Page 1
[Standard Level - Nortel Networks Confidential]
VersionMCP1.1FP1(02.02)
Part No. NN10043-113
April 2003
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 2

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
ii
Copyright © 2003 Nortel Networks
All rights reserved. April 2003.
The informationin this document is subjectto change without notice. The statements, configurations,technicaldata, and
recommendationsin this document are b elieved to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The
information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks Inc.
The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement and may be used only in accordance
with the terms of that license. The software license agreement is included in this document.
Trademarks
Nortel Networks, the Nortel Networks logo, the Globemark, Unified Networks, CallPilot, and i2004 Internet Telephone
are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Adobe and Acrobat Reader are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT, Internet Explorer and Outlook are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Netscape is a trademark of Netscape Communications Corporation.
The asterisk after a name denotes a trademarked item.
Restricted rights legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United States Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph
(c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013.
Notwithstanding any other license agreement that m ay pertain to, or accompany the delivery of, this computer software,
the rights of the United States Government regarding its use, reproduction, and disclosure are as set forth in the
Commercial Computer Software-Restricted Rights clause at FAR 52.227-19.
Statement of conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, Nortel Networks Inc. reserves the
right to make changes to the products described in this document without notice.
Nortel Networks Inc. does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or
circuit layout(s) described herein.
Portions of the code in this software product may be Copyright © 1988, Regents of the University of California. All
rights reserved. Redistribution and use in source and binary forms of such portions are permitted, provided that the
above copyright notice and this paragraph are duplicated in all such forms and that any documentation, advertising
materials, and other materials related to such distribution and use acknowledge that such portions of the software were
developed by the University of California, Berkeley. The name of the University may not be used to endorse or promote
products derived from such portions of the software without specific prior written permission.
SUCH PORTIONS OF THE SOFTWARE ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES,INCLUDING,WITHOUT LIMITATION,THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
In addition, the program and informationcontainedherein are licensed only pursuant to a license agreement that contains
restrictions on use and disclosure (that may incorporate by reference certain limitations and notices imposed by third
parties).
NN10043-113
Page 3

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Nortel Networks Inc. software license agreement
This Software License Agreement (“License Agreement”) is between you, the end-user (“Customer”) and Nortel
Networks Corporation and its subsidiaries and affiliates (“Nortel Networks”). PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING
CAREFULLY. YOU MUST ACCEPT THESE LICENSE TERMS IN ORDER TO DOWNLOAD AND/OR USE THE
SOFTWARE. USE OF THE SOFTWARE CONSTITUTES YOUR ACCEPTANCE OF THIS LICENSE
AGREEMENT. If you do not accept these terms and conditions, return the Software, unused and in the original shipping
container, within 30 days of purchase to obtain a credit for the full purchase price.
“Software” is owned or licensed by Nortel Networks, its parent or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates, and is copyrighted
and licensed, not sold. Software consists of machine-readable instructions, its components, data, audio-visual content
(such as images, text, recordings or pictures) and related licensed materials including all whole or partial copies. Nortel
Networks grants you a license to use the Software only in the country where you acquired the Software. You obtain no
rights other than those granted to you under this License Agreement. You are responsible for the selection of the
Software and for the installation of, use of, and results obtained from the Software.
1. Licensed Use of Software. Nortel Networks grants Customer a nonexclusive license to use a copy of the Software
on only one machine at any one time or to the extent of the activation or authorized usage level, whichever is applicable.
To the extent Software is furnished for use with designated hardware or Customer furnished equipment (“CFE”),
Customer is granted a nonexclusive license to use Software only on such hardware or CFE, as applicable. Software
contains trade secrets and Customer agrees to treat Software as confidential information using the same care and
discretion Customer uses with its own similar information that it does not wish to disclose, publish or disseminate.
Customer will ensure that anyone who uses the Software does so only in compliance with the terms of this Agreement.
Customer shall not a) use, copy, modify, transfer or distribute the Software except as expressly authorized; b) reverse
assemble, reverse compile, reverse engineer or otherwise translate the Software; c) create derivative works or
modifications unless expressly authorized; or d) sublicense, rent or lease the Software. Licensors of intellectual property
to Nortel Networks are beneficiaries of this provision. Upon termination or breach of the license by Customer or in the
event designated hardware or CFE is no longer in use, Customer will promptly return the Software to Nortel Networks
or certify its destruction. Nortel Networks may audit by remote polling or other reasonable means to determine
Customer’s Software activation or usage levels. If suppliers of third party software included in Software require Nortel
Networks to include additional or different terms, Customer agrees to abide by such terms provided by Nortel Networks
with respect to such third party software.
2. Warranty.Except as may be otherwise expressly agreed to in writing between Nortel Networks and Customer,
Software is provided “AS IS” without any warranties (conditions) of any kind. NORTEL NETWORKS DISCLAIMS
ALL WARRANTIES (CONDITIONS) FOR THE SOFTWARE, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING,
BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITYAND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND ANY WARRANTY OF NON-INFRINGEMENT. Nortel Networks is not obligated to
provide support of any kind for the Software. Some jurisdictions do not allow exclusion of implied warranties, and, in
such event, the above exclusions may not apply.
3. Limitation of Remedies. IN NO EVENT SHALL NORTEL NETWORKS OR ITS AGENTS OR SUPPLIERS BE
LIABLE FOR ANY OF THE FOLLOWING: a) DAMAGES BASED ON ANY THIRD P ARTY CLAIM; b) LOSS OF,
OR DAMAGE TO, CUSTOMER’S RECORDS, FILES OR DATA; OR c) DIRECT, INDIRECT,SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING LOST PROFITS OR SAVINGS),
WHETHER IN CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE) ARISING OUT OF YOUR
USE OF THE SOFTWARE, EVEN IF NORTEL NETWORKS, ITS AGENTS OR SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN
ADVISED OF THEIR POSSIBILITY. The forgoing limitations of remedies also apply to any developer and/or supplier
of the Software. Such developer and/or supplier is an intended beneficiary of this Section. Some jurisdictions do not
allow these limitations or exclusions and, in such event, they may not apply.
4. General
a. If Customer is the United States Government, the following paragraph shall apply: All Nortel Networks
Software available under this License Agreement is commercial computer software and commercial computer
software documentation and, in the event Software is licensed for or on behalf of the United States
iii
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 4

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
iv
Government, the respective rights to the software and software documentation are governed by Nortel
Networks standard commercial license in accordance with U.S. Federal Regulations at 48 C.F.R. Sections
12.212 (for non-DoD entities) and 48 C.F.R. 227.7202 (for DoD entities).
b. Customer may terminate the license at any time. Nortel Networks may terminate the license if Customer fails to
comply with the terms and conditions of this license. In either event, upon termination, Customer must either
return the Software to Nortel Networks or certify its destruction.
c. Customer is responsible for payment of any taxes, including personal property taxes, resulting from Customer’s
use of the Software. Customer agrees to comply with all applicable laws including all applicable export and
import laws and regulations.
d. Neither party may bring an action, regardless of form, more than two years after the cause of the action arose.
e. The terms and conditions of this License Agreement form the complete and exclusive agreement between
Customer and Nortel Networks.
f. This License Agreement is governed by the laws of the country in which CustomeracquirestheSoftware.If the
Software is acquired in the United States, then this License Agreement is governed by the laws of the state of
New York.
NN10043-113
Page 5

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Contents
Welcome.....................................................xix
Overview ...........................................................xix
Audience ...........................................................xix
Whatisnotcovered ...................................................xix
Textandgraphicconventions............................................xx
Acronyms...........................................................xx
Relatedpublications...................................................xxi
Howtogethelp .....................................................xxii
Chapter 1
GettingStarted.................................................1
SIPProvisioningClientoverview ..........................................1
SIPProvisioningClientfeatures...........................................2
Systemrequirements...................................................2
Minimumhardwareandsoftwarerequirements............................2
Recommendedhardwareandsoftwarerequirements.......................3
StartingtheSIPProvisioningClient ........................................3
Usingtheonlinehelp ...................................................5
Settinguptimezones...................................................5
SettinguptimeszonesintheUnitedStates ..............................6
Selectingatimezone ...............................................6
Creatinganewtimezone ............................................8
ModifyingorDeletingatimezone ......................................8
Changingtheadminpassword............................................9
ExitingtheSIPProvisioningClient.........................................9
v
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 6

vi Contents
Chapter 2
AdministrationOverview........................................11
Introduction .........................................................11
SIPProvisioningroles,rights,andtasks ...................................12
Understandingprovisioningrolesandrights ................................15
Creatinganewprovisioningrole .........................................16
Listingprovisioningroles ...............................................17
Creatinganewadministrator............................................19
Listingadministrators ..................................................20
Chapter 3
Domain Management. . .........................................23
Introductiontodomains ................................................23
Domaintypes........................................................24
Addingalocalrootdomain..............................................26
Addingasubdomain ..................................................31
Addingaforeigndomain ...............................................33
Listing/modifyingalocalorforeigndomain .................................33
Deletingalocaldomain ................................................35
Deletingaforeigndomain ..............................................36
Banningauser.......................................................36
Defininguserdevicestatusreasons ......................................38
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Limitingaccesstoadomain .........................................15
Systemadministratorprovisioningrole .................................16
Rootdomain .....................................................24
Subdomain ......................................................24
Foreigndomain ...................................................25
Settingupbanlist .................................................36
Viewingalistofbannedusers........................................37
Addingastatusreason .............................................38
Viewingstatusreasons .............................................39
Chapter 4
IPCMs .......................................................41
WhatisanIPCM? ....................................................41
NN10043-113
Page 7

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
AddinganIPCMcluster ................................................42
AssigningandmodifyingIPCMstoadomain................................44
DeletinganIPCMcluster ...............................................46
ListingphysicalIPCMs.................................................47
Chapter 5
VoiceMailServers.............................................49
Introduction .........................................................49
Voicemailservertypes ................................................50
ProvisioningaSIP-basedvoicemailserver.................................50
AddingaSIP-basedvoicemailserver..................................51
Addingaphantomvoicemailserveruser ...............................53
ProvisioningaTrunk-basedvoicemailserver ...............................54
AddingaTrunk-basedvoicemailserver ................................55
ProvisioningaLine-basedvoicemailserver ................................60
AddingaLine-basedvoicemailserver .................................61
Assigningausertoaprovisionedvoicemailserver ..........................67
Listing/modifying/deletingavoicemailserver ...............................68
UsingCPLscriptswithvoicemail ........................................69
Contents vii
Chapter 6
DefiningandAssigningServices.................................71
Definingserviceparameters ............................................71
Assigningservicestoadomain ..........................................75
Chapter 7
Assigning Services and Creating Service Packages .................79
Understandingservicepackages.........................................79
Listingavailableservices ...............................................79
Assigningservicestoaservicepackage ...................................83
Creatingaservicepackage .............................................86
Listing/modifying/deletingservicepackages ................................87
Assigningservicepackagestodomainsandsubdomains......................89
Upgradinganddowngradingservicepackages ..............................90
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 8

viii Contents
Chapter 8
User Management .............................................91
Managinguserfunctions ...............................................91
Addingausertoadomainorsubdomain ..................................92
Addingablendeduser.................................................95
Addingi2004InternetTelephonecapabilityforauser.........................99
Addingaconferenceserveruserandroute................................101
Adding a conference server user and route using the SIP Provisioning Client . .101
Adding conference server routes using the SIP Personal Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Settinguprulesfortheconferenceserverroute .........................104
Customizingservicepackages..........................................104
Listing/modifying/deletingusers.........................................105
Listing/modifying/deletingaliases........................................107
Listing/modifying/deletingblendedaliases.................................109
Chapter 9
Managing i2004 Internet Telephones .............................111
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Introduction ........................................................111
Adding an i2004 Internet Telephone . . . . . ................................111
Listingani2004InternetTelephone ......................................116
Deletingani2004InternetTelephone ....................................119
Chapter 10
Telephony Routes ............................................121
AddingClassofService(COS)information................................122
Addingatelephonyroute..............................................124
Listingatelephonyroute ..............................................128
Addingaroutelist ...................................................128
Listingaroutelist ....................................................130
Usingthetranslationverificationtool .....................................131
Setting up an interworking profile with the Communications Server 2000 (CS2000) .133
Chapter 11
Gateways ...................................................135
Introductiontogateways ..............................................135
NN10043-113
Page 9

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Addingagateway....................................................136
Listingagateway ....................................................137
Addingagatewayroute ...............................................138
Listingagatewayroute ...............................................140
Addingagatewaytrunkgroup ..........................................141
Listingagatewaytrunkgroup ..........................................142
Appendix A
Provisioning Sequence ........................................145
Sequenceoftasks ...................................................145
Appendix B
Understanding Telephony Routing and Translations................149
Telephony routing concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . ................................149
Subdomains.....................................................149
ClassofService..................................................150
SIPApplicationModuleroutingstages ................................151
Telephony routing terminology . . . . . . . . . . ................................152
Routelists ......................................................152
Example of telephony route redirection between domains . . . . . . . . . . . . . .153
Example of telephony route redirection between subdomains . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Routes .........................................................154
Privatetelephonyroutes ........................................155
SIPandgatewayroutes ........................................155
Sample dial plan for telephony routes . . . . ................................155
Provisioningdomains,subscribers,andCOS ...........................155
Exampledialplanassignments......................................157
Dialplandescription ..............................................157
AssociatingCOSandtheroute ......................................158
Telephony route provisioning scenario and examples . . . . . . . . ................158
Step1:Createtheparentandsubdomains.............................159
Step2:CreatetheCOS............................................161
Step3:CreatethesubscribersandassigntheCOS......................162
Step4:Creategateways,gatewayroutesandtrunkgroups................165
Step 5: Create the telephony routes . . ................................166
Contents ix
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 10

x Contents
Appendix C
911 Emergency Notification ....................................181
911emergencynotificationtermsandconcepts ............................181
SettingupInstantMessageNotifications..................................182
Using the SIP Provisioning Client to add emergency subscribers and telephony routes .
183
Using the SIP Personal Agent to route 91 1emergency notifications . . . . . . . . . . . . .192
Index .......................................................195
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Addingaprivateroutetosubdomainrich.abc.com....................167
AddingSIProutestoabc.comandxyz.com .........................169
Addingagatewayroutetoabc.com ...............................172
Step 6: Create the telephony route lists and assign COS . . ................174
Step7:Testthetelephonyroutingconfiguration .........................178
CreatingaCOSforthe911notification ................................184
Addingagateway,gatewayroute,andtrunkgroup.......................185
Addingaprivatetelephonyroute.....................................187
Addingagatewaytelephonyroute ...................................189
Addinganemergencysubscriber ....................................190
AddinganOSNsubscriber .........................................192
Settinguparoutelistfortheemergencysubscriber ......................192
Settinguparulefortheemergencynotificationroute.....................193
NN10043-113
Page 11

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figures
Figure1 SIPProvisioningClientloginwindow..............................4
Figure2 SIPProvisioningClientwelcomewindow..........................4
Figure3 Sessioninactivitymessage ....................................5
Figure4 TimeZonedetailswindow .....................................7
Figure5 Addnewtimezone...........................................8
Figure6 AddaNewRolewindow......................................17
Figure7 ListSystemRoleswindow ....................................18
Figure 8 Role details window . . . . . . . . .................................19
Figure9 Createnewadmin ..........................................20
Figure10 Adminswindow.............................................21
Figure11 AdminDetailswindow........................................22
Figure12 Domainsandsubdomains ....................................25
Figure13 Createnewdomainwindow ...................................27
Figure14 Createnewsubdomainwindow ................................32
Figure15 Createnewdomainwindow ...................................33
Figure16 ListDomainswindow-step1..................................34
Figure17 Listdomains-step2 ........................................35
Figure18 AddapartytoDomainBanListwindow..........................37
Figure19 DomainBanListwindow .....................................38
Figure20 AddStatusReasonwindow ...................................39
Figure21 StatusReasonswindow ......................................40
Figure22 Modifystatusreasonwindow ..................................40
Figure23 CreatenewIPCMwindow ....................................43
Figure24 ListIPCMClusterswindow....................................44
Figure25 ModifyIPCMwindow ........................................45
Figure 26 IPCM Domain Relation window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .................46
Figure27 IPCMDeleteconfirmationdialogbox ............................47
Figure28 ListingphysicalIPCMs .......................................48
Figure29 DeletephysicalIPCMconfirmationdialogbox .....................48
xi
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 12

xii Figures
Figure30 Createnewvoicemailserverwindow(SIP)-step .................51
Figure31 Createnewvoicemailserverwindow(SIP)-step2 ................52
Figure32 VoiceMailServerswindow(SIP) ...............................53
Figure33 Userrouteswindow .........................................54
Figure34 Createnewvoicemailserverwindow(Trunk-based)-step1 .........55
Figure35 Createnewvoicemailserverwindow(Trunk-based)-step2 .........56
Figure36 Createnewvoicemailserverwindow(Trunk-based)-step3 .........58
Figure37 VoiceMailServerswindow(Trunk-based) ........................60
Figure38 Createanewvoicemailserverwindow(Line-based)-step1.........61
Figure39 Createnewvoicemailserverwindow(Line-based)-step2 ..........62
Figure40 Createnewvoicemailserverwindow(Line-based)-step3 ..........64
Figure41 Createnewvoicemailserverwindow(Line-based)-step4 ..........66
Figure42 VoiceMailServerswindow(Line-based) .........................67
Figure43 Listofvoicemailservers .....................................68
Figure44 Listofavailableserviceswindow ...............................72
Figure45 Addnewparametervalueswindow .............................75
Figure46 Assignserviceswindow ......................................76
Figure47 Assignservicestoadomainwindow ............................77
Figure48 Listofavailableservices......................................80
Figure49 Assignserviceswindow ......................................84
Figure50 Assignservicestodomainswindow .............................85
Figure51 Createnewpackagewindow ..................................86
Figure 52 List of packages domain window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .................88
Figure53 Assignpackagetodomainswindow.............................89
Figure54 Addnewuser ..............................................92
Figure55 Addnewuser-blended ......................................96
Figure 56 Blended User added successfully confirmation . . . .................97
Figure57 Servicepackagecustomizationforablendeduser .................98
Figure 58 User details window (i2004) . . .................................99
Figure59 Conferenceuser-addroute..................................102
Figure 60 Conference user - route added ................................103
Figure61 Customizeservicepackagelink ...............................105
Figure62 ListUserswindow..........................................106
Figure63 Listuserssearchresults.....................................106
Figure64 Userdetailswindow ........................................107
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
NN10043-113
Page 13

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 65 List aliases window . . . . . . . . . ................................108
Figure66 Listaliasessearchresults....................................109
Figure67 BlendedAliasessearchresultswindow .........................110
Figure68 Addingadevice ...........................................112
Figure69 Adddevice-IPCMdevicecreated .............................115
Figure70 DeviceUsers-assigningusers ...............................116
Figure 71 List Devices window . . . . . . . . ................................117
Figure72 Listdevicessearchresults ...................................118
Figure73 Modifyingadeviceinadomainwindow .........................118
Figure74 DevicesinDomainwindow(searchresults)......................119
Figure75 ClassofServiceinformationfordomainwindow ..................123
Figure76 CreateNewTelephonyRoutewindow ..........................124
Figure 77 Telephony Route Listing window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ................126
Figure 78 Telephony route listing window ................................128
Figure79 CreateaNewRouteListwindow ..............................129
Figure80 Listroutelistswindow.......................................131
Figure81 TranslationVerificationToolwindow............................132
Figure82 Translationtoolresultswindow................................133
Figure83 SetProfileforDomainwindow ................................133
Figure84 Createnewgatewaywindow .................................136
Figure85 Gatewayswindow..........................................137
Figure86 Gatewayswindow(ListGateways).............................138
Figure87 Createnewgatewayroutewindow.............................139
Figure88 Gatewayrouteswindow .....................................139
Figure89 Gatewayrouteswindow(ListRoutes) ..........................140
Figure90 Reordertrunkgroupswindow.................................141
Figure91 Createnewtrunkgroupwindow ...............................142
Figure92 TrunkGroupswindow .......................................142
Figure93 TrunkGroupswindow(ListTrunkGroup).........................143
Figure94 Exampledomaintree .......................................150
Figure95 SIPApplicationModuleroutingstages..........................152
Figure96 Routelistredirect(domaintodomain) ..........................153
Figure97 Routelistredirect(betweensubdomains) .......................154
Figure98 Domains/subscribersusedforthesampledialplan ................156
Figure99 Parentdomainprovisioningmenu .............................160
Figures xiii
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 14

xiv Figures
Figure100 Subdomainprovisioning.....................................161
Figure101 CreatingCOS .............................................162
Figure102 Assigningservicepackagestosubdomains......................163
Figure103 AddingasubscriberwithCOS ................................164
Figure104 Addingagatewaytoabc.com ................................165
Figure105 Addingagatewayroute .....................................166
Figure106 Addingatrunkgrouptoagatewayroute ........................166
Figure107 Menutoaddroutesinsubdomain .............................167
Figure108 Addingaprivateroutetorich.abc.com..........................168
Figure109 Privateroutecreated .......................................168
Figure110 SettingtheSubscriberNotFoundoption ........................168
Figure111 Listingaprivateroute .......................................169
Figure112 AddingaSIProutetoabc.com................................170
Figure113 SIProutechangeparameters.................................170
Figure114 SIProuteoptions ..........................................171
Figure115 ListingSIProutesinabc.com .................................171
Figure116 SIProutetoabc.com .......................................171
Figure117 Addingagatewayroute .....................................172
Figure118 Gatewaychangeparameters .................................173
Figure119 Gatewayrouteoptions ......................................173
Figure120 Listingabc.comroutes ......................................174
Figure121 Addingaroutelisttoabc.com ................................175
Figure122 AddingaroutelistwithPSTNroutetoabc.com ...................175
Figure123 Listingofabc.comroutelists .................................176
Figure124 Listingofxyz.comroutelists..................................176
Figure125 Addingaroutelisttorich.abc.com .............................177
Figure126 Listingofrich.abc.comroutelists ..............................177
Figure127 Subdomain5digittranslationstrace ...........................178
Figure128 Gatewayroutetranslationstrace ..............................179
Figure129 SIProutetracefromabc.comtoxyz.com........................180
Figure130 Restrictedroutetrace .......................................180
Figure131 CreatingaCOSforthe911notification .........................185
Figure132 Addinganewgateway ......................................186
Figure133 Listofgateways ...........................................186
Figure134 Creatinganewgatewayroute ................................186
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
NN10043-113
Page 15

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure135 Creatinganewtrunkgroup ...................................187
Figure136 Createnewtelephonyroutewindow ...........................188
Figure137 Changeparameters ........................................188
Figure138 Creatinganewroutelist.....................................189
Figure 139 Create gateway telephony route to PSAP . . . . . . . ................190
Figure140 Gatewayrouteoptions ......................................190
Figure141 Adduser-emergencysubscriber..............................191
Figures xv
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 16

xvi Figures
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
NN10043-113
Page 17

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Tables
Table1 SIPProvisioningtasksoverview................................12
Table2 Exampleofrolesandrights ...................................15
Table3 Createnewdomainnamerestrictions ...........................28
Table4 Createnewdomainparameters ................................28
Table5 CreatenewIPCMparameters .................................43
Table6 Voicemailservertypes.......................................50
Table7 SIP-basedvoicemailparameters...............................52
Table8 SMDIparameters ...........................................57
Table9 PRIGatewayconnectionparameters............................59
Table10 Line-basedvoicemailserverSMDIparameters....................63
Table11 Line-basedvoicemailservergeneralparameterinformation..........65
Table12 Line-basedvoicemailserverparameters.........................67
Table13 Servicesparametersandoptions ...............................73
Table14 Servicesparametersandoptions ..............................81
Table15 Adduserparameterdescriptions ...............................93
Table16 i2004properties ...........................................100
Table17 i2004InternetTelephoneparameters...........................113
Table 18 Click Save. The IPCM Device Created window appears (Figure 69). . . 115
Table 19 Telephony route parameter information . . . . . . . . . ................125
Table 20 Telephony route parameters window (Private, SIP, Gateway) . . . . . . . .127
Table21 Callroutingoptions.........................................130
Table22 SIPProvisioningClientprovisioningsequence ...................145
Table23 Exampledialplandata ......................................157
Table24 Dialplanforabc.comandxyz.com.............................157
Table25 AssociationbetweenCOSandRoutes .........................158
Table26 Subscribersinrich.abc.com ..................................166
Table27 DataforSIProutes .........................................169
xvii
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 18

xviii Tables
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
NN10043-113
Page 19

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Welcome
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Provisioning Client is a web-based
Graphical User Interface (GUI) for service providers to complete administrative
tasks, for example, provisioning administrators, domains, IP Client Managers
(IPCMs) and IPCM clusters.
Overview
Service providers access the SIP Provisioning Client with any web browser. Being
a web-based system, the SIP Provisioning Client provides the service providers
with an highly efficient access from anywhere capability.
Note: The provisioning abilities visible to a n administrator in the SIP
Provisioning Client GUI depends on the level of authority assigned to
their account.
xix
Audience
This guide is intended for service providers and administrators (with varying
levels of privileges) assigned to manage customer domains.
What is not covered
This document does not cover
• Configuration
• System Management Console
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 20

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
xx Welcome
Text and graphic conventions
This guide uses the following text and graphic conventions:
bold text Indicates a menu option, link, or command key you
need to click. Example: Click Ok.
italic text Indicates
• a domain name or subdomain name
•adocumenttitle
• a variable name
separator ( > ) Shows menu paths.
Example: Gateway > Add Gateway
Indicates a top level menu item in the SIP Provisioning
Client menu hierarchy.
Indicates a sub menu item in the SIP Provisioning
Client menu hierarchy.
Acronyms
NN10043-113
Indicates a form in the SIP Provisioning Client menu
hierarchy.
This guide uses the following acronyms
CAS Channel Associated Signalling
CPL Call Processing Language
COS Class of Service
CS2000 Communication Server 2000
DSL Digital Subscriber Line
GMT Greenwich Mean Time
Page 21

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DIGMAN Digit Manipulation
GUI Graphical User Interface
IP Internet Protocol
IPCM Internet Protocol Client Manager
MAddr Media Access Control Address
MCP Multimedia CommunicationsPortfolio
MSD Most Significant Digit
MWI Message Waiting Indicator
PDIL Partial Dial
PRI Primary Rate Interface
PSEIZ Permanent Seizure
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network
SA System Administrator
SIP Session Initiation Protocol
SMDI Simplified Message Desk Interface
TDM Time Division Multiplex
UNIStim Unified Network IP Stimulus
URI Uniform Resource Identifier
URL Uniform Resource Locator
VMS Voice Mail Server
VPN Virtual Private Network
Welcome xxi
Related publications
• SIP Personal Agent Getting User Guide (Part No. NN10039-112)
• SIP Multimedia Web Client User Guide (Part No. NN10040-112)
• SIP Multimedia PC Client User Guide (Part No. NN10041-112)
• i2004 Internet Telephone User Guide (Part No. NN10042-113)
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 22

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
xxii Welcome
You can print selected technical manuals and release notes free, directly from the
Internet. Go to the www.nortelnetworks.com/documentation URL. Find t he
product for which you need documentation. Then locate the specific category and
model or version for your hardware or software product. Use Adobe* Acrobat
Reader* to open the manuals and release notes, search for the sections you need,
and print them on most standard printers. Go to Adobe Systems at the
www.adobe.com URL to download a free copy of the Adobe Acrobat Reader.
How to get help
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel Networks product from a
distributor or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that
distributor or reseller for assistance.
If you purchased a Nortel Networks service program, contact Nortel Networks
Technical Support. To obtain contact information online, go to the
www.nortelnetworks.com/cgi-bin/comments/comments.cgi URL, then click on
Technical Support.
NN10043-113
From the Technical Support page, you can open a Customer Service Request
online or find the telephone number for the nearest Technical Solutions Center.
If you are not connected to the Internet, you can call 1-800-4NORTEL
(1-800-466-7835) to learn the telephone number for the nearest Technical
Solutions Center.
An Express Routing Code (ERC) is available for many Nortel Networks products
and services. When you use an ERC, your call is routed to a technical support
person who specializes in supporting that product or service. To locate an ERC for
your product or service, go to the http://www.nortelnetworks.com/help/contact/
erc/index.html URL.
Page 23

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Topics in this section:
• “SIP Provisioning Client overview” on page 1
• “SIP Provisioning Client features” on page 2
• “System requirements” on page 2
• “Using the online help” on page 5
• “Setting up time zones” on page 5
• “Changing the admin password” on page 9
• “Exiting the SIP Provisioning Client” on page 9
SIP Provisioning Client overview
1
The SIP Provisioning Client is a web-based GUI that you use to perform the
following administrative and provisioning tasks:
• define administration roles and privileges
• manage (list add, modify, or delete) users and devices
• define multiple service packages
• assign services to service packages
• assign service packages to domains
• assign translation information specific to a domain or subdomain
• provision voice mail servers
• provision 911 emergency notification
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 24

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
2 Chapter 1 Getting Started
SIP Provisioning Client features
The SIP Provisioning Client gives service providers the capability to create and
set security,access, and permissions for the following components and roles of the
user framework:
• administration
• domains and subdomains (users, devices, telephony routes)
• gateways
• IPCM clusters
• voice mail servers
•services
•system
Note: The provisioning capabilities visible to an administrator in the SIP
Provisioning Client menu depend on the level of authority (rights)
assigned to their account.
System requirements
The following section describes the minimum and recommended hardware and
software requirements for the SIP Provisioning Client.
Minimum hardware and software requirements
• 200MHz Pentium class or equivalent processor
• No additional free RAM is required. (The minimum memory requirements of
your browser must be met. See your browser documentation for more
information.)
• No additional harddrive space is required. (Local caching of web pages is
performed by your web browser. See your browser documentation for
information on the minimum disk space requirements.)
• Mouse (optional)
• 640x480 @8bpp (256 colors) VGA graphics card
NN10043-113
Page 25

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
• Microsoft* Windows* 98 Second Edition (SE), Microsoft Windows
Millennium Edition (Me), Microsoft Windows 2000, Microsoft XP, or
Microsoft Windows NT* 4.0 with Service Pack 5 (SP5)
• 28.8Kbps modem
• Netscape* Communicator 4.77 or Internet Explorer 5.0
• Cookies and javascript enabled
Recommended hardware and software requirements
• 300MHz (or higher) Pentium class
• No additional free RAM is required. (The minimum memory requirements of
your browser must be met. See your browser documentation for more
information.)
• No additional harddrive space is required. (Local caching of web pages is
performed by your web browser. See your browser documentation for more
information on the minimum disk space requirements.)
• Mouse (required)
• 800x600 or higher @16bpp (65,536 colors) VGA or better video graphics
card
• Microsoft Windows 98 Second Edition (SE), Microsoft Windows 2000,
Microsoft XP, or Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 with Service Pack 5 (SP5)
• 56Kbps modem or other high speed connection (For example, cable modem,
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) modem, 10baseT ethernet, an so forth)
• Netscape Communicator 4.77 or greater, or Internet Explorer 5.0 or greater
• Cookies and javascript enabled
Chapter 1 Getting Started 3
Starting the SIP Provisioning Client
To start the SIP Provisioning Client from your PC
1 Start any supported web browser.
2 Enter the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) for the SIP Provisioning Client.
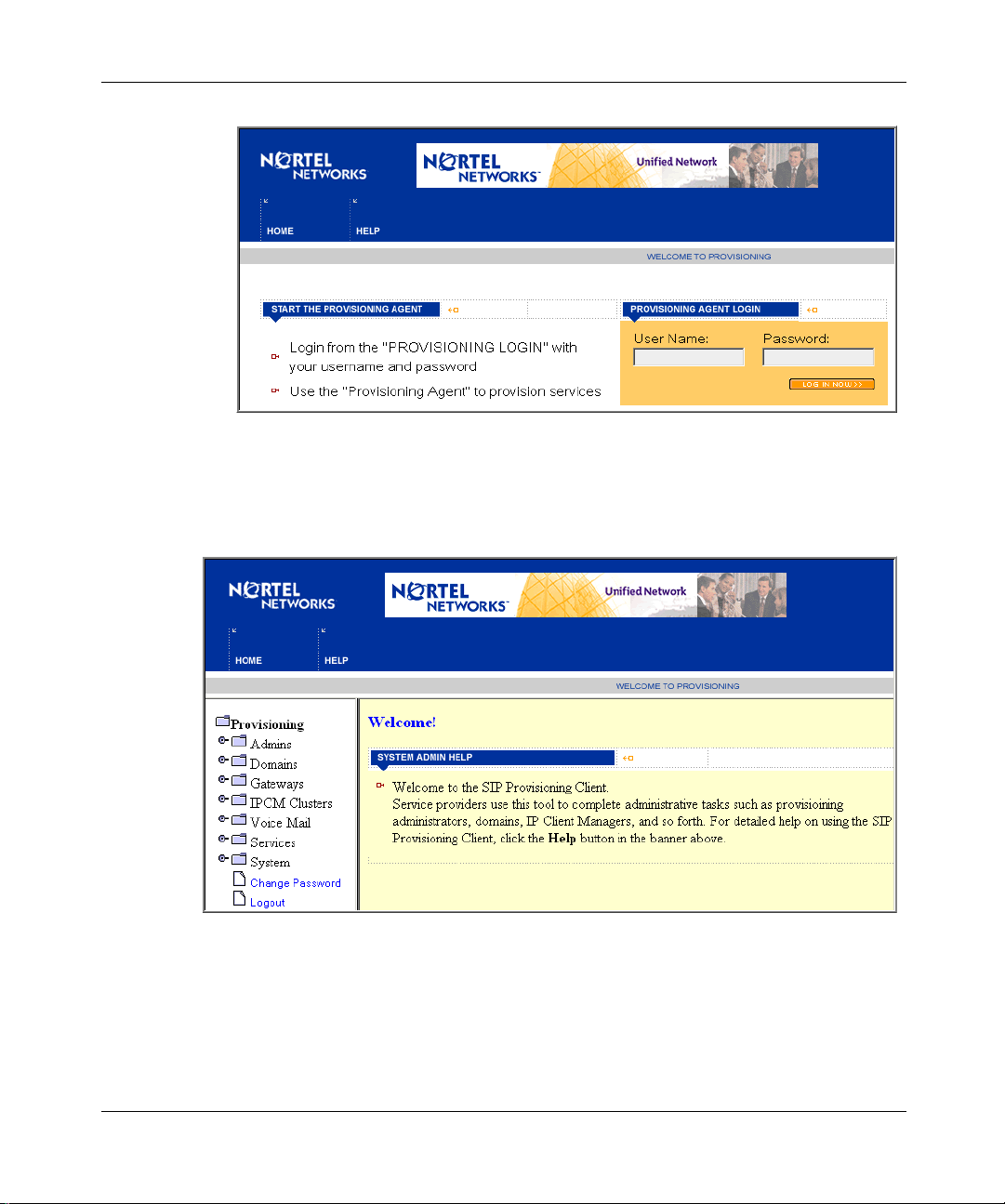
The SIP Provisioning Client Login window appears (Figure 1).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 26
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
4 Chapter 1 Getting Started
Figure 1 SIP Provisioning Client login window.
3 Enter your username and password in the respective fields.
4 Click LOG IN NOW to log in. Upon a successful login, the SIP Provisioning
Client Welcome window appears.
Figure 2 SIP Provisioning Client welcome window
NN10043-113
If the SIP Provisioning Client GUI is inactive for a period of time, your session
will expire. The following message appears:
Page 27

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 3 Session inactivity message
To restart the SIP Provisioning Client, click on the link to login again. Contact
your service provider to request a change to the session expiration time limit.
Using the online help
There are several ways that you can access SIP Provisioning Client help:
• online help - from the SIP Provisioning Client screen, click the Help button to
view a t ask-based help system. The online help provides:
— help pages containing forward and backward navigation icons
— procedures that help you use the SIP Provisioning Client
— a Table of Contents with hypertext links
— an Index with hypertext links
• questionmarkhelp.Clickthequestionmarkicontodisplayadescriptionand
possible values for parameter fields on a form.
Chapter 1 Getting Started 5
Settinguptimezones
The SIP Provisioning C lient allows you to define and manage as many time zones
as you require to meet your needs, and to create your own time zones for easy
reference. Time zones define the time zone from which a subscriber normally
accesses the system (that is, the subscribers’s local time zone). Time zones are
used in the SIP Personal Agent Call Manager function to set a screening rule that
applies during a certain time. This time is dependent on the time zone selected.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 28
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
6 Chapter 1 Getting Started
The SIP Provisioning Client is initially set up with the standard 24 time zones:
plus or minus 12 hours from the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) format. However,
there are more than 300+ time zones. What defines a time zone is not just the
offset from the GMT.It is also whether or not the time zone uses Daylight Saving
Time, when Daylight Saving Time occurs, and what the offset is.
Setting up times zones in the United States
As an example, the time zones you would set up across the United States from
East to West are listed in the following table:
Zone Standard Time Daylight Saving Time
Atlantic AST ADT
Eastern EST EDT
Central CST CDT
Mountain MST MDT
Pacific PST PDT
Alaska AKST AKDT
Hawaii HST Not Observed
Selecting a time zone
NN10043-113
To select a time zone
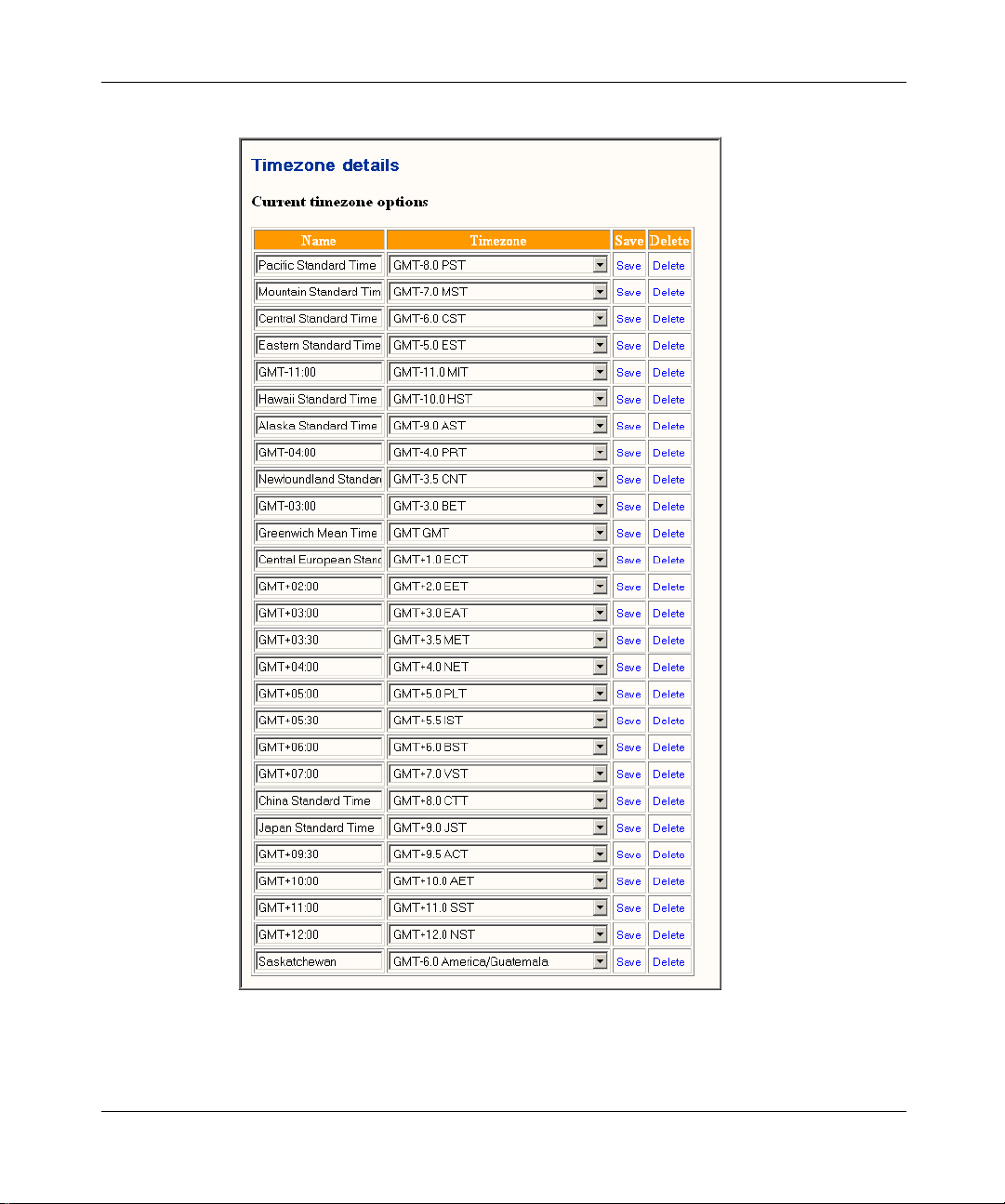
1 Click the System menu option.
2 Click the Timezones form. The Timezone details window appears.
Page 29
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 4 Time Zone details window
Chapter 1 Getting Started 7
3 Select a zone from the list of time zones.
4 From the drop down list, select a time zone.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 30
[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
8 Chapter 1 Getting Started
5 Click Save.
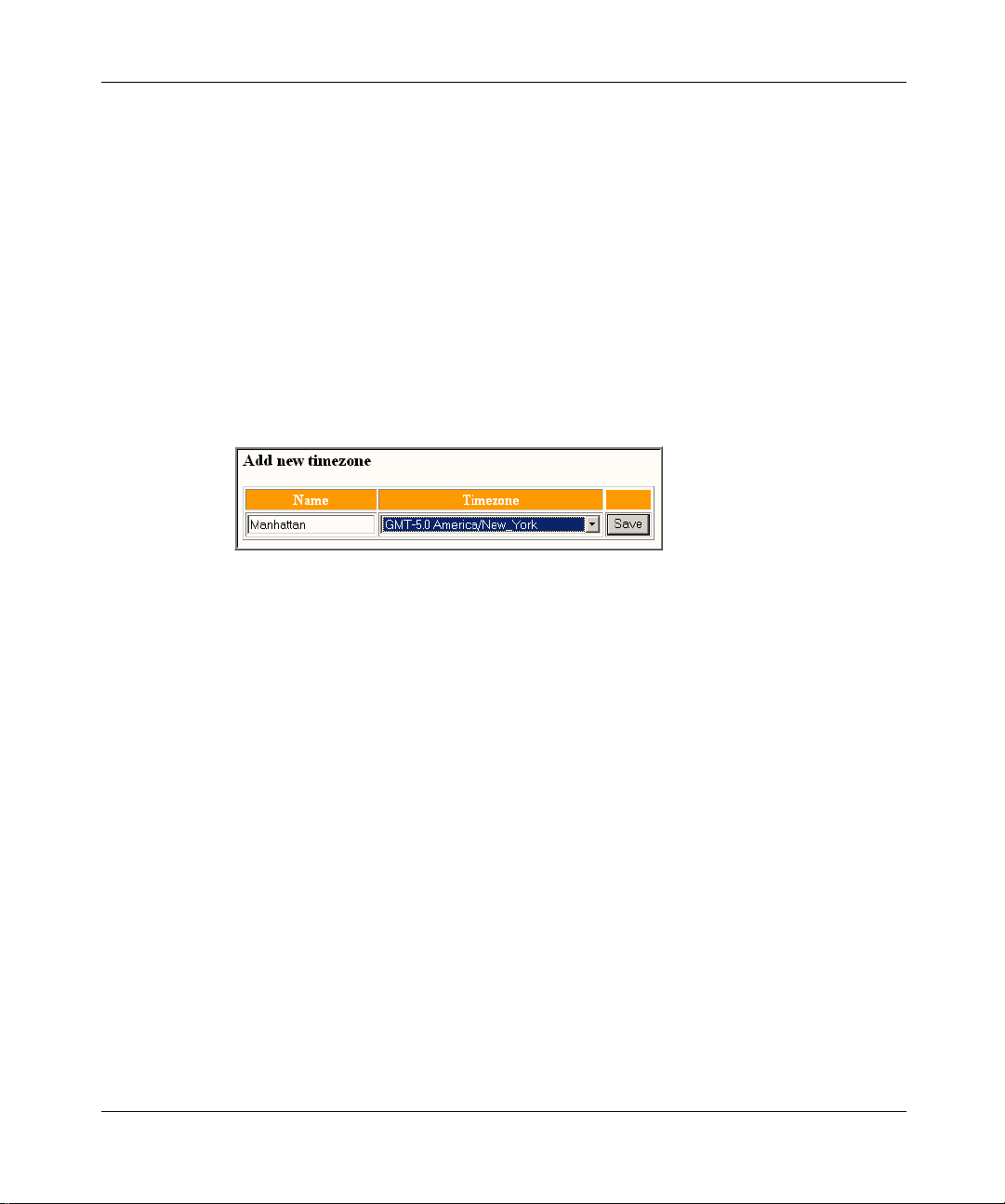
Creating a new time zone
To create a new time zone
1 Click the System m enu option.
2 Click the Timezones form. The Timezone details window appears.
3 In the Add new timezone box, enter a meaningful name for the time zone in
the Name field. (This field is visible to subscribers.) Both the name and the
time zone need to be unique.
Figure 5 Add new time zone
4 Click Save to save the new time zone. Click View details to see the list of
time zones.
Modifying or Deleting a time zone
The SIP Provisioning Client is preloaded with a number of default times zones.
You may wish to modify or delete a time zone to prevent the time zone from
showing up in the drop down list that is available when creating or modifying a
user.
To modify or delete a time zone
1 Click the Services menu option.
2 Click the Timezones form. The Timezone details window appears.
3 Select the time zone that you wish to delete. Click the Delete link next to any
time zone that you do not need. In the confirmation dialog box, Click Ok to
permanently delete the time zone or Cancel to abort the action.
NN10043-113
Page 31

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Tip: You cannot modify or delete a time zone that is currently in use.
Changing the admin password
To change the admin password
1 Click the System m enu option.
2 Click the icon for the Change Password form. The Change Admin Password
window appears.
3 Enter your new password.
4 Confirm your new password.
Chapter 1 Getting Started 9
5 Enter your current password.
6 Click Save. Your new password is activated upon your next login.
Exiting the SIP Provisioning Client
To close the SIP Provisioning Client window and exit the SIP Provisioning Client,
click the Logout menu option.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 32

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
10 Chapter 1 Getting Started
NN10043-113
Page 33

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 2 Administration Overview
Topics in this section:
• “Introduction” on page 11
• “SIP Provisioning roles, rights, and tasks” on page 12
• “Understanding provisioning roles and rights” on page 15
Introduction
In the SIP Provisioning Client, a provisioning role is defined as a collection of
access rights and privileges t hat allow an administrator to perform various
provisioning tasks. As a System Administrator, you can create any number of
administratorroles, depending on your particular needs. For example, you can add
a provisioning role to allow an administrator to perform multiple tasks, however,
giving them the rights to only a subset of everything available.
11
After logging in to the SIP Provisioning Client, you will see a menu list on the left
side of your screen. This list varies based on the privileges available to you. The
types of tasks you can perform as an administrator is based on the scope of your
defined role.
Note: The provisioning abilities visible to a n administrator in the SIP
Provisioning Client GUI depends on the rights assigned to their
provisioning role.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 34

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
12 Chapter2 Administration Overview
SIP Provisioning roles, rights, and tasks
The following table provides an overview of the SIP Provisioning tasks.
Table 1 SIP Provisioning tasks overview
If you have the right
for Use this Provisioning menu option... To perform these tasks...
Full domain access Administer all current domains and
Domain management List, add, modify, or delete domains
IPCM cluster
provisioning
Service Package
Creation
Device Management Add, list, modify, or delete i2004
future domains regardless of initial
provisioning. This allows the
administrator with this role to see all
domains, versus other administrators
that can see only a subset of
domains.
and subdomains.
Add, list, modify,or delete an IPCM or
IPCM cluster. If you add an IPCM
through the SIP Provisioning Client,
the Management Console GUI will not
know that the IPCM exists. It is
recommended that you deploy an
IPCM through the System
Management Console.
Add, list, modify, or delete services
and service packages to a particular
domain or all domains. If you have the
administrator privileges to add a
domain or m ultiple domains, then you
can add or create service packages
within that domain.
devices.
NN10043-113
Page 35

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 2 Administration Overview 13
Table 1 SIP Provisioning tasks overview
If you have the right
for Use this Provisioning menu option... To perform these tasks...
Telephony Route/Digit
Manipulation
Admin Add, list, modify, or delete
Gateway Management Add,list,modify,remove,reorder,new
Add, list, modify, or delete telephony
routes
administrators and roles.
or existing gateways, routes, and
trunk groups. When you deploy and
provision a gateway through the
management console, you must
provision the gateway with the similar
trunk groups and routes through the
SIP Provisioning Client to ensure that
the information is saved into the
database that the SIP Application
Module uses.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 36

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
14 Chapter2 Administration Overview
Table 1 SIP Provisioning tasks overview
If you have the right
for Use this Provisioning menu option... To perform these tasks...
Voice Mail Management Add, list, modify, or remove new or
User Management Add, list, modify, or delete users,
existing voice mail servers. If voice
mail is enabled in a service package,
a customer can select from the
following voice mail server types:
• SIP based - a forward to your
voice mail system using SIP.
• Trunk based - a Primary Rate
Interface (PRI) or Channel
Associated Signalling (CAS) trunk
is associated with the line.
• Line based - a particular phone
number is associated to the line.
aliases, blended aliases, and i2004
Internet Telephone properties
(available from the domain or
subdomain menu option).
NN10043-113
Page 37

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 2 Administration Overview 15
Understanding provisioning roles and rights
Administrators can create, or define, all the necessary provisioning roles to
support their system. They can allow or restrict provisioning roles to carry out
specific actions. The following table provides examples of several administrator
provisioning roles and the rights based restrictions associated with various
provisioning tasks.
Table 2 Example of roles and rights
Provisioning
Role example Rights given Allowed tasks
User
administrator
Device
administrator
System
Administrator
• User management with read,
write, and delete access
• Domain management with
read access only
• Domain management with
read access
• Devicemanagementwith read,
write, and delete access
• Full domain access Cansee all domains,regardlessof
Limiting access to a domain
Complementing the rights-based restrictions, administrators can be provisioned
against certain domains in order to limit access to within those domains. This
prevents an administrator from domain xyz from viewing or modifying details in
domain abc, even though they are hosted from the same system. Administrators
can then delegate work for subdomains to other administrators without giving
them access to their own data.
Can view domain details, and add,
delete, or modify users. Does not
have access to other parts of the
system, for example voice mail,
service packages, and so forth.
Cannot add or modify users.
Allowed to add, modify or delete
devices.
who created the domain, or the list
ofdomainsprovisionedagainstthe
administrator.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 38

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
16 Chapter2 Administration Overview
For example, if an administrator assigned to the User Administrator provisioning
role was given access to suba.xyz (a subdomain of domain xyz), this administrator
can add, modify, and delete users in the subdomain, but does not have access to
the parent domain, domain xyz. This allows for the delegation of task on both the
rights-level and the domain-level.
Note: Access to any domain implies access to all of its descendant
subdomains. For example, access to domain xyz implies access to
suba.xyz. Full domain access will override this domain allocation and
allow any administrator assigned with a provisioning role that includes
this right, to see all domains regardless of what the administrator is
provisioned against.
System administrator provisioning role
The System Administrator (SA) is the highest level administrator and is the only
provisioning role that is preloaded when the SIP Provisioning Client is deployed.
The SA has full access and rights to all provisioning features and functions.
The SA can designate someone as an Administrative user with the Add Admin
menu option, and grant specific administrator rights to that administrative user
with the Add Roles menu option.
Note: The System Administrator role is the only role that cannot be
changed.
Creating a new provisioning role
To create a new provisioning role
1 Click the Admins menu option.
2 Click the Add Roles sub menu option. The Add a New Role window appears
(Figure 6).
NN10043-113
Page 39

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 6 Add a New Role window
Chapter 2 Administration Overview 17
3 Enter a name for the provisioning role in the Role Name field (required).
4 Enter a description for the provisioning role in the Role Description field.
5 To define the level of administrator access, select the checkboxes for Read,
Write,or Delete next to each privilege.
6 Click Add. A message appears that the role has been successfully created.
Listing provisioning roles
To view details about a provisioning role to modify or delete the role
1 Click the Admins menu option.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 40

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
18 Chapter2 Administration Overview
2 Click the List Roles sub menu option. The List SystemRoles window appears
(Figure 7).
Figure 7 List System Roles window
NN10043-113
3 To view details about a provisioning role or description, click the View
Details link. The Role Details window appears (Figure 8). To delete a
provisioning role, click the Delete link next to the role.
Page 41

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 8 Role details window
Chapter 2 Administration Overview 19
4 To change the provisioning role description, enter a new description in the
Role Description box. To modify privileges, select or deselect privileges in
the checkbox next to the privilege.
5 Click Save to save your changes. A message appears that the provisioning
role was modified successfully.
Creating a new administrator
To add an administrator
1 Click the Admins menu option.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 42

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
20 Chapter2 Administration Overview
2 Click the Add Admin sub menu option. The Create new admin window
appears (Figure 9).
Figure 9 Create new admin
3 Enter the username of the administrator (required) and other information in
the fields provided.
4 Click Add. A message appears that the administrator was successfully added.
Listing administrators
To view details about an administrator or to modify or delete an administrator
1 Click the Admins menu option.
NN10043-113
Page 43

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
2 Click the List Admins sub menu option. The Admins window appears
(Figure 10). To delete an administrator, click the Delete link next to the
administrator username.
Figure 10 Admins window
Chapter 2 Administration Overview 21
3 To modify administrator information, enter the changes in the fields provided
(Table 11).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 44

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
22 Chapter2 Administration Overview
Figure 11 Admin Details window
NN10043-113
4 Click Save to save your changes. A message appears that the administrator
was modified successfully.
Page 45

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 3 Domain Management
Topics in this section:
• “Introduction to domains” on page 23
• “Domain types” on page 24
• “Adding a local root domain” on page 26
• “Adding a subdomain” on page 31
• “Adding a foreign domain” on page 33
• “Listing/modifying a local or foreign domain” on page 33
• “Deleting a local domain” on page 35
• “Banning a user” on page 36
• “Defining user device status reasons” on page 38
23
Introduction to domains
A domain is used as a control mechanism of users, services, devices and
translation. The SIP Provisioning Client is used to provision a domain. The
provisioning of domains allows service providers to define a domain and service
packages available for the domain.
Once the domain and service packages are defined, service providers can define
subdomains and assign the following:
• services to service packages
• service packages to domain and users
• translation information specific to a domain or a subdomain
• devices for users to an IPCM (IP Client Manager)
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 46

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
24 Chapter 3 Domain Management
If you have full domain access, you can see all provisioned domains. Otherwise,
you will only be able to see the domains/subdomains you are provisioned against.
The management rights assigned to a domain administrator dictates what you can
do with the domains.
Domain types
There are three types of domains:
• root domain
• subdomain
• foreign domain
Root domain
A root domain is the highest level domain. A service provider can create a root
domain for each of their customers. An example of a root domain is
nortelnetworks.com.
Subdomain
NN10043-113
A subdomain is a category of domains. Subdomains a llow you to divide
subscribersunder a domain into smaller groups. The groups can be used to control
routing and access to services by members of the group.
Under each subdomain, you can add subdomains, service packages, users,
devices, and telephony routes. There are no limits to the levels of nesting of
subdomains. Each subdomain inherits the parameter values from the root domain.
A typical application of subdomains is based on geographical divisions. For
example, using Nortel Networks, you could have nortelnetworks.com as the root
domain, with subdomains of Richardson and Ottawa. Under each of these
subdomains there could be further subdomains as shown in the following
illustration (Figure 12).
Page 47

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 12 Domains and subdomains
Chapter 3 Domain Management 25
Foreign domain
A foreign domain is a domain that is not served by any SIP Application Modules
in your system. When adding a domain, you must determine whether or not t he
domain is a foreign domain or not. A foreign domain uses foreign routes, while a
local domain uses SIP routing or telephony routes.
A domain that is not local is considered foreign. Usually, a foreign domain is
resolved through DNS and would not need to be provisioned. However, since
some deployment scenarios may not involve a DNS server, you (as the system
administrator) can datafill routes for a foreign domain.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 48

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
26 Chapter 3 Domain Management
For example, if the SIP Application Module serving nortelnetworks.com does not
have a DNS server, and there is a need for users to be able to make calls to the
xyz.com domain, then you could add the abc.com domain as a foreign domain and
provide a route to abc’s proxy.
Note: A foreign domain is not controlled by the system. Therefore it
will not be displayed under the domain folder in the menu area, and the
you will not be able to provision users, service packages, devices, and so
forth to these domains.
Adding a local root domain
To add a local root domain
1 Click the Domains menu option.
2 Click Add Domain. The Create new domain window appears (Figure 13).
NN10043-113
Page 49

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 13 Create new domain window
Chapter 3 Domain Management 27
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 50

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
28 Chapter 3 Domain Management
3 Enter the name of the new local domain. The domain name m ust not be more
then 60 chars in length and cannot contain the following symbols or
characters as described in the following table:
Table 3 Create new domain name restrictions
‘$()|;
~%_[]/
!^ {}?
@& + “ ,
#*=:<>
4 Select No. There may be times when you want two domains on different
systems to communicate with each other. If Yes, enter the URL destination(IP
address) of where the domain is located in the Foreign Dest: field.
Tip: Domain parameters are not necessary for foreign domains. When
adding a foreign domain, the parameters can be ignored.
5 Enter parameter information in the fields provided. See the following table for
parameter values and descriptions (Table 4).
Table 4 Create new domain parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
i2004 Locale String;
select from
drop-down
list
Location String 0-50
Idle Display String Up to 30
NN10043-113
Restricted
to English
in the
current
release.
characters
characters
N/A Indicates the language in which the i2004
Internet Telephone will display. Future
releases will include more supported
languages.
N/A Textdescribingl ocation of device.A specific
format of this string is scheduled for a future
release.
N/A Idle telephone display heading.
Page 51

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 3 Domain Management 29
Table 4 Create new domain parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
WD Phone Timer Integer 13-10000 150 Lengthof time the i2004 Internet Telephone
WD Timer Integer 30-10000 15 Howoften (in seconds) the IPCM will send
Time FMT Select from
drop down
list:
• 12-hour
•French
• 24-hour
Date FMT Numeric
Standard
MM/DD or
Numeric
Inverse:
DD/MM
PSEIZ Timer Integer N/A 15 Time-out for first dialed digit.
PDIL Timer Integer
(seconds)
Alpha Boolean True/False False Enablesalphanumericdialing as the default
Default Proxy Port 5060 Any valid
Behind Firewall Boolean True/False True Boolean indicating whether there is a
Allow All Codecs Boolean True/False False Allow all codecs (true) or only selected
0,1,2 0 Thetimeformat of theproxy used as default
2,3 2 2-numeric standard (09/16); 3-numeric
N/A 4 Interdigittime-out (seconds).
5060 Default proxy SIP port.
port
waits before determining that is has lost
connection to the IPCM. Should be greater
than WD_Timerby X amount. Where X is
difference between MAX expected network
latency and MIN expected network.
a “reset watchdog timer” message to a
connected I2004 device. When the I2004
receives this watch dog message, it knows
that it is still connected to the IPCM.
for the i2004 Internet telephone 0-> 12 hour
clock
inverse (16/09).
dialing style. If disabled, I2004 defaults
dialing style to numeric.
No validation is done on this field to ensure
validity.
firewall between the IPCM and the i2004
Internet Telephone.
codec (false). See Vocoder parameter
(below).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 52

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
30 Chapter 3 Domain Management
Table 4 Create new domain parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
Active Proxy Boolean True/False True Determines if default proxy is used. Used
Default Proxy Host String (30) Any valid IP
address
Time Zone Integer;
select from
drop down
list
Vocoder:PacketTime Integer;
select from
drop down
list
Contrast Integer;
select from
drop down
list
Server Home String(60) Up to 60
Realm for a domain String (120) Up to 120
Up to 30
characters
0,4,8,10,18 0 DefaultCodec Setting: 0 – G711Mulaw; 4 –
0 - 15 8 i2004 display contrast setting.
characters
characters
N/A IP Address of proxy used as default for the
N/A Time zone of the user.
N/A Specifies the SIP Application Module that
Realm Identifies the domain for subscribers when
for SIP messaging. If yes, calls will route
through the default proxy. No other routing
is currently supported for the IPCM.
i2004 telephone. No validation is done on
this field to ensure validity.
G723\6.3kbps; 8 – G711\Alaw; 10 – L16; 18
– G729A.
will host the users in this domain. This is
used in an N+M environment. All SIP
Application Modules that are not the home
SIP Application Module will forward
requests for users in this domain to the
specified address as appropriate.
(Example: 10.0.0.8) If no host address is
supplied, or the host address is 0.0.0.0., no
homing is performed.
they are being authenticated. Subscribers
may register in multiple domains. When
they are required to enter a password
during authentication, they need to know
whichdomain i t is so that they can enter the
appropriate password.
NN10043-113
Page 53

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 3 Domain Management 31
Table 4 Create new domain parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
Always Use Media
Portal
Maximum Number of
Presence
Subscriptions
Accepted
6 Click Add.
String True/False False Directs the Application Server to use the
RTP Media Portal when set to true.The
purposeistousetheRTPMediaPortal
function in dealing with special SIP
scenarios. For example, a domain that
straddles multiple sites contains users who
do not have Internet Protocol (IP)
connectivity between them due to firewalls
at different sites. This domain requires the
Always Use Media Portal to be set to True
to negotiate between the firewalls to set up
SIP sessions.
Integer N/A 0 Maximum number of inbound subscriptions
to any given user in this domain.The SIP
Personal Agent, the SIP Multimedia PC
Client, and the SIP Multimedia Web Client
will use this limit when allowing a particular
username to be added to a subscriber's list
of buddies.
Tip: In order to see the new root domain added to the list of domains,
you must close and reopen the domains folder to refresh the list of
domains.
Adding a subdomain
To add a subdomain
1 Click the Domains menu option
2 Under the root domain where you want to add a subdomain, click the
Sub-Domains > Add Sub Domain menu option. The Create new subdomain
window appears with a list of parameters inherited from the parent domain
(Figure 14).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 54

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
32 Chapter 3 Domain Management
Figure 14 Create new subdomain window
NN10043-113
3 Enter a name for the subdomain.
4 Select a COS (Class of Service) for the subdomain from the drop down list of
routing services.
5 Click Save.
Page 55

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Adding a foreign domain
To add a foreign domain
1 Click the Domain > Add Domain menu option. The C reate new domain
window appears (Figure 15). Since parameter fields are not used for foreign
domains, only the fields at the top of the window need to be completed.
Figure 15 Create new domain window
2 Enter a name for the foreign domain.
3 Select Yes from the Foreign drop down box.
Chapter 3 Domain Management 33
4 Add a foreign destination into the Foreign Destination box using the
following format
SIP<IP_Addr>:port
5 Click Add.
Listing/modifying a local or foreign domain
To list/modify a local or foreign domain
1 Click the Domains > List Foreign Domains menu option. The Domains
window appears (Figure 16).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 56

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
34 Chapter 3 Domain Management
Figure 16 List Domains window - step 1
2 From the Criteria Selection drop down list, select one of the following as a
search criteria:
NN10043-113
—DomainName
— Is a Foreign domain
—ID
or enter the name of the domain, foreign domain, or ID in the criteria selection
text box.
3 Click Add Criteria. The search criteria you selected appears in the lower
window and is used to refine your search.
4 Repeat steps 1 -3 to list additional domains.
5 In the lower window area, select whether to search by All or Any of the
criteria specified. Note that you do not have to add any criteria if you want to
see all the domains in the network.
6 Click Search to begin the search, or Remove to remove a search criteria from
the search list. A list of domains (based on the search criteria specified)
appears (Figure 17).
Page 57

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 17 List domains - step 2
7 In the Domains window, select a domain and click the Details link. The
details for the selected domain, or domains, displays.
8 Modify domain information in the parameter fields.
9 Click Save.
Deleting a local domain
Caution: Exercise extreme caution when deleting a domain as this will
permanently remove all users, devices, routes, service packages, and so
forth, associated with the domain. This is an irreversible operation that
could be a service-affecting change. For example, any calls in progress to
users or devices in the domain will terminate.
Chapter 3 Domain Management 35
To delete a local domain or subdomain
1 Click the Domains menu option.
2 Click the domain or subdomain you want to delete from the list of domains.
Tip: In order to delete a domain or subdomain you must first delete all of
its children subdomains.
3 Click Delete to delete the domain or subdomain you want to delete.
4 Click OK in the confirmation dialog box to delete the domain, or Cancel to
cancel the delete operation.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 58

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
36 Chapter 3 Domain Management
Deleting a foreign domain
Caution: Exercise extreme caution when deleting a foreign domain as
this will permanently remove all users, devices, routes, service packages,
and so forth, associated with the domain.This is an irreversible operation
that could be a service affecting change. For example, any calls in
progress to users or devices in the domain will terminate.
To delete a foreign domain
1 Click the Domains > List Foreign Domains menu option.
2 Click the Delete link for the foreign domain you want to delete.
3 Click OK in the confirmation dialog box to delete the foreign domain, or
Cancel to cancel the delete operation.
Banning a user
You can ban an individual user or a group of users in a domain or from viewing
the presence information (online status) of a user or group of users in a domain.
The banning takes effect for all subdomains under the domain.
Setting up ban list
To ban a user or a group of users
1 Click the Domains menu option.
2 Under the domain where you want to ban a user or users, click the Banned
Users > Ban User menu option. The Add a party to Domain Ban List window
appears (Figure 18).
NN10043-113
Page 59

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 18 AddapartytoDomainBanListwindow
3 Enter the party to ban in the text boxes provided. To ban an individual user,
use the following format:
Chapter 3 Domain Management 37
<username>@<domain_name.com>
To ban a group of users in a domain, use the following wildcard format:
<*>@<domain_name.com>
4 Enter a reason for banning the user or group of users to the domain list in the
Description text box.
5 Click Save. A message displays that the party was successfully added to the
ban list.
Viewing a list of banned users
To view a list of users banned from viewing the presence information (online
status) of a user or a group of users in a domain
1 Click the Domains menu option.
2 Under domain where you want to view a list of banned users, click the
Banned Users > List Banned User menu option. The D omain Ban List
window appears (Figure 19).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 60

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
38 Chapter 3 Domain Management
Figure 19 Domain Ban List window
3 To delete a user or a group of users from the ban list, click the Delete link next
to the party to ban.
4 Click OK at the deleteconfirmation dialog box, or Cancel to cancel the delete
operation.
Defining user device status reasons
The Status Reason menu option allows you to define a list of reasons for an
inactive user device status.
When a user is inactive, the user cannot register to the SIP Application Module.
This means that the user cannot use any of the services provided by the SIP
Application Module, including making calls or subscribing to other users'
presence. However, the inactive user can log in t o the SIP Personal Agent and
view the reason for their INACTIVE status.
Adding a status reason
To define a status reason for a user device
1 Click the Domains menu option.
2 Under the domain where you want to define a status reason, click Status
Reason > Add Reason. The Add Status Reason window appears (Figure 20).
NN10043-113
Page 61

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 20 Add Status Reason window
Chapter 3 Domain Management 39
3 From the Status drop down list, select INACTIVE.
4 In the Name field (required) enter a name to identify the status reason.
5 In the Description field, enter a description for the inactive status. For
example, if a user has not paid their bill, the reason for the inactive status
could be “Inactive for at least 6 months”.
6 In the URL field, enter a web page address. This is the web page that the
originator of a call to the user will be presented with, along with the status
reason description, to explain the called user’s inactive status.
7 Click Save. A message displays that the status reason was successfully added.
Viewing status reasons
To view a list of status reasons for a user device status
1 Click the Domains menu option.
2 Under the domain where you want to view the status reasons, click the Status
Reason > List Reasons menu option. The List Reasons window appears
(Figure 21).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 62

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
40 Chapter 3 Domain Management
Figure 21 Status Reasons window
3 To view or modify status reason information, click the Details link for
information about the status reason. The Modify Status Reason window
appears (Figure 22).
Figure 22 Modify status reason window
NN10043-113
4 Enter changes in the fields provided to modify information in the status
reasons fields.
5 Click Save. A message displays that the status reason was successfully
modified.
6 To delete a status reason, click the Delete link.
7 At the delete confirmation dialog box, click OK to delete the status reason, or
Cancel to return to the Status Reasons details window.
Page 63

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 4 IPCMs
Note: You must have IPCM provisioning rights to perform the tasks in
this section.
Topics in this section:
• “What is an IPCM?” on page 41
• “Adding an IPCM cluster” on page 42
• “Assigning and modifying IPCMs to a domain” on page 44
• “Deleting an IPCM cluster” on page 46
• “Listing physical IPCMs” on page 47
41
What is an IPCM?
The IP Client Manager (IPCM) is a network application capable of managing
many internal i2004 Internet Telephones while maintaining the call state and
phone settings. The IPCM also implements features (for example, stock queries
and personal directory) on the i2004 Internet Telephones. An IPCM Cluster may
span multiple domains and/or contain multiple domains.
Note: Users and devices are linked to IPCM Clusters, and not to
individual IPCMs. An IPCM Cluster may contain a single IPCM or a pair
of IPCMs. The IPCM cluster contains a primary and standby IPCM for
each i2004 Internet Telephone. Clustering of IPCMs ensures that each
IPCM retrieves the same user and device data from the database and that
each receives notification of database modifications.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 64

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
42 Chapter 4 IPCMs
In order for the IPCM to manage i2004 Internet Telephones, information
pertaining to the IPCM in general, the i2004 telephones, and users that will use
i2004s, must be provisioned. For more information, see the SIP IP Client
Manager Basics documentation.
i2004 Internet Telephone information can be provisioned in the following ways:
• Provision each individual i2004 using the SIP Provisioning Client.
• Set up default device properties for a domain, assign an activation key to the
domain,and then use the IPCM to auto-provision each i2004 device whenever
a user enters the desired activation key. (See the SIP IP Client Manager
Basics documentation and the i2004 Internet Telephone User Guide for more
information.)
Note: Normally, the IPCM is deployed prior to provisioning the IPCM.
If this is the case, it is still necessary to assign domains to the IPCM
cluster and to assign a provisioned capacity for the IPCM cluster and
domain. If the IPCM has been deployed, see “Assigning and modifying
IPCMs to a domain.” If the IPCM has not been deployed, and it is
desired to pre-provision the IPCM, see “Adding an IPCM cluster.”
Adding an IPCM cluster
Adding an IPCM cluster creates a virtual IPCM to which users, i2004 devices, and
domains may be assigned. It does not actually create a physical IPCM, nor does it
deploy IPCM software onto a server. The association of the physical IPCM to this
IPCM cluster is performed when the physical IPCM is deployed and configured.
To add an IPCM cluster
1 Click the IPCM Cluster > Add IPCM Cluster menu option. The Create new
IPCM window displays. The following figure (Figure 23) shows an example
of creating an IPCM named LAB IPCM. The maximum provisioned capacity
is 1000, i2004 Internet Telephones. Note that the IPCM name is case
sensitive.
NN10043-113
Page 65

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 23 Create new IPCM window
Chapter 4 IPCMs 43
The following table (Table 5) lists the Create new IPCM parameters and values to
use when creating a new IPCM.
Table 5 Create new IPCM parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
IPCM Name String(100) Up to 100
characters
Prov. Capacity Integer Maximum
of 10,000
per IPCM
None ThenameofthisIPCM.
ThenameoftheIPCM
must be a unique name.
None The number of i2004
Internet Telephones that
are allowed to be
provisioned for this IPCM
(across all domains).
2 Click Save.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 66

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
44 Chapter 4 IPCMs
Assigning and modifying IPCMs to a domain
An IPCM is not usable until it is assigned to a domain. To assign an IPCM to a
domain
1 Click the IPCM Clusters > List IPCM Clusters menu option. A list of
deployed IPCMs appears (Figure 24).
Note: Upon first assignment of an IPCM, the list of deployed IPCMS
may be empty. However, in many cases, the IPCM would have already
been deployed using the System Management Console and will appear in
the list.
Figure 24 List IPCM Clusters window
NN10043-113
2 Click the Details link for the IPCM you want to assign to a domain. The
Modify IPCM window appears (Figure 25).
Page 67

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 25 Modify IPCM window
3 If necessary, modify the IPCM Name or Prov. Capacity parameters and click
Save.
Chapter 4 IPCMs 45
Tip: The Avail Capacity field is a read only field calculated by adding
the Assigned Capacity of domains to which this IPCM is assigned and
subtracting that value from the Prov. Capacity of the IPCM.
4 Select a domain from the list of available domains in the Assign New Domain
area of the window. Enter information in the following fields for the domain
you are assigning to the IPCM:
Field Description
Assigned Capacity: The number of i2004 Internet Telephones you want
to allow in this assigned domain.
Activation Key: A unique string (number) per IPCM/domain
combination that associates default device
properties with this particular domain. The
administratormust pick a unique string (number) for
each domain. If the IPCM is used to auto-provision
i2004 devices, the installer will be prompted for this
activation key during the installation process.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 68

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
46 Chapter 4 IPCMs
5 Click Save. The IPCM Domain Relation window appears (Figure 26).
Figure 26 IPCM Domain Relation window
6 Enter your changes and click Save. A confirmation messages displays
confirming your changes.
7 To assign another domain to the IPCM, select a domain from the list in the
Assign New Domain area. Enter information in the parameter fields and click
Save.
Deleting an IPCM cluster
Caution: Exercise extreme caution when deleting an IPCM as this will
permanently remove all i2004 Internet Telephones and users' i2004
capabilities associated with the IPCM that you are deleting.
To delete an IPCM cluster
1 Click the IPCM Clusters > List IPCM Clusters menu option.
NN10043-113
Page 69

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
2 Click the Delete link for the IPCM cluster you want to delete.
3 Click OK in the confirmation dialog box to delete the IPCM cluster, or
Cancel to cancel the delete operation (Figure 27).
Figure 27 IPCM Delete confirmation dialog box
Listing physical IPCMs
The List Physical IPCMs menu option allows you to view the physical IP Address
of the server on which the IPCM resides.
To list the physical IP address of the IPCM
Chapter 4 IPCMs 47
1 Click the IPCM Clusters > List Physical IPCMs menu option. The Physical
IPCMs window appears (Figure 28) listing the following fields:
Field Description
IPCM Cluster: The name that identifies the virtual IPCM
cluster.
Physical IPCM: The physical IP Address of the server on
Delete Physical IPCM: Allows you to delete the mapping of the
which the IPCM resides.
physical IPCM to the IPCM Cluster.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 70

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
48 Chapter 4 IPCMs
Figure 28 Listing physical IPCMs
2 To delete a physical IPCM, click the Delete link in the Delete Physical IPCM
column. At the delete confirmation dialog box, click Ok to delete the physical
IPCM or Cancel to cancel the delete operation (Figure 29).
Figure 29 Delete physical IPCM confirmation dialog box
NN10043-113
Page 71

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
Note: You must have Voice Mail provisioning rights to perform the tasks
in this section.
Topics in this section:
• “Introduction” on page 49
• “Voice mail server types” on page 50
• “Provisioning a SIP-based voice mail server” on page 50
• “Provisioning a Trunk-based voice mail server” on page 54
• “Provisioning a Line-based voice mail server” on page 60
• “Assigning a user to a provisioned voice mail server” on page 67
• “Listing/modifying/deleting a voice mail server” on page 68
• “Using CPL scripts with voice mail” on page 69
49
Introduction
The SIP Provisioning Client allows you to provision third-party voice mail server
information to:
• set up and route calls to voice mail
• associate users to a voice mail server
• set up a voice mail server to receive message waiting indication (MWI)
notifications
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 72

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
50 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
Voice mail server types
The following voice mail server types are supported as described in the following
table (Table 6).
Table 6 Voice mail server types
Voice mail server type Description
SIP-based AnIP based voice mail server that uses the SIP protocol.
Line-based A v oice mail server with multiple lines, each identified by
Trunk-based A legacy Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)
This server type does not need a PSTN gateway.
a 10 digit phone number that goes into the voice mail
server. When people leave messages, the individual
lines are used in a round robin manner to connect to the
voice mail server to allow someone to leave a message.
TheSIPApplicationModulesendsanSMDImessageto
the voice mail server to help establish the connection to
the SIP Application Module that uses SMDI to obtain
Message WaitingIndication (MWI) information from the
voice mail server.
based voice mail server that uses a Primary Rate
Interface (PRI) or Channel Associated Signalling (CAS)
gateway.The SIP Application Module uses SMDI to send
call setup information using a Call Detail Message to get
Message WaitingIndication (MWI) information from the
voice mail server.
Provisioning a SIP-based voice mail server
Provisioning a SIP-based voice mail server allows the administrator to configure
the SIP Application Module to communicate with a voice mail server using the
SIP protocol.
NN10043-113
The SIP Application Module is given information on what to query to find the
location of the voice mail server. The SIP Application Module will use this
information to send SIP calls to the voice mail server when calls are routed to
voice mail.
Page 73

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Adding a SIP-based voice mail server
To add a SIP-based voice mail server
1 Click the VoiceMail > Add Voice Mail Server menu option. The Create new
voice mail server window appears (Figure 30).
Figure 30 Create new voice mail server window (SIP) - step
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers 51
2 Choose SIP-Based Server from the drop down and click Next. The second
page of the Create new voice mail server appears (Figure 31).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 74

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
52 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
Figure 31 Create new voice mail server window (SIP) - step 2
3 Enter information about the SIP-based voice mail server in the parameter
fields. The following table (Table 7) lists the SIP-based voice mail
parameters.
Table 7 SIP-based voice mail parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
Description String(100) Up to 100
URI to query to find
Voice Mail Server
String(100) Up to 100
characters
characters
NN10043-113
None The description for the server that
identifies the SIP-based voice
mail server.
None The SIP address of the user that
the SIP Application Module will
look up to find the address of the
voice mail server.
Page 75

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers 53
Table 7 SIP-based voice mail parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
Client contact String(100) Up to 100
Application Server String(60) Up to 60
Domains String(60)
characters
characters
characters
Up to 60
characters
4 Click Save. The SIP-based voice mail server you added now appears in a list
of voice mail servers (Figure 32).
Figure 32 Voice Mail Servers window (SIP)
Voice mail Thefieldusedto route voicemail.
ServerHome. With
this default, each
SIP Application
Module will ignore
this field and forward
SIP requests to the
voice mail server
insteadofforwarding
them to a "home"
Application Server.
None The domains that will use this
In most cases, you will use the
default(voicemail).Ifyourequire
a different client contact, contact
your Nortel Networks support
representative.
Specifies the SIP Application
Module will host the voice mail
server being provisioned. This is
used in an N+M environment. All
SIP Application Modules that are
not the home SIP Application
Module will forward requests
destined to voice mail to the
address s pecified in this field.
voice mail server.Use the
Ctrl-click key to select multiple
domains to use the same voice
mail server.
Adding a phantom voice mail server user
After you add a voice mail server, you then need to create a phantom user named
voicemail for the domain that will use the SIP-based voice mail server.
To create a phantom user for the SIP-based voice mail server
1 Click the Domains menu option.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 76

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
54 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
2 Under the domain where you want to add a phantom user, click the Add User
menu option.
3 In the Add User form, enter the text "voice mail" for the User Name, Last
Name, First Name, fields. In the password field, enter any password.
4 Click Save. The User details screen displays a message that the user was
added successfully.
5 At the top of the window, click the Routes link to specify the route to the
voice mail server. Enter the SIP address that the voice mail server is
expecting, along with the domain and IP address (Figure 33).
Figure 33 User routes window
6 Click Add.
7 Click Save.
Note: For CAS/CallPilot, it is recommended that you do not create a
phantom user.
Provisioning a Trunk-based voice mail server
Provisioning a Trunk-based voice mail server allows the administrator to
configure the SIP Application Module so that it can communicate with a voice
mail server using a PRI or CAS gateway.
NN10043-113
Page 77

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
The SIP Application Module is given information on what to query to find the
correct gateway to send SIP calls to the voice mail server when calls are routed to
voice mail. An SMDI TELNET session is configured to allow the SIP Application
Module to send call setup information using a SMDI Call Detail Message to
receive SMDI MWI messages.
Adding a Trunk-based voice mail server
To add a Trunk-based voice mail server
1 Click the VoiceMail > Add Voice Mail Server menu option. The Create new
voice mail server window appears (Figure 34).
Figure 34 Create new voice mail server window (Trunk-based) - step 1
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers 55
2 Choose Trunk-BasedServerfrom the drop down and click Next. The second
page of the Create new voice mail server appears (Figure 35).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 78

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
56 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
Figure 35 Create new voice mail server window (Trunk-based) - step 2
NN10043-113
3 Enter SMDI parameter information for the Trunk-based voice mail server.
The following table (Table 8) lists the SMDI parameters.
Page 79

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Table 8 SMDI parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers 57
Address String(100) Up to 100
characters
Port Integer None None The port for the SMDI
SMDI Version Float None None The SMDI version. There
Username String(60) Up to 60
characters
Password String(20) Up to 20
characters
N/A The IP address of the
terminal (SMDI) server.
server to TELNET to.
are only 2 versions of the
SMDI protocol (Version 1
and Version 2). Version 2
is the latest draft and is
supported by most voice
mail servers.
N/A The TELNET username
for logging in to the SMDI
TELNET server. Used by
the SIP Application
Moduletologinintothe
terminal server.
N/A The TELNET password
for logging in to the SMDI
TELNET server.
4 Click Next to enter information about the gateway connection. The Create
new voice mail server window appears (Figure 36).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 80

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
58 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
Figure 36 Create new voice mail server window (Trunk-based) - step 3
NN10043-113
Page 81

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers 59
5 Enter information about the Trunk-based voice mail server gateway
connection in the parameter fields. The following table (Table 9) lists the
gateway connection parameters.
Table 9 PRI Gateway connection parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
Description String(100) Up to 100
characters
URI to query to
find gateway
Type of Trunk Drop List NA PRI_TRUNK A specification of whether the voice
Client contact String(100) Up to 100
String(100) Up to 100
characters
characters
None The description for the server that
identifies the Trunk-based voice
mail server.
None For PRI Gateway: The address (in
either 10 digit phone number and
domainname format or in SIP:voice
mail@nortelnetworks.com format)
of the machine that will host this
voice m ail server. The SIP
Application Module performs
translations on the phone number
and domain to understand which
gatewayto use. Youcanchange the
translations to use a different
gateway, and do nothave to change
this field.
For CAS Gateway (CallPilot): The
SIP address for the CAS Gateway
that routes to the CallPilot. The
addressis made up of a DN that the
gateway routes to the CallPilot, and
an maddr specification for the CAS
Gateway. (For example,
sip:66250@nortelneworks.com;ma
ddr=46.10.11.219).
mail Gateway is PRI or CAS.
Voice mail Thefield used to route voice mail. In
most cases, you will use the default
(voice mail). If you require a
different client contact, contact your
Nortel Networks support
representative.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 82

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
60 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
Table 9 PRI Gateway connection parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
Application
Server
Domain name String(60) Up to 60
String(60) Up to 60
characters
characters
6 Click Save. The Trunk-based voice mail server you added now appears in the
list of voice mail servers (Figure 37).
Figure 37 Voice Mail Servers window (Trunk-based)
ServerHome. With
this default, each SIP
Application Module
will ignore this field
and forward SIP
requests to the voice
mail server instead of
forwarding them to a
"home" Application
Server.
None The domains that will use this
Specifies the SIP Application
Module will host the voice mail
server being provisioned. This is
used in an N+M environment. All
SIP Application Modules that are
not the home SIP Application
Module will forward requests
destined to voice mail to the
address s pecified in this field.
Trunk-based voice mail server.Use
the Ctrl-click key to select multiple
domainstousethesamevoicemail
server.
Provisioning a Line-based voice mail server
Provisioning a Line-based voice mail server allows the administrator to configure
the application so that it can communicate with a voice mail server using a Lines
Gateway. The SIP Application Module is given information on which Lines
Gateway to use and which line numbers to use for sending calls to the gateway
when routing a call to voice mail.
In addition, an SMDI TELNET session is configured to allow the SIP Application
Module to directly communicate call setup information to the voice mail server.
The SMDI link is also used by the SIP Application Module to receiveSMDI MWI
messages.
NN10043-113
Page 83

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Adding a Line-based voice mail server
To add a Line-based voice mail server
1 Click the Voice Mail > Add Voicemail Server menu option. The Create new
voice mail server window appears (Figure 38).
Figure 38 Create a new voice mail server window (Line-based) - step 1
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers 61
2 Choose Line-Based Server from the drop down and click Next. The second
window of the Create new voice mail server appears (Figure 39).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 84

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
62 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
Figure 39 Create new voice mail server window (Line-based) - step 2
NN10043-113
3 Enter SMDI parameter information about the Line-based voice mail server.
The following table (Table 10) lists the Line-based voice mail server SMDI
parameters.
Page 85

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Table 10 Line-based voice mail server SMDI parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers 63
Address String(100) Up to 100
characters
Port Integer None None The port for the SMDI
SMDI Version Float None None The SMDI version. There
Username String(60) Up to 60
characters
Password String(20) Up to 20
characters
N/A The IP address of the
terminal (SMDI) server.
server to TELNET to.
are only 2 versions of the
SMDI protocol: Version 1
and Version 2. (Version 2
is the latest draft and is
supported by most voice
mail servers.)
N/A The TELNET username
for logging in to the SMDI
TELNET server.
N/A The TELNET password
for logging in to the SMDI
TELNET server.
4 Click Next to enter general information about the Line-based server
(Figure 39).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 86

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
64 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
Figure 40 Create new voice mail server window (Line-based) - step 3
NN10043-113
Page 87

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers 65
5 Enter general information about the Line-based voice mail server in the
parameter fields. The following table lists the Line-based parameter
information.
Table 11 Line-based voice mail server general parameter information
Parameter Type Range Default Description
Description String(100) Up to 100
characters
Client contact String(100) Up to 100
characters
Application Server String(60) Up to 60
characters
Maximum Call
Duration
Domain name String(60) Up to 60
Digit 1-99 None The period of time that the SIP
characters
None Thedescriptionforthe server that
identifies the Line-based voice
mail server.
Voice mail The field used to route voice mail.
In most cases, you will use the
default(voice mail). If you require
a different client contact, contact
your Nortel Networks support
representative.
ServerHome. With
this default, each SIP
Application Module
will ignore this field
and forward SIP
requests to the voice
mail server instead of
forwarding them to a
"home" Application
Server.
None The domains that will use this
Specifies the SIP Application
Module will host the voice mail
server being provisioned. This is
used in an N+M environment. All
SIP Application Modules that are
not the home SIP Application
Module will forward requests
destined to voice mail to the
address specified in this field.
Application Module allows a
caller to stay connected to the
Line-based voice mail server
when someone is trying to leave
a voice mail message.
voice mail server. Use the
Ctrl-click key to select multiple
domains to use the same voice
mail server.
6 Click Next to provision the lines for the gateway (Figure 41).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 88

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
66 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
Figure 41 Create new voice mail server window (Line-based) - step 4
NN10043-113
7 Enter the Line-based parameter information to provision the l ines for the
gateway. The following table (Table 12) lists the Line-based voice mail server
parameters.
Page 89

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Table 12 Line-based voice mail server parameters
Parameter Type Range Default Description
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers 67
Gateway String 1-100
Line Digit 0-38 digits None The 10-digit telephone
Message
Desk
Position
Number
3 digits 000-999 None A 3-digit number used by
4 digits 0000-9999 None A 4-digit number used to
characters
domain.com;
norteltrkgrp=1;ma
ddr=0.0.0.0
The trunk group, domain
name and IP address of
the gateway.
number that identifies the
line from the gateway’s
point of view.
the SMDI protocol to
determine where to store
an incoming message.
determine where to put
an incoming message.
8 Click Add Line. To add multiple lines, continue to enter the gateway
parameter information and click Add Line.
9 When you are finished adding lines for this gateway, click Set New Line to
have more than one gateway with lines going into the same voice mail server.
10 Click Save. The Line-based voice mail server you added now appears in the
list of voice mail servers (Figure 42).
Figure 42 Voice Mail Servers window (Line-based)
Assigning a user to a provisioned voice mail server
In order for a user to have voice mail, you must associate a voice mail server and
mail box for that user.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 90

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
68 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
To associate a user with a voice mail server that has been previously provisioned
1 Click the Domains menu option
2 Click the domain for the user.
3 Click the Users > List Users menu option.
4 Click Search at the bottom of the screen to display a list of users in the
domain.
5 Click the Details link for the user you want to associate with a voice mail
server.
6 Scroll down the screen to the voice mail server field. Select a voice mail
server to use when sending calls for this user to voice mail from the drop
down list of provisioned voice mail servers for this domain.
7 Enter the information for the user’s voice mail box in the Voice mail field.
8 Click Save.
Listing/modifying/deleting a voice mail server
To view details of a provisioned SIP, Trunk, or Line-based voice mail server
1 Click the VoiceMail > List Voice Mail Servers menu option. The V oice Mail
Server window appears (Figure 43).
Figure 43 List of voice mail servers
2 To view the details of a voice mail server, click the link of the voice mail
server in the Description column. The Create new voice mail server form
appears where you can modify information.
3 Click Save to save your changes or Back to return to the list of voice mail
servers.
NN10043-113
Page 91

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
4 To delete a voice mail server, click the Delete link for the voice mail server
you wish to delete. At the confirmation dialog box, click OK to delete the
voice mail server, or Cancel to cancel the operation.
Using CPL scripts with voice mail
A user will only have voice mail service if there is a Call Processing Language
(CPL) script that specifies a route to sip:voicemail@domain.com (usually the last
route).
To specify a route, you need to provision the following voice mail parameters in
the SIP Provisioning Client:
Voice mail parameter Description
Client Contact Must match the username in the CPL script and
should always be set to voicemail (unless you are
working with Nortel Networks technical support).
If this parameter is set to something else, properties
in the IPCM and Web Client will require changes.
Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers 69
URI to Query to Find
Gateway
To create a CPL script that has sip:voicemail@domain.com as the last route
1 Log in to the SIP Personal Agent.
2 Click the Call Manager icon.
3 In the Default Behavior window, select the TrytoFindMeoption.
4 Click Save
Tip: Unless a user logs into t he SIP Personal Agent and clicks Save in the
Call Manager window, they will not have a CPL Script and thus calls to
them will never route to voice mail as a final route.
Point to a static route, a user with a static route, or
have a number that can be translated by the
Telephony routing to go to the correct gateway.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 92

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
70 Chapter 5 Voice Mail Servers
NN10043-113
Page 93

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 6 Defining and Assigning Services
Note: You must have Services provisioning rights to perform the tasks in
this section.
Topics in this section:
• “Defining service parameters” on page 71
• “Assigning services to a domain” on page 75
Defining service parameters
The SIP Provisioning Client allows you to define and assign services to domains.
You can assign all or a subset of the pre-defined services to a domain.
71
When you define the service parameters for service package, you are essentially
defining its contents. Services are set up much like convenience packages for the
domain. The service provider then has the flexibility to set up services and create
a standard set of services for their customers according to their own
specifications.
To define service parameters
1 Click the Services > Define Service Parameters menu option.
The list of available services window appears (Figure 44).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 94

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
72 Chapter 6 Defining and Assigning Services
Figure 44 List of available services window
NN10043-113
2 From the list of available services window, select a value for a service
parameter from the drop down list. The following table (Table 13) lists the
service parameters and options.
Page 95

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Chapter 6 Defining and Assigning Services 73
Table 13 Services parameters and options
Service Option Parameter Description Client enforced Server enforced
Enable/disable
Voicemail
Enable/disable
Audio
Conference
Enable/disable
Presence
None Retrieve voice mail or for other
Maximum
number of
ports
Maximum
size of client
list of
buddies
Maximum
number of
subscriptions
generated
subscribers, to leave a voice mail
message. Voice mail is retrieved
from a network server.Theuser is
aware of deposited voice mail since
their client's MWI (message waiting
indicator) is enabled.
Initiate an audio conference call
utilizing a SIP audio server.The
number of users in the conference
call is limited by the maximum
number of ports assigned. Values
beyond above thirty two are not
allowed.
Specifies the number of people in a
list of buddies. This is the number of
peoplethat a user is subscribing to in
order to view their presence.
Although a user can be logged into
numerousdevices,the list of buddies
is a shared resource. For example, if
the max list of buddies size is set to
10, there can be 10 buddies on each
of the client devices (the same 10
buddies, not 10 per device). The
client has the option of sending any
of the buddies.
Allowsausertobeloggedinto
multiple devices (i2004 Internet
Telephone, SIP Multimedia PC
Client, SIP Multimedia Web Client).
Each such device performs
messaging to determine the
presence (online status) of each of
the buddies in the list. There is a
need for limiting the number of
devicesandbuddies to limitresource
contention issues. The maximum
number of presence subscriptions is
defined by the following formula:
maximum number of subscriptions
generated= (maximum# of clients)*
(maximum number of allowed
buddies).
Yes. Optional.
Enabled through
the SIP
Application
Module.
Yes. Optional.
Enabled through
the SIP
Application
Module.
Yes
Yes.
Mandatory.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 96

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
74 Chapter 6 Defining and Assigning Services
Service Option Parameter Description Client enforced Server enforced
Enable/disable
Video
Simultaneous
Network Call
Restriction
Enable/disable
Advanced
Screening
Enable/disable
QoS
Enable/disable
Blended User
None Use of point to point video service
Maximum
number of
ringlist
entries
- Enables the ability to perform
QoSDiffServ
Code for
Signalling
QoSDiffServ
Code for
Audio
QoSDiffServ
Code for
Video
QoS 802.1p
Service
Priority
None Enables the use of a traditional
between web c lients and PC clients.
Specifies the maximum number of
users that are defined in a route in
the Call Manager portion of the SIP
Personal Agent. The users in the
ringlist are simultaneously rung.
address screening (based on the
user’s current address book entries)
and time screening (time of day, day
of week) in the Call Manager area of
the SIP Personal Agent.
Specifies quality of service for client
signaling, audio and video (up to 64).
phone for voice calls and the SIP
Multimedia PC for multimedia
communicationand collaboration.
Yes.
Yes.
Yes.
Yes.
Yes
NN10043-113
3 To create new values for the service parameter, click [Edit].
The Add new parameter values window appears (Figure 45).
Page 97

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 45 Add new parameter values window
Chapter 6 Defining and Assigning Services 75
4 For the selected parameter, select a value from the list, using the UP and
DOWN buttons to set the priority of the value.
5 To add a new value, click Add. The new value appears in the list of parameter
values.
6 Click Set as Default to set the value in the list as the default value for the
service parameter.
7 Click Save to save your service parameter changes.
Assigning services to a domain
Once you add a value for a service parameter, you can select a domain to assign
the services to.
To assign services to a domain
1 Click the Services > Assign Services menu option. The Assign Services
window appears (Figure 46).
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 98

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
76 Chapter 6 Defining and Assigning Services
Figure 46 Assign services window
2 Select a domain from the drop down list and click Continue. To assign
services to more than one domain, click the link to assign services to multiple
domains in the Assign Services window. The Assign services to domains
window appears (Figure 47).
NN10043-113
Page 99

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
Figure 47 Assign services to a domain window
Chapter 6 Defining and Assigning Services 77
3 Select the services and service parameter values you want to assign to the
selected domain or multiple domains (Use the Ctrl-click key to choose
multiple domains.) To enable all services, check the Enable all Services
checkbox.
4 Click Save. A confirmation message displays that your service was assigned
successfully.
Once services have been defined and assigned to domains, you can list all the
services that are available for a domain (or multiple domains) and create and
assign packages accordingly. For a subdomain, services are assigned from the root
domain.
SIP Provisioning Client User Guide
Page 100

[Standard - Nortel Networks Confidential]
78 Chapter 6 Defining and Assigning Services
NN10043-113
 Loading...
Loading...