NOVUS superview User Manual

www.superview.com.br
INSTRUCTIONS MANUAL
V2.9x
INDEX
INDEX ................................................................................................................................................................................. 1
INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................................................. 3
INSTALLATION ................................................................................................................................................................... 4
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS .......................................................................................................................................... 4
INSTALLATION PROCEDURES ................................................................................................................................... 4
FIRST STEPS ..................................................................................................................................................................... 5
SETTING UP A BASIC APPLICATION ......................................................................................................................... 5
START SUPERVIEW ............................................................................................................................................... 5
CREATE A NEW APPLICATION ............................................................................................................................. 6
REGISTERING DEVICES IN THE NETWORK ........................................................................................................ 6
REGISTERING THE VARIABLES OF EACH DEVICE – TAGS .............................................................................. 7
CREATING SUPERVISION FORMS ....................................................................................................................... 8
DEFINE THE NETWORK COMMUNICATION PARAMETERS ............................................................................. 10
SAVING AND OPENING AN APPLICATION ......................................................................................................... 11
START SUPERVISION .......................................................................................................................................... 11
REGISTERING THE SUPERVIEW COPY .................................................................................................................. 12
REGISTER USING A HARDKEY ........................................................................................................................... 12
OPERATION MODES WITH A HARDKEY ............................................................................................................ 12
REGISTER USING A SOFTKEY – USE LICENSE AND REGISTRATION NUMBER ........................................... 12
VALIDATING THE REGISTRATION NUMBER ..................................................................................................... 12
PROCEDURE FOR REGISTRATION USING A SOFTKEY .................................................................................. 13
OPERATION MODES WITH A SOFTKEY............................................................................................................. 13
ADDITIONAL FEATURES ................................................................................................................................................. 14
USERS MANAGEMENT.............................................................................................................................................. 14
ALARM MONITORING, PRESENTATION AND NOTIFICATION ............................................................................... 15
CREATING ALARM GROUPS ............................................................................................................................... 15
DEFINING THE ALARM PARAMETERS OF A TAG ............................................................................................. 16
INCLUDING AN ALARM TABLE OBJECT............................................................................................................. 17
ACKNOWLEDGING ALARMS ............................................................................................................................... 17
CONFIGURING THE E-MAIL SERVER ................................................................................................................. 18
HISTORIC LOG ........................................................................................................................................................... 18
CREATING A HISTORIC ....................................................................................................................................... 19
INCLUDING A HISTORIC LIST TYPE OBJECT .................................................................................................... 19
VISUALIZING, COPYING AND EXPORTING HISTORICS. .................................................................................. 20
CREATING REPORTS .......................................................................................................................................... 21
REPORTS MANAGER ................................................................................................................................................ 21
USING SUPERVIEW WITH THE FIELD LOGGER ..................................................................................................... 22
FIELD LOGGER I/O ............................................................................................................................................... 22
FIELDLOGGER MEMORY DOWNLOAD (NEW GENERATION) .......................................................................... 22
REGISTERING EVENTS IN SUPERVIEW .................................................................................................................. 24
LOGS VISUALIZER ..................................................................................................................................................... 25
CONFIGURING TASKS .............................................................................................................................................. 26
CONFIGURING FORMULAS ...................................................................................................................................... 27
CONFIGURING THE COLOR TEMPLATES ............................................................................................................... 28
INFORMA TI ON TA B L E ............................................................................................................................................... 29
VIRTUAL KEYBOARD................................................................................................................................................. 30
APPLICATION GENERAL OPTIONS .......................................................................................................................... 30
PRINT SETTING ......................................................................................................................................................... 31
DATABASE OF MODBUS DEVICES PARAMETERS ................................................................................................ 31
NOVUS AUTOMATION 1/38

CONFIGURING THE COMMUNICATION WITH DEVICES FROM OTHER VENDORS ............................................ 32
REGISTERING DEVICES IN THE NETWORK ...................................................................................................... 32
REGISTERING THE VARIABLES OF EACH DEVICE – TAGS ............................................................................ 32
ADVANCED SCREEN EDITION ................................................................................................................................. 33
OBJECTS GROUPING .......................................................................................................................................... 33
BRINGING OBJECTS TO FRONT / SENDING BACK .......................................................................................... 33
OBJECTS ALIGNMENT......................................................................................................................................... 33
STANDARDIZING THE SIZE OF OBJECTS ......................................................................................................... 33
COPY / PASTE OBJECTS..................................................................................................................................... 34
EXPORTING AND IMPORTING A COMPLETE SUPERVISION FORM ............................................................... 34
START SUPERVISION WHEN WINDOWS IS STARTED .......................................................................................... 34
DISTRIBUTED SUPERVISION ......................................................................................................................................... 35
DEFINING THE DISTRIBUTED COMMUNICATION PARAMETERS ......................................................................... 35
CONFIGURE REMOTE VARIABLES -TAGS .............................................................................................................. 36
CONFIGURE REMOTE VARIABLES –OBJECT TAG ................................................................................................ 37
ACTIONS DURING SUPERVISION .................................................................................................................................. 37
PRINT A SUPERVISION SCREEN VIEW ................................................................................................................... 37
VISUALIZE, PRINT, IMPORT AND EXPORT AND CHECK HISTORY....................................................................... 37
MODBUS TCP AND MODBUS OVER TCP ...................................................................................................................... 38
NOVUS AUTOMATION 2/38
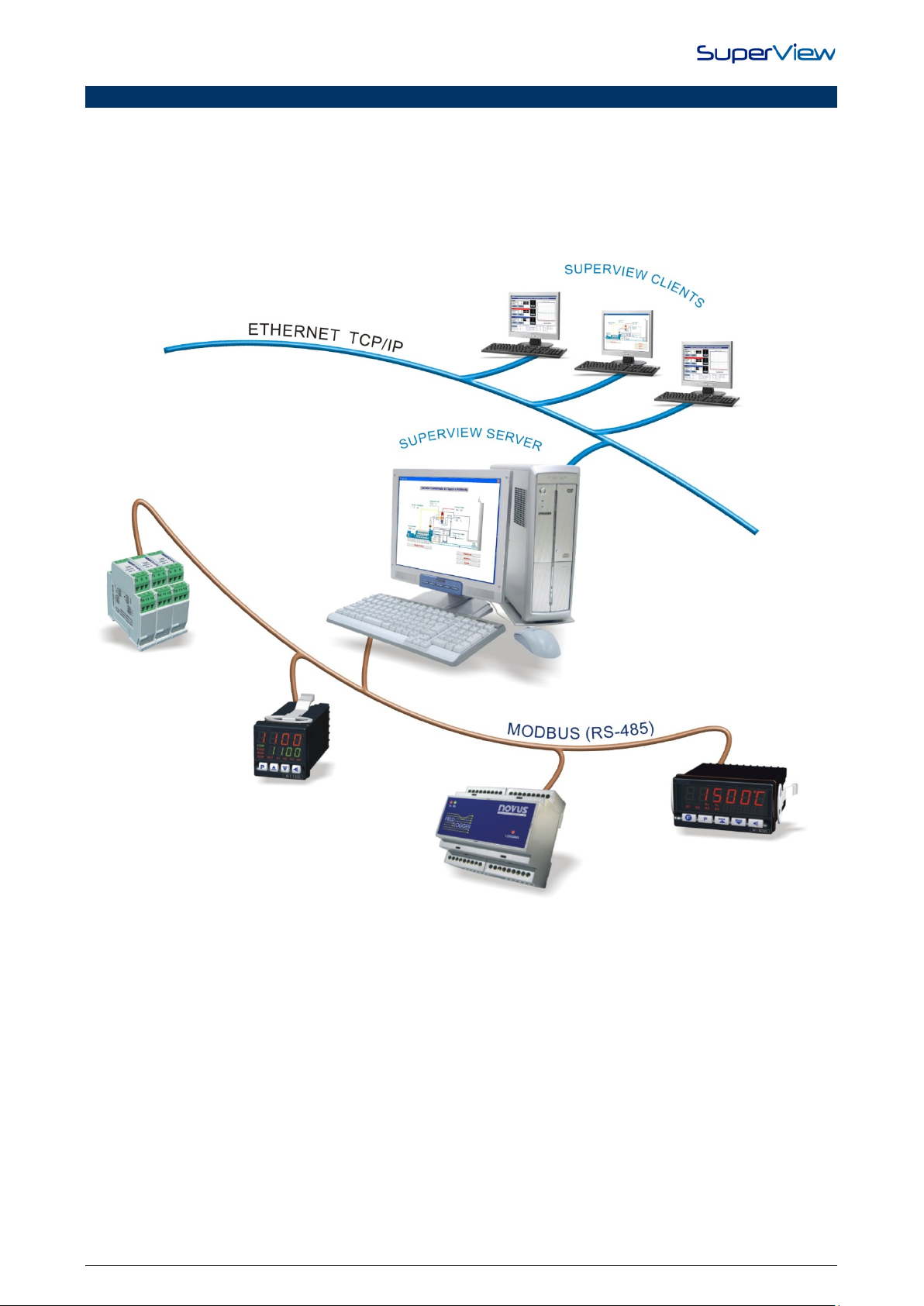
INTRODUCTION
Flexible, func tional and user-friendly, SuperView i s a SCADA – Supervis ory Control and Dat a Acquisition s ystem focused on
supervision of l ocal and g eo gra phi cal ly di s tr i buted appl ic at ions . It s simpl ic it y of conf i gurat ion c ol labor at e in t he pr oc es s o f tak i ng
decisions on how to develop mimic diagrams that represent s real supervision environment.
Acting as a control for super vis ion, the us er have a set of tool s that all ows des cribe l ogics t o read and wri te to M odbus devices.
There are diff erent kinds of alar m for each Tag (c hannel) with cus tomized notificat ions methods, adding security to deal wi th
them.
Electronic registers can be viewed and exported to well-known file formats (XLS, PDF, RTF, XML, HTML, DBF, TXT,
CSV). User’s authentication, t ask management, mathematic al formulas and audit trail of users acti on completes mai n features
of the system.
SuperView achieves t echnical requirem ents of FDA 21 CFR Part 11 for c omputer syst em validation. User s can acknowledge
alarms using elec tronic signature, el ectronic records ar e protected with encr ypted, strong mechanis m of authenticati on using
unique password and log of event’s applicati on (Audit Trai l) for traceabil ity. Vali dation protocol s and the executi on of validation
are optional to additional this product.
This manual describes the steps required to start using SuperView. A detailed description of each SuperView setting
window is available at the help system, accessible through the menu HELP/SUPERVIEW HELP, or by pressing F1.
NOVUS AUTOMATION 3/38

INSTALLATION
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
The following are necessary for using SuperView:
• A PC-Compatible computer running Windows XP or higher operational system. The minimum specification for this
computer is:
Processor AMD or INTEL 2 GHz
Free space on dick: 300 MB
RAM: 1 GB (2 GB Recommended)
Mouse, Keyboard, SVGA Monitor, Serial or USB Ports
NETWORK Interface
• In order to execute SuperView s et up in Server or Local mode, one or more devices with communication through
the MODBUS RTU Slave or MODBUS TCP protocol are necessary. If this device uses a RS485 communication
interface, a converter RS232/RS485 will also be necessary (if communication through the PC serial port is used)
or a USB/RS485 converter (if communication through the PC USB port is used – Requires Windows 2000, XP or
higher).
INSTALLATION PROCEDURES
To provide the SuperView installation, the computer user shall have the privilege of an administrator and an
unrestricted access to the Windows folders.
For the SuperView installation on your computer follow the steps below:
1. Insert the installation CD in the CD driver
2. The SuperView installation program shall start automatically in a few moments. If it does not launch automatically,
run it manually from D:\Setup.exe (considering that D: is the letter that identifies your CD driver).
3. Follow the instructions prompt ed on the screen til l the installation i s complete.
NOVUS AUTOMATION 4/38
FIRST STEPS
The use of SuperView can be divided into four stages:
• Setting up a basic application
• Registering SuperView
• Widening the application
• Supervision
The three first stages shall be performed by a user registered with the Administrator’s privileges. The supervision can be
accomplished by Administrator, Operator or Monitor user.
For the basic application set-up, the following basic steps shall be fulfilled.
• Start SuperView.
• Create a new application.
• Inform SuperView about the NOVUS networked devices in the supervisory system (it is possible to communicate
with Modbus RTU devices from other vendors, as described in “Configuring the Communication With Devices
From Other Vendors”).
• Inform SuperView which the interest variables are (TAGS) within each device in the network.
• Create one or more supervision screens, containing images, texts, buttons and graphics associated to the
variables read in the communication network.
• Define the network communicat ion paramet ers.
• Save the application.
• Start supervision.
The registration consists of registering a license number in SuperView designated by NOVUS when a user license is
purchased. The registration number is unique and is associated to the serial number of one of NOVUS devices
connected to the communication network.
Some additional steps may be required to widen the application:
• Create application’s users, with different privileges.
• Create alarm groups, defining actions for alarm events.
• Define alarm ranges for the critical variables monitored by the system.
• Set up the history register of the system important variables.
• Set up sending e-mail messages in alarm conditions.
• Set up the log of events and actions of the supervision system.
To setup a distributed supervision, the following steps shall be fulfilled.
• Set up the Server Mode to allow TCP/IP communication between two or more SuperView stations.
• Set up the applications to operate in Client mode.
Once the application is created, SuperView shall be normally used only in the Supervision mode, showing the operator
the different information about the supervised process.
SETTING UP A BASIC APPLICATION
START SUPERVIEW
In order to start SuperView, select the icon SuperView from the Start menu. The initial window will pop up in a few
seconds, as on the figure below.
NOVUS AUTOMATION 5/38
CREATE A NEW APPLICATION
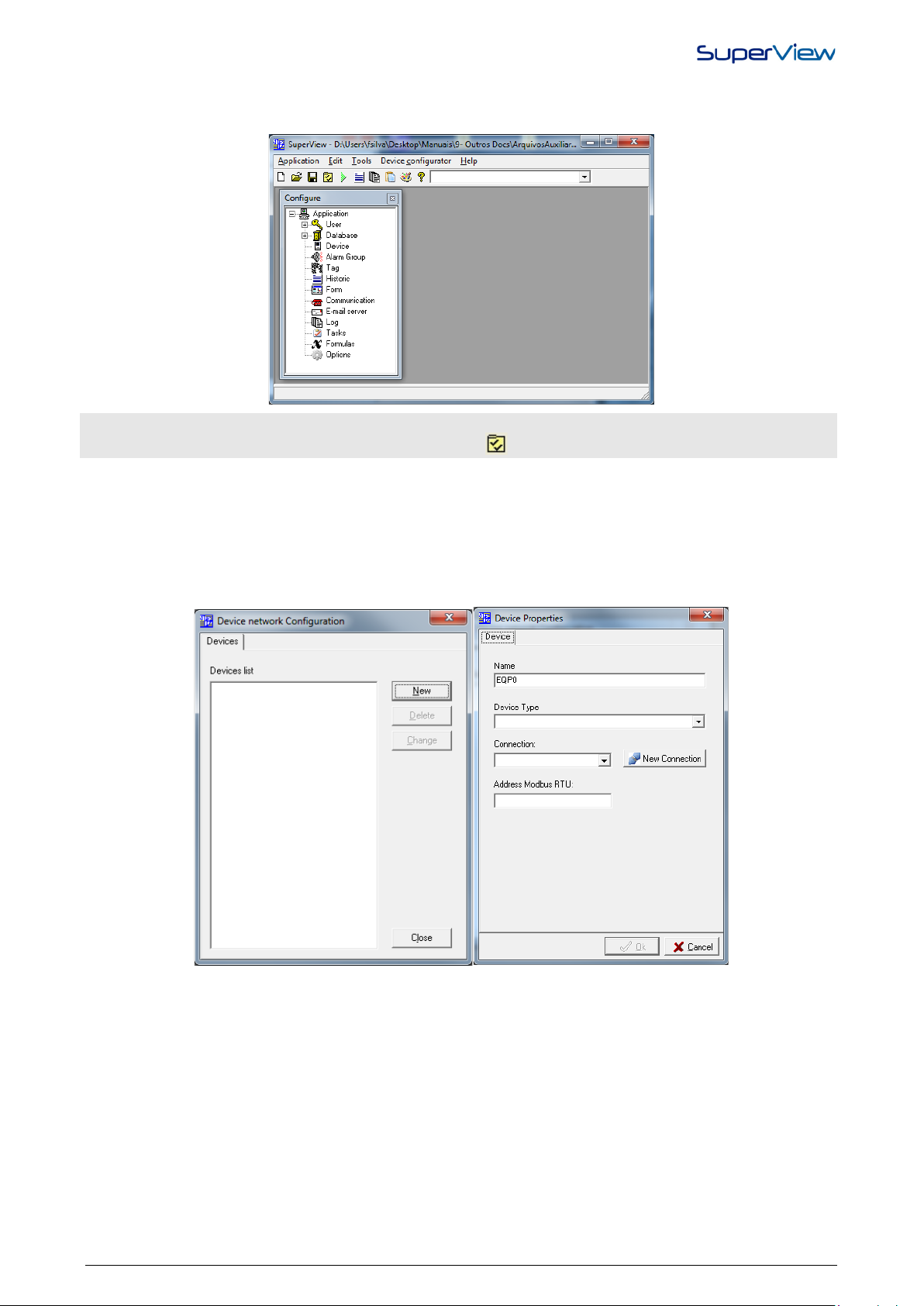
If the CONFIGURE window is closed, it can be opened again selecting the option from the menu
To create a new application in SuperView, select the option APPLICATION/NEW. The CONFIGURE window will be
displayed, as on the figure below.
REGISTERING DEVICES IN THE NETWORK
Establishing communication is only possible with registered devices. To register the devices in the SuperView network,
proceed as indicated below:
1. Double click the icon DEVICES in the CONFIGURE window. The window DEVICE NETWORK CONFIGURATION
2. Click NEW and the DEVICE PROPERTIES window will display. Examples of these two windows are presented on
APPLICATION/CONFIGURE, or pressing the button .
will be displayed.
the figure below.
3. Define the name, in the NAME field, which will identified it in SuperView; in the drop-down list DEVICE TYPE,
select the NOVUS device model that you want to be included in the network; in the field CONNECTION select the
connection that this device will use (for further information about connections, see the topic “Define network
communication parameters”) and in the field ADDRESS, type the address of the Modbus network that identifies this
device. The informed Modbus address must be the same as the one defined for the device, and it must be unique in
the network (only one device in the network can have this address). The name selected for the device will be used
to identify it when configuring the communication variables (TAGS).
4. After entering all these information, click the OK button and check if the new device was added to the registered
device list in the NETWORK DEVICES CONFIGURATION window.
5. Proceed with registering all devices in the network. When finished, close the window CONFIGURE DEVICES
NETWORK.
6. To change data of an existing device, select the device from the list in the CONFIGURE DEVICES NETWORK
window and press the button CHANGE.
The devices available for selection in the DEVICES TYPES list are registered in the SuperView devices database. For
further information about the database, see “Database of Modbus Devices Parameters”. To register Modbus devices
from other vendors, see “Configuring the Communication With Devices From Other Vendors”.
NOVUS AUTOMATION 6/38
The device registered with the address 1 must be a Novus device, and its electronic serial number must be
the one listed in the SuperView Use License purchased from Novus. This condition is necessary when
for more information on SuperView registering and licensing.
SuperView is used in the Full Registered mode. See chapter “REGISTERING THE SUPERVIEW COPY”
REGISTERING THE VARIABLES OF EACH DEVICE – TAGS
The basic element of information to the displayed on SuperView screens is the TAG. A TAG identifies numeric
information and can be one of the following types:
Physical Tag: Identifies a variable associated to a Modbus register in a NOVUS network device. This tag value
represents, for example, the current temperature reading of a controller or the required pressure
(set point) in another one. Only 16-bit value can be associated to a physical tag (values ranging
from -32768 to 32767 or from 0 to 65535).
Constant Tag: Identifies a variable in the computer memory, not associated to a device in the network. Typically
used to perform more advanced functions.
Date/Time Tag: Identifies a variable that contains information about date or time, as indicated by the computer
internal clock. Used when you want the current date and time to be displayed on the SuperView
screen.
Timer Tag: Identifies a variable that counts time in hours, minutes and seconds. Used when you want to
indicate how long the SuperView application is running for. A Timer Tag can be controlled by
writing operations using buttons or alarm groups. To pause or resume the count after a pause:
write -1 to the Tag. To reset the count: write 0 (zero) to the Tag.
Collect Tag: Identifies a variable associated to the data memory content of a NOVUS data logger, Field Logger
model. Used when there are historic data stored in this logger that must be transferred to a
SuperView historic file.
Custom Tag: Identifies a variable associated to a Modbus register in a networked device (like the Physical Tag,
but the device can be from other vendors). The configuration of the Custom Tag requires
parameterization of the Modbus command to be used to read from and write to the device. Onl y
Custom devices can use a Custom Tag type. See “Configuring the Communication With Devices
From Other Vendors” for additional information on communication with Custom devices.
Object Tag: The Object Tag is automatically created when the user creates a history, task or formula. Upon
creating a history, a Tag is created for it with the identification [HST]. Upon creating a task, a Tag
is created for it with the identification [TSK], and upon creating a formula a Tag is creat ed for it
with the identification [FOR]. If desired, the user can create an Object Tag for remote access. For
this purpose, the Object Tag shall be created through the Tags creation window.
Reading and writing operations in a physical or custom tag are associated to reading or writing operations through the
Modbus or TCP/IP communication network. When configuring a simple application, the Physical tag is of greater interest.
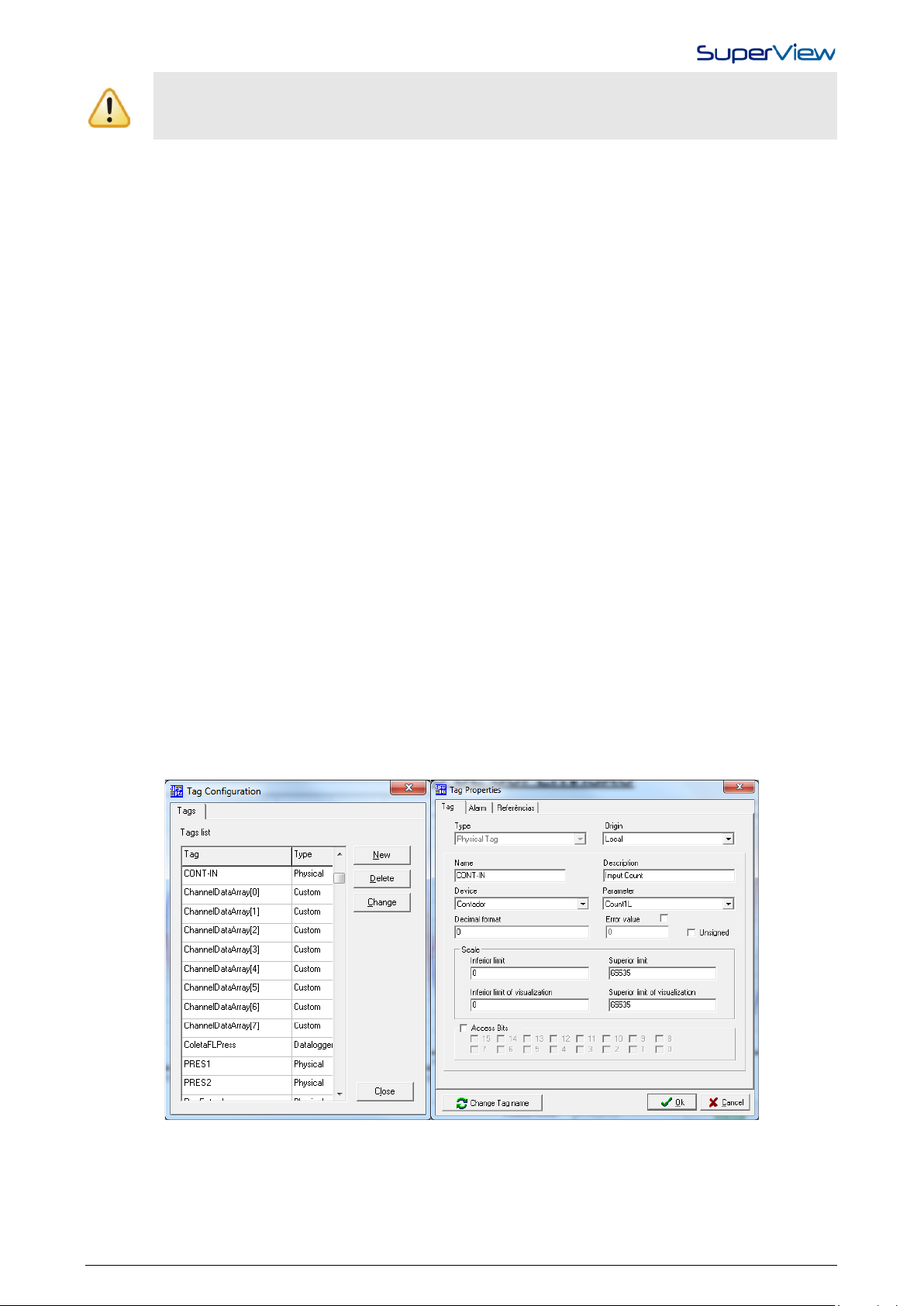
To register the physical tags that shall be read by the network devices, proceed as indicated below:
1. Double click the icon TAGS in the CONFIGURE window. The TAG CONFIGURATION window will be displayed.
2. Click the NEW button and the TAG PROPERTIES window will be displayed. Examples of these two windows are
shown below.
3. In the TYPE drop-down menu, select PHYSICAL TAG.
4. In the field ORIGIN, select LOCAL to read the tag from a RTU Modbus network.
5. In the field NAME assign the tag a unique name, which will identify it in all further set up steps of this SuperView
application.
6. Filling the field DESCRIPTION is optional, and this information is displayed only here.
7. In the DEVICE drop-down menu, select the registered device this tag belongs to.
NOVUS AUTOMATION 7/38
8. In the PARAMETER drop-down menu, select which register of the device will be associated to the tag. Note that
SuperView displays only devices that were already registered, and once the device is selected, the parameter list
corresponds to Modbus registers that are specific of this device model.
9. Select the number of decimal points that will be presented when the value of this tag is displayed on the screen.
10. Determine an ERROR VALUE that will be assigned to the TAG in case its value cannot be read from the associated
Modbus device (due to a communication error or disconnection of the device).
11. Check the box NO SIGNAL in case you want the TAG to undertake positive values higher than 32767, up to the
limit of 65535.
12. After entering all these information, press the OK button and check if the new tag was added to the list of registered
tags in the TAG CONFIGURATION window.
13. Proceed with registering all tags. When finished, closed the TAG CONFIGURATION window.
14. To change data of an existing TAG, select the tag from the TAG CONFIGURATION window list and press the
CHANGE button.
15. To change the name of a tag that has already been created, it is necessary to click on the “Change Tag Name”
button, thus the name is changed in all places where the tag is referenced in, too.
16. In the tab “References”, it is possible to see where the tag is being used, in order to locate the application
components used by the tag.
To set up a TAG in a Modbus device from another vendor, see “Configuring the Communication With Devices From
Other Vendors”.
CREATING SUPERVISION FORMS
Supervision forms are the core features of a SuperView application. Typically, each form presents a different vision of
the process under supervision, and can contain the following types of objects:
• Images
• Fixed texts
• Text box with tags
• Graphs with TAGS values through the time
• Bargraphs (Bargraph)
• Alarm table
• Buttons
• Historic control
• Gauge
• Angular Gauge
• Line Meter
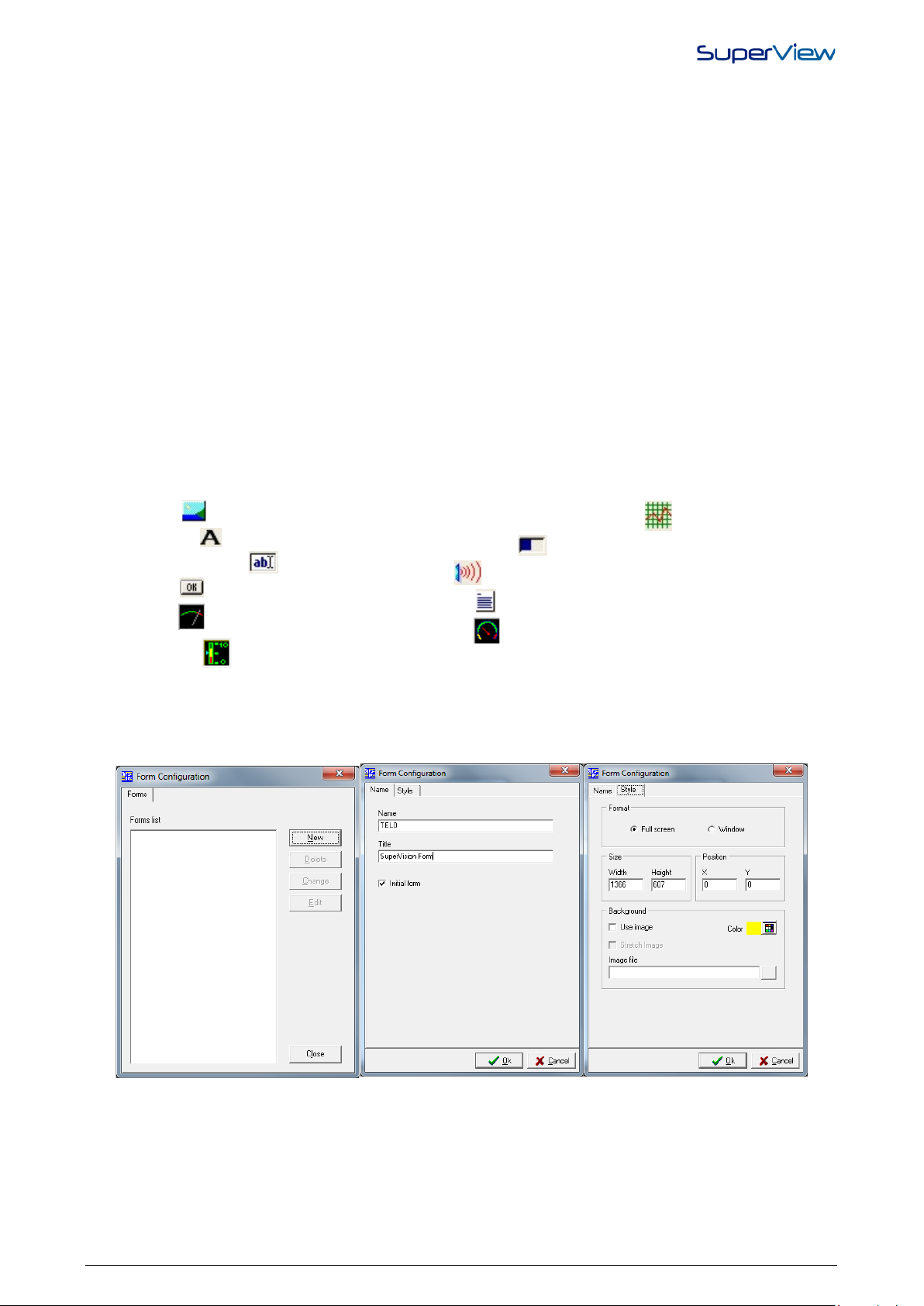
To create a new supervision form on SuperView, proceed as describ ed below :
1. Double click the icon FORM in the CONFIGURE window. The FORM CONFIGURATION window will be displayed.
2. Click on the NEW button and the FORM PROPERTIES window will display. Examples of these two windows are
shown below.
3. In the NAME tab, assign name and title to the form. The name will be used to identify the form in other set up steps
of SuperView, and the title will be presented at the upper part of the form during supervision.
4. Check the option INITIAL FORM to define this form as default whenever this SuperView application is started.
5. In the STYLE tab, define the form appearance (format, size and position). In BACKGROUND section, a color or an
image can be defined to be displayed at the screen background.
6. After entering all these information, click the OK button and check if the new form was added to the list of registered
forms in the FORM CONFIGURATIO N window .
7. To change data of an existing form, select the form from the FORM CONFIGURATION window list and press the
CHANGE button.
NOVUS AUTOMATION 8/38
Once the form is created, the objects that define its appearance and features must be positioned. If multiple forms were
click the first object and then press the Ctrl key. With the Ctrl key
click on the other objects. Multiple selected objects can be dragged (moved)all together with the
created, you can select the one that will be edited using the FORM CONFIGURATION window list, clicking on the EDIT
button. The form to be edited can also be selected from the list located on the upper tool bar of the SuperView screen,
as illustrated on the figure below. Select the form to be edited form this list.
The selected form will be displayed at the desktop. The bottom tool bar contains tools for the inclusion of different
supervision objects in the form area, as presented in the following figure.
The steps required to create a form containing a graphic object ( ),a text box with a tag ( ),two buttons ( ),an
image ( )and a fixed text ( ) are listed below.
1. Select the form to be edited from the forms list located on the upper tool bar. In this example the form called “Initial”
is selec ted.
2. Select the object that will be inserted clicking on the corresponding tool. It will be recessed while active. In the
empty area of the form under creation, left-click the mouse and drag it, defining a rectangle with the dimension
required for the object. When you release the mouse button, the selected object will be placed on the form. To place
another type of object, select the corresponding tool and repeat the procedure to place it on the form. To disable the
selected tool, click on the recessed one or on the arrow tool ( ).When no tool is selected (recessed), the mouse
can be used to move and change the dimensions of the already placed objects. The following figure shows an
example of a form with all objects positioned.
To select more than one object, left-
pressed,
mouse.
NOVUS AUTOMATION 9/38
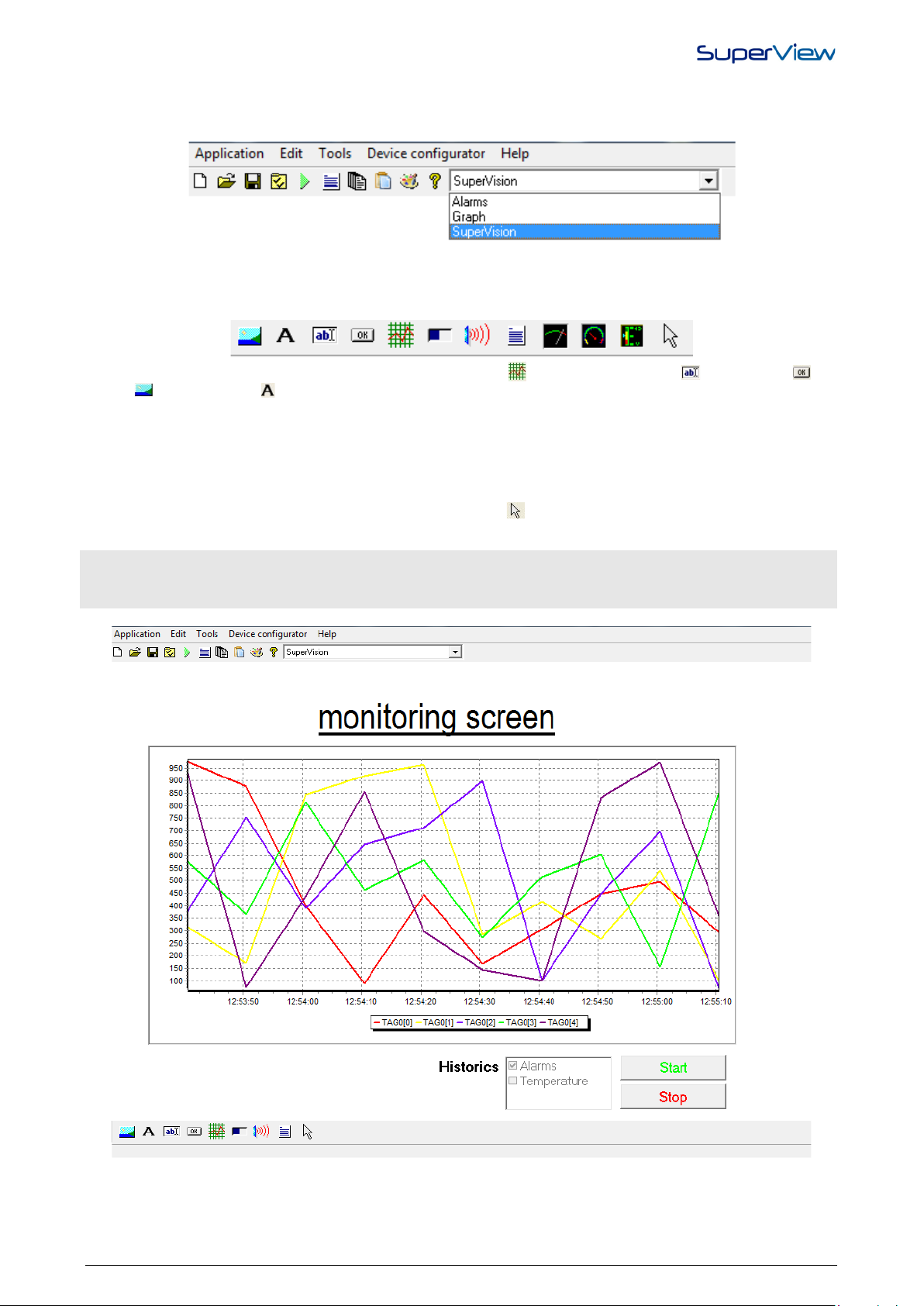
3. Define the properties for each object placed on the form. These properties specify the object appearance and
features. To access the properties window of each object, right-click the object and select PROPERTIES from the
pop-up menu, which will be displayed. The figure below shows the properties windows of the text box with tags
(ELM3 in the previous figure). For further information on the properties of the other objects, refer to the SuperView
help.
4. In the CONTENT tab, select among showing a Tag value, the user name, the number of the application version, you
can use the text box to perform the created routine, only typing the value code in the text box, and at the end, it can
be used as a text box for inserting simple texts.
5. If the user selects the option to show the value of a tag, the list of existing Tags is shown in the box under it, only
tags that have already been registered can be associated to a screen object. Display the list of tags available for
selection clicking on . Define the update rate of the value displayed in the text box. In case the associated tag is
of the Physical type, this rate will define the interval between the tag readings from the communication network. Use
the maximum acceptable value to reduce network traffic. If the associated tag allows write operations, define
whether it can be changed during the supervision through this text box.
6. In case the user selects the option “execute routines”, in the field “routines directory”, the directory, which serves as
repository for the routines files shall be informed.
7. In the STYLE tab you can define visual properties as: font type, background color, border and text alignment.
8. The SIZE/POSITION tab is more informative, once both size and position of form objects can be defined using the
mouse.
9. After the configuration is complete, clic k OK.
10. Define the properties for all objects on the screen. Each type of object presents a specific set of properties, which
are not described in this manual. For further information about the particular properties of each object type, see the
SuperView help by pressing F1 key upon visualization of the window which the help is necessary in.
DEFINE THE NETWORK COMMUNICATION PARAMETERS
The communication through the Modbus RTU network for the reading and writing operations from the Physical Tags is
accomplished through a serial communication port of the computer (COM port). The COM port to be used for
communication, as well as its parameters, shall be set up in SuperView. For this set-up, proceed as described below:
1. Open the CONFIGURE window by clicking in the upper tool bar.
2. Double click the COMMUNICATION icon. The window with the existing Types of communication in SuperView will
be displayed, select SERIAL COMMUNICATION, and the window will shown as the figure below.
NOVUS AUTOMATION 10/38
3. SuperView operates with multiple connections, so different COM port connections can be created, further to the
Upon opening an application, the user name and password will be requested. In case users have not been
possibility to create connection for communication with Modbus TCP protocol.
4. In NAME, select the name for the connection, in CONNECT USING, select the communication port which the
devices to be supervised will be connected to. The other fields will be self guiding.
5. After the configuration is complete, clic k OK.
6. The User can confirm more connection without leaving this window, it is enough to save the existing connection
clicking on the button and then clicking on the button , to start the set-up of the new connection. The
connections shall use different COM ports.
To set up the parameters of the distributed communication, see DISTRIBUTED SUPERVISION.
SAVING AND OPENING AN APPLICATI ON
The application created for SuperView must be saved to avoid losing the last changes. Multiple applications can be
created and saved in different files. To save the current application, select APPLICATION/SAVE or click on the upper
tool bar.
To open a previously created application, select the FILE/OPEN option from the menu or click the button on the upper
tool bar.
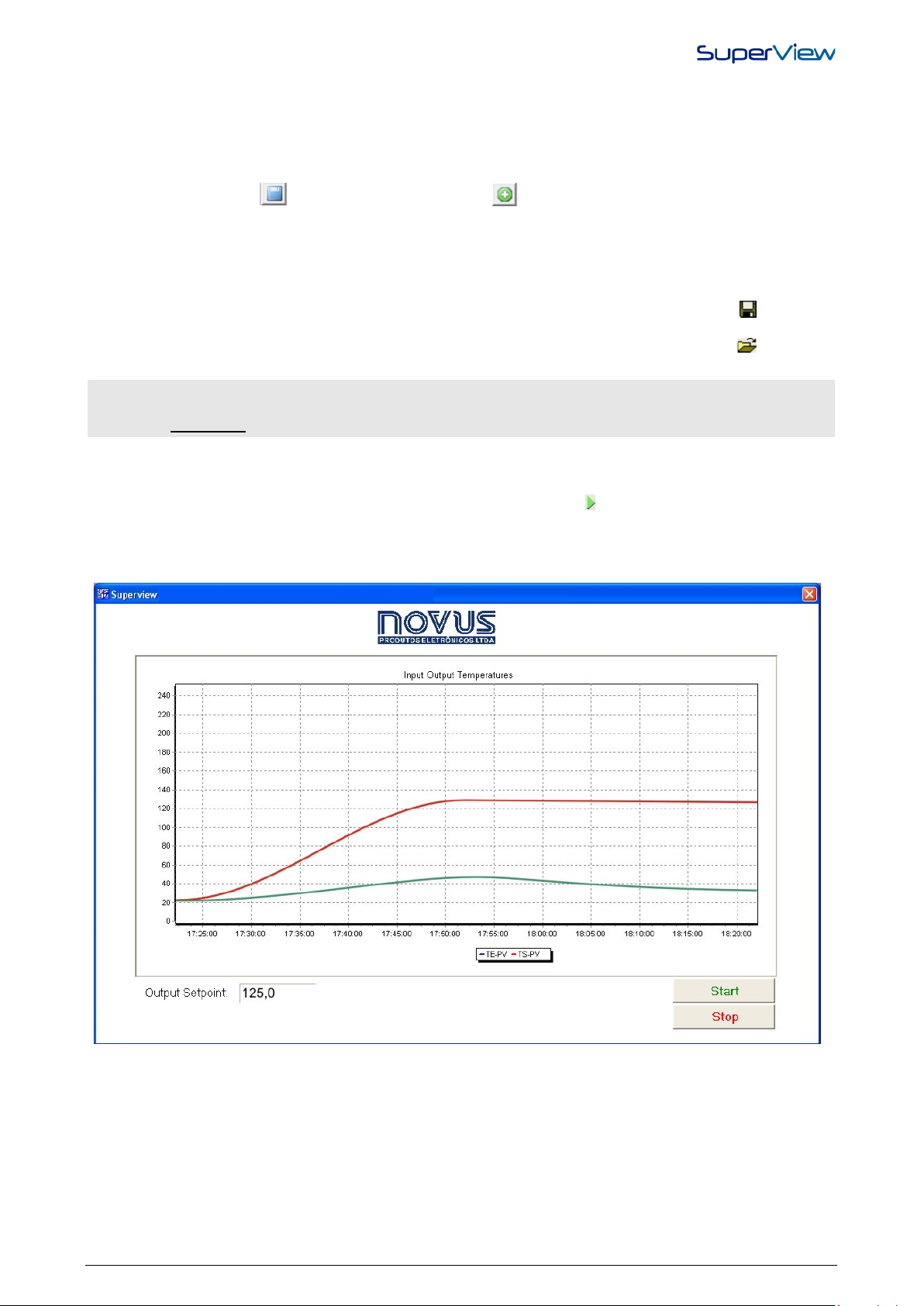
START SUPERVISION
A non-registered copy of SuperView is able to operate in the supervision mode for 20 minutes. This is enough time to
check how the application created is working. To start supervision, click from the upper tool bar, or select
APPLICATION/SUPERVISE option from the menu. SuperView will show a message informing that anon-registered copy
will operate during 20 minutes only, and the communication with the devices will be started. The form defined as initial
will be shown. The sample screen presented before is shown in the supervision mode, according to the figure below (the
tags values depend on the values read from the netw ork dev ices).
defined upon creating this application, or the standard users’ set-up has not been changed, use the word
SuperView as a user name and password (all lower case characters).
All steps described in this chapter for “Configuring a Basic application” are necessary to create a simple supervisory
application and enough to get acquainted with its use. For more complex applications, additional features must be
included in the application, and are described in the “Additional Features” chapter. To operate in supervision for more
than 20 minutes, SuperView must be registered. The registering procedure is described in the chapter “Registering the
SuperView Copy”.
NOVUS AUTOMATION 11/38

REGISTERING THE SUPERVIEW COPY
• It is important to point out that SuperView requir es the machi ne administrator privileges, a free USB
in the Server mode. in case no Clients number is specified,
The Novus device related to the registration number is present in the Modbus network, with address 1
The SuperView register can be done in two ways, the first is using a Hardkey, which shall be plugged in a USB port of
the computer when the SuperView is installed, or using the Softkey system, where it is necessary to have a Novus
device connected to a modbus network, so that the validation of the software register number is provided, based on the
device serial number.
REGISTER USING A HARDKEY
In order to register your SuperView license, it is enough to purchase a Hardkey with the respective license and connect
it to a USB port in the computer where SuperView will supervise, with no need to install any kind of driver. In order to
check whether the Hardkey is working in the selected USB port, it is enough to check whether the indicator light is lit
green.
port and that the energy options cannot switch the USB off during the supervision.
• SuperView will periodically check the Hardkey, so in order for the software to continue monitoring in
full mode, it is necessary to keep the Hardkey plugge d in the computer .
The users have the possibility to purchase six types of Hardkey for SuperView:
- SuperView Software SCADA for Modbus devices with a Hardkey;
- SuperView + License for 1 remote connection with Hardkey;
- SuperView + License for 2 remote connections with Hardkey;
- SuperView + License for 3 remote connections with Hardkey;
- SuperView + License for 4 remote connections with Hardkey;
- SuperView + License for 9 remote connections with Hardkey;
In the SuperView installation pack, there is software for the performance of a set of maintenance actions for the
Hardkey.
OPERATION MODES WITH A HARDKEY
When the supervision is started, SuperView can operate in three different modes, according to the situation of its
register:
Demonstration Mode: In this operation mode all SuperView features are available, but once the supervision is started,
a warning is shown, and after 20 minutes, the supervision mode is interrupted. To be able to re-start the supervision the
hardkey shall be inserted in a USB port in the computer which the SuperView is installed on, thus, next time the software
carries out the register verification, the supervision will be restarted. SuperView operates in this mode when:
• A valid Hardkey has not been found in the computer USB port.
Full Register Mode: In this operation mode, all SuperView features are available, there is no any warning regarding the
register and the Supervision mode can be used indefinitely, provided that a valid Hardkey is plugged in a USB port of the
computer which SuperView is installed on. Thus, SuperView operates in this mode only when:
• SuperView finds a valid hardkey plugged in a USB port of the computer which it is installed on.
• When the Hardkey being used for the register does not have a license for remote connections, the supervision in
distributed mode will be performed in a Demonstration Mode.
REGISTER USING A SOFTKEY – USE LICENSE AND REGISTRATION NUMBER
For licensing of one SuperView copy use, it is necessary to purchase from Novus a Use License containing Registration
Number of the product. The utilization of SuperView with a Registration Number in a computer, without the
corresponding Use Licen se is forbid den.
VALIDATING THE REGISTRATION NUMBER
The SuperView Registration Number is associated to the serial number of a Novus device and to a quantity
of Clients that can connect to SuperView
SuperView will allow a Client connection in the demonstration mode for 20 minutes. The SuperView copy
will operate fully and without warnings only in case:
• A valid registration number has been inserted.
•
(one) or 255 (two hundred and fifty fife).
NOVUS AUTOMATION 12/38
 Loading...
Loading...