Page 1
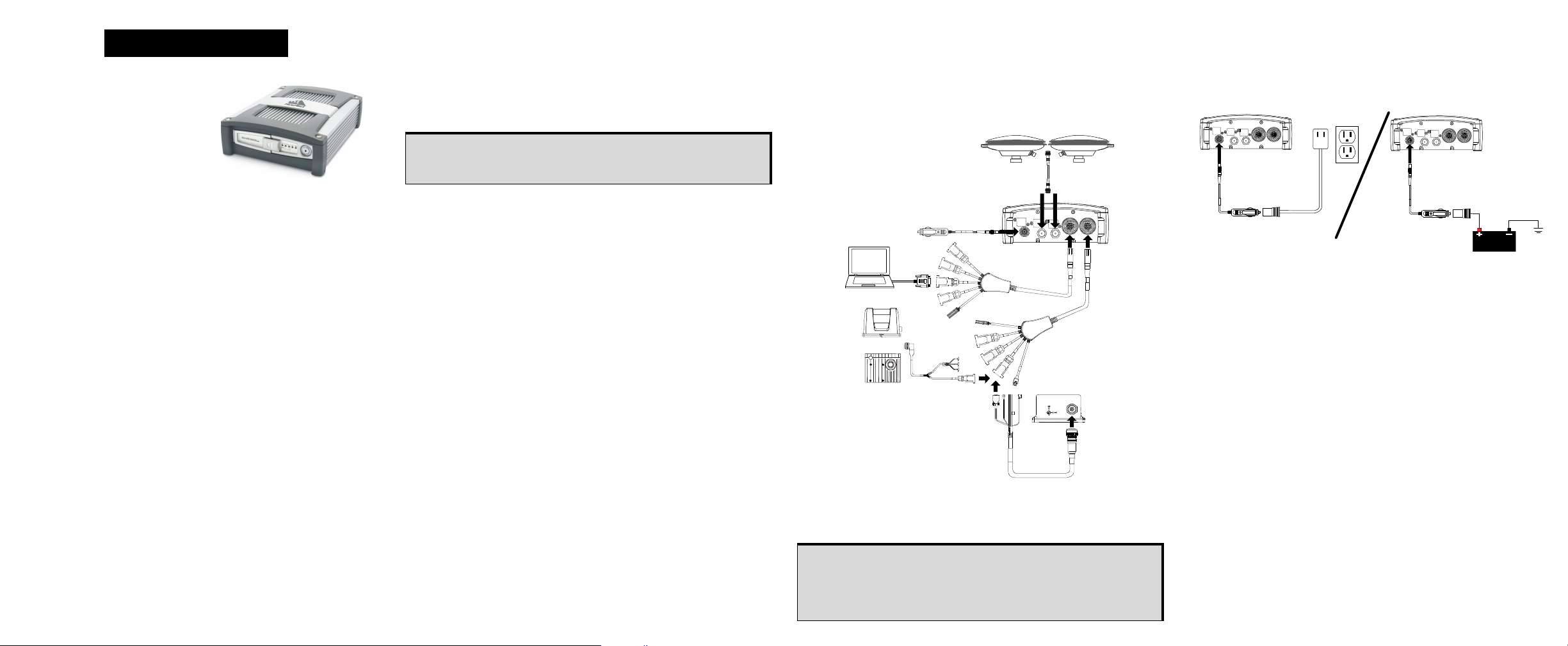
SPAN-SE Receiver
QUICK START GUIDE
OR
OR
GM-14915082 Rev 3 May/2012
This guide provides the basic
information you need to set up
and begin using your SPAN-SE
receiver.
BOX CONTENTS
In addition to this Quick Start
Guide, the following is provided in your SPAN-SE package:
• 1 SPAN-SE receiver
• 2 multi-connector cables
• 1 mounting bracket with screws
• 1 6-foot USB 2.0 cable
• 1 industrial SD memory card
• 1 power cable
• 1 multi I/O connector cover
• 1 CD containing PC Utilities and product documentation
• 1 patent notice and manual request postcard
ADDITIONAL EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
The following additional equipment is needed for a basic setup:
®
• A Windows
or Ethernet port
• A power supply that produces 12 – 28 volts DC
• A quality dual frequency GNSS antenna such as the
GPS-702, the GPS-702-GG, the ANT-A72GA-TW-N for
airborne/high speed applications, or the GPS-702L
antenna for L-Band corrections
• A TNC to appropriate antenna connector RF cable
• A SPAN-supported IMU such as NovAtel numbers:
IMU-H58, IMU-H62, IMU-H00, IMU-LN200,
IMU-FSAS-EI, IMU-FSAS-EI-O, IMU-CPT, UIMU-LCI,
IMU-HG1900 or IMU-HG1930
-based computer with an RS-232 DB9, USB
INSTALLING NOVATEL PC UTILITIES
Before setting up your SPAN-SE system, install NovAtel’s PC
Utilities
on the Windows-based computer that you will use to
communicate with it.
1. Start the computer.
2. Insert the accompanying CD in the CD-ROM drive.
To access and download the most current version of our OEMV PC
Utilities, go to the Support page of the NovAtel web site at
www.novatel.com.
3. Select Install the OEMV PC Utilities from the window that is
automatically displayed. If the window does not
automatically open when the CD is inserted, select Run from
the Start menu and select the Browse button to locate
Setup.exe on the CD drive.
4. Install the PC Utilities by advancing through the steps
provided in the NovAtel GPS PC Utilities setup program.
SPAN HARDWARE SET-UP
Complete the following steps to set up and power your
SPAN-SE.
1. Mount the IMU and antenna securely to a vehicle. Ensure
that the devices cannot move and that the distance and
relative direction between them is fixed.
2. Connect the 30-pin connector of the I/O 2 Yellow Cable to
the yellow port labelled I/O 2 on the SPAN-SE. The cable
clicks when connected properly.
3. Connect the GNSS antenna to the port labelled GPS1 on the
receiver using an appropriate antenna cable.
4. Connect a communications cable from your computer to the
SPAN-SE.
If you want to connect via a serial connection, connect the
COM1 connector of the I/O 2 Yellow Cable to a computer
using a straight-through serial cable.
If you want to connect via USB, connect a USB cable from
the computer to the USB Device port on the SPAN-SE.
If you want to connect via Ethernet, connect a shielded
network cable from the computer to the Ethernet port on the
SPAN-SE.
See the SPAN-SE User Manual for information on
communication connection options.
5. Connect the IMU connector of the I/O 2 Yellow Cable to an
IMU with the IMU interface cable.
6. Insert the SD card into the slot behind the front panel door.
Files stored on the SD card can be transferred to a host computer
for data analysis or other types of post-processing by using the FTP
functionality built into the SPAN-SE or by removing the SD card and
inserting it into a host computer that has an SD card slot or an
adapter attached.
7. Apply power to the receiver. Do not press the power button;
the receiver powers up automatically. If possible, add a
back-up battery between the receiver and its voltage supply
if installed in a vehicle. The backup battery acts as a buffer
to prevent power dips that can cause the receiver and IMU
to lose lock and calibration settings.
8. Connect additional serial communications equipment as
needed. The following ports are available:
• 4 UART serial (RS-232/RS-422 configurable)
• 1 USB
• 1 Ethernet
Refer to the SPAN-SE User Manual for detailed information on
configuring the SPAN-SE communication ports.
LED STATUS INDICATORS
There are six LEDs on the front of the SPAN-SE receiver that
represent the following status categories:
•Power
• SD card memory
• Internal OEMV-3 card status (GPS 1)
• Internal OEMV-2 card status (GPS 2)
• INS filter
• IMU communication
Page 2
The following table details the states of each LED, which remain
solid unless the table indicates a flashing condition.
Table 1: SPAN-SE LEDs
LED Off Green Orange Red
Powered and the
Power
SD No card
OEMV3 No board
OEMV2 No board
INS GPS only
IMU No IMU
No power
to the unit
unit is off
Flashing:
powered and the
unit is on
Card in
Flashing:
file open
Solution complete
+ fine steering
Flashing:
coarse steering
Solution complete
and fine steering
Flashing:
coarse steering
Solution good
Flashing:
alignment
complete
Good RAWIMU
packets
N/A N/A
Card in, low space
Flashing:
file open
Insufficient
observations
Insufficient
observations
Aligning
Flashing:
solution bad
No RAWIMU (IMU
type not set)
Card in, full
Receiver status
error
(bits: 0,1,2, 7)
Receiver status
error
(bits: 0,1,2, 7)
INS inactive
IMU status
error bits
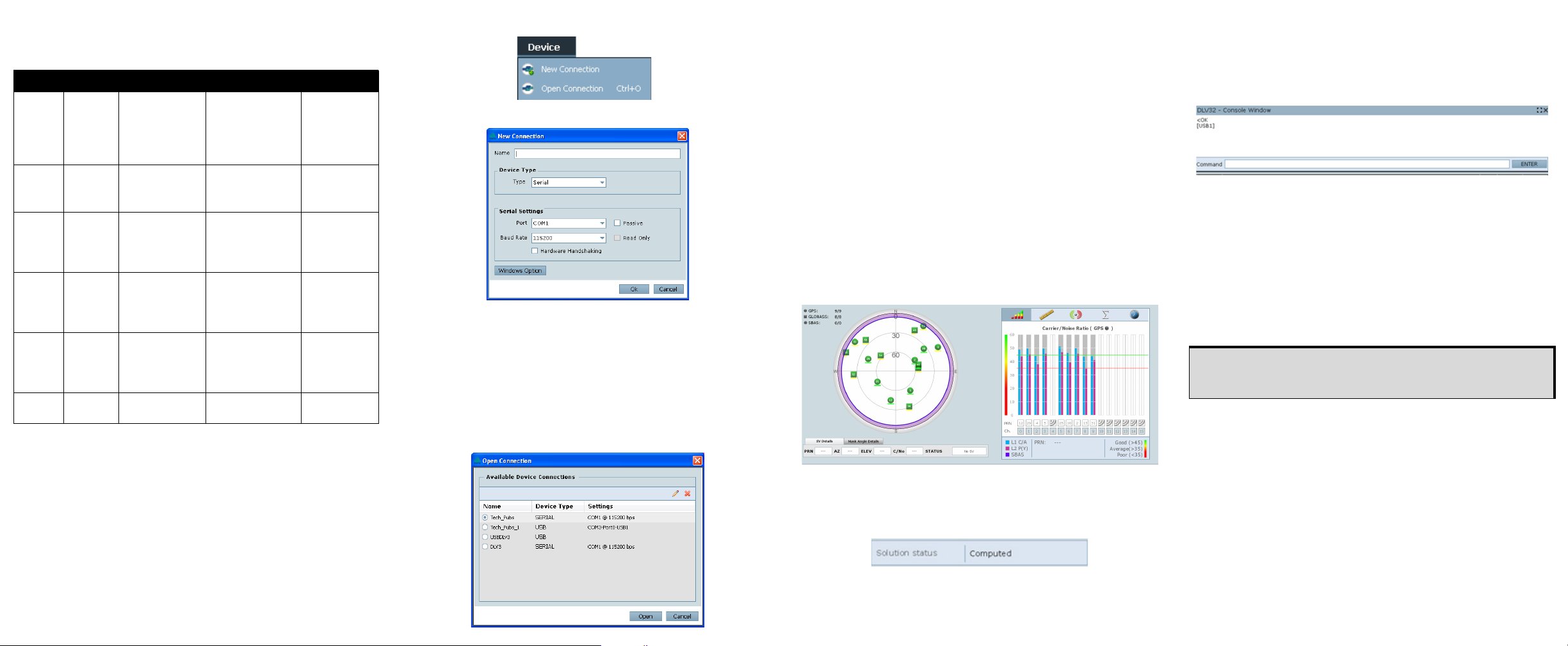
ESTABLISHING RECEIVER COMMUNICATION
To open a serial port to communicate with the receiver, complete
the following:
1. Launch Connect from the Start menu folder specified during
the installation process. The default location is Start | All
Programs | NovAtel PC Software | NovAtel Connect.
2. Select New from the Device menu.
3. Enter a name for the Connection setup.
4. Select Serial from the Typ e list.
5. Select the computer port that the SPAN-SE is connected to
from the Port list.
6. Select 115200 from the Baud Rate list.
7. Ensure the Hardware Handshaking check box is cleared.
8. Click the OK button to save the new device settings.
9. From the Device menu, select Open Connection.
10. Select the new configuration from the Available Device
Connections area of the Open Connection dialog and click
the Open button.
Connect establishes a communication session with the
receiver and displays the progress. Once connected, the
progress box disappears and several windows open,
including the Console window. Connect is now ready for use
to view status information, enter commands or log data.
Using Connect
Connect provides access to key information about your receiver
and its position. The information is displayed in windows
accessed from the View menu. For example, select Position
Window from the View menu to display the position solution of
the receiver. To show details of the GNSS and geostationary
(SBAS) satellites being tracked, select the Tracking Status
Window from the View menu. Select Help from the main menu
for more details on Connect, its windows and features.
Determining When the Position is Valid
When the receiver has a valid position, the Solution Status field
in the Connect Position window shows Computed:
Entering Commands
The SPAN-SE uses a comprehensive command interface.
Commands can be sent to the receiver using the Console
window in Connect, which is opened from the View menu. Enter
commands in the text box at the bottom of the Console window.
The OEMV Family Quick Reference Guide, available on the CD
or on our Web site, provides comprehensive information about
available commands. The SPAN-SE User Manual provides
information on a subset of these commands; in particular, the
ones commonly used with the SPAN-SE.
SAVECONFIG Command
If you change the configuration of a function and want to save
the new settings for your next session, use the SAVECONFIG
command.
When using NovAtel Connect to configure your receiver, ensure all
of the graphical windows are closed before you issue the
SAVECONFIG command.
CONFIGURING GNSS
Depending on the accuracy of the solution required, GNSS can
be augmented with a number of correction sources including
SBAS, L-Band and RTK (RTCA, RTCM, RTCM V3 and CMR).
Refer to the SPAN-SE User Manual for SBAS, L-Band or RTK
setup and operation.
Page 3

Enabling Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) Positioning
Corrections can be transmitted from a base station to a rover
station to improve position accuracy. The base station is the
GNSS receiver that acts as the stationary reference. It has a
known position and transmits correction messages to the rover
station. The rover station is the GNSS receiver that does not
know its exact position and can receive correction messages
from a base station to calculate differential GNSS positions.
You must create a data link between the base station and rover
station (two NovAtel receivers) to transfer corrections. SBAS
and L-band corrections can be accomplished with one receiver
and are exceptions to the base/rover concept. A link capable of
at least 9600 bits per second and less than 4.0 seconds of
latency is recommended. When connecting a base station to a
SPAN-SE, the data link must connect to the SPAN-SE OEMV3
COM port, found on the I/O 1 Green Cable.
When the base and rover stations are set up, you can configure
them for RTCA, RTCM, RTCMV3, CMR+ or CMR corrections.
Below is an RTCM example. Replace the latitude, longitude and
height coordinates shown with those of your base:
Base
interfacemode com2 none rtcm off
fix position 51.11358042 -114.04358013 1059.4105
log com2 rtcm3 ontime 10
log com2 rtcm22 ontime 10 1
log com2 rtcm1819 ontime 1
log com2 rtcm1 ontime 5
log com2 rtcm31 ontime 5,1
(optional GLONASS PSRDIFF)
log com2 rtcm32 ontime 10,2
Rover
gnsscardconfig rtcm none off
RT-2 and RT-20-capable SPAN-SE receivers with AdVance RTK
are real-time kinematic products developed by NovAtel. Optimal
RTK performance requires both the base and rovers be NovAtel
products. However, AdVance RTK operates with equipment from
other manufacturers when using RTCM messaging.
RT-2 and RT-20 are supported by GPS+GLONASS and GPSonly OEMV-based models. Also, RT-20 with GPS+GLONASS
provides faster convergence.
1.Refer to the GPGST log’s usage box in the OEMV Firmware
Reference Manual for a definition of RMS and other statistics.
2.For more base/rover configurations, search for “rover base” on
our Knowledge Database at: http://support.novatel.com/home.
CONFIGURING THE SPAN IMU
Configure SPAN with Connect
Follow these steps to enable INS as part of the SPAN system
using the NovAtel Connect software utility:
1. Select Wizards | SPAN Alignment from the Connect toolbar.
This wizard takes you through the steps to complete a
coarse or fast alignment, select the type of IMU and
configure the receiver to IMU port to accept IMU data.
When you have made your selections in the SPAN wizard, click
the OK button to enable the SPAN system. When the system is
enabled, raw IMU data becomes available and the INS filter
starts.
Configure SPAN Manually
Follow these steps to enable INS as part of the SPAN system
using software commands:
1. Issue the SETIMUTYPE command to specify the IMU.
Table 2: Enable INS Commands
IMU Type SETIMUTYPE
LN-200 IMU_LN200
iIMU-FSAS IMU_IMAR_FSAS
IMU-CPT IMU_KVH_COTS
UIMU-LCI IMU_LITEF_LCI
IMU_HG1700_AG11, or
IMU-HG1700
IMU-HG1900 IMU_HG1900_CA29
IMU-HG1930 IMU_HG1930_AA99
The inertial filter starts when the GNSS solution is solved and
the IMU is connected.
A GNSS antenna must be connected and actively tracking satellites
for correct operation.
2. Use the SETIMUTOANTOFFSET command to set the
distance from the IMU to the GNSS antenna. The offset
between the antenna phase centre and the IMU axes must
remain constant and be accurate (m). The X (pitch), Y (roll)
and Z (azimuth) directions are clearly marked on the IMU
enclosure. The SETIMUTOANTOFFSET parameters are
(where the standard deviation fields are optional):
x_offset y_offset z_offset [x_stdev] [y_stdev] [z_stdev]
IMU_HG1700_AG17, or
IMU_HG1700_AG58, or
IMU_HG1700_AG62
A typical RTK GNSS solution is accurate to within a few
centimeters. For the integrated INS/GNSS system to have
this level of accuracy, the offset must be measured to within
a millimetre. Any bias between the two systems appears in
the output position. For example, a 10 cm error in recording
this offset will result in at least a 10 cm error in the output.
If you cannot measure the IMU to GNSS antenna offset
precisely, perform the lever arm calibration routine to
estimate offset. Refer to the SPAN-SE User Manual for
details.
Configuration for Alignment
A coarse alignment routine requires the vehicle to remain
stationary for at least 1 minute. If that is not possible, an
alternate fast alignment routine is available. The fast or moving
alignment is performed by estimating the attitude from the GPS
velocity vector and injecting it into the SPAN filter as the initial
system attitude.
A static coarse alignment is not available for the IMU-CPT or
IMU-HG1930 IMUs. The fast, or kinematic alignment must be
used instead. A stationary alignment is only possible with a dual
antenna SPAN-SE-D, or if the SETINITAZIMUTH or
SETINITATTITUDE commands are issued. See the SPAN-SE
User Manual for more information.
If your have a dual antenna system (SPAN-SE-D), the default
alignment mode is a dual antenna alignment. Once you enter
the primary and secondary antenna offsets (with
SETIMUTOANTOFFSET and SETIMUTOANTOFFSET2
respectively) the system will automatically align as soon as it
computes a dual antenna solution. See the SPAN-SE User
Manual for more information.
Page 4

LOGGING DATA
NovAtel, SPAN, Inertial Explorer, Waypoint and OEMV are registered trademarks of
NovAtel Inc.
SPAN-SE is a trademark of NovAtel Inc.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
© Copyright 2012 NovAtel Inc. All rights reserved.
Printed in Canada on recycled paper. Recyclable.
Unpublished rights reserved under international copyright laws.
You can collect data logs through any I/O port on the SPAN-SE
receiver into any data capture software, including Connect.
SPAN-SE also has a SD card for data collection. To send data to
the SD card, open a file, then use FILE as the port designator in
log requests. You must close the file when collection is
complete.
For example:
LOGFILE OPEN TEST.GPS
LOG FILE RANGECMPB ONTIME 1
LOGFILE CLOSE
The SPAN-SE has a default logging profile with all raw data
needed for post-processing. If you press the SD logging button,
this profile automatically logs to a uniquely named file until the
SD logging button is pressed again. To change the default
logging profile, send the log requests that you want, the
command: SETAUTOLOGGING ON and then SAVECONFIG.
The newly-defined profile is automatically logged to the SD card
on power up.
Save logs and commands with the SAVECONFIG command to
ensure that the same logging configuration starts whenever the
receiver is powered on. Remove the SD card from the receiver
and plug it into a computer to download data from the card. The
data logging button, located beside the SD card, stops and starts
the data logging if you must change cards during operation.
You can monitor the logs’ output to determine the system status.
Multiple Connect windows show the status of various receiver
subsystems. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) on the front of the
SPAN-SE receiver also show the status of many subsystems.
Log SPAN Data
Raw GNSS, IMU and navigation data (position, velocity and
attitude) are available from the system as ASCII or binary logs.
Data can be collected through Connect using the Logging
Control window, or sent through the receiver COM port to usersupplied data collection software.
For post-processing applications, collect the data shown in the
Post-Processing section of this guide.
OPERATING THE SPAN SYSTEM
Observe the status of the system in the Connect INS window or
in the status field of any of the INS solution logs (for example
INSPOS, INSVEL, INSATT and INSPVA).
INS data is available when the GNSS solution has solved for time
(i.e., FINESTEERING status). An antenna must be connected and
tracking satellites for the system to function.
If performing a static alignment, allow the system to be
stationary for at least one minute after the GNSS solution is
computed for its initial system alignment.
If performing a kinematic alignment, move the vehicle forward at
a speed faster than 1.15 m/s.
If performing a dual antenna alignment, allow the system to
begin alignment, and wait approximately thirty seconds for a
dual antenna solution to be computed.
The following status stages may be observed:
• The status changes from INS_INACTIVE to INS_ALIGNING
when the alignment starts
• The status changes to INS_ALIGNMENT_COMPLETE
when the alignment is complete. Typically, this state continues until the system senses motion.
After some motion (stops, starts, and turns), the attitude
solution converges to within specifications, and the status
changes to INS_SOLUTION_GOOD.
The status may occasionally change to
INS_BAD_GPS_AGREEMENT. This status indicates that the
inertial solution has detected poor quality GNSS positions from
the receiver due to limited satellite visibility or high multipath
conditions. The inertial filter may choose to disregard this
information and wait for the GNSS quality to improve. The
solution is still valid during this status, but it is a warning that the
GNSS/INS solution is more reliable than the GNSS-only
solution.
POST-PROCESSING
Post-processing requires collection of simultaneous data from
the base and rover stations. This includes accurate coordinates
of the base station and accurate measurement of the IMU to
antenna separation.
The following logs are required for post-processing:
• From the base station
• RANGECMPB ontime 1
• RAWEPHEMB onchanged
• From the rover station(s)
• RANGECMPB ontime 1
• RAWEPHEMB onchanged
• RAWIMUSB onnew
In addition, the following is required to log GLONASS:
• GLOEPHEMERISB onchanged
• GLOCLOCKB onchanged
The SPAN-SE system output is compatible with post-processing
software from the Waypoint Products Group, NovAtel Inc. Visit
their web page at www.novatel.com/products/waypoint-software
for more details.
QUESTIONS OR COMMENTS
If you have any questions or comments regarding your
SPAN-SE system, please contact NovAtel Customer Service by:
Email: support@novatel.ca
Web: www.novatel.com
Phone: 1-800-NOVATEL (U.S. & Canada)
1-800-668-2835
1-403-295-4900 (International)
Fax: 1-403-295-4901
 Loading...
Loading...