Page 1

297-2183-912
Nortel Networks Symposium Call Center
Server
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide
Product release 5.0 Standard 1.0 April 2004
Page 2

Page 3

Nortel Networks Symposium Call Center Server
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide
Publication num ber: 297-2183-912
Product release: 5.0
Document release: Standard 1.0
Date: April 2004
Copyright © 2004 Nortel Networks, All Rights Reserved
Information is sub ject to chan ge wi thout not ice . Nortel Networks rese rves the right to mak e cha nges
in design or components as progress in engineering and manufacturing may warrant.
The process of transmitting data and call messaging between the Meridian 1 and Symposium Call
Center Server is proprietary to Nortel Networks. Any other use of the data and the transmission
process is a violation of the us er li ce ns e unl es s sp ec ifi cal ly auth orized in writing by Nortel Networks
prior to such use. Violations of the license by alternative usage of any portion of this process or the
related hardware constitutes grounds for an immediate termination of the license and Nortel
Networks reserves the right to seek all allowable remedies for such breach.
*Nortel Networks, the Nortel Networks logo, the Gl obe ma rk, DMS , DMS-100 , IVR, MAP, Meridian,
Meridian 1, and Symposium are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
CALLPATH is a trademark of Genesys Telecommunications Laboratories, Inc.
CRYSTAL REPORTS is a trademark of Crystal Decisions, Inc.
MICROSOFT, MS-DOS, POWERPOINT, WINDOWS, and WINDOWS NT are trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation.
PCANYWHERE is a trademark of Symantec Corporation.
Page 4

Page 5

Publicat i on hist ory
April 2004
The Standard 1.0 version of the Nortel Networks Symposium
Call Center Server Symposium and
DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide Release 5.0, is released.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide v
Page 6

Publication history Standard 1.0
vi Symposium Call Center Server
Page 7

Contents
1 Getting started 9
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Skills you need . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
What’s new in Release 5.0? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
How Symposium Call Center Server communicates with the switch . . . . . . 19
Support for switch features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Preinstallation checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Configuration tasks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2 Configuring the switch 35
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Section A: Configuring the ICM link parameters 37
Overview of configuring the server logon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Configuring SCAICOMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Configuring BGDATA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Configuring SCAIGRP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Configuring SCAISSRV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Configuring SCAIPROF. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Configuring CUSTNTWK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Section B: Configuring switch resources 53
Overview of configuring switch resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Configuring RAN and music routes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Configuring ACD groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Configuring ACD subgroups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Configuring DNs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Configuring agent phonesets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Configuring supervisor phonesets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Configuring logon IDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Section C: Checking the server configuration 79
Overview of server configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Checking the server configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Relationship of server configuration and switch datafill . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide vii
Page 8

Contents Standard 1.0
3 Verifying the configuration 87
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Verifying that the server can log on to the switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Verifying ACD groups and subgroups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Verifying that phonesets are correctly configured . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Verifying that agents are correctly configured . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Verifying that the CDNs are correctly configured . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Verifying that music and RAN routes are correctly configured. . . . . . . . . . . 97
Verifying that DNISs are correctly configured. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
4 Troubleshooting 101
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Subsystem link problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Resource configuration problems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
A Preinstallation chec klist 111
Preinstallation checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Glossary 115
Index 137
viii Symposium Call Center Server
Page 9

Chapter 1
Getting started
In this chapter
Overview 10
Skills you need 11
What’s new in Release 5.0? 12
Components 13
How Symposium Call Center Server communicates with the switch 19
Support for switch features 24
Preinstallation checklist 31
Configuration tasks 32
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 9
Page 10

Getting started Standard 1.0
Overview
Throughout this guide, the term DMS switch applies to the following switch
types:
! DMS Switch
! MLS-100
! Succession 2000
! Nortel Networks Communication Server 2100
Symposium Call Center Server works in conjunction with othe r systems to
ensure that calls entering your call center are successfully routed to agents
qualified to handle the calls. To enable the features of your Symposium Call
Center Server, you must configure the following systems:
! the DMS/MSL-100 switch
! Intelligent Call Manager (ICM), formerly CompuCA LL
! Symposium C all Center S erver
This guide explains how to configure the switch to work with Symposium Call
Center Server. To find out how to configure the server, refer to the
Administrator’s Guide. If you are using the Symposium Call Cente r Web Client,
refer to the Symposium Call Center Web Client Guide and online Help for
detailed instructions.
This guide assumes that you have already configured ICM to work with the
switch.
Note: This guide assum es that the switch has be en correctly installed and is
operational with al l cu rr ent Product Enhancement Pa ckages (PEPs) applied. For
information on which PEPs to install on the switch, contact your Nortel
Networks customer support representative.
10 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 11

April 2004 Getting started
Skills you need
Introduction
This section describes the skills and knowledge you need to use this guide
effectively.
Nortel Networks product knowledge
Knowledge of, or experience with, the following Nortel Networks products can
be of assistance when configuring the switch to communicate with Symposium
Call Center Server:
! Symposium C all Center S erver
! DMS switch
! Switch release CCM010/SCAI12 to CCM017/SCAI17
! Intelligent Call Manager switch translation release ICM00001 to
ICM00075
! Maintenance Administration Position (MAP) terminal
! Service Orders (servord) utility
! Switch Translation Guide
! Automatic Call Distribu tion (ACD)
! other switch administration and monitoring tools
PC experience or knowledge
Knowledge of, or experience with, the following PC products is of assistance
when administering the Symposium Call Center Server:
! Microsoft Windows 2000 or Windows XP
Other experience or knowledge
Other types of experience or knowledge that might be of use include
! TCP/IP networking
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 11
Page 12

Getting started Standard 1.0
What’s new in Release 5.0?
Skillset display on phoneset
Symposium Call Center Server Release 5.0 with Common Command Module
(CCM)16 or Switch Compu t er Application Interface (SC AI)17 (or later)
supports the display of skillset names on the agent and supervisor phonesets.
The phoneset displays only the first 15 characters of the skillset name, and only
displays the characters A through Z, and the numbers 0 through 9.
SCAI17 support
Symposium Call Center Server Release 5.0 provides SCAI17 support with
backward compatibility to SCAI12.
Hold/Unhold reporting
Symposium Call Center Server Release 5.0 with CCM15/SCAI17 (or later)
supports Hold/Unhold reporting which records the hold time associated with a
call.
iButton
Release 5.0 provides support for iButton as an alternative to such legacy I/O
devices a s parall el port s. iButto n pro vides the abil ity for Symposium Call Center
Server to support le g ac y-f ree servers. This feature is not dep endent on a ny SCAI
level.
12 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 13

April 2004 Getting started
Components
Introduction
Symposium Call Center Server consists of three key components: telephony,
server, and client.
Telephony component
The telephony component includes the switch, the Ethernet Interface Unit (EIU),
Intelligent Call Manager (ICM), and the agent and supervisor phonesets.
Server component
The server in Symposium Call Center Server can be located at either the central
office or customer site.
Client component
The client is installed on the supervisor workstations and accesses the server
over the customer’s LAN.
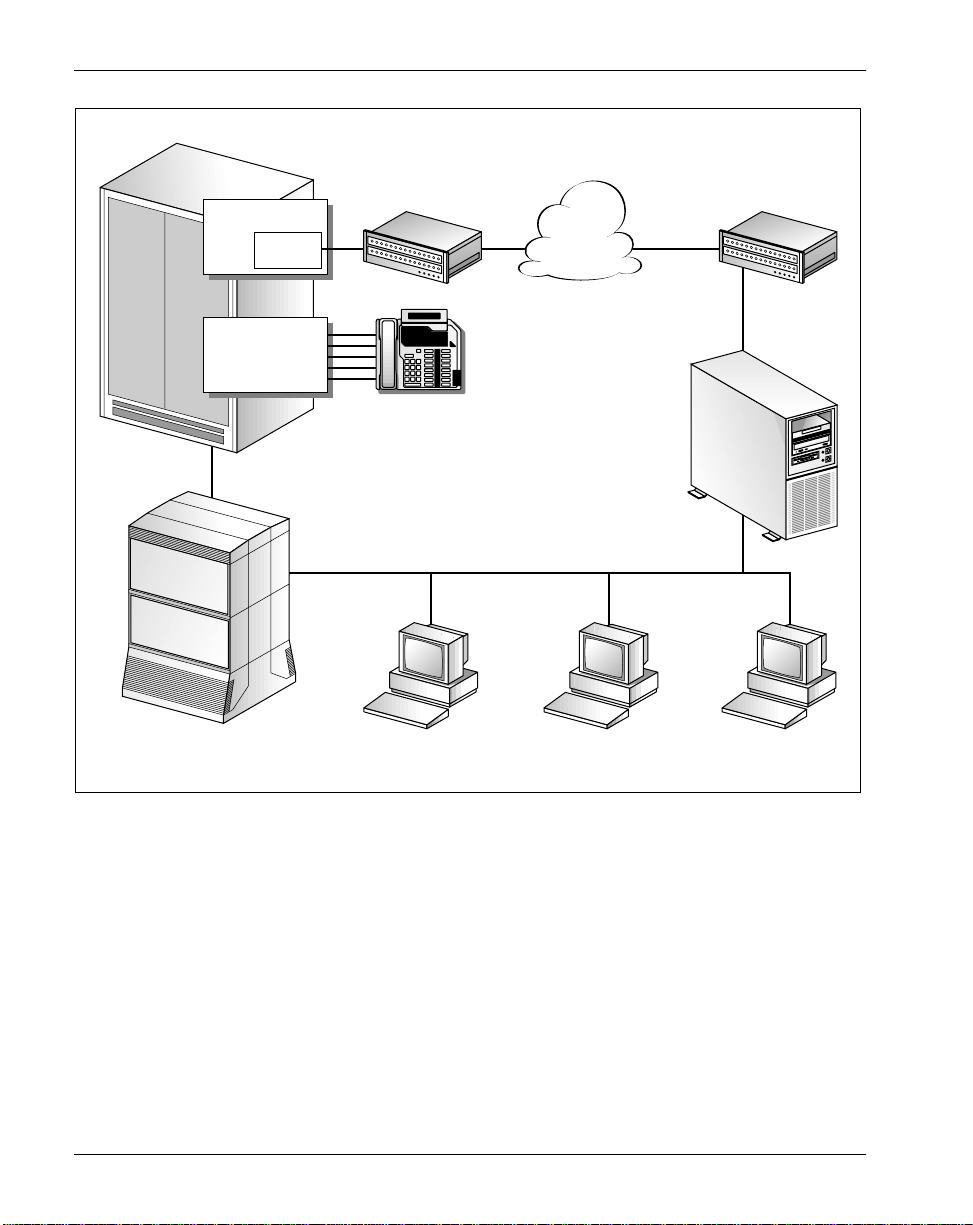
Symposium Call Center Server components
The followin g illus trat ion shows the relationship of the components req uired f or
Symposium C all Center S erver:
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 13
Page 14
Getting started Standard 1.0
Switch
ICM
ACD
Voice port lines
Front-end IVR
(optional)
EIU
Router Router
Agent
phonesets
Client PC
(administrator)
Network
CLAN
Client PC
(supervisor)
ELAN
Symposium
Call Center
Server
Third-party
application
G101333
Switch
The switch is the hardware and software component that provides telephony
services. The switch sends and receives calls to and from Symposium Call
Center Server. When a call arrives at the switch, the switch notifies the server,
which performs call processing and routing.
To work with the Symposium Call Center Server, the switch must be running
software load CCM010/SCAI12 or later.
14 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 15

April 2004 Getting started
Symposium Call Center Server supports the DMS, MLS-100, Succession 2000,
and Communication Server 2100 switches. Throughout this guide, the term
DMS Switch applies to all the supported switch types.
Note: If the link to the s erver goes down, ACD r out ing configured on t he switch
provides a backup method for handling calls.
3PC
The Third-Party Core (3PC ) card (also known as the Call Agent Card) provides
processing power for the Communication Server 2100 compact configurations.
EIU
The Ethernet Interface Unit (EIU) enables the switch to connect to an Ethernet
network for communication with Symposium Call Center Server.
Note: The rules for the EIU also apply to the 3PC card.
ICM
The Intelligent Call Manager (ICM) serves as an interface between Symposium
Call Center S erver and the switch. The ICM receives information from the
switch and transmits it to Symposium Call Center Server. It receives information
from the server and transmits it to the sw itch.
The number av ailable for Symposium Call Center Server dep ends on the number
of other ICM-based applications connecting to the switch. The switch can
support up to 16 ICM connections for CCM05/SCAI07 through CCM13/
SCAI15, and up to 96 for CCM14/ SCAI15 an d higher. (This value is deter mined
by the data in the iphost.)
Symposium Call Center Server requires software packages ICM00001,
ICM00010, or ICM00020 MSL09.
Note: You must configure certain parameters to establish a secure ICM session.
For more information about configuring ICM security, see the Administrator’s
Guide.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 15
Page 16

Getting started Standard 1.0
Server
The server component, which uses Microsoft Windows 2000 software, is
responsible for functio ns such as
! the logic for call processing
! call treatm ent
! call handling
! call presentation
! administration of agent s, skillsets , and supervisors, and agent to skillse t and
agent to supervisor assignments
! accumulation of histor ical and real-time statis tics
Classic Client
The Classic Client component, located on the call center manager’s or
supervisor’s desktop, has a graphical user interface based on Microsoft 2000 or
Windows XP. The client provides meaningful real-time call center statistics and
an easy-to-use interface for the management of the call center.
Web Client
Symposium Web Client is a browser-based thin client for administrators and
supervisors. Through the Internet Explorer browser located on a client PC, you
can connect to the Symposium Web Client application server to manage and
configure a call center and its users, define access to data, and view real-time
and historical reports.If you are using the Symposium Web Client, refer to the
Symposium Call Center Web Client Guide and online Help.
CLAN
The agent and supervisor workstations are connected to the customer LAN
(either an Ethernet or a Token Ring LAN). The customer LAN also provides
connections to optional third-party applications, such as an Interactive Voice
Response system.
16 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 17

April 2004 Getting started
ELAN
The embedded LAN (ELAN) is a dedicated Ethernet TCP/IP LAN connecting
the Symposium Call Center Ser ver and the switch. The ELAN mus t be a pr ivate
isolated network t hat i s dedi cated to the switch and t o the call cente r. The ELAN
must not have a physical or logical connection with the customer network. This
eliminates the potential impact of caller network traffic on call processing.
Front-end IVR system (optional)
The switch can dir ec t c al ls to an optional t hir d-party Interactive Voice Response
(IVR) system. This system plays voice prompts to callers and collects their
responses. After the calls receive IVR treat ment, the IVR system delivers th e
responses for the calls to Symposium Call Center Server. The se rver then gains
control of the calls.
Third-party applications (optional)
Optional third-party applications provide the following functionality to
Symposium C all Center S erver:
! the ability to exchange data with the server, using Host Data Ex change
(HDX)
! the ability to receive real-time updates from the server, using the real-Time
API (RTI)
! the ability to rec ei ve re al-tim e updates f rom the se rver, using the Real-Time
Statistical Multicast stream (RSM)
! the ability to access con figuration and st atistical data in the Symposium
Call Center Server database, using Open Database Connectivity (ODBC)
database drivers
! the ability to trigger screen pops for inbound triggers, using Meridian Link
ICM applications using LinkPlexer 1.2 (optional)
LinkPlexer 1.2 is a Windows 2000 application that acts as a proxy to enable
multiple ICM applications to share the same session and DMS/MSL-100
resources. LinkPle xe r 1.2 allo ws appli cations to sh are a DN (Directo ry Number)
association between different eBusiness applications. LinkPlexer 1.2 is
necessary for systems where
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 17
Page 18

Getting started Standard 1.0
! Interactive Voice Response (IVR) voice ports are controlled by IVR and
monitored by Symposium Call Center Server
! Symposium Call Center Server performs the call rou ting, IVR con trols the
voice response system, and Symposium TAPI Server/Symposium Agent
controls softphones and screen pops
! agent po sitions are controlled by TAPI Server/Sympo sium Agent (or
desktop CTI) and monitored by Symposium Call Center Server
! call queues and agent positions are monitored by third-party applications,
such as voice recorders
Note: For more information, see the LinkPlexer 1.2 Installation and
Configur ati on Guide .
18 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 19

April 2004 Getting started
How Symposium Call Center Server communicates with the switch
Introduction
Symposium Call Center Server and the s witch must be able to exchang e
information if calls are to be successfully routed in Symposium Call Center
Server. You must ensure that this communication is enabled by configuring the
resources shared by both the switch and Symposium Call Center Server.
A Controlled Directory Number (CDN) is the initial point of entry for any call
processed in Symposium Call Center Server. A CDN serves as a holding place
while information is gathered from the call (for example, Calling Line
Identification number [CLID]) and treatments are applied to the call (for
example, recorded announcements).
For any call proces sing to be gi n in Symposi um Call Cente r Serv er, t he call must
arrive at a CDN on the switch that is controlled by Symposium Call Center
Server. Information that is gathered from the CDN and sent from the switch to
Symposium Call Center Serv er is used to enabl e Symposium Cal l Center Serv er
to define the path the call follows through the call center.
How Controlled Directory Numbers operate
A Controlled Directory Number (CDN) is a logical entity identified by a
Directory Number (DN) that holds onto calls waiting to be routed using
Symposium Call Center Server routing instructions. Symposium Call Center
Server can route calls to any local or third party with a valid address, including
agent positions and e ven other CDNs. In addition, call treatments (music, RAN,
silence, and ringback) can be applied to calls while they are waiting for
instructions from Symposium Call Center Server. Other treatments such as busy,
fast busy, and disconnect can
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 19
be applied to a call.
Page 20

Getting started Standard 1.0
For each call arriving at a CDN, the switch informs Symposium Call Center
Server of the call’s arrival and starts a timer while waiting for the routing
instructions. Th e switch h andles th e call a ccording t o the re sponse returned from
Symposium Call Center Server. If the timer expires before a response is
receiv e d, the swit ch rou te s the call to a default ACD group, which is defined for
the CDN on the switch. For more information about default ACD routing, see
“Configuring CDNs in controlled and default mode” on page 62.
ATTENTION
The timer value configured on Symposium Call Center Server
must be set to a value lower than the timer value configured on
the switch.
CDN operation is based on the existing ACD model on the switch. A CDN can
be viewed as an “ACD group” with the following characteristics:
! In the normal oper ation, the swi tch do es not cont rol the o v er flo w or rout in g
for a CDN ACDGRP. Calls in the CDN are handled by Symposium Call
Center Server.
! There are no agents or supervisors associated with a CDN.
! In the servord utility, ACD agents c annot be define d for a CDN’s
ACDGROUP.
Note: Never add options to the tables.
! There are no subgroups assigned to a CDN.
A subgroup cannot be defined for a CDN in table ACDSGRP.
! The CDN priority is set to zero.
In table DNROUTE , the priority of the primary DN and the p riority of the
secondary DN of a CDN ACDGROUP is set to zero.
! A CDN group can be defined in an NACDGRP table as a networked
acdgroup; however, the timers must be set correctly to keep the switch from
taking the call back and sending it to another switch and agent.
! The existing table ACDGRP fields, such as ACD Ring Threshold, Priority
Promotion, and Forced Night Service, are not applicable to an ACDGRP
that has the CDN option.
! A CDN does not have the following call queues: Overflow In Queue,
Overflow Out Queue, or Call Transfer Queue.
20 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 21

April 2004 Getting started
! A CDN has a default ACD group, which is datafilled on the switch.
The default ACD group is datafilled in table ACDGRP.
! A CDN can have the following states:
! Controlled
Incoming calls are handled by Symposium Call Center Server. For an
example of controlled call routing, see “Call routing in controlled and
default mode” below.
! Default
Incoming calls are routed to the default ACD group. For an example of
default call routing, see “Call routing in controlled and default mode”
below.
! Revert to Default
All incoming calls and existing calls in the CDN queues are routed to the
default AC D grou
p.
In addition , the state can be set by Symposium Call Center Server or the
switch.
! To apply MUSIC to a CDN by Symposium Call Center Server, the AUDIO
option must be datafilled in table ACDG ROUP.
! The current limit of the number of calls on a single CDN queue (DMS
switch) is 512.
Call routing in controlled and default mode
The diagram on the next page illustrates how calls can be routed in both
controlled and def aul t mode . The te xt foll o wing the illu str ation explains how the
call is processed depending on whether it i s ro uted through controlle d or default
mode.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 21
Page 22
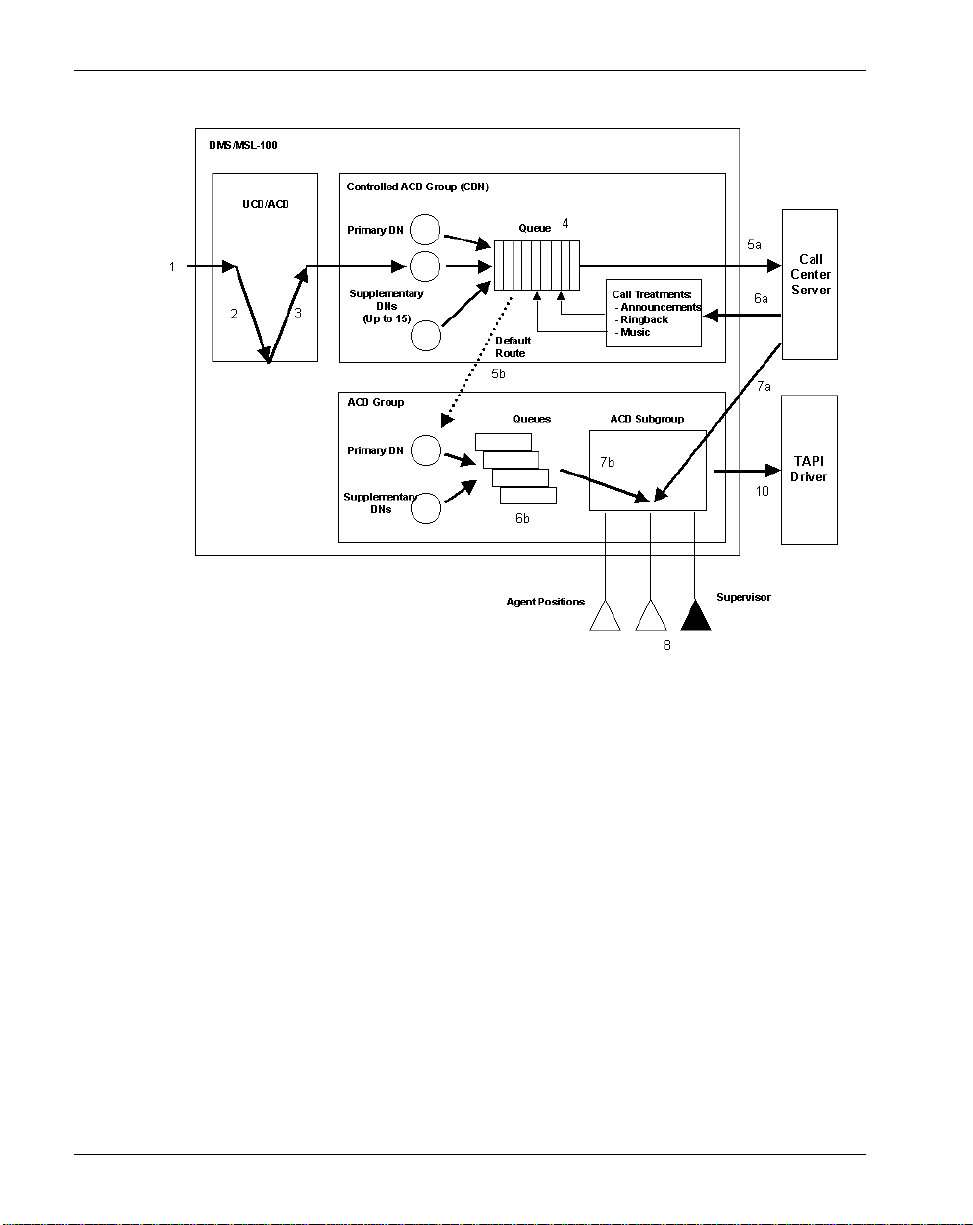
Getting started Standard 1.0
1. An incoming call arrives at the switch.
2. The call is routed to an IVR port (optional).
3. The IVR transfers the call to a CDN after the caller enters digits (optional).
4. The call is routed to an IVR port.
5. The caller receives an IVR treatment, prompting him or her to respond
through the use of phoneset keys.
6. The IVR transfers the call to a CDN after the caller enters digits.
7. The call remains queued in the CDN awaiting further call processing.
8. The switch sends a call notification to Symposium Call Center Server. The
call is routed in either of the following ways:
22 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 23

April 2004 Getting started
! If Symposium Call Center Server receives the notification, a return
notification is sent to the switch. The call remains on the CDN under the
control of Symposium Call Center Server. A call is defaulted from
Symposium Call Center Server if the specified ICCM timer (defined in
table ACDGRP in the option CDN) expired without any response from
Symposium C all Center S erver.
! If Symposium Call Center Server does not respond to the notification
due to a link or server problem, the call is routed in default mode. The
call is route d to the default ACD after the timeout expires.
9. The call follows a path as defined in either the controlled or default call
routing mode.
! In the controlled call routing mode, Symposium Call Center Server
provides treatments as spec ified in the scrip t.
! In the defaul t call routing mode, the call is removed from the queue on
the CDN, and then it is sent to the default ACD group awaiting an
available agent to answer the call.
10. The call follows a path as defined in either the controlled or default call
routing mode.
! In the controlled call routing mode, Symposium Call Center Server
routes the call to an agent qualified and available to answer the call.
! In the default call routing mode, the call is routed to an available agent
in the defaul t ACD group.
11. The call is answered by an available agent.
12. If you have purcha sed the Symposium Agent fea ture, call data sent by TAPI
enables a screen pop to appear on the agent’s screen.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 23
Page 24

Getting started Standard 1.0
Support for switch features
Introduction
This section describes features configurable on the switch, and explains how
they interact with Symposi um Call Center Server.
ACD
You must configure Automati c Call Dist rib ution (A CD) on the switch t o pro vide
default AC D routing when Symposium Call Center Server is not available. All
calls are routed by Symposium Call Center Server. If an ACD call is sent to a
group configured by Symposium Call Center Server, the priority is given to the
call that ge ts there first.
Announcements
Announcements held in Digitally Recorded Announcement Machine (DRAM)
or Enhanced Digitally Recorded Announcement Machine (EDRAM) on the
switch are supported to provide Hold in Queue announcements controlled by
Symposium C all Center S erver.
Controlled and default call routing
Incoming calls can be routed to a default ACD group in the event that
Symposium Call Center Serv er does not gain control of the calls af te r they have
been forwarded from the switch. For more information about controlled and
default call routing, see “Configuring CDNs in controlled and default mode” on
page 62.
Phoneset keys
This section describes special considerations for the use of phoneset keys.
24 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 25

April 2004 Getting started
Unsupported keys on agent phonesets
Do not configure the following keys on agent phonesets. Use of these keys
results in the incorrect a gent status on the real-time displays (RTDs):
! Hotline
! Priv a te li ne
! Voice call
! Dial Intercom
Transfers and conferences
A call is pegged as a transfer when the agent uses the Fast Transfer key. It is
pegged as a conference when the agent uses the 3-way calling (3WC) key.
Note: The transfer or conference is pegged when the agent completes the
transfer or conference by pressing the key the second time. Prior to this, RTD
displays the agent in ConsultInit status.
Secondary DN keys
An agent phoneset can contain multiple secondary DN keys. However, in this
release, Symposium Call Center Server can only monitor one DN key on each
phoneset. Therefore, Nortel Networks recommends that you configure only one
DN key on each agent phoneset.
You must add the ECM option against the secondary DN before the DN can be
acquired by Symposium Call Center Server.
Note: Symposium Call Center Server does not support multiple appearance
DNs.
Emergency key
The Emergenc y ke y ena ble s an agen t to for w ard a ca ll to h is or he r super vis or in
the event of an emergency. When an agent presses the Emergency key, the
supervisor configured as the agent’s reporting supervisor on Symposium Call
Center Server is notified. The Emergency key on the supervisor phoneset rings,
and, if the supervisor is logged on to the server, the Emergency Indicator
appears.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 25
Page 26

Getting started Standard 1.0
Once the agent has forwarded the call to his or her supervisor, the light next to
the agent’s Emergency key flashes. If the supervisor answers the call within 30
seconds, the light next to the agent’s Emergency key no longer flashes, but
remains on until the supervisor disconnects from the call.
If the reporting super vis or does not answer the cal l withi n 30 second s, t he call is
forwarded to a backup associated supervisor, if one has been configured on
Symposium Call Center Server. To enable emergency calls to be forwarded to
the associated supervisor’s phoneset, you must define the associated supervisor
as a member of a hunt group for the ACD subgroup to which the agent belongs.
The agent is disconnected from the call if either the reporting supervisor or the
associated supervisor answers within 30 seconds of the call being forwarded to
them. If neither the reporting supervisor nor the associated supervisor answers
the call within 30 seconds, the agent can press the Emergency key again to
repeat the p rocess or the agent can answer the call.
Note: The switch does not allow agents to press the Emergency key while they
are in conference with another agent.
Display Waiting Calls key
Call queuing occurs on Sympo sium Call Cent er Serv er r ather t han on th e switch ,
so the switch and ICM cannot provide meaningful call waiting statistics.
Phoneset displays
Agent and supervisor phonesets can display information such as the Calling
Line Identification (CLID) number of the caller. The information displayed on
the phoneset is not controlled by Symposium Call Center Server but must be
configured on the switch.
Skillset display on phoneset
Common Command Model (CCM)16/SCAI17 or later supports skillset name
display on the agent and supervisor phonesets. Howeve r, the phoneset will
display only the f irs t 15 c harac te rs of the s kill set na me, a nd will only displ ay the
characters A through Z, and the numbers 0 through 9.
26 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 27

April 2004 Getting started
LOB codes
Line of Business (LOB) codes, or activity codes, identify the type of call. For
example, an activity code can indicate a Sales or a Support call. To use activity
codes, you must enable the LOB feature on the switch. If you want to assign
names to the activity codes (for example Sales or Support) for reporting
purposes, you must also define the activity codes on Symposium Call Center
Server. Agents can enter up to three LOB codes during a call.
Agent actions/events DMS actions
Enters the first LOB code for the
Buffers the code.
call.
Enters another LOB code during
the same call.
Sends the first LOB code to the host.
Buffers the new code.
The call is released. Sends the pre vious ly b uffered code in
dv-LOB-Event-U message. I f no code
is buffered, no code is sent (even if a
default code was datafilled for the
ADC Group).
Cancels the last LOB code entered. Erases the code lying in the buffer.
Note: Only the last code may be
erased, and none before the last is
erased.
Does not enter any code dur ing the
entire call.
Does not send dv-LOB-Event-U
message.
Note: This action is dif ferent from the
ACD MIS that, if datafilled, reports
the default codes.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 27
Page 28

Getting started Standard 1.0
Agent actions/events DMS actions
Enters more than three LOB codes. Sends all of the entered codes to the
host.
Note: This action is different from the
ACD MIS that reports only the first
three codes.
Enters an LOB code after the caller
hangs up.
Waits for a fixed amount of time (2.5
seconds) before tearing the call. If an
agent presses th e LOB key dur ing this
interval, it waits for the agent to finish
entering the code, and then sends the
code in a dv-LOB-Event-U message.
Enters an invalid LOB code. Validates all the co des. Accepts only
the codes from ‘000’ through ‘999’
and the special code of ‘***.’ Sends
the dv-LOB-Event-U message only
for the valid codes.
Presses the LOB ke y twice in quick
succession.
Restarts the LOB feature on the
second pressing of the key.
Note: This action is different from
that of Nortel Networks’ PBX
offering for wh ich this action is a
shortcut fo r the agent to e nter the
default code.
Notes:
1. The switch does not allow agents to press the LOB key wh ile they are in
conference with another agent.
2. The server does not monitor activity codes for DN calls.
28 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 29

April 2004 Getting started
V ariable Wrap feature
When an agent releases a call, the Variable Wrap feature prevents another call
from being presented to the agent for a specific period of time. Agents can us e
this time to perform any required post-call processing. For Symposium Call
Center Server to support Variable Wrap, the feature must be configured on the
switch.
There are two options available when configuring Variable Wrap:
! If Variable Wrap is set to a v alue great er th an z ero ( 0), once an act ive call is
released, the agent is not a vailable to receive an y new calls for the length of
time specified. For example, if Variable Wrap is set to a value of 20, the
agent has 20 seconds to record call-related information before becoming
available to receive new calls.
! If Variable Wrap is set to the value zero (0), once the active call is released,
the agent immediately becomes available to receive new calls.
Note: If you do not configure Variable Wrap on the switch, the Release Guard
feature is enabled. Release Guard prevents calls from being presented to the
agent for 1 second after an active call is released.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 29
Page 30

Getting started Standard 1.0
Night service feature
Skillsets go out of service under the following conditions:
! automatically, when all agents have logged off
! manually, when you change the skillset mode on the Skillset Properties
window on the Symposium Call Center Server client
T wo out-of-servic e modes are a vai lable: tr ansition mode an d night servi ce mode.
You must put skillsets into transition mode manually. In transition mode,
Symposium Call Center Server refuses any new calls, but continues to present
queued calls to agents. When no more ca lls are waiting, the server puts the
skillset into night service mode.
Skillsets go into night service mode automatically when all agents log off; you
can also put them into night service mode manually. In night service mode, the
server refus es call s for th e ski llset, an d gives night treatment to any queued ca lls.
ATTENTION
Do not configure the ni ght se rvice key on superv isor
phonesets. Symposium Call Center Server does not support
this feature.
30 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 31

April 2004 Getting started
Preinstallation checklist
Completing a preinstallation checklist
Before attempting to configure the switch for Symposium Call Center Server,
Nortel Networks recommends that you complete a checklist of the required and
optional components for the switch, the network and router system, and the
CPE. For information about completing the checklist, refer to the example in
Appendix A, “Preinstallation checklist” on page 112.”
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 31
Page 32

Getting started Standard 1.0
Configuration tasks
Introduction
Configuration of the switch to communicate with Symposium Call Center
Server involves installing and configuring the EIU, installing and configuring
ICM, configuring the switch, and configuring Symposium Call Center Server.
Note: The rules for the EIU also apply to the 3PC card.
Before you begin
Before you begin to install and configure either the EIU or the ICM link, you
must ensure you have performe d all tasks and recorded all required information
as detailed in the following list:
! Obtain an EIU Media Access Control (MAC) address from Nortel
Networks. You can request a MAC address by e-mailing a request to Nor tel
Networks at the following ad dress:
macadd@nortelnetworks.com
! Ensure that Nortel Networks enabled the DMS feat ures for ACD routing
and the ICM link (Software Option Control [SOC]).
! Configure ACD groups and the included agents on the switch.
! Install the three required DMS EIU circuit packs.
! Datafill the DMS IP interface tables.
! Install the necessary client drivers (for example, an IVR and TAPI).
! Test the TCP/IP link between the client application and the DMS EIU
interface.
! Install all required applications (for example, IVR system and Symposium
Call Center S erver).
If your installation of Symposium Call Center Server includes a router system
and firewall, you must also complete these tasks:
! Install the network cable from the EIU to the router and firewall.
! Configure the DMS side router and firewall.
32 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 33

April 2004 Getting started
! Install the network cable from the router to the Channel Service Unit (CSU)
or any other transport device.
! Install the client CSU.
! Configure the connection between the DMS CSU and the client CSU.
! Configure the connection between the DMS CSU and the client router and
firewall.
! Configure the connection between the client router and firewall, and the
client applications (for example, IVR system, Windows 2000 Server, and
Symposium C all Center S erver).
! Configure the client-side router and firewall.
Installing and configuring the EIU
To install and configure the EIU, you must perform these tasks on the switch:
! Install the EIU on the switch.
! Confirm the EIU is present and lists all entries as dis played in tabl e
LIUINV.
! Configure an IP address for the switch in table IPNETWRK.
! Configure IP addresses for the EIU in table IPHOST.
! Configure the EIU in table IPTHRON.
For more information, refer to the Ethernet Interface Unit User Guide
(NTP 297-8991-910) and the ICM Router Guide (NTP 297-2233-903).
Installing and configuring ICM
To install and configure ICM, you must ensure that the following tasks have
been performed on the switch:
! Install ICM on the EIU.
! Configure the office parameters in the following table:
OFCENG Allocates resources for switch activiti es.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 33
Page 34

Getting started Standard 1.0
OFCOPT Categorizes ICM messages in groups (this table is
maintained by Nortel Networks ).
Note: For ICM CCM010 (SCAI12), do not enable the
Network_ICM_Active feature.
OFCVAR Contains the operating parameters that the operating
company can change.
34 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 35

Chapter 2
Configuring the switch
In this chapter
Overview 36
Section A: Configuring the ICM link parameters 37
Section B: Configuring switch resources 53
Section C: Checking the server configuration 79
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 35
Page 36

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Overview
This chapter provides procedures for configuring the switch to work with
Symposium Call Center Server. It assumes that the switch is running software
load CCM010/SCAI12 or later; an EIU has been provisioned for the ICM link;
and the ICM software is load ICM00001 or higher.
36 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 37

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Section A: Configuring the ICM link
parameters
In this section
Overview of configuring the server logon 38
Configuring SCAICOMS 43
Configuring BGDATA 44
Configuring SCAIGRP 46
Configuring SCAISSRV 47
Configuring SCAIPROF 49
Configuring CUSTNTWK 51
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 37
Page 38

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Overview of configuring the server logon
Introduction
Symposium Call Center Server must log on to the switch using an ICM linkset
before it can acquire switch r esour ces and exchange messages. Up to 96 linksets
can be configured on each switch. A linkset can only be associated with one
installation of Symposium Call Center Server. Similarly, Symposium Call
Center Server can only be associated with one linkset to the switch. To allow
Symposium Call Center Server to log on to the switch, you must configure the
following tables on the switch:
SCAICOMS Defines linkset names and assigns them to the appropriate
hardware device. This enables a logical pathway through the
EIU to Symposium Call Center Server.
BGDATA Allows mu ltiple switches to share MDC features. This table
associates a business group ID (BGID) with a customer group.
SCAIGRP Associates a business group ID for a customer group with a
linkset. The parameters specified allow Symposium Call
Center Server to log on to the switch.
SCAISSRV Defines a series of profiles for ICM messages, and what
information is included in the messages.
SCAIPROF Assigns services to Symposium Call Center Server by
associatin g them with a linkset.
CUSTNTWK Assigns a network ID to your organization’s network. The
network ID identifies your organization’s network within the
telephony environment.
Before you begin
Before you perform this procedure, log on to the switch from a Maintenance
Administration Positi on (MAP) terminal with a u ser ID that has the privilege
levels required to ch ange these ta bles.
38 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 39

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Configuring ICM security
In order to establish a secure ICM session, you must configure the following
parameters on the switch:
! Linkset name
This is the u ser-defined name for the server in Symposium Call Center
Server as it is known to the switch. The linkset name creates a logical
pathway to the server on the EIU. The linkset name is configured in table
SCAICOMS. For information on the linkset name and other parameters
that can be configured in table SCAICOMS, see “Configuring
SCAICOMS” on page 43.
! Remote host IP address
The remote host IP a ddress entered must matc h the IP address of th e s erver
in Symposium Call Center Server on th e ELAN. The remote host I P
address is configured in table SCAICOMS. For information on the remote
host IP address and other parameters that can be configured in table
SCAICOMS, see “Configuring SCAICOMS” on page 43.
! Linkset password
The security feature, along with a valid user ID, enables a user to log on to
the switch. Customers assign passwords. The Linkset password is
configured in table SCAIGRP. For information on the Linkset password
and other parameters that can be configured in table SCAIGRP, see
“Configuring SCAIGRP” on page 46.
For information on firewalls and packet filtering, see the ICM Router
Guide.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 39
Page 40

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Configuring logon
The following illustration displays the tables you must update to allow
Symposium Call Center Server to log on to the switch. The illustration displayed
is an example. Data varies depending on the specific conditions of your call
center.
SCAISSRV
SUBSERV
CTXEVENT10$
ACDEVENT11$
.
.
.
SCAIPROF
PROFKEY PROFILE
BESTAIRTOR1 11 (CTXEVENT10$) (ACDEVENT11$)
(ACDEVENT11$) (TPCC09$) (RESOURCE11$)
(TPAC36$) (SCAI3WC09$) (DNQUERY07$)
(TPQC10$) (ICCM10$)
SCAICOMS
LINKSET SCAILNKS (IP address of the server)
BEST AIRT OR1 TCP 50.100.77.65
CUSTENG
CUSTNAME
BESTAIR
CUSTNTWK
CUSTNAME NETNAME NETCGID OPTIONS
BESTAIR PUBLIC 50$ (CLID OFFNET) (ECM) $
BGDATA
BGID OPTIONS
LOCAL 5 $ (CUSTGRP BESTAIR N 10 Y 0 0 ) $
SCAIGRP
SCAIGNAM PASSWORD NETNODID BGID OPTIONS
BESTLOGIN1 BESTPWD 50 LOCAL 5 (LINKSET BESTAIRTOR1)
G101335
40 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 41

April 2004 Configuring the switch
The following illustration sh ows th e relationships between the parameters in
these tables:
SCAISSRV
SUBSERV
CTXEVENT10$
ACDEVENT11$
.
.
.
SCAICOMS
LINKSET SCAILNKS (IP address of the server)
BESTAIR T OR1 TCP 50.100.77.65
CUSTENG
CUSTNAME
BESTAIR
Customer group name
Service Service
Linkset name
SCAIPROF
PROFKEY PROFILE
BESTAIRTOR1 11 (CTXEVENT10$) (ACDEVENT11$)
(ACDEVENT11$) (TPCC09$) (RESOURCE11$)
(TPAC36$) (SCAI3WC09$) (DNQUERY07$)
(TPQC10$) (ICCM10$)
CUSTNTWK
CUSTNAME NETNAME NETCGID OPTIONS
BESTAIR PUBLIC 50$ (CLID OFFNET) (ECM) $
BGDATA
BGID OPTIONS
LOCAL 5 $ (CUSTGRP BESTAIR N 10 Y 0 0 ) $
SCAIGRP
SCAIGNAM PASSWORD NETNODID BGID OPTIONS
BESTLOGIN1 BESTPWD 50 LOCAL 5 (LINKSET BESTAIRTOR1)
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 41
Customer group ID
Linkset
name
G101336
Page 42

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
To enter and edit data in the tables
If you have entered an incorrect parameter in a table, you can change the
parameter without discarding the parameters that have been entered correctly.
To change an incorrect parameter.
1 Access the table for which you want to edit the incorrect parameter by
typing table <table name> at the prompt (>), and then press Enter.
2 Type CHA at the prompt, and then press Enter. This allows you to step
through each parameter in the table.
3 If each parameter is correct, press Enter. If not, edit the parameter, and
then press Enter.
4 Continue to press Enter until the prompt appears before the incorrect
parameter.
5 Delete the incorrect parameter and enter the correct parameter.
6 To save the changes, type quit, and then press Enter.
7 Press Enter to exit the table.
Printing data in the tables
You might want to refer to inf ormati on conf igured in the serv er log on tables. F or
example, you might w ant to identify, as part of the project management function,
information such as ACDGRP information, RAN and music routes, and
threshold s routes. Prin t a hard copy of this information during configuration of
the switch to quickly be ab le to referenc e the informati on if you intend to modi fy
the configuration parameters at a later date.
42 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 43

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Configuring SCAICOMS
Introduction
Table SCAICOMS defines linkset names and assigns them to the appropriate
hardware de vice. This ena bles a logical pat hway th rough the EIU to Symposi um
Call Center Server.
To update table SCAICOMS
1 Edit the SCAICOMS table by typing table SCAICOMS and pressing Ente r.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 Type add and press Enter.
Result: The LINKSET prompt appears.
3 For LINKSET, type a name for the server in Symposium Call Center Server
as it is known to the switch, then press Enter. The LINKSET name creates
a logical pathway to the server on the EIU.
Result: The LINKSEL prompt appears.
4 Identify the connection type as TCP and press Enter.
Result: The IP_ADDR prompt appears.
5 The IP address entered must match the IP address of the server in
Symposium Call Center Server on the ELAN. To obtain the IP address of
the server in Symposium Call Center Server, follow the procedure in
“Checking the server configuration” on page 81.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new linkset.
6 Type Y and press Enter.
7 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 43
Page 44

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Configuring BGDATA
Introduction
T able BGDATA allows you to configure multiple switches so that they can share
MDC features. This table associates a business group ID (BGID) with a
customer group. A business group is an entity that represents your organization
on the switch.
Note: In CCM010/SCAI12, the switch network ID is used as the node ID.
To update table BGDATA
1 Edit the BGDATA table by typing table BGDATA and pressing Enter.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 Type add and press Enter.
Result: The BGID prompt appears.
3 Type the Business Group ID, in the format LOCAL GRPNUM, and pres s
Enter.
Result: The BGXLA prompt appears.
4 Type $ and press Ente r.
Result: The OPTIONS prompt appears.
5 Type CUSTGRP and press Enter.
Result: The CUSTGRP prompt appears.
6 Type the name of your customer group and press Enter.
Result: The MBG prompt appears.
7 Type n and press Enter.
Result: The NUMLINES prompt appears.
8 Type 0 (zero) and press Enter.
Result: The INTRAGRP prompt appears.
9 Type y and pres s Ente r.
44 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 45

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Result: The LSCFN prompt appears.
10 Type $ and press Enter.
Result: The LCSINCPT prompt appears.
11 Type 0 (zero) and press Enter.
Result: The OPTION prompt appears.
12 Type 0 (zero) and press Enter.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new business group ID.
13 Type Y and press Enter.
14 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 45
Page 46

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Configuring SCAIGRP
Introduction
Table SCAIGRP associates a business group ID for a customer group with one
or more linksets. Each group is given a password, network node ID, links et , and
an associa ted BGID. Th ese parameters allow Symposium Call Center Server to
log on to the switch.
To update table SCAIGRP
1 Edit the SCAIGRP table by typing table SCAIGRP and pressing Enter.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 Type add and press Enter.
Result: The SCAIGNAM prompt appears.
3 Enter the SCAIGRP name.
Result: The PASSWORD prompt appears. For more information, see,
“Switch Password” on page 85.
4 Enter the password that Symposium Call Center Server uses to log on to
the switch.
Result: The NETNODID prompt appears.
5 Enter the customer network ID that you defined in table CUSTNTWK.
Result: The BGID prompt appears.
6 Enter the business group ID that you defined in table BGDATA.
Result: The OPTIONS prompt appears.
7 Configure the following option for Symposium Call Center Server:
Option Value
LINKSET The linkset name defined for the server in table SCAICOMS.
You must type $ after the last linkset name for the group.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new configuration.
8 Type Y and press Enter.
9 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
46 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 47

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Configuring SCAISSRV
Introduction
Table SCAISSRV defines a series of profiles for ICM messages, and specifies
what information is includ ed in th e mess ages. The switch m ak es thes e mes sages
available to Symposium Call Center Server.
The table below indicates the default configuration of table SCAISSRV. Nortel
Networks recommends that you use the default configuration for Symposium
Call Center Server.
Note: If yo u edit the parameters in table SCAISSRV, you must restart
Symposium Call Center Server for the ch anges to take e ffect. You ca nnot make
any changes to the default services (any service with a $ at the end). You must
build custom services to make the changes you require.
SUBSERV SPROFILE
ACDEVENT11$ ACDEVENT (CALLQ UED Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y ) (CALLOFFR Y Y Y
Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y) (CALLANSWR Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Y) (CALLREL Y Y Y Y Y)
(AGTLGDIN Y Y Y) ( AGTLGDOUT Y Y) (AGTREADY Y
Y)
(AGTNREAD Y Y Y N) (LOBEVENT Y Y Y) (EMKEVENT
Y Y Y Y Y Y)$
CALLINIT07$ CALLINIT (MAKECALL Y Y )$
CTXEVENT10$ CTXEVENT (SETOFFHK Y Y ) (CALLOFFR Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Y Y)
(CALLANSWR Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y) (CALLREL
Y Y Y) (CALLNAME Y Y Y Y Y)$
DNQUERY07$ DNQUERY (DNQUERY Y)$
ICCM10$ ICCM (SETCDNST )$
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 47
Page 48

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
SUBSERV SPROFILE
RESEVENT10$ RESEVENT (SETOFFHK Y Y ) (CALLOFFR Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Y Y)
(CALLANSWR Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y) (CALLREL
Y Y Y) (CALLNAME Y Y Y Y Y)$
RESOURCE11$ RESOURCE (ACDQUERY ) (APPSTQRY Y Y Y Y Y)$
ROUTING35$ ROUTING (CALLRECDC Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y) (CALLREDIR Y Y
Y)$
SCAI3WC09$ SCAI3WC (CONSULTEV Y) (CONFEVNT Y) (TRANSFEREV Y)
(ADDPT Y Y Y Y) (CONFPTY Y) (DROPPTY Y Y)
(TRANPTY Y)$
SCAICC08$ SCAICC (ANSWCALL ) (RELSCALL Y) (HOLDCALL )
(UNHOLDCALL ) (CALLUNHELD Y)$
SCAIMWTI07$ SCAIMWTI (MSGWAIT Y Y Y)$
TPAC36$ TPAC (LOGINAGT Y Y N) (LOGOUTAGT Y) (READYAGT Y)
(NREADYAGT Y N)$
THIRDPTY$ TPAC ( ADDPTY Y Y Y) (DROPPTY Y Y) (MAKECALL YY)$
TPCC09$ TPCC (ANSWCALL ) (RELSCALL Y) (CONSULTEV Y)
(CONFEVNT Y) (TRANSFEREV Y) (HOLDCALL )
(UNHOLDCALL ) (CALLUNHELD Y) (ADOPTY Y Y Y)
(CONFPTY Y) (DROPPTY Y Y) (TRANPTY Y)
(MAKECALL Y Y)$
TPCC11$ TPCC (CONSULTEV Y) (CONFEVNT Y) (TRANSFEREV Y)
(ANSWCALL) (RELSCALL Y) (HOLDCALL)
(UNHOLDCALL) (CALLUNHELD Y) (ADOPT Y Y Y Y
Y) (CONFPTY Y) (DROPPTY Y Y) (TRANPTY Y)
(MAKECALL Y Y)$
TPQC10$ TPQC (ROUTECALL) (GIVETRMT) (TRMTCOMP)$
48 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 49

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Configuring SCAIPROF
Introduction
Table SCAIPROF defines the types of information sent by the switch to
Symposium C all Center S erver.
Note: If yo u edit the para meters in table SCAIPROF, you must r estart
Symposium C all Center Server for the changes to take effect.
To update table SCAIPROF
1 Edit the SCAIPROF table by typing table SCAIPROF and pressing Enter.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 Type add and press Enter.
Result: The utility prompts for the LINKSET.
3 Enter the linkset name from table SCAICOMS.
Result: The utility prompts for the SRVCID.
4 Enter the Service ID. For more information, see “Service ID” on page 85.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 49
Page 50

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
5 Respond to the prompts to create the group. The following prompts require
special values for use with Symposium Call Center Server:
Prompt Value
PROFKEY Enter the linkset name and service ID.
PROFILE CTXEVENT10$ (to support secondary DN keys)
PROFILE ACDEVENT11$ (to support ICM)
PROFILE ROUTING35$
PROFILE TPCC11$ (to allow Symposium Call Center Server to transfer
calls)
PROFILE RESOURCE11$ (to support status messages)
PROFILE TPAC36$ (to support agent logon/logoff, make ready/not
ready, walkaway codes)
PROFILE CALLINIT07$
PROFILE SCAI3WC09$ (to allow monitoring of secondary DN keys for
transfer and conference s)
PROFILE DNQUERY07$ (to report the state of secondary DN keys)
PROFILE SCAICC08$ (to release or answer calls on the secondary DN)
PROFILE TPQC10$ (to support call treatments)
PROFILE ICCM10$ (to support CDNs and call routing)
When you finish entering responses, type $. For information about the
prompts, refer to the Translations Guide.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new configuration.
6 Type Y and press Enter.
7 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
50 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 51

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Configuring CUSTNTWK
Introduction
The table CUSTNTWK assigns a net w ork ID to a customer group. The network
ID identifies your organization’s network within the telephony environment.
Follow the procedure in this section to configure the ECM option.
Before you begin
Ensure that the network name is defined in table NETNAMES.
To configure the ECM option
1 Edit the CUSTNTWK table by typing table CUSTNTWK and pressing
Enter.
2 Type $ and press Ente r.
Result: The OPTIONS prompt appears.
3 You must add ECM to the last entry.
4 Set the following option for use with Symposium Call Center Server:
Option Description
ECM This option configur es the network to rec eiv e SCAI message s
from the switch.
5 Type Y and press Enter.
6 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 51
Page 52

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
52 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 53

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Section B: Configuring switch resources
In this section
Overview of configuring switch resources 54
Configuring RAN and music routes 56
Configuring ACD groups 57
Configuring ACD subgroups 65
Configuring DNs 66
Configuring agent phonesets 69
Configuring supervisor phonesets 74
Configuring logon IDs 76
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 53
Page 54

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Overview of configuring switch resources
Introduction
You must ensure that the following resources are correctly configured on the
switch:
! RAN and music routes
! ACD groups and subgrou ps
! hunt groups
! directory numbers (DNs)
! agent phonesets
! agent logon IDs
Note: The resources configured on the switch must have matching data
configured on Sympo sium Call Center Ser ver. If, at an y time, y ou edit an y of th e
data on Symposium Call Center Server, you must reconfigure the resource on
the switch.
Configuring the switch to communicate with Symposium Call Center
Server
To enable Symposium Call Center Server to communicate with the switch,
perform the following tasks on the switch:
! Configure the switch to enable it to connect with the server. This involves
datafilling the following tables: SCAICOMS, SCAISSRV, SCAIPROF,
CUSTNTWK, BGDATA, and SCAIGRP.
! Configure recorded announcements (RANs) and music routes.
! Configure ACD groups. Each Controlled Directory Number (CDN),
primary or supplementary ACD-DN, and phoneset must be assigned to an
ACD group.
! Configure ACD subgroups. You can use subgroups to divide agents into
smaller groups for sup por t and mon it ori ng. Ea ch sub g ro up ca n be assigned
a supervisor.
54 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 55

April 2004 Configuring the switch
! Configure each CDN to be acquired by the server and each primary or
supplementary ACD-DN to be monitored by the server.
! Configure the phonesets to be acquired and monitored by the server.
! Configure the logon IDs that agents and supervisors use to log on to their
phonesets (this is only required if it is required by the office parameters).
Configuring the server
To configure Symposium Call Center Server to acquire and monitor switch
resources, you must perform these tasks from the System window on the client:
! Configure and acquire CDNs.
! Configure and acquire phonesets.
! Configure RAN and music routes.
! Configure Di aled Number Identificatio n Services (DNISs) that you want
the server to monitor.
! Configure agents and supervisors.
For detailed i nstruc tions , refer to the Admi nistr at or’s Guide. If you are using the
Symposium Web Client, refer to the Symposium Call Center Web Client Guide
and online Help for detailed instructions.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 55
Page 56

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Configuring RAN and music routes
Introduction
You can use RAN and music routes t o pro vide feedba ck to c aller s whil e the y ar e
waiting in queue. You might want to configure a RAN informing callers of the
amount of time they can expect to remain in que ue b ef ore their call is a nswe re d.
While they wait in queue, you can define a specific type of music that they hear.
Configuration of RAN and music routes involves the following tasks:
1. Define trunks to be used for music and RAN in table CLLI (Common
Language Locator Identifier).
2. Define RAN circuits in table DRAMS (Digitally Recorded Announcement
Machine).
3. Configure announcements and music in table ANN.
4. Associate announcements and musi c wi th t runk cards in table ANNMEMS.
5. Record announcements with the DRAMREC utility.
6. Define treatments in table AUDIO.
Note: Table AUDIO defines audio routes available for broadcast for ACD
groups. If you use a GIVE RAN or a GIVE MUSIC command in a script,
you must include a parameter specified in the AUDIO table.
7. Associate treatments with routes in table OFRT (office route) or IBNRTE.
Assign the ACDQ parameter to routes you w ant to make available to
Symposium C all Center S erver.
8. Associate routes with ACD groups in table ACDGRP.
9. Define overflow treatments in table A CDRTE. (This is not requir ed for call
center functionality. It is only required for enhanced default routing).
For detailed i nstructions, see the Translations Guide.
56 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 57

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Configuring ACD groups
Introduction
An ACD grou p is a l ogical group that contai ns a set of prima ry or sup plementary
ACD-DNs, phonesets, and agents. You must create at least two types of ACD
groups—one for the CDNs acquir ed b y Symposium Cal l Center Ser ve r, and one
for phonesets and agents.
If you want to prevent calls from immediately being presented to agents after
they release a call, you can configure options such as Variable Wrap or Not
Ready on Secondary DN for an ACD group.
Notes:
1. Alternatively, you can configure the Variable Wrap or Not Ready on
Secondary DN options for groups.
2. Do not configure the night service option for your ACD groups.
Note: An agent can log on t o any phoneset pr ovid ing th at he or s he enter s a v alid
logon ID. However, to ensure that the agent can use all of the key-enabled
features av aila ble, the agent mus t log on to the phone set that has be en confi gured
as his or her unique Positi on ID. F or re porti ng purpos es, an agent must log on to
a phoneset configured as part of the ACD group to which the agent belongs.
Before you begin
Before you perform this procedure, you must perform the following tasks:
! Log on to the switch from a MAP terminal with a user ID that has the
privilege levels required to change the ACDGRP tables.
To configure ACD groups for the CDN
1 Edit the ACDGRP table by typing table ACDGRP and pressing Enter.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 Type add and press Enter.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 57
Page 58

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Result: The ACDNAME prompt appears.
3 Enter a name for the ACD group.
Result: The utility prompts you for the CUSTGRP.
4 Enter a name for the customer group of the ACD-DN.
Result: The utility prompts you for the ACDRNGTH.
5 Enter a valid value. (The default value is 0.)
Result: The utility prompts you for the THROUTE.
6 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the NSROUTE.
7 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the PRIOPRO.
8 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the DBG.
9 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the MAXCQSIZ.
10 Enter a value between 0–511.
Note: Nortel Networks recommends you use a number around 511 for
CDNs. For acdgroups, you can use a number based on the number of
agents and the hold time you want.
Result: The utility prompts you for the MAXWAIT.
11 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the ACDMIS.
12 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the MSQS.
13 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the DISTRING.
14 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the OBSWTONE.
15 Enter a valid value.
58 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 59

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Result: The utility prompts you for the FRCNGTSV.
ATTENTION
Do not set this value for the CDN.
16 Enter a valid value.
Result: The OPTION prompt appears.
17 Enter a valid CDN.
Result: The DEFAULTGRP prompt appears.
18 Enter the name of the ACD group to which calls are sent when Symposium
Call Center Server is not responding.
Result: The RESPTM prompt appears.
19 Enter the time, in seconds, that elapses before calls are sent to the default
ACD group when Symposium Call Center Server is not responding. Nortel
Networks recommends that you enter a value of 60 seconds.
20 The NETICM prompt appears.NETICM must be defined for use with
CCM010/SCAI12 and subsequent versions. This causes the ACD to use
the node ID defined on the switch, rather than the business group ID
defined in BGDATA, to identify calls.
CAUTION
Risk of malfunction
.
Do not use this option unless you are using a network ACD.
Network ACDs are not supported by Symposium Call Center
Server. If you use a network ACD, the switch will take the call and
send it to an agent on another switch.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new ACD group.
21 Type Y and press Enter.
22 Repeat steps 2 through 21 for each ACD group of this type that you want to
create.
23 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 59
Page 60

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
To configure ACD groups for ACD-DNs, phonesets, and agents
Note: Any modifications to the ACDGRP table must be applied to the default
ACD group, not the CDN.
1 Edit the ACDGRP table by typing table ACDGRP and pressing Enter.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 At the > prompt in the ACDGRP table, type add and press Enter.
Result: The utility prompts you for the ACDNAME.
3 Enter a name for the ACD group.
Result: The utility prompts you for the CUSTGRP.
4 Enter a name for the customer group of the ACD-DN.
Result: The utility prompts you for the ACDRNGTH.
5 Enter a valid value.
Note: The timer value configured on Symposium Call Center Server must
be set to a value lower than the timer value configured on the switch.
Result: The utility prompts you for the THROUTE.
6 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the NSROUTE.
7 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the PRIOPRO.
8 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the DBG.
9 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the MAXCQSIZ.
10 Enter a value between 0–511.
Result: The utility prompts you for the MAXWAIT.
11 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the ACDMIS.
12 Enter a valid value.
60 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 61

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Result: The utility prompts you for the MSQS.
13 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the DISTRING.
14 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the OBSWTONE.
15 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the FRCNGTSV.
16 Enter a valid value.
Result: The utility prompts you for the AGTASSN.
17 Enter a valid value. This is required for ICM.
Result: The FORCING prompt appears. Forcing is an option that is not
datafilled unless you are using it in the existing ACD groups.
18 Set FORCING to NONE.
Result: The VARWRAP prompt appears.
19 When an agent releases a call, the Variable Wrap feature prevents another
call from being presented to the agent for a specific period of time. You
must select the Variable Wrap feature and define TIMER (the length of the
wrap period) in seconds.
If TIMER is set to a value greater than 0, once an active call is released, the
agent is not available to receive any new calls for the length of time
specified.
If TIMER is set to the value 0, once the active call is released, the agent
immediately becomes available to receive new calls.
If you do not configure Variable Wrap on the switch, the Release Guard
feature is enabled. Release Guard prevents calls from being presented to
the agent for 1 second after an active call is released.
Result: The NRONSDN prompt appears.
20 Select this option if you do not want Symposium Call Center Server to
present calls to agents who are active on their secondary DN. The server
can only acquire and monitor one secondary DN on each phoneset.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new ACD group.
21 Type $ to end the datafill for the group.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 61
Page 62

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
22 Type Y to save the TUPLE and press Enter.
23 Repeat steps 2 through 21 for each ACD group of this type that you want to
create.
24 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
Configuring CDNs in controlled and default mode
Table ACDGRP defines an ACD group’s configuration and the options
associated with the group. Table ACDGRP must be changed to add the CDN
option. The CDN option is used to ind icate a contro lled DN tha t holds incoming
calls that are routed by Symposium Call Center Server. Also, the default ACD
group and the ICCM_RESP timer are suboptions of the CDN option.
When the CDN is in the CONTROLLED state, the switch does not control the
Audio, Overflow, or Routing for a CDN ACDGRP. Calls in the CDN are
handled by Symposium Call Center Server. The existing ACDGRP fields, such
as ACD Ring Threshold, Priority Promotion, and Forced Night Service, are not
meaningful with an ACDGRP that has the CDN option.
You must ensure that the relevant ACD ring thresholds in the ACD group table
are set to 0. When you set the ACD ring threshold to 0, the system is able to
redirect calls that are not answered quickly enough to another agent. Calls in an
ACD group are based on the AC D routing table on the switch. If you do not set
the ACD ring threshold to 0, the call might be terminated.
The following table shows all of the fields in table ACDGRP and whether the
fields are applicable for a CDN. The fields that are not valid for a CDN
ACDGRP can be datafilled in table ACDGRP, but are not used.
Brief descriptions
(default value for CDN
Field name
CUSTGRP TYPE IS
ACDRNGTH any valid entry (for
62 Symposium Call Center Server
ACDGRP)
ACD_RING_THRESHOL
D {0 to 60}
example, OFRT 1)
Validity for a
CDN
ACDGRP
Y
N
Page 63

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Brief descriptions
(default value for CDN
Field name
THROUTE any valid route (for
NSROUTE any valid route (for ex ample
PRIOPRO 0 N
DBG N N
MAXCQSIZ 0-511
MAXWAIT 0 N
ACDMIS N Y
MSQS N N
DISTRING NONE N
OBSWTONE N N
ACDGRP)
example, OFRT 1)
OFRT 1)
CDN queue size
Validity for a
CDN
ACDGRP
N
N
Y
FRCNGTSV N N
The followi ng ta ble sh o ws all o f the optio ns in ta ble ACDGRP and whether they
are compatible for a CDN:
Compatible
with CDN
ACDGRP Option
AUDIO N
NARS N
MAXCQLMT N
ACDPSAP N
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 63
(Y/N)
Page 64

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Compatible
with CDN
ACDGRP Option
SCAIREDIR N (only compatible for redirection)
OVFLINQ N
TMDELOFL N
ACDDISP N
MGTRPT N
ACDADMIN N
QSL N
NRONSDN N
ACDCPK N
ORGANN N
(Y/N)
FORCING N
VARW RAP N
TIMECXR N
NONIMCUT N
ACDXFER N
OBSREST
3OVNS
QTOMSB
N
N
N
Table ACDRTE defines the enhanced overflow routes that a group can take. It
also defines t he audio tr eatments t hat A CD g roups use. The ro utes de fined f or an
ACD group in table ACDRTE are not applied for calls in the CDN.
64 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 65

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Configuring ACD subgroups
Introduction
You can use subgroups to divide agents into smaller groups for support and
monitoring. Assign a superviso r to each subgroup. The super visor must log on at
the phoneset in that subgroup that is configured as the supervisor phoneset.
Before you begin
Before you perform this procedure, you must complete the following tasks:
! Log on to the switch from a MAP terminal with a user ID that has the
privilege levels required to change the ACDGRP table.
! Define the ACD group to which the ACD subgroup belongs in table
ACDGRP (see “Configuring ACD groups” on page 57).
To configure ACD subgroups
1 Edit the ACDSGRP table by typing table ACDSGRP and pressing Enter.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 Type add and press Enter.
Result: The ACDNAME prompt appears.
3 Enter the name of the ACD group to which this subgroup belongs.
Result: The utility prompts for the subgroup number.
4 Enter the number of the subgroup.
5 Continue responding to the prompts to define the subgroup. (For more
information about the prompts, see the Translations Guide.)
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new ACD subgroup.
6 Type Y and press Enter.
7 Repeat steps 2 through 6 for each subgroup that you want to define.
8 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 65
Page 66

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Configuring DNs
Introduction
In table DNROUTE, you must configure each of the Controlled Directory
Numbers (CDNs) that Symposium Call Center Server monitors. You must also
configure any ACD-DNs and supplementary DNs that you are using.
In the event that Sym posium Call Center Server is unable to h andle calls,
ACD-DNs provide a backup call distribution system to route calls.
Note: Supplementary DNs are usually used for 1-800 numbers.
Before you begin
Before configuring DNs, you must perform the following tasks:
! Log on to the switch from a MAP terminal with a user ID that has the
privilege levels required to change the DNROUTE table.
! Define the ACD group to which the DNs belong in table ACDGRP (see
“Configuring ACD groups” on page 57).
! Define the are a code (SPA) and exchange (office code) in table
TOFCNAME (see the Translations Guide).
To config ure a CD N
1 Edit the DNROUTE table by typing table DNROUTE and pressing Enter.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 Type add and press Enter.
Result: The AREA prompt appears.
3 Enter the area code for the CDN.
Result: The OFC prompt appears.
4 Enter the office code for the CDN.
66 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 67

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Result: The STAT prompt appears.
5 Enter the remainder of the directory number for the CDN.
Result: The DN_SEL prompt appears.
6 Type FEAT and press Enter.
Result: The FEATURE prompt appears.
7 Type ACD and press Enter.
Result: The ACDGRP prompt appears.
8 Type the name of the ACD group you defined for this CDN in table
ACDGRP and press Enter.
Result: The DNTYPE prompt appears.
9 If you are assigning the first DN to the group, type PRIM and press Enter.
You must define all other DNs as SUPP.
Result: The TRUNK prompt appears.
10 Type 0 (zero) and press Enter.
Result: The LINE prompt appears.
11 Type 0 (zero) and press Enter.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new CDN.
12 Type Y and press Enter.
13 Repeat steps 2 through 12 for each CDN that you want to define.
14 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
To config ure an ACD-DN or supplementary DN
1 Edit the DNROUTE table by typing table DNROUTE and pressing Enter.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 Type add and press Enter.
Result: The DN prompt appears.
3 Enter the DN for the ACD-DN or supplementary DN.
Result: The DN_SEL prompt appears.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 67
Page 68

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
4 Type FEAT and press Enter.
Result: The FEATURE prompt appears.
5 Type ACD and press Enter.
Result: The ACDGRP prompt appears.
6 Continue responding to the prompts to define the ACD-DN or
supplementary DN. (For more information about the prompts, see the
Translations Guide.) To define an ACD-DN, at the DNTYPE prompt, type
PRIM. To define a supplementary DN, at the DNTYPE prompt, type SUPP.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new ACD-DN or supplementary
DN.
7 Type Y and press Enter.
8 Repeat steps 2 through 7 for each ACD-DN that you want to define.
9 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
Configuring CDNs on the server
CDNs configured on the switch must have matching data configured on
Symposium Call Center Server. If, at any time, you edit any of the data on
Symposium Call Center Server, you must reconfigure the resource on the
switch. For more information, refer to the Administrator’s Guide. If you are
using the Symposium Ca ll Center Web Client, refer to the Symposium Call
Center Web Client Guide and online Help for detailed instructions.
Note: If you intend to reconfigure a CDN, you must first deacquire the CDN,
edit the configuration parameters, and then reacquire the CDN.
Configuring DNISs on the server
If you want Symposium Call Center Server to report on calls to your primary
and supplementary ACD-DNs, you must configure them as Dialed Number
Identifi cat ion Services (DNISs) o n t h e ser ver. For more information, refe r t o the
Administrator’s Guide. If you are using the Symposium Call Cente r Web Client,
refer to the Symposium Call Center Web Client Guide and online Help for
detailed instructions.
68 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 69

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Configuring agent phonesets
Introduction
You must configure e ach phoneset that Symposium Call Center Server acquires.
The server must acquire phonesets so that it can
! monitor the status of each phoneset
! present calls to each phoneset
Phoneset keys
An agent can log on to an y phonese t pro viding that he or s he enters a va lid logon
ID. However, to ensure that the agent can use all of the key-enabled featur es
available to him or her, the agent must log on to the phoneset that has been
configured as his or her unique Position ID.
Note: For reporting purposes, an agent must log on to a phoneset configured as
part of the ACD group to which the agent belongs.
The following ta ble lists special considerations for ag ent phoneset keys when
you are using Symposium Call Center Server:
3-Way
Conference
Fast
Transfer
A call is pegged as a conference when the agent presses the 3WC
key, and then co mpletes the c all.
A call is peg ged as a t ransfer when the a gent u ses the F ast Transfer
key, and then co mpletes the c all.
DN The Secondary DN key is usually used for personal calls.
Symposium Call Center Server can only acquire and monitor one
secondary DN on each agent phoneset.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 69
Page 70

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Line of
Business
Symposium Call Center Server can report on the time agents
spend on different types of calls. To use this feature, you must
enable the LOB feature on the switch, and def ine all acti vit y codes
on Symposium Call Center Server. When you define activity
codes on the server, it allows you to give useful names to the
activity codes (for example, Sales or Support) for reporting
purposes.
Not Ready Nortel Networks r ecomme nds tha t you co nf i gure a Not Ready ke y
on the phoneset. If you do not do this, Symposium Call Center
Server cannot report when the agent is in Not Ready status. Agents
can use the Not Ready key in conjunction with an activity code to
indicate the reason they are in Not Ready status.
Emergency
Key
To enable the emergency screen pop on the supervisor’s
workstation, configure EMK for Position ID instead of DN. When
an agent presses the Emergency key, Symposium Call Center
Server uses the Position ID to identify the correct supervisor.
Dial
Intercom
Nortel Networks recommends that you do not configure this key
on the agent phoneset. If agents use this key, the agent status is
incorrectl y reported on the real-tim e display.
Hotline Nortel Networks recommends that you do not configure this key
on the agent phoneset. If agents use this key, the agent status is
incorrectl y reported on the real-tim e display.
Private
Line
Nortel Networks recommends that you do not configure this key
on the agent phoneset. If agents use this key, the agent status is
incorrectl y reported on the real-tim e display.
Voice Call Nortel Networks recommends that you do not configure this key
on the agent phoneset. If agents use this key, the agent status is
incorrectl y reported on the real-tim e display.
Before you begin
Before configuring a phoneset, you must perform the following tasks:
! Log on to the switch from a MAP terminal with a user ID that has the
privilege levels required to access the SERVORD utility.
70 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 71

April 2004 Configuring the switch
! Define the ACD group to which the agent phoneset belongs in table
ACDGRP (see “Configuring ACD groups” on page 57).
! Define the ACD subgroup to which the agent phoneset belongs in table
ACDSGRP (see “Configuring ACD subgroups” on page 65).
Configuring agent phonesets
1 Start the Service Orders utility by typing SERVORD and pressing Enter.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 Type new $ and press Enter.
Result: The DN prompt appears.
3 Enter the DN for the In Calls key on the phoneset.
Result: The LCC_ACC prompt appears.
4 Enter a valid value. This is the value of the set type (for example, m2616).
The result that appears after you enter this value varies depending on the
type of set you are using.
Result: The GROUP prompt appears.
5 Type the name of the customer group to which you added the ECM in the
CUSTNTWK table.
Result: The SUBGRP prompt appears.
6 Type the name of the customer subgroup to which the agent phoneset
belongs (usually 0) and press Enter.
Result: The NCOS prompt appears.
7 Enter a valid value.
Result: The SNPA prompt appears.
8 Enter a valid value.
Result: The KEY prompt appears.
9 Enter a valid value.
Result: The RINGING prompt appears.
10 Type Y and press Enter.
Result: The LEN_OR_LTID prompt appears.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 71
Page 72

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
11 Enter a valid value.
Result: The OPTKEY prompt appears.
12 Type $ and press Enter.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new phoneset settings.
Tip: Before you save the configuration, ensure that you perform the
following tasks:
! Assign the phoneset a valid DN.
! Assign Make Set Busy (MSB) to valid keys.
! Define any of the following keys, if required:
! secondary DN (only one)
! 3-Way Conference (3WC)
! Line of Business key (LOB)
! Emergency key (EMK)
! Fast Transfer key (FXR)
Notes:
! If you use the EMK, configure it for SuprPosID.
! If you define a secondary DN, the ECM option must be specified for the
secondary DN key.
13 Type Y and press Enter.
14 Repeat steps 2 through 13 for each phoneset you want to define.
Configuring agent phonesets on the server
After configuring agent phonesets on the switch, you must configure them on
Symposium C all Center Server. To do so, refer to the Administrator’s Guide. If
you are using the Sympos ium Call Center Web Client, refer to the Symposium
Call Center Web Client Guide and online Help fo r detailed ins tructions.
72 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 73

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Notes:
1. The agent phonesets configured on the switch must have matching data
configured on Symposium Call Center Server. If, at any time, you edit any
of the data on Symposium Call Center Server, you must reconfigure the
resource on the switch.
2. If you intend to reconfigure an agent phoneset, you must first deacquire the
phoneset, edit the configuration parameters, and then reacquire the
phoneset.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 73
Page 74

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Configuring supe rvisor phonesets
Introduction
In each ACD subgroup, you must configure one supervisor phoneset.
Symposium Call Center Serv er must acqui re thi s phonese t so tha t it can monitor
the status of the phoneset.
Phoneset keys
The following table lists special considerations for supervisor phoneset keys
when you are using Symposium Call Center Server:
Night
Service
Nortel Networks recommends that you do not configure this key
on the supervisor phoneset. Symposium Call Center Server does
not support this feature.
Before you begin
Before configuring a phoneset, you must perform the following tasks:
! Log on to the switch from a MAP terminal with a user ID that has the
privilege levels required to access the SERVORD utility.
! Define the ACD group to which the supervisor phoneset belongs in table
ACDGRP (see “Configuring ACD groups” on page 57).
! Define the ACD subgroup to which the supervisor phoneset belongs in
table ACDSGRP (see “Configuring ACD subgroups” on page 65).
To configure a super visor phoneset
1 At the > prompt in the servord utility, type new and press Enter.
Result: The DN prompt appears.
2 Enter the DN for the In Calls key on the phoneset.
74 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 75

April 2004 Configuring the switch
3 Continue responding to the prompts to define the phoneset. Be sure to
define the following options:
! position ID
! Observation key (OBS)
! Answer Emergency key (AEMK)
! Agent Status key (ASK)
For more information about these and other available options, see the
SERVORD Reference Manual.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new phoneset.
4 Type Y and press Enter.
5 Repeat steps 1 through 4 for each supervisor phoneset you want to define.
6 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
Configuring supervisor phonesets on the server
After configuring supervisor phonesets on the switch, you must configure them
on Symposium Call Center Se rver. To do so, ref er to the Administrator’s Guide.
If you are using the Symposium Call Center Web Client, refer to th e Symposium
Call Center Web Client Guide and online Help for detailed instructions .
Notes:
1. The supervisor phonesets configured on the switch must have matching
data configured on Symposium Call Center Server. If, at any time, you edit
any of the d ata on Sympo sium Call Cent er Serv er, you must rec onfi gure the
resource on the switch.
2. If you intend to reconfigure a su pervis or p honeset , you must f i rst de acquir e
the phoneset, edit the configuration parameters, and then reacquire the
phoneset.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 75
Page 76

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Configuring logon IDs
Introduction
You must configure the logon ID of each agent who logs on to a phoneset
monitored by Symposi um Call Cen ter Serv er. I f you add an agent in Symposi um
Call Center Server , you must configure the ma tc hin g agent logon parameters on
the switch.
Note: An agent can log on to any phoneset providing he or she enters a valid
logon ID. However, to ensure that the agent can use all of the key-enabled
features av aila ble, the agent mus t log on to the phone set that has be en confi gured
as his or her unique Positi on ID. F or re porti ng purpos es, an agent must log on to
a phoneset configured as part of the ACD group to which the agent belongs.
Before you begin
Before configuring a logon ID, you must log on to the switch from a MAP
terminal with a user ID that has the privilege levels required to change the
ACDLOGIN table.
To configure an agent login
1 Edit the ACDLOGIN table by typing table ACDLOGIN and pressing Enter.
Result: The > prompt appears.
2 Type add and press Enter.
Result: The LOGINID prompt appears.
3 Enter the numeric ID that the agent uses to log on to the phoneset.
Result: The CUSTSEL prompt appears.
4 Type N and press Enter.
Result: The PSWDSEL prompt appears.
76 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 77

April 2004 Configuring the switch
5 Type N and press Enter.
Result: The OPTION prompt appears.
6 Select the VARWRAP option.
Result: The VARWRAP prompt appears.
7 When an agent releases a call, the Variable Wrap feature prevents another
call from being presented to the agent for a specific period of time. You
must select the Variable Wrap feature and define TIMER (the length of the
wrap period, in seconds).
If TIMER is set to a value greater than zero (0), once an active call is
released, the agent is not available to receive any new calls for the length of
time specified.
If TIMER is set to the value zero (0), once the active call is released, the
agent immediately becomes available to receive new calls.
If you do not configure Variable Wrap on the switch, the Release Guard
feature is enabled. Release Guard prevents calls from being presented to
the agent for 1 second after an active call is released.
Result: The FORCING prompt appears.
8 Set FORCING to NONE.
Result: The utility prompts you to save the new agent login ID.
9 Type Y and press Enter.
10 Repeat steps 2 through 9 for each agent login ID that you want to define.
11 To exit from the table, type quit and press Enter.
Configuring agents on the server
After configuring agent logons on the switch, you must configure them on
Symposium C all Center Server. To do so, refer to the Administrator’s Guide. If
you are using the Sympos ium Call Center Web Client, refer to the Symposium
Call Center Web Client Guide and online Help fo r detailed ins tructions.
Note: The agent phonesets configured on the switch must have matching data
configured on Sympo sium Call Center Ser ver. If, at an y time, y ou edit an y of th e
data on Symposium Call Center Server, you must reconfigure the resource on
the switch.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 77
Page 78

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
78 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 79

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Section C: Checking the server
configuration
In this section
Overview of server configuration 80
Checking the server configuration 81
Relationship of server configuration and switch datafill 83
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 79
Page 80

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Overview of server configuration
Installation of Symposium Call Center Server enables you to configure the
connection to the switch. After the installation, you can view the configuration
information to confirm that it was entered correctly.
Note: This section describes how to view the configuration from a client PC.
You can also use the Feature Reports utility on the server. For more information
about this utility, refer to the Installation and Maintenance Guide.
80 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 81

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Checking the server configuration
Introduction
This section describes checking the switch connection.
To check the switch connection
1 From the SMI window, choose System Administration ➝ System
Configuration ➝ Server Settings.
Result: The Switch Resource property sheet appears. This property sheet
shows the type of switch to which the server is connected, and how the
server is configured on the switch.
Note: The following section shows the relationships between these fields
and the tuples (parameters and values) in the DMS tables.
2 Click the Advanced button.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 81
Page 82

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Result: The Switch configuration property sheet appears. This property
sheet contains additional information about the server configuration on the
switch.
3 Click Close to return to the Switch Resource property sheet.
4 Click Close to return to the SMI window .
82 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 83

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Relationship of server configuration and switch datafill
Introduction
This section shows the relationships between fields in the Symposium Call
Center Server configuration and tuples in the DMS tables.
Table of relationships
The following table shows the DMS tuples that must match the fields on the
Symposium Call Center Server Switch Configuration property page:
Symposium Call
Center Server
parameter DMS table Data
Switch IP Address IPNETWRK CMIPADDR
Network Node SCAIGRP NETNODEID
Business Group SCAIGRP BGID
Linkset Name SCAIGRP LINKSET
Switch Password SCAIGRP PASSWORD
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 83
Page 84

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
Predefined values
The following fields in the Symposium Call Center Server configuration have
predefined values:
Symposium Call
Center Server
parameter Value Meaning
Service ID 0–255
(from table
SCAIPROF)
Identifies the connection profile
parameters for communica ti on
between the switch and
Symposium Call Center Server.
Application ID Any user-defined value Symposium Call Center Server
Service Version 12
13
14
15
16
17
Release CCM010
Release CCM011
Release CCM012
Releases: CCM013, CCM014
Release CCM015
Releases: CCM016, CCM017
Note: To change the Service ID or Service Version, use the Feature Reports
utility on the server. These fields must be set correctly to allow you to take
advantage of the features of the operating system that you are using.
Symposium Call Center Server logon parameters
Network Node
! uniquely i dentifies a switch (CO switch or PBX) in a customer’s network.
The customer assigns the network node ID to assure a uniqueness in
network that might consist of public and private nodes.
! must be a number between 0–32767
! is keyed to the NETNODID field of the SCAIGRP table
84 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 85

April 2004 Configuring the switch
Business Group
! uniquely identifies a Meridian Business Group (MBG) customer within a
public network
! is assigned by the telephone company, distributor, or end-user
! is keyed to the BGID field of the SCAIGRP table
! must be a number between 1–4194304
Note: An MBG customer is a telephone company customer who uses public
facilities to carry customer-specific information. This parameter uniquely
identifies a given telephone company MBG customer across a number of
switches in a given network, and not only wit hin a given swi tc h. As a r esult, any
host applications that establish application-level sessions wi th multiple switches
only need to be datafilled with one business group ID per network rather than
per switch.
Switch Password
! is a security f eatur e th at, a long wi th a valid user ID, enables a user t o log on
to the switch. The customer assigns passwords.
! maintains a one-to- one rela tions hip wi th th e b usin ess group ID. All Servi ce
IDs of a customer are under the same password.
! is keyed to the PASSWORD field of the SCAIGRP table
! must be between 1–8 characters in length
Service ID
! uniquely identifies a service profile for a session. An operating company
can define functions and parameters in service profiles on the switch. The
operating company can assign a customer up to eight service IDs.
! is assigned by the telephone company
! is referenced to the PROFKEY field of the DMS SCAIPROF table
! must be a number between 0–255
Application ID
! uniquely identifies Symposium Call Center Server in a customer’s
network—in other w or ds, within the set of publ ic an d pri vate switches with
which a customer’s host application can establish a session
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 85
Page 86

Configuring the switch Standard 1.0
! identifies the specific customer host application (for example, Symposium
Call Center Server, OPEN IVR, TAPI Driver) initiating the logon request
! assigned by the customer
! must be a number between 1–32767. This number must be different for all
the other applications connected to the linkset.
Service Version
! uniquely identifies the application level signaling version on a specific
switch
Succession
CCM release SCAI version DMS release MLS release
rate
CCM10 SCAI12 NA10 MSL12
CCM11 SCAI13 NA11
CCM12 SCAI14 NA12 MSL14
CCM13 SCAI15 NA13
CCM14 SCAI15 NA14 MSL15
CCM15 SCAI16 NA15
CCM16 SCAI17 NA16
CCM17 SCAI17 NA17 MSL17 SE06
Note: Symposium Call Center Server supports a minimum of CCM10. The
switch releases must be able to support the intended SCAI version; however, a
lower SCAI version can be run from a more recent version of software .
! must be a number between 0–65535
86 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 87

Chapter 3
Verifying the configuration
In this chapter
Overview 88
Verifying that the server can log on to the switch 89
Verifying ACD groups and subgroups 91
Verifying that phonesets are co rrec tl y con fig ur ed 92
Verifying that agents are correctly configured 94
Verifying that the CDNs are correctly configured 95
Verifying that music and RAN routes are correctly configured 97
Verifying that DNISs are correctly configured 99
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 87
Page 88

Verifying the configuration Standard 1.0
Overview
Introduction
This section describes how to verify that the switch has been set up correctly.
Before you continue, ensure that you have configured Symposium Call Center
Server as described in the Administrator’s Guide.
Verifying the configuration
You must verify that the switch has been configured correctly. This section
explains the procedure you must follow to verify the following configurations:
! Symposium Call Center Server can log on to the switch over the ICM link.
! ACD groups and subgroups are correctly configur ed.
! Agent phonesets are correctly configured.
! Agents and supervisors are configured to log on.
! CDNs are correctly configured.
! Music and RAN routes are correctly configured.
! DNISs (primary and su pplementary ACD-DNs) are correctly configured.
88 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 89

April 2004 Verifying the configuration
Verifying that the server can log on to the switch
Introduction
Symposium Call Center Server attempts to log on to the switch at startup and—
if the link goes do wn—whene v er the li nk becomes a v ailabl e. To allow the serv er
to log on, the following conditions must be met:
! The ICM link between the switch and Symposium Call Center Server must
be correctly configured.
! The server logon parameters must be correctly configured.
To verify the integrity of the ICM link
1 At the switch, use the SNPINGCI utility to ping the ELAN IP address of the
server in Symposium Call Center Server. (For more information about the
SNPINGCI utility, refer to the DMS Utilities Guide.)
2 On Symposium Call Center Server, open a DOS window and use the PING
command to ping the switch IP address (specified for parameter
CMIPADDR in table IPNETWORK).
If the connection fails, th e link is incorrectly configured. Yo u must confirm that
the configuration information entered on Symposium Call Center Server
matches the information defined in the resources configured on the switch.
Note: If you receive the message “destination net unreachable” when using the
ping command, it might be necessary to add a static route to the switch.
To create a static route
1 On Symposium Call Center Server, from the Start menu, select Programs
➝ MS-DOS Prompt.
Result: The MS-DOS Prompt window appear s.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 89
Page 90

Verifying the configuration Standard 1.0
2 Type the following text:
route add -p cmipaddr route
where cmipaddr is the actual IP address of the server in Symposium Call
Center Server, and “route” is the IP address of the nearest router or ICM
link on the EIU.
Logon failure
If the logon process is incorrectly configured, Symposium Call Center Server is
unable to log on to the switch, and the server cannot acquire CDNs, phonesets,
or voice p ort s. These resources display the status “Acquire Fai le d” in the CDNs,
Phonesets, and Voice Ports windows on Symposium Call Center Server.
90 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 91

April 2004 Verifying the configuration
Verifying ACD groups and subgroups
Introduction
To verify that ACD groups and subgroups are correctly defined, use the
ACDSHOW utility.
Before you begin
Before verifying the ACD configuration, you must log on to the switch from a
MAP termina l with a user ID that has the privilege levels required to ac cess the
ACDSHOW utility.
To verify ACD configurations
Check the ACD configuration using the ACDSHOW command. (For more
information about this command, refer to the Translations Guide.) Ensure that
the following conditions have been met for each ACD group to which
ACD-DNs, phonesets, and agents are assigned:
! The AGTASSN option is enabled.
! The Variable Wrap (VARWRAP) option is enabled . When an agent rel eases
a call, the Variable Wrap featur e pre vent s anoth er call from be ing present ed
to the agent for a specific period of time. If you do not want to allow wrapup time at the end of a call, set the wrap time to zero (0).
! The Not Ready on Secondary DN (NROSDN) option is enabled. Use this
option if you do not want Symposi um Call Cente r Serv er to pr esent calls to
agents who are active on their secondary DN.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 91
Page 92

Verifying the configuration Standard 1.0
Verifying that phonesets are correctly configured
Introduction
T o verify that a phoneset is correctly configured, ensure that it is configured as a
type Meridian Digital Centr ex (MDC), and that all ke ys are cor rectly conf igured.
(For information about the interaction of keys and Symposium Call Center
Server, see “Configuring agent phonesets” on page 69, and “Configuring
supervisor phonesets” on page 74.)
Before you begin
Before verifying the phoneset, you must log on to the switch from a MAP
terminal with a us er ID t hat has the pr ivilege levels req uired to acc ess the QLEN
utility.
Verifying agent phoneset configurations
To verify that phonesets are correctly configured, check the phoneset
configuration using the QLEN command. (For more information about this
command, see the SERVORD Reference Manual.) Ensure that the following
conditions have been met for each agent phoneset:
! The phoneset type is MDC.
! The phoneset is configured for position ID.
! The phoneset has a Not Ready key.
! The phoneset has an Emergency key.
! The phoneset does not have the following keys: Dial Intercom, Hotline,
Private Line, or Voice Call. Only supervisor phonesets should have these
keys configured.
! If you want to use the LOB (activity) c ode f ea tur e, t he p honeset has a LOB
key .
! If you want to distinguish between conferences and transfers, the phoneset
has 3-Way Conference and Fast Transfer keys.
! The ECM option is set on the secondary DN.
92 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 93

April 2004 Verifying the configuration
Verifying supervisor phoneset configurations
To verify that supervisor phoneset s a re cor rec tly configured, c heck the phoneset
configuration using the QLEN command. (For more information about this
command, see the SERVORD Reference Manual.) Ensure that the following
conditions have been met for each supervisor phoneset:
! The phoneset type is MDC.
! The phoneset has an Emergency key.
! The phoneset does not have a Night Service key. Only agent phonesets
should have this key configured.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 93
Page 94

Verifying the configuration Standard 1.0
Verifying that agents are corre ctly configured
Introduction
If agents are correctly configured, agents can log on to a phoneset, and their
status is correctly repo rted in the agent real-time display.
Before you begin
Ensure that the phoneset has been acquired on Symposium Call Center Server.
On a client workstation , open an Agent real-time display window.
To verify agent logons
1 At a phoneset configured as an agent set, pick up the handset.
2 Press the Make Set Busy (MSB) key.
3 Press the Incalls key.
4 Enter the agent’s logon ID.
Result: The Not Ready light goes on and the Make Set Busy indicator goes
off. On the Agent real-time display window, the agent appears with the
value “Not Ready” in the In Calls Status column.
5 Press the Not Ready key.
Result: On the Agent real-time display window , the agent’s In Calls Statu s
changes to Idle.
94 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 95

April 2004 Verifying the configuration
Verifying that the CDNs are corr ectly configured
Introduction
If a Controlled Directory Number (CDN) is correctly configured, Symposium
Call Center Server can acquire that CDN, and calls to that CDN are correctly
routed.
Before you begin
Before using this procedure, comple te these tasks:
1. Define two CDNs. Ensure that they are correctly configured on both the
switch and Symposium Call Center Server.
2. Define two agents. Ensure that the agents are correctly configured on both
the switch and Symposium Call Center Server.
3. Define two skillsets on Symposium Call Center Server. Fo r inf or mati on on
defining skillsets, refer to the Administrator’s Guide. If you are using the
Symposium C all Center Web Client, refer to the Symposium Call Center
Web Client Guide and online Help for detailed instructions.
4. Assign one agent to each skillset on the server. For information on
assigning skillsets to agents, refe r to the Administrator’s Guide. If you are
using the Symposium Cal l Center Web Client, refer to the Symposium Call
Center Web Client Guide and online Help for detailed instructions.
5. Create a Master script similar to the following sample, validate it, and
activate it. For information on creating a Master script, refer to the
Scripting Guide.
Note: The sample script uses the skil lsets skillset_A_sk and skillset_B_sk, and
the CDNs 416-555-7890 and 416-555-4891.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 95
Page 96

Verifying the configuration Standard 1.0
Sample script
GIVE RINGBACK
WAI T 2
IF (CDN = 4165557890) THEN
QUEUE TO SKILLSET skillset_A_sk
WAI T 2
LOG “queued at CDN A”
QUIT
END IF
IF (CDN = 4165557891) THEN
QUEUE TO SKILLSET skillset_B_sk
WAI T 2
LOG “queued at CDN B”
QUIT
END IF
WAI T 5
LOG “did not arrive at either CDN”
QUIT
To verify CDN configurations
1 On Symposium Call Center Server, acquire the CDN by selecting it in the
CDNs window and choosing File ➝ Acquire.
Result: The CDN status changes to Acquire Pending, and then to
Acquired.
2 Log on each agent to a phoneset.
3 Make a call to each CDN.
Result: The call is routed to the correct agent.
96 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 97

April 2004 Verifying the configuration
Verifying that music and RAN routes are correctly configured
Introduction
If music and RAN routes are correctly configured, calls receive the correct
recorded announcement or music treatment.
Before you begin
Before using this procedure, comple te these tasks:
1. Define a CDN. Ensure that it is corr ectl y conf ig ured on bo th t he swit ch and
Symposium C all Center S erver.
2. Define two RAN routes. Ensure that the routes are correctly configured on
both the switch and Symposium Call Center Server. For information on
defining RAN routes, refer to the Administrator’s Guide. If you are using
the Symposium Call Cen ter Web Client, refer to the Symposium Call
Center Web Client Guide and online Help for detailed instructions.
3. Define two music routes. Ensure that the routes are correctly configured on
both the switch and Symposium Call Center Server. For information on
defining music routes, refer to the Administrator’s Guide. If you are using
the Symposium Call Cen ter Web Client, refer to the Symposium Call
Center Web Client Guide and online Help for detailed instructions.
4. Create a Master script similar to the following sample, validate it, and
activate it. For information on creating a Master script, refer to the
Scripting Guide.
Sample script
GIVE RINGBACK
WAI T 2
GIVE MUSIC pop_music_gv
WAI T 2
GIVE MUSIC classical_music_gv
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 97
Page 98

Verifying the configuration Standard 1.0
WAI T 2
GIVE RAN welcome_RAN_gv
WAI T 2
GIVE RAN holiday_RAN_gv
QUIT
Verifying music/RAN route configurations
To verify that RAN or music routes are correctly configured, make a call to the
CDN for which RAN or music treatment is configured. The correct treatment
should be received.
98 Symposium Call Center Server
Page 99

April 2004 Verifying the configuration
Verifying that DNISs are correctly configured
Introduction
To enable Symposium Call Center Server to monitor dialed numbers (primary
and supplementary ACD-DNs), you must configure them on the switch and
define them as DNISs on the server. If DNISs are correctly configured, calls to
DNISs receive the correct treatment.
Before you begin
Before using this procedure, comple te these tasks:
1. Define a CDN. Ensure that it is corr ectl y conf ig ured on bo th t he swit ch and
Symposium C all Center S erver.
2. Define one DNIS. Ensure that the DNIS is correctly conf i gured on bot h the
switch and Symposium Call Center Server.
3. Define an agent. Ensure that the agent is correctly configured on both the
switch and Symposium Call Center Server.
4. Define a skills et on Symposium Call Cen ter Server. For information on
defining skillsets, refer to the Administrator’s Guide. If you are using the
Symposium C all Center Web Client, refer to the Symposium Call Center
Web Client Guide and online Help for detailed instructions.
5. Assign the agent to the skillset on the server. For information on assigning
agents to skillsets, refer to the Administrator’s Guide. If you are using the
Symposium C all Center Web Client, refer to the Symposium Call Center
Web Client Guide and online Help for detailed instructions.
6. Create a Master script similar to the following sample, validate it, and
activate it. For information on creating a Master script, refer to the
Scripting Guide.
Note: The sample script uses the skillset skillset_A_sk and the DNIS
800-555-4567.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide 99
Page 100

Verifying the configuration Standard 1.0
Sample script
GIVE RINGBACK
WAI T 2
IF (DNIS = 8005554567) THEN
QUEUE TO SKILLSET skillset_A_sk
WAI T 2
LOG “using DNIS”
QUIT
END IF
WAI T 5
LOG “did not have DNIS”
QUIT
Verifying DNIS configurations
To verify that DNISs are correctly config ured, mak e a call to the DNIS. The call
should be queued to the correct skillset.
100 Symposium Call Center Server
 Loading...
Loading...