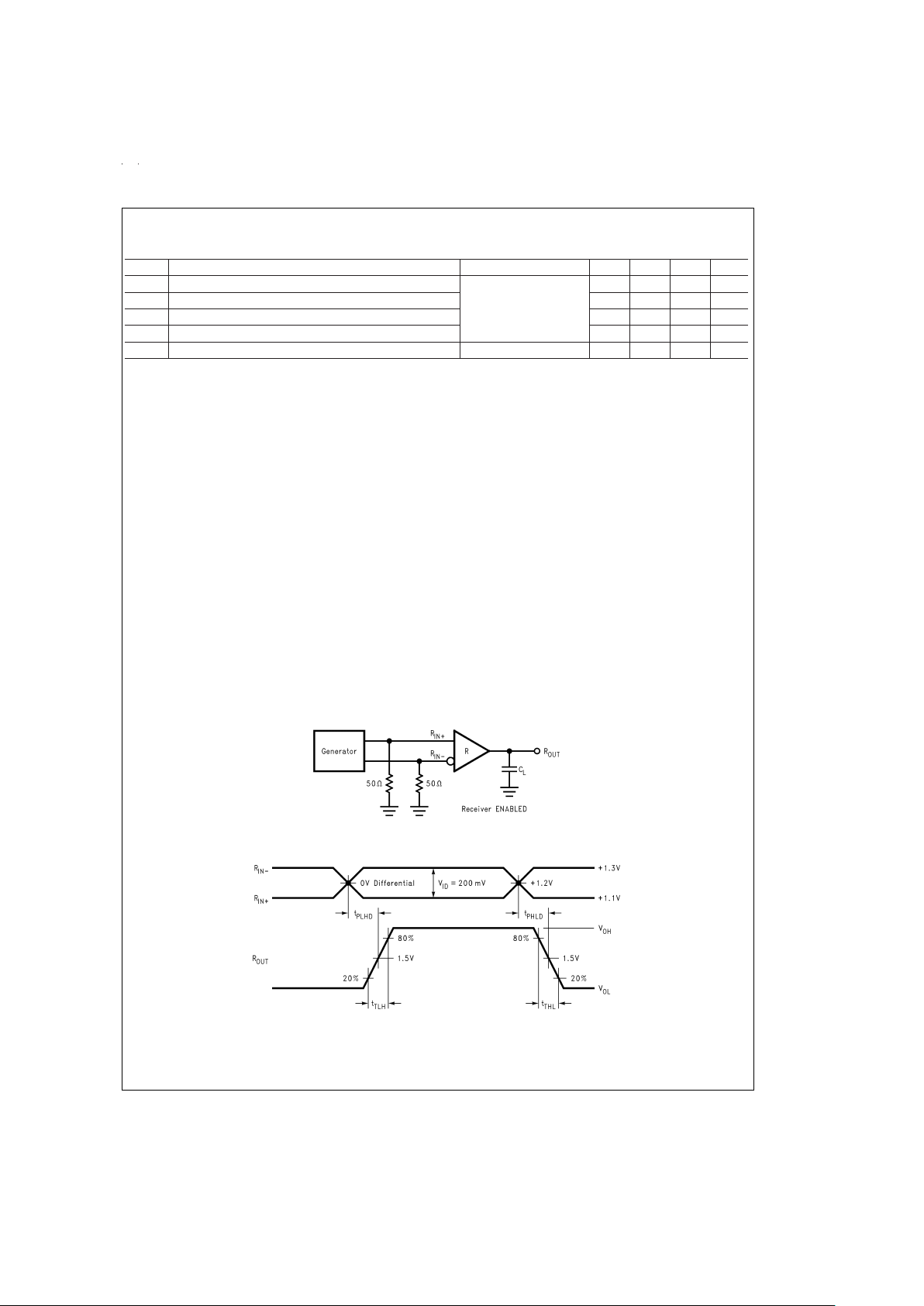
Parameter Measurement Information
DS100888-3
FIGURE 1. Receiver Propagation Delay and Transition Time Test Circuit
DS100888-4
FIGURE 2. Receiver Propagation Delay and Transition Time Waveforms
www.national.com3
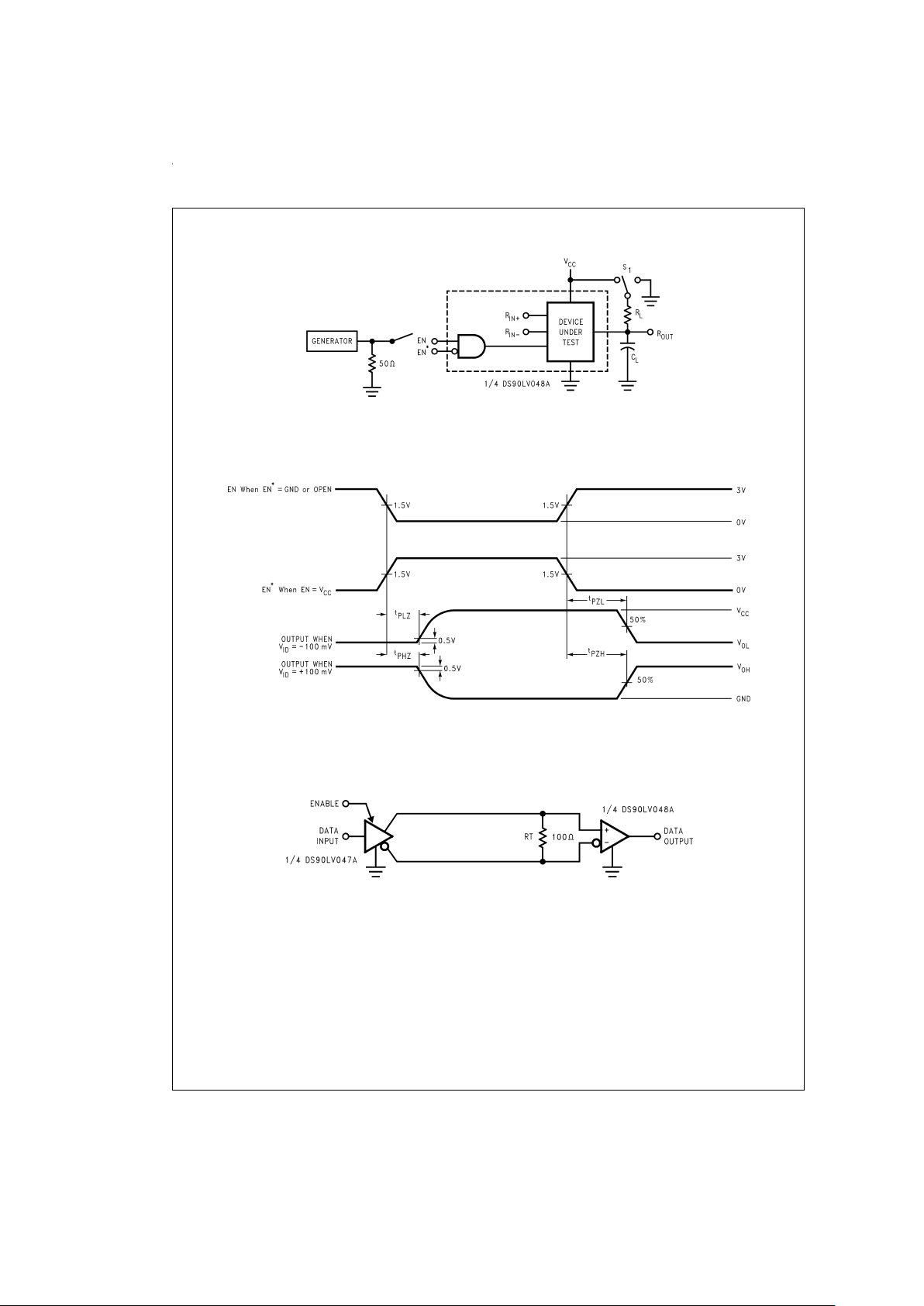
Parameter Measurement Information (Continued)
Typical Application
Applications Information
General application guidelines and hints for LVDS drivers
and receivers may be found in the following application
notes: LVDS Owner’s Manual (lit #550062-001), AN808,
AN977, AN971, AN916, AN805, AN903.
LVDSdriversand receivers are intendedto be primarily used
in an uncomplicated point-to-point configuration as is shown
in
Figure 5
. This configuration provides a clean signaling environment for the fast edge rates of the drivers. The receiver
is connected to the driver through a balanced media which
may be a standard twisted pair cable, a parallel pair cable, or
simply PCB traces. Typically,the characteristic impedance of
the media is in the range of 100Ω. A termination resistor of
100Ω (selected to match the media), and is located as close
to the receiver input pins as possible. The termination resistor converts the driver output (current mode) into a voltage
that is detected by the receiver. Other configurations are
possible such as a multi-receiver configuration, but the effects of a mid-stream connector(s), cable stub(s), and other
impedance discontinuities as well as ground shifting, noise
margin limits, and total termination loading must be taken
into account.
DS100888-5
CLincludes load and test jig capacitance.
S
1=VCC
for t
PZL
and t
PLZ
measurements.
S
1
= GND for t
PZH
and t
PHZ
measurements.
FIGURE 3. Receiver TRI-STATE Delay Test Circuit
DS100888-6
FIGURE 4. Receiver TRI-STATE Delay Waveforms
Balanced System
DS100888-7
FIGURE 5. Point-to-Point Application
www.national.com 4
 Loading...
Loading...