Page 1

Part No. 312865-C
January 2002
4401 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054
Installing Gigabit
Interface Converters,
SFP, and CWDM SFP
Gigabit Interface
Converters
*312865-C*
Page 2

Copyright © 2002 Nortel Networks
All rights reserved. January 2002.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The
statements, configurations, technical data, and recommendations in this document
are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products
specified in this document. The information in this document is proprietary to
Nortel Networks Inc.
Trademarks
Nortel Networks, the Nortel Networks logo, and the Globemark and are trademarks
of Nortel Networks.
Adobe and Acrobat Reader are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Statement of conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability,
Nortel Networks Inc. reserves the right to make changes to the products described in
this document without notice.
Nortel Networks Inc. does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or
application of the product(s) or circuit layout(s) described herein.
EMI Compliance
Meets requirements of:
FCC Part 15, Subparts A and B, Class A
EN55022: 1998/CISPR22:1997), Class A
General License VDE 0871, Class B
(AmtsblVfg No. 243/1991, Vfg 46/1992) VCCI Class A ITE
EN55024:1998/CISPR24:1997
Caution: Use of controls or adjustments, or performance
of procedures other than those specified herein may
result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Page 3

Caution: Only qualified technicians should install this
equipment.
Place all printed circuit boards on an antistatic mat until you
are ready to install them. If you do not have an antistatic
mat, wear a discharge leash to free yourself of static before
touching any of the printed circuit boards, or free yourself of
static by touching a grounded metal object before handling a
printed circuit board.
Product Safety
Meets requirements of:
CSA 22.2 No. 950-M95/UL1950, 3rd ed.
EN60950: 1992 /A1:1993 /A2:1993 /A3:1995 /A4:
199721CFR, Chapter I
EN60825-1:1994 /A11:1996
Warning: Fiber optic equipment can emit laser or infrared light that can
injure your eyes. Never look into an optical fiber or connector port.
Always assume that fiber optic cables are connected to a light source.
Vor si ch t: Glasfaserkomponenten können Laserlicht bzw. Infrarotlicht
abstrahlen, wodurch Ihre Augen geschädigt werden können. Schauen
Sie niemals in einen Glasfaser-LWL oder ein Anschlußteil. Gehen Sie
stets davon aus, daß das Glasfaserkabel an eine Lichtquelle
angeschlossen ist.
Avertissement: L’équipement à fibre optique peut émettre des
rayons laser ou infrarouges qui risquent d’entraîner des lésions
oculaires. Ne jamais regarder dans le port d’un connecteur ou d’un
câble à fibre optique. Toujours supposer que les câbles à fibre optique
sont raccordés à une source lumineuse.
1
Page 4

Advertencia: Los equipos de fibra óptica pueden emitir radiaciones
de láser o infrarrojas que pueden dañar los ojos. No mire nunca en el
interior de una fibra óptica ni de un puerto de conexión. Suponga
siempre que los cables de fibra óptica están conectados a una fuente
luminosa.
Avvertenza: Le apparecchiature a fibre ottiche emettono raggi laser o
infrarossi che possono risultare dannosi per gli occhi. Non guardare
mai direttamente le fibre ottiche o le porte di collegamento. Tenere in
considerazione il fatto che i cavi a fibre ottiche sono collegati a una
sorgente luminosa.
Introduction to Gigabit Interface Converters
This section describes the Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC)
and label, and provides a GBIC model list.
Product description
Gigabit Interface Converters (GBICs) are hot-swappable
input/output enhancement components designed for use with
Nortel Networks*
link with fiber optic networks.
Figure 1 shows the two GBIC insertion and removal
mechanisms—extractor tabs and extractor handle.
products to allow Gigabit Ethernet ports to
2
Page 5
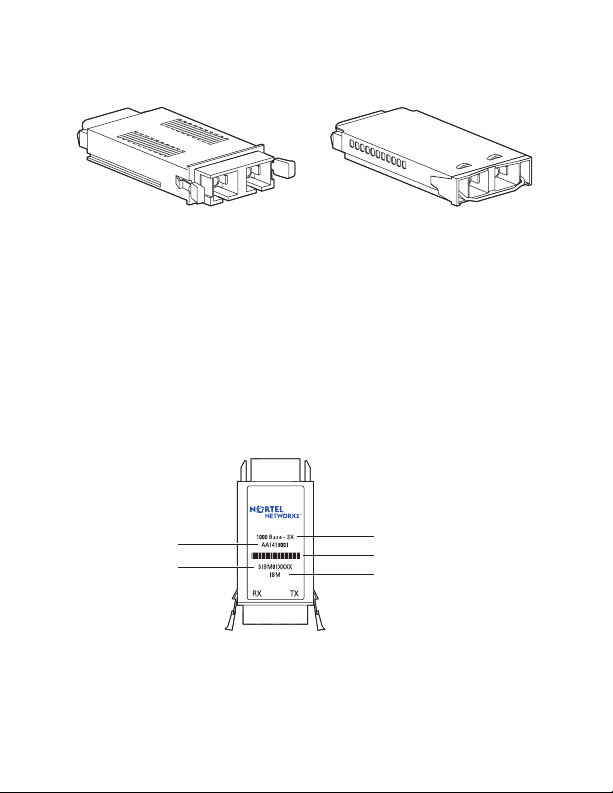
Figure 1 GBIC extraction tabs and extractor handle
GBIC model with
extractor tabs
GBIC model with
extractor handle
9702FA
GBIC labeling
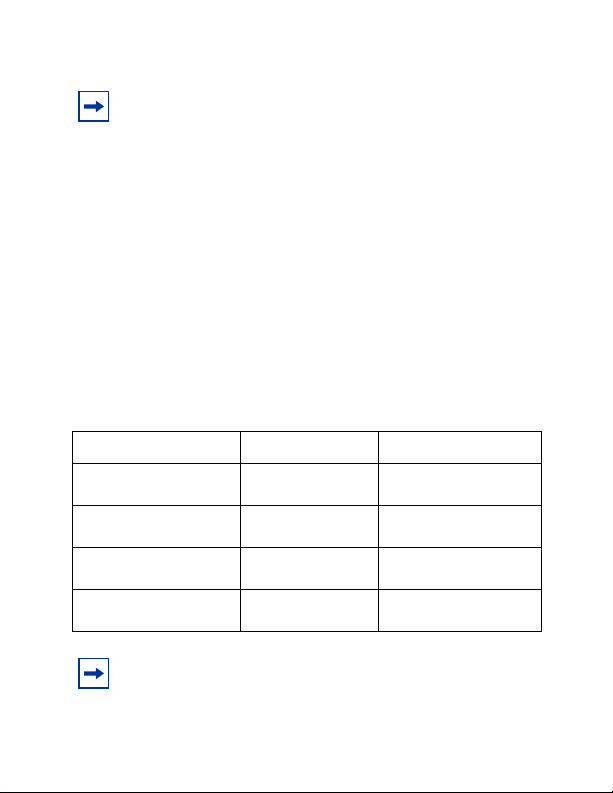
The Nortel Networks label on a typical GBIC (Figure 2) contains
a Nortel Networks serial number, a bar code, a manufacturer’s
code, an interface type, and a part number.
Figure 2 Nortel Networks GBIC label
Part number
Serial number
3
GBIC interface type
Bar code
Manufacturer code
9706EA
Page 6
Note: When you contact a Nortel Networks service
representative for troubleshooting purposes, you must
have the following information available:
• Nortel Networks serial number
• Manufacturer’s code
• Interface type
• GBIC part number
GBIC and SFP GBIC model list
Table 1 lists and describes the Nortel Networks GBIC and SFP
GBIC models.
Table 1 Nortel Networks GBIC and SFP GBIC models
Model number Product number Description
1000BASE-SX AA1419001 Short wavelength/
1000BASE-LX AA1419002 Long wavelength
1000BASE-XD AA1419003 Extended distance 50
1000BASE-ZX AA1419004 Extended distance 70
distance 550 m
distance 5 km
km
km
Note: GBIC wavelength distance may vary, depending
on the quality of fiber optic cable used.
4
Page 7

Handling, safety, and environmental guidelines
Before installing your GBIC, read the following handling, safety,
and environmental guidelines:
• GBICs are static sensitive. To prevent damage from
electrostatic discharge (ESD), follow your normal board
and component handling procedures.
• GBICs are dust sensitive. When you store a GBIC, or when
you disconnect it from a fiber optic cable, always keep the
dust cover over the GBIC’s optical bores.
• To clean contaminants from the optical bores of a GBIC,
use an alcohol swab or equivalent to clean the ferrules of
the optical connector.
• Dispose of this product according to all national laws and
regulations.
Warning: Fiber optic equipment can emit laser or
infrared light that can injure your eyes. Never look into
an optical fiber or connector port. Always assume that
fiber optic cables are connected to a light source.
Installing a GBIC
This section lists the steps to install a GBIC.
To install a GBIC:
1 Remove the GBIC from its protective packaging.
5
Page 8
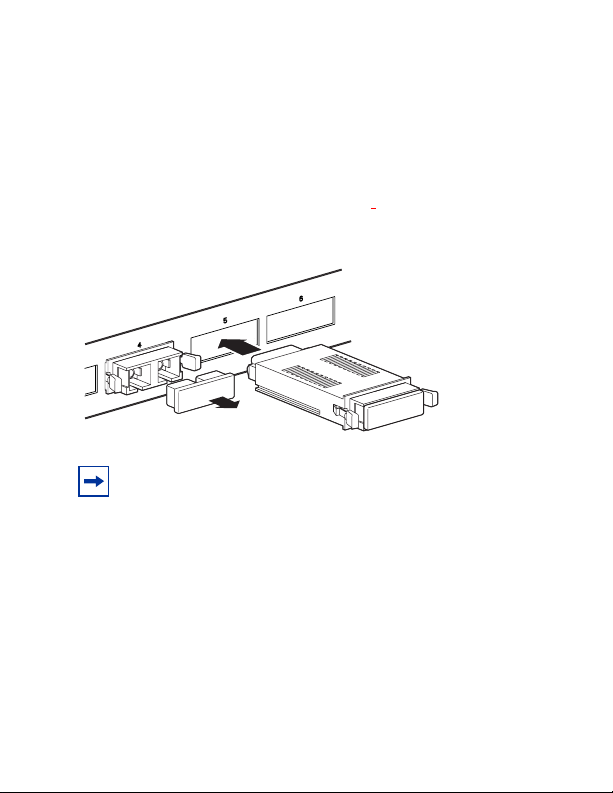
2 Verify that the GBIC is the correct model for your network
configuration (Table 1 on page 4).
3 Remove the dust cover from the GBIC’s optical bores.
4 Grasp the GBIC between your thumb and forefinger.
5 Insert the GBIC into the slot on the front panel of the Gigabit
Ethernet switching module (Figure 3) .
Figure 3 Inserting the GBIC into the switching module
Note: GBICs are keyed to prevent incorrect insertion.
Removing a GBIC
This section lists the steps for removing a GBIC.
To remove a GBIC:
1 Disconnect the network fiber cable from the GBIC
connector.
6
Page 9
2 Depending on your GBIC model, either grasp the extraction
tabs (Figure 1) located on either side of the GBIC with your
thumb and forefinger, or lift the extractor handle (Figure 1)
attached to the GBIC.
3 Slide the GBIC out of the Gigabit Ethernet module slot.
4 If the GBIC does not slide easily from the module slot, use a
gentle side-to-side rocking motion while firmly pulling the
GBIC from the slot.
5 Dispose of the GBIC according to all national laws and
regulations.
Note: If you are storing a GBIC, remember to place a
dust cover over the fiber optic bores.
GBIC specifications
Table 2 describes general GBIC specifications.
Table 2 GBIC specifications
Specification Descriptions
Dimensions (H x W x D) 0.39 x 1.18 x 2.56 inches
(1 x 3 x 6.5 cm)
Connectors Multimode fiber optic: SC
Single-mode fiber optic: SC
7
Page 10
Standards, connectors, cabling, and distance
This section describes GBIC standards, connectors, cabling, and
distance; and provides specifications for the following GBICs:
• “1000BASE-SX,” next
• “1000BASE-LX” on page 9
• “1000BASE-XD” on page 11
• “1000BASE-ZX” on page 13
• “1000BASE-T” on page 15
GBIC ports for both multimode and single-mode fiber have
SC-type connectors and a minimum cable distance of 6.5 feet (2
m).
1000BASE-SX
The Model 1000BASE-SX GBIC provides 1000BASE-SX (850
nm, short wavelength, Gigabit Ethernet) connectivity using SC
duplex multimode fiber connectors.The Model 1000BASE-SX
GBIC supports full-duplex operation only
Table 3 describes standards, connectors, cabling, and distance for
the Model 1000BASE-SX GBIC.
Table 3 1000BASE-SX specifications
.
Type Specifications
Standards Conformity to the following standards:
802.3z, 1000BASE-SX
8
Page 11
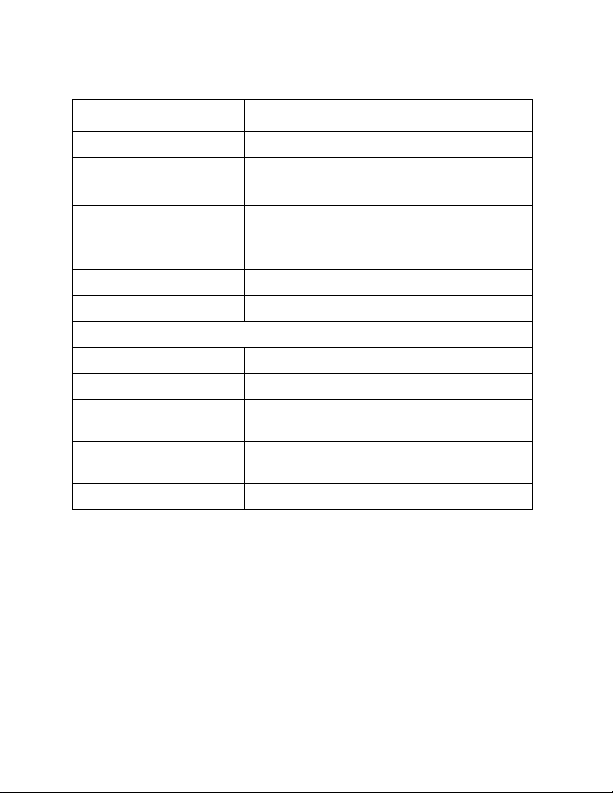
Table 3 1000BASE-SX specifications (continued)
Type Specifications
Connectors Duplex SC fiber optic connector
Cabling 62.5 µm
Distance 902 ft. (275 m) using 62.5 µm
Wavelength 850 nm
Optical budget 7 dB
Laser Transmitter Characteristics
Minimum launch power -10 dBm
Maximum launch power -4 dBm
Receiver
Characteristics
Minimum receiver
sensitivity
Maximum input power 0 dBm
MMF optic cable
50 µm MMF optic cable
MMF optic
cable
1804 ft. (550 m) using 50 µm MMF optic cable
-17 dBm
1000BASE-LX
The Model 1000BASE-LX GBIC provides 1000BASE-LX
(1300 nm, wavelength, Gigabit Ethernet) connectivity using
SC duplex fiber connectors. The long wavelength optical
transceivers used in the LX model provide variable distance
ranges using both multimode and single-mode fiber optic
cabling. The Model 1000BASE-LX GBIC supports full-duplex
operation only
.
9
Page 12

Table 4 describes standards, connectors, cabling, and distance for
the Model 1000BASE-LX GBIC.
Table 4 1000BASE-LX specifications
Type Specifications
Standards Conformity to the following standards:
802.3z, 1000BASE-LX
Connectors Duplex LC fiber optic connector
Cabling 62.5 µm
Distance 1804 ft. (550 m) using 62.5 µm
Wavelength 1300 nm
Optical budget 10.5 dB
Laser Transmitter Characteristics
Minimum launch power -9.5 dBm
Maximum launch power -3 dBm
Receiver Characteristics
Minimum receiver
sensitivity
Maximum input power -3 dBm
MMF optic cable
50 µm MMF optic cable
10 µm SMF optic cable
cable
1804 ft. (550 m) using 50 µm
16405 ft. (5 km) using 10 µm
-20 dBm
MMF optic
MMF optic cable
SMF optic cable
10
Page 13

Note: When multimode fiber is used in long-distance
applications, external, removable, mode-conditioning
patch cords may be required to prevent differential mode
delay (DMD). You can order mode conditioning patch
cords through Nortel Networks:
• SC-SC Mode-Conditioning Patch Cord 62.5/125
(part number AA0018035)
• SC-SC Mode-Conditioning Patch Cord 50/125
(part number AA0018036)
1000BASE-XD
The Model 1000BASE-XD GBIC provides Gigabit Ethernet
connectivity using SC duplex single-mode fiber connectors.
High-performance optical transceivers enable Gigabit Ethernet
link distances up to 50 kilometers (km) over single-mode fiber.
The ports operate in full-duplex mode only.
Note: The Model 1000BASE-XD GBIC is based on
proprietary signaling and is compatible with Accelar
1000 Series XD modules.
Table 5 describes standards, connectors, cabling, and distance for
the Model 1000BASE-XD GBIC.
Table 5 1000BASE-XD GBIC specifications
Type Specifications
Standards Conformity to the following standards:
802.3z, Ethernet full duplex
11
Page 14

Table 5 1000BASE-XD GBIC specifications (continued)
Type Specifications
Connectors Duplex SC single-mode fiber optic
Cabling Single-mode fiber optic cable
Distance Up to 50 km using single-mode fiber
Optical budget 17 dB
Laser Transmitter Characteristics
Wavelength 1550 ± 10 nm
Maximum spectral width 0.2 nm
Maximum launch power 0 dBm or 1.0 mW
Minimum launch power into
fiber
Distance 50 km
Receiver Characteristics
Wavelength 1200 to 1550 nm
Minimum receiver sensitivity -22 dBm
Maximum input power -3 dBm
connector
cable, depending on the quality of the fiber
-5 dBm or 0.3 mW
Note: Nortel Networks recommends that you use an
in-line attenuator for shorter link distances to avoid
overloading the receiver.
12
Page 15

1000BASE-ZX
The Model 1000BASE-ZX GBIC provides Gigabit Ethernet
connectivity using SC duplex single-mode fiber connectors.
High-performance optical transceivers enable Gigabit Ethernet
link distances up to 70 km over single-mode fiber cable. The
ports operate in full-duplex mode only.
Note: The 1000BASE-ZX Model GBIC is based on
proprietary signaling. Nortel Networks recommends that
this product be used only with other Nortel Networks
1000BASE-ZX GBICs.
Table 6 describes standards, connectors, cabling, and distance for
the Model 1000BASE-ZX GBIC.
Table 6 1000BASE-ZX GBIC specifications
Type Specifications
Standards Conformity to the following standards:
Connectors Duplex SC single-mode fiber optic connector
Cabling Single-mode fiber cable
Distance Up to 70 km using single-mode fiber cable,
Optical Budget 22 dB
Laser Transmitter Characteristics
Wavelength 1550 ± 10 nm
Maximum spectral width 0.2 nm
Maximum launch power 5 dBm or 3.0 mW
Minimum launch power 0 dBm
802.3z, Ethernet full duplex
depending on the quality of the fiber
13
Page 16

Table 6 1000BASE-ZX GBIC specifications (continued)
Type Specifications
Distance 70 km
Receiver Characteristics
Wavelength 1200 to 1550 nm
Minimum receiver sensitivity -22 dBm
Maximum input power -3 dBm
Note: When shorter lengths of single-mode fiber cable
are used, there is a risk of overloading the receiver. It
may be necessary to insert an in-line optical attenuator
in the link to prevent overloading, as follows:
• Insert a 10 dB in-line optical attenuator between the
fiber optic cable plant and the receiving port on the
1000BASE-ZX GBIC, at each end of the link, if the
fiber optic cable span is less than 25 km.
• Insert a 5 dB in line optical attenuator between the
fiber optic cable plant and the receiving port on the
1000BASE-ZX GBIC, at each end of the link, if the
fiber optic cable span is less than 50 km.
14
Page 17

1000BASE-T
The Model 1000BASE-T GBIC provides 1000BASE-T (Gigabit
Ethernet) connectivity.
Table 4 describes standards, connectors, cabling, and distance for
the Model 1000BASE-LX GBIC.
Table 7 1000BASE-LX specifications
Type Specifications
Standards Conformity to the following standards:
IEEE 802.3z and IEEE 802.3AB
Connectors RJ-45 connector
Cabling
Distance 100 m maximum
Receiver Characteristics
Minimum receiver
sensitivity
Maximum input power 2.00 volts
0.50 volts
15
Page 18

Introduction to Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) Gigabit Interface Converters
This section describes the Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP)
Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) and label, and provides a
SFP GBIC model list.
Product description
Small Form Factor Pluggable Gigabit Interface Converters (SFP
GBICs) are hot-swappable input/output enhancement
components designed for use with Nortel Networks*
allow Gigabit Ethernet ports to link with fiber optic networks.
Figure 4 shows the SFP GBIC
Figure 4 SFP GBIC
products to
MTRJ GBIC model with
extractor button
LC GBIC model with
extractor tab
16
10515FA
Page 19

SFP GBIC labeling
The Nortel Networks label on a typical SFP GBIC (Figure 5)
contains a Nortel Networks serial number, a bar code, a
manufacturer’s code, an interface type, and a part number.
Figure 5 Nortel Networks SFP GBIC label
Part number
GBIC interface type
AA141901x
SFP 1000 BASE-xx
21CFR(J) CLASS1
Bar code
Serial number
Note: When you contact a Nortel Networks service
representative for troubleshooting purposes, you must
have the following information available:
• Nortel Networks serial number
• Manufacturer’s code
• Interface type
• GBIC part number
17
Top view
Side view
10516EA
Page 20

SFP GBIC model list
Table 8 lists and describes the Nortel Networks SFP GBIC
models.
Table 8 Nortel Networks SFP GBIC models
Model number Product number Description
1000BASE-SX (LC
Type)
1000BASE-SX
(MT-RJ Type)
1000BASE-LX (LC
Type)
AA1419013 Small Form Factor
AA1419014 Small Form Factor
AA1419015 Small Form Factor
Pluggable, short
wavelength 550 m
Pluggable, short
wavelength 550 m
Pluggable, long wavelength
5 km
Note: The cable distance may vary depending on the
quality of fiber optic cable used.
Handling, safety, and environmental guidelines
Before installing your SFP GBIC, read the following handling,
safety, and environmental guidelines:
• SFP GBICs are static sensitive. To prevent damage from
electrostatic discharge (ESD), follow your normal board
and component handling procedures.
18
Page 21

• SFP GBICs are dust sensitive. When you store a SFP GBIC,
or when you disconnect it from a fiber optic cable, always
keep the dust cover over the SFP GBIC’s optical bores.
• To clean contaminants from the optical bores of a SFP GBIC,
use an alcohol swab or equivalent to clean the ferrules of
the optical connector.
• Dispose of this product according to all national laws and
regulations.
Warning: Fiber optic equipment can emit laser or
infrared light that can injure your eyes. Never look into
an optical fiber or connector port. Always assume that
fiber optic cables are connected to a light source.
Installing a Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) GBIC
This section lists the steps to install a SFP GBIC.
To install a SFP GBIC:
1 Remove the SFP GBIC from its protective packaging.
2 Verify that the SFP GBIC is the correct model for your
network configuration (Table 8 on page 18).
3 Remove the dust cover from the SFP GBIC’s optical bores.
4 Grasp the SFP GBIC between your thumb and forefinger.
5 Insert the SFP GBIC into the slot on the front panel of the
Gigabit Ethernet switching module (Figure 7)
.
19
Page 22

Figure 6 Inserting a LC SFP GBIC
Figure 7 Inserting a MT-RJ SFP GBIC
Link
Act
BPS2000-2GE MDA
Link
Act
BPS2000-2GE MDA
Note: SFP GBICs are keyed to prevent incorrect
insertion.
20
Page 23

Removing a Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) GBIC
This section lists the steps for removing a GBIC.
To remove a GBIC:
1 Disconnect the network fiber cable from the SFP GBIC
connector.
2 Depending on your SFP GBIC model, either pull the LC
extraction tab located in the front of the SFP GBIC (below
right) with your thumb and forefinger, or press the button on
the botton of the MT-RJ SFP GBIC (below left).
Figure 8 Removing a SFP GBIC (Bottom view)
MT-RJ
SFP GBIC
3
Slide the SFP GBIC out of the Gigabit Ethernet module slot.
4 If the SFP GBIC does not slide easily from the module slot,
LC SFP GBIC
10518FA
use a gentle side-to-side rocking motion while firmly pulling
the SFP GBIC from the slot.
21
Page 24

5 Dispose of the SFP GBIC according to all national laws and
regulations.
Note: If you are storing a SFP GBIC, remember to place
a dust cover over the fiber optic bores.
Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) GBIC specifications
Table 9 describes general SFP GBIC specifications.
Table 9 Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) GBIC
specifications
Specification Descriptions
Dimensions (H x W x D) 0.53 x 0.33 x 2.22 inches
(13.4 x 8.5 x 56.4 mm)
Connectors Multimode fiber optic: LC or MT-RJ
Single-mode fiber optic: LC or MT-RJ
Standards, connectors, cabling, and distance
This section describes SFP GBIC standards, connectors, cabling,
and distance; and provides specifications for the following SFP
GBICs:
• “1000BASE-SX (LC Type)” on page 23
• “1000BASE-LX (LC Type)” on page 24
• “1000BASE-SX (MT-RJ Type)” on page 25
22
Page 25

1000BASE-SX (LC Type)
The Model 1000BASE-SX SFP GBIC provides 1000BASE-SX
(850 nm, short wavelength, Gigabit Ethernet) connectivity using
LC duplex multimode fiber connectors.The Model 1000BASESX SFP GBIC supports full-duplex operation only
.
Table 10 describes standards, connectors, cabling, and distance
for the Model 1000BASE-SX SFP GBIC.
Table 10 1000BASE-SX SFP GBIC specifications
Type Specifications
Standards Conformity to the following standards:
802.3z, 1000BASE-SX
Connectors Duplex LC fiber optic connector
Cabling 62.5 µm
Distance 902 ft. (275 m) using 62.5 µm
Wavelength 850 nm
Optical budget 7 dB
Laser Transmitter Characteristics
Minimum launch power -10 dBm
Maximum launch power -4 dBm
Receiver
Characteristics
Minimum receiver
sensitivity
MMF optic cable
50 µm MMF optic cable
cable
1804 ft. (550 m) using 50 µm MMF optic cable
-17 dBm
MMF optic
23
Page 26

Table 10 1000BASE-SX SFP GBIC specifications
Type Specifications
Maximum input power 0 dBm
1000BASE-LX (LC Type)
The Model 1000BASE-LX SFP GBIC provides 1000BASE-LX
(1300 nm, wavelength, Gigabit Ethernet) connectivity using
LC duplex fiber connectors. The long wavelength optical
transceivers used in the LX model provide variable distance
ranges using both multimode and single-mode fiber optic
cabling. The Model 1000BASE-LX GBIC supports full-duplex
operation only
.
Table 11 describes standards, connectors, cabling, and distance
for the Model 1000BASE-LX GBIC.
Tab l e 11 1000BASE-LX SFP GBIC specifications
Type Specifications
Standards Conformity to the following standards:
802.3z, 1000BASE-LX
Connectors Duplex LC fiber optic connector
Cabling 62.5 µm
Distance 1804 ft. (275 m) using 62.5 µm
MMF optic cable
50 µm MMF optic cable
10 µm SMF optic cable
cable
1804 ft. (275 m) using 50 µm
16405 ft. (5 km) using 10 µm
MMF optic
MMF optic cable
SMF optic cable
24
Page 27

Tab l e 11 1000BASE-LX SFP GBIC specifications
Type Specifications
Wavelength 1300 nm
Optical budget 10.5 dB
Laser Transmitter Characteristics
Minimum launch power -9.0 dBm
Maximum launch power -3 dBm
Receiver Characteristics
Minimum receiver
sensitivity
Maximum input power -3 dBm
-20 dBm
1000BASE-SX (MT-RJ Type)
The Model 1000BASE-SX (MT-RJ Type) SFP GBIC provides
Gigabit Ethernet connectivity using MT-RJ multi-mode fiber
connectors.
Table 12 describes standards, connectors, cabling, and distance
for the Model 1000BASE-SX (MT-RJ Type) SFP GBIC.
Table 12 1000BASE-SX (MT-RJ Type) SFP GBIC
specifications
Type Specifications
Standards Conformity to the following standards:
802.3z, Ethernet full duplex
Connectors Duplex MT-RJ fiber optic connector
25
Page 28

Table 12 1000BASE-SX (MT-RJ Type) SFP GBIC
specifications (continued)
Type Specifications
Cabling 62.5 µm
Distance 275 mm (62.5 µm
Optical budget 7 dB
Laser Transmitter Characteristics
Wavelength 850 nm
Maximum spectral width 0.85 nm
Maximum launch power -4.0 dBm
Minimum launch power into
fiber
Receiver Characteristics
Wavelength 850 nm
Minimum receiver sensitivity -17 dBm
Maximum input power 0 dBm
MMF optic cable
50 µm MMF optic cable
MMF optic cable)
550 mm (50 µm MMF optic cable)
-9.5 dBm
26
Page 29

Introduction to Coarse Wavelength Division
Multiplexed (CWDM) Small Form Factor
Pluggable (SFP) Gigabit Interface Converters
This section describes how the Nortel Networks* coarse
wavelength division multiplexed Small Form Factor Pluggable
Gigabit Interface Converter (CWDM SFP GBIC) works within
the optical routing system. It also provides a list of CWDM SFP
GBICs by wavelength and shows how they are labeled and colorcoded.
CWDM SFP GBIC description
CWDM SFP GBICs are transceivers that link Gigabit Ethernet
ports with fiber optic networks. WDM technology consolidates
multiple optical channels, using specific wavelengths to expand
available bandwidth, on a common optical fiber.
About the optical routing system
CWDM SFP GBICs are a component in the optical routing
system designed to support high speed data communication for
Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs). The system uses a grid of
eight CWDM optical wavelengths in both ring and point-to-point
configurations. All components are color-coded by wavelength.
27
Page 30

CWDM SFP GBIC Listing
Table 13 lists the Nortel Networks CWDM SFP GBICs and
describes their wavelengths, color codes, part numbers, and cable
lengths.
Table 13 Nortel Networks CWDM SFP GBIC List
CWDM SFP GBIC Product number Cable Length
1470nm/Gray AA1419025
AA1419033
1490nm/Violet AA1419026
AA1419034
1510nm/Blue AA1419027
AA1419035
1530nm/Green AA1419028
AA1419036
1550nm/Yellow AA1419029
AA1419037
1570nm/Orange AA1419030
AA1419038
1590nm/Red AA1419031
AA1419039
1610nm/Brown AA1419032
AA1419040
40 KM
70 KM
40 KM
70 KM
40 KM
70 KM
40 KM
70 KM
40 KM
70 KM
40 KM
70 KM
40 KM
70 KM
40 KM
70 KM
Note: The cable distance may vary depending on the
quality of fiber optic cable used.
28
Page 31

Note: CWDM SFP GBICs are installed and removed
like any other LC type SFP GBIC.
CWDM SFP GBIC specifications
Table 14 CWDM SFP GBIC specifications
Item Specification
Physical dimensions 0.457 X .604 X 2.18 inches
Connectors Duplex LC fiber optic
Cabling SMF, 9 µm
Data rate Nominal
Average launch power minimum
Transmitter extinction ratio minimum 9 dB
Data format 8 B/10 B
Average receive power minimum
Power supply maximum 3.15 to 3.45 V, 40 mA
Operating temperature range 0
Regulatory Class 1 devices per FDA/CDRH and
range
maximum
maximum
1EC8251 Laser Safety Regulations
(11.6 X 15.3 X 55.43 mm)
1.0625 to 1250 Mbaud
-40 dBm
+2 dBm
-23 dBm
-3 dBm
o
C to 60oC
29
Page 32

Note: A minimum attenuation of 5 dB must be present
between the transmitter and receiver. To avoid receiver
saturation, you must insert a minimum attenuation of 5
dB when:
• testing the CWDM SFP GBIC in loopback mode
• using short runs of fiber with no intermediate
CWDM OADM or CWDM OMUX
To determine the expected signal loss for a CWDM
OADM, CWDM OMUX, or fiber length, see Installation
and Networking Guidelines for Optical Routing, part
number 212257-A.
Given a loss budget of 24 dB and assuming fiber loss of
.25 dB/km, up to 96 km reach is supported with no
intermediate CWDM OADM or CWDM OMUX.
30
Page 33

Connecting to Nortel Networks online
This section describes products, services, and support systems
that can be accessed online.
Hard-copy technical manuals
You can print selected technical manuals and release notes free,
directly from the Internet. Go to the www.nortelnetworks.com/
documentation URL. Find the product for which you need
documentation. Then locate the specific category and model or
version for your hardware or software product. Use Adobe*
Acrobat Reader* to open the manuals and release notes, search
for the sections you need, and print them on most standard
printers. Go to Adobe Systems at the www.adobe.com URL to
download a free copy of the Adobe Acrobat Reader.
You can purchase selected documentation sets, CDs, and
technical publications through the Internet at the
www1.fatbrain.com/documentation/nortel/ URL.
How to get help
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel Networks
product from a distributor or authorized reseller, contact the
technical support staff for that distributor or reseller for
assistance.
31
Page 34

If you purchased a Nortel Networks service program, contact one
of the following Nortel Networks Technical Solutions Centers:
Technical Solutions Center Telephone
Europe, Middle East, and Africa (33) (4) 92-966-968
North America (800) 4NORTEL or (800) 466-7835
Asia Pacific (61) (2) 9927-8800
China (800) 810-5000
An Express Routing Code (ERC) is available for many Nortel
Networks products and services. When you use an ERC, your
call is routed to a technical support person who specializes in
supporting that product or service. To locate an ERC for your
product or service, go to the www12.nortelnetworks.com/ URL
and click ERC at the bottom of the page.
32
 Loading...
Loading...