NSC ADC10738CIWM, ADC10734CIMSA, ADC10732CIWM, ADC10731CIWM Datasheet
ADC10731/ADC10732/ADC10734/ADC10738
10-Bit Plus Sign Serial I/O A/D Converters with Mux,
Sample/Hold and Reference
General Description
This series of CMOS 10-bit plus sign successive approximation A/D converters features versatile analog input multiplexers, sample/hold and a 2.5V band-gap reference. The 1-, 2-,
4-, or 8-channel multiplexers can be software configured for
single-ended or differential mode of operation.
An input sample/hold is implemented by a capacitive reference ladder and sampled-data comparator. This allows the
analog input to vary during the A/D conversion cycle.
In the differential mode, valid outputs are obtained even
when the negative inputs are greater than the positive because of the 10-bit plus sign output data format.
The serial I/O is configured to comply with the NSC MICROWIRE
face to the COPS
can easily interface with standard shift registers and microprocessors.
™
serial data exchange standard for easy inter-
™
and HPC™families of controllers, and
Features
n 0V to 5V analog input range with single 5V power
supply
n Serial I/O (MICROWIRE compatible)
n 1-, 2-, 4-, or 8-channel differential or single-ended
multiplexer
n Software or hardware power down
n Analog input sample/hold function
n Ratiometric or absolute voltage referencing
n No zero or full scale adjustment required
n No missing codes over temperature
n TTL/CMOS input/output compatible
n Standard DIP and SO packages
Key Specifications
n Resolution 10 bits plus sign
n Single supply 5V
n Power dissipation 37 mW (Max)
n In powerdown mode 18 µW
n Conversion time 5µs (Max)
n Sampling rate 74 kHz (Max)
n Band-gap reference 2.5V
Applications
n Medical instruments
n Portable and remote instrumentation
n Test equipment
May 1999
±
2%(Max)
ADC10731/ADC10732/ADC10734/ADC10738 10-Bit Plus Sign Serial I/O A/D Converters with Mux,
Sample/Hold and Reference
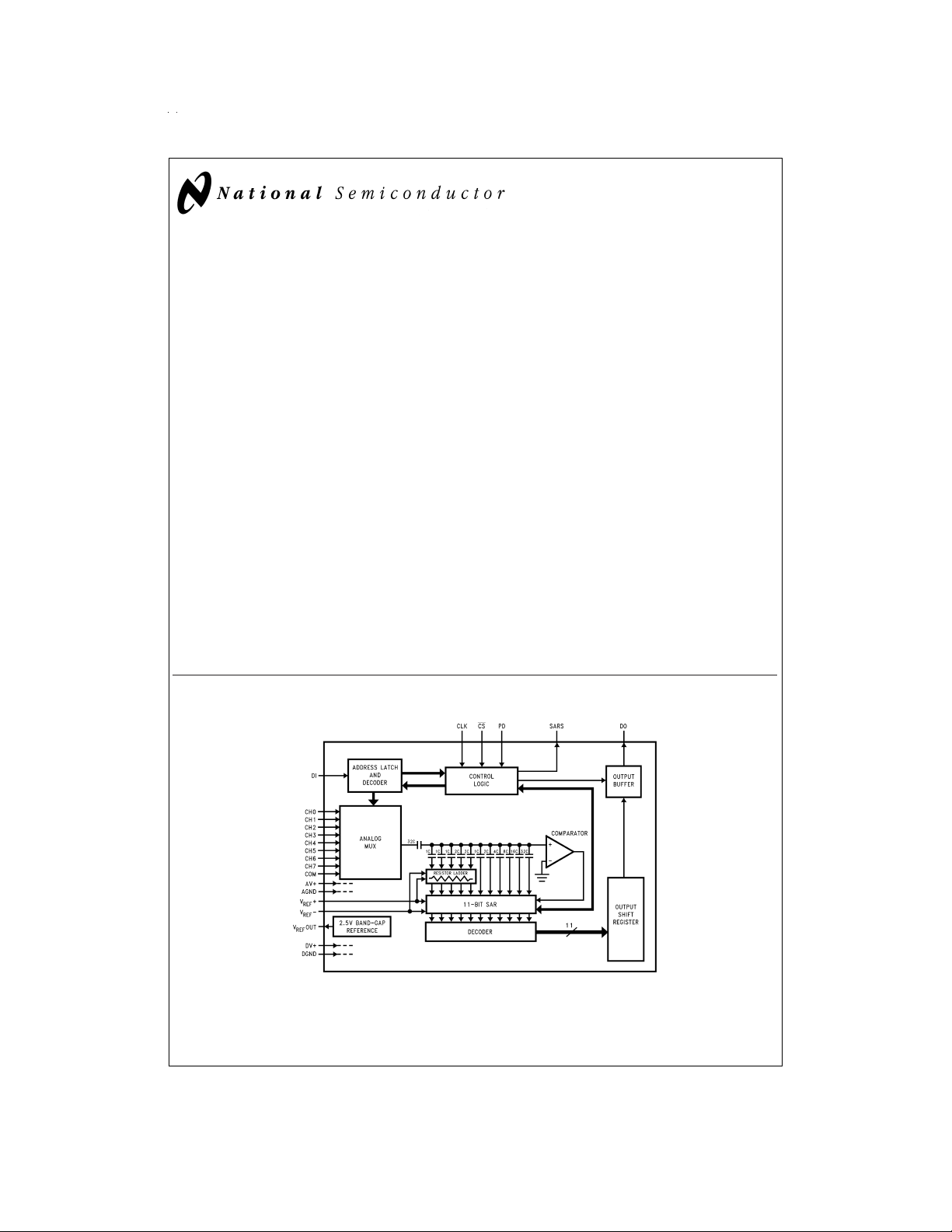
ADC10738 Simplified Block Diagram
DS011390-1
COPS™, HPC™and MICROWIRE™are trademarks of National Semiconductor Corporation.
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS011390 www.national.com
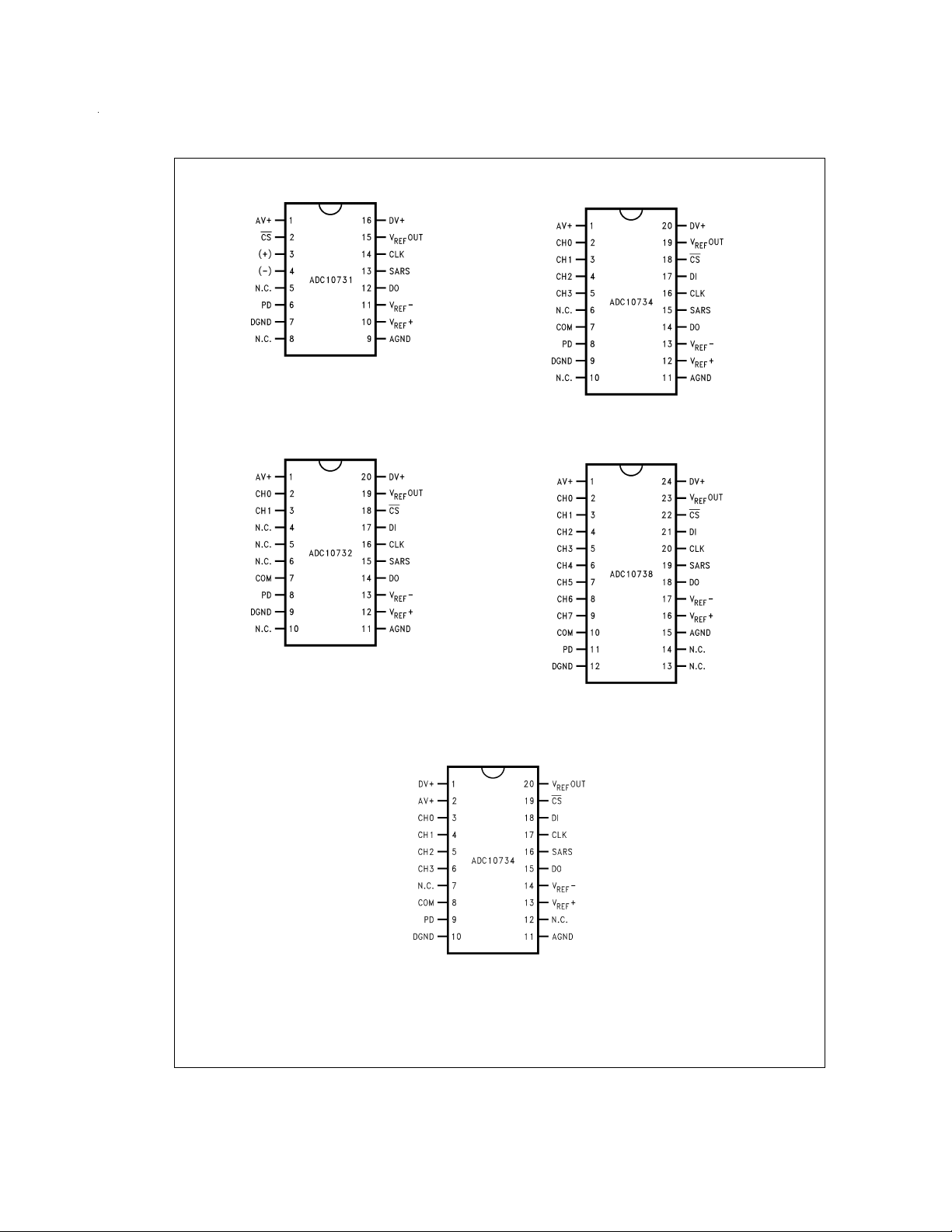
Connection Diagrams
Top View
See NS Package Number M16B
DS011390-2
DS011390-4
Top View
See NS Package Number M20B
DS011390-3
Top View
See NS Package Number M20B
SSOP Package
See NS Package Number MSA20
www.national.com 2
DS011390-5
Top View
See NS Package Number M24B
DS011390-34
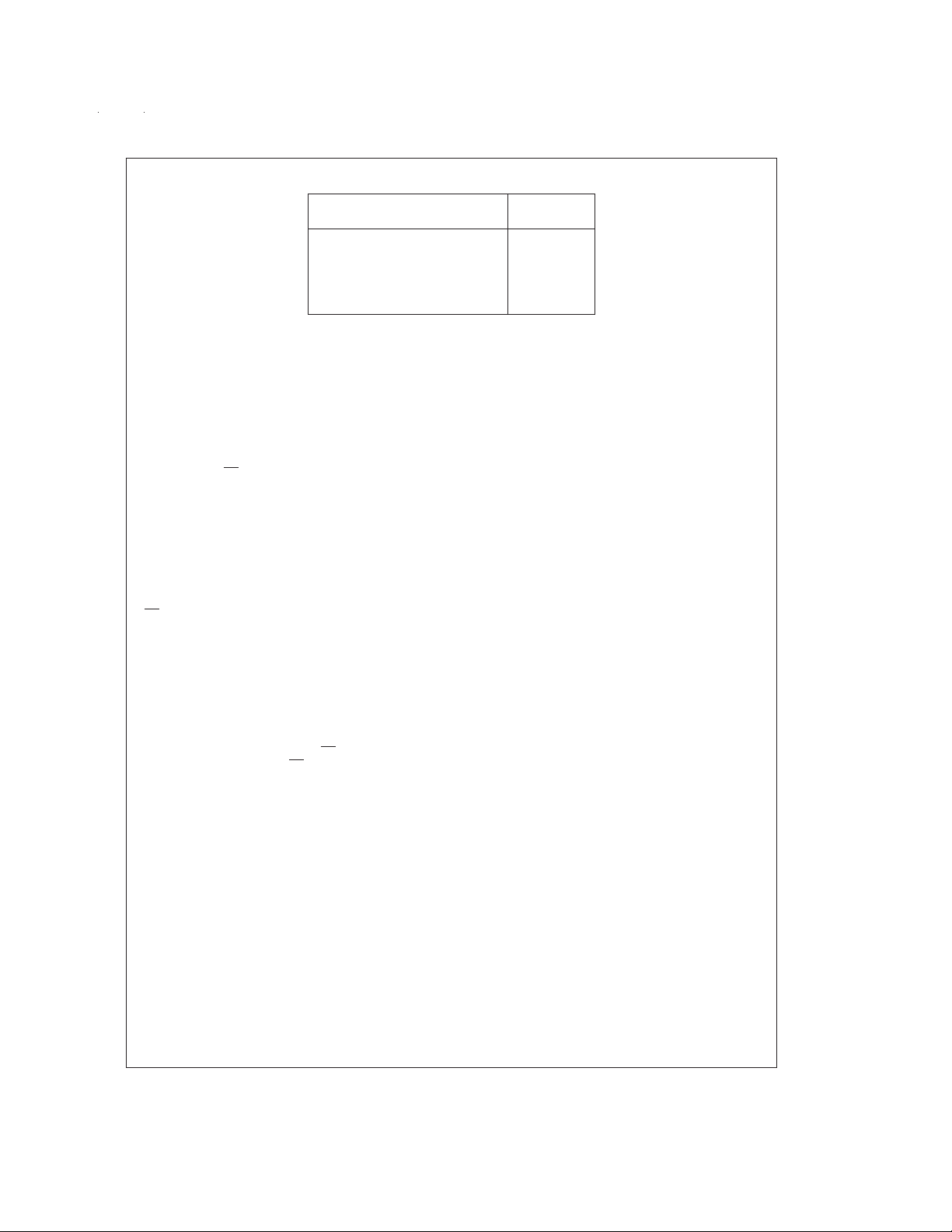
Ordering Information
Industrial Temperature Range Package
−40˚C ≤ T
≤ +85˚C
A
ADC10731CIWM M16B
ADC10732CIWM M20B
ADC10734CIMSA MSA20
ADC10734CIWM M20B
ADC10738CIWM M24B
Pin Descriptions
CLK The clock applied to this input controls the suc-
DI This is the serial data input pin. The data applied
DO The data output pin. The A/D conversion result
CS
PD This is the power down input pin. When a logic
SARS This is the successive approximation register
CH0–CH7 These are the analog inputs of the MUX. A chan-
COM This pin is another analog input pln. It can be
V
REF
cessive approximation conversion time interval,
the acquisition time and the rate at which the serial data exchange occurs. The rising edge loads
the information on the DI pin into the multiplexer
address shift register. This address controls
which channel of the analog input multiplexer
(MUX) is selected. The falling edge shifts the
data resulting from the A/D conversion out on
DO. CS enables or disables the above functions.
The clock frequency applied to this input can be
between 5 kHz and 3 MHz.
to this pln is shifted by CLK into the multiplexer
address register.
Tables 1, 2, 3
show the multi-
plexer address assignment.
(DB0-SIGN) are clocked out by the failing edge
of CLK on this pin.
This is the chip select input pin. When a logic low
is applied to this pin, the rising edge of CLK
shifts the data on DI into the address register.
This low also brings DO out of TRI-STATE after
a conversion has been completed.
high is applied to this pin the A/D is powered
down. When a low is applied the A/D is powered
up.
status output pin. When CS is high this pin is in
TRI-STATE. With CS low this pin is active high
when a conversion is in progress and active low
at all other times.
nel input is selected by the address information
at the DI pin, which is loaded on the rising edge
of CLK into the address register (see
3
).
The voltage applied to these inputs should not
exceed AV
+
or go below GND by more than
Tables1, 2,
50 mV. Exceeding this range on an unselected
channel will corrupt the reading of a selected
channel.
used as a “pseudo ground” when the analog
multiplexer is single-ended.
+ This is the positive analog voltage reference in-
put. In order to malntaln accuracy, the voltage
range V
REF(VREF
5.0 V
and the voltage at V
DC
+
AV
+50 mV.
=
+–V
V
REF
−) is 0.5 VDCto
REF
+ cannot exceed
REF
V
− The negative voltage reference input. In order to
REF
maintain accuracy, the voltage at this pin must
not go below GND − 50 mV or exceed AV
+50mV.
+
,DV+These are the analog and digital power supply
AV
pins. These pins should be tied to the same
power supply and bypassed separately.The operating voltage range of AV
+
and DV+is 4.5 V
to 5.5 VDC.
DGND This is the digital ground pin.
AGND This is the analog ground pin.
+
DC
www.national.com3

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes 1, 3)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
+
+
Supply Voltage (V
=
AV
Total Reference Voltage
+–V
(V
REF
−) 6.5V
REF
Voltage at Inputs and Outputs V
Input Current at Any Pin (Note 4) 30 mA
Package Input Current (Note 4) 120 mA
Package Dissipation at T
(Note 5) 500 mW
ESD Susceptability (Note 6)
Human Body Model 2500V
Machine Model 150V
Soldering Information
N packages (10 seconds) 260˚C
SO Package (Note 7)
+
=
) 6.5V
DV
=
25˚C
A
+
+ 0.3V to −0.3V
Vapor Phase (60 seconds) 215˚C
Infrared (15 seconds) 220˚C
Storage Temperature −40˚C to +150˚C
Operating Ratings (Notes 2, 3)
Operating Temperature Range T
ADC10731CIWM,
ADC10732CIWM,
ADC10734CIWM,
ADC10734CIMSA,
ADC10738CIWM −40˚C ≤ T
Supply Voltage
+
+
=
AV
(V
+AV
V
REF
−AV
V
REF
V
REF(VREF
+
=
) +4.5V to +5.5V
DV
+–V
−) +0.5V to V
REF
≤ TA≤ T
MIN
+
+50 mV to −50 mV
+
+50 mV to −50 mV
≤ +85˚C
A
MAX
+
Electrical Characteristics
The following specifications apply for V
Characteristics, VIN−=GND for Unsigned Characteristics and f
ply for T
=
=
T
A
to T
T
J
MIN
MAX
+
+
=
AV
; all other limits T
+
=
=
DV
+5.0 V
=
=
T
+25˚C. (Notes 8, 9, 10)
A
J
+=2.5 VDC,V
DC,VREF
=
2.5 MHz unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits ap-
CLK
−=GND, VIN−=2.5V for Signed
REF
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical Limits Units
(Note 11) (Note 12) (Limits)
SIGNED STATIC CONVERTER CHARACTERISTICS
Resolution with No Missing Codes 10 + Sign Bits
TUE Total Unadjusted Error (Note 13)
INL Positive and Negative Integral
±
2.0 LSB(max)
±
1.25 LSB(max)
Linearity Error
Positive and Negative
±
1.5 LSB(max)
Full-Scale Error
Offset Error
±
1.5 LSB(max)
Power Supply Sensitivity
Offset Error V
+ Full-Scale Error
− Full-Scale Error
DC Common Mode Error (Note 14) V
Multiplexer Channel to
±
10
+5.0V
+=VIN−=VINwhere
IN
5.0V ≥ V
≥ 0V
IN
%
±
0.2
±
0.2
±
0.1
±
0.1
±
0.1 LSB
±
1.0 LSB(max)
±
1.0 LSB(max)
±
0.75 LSB(max)
±
0.33 LSB(max)
+
=
Channel Matching
UNSIGNED STATIC CONVERTER CHARACTERISTICS
Resolution with No Missing Codes 10 Bits
TUE Total Unadjusted Error (Note 13) V
INL Integral Linearity Error V
Full-Scale Error V
Offset Error V
+=4.096V
REF
+=4.096V
REF
+=4.096V
REF
+=4.096V
REF
±
0.75 LSB
±
0.50 LSB
±
1.25 LSB(max)
±
1.25 LSB(max)
Power Supply Sensitivity
+
=
Offset Error V
Full-Scale Error V
DC Common Mode Error (Note 14) V
Multiplexer Channel to Channel
Matching
±
10
+5.0V
+=4.096V
REF
+=VIN−=VINwhere
IN
+5.0V ≥ V
V
REF
≥ 0V
IN
+=4.096V
%
±
0.1 LSB
±
0.1 LSB
±
0.1 LSB
±
0.1 LSB
www.national.com 4
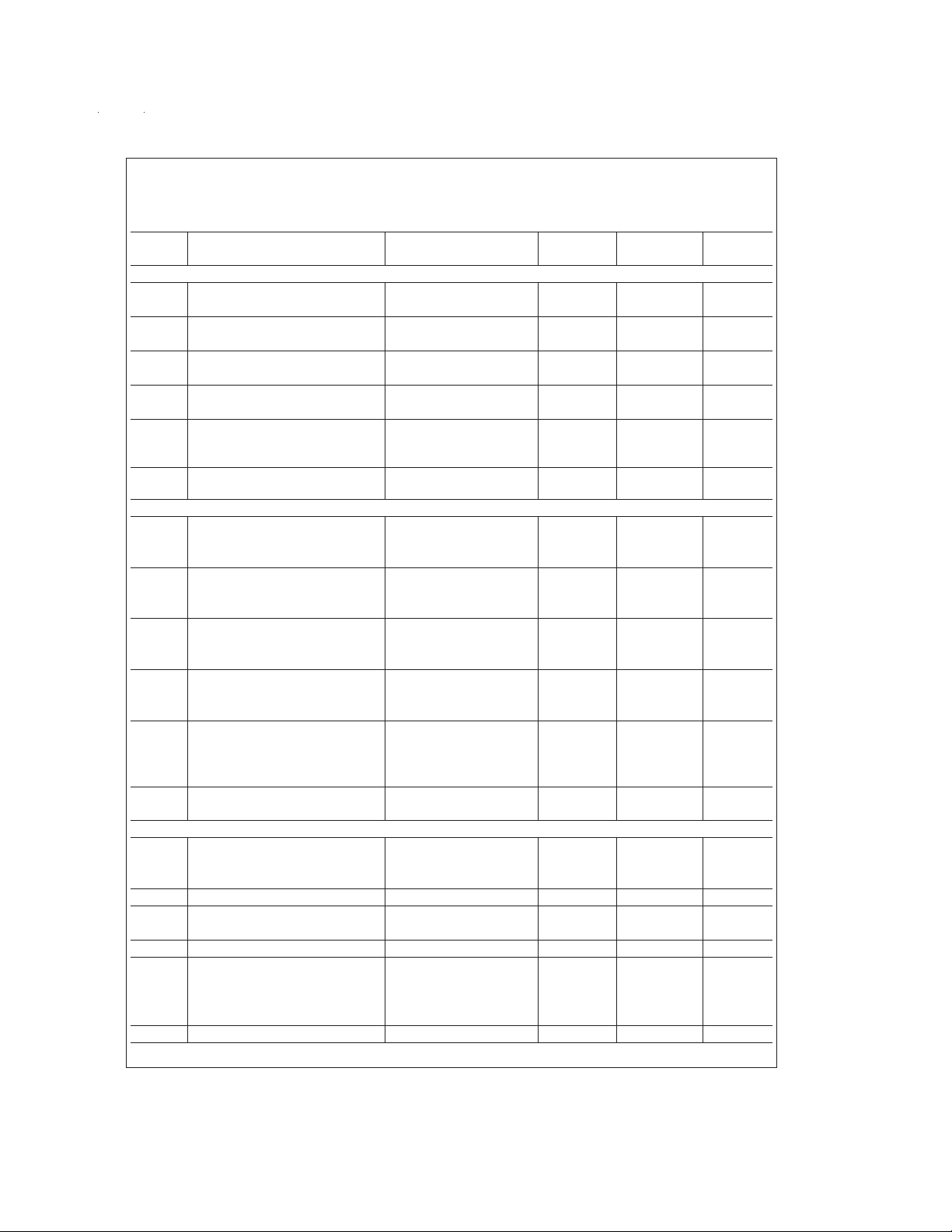
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
+
+
The following specifications apply for V
Characteristics, VIN−=GND for Unsigned Characteristics and f
ply for T
=
=
T
A
to T
T
J
MIN
MAX
=
AV
; all other limits T
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical Limits Units
DYNAMIC SIGNED CONVERTER CHARACTERISTICS
S/(N+D) Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion Ratio V
ENOB Effective Number of Bits V
THD Total Harmonic Distortion V
IMD Intermodulation Distortion V
Full-Power Bandwidth V
Multiplexer Channel to Channel
Crosstalk
DYNAMIC UNSIGNED CONVERTER CHARACTERISTIC
S/(N+D) Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion Ratio V
Effective Bits V
THD Total Harmonic Distortion V
IMD Intermodulation Distortion V
Full-Power Bandwidth V
Multiplexer Channel to Channel f
Crosstalk V
REFERENCE INPUT AND MULTIPLEXER CHARACTERISTICS
Reference Input Resistance 7 kΩ
C
REF
Reference Input Capacitance 70 pF
MUX Input Voltage −50 mV(min)
C
IM
MUX Input Capacitance 47 pF
Off Channel Leakage Current
(Note 15)
On Channel Leakage Current On Channel=5V and 0.4 3.0 µA(max)
+
=
=
DV
+5.0 V
=
=
T
+25˚C. (Notes 8, 9, 10)
A
J
+=2.5 VDC,V
DC,VREF
=
2.5 MHz unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits ap-
CLK
−=GND, VIN−=2.5V for Signed
REF
(Note 11) (Note 12) (Limits)
IN
and f
IN
and f
IN
and f
IN
and f
IN
=
IN
=
IN
=
IN
=
IN
=
,67 dB
4.85 V
PP
=
1 kHz to 15 kHz
, 10.8 Bits
4.85 V
PP
=
1 kHz to 15 kHz
, −78 dB
4.85 V
PP
=
1 kHz to 15 kHz
, −85 dB
4.85 V
PP
=
1 kHz to 15 kHz
, where 380 kHz
4.85 V
PP
S/(N + D) Decreases
3dB
=
f
15 kHz −80 dB
IN
+=4.096V,
REF
=
V
IN
=
f
IN
REF
=
V
IN
=
f
IN
REF
=
V
IN
=
f
IN
REF
=
V
IN
=
f
IN
=
IN
V
REF
, and 60 dB
4.0 V
PP
1 kHz to 15 kHz
+=4.096V,
, and 9.8 Bits
4.0 V
PP
1 kHz to 15 kHz
+=4.096V,
, and −70 dB
4.0 V
PP
1 kHz to 15 kHz
+=4.096V,
, and −73 dB
4.0 V
PP
1 kHz to 15 kHz
,
4.0 V
PP
+=4.096V, 380 kHz
where S/(N+D) decreases
3dB
=
15 kHz,
IN
REF
+=4.096V
−80 dB
5.0 kΩ(min)
9.5 kΩ(max)
+
AV
+50 mV (max)
On Channel=5V and −0.4 −3.0 µA(max)
Off Channel=0V
On Channel=0V and 0.4 3.0 µA(max)
Off Channel=5V
www.national.com5
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
+
+
The following specifications apply for V
Characteristics, VIN−=GND for Unsigned Characteristics and f
ply for T
=
=
T
A
to T
T
J
MIN
MAX
=
AV
; all other limits T
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical Limits Units
REFERENCE INPUT AND MULTIPLEXER CHARACTERISTICS
(Note 15) Off Channel=0V
REFERENCE CHARACTERISTICS
V
Out Reference Output Voltage 2.5V±0.5
REF
∆V
/∆TV
REF
∆V
/∆ILLoad Regulation, Sourcing 0 mA ≤ IL≤ +4 mA
REF
∆V
/∆ILLoad Regulation, Sinking 0 mA ≤ IL≤ −1 mA
REF
Out Temperature Coefficient
REF
Line Regulation 5V
I
SC
Short Circuit Current V
Noise Voltage
∆V
/∆t Long-term Stability
REF
t
SU
Start-Up Time C
DIGITAL AND DC CHARACTERISTICS
V
IN(1)
V
IN(0)
I
IN(1)
I
IN(0)
V
OUT(1)
V
OUT(0)
I
OUT
+I
SC
−I
SC
I
+ Digital Supply Current CS=HIGH, Power Up 0.9 1.3 mA(max)
D
Logical “1” Input Voltage V
Logical “0” Input Voltage V
Logical “1” Input Current V
Logical “0” Input Current V
Logical “1” Output Voltage V
Logical “0” Output Voltage V
TRI-STATE Output Current V
Output Short Circuit Source Current V
Output Short Circuit Sink Current V
(Note 17) CS=HIGH, Power Down
I
+ Analog Supply Current CS=HIGH, Power Up 2.7 6.0 mA(max)
A
(Note 17) CS=HIGH, Power Down
I
REF
Reference Input Current V
AC CHARACTERISTICS
f
CLK
Clock Frequency 3.0 2.5 MHz(max)
Clock Duty Cycle 40
t
C
t
A
Conversion Time 12 12 Clock
Acquisition Time 4.5 4.5 Clock
+
=
=
DV
+5.0 V
=
=
T
+25˚C. (Notes 8, 9, 10)
A
J
+=2.5 VDC,V
DC,VREF
=
2.5 MHz unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits ap-
CLK
−=GND, VIN−=2.5V for Signed
REF
(Note 11) (Note 12) (Limits)
On Channel=0V and −0.4 −3.0 µA(max)
Off Channel=5V
%
±
40 ppm/˚C
±
0.003
±
0.2
±
%
10
Out=0V 13 22 mA(max)
REF
10 Hz to 10 kHz,
=
100 µF
C
L
=
100 µF 100 ms
L
+
=
5.5V 2.0 V(min)
+
=
4.5V 0.8 V(max)
=
5.0V 0.005 +2.5 µA(max)
IN
=
0V −0.005 −2.5 µA(max)
IN
+
=
4.5V, I
+
=
V
4.5V, I
+
=
4.5V, I
=
OUT
=
V
OUT
=
OUT
=
OUT
=
−360 µA 2.4 V(min)
OUT
=
−10 µA 4.5 V(min)
OUT
=
1.6 mA 0.4 V(min)
OUT
0V −0.1 −3.0 µA(max)
5V +0.1 +3.0 µA(max)
+
=
0V, V
V
4.5V −30 −15 mA(min)
+
=
4.5V 30 15 mA(min)
±
0.3
5µV
±
120 ppm/kHr
%
2.5V±2
±
0.05
±
0.6
±
2.5 mV(max)
0.2 0.4 mA(max)
CS=HIGH, Power Down,
0.5 50 µA(max)
and CLK Off
3 15 µA(max)
+=+2.5V and 0.6 mA(max)
REF
CS=HIGH, Power Up
5 kHz(min)
60
5 5 µs(max)
2 2 µs(max)
V(max)
%
/mA(max)
%
/mA(max)
%
(min)
%
(max)
Cycles
Cycles
www.national.com 6
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
+
+
The following specifications apply for V
Characteristics, VIN−=GND for Unsigned Characteristics and f
ply for T
=
=
T
A
to T
T
J
MIN
MAX
=
AV
; all other limits T
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical Limits Units
AC CHARACTERISTICS
t
SCS
CS Set-Up Time, Set-Up Time from
Falling Edge of CS to Rising Edge of
Clock
DI Set-Up Time, Set-Up Time from
t
SDI
Data Valid on DI to Rising Edge of
Clock
DI Hold Time, Hold Time of DI Data
t
HDI
from Rising Edge of Clock to Data
not Valid on DI
DO Access Time from Rising Edge of
t
AT
CLK When CS is “Low” during a
Conversion
DO or SARS Access Time from CS ,
t
AC
Delay from Falling Edge of CS to
Data Valid on DO or SARS
Delay from Rising Edge of Clock to
t
DSARS
t
HDO
Falling Edge of SARS when CS is
“Low”
DO Hold Time, Hold Time of Data on
DO after Falling Edge of Clock
DO Access Time from Clock, Delay
t
AD
t
1H,t0H
t
DCS
t
CS(H)
t
CS(L)
t
SC
t
PD
t
PC
C
IN
C
OUT
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur.
Note 2: Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifcations and
test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The guaranteed specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics may degrade when the device is not operated under the listed test conditions.
Note 3: All voltages are measured with respect to GND, unless otherwise specified.
Note 4: When the input voltage (V
The 120 mA maximum package input current rating limits the number of pins that can safely exceed the power supplies with an input current of 30 mA to four.
Note 5: The maximum power dissipation must be derated at elevated temperatures and is dictated by T
allowable power dissipation at any temperature is P
T
from Falling Edge of Clock to Valid
Data of DO
Delay from Rising Edge of CS to DO
or SARS TRI-STATE
Delay from Falling Edge of Clock to
Falling Edge of CS
CS “HIGH” Time for A/D Reset after
Reading of Conversion Result
ADC10731 Minimum CS “Low” Time
to Start a Conversion
Time from End of Conversion to CS
Going “Low”
Delay from Power-Down command to
10%of Operating Current
Delay from Power-Up Command to
Ready to Start a New Conversion
Capacitance of Logic Inputs 7 pF
Capacitance of Logic Outputs 12 pF
) at any pin exceeds the power supplies (V
IN
=
(T
=
150˚C. The typical thermal resistance (θ
Jmax
D
) of these Paris when board mounted can be found in the following table:
JA
+
=
=
DV
+5.0 V
=
=
T
+25˚C. (Notes 8, 9, 10)
A
J
+=2.5 VDC,V
DC,VREF
=
2.5 MHz unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits ap-
CLK
−=GND, VIN−=2.5V for Signed
REF
(Note 11) (Note 12) (Limits)
14 30 ns(min)
(1 t
CLK
(1 t
CLK
−14ns) −30 ns)
16 25 ns(min)
2 25 ns(min)
30 50 ns(min)
30 70 ns(max)
100 200 ns(max)
20 35 ns(max)
40 80 ns(max)
40 50 ns(max)
20 30 ns(min)
1 CLK 1 CLK cycle(min)
1 CLK 1 CLK cycle(min)
5 CLK 5 CLK
1µs
10
<
GND or V
IN
)/θJAor the number given In the Absolute Maximum Ratings, whichever is lower. For this device,
Jmax−TA
>
AV+or DV+), the current at that pln should be limited to 30 mA.
IN
, θJAand the ambient temperature, TA. The maximum
Jmax
(max)
cycle(min)
µs
www.national.com7
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Part Number Thermal Resistance Package
Type
ADC10731CIWM 90˚C/W M16B
ADC10732CIWM 80˚C/W M20B
ADC10734CIMSA 134˚C/W MSA20
ADC10734CIWM 80˚C/W M20B
ADC10738CIWM 75˚C/W M24B
Note 6: The human body model is a 100 pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5 kΩ resistor into each pin. The machine model is a 200 pF capacitor discharged di-
rectly into each pin.
Note 7: SeeAN-450 “Surface Mounting Methods and Their Effect on Product Reliability” or the section titied “Surtace Mount” found in any post 1986 National Semiconductor Linear Data Book for other methods of soldering surtace mount devices.
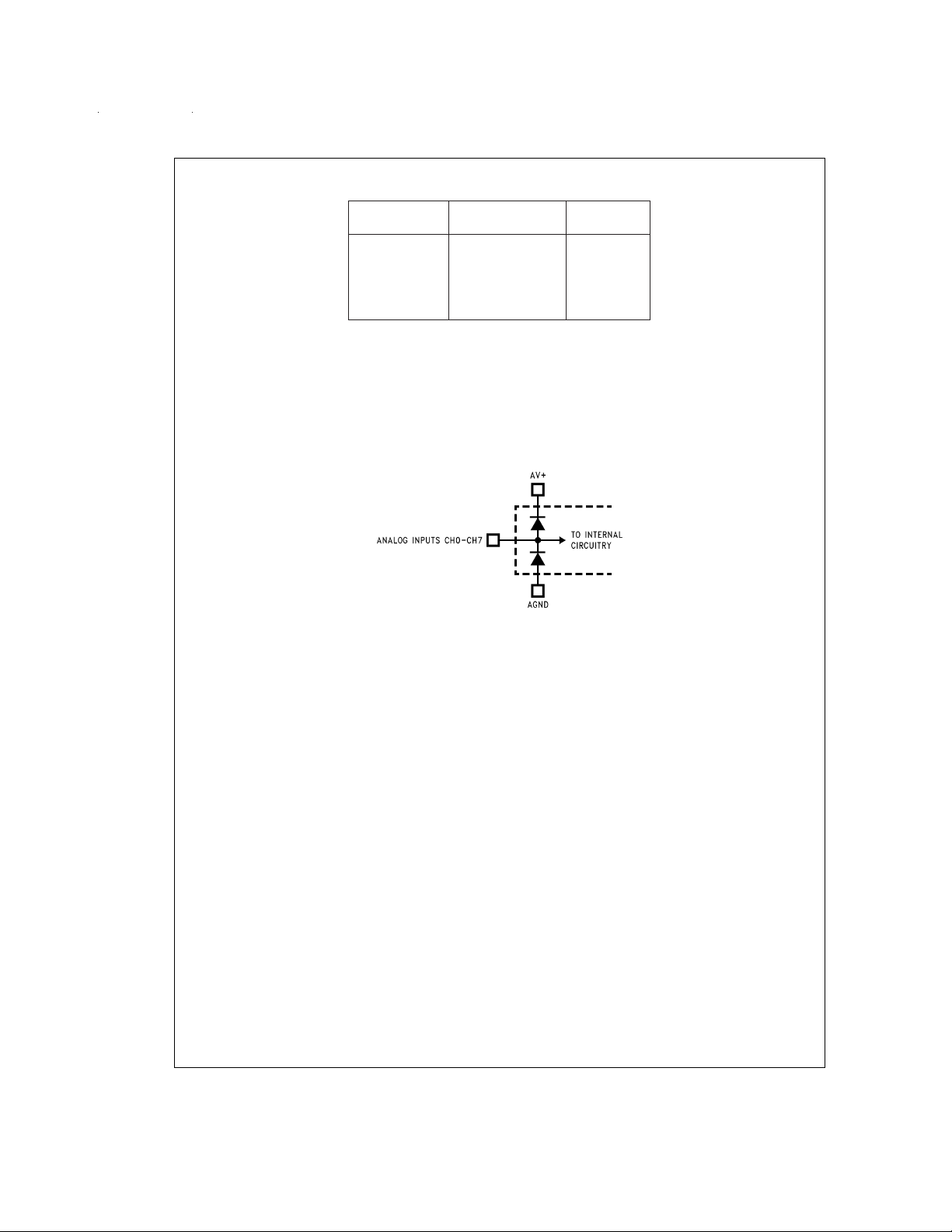
Note 8: Twoon-ohip diodes are tied to each analog input as shown below. They will forward-conduct for analog input voltages one diode drop below ground or one
diode drop greater than V
at elevated temperatures, which will cause errors In the conversion result. The specification allows 50 mV forward bias of either diode; this means that as long as
the analog V
the reading of a selected channel. If AV
Note 9: No connection exists between AV
To guarantee accuracy, it is required that the AV
Note 10: One LSB is referenced to 10 bits of resolution.
Note 11: Typicals are at T
Note 12: Tested limits are guaranteed to National’s AOQL (Average Outgolng Quality Level).
Note 13: Total unadjusted error includes offset, full-scale, linearity, multiplexer, and hold step errors.
Note 14: The DC common-mode error is measured in the differential multiplexer mode with the assigned positive and negative input channels shorted together.
Note 15: Channel leakage current is measured after the channel selection.
Note 16: All the timing specifications are tested at the TTL logic levels, V
to 1.4V.
Note 17: The voltage applied to the digital inputs will affect the current drain during power down. These devices are tested with CMOS logic levels (logic Low=0V
and logic High=5V). TTL levels increase the current, during power down, to about 300 µA.
IN
+
supply.Becareful during testing at low V+levels (+4.5V), as high level analog inputs (+5V) can cause an input diode to conduct, especially
does not exceed the supply voltage by more than 50 mV, the output code will be oorrect. Exceeding this range on an unselected channel will corrupt
J
+
and DV+are minimum (4.5 VDC) and full scale must be ≤+4.55 VDC.
+
and DV+on the chip.
+
and DV+be connected together to a power supply with separate bypass filter at eacn V+pin.
=
=
T
25˚C and represent most likely pararmetric norm.
A
=
0.8V for a falling edge and V
IL
DS011390-6
=
2.0V for a rising. TRl-STATE voltage level is forced
IH
www.national.com 8
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
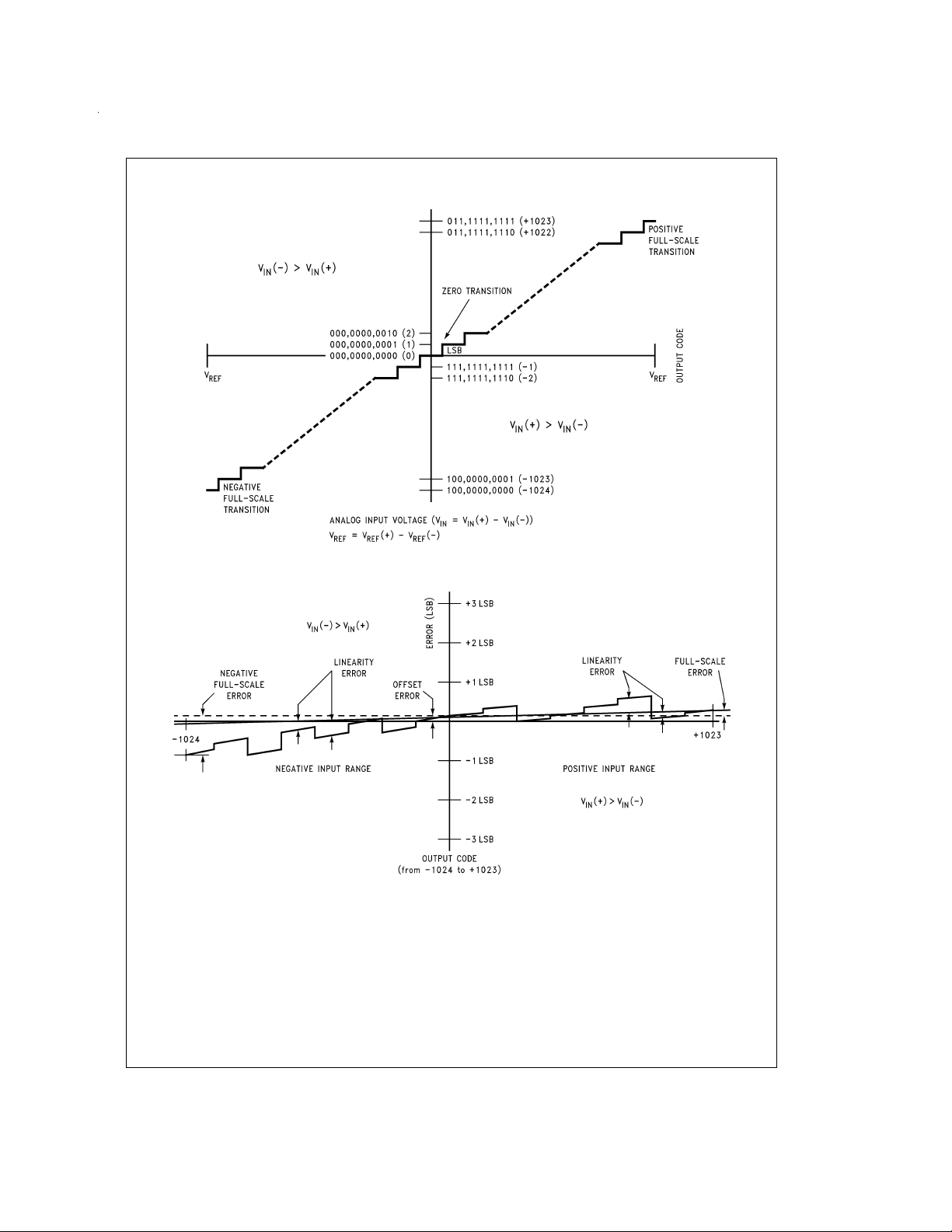
FIGURE 1. Transter Characteristic
DS011390-8
FIGURE 2. Simplified Error Curve vs Output Code
DS011390-26
www.national.com9
 Loading...
Loading...