Page 1

Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100
Page 2

Document status: Standard
Document issue: 01.01
Document date: 03 June 2008
Product release: Release 6.0
Job function: Product Fundamentals
Type: NTP
Language type: English
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Sourced in Canada and the United States
Nortel, the Nortel logo and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Page 3

Contents
New in this release 5
Features 5
Other changes 5
Introduction 6
MAS installation 7
Architecture and supported hardware and software 7
Session controller 8
VXML browser 8
SIP Multimedia Conductor (SIPMC) 8
Multimedia Controller 8
IVR media processor (IVRMP) 9
Conference media processor 9
Multimedia Content Store 9
Stream source 9
Reporter 9
MAS installation 9
Options for MAS application deployment 10
Application deployment options 11
Maintenance Releases 12
- 3 -
Contents
MAS commissioning 13
AS 5300 commissioning for MAS 13
Packaged applications 13
MAS clusters 14
SIP signaling 17
Media conferencing 19
Media settings 21
Continuous streaming 24
MAS administration and security 26
Access security setup 26
Remote Desktop Protocol 28
IPSEC configuration 29
Security tools 29
Certificate management 30
Service and configuration data backup 31
Automatic and manual backups 31
System maintenance 33
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 4
- 4 -
Contents
MAS performance management 34
MAS fault management 35
Fault management architecture 35
SNMP management 36
Supported MIBs 36
Syslog 37
Event logs 37
Security Logs 38
Alarms 39
Nortel MAS Console 42
Counters & Gauges 42
Nortel MAS Console 43
Dialog boxes 45
Terminology 58
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 5

New in this release
The following sections detail what is new in Media Application Server 6.0 for
AS 5300 Fundamentals (NN44470-100).
Navigation
• Features (page 5)
• Other changes (page 5)
Features
See the following sections for information about feature changes:
• MAS and AS 5300 integration (page 5)
• Administration and security (page 5)
MAS and AS 5300 integration
The Media Application Server (MAS) 6.0 supports integration with the
Application Sever (AS) 5300. For more information, see see the figure MAS
commissioning.
Administration and security
The MAS 6.0 for AS 5300 release contains new features that include SIP TLS,
Secure SRTP, and platform security. For more information, see see the figure
MAS administration and security.
Other changes
The MAS 6.0 documentation suite contains reorganized content from the
MAS 5.1, 5.0, and 4.0 documentation suites.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Nortel Confidential
Page 6

Introduction
The Media Application Server (MAS) is a software platform for hosting
multimedia applications. This document explains MAS platform fundamentals.
Navigation
• MAS installation (page 7)
• MAS commissioning (page 13)
• MAS administration and security (page 26)
• MAS performance management (page 34)
• MAS fault management (page 35)
• Nortel MAS Console (page 42)
• Terminology (page 58)
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 7

MAS installation
This chapter explains MAS installation fundamentals. For step-by-step
information about how to install the MAS platform, see Nortel Media
Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Installation
Navigation
• Architecture and supported hardware and software (page 7)
• MAS installation (page 9)
• Options for MAS application deployment (page 10)
• Maintenance Releases (page 12)
Architecture and supported hardware and software
This section details the system architecture for MAS 6.0 for Application Server
(AS) 5300 release as well as the supported hardware and software for that
platform. For more information, refer to Media Application Server 6.0 for AS
5300 Planning and Engineering (NN44470-200).
System architecture
The MAS platform is a software-based, media processing server. Software on
the host server performs all media processing. The MAS architecture permits
scalability for all core functions of the platform, including signaling, application
execution, content management, and media processing.
(NN44470-300).
Network architecture
The MAS platform can scale from a small, duplex server solution. The system
exploits a multiprocess, multithreaded architecture that is designed to take
advantage of multiple processor core and hardware platforms. The server
achieves scalability across multiple computers by replicating the entire
system.
Supported hardware and software
The MAS platform uses commercial operating systems and commercial
hardware platforms for all processing.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 8

- 8 -
MAS installation
Supported hardware platform
You can install the MAS software on an IBM X3550. The X3550 has an Intel
XEON 5140 2.33 GHZ processor, 2 GB of RAM and a SCSI hard drive.
Supported operating system
You can install the MAS software on Windows 2003 operating system (OS). To
comply with the Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) Security
Technical Implementation Guideline (STIG) and GR-815 compliancy,
install additional OS hardening patches
and security software must be installed
you must
on the MAS before you install MAS platform or MAS application software.
MAS platform core components
The MAS platform software includes the following core components:
• Session controller (page 8)
• VXML browser (page 8)
• SIP Multimedia Conductor (SIPMC) (page 8)
• Multimedia Controller (page 8)
• IVR media processor (IVRMP) (page 9)
• Conference media processor (page 9)
• Multimedia Content Store (page 9)
• Stream source (page 9)
• Reporter (page 9)
Session controller
The Session Controller (SC) provides the application execution environment
and manages all platform resources. The Media Controller provides the
conduit for communication between components and is the core of the
platform.
VXML browser
The VXML Browser (VXMLI) provides the execution environment for VXML
based applications.
SIP Multimedia Conductor (SIPMC)
The SIP Multimedia Conductor (SIPMC) provides SIP signalling and session
management capabilities.
Multimedia Controller
The Multimedia Controller (also called the SoftIVR Controller, or SC) is the
core of the MAS platform. The SC provides the conduit for communication
between components, provides the environment for application execution,
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Fundamentals
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 9

and manages all platform resources. The SC is a client with respect to all other
components. The SC connects to all components identified as part of one
virtual system.
IVR media processor (IVRMP)
The IVR media processor IVRMP provides audio and video streaming, digit
collection, automatic speech recognition (ASR) and Text-to-Speech (TTS)
capabilities.
Conference media processor
The Conference media processor (ConfMP) provides audio and video
conferencing functions to the remainder of the platform.
Multimedia Content Store
The Multimedia Content Store (CStore) manages all content types and
ensures that you can access content reliably and consistently within a
platform cluster.
Stream source
The Stream source (streamsource) provides continuous pretranscoded realtime audio to the IVRMP to facilitate a radio broadcast effect. Multiple IVRMP
channels use this feature to listen to the same real-time audio stream without
transcoding the stream on each channel or connecting each channel to a
remote server. Primarily, the SSRC is used for music-on-hold streaming or
connecting to Internet streaming radio servers.
- 9 -
MAS installation
Reporter
Reporter (reporter) generates scheduled reports (CSV, HTML) with optional
FTP/SMTP delivery. Reporter also replicates OM and call detail records.
MAS installation
The MAS platform and its associated applications are installed together on a
commercial off-the shelf (COTS) server. The server is shipped with a
hardened version of Microsoft Windows Server 2003 preinstalled. After you
power on the server, change the IP address, netmask, gateway, and host
name. A Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) (recommended) or 100 MB full-duplex
network connectivity is required. Quality of service (QoS) policies on the
switch connecting directly to the server must trust the server to allow
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) markings to flow through the
switch.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 10

MAS installation
Uninstallation
Under normal circumstances, you need not uninstall the MAS platform unless
you want to perform a clean installation. Before you install the platform, you
must uninstall all applications and close all instances of the Nortel MAS
Console. If instances of the Nortel MAS Console are running when you
uninstall the MAS platform, you must restart the server.
Reinstallation
If you need to reinstall the MAS platform, you can use the MAS installation
DVD. The MAS installation DVD contains an automated installer. The MAS
platform is contained in a single installer; each application is bundled in a
separate installer. After you insert the DVD, locate and run the setup program.
MAS installation verification
After you install the MAS platform, you must verify that the IP address and
host name are correct.
Supported third-party software
Nortel supports McAfee VirusScan Enterprise Edition 8.5 only.
- 10 -
Options for MAS application deployment
The following sections provide an overview of the applications. available for
use on the MAS 6.0 platform, as well as the application deployment options
for the platform.
Meet Me Conferencing
The Meet Me Conferencing application provides reservation-less audio
conferencing on the MAS platform. You can use Meet Me Conferencing for
private conferencing at any time. Meet Me Conferencing is controlled by the
chairperson, who is assigned the role by an Application Administrator (AA).
For more information about Meet Me Conferencing, see Nortel Media
Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Meet Me Conferencing Fundamentals
(NN44470-103).
Ad Hoc Conferencing
Use Ad Hoc Conferencing to join together multiple simultaneous calls into a
single conference call. You can initiate a conference call from any client. To
initiate a conference, place a number of calls on hold and then select the Join
button in the Multimedia PC Client to transfer the calls to the conference
server and start the conference. The conference originator may leave the
conference without interrupting the call. The conference server terminates
the call when there is only one participant left. For more information about Ad
Hoc Conferencing, see Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Ad
Hoc Conferencing Fundamentals (NN44470-104).
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 11

Music On Hold
With the Music On Hold application, a system administrator can provision the
MAS system to play music while a caller is hold. The Music on hold application
lets a caller know that the call is still connected. It is possible to implement the
Music on Hold application for the following types of hold: end-user, transfer,
and Call park. This application continuously plays for the user on hold and
does not restart the tune each time a user is put on hold. For more information
about Music on Hold, see Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Music on Hold Fundamentals (NN44470-106).
Announcements
The Announcements application plays recordings for branding, causes, and
treatments. You can use announcements to indicate the status of calls and
internal session manager conditions (treatments); which are used in all-circuit
busy situations. Announcements also provides treatment when calls fail to
complete, and provides branding (for example, Welcome to Nortel Networks).
For more information about Announcements, see Nortel Media Application
Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Announcements Fundamentals (NN44470-105).
- 11 -
MAS installation
Unified Communications
The Unified Communications application provides users with integrated
access to their voice-mail messages from a preferred client device, such as a
PC, voice over IP (VoIP) phone, wireless phone, or a traditional circuit
switched telephone. One single mailbox can be used by multiple telephony
devices and the messages deposited in this common mailbox may optionally
be mailed to a user’s e-mail client, offering another convenient access option
for voice mail message playback. Users manage their account through a
traditional Telephony User Interface (TUI) or through the web-based Personal
Agent (PA), which may be optionally configured for the user. For more
information about Unified Communications, see Nortel Media Application
Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Unified Communications Fundamentals (NN44470-
102).
Application deployment options
In Release 6.0, Media Application Servers are deployed as duplex clusters
(pairs) to ensure redundancy. In a duplex cluster, the MAS applications are
installed on both servers. The only exception to this rule is Meet Me, which can
be installed in an N+1 cluster configuration. You can deploy MAS applications
in one of three different deployment scenarios:
• Dedicated Deployment
• Co-resident Application Deployment (including Meet Me)
• Co-resident Application Deployment (excluding Meet Me)
The deployment scenario you select is determined by your capacity
requirements.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 12

Dedicated deployment
In a dedicated deployment scenario, each application is deployed on its own
MAS pair to the maximum capacity of that single application. However, for the
most efficient use of resources, a combination of dedicated deployment and
multi application deployment is required.
Co-resident deployment
In a co-resident deployment, up to five MAS applications (Meet-Me, Ad Hoc,
Music on Hold, Announcements, and Unified Communications) can be
deployed on the same MAS duplex.
If you choose a co-resident deployment, you must stay within the engineered
capacity limits for that co-resident deployment. You cannot, for example,
expand the capacity for Meet Me and balance that by reducing Unified
Communications capacity. If you require additional application capacity, you
can add an additional MAS pair and deploy a dedicated service to
accommodate the additional capacity requirements for that service. For
example, if you currently have a combination five deployment, and you require
additional Meet Me capacity, you can purchase additional Meet Me licenses
and servers and deploy a dedicated Meet Me server cluster to handle the
increased capacity.
- 12 -
MAS installation
The available co-resident deployment options are defined in the following
sections.
Co-resident Application Deployment (including Meet Me)
In a Co-resident Application Deployment (excluding Meet Me), all five MAS
applications are deployed on the same MAS pair.
Co-resident Application Deployment (excluding Meet Me)
In a Co-resident Application Deployment (including Meet Me), Ad Hoc, Music
on Hold, Announcements, and Unified Communications are deployed on one
MAS pair and a separate MAS pair is dedicated to Meet Me Conferencing.
Maintenance Releases
The MAS is updated or downgraded using executable installers (DVDs). To
update the MAS to the latest maintenance release, you must obtain the latest
maintenance release DVD and install the software. To downgrade to an earlier
maintenance release, you must run the installer on desired maintenance
release DVD. For the procedures to update and downgrade maintenance
releases, see Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Installation
(NN44470-300).
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 13

MAS commissioning
This chapter describes the items that you can configure on the MAS platform.
For detailed information, see Nortel Media Application Server Commissioning
(NN44470-301).
Navigation
• AS 5300 commissioning for MAS (page 13)
• MAS clusters (page 14)
• SIP signaling (page 17)
• Media conferencing (page 19)
• Media settings (page 21)
• Continuous streaming (page 24)
AS 5300 commissioning for MAS
For more information about commissioning the Application Server (AS) 5300
system for use with MAS, see Nortel Media Application Server
Commissioning (NN44470-301) and the AS 5300 documentation suite.
Packaged applications
You can deploy packaged applications on the MAS platform. Packaged
applications are prepackaged applications that you configure on the system
using an installer.
Attention: This release does not currently support custom applications.
Packaged application installation and licensing
You can install packaged applications after you install and configure the MAS
platform. As part of the installation process, you must configure license keys
for all packaged applications that you install.
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Fundamentals
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 14

To view installed packaged applications, use the Nortel MAS Console. The
Nortel MAS Console lists the application version and the current operational
state for that application. An example of a packaged application would be
Recorder.
Configuration data
Each packaged application has one or more configuration parameters that
you can modify to alter the behavior of the application. To view and modify
these application-specific parameters, use the Nortel MAS Console.
Operational state
Each packaged application has an operational state that you can view and
modify. To view and modify the operational state of an application, use the
Nortel MAS Console.
You can select one of the following operational states:
• Unlocked—This is the default. Normal call processing is performed for the
application.
• Locked—When the application enters a Locked state, existing sessions for
that application are terminated and the system redirects new traffic. You
typically place the application into a Locked state when performing
maintenance (for example, application upgrades) to the application.
- 14 -
MAS commissioning
MAS clusters
• Pending Lock—When the application enters a Pending Locked state, the
system redirects new traffic for that application, while existing sessions are
preserved.
A MAS cluster is a collection of MAS nodes that work closely together. A MAS
cluster shares the following resources:
• SNTP server for clock synchronization
• persistent content storage
• Controller Peer Ring
• redundant license servers
A cluster consists of N+1 active MAS servers where N is a maximum of 7 for
high availability and redundancy. An additional server is used as a spare to
accommodate one server failure. The spare server is active and handling
traffic, but the entire system is engineered to N servers of capacity (not N+1).
This ensures that enough remaining capacity is available to handle peak traffic
if one server fails.
The following terminology describes the different cluster types:
• Duplex—a cluster consisting of two MAS nodes
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 15
MAS commissioning
• N-way—a cluster consisting of three or more MAS nodes
Because the cluster is based on system replication, you must configure the
same applications on all of the MAS servers in the same cluster and provision
any application data (such as subscriber information) for that cluster. The SIP
proxy must support load balancing across multiple MAS nodes in the same
cluster.
Persistent content storage
Configuration of the persistent content storage depends on
• the number of nodes in a cluster
• the applications that are provisioned for that cluster
• how those applications make use of the persistent content storage
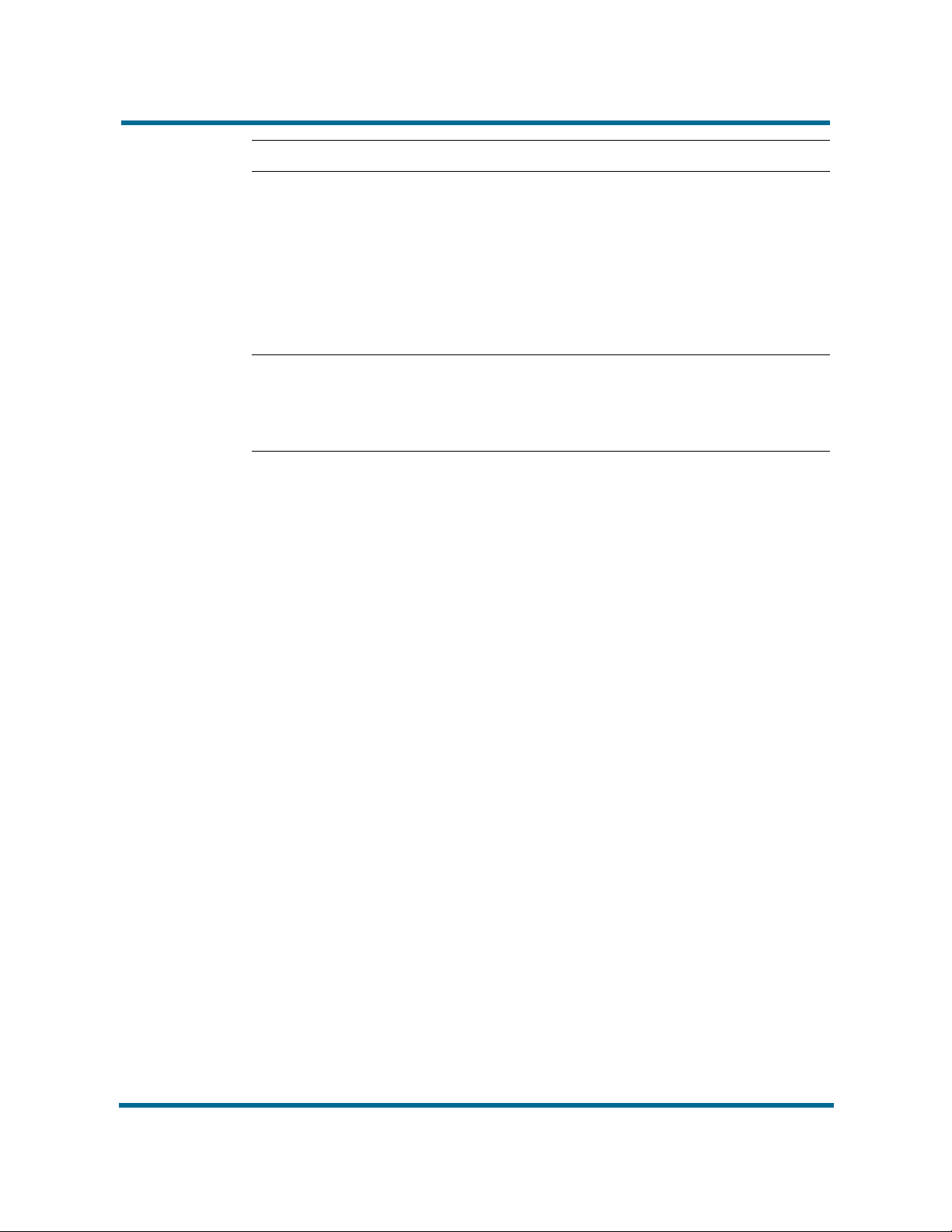
For duplex configuration, the cluster consists of two nodes. On both nodes,
configure the Content Store Local Function key to Master, configure the
Content Store Peer Master Server key to contain the IP address of the peer
master node, and configure the Content Store Remote Server(s) key to a
blank value. To view an example of a duplex cluster, see CStore duplex cluster
configuration (page 15).
- 15 -
CStore duplex cluster configuration
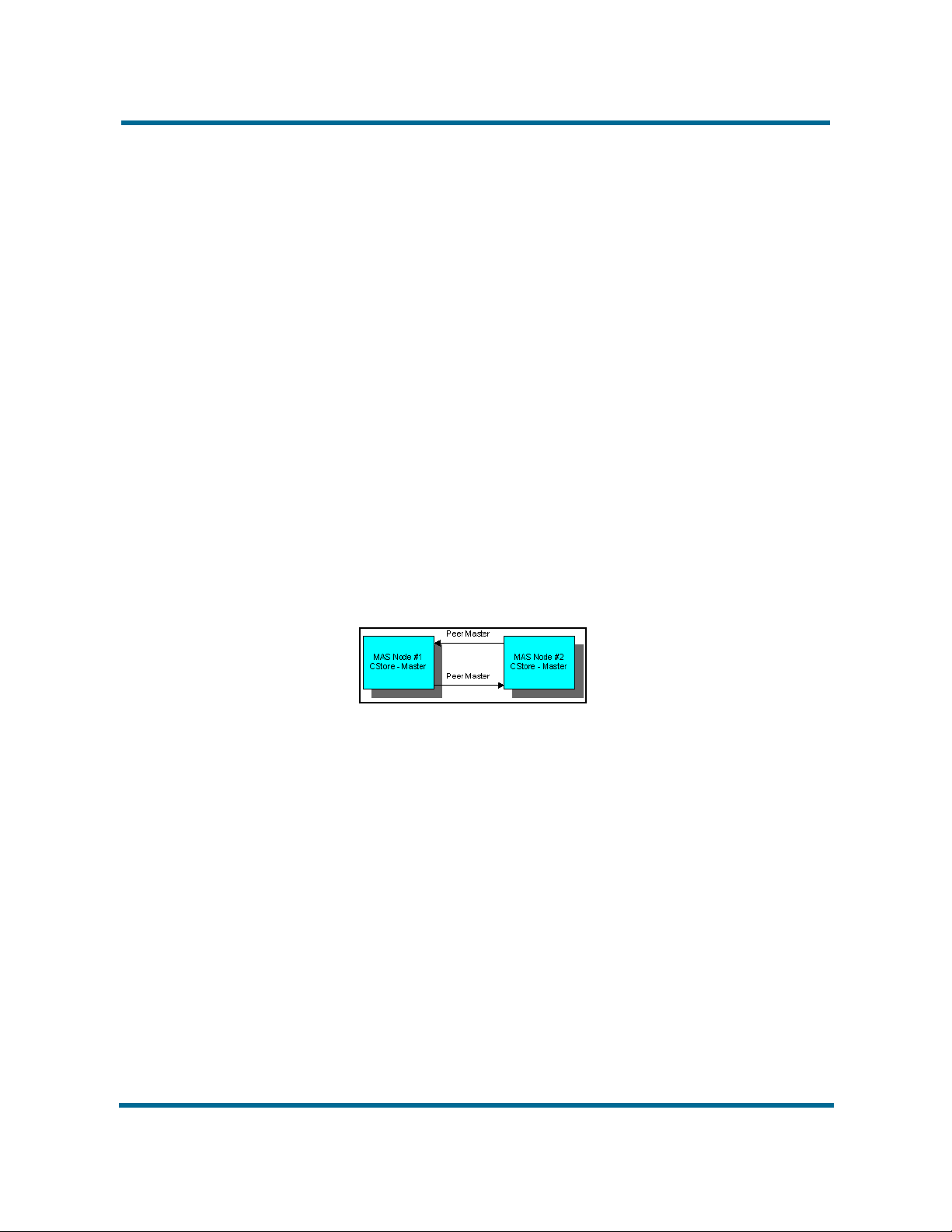
For N-way configuration, the cluster consists of three or more nodes. On the
first two nodes, configure the Content Store Local Function key to Master,
configure the Content Store Peer Master Server key to contain the IP address
of its peer master node, and configure the Content Store Remote Server(s)
key to a blank value. Disable the CStore for all other nodes.
For all other nodes, configure Content Store Local Function to Idle and
configure the Content Store Remote Server(s) key to contain the IP address
of both CStore masters. Configure the Content Store Peer Master Server key
to blank. To view an example of an N-way cluster, see CStore N-way cluster
configuration (page 16).
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 16
CStore N-way cluster configuration
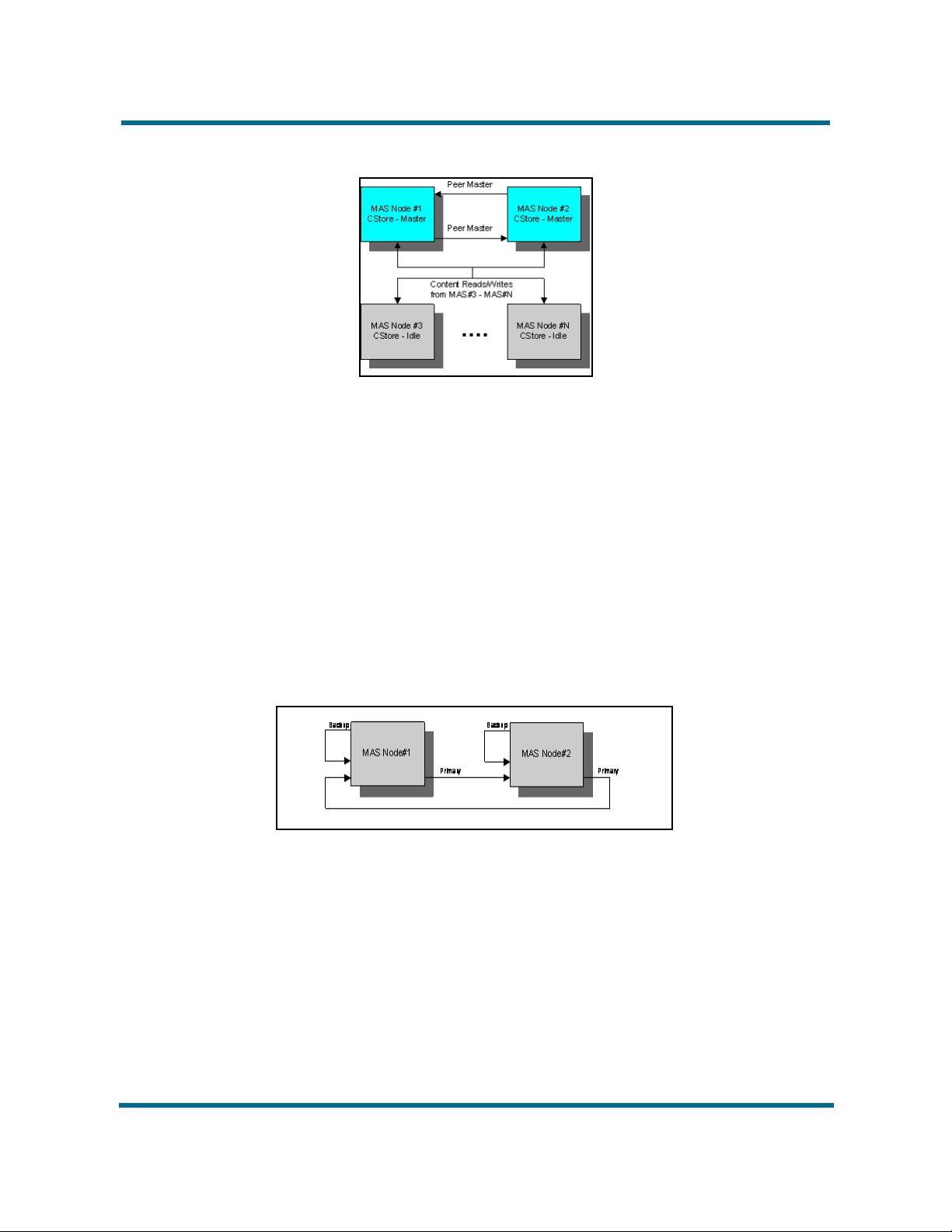
Controller Peer Ring
Applications use the Controller Peer Ring to send and receive events to the
various MAS nodes in the cluster. Configuration of the Controller Peer Ring
depends on the number of nodes in the cluster and if the provisioned
applications use the Controller Peer Ring. To create the ring, configure each
MAS node with a primary and backup controller peer. You can then
dynamically add or remove MAS nodes to and from the Controller Peer Ring.
- 16 -
MAS commissioning
For duplex configuration, configure the Controller Peer Primary Server key to
the IP address of the other media server and configure the Controller Peer
Backup Server key to the IP address of the same server. To view an example
of a duplex controller ring, see Duplex controller ring (page 16).
Duplex controller ring
For an N-way configuration, for Node n, configure the Controller Peer Primary
Server key to the IP address of Node n+1 and the Controller Peer Backup
Server key to the IP address of Node n+2. To view an example of a 4-way
controller ring, see 4-Way controller ring (page 17).
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 17
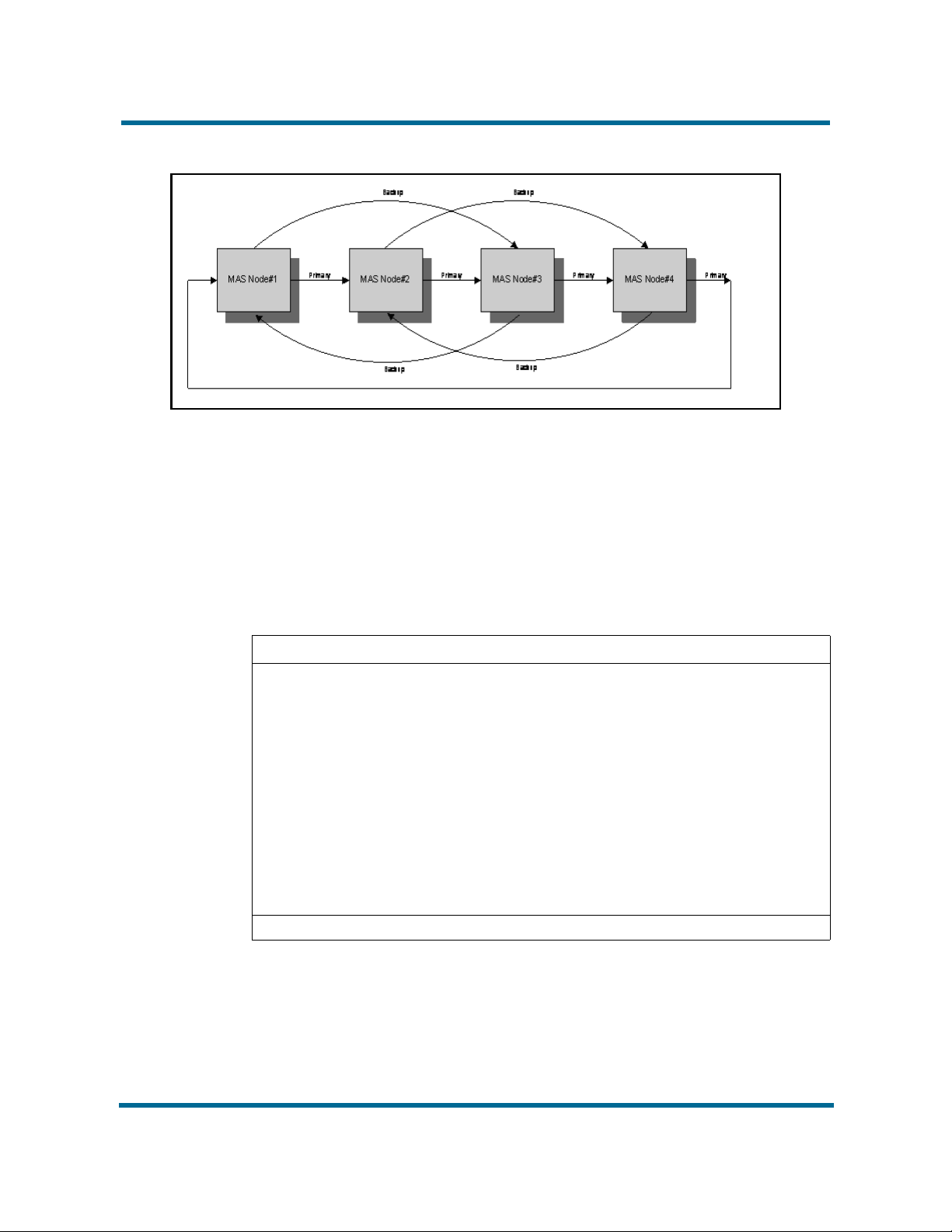
4-Way controller ring
SIP signaling
SIP configuration is broken into the following categories: General, Domains,
Accounts, Trusted Nodes, and Routes. The following sections describe these
categories in more detail.
- 17 -
MAS commissioning
SIP properties
You can modify the following SIP properties.
SIP properties
Property Description
Always use SIP default
outbound proxy
Answer Delay (rings) Represents the number of rings before an
Hide SIP User-Agent Header If enabled, the User-Agent header is not included
SIP domains
You must define all SIP domains on the MAS. You must configure a SIP
domain before you can configure SIP accounts and routes.
If enabled, the system routes SIP requests, which
do not match domain proxy configuration, through
the default outbound proxy (if configured), even if
the IP address is specified in the host portion of the
destination Universal Resource Indicator (URI).
incoming SIP call is answered. To configure the
duration of a ring, use the Ring Interval engineering
parameter. Zero rings means that the call is
immediately answered.
in SIP messaging.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 18

The platform has an internal domain called the wildcard domain, which is
represented with an asterisk and is the default domain if no matching domain
is found.
SIP accounts
SIP accounts are used for application registration in the SIP network. The
MAS registers all accounts against the registrar servers. For information about
the servers, see SIP registrar servers (page 19). You can view, add, and
delete SIP accounts.
SIP trusted nodes
MAS processes SIP traffic from trusted nodes only (for example, proxies and
gateways). Any requests from a nontrusted node are rejected. You can view,
add, and delete trusted nodes.
Attention: If you add or delete a trusted node, you must restart the platform
for the change to take effect.
SIP routes
Use SIP routes to define all proxy and registrar servers with which a MAS
node communicates. You can configure up to 32 routes for each domain.
- 18 -
MAS commissioning
SIP proxy servers
A SIP proxy server accepts MAS requests and queries the SIP registrar server
to obtain the recipient addressing information. The proxy server then forwards
the request directly to the recipient if the recipient is in the same domain or to
another proxy server if the recipient is in a different domain.
The MAS platform uses proxy server routes to route outbound SIP requests
to the appropriate proxy server for outbound traffic load sharing and failover.
Routes are selected based on the domain (or subdomain) lookup. If no
matching domain is configured, the default wildcard (*) route is used. For
example, if an outbound call is made to janedoe@techtrial.com, the routes
associated with the techtrial.com domain are selected.
On the first routing attempt, the MAS platform selects active routes that are
online based on the lowest priority only. The weight is used to select routes
within the same priority level. Route selection from the next priority level is
chosen automatically only if the lower priority routes are either offline or fail to
respond.
For load sharing configurations, you can define multiple routes with the same
priority. For failover configurations, configure the primary routes with
priority = 0 and weight = 10 and configure the secondary routes with
priority = 1 and weight = 10.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 19

SIP registrar servers
A SIP registrar server is a database that contains the location of all user
agents within a domain. MAS registers its applications with all configured SIP
registrars. Registration is optional based on MAS configuration. Digest
authentication is supported.
Media conferencing
MAS supports multimedia conferencing for both audio and video streams. You
can use one of the following conferencing algorithms: basic and premium.
Basic conferencing algorithm
The basic conferencing algorithm mixes the two audio streams with the
highest energy and provides the mixed audio to the remaining participants.
The two participants with the highest energy audio streams receive only the
other active participant's audio so they do not hear themselves. The
participant with the highest energy with of the two highest energy speakers is
known as the primary active speaker. The other participant is the secondary
active speaker. (The system continually monitors the energy of all participants
in a conference, and using threshold algorithms, changes the conference
focus point.)
- 19 -
MAS commissioning
When some or all of the participants in the conference have corresponding
video streams, the video streams of the primary active speaker are replicated
and sent to those participants. The primary and secondary speakers see only
each other if they have video-enabled clients. The system attempts to provide
video participants with video when possible. If the active speaker does not
have video capabilities, participants receive a configurable replacement video,
which by default is an icon of a megaphone.
Premium conferencing algorithm
A more advanced conferencing algorithm (called premium conferencing)
mixes up to four parties simultaneously. Each channel runs a voice activity
detector (to determine speech versus background noise), an automatic gain
control algorithm, and a dynamic jitter buffer with compaction and packet loss
concealment. This algorithm is suitable for mixing large conferences.
Number of conferences and participants
MAS has no hard limitations on how many simultaneous conferences can
exist on the system, or how many participants can be in each conference. The
maximum number of participants in a single conference, without bridging
multiple conferences together, is limited only by the capacity of the scaled
system, which can vary based on hardware and the operating system.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 20

Mixing different codecs
The system can mix participants with potentially different codecs in the same
conference. To achieve this, the system transcodes the incoming streams into
a common format, mixes, and then provides each participant with the correctly
mixed audio. The system optimizes for multiple participants by transcoding the
resulting mixed audio based upon a grouping of conference participants. If
every participant uses identical codecs, at least three groups exist in a
conference.
The first group contains the primary speaker, the second group contains the
secondary speaker, and the third group contains the remainder of the
participants. The groups describe the different versions of the mixed audio
required in a conference. The first and second groups exist because the
primary and secondary speakers do not hear their own voice, thus they must
receive a different version of the audio than other participants. The third group
is for all other participants who require the mixed audio of both active
speakers.
The system must transcode all incoming audio streams to test for energy.
However, if the basic conference algorithm is used, the system must
transcode only the audio of each group and then replicate for each participant
as needed. This conserves system resources. If multiple codecs exist in a
single conference or if the premium conference algorithm is used, additional
groups are required. The system can, therefore, optimize conferences with
more than three participants because the additional system resources
required for each participant includes transcoding the incoming audio stream
and testing for energy. The additional participants are assigned to existing
groups as needed so they receive the same audio as other group members.
- 20 -
MAS commissioning
The MAS can provide additional media processing functions for conferences
on a global conference basis or for each participant. Optionally, the system
can allocate a global announcement port that provides broadcast
announcement capability to all participants. Additionally, the system can
allocate a pseudo resource for each participant that enables the system to
perform digit collection, speech recognition, and whisper-like functions for a
specific individual.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 21

Media settings
This section describes audio codecs, video codecs, and digital relay.
Audio codecs
To configure audio codec settings, use the Nortel MAS Console. You can
complete the following configuration tasks for audio codecs:
• Enable or disable audio codecs. The following audio codecs are
• Configure the preferred order of enabled codecs for negotiation (Session
• Enable packet time (ptime) for each codec.
• Configure the default ptime for each codec.
- 21 -
MAS commissioning
supported:
— G.711-ULAW
— G.711-ALAW
— G.729A
— EVRC-0
Description Protocol [SDP] answer) or default SDP (SDP offer).
Video codecs
To configure video codec settings, use the Nortel MAS Console. You can
configure the following video codec settings:
• Enable or disable video codecs. The following video codecs are
supported:
— H.263
— H.263+
— H.263++
— NNVC
• Configure the preferred order of enabled codecs for negotiation (SDP
answer) or default SDP (SDP offer).
• Enable frame rates for each codec.
• Configure the Annex profile for each codec (if required).
Digit relay
To configure digit relay, use the Nortel MAS Console. You can configure the
following digit relay properties:
• Enable or disable the dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) relay method.
The following DTMF relay methods are supported:
— INFO Digits
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 22

— RFC2833
Attention: If you remove all methods, inband DTMF detection is forced,
which is not recommended because it degrades system capacity.
• Configure the preferred order of enabled DTMF relay methods for
negotiation (SDP answer) or default SDP (SDP offer).
• Configure the RFC2833 payload type. Nortel recommends that you select
the default payload type, which is determined dynamically. However, some
clients require a fixed payload type.
Conferencing
To configure conferencing, use the Nortel MAS Console. You can configure
the following conferencing properties:
• Enable or disable the Automatic Gain Control. The default is enabled.
• Enable or disable the Customized Replacement Video property. When
enabled, customer-supplied replacement video files are used. The default
selection is enabled.
- 22 -
MAS commissioning
• Enable or disable the
When enabled, the first party determines the video format. If the first party
is audio-only, the conference has no video. When disabled, the first party
with active video determines the video format. The default is enabled.
• Enable or disable the Replacement Video For Active Speaker property.
When enabled, the active speaker receives replacement video in
conferences where one or more than two (but not two) parties are enabled
to speak. The default is enabled.
• For the Silent Conference Teardown Delay (sec) property, configure the
number of seconds a conference must be silent before it is terminated (0
indicates no termination). The default value is one hour.
Quality of Service
MAS supports Differentiated Services (DiffServ) packet marking on outgoing
Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) streams. The system sets the DiffServ
Control Point (DSCP) to expedited forwarding (EF), which is a widely
supported indicator for QoS-enabled networks carrying real-time audio and
video data. Network routers that are QoS-enabled examine the type of service
bits in the IP header and provide priority (with respect to routing and handling)
to those packets marked with expedited forwarding. In addition to marking
packets, MAS uses high resolution, interrupt-driven timers to drive RTP
packetization at precise intervals.
Lock Video Format on First Party in Conference property.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 23

- 23 -
MAS commissioning
MAS uses flow specifications for each codec to identify packet delivery
characteristics to the operating system, enabling it to prioritize (internally)
packets destined to and from the network interface card (NIC). The framework
ensures that QoS marked packets sent from MAS media processors are not
dropped or delayed in their delivery to the wire. MAS can reserve a
percentage of NIC bandwidth for its media processors. This ensures that
management and signaling does not affect the quality of the audio or video
streams in use on the platform. Use of flow specifications also offers some
denial of service protection as the transport layers discard packets (instead of
attempting to process them) that do not conform to the flow specification.
MAS contains the Telchemy VQMON agent for QoS monitoring and RTCP-XR
support. R-Factor, jitter, and packet loss are continually monitored for each
call. Calls that fall below a configured R-Factor threshold are logged. All QoS
statistics are archived with session detail records for analysis.
To configure QoS, use the Nortel MAS Console. You can configure the
following QoS properties.
QoS properties
Property Description
QOS Maximum Bandwidth Per
H.263 Video Flow (Bytes)
QOS Maximum Bandwidth Per
NNVC Video Flow (Bytes)
QOS Monitoring Enable or disable QoS monitoring and reporting.
QOS Monitoring Critical R
Threshold (%)
QOS Monitoring Warning R
Threshold (%)
QOS Monitoring Maximum
Alerts
QOS Monitoring Alert Interval
(sec)
QOS Monitoring Refresh
Interval (sec)
The QoS maximum bandwidth for H.263 video flow
in bytes. The default is 300 kbytes.
The QoS maximum bandwidth for NNVC video
flow in bytes. The default is 300 kbytes.
The R-Factor threshold, which generates a critical
alert when the threshold is crossed. The default
value is 70%.
The R-Factor threshold, which generates a
warning alert when the threshold is crossed. The
default is 80%.
The maximum number of alerts that can be
generated during a particular interval (QoS
Monitoring Alert Interval). This property reduces
network traffic. The default value is 100.
The minimum time between QoS alert monitoring
(the alert refresh interval). The default value is 60
seconds.
The minimum time between QoS statistic
reporting. The default is 15 seconds. Nortel
recommends that you do not modify this property.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 24

Continuous streaming
The MAS platform supports continuous streaming of pretranscoded real-time
audio that applications can use to facilitate a radio broadcast effect. With this
feature, applications can give sessions music-on-hold streaming or connect
the sessions to Internet-streaming radio servers. Multiple sessions can listen
to the same real-time audio stream without the cost of transcoding the stream
on each session or connecting each session to a remote server.
The MAS platform can stream from the following providers: Directory or RSS.
The following sections describe these providers in detail.
To adjust the continuous stream volume, use the Nortel MAS Console to edit
the Continuous Streaming Volume Adjustment (dB) property (specify the
value in decibels [dB]).
Directory provider
With the directory provider, files in a local directory can be transcoded,
cached, and played indefinitely in alphabetic order. Continuous playback is
achieved by repeating the sequence. The platform monitors the directory and
detects any changes made for dynamic updates.
- 24 -
MAS commissioning
To configure the Directory Provider you must create a directory inside
%BASEDIR%\platdata\StreamSource\ChannelRoot. This directory name is
the channel name that the application specifies and is used to stream from this
source. Nortel recommends that you place all audio files in this directory.
RSS provider
The RSS provider can retrieve and parse Real Simple Syndication (RSS)
documents. The RSS provider downloads the contents of these documents so
the directory provider can play them. The RSS provider supports the following
features:
• automatic RSS feed synchronization —to automatically add and remove
content
• time-to-live attribute—to update content
• fault tolerance—to preserve local files until files are safely downloaded
• MP3 and WAV content types
RSS is a dialect of Extensible Markup Language (XML) and the platform
currently supports RSS 2.0. For more information, see the RSS 2.0
specification document at www.rss-specification.com.
The platform is currently limited to RSS documents that are no larger than
260 kbytes. The following illustration shows a sample RSS 2.0 document.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 25

RSS 2.0 sample document
- 25 -
MAS commissioning
To enable the RSS provider, you must configure the URL of the RSS
document. This document is fetched when you start the MAS platform or
change the URL. The RSS provider automatically adds or deletes content
when you change the URL. To configure the URL, use the Nortel MAS
Console.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 26

MAS administration and security
This chapter describes the administration tasks and security tools associated
with MAS operation and management.
Navigation
• Access security setup (page 26)
• Remote Desktop Protocol (page 28)
• IPSEC configuration (page 29)
• Security tools (page 29)
• Certificate management (page 30)
• Service and configuration data backup (page 31)
• Automatic and manual backups (page 31)
• System maintenance (page 33)
Access security setup
Administrative access to the MAS is obtained using the Microsoft Remote
Desktop Connection Client. This client is based on the Remote Desktop
Protocol (RDP), which provides access over separate virtual channels.
For the purposes of enhanced security, management access control is
restricted to a limited number of authorized IP addresses. The number of
authorized IP addresses must be less than or equal to the number of network
administrators.
A timeout feature, set to a default value of 15 minutes, is used to disconnect
idle connections. In addition, management ports that receive three
consecutive failed login attempts are made unavailable for at least 60
seconds, and network connected management ports drop a connection or
session that becomes disconnected for any reason, within 15 seconds.
RDP is separated from other traffic through the use of a virtual local area
network (VLAN). A VLAN is added through the Broadcom Advanced Control
Suite and a virtual adapter is created for each VLAN added.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 27

User accounts
This section introduces the concept of multiple users and user roles. To
accommodate customers who wish to use the shared account methodology,
support for the use of the shared administrator account is provided.
When a user is added to the system, it is defined as filling one of these user
roles assumes the ability to perform the administrative functions associated
with that role.
Individual user accounts provides full accountability and monitoring of
individual user actions on the system. User accounts are managed on an
individual basis for each server; it is the responsibility of the customer to
create each individual user account and to ensure that identical users are
created on each server within the MAS environment.
Each individual user account has a password that is processed through the
password complexity profile and can be enabled or disabled by a Security
System Administrator as required.
To maintain the accountability with individual users for the security of their
account, each individual user should be knowledgeable of only their own
password and not of the passwords of other users.
- 27 -
MAS administration and security
The following user roles (Windows User Groups) are identified with the MAS
system:
System Security Administrator (SSA)
The System Security Administrator is ultimately responsible for the complete
range of system administration functions, as follows:
• Maintaining Operating System configuration.
• Maintaining hardware and network configuration.
• Maintaining security policy configuration.
• Performing user management functions such as add, delete, or modify
accounts.
• Performing certificate management functions.
• Installing and upgrading MAS platform and application software.
• Performing any task or operation within the MAS Console.
Security Auditor (SA)
The Security Auditor (SA) monitors security related events on the MAS
system, and manages the security log files, including viewing the security log
files and creating backup archives of the security logs.
The Security Auditor does not have permission to run the MAS Console.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 28

- 28 -
MAS administration and security
Application Administrator (AA)
The Application Administrator (AA) performs administrative functions that
relate to the operation of applications on the MAS system, and can perform all
operations within the MAS Console. The Application Administrator can install
MAS software patches, but cannot access Event Viewer Security Logs.
Logon banners
A logon banner is a message screen that is displayed to users before a logon
to the system is attempted.
The logon banner does the following:
• informs users that they are logging onto a secure and private system, and
warns unauthorized users that unless they are authorized they should not
proceed.
• warns both authorized and unauthorized users that they are subject to
monitoring to detect unauthorized use.
A logon banner can be displayed to users before the login screen for the MAS
platform is displayed. Using a logon banner is optional. The banner title and
text values can be configured to display information for the system. The logon
banner is configured with default values when system is installed. After
installation, the customer is responsible for modifying the logon banner
settings if the default banner is not sufficient for their system.
Remote Desktop Protocol
Existing administrative access to the MAS is accomplished using the
Microsoft Remote Desktop Connection Client. This client is based on the
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) that provides for separate virtual channels.
IPSEC policy (with preshared key) is used to secure RDP. The RDP feature
for MAS 6.0 for AS 5300 continues to leverage IPSEC policy, however
replaces the preshared key with a TLS certificate (PKCS-12 format).
The following requirements apply to the MAS 6.0 for AS 5300 release:
• Management access control is restricted to a limited number of
authorized IP addresses. The number of IP addresses must be equal to
or less than the number of network administrators. A valid username and
password is required for access to the MAS.
• A timeout feature, set to 15 minutes, is used to disconnect idle
connections.
• Management ports that receive three consecutive failed logon attempts
are unavailable for at least 60 seconds (port 3389 for RDP).
• Network connected management ports drop a connection or session that
is interrupted for any reason within 15 seconds.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 29

• RDP is separated from other traffic by using a virtual local area network
(VLAN). A VLAN is added through the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite.
A virtual adapter is created for each VLAN added. The VLAN for RDP is
identified as the Management VLAN. The VLAN for all other network traffic
is identified as the Service VLAN.
• The only protocol assigned to the Mgmt VLAN in this release is RDP.
• Only accept RDP connections on the Mgmt VLAN
IPSEC configuration
IPSec is used to encrypt and authenticate communications between servers.
Each IPSec policy is made for both the source IP and for the destination.
There are three IPSec encryption algorithms available:
• DES (56bit key)
• AES (128bit key)
• 3DES (168bit key)
IPSec can be used to protect communications with servers outside of the
trusted system.
- 29 -
MAS administration and security
For detailed information about configuring IPSec, see Media Application
Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Commissioning (NN44470-301).
Security tools
This section details the security tools included with the MAS 6.0 for AS 5300
platform install. To preserve system security and file integrity, Nortel
recommends that the security tools are run continuously or periodically by the
onsite System Administrator to monitor potential security breaches.
Virus Protection using McAfee VirusScan Enterprise Edition 8.5
The virus protection software must be installed and configured to run
automatically on a weekly basis on every server. The McAfee VirusScan
Command Line Scanner software is included with the OS during installation
and comes preconfigured to run a scheduled scan once per week and to scan
the entire file system (excluding configured system directories) for potential
problems due to viruses.
When a virus scan is completed, the status is reported to the system log. Any
problems found are logged as critical in the system log and full details of the
error are then placed in the security log. Any files with suspected virus
infection are moved to a configured quarantine location. It is the responsibility
of a System Security Administrator to remove these files manually.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 30

- 30 -
MAS administration and security
The default scheduled time for a scan to run is on Sundays at 4:22 AM. A
script is provided to allow the configuration of a different day and time for when
the scan is executed, or to disable automatic scanning entirely if this is
desired. Scanning the entire file system (excluding configured system
directories) takes at least 20 minutes under no load. This should be taken into
account when determining the day and time when the scanner is to be run.
Retrieving the latest virus definition files from McAfee and manually loading
them on the system is the responsibility of the onsite System Security
Administrator.
File system integrity and the fcheck tool
The file system integrity security tool allows an System Security Administrator
create a baseline of cryptographic hashes for a subset of files on the file
system. Once a baseline is created, future baselines can then be compared
against previous baselines to give the System Security Administrator an
indication of what files have changed on the system since the last time the tool
was run. Depending on which files were changed, added, or deleted since the
last baseline was taken, the System Security Administrator can determine
whether or not a security breach has occurred.
The file system integrity tool fcheck is the baselining tool used in this process,
and is included with the OS installation. The fcheck tool must be run manually
by an onsite System Security Administrator and must not be scheduled to run
automatically by the system. The System Security Administrator must
determine how frequently (weekly, for example) and under what conditions a
baseline should be taken.
The purpose of the file security integrity tool is to track files that should not
change very often. The tool allows a list of excluded directories and files to be
used.
Usage instructions and documentation are included in the default directory
location (C:\fcheck).
Certificate management
MAS 6.0 for AS 5300 uses the X.509 certificate type, that contains the public
key for a server and a signature from the certification authority (CA). A
certification authority is a trusted entity that issues, renews, and revokes
certificates.
A server uses a certificate to identify itself. A TLS or SSL connection or an
IPSec channel between two servers is established after two servers exchange
certificates and authentication is completed when the certificates are verified.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 31

- 31 -
MAS administration and security
To create and install a valid certificate, you must do the following:
• Generate a public and private key pair.
• Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
• Send CSR to CA to request the certificate.
• Transfer CA-signed certificate to the MAS using SFTP.
• Install the certificate using the MAS Console.
A certificate may also be revoked by the CA. A Certificate Revocation List
(CRL) must be obtained from the CA and installed on the server. When a new
CRL is available from the CA, the previously installed CRL on the server is
replaced.
• The CRL is obtained from the CA using a secure method.
• The CRL is installed in a designated location on the server.
Service and configuration data backup
The following sections define configuration data and application data.
Configuration data
Configuration data is the system configuration data that includes all the
configuration parameters. You can use the Nortel MAS Console to view the
configuration parameters.
Service data
Application data is the user data that resides on disk in the managed storage
area of the Content Store.
Automatic and manual backups
This section explains the backup and restore capabilities on the MAS
platform. To back up and restore configuration and service data, you can use
the Nortel MAS Console.
You can use the automatic backup task menu to create regularly scheduled
backups to run, for example, daily, weekly, and biweekly. You can configure the
local destination directory using the properties panel. In the automatic backup
task menu, you can transfer the archive to a remote server through the File
Transfer Protocol (FTP). You can use the properties panel to access the FTP
host, user name, password, destination path, and the option to delete the local
file after transfer.
The following sections explain backup and restore functions for configuration
data and service data.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 32

MAS administration and security
Backup of configuration data
You can back up configuration data while the system is online, but the MAS
must be offline before you can perform a restore operation.
The configuration data backup file contains the following files:
• an SQL database dump that contains data from the system configurationrelated database
• a text file that contains metadata for the load
• a text file that contains metadata for the schema versions
Restrictions
The backup zip file contains metadata that defines the complete load version,
for example, 5.0.193. You can perform restore operations only if the load
version metadata in the backup file is identical to the running load version.
Attention: You must create a backup file after any installation or upgrade to
ensure a compatible backup is available for restoration. If you do not create
a backup file, you cannot restore the currently running version.
- 32 -
Service data (Content Store data)
You can back up service data while the system is online, but the MAS must be
offline before you can perform a restore operation.
The service data backup file contains the following files:
• an SQL database dump that contains data from the Content Store-related
database
• a zip file of all files on disk in the managed storage area of the Content
Store
• a text file containing the metadata for the load
• a text file containing the schema versions
Restrictions
The backup zip file contains metadata that defines the complete load version,
for example, 5.0.193. You can perform restore operations only if the major load
version in the backup file matches the running major load version. Minor
version, load build number, and schema version are not considered.
Attention: You must create a backup file after any installation or upgrade to
ensure a compatible backup is available for restoration. However, unlike
configuration data, you can perform a restoration from a noncompatible
backup file only if you perform an upgrade from a previous release or the
major load version is 5, for example MAS 1.0.193.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 33

System maintenance
It is good practice to perform routine maintenance tasks to avoid problems that
can affect server performance or cause the server to fail. The MAS platform
includes a number of useful tools and indicators to help you monitor your
server performance quickly and easily. With these tools, you can perform
regular maintenance routines.
Event logs
To ensure you are aware of service-affecting events so that you can take
appropriate action, check your event logs daily. Investigate any unusual
alarms or events, changes in alarm patterns, or inordinate alarm volumes.
Backups
To protect your site against data loss, maintain up-to-date backups. Ensure
you have a full system backup scheduled at regular intervals, even on systems
equipped with Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID). A full system
backup is critical to prevent data loss if a system failure occurs, such as a disk
drive failure or data corruption. Nortel also recommends that you perform a full
system backup before you upgrade or install new software. You can schedule
backups to run online while the system is still in service; however, Nortel
recommends that you schedule backups for off-peak hours.
- 33 -
MAS administration and security
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 34

MAS performance management
Performance management includes report generation and Operational
Measurements. For detailed information about MAS performance
management, see Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Performance
Management (NN44470-701).
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 35

MAS fault management
This chapter describes fault management on the MAS platform. For step-bystep information, see Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Troubleshooting and Fault Management (NN44470-700).
Navigation
• Fault management architecture (page 35)
• SNMP management (page 36)
• Supported MIBs (page 36)
• Syslog (page 37)
• Event logs (page 37)
• Alarms (page 39)
Fault management architecture
This section describes the fault management architecture.
Polling management data
The MAS supports the polled management model of the Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP) to facilitate well-controlled network
management traffic and to enable reliable data synchronization through a
request-response interaction. By maintaining Management Information Base
(MIB) tables and variables, the Internet Protocol (IP) Multimedia System (IMS)
enables the following functions:
• To recover the missing data due to lost notifications. This is referred to as
auditing and is described in the next section.
• To perform initial data synchronization for the active alarm list.
• To monitor the status of operation, administration, and maintenance
(OAM) communications with the agents and resynchronize all data after
recovering from communication loss.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 36

Auditing
Auditing includes regular auditing and data auditing. With regular auditing, you
can use the SNMP agent to poll the value of the following MIB variables:
• sysUpTime (1.3.6.1.4.1.562.29.1.1.3)
• currentTxNotificationSequenceNum (1.3.6.1.4.1.562.29.1.6.1)
Active alarm status
A management application can determine the latest alarm for a particular
network element. When the network element instance restarts, the value is
reset to zero.
SNMP management
The MAS platform provides SNMP management. SNMP management
supports outgoing traps for logs and alarms to remote SNMP-based Network
Management Stations (NMS). In addition, NMS can query alarm table and
audit services. Use the Nortel MAS Console to activate the Windows SNMP
service and configure system parameters.
- 36 -
MAS fault management
Traps
Traps use the Nortel Reliable MIB format to support active and cleared alarm
notifications as well as informational log messages. To enable or disable
alarm-related traps and information log traps, use the Nortel MAS Console.
MAS SNMP agent
The MAS SNMP agent supports queries on the ActiveAlarm table and audits
for resynchronization with the management server. These queries can be in
the form of Get requests on specific fields or GetNext requests for table
traversal.
SNMPv1/v2
SNMPv1/v2 uses community names to authenticate messages. The
community name is like a password shared by the SNMP NMS and the MAS
SNMP agent. The community name must be the same value on both the NMS
and the MAS SNMP agent.
Supported MIBs
Nortel supports the following MIBs. You must load MIBs in the following order:
1nortel.mib
2 nortelGenericMIBs-smi2.mib
3 nortelNMItextConv-smi2.mib
4 nortelNMIconfigMgmt-smi2.mib
5 nortelNMIconformance-smi2.mib
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 37

- 37 -
MAS fault management
6 nortelNMImibGroups-smi2.mib
7 nortelNMIresourceMgmt-smi2.mib
8 nortelNMInotifications-smi2.mib
9 nortelNMIneInventory-smi2.mib
10 nortelNMIconfigNoti-smi2.mib
11 nortelNMIfaultMgmt-smi2.mib
12 nortelNMIfaultNoti-smi2.mib
13 nortelNMIalarmSurv-smi2.mib
14 nortelNMIstateInfo-smi2.mib
15 nortelNMIappComplianceIndications-smi2.mib
16 nortelNMIappRequirements-smi2.mib
17 nortelCSMOAappRequirements-smi2.mib
18 nortelCSMOAappComplianceIndications-smi2.mib
Syslog
Event logs
Syslog is a standard for forwarding log messages in an IP network. The MAS
platform optionally supports syslog over User Datagram Protocol (UDP) for
the delivery of logs and alarm history to one or more syslog server
destinations.
To enable or disable syslog delivery, use the Delivery of SYSLOG property
(found in the Nortel MAS Console). To configure one or more syslog server
destinations, use the SYSLOG Destination Server List property (found in the
Nortel MAS Console). You can enter the syslog server host name or IP
address; separate each entry with a semicolon.
Event logs provide a historical view of events that occur on the system. Event
logs are delivered to all configured destinations, which may include the MAS
management console, syslog destinations, SNMP destinations, and the local
Microsoft Event Viewer. The system automatically archives and rotates the
logs as needed.
Every log is assigned one of the following severities: Error, Warning, or
Informational. Errors are the most severe and provide further details on alarm
conditions. Warnings are less severe and are generated for events such as
raising or clearing an alarm. Informational logs are the least severe and
provide indication of processing, such as new connections initialized for each
component during startup.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 38

- 38 -
MAS fault management
You can configure logs to syslog destinations and to be sent as SNMP traps
when generated.
To view event logs, use the Nortel MAS Console. The following table describes
the information that you can view in each event log.
Field Description
Type Event log severity. (Error, Warning, or
Informational). In addition, a colored icon
represents the log type. Red indicates Error, yellow
indicates Warning, and white indicates
Informational.
Timestamp Timestamp of when the event was logged. You can
configure the timestamp to display as either local
time or Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) time.
UTC time is useful for correlating logs with events
in other time zones.
Id Identifier assigned to the event log.
Description A description of the event log.
Source The platform component that generated the log.
Security Logs
Security logs provide Security Administrators and Auditors the ability to track
critical operations of the system and to analyze historical data should a
security breach occur. Security logs are viewed using the Event Viewer
Administrative tool.
Security logs are archived using the Save Log File As... popup menu option in
the Event Viewer. It is the responsibility of onsite personnel to transfer these
files off of the system if a backup of the security logs is required.
Access to security logs is restricted to either SSA or SA users.
The following parameters are set during installation:
• MaximumLogSize = 81920 KB
• AuditLogRetentionPeriod = 2
Windows OS Security Logs
All system events such as logins, file access, file handling, and network
access are all tracked using various Windows operating system services.
The rules that govern these logs are factory configured and installed on
the server during installation.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 39

MAS fault management
At a minimum, the following are monitored and logged by the OS:
• User authentication attempts
• Unauthorized attempts to access resources (files or programs on the
server, for example)
• User login attempts (both successes and failures)
• Changes made to a user security profile or to user attributes
• Disabling and enabling of a user profile
• Changes made to security profile or attributes associated with a channel
or port
• Changes made to access rights associated with resources
• Changes made in the security configuration
MAS Console security logs
The MAS Console generates security logs for the following operations:
• Software stops, starts, and restarts
- 39 -
Alarms
• Operational state changes (lock, pending-lock, or lock) for platform or
applications
• Changes made to configuration data
• Backups and Restores (system or service data)
• Active sessions control (mute, un-mute, and delete)
• Generate Report (control panel)
A critical event viewer application log is generated if the console is unable to
write to a security log. The contents of the log are as follows:
• Description
• Date and Time
•User ID
• Type of Operation (for example, stops, starts, or configuration data
changes)
• Source (client) IP address
• Success and Failure of operations
When a serious error is detected and corrective action is required, the MAS
platform generates an alarm. Alarms generate an event log each time an
alarm is raised or cleared and this provides a clear record of all state changes
on the platform.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 40

- 40 -
MAS fault management
Every alarm is assigned one of the following severities:
•Critical
• Major
• Minor
• Warning
Optionally, you can configure alarms to be sent as SNMP traps when alarms
are raised or cleared, which is described in SNMP management (page 36). A
network management station can use SNMP to poll the platform to determine
which alarms are active.
To view active alarms, use the Nortel MAS Console. The following table
describes the information that you can view for each alarm.
Field Description
Alarm ID A globally unique identifier assigned to the alarm. In addition a
colored icon represents the alarm severity. Red indicates Critical
and yellow represents all other alarms.
Name Descriptive text associated with the alarm.
Severity The severity of the alarm, which can be one of the following (listed
from most to least severe): Critical, Major, Minor, and Warning.
Timestamp Timestamp of when the alarm was raised. You can configure
timestamps to display as either local time or UTC time. UTC time
is useful for correlating alarms with events in other time zones.
(1 of 2)
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 41

- 41 -
MAS fault management
Field Description
Type Alarm type. The following is a list of alarm types:
• GENERIC
• ATTRCHANGE
• COMMALARM
• ENVIRONALARM
• EQUIPALARM
• INTEGRITYVIOLATION
• OBJCREATION
• OBJDELETION
• OPERATIONALVIOLATION
• PHYSICALVIOLATION
• PROCESSINGERROR
• QOSALARM
• QOSALARM
• RELATIONCHANGE
• SECURITYVIOLATION
• STATECHANGE
• TIMEDOMAINVIOLATION
Probable Cause A description of what probably caused this alarm to be raised.
Corrective
Suggested corrective action to resolve this error.
Action
(2 of 2)
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 42

Nortel MAS Console
This chapter describes the Nortel MAS Console application. You can use the
Nortel MAS Console to manage, monitor, and configure the MAS platform.
The Nortel MAS Console is a Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in
and is installed with the platform. To access the Nortel MAS Console, you
must use a Remote Desktop Connection. The Nortel MAS Console provides
nodal access only. Alternatively, you can use the Remote Console to
configure, manage, and monitor multiple MASs from a user desktop.
Navigation
• Counters & Gauges (page 42)
• Nortel MAS Console (page 43)
• Dialog boxes (page 45)
Counters & Gauges
You can complete the following tasks in the Counters & Gauges view.
• create a new counter set
• view current activity
• view log data
• view graph
• view histogram
• view report
• add counters
• view system monitor properties
• freeze display
• update data
For more information about Counters and Gauges, see Media Application
Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Performance Management (NN44470-701). For
detailed information about using the Counters & Gauges view, see the online
Help that is available with this view.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 43

Nortel MAS Console
You can view or configure the following items in the Nortel MAS Console view
of the Nortel MAS Console application.
Command Description
Active Sessions Use the Active Sessions command to view active sessions. You
Log Viewer Use the Log Viewer command to view all system logs. You
Statistics Use the Statistics command to view system statistics. You can
Configuration Use the Configuration command to access the following
- 43 -
Nortel MAS Console
cannot configure active sessions.
cannot configure system logs.
configure system statistics.
For more information about configuration, see Media Application
Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Performance Management
(NN44450-701).
sections:
• IP Interfaces (page 43)
Alarms Use the Alarms command to view active alarms. You cannot
Control Panel Use the Control Panel command to perform administrative type
IP Interfaces
Use the IP Interfaces menu option to configure general settings for the MAS
platform, for example, IP address and node name.
• Logging (page 44)
• Applications (page 44)
• Licensing (page 44)
• Signaling (page 44)
• Media Settings (page 44)
• Management (page 44)
• Clustering (page 44)
• Reporter (page 44)
• Advanced Settings (page 44)
For more information about configuration, see Media Application
Server 6.0 for AS 5300 Commissioning (NN44470-301).
configure active alarms.
of operations.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 44

Logging
Use the Logging command to view and configure trace logs, the syslog, the
Session Detail Record archive, and the Operational Measurement (OM)
archive.
Applications
Use the Applications command to:
• view and modify installed packaged applications
• view and modify the operational state of packaged applications
• create, delete, view, and modify translations
Attention: This release does not support custom applications.
Licensing
Use the Licensing command to configure license keys and servers.
- 44 -
Nortel MAS Console
Signaling
Use the Signaling command to view and configure SIP domains, SIP
accounts, SIP trusted nodes, SIP routes, and general SIP settings.
Attention: This release does not support MRCP.
Media Settings
Use the Media Settings command to configure media-related settings, such
as audio codecs, video codecs, DTMF relay, streaming, conference settings,
and QoS.
Management
Use the Management command to configure remote management (SNMP or
SOAP) and users.
Clustering
Use the Clustering command to configure a cluster of MAS platform nodes.
Reporter
Use the Reporter command to configure report generation.
Advanced Settings
Use the Advanced Settings command to view and configure trace logging,
media processing, network settings, and engineering parameters.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 45

Dialog boxes
- 45 -
Nortel MAS Console
Attention: Nortel recommends that you change advanced settings only if
Nortel product development instructs you to do so.
This section describes the following dialog boxes:
• Configuration properties (page 45)
• Translation properties (page 46)
• SIP domain properties (page 48)
• SIP account properties (page 49)
• SIP Trusted Nodes properties (page 50)
• SIP route properties (page 50)
• Audio codec configuration (page 52)
• Video codec configuration (page 53)
• Digit relay configuration (page 55)
• Users properties (page 56)
Configuration properties
You can use the Configuration Properties dialog box (page 46) to view the
properties for:
• Logging
• Licensing
• SIP General Settings
• Media Settings
• Management General Settings
•Clustering
• Reporter
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 46

- 46 -
Nortel MAS Console
Configuration Properties dialog box
The following table describes the Configuration Properties dialog box fields
and buttons.
Field Description
Key This is a read-only field. It is the configuration
parameter name.
Description This is a read-only field. It provides a description of
Restart required This is a read-only field. It indicates whether a
Value The Value field represents the current value of the
Restore Default Click Restore Default to restore the configuration to
OK Click OK to close the dialog box.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving
Apply Click Apply to save property changes.
Translation properties
The following figure shows an example of a Translation Properties dialog box.
the selected configuration item.
restart is required if you modify the properties for
this configuration item. Values are Yes and No.
Yes indicates a platform restart is required for the
configuration change to take effect.
configuration parameter.
the factory default value.
changes.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 47

- 47 -
Nortel MAS Console
Translation Properties dialog box
The following table describes the Translation Properties dialog box fields and
buttons.
Field Description
Application Name After you create and save a translation, this field is
read-only.
Mode The mode applied to the algorithm. You can select
one of the following modes:
• None
• SIP Request URI
• Called DN
• Calling DN
• SIP Request URI User
• SIP To
• SIP From
(1 of 2)
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 48

- 48 -
Nortel MAS Console
Field Description
Algorithm The algorithm is used to determine if there is a
match between the translation and the SIP
request.You can select one of the following
algorithms:
• None
• Substring Match
• Regular Expression
• Exact Match
• Case Insensitive Match
• Hash
• Dial Plan Notation
Pattern Regular expression that is used when the
application determines if the algorithm finds a
match.
Rank The order in which to apply translations if multiple
translations match. If translations have the same
rank, the translations are selected in the order that
it is defined.
OK Click OK to close the dialog box.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving
Apply Click Apply to save property changes.
SIP domain properties
The following figure shows an example of a SIP Domain Properties dialog box.
SIP Domain Properties dialog box
changes.
(2 of 2)
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 49

The following table describes the SIP Domain Properties dialog box fields and
buttons.
Field Description
Edit Domain Name Type the new SIP domain name.
OK Click OK to close the dialog box.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving
Apply Click Apply to save property changes.
SIP account properties
The following figure shows an example of a SIP Account Properties dialog
box.
SIP Account Properties dialog box
- 49 -
Nortel MAS Console
changes.
The following table describes the SIP Account Properties dialog box fields and
buttons.
Field Description
Name Type the new SIP account name.
Password Type the new password
Domain Select a SIP domain for this SIP account.
OK Click OK to close the dialog box.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving
Apply Click Apply to save property changes.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
changes.
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 50

Nortel MAS Console
SIP Trusted Nodes properties
The following figure shows an example of a SIP Trusted Nodes Properties
dialog box.
SIP Trusted Nodes Properties dialog box
The following table describes the SIP Trusted Nodes Properties dialog box
fields and buttons.
- 50 -
Field Description
Host or IP Type the host name or IP address for the trusted
Restart Required This is a read-only field. It indicates whether a
OK Click OK to close the dialog box.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving
Apply Click Apply to save property changes.
SIP route properties
The following figure shows an example of a Modify SIP Route dialog box.
node.
Attention: If you use a host name, you must use
a Domain Name System (DNS) server to resolve it.
restart of the server is required if you modify the
trusted node host name or IP address. Values are
Yes and No. Yes indicates a platform restart is
required for the configuration change to take effect.
changes.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 51

- 51 -
Nortel MAS Console
Modify SIP Route dialog box
The following table describes the Modify SIP Route dialog box fields and
buttons.
Field Description
Domain Select the domain to associate with this SIP route.
If no route is configured for a domain, routes
associated with the wildcard domain are used.
Trusted Node Select the trusted node to associate with this route.
Transport Select the one of the following SIP transports:
UDP, TCP, or TLS.
Attention: TLS is not supported.
Remote Port Type the remote port on which the route is
accepting SIP requests.
Priority Priority values with a range of 0 – 65535. The
lowest value is the highest priority. The default
priority is 0.
Weight Priority values range from 0 – 65535. The default
priority is 10.
Role(s) Select the roles that this SIP route performs. You
can select Proxy and Registrar.
Enabled Select the Enabled check box to enable or disable
a selected route. Typically routes are enabled, but
you can disable a route to remove it temporarily
without reconfiguring the system.
(1 of 2)
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 52

Nortel MAS Console
Field Description
Restart Required This is a read-only field. It indicates whether a
OK Click OK to close the dialog box.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving
Audio codec configuration
The following figure shows an example of an Audio Codec Configuration
Dialog box.
Audio Codec Configuration dialog box
- 52 -
restart of the server is required if you modify the
trusted node host name or IP address. Values are
Yes and No.
changes.
(2 of 2)
The following table describes the Audio Codec Configuration dialog box fields
and buttons.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 53

- 53 -
Nortel MAS Console
Field Description
Supported Audio Codecs The following audio codecs are supported: G.711-
ULAW, G.711-ALAW, EVRC-0, and G.729A. To
enable an audio codec, from the Available list,
select an audio codec, and then click the right
arrow. Use the left arrow to remove an audio
codec.
Add Click Add to enable an audio codec. From the
Available list, select an audio codec, and then click
Add.
Add All Click Add to enable all audio codecs. From the
Available list, select an audio codec, and then click
Add All.
Remove Click Remove to disable an audio codec. From the
Enable list, select an audio codec, and then click
Remove.
ptimes Select the packet times (ptimes) to enable for each
enabled audio codec.
Default Select the default packet time for each enabled
Restart Required This is a read-only field. It indicates whether a
OK Click OK to close the dialog box.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving
Video codec configuration
The following figure shows an example of a Video Codec Configuration dialog
box.
audio codec.
restart of the server is required if you modify the
trusted node host name or IP address. Values are
Yes and No. Yes indicates a platform restart is
required for the configuration change to take effect.
changes.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 54

- 54 -
Nortel MAS Console
Video Codec Configuration dialog box
The following table describes the Video Codec Configuration dialog box fields
and buttons.
Field Description
Supported Audio Codecs Lists the following supported video codecs that you
can enable or disable: H.263 and NNVC.
Add Click Add to enable a video codec. From the
Available list, select a video codec, and then click
Add.
Add All Click Add to enable all video codecs. From the
Available list, select a video codec, and then click
Add All.
Remove Click Remove to disable a video codec. From the
Enable list, select a video codec, and then click
Remove.
Remove All Click Remove All to disable all video codecs. From
the Enable list, select a video codec, and then click
Remove All.
Up and Down Use the Up and Down buttons to change the order
of the enabled video codecs.
Allowed Frame Rates Select the frame rates for each enabled video
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
codec.
(1 of 2)
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 55

- 55 -
Nortel MAS Console
Field Description
Default Rates Select the default frame rate for each enabled
video codec.
Preferred Format Select the preferred format for each enabled video
codec.
Annex Profile Select the annex profile for each enabled video
codec.
Restart Required This is a read-only field. It indicates whether a
restart of the server is required if you modify the
trusted node host name or IP address. Values are
Yes and No. Yes indicates a platform restart is
required for the configuration change to take effect.
OK Click OK to close the dialog box.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving
changes.
(2 of 2)
Digit relay configuration
The following figure shows an example of a Configure Digit Relay dialog box.
Configure Digit Relay dialog box
The following table describes the Configure Digit Relay dialog box fields and
buttons.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 56

- 56 -
Nortel MAS Console
Field Description
Supported Digital Relay
Methods
You can enable or disable the following supported
digital relay methods: INFO Digits and RFC2833.
Attention: Nortel recommends that you do not
disable all methods. If you disable all methods,
inband DTMF detection is enforced and system
capacity degrades.
Add Click Add to enable a digital relay method. From
the Available list, select a digital relay method, and
then click Add.
Add All Click Add All to enable all digital relay methods.
From the Available list, select a digital relay
method, and then click Add All.
Remove Click Remove to disable a digital relay method.
From the Enable list, select a digital relay method,
and then click Remove.
Remove All Click Remove All to disable all digital relay
methods. From the Enable list, select a digital relay
method, and then click Remove All.
Up and Down Use the Up and Down buttons to change the order
of the enabled digital relay methods.
Assign RFC 2833 Payload
Type Dynamically
This check box is selected by default. Nortel
recommends that RFC 2833 payload type is
assigned dynamically. However, some clients
require a fixed payload type.
Specify Type If you require a fixed payload type, clear the Assign
Restart Required This is a read-only field. It indicates whether a
OK Click OK to close the dialog box.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving
Users properties
The following figure shows an example of a Users Properties dialog box.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
RFC 2833 Payload Type Dynamically check box,
and then in the Specify Type box, type the payload
type.
restart of the server is required if you modify the
trusted node host name or IP address. Values are
Yes and No. Yes indicates a platform restart is
required for the configuration change to take effect.
changes.
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 57

- 57 -
Nortel MAS Console
User Properties dialog box
The following table describes the User Properties dialog box fields and
buttons.
Field Description
Key This is a read-only field.
Description This is a read-only field. It provides a description
for the selected configuration item.
Restart required This is a read-only field. It indicates whether a
restart is required if you modify the properties of
this configuration item. Values are Yes and No.
Yes indicates a platform restart is required for the
configuration change to take effect.
Enable Account Select the Enable Account check box to modify the
user name and password fields or reset the
password.
User name and Password Enter the user name and password in these fields.
Reset Password Use to reset the password.
OK Click OK to close the dialog box.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving
changes.
Apply Click Apply to save property changes.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 58

Terminology
A
digest access authentication
A method which web page can use to establish user identity (using the
Hypertext Transfer Protocol) without having to send a password in plaintext
over the network.
audio codec
A computer program that compresses and decompresses digital audio data
according to a given audio file format or streaming audio format.
ASR
See automatic speech recognition.
automatic speech recognition
The process of converting a speech signal to a sequence of words, by means
of an algorithm implemented as a computer program.
C
Call Control Extensible Markup Language
An Extensible Markup Language (XML) standard designed to provide
telephony support to VoiceXML. Informs the voice browser how to handle the
telephony control of the voice channel. See also Voice Extensible Markup
Language.
CCXML
See Call Control Extensible Markup Language.
D
Differentiated Services
A computer networking architecture that specifies a simple, scalable, and
coarse-grained mechanism for classifying, managing network traffic, and
providing Quality of Service (QoS) guarantees on IP networks.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 59

M
- 59 -
Terminology
Differentiated Services Code Point
A field in an IP packet that enables different levels of service to be assigned
to network traffic. This is achieved by marking each packet on the network with
a DSCP code and assigning to it the corresponding level of service.
DSCP
See Differentiated Services Code Point.
DTMF
See dual-tone multi-frequency.
dual-tone multi-frequency
A system of signal tones used in telecommunications. Also known as touchtone.
Management Information Base
A type of database used to manage the devices in a communications network.
It comprises a collection of objects in a (virtual) database used to manage
entities (such as routers and switches) in a network.
R
MAS
See Media Application Server.
Media Application Server
A media services platform that supports a diverse range of multimedia
services and applications.
MIB
See Management Information Base.
Media Server Link
A proprietary network messaging protocol.
MSLink
See Media Server Link.
RAID
See Redundant Array of Independent Disks.
Real-time Transport Protocol
A standardized packet format for delivering audio and video over the Internet.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 60

S
- 60 -
Terminology
Redundant Array of Independent Disks
A category of disk drives that employ two or more drives in combination for
fault tolerance and performance. RAID disk drives are used frequently on
servers.
RTP
See Real-time Transport Protocol.
SDP
See Session Description Protocol.
Session Description Protocol
Session Description Protocol (SDP), is a format for describing streaming
media initialization parameters. SDP is intended for describing multimedia
sessions for the purposes of session announcement, session invitation, and
other forms of multimedia session initiation.
Session Information Protocol
An application-layer control protocol that can establish, modify and terminate
multimedia sessions or calls.
T
Simple Network Management Protocol
Used by network management systems to monitor network-attached devices
for conditions that warrant administrative attention. Simple Network
Management Protocol consists of a set of standards for network
management, including an Application Layer protocol, a database schema,
and a set of data objects
Simple Network Time Protocol
An Internet protocol used to synchronize computer clocks in the Internet.
SIP
See Session Information Protocol.
SNMP
See Simple Network Management Protocol.
SNTP
See Simple Network Time Protocol.
Text-to-speech
A text-to-speech (TTS) system converts normal language text into speech.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 61

U
- 61 -
Terminology
TTS
See Text-to-speech.
UDP
See User Datagram Protocol.
Universal Resource Indicator
A short string of characters that represent the address or location of
resources, typically on the Internet, and how that resource should be
accessed.
URI
See Universal Resource Indicator.
User Datagram Protocol
One of the core protocols of the Internet protocol suite. Using UDP, programs
on networked computers can send short messages to one another
V
video codec
A computer program that compresses and decompresses digital video data
according to a given video file format or streaming video format.
VXML
See Voice Extensible Markup Language
Voice Extensible Markup Language
A standard XML format for specifying interactive voice dialogues between a
human and a computer.
Copyright © 2008, Nortel Networks
Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
NN44470-100 01.01 Standard
Release 6.0 03 June 2008
Page 62

Page 63

Nortel Media Application Server 6.0 for AS 5300
Fundamentals
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Sourced in Canada and the United States
Publication: NN44470-100
Document status: Standard
Document issue: 01.01
Document date: 03 June 2008
Product release: Release 6.0
Job function: Product Fundamentals
Type: NTP
Language type: English
Nortel, the Nortel logo and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Microsoft Event Viewer, and Microsoft Management Console are
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
To provide feedback or report a problem with this document, go to www.nortel.com/documentfeedback.
 Loading...
Loading...