Page 1

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Operator’s
Instruction
Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Date: 30 January 2004
© 2004 Draeger Medical, Inc.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile
Anesthesia System
W ARNING: For a full understanding of the performance characteristics of this anesthesia
machine, the user should carefully read this manual before operating.
Page 2

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 3

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Contents
Section 1. Safety Summary
Operator's Responsibility for Patient Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
Limitation of Liability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3
Restriction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3
Copyright. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3
Trademark Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3
Disclaimer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Recommendations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Purpose of This Manual. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Symbol Definition. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Warnings and Cautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Section 2. General Description
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-3
Gas Delivery System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-5
Anesthetic Vaporizer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-14
Absorber System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-15
Scavenger System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-19
Anesthesia Ventilator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-20
Power Supply System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-22
System Interface Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-24
Remote Display and Support Arm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-24
Monitoring System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-25
Alarm System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-26
Section 3. Specifications
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-2
Environmental . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-2
Electrical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-2
Gas Delivery System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
Ventilator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-4
Absorber System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-4
Oxygen Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-4
Breathing Pressure Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-5
Respiratory Volume Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-5
Serial Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-6
Section 4. Daily and Preuse Checkout Procedures
Daily Checkout Procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-3
Preuse Checkout Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-11
Section 5. Operating the Anesthesia Machine
Gas Delivery System Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
Anesthetic Vaporizer Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-4
Absorber System Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-7
Scavenger Interface Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-11
Anesthesia Ventilator Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-12
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: FNarkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Page 4

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section 6. Using the Monitoring System
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-3
Power-On Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-3
Monitor Screen and Controls. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-4
Using the Alarm Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-10
Oxygen Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-12
Respiratory Volume Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-18
Breathing Pressure Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-23
Section 7. Routine Maintenance and Cleaning
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-3
Routine Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-3
Removing Parts for Cleaning and Disinfection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-9
Disassembling Parts for Cleaning and Disinfection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-14
General Guidelines for Cleaning and Disinfection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-16
Reassembly Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-24
Section 8. Troubleshooting
Absorber System Problem Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-2
Ventilator Problem Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-4
Oxygen Monitoring Problem Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-5
Respiratory Volume Monitoring Problem Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-6
Breathing Pressure Monitoring Problem Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-6
Appendix: Spare and Replacement Parts
ii
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 5
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
Safety Summary
Table of Contents
Operator's Responsibilit y for Patient Safety .... .. .. ............... 1-2
Limitation of Lia b i l ity ........................................... ............... 1-3
Restricti on .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ..... .. .... ..... .. ..... .... .. .... 1-3
Copyright ........................................................................... 1-3
Trademark Notices .......................................................... ... 1-3
Disclaimer .. ................. .................... .................... ............... 1-4
Recommendations ............................................................. 1-4
Purpose of This Manual ..................................................... 1-4
Symbol Definition .. ............... ............................. ................. 1 -5
Warnings and Ca u tio n s .............. ............................. .......... 1-5
Warnings ....... ...... ..... ...... ....... .... ....... ...... ..... ....... ...... .... 1-6
Moving the Unit ........................... ................................. 1-6
Cautions .............................. ............................ ............. 1-8
Vaporizer Storage ........................................................ 1-9
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s ManualPart Number: 4115139-001
Page 6

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
Operator's Responsibility for Patient Safety
Draeger Medical anesthesia products are designed to provide the greatest
degree of patient safety that is practically and technologically feasible. The
design of the equipment, the accompanying literature, and the labeling on
the equipment take into consideration that the purchase and use of the
equipment are restricted to trained professionals, and that certain inherent
characteristics of the equipment are known to the trained operator.
Instructions, warnings, and caution statements are limited, therefore, to
the specifics of the Draeger Medical design. This publication excludes
references to hazards that are obvious to a medical professional, to the
consequences of product misuse, and to potentially adverse effects in
patients with abnormal conditions. Product modification or misuse can be
dangerous. Draeger Medical disclaims all liability for the consequences of
product alterations or modifications, as well as for the consequences that
might result from the combination of Draeger Medical products with
products supplied by other manufacturers if such a combination is not
endorsed by Draeger Medical.
The operator of the anesthesia system must recognize that the means of
monitoring and discovering hazardous conditions are specific to the
composition of the system and the various components of the system. It is
the operator, and not the various manufacturers or suppliers of components,
who has control over the final composition and arrangement of the
anesthesia system used in the operating room. Therefore, the responsibility
for choosing the appropriate safety monitoring devices rests with the
operator and user of the equipment.
Patient safety may be achieved through a variety of different means
depending on the institutional procedures, the preference of the operator,
and the application of the system. These means range from electronic
surveillance of equipment performance and patient condition to simple,
direct contact between operator and patient (direct observation of clinical
signs). The responsibility for the selection of the best level of patient
monitoring belongs solely to the equipment operator. To this extent, the
manufacturer, Draeger Medical, disclaims responsibility for the adequacy of
the monitoring package selected for use with the anesthesia system.
However, Draeger Medical is available for consultation to discuss
monitoring options for different applications.
1-2
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 7

Limitation of Liability
Draeger Medical's liability, whether arising from or related to the
manufacture and sale of the products, their installation, demonstration,
sales representation, use, performance, or otherwise, including any liability
based upon Draeger Medical's product warranty, is subject to and limited to
the exclusive terms of Draeger Medical's limited warranty, whether based
upon breach of warranty or any other cause of action whatsoever, regardless
of any fault attributable to Draeger Medical and regardless of the form of
action (including, without limitation, breach of warranty, negligence, strict
liability, or otherwise).
Draeger Medical shall in no event be liable for any special,
incidental, or consequential damages (including loss of profits)
whether or not foreseeable and even if Draeger Medical has been
advised of the possibility of such loss or damage. Draeger Medical
disclaims any liability arising from a combination of its product
with products from another manufacturer if the combination has
not been endorsed by Draeger Medical. Buyer understands that the
remedies noted in Draeger Medical's limited warranty are its sole
and exclusive remedies.
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
Furthermore, buyer acknowledges that the consideration for the
products, equipment, and parts sold reflects the allocation of risk
and the limitations of liability referenced herein.
Restriction
Federal law restricts this device to sale by, or on the order of, a physician.
Copyright
Copyright 2004 by Draeger Medical, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this
publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, or stored in a
retrieval system in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
including photocopying and recording, without written permission of
Draeger Medical, Inc.
Trademark Notices
Datagrip, DrägerService, Narkomed, Narkomed GS, ORM,
Quality Service For Life, Vigilance Audit, Vitalert, and Vitalink are
registered trademarks of Draeger Medical, Inc. All other products or name
brands are trademarks of their respective owners.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s ManualPart Number: 4115139-001
1-3
Page 8

1
Disclaimer
The content of this manual is furnished for informational use only and is
subject to change without notice. Draeger Medical, Inc. assumes no
responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies that may appear in
this manual.
Recommendations
In the interest of patient safety, Draeger Medical strongly advocates the use
of an oxygen analyzer, pressure monitor, and either a volume monitor or an
end-tidal CO
Because of the sophisticated nature of Draeger Medical anesthesia
equipment and its critical importance in the operating room setting, it is
highly recommended that only appropriately trained and experienced
professionals be permitted to service and maintain this equipment. Contact
an authorized representative of DrägerService for service of this equipment.
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
monitor in the breathing circuit at all times.
2
Draeger Medical also recommends that its anesthesia equipment be
serviced at three-month intervals. Periodic Manufacturer's Service
Agreements are available for equipment manufactured by Draeger Medical.
For further information concerning these agreements, contact
DrägerService at (800) 543-5047.
Purpose of This Manual
This manual provides operating instructions for the Narkomed Mobile
Anesthesia System. It is intended for use by trained clinical professionals
familiar with accepted medical procedures, practices, and terminology used
in delivery of anesthesia and patient monitoring.
1-4
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 9
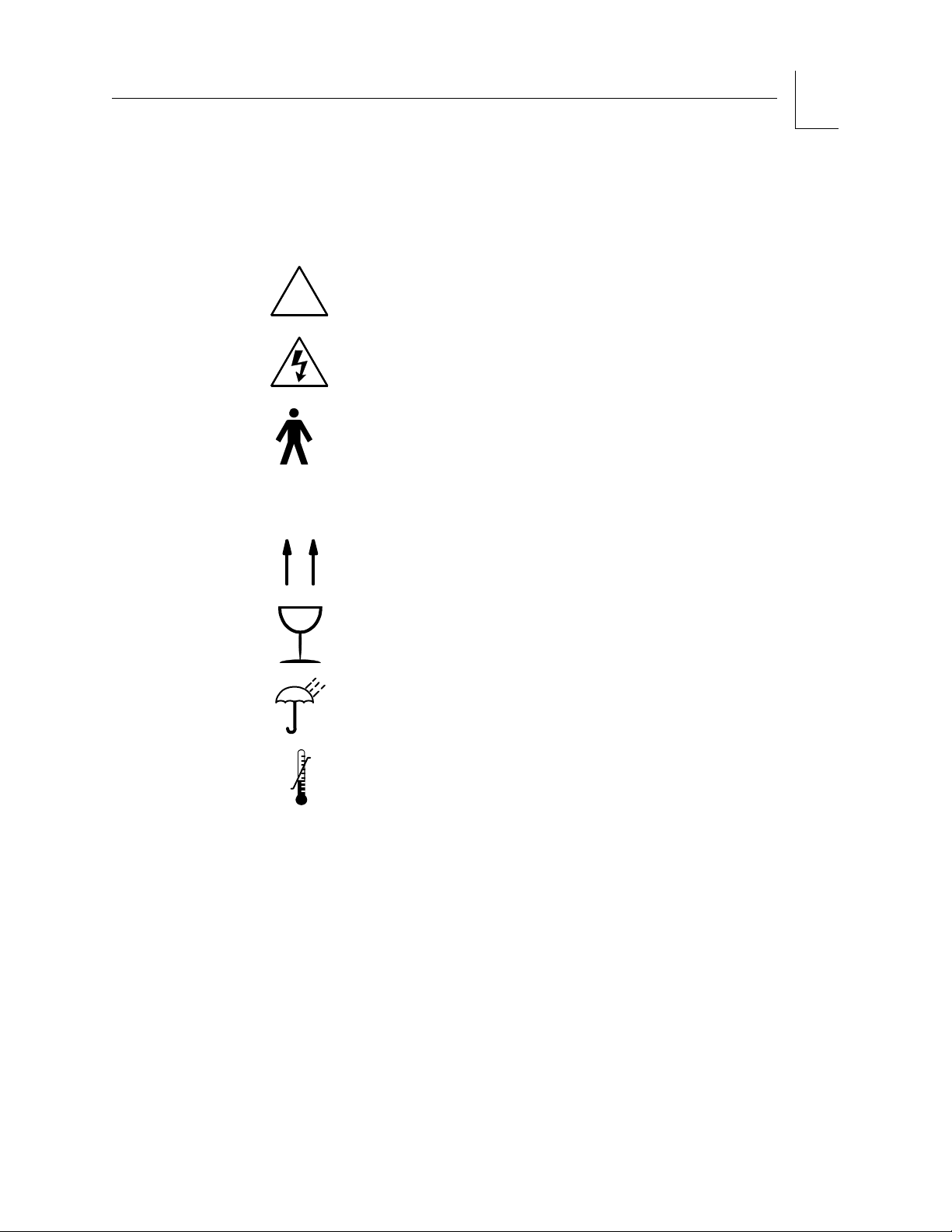
Symbol Definition
The following symbols appear on the label on the back of the
Narkomed Mobile unit.
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
CAUTION: Refer to accompanying documents before
operating equipment.
!
CAUTION: Risk of electric shock, do not remove cover.
Refer servicing to a qualified technical
service representative.
Degree of protection against electric shock:
Type B.
The following symbols appear on the shipping container of the
Narkomed Mobile unit.
60ºC
-20ºC
Warnings and Cautions
This manual contains warning and caution statements about the Narkomed
Mobile unit.
• Warni n g statements provide important information that, if
ignored, could lead directly to personal injury.
WARNI N G: This end up.
WARNI N G: Handle with care.
WARNI N G: Keep dry.
WARNI N G: Minimum and maximum storage
temperatures.
• Caution statements provide important information that, if
ignored, could lead directly to equipment damage and indirectly
to personal injury.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s ManualPart Number: 4115139-001
1-5
Page 10

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
Warnings The instruction manual provides important information about patient and
operator safety. Anyone involved with the setup, operation, or maintenance
of the Narkomed Mobile anesthesia system must be thoroughly familiar
with this instruction manual.
This anesthesia system will not respond automatically to certain changes in
patient condition, operator error, or failure of components. The system is
designed to be operated under the constant surveillance and control of a
qualified operator. Constant surveillance is necessary to ensure patient
safety.
Do not attach third-party components to the anesthesia machine, ventilator,
or breathing system (except for certain approved exceptions). These devices
may affect the safe operation of the anesthesia machine. Contact
DrägerService at (800) 543-5047 for further information.
Moving the
Unit
Prior to moving the Narkomed Mobile unit, the following functions must be
performed:
1. Disconnect the power cord from the mains and store properly.
2. Disconnect all gas supply lines from the wall supply. Ensure that these
supply lines are not in a position to interfere with the movement of the
machine.
3. Make sure the Vaporizer has been placed in the “0” position. Remove
and store the Vaporizer in the vaporizer holding area located on the base
of the unit. For more detailed information on storing the Vaporizer refer
to “Vaporizer Storage” on page 1-9. Move the monitor to its parked
position.
4. Move the absorber system to its parked position.
5. Unlock the caster brakes located on the two front wheels of the unit.
Before moving the assembled anesthesia machine, remove all monitors from
the top shelf of the machine, and use only the machine handles to push or
pull the unit. The anesthesia machine should only be moved by people who
are physically capable of handling the weight. Take special care that the
machine does not tip when moving up or down ramps and across thresholds
(i. e., door thresholds, elevator entrances etc.).
The Narkomed Mobile patient breathing system must not be used in
conjunction with any additional components that establish a flow direction.
1-6
Hoses and bags attached to the 22 mm hose terminals of the inspiratory
valve, expiratory valve, ventilator hose connect, and breathing bag mount
must comply with current ANSI standards.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 11
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
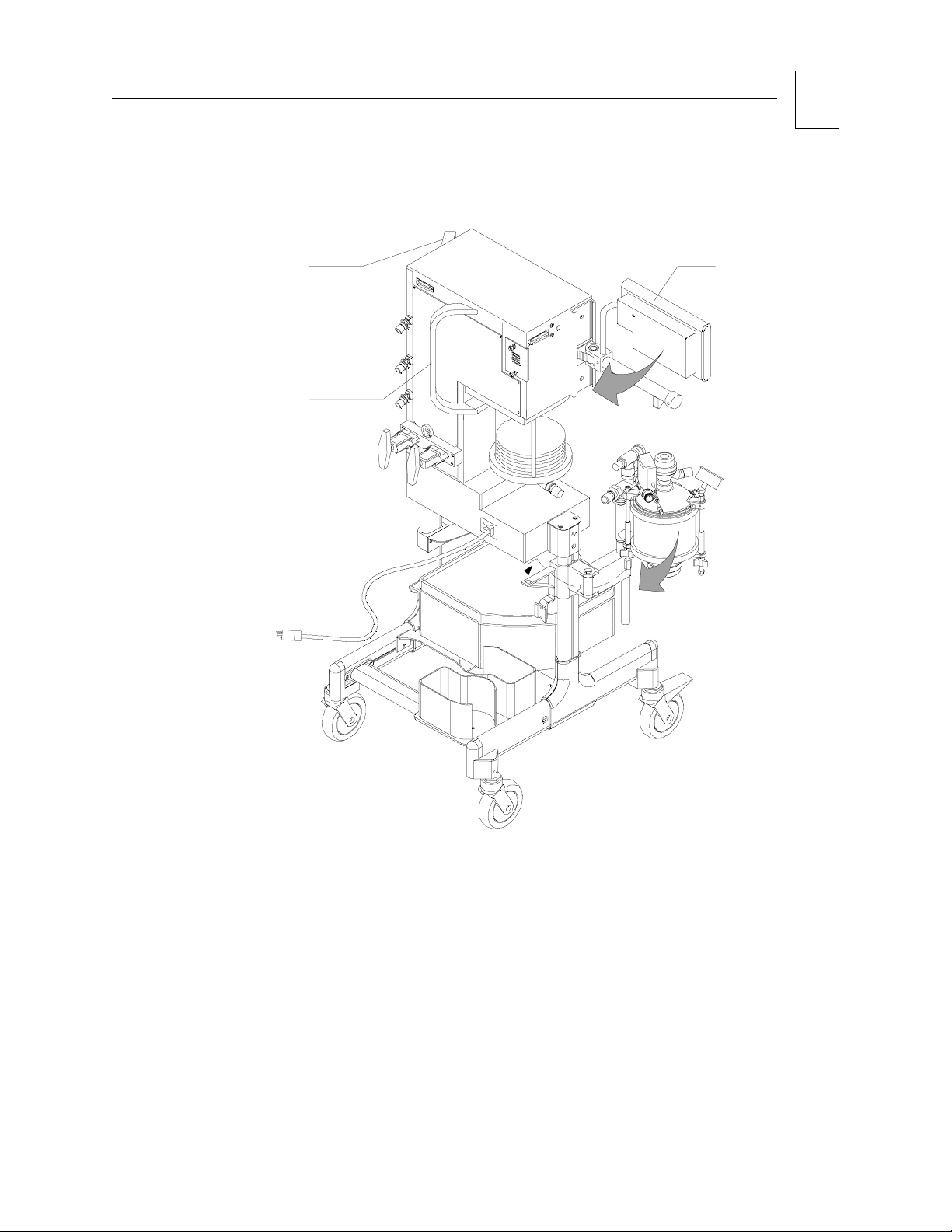
Figure 1-1. Narkomed Mobile Showing Handle Locations.
1
HANDLE
(SIDE)
HANDLE
(REAR)
ROTATE MONITOR
INTO PARKED POSITION
ROTATE ABSORBER,
ELEVATE SLIGHTLY,
AND INSERT INTO
BRACKET OPENING FOR
PARKED POSITION
Rev: F
OP00104
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s ManualPart Number: 4115139-001
1-7
Page 12

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
Oil and grease may combine explosively with oxygen or nitrous oxide. For
this reason, oil and grease must never come in contact with pipelines,
cylinders, cylinder valves, gauges, fittings, etc., that conduct oxygen or
nitrous oxide within the machine. For further information regarding safety
precautions in the use of medical gases, consult Compressed Gas
Association pamphlet P-2 and appropriate sections of the National Fire
Protection Association Standard 99.
In circle systems, the gas mixture in the patient circuit is not necessarily
the same as that in the fresh gas flow. This is particularly true at low fresh
gas flow rates when the patient rebreathes a significant amount of
previously exhaled gases. It is important that the gas mixture in the patient
circuit is monitored and that the fresh gas flow is adjusted to meet the
requirements of the patient and to compensate for patient intake, any
system leakage, or any gas drawn through sample lines and not returned.
Waste gas scavenging systems used with Draeger Medical absorber systems
must have safety features to ensure that excessive subatmospheric pressure
(lower than –0.5 cmH
+10 cmH
O) are not possible at the connection point.
2
O) and excessive positive pressure (higher than
2
Because the vaporizer funnel filling system does not limit the type of agent
poured into the vaporizer, using an agent monitoring device is
recommended to verify the agent.
Do not inhale anesthetic vapors while filling or draining the vaporizer.
Uncontrolled inhalation of anesthetic vapors is injurious to health.
Do not insert any additional components into, or modify, the anesthesia
system after any checkout procedure is started. Doing so can invalidate the
checkout results and could affect the patient's safety.
There is a possible explosion hazard if the Narkomed Mobile is used in the
presence of flammable anesthetics.
Cautions Although the Narkomed Mobile is designed to minimize the effects of
ambient radio-frequency interference, machine functions may be adversely
affected by the operation of electrosurgical equipment or shortwave or
microwave diathermy equipment in the vicinity.
Communications with external equipment may be temporarily affected by
electromagnetic interference due to the use of electrosurgical equipment.
Do not place sensitive electronic equipment on or adjacent to the display
screen.
The vaporizer is specifically designed and calibrated for one particular
anesthetic agent. Do not fill a vaporizer with any other anesthetic.
1-8
Do not place more than 35 pounds on top of the Narkomed Mobile unit.
Always operate the Narkomed Mobile on a level surface.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 13
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
Vaporizer
Storage
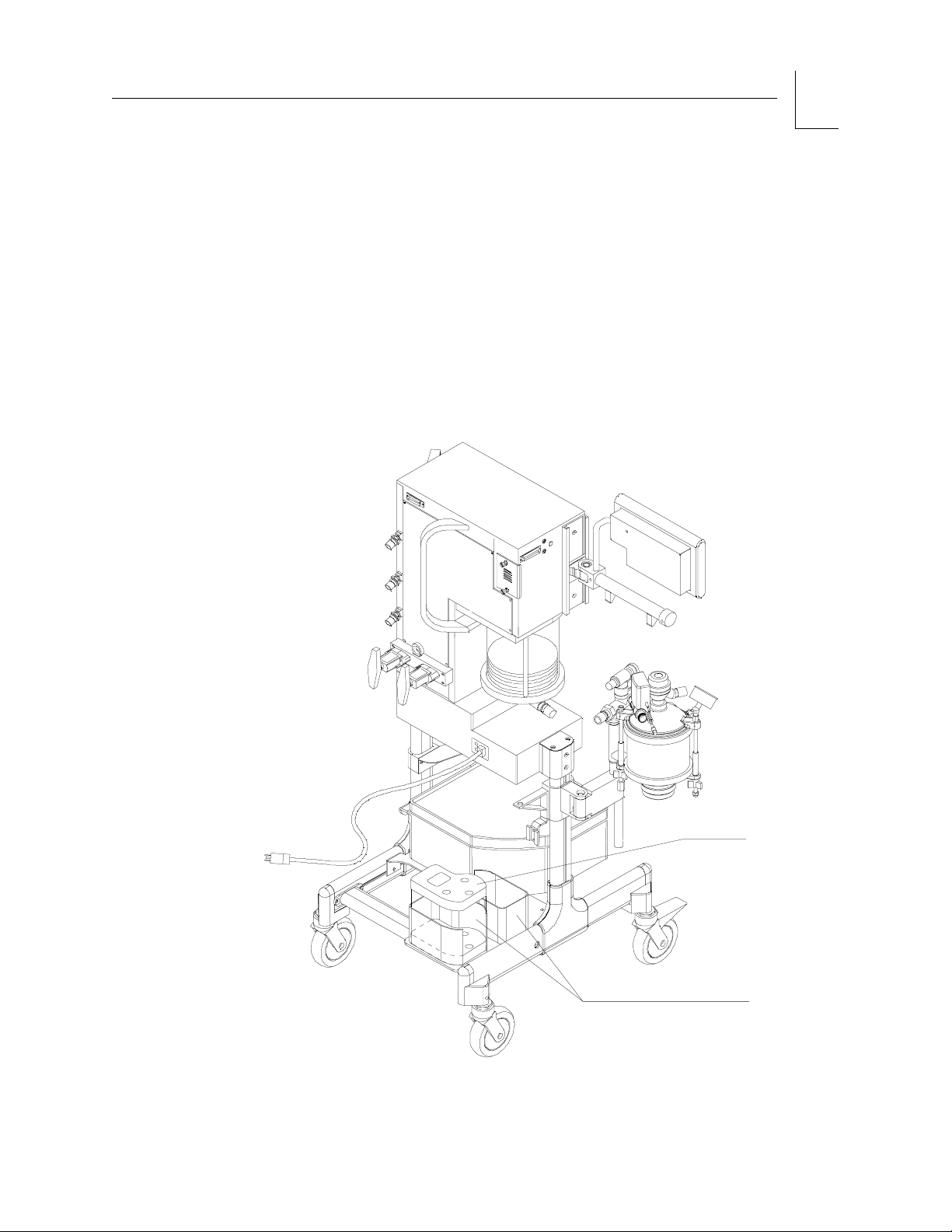
Two vaporizer holders are located on the lower rear frame rail as shown in
the illustration.
Each holder will accommodate a single Dräger Vapor unit. For storing a
Dräger Vapor unit with a flat bottom, a single foam cushion is used. For
Dräger Vapor units that are not the flat bottom style (three exposed pads on
the bottom of the unit) you will need to place an additional foam cushion in
the holder. There are two additional foam cushions supplied with the
machine and are located in the drawer.
Figure 1-2. Vaporizer Storage Locations
SU00045
Rev: F
ADDITIONAL
FOAM PAD
(IF NEEDED)
VAPORIZER
HOLDERS
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s ManualPart Number: 4115139-001
1-9
Page 14

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 15
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
General Description
Table of Contents
Overview .... ........... ........... ......... ........... ........... ......... .......... 2-3
Gas Delivery S y stem . .. .. .......................................... .... 2-5
Piping, Hoses, and Fittings ..................... ................ ..... 2-5
Oxygen Supply Pressure Failure Protection Device .... 2-9
Flowmeters .................................................................. 2-9
Minimum Oxygen Flow .............................................. 2-10
Oxygen Flus h ............... ............................. ................. 2 -1 1
Oxygen Rati o C o n troller .. ... ............... ........................ 2-12
Fresh Gas Outlet (15 mm) ......................................... 2-12
Auxiliary Oxygen Flowmeter ...................................... 2-12
Anesthetic Vaporizer ........................................................ 2-14
Absorber Sy st e m ............................ ............................. .... 2 -15
Inspiratory and Expiratory V alves .............................. 2-16
Canister ..................................................................... 2-17
Dust Cup ................................. ............................. ...... 2-17
Fresh Gas Hose ........... ............... ............................. .. 2-1 7
Breathing System Pressure Gauge ........................... 2-17
Pressure Se ns ing Hose Asse mbly ........ ... ............... .. 2-1 7
Manual/Automatic Se l e ctor Valve ............. .. ............... 2-1 7
Adjustable Press u re Limiter (APL) Valve ................. .. 2-1 7
Respiratory Volume Monitor Sensor .......................... 2-17
Oxygen Sen so r ..................... ............................. ........ 2-18
Positive End-Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) Valve ........ 2-18
Scavenger System ........................................................... 2-19
Anesthesia Ventilator ....................................................... 2-20
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Page 16

2
Table of Contents (continued)
Power Supply System .................................................... 2-22
System Power Switch ........................................... ...... ..... 2-22
Circuit Breakers ............................................................... 2-22
Backup Battery System .................................................... 2-23
System Interface Panel .................................................. 2-24
Remote Display and Support Arm ................................. 2-24
Monitoring System ......................................................... 2-25
Monitor Screen and Controls ........................................... 2-25
Alarm Sys tem .. ... ............... ............................. ............... 2-26
Alarm Display ................. ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ..... 2-26
Alarm Annunciation ........ ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ..... 2-27
Ventilation Alarms ............................................................ 2-27
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2-2
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 17
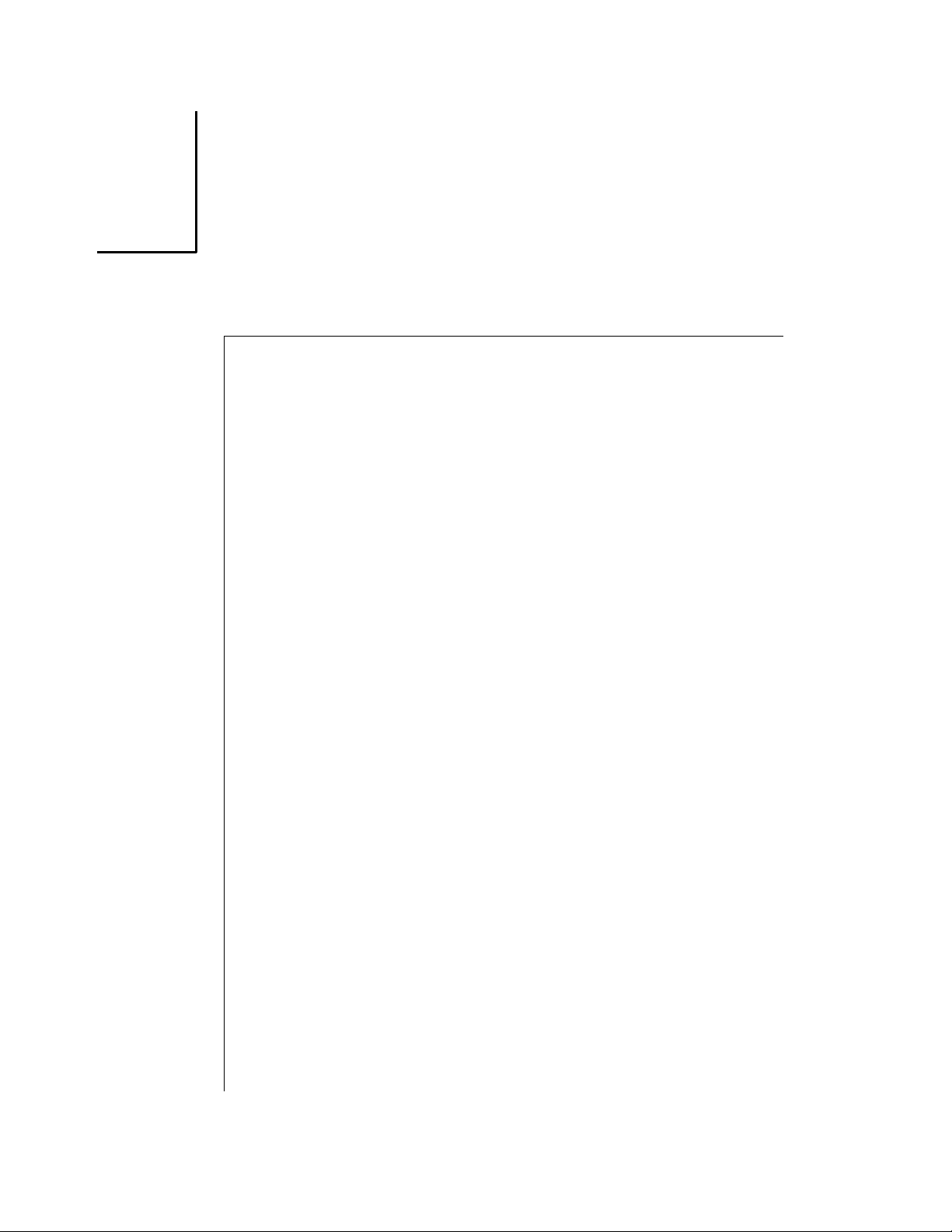
Overview
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
The Narkomed Mobile is a compact, lightweight, continuous flow anesthesia
system. All Narkomed Mobile machines are equipped with a monitoring
system and pneumatic circuitry for delivering gases and anesthetic vapor
for adult and pediatric patients.
Figure 2-1.
VENTILATOR
CONTROLS
DISPLAY
ASSEMBLY
BELLOWS
ULTRASONIC
FLOW SENSOR
Narkomed Mobile Front View
OP00087
HANDLE
FLOWMETER
BANK
AUXILIARY
OXYGEN
FLOWMETER
PRESSURE
GAUGES
VAPORIZER
ABSORBER
SYSTEM
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
SUPPORT
FRAME
2-3
Page 18
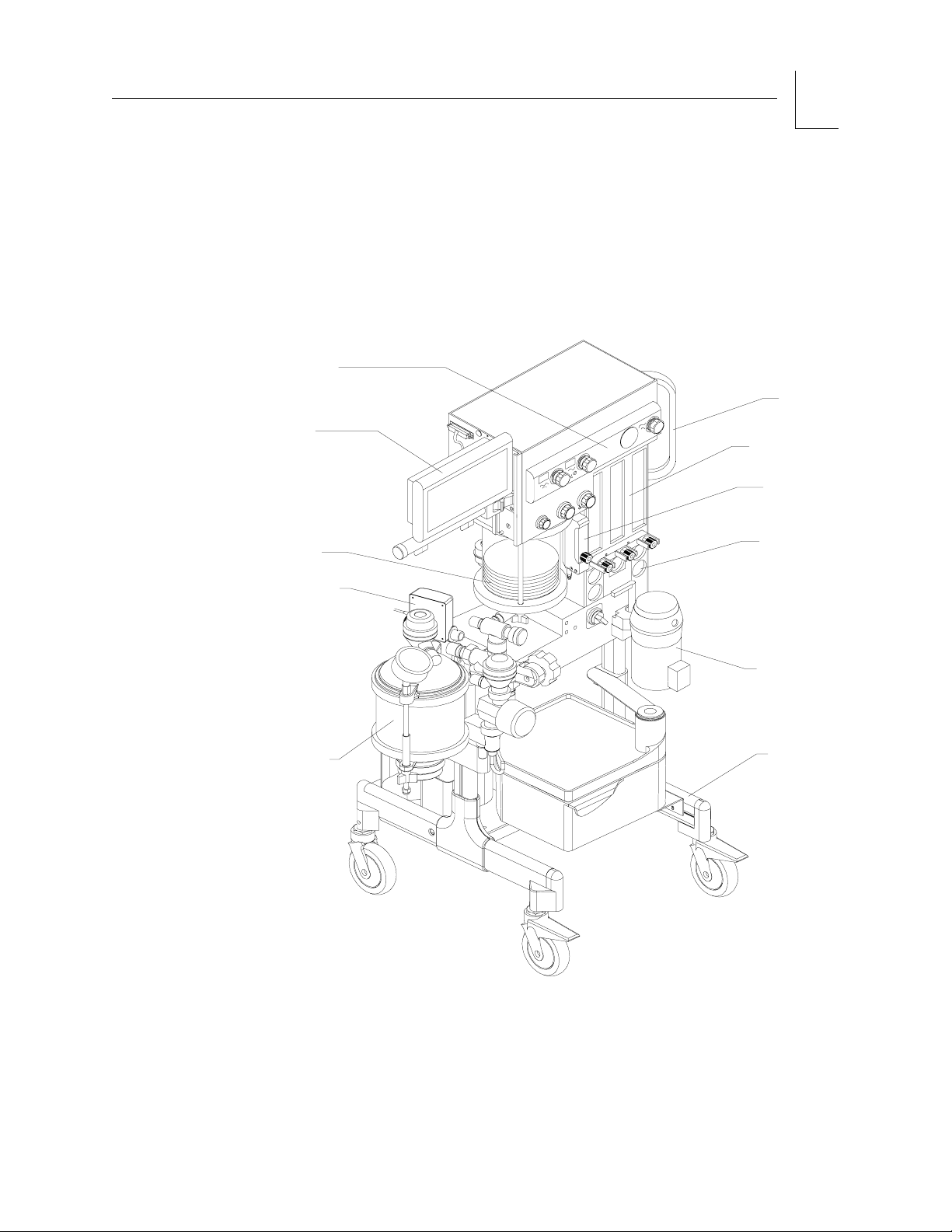
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
The Narkomed Mobile consists of these major systems:
• gas delivery
• vaporizer
• absorber
•scavenger
• ventilator
• power supply
• system interface
• monitoring/alarms.
Figure 2-2. Narkomed Mobile Back View
PIPELINE
GAS INLET
CYLINDER
YOKE
SYSTEM INTERFACE PANEL
2-4
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
OP00086
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 19
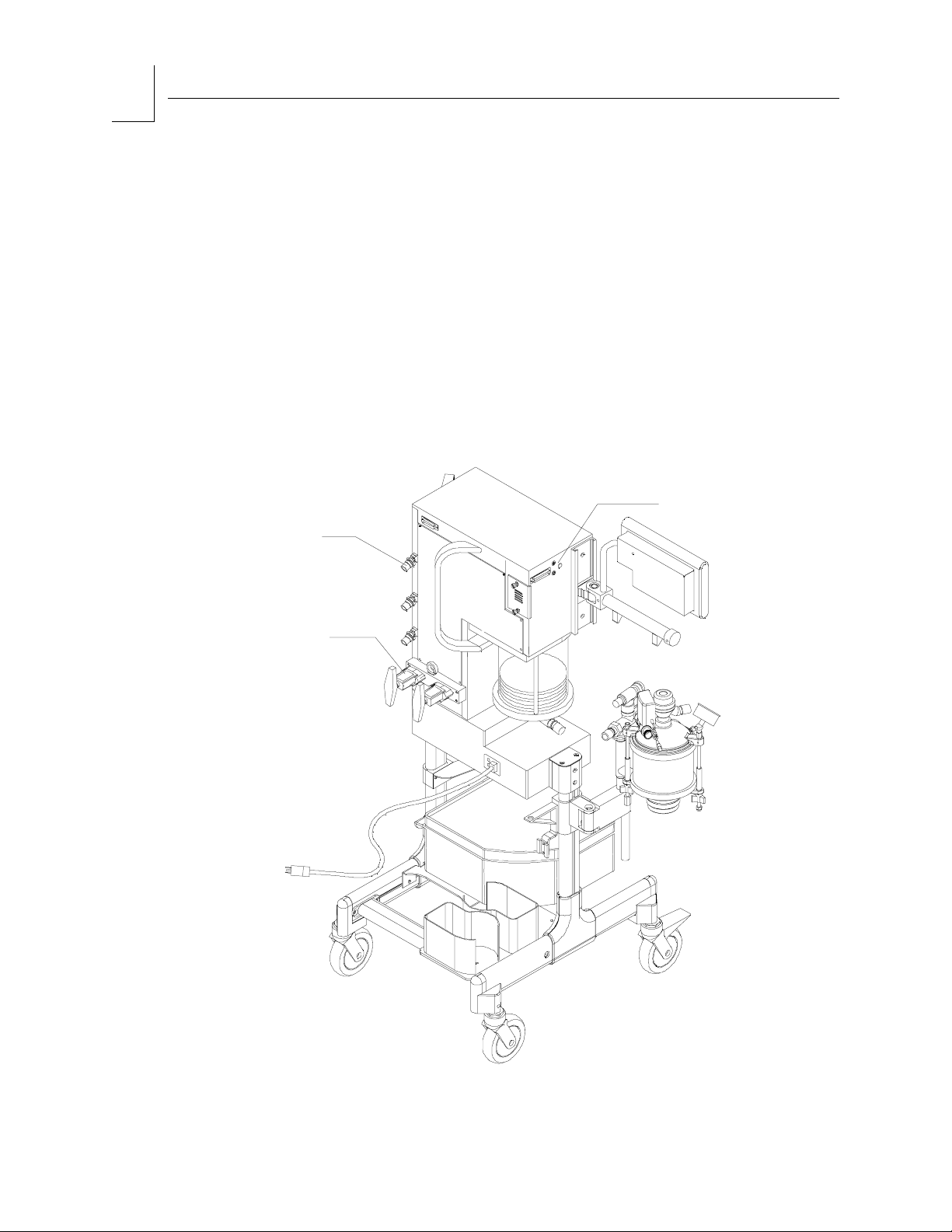
Gas Delivery System
The pneumatic system can simultaneously deliver up to three gases and one
anesthetic agent. Gas is supplied to the system through pipelines and
cylinders. Pipeline connections for oxygen, air, and nitrous oxide are
standard. Gas cylinder yokes for one oxygen and one nitrous oxide cylinder
connection are provided. As a factory installed option, these gas cylinder
connections can be configured for two oxygen cylinders. Pipeline connectors
and the gas cylinder yokes are located on the back of the anesthesia
machine.
Figure 2-3. Gas Delivery Connections
PIPELINE
GAS SUPPLY
CONNECTIONS
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
OP00085
Piping,
Hoses, and
Fittings
Color Coding
O2
AIR
N2O
CYLINDER YOKES
Each connection, valve, gauge, and flowmeter is labeled and color-coded for
the appropriate gas, as shown in the table below.
GAS SYSTEM COLOR CODING
GAS MARKING COLOR
Air AIR Yellow
Nitrous Oxide N2O Blue
Oxygen O2 Green
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-5
Page 20

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Pipeline Gas
Entry
Pipeline
Pressure
Gauges
Gas from the pipeline supply enters the system through hoses connected to
indexed pipeline inlets. The indexed connector system reduces the risk of
delivering the wrong gas to a patient by preventing incorrect connection of
gas lines. The inlets have check valves that prevent backflow leakage into
the atmosphere when supply hoses are not connected or backflow into the
attached supply hoses when the cylinder is used. Each pipeline connection
is equipped with a filter to prevent foreign material from entering the
internal gas piping. Pipeline gases should be supplied at 50—55 psi.
Pipeline pressure gauges for oxygen, air, and nitrous oxide are standard.
These gauges are labeled and color-coded for their respective gases on the
flowmeter shield. The gauges are located directly below their corresponding
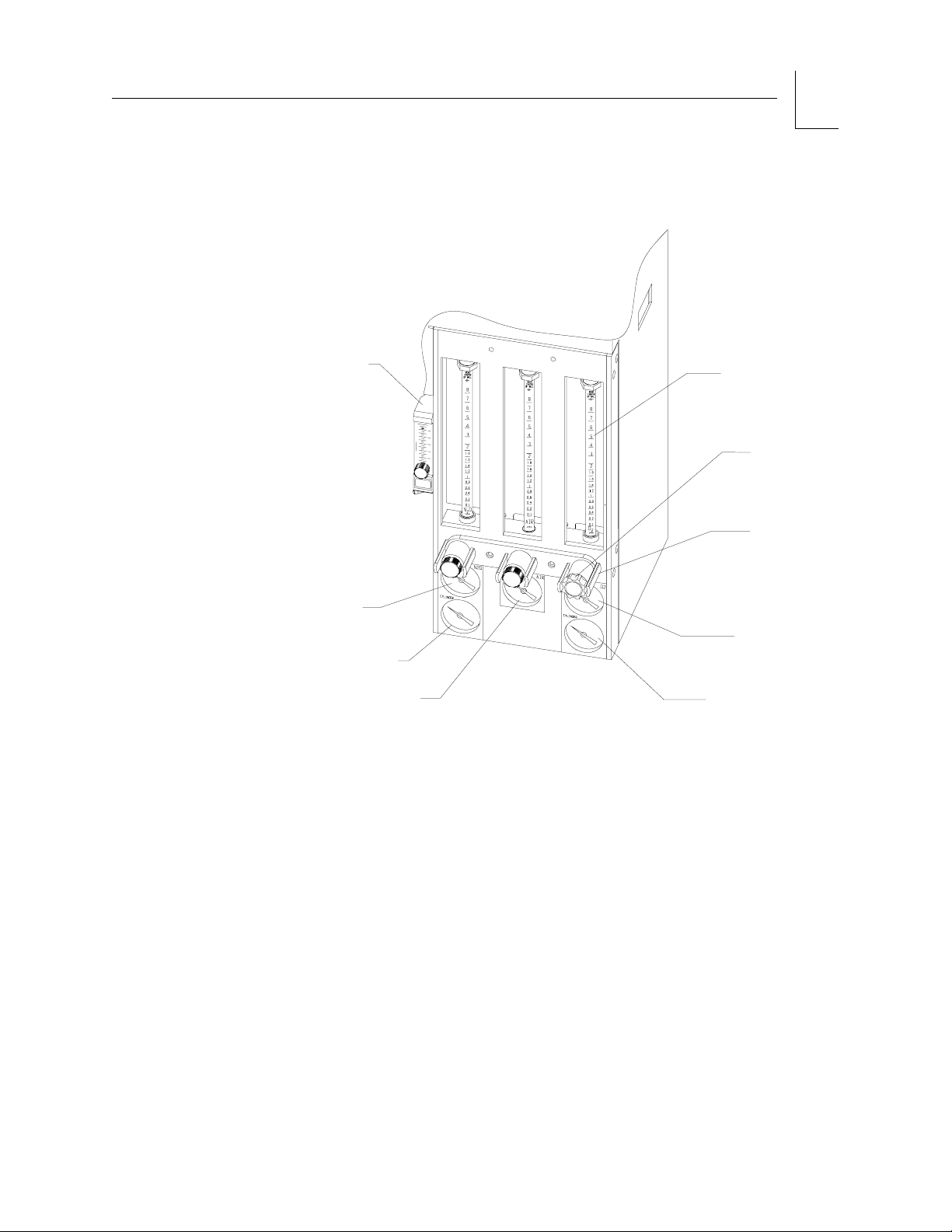
flowmeters and flow control valves. Pressure is indicated in psi and kPa.
The pressure gauge and flowmeter arrangements are shown in Figure 2-4
on page 2-7.
2-6
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 21
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Figure 2-4. Flowmeter and Pressure Gauge Assembly
OP00211
2
AUXILIARY
O2
FLOWMETER
PIPELINE
PRESSURE
GAUGE (N2O)
(N2O) CYLINDER
PRESSURE GAUGE
PIPELINE PRESSURE
GAUGE (AIR)
FLOW TUBE
(l/min)
FLOW
CONTROL
VALVE
FLOW
GUARD KNOB
N2O
AIR
O
2
PIPELINE
PRESSURE
GAUGE (O2)
(O2) CYLINDER
PRESSURE GAUGE
When the machine is connected to an active pipeline supply, each gauge
should indicate 50—55 psi. A deviation from within this range indicates
that the pipeline gas supply system is improperly adjusted and can
adversely affect operation. A fluctuating pipeline supply pressure, for
example, would cause a corresponding fluctuation of the gas flow delivered
from that pipeline. An excessively low pipeline pressure can activate the O
and N
the open position).
Part Number: 4115139-001
O cylinders and deplete their contents (if the cylinder valve is left in
2
Caution: To ensure gas supplies are adequate, pipeline pressure
gauges should show steady pressures of 50—55 psi.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-7
2
Page 22

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Cylinder Gas
Entry
The Narkomed Mobile is equipped with a two cylinder hanger yoke
assembly. The standard combination is one O
cylinder. A factory installed option for the mounting of two O
2 cylinder and one N2O
2 cylinders is
available. If this option is installed, the appropriate color coding scheme and
cylinder pin-index safety sytems will show this difference. To prevent a
cylinder from being improperly connected, the yoke is labeled, color-coded,
and keyed for oxygen and nitrous oxide cylinders using the pin-indexed
safety system.
A filter in the yoke prevents foreign material from entering the internal gas
piping. A check valve in the yoke prevents leakage into the atmosphere
when a cylinder is not mounted on the yoke. If a cylinder is not mounted to
the yoke, the attached yoke plug should be placed between the yoke bolt and
the yoke's gas inlet.
When attaching a cylinder, make sure that only one washer is installed
between the cylinder and the yoke gas inlet. Using multiple washers can
compromise the pin-indexed safety system. Be sure to verify the integrity of
both index pins when installing a new cylinder.
Warning: Make sure the cylinder yoke has two intact index pins each
time the cylinder is replaced. Use only one cylinder gasket.
Using more than one gasket can cause cylinder gas leakage
and compromise the pin-indexed safety system.
Cylinder
Pressure
Gauge
The cylinder attached to the hanger yoke must contain the proper gas at the
recommended pressures outlined in the table below. Any cylinder that
contains less than the recommended minimum shown in the table should be
replaced with a new, full cylinder.
GAS
Oxygen 1900
Nitrous Oxide 745 600
* Indicated pressure is for an E-size cylinder at 70 °F (21 °C).
† Due to differences in manufacture’s specifications and topping off during
refill of E-type cylinders, a full cylinder can be as high as 2015 psi.
PSI - FULL
*
PSI - MIN
†
1000
Within the cylinder gas circuit are the cylinder pressure gauges. These
gauges are labeled and color-coded on the flowmeter housing. When a
cylinder valve is opened, the associated pressure gauge indicates the gas
pressure in that cylinder. Pressure is indicated in psi and kPa. The
indicated pressure is proportional to the gas content of the cylinder.
2-8
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 23

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Oxygen
Supply
Pressure
Failure
Protection
Device
The oxygen failure protection device (OFPD) is a pneumatically operated
valve that protects the patient in the event of partial or complete loss of
oxygen pressure. The valves are located in the internal supply lines for all
gases except oxygen. The gas pressure in the oxygen supply line controls the
valves. When the oxygen pressure is adequate, the valves remain open with
an unrestricted gas flow. Oxygen pressure loss causes the valves to close
proportionally to the loss of pressure. As a result, OFPD-controlled gases
can be restricted or shut down in response to loss of oxygen pressure.
Gas flow reductions are indicated on the flowmeter. When the oxygen
supply from the pipeline or cylinder pressure drops below about 37 psi:
• an O2 SUPPLY LOW Caution message appears in the Alarm
window on the monitor
• an intermittent alarm sounds.
Note: If only one source of oxygen supply pressure (either the cylinder or
pipeline) fails and the other source maintains proper supply
pressure in the oxygen supply lines, the OFPD and the alarm are not
activated.
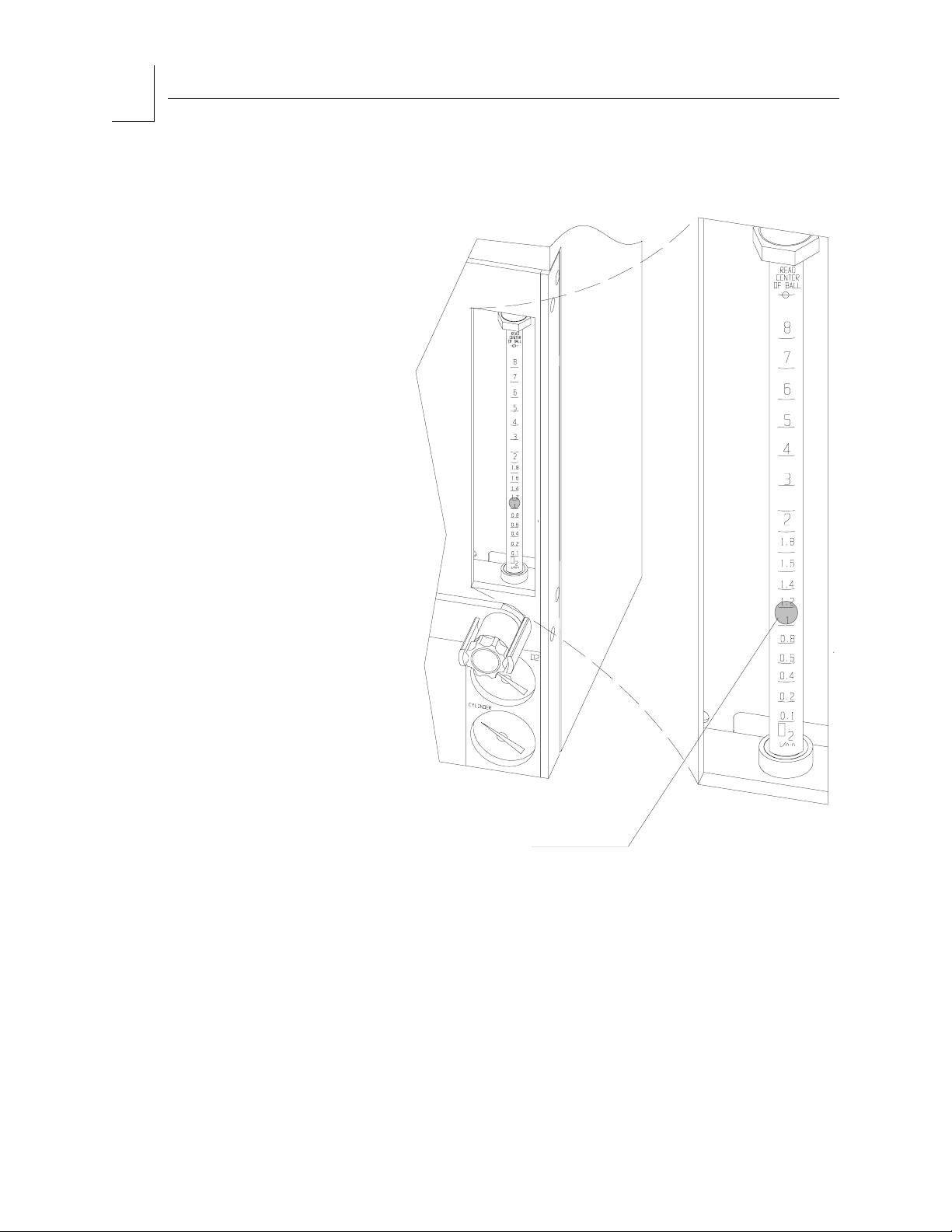
Flowmeters The individual flowmeters for each gas are located directly above their
corresponding flow control valves. The flowmeters indicate the delivered
flow rate of each gas in the fresh gas mixture. The specific gas is labeled at
bottom of the flowtube.
Each flowmeter has a float indicator. To determine the flow rate, read the
flowmeter scale at the center of the float.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-9
Page 24
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Figure 2-5. Flowmeter and Indicator Float
OP00213
Minimum
Oxygen Flow
O
2
INDICATOR FLOAT
The oxygen dispensing system has a calibrated bypass flow of
150 ±50 mL/min (at 50 psi pipeline pressure) that delivers this flow of
oxygen even if the oxygen flow control valve is fully closed.
2-10
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 25
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Flow Control
Valves
Oxygen
Flush
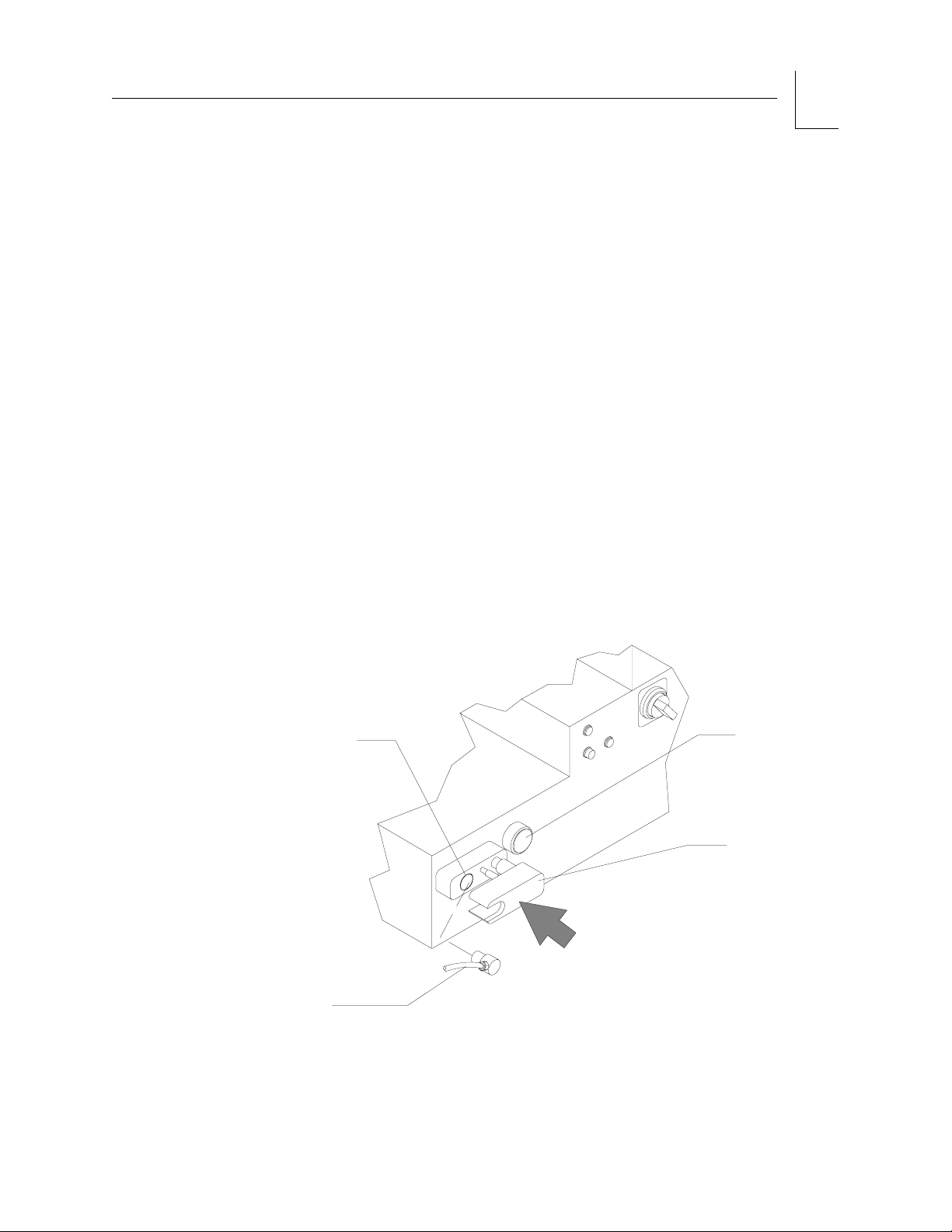
A valve located below each flowmeter tube is used to adjust the gas flow.
Turning the valve knob counterclockwise increases flow. Turning the knob
clockwise decreases flow. A zero-stop prevents damage to the flow control
valve seats. If necessary, an authorized representative of Dräger Service can
readjust the stop.
Each flow control knob is identified by its color code and chemical symbol.
The oxygen flow control valve is also touch-coded with a deeply fluted knob.
Each knob has a guard to prevent accidental adjustment to gas flow.
Caution: The oxygen flow cannot be completely shut off. Do not force
the oxygen flow control knob in an effort to shut off the
minimum flow (150 ±50 mL/min). Forcing the knob can
damage the valve seat.
A manually operated, self-closing oxygen flush valve is located on the front
of the power supply area of the machine. A bezel is mounted around the
push-button to prevent accidental engagement. When pressed, the valve
delivers an unmetered oxygen flow of about 55 L/mi directly to the fresh gas
common outlet. The SYSTEM POWER switch does not have to be on to use
the oxygen flush.
Figure 2-6. O
Flush Button
2
OP00097
FRESH GAS
OUTLET
FRESH
GAS HOSE
RELEASE TO LOCK
PULL TO INSERT OR
REMOVE HOSE
O2 FLUSH
CONTROL
FRESH GAS
LOCKING BAR
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-11
Page 26

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Oxygen Ratio
Controller
The Oxygen Ratio Controller (ORC) is a pneumatic oxygen/nitrous oxide
interlock system that maintains a fresh gas oxygen concentration of 25 ±4%.
The ORC allows independent control of the oxygen and nitrous oxide flows.
The ORC proportionally limits the nitrous oxide flow whenever the selected
oxygen and nitrous oxide flow control valve settings would otherwise result
in a hypoxic fresh gas mixture.
For example, if you open the nitrous oxide flow control valve excessively
without making a corresponding increase in the oxygen flow control valve
setting, the flow of nitrous oxide will not increase even though its flow
control valve setting was greatly increased. Similarly, if you decrease the
oxygen flow without also decreasing the nitrous oxide flow, the nitrous oxide
flow will automatically drop in proportion to the oxygen flow.
Warning: In circle systems, the gas mixture in the patient circuit is not
necessarily the same as that in the fresh gas flow. This is
particularly true at low fresh gas flow rates when the patient
rebreathes a significant amount of previously exhaled gases.
It is important that the gas mixture in the patient circuit is
monitored and that the fresh gas flow is adjusted to meet the
requirements of the patient and to compensate for patient
intake, any system leakage, or any gas drawn through
sample lines and not returned.
Fresh Gas
Outlet
(15 mm)
Auxiliary
Oxygen
Flowmeter
The fresh gas outlet (Figure 2-7 on page 2-13) delivers the fresh gas mixture
(consisting of oxygen, nitrous oxide, and air) and vapors of a liquid
anesthetic to the patient breathing system. The outlet is located on the front
of the anesthesia machine.
The 15 mm cylindrical female fitting accepts a 15 mm male fitting on the
absorber fresh gas hose. The male fitting slides into a retaining slot in the
spring-loaded safety locking bar to prevent inadvertent disconnection of the
fresh gas hose. The 15 mm male fitting on the fresh gas hose is unique to
Draeger Medical design and should not be replaced by a hose from any other
manufacturer.
For the delivery of a metered flow of pure oxygen (for example, delivery of
oxygen through a nasal cannula), an auxiliary oxygen flowmeter is mounted
on the left side of the flowmeter bank (Figure 2-6 on page 2-11). This
flowmeter can be used when the machine is turned off.
2-12
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 27
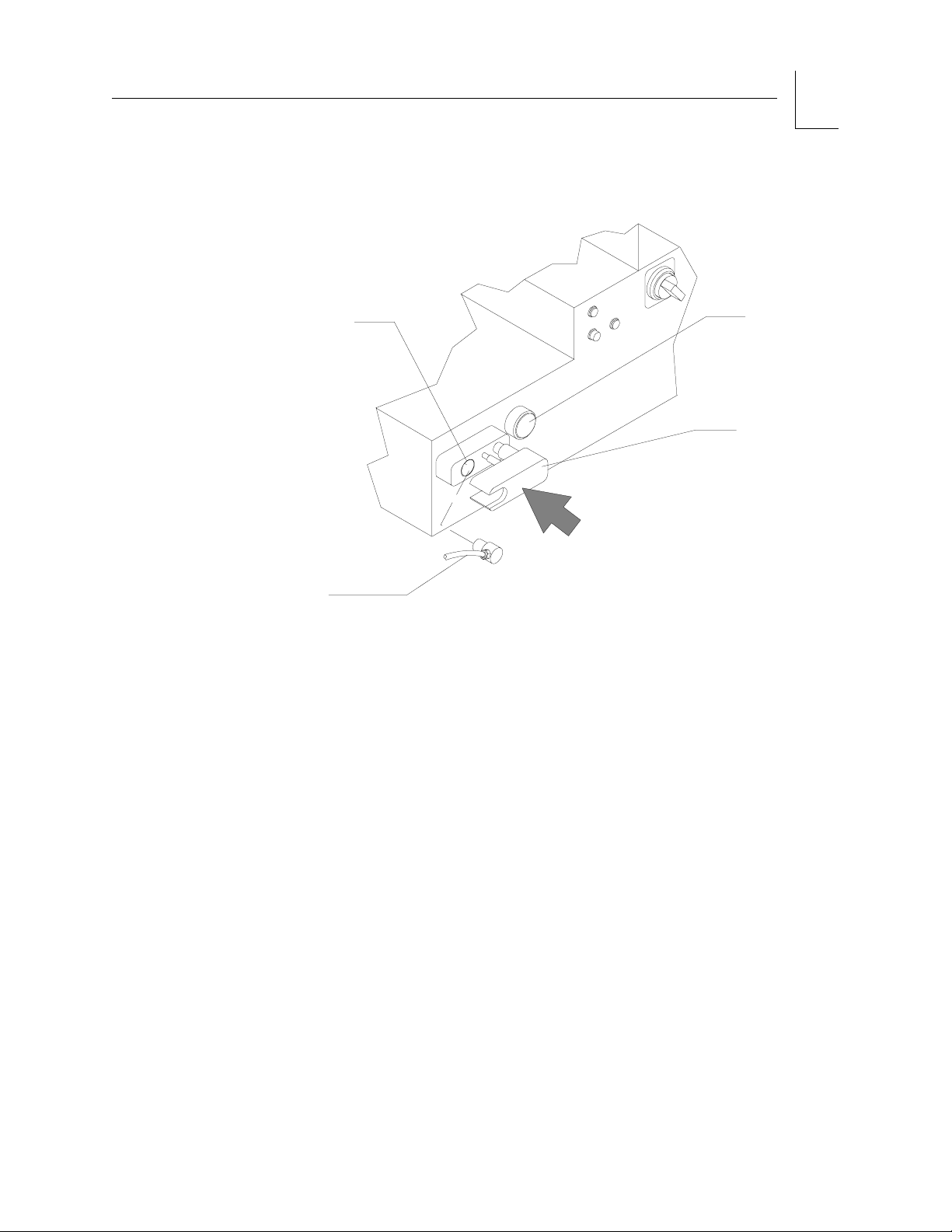
Figure 2-7. Fresh Gas Outlet
OP00097
FRESH GAS
OUTLET
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
O2 FLUSH
CONTROL
FRESH GAS
LOCKING BAR
FRESH
GAS HOSE
RELEASE TO LOCK
PULL TO INSERT OR
REMOVE HOSE
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-13
Page 28
2
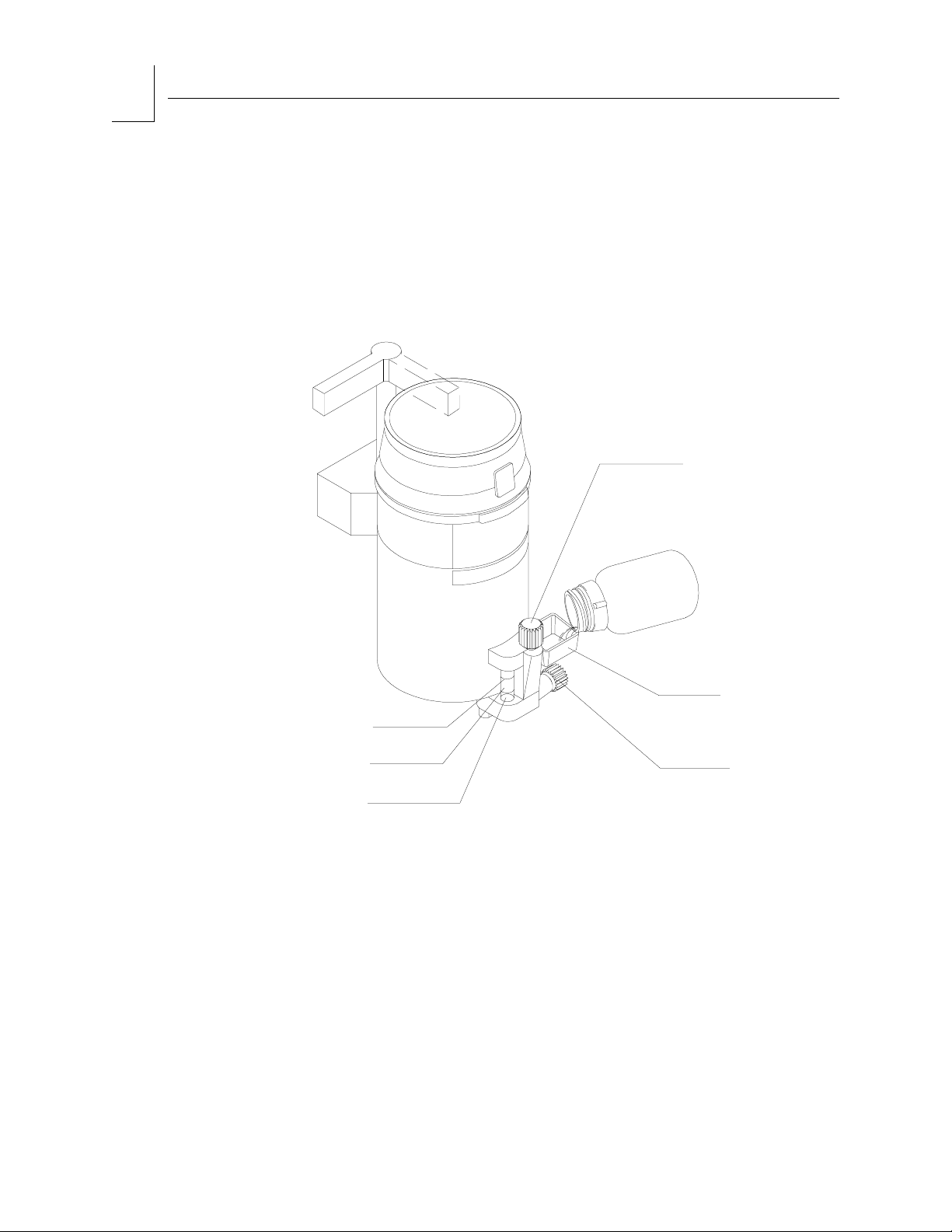
Anesthetic Vaporizer
The Narkomed Mobile is equipped with a Dräger-Vapor 19.3 vaporizer. This
vaporizer enriches fresh gas with precisely metered vapor of liquid
anesthetic agent. The vapor is inserted into the fresh gas line. It is
connected between the fresh gas metering unit and the fresh gas outlet.
Figure 2-8. Dräger-Vapor 19.3 Vaporizer
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
OP00329
INLET VALVE
FILLING
SPOUT
MAX FILL LINE
SIGHT GLASS
MIN FILL LINE
DRAIN
VALVE
Warning: If the wrong anesthetic is used, the delivered concentration
can be higher or lower than the concentration set on the
handwheel.
Warning: Be sure to fill the vaporizer in an upright position. Filling the
vaporizer in a tilted position can cause overfilling. Overfilling
causes the anesthetic concentration rate to be higher or lower
than the handwheel setting.
Caution: Handle the vaporizer with care. Do not drop, carry by the
handwheel, sealing plugs, or locking lever. Damage to the
vaporizer will result.
Caution: Ensure that the Vapor 19.3 handle is in the locked position
prior to use.
2-14
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 29
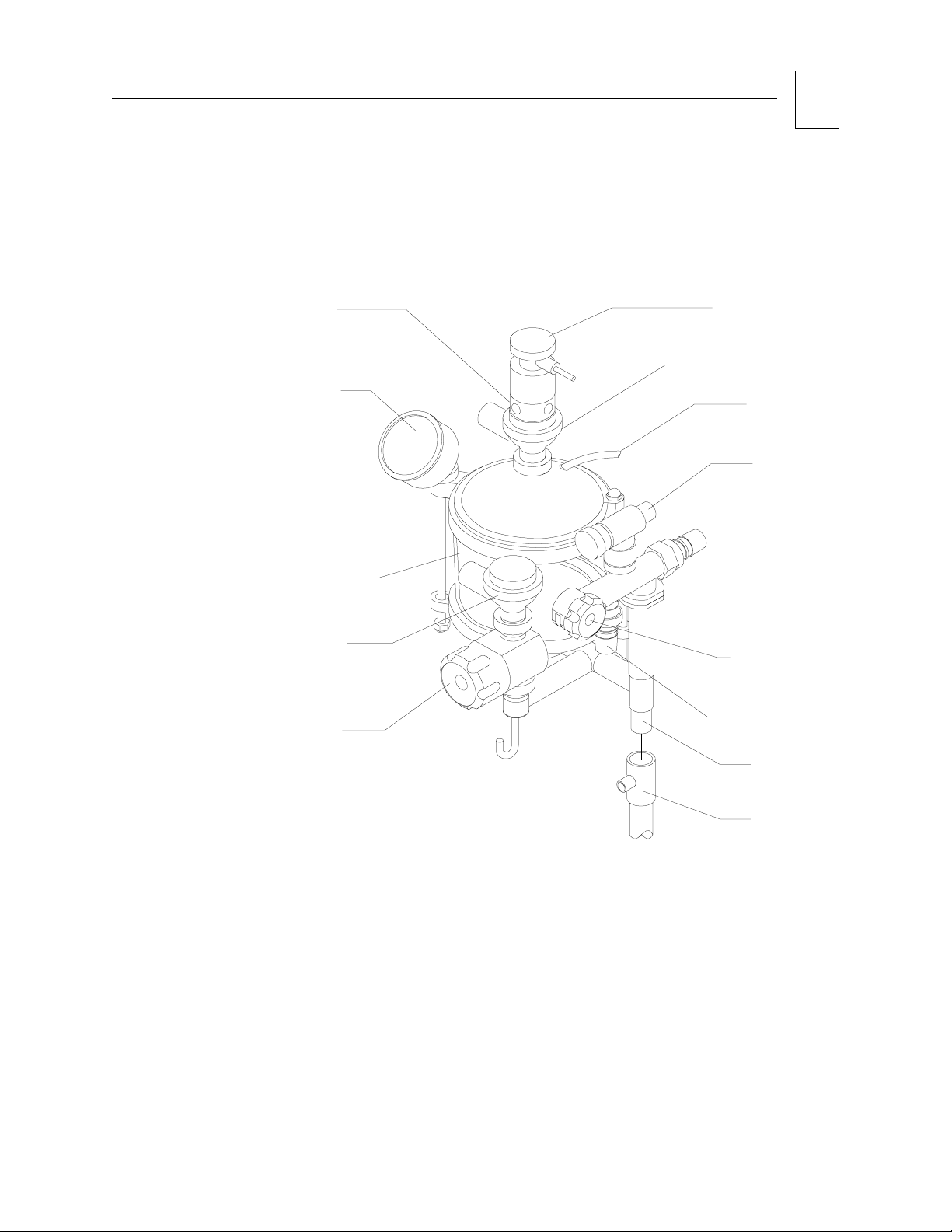
Absorber System
A single-canister system absorbs exhaled carbon dioxide in the rebreathing
circuit of the anesthesia machine.
Figure 2-9. Absorber System
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
PRESSURE
SENSOR ADAPTER
BREATHING
SYSTEM
PRESSURE
GAUGE
ABSORBENT
CANISTER
EXPIRATORY
VALVE
PEEP VALVE
OP00079
OXYGEN SENSOR
INSPIRATORY
VALVE
FRESHGAS
HOSE
APL VALVE
MANUAL/AUTO
SELECTOR
VALVE
BREATHING
BAG FITTING
ABSORBER
MOUNTING STUD
The absorber system is equipped to accommodate sensors to monitor oxygen
concentration, tidal volume, respiratory minute volume, pressure, and
respiratory frequency. The PEEP valve regulates positive end-expiratory
pressure in the patient breathing circuit.
The absorber system handles spontaneous, manually assisted, or automatic
ventilation. The preferred mode of operation is selected with the manual/
automatic selector valve. The “AUTO” position of the valve enables
automatic ventilation. The “BAG” position enables Manual/Spontaneous
ventilation.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
ABSORBER
POLE
2-15
Page 30

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
The absorber system includes:
• an inspiratory valve and an expiratory valve
• an absorber canister and dust cup
• a breathing system pressure gauge
• a pressure sensing hose assembly
• fresh gas hose
• manual/automatic (ventilation) selector valve
• an adjustable pressure limiter (APL) valve
• respiratory volume sensor
• oxygen concentration sensor
• a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) valve.
Inspiratory
and
Expiratory
Valves
The inspiratory and expiratory valves control the gas flow direction in the
absorber system. The valves are unidirectional, meaning they permit gas
flow in one direction only:
• The inspiratory valve allows gas to flow toward the patient only,
without backflow to the absorber.
• The expiratory valve allows gas to flow to the absorber only, with
no backflow to the patient.
The valves are
not interchangeable. They must be connected to the correct
mounts to ensure proper flow direction through the absorber system.
Different size mounting threads on each valve prevent connecting a valve to
the wrong vent.
Warning: Do not use the anesthesia machine if:
• a pin in the valve domes or valve body is bent, damaged,
or missing
• the valve disks are missing or damaged
• the valve seat is damaged.
The inspiratory valve dome is equipped with a pressure sensor adapter.
This adapter contains a port for the pressure sensor hose assembly. The
oxygen concentration sensor fits on top of the pressure sensor adapter. A cap
is tethered to the absorber for plugging into the inspiratory valve dome
when the oxygen sensor and pressure sensor hose assembly are not in place.
2-16
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 31

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Canister The absorber system has a transparent plastic canister that houses the
absorbent. The absorbent—soda lime or barium hydroxide lime—is
available in either loose, granular form or in a prepacked cartridge.
When using loose absorbent, do not fill above the maximum fill level line
located about a quarter-inch from the top of the canister. The clearance and
the ratio of canister diameter to screen opening minimize the potential for
channeling. In channeling, gas flows through the canister along the path of
least resistance. The gas depletes the efficiency of the absorbent along this
route, bypassing absorbent in other areas of the absorber. Draeger Medical
recommends the use of DrägerSorb for the absorber system.
Dust Cup A removable cup at the bottom of the absorber canister assembly collects
absorbent dust and excess moisture that can cause increased flow resistance
in the system.
2
Fresh Gas
Hose
Breathing
System
Pressure
Gauge
Pressure
Sensing
Hose
Assembly
Manual/
Automatic
Selector
Valve
The fresh gas hose is connected to the upper absorber dome. This flexible
hose delivers fresh gas to the breathing system. It has a 15 mm male fitting
designed to fit the Draeger Medical fresh gas outlet and must not be
replaced by another manufacturer's fitting.
The absorber system has a pressure gauge for quick visual readings of
breathing circuit pressure. The gauge is marked for measurements from
–20 to +80 cmH
O in increments of 2 cmH2O. The pressure gauge line is
2
connected to the absorber at the pressure sensing adapter.
Warning: Frequent observation of the breathing system pressure gauge
is mandatory to ensure adequate pressure buildup and relief,
regardless of the mode of operation.
Pressure is monitored at the absorber. A pilot line connects the anesthesia
system pressure monitoring and alarm system.
The manual/automatic selector valve has two-position control knob for
selecting gas pathways for automatic or manually assisted ventilation.
Turning the knob clockwise sets the system to AUTO. Turning the knob
counterclockwise, sets the system to BAG.
Adjustable
Pressure
Limiter (APL)
Valve
Respiratory
Volume
Monitor
Sensor
Part Number: 4115139-001
The APL valve relieves excess gas from the breathing circuit into the
scavenger system. The APL valve expels excess gas containing expired
carbon dioxide before it contacts the absorbent, which extends the life of the
absorbent.
The respiratory volume sensor is an ultrasonic flow sensor that monitors
tidal volume, respiratory minute volume, and respiratory frequency.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-17
Page 32

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Oxygen
Sensor
Positive EndExpiratory
Pressure
(PEEP) Valve
The oxygen sensor analyzes oxygen concentration in the patient circuit. The
sensor mounts in the port at the top of the pressure sensor adapter, which is
connected to a port in the inspiratory valve dome. A plug for closing off the
port when an oxygen sensor is not in place is tethered on the absorber
system. Draeger Medical strongly advocates using an oxygen concentration
sensor in the patient circuit.
The PEEP valve regulates the positive end-expiratory pressure in the
patient breathing circuit. PEEP is increased by turning the knob clockwise
and diminished by turning the knob counterclockwise. The adjustment
range is about 2 to 15 cmH
O. The pressure gauge reading includes the
2
PEEP.
Warning: Waste gas scavenging systems used with Draeger Medical
absorber systems must have safety features to ensure that
excessive subatmospheric pressure (lower than
–0.5 cmH
+10 cmH
O) and excessive positive pressure (higher than
2
O) are not possible at the connection point.
2
2-18
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 33

Scavenger System
The scavenger interface is an exhaust collector manifold. It is intended for
use with suction (vacuum) or passive waste gas disposal systems.
The suction approach uses continuous suction to transfer the gas from the
scavenger to the disposal system. Passive systems rely on the pressure of
the waste gas to convey the waste gas to the exhaust system.
This is a closed system that has one spring-loaded valve for positive
pressure relief and one for negative pressure relief.
Figure 2-10. Scavenger Interface
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
VACUUM NEGATIVE
PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
OP00088
19MM OUTLET
HOSE CONNECTION
(PASSIVE)
OR
3.0 LITER RESERVOIR
BAG (ACTIVE)
POSITIVE RESSURE
RELIEF VALVE
19MM INLET
HOSE
CONNECTION
NEEDLE VALVE
ADJUSTMENT KNOB
(SHOWN DOTTED)
SUCTION
HOSE BARB
The exhaust collector manifold has two 19 mm male fittings to connect
19 mm hoses from the ventilator and absorber APL valve to the exhaust
system.
The exhaust collector manifold connects to a suction waste gas disposal
system with the hose barb. An adjustable needle valve regulates the waste
gas exhaust flow. A 3.0 liter reservoir bag contains the excess waste gas.
This system accommodates a variety of waste gas flow rates from the
patient breathing system.
A 19 mm hose connects to the fitting below the hose barb for passive
exhaust systems. A relief valve guards against excessive pressure build-up
if the exhaust hose is restricted.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-19
Page 34

2
Anesthesia Ventilator
The anesthesia ventilator is a volume-preset, time-cycled, pressure-limited
ventilator with electronic timing, pneumatic circuitry, and independent
controls for frequency, inspiratory-to-expiratory (I:E) ratio, inspiratory flow
rate, tidal volume, and inspiratory pressure limiting.
Figure 2-11. Anesthesia Ventilator Assembly
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
I:E RATIO CONTROL
I:E RATIO DISPLAY
EXTENDED RANGE ACCESS
FREQUENCY CONTROL
FREQUENCY DISPLAY
INSPIRATORY PRESSURE LIMIT
BELLOWS CANISTER
cmH2O
3
0
MIN MAX
OP00096
INSIRATORY FLOW GAUGE
INSPIRATORY
FLOW CONTROL
VENTILATOR
ON-OFF
CONTROL
TIDAL VOLUME
CONTROL
PRESSURE
LIMIT CONTROL
2-20
TIDAL VOLUME
SETTING INDICATOR
BREATHING CIRCUIT
CONNECTOR
Pneumatic power (bellows drive gas) to the ventilator is supplied through
the hospital pipeline supply or through the cylinder. A switch on the right
side of the housing is used to select either oxygen or air as the drive gas
(Figure 2-12 on page 2-21). The ventilator will not function properly if this
pressure drops below 32 psi. Electrical power is supplied by the AC power
source, or, in event of AC power failure, by the backup battery. A fully
charged battery can power the ventilator for at least 90 minutes.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 35

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Figure 2-12. Drive Gas Selector Switch
DRIVE GAS
SELECTOR SWITCH
AIR
VENTILATOR
DRIVE GAS
OP00078
2
O
2
N2O
AIR
O
2
FLOWMETER HOUSING
The anesthesia ventilator is designed for use with a Draeger Medical
absorber with a manual/automatic selector valve. This valve is for selecting
either the breathing bag using the adjustable pressure limiter (APL) valve
for manual ventilation, or the ventilator bellows for automatic ventilation.
During automatic ventilation, the manual/automatic selector valve isolates
the absorber's breathing bag and APL valve from the breathing system. To
compensate for the continuous introduction of fresh gas into the breathing
system, the ventilator has a relief valve mounted behind the bellows
chamber.
When the bellows is completely filled, any excess gas in the system is
released to the scavenging system through the ventilator relief valve. As in
any ascending bellows, the force needed to overcome gravity acting on the
bellows causes a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) within the
breathing system. For the Narkomed Mobile, the PEEP is approximately
2cmH
O.
2
The pressure limit control is used to set the peak inspiratory pressure
produced by the ventilator to limit the maximum pressure to the patient.
The pressure limit control can also improve ventilation for patients with
reduced lung compliance (neonatal/pediatric patients and patients with
adult respiratory distress syndrome).
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-21
Page 36

2
Power Supply System
The Narkomed Mobile has a central power supply for the ventilator, alarm
system, and monitoring system. When in use, the Narkomed Mobile must be
plugged into an active AC outlet. Do not use “cheater” plugs. The term
“cheater” plug implies any and all electrical plugs or other devices that can
inhibit or prohibit the proper grounding of the anesthesia machine.
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
System
Power Switch
The SYSTEM POWER switch is located at the front of the power supply. It
has two positions; ON and STANDBY. In the ON position, the gas
(pneumatic) and electric power circuits are actuated. In the STANDBY
position, the switch shuts down the fresh gas supply, the monitoring system,
and all electrical power to the machine except the battery charging circuit.
When power is on, the green LED power-on indicator illuminates.
Figure 2-13. System Power Supply
POWER APPLIED
INDICATOR
OP00098
SYSTEM
POWER
SWITCH
BATTERY TEST
BUTTON
BATTERY TEST
INDICATOR
Circuit
Breakers
2-22
The electrical system has two magnetic circuit breakers to protect machine
functions (primary AC power input and backup battery power). The circuit
breakers are located on the lower part of the power supply in the back of the
machine.
A circuit breaker is in its normal, closed position when the plunger is flush
with the surface of its base. A circuit breaker is open (tripped) when its
plunger extends beyond its base. If a breaker is tripped, the cause must be
found and corrected before using the anesthesia system.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 37

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Backup
Battery
System
Machine
Functions on
Backup
Battery Power
The backup battery system consists of a rechargeable battery and a built-in
battery charging system.
The backup battery system automatically provides power with no delay
during the period between line power failure and activation of an emergency
generator during a power outage. It also provides power if the cord is
accidentally unplugged during a case. The system automatically switches
back to AC power and recharges its battery when power is restored.
The battery charging system charges the battery any time the power cord is
connected to an active AC power source. The charger can recharge a fully
discharged battery in about 12 hours.
If the machine is getting AC power, but the battery voltage level is low due
to a problem with the battery charging circuit or similar hardware
malfunction, the Advisory message RESERVE BATT LOW is displayed.
These events signal backup battery system activation:
• The Caution message AC POWER FAIL is displayed.
• A three-pulse pattern audio alarm sounds every 30 seconds.
These alarms signify that about 90 minutes of backup battery power
remains from the time the alarm is activated if the battery was fully
charged. All monitoring functions continue to operate, using the battery for
power.
Battery Test
Indicator and
Button
When the battery reserve approaches depletion after an AC power loss, the
Caution message AC BATTERY FAIL is displayed.
This alarm signifies that about 10 minutes of backup battery power remains
from the time the message is activated.
The gas supply system remains operative. Because the ventilator is
inoperative when battery power is cut off, you must perform manual
ventilation by bag. The machine cannot provide monitoring or alarm
functions until AC power is restored.
Note: If the power cord is not plugged into an active AC outlet for a period
of 30 days or more, the backup battery can become depleted.
Plugging the power cord into an active AC outlet for about 12 hours
will recharge a depleted battery.
The battery test button and indicator located near the system power switch
are used to determine the backup battery status (Figure 2-13 on page 2-22).
A detailed testing procedure is included in the checkout procedures in this
manual.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-23
Page 38

2
System Interface Panel
The system interface panel has receptacles for the remote display, oxygen
sensor cord, the breathing pressure pilot line, and the respiratory volume
sensor cord. The panel is located on the display side of the anesthesia
machine near the top of the housing.
Figure 2-14. System Interface Receptacles
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
REMOTE
DISPLAY
INTERFACE
OP00083
FROM: ULTRASONIC
FLOW SENSOR
Remote Display and Support Arm
The remote display (monitor screen and controls) is mounted on the
absorber side of the machine. The display can be adjusted up or down to
place it in the most convenient position. The support arm below the monitor
screen supports an external patient monitor.
REMOTE DISPLAY
VOLUME
SENSOR
OXYGEN
SENSOR
BREATHING
PRESSURE
BREATHING
PRESSURE
MONITOR
INTERFACE
OXYGEN ANALYZER
INTERFACE
2-24
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 39

Monitoring System
The monitoring system integrates the functions of the electronic monitors
and organizes information from these monitors on the monitor screen.
The Narkomed Mobile monitors:
• oxygen concentration
• breathing pressure
• respiratory volume
• oxygen supply pressure
•system status.
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Monitor
Screen and
Controls
All monitoring data and alarm messages are displayed on the monitor
screen. Use the control keys on either side of the screen to establish
monitoring settings. With the left keypad, you can control system-wide
settings, such as alarm annunciation and monitor configuration. With the
right keypad, you can control settings for specific monitors oxygen
concentration, breathing pressure, and respiratory volume.
Figure 2-15. Monitor Screen and Controls
OP87005
Config
Alarms
All
Stby
LEFT
KEYPAD
WARNING:
ADVISORY:
TID VOL
0.35
CAUTION:
35
12
INSP O2 LOW
SUB ATM PRESSURE
AC / BATTERY FAIL
O2 SUPPLY LOW
SERVICE VENT MON
PORT A ERROR
BPM
10
MONITOR
SCREEN
OXYGEN
32
MIN VOL
3.5
PEAK
MEAN
PEEP
100
18
Oxygen(%)
High
Limit
30
Breathing Volume
Low
Limit
Breathing Pr essure
2.0
High
Limit
7
2
Low
Limit
On
On
Auto
Set
Cal
(Liters)
Off
(cm H O)
Off
2
RIGHT
KEYPAD
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-25
Page 40

2
Alarm System
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Alarms are organized into three categories, depending on the urgency of the
alarm condition.
Warn i ngs The highest priority alarms requiring an
immediate response
Cautions Second priority alarms requiring a prompt
response
Advisories The lowest priority alarms requiring the
operator's awareness
Visual and audible notification announce the most urgent conditions.
Alarm
Display
Messages for active alarm conditions appear in the Alarm window at the top
of the monitor screen. Messages are displayed for up to six of the highest
priority active alarm conditions. Any additional lower priority active alarm
conditions are retained in the monitor's memory. Messages for these lower
priority conditions are displayed when the higher priority alarm conditions
are resolved and their messages are removed from the display.
Figure 2-16. Alarm Window Display
ALARM WINDOW
WARNING:
CAUTION:
ADVISORY:
TID VOL
0.35
35
INSP O2 LOW
SUB ATM PRESSURE
AC / BATTERY FAIL
O2 SUPPLY LOW
SERVICE VENT MON
PORT A ERROR
BPM
10
OXYGEN
32
MIN VOL
3.5
100
30
2.0
PEAK
18
12
OP87001
MEAN
7
PEEP
2
2-26
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 41

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Alarm
Annunciation
Ventilation
Alarms
Each alarm category has a specific audible signal:.
Warn i ngs A three-pulse tone pattern that is
initially repeated every few seconds in a
series of descending volumes, and then
constantly at full volume until the alarm
condition is resolved
Cautions A three-pulse tone pattern that is
repeated every 30 seconds
Advisories A single tone or no sound at all,
depending on the urgency of the advisory
The alarm sounds only for the highest-priority, currently active alarm
condition. Tones for lower priority alarm conditions are temporarily
suppressed eliminate simultaneous alarms. If the primary speaker fails, the
Advisory message SERVICE SPEAKER appears in the Alarm window.
When the system power switch is turned ON, the volume and pressure
apnea alarms default to Standby to allow machine setup without sounding
alarms. An interlock with the ventilator ensures that when the ventilator is
turned on, the alarms are enabled. You can also enable the alarms
individually using the keypad.
When the ventilator is turned off:
• If the pressure apnea threshold was greater than 15 cmH
O
2
when the ventilator was turned off, the threshold setting is
changed to 15 cmH
than 15 cmH
O when the ventilator was turned off, the threshold
2
O. (If the pressure apnea threshold was less
2
retains its setting.)
• The Cautions and Warnings associated with apnea alarms
change from activation after 15 and 30 seconds of apnea to
30 and 60 seconds, respectively.
When the ventilator is turned back on, the pressure apnea threshold is
restored to its previous set value and the apnea alarms revert to activation
after 15 seconds (Caution) and 30 seconds (Warning) of apnea.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
2-27
Page 42

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 43

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
3
Specifications
Table of Contents
General .............................................................................. 3-2
Environmental .. ........... .............. ............. ........... ............. .... 3-2
Storage ........................................................................ 3-2
Operating ... ........................... ....................................... 3-2
Electrical .................................................... ........................ 3-2
Main Power Supply ...................................................... 3-2
Backup Battery ........ .......................................... .......... 3-2
Gas Delivery S y stem ......... .. ................ ............................ .. 3-3
Cylinder Gas Pressure .......................... ................ ....... 3-3
Flowmeter Accuracy (at 20 °C and 760 mmHg) .......... 3-3
Ventilator ...... ............. ........... ............. .............. ........... ........ 3-4
Absorber Sy st e m ............................ ............................. ...... 3-4
Inspiratory Valve .......................................................... 3-4
Expiratory Valve ........................................................... 3-4
PEEP Valve ................................................................. 3-4
APL Valve .................................................................... 3-4
Bag Mount ............................................... .................... 3-4
Oxygen Mon it o ring . .. ................ ......................................... 3-4
Breathing Pr e ss u r e M o n it o ring ....... ................ ................... 3 -5
Respiratory Volume Monitoring ........... .. .. .......................... 3-5
Minute Volume ............................................................. 3-5
Tidal Volume .............. .. ............................. ................... 3 -5
Respiratory Rate .......................................................... 3-5
Serial Inte r face ..... .. ............... ............................. ............... 3-6
Serial Port s ......... ................ ............................ ............. 3-6
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Page 44

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
3
General
Anesthesia machine dimensions (approx.)
(W x H x D). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23½ x 53½ x 24½ inches
Anesthesia machine Weight (Approx). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .163 lbs.
Environmental
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–20—+60 °C
Humidity . . . . . . . . . . . .10—90% relative humidity (noncondensing)
Barometric Pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 787—523 mmHg
Operating Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10—35 °C
Humidity . . . . . . . . . . . .30—70% relative humidity (noncondensing)
Barometric Pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 787—523 mmHg
Electrical
Equipment class UL 2601 Class 1, Type B, continuous operation, IPXO
Main Power
Supply
Leakage current
Ground impedance
Dielectric withstand
Chassis resistance (between any metallic point
and ground pin on power cord)
Primary input voltage (acceptable range) .100—240 VAC (@ 50/60 Hz)
Primary input current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .≤ 2.5 amps (@ 50/60 Hz)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ≤ 300 microamps (UL 2601)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ≤ 0.1 ohm (60 Hz source)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ≥ 1500 VAC (UL 2601)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .≤ 0.1 ohm
Backup
Battery
3-2
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Sealed Lead Acid, 12 VDC, 3.4 Ah
Charging time
Reserve power time (from full charge) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90 min
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ≤ 12 hours
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 45

Gas Delivery System
Pipeline inlet connections . . . . . . . . . . DISS/male (ANSI B57.1-1977)
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
3
Cylinder Gas
Pressure
Pipeline inlet pressure. . . . 50—55 psi (345—380 kPa) (O
, N2O, Air)
2
Pipeline gauge accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±3 psi (0—25 psi)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±2 psi (25—75 psi)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±3 psi (75—100 psi)
Cylinder connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pin-indexed hanger yoke
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (ANSI/CGA V-1-1987)
Over pressure relief valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95 psi (655 kPa)
Fresh gas common outlet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 mm female
Fresh gas oxygen concentration (ORC). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 ±4%
Oxygen flush flow rate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 (±10) L/min
Minimum oxygen flow (at 50 psi pipeline pressure) 150 ±50 mL/min
Low oxygen supply pressure alarm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34—40 psi
Cylinder gauge accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±90 psi (0—750 psi)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±60 psi (750—2250 psi)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±90 psi (2250—3000 psi)
Oxygen . . . . . . 1900 psi (13100 kPa) E-size cylinder (at 70 °F, 21 °C)
Nitrous Oxide . . . 745 psi (5130 kPa) E-size cylinder (at 70
°F, 21 °C)
Flowmeter
Accuracy (at
20 °C and
760 mmHg)
Part Number: 4115139-001
Oxygen, Nitrous Oxide, Air
Dual Tapered 0—8 L/min . . . . . . . . . . . .0.1—0.2 L/min ± 50 mL/min
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.2—1.0 L/min ±100 mL/min
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0—8.0 L/min ±5% FS
Oxygen (Auxiliary Oxygen) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0—10 L/min ±5% FS
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
3-3
Page 46

3
Ventilator
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Frequency. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1—99, ±1 BPM (in 1 BPM increments)
I:E ratio
. . . Standard range: 1:1—1:4.5, ±0.1 (in increments of 0.5);
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Extended range: 4:1, 3:1, 2:1
Inspiratory flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10—100 L/min (uncalibrated)
Tidal volume. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20—1500 mL, ±100 mL
Pressure limit control adjustment range . . . . . . . . . .15—120 cmH
Absorber System
Inspiratory
Valve
Expiratory
Valve
PEEP Valve Range . . . . . . . . . . . approx. 2—15 cmH
APL Valve APL Valve Nominal low flow resistance . . . . . . . 2 cmH
Mounting ring nut size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . M35 x 1
Hose terminal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 mm male
Mounting ring nut size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . M33 x 1
Hose terminal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 mm male
O (continuously adjustable)
2
Hose terminal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 mm male
O at 8 L/min
2
O
2
Bag Mount Breathing Bag Terminal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 mm male
Oxygen Monitoring
Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10—100 vol % O
Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 vol % O
Accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±3 vol % O2
(When calibrated within 18 hrs, and constant temperature and pressure)
Response time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .≤ 25 sec (T90)
Zero drift. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Span drift
Temperature error
Sensor service life
. . . 50% relative humidity, 50% O
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ≤ 1 vol % O
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . ≤ ± 3% of reading (15 °C—40 °C)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ≥ 8 months at 25 °C,
gas mixture (or ≥ 5000% hr CO
2
≤0.1 vol % O
/month
2
/8 hours
2
2
2
2
)
3-4
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 47

Breathing Pressure Monitoring
Numeric display range. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–10—+125 cmH2O
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
3
Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 cmH
Accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±3 cmH
O or ±10% of reading,
2
O
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . whichever is greater
Waveform display range - full . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0—100 cmH
Waveform resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 cmH
Waveform accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±3 cmH
O or ±10% of reading,
2
O
2
O
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . whichever is greater
Waveform display scales . . . . . . . . . . . . 0—20, 0—50, 0—100 cmH
O
2
Respiratory Volume Monitoring
Minute
Volume
Tidal Volume Display Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.01—2.01 L
Display Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.1—50.0 L
Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 L
Accuracy
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±10% of reading or 0.01 L x breath rate
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . whichever is greater*
NOTE:
The standard bellows will deliver up to 1.5 L
Respiratory
Rate
Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.01 L
Accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±10% of reading or 0.015 L,
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . whichever is greater*
Volume Apnea Threshold. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.02 L
Numeric display range. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2—99 BPM
Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 BPM
Accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±10% of reading or ±1 BPM,
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . whichever is greater
Exclusive of hose compliance
*
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
3-5
Page 48

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
3
Serial Interface
Serial Ports Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . RS-232/422
Baud Rate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300—38400
Parity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Odd, Even, or None
Data Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 or 8
Stop Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 or 2
Protocols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Vitalink
3-6
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 49

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
Daily and Preuse Checkout Procedures
Table of Contents
Daily Checkout Procedure ................................................. 4-3
Initial Setup a nd Verification .......... .. ............................ 4-3
System Software Diagnostics ...................................... 4-3
Battery Power Verification ............................................ 4-3
Emergency Ventilation Equipment V erification ............ 4-3
High Pressure System Verification .............................. 4-4
Pipeline Supply System Verification ............................ 4-4
System Gas C ir c uit Verificatio n ........... ................ ........ 4-4
Low Pressure Sys t e m Verification . .. ............... ............. 4-5
Oxygen Mon it o r C al ibration .......................... ............... 4-5
OFPD Verification ............ ............................. ............... 4-5
ORC Verification ............................ .............................. 4 -5
Oxygen Flus h Verification .................. .......................... 4-5
Fresh Gas Verificatio n .. ............... ............................. .... 4-5
Absorber Sy st e m Verification ........... .. ................ .......... 4-6
APL Valve Verification .................................................. 4-7
Breathing System Leak Test ........................................ 4-7
Scavenger System Verification .................................... 4-8
Manual and Automat ic Ventilation System s ............. .. .. 4-9
Monitors ... ...................... ........................ .................... 4 -10
System Flush .............................................. ............... 4-1 0
Final Position ...... ............................. .......................... 4-10
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s ManualPart Number: 4115139-001
Page 50

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
Table of Contents (continued)
Preuse Checkout Procedur e .......... ...................... .......... 4-11
Reserve Power Verification .............................................. 4-11
Absorber System Verification ........................................... 4-11
APL Valve .......................................... ....... ...... ....... ...... ..... 4-12
Breathing System Leak Test ............................................ 4-13
Scavenger System ........................................................... 4-14
Manual and Automatic Ventilation Systems ..................... 4-15
Monitor ............................................................................. 4-16
System Flush ................................................................... 4-16
Final Position .................................................................... 4-16
4-2
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 51

Daily Checkout Procedure
Before operating the Narkomed Mobile, the following checkout procedure
must be performed to make sure the machine is ready for use. This is a
recommended procedure. Follow your institution's policies for specific
checkout procedures. If the anesthesia system fails any procedures
identified by an important note symbol , do not use the machine. Contact
an authorized representative of DrägerService for inspection of the unit.
Note: Do not insert any additional components into, or modify, the
anesthesia system after the checkout procedure is started.
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
!
Initial Setup
and
Verification
System
Software
Diagnostics
Battery
Power
Verification
1. Enter the serial number of the anesthesia machine. The serial number
is located on the leg of the transport trolley assembly.
2. Make sure there is a valid inspection sticker on the back of the machine
indicating that the anesthesia machine was serviced and inspected by
an authorized representative of DrägerService.
3. Verify that a cylinder wrench is tethered next to the cylinder yoke.
4. If the anesthesia machine is not already plugged in, connect the
electrical power cable to an active AC outlet that accepts and properly
grounds the power cable. Do not use “cheater” plugs. The term
“cheater” plug implies any and all electrical plugs or other devices that
can inhibit or prohibit the proper grounding of the anesthesia machine.
5. Turn the SYSTEM POWER switch to the ON position. Wait for the
!
machine to complete its diagnostic checks. Make sure the system is
functional.
6. Check the reserve battery power. Remove the power cable from the
!
outlet. Press the BATTERY TEST button. The green indicator must
light. Plug the power cable back into the electrical outlet.
NOTE:
This test assumes that the anesthesia machine has been plugged in for 12 hours.
The battery charging system works only when the machine is connected to an
active AC power source. The charging system takes about 12 hours to charge a
fully discharged battery.
Emergency
Ventilation
Equipment
Verification
Part Number: 4115139-001
7. Verify that backup ventilation equipment is available and
!
functional.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
4-3
Page 52

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
High
Pressure
System
Verification
8. Check the oxygen and nitrous oxide cylinder supplies.
!
a. Disconnect all pipeline gas supply hoses and drain the system.
b. Close the both cylinder valves and remove the cylinders from the
yoke. Verify that there is one cylinder gasket and there are two index
pins at each cylinder mounting point. Verify that the cylinders match
the yoke label. Replace the cylinders.
c. Open the oxygen cylinder and check the cylinder pressure gauge. A
†
1900
full oxygen cylinder registers about
psi. Replace any cylinder
with pressure less than 1000 psi. To check for a high pressure leak,
close the cylinder and observe the cylinder pressure gauge for a
prominent decrease in the pressure. With the oxygen cylinder closed,
press the oxygen flush button on the front of the anesthesia machine.
Hold the button in until the pressure gauges indicate no pressure.
d. Open the nitrous oxide cylinder and check the cylinder pressure
gauge. A full oxygen cylinder registers about 745 psi. Replace any
cylinder with pressure less than 600 psi. To check for a high pressure
leak, close the cylinder and observe the cylinder pressure gauge for a
prominent decrease in the pressure.
The full and minimum pressures for the oxygen and nitrous oxide cylinders:
GAS
Oxygen 1900
Nitrous Oxide 745 600
PSI - FULL
*
PSI - MIN
†
1000
Pipeline
Supply
System
Verification
System Gas
Circuit
Verification
* Indicated pressure is for an E-size cylinder at 70 °F (21 °C).
† Due to differences in manufacture’s specifications and topping off during
refill of E-type cylinders, a full cylinder can be as high as 2015 PSI.
9. Pipeline Supply Verification
!
a. Inspect the supply hoses for cracks or wear.
b. Connect the appropriate pipeline supply hoses to the pipeline inlet
connectors.
c. Check for sufficient pipeline pressure readings for each gas on the
pipeline pressure gauges located below the flow control valves. The
pressure for each gas must be between 50—55 psi. Open the flow
control valve for each gas over the full range. The pressure indicated
at the pipeline pressure gauge must not decrease more than 5 psi.
d. Verify that the correct gases are supplied to the anesthesia machine
inlets.
10. Check the flowmeters. Adjust the flow control knob for each gas and
!
verify the proper operation of the corresponding flowmeters. The float
must move freely over the full range of each flowmeter.
4-4
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 53

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
Low Pressure
System
Verification
Oxygen
Monitor
Calibration
OFPD
Verification
11. Vaporizer Verification
!
a. Check for sufficient supply of liquid anesthetic in the vaporizer. Fill
the vaporizer with liquid anesthetic to the maximum fill line.
b. Make sure the cap is on the spout and the drain is completely closed.
c. Make sure the handwheel is set to 0.
d. d. Vapor handle is in the locked position
12. Calibrate the oxygen monitor by exposing the sensor to ambient air
!
and activate the calibration key. (See
Operation - Oxygen Monitoring
“Calibrating the Oxygen Sensor” in Section 5 for more information.)
a. Place the oxygen sensor securely in the sensor mount.
b. Verify that the correct gas concentration is supplied to the
anesthesia system from the pipeline and cylinder supplies.
c. Close the cylinder supply and deplete the pressure from the system.
13. Check the oxygen failure protection device. With all gases available
!
on the machine set to a flow of about 4 L/min, close the oxygen supply by
disconnecting the oxygen pipeline supply hose and closing the oxygen
cylinder. The flow of all other gases indicated by their flowmeters must
decrease in proportion to the decrease in oxygen flow and eventually
shut off.
ORC
Verification
Oxygen
Flush
Verification
Fresh Gas
Verification
14. Check the function of the ORC. With the nitrous oxide flow control
!
valve open to a flow of 8 L/min, vary the oxygen flow with the oxygen
flow control valve. The nitrous oxide flow indicated on the nitrous oxide
flowmeter must automatically vary in response to the adjustment of the
oxygen flow control valve.
The ORC must maintain a fresh gas oxygen/nitrous oxide flow ratio of at
least 21% oxygen.
15. Check the oxygen flush:
!
a. Press the oxygen flush button and listen for an audible gas flow
sound, accompanied by a marked increase in oxygen concentration in
the breathing system.
b. Check the delivered oxygen concentration. Repeatedly flush the
patient breathing system by pressing the oxygen flush button. Close
all the other flow control valves. The oxygen measurement display
area should indicate 97% to 100% oxygen concentration.
16. Make sure the handwheel is set to 0. Open the oxygen flow control
!
valve to an 8 L/min flow and close all other flow control valves. Sniff the
gas coming from the fresh gas common outlet. There should be no
noticeable odor.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
4-5
Page 54

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
Absorber
System
Verification
17. To check the absorber system:
!
a. Check the hose connections in the breathing system.
b. Make sure the fresh gas hose of the breathing system is securely
connected to the fresh gas outlet.
c. Make sure a 22 mm patient breathing circuit is connected between
the inspiratory valve and the expiratory hose terminal on the
ultrasonic flow sensor.
d. Make sure a 22 mm breathing hose is connected between the
ventilator hose terminal and the manual/automatic selector valve
breathing hose terminal.
e. Make sure a breathing bag of proper capacity and appropriate
construction is connected to the breathing bag terminal of the
breathing system.
f. Make sure the breathing pressure hose assembly is properly
connected between the pressure sensor adapter and the system
interface panel.
g. Make sure the oxygen sensor and respiratory volume sensor are
properly installed.
18. Make sure the absorber canister is filled with CO
!
absorbent.
2
Consult the absorbent manufacturer's literature for information on
what signs to expect when the absorbent is exhausted. Draeger Medical
recommends the use of DrägerSorb. Make sure that the color change
represents the absorbent's true state of depletion and is not due to
regeneration after a rest period. Flushing the anesthesia machine
continuously for at least one minute with 100% oxygen before the first
case of the day is recommended.
4-6
If the anesthesia machine has been out of use or in storage, replace the
absorbent before using the machine. Draeger Medical recommends
establishing a routine schedule with a sufficient safety margin for
replacing the absorbent.
Remove accumulated absorbent dust and water from the absorber dust
cup.
WARNING:
NOTE: When changing the CO
Absorbent is caustic and is a strong eye, skin, and respiratory tract
irritant. When emptying the absorber dust cup, take care not to spill
its caustic contents.
absorbent, take care not to chip or crack the
absorbent canister. Check the canister for signs of damage, especially
along the rim before reinstallation.
2
19. Close the vaporizer and all gas flow sources. Check for free gas passage
in the patient breathing system. Wear a surgical mask to inhale and
exhale through the breathing system (each limb individually, if
possible). Verify the unidirectional flow in each limb and then reconnect
the tubing.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 55

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
APL Valve
Verification
Breathing
System Leak
Test
20. Check the APL valve to be sure it can relieve excess gas from the
!
breathing system into the scavenger system.
To check the APL valve's flow resistance:
a. Set the manual/automatic selector valve to BAG.
b. Set the PEEP valve to its minimum position.
c. Remove the bag from the bag mount.
d. Interconnect the inspiratory valve and the expiratory hose terminal
on the ultrasonic flow sensor with a 22 mm hose.
e. Completely open the APL valve by turning the control knob fully
counterclockwise to its stop position.
f. Turn the SYSTEM POWER switch to ON.
g. Open the oxygen flow control valve to a flow of 8 L/min.
h. Occlude the bag mount opening and watch for a pressure increase on
the breathing system pressure gauge. This pressure increase must
not exceed 3 cmH
O.
2
21. Perform a breathing and fresh gas delivery system pressure test. This
test detects leaks from the patient breathing system and fresh gas
delivery system.
To perform the test:
a. Close all flow control valves on the anesthesia machine.
b. Turn the SYSTEM POWER switch to the STANDBY position.
c. Turn the vaporizer to 0% concentration.
d. Interconnect the inspiratory valve and the expiratory hose terminal
on the ultrasonic flow sensor with a 22 mm breathing hose.
e. Set the manual/automatic selector valve to BAG.
f. Close the APL valve by turning the knob fully clockwise to its stop
position.
g. Check that the breathing pressure gauge is on 0.
h. Attach the supplied test terminal to the breathing bag mount.
i. Connect a sphygmomanometer squeeze bulb (available from Draeger
Medical) to the hose barb on the test terminal.
j. Pump the squeeze bulb by hand until the breathing system pressure
gauge indicates pressure of at least 50 cmH
80 cmH
2
O).
O (not to exceed
2
k. Observe the pressure drop at the breathing system pressure gauge.
When the pressure is at 50 cmH
pressure must not drop more than 20 cmH
O, begin counting seconds. The
2
O in 30 seconds.
2
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
4-7
Page 56

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
Scavenger
System
Verification
22. Verify the performance of the scavenger system.
!
To test negative pressure relief:
a. Connect a 19 mm scavenger hose to the ventilator relief valve and
the scavenger interface.
b. Connect a 19 mm scavenger hose between the APL valve and the
scavenger interface.
c. Connect the 3.0 liter reservoir bag to the reservoir bag terminal.
d. Connect the scavenger to the suction waste gas disposal system.
e. Short circuit the inspiratory valve and the expiratory hose terminal
on the ultrasonic flow sensor with a 22 mm breathing hose.
f. Set the absorber's manual/automatic selector valve to BAG.
g. Turn the APL valve fully counterclockwise.
h. Verify that the suction waste gas disposal system is active.
i. Open the scavenger needle valve enough to allow typical suction
through the scavenger.
j. Close all flow control valves on the anesthesia machine.
k. Occlude the absorber breathing bag mount. At this point, the
breathing pressure gauge should indicate a negligible negative
pressure no lower than –1.0 cmH
O.
2
To test positive pressure relief:
a. Connect a 19 mm scavenger hose to the ventilator relief valve and
the scavenger interface.
b. Connect a 19 mm scavenger hose between the APL valve and the
scavenger interface.
c. Connect the 3.0 liter reservoir bag to the reservoir bag terminal.
d. Connect the scavenger to the suction waste gas disposal system.
e. Short circuit the absorber's inspiratory and expiratory valves with a
22 mm breathing hose.
f. Set the absorber's manual/automatic selector valve to BAG.
g. Turn the APL valve fully counterclockwise.
h. Verify that the suction waste gas disposal system is active.
i. Turn the PEEP valve control knob fully counterclockwise to its
lowest setting.
j. Turn the scavenger needle valve fully counterclockwise.
k. Push the O
flush button to inflate the scavenger reservoir bag.
2
4-8
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 57

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
l. Open the oxygen flow control valve to a flow of 8 L/min.
m. Occlude the absorber breathing bag terminal. The oxygen flow
should exit through the positive pressure relief valve. The pressure
gauge should indicate pressure less than 10 cmH
O.
2
n. Adjust the scavenger needle valve to a proper initial setting.
To test the scavenger interface for passive systems:
a. Make sure a 19 mm scavenger hose is connected between the
ventilator relief valve and the scavenger interface.
b. Make sure a 19 mm scavenger hose is connected between the APL
valve and the scavenger interface.
c. Make sure a 19 mm scavenger hose is connected between the bottom
scavenger interface and the hospital exhaust system.
4
Manual and
Automatic
Ventilation
Systems
d. Check for moisture accumulation in the breathing and scavenger
hoses. Remove any moisture found.
e. Short-circuit the inspiratory valve and the expiratory hose terminal
on the ultrasonic flow sensor with a 22 mm breathing hose.
f. Set the absorber’s manual/automatic selector valve to AUTO.
g. Turn the PEEP valve control knob fully counterclockwise to its
lowest setting.
h. Open the oxygen flow control valve to a flow of 10 L/min and occlude
the 19 mm scavenger terminal labeled EXHAUST.
i. After the ventilator bellows inflates, the flow of oxygen exits the
system through the positive pressure safety relief valve. At this
point, the absorber system’s breathing pressure gauge must indicate
a pressure of less than 5 cmH2O.
23. Test the ventilator.
!
a. Check for proper pressure and flow at the Y-piece during the
inspiratory and expiratory phases. Turn the SYSTEM POWER
switch and ventilator power switch to their ON positions. Place the
manual/automatic selector valve in the AUTO position. Adjust the
oxygen flow control valve to a 3 L/min flow. Set the ventilator
frequency to 3 BPM, the I:E ratio to 1:2, and the tidal volume to
about 1 liter.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Adjust the ventilator flow control to the maximum of the “low” zone
on the flow gauge. Occlude the patient side of the Y-piece. Fill the
ventilator bellows by pressing the oxygen flush button. Observe the
breathing system pressure gauge as the ventilator cycles.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
4-9
Page 58

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
The pressure gauge must indicate a pressure over 30 cmH2O when
the bellows completes its downward travel. The pressure should not
exceed 3 cmH
completes its upward travel.
b. Verify the PEEP valve's performance. Attach a breathing bag to the
patient Y-piece with an appropriate adapter such as a Draeger
Medical combination mask elbow with a 22 mm male fitting for the
breathing bag and 15 mm male fitting for the Y-piece. With the
manual/automatic selector in the AUTO position, set the ventilator
to the preferred frequency.
Then adjust the PEEP valve to different values and observe the
breathing system pressure gauge to verify performance. Turn the
PEEP valve control knob fully counterclockwise to its lowest setting
after the test is completed.
O at the end of the expiratory phase when the bellows
2
Monitors 24. Check the alarm limit settings. The monitor alarm limits are
automatically set to a default configuration when the SYSTEM POWER
switch is turned on. Check these settings and adjust them if necessary.
Alarm limits can be adjusted at the beginning of or during a procedure.
Also, make sure that any external monitors (if any) are connected
properly and that the alarms sound through the anesthesia machine's
central audio annunciator.
25. Test the alarm functions for all monitors. Simulate alarm conditions
!
and check for appropriate alarm signals.
System Flush 26. Flush the system for at least one minute with 100% oxygen by pressing
the oxygen flush button.
Final Position 27. When the daily checkout procedure is complete, verify that:
a. the vaporizer is off (the handwheels is set to zero)
b. the vaporizer is filled to the maximum fill line
c. Vaporizer properly locked into position.
d. the APL valve is open (fully counterclockwise)
e. the manual/automatic selector is set to BAG
4-10
f. all flowmeters indicate 0 (or minimum)
g. the breathing system is ready to use (the bag is in place and all hoses
are connected properly).
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 59

Preuse Checkout Procedure
Perform the following abbreviated checkout procedure when the Narkomed
Mobile is used in successive cases. It may be performed only after the initial
daily checkout procedure given in Section 3 was performed. This is a
recommended procedure. Follow your institution's policies regarding
specific checkout procedures. If the anesthesia system fails any procedures
identified by an important note symbol , do not use the machine. Contact
an authorized representative of DrägerService for inspection of the unit.
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
!
Reserve
Power
Verification
Absorber
System
Verification
NOTE:
1. Check the reserve battery power. Turn the SYSTEM POWER switch
Do not insert any additional components into or modify the anesthesia system
after the checkout procedure is started.
!
to the ON position. Remove the power cable from the outlet. Press the
BATTERY TEST button located to the left of the SYSTEM POWER
switch. The green indicator to the right of the test button must
illuminate. Plug the power cable back into the electrical outlet.
NOTE:
2. To check the absorber system:
This test assumes that the anesthesia machine has been plugged in for 12 hours.
The battery charging system works only when the machine is connected to an
active AC power source. The charging system takes about 12 hours to charge a
fully discharged battery.
!
a. Check the hose connections in the breathing system.
b. Make sure the fresh gas hose of the breathing system is securely
connected to the fresh gas outlet.
c. Make sure a 22 mm patient breathing circuit is connected between
the inspiratory valve and expiratory hose terminal on the ultrasonic
flow sensor.
d. Make sure a 22 mm breathing hose is connected between the
ventilator hose terminal and the manual/automatic selector valve
breathing hose terminal.
Part Number: 4115139-001
e. Make sure a breathing bag of proper capacity and appropriate
construction is connected to the breathing bag terminal of the
breathing system.
f. Make sure the breathing pressure hose assembly is properly
connected to the pressure sensor adapter and the system interface
panel.
g. Make sure the oxygen sensor and respiratory volume sensor are
properly installed.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
4-11
Page 60

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
3. Check the CO2 absorbent in the absorber system. Make sure the
!
absorber canister is filled with CO
manufacturer's literature for information on what signs to expect when
the absorbent is exhausted. Draeger Medical recommends the use of
DrägerSorb. Make sure that the color change represents the absorbent's
true state of depletion and is not due to regeneration after a rest period.
Flushing the anesthesia machine continuously for at least one minute
with 100% oxygen before the first case of the day is recommended.
If the anesthesia machine has been out of use or in storage, replace the
absorbent before using the machine. Draeger Medical recommends
establishing a routine schedule with a sufficient safety margin for
replacing the absorbent.
Remove accumulated absorbent dust and water from the absorber dust
cup.
absorbent. Consult the absorbent
2
WARNING:
NOTE: When changing the CO
Absorbent is caustic and is a strong eye, skin, and respiratory tract
irritant. When emptying the absorber dust cup, take care not to spill is
caustic contents.
absorbent, take care not to chip or crack the
absorbent canister. Check the canister for signs of damage, especially
around the rim, before reinstallation.
2
4. Close the vaporizer and flow control valves. Check for free gas passage
in the patient breathing system. Wear a surgical mask to inhale and
exhale through the breathing system (each limb individually if possible).
Verify the unidirectional flow in each limb and then reconnect the
tubing.
APL Valve 5. Check the APL valve. The APL valve must be capable of relieving
!
excess gas from the breathing system into the scavenger system.
To check the APL valve's flow resistance:
a. Set the manual/automatic selector valve to BAG.
b. Remove the bag from the bag mount.
c. Interconnect the inspiratory valve and the expiratory hose terminal
on the ultrasonic flow sensor with a 22 mm hose.
d. Completely open the APL valve by turning the control knob fully
counterclockwise to its stop position.
4-12
e. Turn the SYSTEM POWER switch to ON.
f. Open the oxygen flow control valve to a flow of 8 L/min.
g. Occlude the bag mount opening and watch for a pressure increase on
the breathing system pressure gauge. This pressure increase must
not exceed 3 cmH
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
O.
2
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 61

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
Breathing
System Leak
Test
6. Perform a breathing and fresh gas delivery system pressure test. This
test detects leaks from the patient breathing system and fresh gas
delivery system.
To perform the test:
a. Close all flow control valves on the anesthesia machine.
b. Turn the SYSTEM POWER switch to the STANDBY position.
c. Turn the vaporizers to 0% concentration.
d. Interconnect the inspiratory valve and the expiratory hose terminal
on the ultrasonic flow sensor with a 22 mm breathing hose.
e. Set the manual/automatic selector valve to BAG.
f. Close the APL valve by turning the knob fully clockwise to its stop
position.
g. Check that the breathing pressure gauge is on 0.
h. Attach the supplied test terminal to the breathing bag mount.
i. Connect a sphygmomanometer squeeze bulb (available from Draeger
Medical) to the hose barb on the test terminal.
j. Pump the squeeze bulb by hand until the breathing system pressure
gauge indicates pressure of at least 50 cmH
80 cmH
2
O).
O (not to exceed
2
k. Observe the pressure drop at the breathing system pressure gauge.
When the pressure is at 50 cmH
O, begin counting seconds. Thirty
2
seconds or longer are needed for a pressure drop from
50—30 cmH
0.
2
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
4-13
Page 62

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
Scavenger
System
7. Verify the performance of the scavenger system.
!
To test negative pressure relief:
a. Connect a 19 mm scavenger hose to the ventilator relief valve and
the scavenger interface.
b. Connect a 19 mm scavenger hose between the APL valve and the
scavenger interface.
c. Connect the 3.0 liter reservoir bag to the reservoir bag terminal.
d. Connect the scavenger to the suction waste gas disposal system.
e. Short-circuit the inspiratory valve and the expiratory hose terminal
on the ultrasonic flow sensor with a 22 mm breathing hose.
f. Set the absorber's manual/automatic selector valve to BAG.
g. Turn the APL valve fully counterclockwise.
h. Verify that the suction waste gas disposal system is active.
i. Open the scavenger needle valve enough to allow typical suction
through the scavenger.
j. Close all flow control valves on the anesthesia machine.
k. Occlude the absorber breathing bag mount. At this point, the
breathing pressure gauge should indicate a negligible negative
pressure no lower than –1.0 cmH
O.
2
To test positive pressure relief:
a. Connect a 19 mm scavenger hose to the ventilator relief valve and
the scavenger interface.
b. Connect a 19 mm scavenger hose between the APL valve and the
scavenger interface.
c. Connect the 3.0 liter reservoir bag to the reservoir bag terminal.
d. Connect the scavenger to the suction waste gas disposal system.
e. Short circuit the absorber's inspiratory and expiratory valves with a
22 mm breathing hose.
f. Set the absorber's manual/automatic selector valve to BAG.
g. Turn the APL valve fully counterclockwise.
h. Verify that the suction waste gas disposal system is active.
i. Turn the PEEP valve control knob fully counterclockwise to its
lowest setting.
j. Turn the scavenger needle valve fully counterclockwise.
k. Push the O
flush button to inflate the scavenger reservoir bag.
2
4-14
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 63

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
l. Open the oxygen flow control valve to a flow of 8 L/min.
m. Occlude the absorber breathing bag terminal. The oxygen flow
should exit through the positive pressure relief valve. The pressure
gauge should indicate pressure less than 10.0 cmH
O.
2
n. Adjust the scavenger needle valve to a proper initial setting.
To test the scavenger interface for passive systems:
a. Make sure a 19 mm scavenger hose is connected between the
ventilator relief valve and the scavenger interface.
b. Make sure a 19 mm scavenger hose is connected between the APL
valve and the scavenger interface.
c. Make sure a 19 mm scavenger hose is connected between the bottom
scavenger interface and the hospital exhaust system.
4
Manual and
Automatic
Ventilation
Systems
d. Check for moisture accumulation in the breathing and scavenger
hoses. Remove any moisture found.
e. Short-circuit the inspiratory valve and the expiratory hose terminal
on the ultrasonic flow sensor with a 22 mm breathing hose.
f. Set the absorber’s manual/automatic selector valve to AUTO.
g. Turn the PEEP valve control knob fully counterclockwise to its
lowest setting.
h. Open the oxygen flow control valve to a flow of 10 L/min and occlude
the 19 mm scavenger terminal.
i. After the ventilator bellows inflates, the flow of oxygen exits the
system through the positive pressure safety relief valve. At this
point, the absorber system’s breathing pressure gauge must indicate
a pressure of less than 10 cmH
8. Test the ventilator.
!
O.
2
a. Check for proper pressure and flow at the Y-piece during the
inspiratory and expiratory phases. Turn the SYSTEM POWER
switch and ventilator power switch to their ON positions. Place the
manual/automatic selector valve in the AUTO position. Adjust the
oxygen flow control valve to a 3 L/min flow. Set the ventilator
frequency to 3 BPM, the I:E ratio to 1:2, and the tidal volume to
about 1 liter.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Adjust the ventilator flow control to the maximum of the “low” zone
on the flow gauge. Occlude the patient side of the Y-piece. Fill the
ventilator bellows by pressing the oxygen flush button. Observe the
breathing system pressure gauge as the ventilator cycles.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
4-15
Page 64

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
4
The pressure gauge must indicate a pressure over 30 cmH2O when
the bellows completes its downward travel. At the end of the
expiratory phase, when the bellows completes its upward travel, the
pressure should not exceed 3 cmH
b. Verify the PEEP valve's performance. Attach a breathing bag to the
patient Y-piece with an appropriate adapter such as a Draeger
Medical combination mask elbow with a 22 mm male fitting for the
breathing bag and 15 mm male fitting for the Y-piece. With the
manual/automatic selector valve in the AUTO position, set the
ventilator to the preferred frequency.
Then adjust the PEEP valve to different values and observe the
breathing system pressure gauge to verify performance. Turn the
PEEP valve control knob fully counterclockwise to its lowest setting
after the test is completed.
O.
2
Monitor 9. Check the alarm limit settings. The monitor alarm limits set
automatically to a default configuration when the SYSTEM POWER
switch is turned on. Check these settings and adjust them if necessary.
Alarm limits may be adjusted at the beginning of or during a procedure.
Also, make sure that any external monitors are connected properly and
that the alarms sound through the anesthesia machine's central audio
annunciator.
10. Test the alarm functions of all monitors. Simulate alarm conditions
!
and check for appropriate alarm signals.
System Flush 11. Flush the system with 100% oxygen by pressing the oxygen flush button.
Final Position 12. At the completion of the checkout procedure, verify that:
a. the vaporizer is off (handwheel is set to zero)
b. the vaporizer is filled to the maximum fill line
c. the APL Valve is open (fully counterclockwise)
d. the manual/automatic switch is set to BAG
e. all flowmeters indicate 0 (or minimum)
f. the patient suction level is adequate
4-16
g. the breathing system is ready to use (bag is in place and all hoses
connected are properly).
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 65

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
Operating the Anesthesia Machine
Table of Contents
Gas Delivery System Operation ........................................ 5-3
Adjusting the G a s Flow .......................................... ...... 5-3
Using the Oxygen Flush .............................................. 5-4
Anesthetic Vaporizer Operation ......................................... 5-4
Turning the Vaporizer On ............................................. 5-5
Turning the Vaporizer Off ............................................. 5-5
Filling the V aporizer During a Case ............................. 5-6
Absorber Sy st e m O p era tion ......... .. .. ................................. 5-7
Using the Manual/ Automatic Selector Valve ............... 5-8
Using the APL Valve .................................................... 5-9
Using the PEEP Valve ............................. .. ................ 5-10
Part Number: 4115139-001
Scavenger Interface Operation ........................................ 5-11
Needle Valve Adjustment for Suction Systems .......... 5-12
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Page 66

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
Table of Contents (continued)
Anesthesia Ventilator Operation .................................... 5-12
Activating the Ventilator .................................................... 5-14
Using the Ventilator On/Off Control .................................. 5-14
Adjusting the Tidal Volume ............................................... 5-14
Setting the Respiratory Frequency ................................... 5-15
Setting the Inspiratory/Expiratory (I:E) Phase Time Ratio 5-15
Setting the Inspiratory Flow Rate ..................................... 5-15
Setting the Inspiratory Pressure Limit .............................. 5-15
Selecting the Bellows Drive Gas ...................................... 5-16
5-2
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 67

Gas Delivery System Operation
The Narkomed Mobile is a continuous flow anesthesia system with
pneumatic circuitry for mixing and delivering fresh gas and anesthetic
agent vapor. The pneumatic system can deliver up to three gases (oxygen,
nitrous oxide, and air) and one anesthetic agent simultaneously.
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
Adjusting the
Gas Flow
To adjust the gas flow:
1. Turn the flow control knob located below the flowmeter tube for the gas
you want to adjust. Turning the valve knob counterclockwise increases
flow. Turning the knob clockwise decreases flow.
2. As you adjust the flow control knob, observe the flow rate. Flow rate is
indicated by the flowmeter scale reading at the center of the float.
Caution: The oxygen flow cannot be completely shut off. Do not force
the oxygen flow control knob in an effort to shut off the
minimum flow (150 ±50 mL/min). Forcing the knob can
damage the valve seat.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
5-3
Page 68

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
Using the
Oxygen
Flush
To use the oxygen flush, press the oxygen flush button, located on the front
of the Narkomed Mobile. This introduces an unmetered flow of pure oxygen
into the breathing circuit at a rate of about 55 L/min.
Figure 5-1. Oxygen Flush Button
OP00097
FRESH GAS
OUTLET
FRESH
GAS HOSE
Anesthetic Vaporizer Operation
The Dräger-Vapor 19.3 adds an anesthetic gas to the fresh gas stream by
producing a precisely metered amount of the vapor of a particular liquid
anesthetic. The vaporizer is installed in the fresh gas line upstream of the
patient breathing system (semi-closed, semi-open system). Refer to the
Dräger-Vapor 19.n Anesthetic Vaporizer Instructions for Use for detailed
information about operating the vaporizer.
RELEASE TO LOCK
PULL TO INSERT OR
REMOVE HOSE
O2 FLUSH
CONTROL
FRESH GAS
LOCKING BAR
5-4
Warning: The vaporizer must not be connected downstream of the fresh
gas outlet of the anesthesia machine.
For low flow (fresh gas flows lower than 250 mL/min) or closed system
anesthesia, breathing circuit concentrations may differ considerably from
the vaporizer setting. When performing anesthesia with low flow or closed
system techniques, it is essential to monitor inspiratory and expiratory
anesthesia concentration, oxygen concentration, expiratory volume, and
airway pressure in the circuit.
Warning: Be sure to fill the vaporizer in an upright position. Filling the
vaporizer in a tilted position can cause overfilling. Overfilling
causes the anesthetic concentration rate to be higher or lower
than the handwheel setting.
Before each case, perform the preuse checkout procedures and check the
following:
1. Make sure the drain valve is closed and the locking lever is in the locked
position.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 69

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
2. Set the handwheel to 0 (zero-point interlock) and make sure the button
is engaged. Then press the 0 button and turn the handwheel to 0 and
engage the button. Wait 5 seconds for the pressure to equalize.
Figure 5-2. Locking Lever Open/Handwheel Moved to Zero
LOCKING LEVER
(LOCKED)
LOCKING LEVER
(UNLOCKED)
Turning the
Vaporizer On
Turning the
Vaporizer Off
HANDWHEEL
OP00330
3. Fill the vaporizer to the maximum fill line.
4. Tighten the filler sealing plug.
To turn the vaporizer on:
1. Adjust the fresh gas flow.
2. Turn the vaporizer handwheel to the preferred anesthetic concentration.
Do not set the handwheel between 0 and 0.2% volume concentration.
This part of the handwheel actuates the on/off switch and cannot be
calibrated.
Note: Verify that the scavenger system, to collect and remove vented gas
from the operating room, is properly functioning.
To turn the vaporizer off, turn the vaporizer handwheel to 0 (zero-point
interlock) and make sure the button engages. Do not interrupt the fresh gas
flow until the vaporizer is turned off.
Note: Drain the anesthetic agent if the vaporizer will not be used for longer
Part Number: 4115139-001
than six months or if the vaporizer will be removed from the
anesthesia machine.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
5-5
Page 70

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
Filling the
Vaporizer
During a
Case
Be extremely careful when filling the vaporizer during a case. The
vaporizing chamber is pressurized when fresh gas is flowing and the
vaporizer is turned on.
To safely add anesthetic agent while the machine is in use, depressurize the
vaporizer by setting the handwheel to 0 (zero-point interlock). Make sure
the button engages in the locked position. Allow at least 5 seconds for the
vaporizing chamber to depressurize, then add the anesthetic agent.
Warning: The vaporizer handwheel must be set to 0 (zero-point
interlock) before the vaporizer can be filled. If the vaporizer is
not depressurized before unsealing the filling spout, liquid
anesthetic can gush out.
Warning: Because the vaporizer funnel filling system does not limit the
type of agent poured into the vaporizer, using an agent
monitoring device is recommended to verify the agent.
5-6
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 71

Absorber System Operation
A single-canister system absorbs exhaled carbon dioxide in the rebreathing
circuit of the anesthesia machine.
Figure 5-3. Absorber System
PRESSURE
SENSOR ADAPTER
BREATHING
SYSTEM
PRESSURE
GAUGE
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
OXYGEN SENSOR
INSPIRATORY
VALVE
FRESHGAS
HOSE
APL VALVE
ABSORBENT
CANISTER
EXPIRATORY
VALVE
PEEP VALVE
OP00079
The absorber system includes:
• an inspiratory valve and an expiratory valve
• an absorber canister and dust cup
• a breathing system pressure gauge
• a pressure sensing hose assembly
• fresh gas hose
MANUAL/AUTO
SELECTOR
VALVE
BREATHING
BAG FITTING
ABSORBER
MOUNTING STUD
ABSORBER
POLE
• manual/automatic ventilation selector valve
• an adjustable pressure limiter (APL) valve
• respiratory volume sensor
• oxygen concentration sensor
• a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) valve.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
5-7
Page 72

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
The absorber system handles spontaneous, manually assisted, or automatic
ventilation. The preferred mode of operation is selected with the manual/
automatic selector valve.
Warning: Waste gas scavenging systems used with Draeger Medical
absorber systems must have safety features to ensure that
excessive subatmospheric pressure (lower than
–0.5 cmH
+10 cmH
O) and excessive positive pressure (higher than
2
O) are not possible at the connection point.
2
Using the
Manual/
Automatic
Selector
Valve
The manual/automatic selector control knob must be positioned properly for
either the ventilator bellows or the breathing bag to be properly engaged in
the breathing circuit. Turn the knob counterclockwise for the BAG setting.
Turn the knob to the clockwise for the AUTO setting. The settings are
labeled on the control knob. The current setting appears near the top.
Set the knob to BAG for spontaneous breathing or manually assisted
ventilation. Set the knob to AUTO for automatic ventilation.
Selecting the ventilator (AUTO) pathway removes the APL valve and the
breathing bag from the active gas pathway of the absorber. When the
system is set in the automatic mode, excess gas is relieved from the
breathing circuit through a relief valve mounted on the ventilator bellows.
Selecting BAG eliminates the ventilator and its relief valve from the active
gas pathway and includes the APL valve and breathing bag. In this mode,
the breathing bag acts as a passive reservoir for breathing gases and the
patient's thoracic movements drive the gases through the breathing circuit.
When breathing is manually assisted, the breathing bag contains breathing
gases and functions as the sole means of driving them through the
breathing circuit when the bag is squeezed.
Warning: Do not use the anesthesia machine if:
• The pins in the I E valves or valve body(ies) are bent, damaged, or
missing,
5-8
• The valve disks are missing or damaged.
• The valve seat is damaged.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 73

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
Using the
APL Valve
The APL valve relieves excess gas from the breathing circuit into the
scavenger system during spontaneous or manual ventilation. The APL valve
expels excess gas containing expired carbon dioxide before it contacts the
absorbent, which extends the life of the absorbent.
Turning the APL valve knob clockwise increases the flow resistance into the
scavenging system. Complete clockwise rotation eliminates all flow through
the valve. Turning the knob counterclockwise decreases the flow resistance.
In addition to regulating the amount of waste gas flow, adjusting the APL
valve also affects the patient peak inspiratory pressure during manual
ventilation. Turning the APL valve knob counterclockwise reduces the
valve's flow resistance and lowers the peak inspiratory pressure. Turning
the APL valve knob clockwise increases the valve's flow resistance and
raises the peak inspiratory pressure. However, a variety of additional
factors, such as fresh gas flow rate and the method used to squeeze the
breathing bag, also affect patient peak inspiratory pressure during manual
ventilation.
During spontaneous ventilation, the APL valve control knob must be fully
open (turned fully counterclockwise) to minimize mechanical resistance to
patient exhalation.
Figure 5-4. APL Valve
APL VALVE
CONTROL
KNOB
OP00089
A gravity-loaded check valve within the APL valve prevents gas flow from
the scavenging system into the breathing system. For instance, during
spontaneous ventilation when patient inspiratory effort produces a negative
pressure on the breathing circuit side of the check valve, the valve closes
and prevents gas from the scavenger system from entering the breathing
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
5-9
Page 74

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
circuit. Also, the check valve minimum opening pressure of about 1 cmH2O
enables the breathing bag to reinflate before the valve opens.
Warning: To minimize mechanical resistance to the patient's exhalation
during spontaneous breathing, the APL valve's control knob
must be turned fully counterclockwise. For manually assisted
or manually controlled ventilation, APL valve resistance
must be increased as needed by turning the APL valve
control knob clockwise.
Using the
PEEP Valve
The absorber system regulates positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
through the PEEP valve. The PEEP valve is located on the absorber
downstream of the breathing system pressure gauge As a result, the
pressure gauge reading includes PEEP. Its integral design also prevents
accidents that are possible with accessory PEEP valves, such as inadvertent
reversal and misplacement in the inspiratory limb.
Turning the PEEP control knob clockwise increases PEEP, and turning the
knob counterclockwise reduces PEEP. The actual PEEP in the system is
indicated on the absorber pressure gauge at the end of exhalation and can
be adjusted from about 2—15 cmH
O.
2
5-10
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 75

Scavenger Interface Operation
The scavenger interface is an exhaust collector manifold. It is intended for
use with suction (vacuum) or passive waste gas disposal systems.
The suction approach uses continuous suction to transfer the gas from the
scavenger to the disposal system. Passive systems rely on the pressure of
the waste gas to convey the waste gas to the exhaust system.
This is a closed system that has one spring-loaded valve for positive
pressure relief and one for negative pressure relief.
Figure 5-5. Scavenger Interface
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
VACUUM NEGATIVE
PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
OP00088
19MM OUTLET
HOSE CONNECTION
(PASSIVE)
OR
3.0 LITER RESERVOIR
BAG (ACTIVE)
POSITIVE RESSURE
RELIEF VALVE
19MM INLET
CONNECTION
NEEDLE VALVE
ADJUSTMENT KNOB
(SHOWN DOTTED)
SUCTION
HOSE BARB
Warning: The scavenger interface for suction systems requires proper
adjustment for safe operation. The needle valve regulates the
waste gas exhaust flow. During a case, the needle valve must
be readjusted as needed. Needle valve adjustment depends on
several factors, including the fresh gas flow rate and type of
suction disposal system.
HOSE
Part Number: 4115139-001
Warning: The positive pressure relief valve must be inspected and
cleaned (if necessary) at six month intervals.
Warning: Waste gases vented through the positive pressure relief valve
enter the operating room. Properly adjusting the needle valve
keeps such venting to a minimum.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
5-11
Page 76

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
Needle Valve
Adjustment
for Suction
Systems
1. Attach breathing hoses and a Y-piece to the absorber system.
2. Attach a breathing bag to the Y-piece, using an appropriate adapter such
as a Draeger Medical combination mask elbow with a 15 mm male
fitting for the Y-piece and a 22 mm male fitting for the breathing bag.
3. Set the manual/automatic selector valve to AUTO and set the ventilator
to the preferred frequency.
4. Adjust the O
flow control valve to the expected total flow of all gases.
2
5. Verify that the suction disposal system is active.
6. Watch the scavenger reservoir bag as the oxygen flow passes through
the scavenger. The bag should not overextend or collapse.
7. Adjust the needle valve to provide either more or less suction.
Anesthesia Ventilator Operation
The anesthesia ventilator is a volume preset, time cycled, pressure limited
ventilator with electronic timing, pneumatic circuitry and independent
controls for frequency, inspiratory to expiratory (I:E) ratio, inspiratory flow
rate, tidal volume, and inspiratory pressure limit.
5-12
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 77

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Figure 5-6. Anesthesia Ventilator Components and Controls
5
I:E RATIO CONTROL
I:E RATIO DISPLAY
EXTENDED RANGE ACCESS
FREQUENCY CONTROL
FREQUENCY DISPLAY
INSPIRATORY PRESSURE LIMIT
BELLOWS CANISTER
cmH2O
3
0
MIN MAX
OP00096
INSIRATORY FLOW GAUGE
INSPIRATORY
FLOW CONTROL
VENTILATOR
ON-OFF
CONTROL
TIDAL VOLUME
CONTROL
PRESSURE
LIMIT CONTROL
TIDAL VOLUME
SETTING INDICATOR
BREATHING CIRCUIT
CONNECTOR
Pneumatic power (bellows drive gas) to the ventilator is supplied through
the hospital pipeline supply or through reserve cylinders on the anesthesia
machine. A switch on the side of the machine allows the use of either oxygen
or air as the drive gas. The ventilator will not function if this pressure drops
below 32 psi. Electrical power is supplied by the Narkomed Mobile's AC
power source, or, in event of AC power failure, by the backup battery. A fully
charged battery can power the ventilator for at least 90 minutes.
The anesthesia ventilator is designed for use with a Draeger Medical
absorber system, which incorporates a manual/automatic selector valve.
This valve allows you to select either the breathing bag and adjustable
pressure limiter (APL) valve for manual ventilation, or the ventilator
bellows for automatic ventilation.
During automatic ventilation, the manual/automatic selector valve isolates
the absorber's APL valve from the breathing system. To compensate for the
continuous introduction of fresh gas into the breathing system, the
ventilator incorporates a relief valve mounted behind the bellows chamber.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
5-13
Page 78

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
When the bellows is completely filled, any excess gas in the system is
released to the scavenging system through the ventilator relief valve. As in
any ascending bellows, the force needed to overcome gravity acting on the
bellows causes a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) within the
breathing system. The PEEP is approximately 2 cmH
The monitoring system's breathing pressure and expiratory flow waveform
displays can be used as an aid in adjusting the ventilator and establishing
alarm criteria.
Warning: Regardless of the indications of any alarm or monitoring
device, patient chest movement shall be the primary
indication of a securely connected, properly ventilated
patient.
O.
2
Activating
the Ventilator
Using the
Ventilator On/
Off Control
Adjusting the
Tidal Volume
The ventilator is activated by using the ventilator on/off control. The
anesthesia machine's SYSTEM POWER switch located at the bottom of the
flowmeter housing must be set to ON for the ventilator to function.
The ventilator power switch controls the pneumatic and electrical power to
the ventilator. In the OFF position, the FREQUENCY and I:E RATIO
displays remain lighted, but the ventilator will not function. The ON
position activates the ventilator. The monitoring system's volume and
pressure alarms are automatically enabled when the power switch is in the
ON position.
The tidal volume is adjusted using a self-locking knob, located above the
bellows assembly. The control knob positions a stop within the bellows
canister that limits the upward travel of the bellows and sets the maximum
tidal volume of gas delivered to the patient.
To adjust the tidal volume, press the self-locking knob in so it can turn, then
set the tidal volume by the setting indicator on the bellows chamber scale
(marked 200—1400 mL). The tidal volume can be adjusted for volumes
between 20 and 1500 mL ±100mL.
Smaller tidal volumes can be adjusted by setting the pointer below the
200 mL marking on the bellows chamber. Larger tidal volumes can be
selected by setting the pointer above the 1400 mL calibration.
5-14
As in any volume-preset anesthesia ventilator, the actual tidal volume
delivered to the patient's lungs may differ from the preset volume at the
bellows due to the compliance of the breathing system and fresh gas flow. To
accurately set the tidal volume, refer to the tidal and minute volume
measurements.
The position of the tidal volume indicator can be calibrated for a specific
combination of fresh gas flow and equipment compliance by an authorized
representative of DrägerService.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 79

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
Setting the
Respiratory
Frequency
Setting the
Inspiratory/
Expiratory
(I:E) Phase
Time Ratio
Setting the
Inspiratory
Flow Rate
Use the frequency control knob to set the respiratory frequency from 1 to 99
breaths per minute (BPM) in 1 BPM increments.
Clockwise rotation of the control knob increases the frequency setting, while
counterclockwise rotation decreases the frequency setting.
Use the I:E ratio control knob to set the inspiratory/expiratory (I:E) phase
time ratio. The standard range of ratios is from 1:1 through 1:4.5, adjustable
in increments of 0.5.
An extended range of ratios is also available that allows the setting of
inverse I:E ratios. The specific extended range settings are: 4:1, 3:1, and
2:1. The extended range settings are accessible by pressing the
EXTENDED RANGE switch while rotating the I:E ratio control knob.
Clockwise rotation of the control knob increases the I:E ratio setting, while
counterclockwise rotation decreases the I:E ratio setting.
Warning: Using inverse I:E ratios will introduce auto-PEEP.
Use the inspiratory flow control knob to set the inspiratory flow in the range
of 10 L/min to 100 L/min. This setting controls the flow rate of gas into the
bellows canister, affecting the flow rate of gas delivered to the patient.
Because of patient circuit variables such as lung compliance, fresh gas flow,
airway resistance and equipment compliance, the flow gauge is labeled with
nominal zones of LOW, MEDIUM, and HIGH.
Setting the
Inspiratory
Pressure
Limit
Adjust the flow setting to a point where the ventilator bellows is fully
compressed (but not deformed) at the end of the inspiratory phase of the
breathing cycle.
The inspiratory flow control can be used to create an inspiratory plateau at
the end of the inspiratory cycle and to affect the potential peak inspiratory
pressure within the patient breathing system. Always check the pressure
indicated by the breathing system pressure gauge and waveform when
adjusting the inspiratory flow control.
The pressure limit control, located above the bellows canister, is used to
adjust the pressure limit over a scale labeled MIN-30-MAX (see Figure 5-6).
This control determines the maximum pressure that can be delivered by the
ventilator during the inspiratory phase of the respiratory cycle. Because of
patient circuit variables, the scale is only a reference. The pressure should
be read from the breathing system pressure gauge or the anesthesia
machine's pressure monitoring system.
When the pressure limit control is turned fully counterclockwise, the peak
inspiratory pressure is less than or equal to 15 cmH
O. When the control is
2
turned fully clockwise, the peak inspiratory pressure is less than or equal to
120 cmH
O.
2
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
5-15
Page 80

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
5
Selecting the
Bellows Drive
Gas
A toggle switch located on the side of the flowmeter housing is for selecting
the bellows drive gas. To select oxygen as the drive gas, move the switch to
the O
position. To select air as the drive gas, move the switch to the AIR
2
position.
Figure 5-7. Drive Gas Selector Switch
DRIVE GAS
SELECTOR SWITCH
AIR
VENTILATOR
DRIVE GAS
OP00078
O
2
N2O
AIR
O
2
FLOWMETER HOUSING
5-16
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 81

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
Using the Monitoring System
Table of Contents
Overview .... ........... ........... ......... ........... ........... ......... .......... 6-3
Power-On Screen ............................ ................ ................. . 6-3
Monitor Screen and Controls .......................................... ... 6-4
Monitor Screen ............................................................ 6-4
Left Keypad ............................ ................. ................ ..... 6-6
Right Keypad ........................... ...................... .............. 6-7
Configur i ng th e A nesthesia Mac h in e .......... ................. 6 -7
Displaying the Configure Screen ................................. 6-8
Understanding the Keys ............................................... 6-8
Changing Par a meter Values ............................ ............ 6-9
Exiting the Configure Screen ............................ .. ......... 6-9
Part Number: 4115139-001
Using the Alarm Log ........................................ ................ 6-10
Displaying the Alarm Log ........................................... 6-10
Clearing the Alarm Log .................................. .. .......... 6-10
Exiting the Ala rm Log ......... .. ............... ...................... 6-11
Setting Alarms to Standby ......................................... 6-11
Silencing Ala rms .............. ............................. ............. 6-11
Oxygen Mon it o ring . .. ............................. .......................... 6-12
Oxygen Mon it o ring Display . .. .. ............................. ...... 6-12
Oxygen Mon it o r C on t ro ls . ... ............................ ........... 6-13
Setting Alarm Limits ................................................... 6-13
Calibrating the Oxygen Sensor .................................. 6-14
Unsucessfu l C a libration ........ .. ............... .................... 6-15
Oxygen Alarm Messages .......................................... 6-17
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Page 82

6
Table of Contents (continued)
Respiratory Volume Monitoring ..................................... 6-18
Respiratory Volume Display ............................................. 6-19
Respiratory Volume Monitor Controls .............................. 6-20
Setting the Minute Volume Low Alarm Limit ..................... 6-20
Turning Respiratory Volume Alarms Off ........................... 6-21
Turning Respiratory Volume Alarms On ........................... 6-21
Respiratory Volume Alarm Messages .............................. 6-21
Breathing Pressure Monitoring ...................................... 6-23
Breathing Pressure Monitoring Displays .......................... 6-23
Breathing Pressure Monitor Window ............................... 6-24
Breathing Pressure Trace Window ................................... 6-24
Breathing Pressure Monitor Controls ............................... 6-26
Setting the Pressure High Alarm Limit ............................. 6-27
Setting the Threshold Pressure Alarm Limit .................... 6-27
Manually Setting the Threshold Limit ............................... 6-28
Automatically Setting the Threshold Limit ........................ 6-28
Turning the Apnea Pressure Alarm Off ............................ 6-30
Turning the Apnea Pressure Alarm On ............................ 6-30
Breathing Pressure Alarm Messages .............................. 6-31
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6-2
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 83

Overview
In addition to monitoring clinical parameters, the Narkomed Mobile
performs diagnostic self-tests every time the machine is turned on. After the
initial power-on screen appears, the Monitor screen is displayed. This
section of the manual describes these screens, and explains how to establish
general monitoring settings.
Power-On Screen
When you turn the SYSTEM POWER switch ON, the Narkomed Mobile
performs extensive self-tests on its internal hardware. As these diagnostics
are performed, each test and its result appear on the screen. The result,
PASS or FAIL, indicates the status of the tested component.
Figure 6-1. Power-On Screen
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
(%)
Config
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
FIRMWARE
RAM
VIDEO
Alarms
A/D CONVERTER
AUDIO - PRIMARY
All
- BACKUP
Stby
SERIAL I/O
CLOCK
NON-VOLATILE M EMORY
COPYRIGHT, NAD INC.
VERSION:
SOFTWARE ID:
PASS
PASS
PASS
PASS
PASS
PASS
PASS
PASS
PASS
Oxygen
Low
High
Limit
Limit
Breathing Volum e
Low
On
Limit
Breathing Pressure
High
Limit
Auto
Set
Cal
(Liters)
Off
(cm H O)
OffOn
2
FUNCTIONAL
OP00215
At the end of the self-diagnostics, one of three possible conclusions to the
self-tests is posted on the screen:
FUNCTIONAL
The monitoring system is in satisfactory operational
order. After a brief delay, the Monitor screen appears.
CONDITIONALLY
FUNCTIONAL
A noncritical fault was detected, such as a speaker
failure. The Narkomed Mobile may be used, but an
authorized representative of DrägerService should be
notified to correct the problem. When you are ready
to resume operation, press any key on the keypad.
NONFUNCTIONAL
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
A serious fault was detected and operation of the
monitor is inhibited. Do not use the machine.
Immediately notify an authorized representative of
DrägerService to correct the problem.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
6-3
Page 84

6
Monitor Screen and Controls
Following a successful power-up, monitoring information is displayed on the
Monitor screen. The control keys to the left and right of this screen allow
you to establish monitoring settings.
Figure 6-2. Monitor Screen and Controls
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
OP87005
Monitor
Screen
Config
Alarms
All
Stby
WARNING:
ADVISORY:
TID VOL
0.35
CAUTION:
35
12
INSP O2 LOW
SUB ATM PRESSURE
AC / BATTERY FAIL
O2 SUPPLY LOW
SERVICE VENT MON
PORT A ERROR
BPM
10
OXYGEN
32
MIN VOL
3.5
PEAK
MEAN
PEEP
100
18
Oxygen (%)
High
Limit
30
Breathing Volume
Low
Limit
Breathing Pres sure
2.0
High
Limit
7
Low
Limit
On
On
Auto
Set
(Liters)
(cm H O)
2
LEFT
KEYPAD
MONITOR
SCREEN
The Monitor screen displays information in five separate windows.
Figure 6-3. Monitor Screen Window Locations
ALARM WINDOW
OXYGEN
MONITOR WINDOW
Cal
Off
2
Off
RIGHT
KEYPAD
6-4
WARNING:
CAUTION:
ADVISORY:
TID VOL
0.35
35
12
INSP O2 LOW
SUB ATM PRESSURE
AC / BATTERY FAIL
O2 SUPPLY LOW
SERVICE VENT MON
PORT A ERROR
BPM
10
BREATHING PRESSURE
TRACE WINDOW
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
OXYGEN
32
MIN VOL
3.5
100
30
RESPIRATORY
2.0
PEAK
VOLUME
MONITOR WINDOW
18
MEAN
7
PEEP
2
BREATHING PRESSURE
MONITOR WINDOW
Part Number: 4115139-001
OP87006
Rev: F
Page 85

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
• Alarm Window—Displays up to six of the highest priority alarms.
• Oxygen Monitor Window—Displays the patient's oxygen
concentration and the anesthesia machine's oxygen alarm limits.
• Respiratory Volume Monitor Window—Displays the
patient's tidal volume, respiratory rate (breaths per minute), and
minute volume, as well as the anesthesia machine's minute
volume low alarm limit.
• Breathing Pressure Monitor Window—Displays the
patient's peak airway pressure, mean airway pressure, and
positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP).
• Breathing Pressure Trace Window—Displays a trace, or
waveform, of the patient's breathing pressure, and the
anesthesia machine's breathing pressure alarm limits (to the left
of the waveform).
6
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
6-5
Page 86

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
Left Keypad You use the left keypad to initiate system-wide monitoring functions.
Figure 6-4. Left Keypad
Config
Alarms
All
Stby
OP87007
All
Standby
When the ventilator is off,
turns off audible tones
and message displays
associated with the
breathing pressure alarm
and respiratory volume
alarms, until a valid
breath is detected.
Silence
Alarms
Silences all audible alarm
tones for 2 minutes.
Configure Displays the Configure
screen, where you can set
system parameters, such
as the time, date, and
alarm volume. You also
enter the Alarm Log by
way of the Configure
screen.
6-6
These functions are described in detail later in this section.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 87

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Right Keypad You use the right keypad to perform functions associated with a specific
monitor. These functions are described in the following sections: “Oxygen
Monitoring,” “Respiratory Volume Monitoring,” and “Breathing Pressure
Monitoring.”
Figure 6-5. Right Keypad
(%)
Oxygen
High
Limit
Breathing Volume
Low
Limit
Breathing Pressure
High
Limit
Low
Limit
On
On
Cal
(Liters)
Off
(cm H O)
Off
2
6
Configuring
the
Anesthesia
Machine
Auto
Set
OP87008
You can configure the following parameters on the Narkomed Mobile:
• Trace Speed—Speed of the breathing pressure waveform trace:
either FAST or SLOW
• Alarm Volume—Volume of annunciated alarms
• Current Time—The current hour and minute in 24-hour format
hour:minute)
(
• Current Date—The current day, month, and year
• Display Alarms—On/Off status of the anesthesia machine's
Alarm window.
The Display Alarms parameter is configurable only when the anesthesia
machine is connected to another Narkomed product that can display the
anesthesia machine's alarms on a central alarm display. An On status
indicates that the anesthesia machine's Alarm window will continue to
display alarms as usual. An Off status indicates that the anesthesia
machine's Alarm window will not display alarms; instead, alarms will be
displayed on the other product's central alarm display.
When you start the anesthesia machine, it uses the values that were
established the last time the machine was configured. You can view or
change these values on the Configure screen.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
6-7
Page 88

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
Displaying
the Configure
Screen
Understanding the
Keys
To display the Configure screen, press the Config key, which is located on
the left keypad.
The Configure screen replaces the standard Monitor screen. You must begin
configuration within 1 minute, or the Monitor screen will replace the
Configure screen.
Figure 6-6. Configure Screen
ALARM
WINDOW
CONFIGURE
SCREEN
WARNING:
ADVISORY:
TRACE SPEED:
ALARM VOLUME:
TIME:
DATE:
DISPLAY ALARMS:
INSP O2 LOW
SUB ATM PRESSURE
CAUTION:
AC / BATTERY FAIL
O2 SUPPLY LOW
SERVICE VENT MON
PORT A ERROR
CONFIGURE SCREEN
SLOW
11:10
18 JUN 1996
ON
ALARM
LOG
SELECT
EXIT
OP87009
KEY LABELS
When the Configure screen is displayed, the system control keys function
according to the labels on the screen.
Key Label Function
ALARM
LOG
Displays the Alarm Log, a
separate screen that lists
cautions and warnings
that have occurred
SELECT Selects a parameter by
highlighting it with a box
EXIT Exits the Configure screen
and returns to the
Monitor screen
6-8
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 89

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
Changing
Parameter
Values
Exiting the
Configure
Screen
Follow this procedure for each parameter you want to change.
1. Press the SELECT key until the variable you want to change is
highlighted with a box.
2. Press the up or down arrow key to increase or decrease the value of the
highlighted variable.
To exit the Configure screen immediately, press the EXIT key.
NOTE:
The monitoring system automatically exits the Configure screen if a minute
passes and no keys are pressed.
When you exit the Configure screen, the values displayed on the screen are
saved. The monitoring system uses these values until they are changed.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
6-9
Page 90

6
Using the Alarm Log
If you miss a warning or caution message in the Alarm window, you can look
for it in the Alarm Log. It contains up to 100 of the most recent warning and
caution messages. When there are more than 100 warnings and cautions,
the oldest message is deleted to make room for the newest.
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
Displaying
the Alarm
Log
Follow this procedure to display the Alarm Log.
1. From the Monitor screen, press the Config key.
The Configure screen is displayed.
2. From the Configure screen, press the ALARM LOG key.
The Alarm Log appears, with the first warning or caution that occurred
at the top of the list.
3. If the list extends beyond the page, scroll forward by pressing the down
arrow key, and scroll backward by pressing the up arrow key.
Figure 6-7. Alarm Log Screen
OP87029
CLEAR
LOG
ALARM LOG
TIME
12:49
14:03
14:03
14:03
14:03
14:03
MESSAGE
INSP O2 LOW
APNEA - PRESSURE
APNEA - VOLUME
APNEA - PRESSURE
APNEA - VOLUME
MINUTE VOLUME LO
EXIT
Clearing the
Alarm Log
6-10
To delete all of the messages from the Alarm Log, press the CLEAR LOG
key.
The messages are permanently deleted from the LOG.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 91

Exiting the
Alarm Log
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
To exit the Alarm Log immediately, press the EXIT key.
Note: The monitoring system automatically exits the Alarm Log if a
minute passes and no keys are pressed.
When you exit the Alarm Log, you return to the Monitor screen.
Setting
Alarms to
Standby
Silencing
Alarms
When the ventilator is off, you can use the All Stby key to turn off audible
tones and message displays associated with the breathing pressure alarm
and respiratory volume alarms. The alarms remain in this standby
condition until the monitor detects a valid breath.
Note: If the ventilator is on, setting alarms to standby has no effect on the
pressure alarm. The pressure alarm cannot be turned off when the
ventilator is on.
To set alarms to standby, press the All Stby key.
The LED next to the All Stby key lights to indicate the standby condition.
You can silence all audible alarm tones for 2 minutes while retaining the
alarm message display on the monitor.
To silence alarm tones for 2 minutes, press the Silence Alarms key.
The LED next to the Silence Alarms key lights and remains lit for the
duration of the silence period. Pressing the Silence Alarms key while the
LED is lit restarts the 2-minute silence period.
If a new alarm condition occurs during the silence period, a single tone
pattern sounds corresponding to the priority of the alarm.
After the silence period, one of the following occurs:
• If no alarm conditions are active, audio annunciation reverts to
• If any Warning or Caution conditions are active, the tone
Note: All continuous audible alarms are automatically silenced for 2
Part Number: 4115139-001
normal.
associated with the highest existing alarm condition sounds. The
alarm continues to sound once every minute, for up to 3 minutes,
or until alarm conditions have been cleared for 10 seconds.
minutes following power-up. During this period, the occurrence of a
new alarm produces a non-repeating tone pattern appropriate for
that alarm's level of urgency.
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
6-11
Page 92

6
Oxygen Monitoring
Inspiratory oxygen concentration is measured with a dual galvanic cell
sensor, which is attached to the inspiratory valve dome. The sensor contains
two independent electrochemical cells, or sensor halves. When the sensor
takes in oxygen, an electrochemical reaction occurs within each cell. The
oxygen monitor reads the voltage produced in each cell, computes an
average for the two cells, and translates the average into an oxygen
concentration measurement.
Caution: Never remove an oxygen sensor from its housing, except to
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
replace it. If a sensor is removed from its housing, you must
do the following before continuing normal operations:
• Reinstall the sensor in the housing.
• Wait for a period equal to the time that the sensor spent
outside the housing.
Oxygen
Monitoring
Display
• Calibrate the sensor.
Note: When the machine is not in use, remove the oxygen sensor assembly
from the inspiratory valve dome, and insert the inspiratory valve
dome plug into the inspiratory valve dome.
Information about the oxygen analysis is presented in the Oxygen Monitor
window at the top right of the monitor display. The numerical value for
inspiratory oxygen concentration is shown in large type. To the right of this
figure, in small type, are the high and low oxygen concentration alarm
limits.
Figure 6-8. Oxygen Monitor Window
OP87010
WARNING:
CAUTION:
ADVISORY:
TID VOL
0.35
35
12
INSP O2 LOW
SUB ATM PRESSURE
AC / BATTERY FAIL
O2 SUPPLY LOW
SERVICE VENT MON
PORT A ERROR
BPM
10
OXYGEN
32
MIN VOL
3.5
100
30
2.0
PEAK
18
MEAN
7
PEEP
INSPIRATORY
OXYGEN
CONCENTRATION
HIGH OXYGEN
CONCENTRATION
ALARM LIMIT
LOW OXYGEN
CONCENTRATION
ALARM LIMIT
2
6-12
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 93

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
Oxygen
Monitor
Controls
Setting Alarm
Limits
You use the oxygen monitor control keys and the arrow keys on the right
keypad to set oxygen concentration alarm limits and calibrate the oxygen
sensor. The oxygen monitor control keys are located next to the Oxygen
Monitor window.
Figure 6-9. Oxygen Monitoring Control Keys
HIGH OXYGEN
CONCENTRATION
ALARM LIMIT KEY
LOW OXYGEN
CONCENTRATION
ALARM LIMIT KEY
OP87011
Oxygen (%)
High
Limit
Breathing Volume
Low
Limit
Breathing Pressure
High
Limit
Low
Limit
On
On
Auto
Set
Cal
(Liters)
Off
(cm H O)
Off
2
CALIBRATION
ARROW
KEYS
KEY
At power-up, the oxygen high and low alarm limits are automatically set to
their system defaults. You can adjust these limits within specified ranges.
Valid settings for the alarm limits, and their system defaults, are shown in
the following table.
Alarm Limit Default Valid Settings
High 100% 19%—100%; must be greater
than low alarm limit
Low 30% 18%—99%; must be less than
high alarm limit
Follow these steps to change the high or low alarm limit:
1. Press the Oxygen High Limit or Low Limit key, depending on which
alarm limit you want to change.
A box is drawn around the selected alarm limit.
2. Press the up arrow or down arrow key to increase or decrease the
highlighted alarm limit.
3. To save the new value, stop pressing arrow keys until the highlighting
box disappears (5 seconds), or press a different alarm Limit key.
The new value is saved as the alarm limit.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
6-13
Page 94

6
Calibrating
the Oxygen
Sensor
RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
To calibrate the oxygen sensor correctly, make sure it is exposed only to
room air during the entire calibration period. You should calibrate the
oxygen sensor as part of the daily preoperative setup of the anesthesia
equipment.
1. Remove the sensor assembly from the inspiratory valve dome and close
off the dome with the inspiratory valve dome plug. (Do not disassemble
the sensor assembly further.)
2. Expose the sensor to ambient air only (21% oxygen concentration) and
allow it to stabilize for several minutes. To ensure an ambient air
exposure, hold the sensor away from any open part of the breathing
system.
3. With the sensor exposed only to room air, press the Cal key.
Calibration begins.
4. View the monitor screens to track progress of the calibration.
• During calibration, the LED next to the Cal key lights,
and the label CAL appears in the Oxygen Monitor
window.
• Following successful calibration, the currently sensed
oxygen concentration appears in the Oxygen Monitor
window. (If the calibration was not successful, the Oxygen
Monitor window is blank. See “Unsuccessful Calibration”
in this section for further information.)
Typically, calibration lasts less than 30 seconds. However, the time may
vary depending on the amount of oxygen the sensor was exposed to
before calibration.
Oxygen
Exposure
Typical Calibration
Time
21% 10 seconds
> 21% up to 50 seconds
6-14
5. When the Narkomed Mobile successfully completes the calibration, pull
the inspiratory valve dome plug and reinsert the sensor assembly.
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 95

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
Unsucessful
Calibration
If, at the end of the calibration period, if the Oxygen Monitor window is
blank, the calibration was not successful. (This condition is also indicated by
the CAL O2 SENSOR Advisory message in the Alarm window.)
An unsuccessful calibration can be caused by several conditions.
Cause Solution
Sensor was exposed to an
excessively lean or excessively
rich oxygen calibration mixture.
Sensor was exposed to a
constantly changing calibration
mixture.
Sensor did not receive the proper
waiting period.
Make sure that the sensor is
exposed to room air only for the
entire calibration period.
Make sure that the sensor is
exposed to room air only for the
entire calibration period.
If the sensor capsule was
removed from the sensor
assembly, a waiting period equal
to the time that the capsule spent
outside the sensor assembly (up
to one week) is necessary prior to
calibration. New sensors require
a 15-minute waiting period.
Sensor is exhausted. If the oxygen sensor has decayed
beyond its useful service life (see
the “Specifications” section of the
manual), replace the decayed
sensor with a new sensor and
allow the proper waiting period.
Sensor failure. If there is too great a difference
between the outputs of the two
sensor halves, replace the failed
sensor with a new sensor, and
allow the proper waiting period
prior to calibration.
Sensor is disconnected. When the sensor is disconnected,
the display area is blank, and the
message 02 SENSOR DISC
appears in the Alarm window. If
this happens, reconnect the
sensor cord to the OXYGEN
SENSOR interface beneath the
rear panel of the ventilator box
and try to calibrate the oxygen
sensor again.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
6-15
Page 96

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
If the oxygen sensor is improperly calibrated, it can cause inaccurate
measurements. When a calibration gas mixture is excessively rich or lean in
oxygen, the Narkomed Mobile will not complete an attempted calibration;
however, if the calibration gas is rich or lean but is within certain limits, the
Narkomed Mobile will complete the calibration. As a result, when
displaying sensor measurements, the Narkomed Mobile displays an oxygen
percentage either greater or less than the actual oxygen percentage.
Therefore, make sure that the sensor is exposed only to room air during the
entire calibration period.
The following figure illustrates the relationship between the calibration
mixture and the accuracy of oxygen measurement.
Figure 6-10. Relationship Between Calibration Mixture and Oxygen Measurement
Accuracy
100
2
E
O
G
A
D
T
E
N
Y
E
A
L
C
P
R
S
E
I
P
D
OP10098A
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
At calibration, sensor exposed
to < 21% O2. Thus, displayed % O2
will be higher than actual O2.
Correct calibration of room air
(21% O2) for entire calibration period.
Displayed % O2 = actual % O2.
At calibration , sensor exp osed
to > 21% O2. Thus, displayed % O2
lower than actual % O2.
will be
0
100908070605040302010
ACTUAL O2 PERCENTAGE
6-16
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 97

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
Oxygen
Alarm
Messages
INSP O2 LOW
(Warning)
INSP O2
HIGH
(Advisory)
O2 SENSOR
DISC
(Advisory)
REPLACE O2
CELL
(Advisory)
The following list contains all warning, caution, and advisory alarms
associated with oxygen monitoring.
The Narkomed Mobile continuously compares the current inspiratory
oxygen percentage with the preset low oxygen alarm limit. If the measured
oxygen concentration falls below the low alarm limit, the Warning message
INSP O2 LOW appears in the Alarm window, and a continuous audible
alarm sounds.
If the measured inspiratory oxygen concentration exceeds the preset high
alarm limit, the Advisory message INSP O2 HIGH appears in the Alarm
window, and a single-tone audible alarm sounds.
If the oxygen sensor cord becomes disconnected (or is damaged enough to
cause an open circuit), the Advisory message O2 SENSOR DISC appears in
the Alarm window, and a single-tone audible alarm sounds.
During oxygen sensor calibration and monitoring, the Narkomed Mobile
checks for a difference between the outputs of the two sensor channels. If
the difference exceeds a predetermined percentage, the Advisory message
REPLACE O2 CELL appears in the Alarm window.
During oxygen sensor calibration, the Narkomed Mobile also checks the
sensor's output against a range of acceptable output voltages. There are
three possible causes for deviation from within this range.
CAL O2
SENSOR
(Advisory)
Exhausted sensor. If the sensor's capacity is exhausted, its output
•
voltage will not meet the required minimum.
•
Incorrect calibration environment. If the sensor is exposed to an
excessive oxygen during calibration, the sensor's output will be
above or below the acceptable output range.
Improper waiting. If the proper waiting period is not allowed for
•
a new sensor or for a sensor removed from the sensor housing,
the sensor's output may be above or below the acceptable output
range.
If a sensor error condition is detected during monitoring, the Advisory
message REPLACE O2 CELL appears in the Alarm window and operation
continues. Try to recalibrate the sensor; if the message remains, replace the
sensor cell.
The Advisory message CAL O2 SENSOR appears in the Alarm window in
the following instances:
• the oxygen sensor enters a noncalibrated state
• the Narkomed Mobile is unable to calibrate the oxygen sensor
• more than 18 hours have elapsed since the last calibration
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
6-17
Page 98

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
SERVICE
VENT MON
(Advisory)
If the Narkomed Mobile detects an internal electronic failure that would
prevent proper operation, the Advisory message SERVICE VENT MON
appears in the Alarm window. If this happens, contact an authorized
representative of DrägerService.
Respiratory Volume Monitoring
Respiratory volume is measured by an ultrasonic flow sensor which is
attached to the expiratory valve and mounted to the top of the absorber
assembly. The ultrasonic flow sensor has two transducers that measure the
time of flight of ultrasonic pulses transmitted upstream and downstream in
the respiratory flow path. The difference in the time of flight is used to
determine the velocity and the flow rate of gas through the patient circuit.
The flow sensor output is converted to meaningful readings for minute
volume, tidal volume, and respiratory rate displays
Warning: The ultrasonic flow sensor can be used with all normal
anesthetic gases except oxygen-helium (heliox). Incorrect
flow measurements will result if heliox is used.
Caution: Although the Narkomed Mobile is designed to minimize the
effects of ambient radio-frequency interference, the
functioning of the respiratory volume monitor may be
adversely affected by the operation of electrosurgical
equipment or short wave or microwave diathermy equipment
in the vicinity.
Note: Sudden, irregular expiratory flow may cause erratic tidal volume
and respiratory rate displays. To avoid such erroneous
measurements, defer reading the display until a full minute has
elapsed after the irregular flow has stopped.
6-18
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Page 99

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
Respiratory
Volume
Display
Information about the patient's respiratory volume is presented in the
Respiratory Volume Monitor window in the middle of the monitor display.
From left to right, numerical values are shown in large type for tidal
volume, respiratory rate, and minute volume. At the extreme right, in small
type, is the minute volume low alarm limit.
Figure 6-11. Respiratory Volume Monitor Window
WARNING:
CAUTION:
ADVISORY:
TID VOL
0.35
35
12
INSP O2 LOW
SUB ATM PRESSURE
AC / BATTERY FAIL
O2 SUPPLY LOW
SERVICE VENT MON
PORT A ERROR
BPM
10
OXYGEN
32
MIN VOL
3.5
PEAK
MEAN
PEEP
100
30
MEASUREMENT
2.0
18
7
OP87012
MINUTE
VOLUME
(l/min)
MINUTE
VOLUME
ALARM LIMIT
2
TIDAL VOLUME
MEASUREMENT (l)
BREATHING RATE
MEASUREMENT
(breaths/min)
• Tidal Volume Measurement (TID VOL)—Displays the
volume for each valid breath (at least 20 mL). If the monitor does
not detect a valid breath within 30 seconds, the display area goes
blank.
• Breathing Rate Measurement (BPM)—Shows the number of
breaths during the previous minute of respiration. If the BPM
display is blank, a full minute of respiration has not occurred.
• Minute Volume Measurement (MIN VOL)— Continuously
displays the volume of exhaled gas accumulated during the
previous minute of respiration. A blank MIN VOL display area
indicates that a full one-minute history of exhaled volume is not
available.
• Minute Volume Alarm Limit—Indicates the volume below
which an alarm condition occurs.
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
6-19
Page 100

RETURN TO THIS MANUAL'S TABLE OF CONTENTS
RETURN TO CD-ROM TABLE OF CONTENTS
6
Respiratory
Volume
Monitor
Controls
You use the respiratory volume monitor control keys and the arrow keys on
the right keypad to set the minute volume low alarm limit and to turn the
volume alarms on and off. The respiratory volume monitor control keys are
located next to the Respiratory Volume Monitor window.
Figure 6-12. Respiratory Volume Monitor Control Keys
Oxygen (%)
Low
Limit
On
On
Auto
Set
Cal
(Liters)
Off
(cm H O)
Off
VOLUME
ALARMS
OFF KEY
2
ARROW
KEYS
LOW MINUTE
VOLUME
ALARM LIMIT KEY
VOLUME
ALARMS ON KEY
OP87013
High
Limit
Breathing Volume
Low
Limit
Breathing Pressure
High
Limit
Fixed alarms are provided for low tidal volume (apnea-volume), low minute
volume, and reverse flow through the sensor. While the ventilator is on,
apnea volume alarms are generated at 15 seconds (Caution) and 30 seconds
(Warning) if the respiratory volume monitor does not sense a valid breath.
While the ventilator is off, these alarms are generated at 30 seconds
(Caution) and 60 seconds (Warning).
Setting the
Minute
Volume Low
Alarm Limit
The Narkomed Mobile's volume alarms are automatically enabled when the
ventilator power switch is turned to the ON position. A disconnected or
damaged sensor causes a sensor failure alarm.
If the low minute volume falls below the minute volume low alarm limit, an
alarm condition occurs. The alarm limit is automatically set to a default of
1.0 liter at power-up. You can change the default to a value within the range
of 0.2 liters to 10.0 liters.
Follow these steps to adjust the minute volume low alarm limit:
1. Press the Breathing Volume Low Limit key.
A box is drawn around the minute volume low alarm limit.
2. Press the up arrow or down arrow key to increase or decrease the
highlighted alarm limit.
3. To save the new value, stop pressing arrow keys until the highlighting
box disappears (5 seconds), or press a different alarm Limit key.
The new value is saved as the alarm limit.
6-20
Narkomed Mobile Operator’s Manual
Part Number: 4115139-001
Rev: F
 Loading...
Loading...