Page 1

Page 2

Contents
Overview................................................................................................................................5
NB5Plus4/W Package Contents ......................................................................................6
Minimum System Requirements ......................................................................................7
Do I need a Micro lter? .................................................................................................8
LED Indicators .................................................................................................................9
Back Panel Ports ...........................................................................................................10
Restoring Factory Defaults ............................................................................................ 11
Default Settings .............................................................................................................12
LAN (Management) ..................................................................................................12
WAN (Internet) .........................................................................................................12
Modem Access .........................................................................................................12
Connecting your NB5Plus4/W .............................................................................................13
Connecting your NB5Plus4/W ADSL Modem via ETHERNET ........................................... 13
Connecting your NB5Plus4/W ADSL Modem via USB .....................................................14
Installing the USB driver (Windows 98/Me/2000/XP only) .......................................14
NB5Plus4W Antenna Instructions ..................................................................................15
Conguring your NB5Plus4/W .............................................................................................16
Computer Hardware Conguration .....................................................................................18
Windows® XP PCs ........................................................................................................18
Windows 2000 PCs .......................................................................................................18
Windows Me PCs ..........................................................................................................18
Windows 95, 98 PCs .....................................................................................................19
Advanced Settings ..............................................................................................................20
Setup .............................................................................................................................21
Setup>LAN Conguration ........................................................................................22
Interfaces ............................................................................................................22
LAN Groups ........................................................................................................22
Conguring LAN Groups ....................................................................................24
IP Settings ..........................................................................................................25
Services ..............................................................................................................27
Ethernet Switch ..................................................................................................27
WAN Setup>New Connection ..................................................................................28
PPPoA Connection Setup...................................................................................33
Static Connection Setup .....................................................................................34
DHCP Connection Setup ....................................................................................35
Bridge Settings ...................................................................................................35
CLIP Connection Setup ......................................................................................36
WAN Setup>Modem ................................................................................................37
Logout.................................................................................................................38
Advanced .......................................................................................................................39
Advanced>UPnP ......................................................................................................40
Advanced>SNTP ......................................................................................................41
Advanced>IPQoS ....................................................................................................45
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
2 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 3

QoS Setup Page ......................................................................................................45
Rules Conguration Page ........................................................................................46
Trafc Queuing Conguration ..................................................................................47
Queue Priorities: .................................................................................................47
Conguration: .....................................................................................................47
En-queuing Policy ....................................................................................................47
Conguration: .....................................................................................................47
De-queuing Policy ....................................................................................................47
WRR Queue Scheduler for Medium and Low priority queues ............................48
Conguration: .....................................................................................................48
Low Latency Queue (Fragmentation and Interleaving) for Voice Trafc.............48
TOS-to-Priority Mapping .....................................................................................48
Advanced>Port Forwarding .....................................................................................50
More about Port Forwarding ...............................................................................50
Well-know and registered Ports .........................................................................51
Easy Port Forwarding: Applying Pre-Dened Rules ...........................................52
DMZ Settings ......................................................................................................53
Advanced Port Forwarding: Creating Custom Rules ..........................................54
Adding Custom Rules to Applied Rules List .......................................................55
Advanced > IP Filters ...............................................................................................56
Advanced > LAN Isolation ........................................................................................58
Advanced > Bridge Filters ........................................................................................59
Enable/Disable Bridge Filtering ..........................................................................59
Create Bridge Filter Rules ..................................................................................59
Edit or Delete Bridge Filter Rules .......................................................................60
Hidden Bridge Filter Rules..................................................................................60
Advanced > Multicast ...............................................................................................61
Advanced > Static Routing .......................................................................................62
Conguring Static Routing: .................................................................................62
Advanced>Dynamic Routing ....................................................................................63
Advanced > Access Control .....................................................................................64
Tools ..............................................................................................................................65
Tools>System Commands .......................................................................................66
Tools>User Management .........................................................................................67
Tools>Update Firmware ...........................................................................................68
Tools>Ping Test ........................................................................................................69
Tools>Modem Test ...................................................................................................70
Status .............................................................................................................................71
Status>Network Statistics ........................................................................................72
Status > Connection Status .....................................................................................73
Status > DHCP Clients .............................................................................................74
Status > Modem Status ............................................................................................75
Status > Product Information ...................................................................................76
Status > System Log ................................................................................................77
EasyCong ....................................................................................................................78
Help ...............................................................................................................................79
Appendix A: NB5Plus4W Wireless Features .......................................................................80
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 3
Page 4

Wireless Main Screen ....................................................................................................80
Wireless>Setup ........................................................................................................81
Wireless Setup Field Descriptions ......................................................................81
User Isolation .....................................................................................................83
Save Your Changes ............................................................................................83
Wireless>Conguration ............................................................................................84
Wireless>Security ....................................................................................................86
Wireless>Security>WEP ....................................................................................87
Wireless > Security > 802.1x ..............................................................................89
Wireless>Security>WPA .....................................................................................90
Wireless>Management ............................................................................................91
Wireless>Management>Access List ..................................................................91
Wireless > Management > Associated Stations .................................................92
Wireless > Management > Multiple SSID ...........................................................93
Status .............................................................................................................................94
Log out ...........................................................................................................................95
Appendix B: Specication ...................................................................................................96
Appendix C: Cable Connections.........................................................................................98
RJ-45 Network Ports ...............................................................................................98
Straight and crossover cable conguration ...................................................................99
Straight-Through Cabling .........................................................................................99
Cross-Over Cabling ..................................................................................................99
RJ11 connector and cable ......................................................................................100
605 to RJ-11 adapter ..............................................................................................100
Appendix D: Glossary .......................................................................................................101
Appendix E: Registering your NetComm Product ............................................................109
Contact Information .....................................................................................................109
Appendix F: Legal & Regulatory Information ....................................................................110
Customer Information .................................................................................................. 110
Product Warranty ......................................................................................................... 110
Limitations of Warranty ................................................................................................ 111
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
4 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 5

Overview
Thank you for purchasing the NetComm NB5Plus4/W ADSL/ADSL2 Modem Router.
NetComm brings you the Next Generation of ADSL technology with ADSL-2*, which
boosts ADSL’s performance, improves interoperability, and supports new applications, services and deployment conditions.
NetComm’s implementation of ADSL-2* and ADSL-2+* ensures that the NB5Plus4/
W operates with existing ADSL services while delivering optimal performance in
all modes of operation. Powered by the latest ADSL-2* TI chipset, NetComm’s
NB5Plus4/W increases downstream data rates by up to 50% (12Mbps) and 100%
(25Mbps) for ADSL2 Plus* mode ensuring that you can surf the net or download
your les quicker than ever before.
Security is a key issue with Broadband users and NetComm’s NB5Plus4/W does not
leave you exposed. Employing the latest Active Firewall technology, the NB5Plus4/
W checks every packet of data that comes in ensuring your defences are rock-solid
against hackers, unauthorised entries, probes and even Denial of Service attacks.
What’s more, the NB5Plus4/W is equipped with a VPN pass-through feature allowing
you to use a standard VPN client for Point-to-Point communication even while your
Firewall is active.
The NB5Plus4/W delivers the connection versatility needed to cater for today’s ADSL
users. You can simply attach the NB5Plus4/W to a single PC by using the USB port
or Ethernet port. Alternatively, should you wish to share your Internet connection,
the NB5Plus4/W is equipped with an in-built Router and four 10/100 Ethernet ports
for connection to a network. If you have the NB5Plus4W modem, you can share
your Internet connection wirelessly.
The NB5Plus4/W’s Port Forwarding and UPnP functions have made it easier for
today’s Internet users to congure and setup the myriad of Network Port Rules
needed by Internet applications such as On-Line Gaming, Peer-To-Peer le sharing
and Messenger services to operate. NB5Plus4/W has a number of pre-congured
rules for several games, just click on the game you wish to play on-line and the rest
is done for you.
Added to this, the NB5Plus4/W introduces a QoS (Quality of Service) feature that
gives you control over which types of outgoing data are given priority by the router.
With QoS you can tailor your router settings to ensure that you can keep gaming or
browsing even though your upstream bandwidth may be saturated by applications
such as Peer-To-Peer le sharing.
* Your ISP must support and provide you with an ADSL-2 or ADSL-2+ service for these features to be available. This
product will operate as a standard ADSL Modem Router when an ADSL-2 service is not available.
This reference manual assumes that the reader has an installed Ethernet card in the computer to be connected and
has basic to intermediate computer and Internet skills. However, basic Computer Networking, Internet, and Firewall
technology information is available from the NetComm Web site. See www.netcomm.com.au.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 5
Page 6

NB5Plus4/W Package Contents
Your NB5Plus4/W Package contains the following items:
• The NB5Plus4 or NB5Plus4/W Mo-
dem Router (both models shown
above)
• Telephone Cable (RJ-11)
• RJ-11 to 605 Adaptor
• USB Cable
• Driver and Manual CD
• CAT-5 UTP Straight Ethernet
Network Cable (RJ-45)
• NB5Plus4/W Quick Start Guide
and Package Contents Note
If any of the above items are damaged or missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
6 www.netcomm.com.au
• Power Adaptor (AC 15V)
Page 7

Minimum System Requirements
Before continuing with the installation of your NB5Plus4/W, please conrm that you
comply with the minimum system requirements.
• Pentium® MMX 233MHz
• A CD-ROM Drive
• Ethernet card installed with TCP/IP Protocol (required only if you are connecting
to the ETHERNET port of your ADSL Router)
• USB Port (required only if you are connecting to the USB Port of your ADSL
Router)
• Host Operating Systems support for USB:
• Windows® 98 Second Edition
• Windows® 2000
• Windows® Me
• Windows® XP (recommended)
• OS independent for Ethernet
• Web Browser support:
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 (or later versions)
• Netscape® Navigator 4.0 (or later versions)
• Most popular browsers
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 7
Page 8
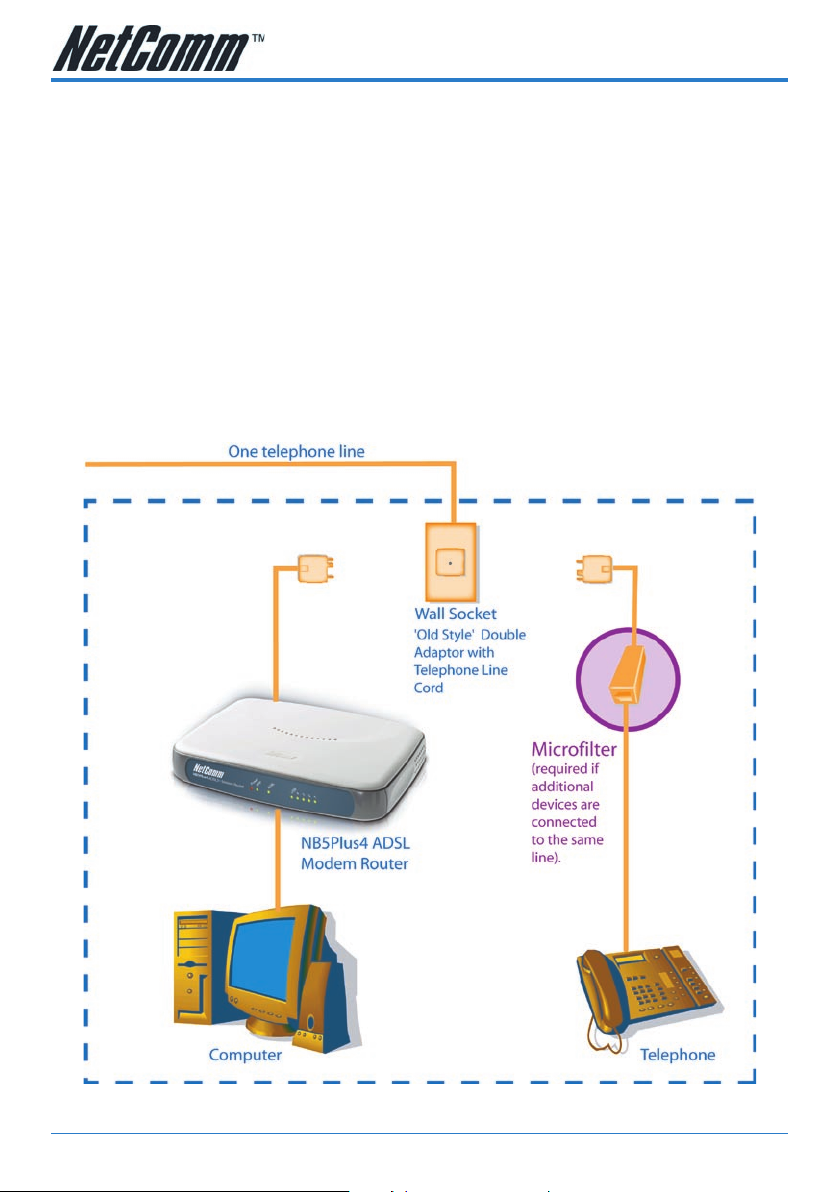
Do I need a Micro filter?
Micro lters are used to prevent common telephone equipment, such as phones,
answering machines and fax machines, from interfering with your ADSL service. If
your ADSL enabled phone line is being used with any other equipment other than
your ADSL Modem then you will need to use one Micro lter for each phone device.
Splitters may be installed when your ADSL line is installed or when your current
phone line is upgraded to ADSL. If your telephone line is already split you will not
need to use a Microlter - check with your ADSL service provider if you are unsure.
Each micro lter is connected in-line with your telephone or fax machine so that all
signals pass through it. Telephones and/or facsimiles in other rooms that are using
the same extension will also require Microlters. The following diagram gives an
example of connecting your ADSL Modem/Router using a Microlter.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
8 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 9

LED Indicators
The LED Indicators are located on the front of the unit, they are green in colour,
except the Power LED which is red. The meanings are as follows:
Label Status Indicates
Power On Power is on.
Off Power is off.
PPP Flashing Trying to authenticate with ISP’s PPP
On PPP link is up.
Off No PPP link available.
ADSL On A valid ADSL connection.
Flashing An active WAN session.
WLAN (NB5Plus4W) On Wireless link is enabled on NB5Plus4W.
Flashing Data is being transmitted wirelessly.
USB On PC connected to USB port.
Flashing Data is being transmitted between NB-
LAN 4, 3, 2 & 1 Flashing Flashes when data is being sent or re-
On Indicates a link to your LAN or Network
Off Indicates no link to LAN.
server.
5Plus4/W and PC.
ceived on the LAN connection.
card is active.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 9
Page 10

Back Panel Ports
Power jack
for AC power
adaptor
Power Connect the Power Adapt0r that comes with your package.
1, 2, 3, 4 4 x 10/100 Base-T Ethernet jack (RJ-45) to connect to your Ethernet
Network card or Ethernet Hub / Switch.
Reset To reset your ADSL Router to factory default settings. (All custom-
ised settings that you have saved will be lost!)
Please refer to the section below on how to use the
reset function.
USB USB Port (requires Drivers from accompanying CD).
Line Telephone jack (RJ-11) to connect to your
Telephone Wall Socket (ADSL line).
4 x RJ-45
Ports for 10/100
Ethernet LAN
Rear Panel of the NB5Plus4
Reset
factory
defaults
USB
Port
NB5Plus4W
antenna
RJ11 for ADSL
connection to
telephone line
Power jack
for AC power
adaptor
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
10 www.netcomm.com.au
4 x RJ-45
Ports for 10/100
Ethernet LAN
Rear Panel of the NB5Plus4W
Reset
factory
defaults
USB
Port
RJ11 for ADSL
connection to
telephone line
Page 11

Restoring Factory Defaults
This feature will reset the Modem to its factory default conguration. Occasions may
present themselves where you need to restore the factory defaults on your modem.
Typical situations are:
• You have lost your username and password and are unable to login to the mo-
dem.
• You have purchased the modem from someone else and need to recongure the
device to work with your ISP.
• You are asked to perform a factory reset by a member of the NetComm Support
staff.
In order to restore your modem to its factory default settings, please follow these
steps:
• Ensure that your Modem is powered on (for at least 10 seconds).
• Use a paper clip or a pencil tip to depress the reset button for ten seconds and
release. At this point, the reset is in progress. Do not power off the unit at this
point.
• When indicator lights return to steady green, reset is complete. The default set-
tings are now restored. The entire process takes about 45 seconds to complete.
• Once you have reset the modem to its default settings you will be able to access
the device's conguration web interface using http://192.168.1.1 with username
'admin' and password 'admin'.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 11
Page 12

Default Settings
LAN (Management)
Field Setting Details
Static IP Address: 192.168.1.1 *
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 *
Default Gateway: blank
WAN (Internet)
Field Setting Details
User Name: username@isp
Password: ****
Protocol: PPPoE
VPI: 8 *
VCI: 35 *
IP Address: 192.168.1.1 *
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 *
Default Gateway: 0.0.0.0 *
Modem Access
Field Setting Details
User Name: admin
Password: admin
* Default Setting. Although in most cases you will not be required to alter
these default settings for your NB5Plus4/W, your ISP may identify specic
settings to enable connection to their service. Please refer to your ISP or
Network Administrator for further information.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
12 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 13
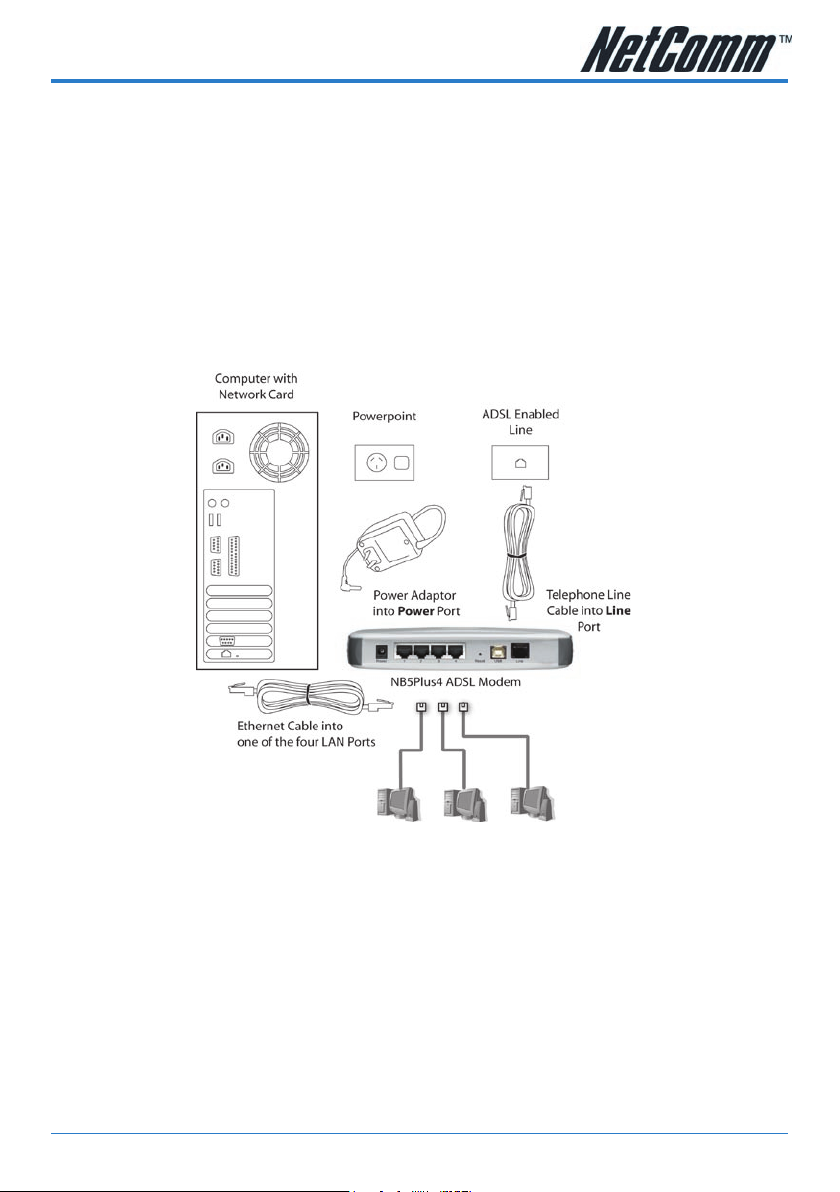
Connecting your NB5Plus4/W
The NB5Plus4/W can be connected via a USB cable or an Ethernet cable or both. The USB
connection is simply an ethernet simulation. As far as your computer is concerned the
USB connection is an Ethernet connection, hence DHCP and other protocols will work the
same as for Ethernet.
To connect to your ADSL Router, you need to have either an Ethernet Port or a USB
Port present on your Computer/Notebook.
Connecting your NB5Plus4/W ADSL Modem via ETHERNET
1. Connect your NB5Plus4/W to either a computer directly or a network hub or
switch using CAT5 ethernet cables.
2. Connect the power pack to the ADSL Modem and switch on the power switch.
3. Ensure that there is a LAN link light on the NB5Plus4/W.
4. Ensure that the computer you intend to use has an IP address in the same
subnet as the NB5Plus4/W ADSL Modem. (e.g. the NB5Plus4/W’s default IP is
192.168.1.1 - your computer should be on 192.168.1.100 or similar.) If you
have DHCP enabled on your computer, the NB5Plus4/W will assign your computer a suitable IP address.
5. Ensure that your computer has a LAN link light.
6. Connect one end of the ADSL phone line to the NB5Plus4/W ADSL Modem and
the other end to the wall socket.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 13
Page 14
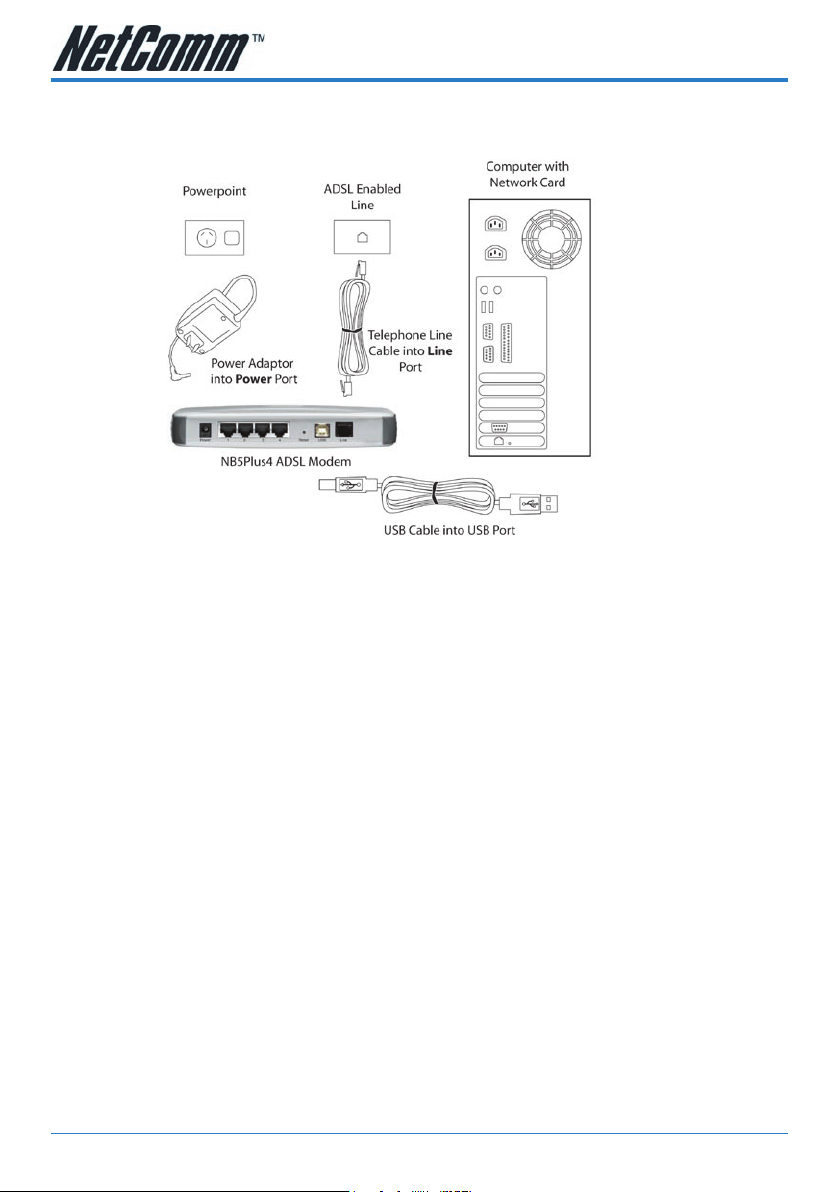
Connecting your NB5Plus4/W ADSL Modem via USB
1. Connect the power pack to the NB5Plus4/W ADSL Modem and switch on the
power switch.
2. Connect your NB5Plus4/W to a computer directly via USB cable.
3. When the computer is booted, the Add New Hardware Wizard will launch and
prompt you to provide a driver for your NB5Plus4/W ADSL Modem. Insert the
CD provided.
4. Follow the on-screen prompts to load the driver. Refer to the section below for
more detailed information. (You may need to restart your computer).
5. Connect one end of the ADSL phone line to the NB5Plus4/W ADSL Modem and
the other end to the wall socket.
Installing the USB driver (Windows 98/Me/2000/XP only)
When you install the USB driver on your computer it creates a Virtual Ethernet
Adapter, which can be congured in the same way as a Network Interface card with
DHCP or static IP address. To install the USB driver please follow the steps below:
1. Boot your machine into Windows 98/Me/2000/XP.
2. Insert your NetComm NB5Plus4/W CD into your CD-ROM drive.
3. Plug power up to your NB5Plus4/W and switch ON.
4. Plug a USB cable from the back of the unit into a spare USB socket on your computer.
5. The Windows “Add New Hardware Wizard” should appear. Click Next to continue.
6. Ensure the option “Search for the best driver….” is chosen and click Next.
7. Choose “Specify location”, untick any other boxes and click on the Browse button. Open the CD-ROM drive location of your NetComm NB5Plus4/W CD and
then select the ‘USBdriver’ folder. The USB driver will be installed.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
14 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 15

NB5Plus4W Antenna Instructions
Before continuing with the Hardware installation, you may need to connect the
Antenna
1. The antenna has a retaining nut which must be screwed into the SMA connector
on the back of the modem. Place the screw retaining nut over the antenna connection on the rear of the NB5Plus4W and turn it clockwise.
Note: Do not over-tighten the attaching nut - but do make sure that you have
screwed it all the way to its end.
Screw retaining
nut clockwise
over the antenna
connection
Bend antenna
to a 90o angle
2. Bend the antenna to a 90o angle.
Note: Please note that you may have to rotate the complete antenna assembly to
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 15
do this and have the antenna pointing vertically.
Page 16
Configuring your NB5Plus4/W
You will need to log directly into the conguration page of the modem and congure
the basic settings for your Internet connection. Your ISP should provide you with the
necessary information to complete this step.
The settings that you most likely need to change to access the Internet are grouped onto
a single EasyCong page.
To congure your modem follow the steps below:
Note: Ensure that your PC is setup as a DHCP client. Refer to the Computer
1. Insert the CD into your CD-ROM drive. An autorun screen will appear. Click on
(Alteratively, if the CD-ROM is ot available, you ca ope a web
2. The login page will be displayed. Enter the modem’s username and password.
The default username is admi.
Hardware Conguration section for instructions on how to set this up with
different Operating Systems.
Coure Modem.
browser ad type http://192.168.1.1 i the locatio bar to access the
modem’s EasyCo setup scree directly.)
The default password is admi.
Click on Log In.
3. The EasyCong page will be displayed.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
16 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 17
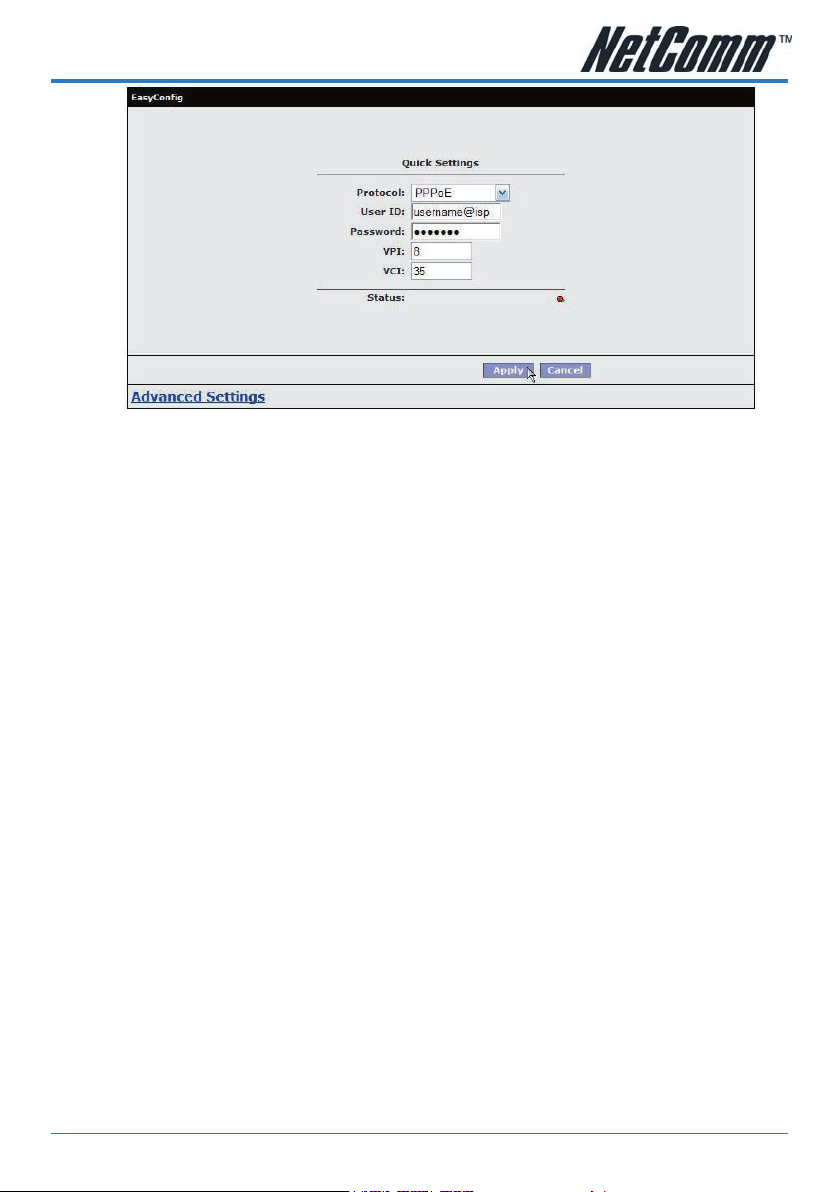
4. Check with your ISP what Protocol your modem needs to use to connect to the
Internet. If unsure, leave the default selection of PPPoE.
5. In the User ID eld, enter the Username that your ISP has provided. In the
password eld, enter the password that your ISP has given you.
Note: If your ISP has provided you with Static addressing details you will need
6. The default VPI / VCI settings for most connections is 8 / 35 in Australia. Do not
7. Click on the Apply button to save the settings you have entered. The modem will
8. If the settings you entered were correct and you have an ADSL connection es-
9. You should now be able to access the Internet with a web browser, email client
10. If the status light remains red after 45 seconds and you have refreshed your
TIP: To test your Internet connection while the modem is attempting to apply
to access the Advanced Settings of your modem to congure these. Please
refer to the section on Advanced Settings in this manual for instructions.
change these unless your ISP has instructed you to do so.
automatically reboot. Refresh the web page after 20 seconds.
tablished the Status light will change to green.
or other Internet application.
web page several times, check the following:
• ADSL Link light on your modem is solid green; If not, you do not have a
connection established with your local DSLAM. Please call your ISP who will
assist in resolving this.
• If you have a solid green light on your modem for the ADSL Link, check that
the username / password you entered are correct and try again;
• If the above two suggestions don’t resolve the issue, please contact your ISP;
the settings, you can open a DOS prompt (Start > Run > cmd) and execute
a continual ping command to a public server’s IP address on the Internet.
Once you receive a reply from the server you know that you are connected.
This can take up to 30 seconds. e.g: c:/ ping 210.0.111.111 -t
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 17
Page 18

Computer Hardware Configuration
This section provides instructions for conguring the TCP/IP (Network) settings on your
computer to work with your Modem. These steps are only required if you are having
trouble accessing your Modem.
Windows® XP PCs
1. In the Windows task bar, click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
2. Click on Network & Iteret Coectios icon. (Category mode only).
3. Click the Network Coectios icon.
4. In the LAN or High-Speed Internet window, right-click on the icon corresponding
to your network interface card (NIC) and select Properties. (Often, this icon is
labelled Local Area Coectio).
5. The Local Area Connection dialog box displays with a list of currently installed
network items. Ensure that the check box to the left of the item labelled In-
teret Protocol (TCP/IP) is checked. Select Iteret Protocol TCP/IP and
click on Properties.
6. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click the radio button
labelled Obtai a IP address automatically. Also click the radio button labelled Obtai DNS server address automatically.
7. Click OK twice to conrm your changes, and close the Control Panel.
Windows 2000 PCs
First, check for the IP protocol and, if necessary, install it:
1. In the Windows task bar, click the Start button, point to Settings, and then
click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network ad Dial-up Coectios icon.
3. In the Network ad Dial-up Coectios window, right-click the Local Area
Coectio icon, and then select Properties.
4. In the Local Area Coectio Properties dialog box, select Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP), and then click Properties
5. In the Iteret Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click the radio
button labelled Obtain an IP address automatically. Also click the radio button
labelled Obtain DNS server address automatically.
6. Click OK twice to conrm and save your changes, and then close the Control
Panel.
Windows Me PCs
1. In the Windows task bar, click the Start button, point to Settings, and then
click Control Panel.
2. Click on View All Cotrol Pael Optios.
3. Double-click the Network icon.
4. The Network Properties dialog box displays with a list of currently installed
network components. If the list includes Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then the
protocol has already been enabled. Skip to step 10.
5. If Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) does not display as an installed component, click
Add…
6. In the Select Network Compoet Type dialog box, select Protocol, and
then click Add…
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
18 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 19

7. Select Microsoft in the Maufacturers box.
8. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) in the Network Protocols list, and then click
OK. You may be prompted to install les from your Windows ME installation CD
or other media. Follow the instructions to install the les. If prompted, click OK
to restart your computer with the new settings.
Next, congure the PC to accept IP information assigned by the modem:
9. Follow steps 1 – 4 above..
10. In the Network Properties dialog box, select TCP/IP, and then click Properties.
If you have multiple TCP/IP listings, select the listing associated with your network card or adapter.
11. In the TCP/IP Settis dialog box, click the radio button labelled Obtai a
IP address automatically.
12. Click OK twice to conrm and save your changes, and then close the Control
Panel.
Windows 95, 98 PCs
First, check for the IP protocol and, if necessary, install it:
1. In the Windows task bar, click the Start button, point to Settings, and then
click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network icon.
3. The Network dialog box displays with a list of currently installed network
components. If the list includes TCP/IP, and then the protocol has already been
enabled. Skip to step 9.
4. If TCP/IP does not display as an installed component, click Add… The Select
Network Compoet Type dialog box displays.
5. Select Protocol, and then click Add… The Select Network Protocol dialog box
displays.
6. Click on Microsoft in the Maufacturers list box, and then click TCP/IP in the
Network Protocols list box.
7. Click OK to return to the Network dialog box, and then click OK again. You
may be prompted to install les from your Windows 95/98 installation CD. Follow
the instructions to install the les.
8. Click OK to restart the PC and complete the TCP/IP installation.
Next, congure the PCs to accept IP information assigned by the Modem:
9. Follow steps 1 – 3 above.
10. Select the network component labelled TCP/IP, and then click Properties. If
you have multiple TCP/IP listings, select the listing associated with your network
card or adapter.
11. In the TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click the IP Address tab.
12. Click the radio button labelled Obtai a IP address automatically.
13. Click OK twice to conrm and save your changes. You will be prompted to restart Windows.
14. Click Yes.
Note: For detailed information regarding the advanced features of this prod-
uct, please refer to the conguring sections in the NB5Plus4/W User
Guide on the supplied CD-ROM.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 19
Page 20
Advanced Settings
To access the Advanced Settings of your modem you click on the Advanced Settings
link on the EasyCong web page. To access this page, enter http://192.168.1.1 and
login with username ‘admin’ and password ‘admin’.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
20 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 21
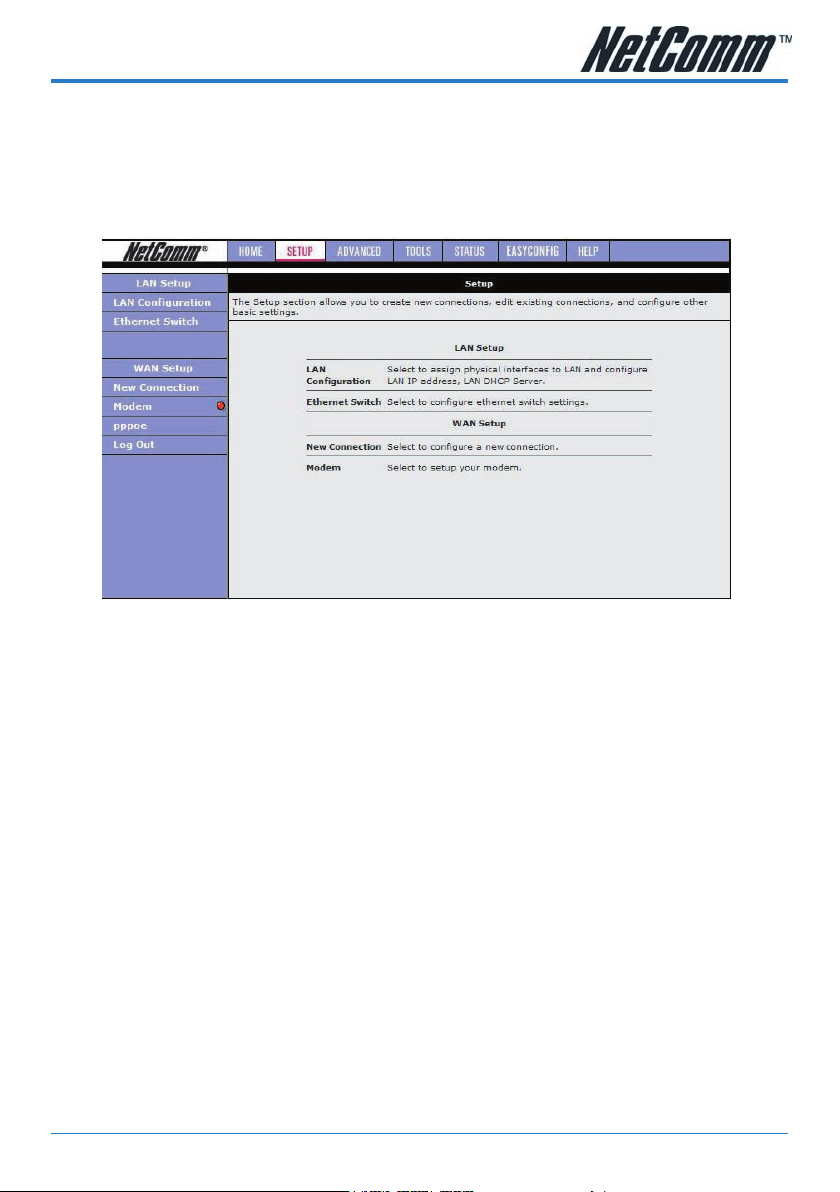
Setup
Click the Setup tab.
The Setup screen allows you to change current settings for your LAN (Local Area
Network), Ethernet Switch and WAN (Wide Area Network). You can also create new
connection proles.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 21
Page 22
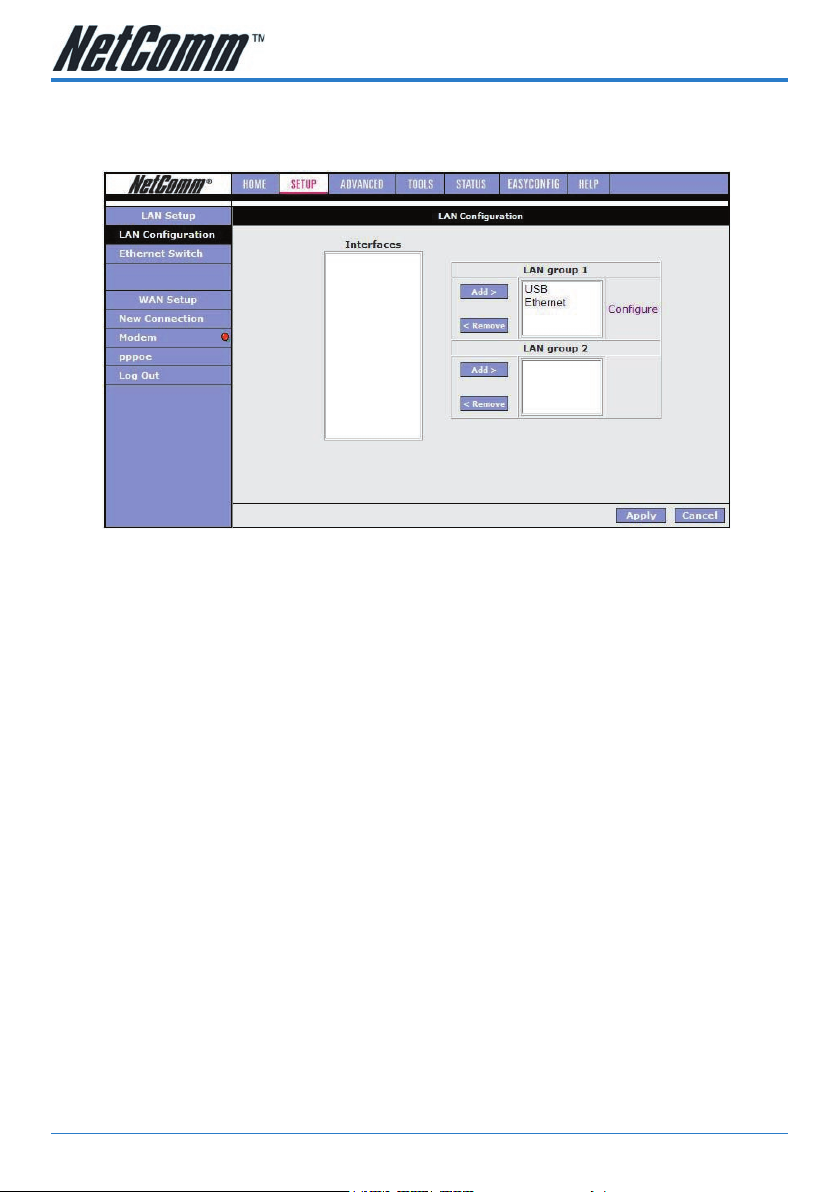
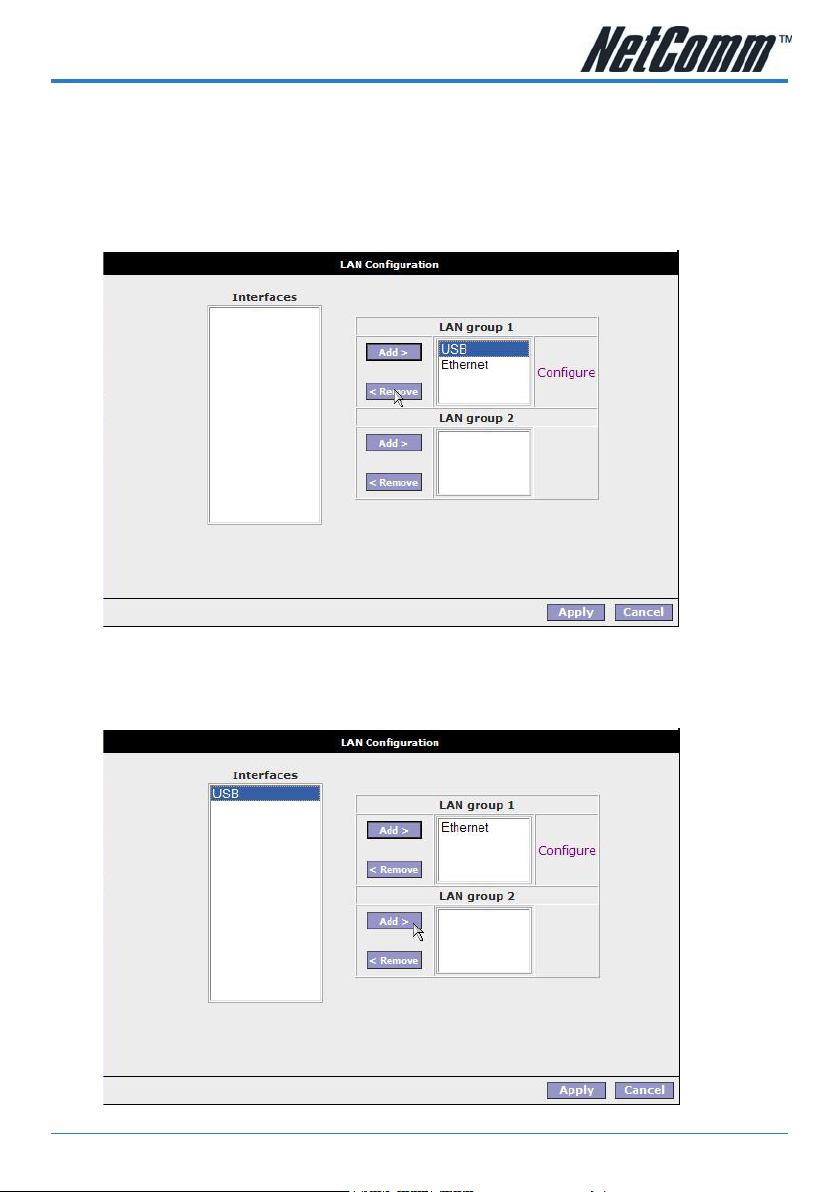
Setup>LAN Configuration
Click on the LAN Conguration link under the Setup menu to congure your Local
Area Network settings.
Interfaces
This section displays the available interfaces on your modem that have yet to be
congured. The default setting is to have all interfaces in LAN group 1.
It is possible to have separate LAN groups:
• three if you have the NB5Plus4W:
i) USB;
ii) Ethernet;
iii) WLAN (Wireless LAN);
• two if you have the NB5Plus4:
i) USB;
ii) Ethernet;
LAN Groups
Conguring LAN Groups with static IP addresses must be done in such a way that
the range of assignable IP addresses in each of the LAN groups should not overlap
with other LAN groups. A rule of thumb would be that each LAN group should be
on its own network or subnet. For example, say you have 3 LAN groups each being
setup with static IP addressing. Below is a sample conguration:
LanGroup #1
IP Address 192.168.1.1
NetMask 255.255.255.0
LanGroup #2
IP Address 192.168.2.1
NetMask 255.255.255.0
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
22 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 23
LanGroup #3
IP Address 192.168.3.1
NetMask 255.255.255.0
The above example shows that each LAN group is on its own network and that there
is no overlap in assignable IP address based on netmask.
To remove an interface from LAN group 1, click on the interface (e.g. USB) and click
the Remove button:
To add the available interface from the Interfaces section to a LAN group, highlight
the interface and click the Add button of the appropriate LAN group. To add the
available USB interface to LAN group 2 highlight the USB interface in the Interfaces
section and click the Add button for LAN group 2:
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 23
Page 24
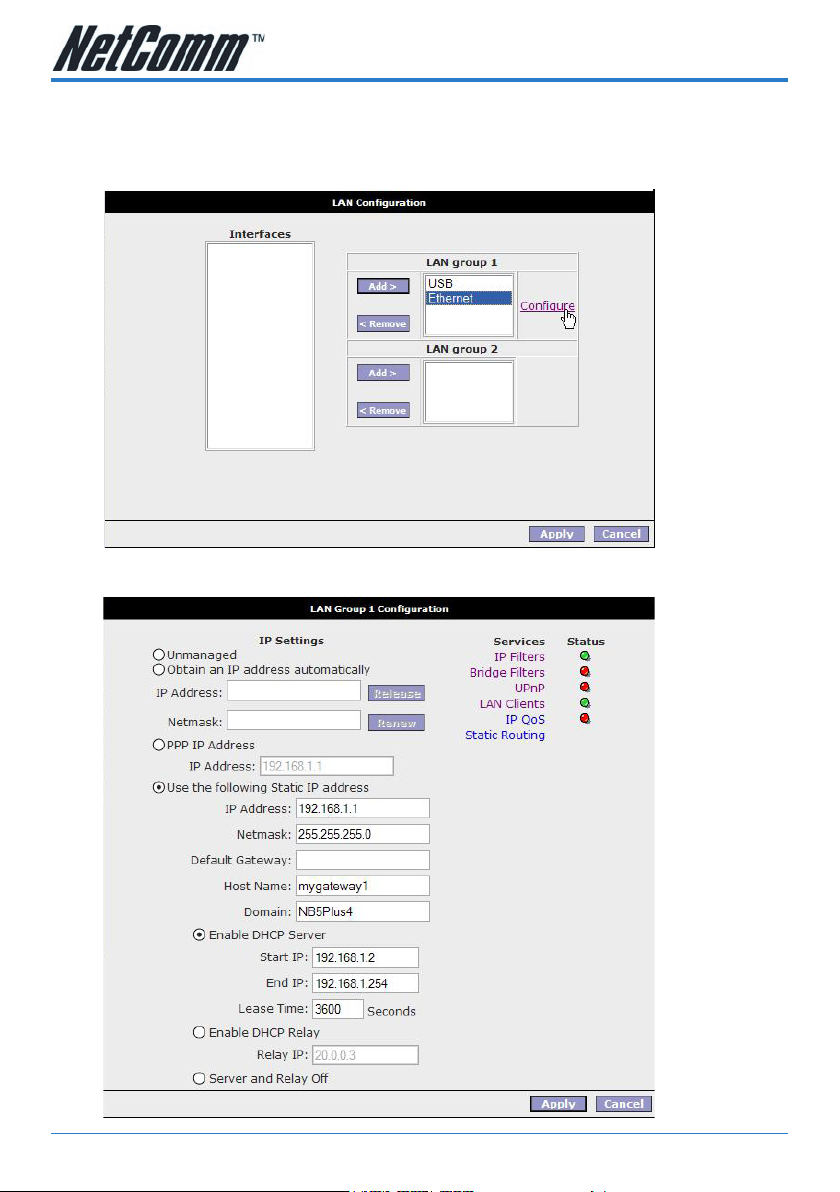
Configuring LAN Groups
To congure an interface of a LAN group click the interface and click the Congure
hyperlink. E.g. to congure the Ethernet interface for LAN group 1 click the Ethernet
interface and click the Congure hyperlink:
You will be presented with the following screen:
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
24 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 25

IP Settings
The IP address is usually 192.168.1.1 but you can change it to another suitable
number (e.g. 192.168.0.1 or 10.0.0.1 or 172.16.1.1) to suit any existing network
devices you already have installed. The NetMask describes how big your network is,
the default 255.255.255.0 will allow for 253 computers and generally does not need
to be changed unless to suit existing network requirements.
Note: If you change your IP address the DHCP server in your modem will auto-
Option Description
IP Address: Private IP address for connecting
Netmask: Netmask for the local private network
Default Gateway: This eld is optional. Enter in the IP ad-
Host Name: Required by some ISPs. If the ISP does
Domai Name: www.dyndns.org will provide you with
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Conguration Protocol. Your Modem has its DHCP
Server enabled by default. This means it will assign valid IP addresses to each
computer connected to it and will direct those computers to use the Modem as the
gateway to the Internet. Having the DHCP server enabled is the recommended
choice.
When selecting certain radio buttons you will notice that some of the options avail-
able for conguration will be greyed out. For example, when selecting ‘Unmanaged’
you will notice that all elds under IP Settings are greyed out. This means that no
settings are congurable if the interface is unmanaged.
Option Description
Umaaed Interface is ignored.
Obtai a IP Address automatically Interface will be allocated an IP address
IP Address The IP address assigned to the interface
Netmask: The subnet mask assigned to the inter-
Release butto It is possible to release the IP address
matically change the IP address range (DHCP pool) it hands out accordingly.
to a local private network (Default:
192.168.1.1).
(Default: 255.255.255.0).
dress of the router on your network.
not provide the Host name, please leave
it blank.
a Domain Name. Enter this name in the
“Domain Name” eld.
by a DHCP server.
by a DHCP server on your network.
face by a DHCP server on your network.
by clicking the Release button.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 25
Page 26
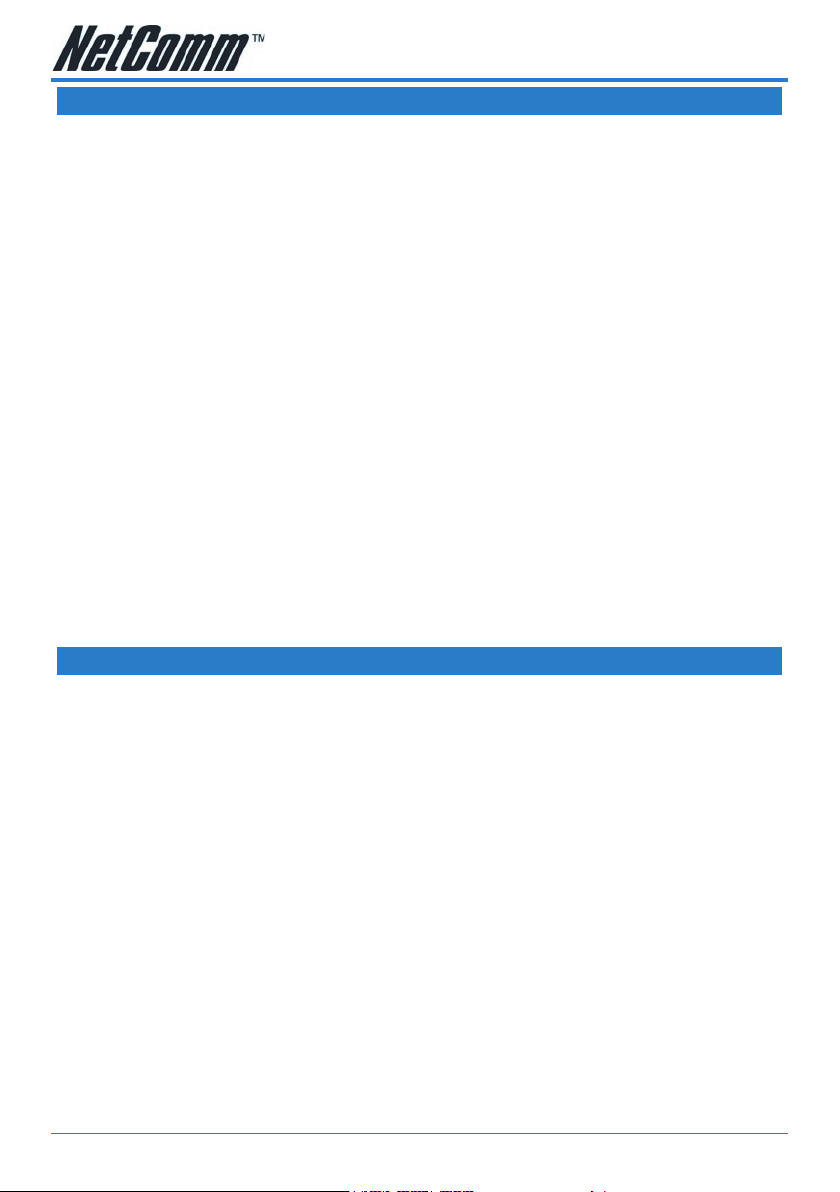
Option Description
Reew butto It is possible to renew the IP address by
PPP IP Address The IP address to be used during a PPP
Use the followi static IP address (Default) This is the IP address of your
Note: If Server and Relay are turned off you need to assign IP addresses within
the same range to the PCs connected to the modem else they will not
be able to communicate with the modem. For example, if your modem’s Ethernet interface address is 192.168.1.1 with a subnet mask of
255.255.255.0 you need to assign static addresses starting at 192.168.1.2
up to 192.168.1.253.
If you disable the DHCP server in the Modem you will need to either manually (statically) assign IP address information to each computer or use another device/computer as DHCP server.
Note: It is not recommended that you have more than one DHCP server enabled
on your network.
Option Description
Server O: Enables the DHCP server.
Start IP: Sets the start IP address of the IP ad-
Ed IP: Sets the end IP address of the IP ad-
Lease time: The lease time is the amount of time an
Eable DHCP Relay: Allow PCs on LAN to request IP address
clicking the Release button.
session. This defaults to the IP address
of the interface.
Modem on your local network. This IP
address is specied on all computers
on your network as the Gateway IP
address. The IP address is also the IP
address you type into your browser location bar to login to your modem’s web
interface.
dress pool.
dress pool.
IP address issued by the DHCP service
of your modem is valid before being
updated. If all elds are 0, the allocated
IP address will be effective forever.
from other DHCP server.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
26 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 27
Services
It is possible to set the services for an interface by clicking on the hyperlink which
will take you to the page to congure them. Please refer to the relevant section in
this manual for information on the settings for these services.
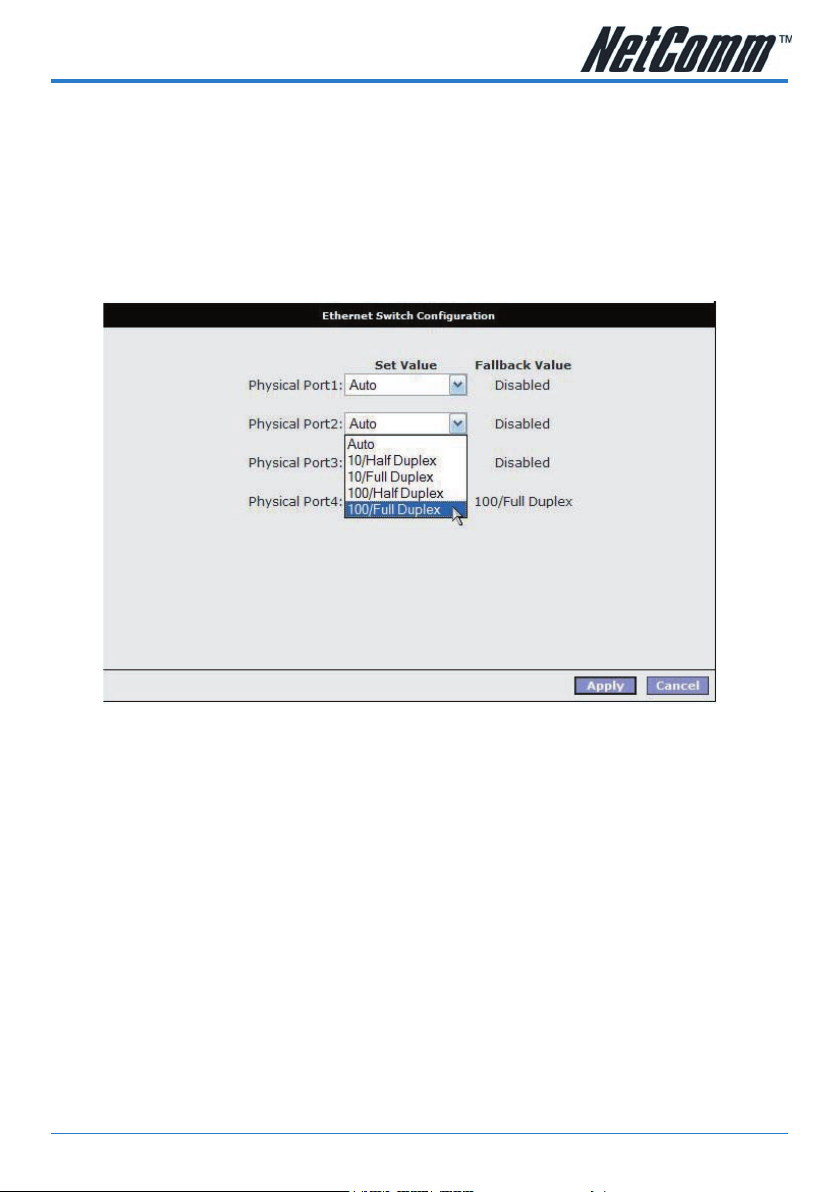
Ethernet Switch
The 4-port Ethernet switch of your modem is set to automatically adapt to the type
of connection plugged into a specic port. To force a port to connect at a specic
speed, select the setting from the dropdown menu of a port.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 27
Page 28
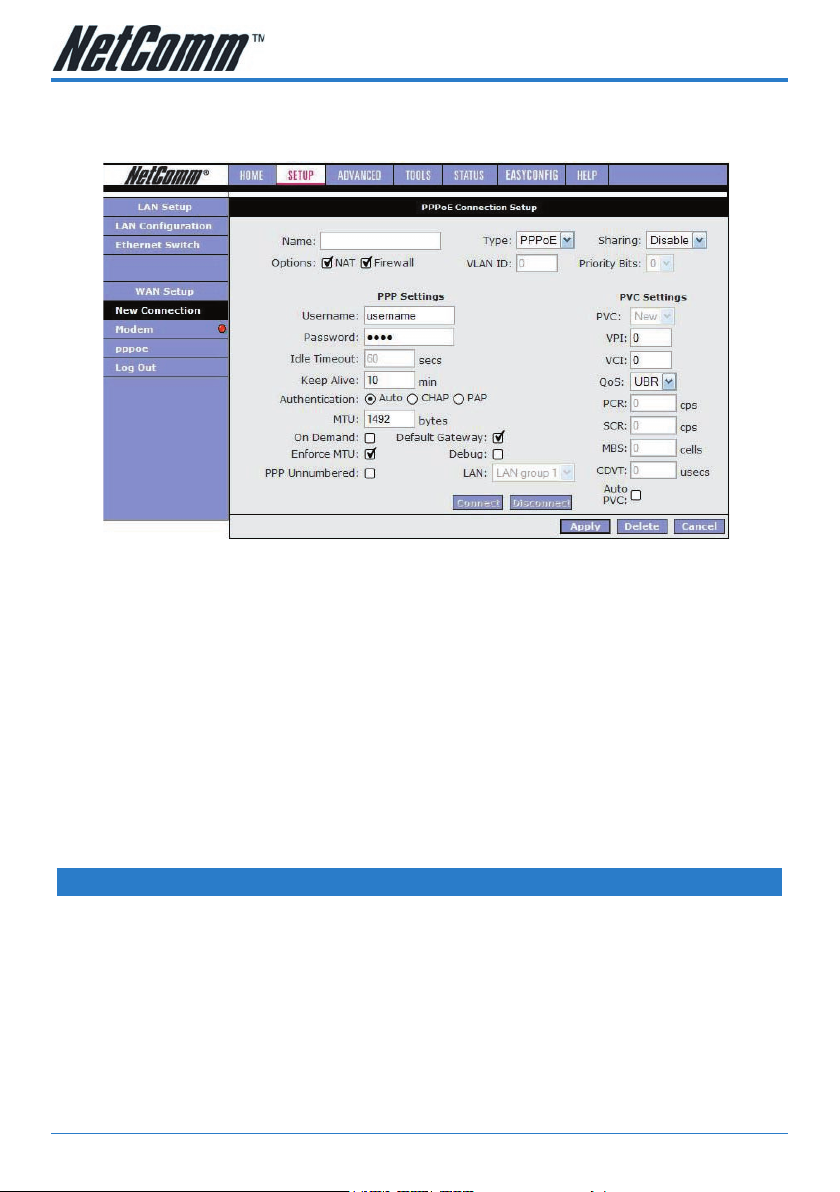
WAN Setup>New Connection
If you click ‘New Connection’ you will see the screen shown below.
The Connection setup page requires you to choose the correct settings to work with
your ADSL connection as specied by your ISP. The screen will add or remove non-
applicable choices as you change options. There are a few main settings you will
need to conrm with your ISP before you can complete this page, these are;
• Type of Connection (e.g. PPPoE, PPPoA, Static, DHCP, Bridge, CLIP)
• Username & Password (usually only required for PPPoE or PPPoA types)
• VPI & VCI (usually VPI=8 and VPI =35)
• Authentication (Usually AUTO will work otherwise check with your ISP)
Most other choices on this screen are personal preference and not critical to getting
your connection working.
Note: The Username & Password you need to type in here is for your ISP’s ac-
PPPoE Connection Setup Fields
Option Description
Name You need to provide for a connection
Type Select the type of connection for this
Sharing Decide whether you want to share this
count and it will be supplied to you by your ISP.
(e.g. MyISP)
prole.
connection. You can share a connection
using a VLAN (Virtual LAN) or by a PVC
(Private Virtual Circuit).
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
28 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 29

Option Description
Optios: NAT / Firewall NAT (Network Address Translation al-
lows you to share the public IP address assigned to the WAN (Wide Area
Network) interface of your modem with
multiple clients on your LAN (Local
Area Network). NAT also acts as a basic
rewall. The rewall feature protects the
PCs on your LAN from malicious attacks
from people on the Internet (e.g. DOS
attacks).
VLAN ID If you decide to share this connection
with a VLAN, this eld will be enabled
and you need to select your VLAN ID.
For example, if you have your Ethernet
interface in LAN Group 1 and your USB
interface in LAN Group 2 you can create
a VLAN for both groups to access each
1
other.
Priority Bits Set the priority bit of the Ethernet frame
if using a VLAN.
1
For more information on VLANs visit http://www.javvin.com/protocol/VLAN.html.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 29
Page 30
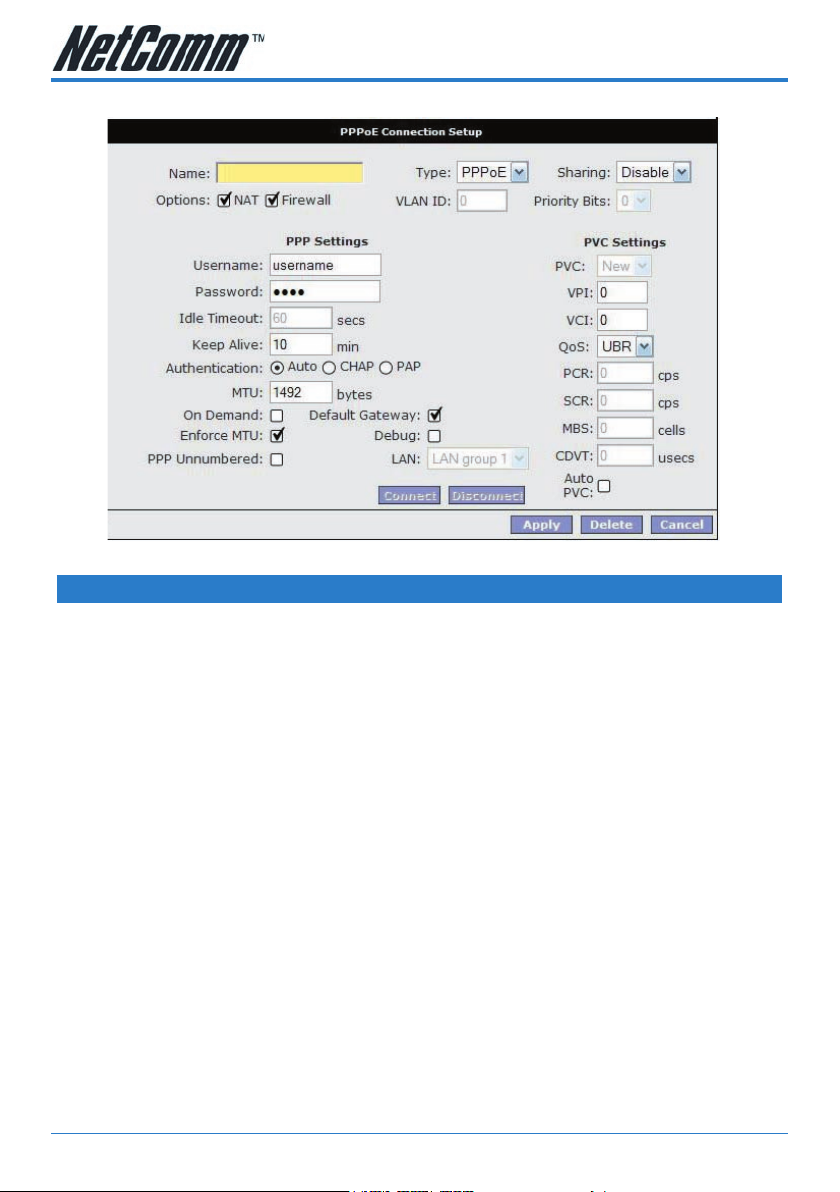
PPPoE Connection Setup
PPP Settings
Option Description
Userame: Enter the username provided by your
Password: Enter the password provided by your
Idle Timeout: Idle timeout means the router will
Keep Alive: If mode is LCP, This is the Keep Alive
Autheticatio: Default is Auto. However, if your ISP
MTU Maximum Transmission Unit indicates
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
30 www.netcomm.com.au
ISP.
ISP.
disconnect after being idle for a preset
amount of time. The default is 60 seconds. If you set the time to 0, the ADSL
connection will remain always connected
to the ISP.
timer. If a reply to the LCP echo is not
received in this amount if time, the connection is dropped. The Default is 10.
asks you to specify the authentication
type, you can select it here (CHAP or
PAP).
the largest packet size in bytes that the
modem transmits. Any packets larger
than the MTU setting are fragmented
into smaller packets before being transmitted.
Page 31

Option Description
O Demad: If enabled the Idle Timeout eld can be
Default Gateway: Species that this connection will be the
Eforce MTU: Species that the MTU setting will be
Debu: Enable to turn on the debugging mode
PPP Uumbered: An unnumbered interface does not have
modied. On Demand species that the
modem will connect to the Internet on
demand.
default gateway for other LAN groups to
access the Internet.
enforced.
of your modem. Your ISP may ask you
to do this should you be experiencing
problems connecting to the Internet.
an IP address assigned to it. An unnumbered interface is often used in point-topoint connections where an IP address
is not required. You’ll notice that once
PPP Unnumbered is enabled you need
to choose the LAN group to which this
applies.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 31
Page 32

PVC (Private Virtual Circuit) Settings
Option Description
VPI: (Virtual Path Identier) If instructed
VCI: (Virtual Channel Identier) If instructed
Your modem can support up to 8 PVCs.
QoS: Default is UBR (Unspecied Bit Rate).
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the
MBS: Maximum Burst Rate. Represents the
CDVT: Cell Delay Variation Tolerance. If your
Auto PVC: If enabled your modem will automatical-
Coect /
Discoect Buttos: Click Connect button to attempt to con-
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
to change this, type in the VPI value
for the initial connection (using PVC 0).
Default = 0.
to change this, type in the VCI value
for the initial connection (using PVC 0).
Default = 0.
For example, you could have one PVC
(8/35) for your Internet trafc, and
another PVC (9/35) for your VoIP trafc.
Contact your ISP for further details.
Change this setting if your ISP instructs
you to do so. The other settings are CBR
(Constant Bit Rate) and VBR (Variable
Bit Rate).
(the size of an ATM cell) to nd the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum
rate at which the sender can send cells.
average cell rate (long-term) that can
be transmitted.
maximum number of cells accepted
over a period of time. When the cell rate
exceeds the MBS cells can be dropped.
PVC is a CBR service you need to set
the PCR and CDVT parameters. Ask your
ISP what the best settings are for these
on their network.
ly detect your PVC (VPI/VCI) settings.
nect using the settings you have speci-
ed. Click Disconnect button to disconnect the current prole.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
32 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 33

PPPoA Connection Setup
When specifying your connection Type to be PPPoA you are able to change the En-
capsulation to either LLC (Logical Link Control) or VC (Virtual Circuit) encapsulation.
The default is LLC so do not change this setting unless your ISP instructs you to do
so.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 33
Page 34

Static Connection Setup
Option Description
Ecapsulatio: Select the method of encapsulation used
IP Address: If your ISP has issued you with a static
Mask: The subnet mask specied by your ISP.
Default Gateway: The default gateway specied by your
DNS: You have the choice to specify up to
Mode: Bridged and Routed
by your ISP. The default is LLC, so only
change this to VC if your ISP asks you
to.
public IP address, you need to specify it
here. (e.g. 210.1.123.123).
ISP.
three DNS (Domain Name Service)
servers. The function of a DNS server
is to map URL names (e.g. www.
google.com.au) to their IP addresses
(e.g.66.102.7.147). If DNS 1 is down,
your modem will use DNS 2.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
34 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 35

DHCP Connection Setup
Option Description
Ecapsulatio: Select the method of encapsulation
IP Address: The IP address assigned by an external
Mask: The subnet mask assigned by an exter-
Gateway: The gateway assigned by your DHCP
Default Gateway: Enable this if you want to use this pro-
used by your ISP from the drop-down
list box. Choices vary depending on the
mode you select in the Mode eld.
DHCP server.
nal DHCP server.
server.
le connection as the default gateway
for clients to connect to the Internet.
Bridge Settings
Ecapsulatio: Select the method of encapsulation
Select LAN: Select the LAN group to which you want
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 35
used by your ISP from the drop-down
list box. Choices vary depending on the
mode you select in the Mode eld.
to bridge this connection to. Having a
Bridged Connection places the modem
into a ‘dumb’ mode. The modem connects to the ISP, but does not perform
authentication, routing or rewalling
functions. You will need to have an additional router plugged into a LAN port of
your modem to perform these functions.
Page 36

CLIP Connection Setup
Option Description
IP Address: The public IP address assigned by your
Mask: The subnet mask issued by your ISP for
ARP Server: The ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
Default Gateway: Specify the default gateway used by
ISP for the Classical IP over ATM connection.
the CLIP connection.
server used by your modem.
your modem (issued by your ISP).
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
36 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 37

WAN Setup>Modem
Here you can choose one of four ADSL handshake types, typically MMode (Multimode) will work on Australian ADSL lines. You should not need to change this setting unless advised by your ISP.
Option Description
T1413: Full-Rate (ANSI T1.413 Issue 2) with
GDMT: Full-Rate (G.dmt, G992.1) with line rate
GLITE: G.lite (G.992.2) with line rate support
MMODE: Support Multi-Mode standard (ANSI
Click Apply to save the changes.
line rate support of up to 8 Mbps downstream and 832 Kbps upstream.
support of up to 8 Mbps downstream
and 832 Kbps upstream.
of up to 1.5 Mbps downstream and 512
Kbps upstream.
T1.413 Issue 2; G.dmt(G.992.1);
G.lite(G.992.2)).
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 37
Page 38

Logout
Click Log Out to logout of the modem’s conguration interface.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
38 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 39

Advanced
The Advanced menu allows you to congure a number of features of your modem.
This section deals with these features.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 39
Page 40

Advanced>UPnP
Your modem is Universal Plug ‘n Play Capable, for security this feature is disabled by
default. UPnP is a method of allowing devices and computer software on your Net-
work to be able to congure ‘unblocked’ ports through your modem (and through
your modem’s rewall). This makes it easier to run Network games and Programs
like Microsoft Messenger etc.
To Enable UPnP click the Enable UPnP box and choose the WAN connection (usually
‘PPPoE’). Select the LAN Connection (e.g. LAN Group 1) to which UPnP is to be applied to.
Option Description
Eable UPNP: Enable the UPnP.
Click Apply to save the changes.
2
For more information on Universal Plug and Play, see http://www.microsoft.com/
technet/prodtechnol/winxppro/evaluate/upnpxp.mspx.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
40 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 41

Advanced>SNTP
SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) allows your modem to update its time automatically using an SNTP server. To enable this feature, click the Enable SNTP tick
box.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 41
Page 42

Option Description
Primary, Secodary,
Tertiary SNTP Servers This allows you to enter three different
Timeout: The number of seconds your modem will
Polli Iterval: The interval that your modem will up-
Retry Cout: The number of attempts at connecting
Time Zoe: Select the time zone you are in.
Day Liht: Enable this to enable daylight savings
Click Apply to save the settings.
To check that your NB5Plus4/W modem is talking to an NTP server, follow these
instructions for Windows Operating Systems:
1. Open a Command Prompt (Start > Run > cmd).
2. Type telnet 192.168.1.1 (or the IP address of your modem) and enter.
3. Type your login and password.
Login: admin
Password: admin
4. date [ENTER key]
5. Note that the date is set correctly.
SNTP server addresses. If one of these
servers is unavailable your modem
will use an alternative. An example
of an NTP server on the Internet is
128.250.36.3.
attempt to connect to an SNTP server
before trying an alternative server
should the server you are trying to connect to be unavailable.
date its time with an SNTP server.
to an SNTP server.
for the time on your modem.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
42 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 43

Advanced>IPQoS
IP QoS (Quality of Service) allows you to set priorities for trafc travelling through
your modem. For example, you may want to prioritize your UDP trafc over your
TCP trafc. Typical UDP trafc would be your VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol)
trafc. This section describes how to make use of your modem’s IPQoS feature.
The NB5Plus4/W should have two primary sections for setting up IP QoS services:
1. A QoS setup page to congure the upstream/downstream connection queue
priorities, and
2. A Rules conguration page.
QoS Setup Page
The QoS setup page will have 2 primary elds:
1. Connection name selection,
2. A table to select queue weights for the system transmit queues.
IP QoS trafc shaping is associated with any transmitted trafc from the perspective
of the NB5Plus4/W. Each interface has 3 priority queues associated with transmit
data. The web UI will allow the user to choose any interface connection and select
the priority weights associated with that connection. For Example; the user could
have a connection named WAN1 or a connection named LAN1. If the user selects
WAN1 the transmit queues will be associated with that connection, and likewise
with LAN1 (Refer to the following diagrams). All interfaces on the LAN are currently
bridged and therefore the only connection name is that name associated with the
LAN.
Transmit queues associated with WAN connection
Transmit queues associated with LAN connection
The high priority queue has strict priority over the medium and low priority queue,
and therefore can exhaust all available bandwidth. The web UI will allow the user to
select the weights of the medium and low priority queues in increments of 10 percent so that the sum of the weights of the 2 queues is equal to 100 percent. These
queues will be serviced on a Round Robin priority basis according to the weights
assigned, after the high priority queue has been completely serviced.
Rules Configuration Page
The Rules conguration page will allow the user to dene IP matching elds to associate with the priority queues associated with the named connections selected above
in the “QoS Setup Page” section.
There will be three primary elds for the user to select: 1.) A Trusted mode check
box. 2.) A trafc priority choice (High, Medium, Low), and 3.) An IP rules matching
selection area.
The NB5Plus4/W has two primary modes of operation with regard to queue trafc
prioritization; Trusted, and Un-trusted. The Web UI will provide one check box to
enable trusted mode. In trusted mode all rules will be applied rst regardless of the
setting of the TOS bits. After the rules have been exhausted the existing TOS bit
settings will be honoured. If the “Trusted mode” box is unchecked this will indicate
the “Un-trusted mode.” “Un-trusted” mode will match rst against all rules as in
“Trusted” mode. The difference is that if there is no match then a default rule will be
used. The default rule will have an associated queuing priority.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 43
Page 44

Rule denitions will be dened by the user by allowing the user to select matching
based on Source IP, Destination IP, IP Protocol, Source Port, Destination Port, and
Incoming Mac Port (switched LAN Port). These selections will dene a rule and be
associated with a particular queue priority: High, Medium, and Low.
Traffic Queuing Configuration
Based on the TOS (DSCP) marking, the NB5Plus4/W shall prioritize the trafc servicing on the outgoing interface (facing the Access Network) using a 3-band priority
mechanism as described below.
Queue Priorities:
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
44 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 45

One Expedited Forwarding (EF) Queue: High Priority queue with non-preemptible
service. The EF queue is always scheduled rst prior to the medium and low priority
queues and runs to completion
Two Queues (Medium and Low Priority) with Weighted Round Robin service. Based
on the associated weights, packets on these queues share the remaining link
bandwidth (after the EF service). The low priority queue corresponds to Best Effort
service. Looking forward, the medium priority queue will play the role of Assured
Forwarding Queue.
Configuration:
a.) The Medium, and Low Priority Queue weights will be selectable via the Web UI.
User weights for these two queues are entered as a percentage in increments of
10%. The sum of the 2 weights must be equal to 100 percent.
En-queuing Policy
Inter-queue isolation to make greed work on the Residential Gateway: the transmit
interface buffer (a common pool for all queues) can be monopolized by a greedy
ow on the low priority queue thus preventing en-queuing high priority trafc. To
prevent such conditions the en-queuing process is using a simple congurable allocation of per-queue lengths, adding up to the total queue length.
Configuration:
The Expedited Forwarding queue (fast service queue) length will be congurable via
the cong.xml le. This parameter will not be congurable via the Web UI. Please
call NetComm Support and request to speak with an engineer should you require
this XML le to edit.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 45
Page 46

The Medium and Low priority queue lengths will be proportionally calculated via the
queue weights selected in 1.) Queue Priorities above.
Total queue length for all three queues will sum to the transmit queue length set in
the system.
Packets overowing their queues will be tail-dropped, penalizing stochastically the
greediest ow within each queue.
Future implementations may introduce a “buffer stealing” policy. This policy will re-
move the xed buffer limits and allow a particular queue buffer to decrease to some
predened minimum limit.
De-queuing Policy
Expedited Forwarding Queue (High Priority) is always serviced rst at each packet
scheduling cycle and serviced to extinction. Therefore, the EF queue is non-preemtible by the Medium and Low priority queues.
WRR Queue Scheduler for Medium and Low priority queues
The L and M weights will be congured from the Web UI as stated above in 1.)
Queue Priorities.
A service scheduling array will be pre-computed for the Medium and Low priority
queues based on the user congurable weights assigned to these queues. Each array slot corresponds to a scheduling cycle. The pre-computed algorithm will allo-
cate scheduling slots for each queue based on the Medium and Low priority queue
weights and uniformly interleave them through the scheduling array. This array will
provide an O(1) scheduler with a minimum possible average latency for each of the
two queues.
Configuration:
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
46 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 47

The weighted values used for the WRR scheduler will be calculated based on the
percentage weights the user inputs in the Web UI as stated above in 1.) Queue
Priorities.
Example: User selects a Medium Queue Weight = 60 %, and Low Queue Weight =
40%. Then the O(1) scheduling array will look like {L, M, M, L, M, M, L, M, M, L}
where L and M represents a scheduling cycle for the respective Low and Medium
queues.
Low Latency Queue (Fragmentation and Interleaving) for Voice Traffic
With Voice trafc shared over same PVC with Data trafc, the simple packet classication and prioritization will not sufce to achieve the low latency required by voice.
In this case, a voice call triggers dynamic ushing of existing data packets from
device queues (including DSL device driver) for Head of Line Blocking removal, and
IP MTU resizing based on uplink bandwidth for fragmentation and packet interleaving of voice and data. Below is an example of MTU calculations:
Total delay PSTN delay Maximum Data Fragment size
end-to-end budget based on upstream bandwidth (bytes)
VIF (ms) (ms) 100kbps 150kbps 200kbps 250kbps
10ms 200 100 207 363 519 675
20ms 200 100 82 175 269 363
30ms 200 100 x x 19 50
For Voice trafc priority an extra EF queue was added to PRIOWRR. This extra
queue should not be exposed via WebUI cong for data usage. Its use is triggered
internally by the voice app using the socket options system calls. Voice packets are
using this EF queue. Signalling for Voice uses the next EF queue that’s also exposed
on the web cong. This means that voice signalling can be mixed with data if user
congures data for High Priority.
TOS-to-Priority Mapping
High Priority Marking for Expedited Forwarding Queue: DSCP Mark: xx1000
Medium Priority Marking: DSCP Mark: xx0100
Low Priority Marking for Best Effort: DSCP Mark: xx0000
The four TOS bits (the ‘TOS eld’) are dened as:
Binary Meaning
1000 Minimize delay (md)
0100 Maximize throughput (mt)
0010 Maximize reliability (mr)
0001 Minimize monetary cost (mmc)
0000 Normal Service
TOS Bits Means Linux Priority Queue Priority Band
0x0 0 Normal Service 0 Best Effort 2
0x2 1 Minimize Monetary Cost 1 Filler 2
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 47
Page 48

0x4 2 Maximize Reliability 0 Best Effort 2
0x6 3 mmc+mr 0 Best Effort 2
0x8 4 Maximize Throughput 2 Bulk 1
0xa 5 mmc+mt 2 Bulk 1
0xc 6 mr+mt 2 Bulk 1
0xe 7 mmc+mr+mt 2 Bulk 1
0x10 8 Minimize Delay 6 Interactive 0
0x12 9 mmc+md 6 Interactive 0
0x14 10 mr+md 6 Interactive 0
0x16 11 mmc+mr+md 6 Interactive 0
0x18 12 mt+md 4 Int. Bulk 1
0x1a 13 mmc+mt+md 4 Int. Bulk 1
0x1c 14 mr+mt+md 4 Int. Bulk 1
0x1e 15 mmc+mr+mt+md 4 Int. Bulk 1
The Default queue priority for non-mapped TOS values is Best Effort.
Advanced>LAN Clients
LAN Client names are a way of applying specic Port-forwarding and Access Control rules to individual computers on the LAN. If DHCP is used, all DHCP clients are
automatically assigned and are designated as a LAN client.
To add a LAN client, click Advanced>LAN Clients.
Option Description
Select LAN Group: Select the LAN group you would like to
Eter IP Address: Enter the IP address of the LAN client to
Hostame: Enter the Hostname.
MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the new cli-
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
add a LAN client to.
be added.
ent. To nd out the MAC address of the
client, open a command prompt and
execute an ipcong/all command (Windows 2000/XP). Note, it is optional to
add the MAC address of the device. The
format to add the MAC address is xx:xx:
xx:xx:xx:xx.
Advanced > LAN Isolation
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
48 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 49

You are able to restrict communication between clients in different LAN groups. If
you have the NB5Plus4 you can restrict trafc between two LAN groups. If you have
the NB5Plus4W you can restrict trafc between three LAN groups (Ethernet, USB,
Wireless).
Advanced > Bridge Filters
Bridge ltering enables rules to be dened which allow or deny data to pass through
the Router based on the source and destination Bridge address and data type of
each data frame.
To access Bridge Filters Control, click on Advanced>Bridge Filters.
Usage examples of Bridge Filter Rules are: to specify which computers on a network
are allowed Internet access; or to determine which particular computers are allowed
to access services provided by the Router (the last point is particularly relevant for
routers serving Wireless Networks as it can be used to prevent unauthorised people
from attaching themselves to a wireless LAN).
Enable/Disable Bridge Filtering
To enable Bridge ltering, navigate to the Bridge Filter Control Screen and select the
Enable Bridge Filters check box.
If the check box is selected, Bridge ltering is enabled according to the list of Bridge
Filter Rules that has been created.
If the box is de-selected, Bridge Filtering will not be enabled, even if Bridge Filter
Rules have been created.
Create Bridge Filter Rules
Enter the Source Bridge and Destination Bridge details. Entering zeros or blanks
into the Source or Destination elds enters a null value.
‘Protocol’ provides the choice of protocol type for the rule.
‘Mode’ provides the choice of Allow or Deny for the rule.
When all selections are made, click on Add to add the rule to the list of rules. A
maximum of 20 Bridge Filter Rules can be dened and saved.
To save changes, click on Apply.
Edit or Delete Bridge Filter Rules
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 49
Page 50

Option Description
WAN Coectio: Refers to the active Connection Prole.
Allow Icomi Pi: Enabling this feature allows users on
the WAN side of your modem to receive
replies to an ICMP ping command. Useful for testing remote connection to your
modem.
Select LAN Group: Select the LAN group for which you are
LAN IP: Select the device (PC) to which you will
New IP: If you wish to manually add a LAN client
setting up the port forwarding rules for.
be port forwarding data to. The default
will be the LAN device currently logged
in to the modem’s web interface. For
example, if you had a web server with
IP address 192.168.1.100, you would
select this from the drop-down list.
so that you can apply rules to it, click
on the New IP Button and enter Host
Name, MAC Address and IP Address.
Note: The MAC address needs to be
entered in the format xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:
xx. You do not need to enter a MAC address.
DMZ Settings
A DMZ (demilitarized zone) is a computer host or small network inserted as ‘neutral
territory’ between a private LAN and the Internet. It prevents outside users from
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
50 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 51

getting direct access to LAN computers while still being able to access services
hosted on the designated DMZ Computer.
When using NAPT to share your internet connection, LAN computers will still be able
to access the Internet when the DMZ host is enabled. Any direct communication
to the WAN port of your Modem that is not a reply to the original NAPT request is
forwarded to the DMZ host.
Option Description
Select your WAN
Coectio: Select the connection to which your
Select LAN roup: Select the LAN group in which you want
Select a LAN IP
Address: Select the LAN IP address of the DMZ
LAN Cliets: Click the LAN clients hyperlink to manu-
Click the Apply button to save the settings.To remove a rule from the Applied Rules
box, select the Rule and click on the Remove Button.
To save changes, click on Apply.
DMZ client is connected to.
to place the DMZ client.
client.
ally add a LAN client.
Advanced Port Forwarding: Creating Custom Rules
Click the Custom Port Forwarding link to setup a custom rule.
If there is no pre-dened Port Forwarding Rule for a particular application, a User
Rule can be created which denes the required Port(s), Protocol(s) and Internal Port
forwarding rules.
To create a custom rule you will need to know the specic port number(s) and port
type [UDP or TCP] that the application requires. These will be the outside port num-
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 51
Page 52

bers. Some applications specify a range of ports in which case you will need to know
both the starting and ending port numbers in the range, which are mapped by the
start port and end port elds.
The Destination Port Map eld species the internal port that the data will be
directed to on the LAN Client. When dealing with port ranges, the Internal Port (des-
ignated by the Port Map eld) will be the same as the rst port in the range. When
you simply want to forward a single port from outside (i.e. WAN side) to inside (i.e.
LAN side), then all three elds (Port Start, Port End and Port Map) will have the
same port number.
Option Description
Coectio: Choose the connection to which the rule
Applicatio: Provide a name for the application (e.g.
Protocol: Can be either TCP or UDP, or both.
Option Description
Source IP Address: The client on the Internet sending the
Source Netmask: The subnet mask of the client connect-
Destiatio IP Address: The LAN IP address of the device on
Destiatio Netmask: The subnet mask of the LAN device.
is to be applied to.
Azureus). The name must be unique,
must not contain spaces and cannot
begin with a number.
data (e.g. 202.44.55.66). Note, if you
do not know the IP address of the client
use 0.0.0.0 for any client on the Internet.
ing to you. Note, if you do not know the
Netmask use 0.0.0.0.
your network to which packets of data
will be forwarded to (e.g. 192.168.1.2).
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
52 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 53

Destination Port Start
& Destiatio Port Ed. The ports on the remote client from
Destiatio Port Map: This is the port number that the data
TIP: It is possible to map outside port numbers, or ranges [i.e. port start…port
end] to a different inside port numbers [port map] for reasons of security
or convenience.
Click ‘Apply’.
The Port Rule settings dened by this process will then be displayed in a table at the
bottom of the Rule Management panel.
If you wish to add more ports to this rule, leave the text name in the Rule Name
eld and enter the new port settings. Click ‘Apply’ and the new settings will be
added to the list.
which data is being sent to your modem’s corresponding ports. These will
be the same if you are forwarding only
a single port. If there is a range, then
port start is the rst number in the
range, and port end will be the last
number.
should be forwarded to on the speci-
ed LAN IP (i.e. the inside port). This
is usually the same as the port start
gure.
Adding Custom Rules to Applied Rules List
When you have assigned all necessary ports to the Rule and they appear in the
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 53
Page 54

table, click on the Port Forwarding menu item to return to the main Port Forwarding
screen.
User-created rules will be shown in the Available Rules list when the User Category
radio button is selected. You can now apply the rule(s) by selecting it and clicking
Add. This will add the rule to list of applied rules.
Advanced > IP Filters
The IP lters page allows you to specify Normal Port Forwards, Block ALL trafc
to specic LAN Clients or specify Custom IP lters that will control the ow of data
across the router.
Custom IP Filters (often also referred to as ‘Access Control Lists’ ) allow you to
specify individual rules that will deny trafc by dening the following:
• Source IP address or IP Subnet
• Destination IP address or Subnet
• Port or Port range
• Protocol
Custom IP lters are different from Port forwards, or Block All trafc because they
allow greater scopes of IP addresses to be included in the block.
Note: You must have at least one LAN Client in your LAN clients table before IP
lters can be created. To create a LAN Client, see the section below on LAN
Clients under the Advanced Menu.
Advanced > Access Control
Use Access Control to congure advanced security functions by customising the
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
54 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 55

Modem Firewall. The default ‘Firewall On’ setting blocks all anonymous Internet
trafc. Access control enables the user to selectively direct such trafc, for example
to a Web Host in the DMZ or to specic ports opened for such applications as Web,
Telnet or FTP.
CAUTION: This dialog box indicates that you should not disable LAN Web Access
To congure Access Control, click on Advanced>Access Control. This will reveal the
Enable Access Control screen. The default conguration enables Telnet, Web, FTP
and SSH access FROM the LAN TO the WAN. Access FROM the WAN to the LAN is
not available in the default conguration.
Enable Access Control: check this box to enable selective access from the WAN to
your LAN for applications of the class indicated by the relevant check boxes. If Access Control is not enabled, the individual check boxes cannot be checked.
If Access Control is enabled, and an Enable WAN checkbox is selected, then WAN
access to the matching service is enabled. In other words, for example, if your
were to enable Telnet access on the WAN you could then manage and congure
your modem from anywhere on the Internet via Telnet.
Caution: Enabling WAN access to your modem reduces security.
IP Access List: This enables you to specify which LAN/WAN IP addresses are allowed
access to the modem conguration services specied.
or else you might not be able to connect to the device. If you become
locked out of the device perform a Restore Factory Default as detailed
earlier in this manual.
Tools
The Tools section allows you to save the conguration, restart the gateway, update
the gateway rmware, setup user and remote log information and run Ping and
Modem tests.
Tools>System Commands
System commands allow you to carry out basic system actions. Press the button to
execute a command. Here you will nd the following functions:
• Save All
• Restart
• Restore Defaults (same as pressing and holding the button on the back to clear
and reset to factory default.
Note: If you Restore Defaults you will need to recongure your internet connec-
tion settings, ISP Username & Password etc.
Tools>User Management
User Management is used to change your NB5Plus4/W’s User Name or Password.
Option Description
User Name: Default is ‘admin’.
Password: Default is ‘admin’.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 55
Page 56

Idle Timeout: If there is no activity by the admin user
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
logged into the modem for the number
of minutes specied in this eld, the
user will be required to login again.
WARNING: It is strongly recommended that you change the default username and
password to something unique.
Tools>Update Firmware
To update your NB5Plus4/W’s rmware, browse an update image le or conguration le and then click the Update Gateway button.
Additionally, you may download your conguration le from the system by clicking
“Get Conguration” so that you can store a backup of your conguration to restore
it at a later date.
Tools>Ping Test
The Ping test allows you to ping local and remote IP addresses to check for connec-
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
56 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 57

To edit an existing Bridge Filter Rule, click the radio button adjacent to the Filter
Rule name. The Rule will then appear in the top half of the Bridge Filter control
screen where it can be edited. When editing is complete, click ‘Add’ to return the
Rule to the list of existing rules.
To delete Bridge Filter Rules, click on the ‘Delete’ tick box; multiple deletions can be
made by shift-clicking Delete tick boxes; Select All will select every rule. When the
desired selections are made, effect deletion by clicking on Apply.
To save changes, click on Apply.
Hidden Bridge Filter Rules
The Bridge lter table contains three hidden rules. These rules are built into the
Router to ensure the user does not become locked out by entering a rule which
prevents further access to the router.
The rst rule allows any and all ARP frames through the system.
The second rule allows all IPv4 frames with the destination Bridge address of the
bridge to go through.
The third rule allows all IPv4 frames with the source MAC address of the bridge to
go through.
TIP: To nd the MAC address of a Windows-based computer, at the DOS prompt
type: ipcong /all.
Advanced > Multicast
IGMP [=Internet Group Management Protocol] Multicast enables communication
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 57
Page 58

between a single sender and multiple receivers on a network. It is used when data
needs to be sent from one to many devices. Typical uses might include the updat-
ing of mobile personnel from a home ofce or the periodic publishing of an online
newsletter. Multicasting provides efciencies which enable it to use less network
bandwidth than the sending of the same data by other means [e.g. SMTP].
To access Multicasting, click on Advanced>Multicast.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
58 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 59

To enable Multicast, open the multicast screen and select the Enable IGMP Multicast.
If you have multiple connections setup on your modem you will be able to choose
which connection to enable IGMP Multicast for.
Click the Apply button to save the settings.
Advanced > Static Routing
If the Router is required to serve more than one network, you will need to set up a
Static Route between the networks. Static routing can be used to allow users from
one IP domain to access the Internet through the Router in another domain. A
Static Route provides the dened pathway that network information must travel to
reach the specic host or network which is providing Internet access .
To access the Static Routing controls, click on Advanced> Static Routing.
Configuring Static Routing:
Choose a Connection: presents list of Saved Connections. Select appropriate connection from list.
The New Destination IP is the address of the remote LAN network or host to which
you want to assign a static route. Enter the IP address of the host for which you
wish to create a static route here. For a standard Class C IP domain, the network
address is the rst three elds of the New Destination IP, while the last eld should
be 0. The Subnet Mask identies which portion of an IP address is the network por-
tion, and which portion is the host portion. For a full Class C Subnet, the Subnet
Mask is 255.255.255.0. The Gateway IP address should be the IP address of the
gateway device that allows for contact between the Gateway and the remote network or host.
Gateway: IP address refers to the IP address of the near device that is to connect
with the remote network or host. If the Modem is fullling this function then its IP
address will be entered in this eld.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 59
Page 60

To save changes, click on Apply.
Advanced>Dynamic Routing
Dynamic Routing makes use of the RIP Protocol to allow the ADSL Router to automatically adjust to physical changes in the network. The NB5Plus4/W, using the
RIP protocol, will determine the network packet route based on the least number of
hops between the Source and the Destination. The RIP protocol regularly broadcasts
routing information to other Routers on the network and is part of the IP Suite.
To access Dynamic Routing click Advanced>Dynamic Routing.
Option Description
Eable RIP: If this box is checked, Dynamic Routing
Protocol: Choice is dependent upon the network
Eable Password: Enable to password protect the Dynamic
Directio: Determines the direction that RIP routes
is enabled.
environment. Most networks support Rip
v1. If RIP v1 is selected, routing data
will be sent in RIP v1 format. If Rip V2 is
selected, routing data will be sent in RIP
v2 format using Subnet Broadcasting. If
Rip V1 Compatible is selected, routing
data will be sent in RIP v2 format using
Multicasting.
Routing settings.
will be updated.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
60 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 61

Select ‘I’: The NB5Plus4/W will only incorporate
Select ‘Out’: The NB5Plus4/W will only send out RIP
Select ‘Both’: The NB5Plus4/W will both incorporate
received RIP information.
information.
received RIP information and send out
updated RIP information.
Advanced>Port Forwarding
Port Forwarding is necessary because NAT [=Network Address Translation] only
forwards trafc from the Internet to the LAN if a specic port mapping exists in the
NAT translation table. Because of this, the NAT provides a level of protection for
computers that are connected to your LAN. However, this also creates a connectivity
problem when you want to make LAN resources available to Internet clients, which
you may want to do to play network games or host network applications.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 61
Page 62

Thus Port Forwarding is necessary to run certain games, chat clients, video-conferencing and other kinds of applications. You might also need to congure port-forwarding if you intend to host a web server or mail server that is to be visible outside
your LAN.
TIP: In situations where you are hosting a Web Site or, for example, setting up
a regular NetMeeting link, it is advisable to consider implementing a Fixed
IP address, otherwise the dynamic IP address allocated by DHCP will need
to be communicated prior to every user session.
More about Port Forwarding
In TCP/IP and UDP networks a port is a 16-bit number used to identify which application program (usually a server) incoming connections should be delivered to.
Some ports have numbers that are pre-assigned to them by the IANA (the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority), and these are referred to as “well-known ports”.
Servers follow the well-known port assignments so clients can locate them.
If you wish to run a server on your network that can be accessed from the WAN
(i.e. from other machines on the Internet that are outside your local network), or
any application that can accept incoming connections (e.g. Peer-to-peer/P2P soft-
ware such as instant messaging applications and P2P le-sharing applications) and
are using NAT (Network Address Translation), then you will usually need to congure your router to forward these incoming connection attempts using specic ports
to the PC on your network running the application. You will also need to use port
forwarding if you want to host an online game server.
The reason for this is that when using NAT, your publicly accessible IP address will
be used by and point to your router, which then needs to deliver all trafc to the
private IP addresses used by your PCs.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is the central coordinator for the
assignment of unique parameter values for Internet protocols. Port numbers range
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
62 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 63

from 0 to 65535, but only ports numbers 0 to 1023 are reserved for privileged services and are designated as “well-known ports”. The registered ports are numbered
from 1024 through 49151. The remaining ports, referred to as dynamic ports or
private ports, are numbered from 49152 through 65535.
Examples of well-known and registered port numbers are shown in Table 4, for further information, please see IANA’s website at: http://www.iana.org/assignments/
port-numbers
Well-know and registered Ports
Port Number Protocol Description
20 TCP FTP Data
21 TCP FTP Control
22 TCP & UDP SSH Remote Login Protocol
23 TCP Telnet
25 TCP SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
53 TCP & UDP DNS (Domain Name Server)
69 UDP TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol)
80 TCP World Wide Web HTTP
110 TCP POP3 (Post Ofce Protocol Version 3)
119 TCP NEWS (Network News Transfer Protocol)
123 UDP NTP (Network Time Protocol)
443 TCP & UDP HTTPS
1503 TCP T.120
1720 TCP H.323
4000 TCP ICQ
7070 UDP RealAudio
Easy Port Forwarding: Applying Pre-Defined Rules
Available pre-dened rules are categorised according to the application type. Click
the Radio Button adjacent to the appropriate Category, and then select the required
application name. Click on the Add button to move the application into the Applied
Rules box. In the example shown on the previous page, ‘Delta Force’ has been selected from the list of Available Rules and is about to be copied to Applied Rules. In
the example, this will congure your Modem ports to use with ‘Delta Force’ .
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 63
Page 64

tivity directly from the NB5Plus4/W to the Internet or to a computer on your Network. You must make certain that the IP address that you ping will actually respond
to a ping before interpreting the results of the ping.
Note: Computers and Network devices can be congured to communicate even
though they do not respond to a ping, this can sometimes be done for
security.
Tools>Modem Test
This test can be used to check whether your Modem is properly connected to the
Network. This test may take a few seconds to complete. To perform the test, select
your connection from the list and press the Test button.
Note: Errors or failures on this test do not specically mean your connection is
faulty, only your ISP can tell you if these tests should pass or fail.
Status
The Status section allows you to view the Status/Statistics of different connections
and interfaces.
Status>Network Statistics
You can view data statistics for your Ethernet ports combined or for your ADSL port
in these pages.
Note: The statistics will be reset on loss of power or Reboot/Reset.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
64 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 65

Status > Connection Status
Here you can view the connection status of your Internet connection (usually ‘PPPoE’). You can also see the Public IP address that has been assigned to your modem
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 65
Page 66

as well as other information about the connection.
Status > DHCP Clients
The DHCP Clients page shows the MAC address, IP Address, Host Name and Lease
Time assigned to other computers in your network by the modem.
Status > Modem Status
The Modem Status page shows the modem status and DSL statistics.
Status > Product Information
The Product Information page shows the product information and software versions.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
66 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 67

Status > System Log
The System Log page shows the events triggered by the system.
EasyConfig
The EasyCong menu takes you to the EasyCong page. This is the page you originally congured your modem with.
Help
This menu provides information on various features of your modem. Click the hyperlinks to access the information.
Appendix A: NB5Plus4W Wireless Features
The WLAN tab allows you to perform basic WLAN interface conguration functions
including:
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 67
Page 68

• Access to the WLAN web interface.
• Identify the function of each WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) web interface
page.
• Use the WLAN web interface to congure the NB5Plus4W as an Access Point
(AP).
Wireless Main Screen
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
68 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 69

The screen below shows the Wireless main screen, which can be accessed by clicking on the Wireless tab from the top of the screen. This screen provides access to
the following Wireless conguration screens:
• Setup
• Conguration
• Security
• Management
• Log Out
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 69
Page 70

Wireless>Setup
The screenshot below shows the default Wireless setup screen, which can be accessed by clicking on the Setup link. This screen provides basic local and Wireless
networks parameter settings.
Following is a description of the Wireless Setup options:
Wireless Setup Field Descriptions
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
70 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 71

Option Description
Eable AP Enables/disables the access point.
SSID Service Set Identier of the AP. The
default is ‘wireless’ and you can assign
a unique SSID to your AP. The SSID
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 71
Page 72

is the name of your wireless network.
When scanning for wireless networks
in your area this is what you will see
displayed.
Hidden SSID Enables/disables the Hidden SSID
feature. The AP (Access Point) will not
transmit beacon and thus will not be
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
72 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 73

seen by any other station. This adds an
extra layer of security.
Chael B/G The channel on which the AP and the
wireless stations will communicate.
Different domains will have different
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 73
Page 74

ranges of channels. For ETSI (European
Telecom Standardization Institution) in
2.4GHz, the default is 13.
Option Description
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
74 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 75

Chael B/G (cont’d) The channel can be selected accord-
ing to the band selection. It is good
practise to have your wireless network
transmitting on a different channel to
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 75
Page 76

neighbouring wireless networks.
802.11 Mode You can select from the following mode:
• Mixed mode: Both 11b and 11g
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
76 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 77

devices are able to connect to the
NB5Plus4W. Beacon & Probe Response
Frames are sent in “b” rate.
• 11b only Mode: Only 11b devices are
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 77
Page 78

able to connect to the NB5Plus4W.
• 11b+ Mode: Similar to the “802.11b-
only” mode except that 22Mbps PBCC
rate/modulation is included.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
78 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 79

• 11g only Mode: Only 11g devices are
4X Same as b+ mode, which enables/disa-
able to connect to the NB5Plus4W.
bles the 4x feature. This function is TI
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 79
Page 80

proprietary and is only available when
both NetComm wireless cards (e.g.
NP543 / NP542) and the NB5Plus4W are
used.
User Isolation When checked, wireless users will not
be able to directly access other wireless
users. More details on User Isolation are
discussed in the ‘‘User Isolation’’ section
below.
User Isolation
When User Isolation is enabled, wireless users will not be able to directly access
other wireless users. Access can be controlled by the AP. This is enabled on the
network side.
The gure below demonstrates the User Isolation feature.
1. AP disabled BSS (Basic Service Set) bridging
2. All data sent to WAN (Wide Area Network)
3. Enable/Disable ag
Save Your Changes
Follow these steps to save changes you have made on the Wireless Setup screen.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
80 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 81

CAUTION: Any changes you make to the WLAN screen do NOT get saved auto-
1. Click the Apply button.
2. Click the Restart Access Point link at the bottom of the page, which will take you
to the System Commands screen.
Note: An alternative way to access the System Commands Screen to click on the
3. On the System Commands Screen, click Save All. This will save all the changes
you have made. You will still need to restart the access point for any changes to
take effect.
4. If you only made changes to the WLAN setting(s), click the Restart Access Point
button for the changes to take effect. OR
5. If you also made changes to the DSL setting(s), click the Restart button for all
changes to take effect.
matically. Clicking on the ‘Apply’ button on the individual page is not
sufcient for the changes you made to take effect. For change(s) you
made to any WLAN screen to take effect, you will need to perform these
steps.
Tools tab, then select the System Commands option.
Wireless>Configuration
You can access the Conguration screen by clicking on the Conguration link. This
screen provides an advanced wireless network parameter settings.
Following is a description of the Wireless Conguration elds:
Option Description
Beaco Period The time interval between beacon frame
DTIM period Delivery Trafc Identication Map
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 81
transmissions, which ranges from 0 65535 msec.
Page 82

Period: The number of beacon frame
transmissions before frames, targeted
for stations operating in low-power
mode will be transmitted
RTS threshold Request To Send The number of bytes
Frametatio Threshold The minimum length of a frame that
Power Level The TX Output power percentage com-
Option Description
Multi Domai Capability This feature can only be congured on a
Coutry Stri Please call NetComm support should you
Curret Re. Please call NetComm support should you
Private Re. Please call NetComm support should you
in an MPDU below which an RTS/CTS
handshake will not be performed. The
default value is 2347, however, when 4x
is enabled on the setup page, the RTS
threshold value changes to 4096.
will be fragmented. The default value
is 2346, however, when 4x is enabled
on the setup page, the fragmentation
threshold value changes to 4096.
paring to the maximum TX power: full,
50%, 25%, 12%, and 6%.
hidden page. It is not recommended for
the end users to congure this feature.
Please call NetComm support should you
need to change any of these settings.
need to change any of these settings.
need to change any of these settings.
need to change any of these settings.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
82 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 83

Video Blast Support When checked, priority is given to video
in the trafc to and from the specied
IP. This feature is only available if you
are using a NetComm wireless card and
the NB5Plus4W.
IP Address The LAN-side IP with the preferred
Protocol The protocol used by the IP address.
Destination Port The port number used by the IP ad-
bandwidth. This eld is related to the
Video Blast Support and is enabled
when Video Blast Support is checked.
You can enter up to two IPs for the
Video Blast Support features.
This eld is related to the Video Blast
Support and is enabled when Video
Blast Support is checked. There are
three options: None, TCP, and UDP. You
will need to select TCP or UDP for each
IP.
dress. This eld is related to the Video
Blast Support and is enabled when
Video Blast Support is checked.
Wireless>Security
The screen below illustrates the security settings when no security is enabled.
Option Description
None No security used.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) En-
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 83
able legacy stations to connect to the
Page 84

NB5Plus4W.
802.1x Enable stations with 802.1x capability to
connect to the NB5Plus4W.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) Enable stations
Note: Currently VLAN (Virtual LAN) + Multiple SSID with different security options
is not supported. If you have enabled multiple SSID with security turned
off, when you enable any security option (WEP, 802.1x, or WPA), multiple
SSID will be disabled.
with WPA capability to connect to the
NB5Plus4W.
Wireless>Security>WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent privacy) is a security protocol for Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN). WEP provides security by encrypting the data that is sent over the
WLAN.
The NB5Plus4W supports 3 levels of WEP encryption:
• 64 Bit encryption
• 128Bit encryption
• 256 Bit encryption
With WEP, the receiving station must use the same key for decryption. Each radio
NIC and access point, therefore, must be manually congured with the same key.
The screen below illustrates the default setting of the WEP Wireless Security screen.
WEP is enabled by default.
1. Check Enable WEP Wireless Security.
2. Select Authentication Type
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
84 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 85

3. Enter Encyption key and select Cipher following instructions on screen. You will
need to enter the same key for the rst time conguration of each station
4. To save your settings, refer to the section above.
Following is a description of the WEP eld settings.
Option Description
Eable WEP
Wireless Security Check this eld to enable WEP wireless
Autheticatio Type Authentication algorithm to use when
Ecryptio Key This eld is enabled when the WEP
WEP Cipher This eld is enabled when the WEP
security.
the security conguration is set to
Legacy. When the security conguration
is set to 802.1x or WPA, the authentica-
tion algorithm is always open. This eld
is enabled when the WEP security eld
is checked. There are three options:
• Open: In open-system authentication,
the access point accepts any station
without verifying its identify.
• Shared: Shared-key authentication
requires a shared key (WEP encryption key) be distributed to the stations
before attempting authentication.
• Both: If both is selected, the access
point will perform shared-key authentication, then open-system authentication.
security eld is checked. The key’s value
that is used when the security congu-
ration is set to legacy. The key length
must match the WEP cipher. This eld is
not used when the security congura-
tion is set to 802.1x or WPA.
security eld is checked. You can select
from 64 bits, 128 bits, and 256 bits.
The WEP cipher that is used when the
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 85
Page 86

security conguration is set to Legacy or
802.1x. This eld is not used when the
security conguration is set to WPA.
Wireless > Security > 802.1x
802.1x is a security protocol for Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN). It is a port-
based network access control that keeps the network port disconnected until authentication is completed. 802.1x is based on the Extensible Authentication protocol
(EAP). EAP messages from the authenticator to the authentication server typically
use the RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) protocol. The screenshot below illustrates the default setting of the 802.1x Wireless Security screen.
Following is a description of the 802.1x Security eld settings.
Option Description
Server IP Address The LAN-side RADIUS (Remote Authen-
Port The RADUIS server’s port.
Secret The secret that the AP shares with the
tication Dial-In User Service) server’s IP
address. Used for authentication.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
86 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 87

RADIUS server. You can enter up to 63
characters in this eld.
Group Key Iterval The group key interval that is used to
distribute the group key to 802.1x and
WPA stations.
Wireless>Security>WPA
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) is a security protocol for Wireless Local Area Networks
(WLAN). WPA uses a sophisticated key hierarchy that generates new encryption
keys each time a mobile device establishes itself with an access point. Protocols including 802.1X, EAP and RADIUS are used for strong authentication. Like WEP, keys
can still be entered manually (preshared keys); however, using a RADIUS authentication server provides automatic key generation and enterprise-wide authentication.
The screen below illustrates the default setting of the WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
Wireless Security screen.
Following is a description of the WPA Security eld settings.
Option Description
802.1x When selected, the WPA stations authenticate with the RADIUS
Port The RADIUS server’s port
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 87
server using EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol - Transport Layer Security) over 802.1x.
Page 88

Secret The secret that the AP shares with the RADIUS server
PSK String Pre-Shared Key String. When selected, the WPA stations
do not authenticate with the RADIUS server using EAP-TLS. Instead they share a pre-shared secret with the AP (ASCII format).
The PSK string needs to be entered in the rst time conguration
with each station.
Wireless>Management
The Wireless Management function gives another level of security to your AP. It
allows you to create an allowed access list or a banned access list (not both), and
view a list of stations associated with your access point.
Wireless>Management>Access List
By clicking on Management from the left-hand navigation list, you are taken to the
default Access List screen.
You can create an allowed OR banned access list from the Access List screen by
performing the following procedures.
1. Check Enable Access List.
2. Select Allow to create an allowed access list or Ban to create a banned list.
Note: You can not create both.
3. Enter a MAC (Medium Access Control) address of an allowed or banned station,
then click the Add button. This station will appear in your allowed or banned access list.
4. Repeat this step for each station.
5. To save your settings, refer to the ‘‘Save Your Changes’’ section above.
Wireless > Management > Associated Stations
By clicking on the Associated Stations button under the ‘Management’ option, you
are taken to the Associated Stations screen. This screen allows you to see a list of
all associated stations with the access point. You can ban any station(s) on the list
by clicking on the Ban Station button next to the MAC Address. To save your settings, refer to ‘‘Save Your Changes’’ section above.
Wireless > Management > Multiple SSID
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
88 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 89

You can access the Multiple SSID screen by clicking on the Multiple SSID button un-
der the Management option. The Enable SSID eld will enable you to create multiple
SSIDs for the AP.
Note: Currently VLAN (Virtual LAN) + Multiple SSID with different security op-
You can create multiple SSIDs by performing the following procedures.
tions is not supported. If security is enabled, you will not be able to enable
multiple SSID. You can only enable multiple SSID if your security option is
set to “None”.
Create an Access List
1. Check Enable Multiple SSID.
2. Enter the name of the rst SSID in the SSID eld, then click the Add button.
Repeat this step for each additional SSID. The SSIDs will appear as shown in
below.
3. To delete an SSID, check the SSID, then click Delete in the popup window. To
delete all SSIDs, check Delete All.
4. To save your settings, refer to the ‘‘Save Your Changes’’ section above.
Status
You can access this screen by clicking on the Status button.
Use the following procedures to check your Wireless status.
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 89
Page 90

1. Click on Status from the top of the screen.
2. Select Network Statistics from the left-hand column.
3. Click Wireless.
Log out
By clicking on Log Out, you will log out of the NB5Plus4W (not just the Wireless
interface). Click the Log Out button will take you back to the login screen.
Use the following procedures to log out.
1. Select Log Out from the left-hand column. You will be prompted to conrm in the
screen shown above.
2. Conrm by clicking the Log Out button at the bottom-right corner. You will be
taken back to the login screen (cross-reference).
Appendix B: Specification
ADSL/ATM SUPPORT
• ANSI T1.413 issue 2
• ITU-T G.992.1 (G.dmt) and G.992.2 (G.lite) compliant
• ADSL2/2+, G.992.3/G.992.5
• Rate Adaptive modem at 32 Kbps steps
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
90 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 91

• Dynamic Adaptive Equalisation to improve Carrier’s service area
• Bridge Tap Mitigation support
• Turbo DSL support improving packet throughout performance by 3 times
• ATM Layer with Trafc shaping QoS Support (UBR, CBR, VBR-rt, VBR-nrt)
• AAL ATM Attributes - AAL5
• Multiple PVC up to 8 support
• Spectral compatibility with POTS
• F5 OAM Loopbacks/Send and Receive
ENCAPSULATION SUPPORT
• RFC2684 Bridged and Routed LLC and VC Mux Support
• RFC2364 PPPoA Client Support
• RFC2516 PPPoE Client Support
• RFC2225/RFC1577 Classical IP Support
• Transparent Bridge Support
• PAP/CHAP/MS-CHAP for Password Authentication Support
NETWORK SUPPORT
• Port Forwarding rules for Popular Games/Applications
• Static IP, Dynamic RIP Routing Support
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 91
Page 92

• IP/TCP/UDP/ICMP/ARP/RARP Application Support
• Network Address Translation (NAT)
• Port Mapping/Forwarding
• IGMP Multicast
• SNTP
• NAT Application Level Gateway for Popular Applications
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
92 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 93

• DHCP Server/Relay/Client
• DNS Relay Agent
• DMZ Support
• Single session IP Sec and PPTP/L2TP VPN pass-through support
• PPP Always on with congurable timeout
VoIP
• SIP version 1 & 2, H.323, MGCP
• QoS support for voice packets
SECURITY
• NAT for Basic Firewall and sharing
• Packet Filtering Firewall Support
• Stateful Packet Inspection Support
• Protection against Denial of Service attacks
• Password Authentication to Modem
MANAGEMENT SUPPORT
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 93
Page 94

• Web-based HTTP management GUI (LAN or Remote)
• TFTP/FTP Support For Firmware Upgrade
• Web-based Firmware Upgrade (Local)
• Soft Factory Reset Button via Web GUI
• Diagnostic Test (DSL, OAM, Network, Ping Test)
• Telnet/CLI (Read Only)
• Syslog Support
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
94 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 95

HARDWARE
• Texas Instrument TNETD7300 Single Chip Network Processor/AFE/Line Driver
Chipset
• Dying Gasp Support
• A-Tick approval N367
PLATFORM SUPPORT
• For Ethernet – OS Independent: includes Windows®, Mac, Linux and UNIX
• For USB – Windows® 98SE, ME, 2000, XP, 2003
LED INDICATORS
• 1 x PPP LED
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 95
Page 96

• 1 x Power LED
• 1 x ADSL Link Status LED
• 4 x Ethernet Link/Activity Status LED
• 1 x USB Status LED
• 1 x WLAN Status LED ( NB5Plus4W Only)
Appendix C: Cable Connections
This cable information is provided for your reference only. Please ensure you only
connect the appropriate cable into the correct socket on either this product or your
computer.
If you are unsure about which cable to use or which socket to connect it to, please
refer to the hardware installation section in this manual. If you are still not sure
about cable connections, please contact a professional computer technician or NetComm for further advice.
RJ-45 Network Ports
RJ-45 Network Ports can connect any networking devices that use a standard LAN
interface, such as a Hub/Switch Hub or Router. Use unshielded twisted-pair (UTP)
or shield twisted-pair (STP) cable to connect the networking device to the RJ-45
Ethernet port. Depending on the type of connection, 10Mbps or 100Mbps, use the
following Ethernet cable, as prescribed.
10Mbps: Use EIA/TIA-568-100-Category 3, 4 or 5 cable.
100Mbps: Use EIA/TIA-568-100-Category 5 cable.
Note: To prevent loss of signal, make sure that the length of any twisted-pair
connection does not exceed 100 metres.
Figure 1
Figures 1 and 2 illustrate the use of straight-through and crossover twisted pair
cables along with the connector.
Figure 2
RJ11 connector and cable
An RJ-11 connector is the small, modular plug used for most analog telephones. It
has six pin slots in the head, but usually only two or four of them are used.
Figure 5
605 to RJ-11 adapter
The 605 to RJ-11 adaptor is provided to comply with the older 610 Telstra wall
socket. The 605 to RJ-11 adapter may be used to convert the supplied RJ-11 cable,
if the older connection is required.
Appendix D: Glossary
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
96 www.netcomm.com.au
Page 97

10BASE-T A designation for the type of wiring used by Ethernet
100BASE-T A designation for the type of wiring used by Ethernet
ADSL Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. The most commonly
analog Of data, having a form is analogous to the data’s origi-
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode A standard for high-speed
autheticate To verify a user’s identity, such as by prompting for a
biary The “base two” system of numbers, that uses only two
bit Short for “binary digit,” a bit is a number that can have
bps bits per second
bridi Passing data from your network to your ISP and vice
networks with a data rate of 10 Mbps. Also known as
Category 3 (CAT 3) wiring. See also data rate, Ethernet.
networks with a data rate of 100 Mbps. Also known as
Category 5 (CAT 5) wiring. See also data rate, Ethernet.
deployed type of DSL for home users. The term asymmetrical refers to its unequal data rates for downloading and uploading (the download rate is higher than the
upload rate). The asymmetrical rates benet home users
because they typically download much more data from
the Internet than they upload.
nal waveform. The voice component in DSL is an analog
signal. See also digital.
transmission of data, text, voice, and video, widely used
within the Internet. ATM data rates range from 45 Mbps
to 2.5 Gbps. See also data rate.
password.
digits, 0 and 1, to represent all numbers. In binary, the
number 1 is written as 1, 2 as 10, 3 as 11, 4 as 100, etc.
Although expressed as decimal numbers for convenience,
IP addresses in actual use are binary numbers; e.g., the
IP address 209.191.4.240 is 11010001.10111111.000001
00.11110000 in binary. See also bit, IP address, network
mask.
two values, 0 or 1. See also binary.
versa using the hardware addresses of the devices at
each location. Bridging contrasts with routing, which can
add more intelligence to data transfers by using network
addresses instead. The My ADSL Modem can perform
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 97
Page 98

both routing and bridging. Typically, when both functions
are enabled, the device routes IP data and bridges all
other types of data. See also routing.
broadbad A telecommunications technology that can send different
Broadcast To send data to all computers on a network.
CO Central Ofce A circuit switch that terminates all the local
DHCP Dynamic Host Conguration Protocol DHCP automates
DHCP relay Dynamic Host Conguration Protocol relay. A DHCP relay
RJ-45 Connector
Pin Assignment Normal Assignment
1 Input Receive Data +
2 Input Receive Data -
3 Output Transmit Data +
6 Output Transmit Data -
4,5,7,8 Not used
types of data over the same medium. DSL is a broadband
technology.
access lines in a particular geographic serving area; a
physical building where the local switching equipment is
found. xDSL lines running from a subscriber’s home con-
nect at their serving central ofce.
address assignment and management. When a computer
connects to the LAN, DHCP assigns it an IP address from
a shared pool of IP addresses; after a specied time limit,
DHCP returns the address to the pool.
is a computer that forwards DHCP data between comput-
ers that request IP addresses and the DHCP server that
assigns the addresses. Each of the My ADSL Modem’s
interfaces can be congured as a DHCP relay. See DHCP.
DHCP server Dynamic Host Conguration Protocol server. A DHCP
digital Of data, having a form based on discrete values ex-
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
98 www.netcomm.com.au
server is a computer that is responsible for assigning IP
addresses to the computers on a LAN. See DHCP.
RJ-45 plug attached
to cable
pressed as binary numbers (0’s and 1’s). The data com-
Page 99

Straight and crossover cable configuration
There are two types of the wiring: Straight-Through Cables and Crossover Cables.
Category 5 UTP/STP cable has eight wires inside the sheath. The wires form four
pairs. Straight-Through Cables has same pinouts at both ends while Crossover Cables has a different pin arrangement at each end.
In a straight-through cable, wires 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 and 8 at one end of the cable are
still wires 1~8 at the other end. In a crossover cable, the wires of 1,2,3,6 are reversed so that wire 1 become 3 at the other end of the cable, 2 becomes 6, and so
forth.
To determine which wire is wire 1, hold the RJ-45 cable tip with the spring clip
facing towards the ground and the end pointing away from you. The copper wires
exposed upwards to your view. The rst wire on the far left is wire 1. You can also
refer to the illustrations and charts of the internal wiring on the following page.
Straight-Through Cabling
Figure 3
Wire Becomes
1 1
2 2
3 3
6 6
Cross-Over Cabling
Figure 4
Wire Becomes
1 3
2 6
3 1
6 2
Note: To prevent loss of signal, make sure that the length of any twisted-pair
YML754 Rev1 NB5Plus4/W User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 99
connection does not exceed 100 metres.
Page 100

ponent in DSL is a digital signal. See also analog.
DNS Domain Name System. The DNS maps domain names
RJ-11 Connector
Pin Assignment Normal Assignment
1 Not Connected
2 Not connected
3 Line
4 Line
5 Not Connected
6 Not Connected
into IP addresses. DNS information is distributed hierarchically throughout the Internet among computers
called DNS servers. When you start
to access a web site, a DNS server
looks up the requested domain name
to nd its corresponding IP address.
If the DNS server cannot nd the IP
address, it communicates with higherlevel DNS servers to determine the IP
address. See also domain name.
NB5Plus4/W User Guide YML754Rev1
100 www.netcomm.com.au
 Loading...
Loading...