Page 1

Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
Mobile Communication 3100
and Communication Server 1000
Solution Integration Guide
Release: 3.1
Document Revision: 02.01
www.nortel.com
NN49000-315
.
Page 2

Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
Release: 3.1
Publication: NN49000-315
Document release date: 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
While the information in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable, except as otherwise expressly
agreed to in writing NORTEL PROVIDES THIS DOCUMENT "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF
ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. The information and/or products described in this document are
subject to change without notice.
Nortel, Nortel Networks, the Nortel logo, and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
.
Page 3

.
Contents
New in this release 5
Features 5
Other changes 5
Introduction 7
MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment overview 9
CS 1000 engineering for MC 3100 9
Mobile prefix 15
Data Access Planning 15
Licensing requirements 16
Dialing plans and telephone numbers 17
Service DN 18
Universal Extensions 19
Device Handoff key configuration in PBX telephones 20
3
CS 1000 Source Based Routing 13
SIP Gateway CLID Parameters configuration 13
CS 1000 data access considerations 16
Caller ID table 19
CallPilot MWI Configuration 23
MC 3100 and CS 1000 integration 25
Prerequisites 27
Establishing the system baseline 27
Checking the CS 1000 release from Element Manager 29
Checking the CS 1000 release from the command line 29
Integration worksheet 30
MCG 3100 configuration 37
CS 1000 configuration 39
CS 1000 licensing 41
Verifying package requirements 41
Verifying PCA requirements 42
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 4

4
Configuring ISM requirements 43
Printing system license limits 43
NRS configuration 45
Configuring gateway endpoints on the NRS 46
Adding an NRS Routing rule 47
Adding a User Endpoint 49
CS 1000 configuration for client support 53
Configuring features and keys 54
Configuring the Device Handoff key 55
Configuring the TSC steering codes 56
Configuring dial plan parameters 56
Configuring the Digit Manipulation Index 58
Configuring a Route List Index 59
Configuring Call Forward No Answer 59
MCC 3100 configuration 61
Autoconfiguration settings 62
Validate deployment 63
Validating MCG 3100 registration 63
Validating MCC 3100 for BlackBerry communication 64
Validating MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment 64
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 5
.
New in this release
The following sections detail what’s new in Nortel Mobile Communication
3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
(NN49000-315) for Mobile Communication 3100 (MC 3100) Release 3.1.
•
"Features" (page 5)
•
"Other changes" (page 5)
Features
For information on the features, see Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
Fundamentals (NN42030-109).
Other changes
The following changes were made for MC 3100 Release 3.1:
• updated document to reference the MC 3100 Web User Interface
• ECM is no longer used for MC 3100 administration, so this information
was removed. ECM information related to the CS 1000 is contained in
the CS 1000 documentation suite.
5
•
Renamed the MC 3100 Web Console to Web Administration Console.
MC 3100 Release 3.1 supports Nortel Communication Server 1000
Release 5.5 and Release 6.0.
Revision history
October 2009 Standard 02.01. This document is issued to support Nortel Mobile
Communication 3100 Release 3.1.
June 2009 Standard 01.04. This document is up-issued to add technical information in
Table 3.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 6
6 New in this release
April 2009 Standard 01.03. This document is up-issued to add a new section called
"CallPilot MWI Configuration" and to delete the following sections:
•
Installing the ECM MCG 3100 software
•
Adding the MCG 3100 as an element from the primary ECM
•
Upgrading to a different network framework
•
Accessing the MC 3100 Web Console from the ECM
January 2009 Standard 01.02. This document is up-issued to add a new section called "SIP
Gateway CLID Parameters configuration".
December
2008
Standard 01.01. This document is issued to support Nortel Mobile
Communication 3100 Release 3.0 and Nortel Communication Server 1000
Release 5.5.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 7

.
Introduction
This document describes the interworking of the Mobile Communication
3100 (MC 3100) and Communication Server 1000 (CS 1000). The
MC 3100 consists of the Mobile Communication Gateway 3100
(MCG 3100), the MC 3100 Web User Interface (MC 3100 Web UI), and
the clients: Nortel Mobile Communication Client 3100 (MCC 3100) for
BlackBerry, MCC 3100 for Nokia, and MCC 3100 for Windows Mobile.
For information on the MC 3100 solution, see Nortel Mobile
Communication 3100 Fundamentals (NN42040-109), Nortel Mobile
Communication 3100 Planning and Engineering (NN42030-200), and the
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100 Technology Transfer (located in the
MC 3100 product area of w
In this document, the term Enterprise Communication Server (ECS) refers
to the Nortel Communication Server 1000.
7
ww.nortel.com).
Navigation
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Attention: This document assumes a detailed knowledge of
Communication Server 1000 configuration.
•
"MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment overview" (page 9)
• "MC 3100 and CS 1000 integration" (page 25)
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Page 8

8 Introduction
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 9

.
MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment
overview
This section describes the deployment of the Mobile Communication 3100
(MC 3100) with the Communication Server 1000 (CS 1000).
For information on the planning aspects related to the MC 3100
and CS 1000, see Nortel Mobile Communication 3100 Planning and
Engineering (NN42030-200), which covers the following topics:
• Mobile Communication Client 3100 (MCC 3100) deployment
considerations
• Dialing plans and telephone numbers
•
MC 3100 high availability support
•
MC 3100 port tables
• CS 1000 deployment considerations
9
Navigation
•
"CS 1000 engineering for MC 3100" (page 9)
•
"Data Access Planning" (page 15)
•
"Licensing requirements" (page 16)
•
" Dialing plans and telephone numbers" (page 17)
•
"Service DN" (page 18)
• "CallPilot MWI Configuration" (page 23)
• "Universal Extensions" (page 19)
• "Device Handoff key configuration in PBX telephones" (page 20)
CS 1000 engineering for MC 3100
The MC 3100 Web User Interface, MCC 3100 for BlackBerry, MCC 3100
for Nokia, MCC 3100 for Windows Mobile, and MCG 3100 depend on the
following CS 1000 components:
• Call server
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Page 10

10 MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment overview
— Each user requires one Universal Extension (UEXT). Each UEXT
supports the SIP interface on the client. Configure the UEXT with
the Fixed Mobile Convergence Line (FMCL) subtype.The FMCL
subtype requires an Incremental Software Management (ISM)
independent of the Mobile Extension (MOBX) subtype.
— SIP Access Port license
•
SIP Gateway, operating on the VxWorks Signaling Server platform
•
SPS, using the NRS-SPS on the Linux-based NRS.
— Configure each MCG 3100 as a Dynamic Gateway Endpoint with
an endpoint name. Configure the Dynamic Gateway Endpoint with
authentication turned off.
— Each client requires the configuration of an NRS-SPS User
Endpoint (UE). Clients use the UE for user name and password
information, not for SIP routing. Therefore, the NRS-SPS must
never match a destination number against the client UEs (including
the corresponding UEXT Target DN).
The Direct Inward Dial (DID) number for the Dial in Service DN terminates
on the MCG 3100.
Configure the CS 1000 with a mobility prefix to support the client. The
UEXT target DN uses the mobility prefix as a prefix to identify mobile
users. The mobility prefix is a unique digit sequence that does not conflict
with the CS 1000 Universal Dialing Plan (UDP), Coordinated Dialing Plan
(CDP), and routing configuration.
The Multiple Access Directory Number (MADN) is a DN that appears
on multiple terminal numbers (TN). The Multiple Appearance Directory
Number Redirection Prime (MARP) is a designation that is put on one
of the TNs to identify that specific features apply to the DN that is on
multiple TNs should be configured for the group on the TN that is the
MARP. For more information, see
Features and Services Fundamentals
(NN43001-106).
The CS 1000 NRS-SPS supports the Source Based Routing (SBR)
feature. SBR ensures that, for all users of an MCG 3100, the CLID NCOS
and dial plan they see on their mobile phone is consistent with their desk
phone. The SPS routes all MC 3100 call attempts to the user’s home call
server so that those features configured on the home call server can be
applied to the MC 3100 call. For information about Source Based Routing
(SBR), see "CS 1000 Source Based Routing" (page 13).
Figure 1 "Client with CS 1000 and UDP" (page 11) shows an example of
clients using a CS 1000 UDP.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 11
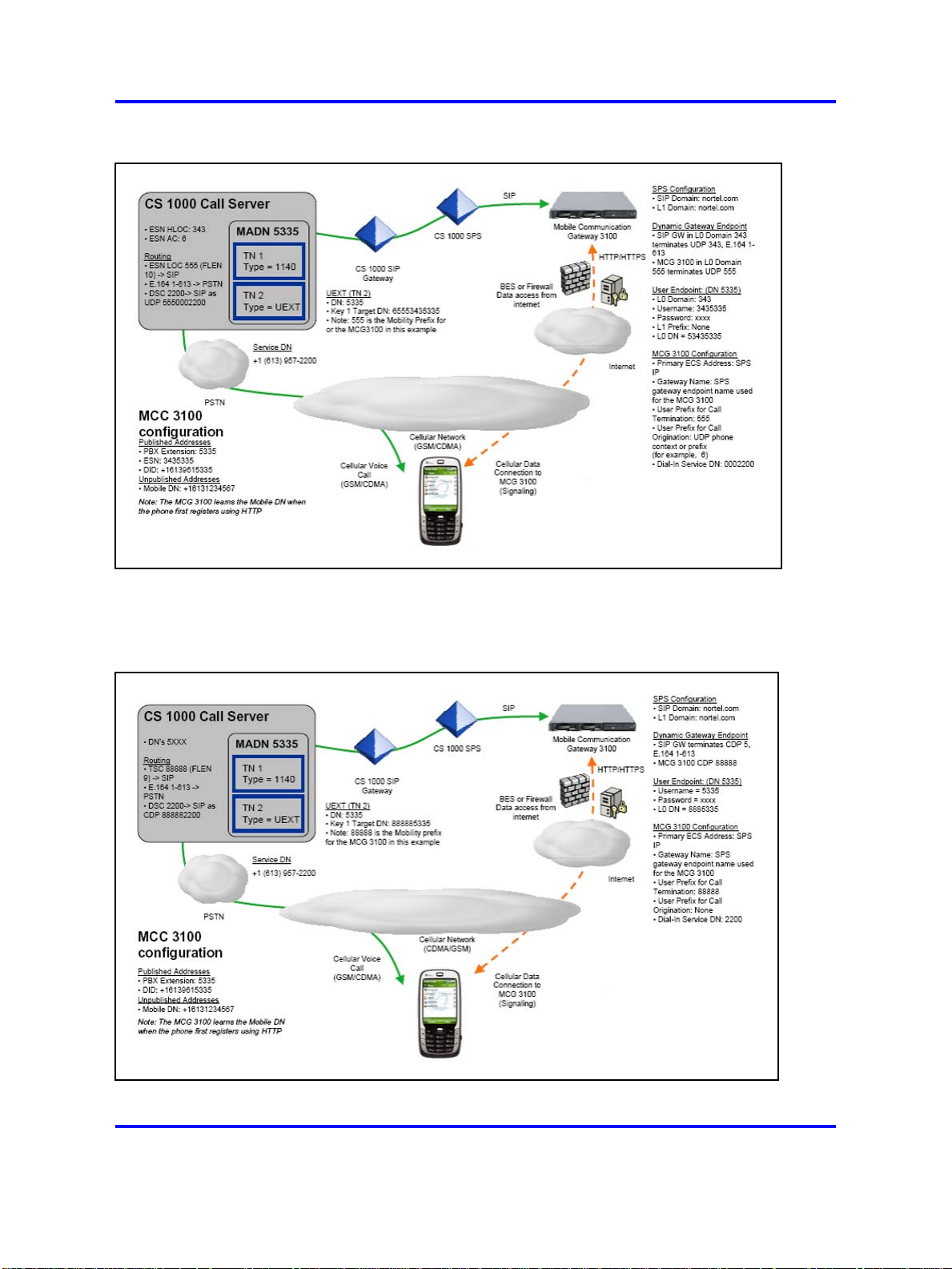
Figure 1
Client with CS 1000 and UDP
CS 1000 engineering for MC 3100 11
Figure 2 "Client with CS 1000 and CDP" (page 11) shows an example of
clients using a CS 1000 CDP.
Figure 2
Client with CS 1000 and CDP
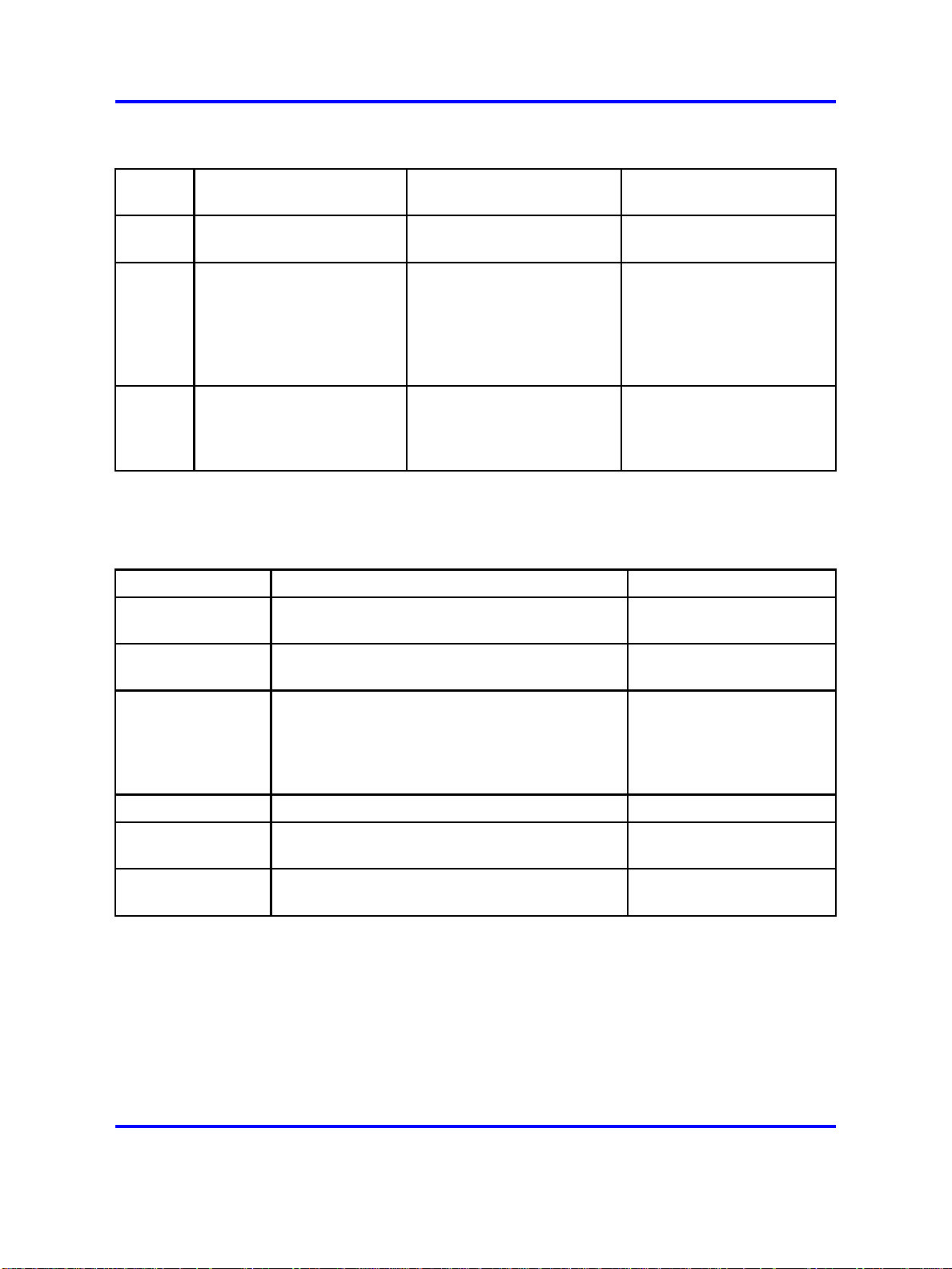
The UEXT configuration requirements are shown in the following table.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 12
12 MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment overview
Table 1
UEXT configuration parameters
Parame
ter
Subtype UEXT subtype; must be
primaryDNOn key 0; this determines
target
DN
Description UDP example
FMCL FMCL
FMCL
5335
the user’s published
addresses for both private
electronic switched network
(ESN) and public direct
inward dial (DID).
Extends the user’s
incoming calls to mobile
clients that are accessible
trough the SIP domain
contributes to an ESN of
3435335 and a DID of
+16139615335
65553435335 888885335
CDP example
5335
contributes to a DN of
3435335 and a DID of
+16139615335
On the NRS-SPS, configure the UE attributes as described in Table 2
"User Endpoint attributes" (page 12).
Table 2
User Endpoint attributes
Parameter Description Example
User name User’s Electronic Switched Network (ESN)
number
3435335
Tandem gateway
endpoint name
L0 DN Based on the user’s directory number (DN).
L1 DN prefix not required
Authentication
enabled
Authentication
password
Endpoint name.
Do not configure this parameter
Cannot match anything in the Coordinated
Dialing Plan or unqualified dialing plan. Can be
the last digit of the mobile prefix with the User’s
ESN DN.
Determines if Authentication is required. Authentication on
The password for authentication
For more information about UEXTs, see Features and Services
Fundamentals – Book 6 of 6 (NN43001-106-B6). For information about
SIP Gateway configuration, see IP Peer Networking Installation and
Commissioning (NN43001-313).
53435335
xxxxxxxx
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 13

CS 1000 Source Based Routing
CS 1000 Source Based Routing (SBR) occurs when the request Uniform
Resource Indicator (URI) of the INVITE message sent from the Mobile
Communication Client 3100 (MCC 3100) or the MCG 3100 contains the
tag x-nt-net-feature=x-nt-home. For example, the following request URI
triggers SBR:
INVITE sip:+16131234567@nortel.com;x-nt-sip-line-service;x-nt-net-featur
e=x-nt-home SIP/2.0
SBR causes the CS 1000 Network Routing Service-SIP Proxy Service
(NRS-SPS) to route the call attempt (INVITE) to the P-Asserted-Id in the
SIP INVITE instead of using the Request URI.
Using SBR means that all calls from a SIP user route to the home call
server for origination, allowing the call server to apply features such as
Calling Line ID (CLID) and Network Class of Service (NCOS) to SIP calls.
In the MCG 3100, use the User Prefix/Phone-context for Call origination
field to configure SBR. For information, see Nortel Mobile Communication
3100 Administration and Security (NN42030-600).
CS 1000 engineering for MC 3100 13
SIP Gateway CLID Parameters configuration
The SIP Gateway CLID parameters are used to adjust the format
of telephone numbers for incoming call appearances. For Mobile
Communication 3100 (MC 3100) these settings impact the format of
numbers that appear on the incoming call popup on the MCC 3100 client.
Figure 3
SIP GW CLID Parameters
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 14

14 MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment overview
For all public calls (subscriber [for example, NXX in North America],
national [for example, NPA in North America], or international) E.164 fully
qualified numbers are used to represent the caller. This is made possible
through the use of the following parameters:
•
Country Code
•
Area Code
•
Subscriber/Number of Digits to strip
• Subscriber/Prefix to insert
•
National/Number of Digits to strip
•
National/Prefix to insert
The E.164 format of subscriber calls (for example, NXX in North America)
is:
+<countrycode><area code><subscriber number>.
The parameters Subscriber/Number of digits to strip and prefix to insert are
used to modify the format of subscriber numbers presented from the PSTN
due to region specific requirements.
The E.164 format of national calls (for example, NPA in North America) is:
• +<countrycode><national number>.
The parameters National/Number of digits to strip and prefix to insert are
used to modify the format of national numbers presented from the PSTN
due to region specific requirements.
Parameter: Country Code
This parameter defines the country code to be used in CLID generation.
Parameter: Area Code
This parameter defines the area code to be used in CLID generation.
Parameter: Subscriber/Number of Digits to strip
For incoming subscriber (NXX) calls this parameter defines the number of
digits to strip from the incoming phone number prior to conversion to E.164
format.
Parameter: Subscriber/Prefix to insert
For incoming subscriber (NXX) calls this parameter defines the prefix to
insert after stripping any digits necessary from the incoming phone number
prior to conversion to E.164 format.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 15

Mobile prefix
Data Access Planning 15
Parameter: National/Number of Digits to strip
For incoming national (NPA) calls this parameter defines the number of
digits to strip from the incoming phone number prior to conversion to E.164
format.
Parameter: National / Prefix to insert
For incoming national (NPA) calls this parameter defines the prefix to
insert after stripping any digits necessary from the incoming phone number
prior to conversion to E.164 format.
Before configuring and deploying the MCC 3100 solution, the administrator
determines the Mobile prefix for the MCG 3100. The mobile prefix is a digit
prefix used to prefix to all calls that will be sent to the MCG 3100. This
includes the target DN number of all UEXTs for MC 3100 users as well as
the service DN calls from MCC 3100 clients. The mobile prefix provides a
unique digit sequence within the SIP domain to route calls to a specific
MCG 3100 that does not conflict with the existing dial plan and routing
configuration for CDP and UDP numbers. If the UEXT target DN did not
have this prefix to distinguish MCC 3100 calls, the UEXT extended SIP
calls would loop back to the UEXT.
mobile prefixes have the following requirements:
• One mobile prefix is required per gateway.
•
On the call server you must configure
— The dial plan to send all calls with this prefix to the NRS.
— All UEXT’s for MCC 3100 users must have a target DN with
the prefix of the MCG 3100 to which their MCC 3100 client is
registered.
— The incoming service DN call must have its digits manipulated so
that the PSTN number dialed for the service DN is mapped to a
number prefixed by the mobile prefix. This mapping will trigger the
NRS to send this call to the MCG 3100 and the MCG 3100 will strip
this prefix as with any other mobile prefix prefixed call to reveal the
service DN configured on the MCG 3100.
•
The NRS must have a routing rule to send all calls with this prefix to
the MCG 3100.
• The mobile prefix is configured on the MCG 3100 in the User Prefix
for Call Termination field.
Data Access Planning
This section describes things to consider when planning data access.
• "CS 1000 data access considerations" (page 16)
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Page 16

16 MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment overview
CS 1000 data access considerations
The MCG 3100 requires data access to the TLAN of the CS 1000. The
MCG 3100 uses the CS 1000 SPS as the SIP Signaling Proxy. The media
for all calls to and from MCC 3100 clients is anchored on the MCG 3100.
The MCG 3100 will accept or transmit RTP to any IP endpoint within the
enterprise (e.g. Media Cards, Other SIP clients, IP sets).
Example
If an UNISTIM set calls a user answering through the MCC 3100 on the
mobile phone the RTP for the active call will be between the MCG 3100
and IP set directly and then forwarded from the MCG 3100 to the CS 1000
media gateway (for the trunk call to the mobile phone)
Careful consideration is required based on the data network and security
requirements of the Enterprise to allow the public internet traffic to
reach the MCG 3100 from the clients while at the same time giving the
MCG 3100 access to the TLAN of the CS 1000 for SIP and RTP.
Licensing requirements
Communication Server licensing requirements
• Requires CS 1000 Release 5.5
• Uses SIP Access Port Licenses for CS 1000 SIP infrastructure support
•
Requires 1 Universal Extension (UEXT) for each MCC 3100 user. The
UEXT is configured with the Fixed Mobile Convergence Line (FMCL)
subtype.
MCC 3100 licensing requirements
•
Each MCC 3100 client requires a license.
• Each license key can only be used once per user.
•
The MCC 3100 licenses are installed on the MCG 3100.
The MCG 3100 allocates the license on a first come, first served basis as
the MCC 3100 registers with the MCG 3100.
• There is no requirement to distribute licenses to each end user.
• The MCG 3100 administrator can revoke licenses on a per user basis,
if necessary, to reclaim user licenses.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 17

Dialing plans and telephone numbers
MC 3100 supports telephone numbers in the following formats
• Dial strings, where the user enters all the digits to be dialed. Examples
of dial strings include 2356, 63432356, 93432356 and 3432356.
• E.164 Fully Qualified International Numbers, where telephone
numbers start with the plus (+) symbol. E.164 Fully Qualified
International Numbers are also known as "plus numbers". Examples
of Fully Qualified International Numbers include +16131234567 and
+31123456789.
The dial plan available from MC 3100 should be the same as the dial plan
for a desk telephone. That is, if the user has a desk telephone and an
MCC 3100 device, the dial plan should be the same.
MC 3100 users should use the E.164 Fully Qualified International Numbers
for all stored Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) numbers in
address books and mobile device applications. By using this format, the
numbers can be dialed from any region or country, within the wireless
network or from the communication server.
Dialing plans and telephone numbers 17
The E.164 Fully Qualified International Numbers ensure that users do not
need to be concerned about dial prefixes or long distance codes. The
network determines how to place the call, based on the user’s location and
network connection.
When the user dials an E.164 Fully Qualified International Number, the
communication server puts the number in the request Uniform Resource
Indicator (URI) of the SIP INVITE message in the following format
sip: +CCCXXXXXXXX@domain; user=phone.
When using the ECS, configure the CNTC, NATC, and INTC parameters
in LD 15 to support E.164 Fully Qualified International Numbers. These
parameters ensure that fully qualified numbers within the same country
are dialed as national numbers, and international numbers are prefixed
correctly.
Example 1 (Switzerland)
ECS is Nortel Communication Server 1000 (CS 1000)
AC1=0, CNTC=41, NATC=0, INTC=00
Call to a number within Switzerland
A user initiates a call to a contact with the phone number +41123456789.
The URI incoming for the SIP INVITE for the call is
sip:+41123456789@domain.com;user=phone
CS 1000 digit processing strips the CNTC and adds <AC1 + NATC> to
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 18

18 MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment overview
produce 00123456789
Call to a number outside Switzerland
A user initiates a call to a contact with the phone number +14161234567.
The URI incoming for the SIP INVITE for the call is
sip:+14161234567@domain.com;user=phone
CS 1000 digit processing adds <AC1 + INTC> to produce
00014161234567
Example 2 (North America)
ECS is CS 1000
AC1=6, CNTC=1, NATC=1, INTC=011
Call to a number within North America
A user initiates a call to a contact with the phone number +14161234567.
The URI incoming for the SIP INVITE for the call is
sip:+14161234567@domain.com;user=phone
Service DN
CS 1000 digit processing strips the CNTC and adds <AC1 + NATC> to
produce 614161234567
Call to a number outside North America
A user initiates a call to a contact with the phone number +41123456789.
The URI incoming for the SIP INVITE for the call is
sip:+41123456789@domain.com;user=phone
CS 1000 digit processing adds <AC1 + INTC> to produce
601141123456789.
The mobile clients use a Service DN to originate calls in direct outbound
mode. The CS 1000 must route the calls to the SPS in the following
format:
<mobile prefix><service DN>
In the following example, 88888 is the mobile prefix and 2200 is the
service Directory Number (DN).
Example: sip:888882200@nortel.com
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 19

Configure the mobile prefix on the MCG 3100 gateway configuration tab as
the incoming prefix for call termination. Configure the Service DN field on
the MCG 3100 gateway configuration with the service DN.
Universal Extensions
A CS 1000 Universal Extension (UEXT) represents each mobile client
instance.
The Primary DN of the UEXT determines the user’s published addresses:
both private electronic serial number (ESN) and public direct inward dialing
DID (for example, Primary DN: 5335 contributes to the ESN address
3435335 and DID address +16139675335).
The mobile prefix is a prefix to all mobile user identities on the UEXT
target DN. The mobile prefix provides a digit sequence that is unique
within the SIP domain to identify a mobile client that does not conflict with
the existing dial plan and routing configuration for their CDP and UDP
numbers.
The Target DN of the UEXT extends the user’s incoming calls to mobile
clients that are accessible through SIP domain. A typical setup would be
AC1 + (mobile prefix) + the user’s ESN number (for example, Target DN:
65553435335).
Universal Extensions 19
Attention: It can be necessary to increase the Forward No Answer
(FNA) timeout for mobile client users. The UEXT extends all calls to the
MCG 3100. The MCG 3100 then presents the incoming call to the MCC
3100 clients over the cellular data channel of the MCC 3100 (using HTTP
or /HTTPS). It can take a few seconds for the data transmission to reach
the client depending on the current state of the mobile phone. If the FNA
timeout is too short users do not have reasonable time to (potentially log
on) and answer the call before the call server invokes FNA and sends the
call to the FNA destination.
Caller ID table
All CS 1000 telephones use the Caller ID table. The Caller ID table is
required for the MCC 3100 to correctly build the Caller ID (CLID) for both
Private network and Public network calls from a number or extension.
Outgoing SIP calls from the MCG 3100 on behalf of the mobile client
use the CLID table configured against the Multiple Appearance Directory
Number Redirection Prime (MARP) TN in the Multiple Access Directory
Number (MADN) group of the MCC 3100 user.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 20

20 MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment overview
Device Handoff key configuration in PBX telephones
To allow an MCC 3100 user to perform Device Handoff between the
MCC 3100 and PBX telephone, a Handoff key must be configured on
the desktop telephone. The MCC 3100 uses the same configuration and
same user interface for device handoff as the Mobile Extension feature
introduced in CS 1000 Release 5.5.
Only one handoff key can be configured for a desktop telephone. Once
configured, the key label on the telephone shows “Handoff” as the text
display for the device handoff key.
Attention: Nortel M3902 telephones do not display the key label for
Handoff key. This label needs to be configured manually on the telephone.
Sample configuration from LD 11:
REQ: PRT
TYPE: 3904
TN4073
DATE
PAGE
DES DESK
TN 004 0 07 03 VIRTUAL
TYPE 3904
CDEN 8D
CTYP XDLC
CUST 0
ERL 0
FDN
TGAR 0
LDN NO
NCOS 7
SGRP 0
RNPG 0
SCI 0
SSU
XLST
SCPW
SFLT NO
CAC_CIS 3
CAC_MFC 0
CLS UNR FBD WTA LPR MTD FND HTD TDD HFA GRLD CRPD STSD
MWD LMPN RMMD SMWD AAA IMD XHD IRD NID OLD VCE DRG1
POD DSX VMD SLKD CCSD SWD LND CNDA
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 21

Device Handoff key configuration in PBX telephones 21
CFTD SFD MRD DDV CNID CDCA MSID DAPA BFED RCBD
ICDD CDMD LLCN MCTD CLBD AUTU
GPUD DPUD DNDA CFXA ARHD CLTD ASCD
CPFA CPTA ABDD CFHD FICD NAID DNAA BUZZ
UDI RCC HBTD AHD IPND DDGA NAMA MIND PRSD NRWD NRCD NROD
DRDD EXR0
USMD USRD ULAD CCBD RTDD RBDD RBHD PGND FLXD FTTC DNDY DNO3
MCBN
FDSD NOVD CDMR MCDD T87D PKCH
CPND_LANG ENG
HUNT
PLEV 02
DANI NO
AST
IAPG 0
AACS NO
ITNA NO
DGRP
MLWU_LANG 0
MLNG ENG
DNDR 0
KEY 00 SCR 7771 0 MARP
ANIE 0
01 HNDO
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 TRN
18 AO6
19 CFW 16
20 RGA
21 PRK
22 RNP
23
24 PRS
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 22

22 MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment overview
25 CHG
26 CPN
27 CLT
28 RLT
29
30
31
DATE 25 MAR 2008
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 23

.
CallPilot MWI Configuration
For CallPilot to send message waiting indicator (MWI) notifications to the
mobile clients, you must configure CallPilot with an alternate DN against
the primary DN for the user. The alternate DN must be equal to the UEXT
target DN used to extend SIP calls to the mobile clients. The format is:
<mobile prefix><MCC 3100 username>
Example: 888881234567
When CallPilot sends the Message Waiting Indicator (MWI) notification,
the following series of events occurs:
1. CallPilot sends the notification to the CS 1000.
2. The CS 1000 sends the notification (an unsolicited SIP message) to
the SPS and on to the MCG 3100.
3. The MCG 3100 sends the MWI notification using HTTP or HTTPS over
the cellular data channel to the mobile client.
23
Attention: In order to support MWI for MC3100 it is necessary to enable
the Premium Service and NMS packages (175, 219). Refer CallPilot
documentation for details on when these packages are required to be
determined for your specific configuration.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 24

24 CallPilot MWI Configuration
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 25

.
MC 3100 and CS 1000 integration
This section describes the tasks required to get the Nortel Mobile
Communication 3100 (MC 3100) working with Communication Server 1000
(CS 1000).
MC 3100 and CS 1000 integration workflow
Figure 4 "MC 3100 and CS 1000 integration workflow" (page 25) shows
the steps required to integrate the MC 3100 and CS 1000.
Figure 4
MC 3100 and CS 1000 integration workflow
25
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 26

26 MC 3100 and CS 1000 integration
Work flow navigation
•
"Prerequisites" (page 27)
• "MCG 3100 configuration" (page 37)
•
"CS 1000 configuration" (page 39)
•
"MCC 3100 configuration" (page 61)
• "Validate deployment" (page 63)
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 27

.
Prerequisites
This section describes the prerequisites for Mobile Communication 3100
(MC 3100) and Communication Server 1000 (CS 1000) integration.
Navigation
•
"Establishing the system baseline" (page 27)
• "Integration worksheet" (page 30)
Establishing the system baseline
To successfully integrate voice services, you must first establish the
system baseline for the CS 1000 and MC 3100 systems so that the
systems are configured and working in a stand-alone environment. Use
the following table to complete system baselines before integration.
27
Task Reference
CS 1000
The Network Numbering Plan
is implemented.
CS 1000 software is Release
5.5.
Basic installation, setup, and
configuration of the Call Server
components are complete.
Dialing Plans: Description
(553-3001-183)
Communication Server 1000M
and Meridian 1: Large System
Installation and Configuration
(553-3021-210)
Communication Server 1000S:
Installation and Configuration
(553-3031-210)
Communication Server 1000E:
Installation and Configuration
(553-3041-210)
Comments
Are you using a Unified Dialing
Plan (UDP) or a Coordinated
Dialing Plan (CDP), or both?
To check the release level, see
"Checking the CS 1000 release
from Element Manager" (page
29) or "Checking the CS 1000
release from the command
line" (page 29).
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 28

28 Prerequisites
Task Reference
The CS 1000 must have the
latest DEP List loaded.
Nortel Mobile Communication
3100 Release Notes
(NN42030-404) (Updates
through Product Bulletins)
SIP Proxy Server (SPS)
SPS software is CS 1000
Release 5.5.
SPS must have the latest SU
loaded
Nortel Mobile Communication
3100 Release Notes
(NN42030-404) (Updates
through Product Bulletins)
MC 3100
Mobile Communication 3100 is
Release 3.0.
If using BlackBerry devices
and the BlackBerry Enterprise
Server (BES), the devices and
BES must have the BlackBerry
Mobile Data Service (MDS)
enabled and the devices
must be able to access the
Fully Qualified Domain Name
(FQDN) or IP address of the
MCG 3100.
Comments
If using mobile devices from
the cellular data network (no
BES), the MCG 3100 requires
am internet-accessible FQDN
and IP address.
MCG 3100 must be able to
access the CS 1000 TLAN
through the firewall.
The MC 3100 must have the
latest patches applied.
MCG 3100 license file installed
to enable MCC 3100 clients
MCG 3100 ports must be
accessible through the firewall.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Nortel Mobile Communication
3100 Release Notes
(NN42030-404) (Updates
through Product Bulletins).
Nortel Mobile Communication
3100 Installation and
Commissioning (NN42030-300)
Nortel Mobile Communication
3100 Planning and Engineering
(NN42030-200)
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Page 29

Establishing the system baseline 29
Checking the CS 1000 release from Element Manager
Use this procedure to check the version of the CS 1000 using Element
Manager.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1
2
Log on to Element Manager.
On the left navigation pane, select Home.
The Home System View page appears.
3
In the Call Server section, the software release is referred to as
Release.
--End--
Checking the CS 1000 release from the command line
Use this procedure to check the version of the CS 1000 using the
command line.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1
2
Log in to the Signaling server or the Enterprise Common
Manager server using the nortel account.
Enter the following command
swVersionShow
The installed software applications and version numbers are
displayed. For an example, see the following figure.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 30

30 Prerequisites
Figure 5
swVersionShow example
--End--
Integration worksheet
Use the following worksheet to capture values that you require during the
integration of MC 3100 and CS 1000. Some of these values will not be
applicable to your system, depending on your CS 1000 dialing plan.
Table 3
Integration worksheet
Related to Dial plan
type
CS 1000
UDP
Parameter Example Value Description
SIP Domain nortel.com
L0 Domain CDP
L1 Domain UDP
ESN mobile
prefix
ESN AC
ESN LOC
FLEN
DSC
E.164
Service DN 1.614E+10
343
6
555
10
2200
1-613
CDP
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
SIP Domain nortel.com
L0 Domain CDP
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 31

Integration worksheet 31
Related to Dial plan
type
NRS
NRS—UDP
Route
Parameter Example Value Description
TSC
FLEN
E.164
DSC
88888
9
1-613
2200
Service DN 1.614E+10
Gateway
MCG3100 Add a gateway endpoint
Endpoint Id
Call Signaling
IP
192.167.13
0.75
This should be the IP of
the MCG once it registers
as a Dynamic Endpoint.
DN Prefix
555
DN Type Private
level 1 reg
ional (UDP
steering
code)
Route Cost
SIP URI
1
UDP
Phone
Context
NRS—CDP
Route
User
Endpoint—U
DP
User
Endpoint—C
DP
DN Prefix
88888
DN Type Private
level 0 reg
ional (CDP
steering
code)
Route Cost
SIP URI
1
CDP.UDP
Phone
Context
L0 Domain
Username
Password
343
3435335
xxx
L1 Prefix None
L0 Domain
Username
Password
L0 DN
53435335
5335
xxxx
8885335
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 32

32 Prerequisites
Related to Dial plan
type
MCG 3100
Parameter Example Value Description
Primary
Gateway
Address
192.167.13
0.75
The IP address that
the local MCG 3100
uses for SIP traffic. This
parameter is unique to
the local server.
Secondary
Gateway
Address (if
applicable)
192.167.13
0.76
The IP address that
the local MCG 3100
uses for SIP traffic. This
parameter is unique to
the local server.
Primary and
Secondary
Gateway SIP
Port
5060
The SIP server port. The
default value is 5060.
This parameter applies
to both servers in the
redundant configuration.
Domain
mcg3100.c
om
The SIP registration
domain defined on
the Enterprise Call
Server (ECS). This
parameter applies to both
servers in the redundant
configuration.
MCG 3100
(continued)
Gateway
Name
Primary ECS
Address
Secondary
ECS Address
MCG3100 The gateway identity
defined on the ECS for
the MCG 3100. This
parameter applies to both
servers in the redundant
configuration.
192.167.10
7.8
The IP address and
port of the primary ECS.
Format: <IP address>
:<port>
192.167.10
7.9
The IP address and port
of the secondary ECS.
Format: <IP address>
:<port>
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 33

Integration worksheet 33
Related to Dial plan
type
MCG 3100
(continued)
MCG 3100
(continued)
Parameter Example Value Description
Phone-context
for Call
Origination
CDP: NoneUser Prefix /
UDP: udp
The user name prefix
or phone context for
call origination. This
prefix applies to calls
originated by the MCG
3100 server and to the
calling address.
User Prefix
for Call
Termination
CDP: 8888
8
UDP: 555
The user name prefix
for call termination. This
prefix applies to calls
received by the MCG
3100 server and to the
called address.
Dial-In ServiceDNCDP: 2200 Enter the Service
Directory Number (DN)
for client calls that will
arrive at the MCG3100
on the SIP network. This
field is mandatory. The
Service DN allows MCC
3100 for BlackBerry,
MCC 3100 for Windows
Mobile, and MCC 3100
for Nokia users to place
calls directly from their
wireless devices to other
parties using Direct
Outbound call mode.
The PSTN numbers
that are dialed by the
mobile on the PSTN are
defined on the device
configuration page.
When the call arrives
at the enterprise the
PSTN number must be
converted to an internal
format for use on the
SIP network, routed by
the NRS, and which will
eventually arrive at the
MCG3100.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 34

34 Prerequisites
Related to Dial plan
type
Parameter Example Value Description
Mobility Prefix
Username 343XXXX The account use name
Password XXXXXXX The account password on
Outgoing Call
Service DN
555
+41123456
789
on the enterprise
network.
the enterprise network
The mobile phone will dial
+41123456789 for direct
outbound calls. This
PSTN number will be
routed to the enterprise
as a DID number. When
the number arrives at
the Enterprise we must
manipulate the PSTN
number (+41123456789)
to be routed on the SIP
network.
Attention: If you
have a mapping on
the incoming trunk
route on the call
server to map a PSTN
service DN number:
+41123456789 to
5550006789, you
would configure the
service DN on the
MCG3100 as 0006789.
In the case where
an enterprise has
multiple service DN’s
all incoming PSTN
service DN calls must
map to the single
service DN number
configured in this field.
Example:+1613132
For
4567 to 5550006789.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 35

Integration worksheet 35
Related to Dial plan
type
MCC 3100
Parameter Example Value Description
Mobile Contac
t
+41123456
789
Connection details for
the primary Enterprise
mobility gateway (EMG).
Username
3435335
The account use name
on the enterprise
network.
Password XXXXXXX The account password on
the enterprise network.
Outgoing Call
Service DN
+1 (613)
957-2200
The service directory
number that enables you
to place calls in Direct
Outbound mode.
Mobile
Contact
+16131234
567
Enter your mobile phone
number or accept the
auto populated value.
Include the country code
prefix.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 36

36 Prerequisites
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 37

.
MCG 3100 configuration
Install the MCG 3100 as described in Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
Installation and Commissioning (NN42030-300), taking into consideration
the following configuration requirements:
•
When configuring the Gateway Settings:
— The User Prefix for Call Termination field which is related to the
mobile prefix. For more information, see "Mobile prefix" (page 15).
— The Dial-In Service DN field must be configured. The Dial-In
Service DN configured on the MCG 3100 is the digits left over
after the mobile prefix is stripped from the incoming call to the
MCG 3100. As noted in "Mobile prefix" (page 15), all calls to the
MCG3100 from the NRS have this prefix. After stripping off this
prefix, you either have an MCC 3100 user name in the case of a
call extended from the UEXT, or in the other case what is left over
after the mobile prefix is stripped is the service DN.
•
When configuring the Device Configurations, ensure that the Service
Number matches the Dial-In Service DN in the Gateway Settings.
37
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 38

38 MCG 3100 configuration
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 39

.
CS 1000 configuration
This section describes the configuration required on the Communication
Server 1000 (CS 1000).
CS 1000 configuration workflow
CS 1000 configuration requires a number of tasks to be completed, as
shown in the following figure.
Figure 6
CS 1000 configuration work flow
39
Work flow navigation
•
"CS 1000 licensing" (page 41)
• "NRS configuration" (page 45)
• "CS 1000 configuration for client support" (page 53)
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Page 40

40 CS 1000 configuration
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 41

.
CS 1000 licensing
This section describes the tasks required for Communication Server 1000
(CS 1000) licensing.
CS 1000 licensing task flow
Figure 7
CS 1000 licensing task flow
41
Task flow navigation
•
"Verifying package requirements" (page 41)
• "Verifying PCA requirements" (page 42)
• "Configuring ISM requirements" (page 43)
• "Printing system license limits" (page 43)
Verifying package requirements
Follow this procedure to verify the Fixed Mobile Convergence Line (FMCL)
Universal Extensions (UEXT) package.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Page 42

42 CS 1000 licensing
Procedure steps
Step Action
1
2 Press enter.
3 Enter the following command to log in to the system.
Connect to your call server.
LOGI admin2
4 Enter the Level 2 password.
5
Enter the following command.
LD 22
6
7 At the TYPE prompt, enter PKG
8
At the REQ prompt, enter PRT
From the results, ensure that Packages 414, 412, 398, and 145
are listed.
Verifying PCA requirements
Use this procedure to verify that the PCA feature is enabled.
Procedure steps
--End--
Step Action
1
2 Press enter.
3
Connect to the call server command line.
Enter the following command to log in to the system.
LOGI admin2
4 Enter the Level 2 password.
5 Enter the following command.
LD 21
6 At the REQ prompt, enter PRT
7 At the TYPE prompt, enter FTR
8 At the PCA prompt, ensure that it is configured to ON.
If the PCA is not on, it must be turned on.
--End--
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Page 43

Configuring ISM requirements
ISM counts are created for each of the Universal Extension subtypes,
according to the following table.
Printing system license limits 43
Universal Extension UXTY
MOBX Mobile Extensions Implemented by this feature
TLSV Telephony Services Microsoft OCS 2007 support
FMCL Converged Mobile Users MC 3100 clients
SIPN Nortel SIP Lines Support for SIP phones made
SIP3 Third Party SIP Lines Support for SIP phones not
ISM
Description
by or for Nortel
made for Nortel
Each mobile user consumes a license out of the total FMCL ISM count.
The FMCL ISM count will be decremented and incremented when a UEXT
is configured as an FMCL unit (when UXTY prompt is configured as
FMCL).
Verify that sufficient ISMs are licensed for your system, using LD 22 (REQ
SLT).
Printing system license limits
When REQ is configured to SLT in LD 22, system License limits are
printed. You can update the value of License limits either through sysload
or the Instant Software License feature. You can print the new License
limits through LD 22 after the update is complete.
In the License limits printout, three parameters are printed for each
License
• The first parameter is the License limit
•
The USED parameter is the number of configured units.
•
The LEFT parameter is the difference between the License limit and
the USED value (LEFT = License limit - USED).
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 Connect to your call server.
2 Press enter.
3
4 Enter the Level 2 password.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Enter the following command to log in to the system:
LOGI admin2
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Page 44

44 CS 1000 licensing
5
Enter the following command:
LD 22
6
7 From the results, ensure from the LEFT parameter that you have
At the REQ prompt, enter SLT
the necessary ISMs available.
--End--
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 45

.
NRS configuration
The Mobile Communication Gateway 3100 (MCG 3100) is defined as a
Dynamic Gateway Endpoint on the Network Routing Server (NRS) SIP
Proxy Server (SPS) and is assigned an endpoint name. Authentication
is turned off. The endpoint name is configured on the MCG 3100 as the
gateway name under the list of gateway configuration parameters.
Each Mobile Communication Client 3100 (MCC 3100) or MC 3100 Web
User Interface user is represented by an NRS-SPS User Endpoint (UE).
The UE is created in the L0 domain that corresponds to the Private Branch
Exchange (PBX) that hosts the user. The NRS-SPS must be configured
so that the NRS-SPS will never match a destination number against the
UE that represents an MCC 3100 (not even the corresponding Universal
Extension [UEXT]).
The user endpoint entry on the NRS-SPS for MCC 3100 defines the
username and corresponding password only, and is not used for SIP
routing.
45
All calls to the MCG 3100 are prefixed with the mobile prefix. A routing rule
is associated with the MCG 3100 endpoint to route all calls with this prefix
to the MCG 3100. This routing rule, and not the user endpoints, ensures
calls route to the MCG 3100.
NRS configuration task flow
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Page 46

46 NRS configuration
Figure 8
NRS configuration task flow
Task flow navigation
•
"Configuring gateway endpoints on the NRS" (page 46)
• "Adding an NRS Routing rule" (page 47)
• "Adding a User Endpoint" (page 49)
Configuring gateway endpoints on the NRS
Perform the following procedure to configure the MCG gateway endpoints
on the Network Routing Service (NRS). You must perform this procedure
for each MCG node on the system.
On NRS redundant systems, perform all configuration on the primary NRS.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 Open NRS Manager by doing one of the following:
In Element Manager, select Dialing and Numbering Plans,
Network Routing Service.
OR
In Internet Explorer, enter the IP address of the NRS into the
address bar.
2 Select the Configuration tab.
3 Click set Standby DB view to switch from active to standby
database view.
4 Click Gateway Endpoints.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 47

Adding an NRS Routing rule 47
5
Ensure that the correct service domain, L1 domain, and L0
domain are selected and click Add.
The View Gateway Endpoint Property page appears.
6 For Endpoint name, type a relevant endpoint name.
Example: MCG3100
7
8
9 Ensure that Tandem Gateway Endpoint name is configured to
For Endpoint description, type a relevant endpoint description.
Clear the Trust Node check box.
Not Configured.
10 Ensure that Endpoint Authentication Enabled is configured to
Authentication Off.
11
12
13
14 Click Save.
15 Click Cut over.
For SIP support, select Dynamic SIP endpoint.
For SIP transport, select the transport protocol type.
Type a value for the SIP port, or leave the default value of 5060.
The Cut over command is issued, and the database is placed
into a Switched over state.
16
In the NRS Manager Navigator, select System, Database.
The Database Web page opens. The Database status is
Switched over.
17
Select Commit.
The Commit command is issued, and the database is placed into
a Committed state.
Adding an NRS Routing rule
Use this procedure to create an NRS Routing rule to route calls to the
MCG 3100.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 Log in to the ECM system.
2 Launch the NRS Element.
The NRS interface opens.
--End--
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 48

48 NRS configuration
3
In the NRS Manager Navigator, select Numbering Plans,
Routes.
The Routes web page opens.
4 Ensure Standby database is selected.
5 The Limit results to Domain drop-down lists, in the Search for
Routing Entries pane, contain configured Service Domains, L1
Domains and L0 Domains. Select a Service Domain,anL1
Domain and an L0 Domain from the respective drop-down lists.
6 Select a Gateway Endpoint from the Endpoint Name drop-down
list in the Search for Routing Entries pane.
7
8 Click Add.
Click Routing Entries.
The Add Routing Entry web page opens.
9
Select the DN type from the DN Type drop-down list.
The six choices are E.164 international, E.164 national, E.164
local (subscriber), Private level 1 regional (UDP location code),
Private level 0 regional (CDP steering code), and Private special.
10
Enter the DN prefix in the text box.
The DN prefix can include 0-9, #, -, ?. The prefix can be up to
30 characters in length; however, the first character must be
numeric.
11 Enter the Route cost in the text box.
The range is 1-255. The cost must be numeric and can be up to
three digits in length. The Route Cost is used to define least-cost
routing. Higher numbers indicate higher costs.
12 Click Save.
The standby database is updated. The Routes web page opens,
displaying the newly added routing entry in the Routing Entries
pane.
13 In the NRS Manager Navigator, select System, Database.
The Database Web page opens
14 Click Cut over.
The Cut over command is issued, and the database is placed
into a Switched over state.
15
In the NRS Manager Navigator, select System, Database.
The Database Web page opens. The Database status is
Switched over.
16 Select Commit.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 49

The Commit command is issued, and the database is placed into
a Committed state.
Adding a User Endpoint
Use this procedure to add a user endpoint to the NRS.
Each mobile client instance is represented by a User Endpoint (UE).
Create the UE in the L0 domain that corresponds to the PBX that hosts the
user. A typical UE attribute configuration is as follows:
• User name: user’s Electronic Switched Network (ESN) number (for
example, 3435335)
•
Tandem gateway endpoint name: (do not configure) none
• L0 directory number (DN): a number based on the user’s DN that can
never match in the Coordinated Dialing Plan (CDP) or Universal Dialing
Plan (UDP). This can be the last digit of the mobile prefix + User’s ESN
DN (for example, 53435335).
•
L1 directory number (DN) prefix: (not required) none
Adding a User Endpoint 49
--End--
• Authentication enabled: Authentication on
•
Authentication password: xxxxxxx
The MCG 3100 registers as a gateway endpoint. As each client logs on,
the MCG 3100 uses the user account on the CS 1000 to validate the
password of the user. Call routing does not use SIP registration.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 In the NRS Manager Navigator, select Numbering Plans,
2 Ensure that the Standby database is selected.
3 The Limit results to Domain menu contains configured Service
4 Click the User Endpoints button. The Endpoints Web page
5 Click the Add button. The Add User Endpoint Web page opens.
Endpoints. The Endpoints Web page opens.
Domains, L1 Domains and L0 Domains. Select a Service
Domain, a L1 Domain and a L0 Domain from the respective
drop-down lists.
displays a list of configured User Endpoints in the Endpoints
pane.
6 Configure the User Endpoint, using the Job Aid.
7 Click the Save button.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 50

50 NRS configuration
The standby database is updated. The Endpoints Web page
opens, showing the newly added User Endpoint in the User
Endpoints pane.
8
If required, click
Add to add additional User Endpoints. The User
Endpoints Web page displays any new endpoints.
Attention: A maximum of 100 user endpoints can be displayed
on the User Endpoints Web page.
Attention: On login, the MCC 3100 users validate their
password against the NRS; however they never will show as
registered against the NRS. To view user status, refer to the
User Info tab on the MCG 3100 Web administration interface.
9
In the NRS Manager Navigator, select System, Database. The
Database Web page opens.
10
Click the Cut over button. The Cut over command is issued, and
the database is placed into a Switched over state.
11 In the NRS Manager Navigator, select System, Database. The
Database Web page opens. The Database status is Switched
over.
12 Select the Commit button.
The Commit command is issued, and the database is placed into
a Committed state.
Job Aid
The following table to understand the Add User Endpoint Web page fields.
Field Description
User name
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Enter a User name for the endpoint. The endpoint’s user name must be
alphanumeric (a…z, A…Z, 0…9) and can be up to 30 characters in length.
The user name, together with the Service Domain names, becomes a
string that is used to build the user’s SIP URI.
Frequently, this field is configured with the user’s extension number.
Example
5340
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
--End--
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Page 51

Field Description
Adding a User Endpoint 51
User endpoint
description
Trust Node
Tandem gateway
endpoint name
L0 directory number
(DN)
L1 directory number
(DN) prefix
E.164 local directory
number (DN) prefix
E.164 Area Code
E.164 Country Code
Authentication
enabled
The endpoint’s description can use most keyboard characters (except
single quotes) and can be up to 120 characters in length.
Frequently, this field is configured with the user’s name.
Example
John Smith
The checkbox should be cleared.
Configure the field to Not Configured.
This field is a number that is based on the user’s directory number. The
number cannot match entries in the dial plan.
Leave as default.
Leave as default.
Leave as default.
Leave as default.
Select Authentication on from the drop-down list to enable authentication
for this endpoint.
Authentication
password
The password must be alphanumeric and can be up to 24 characters in
length.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 52

52 NRS configuration
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 53

.
CS 1000 configuration for client
support
This section describes the configuration required on the Communication
Server 1000 (CS 1000) to support the individual Mobile Communication
Client 3100 (MCC 3100) users.
CS 1000 configuration for client support task flow
Configuring the CS 1000 for client support requires the following
procedures.
Figure 9
CS 1000 configuration for client support task flow
53
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Page 54

54 CS 1000 configuration for client support
Task flow navigation
•
"Configuring features and keys" (page 54)
• "Configuring the Device Handoff key" (page 55)
•
"Configuring the TSC steering codes" (page 56)
•
"Configuring dial plan parameters" (page 56)
• "Configuring the Digit Manipulation Index" (page 58)
• "Configuring a Route List Index" (page 59)
• "Configuring Call Forward No Answer" (page 59)
Configuring features and keys
Use this procedure to configure the features and keys on the CS 1000.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1
2
3 Click Phones link from the left navigation pane. The Search for
4
5 Select UEXT-FMCL-Universal Extension FMCL from the
6 Enter the other applicable details under the Type and Options
Login to ECM using a valid account.
Click on the appropriate call server element. The Element
Manager appears.
Phones page appears.
The phone database and call server database must be kept
synchronized all the time. Necessary configuration of a customer
must already be available for a telephone to be configured (for
example, super loop or customer).
From the Search for Phones page under the Phones heading,
click Add. The New Phones page opens.
Phone Type drop down menu.
Attention: You do not need to configure a UXID.
fields and click Preview.
The Phone Details page appears. The top of the Phone Details
page should show the Phone Type as Universal Extension
FMCL.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 55

Configuring the Device Handoff key 55
7
Navigate to the Keys section of the Phone Details page.
•
Key 0 is configured with the SCR DN.
• Key 1 is configured as a HOT_P key containing the mobile
DN.
8
9 Click Finish.
Job aid
Parameter Description
KEY 1
Enter the required details for Key 0 and Key 1 and click Validate
to perform validation of general properties, features, and keys.
For more information, see the following Job aid.
Configure to the number that will send all calls the MCG 3100 for that user
whenever the user is called.
The format of the input for Key 1 is: HOT P X YYYYY, where X is the
number of digits in YYYYY.
The expected format of YYYYY is
<Dial Plan Digit><Mobility Prefix><MCC 3100 User ID>
--End--
Configuring the Device Handoff key
Use this procedure to configure the handoff key
Procedure steps
Step Action
1
2 Press enter.
3
4 Enter the Level 2 password.
5 Enter the following command:
6
7 At the TYPE prompt, enter the type of device you are changing.
8 At the TN prompt, enter the TN for the device you are changing.
Connect to your call server.
Enter the following command to log in to the system:
LOGI admin2
LD 11
At the REQ prompt, enter CHG
Example: 2004P2
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 56

56 CS 1000 configuration for client support
Example: 100 0 0 29
9 At the KEY prompt, enter 01 HNDO to program the Handoff
feature on key 01 of the device.
Configuring the TSC steering codes
Perform this procedure if you require TSC steering codes.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 Connect to your call server.
--End--
2
3 Enter the following command to log in to the system:
Press enter.
LOGI admin2
4 Enter the Level 2 password.
5 Enter the following command:
LD 87
6
7
At the REQ prompt, enter NEW
At the CUST prompt, enter the Customer Number, as defined in
LD 15.
8 At the FEAT prompt, enter CDP for the Coordinated Dialing Plan.
OR
At the FEAT prompt, enter UDP for the Universal Dialing Plan.
9
10
At the TYPE prompt, enter DSC for the Distant Steering Code.
At the DSC prompt, enter the Distant Steering Code digits, up to
7 digits.
Example: 2200
11 At the FLEN prompt, enter the number of digits that will be
passed to the system.
Example: 9
Configuring dial plan parameters
The CS 1000 requires different parameters, depending on the type of dial
plan: Universal Dial Plan (UDP) or Coordinated Dial Plan (CDP).
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
--End--
Page 57

Configuring dial plan parameters 57
Use your CS 1000 documentation and your existing dial plan to configure
the parameters in the following job aids.
UDP Job Aid
Table 4
UDP parameters
Parameter Description Example
ESN AC The Access code can be
configured in LD 15 while
configuring the CDB
mobile prefix ESN Configure in LD 90 and LD 15 mobile prefix ESN : 343
DMI In LD 86
RLI IN LD 86
Mobility mobile prefix Configured in MCG 3100 "Call
termination field"
mobile prefix configured in
NRS Routing rule , MCG3100
terminates in L0 domain as
555.
UEXT LD 11 - Configuration done
as KEY <AC><mobile
prefix><ESN mobile
prefix><DN>
FLEN Configured in LD 87 as the
total digit count.
AC2 : 6
SIP Gateway in L0 domain 343
555
6 555 343 5335
CDP Job Aid
Table 5
CDP parameters
Parameter Description Example
TSC LD 87
RLI In LD 86
FLEN Configured in LD 87 as the
total digit count.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
88888
9
.
Page 58

58 CS 1000 configuration for client support
Table 5
CDP parameters (cont’d.)
Parameter Description Example
Mobility mobile prefix
UEXT LD 11 - KEY <mobile
Configured in MCG 3100 Call
termination field
Mobility mobile prefix
configured in NRS Routing
rule as 88888.
prefix><DN>
Configuring the Digit Manipulation Index
Create a Digit Manipulation Index (DMI) to take calls from the PSTN, route
it to the SIP Gateway, through the SRS, and finally to the MCG 3100.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1
2 Press enter.
3 Enter the following command to log in to the system:
Connect to your call server.
LOGI admin2
88888 5535
4 Enter the Level 2 password.
5
Enter the following command:
LD 86
6
7
At the REQ prompt, enter NEW
At the CUST prompt, enter the Customer Number, as defined in
LD 15.
8
9 At the DMI prompt, enter the Digit Manipulation Index numbers.
10 At the DEL prompt, enter the number of digits to be deleted.
11 At the INST prompt, enter any leading digits that need to be
At the FEAT prompt, enter DGT.
inserted.
12 At the CTYP prompt, enter the Call Type to be used by the
manipulated digits.
--End--
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Page 59

Configuring a Route List Index
The Route List Index (RLI) defines the trunk characteristics. The RLI is
used to steer calls to the MCG 3100.
Procedure steps
Step Action
Configuring Call Forward No Answer 59
1
2 Press enter.
3
Connect to your call server.
Enter the following command to log in to the system:
LOGI admin2
4 Enter the Level 2 password.
5 Enter the following command:
LD 86
6 At the REQ prompt, enter NEW
7 At the CUST prompt, enter the Customer Number, as defined in
LD 15
8 At the FEAT prompt, enter RLB for the Route List Block.
9
At the RLI prompt, enter a number between 0-127 for the CDP
routing.
10
11 At the ROUTE prompt, enter a number between 0-511 for a Large
At the LTER prompt, enter NO for the local termination entry.
System.
12 At the DMI prompt, enter the Digit Manipulation Index number as
defined in LD 86.
Configuring Call Forward No Answer
To increase the Call Forward No Answer (CFNA) timeout, configure the
CS 1000 using LD 15 and LD 11.
LD 15 configures the CFN0, CFN1 and CFN2 indexes.
LD 15
REQ: chg
TYPE: rdr
TYPE RDR_DATA
CUST 0
OPT
FNAD
FNAT
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
--End--
.
Page 60

60 CS 1000 configuration for client support
FNAL
CFTA
CCFWDN
CFN0
CFN1 6
CFN2
DFN0
DFN1
DFN2
MDID
NDID
MWFB
TRCL
CRTOD
CRDAY
CRHOL
LD 11 configures the number of ringing cycles for CFNA. Configure the
CFN index that corresponds to the RCO entry configured in LD 15 (for
example, RCO 1 uses CFN 1).
LD 11
REQ: chg
TYPE: 1140
TN 100 0 8 23
ECHG yes
ITEM rco 1
ITEM
HNT FNA
HNT FNA
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 61

.
MCC 3100 configuration
On the first login attempt, Mobile Communication Client 3100 (MCC 3100)
users have a minimal set of parameters to configure.
•
Server Address—The Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or IP
address of the MCG 3100
•
Login Name—The user’s account username on the network.
• Login Password—The user’s login password on the network.
•
Mobile Phone Number
Attention: Configure the mobile telephone number using the format
+1XXXXXXXXXX . Example: +16132429900
Upon successful login, the MCC 3100 automatically retrieves all other
configuration settings required for operation of the client as defined by
the MCG 3100 administrator. If the client login fails, consult Nortel Mobile
Communication 3100 Troubleshooting (NN42030-700).
61
For information on installing and configuring the MCC 3100 clients, see
• Nortel Mobile Communication Client 3100 for BlackBerry User Guide
(NN42030-101)
•
Nortel Mobile Communication Client 3100 for Nokia User Guide
(NN42030-102)
• Nortel Mobile Communication Client 3100 for Windows Mobile User
Guide (NN42030-107)
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 62

62 MCC 3100 configuration
Autoconfiguration settings
Autoconfiguration allows a number of the client configuration parameters
to be preset on the MCG 3100 and downloaded to the client during the
first login to the MCG 3100. The automatically-downloaded fields appear
as grey text on the interface unless the administrator allows the user to
override the configuration.
Autoconfiguration insures that all clients registered to each MCG 3100
receive the same configuration.
For information on configuring the autoconfiguration settings, see
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100 Installation and Commissioning
(NN42030-300).
For information on configuring the MCC 3100 clients, see
•
Nortel Mobile Communication Client 3100 for BlackBerry User Guide
(NN42030-101)
•
Nortel Mobile Communication Client 3100 for Nokia User Guide
(NN42030-102)
• Nortel Mobile Communication Client 3100 for Windows Mobile User
Guide (NN42030-107)
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 63

.
Validate deployment
This section describes how to validate that the Mobile Communication
3100 (MC 3100) components and the Communication Server 1000
(CS 1000) integration is correct.
Validating deployment task flow
63
Validating deployment task flow navigation
•
"Validating MCG 3100 registration" (page 63)
• "Validating MCC 3100 for BlackBerry communication" (page 64)
• "Validating MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment" (page 64)
Validating MCG 3100 registration
Use this procedure to determine if the MCG 3100 is registered on the
NRS.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Page 64

64 Validate deployment
Procedure steps
Step Action
1
2 Select Endpoints under the Numbering Plan menu on the left
Login to the NRS.
hand side.
3
4 Select the Gateway Endpoints tab.
5
6 Verify that the Call Signaling IP is the IP address of the
Ensure that you are managing the Active Database.
In the results pane, locate the MCG3100 endpoint ID.
MCG3100 gateway.
If the Call Signaling IP field shows Not Registered, then the
MCG3100 gateway is not currently registered. Check your
configuration and try again.
--End--
Validating MCC 3100 for BlackBerry communication
Use this procedure to ensure that you can connect to the MCG 3100
through the BlackBerry Enterprise Server (BES).
Procedure steps
Step Action
1
On your BlackBerry mobile client, open the BlackBerry Mobile
browser.
2 Navigate to the User Portal of the MCG 3100 server.
If you can view the MCG 3100 User Portal, then you have proper
communication between the client and the MCG 3100 servers.
--End--
Validating MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment
This procedure tests a number of scenarios, in increasing order of
complexity, to ensure that the configuration of the Mobile Communication
Gateway 3100 (MCG 3100), Mobile Communication Client 3100
(MCC 3100), CS 1000, and Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
server interact correctly.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
.
Page 65

Prerequisites
• MCG 3100 has been installed and configured.
• MCC 3100 has been installed and configured on a number of devices.
•
CS 1000 has been configured to support MC 3100.
• LDAP server is accessible.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 Configure the MCG 3100 to not require encryption.
Validating MC 3100 and CS 1000 deployment 65
2
Configure the MCC 3100 for BlackBerry to not require
encryption.
3
Log in to the MCC 3100 for BlackBerry (uses HTTP).
Validates that the MCC 3100 client can register with the
MCG 3100 and SPS.
4 Configure the MCC 3100 for Nokia or MCC 3100 for Windows
Mobile to not require encryption.
5 Log in to the MCC 3100 for Nokia or MCC 3100 for Windows
Mobile (uses HTTP).
Validates that the MCC 3100 client can register with the
MCG 3100 and SPS.
6
Configure one of the clients to require encryption. Use this client
in the remainder of this procedure.
7
Log in to the client using HTTPS.
Validates that certificates are functioning correctly.
8
9
Dial the mobile device from another telephone.
Accept the call using the MCC 3100.
Tests that the UEXT for incoming calls, the Call Server dial plan,
and the SPS routing are configured correctly.
10 Make a Call-me-first call from the client.
Tests that the UEXT for incoming calls, the Call Server dial plan,
and the SPS routing are configured correctly.
11 Make a direct outbound call from the client.
Validates that the service DN routing to the MCG 3100 is correct.
12 Test mid-call features on the client (for example, hold and
retrieve, transfer or conference).
Verifies DTMF handling and more complex call scenarios.
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 66

66 Validate deployment
13
Perform a corporate directory search from the client for a known
user.
Verifies that the LDAP to MCG 3100 connections and data
mapping are correct.
14
15 Send an instant message to the added user.
Add a user from the corporate directory search to the buddy list.
Validates the LDAP field mapping and instant message
functionality.
16
Check that you can see the presence status of the user.
Validates the LDAP field mapping and presence.
--End--
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
NN49000-315 02.01 2 October 2009
.
Page 67

Page 68

Nortel Mobile Communication 3100
Mobile Communication 3100 and Communication Server 1000
Solution Integration Guide
Release: 3.1
Publication: NN49000-315
Document revision: 02.01
Document release date: 2 October 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
While the information in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable, except as otherwise expressly agreed to in writing
NORTEL PROVIDES THIS DOCUMENT "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED. The information and/or products described in this document are subject to change without notice.
Nortel, Nortel Networks, the Nortel logo, and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
To provide feedback or to report a problem in this document, go to www.nortel.com/documentfeedback.
www.nortel.com
.
 Loading...
Loading...