Page 1
Part No. 208963-B
March 2001
4401 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054
Using Optivity Switch Manager Release 1.1.0.0
Page 2

2
Copyright © 2001 Nortel Networks
All rights reserved. March 2001.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and
recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The
information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks NA Inc.
The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement and may be used only in accordance
with the terms of that license. The software license agreement is included in this document.
Trademarks
NORTEL NETWORKS is a trademark of Nortel Networks.
Optivity and Passport are registered trademarks and BayStack is a trademark of Nortel Networks.
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Restricted rights legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United States Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph
(c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013.
Notwithstanding any other license agreement that may pertain to, or accompany the delivery of, this computer software,
the rights of the United States Government regarding its use, reproduction, and disclosure are as set forth in the
Commercial Computer Software-Restricted Rights clause at FAR 52.227-19.
Statement of conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, Nortel Networks NA Inc. reserves
the right to make changes to the products described in this document without notice.
Nortel Networks NA Inc. does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or
circuit layout(s) described herein.
Portions of the code in this software product may be Copyright © 1988, Regents of the University of California. All
rights reserved. Redistribution and use in source and binary forms of such portions are permitted, provided that the
above copyright notice and this paragraph are duplicated in all such forms and that any documentation, advertising
materials, and other materials related to such distribution and use acknowledge that such portions of the software were
developed by the University of California, Berkeley. The name of the University may not be used to endorse or promote
products derived from such portions of the software without specific prior written permission.
SUCH PORTIONS OF THE SOFTWARE ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
In addition, the program and information contained herein are licensed only pursuant to a license agreement that contains
restrictions on use and disclosure (that may incorporate by reference certain limitations and notices imposed by third
parties).
208963-B
Page 3

Nortel Networks NA Inc. software license agreement
NOTICE: Please carefully read this license agreement before copying or using the accompanying software or installing
the hardware unit with pre-enabled software (each of which is referred to as “Software” in this Agreement). BY
COPYING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, YOU ACCEPT ALL OF THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THIS
LICENSE AGREEMENT. THE TERMS EXPRESSED IN THIS AGREEMENT ARE THE ONLY TERMS UNDER
WHICH NORTEL NETWORKS WILL PERMIT YOU TO USE THE SOFTWARE. If you do not accept these terms
and conditions, return the product, unused and in the original shipping container, within 30 days of purchase to obtain a
credit for the full purchase price.
1. License grant. Nortel Networks NA Inc. (“Nortel Networks”) grants the end user of the Software (“Licensee”) a
personal, nonexclusive, nontransferable license: a) to use the Software either on a single computer or, if applicable, on a
single authorized device identified by host ID, for which it was originally acquired; b) to copy the Software solely for
backup purposes in support of authorized use of the Software; and c) to use and copy the associated user manual solely
in support of authorized use of the Software by Licensee. This license applies to the Software only and does not extend
to Nortel Networks Agent software or other Nortel Networks software products. Nortel Networks Agent software or
other Nortel Networks software products are licensed for use under the terms of the applicable Nortel Networks NA Inc.
Software License Agreement that accompanies such software and upon payment by the end user of the applicable
license fees for such software.
2. Restrictions on use; reservation of rights. The Software and user manuals are protected under copyright laws.
Nortel Networks and/or its licensors retain all title and ownership in both the Software and user manuals, including any
revisions made by Nortel Networks or its licensors. The copyright notice must be reproduced and included with any
copy of any portion of the Software or user manuals. Licensee may not modify, translate, decompile, disassemble, use
for any competitive analysis, reverse engineer, distribute, or create derivative works from the Software or user manuals
or any copy, in whole or in part. Except as expressly provided in this Agreement, Licensee may not copy or transfer the
Software or user manuals, in whole or in part. The Software and user manuals embody Nortel Networks’ and its
licensors’ confidential and proprietary intellectual property. Licensee shall not sublicense, assign, or otherwise disclose
to any third party the Software, or any information about the operation, design, performance, or implementation of the
Software and user manuals that is confidential to Nortel Networks and its licensors; however, Licensee may grant
permission to its consultants, subcontractors, and agents to use the Software at Licensee’s facility, provided they have
agreed to use the Software only in accordance with the terms of this license.
3. Limited warranty. Nortel Networks warrants each item of Software, as delivered by Nortel Networks and properly
installed and operated on Nortel Networks hardware or other equipment it is originally licensed for, to function
substantially as described in its accompanying user manual during its warranty period, which begins on the date
Software is first shipped to Licensee. If any item of Software fails to so function during its warranty period, as the sole
remedy Nortel Networks will at its discretion provide a suitable fix, patch, or workaround for the problem that may be
included in a future Software release. Nortel Networks further warrants to Licensee that the media on which the
Software is provided will be free from defects in materials and workmanship under normal use for a period of 90 days
from the date Software is first shipped to Licensee. Nortel Networks will replace defective media at no charge if it is
returned to Nortel Networks during the warranty period along with proof of the date of shipment. This warranty does not
apply if the media has been damaged as a result of accident, misuse, or abuse. The Licensee assumes all responsibility
for selection of the Software to achieve Licensee’s intended results and for the installation, use, and results obtained
from the Software. Nortel Networks does not warrant a) that the functions contained in the software will meet the
Licensee’s requirements, b) that the Software will operate in the hardware or software combinations that the Licensee
may select, c) that the operation of the Software will be uninterrupted or error free, or d) that all defects in the operation
of the Software will be corrected. Nortel Networks is not obligated to remedy any Software defect that cannot be
reproduced with the latest Software release. These warranties do not apply to the Software if it has been (i) altered,
except by Nortel Networks or in accordance with its instructions; (ii) used in conjunction with another vendor’s product,
resulting in the defect; or (iii) damaged by improper environment, abuse, misuse, accident, or negligence. THE
FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND LIMITATIONS ARE EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL
OTHER WARRANTIES EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Licensee is responsible for the security of its
3
Using Optivity Switch Manager Release 1.1.0.0
Page 4

4
own data and information and for maintaining adequate procedures apart from the Software to reconstruct lost or altered
files, data, or programs.
4. Limitation of liability. IN NO EVENT WILL NORTEL NETWORKS OR ITS LICENSORS BE LIABLE FOR
ANY COST OF SUBSTITUTE PROCUREMENT; SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES; OR ANY DAMAGES RESULTING FROM INACCURATE OR LOST DATA OR LOSS OF USE OR
PROFITS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE PERFORMANCE OF THE SOFTWARE, EVEN IF
NORTEL NETWORKS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT
SHALL THE LIABILITY OF NORTEL NETWORKS RELATING TO THE SOFTWARE OR THIS AGREEMENT
EXCEED THE PRICE PAID TO NORTEL NETWORKS FOR THE SOFTWARE LICENSE.
5. Government licensees. This provision applies to all Software and documentation acquired directly or indirectly by or
on behalf of the United States Government. The Software and documentation are commercial products, licensed on the
open market at market prices, and were developed entirely at private expense and without the use of any U.S.
Government funds. The license to the U.S. Government is granted only with restricted rights, and use, duplication, or
disclosure by the U.S. Government is subject to the restrictions set forth in subparagraph (c)(1) of the Commercial
Computer Software––Restricted Rights clause of FAR 52.227-19 and the limitations set out in this license for civilian
agencies, and subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause of DFARS
252.227-7013, for agencies of the Department of Defense or their successors, whichever is applicable.
6. Use of software in the European Community. This provision applies to all Software acquired for use within the
European Community. If Licensee uses the Software within a country in the European Community, the Software
Directive enacted by the Council of European Communities Directive dated 14 May, 1991, will apply to the examination
of the Software to facilitate interoperability. Licensee agrees to notify Nortel Networks of any such intended
examination of the Software and may procure support and assistance from Nortel Networks.
7. Term and termination. This license is effective until terminated; however, all of the restrictions with respect to
Nortel Networks’ copyright in the Software and user manuals will cease being effective at the date of expiration of the
Nortel Networks copyright; those restrictions relating to use and disclosure of Nortel Networks’ confidential information
shall continue in effect. Licensee may terminate this license at any time. The license will automatically terminate if
Licensee fails to comply with any of the terms and conditions of the license. Upon termination for any reason, Licensee
will immediately destroy or return to Nortel Networks the Software, user manuals, and all copies. Nortel Networks is not
liable to Licensee for damages in any form solely by reason of the termination of this license.
8. Export and re-export. Licensee agrees not to export, directly or indirectly, the Software or related technical data or
information without first obtaining any required export licenses or other governmental approvals. Without limiting the
foregoing, Licensee, on behalf of itself and its subsidiaries and affiliates, agrees that it will not, without first obtaining all
export licenses and approvals required by the U.S. Government: (i) export, re-export, transfer, or divert any such
Software or technical data, or any direct product thereof, to any country to which such exports or re-exports are restricted
or embargoed under United States export control laws and regulations, or to any national or resident of such restricted or
embargoed countries; or (ii) provide the Software or related technical data or information to any military end user or for
any military end use, including the design, development, or production of any chemical, nuclear, or biological weapons.
9. General. If any provision of this Agreement is held to be invalid or unenforceable by a court of competent
jurisdiction, the remainder of the provisions of this Agreement shall remain in full force and effect. This Agreement will
be governed by the laws of the state of California.
Should you have any questions concerning this Agreement, contact Nortel Networks, 4401 Great America Parkway, P.O.
Box 58185, Santa Clara, California 95054-8185.
LICENSEE ACKNOWLEDGES THAT LICENSEE HAS READ THIS AGREEMENT, UNDERSTANDS IT, AND
AGREES TO BE BOUND BY ITS TERMS AND CONDITIONS. LICENSEE FURTHER AGREES THAT THIS
AGREEMENT IS THE ENTIRE AND EXCLUSIVE AGREEMENT BETWEEN NORTEL NETWORKS AND
LICENSEE, WHICH SUPERSEDES ALL PRIOR ORAL AND WRITTEN AGREEMENTS AND
COMMUNICATIONS BETWEEN THE PARTIES PERTAINING TO THE SUBJECT MATTER OF THIS
AGREEMENT. NO DIFFERENT OR ADDITIONAL TERMS WILL BE ENFORCEABLE AGAINST NORTEL
NETWORKS UNLESS NORTEL NETWORKS GIVES ITS EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT, INCLUDING AN
EXPRESS WAIVER OF THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT.
208963-B
Page 5

Contents
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Before you begin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Text conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Related publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
How to get help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Chapter 1
Introducing Optivity Switch Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
What is Optivity Switch Manager? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Optivity Switch Manager features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Optivity Switch Manager submanagers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
VLAN Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
MultiLink Trunking Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Multicast Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Log Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
5
Chapter 2
Using Optivity Switch Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Starting Optivity Switch Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Using the Optivity Switch Manager window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Optivity Switch Manager menu bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Finding unsaved configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Using the Optivity Switch Manager shortcut menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Viewing device properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Using the toolbar buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Optivity Switch Manager status bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Optivity Switch Manager contents pane icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 6

6 Contents
Working with the network topology map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Getting help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Chapter 3
Configuring Optivity Switch Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Discovering your network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Accessing devices within different SNMP communities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Adjusting the contents pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Using the scale slider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Loading a saved network topology map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Saving a topology map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Printing a topology map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Finding a device in the topology map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Arranging devices on the topology map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Discovering devices on a network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Restricting discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Layout slider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
208963-B
Chapter 4
Using VLAN Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
What is VLAN Manager? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Spanning Tree Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
VLAN Manager features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Starting VLAN Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
VLAN Manager window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Menu bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Navigation pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Contents pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Status bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Finding network resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Using VLAN Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Port membership . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Viewing the unassigned ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Page 7

Contents 7
Viewing tagged Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Viewing isolated router ports (IRPs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Viewing bridge routing Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Viewing spanning tree groups (STGs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Members . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Viewing and configuring STG parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Status group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Root . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Default VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
VLAN ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Managing spanning tree groups (STGs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Creating a spanning tree group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Editing a spanning tree group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Deleting a spanning tree group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Managing a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Creating a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Creating a port-based VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Creating a source IP subnet-based VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Creating a protocol-based VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
User-defined protocols in a protocol-based VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Creating a source MAC address-based VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Deleting a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Highlighting STGs and VLANs in the Optivity Switch Manager contents pane . . . . . . 93
Viewing VLAN members in Optivity Switch Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Viewing STG port members . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Viewing STG root configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Chapter 5
Using MultiLink Trunking Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
What is MultiLink Trunking Manager? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
MultiLink Trunking Manager features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Starting MultiLink Trunking Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
MultiLink Trunking Manager window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Menu bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 8

8 Contents
Using MultiLink Trunking Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Managing MultiLink Trunks (MLTs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Highlighting devices and MLT links in Optivity Switch Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Navigation pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Contents pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Status bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Finding network resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Viewing trunk connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Viewing no trunk configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Viewing isolated devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Creating an MLT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Creating an MLT with one device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Creating a new MLT on a pair of devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Viewing MLT port information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Editing a port on an MLT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Deleting an MLT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Editing an MLT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
208963-B
Chapter 6
Using Multicast Manager. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
What is Multicast Manager? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Multicast protocols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
DVMRP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
IGMP Snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Multicast Manager features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Starting Multicast Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Multicast Manager window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Menu bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Navigation pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Contents pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Status bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Finding a network resource . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Page 9

Contents 9
Using Multicast Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Viewing IGMP Snoop groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
General tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Receiver tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Sender tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Static tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Access tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Viewing L3-IGMP information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Cache tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Interface tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Group tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Viewing DVMRP information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Globals tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Interface tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Neighbor tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Route tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Next Hop tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Viewing MRoute information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Route tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Viewing Multicast Groups information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Source Subnets tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Receivers tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Viewing Multicast Manager information in Optivity Switch Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Highlighting a multicast device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Highlighting a multicast forwarding path . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Chapter 7
Using Log Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Uploading Passport syslog files to your management station . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Uploading a file using Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Uploading a file using the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Initiating a Telnet session from Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Using the Telnet application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Uploading the syslog file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Passport/Accelar 1000 Series switches (version 2.x) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 10

10 Contents
Starting Log Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Opening a syslog file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Exporting a log file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Locating specific log entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Filtering log entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Appendix A
Additional reference sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Appendix B
Troubleshooting and error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Resolving problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
208963-B
Page 11

Figures
Figure 1 Optivity Switch Manager window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 2 Find Unsaved Configurations dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 3 Shortcut menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 4 Device Properties dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 5 Optivity Switch Manager topology map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 6 Scale slider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 7 Open File dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 8 Save dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 9 Find Device dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 10 Optivity Switch Manager display before Layout command . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 11 Preferences dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 12 Restrict Discovery dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Figure 13 Communities dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 14 VLAN Manager window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Figure 15 VLAN Manager navigation pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Figure 16 Default (1) folder view in the contents pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Figure 17 Find dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Figure 18 Unassigned Ports table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Figure 19 Tagging Ports table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 20 Isolated Routing Ports table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Figure 21 Bridge Routing Ports table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Figure 22 STG folder in the VLAN Manager navigation pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Figure 23 Spanning tree group members table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Figure 24 PortMembers dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Figure 25 Configuration table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Figure 26 Status table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Figure 27 Root table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Figure 28 Default VLAN table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Figure 29 VLAN table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
11
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 12

12 Figures
Figure 30 New STG dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Figure 31 Delete dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Figure 32 New VLAN dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Figure 33 New VLAN dialog box with bySubnet selected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Figure 34 New VLAN dialog box with byProtocolId selected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Figure 35 New VLAN dialog box with bySrcMac selected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Figure 36 Edit Mac - VLAN dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Figure 37 VLAN topology in the Optivity Switch Manager contents pane . . . . . . . . . 94
Figure 38 Viewing STG port members . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Figure 39 Root topology displayed in the Optivity Switch Manager contents pane . 97
Figure 40 MultiLink Trunking Manager window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Figure 41 Contents pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Figure 42 Find dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Figure 43 Trunk table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Figure 44 No Trunk table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Figure 45 Isolated Device table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Figure 46 Insert MLT dialog box — one device selected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Figure 47 Trunk table for a pair of devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Figure 48 Insert MLT dialog box — pair of devices selected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Figure 49 Port dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Figure 50 PortMembers dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Figure 51 Delete dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Figure 52 Trunk table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Figure 53 Highlight topology view in Optivity Switch Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Figure 54 Multicast Manager window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Figure 55 Multicast Manager navigation pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Figure 56 DVMRP Table in the contents pane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Figure 57 Find dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Figure 58 IGMP Snoop Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Figure 59 General tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Figure 60 Receiver tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Figure 61 Sender tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Figure 62 Static tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Figure 63 Access tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Figure 64 IGMP Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
208963-B
Page 13

Figures 13
Figure 65 Cache tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Figure 66 Interface tab (L3-IGMP partial view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Figure 67 Group tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Figure 68 DVMRP Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Figure 69 Globals tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Figure 70 Interface tab (DVMRP) fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Figure 71 Neighbor tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Figure 72 Route tab (DVMRP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Figure 73 Next Hop tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Figure 74 Route tab (MRoute) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Figure 75 Multicast Group table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Figure 76 Source Subnets tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Figure 77 Receivers tab (Multicast Groups) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Figure 78 Optivity Switch Manager with forwarding node highlighted . . . . . . . . . . 162
Figure 79 Optivity Switch Manager window with devices using DVMRP
highlighted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Figure 80 Copy File tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Figure 81 Telnet dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Figure 82 Telnet window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Figure 83 SysLog dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Figure 84 Open sysLog dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Figure 85 Imported log file in SysLog dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Figure 86 Export sysLog dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Figure 87 sysLog - Find dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Figure 88 sysLog - Filter dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 14

14 Figures
208963-B
Page 15

Tables
Table 1 Parts of the Optivity Switch Manager window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 2 Optivity Switch Manager menus and commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 3 Find Unsaved Configurations dialog box items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 4 Device Properties dialog box items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 5 Optivity Switch Manager and submanager toolbar buttons . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 6 Status bar fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 7 Device icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 8 Preferences dialog box items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 9 Communities dialog box fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Table 10 Maximum STGs and VLANs supported by switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Table 11 VLAN Manager window parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Table 12 VLAN Manager menus and commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 13 VLAN Manager status bar fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 14 Port membership types and STGs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Table 15 Unassigned Ports table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 16 Tagging Ports table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Table 17 Isolated Routing Ports table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table 18 Bridge Routing Ports table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Table 19 STG information icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Table 20 Members table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Table 21 Configuration table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Table 22 Status table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Table 23 Root table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Table 24 Default VLAN table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Table 25 New STG dialog box items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Table 26 New VLAN dialog box items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Table 27 Maximum number of MLTs supported in different switches . . . . . . . . . . 100
Table 28 MultiLink Trunking Manager window parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Table 29 MultiLink Trunking Manager submenus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
15
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 16

16 Tables
Table 30 MultiLink Trunking Manager status bar fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Table 31 Trunk table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Table 32 No Trunk table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Table 33 Isolated Device table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Table 34 Insert MLT dialog box items for a single device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Table 35 Insert MLT dialog box items for two nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Table 36 Multicast Manager window parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Table 37 Multicast Manager menus and commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Table 38 Multicast Manager status bar fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Table 39 General tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Table 40 Receiver tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Table 41 Sender tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Table 42 Static tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Table 43 Access tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Table 44 Cache tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Table 45 Interface tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Table 46 Group tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Table 47 Globals tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Table 48 Interface tab—DVMRP fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Table 49 Neighbor tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Table 50 Route tab (DVMRP) fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Table 51 Next Hop tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Table 52 Route tab (MRoute) fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Table 53 Source Subnets tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Table 54 Receivers tab (Multicast Groups) fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Table 55 SysLog dialog box items and buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Table 56 Optivity Switch Manager problems and solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Table 57 Optivity Switch Manager error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
208963-B
Page 17

Preface
Optivity Switch Manager is a Java-based graphical network management
application used to configure and manage select Passport and BayStack switches
and Business Policy Switch 2000 switches operating within the same local area
network.
This guide provides information about installing the Optivity Switch Manager
software and using the features and capabilities of Optivity Switch Manager’s
graphical user interface (GUI).
Before you begin
This guide is intended for network administrators with the following background:
• Working knowledge of networks and Ethernet bridging
• Ability to configure and troubleshoot VLANs, STGs, MLTs, and Multicast
groups
• Familiarity with networking concepts and terminology
• Working knowledge of GUIs
17
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 18

18 Preface
Text conventions
This guide uses the following text conventions:
bold Courier text
italic text Indicates new terms, book titles, and variables in
plain Courier text
separator ( > ) Shows menu paths.
Related publications
Indicates command names and options and text that
you need to enter.
Example: Use the
Example: Enter
command syntax descriptions. Where a variable is two
or more words, the words are connected by an
underscore.
Example: If the command syntax is
show at <valid_route>, valid_route is one
variable and you substitute one value for it.
Indicates command syntax and system output, for
example, prompts and system messages.
Example:
Example: Protocols > IP identifies the IP option on the
Protocols menu.
Set Trap Monitor Filters
dinfo command.
show ip {alerts|routes}.
208963-B
For more information about the protocols used in Optivity Switch Manager or
information about using Device Manager, refer to the publications in this list.
Note: The Passport product line was formerly named Accelar. The
product name on some previously published documents has not yet been
changed.
Page 19

Preface 19
• Networking Concepts for the Accelar 1000 Series Routing Switch Software
Release 2.0 (part number 205588-A)
Provides general information and description of how the Passport 1000 Series
switch handles various networking features, such as VLANs, MultiLink
Trunking, OSPF, RIP, and IPX.
• Installing Optivity Switch Manager for LAN Switch Networks 1.0.0.0
(part number 210274-A)
Describes the steps necessary to install Optivity Switch Manager on the
Windows and Solaris platforms.
• Networking Concepts for the Passport 8000 Series Switch
(part number 207307-C)
Provides general information and description of how the Passport switch
handles various networking features, such as VLANs, MultiLink Trunking,
OSPF, RIP, and IPX.
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Command Line Interface Basic Switch
Management Release 3.1 (part number 211255-A)
Describes the command line interface (CLI) structure and the commands used
to perform basic switch management operations, such as modifying the switch
boot sequence, working with switch files, and setting up security features.
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Command Line Interface Switching
Operations Release 3.1 (part number 207308-D)
Describes the CLI commands and parameters for switching operations. Most
configuration tasks that can be performed using Device Manager can also be
done using the CLI.
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Command Line Interface Routing
Operations Release 3.1 (part number 208967-C)
Describes the CLI commands and parameters for routing operations.
• Reference for Accelar Management Software Switching Operations
Release 2.0 (part number 205586-A)
Describes how to use Device Manager to configure and manage layer 2
(switching) functions with the Accelar 1000 Series routing switch, including
procedures and illustrations of pertinent screens.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 20

20 Preface
• Reference for Accelar Management Software Routing Operations Release 2.0
(part number 205587-A)
Describes how to use Device Manager to configure and manage layer 3
(routing) functions with the Accelar 1000 Series routing switch, including
procedures and illustrations of pertinent screens.
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Management Software Switching
Operations Release 3.1 (part number 207414-D)
Describes how to use Device Manager to configure and manage layer 3
(routing) functions with the Passport routing switch, including procedures and
illustrations of pertinent screens.
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Management Software Routing
Operations Release 3.1 (part number 207415-C)
Describes how to use Device Manager to configure and manage layer 2
(switching) functions with the Passport 8000 Series switch, including
procedures and illustrations of pertinent screens.
• Reference for the BayStack 350/410/450 Management Software Operations
Version 3.1 (part number 210245-B)
208963-B
Describes how to use Device Manager to configure and manage layer 2
(switching) functions with BayStack switches, including procedures and
illustrations of pertinent screens.
You can print selected technical manuals and release notes free, directly from the
Internet. Go to the www25.nortelnetworks.com/library/tpubs/ URL. Find the
product for which you need documentation. Then locate the specific category and
model or version for your hardware or software product. Use Adobe Acrobat
Reader to open the manuals and release notes, search for the sections you need,
and print them on most standard printers. Go to Adobe Systems at the
www.adobe.com URL to download a free copy of the Adobe Acrobat Reader.
You can purchase selected documentation sets, CDs, and technical publications
through the Internet at the www1.fatbrain.com/documentation/nortel/ URL.
Page 21

How to get help
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel Networks product from a
distributor or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that
distributor or reseller for assistance.
If you purchased a Nortel Networks service program, contact one of the following
Nortel Networks Technical Solutions Centers:
Technical Solutions Center Telephone
EMEA (33) (4) 92-966-968
North America (800) 4NORTEL or (800) 466-7835
Asia Pacific (61) (2) 9927-8800
China (800) 810-5000
An Express Routing Code (ERC) is available for many Nortel Networks products
and services. When you use an ERC, your call is routed to a technical support
person who specializes in supporting that product or service. To locate an ERC for
your product or service, go to the www12.nortelnetworks.com/ URL and click
ERC at the bottom of the page.
Preface 21
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 22

22 Preface
208963-B
Page 23

Chapter 1 Introducing Optivity Switch Manager
This chapter introduces Nortel Networks Optivity Switch Manager features and
functions. The chapter includes the following topics:
• What is Optivity Switch Manager? (next)
• Optivity Switch Manager features (page 24)
• Optivity Switch Manager submanagers (page 24)
What is Optivity Switch Manager?
Optivity Switch Manager is a Java-based network management application that
allows you to discover and view up to 100 network devices and their physical
links on a topology map. Once your network is discovered, you can monitor,
manage, and configure protocols and settings in devices in the network using the
following submanagers within Optivity Switch Manager:
23
• VLAN Manager
• MultiLink Trunking Manager
• Multicast Manager
• Log Manager
In addition to these submanagers, Optivity Switch Manager has an associated
standalone application, Device Manager, that provides the ability to completely
configure and manage a single device in the network.
Optivity Switch Manager allows you to manage small to medium-size networks.
Since Optivity Switch Manager is a Java-based tool, it is platform-independent.
Optivity Switch Manager is also a real-time SNMP tool, allowing you to save the
topology map, error log, preferences, and communities in the application.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 24
24 Chapter 1 Introducing Optivity Switch Manager
To use Optivity Switch Manager, you must have the Java Runtime Environment
(JRE) installed on your system. Optivity Switch Manager requires JRE 1.3.
Note: For a description of operating systems, devices, and software
releases supported by Optivity Switch Manager, see Installing Optivity
Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0.
Optivity Switch Manager features
Optivity Switch Manager is a configuration tool for troubleshooting and limited
network monitoring. It has the following features:
• A consistent look across the Solaris and Windows platforms.
• Spring algorithm that balances distances between devices and minimizes
crossing lines when creating the topology map.
• A consistent graphical user interface (GUI) across Optivity Switch Manager
and submanagers and a single point of access to the submanagers.
• Dynamic system updates across submanagers. You can simultaneously query
your device in a submanager application as you view the topology map
through Optivity Switch Manager.
• Access control and security using community strings.
• Network discovery that you can specify to be as large or small as you want.
• Ability to save the layout of a discovered network for future use.
Optivity Switch Manager submanagers
Optivity Switch Manager incorporates submanagers that provide detailed device
information and management capabilities. The submanagers are designed to
provide specialized information in an easy-to-use graphical user interface that is
consistent in layout across the submanagers. A submanager can query Optivity
Switch Manager and instruct the primary application to update the topology view
with information relevant to the submanager view. For example, VLAN Manager
can instruct Optivity Switch Manager to color all the devices in the view that
include members of a particular VLAN.
208963-B
Page 25

Chapter 1 Introducing Optivity Switch Manager 25
The submanagers open in a separate window from Optivity Switch Manager. You
must have the Optivity Switch Manager window open to access all the
submanagers except Device Manager. The submanagers are:
• VLAN Manager
• MultiLink Trunking Manager
• Multicast Manager
• Log Manager
• Device Manager
VLAN Manager
VLAN Manager allows you to:
• Create, delete, or modify VLANs across one or multiple devices
• View VLAN information, membership, and port configuration information in
tabular format
• View Spanning Tree Protocol information such as members of spanning tree
groups (STGs) and Spanning Tree Protocol configuration
• View VLAN nodes across the network
For more information about VLAN Manager, refer to Chapter 4, “Using VLAN
Manager,” on page 55.
MultiLink Trunking Manager
MultiLink Trunking Manager allows you to:
• Create, delete, or modify MultiLink Trunks (MLTs) across one or two devices
• View MLT configuration information such as port and VLAN membership
For more information about MultiLink Trunking Manager, refer to Chapter 5,
“Using MultiLink Trunking Manager,” on page 99.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 26

26 Chapter 1 Introducing Optivity Switch Manager
Multicast Manager
Multicast Manager allows you to:
• View multicast configuration and protocols found in the network
• Display multicast forwarding paths from a selected source or group
For more information about Multicast Manager, refer to Chapter 6, “Using
Multicast Manager,” on page 121.
Log Manager
Log manager allows you to download individual log files from network devices
and view the entire file or selected information.
For more information about Log Manager, refer to Chapter 7, “Using Log
Manager,” on page 165.
208963-B
Device Manager
Device Manager is a standalone application that you can launch either from
Optivity Switch Manager or separately. This application allows you to:
• Download image and configuration files
• Completely manage and configure layer 2 and, if applicable, layer 3 protocols
and features for a single network device
• Monitor traffic flow through the device
• View a device image indicating which ports are active and, for Passport
switches, which modules are installed
For more information about Device Manager, refer to the documents listed in
“Related publications” on page 18.
Page 27

Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
This chapter describes the basic procedures for using Optivity Switch Manager.
For information about how to install Optivity Switch Manager, refer to Installing
Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0.
This chapter includes the following topics:
• Starting Optivity Switch Manager, next
• Using the Optivity Switch Manager window (page 29)
• Working with the network topology map (page 41)
• Getting help (page 46)
27
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 28

28 Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
Starting Optivity Switch Manager
After you install Optivity Switch Manager, you can start the application.
To start Optivity Switch Manager:
Do one of the following:
• From the Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 2000, or Windows NT
Start menu, choose Programs > Nortel Optivity Switch Management
Software > Optivity Switch Manager.
• In a Windows environment, double-click the Optivity Switch Manager
shortcut icon on your desktop, if it is present.
• In a Solaris terminal window, enter
Switch Manager has been installed.
Optivity Switch Manager starts.
./OSM in the location where Optivity
You do not need a password to open the application. However, to discover and
display a network topology, you need to enter an IP address to a device that will
act as a “seed,” and you must have permission to access that “seed” device. Refer
to “Discovering devices on a network” on page 48 for more information.
208963-B
Page 29
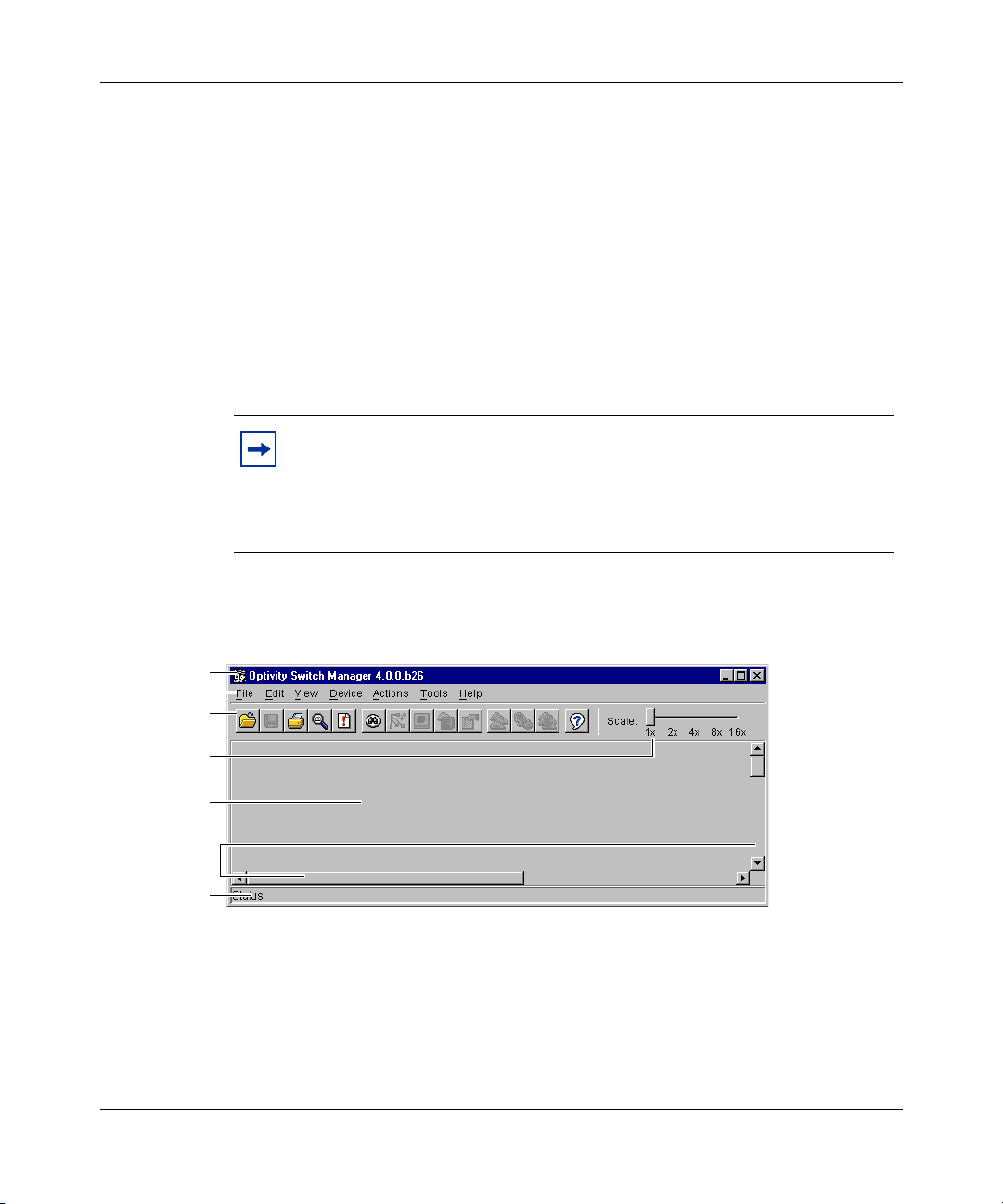
Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager 29
Using the Optivity Switch Manager window
The Optivity Switch Manager window:
• Displays a logical map of a network showing physical connectivity between
devices.
• Provides tools to access other Optivity Switch Manager features.
• Allows you to launch Optivity Switch Manager submanagers.
After the initial discovery, other Optivity Switch Manager submanager
applications allow you to monitor or configure discovered devices.
Note: The Optivity Switch Manager window remains open and can
display highlighted devices after the Optivity Switch Manager
submanager windows open. If you close the Optivity Switch Manager
window while Optivity Switch Manager submanager windows are open,
the submanagers also close.
Title bar
Menu bar
Toolbar
Scale slider
Contents
pane
Scroll bars
Status bar
Figure 1 shows the Optivity Switch Manager window.
Figure 1 Optivity Switch Manager window
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 30

30 Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
Table 1 describes the parts of the Optivity Switch Manager window.
Table 1 Parts of the Optivity Switch Manager window
Part Description
Title bar Displays the application name and software version.
Menu bar Provides access to all Optivity Switch Manager commands.
Toolbar Provides quick access to commonly-used Optivity Switch Manager
Scale slider Provides four zoom levels to magnify the network topology map.
Contents pane Displays the network topology map.
Scroll bars Provide access to an entire map, table, or other text that spans two
Status bar Displays status information and the map legend.
commands.
pages in the contents pane.
When you successfully query a device on the network, the Optivity Switch
Manager contents pane presents a logical map of the network displaying a variety
of information about the network connections. The specific information available
on the network topology map depends on the size of the network discovered. For
example, in a very large network topology, the device IP addresses and port
numbers are not displayed unless you magnify the network topology map using
the scale slider.
208963-B
Optivity Switch Manager menu bar
The menu bar provides menus and commands for operating Optivity Switch
Manager and for accessing Device Manager, VLAN Manager, MultiLink
Trunking Manager, Multicast Manager, and Log Manager. Table 2 lists the
Optivity Switch Manager menus and commands.
Page 31

Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager 31
Table 2 Optivity Switch Manager menus and commands
Shortcut
Menu Command
File Open [Ctrl]+O Opens a topology map.
Save [Ctrl]+S Saves a topology map.
Print [Ctrl]+P Opens the Print dialog box, where you set print parameters.
Exit [Ctrl]+Q Exits Optivity Switch Manager.
Edit Communities Edits SNMP communities accessible by Optivity Switch
Preferences Edits network preferences and identifies seed addresses
Clear Map [Del] Deletes the current network topology displayed in the
Find Device in
Map
Select All Selects all devices within a supported product family
View Link Speeds Displays network link speeds in color on the network
Link Duplex Displays half- and full-duplex links in color on the network
Link Types Displays the media type (Ethernet, POS, or ATM) in color
MultiLink Trunks Displays MultiLink Trunks discovered in the network
Show Port
Address
Error Log Displays the error log for Optivity Switch Manager. You can
keys Description
Manager. Refer to “Accessing devices within different
SNMP communities” on page 53 for more information.
used by Optivity Switch Manager. Refer to Chapter 3,
“Configuring Optivity Switch Manager,” on page 48 for more
information.
contents pane.
[Ctrl]+F Opens the Find Device dialog box, where you set
parameters to find a device in the topology map.
(Passport 1000 Series switches, Passport 8000 Series
switches, or BayStack switches).
topology map. The status bar provides a color legend for
the link speeds (refer to “Optivity Switch Manager status
bar” on page 38).
topology map. The status bar provides a color legend for
the link duplex status (refer to “Optivity Switch Manager
status bar” on page 38).
for the links in the network topology map. The status bar
provides a color legend for the link types (refer to “Optivity
Switch Manager status bar” on page 38).
topology.
Displays IP addresses of isolated routing ports or brouter
ports.
save the error log to a text file.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 32

32 Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
Table 2 Optivity Switch Manager menus and commands (continued)
Shortcut
Menu Command
Device Telnet Starts a Telnet session.
Ping Pings a device to test connectivity.
Device Manager Launches Device Manager to monitor and configure the
Properties Displays the properties of the selected device. Refer to
Report Opens the Report dialog box, which displays the device IP
Dump Topology
to Log
Note: This menu is accessible only if a device is selected on the network map displayed in
the Optivity Switch Manager Contents pane
Actions Discover Map Discovers a network topology map.
Layout Map Rearranges a topology map for better viewing.
Find Unsaved
Configurations
Log Manager Opens Log Manager. Refer to Chapter 7, “Using Log
Tools VLAN Manager [F2] Opens VLAN Manager. Refer to Chapter 4, “Using VLAN
MultiLink
Trunking
Manager
Multicast
Manager
keys Description
selected device.
“Using the Optivity Switch Manager shortcut menu” on
page 34 for a description of this feature.
address, name, type, and description.
Dumps the current topology to the log.
Opens the Find Unsaved Configurations dialog box that lists
the devices with unsaved changes in their configuration
files. The dialog box contains the device IP address, the
time/date when the configuration was last changed, and the
time/date when the device’s configuration was last saved.
Manager,” on page 165, for more information about this
application.
Manager,” on page 55, for more information about this
application.
[F3] Opens MultiLink Trunking Manager. Refer to Chapter 5,
“Using MultiLink Trunking Manager,” on page 99, for more
information about this application.
[F4] Opens Multicast Manager. Refer to Chapter 6, “Using
Multicast Manager,” on page 121 for more information about
this application.
208963-B
Page 33

Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager 33
Table 2 Optivity Switch Manager menus and commands (continued)
Shortcut
Menu Command
Help Contents [F1] Opens a Web browser application and loads Help files.
Online Support Opens a Web browser that loads the Nortel Networks
Legend Displays a key to the icons used in the Optivity Switch
About Optivity
Switch Manager
keys Description
Customer Support Web page.
Manager topology map.
Displays Optivity Switch Manager application information.
Finding unsaved configurations
You can find devices that have unsaved configuration files or changed
configuration files.
To find unsaved configuration files:
From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Actions >
Find Unsaved Configurations.
The Find Unsaved Configurations dialog box opens (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Find Unsaved Configurations dialog box
Table 3 describes the items in the Find Unsaved Configurations dialog box.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 34

34 Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
Table 3 Find Unsaved Configurations dialog box items
Item Description
Device The IP address, system name, or host name of the device.
LastChange The date and time when the device’s configuration was last
LastSavedToNVRam The date and time when the device’s configuration was last
changed.
saved. If the device’s configuration was never saved, this
text box reads “none.”
Using the Optivity Switch Manager shortcut menu
Use the shortcut menu (Figure 3) to start device-related tasks for a selected
device. The shortcut menu commands are similar to those found in the Device
menu and include launching the standalone Device Manager application.
To access the shortcut menu:
Right-click a device on the topology map to open the shortcut menu.
The shortcut menu opens (Figure 3).
Figure 3 Shortcut menu
208963-B
Page 35

Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager 35
Viewing device properties
When you choose Properties from the shortcut menu, you can view properties for
the selected device. The Device Properties dialog box (Figure 4) includes the
name, type, and location of the device, if that information was entered in the
device’s configuration. The bottom of the Device Properties dialog box shows the
port status of the device.
Figure 4 Device Properties dialog box
Table 4 describes the items in the Device Properties dialog box.
Table 4 Device Properties dialog box items
Item Description
Name The IP address, system name, or host name of the device.
Type The chassis type.
SysName The name of the device.
Description The system-assigned name.
Location The physical location of the device.
Contact The contact information for the system administrator. This
item reflects the contact information entered as part of the
system information for this device in Device Manager.
UpTime The time elapsed since the device was last booted.
Ports The device’s port status. The color of the box representing
each port indicates if the port is up (green), has no link (is
down) (orange), or is being tested (blue).
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 36

36 Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
Using the toolbar buttons
The toolbars for Optivity Switch Manager, VLAN Manager, MultiLink Trunking
Manager, Log Manager, and Multicast Manager are located beneath their
respective menu bars. The toolbar buttons provide quick access to commonly used
commands. When a toolbar button is unavailable for a particular configuration or
submanager, it appears dimmed.
When you point to a button, the name of the button and a description of the
command function are displayed.
Table 5 describes the toolbar buttons for Optivity Switch Manager and the
submanagers.
Table 5 Optivity Switch Manager and submanager toolbar buttons
Button Name Description Application
Open Opens a topology map or log file. Optivity Switch Manager,
Log Manager
208963-B
Save Saves a topology map or log file. Optivity Switch Manager,
Print Prints the topology map.
Note: The application does not paginate the
map, that is, break the map printing into
several pages. To print a portion of the map,
ensure that the portion is visible in the window
at the desired zoom level.
Find Allows you to find a device by IP address, a
VLAN by name, an MLT by IP address, or a
multicast group by address. Refer to “Finding
a device in the topology map” on page 44 for
more information.
View Error Log Displays the Optivity Switch Manager error
log.
Discover Network Discovers a seed address in a network. Refer
to “Discovering devices on a network” on
page 48 for more information.
Stop Discovery Stops the discovery process.
Note: This button is available only while
discovery is in process.
Log Manager.
Optivity Switch Manager,
VLAN Manager, MultiLink
Trunking Manager,
Multicast Manager, Log
Manager.
Optivity Switch Manager,
VLAN Manager, MultiLink
Trunking Manager,
Multicast Manager
Optivity Switch Manager
Optivity Switch Manager
Optivity Switch Manager
Page 37

Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager 37
Table 5 Optivity Switch Manager and submanager toolbar buttons (continued)
Button Name Description Application
Layout map Lays out the topology map for better
Log Manager Starts the Log Manager submanager Optivity Switch Manager
Telnet Opens a Telnet session in a separate window. Optivity Switch Manager
Device Manager Starts the Device Manager submanager. Optivity Switch Manager
Show Device
Properties
VLAN Manager Starts the VLAN Manager submanager. Optivity Switch Manager
MultiLink Trunking
Manager
Multicast Manager Starts the Multicast Manager submanager Optivity Switch Manager
Help Opens online Help. Optivity Switch Manager,
Reload Reloads the current submanager folder
Insert Displays the Insert dialog box to add a VLAN,
Delete Deletes a selection. VLAN Manager, MultiLink
Apply Changes Applies changes you have made to the
readability.
Displays the device properties of a particular
device on the discovered network.
Starts the MultiLink Trunking Manager
submanager.
information.
Note: Use this function often to ensure that
the displayed data is the most recent.
STG, or MLT.
configuration.
Optivity Switch Manager
Optivity Switch Manager
Optivity Switch Manager
VLAN Manager, MultiLink
Trunking Manager,
Multicast Manager
VLAN Manager, MultiLink
Trunking Manager,
Multicast Manager
VLAN Manager, MultiLink
Trunking Manager,
Multicast Manager
Trunking Manager,
Multicast Manager
VLAN Manager, MultiLink
Trunking Manager,
Multicast Manager
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 38

38 Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
Table 5 Optivity Switch Manager and submanager toolbar buttons (continued)
Button Name Description Application
Undo Changes Undoes changes you have made to the
configuration if you have not already clicked
Apply Changes.
Copy Copies highlighted information. VLAN Manager, MultiLink
Paste Pastes highlighted information. VLAN Manager, MultiLink
VLAN Manager, MultiLink
Trunking Manager,
Multicast Manager
Trunking Manager,
Multicast Manager, Log
Manager
Trunking Manager,
Multicast Manager
Optivity Switch Manager status bar
The Optivity Switch Manager status bar is at the bottom of the Optivity Switch
Manager main window (see Figure 1 on page 29). Table 6 describes the fields in
the status bar.
Table 6 Status bar fields
Field Description
Message Located on the left, the message field displays information about:
• Menu commands and toolbar buttons
• Optivity Switch Manager and submanager operations
Icon Located on the right, the icon field displays a legend for color-coded
information of Optivity Switch Manager and submanagers. Depending on
what selections are made from the View menu, this legend shows the
following information for Optivity Switch Manager:
• Link Speeds—10Mb/s (pink), 100Mb/s (blue), or 1Gb/s (red)
• Link Duplex—Half-duplex (blue) or full duplex (red)
• Link types—Ethernet (blue), POS (red), or ATM (green)
If none of these items is selected from the View menu, this field is blank.
208963-B
Page 39

Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager 39
Optivity Switch Manager contents pane icons
After you query a device’s seed address, the topology map opens in the Optivity
Switch Manager contents pane (Figure 5).
Figure 5 Optivity Switch Manager topology map
The Optivity Switch Manager topology map uses icons to represent the types of
network devices discovered. Some of the devices are supported by Optivity
Switch Manager; others are not supported but connect supported devices.
To access a legend with these icons and their names:
From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Help > Legend.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 40

40 Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
Table 7 describes the device icons.
Table 7 Device icons
Icon Name Description
Bus Network bus or hub not supported by Optivity
Passport 1K Passport 1000 Series switch. This device can be
Passport 8K Passport 8000 Series switch. This device can be
BayStack or
Business Policy
Switch 2000
Baystack (old) Baystack 310 switch. This device is partially
Other switch A switch not supported by Optivity Switch Manager
Other router A router not supported by Optivity Switch Manager
Switch Manager or its submanagers. You can view
ports connected to BayStack or Passport switches
by choosing View > Show Port Address.
configured and monitored by Optivity Switch
Manager and its submanagers.
configured and monitored by Optivity Switch
Manager and its submanagers.
BayStack 350, 410, or 450 switch or Business
Policy Switch 2000. This device can be configured
and monitored by Optivity Switch Manager and its
submanagers.
supported by Optivity Switch Manager and its
submanagers.
or its submanagers.
or its submanagers.
208963-B
Page 41

Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager 41
Adjusting the contents pane
You can resize the Optivity Switch Manager window or submanager windows by
dragging the edges of the active window. You can also use the scroll bars to adjust
the Optivity Switch Manager contents pane to view a specific portion of the
discovered network topology.
Using the scale slider
To adjust the scale of the topology map:
Move the scale slider (Figure 6) to the right to magnify the map or to the left
to make it smaller.
Figure 6 Scale slider
You can display the map up to sixteen times larger.
Note: Use Edit > Find Device in Map to easily locate the device before
you resize the specific region of the map.
Note: When you use Optivity Switch Manager in a Solaris environment,
you can click the number in the scale slider or drag the slider.
Working with the network topology map
After a network topology map is loaded into the Optivity Switch Manager
contents pane, you can save it and reload it.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 42

42 Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
Loading a saved network topology map
You can reload a saved topology map. If you do not have a specific topology map
saved, the application loads the previously saved topology map. This map is
stored in the default.topo file.
Note: Optivity Switch Manager Release 1.1.0.0 cannot open topology
maps saved in earlier releases.
To open a new topology map, you must use the discovery process described in
“Discovering devices on a network” on page 48.
To reload a saved topology map:
1 Do one of the following:
• From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose File > Open.
• On the keyboard, press [Ctrl]+O.
• On the Optivity Switch Manager toolbar, click Open.
208963-B
The Open File dialog box opens (Figure 7).
Figure 7 Open File dialog box
2 Select the filename (with a .topo extension) that contains your saved network
topology.
Page 43

Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager 43
3 Click Open.
The topology map is displayed in the contents pane.
4 From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Actions > Update
Topology to update your network topology map.
Saving a topology map
When you save a topology map, it is stored with a .topo file extension. If you do
not save a topology with a specific file name, Optivity Switch Manager attempts
to save the current map to the default.topo file.
To save a topology map with another name:
1 Do one of the following:
• From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose File > Save.
• On the keyboard, press [Ctrl]+S.
• On the Optivity Switch Manager toolbar, click Save.
The Save dialog box opens (Figure 8).
Figure 8 Save dialog box
2 Type the file name with a .topo file extension.
3 Click Save.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 44

44 Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
Printing a topology map
To print a topology map:
Do one of the following:
• From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose File > Print.
• On the keyboard, press [Ctrl]+P.
• On the Optivity Switch Manager toolbar, click Print.
Note: Optivity Switch Manager prints only a single page showing the
part of the topology map that starts at the left border of the window. To
print a portion of the map, ensure that the portion is next to the left
border of the window at the desired zoom level.
Finding a device in the topology map
To locate a device in the network topology map:
1 Do one of the following:
• From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Edit > Find Device
in Map.
• On the keyboard, press [Ctrl]+F.
• On the Optivity Switch Manager toolbar, click Find.
The Find Device dialog box opens (Figure 9).
Figure 9 Find Device dialog box
2 Type the name or the IP address of the device.
3 Click Find.
208963-B
Page 45

Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager 45
Arranging devices on the topology map
As Optivity Switch Manager discovers devices, they are arranged by default in a
column (top to bottom/left to right) on the topology map. Figure 10 shows the
Optivity Switch Manager contents pane after a seed address was located. The
devices icons are crowded together, and the port numbers and IP addresses
overlap each other. To improve readability of the map, you can automatically or
manually adjust the layout.
Figure 10 Optivity Switch Manager display before Layout command
To automatically arrange the topology map:
Do one of the following:
• From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Actions > Layout
Map.
• On the Optivity Switch Manager toolbar, click Layout Map.
The nodes are automatically arranged on the map. You may also need to
manually adjust nodes on the map until you have the desired layout.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 46

46 Chapter 2 Using Optivity Switch Manager
To manually arrange the devices discovered in the network topology:
Drag selected devices to desired locations on the topology map.
Getting help
Help in Optivity Switch Manager is arranged by subject. A Web browser, such as
Netscape Navigator or Microsoft Internet Explorer, opens to display Help files.
You can use the contents frame or the Help index to locate information.
To access Help:
Do one of the following:
• From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Help > Contents.
• On the keyboard, press [F1].
• On the Optivity Switch Manager toolbar, click Help.
208963-B
The Help files open in a Web browser.
Page 47

Chapter 3 Configuring Optivity Switch Manager
This chapter describes configuration tools for Optivity Switch Manager, and
includes the following topics:
• Discovering your network (next)
• Accessing devices within different SNMP communities (page 53)
Discovering your network
Optivity Switch Manager builds its logical map of the network by querying the
topology table of the seed device, using the Bay Autotopology Protocol (BTP).
A seed device is a device from which you start learning about the topology of the
network. After getting the information about the neighbors of the seed device,
Optivity Switch Manager queries the neighbor devices for their topology tables.
Optivity Switch Manager then selects the appropriate icon to represent each
device, computes the links between devices, and represents the device information
in a network topology map.
47
Discovery continues until the maximum number of hops is reached. By default,
Optivity Switch Manager does not query neighbors more than five hops away
from the seed device. You can set the number of hops, up to a maximum of 20
hops. Also, you can stop the discovery process at any time by clicking Discovery
from the Optivity Switch Manager toolbar. While the discovery process is
occurring, this button changes to show a red X.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 48

48 Chapter 3 Configuring Optivity Switch Manager
Discovering devices on a network
The topology discovery process begins when you supply Optivity Switch
Manager with one or more network device seed addresses and the application
queries the addresses. The Preferences dialog box specifies the seed address and
defines the scope of the discovery process.
To discover a network:
1 From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Edit > Preferences.
The Preferences dialog box opens (Figure 11).
Figure 11 Preferences dialog box
208963-B
2 In the Seed Address(es) textbox, type the IP address of one or more devices in
the network.
Separate multiple IP addresses with commas.
Page 49

Chapter 3 Configuring Optivity Switch Manager 49
3 In the MaxHops textbox, type the maximum number of hops.
4 Use the Layout slider to indicate whether greater speed or better accuracy is
more important.
5 Select other options in the dialog box to control the appearance of the
topology map.
See Table 8 for a description of the options available.
6 Click Apply.
7 Click OK.
8 From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Actions > Discover
Map.
The topology map is displayed.
Table 8 describes the items in the Preferences dialog box.
Table 8 Preferences dialog box items
Section Item Description
Discovery Seed Address(es) The IP address(es) of one or more devices
that Optivity Switch Manager queries using
SNMP to start the discovery process. For a list
of supported devices, see Installing Optivity
Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0.
Note: If the devices you want to monitor and
configure are not connected to the same
network, you can specify multiple seed
addresses, separated by commas. The
separate networks do not appear to be
connected in the network topology map.
Max Hops The number of hops, between 1 and 20, that
a data packet travels from one router or
intermediate point to another in the network.
(Default is 5 hops.)
Restrict Discovery Opens the Restrict Discovery dialog box to
restrict device discovery to only the devices in
the subnets entered. Refer to “Restricting
discovery” on page 51 for more information.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 50

50 Chapter 3 Configuring Optivity Switch Manager
Table 8 Preferences dialog box items (continued)
Section Item Description
Map Layout Drag the slider to the right (better) or to the left
Show Device by Determines how a device is identified in the
Trim HostName Domains Truncates Internet host name domains.
Non-highlighted area Allows you to select an option for viewing
Automatically Save on Exit If checked, the current network topology map
Automatically Relayout
after discovery
(faster) to indicate how you want Optivity
Switch Manager to lay out devices in the
network topology map. Refer to “Layout slider”
on page 52 for more information.
network topology map. The selections are:
• HostName
• SysName
• IP Address (Default)
Example: nortelnetworks.com becomes
nortelnetworks
inactive devices. The options are:
• Dimmed–Non-highlighted items are
shaded. (Default)
• Invisible–Removes non-highlighted items
from the topology map.
is automatically saved to the default.topo file.
If checked, the network topology map is
adjusted for better viewing as it is loaded in
Optivity Switch Manager.
208963-B
Page 51

Chapter 3 Configuring Optivity Switch Manager 51
Table 8 Preferences dialog box items (continued)
Section Item Description
SNMP Retry Count The number of times, between 0 and 5,
Timeout The amount of time, between 3 and 10
Max Outstanding
Requests
Trace If checked, additional SNMP information is
Optivity Switch Manager tries to connect to a
device using SNMP. (The default is 1.)
seconds, Optivity Switch Manager waits
before trying to connect to a device again.
(The default is 5.)
The number of SNMP requests, between 20
and 250, that Optivity Switch Manager
maintains as open or outstanding. (The
default is 100.)
written to the Optivity Switch Manager error
log, and can provide assistance in
troubleshooting.
Note: Selecting Trace could slightly slow
down performance as extra information is
gathered.
Restricting discovery
You can restrict the discovery process to devices on specified subnets. Use the
Restrict Discovery dialog box to enter IP subnets that are available for discovery
by Optivity Switch Manager. Only devices on a listed subnet are displayed in the
Optivity Switch Manager contents pane.
To restrict discovery to certain subnets:
1 From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Edit > Preferences.
2 Click Restrict Discovery.
The Restrict Discovery dialog box opens (Figure 12).
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 52

52 Chapter 3 Configuring Optivity Switch Manager
Figure 12 Restrict Discovery dialog box
3 Click Insert.
A new row containing 0.0.0.0 appears under the To Subnet heading.
4 Click the row containing 0.0.0.0 and type the subnet address.
5 Click Close.
208963-B
Layout slider
Use the layout slider to improve the readability of the topology map. It adjusts the
layout of the devices in the network topology using the Spring algorithm, which
balances the distances between devices and minimizes the number of crossing
lines.
To use the layout slider:
1 Choose Edit > Preferences.
The Preferences dialog box opens (Figure 11 on page 48).
2 In the Map area, slide the ruler between faster and better to adjust the layout
display.
Optivity Switch Manager retains the locations of nodes until you rediscover
the network.
3 Click Apply.
Page 53

Chapter 3 Configuring Optivity Switch Manager 53
4 To resdiscover the network topology map with new layout, do one of the
following:
• From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Actions > Discover
Map.
• On the Optivity Switch Manager toolbar, click Discover Network.
Accessing devices within different SNMP communities
SNMP community passwords can provide a level of protection by limiting access
to devices. In Optivity Switch Manager, you can access subnets with different
communities by adding the correct SNMP passwords in the Communities dialog
box. SNMP devices, which include those devices supported by Optivity Switch
Manager, typically have two passwords or communities for read and write
operations on that device. The two passwords are “public” (open access) and
“private” (restrictive access).
By default, Optivity Switch Manager reads an ASCII file (snmpcomm.properties)
that contains one entry. That entry allows Optivity Switch Manager to access all
devices in the discovered network using “public” as the community password for
read operations and “private” as the password for write operations. If devices
contain a different SNMP community password, you cannot access them unless
you know their passwords and enter those password into the Optivity Switch
Manager snmpcomm.properties file.
To assign a different SNMP community password to a group or single device:
1 From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Edit > Communities.
The Communities dialog box opens (Figure 13).
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 54

54 Chapter 3 Configuring Optivity Switch Manager
Figure 13 Communities dialog box
2 Click Insert.
An empty row is added to the table.
3 Click on the empty row and enter the IP address and communities.
4 Click Save.
208963-B
The changes are saved to the snmpcomm.properties file.
Table 9 describes the Communities fields in the dialog box.
Table 9 Communities dialog box fields
Fields Descriptions
Address The subnet address of a group of devices or the IP address
of a single device. (Default is 0.0.0.0 to include all devices.)
Note: Optivity Switch Manager uses zero (0) as a wildcard
to associate SNMP communities with groups of devices.
You can place a zero anywhere in the IP address. For
example, the address 10.10.0.0 refers to all addresses in
the 10.10. subnet.
Read The level of permission to view or read configuration
information on a group of devices or single device.
The community string default is public (open access)
Write The level of permission to change configuration information
on a group of devices or single device.
The default community string is private (restrictive access)
Page 55

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
VLAN Manager manages Spanning Tree Groups (STGs) and VLANs across
devices in a network. Optivity Switch Manager is the starting point for VLAN
Manager, and Optivity Switch Manager must be open to use VLAN Manager.
This chapter describes using VLAN Manager to manage VLANs on Passport and
BayStack switches. The chapter includes the following information:
• What is VLAN Manager?, next
• Starting VLAN Manager (page 57)
• VLAN Manager window (page 57)
• Using VLAN Manager (page 63)
• Managing spanning tree groups (STGs) (page 79)
• Managing a VLAN (page 82)
• Highlighting STGs and VLANs in the Optivity Switch Manager contents
pane (page 93)
55
What is VLAN Manager?
VLAN Manager enables you to manage VLAN and STG configurations across a
single device or multiple devices. It supports the rcVlan and rcStg MIBs.
VLAN
A VLAN is a collection of ports on one or more switches that defines a broadcast
domain. You can assign ports to a VLAN or you can create a policy VLAN, which
determines the port’s membership in the VLAN based on the traffic entering that
port. For example, in an IP subnet-based VLAN, the port belongs to the VLAN
only if the traffic passing through the port is on the specified IP subnet.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 56

56 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
You control path redundancy for VLANs by implementing the Spanning Tree
Protocol (STP).
Spanning Tree Protocol
As defined in the IEEE 802.1D standard, the Spanning Tree Protocol detects
and eliminates logical loops in a bridged or switched network. When multiple
paths exist, the spanning tree algorithm configures the network so that a bridge or
switch uses only the most efficient path. If that path fails, the protocol
automatically reconfigures the network to make another path active, thus
sustaining network operations.
The collection of ports in one spanning tree is called a spanning tree group (STG)
and a network may include multiple instances of STGs. All the devices supported
by Optivity Switch Manager support at least one STG. The Passport 1000 Series
switch and the Passport 8600 modules support multiple spanning trees, thus
multiple spanning tree groups.
Table 1 0 lists the maximum number of STGs and VLANs supported by the
different switches.
Table 1 0 Maximum STGs and VLANs supported by switches
Maximum
Switch
Passport 1000 Series switch 25 124
Passport 8100 modules 1 2000
Passport 8600 modules 25 1979
BayStack 350/410/450 switches 1 64
Business Policy Switch 2000 1 64
number of STGs
Maximum
number of VLANs
For more information about VLANs and Spanning Tree Protocol, refer to
Networking Concepts for the Passport 1000 Series Routing Switch Release 2.0
and Networking Concepts for the Passport 8000 Series Routing Switch.
208963-B
Page 57

VLAN Manager features
VLAN Manager allows you to:
• Configure and monitor VLANs and STGs across one or multiple devices.
• View and edit port membership information: ports not belonging to an STG,
or ports belonging to multiple STGs, individual routing ports and brouter
ports.
• View Spanning Tree configuration information In the Optivity Switch
Manager contents pane, such as which ports are blocking or forwarding. You
can also see which device is the root of the Spanning Tree configuration.
The following sections describe the VLAN Manager window and the
management functions available.
Starting VLAN Manager
Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 57
To start VLAN Manager:
Do one of the following:
• From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Tools > VLAN
Manager.
• On the keyboard, press [F2].
• On the Optivity Switch Manager toolbar, click VLAN Manager.
The VLAN Manager window opens (Figure 14).
VLAN Manager window
The VLAN Manager window (Figure 14) contains the parts described in Table 11.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 58

58 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Figure 14 VLAN Manager window
Title bar
Menu bar
Toolbar
Navigation pane
Contents pane
Status bar
Table 11 describes the parts of the VLAN Manager window.
Table 11 VLAN Manager window parts
Part Description
Title bar Displays the submanager name.
Menu bar Provides access to all VLAN Manager commands.
Toolbar Provides quick access to commonly-used VLAN Manager commands.
Navigation pane Provides a navigation tree showing VLAN Manager network folder
Contents pane Displays information selected in the navigation pane.
Status bar Displays status information, including the type of device highlighted
Menu bar
The menu bar provides menus and commands for operating VLAN Manager.
resources.
and command status.
208963-B
Page 59

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 59
Table 1 2 lists the VLAN Manager menus and commands.
Table 1 2 VLAN Manager menus and commands
Menu Command Shortcut Key Description
File Reload [Ctrl]+R Reloads the VLAN Manager
Save
Diagnostic
Info
Print [Ctrl]+P Opens the Print dialog box, where you
Close Closes the VLAN Manager window.
Edit Undo
Changes
Copy [Ctrl]+C Copies the contents of a selected cell.
Paste [Ctrl]+V Pastes the cell contents to a new
Insert [Insert] Opens the Insert dialog box, where you
Delete [Del] Removes a selection and displays a
Apply
Changes
Edit MAC
Address
Find [Ctrl]+F Opens the Find dialog box, where you
View Highlight
Topology
Audit Queries the network configuration to
[Ctrl]+S Saves diagnostic information about the
[Ctrl]+Z Reverses any changes you made to an
[Ctrl]+A When you have made changes to your
information.
STGs and VLAN discovered.
enter print parameters.
item or field.
location.
insert an STG or VLAN on selected
devices.
message to confirm deletion of the
selected VLAN.
VLAN configuration, this command
applies these changes to the devices in
the network.
Allows you to insert the text file
containing the MAC addresses for
MAC-based VLANs.
set parameters to find matching entries
in your network.
Highlights the VLAN topology map in the
Optivity Switch Manager contents pane.
report any discrepancies.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 60

60 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Table 1 2 VLAN Manager menus and commands (continued)
Menu Command Shortcut Key Description
Help Using Opens a Web browser and loads the
Toolb ar
For information about the toolbar buttons available in VLAN Manager, refer to
Table 5 on page 36.
Navigation pane
The VLAN Manager navigation pane (Figure 15) is located on the left side of the
window. It contains a network folder for each STG found in the network. When
you select an STG folder, the tree expands to display the STG configuration
information and then lists the VLANs associated with that STG.
In the navigation pane, select the folder for which you want to view STG or
VLAN information, or choose Edit > Print to print the navigation tree.
Online
Support
About VLAN
Manager
Help files.
Opens a Web browser that loads the
Nortel Networks Customer Support Web
page.
Displays information about VLAN
Manager.
208963-B
Page 61

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 61
Figure 15 VLAN Manager navigation pane
Contents pane
When you select a network resource in the navigation pane, a table opens in the
contents pane (Figure 16).
Figure 16 Default (1) folder view in the contents pane
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 62

62 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
To view the VLAN information in the contents pane:
In the navigation pane, select an STG or VLAN icon.
The example in Figure 16 shows the VLAN membership information for the
Default VLAN. The Default (1) folder opens in the contents pane when you
select Default (1) from the navigation tree.
Status bar
The VLAN Manager status bar (Figure 14 on page 58) is located at the bottom of
the VLAN Manager window and contains two fields. Table 13 describes the
VLAN Manager status bar fields.
Table 1 3 VLAN Manager status bar fields
Field Description
Message Located on the left, the message field displays information about VLAN
Icon Located on the right, the icon field provides a legend for different types of
manager operations.
VLANs found in the network:
• port–a VLAN in which the ports are explicitly assigned to the VLAN.
• subnet–a VLAN in which ports are dynamically added to the VLAN
based on source IP subnet.
• protocol–a VLAN in which ports are dynamically added to the VLAN
based on a network protocol.
• mac–a VLAN in which ports are dynamically added to the VLAN
based on the source MAC address.
Finding network resources
You can locate an entry in a field that contains a particular item of information,
such as text, seed address, or VLAN ID number.
To find a network resource:
1 Click any device in the navigation tree or contents pane, and do one of the
following:
• From the VLAN Manager menu bar, choose Edit > Find.
208963-B
Page 63

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 63
• On the VLAN Manager toolbar, click Find.
The Find dialog box opens (Figure 17).
Figure 17 Find dialog box
2 In the Find text box, type the text or number for your search.
3 In the In section, click the Tree option to search the navigation tree, or click
the Table option to search the contents pane.
4 Click Next.
VLAN Manager starts its search and highlights the first match that it finds or
displays a message that it found no matches.
5 If a first match was found, click Next to find each subsequent match, or click
Previous to go back to your last match.
Using VLAN Manager
Using VLAN Manager, you can monitor, configure, and troubleshoot STGs and
VLANs found in the network.
This section includes the information about the following topics:
• Port membership (ports not belonging to STGs or ports belonging to multiple
STGs)
• Viewing spanning tree groups (STGs)
• VLAN ports
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 64

64 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Port membership
In the navigation pane, the top four icons represent the following types of port
memberships:
• Unassigned
• Tagging
• Isolated Routing Port (IRP)
• Bridge Routing (brouter ports)
Table 1 4 describes the port membership types.
Table 1 4 Port membership types and STGs
Icon Port type Description
Unassigned Port that do not belong to any STG. If no devices in the
Tagging Port that has tagging enabled and can belong to multiple
Isolated Routing
Port (IRP)
Bridge Routing
(brouter ports)
network contain unassigned ports, a table does not open
in the contents pane.
STGs. If a tagged frame is received on a tagged port, with
a VLAN ID specified in the tag, the switch directs it to that
VLAN, if it is present.
Port that can only route IP packets and does not belong to
any STG or VLAN.
Note: IRPs are applicable only to the Passport 1000
Series switch.
Port that can route IP packets as well as bridge all
nonroutable traffic. The routing interface is not subjected
to the Spanning Tree Protocol.
Note: Bridge routing ports, or brouter ports, are available
only on the Passport 1000 Series switch and the Passport
8600 switch.
Viewing the unassigned ports
To view the table associated with the unassigned ports:
In the navigation pane, select Unassigned.
208963-B
Page 65

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 65
The Unassigned Ports table opens in the contents pane (Figure 18). Because
there are no unassigned ports in the discovered network, the table is empty.
Figure 18 Unassigned Ports table
Table 1 5 describes the Unassigned Ports table fields.
Table 1 5 Unassigned Ports table fields
Field Description
Device IP address, system name, or host name of the device.
Ports Ports not currently assigned to an STG.
Viewing tagged Ports
To view the devices and ports associated with tagged ports:
In the navigation pane, select Tagging.
The Tagging Ports table opens in the contents pane (Figure 19).
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 66

66 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Figure 19 Tagging Ports table
Table 1 6 describes the fields in the Tagging Ports table.
Table 1 6 Tagging Ports table fields
Field Description
Device IP address, system name, or host name of the device.
Port Ports on which tagging is enabled.
VlanIds VLAN ID(s) of which the port is a member.
Viewing isolated router ports (IRPs)
To view IRPs on Passport 1000 Series switches:
In the navigation pane, select Isolated Routing.
The Isolated Routing Ports table opens in the contents pane (Figure 20).
208963-B
Page 67

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 67
Figure 20 Isolated Routing Ports table
Table 1 7 describes the fields in the Isolated Routing Ports table.
Table 1 7 Isolated Routing Ports table fields
Field Descriptions
Device IP address, system name, or host name of the device.
Ports Ports that route only IP packets.
Viewing bridge routing Ports
To view bridge routing (brouter) ports on Passport 1000 Series switches and
Passport 8000 Series switches:
In the navigation pane, select Bridge Routing.
The Bridge Routing Ports table opens in the contents pane (Figure 21).
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 68

68 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Figure 21 Bridge Routing Ports table
Table 1 8 describes the fields in the Bridge Routing Ports table.
208963-B
Table 1 8 Bridge Routing Ports table fields
Field Descriptions
Device IP address, system name, or host name of the device.
Ports Port numbers of the port on which frames are received.
Viewing spanning tree groups (STGs)
All devices supported by Optivity Switch Manager support the IEEE 802.1D
Spanning Tree Protocol and at least one instance of a Spanning Tree Group. Refer
to Table 10 on page 56 for the maximum STGs supported by each switch.
To view an STG:
Click the folder for the STG you want to view.
The folder expands to show four icons representing types of information
available about the STG and a list of VLANS in the STG (Figure 22).
Page 69

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 69
Figure 22 STG folder in the VLAN Manager navigation pane
Table 1 9 describes the STG icons displayed in the VLAN Manager navigation
pane.
Table 1 9 STG information icons
Icon Name Representation
Members Devices and ports that are part of the STG.
Config STG configuration information.
Status STG status information, including STG topology
Root Devices that are the STG root.
change information.
Members
To view the ports that are members of the STG:
In the navigation pane, select Members.
The Members table opens in the contents pane (Figure 23).
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 70

70 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Figure 23 Spanning tree group members table
Table 2 0 describes the fields in the Members table.
Table 2 0 Members table fields
208963-B
Field Description
Device IP address, system name, or host name of the device.
PortMembers Ports on the device that are members of the STG.
Adding port members
To add ports to an STG:
1 In the Members table, select a device in the list.
2 Double-click in the PortMembers cell for the device to which you want to add
port membership.
The PortMembers dialog box opens (Figure 24).
Page 71

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 71
Figure 24 PortMembers dialog box
3 Select the port number(s) or click All for all the ports.
4 Click Ok.
Viewing and configuring STG parameters
You can view and configure STG parameters.
To view the configuration information:
In the navigation pane, select Config.
The Configuration table opens (Figure 25) in the contents pane.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 72

72 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Figure 25 Configuration table
Table 2 1 describes the fields in the Configuration table.
Table 2 1 Configuration table fields
Field Description
Device IP address, system name, or host name of the device.
Priority The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) bridge priority, in decimal.
BridgeMaxAge The value in hundredths of a second that all bridges use for
BridgeHelloTime The value in hundredths of a second that all bridges use for
BridgeForwardDelay The value in hundredths of a second that all bridges use for
EnableStp Enables or disables the spanning tree algorithm for the spanning
StpTrapEnable Enables or disables SNMP traps to be sent to trace receiver
The range is 0 (highest priority) to 65535 (lowest priority). The
default is 32768.
MaxAge when this bridge is acting as the root.
Note: The 802.1D-1990 standard specifies that the range for
this parameter is related to the value of dot1dStp\Time.
The default is 2000 (20 seconds).
Hello Time when this bridge is acting as the root. The granularity
of this timer is specified by the IEEE 802.1D-1990 standard to
be in increments of 1/100 of a second. The default is 200
seconds.
Forward Delay when this bridge is acting as the root. The default
is 1500 (15 seconds).
tree group.
every time an STP topology change occurs.
208963-B
Page 73

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 73
Table 2 1 Configuration table fields (continued)
Field Description
TaggedBpduAddress A MAC address; specifically for tagged BPDUs.
TaggedBpduVlanId The VLAN tag associated with the spanning tree group. This ID
is used to tag BPDUs through a non-IEEE tagging bridge to
another Passport switch.
Status group
Use the read-only Status table to view the status of the Spanning Tree Protocol for
each STG that is associated with the network.
To view the Status table:
In the navigation pane, select Status.
The Status table (Figure 26) opens in the contents pane.
Figure 26 Status table
Table 2 2 describes the fields in the Status table.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 74

74 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Table 2 2 Status table fields
Field Description
Device IP address of the bridge.
NumPorts Number of ports controlled by this bridging entity.
ProtocolSpecification An indication of which version of the Spanning Tree
TimeSinceTopologyChange Time in hundredths of a second since the last time a
TopChanges The number of topology changes detected by this bridge
MaxAge Maximum age of STP information learned from the network
HelloTime Amount of time in hundredths of a second between
HoldTime Time interval in hundredths of a second during which no
ForwardDelay Time interval in hundredths of a second that controls how
Protocol (STP) is operating. The IEEE 802.1d
implementations display ieee8021d.
topology change was detected by the bridge entity or STG.
since the management entity was last reset or initialized.
on any port before it is discarded, in units of hundredths of
a second. This is the actual value that the bridge is
currently using. The default value is 2000 (20 seconds).
transmission of configuration bridge protocol data units
(BPDUs) by this device on any port when it is the root of
the spanning tree. The default value is 200 (2 seconds).
more than two configuration BPDUs are transmitted by this
device. The default value is 100 (1 second).
fast a port changes its spanning state when moving toward
the Forwarding state. This value determines how long the
port stays in each of the Listening and Learning states,
which precede the Forwarding state. This value is also
used when a topology change is detected and is under
way, to age all dynamic entries in the Forwarding
Database. The default value is 1500 (15 seconds).
208963-B
Root
The read-only Root table displays information about the device acting as root
within a selected STG.
To view the root table:
In the navigation pane, select Root.
The Root table opens in the contents pane (Figure 27).
Page 75

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 75
Figure 27 Root table
Table 2 3 describes the fields on the Root table.
Table 2 3 Root table fields
Field Description
Device IP address of a device in the STG.
BridgeAddress MAC address used by this bridge when it must be identified in a
DesignatedRoot Bridge identifier of the root of the spanning tree as determined by
RootCost Cost of the path to the root as seen from this bridge.
RootPort Port number of the port that offers the lowest cost path from this
Default VLAN
Passport 8000 Series switches, Passport 1000 Series switches, BayStack 350/410/
450 switches, and the Business Policy Switch 2000 are factory configured with all
ports in a port-based VLAN called the default VLAN. The VLAN ID of the
default VLAN is always 1, and it is always a port-based VLAN. You cannot delete
the default VLAN, although you can remove ports from it.
unique fashion.
the Spanning Tree Protocol as executed by this device. This value
is used as the Root Identifier parameter in all configuration BPDUs
originated by this device.
bridge to the root bridge.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 76

76 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
To view the Default Ports table:
From the navigation tree, select Default(1).
The Default VLAN table opens in the contents pane (Figure 28).
Figure 28 Default VLAN table
208963-B
Table 2 4 describes the fields in the Default VLAN table.
Table 2 4 Default VLAN table fields
Field Description
Device IP address, system name, or host name of the device.
PortMembers Ports that are assigned to the VLAN.
HighPriority In a Passport 1000 Series switch, you can select HighPriority mode
for all traffic in the VLAN.
QosLevel In a Passport 8000 Series switch, you can set the Quality of Service
level for traffic in the VLAN to a level between 1 and 8.
DsField In a Passport 8000 Series switch, you can set the Differentiated
Services field for traffic in the VLAN to a level between 1 and 54.
Page 77

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 77
Table 2 4 Default VLAN table fields (continued)
Field Description
IfIndex Logical interface index assigned to the VLAN. This value can be in
one of the following ranges:
• Passport 1000 Series switch: 257 to 512
• Passport 8000 Series switch: 2049 to 4096
Note: This field does not apply to BayStack or Business Policy Switch
2000 switches.
IpAddress IP address, if any, assigned to the VLAN for routing.
VLAN ports
Ports in a VLAN are always members of a spanning tree group (STG). A VLAN
can include all the ports in a given STG, and there can be multiple VLANs in an
STG, but a VLAN will never have more ports than exist in the STG.
In an STG, VLAN information is displayed in the contents pane when that VLAN
is selected.
The icon that precedes the VLAN name identifies the type of VLAN:
• Port
• Subnet
• Protocol
• Mac
Note: Not all VLAN types are available on all devices that Optivity
Switch Manager supports. Of these four types of VLANs, Passport 8100
switches and the Business Policy Switch 2000 support only port-based
or protocol-based VLANs. BayStack 350/410/450 switches support only
port-based VLANs. Refer to the documentation that was shipped with
your switch for more information.
To view VLANs:
In the navigation pane, select a VLAN.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 78

78 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
The VLAN table opens (Figure 29) in the contents pane.
Figure 29 VLAN table
208963-B
Table 24 on page 76 describes the fields in the VLAN table.
Page 79

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 79
Managing spanning tree groups (STGs)
You can edit STG and STG membership information to manage STGs in any of
the following ways:
• Creating a spanning tree group
• Editing a spanning tree group
• Deleting a spanning tree group
Creating a spanning tree group
On a Passport 1000 Series switch or a Passport 8600 switch, you can create new
STGs. The BayStack switches and the Business Policy Switch 2000 support only
one STG per switch.
To create a new spanning tree group:
1 From the navigation tree, highlight the first Network folder and do one of the
following:
• From the VLAN Manager menu bar, choose Edit > Insert.
• On the VLAN Manager toolbar, click Insert.
The New STG dialog box opens (Figure 30).
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 80

80 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Figure 30 New STG dialog box
2 Insert values or select options in the option boxes.
3 Click Ok.
Table 2 5 describes the items in the New STG dialog box.
Table 2 5 New STG dialog box items
Item Description
Id A number between 1 and 25 that identifies the new spanning tree
TaggedBpduAddress A MAC address, specifically for tagged BPDUs.
TaggedBpduVlanId The VLAN tag associated with the STG. This ID is used to tag
Priority STP bridge priority, in decimal. The range is 0 (highest priority) to
BridgeMaxAge Value in hundredths of a second that all bridges use for MaxAge
group (STG) configured on the network.
BPDUs through a non-IEEE tagging bridge to another Passport
or BayStack switch.
65535 (lowest priority). The default is 32768.
when this bridge is acting as the root.
Note: The 802.1D-1990 standard specifies that the range for this
parameter is related to the value of dot1dStpBridgeHelloTime.
The default is 2000 (20 seconds).
208963-B
Page 81

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 81
Table 2 5 New STG dialog box items (continued)
Item Description
BridgeHelloTime Value in hundredths of a second that all bridges use for Hello
BridgeForwardDelay Value in hundredths of a second that all bridges use for Forward
Enable Stp Enables or disables the spanning tree algorithm for the spanning
Enable Stp Traps Enables SNMP traps to be sent to trace receiver every time an
On All Devices When checked, selects all devices listed in the list. Otherwise,
Time when this bridge is acting as the root. The granularity of this
timer is specified by the IEEE 802.1D-1990 standard to be in
increments of 1/100 of a second. The default is 200 seconds.
Delay when this bridge is acting as the root. The default is 1500
(15 seconds).
tree group.
STP topology change occurs.
select the individual devices to be added to the STG.
Editing a spanning tree group
To edit a spanning tree group:
1 Select an STG folder.
2 In the STG table in the contents pane, click the item that you want to edit.
The field is highlighted, and you can edit directly in the table.
3 Type information in the text boxes, or select from a list.
The changes appear in bold.
4 On the VLAN Manager toolbar, click Apply Changes.
Deleting a spanning tree group
To delete a spanning tree group:
1 In the navigation pane, select an STG folder except STG 1, and do one of the
following:
• From the VLAN Manager menu bar, choose Edit > Delete.
• On the VLAN Manager toolbar, click Delete.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 82

82 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
The Delete dialog box (Figure 31) opens, asking you to confirm the deletion
of the STG.
Figure 31 Delete dialog box
2 Do one of the following:
• Click Yes to confirm the deletion and return to the table view.
• Click No to cancel the deletion and return to the table view.
Note: Multiple STGs are supported only on Passport 1000 and Passport
8000 Series switches.
Managing a VLAN
This section contains information about common operations you can perform
when managing VLANs with VLAN Manager.
Creating a VLAN
When you create VLANs using VLAN Manager, follow these rules:
• VLANs must have unique VLAN IDs and names.
• Trunk (tagged) ports can belong to multiple VLANs and multiple spanning
tree groups.
• A VLAN cannot belong to multiple spanning tree groups.
208963-B
Page 83

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 83
• An access (untagged) port can belong to one and only one port-based VLAN
or it can belong to one and only one policy-based VLAN for the given
protocol.
• If you enable tagging on a port that is in a VLAN, the spanning tree group
configuration for that port is lost.
• A frame’s VLAN membership is determined by the following order of
precedence:
— VLAN ID
— Source MAC-based VLAN
— IP subnet-based VLAN
— Protocol-based VLAN
— Port-based VLAN
Creating a port-based VLAN
To create a port-based VLAN:
1 In the navigation pane, select an STG.
2 Do one of the following:
• From the menu bar, choose Edit > Insert.
• On the toolbar, click Insert.
The New VLAN dialog box opens (Figure 32).
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 84

84 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Figure 32 New VLAN dialog box
208963-B
3 Type the VLAN ID.
The value can be from 1 to 4094, as long as it is not already in use. (The
default VLAN has a VLAN ID of 1.)
4 Type the VLAN name (optional).
If no name is entered, a default is created.
5 For a Passport 8600 switch, select the QoS Level (optional)
6 For a Passport 8600 switch, type the Differentiated Services (DS) Field
(optional).
7 For a Passport 1000 Series switch, specify if the VLAN traffic will be tagged
as High Priority (optional).
8 In the Type option, select byPort.
Other items in the dialog box that apply to a port-based VLAN are activated.
Page 85

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 85
9 Select the device to be configured on the VLAN by doing one of the
following:
• Select from the device list.
• Click On All Devices to select all devices in the list.
10 Click Ok.
Table 2 6 describes the items in the New VLAN dialog box.
Table 2 6 New VLAN dialog box items
Item Description
Id A number between 1 and 4,094 that identifies the new VLAN
Name Name given to the VLAN.
QosLevel For a Passport 8000 Series switch, you can set the Quality of
DsField For a Passport 8000 Series switch, you can set the Differentiated
High Priority For a Passport 1000 Series switch, you can select HighPriority
Type Type of VLAN:
On All Devices Selects all devices in the list.
configured on the network.
Service level for traffic in the VLAN to a level between 1 and 8.
Services field for traffic in the VLAN to a level between 1 and 54.
mode for all traffic in the VLAN.
• Port-based VLAN
• Source IP subnet-based VLAN
• Protocol-based VLAN
• Source MAC address-based VLAN
Creating a source IP subnet-based VLAN
Source IP subnet-based VLANs are supported only on Passport 1000 Series and
Passport 8000 Series switches.
To create a source IP subnet-based VLAN:
1 In the navigation pane, select an STG.
2 Do one of the following:
• From the menu bar, choose Edit > Insert.
• On the toolbar, click Insert.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 86

86 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
The New VLAN dialog box opens (Figure 33).
Figure 33 New VLAN dialog box with bySubnet selected
208963-B
3 Type the VLAN ID.
The value can be from 1 to 4094, as long as it is not already in use. (The
default VLAN has a VLAN ID of 1.)
4 Type the VLAN name (optional).
If no name is entered, a default is created.
5 For a Passport 8600 switch, you the QoS Level (optional)
6 For a Passport 8600 switch, type the Differentiated Services (DS) Field
(optional).
7 For a Passport 1000 Series switch, specify if the VLAN traffic will be tagged
as High Priority (optional).
8 In the Type option, select bySubnet.
Other items in the dialog box that apply to a subnet-based VLAN are
activated.
9 In the Subnet text box, type the source IP subnet address.
Page 87

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 87
10 In the Mask text box, type the IP subnet mask.
11 Select the device to be configured on the VLAN by doing one of the
following:
• Select from the device list.
• Click On All Devices to select all devices in the list.
12 Click Ok.
13 Do one of the following:
• From the VLAN Manager menu bar, choose Apply Changes.
• On the VLAN Manager toolbar, click Apply Changes.
Creating a protocol-based VLAN
To create a protocol-based VLAN:
1 In the navigation pane, select an STG.
2 Do one of the following:
• From the menu bar, choose Edit > Insert.
• On the toolbar, click Insert.
The New VLAN dialog box opens (Figure 34).
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 88

88 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Figure 34 New VLAN dialog box with byProtocolId selected
208963-B
3 Type the VLAN ID.
The value can be from 1 to 4094, as long as it is not already in use. (The
default VLAN has a VLAN ID of 1.)
4 Type the VLAN name (optional).
If no name is entered, a default is created.
5 For a Passport 8600 switch, select the QoS Level (optional)
6 For a Passport 8600 switch, type the Differentiated Services (DS) Field
(optional).
7 For a Passport 1000 Series switch, specify if the VLAN traffic will be tagged
as High Priority (optional).
8 In the Type box, select byProtocolId.
Other items in the dialog box that apply to protocol-based VLANs are
activated.
Page 89

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 89
9 In the ProtocolId box, select the protocol.
If you select UsrDefined, refer to “User-defined protocols in a protocol-based
VLAN” on page 89 for more information.
10 Select the device to be configured on the VLAN by doing one of the
following:
• Select from the device list.
• Click On All Devices to select all devices in the list.
11 Click Ok.
12 In the Ports table, specify the port membership by clicking on one or all of the
following columns and specifying ports:
• ActiveMember
• PotentialMembers
• StaticMembers
• NotAllowedToJoin
13 Do one of the following:
• From the VLAN Manager menu bar, choose Apply Changes.
• On the VLAN Manager toolbar, click Apply Changes.
User-defined protocols in a protocol-based VLAN
You can create a protocol-based VLAN with a user-defined protocol for
integration into existing networks where nonstandard protocols are used.
In the UserDefinedPId text box, enter the PID of the protocol in the format 0x
(protocol type in decimal value).
• For a Passport 8600 switch and Passport 1000 Series switch, the 16-bit PID
assigned to a protocol-based VLAN specifies either an Ethertype, a DSAP/
SSAP, or a SNAP PID, depending on whether the frame encapsulation is
Ethernet 2, 802.2, or LLC-SNAP, respectively.
• For a Passport 8100 switch, the 16-bit PID assigned to a protocol-based
VLAN specifies only an Ethertype for Ethernet 2 frame encapsulation.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 90

90 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Refer to the section on user-defined protocols in Networking Concepts for the
Passport 1000 Series Routing Switch Release 2.0 and Networking Concepts for
the Passport 8000 Series Routing Switch for more information about this topic or
to see the actual values and how they are assigned.
The following PIDs are not valid:
• PID0x0000 through 0x05dc: overlap with the 802.3 frame length
• PIDs of predefined protocols (for example, IP, IPX, AppleTalk)
• PID 0x8100: reserved by 802.1Q to identify tagged frames
• PID0x9000: used by the diagnostic loopback frames
• PID0x8808: used by 802.3x pause frames
• PID0x4242: overlaps with the BPDU DSAP/SSAP
Creating a source MAC address-based VLAN
To create a source MAC address-based VLAN:
1 In the navigation pane, select an STG.
2 Do one of the following:
• From the menu bar, choose Edit > Insert.
• On the VLAN Manager toolbar, click Insert.
The New VLAN dialog box opens (Figure 35).
208963-B
Page 91

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 91
Figure 35 New VLAN dialog box with bySrcMac selected
3 Type the VLAN ID.
The value can be from 1 to 4094, as long as it is not already in use. (The
default VLAN has a VLAN ID of 1.)
4 Type the VLAN name (optional).
If no name is entered, a default is created.
5 For a Passport 8600 switch, select the QoS Level (optional)
6 For a Passport 8600 switch, type the Differentiated Services (DS) Field
(optional).
7 For a Passport 1000 Series switch, specify if the VLAN traffic will be tagged
as High Priority (optional).
8 In the Type option, select bySrcMac.
Other items in the dialog box that apply to source MAC address-based
VLANs are activated.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 92

92 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
9 Select the device to be configured on the VLAN by doing one of the
following:
• Select from the device list.
• Click On All Devices to select all devices in the list.
10 Click Ok.
11 Select the newly created MAC-based VLAN, and choose Edit > Edit Mac
Addresses.
The Edit Mac - VLAN dialog box opens (Figure 36).
Figure 36 Edit Mac - VLAN dialog box
208963-B
12 Select Add From File and enter the file name of the text file containing the
MAC addresses to added to the new MAC-based VLAN.
You can create this file earlier and remember where you saved the text file.
You can use colons (:) or dashes (-) to delineate the MAC address.
13 Click Close.
14 Click Refresh.
Deleting a VLAN
To delete a VLAN:
1 In the navigation pane, select a VLAN and do one of the following:
• From the VLAN Manager menu bar, choose Edit > Delete.
Page 93

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 93
• On the VLAN Manager toolbar, click Delete.
The Delete dialog box opens (Figure 31 on page 82).
2 Click Yes.
Highlighting STGs and VLANs in the Optivity Switch Manager contents pane
Optivity Switch Manager provides dynamic discovery of active STG devices in a
network. From Optivity Switch Manager, you can view the following
information:
• Which ports in the network are configured as unassigned, tagging, or isolated
routing ports (IRPs) and brouter ports
• Which ports are assigned to a particular spanning tree group (STG)
• Which device is the root of an STG, and which ports are in the forwarding and
blocking states.
• Which ports are members of a VLAN or multiple VLANs.
Viewing VLAN members in Optivity Switch Manager
To view the members of a VLAN in Optivity Switch Manager:
1 In the navigation pane, choose a VLAN.
The Ports table opens in the VLAN Manager contents pane.
2 From the VLAN Manager menu bar, choose View > Highlight Topology.
3 Return to the Optivity Switch Manager window.
The highlighted topology view opens in the Optivity Switch Manager
contents pane.
Figure 37 shows that 10.10.40.170 and 10.10.40.235 are members of
VLAN-209.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 94

94 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Figure 37 VLAN topology in the Optivity Switch Manager contents pane
VLAN
members
208963-B
Viewing STG port members
When you select an STG in the VLAN Manager navigation pane, you can view
the devices and ports associated with that STG in the Optivity Switch Manager
network topology map. This view can assist you in troubleshooting by identifying
which ports are already members of the STG selected.
Page 95

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 95
To view STG ports:
1 In the VLAN Manager navigation pane, choose an STG Members icon.
The STG Members table opens in the VLAN Manager contents pane.
2 From the VLAN Manager menu bar, choose View > Highlight Topology.
3 Return to the Optivity Switch Manager window.
The devices containing STG ports are highlighted (Figure 38) with a color
and the device’s IP address. Those device ports that are members of the STG
are outlined in black.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 96

96 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
Figure 38 Viewing STG port members
Some of the
STG port
members
208963-B
Page 97

Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager 97
Viewing STG root configuration
You can get a quick view of which device is the root of the spanning tree group
and which ports are in the forwarding and blocking state by selecting the STG root
icon.
To view STG root configuration in Optivity Switch Manager:
1 In the navigation pane, select an STG Root.
The Root table opens in the contents pane.
2 From the VLAN Manager menu bar, choose View > Highlight Topology.
3 Return to the Optivity Switch Manager window.
The highlighted topology view (Figure 39) opens in the Optivity Switch
Manager contents pane with the root displayed.
Figure 39 Root topology displayed in the Optivity Switch Manager contents pane
STG Root
Forwarding
port
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 98

98 Chapter 4 Using VLAN Manager
In Figure 39, the root of the STG is 10.10.40.153, and the port in forwarding state
is Port 9 on Slot 1 of 10.10.40.32.
Note: Update the View > Highlight topology periodically to refresh the
topology display, because ports may change from forwarding to blocking
and vice versa.
208963-B
Page 99

Chapter 5 Using MultiLink Trunking Manager
MultiLink Trunking is a point-to-point connection that aggregates multiple ports
so that they logically act like a single port with the aggregated bandwidth.
Grouping multiple ports into one logical link allows you to achieve higher
aggregate throughput on a switch-to-switch or server-to-server application.
This chapter describes using MultiLink Trunking Manager to manage single and
multiple device configurations on switches. The chapter includes the following
information:
• What is MultiLink Trunking Manager? (next)
• Starting MultiLink Trunking Manager (page 100)
• MultiLink Trunking Manager window (page 101)
• Using MultiLink Trunking Manager (page 106)
• Managing MultiLink Trunks (MLTs) (page 111)
• Highlighting devices and MLT links in Optivity Switch Manager (page 118)
99
For more information about MLT concepts, refer to Networking Concepts for the
Passport 8000 Series Routing Switch and Networking Concepts for the Passport
1000 Series Routing Switch Release 2.0.
What is MultiLink Trunking Manager?
MultiLink Trunking Manager enables you to configure and monitor MultiLink
Trunks (MLTs) across a single device or two adjacent devices. In MultiLink
Trunking Manager, you can configure an MLT before you physically connect the
ports.
Table 2 7 lists the number of MLTs available with each supported switch type.
Using Optivity Switch Manager, Release 1.1.0.0
Page 100

100 Chapter 5 Using MultiLink Trunking Manager
Table 2 7 Maximum number of MLTs supported in different switches
Switch
Passport 1000 Series switch 8
Passport 8100 switch 6
Passport 8600 switch 32
BayStack 450 switch 6
Business Policy Switch 2000 6
MultiLink Trunking Manager features
MultiLink Trunking Manager supports devices that implement the rcVlan and
rcMlt MIB groups.
MultiLink Trunking Manager allows you to:
Maximum
number of MLTs
• Create, delete, or modify MLTs across one or two devices.
• View MLT configuration information such as port and MLT membership.
• View MLT links in the network topology map.
Starting MultiLink Trunking Manager
To start MultiLink Trunking Manager:
Do one of the following:
• From the Optivity Switch Manager menu bar, choose Tools > MultiLink
Trunking Manager.
• On the keyboard, press [F3].
• On the Optivity Switch Manager toolbar, click the MultiLink Trunking
Manager toolbar button.
The MultiLink Trunking Manager window opens (Figure 40).
208963-B
 Loading...
Loading...