Page 1

Using the Model 3395/3395A
APGEN Utility
SynOptics Communications, Inc.
4401 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95052-8185
(408) 988-2400
893-769-A July 1994
Page 2

© 1994 by SynOptics Communications, Inc. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
SynOptics Communications, SynOptics, Optivity, and LattisNet are registered trademarks of SynOptics
Communications, Inc. System 3000 and SynOptics Press are trademarks of SynOptics Communications,
Inc.
Other brand and product names are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective holders.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, SynOptics
Communications, Inc. reserves the right to make changes to the products described in this document
without notice.
SynOptics Communications, Inc. does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application
of the product(s) or circuit layout(s) described herein.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Statement
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy. If it is not installed and used in accordance with the
instruction manual, it may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required
to take whatever measures may be necessary to correct the interference at their own expense.
Electromagnetic Emissions
Meets requirements of:
FCC Part 15, Subparts A and B, Class A
EN 55 022 (CISPR 22:1985), Class A
General License VDE 0871, Class B (AmtsblVfg No. 243/1991 and Vfg 46/1992)
VCCI Class 1 ITE
ii 893-769-A
Page 3

Table of Contents
Preface
Organization................................................................................................................................................vii
Conventions................................................................................................................................................viii
Related Documentation .............................................................................................................................. ix
SynOptics Customer Support......................................................................................................................ix
Chapter 1 - Introduction to Model 3395 Host-based Management
Support for Load Servers and Parameter Servers....................................................................................... 1-2
SynOptics Network Management Products................................................................................................ 1-3
Optivity................................................................................................................................................ 1-3
SNMP.................................................................................................................................................. 1-3
Terminal Server Host-based Management Features.................................................................................. 1-4
The csportd Daemon............................................................................................................................ 1-4
Command Scripts ................................................................................................................................ 1-4
Dial-back Scripts ................................................................................................................................. 1-5
Nested Menus......................................................................................................................................1-5
The APGEN Utility .................................................................................................................................... 1-5
Chapter 2 - Installing the APGEN Utility
General Network Configuration ................................................................................................................. 2-1
Configuring the Terminal Server for Use with APGEN ............................................................................ 2-2
Defining a UNIX Host as a Parameter Server..................................................................................... 2-2
Defining the UNIX Script Server........................................................................................................ 2-3
Configuring the UNIX Host as a Script Server.......................................................................................... 2-3
Directory Requirements....................................................................................................................... 2-4
The Secure TFTP Option..................................................................................................................... 2-5
Running the APGEN Installation Script..................................................................................................... 2-5
Chapter 3 - Using the APGEN Utility
Using the APGEN Command and Options ................................................................................................ 3-2
Creating the APGEN Script File................................................................................................................. 3-4
Using the -verbose Option................................................................................................................... 3-4
About Comment Lines in the Script.................................................................................................... 3-5
Converting the Entire Parameter File With the -all Option................................................................. 3-5
Converting a Portion of a Parameter File............................................................................................ 3-10
Editing the Script File to Modify Command Lines.................................................................................... 3-11
Changing the Values of Terminal Server Characteristics....................................................................3-11
Entering Terminal Server Passwords .................................................................................................. 3-11
Enabling Configurable and Keyed Features........................................................................................ 3-12
Executing the APGEN Script File..............................................................................................................3-15
Initializing the Terminal Server After Running a Script..................................................................... 3-17
Troubleshooting the Script File........................................................................................................... 3-17
Updating APGEN Script Files.................................................................................................................... 3-18
iii 893-769-A
Page 4

Chapter 4 - Using UNIX Utilities With APGEN Script Files
Using the diff Utility to Compare Two APGEN Script Files .....................................................................4-1
Creating a File with the diff Utility......................................................................................................4-1
Using the grep Utility to Search Through an APGEN file..........................................................................4-3
Displaying Command Lines ................................................................................................................4-3
Creating a Script File ...........................................................................................................................4-4
Appendix A - A Sample APGEN -all Script
Appendix B - A Sample APGEN -verbose Script
Index
iv 893-769-A
Page 5

Figures
1-1 Different types of hosts on the network........................................................................................... 1-1
1-2 A portion of an APGEN script file................................................................................................... 1-6
1-3 Sending APGEN script files to terminal servers on the network..................................................... 1-7
2-1 A network configuration that supports the APGEN utility.............................................................. 2-2
2-2 An example of a script server directory structure............................................................................ 2-4
2-3 APGEN files .................................................................................................................................... 2-6
3-1 A parameter file header from an APGEN script file........................................................................ 3-4
v 893-769-A
Page 6

Preface
This manual introduces some of the tools that you can use to manage the Model 3395 Terminal Server
from a host on the network. In particular, it describes how to use the Model 3395 ASCII Parameter File
Generator (APGEN) utility. This utility converts a binary terminal server parameter file into an ASCII
script file, which you can download from the host to a communications server.
This manual is for network managers who update and maintain Model 3395 Terminal Server parameter
files, and who have some knowledge of the UNIX operating system. This manual assumes that the terminal
server hardware is installed, and that the server is running with a load image and a parameter file. Readers
will use this manual with other terminal server documentation, listed at the end of this Preface.
Organization
This manual contains the following chapters:
Chapter 1 Introduces different Model 3395 host-based management products, including the APGEN
utility.
Chapter 2 Describes how to configure the UNIX host and the terminal server to support the
APGEN utility. This chapter also describes how to install the APGEN utility on the
UNIX host with the Install script.
Chapter 3 Describes how to use the apgen command to create ASCII script files, how to edit these
files, and how to execute a script file from the terminal server.
Chapter 4 Describes how to use UNIX tools, including diff and grep, to analyze APGEN script files.
Appendix A Includes a complete APGEN script created with the -all option.
Appendix B Includes a complete APGEN script created with the -verbose option.
893-769-A vii
Page 7

Preface
Conventions
Throughout this manual, the word “Enter” means type something and then press the <New Line>,
<Return>, or <Enter> key; for example, “Enter the apgen command” means type the word apgen and then
press the <New Line>, <Return>, or <Enter> key.
This manual also uses the following conventions:
command required [optional] [
Where Means
command You must enter the command, or its accepted abbreviation, as shown.
required You must enter an argument, or its accepted abbreviation, as shown.
[optional] You have the option of entering this argument or variable. Do not
[
optional
Additionally, this manual uses certain symbols in special ways:
Symbol Means
TS3395> This is the default Model 3395 command interface prompt at Nonprivileged ports.
TS3395>> This is the default Model 3395 command interface prompt at Privileged ports.
% This is the UNIX C shell prompt.
In examples, this manual uses
This typeface to show your entry and the responses and screens from
the Model 3395 Terminal Server.
This typeface to show responses from remote hosts and devices on the network. This typeface also
shows commands or arguments that are variable, such as “hostname.”
] type the [optional] brackets; they only set off what is optional.
optional
]
viii 893-769-A
Page 8

Preface
Related Documentation
The following manuals provide information that you may find useful with this manual:
Software Management Guide for the Model 3395/3395A Terminal Server (SynOptics part number
893-158-C)
This manual describes the configuration, setup, and management of a terminal server software
communications package, supplied by SynOptics Communications, Inc. This manual is written for
network managers, and terminal server, UNIX, and VAX system managers.
Commands Reference for the Model 3395/3395A Terminal Server (SynOptics part number 893-159-C)
This manual describes individual terminal server commands in detail. It is written for all terminal server
users, although many commands can only be used at privileged ports.
To purchase additional copies of this document or other SynOptics product publications, order by part
number from SynOptics Press™ at the following numbers. You may also request a free catalog of
SynOptics Press product publications.
• Phone: 1-800-845-9523
• FAX: U.S./Canada: 1-800-582-8000, International: 1-916-939-1010
SynOptics Customer Support
For assistance with installing and configuring your SynOptics systems or for post-installation questions or
problems, contact your local reseller. If you cannot contact your local reseller, call the SynOptics Technical
Response Center (TRC) Contract Hotline.
To contact the TRC Contract Hotline, call:
• U.S. and Canada: 1-800-473-4911
• Europe: 011-31-3480-31616
• Rest of the world: 408-764-1000
Technical information is available from the SynOptics InfoFACTS fax-on-demand system by calling:
• U.S. and Canada: 1-800-786-3228
• International: 408-764-1002
You can also access technical information in the SynOptics forum on CompuServe.
For information about our education services, contact the SynOptics Training Coordinator at
1-800-473-4911 or 408-764-1018.
893-769-A ix
Page 9
Chapter 1
Introduction to Model 3395
Host-Based Management
The Model 3395 Terminal Server includes several tools that allow you to manage them from a host on the
network. Command scripts and the ASCII Parameter File Generator utility (APGEN), are part of the
terminal server software package. This chapter briefly describes several different host-based tools and how
they can help you manage your Model 3395. It also introduces the APGEN utility, which the remaining
chapters of this book describe in detail.
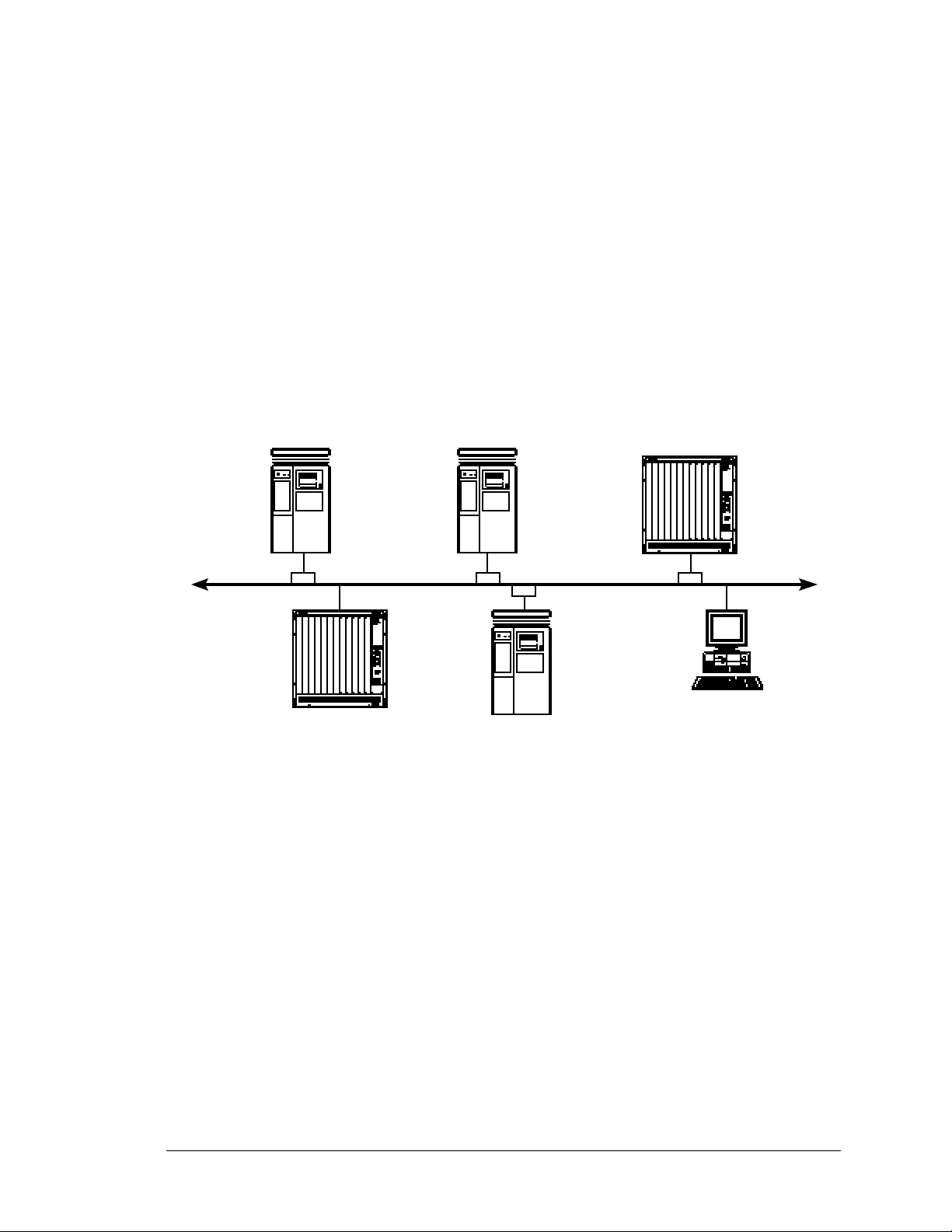
Figure 1-1 shows a local area network (LAN) with different types of hosts that you can use to run the tools
described in this chapter. Not every type of host supports every management tool.
Model 3000 Hub
VAX/ULTRIX Host
UNIX Host
with Model 3395
Terminal Server
Model 3000 Hub
with Model 3395
Terminal Server
Figure 1-1. Different types of hosts on the network
VAX/VMS Host
UNIX SUN
Workstation
893-769-A 1-1
Page 10

Introduction
The host-based management tools that Model 3395 Terminal Server offers to support its product line
include the following:
• Support for Load Servers and Parameter Servers
• SynOptics Network Management Products
• Communications Server Host-Based Management Features
• The APGEN Utility
The remaining chapters of this manual provide detailed information about the APGEN utility.
Support for Load Servers and Parameter Servers
UNIX® hosts and VAX hosts, running VMS or ULTRIX, can supply the operating software, or load
image, to Model 3395 Terminal Servers on the network. These hosts can also maintain the parameter files
for Model 3395 Terminal Servers and receive diagnostic files from these products if a problem occurs.
Hosts that offer these services function as load servers, parameter servers, and dump servers for Model 3395
Terminal Servers.
You can configure one or more hosts as load servers and parameter servers while also using Model 3395
Terminal Servers as load servers and parameter servers. For example, you might use a Model 3395
Terminal Server as the primary load server and parameter server for other Model 3395 Terminal Servers in a
System 3000 chassis. You can also use a host as a backup parameter server and another host as a back up
load server for the products in the chassis.
When you order software from SynOptics, you specify whether you will need a UNIX kit or a VAX/VMS
kit. SynOptics sends you the appropriate software kit and documentation for the load server. For more
information about how to configure UNIX hosts and VAX/VMS hosts as load servers, parameter servers,
and dump servers, see the following manuals:
• Model 3395 Terminal Server Software Installation Guide, UNIX (SynOptics part
number
893-184-B), which describes procedures that you use to install Model 3395 software
on UNIX hosts.
• Model 3395 Terminal Server Software Installation Guide, VMS (SynOptics part
number 893-163-B), which describes procedures that you use to install Model 3395
software on VAX/VMS hosts.
1 -2 893-769-A
Page 11

Introduction
SynOptics Network Management Products
SynOptics offers its own network management product, called Optivity, as well as support for the Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP), which is an industry standard protocol.
Optivity
Optivity is a software package for the management of SynOptics networks. Just as the Model 3395
Terminal Server is integrated into the System 3000 hub, management of the Model 3395 Terminal Server
is integrated into the Optivity network management application. Optivity is designed to work with popular
UNIX- and DOS-based management platforms such as Sun Microsystem's SunNet Manager, Novell's
NetWare Management System, IBM's NetView/6000, and Hewlett-Packard's OpenView.
Contact your local SynOptics representative for more information on Optivity.
SNMP
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet protocol defined by RFC1157 that
specifies how network management information is carried through a network. Model 3395 Terminal
Servers store information defined in RFC 1213, Management Information Base (MIB), as well as many
other standard and Model 3395 MIBs. This information is available when requested through SNMP.
Refer to the software documentation supplied with your Model 3395 Terminal Server for more information
about SNMP support.
893-769-A 1 -3
Page 12

Introduction
Terminal Server Host-based Management Features
The terminal server software package provides several features that you can use on a host to manage
terminal servers on the network. These include the following:
• The Csportd daemon
• Command scripts
• Dial-back scripts
• Nested menus
The Software Management Guide for the Model 3395/3395A Terminal Server describes these features in
detail. The APGEN utility, another communications server host-based management feature, is described in
the next section.
The csportd Daemon
The csportd daemon is a UNIX host-based daemon that you use to make connections to a port and transfer,
or pipe, data to and from that port. You can use this connection to send a file or user data to a port, for
printing to PostScript printers, or as a permanent connection between a host and a specific port. The
csportd daemon is a Model 3395-proprietary daemon that you implement as a utility at a UNIX host. You
can use csportd in place the of the tsvr_ptyd daemon and tsvr_filter, although Model 3395 Terminal Servers
still includes these features in the terminal server software kit.
The csportd daemon comes with an installation script and a MAN page. You copy it from a UNIX media
kit onto the host, and then install it with the installation script. You can install the csportd daemon on any
UNIX host running BSD and AT&T System V UNIX operating systems, and has also been tested on hosts
running the AIX, MIPS, HP/UX, and ULTRIX operating systems.
Command Scripts
The Model 3395 script feature allows you to create a file, or script, that contains one or more Model 3395
commands and to store the script on a host, or script server. UNIX hosts and VAX/VMS hosts can
function as command script servers. When you execute the SCRIPT command on the terminal server, the
host downloads the script to the terminal server. The command processor on the terminal server
automatically executes the commands.
You can configure a terminal server port to request the script file automatically when a user logs on to the
port, or you can allow the user to request the script file. You create script files on the script server using a
text editor. The script server can be a host system that supports the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP).
The way you use scripts to manage terminal server ports depends on the content of the script file and
whether or not you configure the port to execute the script automatically or allow the user to execute the
script.
1 -4 893-769-A
Page 13

Introduction
Dial-back Scripts
If a port on a terminal server is a “dial-back” modem port, you can create a dial-back script to enhance
security on the modem port. The dial-back script specifies the telephone number to dial when a specific
user attempts to log on to the server through a modem. If the terminal server cannot find a script file for
that user, it will not permit the user to log in. If it does find a script file for the user, the server will cause
the modem to dial back that user at a designated telephone number. You can use the dial-back script with a
login script for dial-back ports.
Nested Menus
The Nested Menus feature allows you to create a series of menus with options that can execute terminal
server commands or open another menu. You create the nested menus in a menu file which resides on a
host defined as a script server. The terminal server obtains the menu file from the script server and uses the
menus to override the Model 3395 command interface. You can enable or require nested menus at specific
ports or in a user's login script.
If you require nested menus at a port, you can prevent users at that port from gaining access to the Model
3395 command interface. The users will only have access to the options on the menu. To change these
options, you can modify the menu file on the host.
The APGEN Utility
The ASCII Parameter File Generator (APGEN) utility, which runs on a UNIX host, converts a binary
communications server parameter file to an ASCII script file. The script file contains the Model 3395
DEFINE commands that specify the values for parameters on the terminal server. You download the script
file from the host to a terminal server on the network with the Model 3395 SCRIPT command. The
APGEN utility can convert compressed or uncompressed parameter files.
The following Model 3395 Terminal Server products support the APGEN Utility:
• Terminal servers, running version 5.1 or greater of Model 3395 software
893-769-A 1 -5
Page 14

Introduction
Figure 1-2 represents a part of an APGEN script file for a terminal server. This portion of the script file
lists the commands which define terminal server features.
#echo Server Features
#
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL TELNET ENABLED LAT
ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL PPP ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL SNMP ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL TN3270 DISABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL XPRINTER ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL XREMOTE DISABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL ARAP DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER RLOGIN ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER IPX PROTOCOL ETHERNET ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER IPX PROTOCOL MAC DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS DISABLED
#
Figure 1-2. A portion of an APGEN script file
Chapter 3 and Appendixes A and B include more examples of APGEN script files.
The apgen command, which creates the script file, allows you to convert an entire parameter file or just a
portion of it which includes the commands that define a particular feature. You can create a script file that
includes only the server features in Figure 1-2 for example. These smaller scripts take less time to edit and
execute than larger files, and provide an efficient method changing a limited portion of the parameter file.
Once you create the script file, you can edit it with any ASCII text editor. You can enable and disable
features, specify particular values for characteristics, and change text strings. The result is a script that
represents a tailored parameter file that you can download to terminal servers anywhere on the network.
APGEN script files also provide a record if the parameters available on a particular terminal server and their
status at any given time.
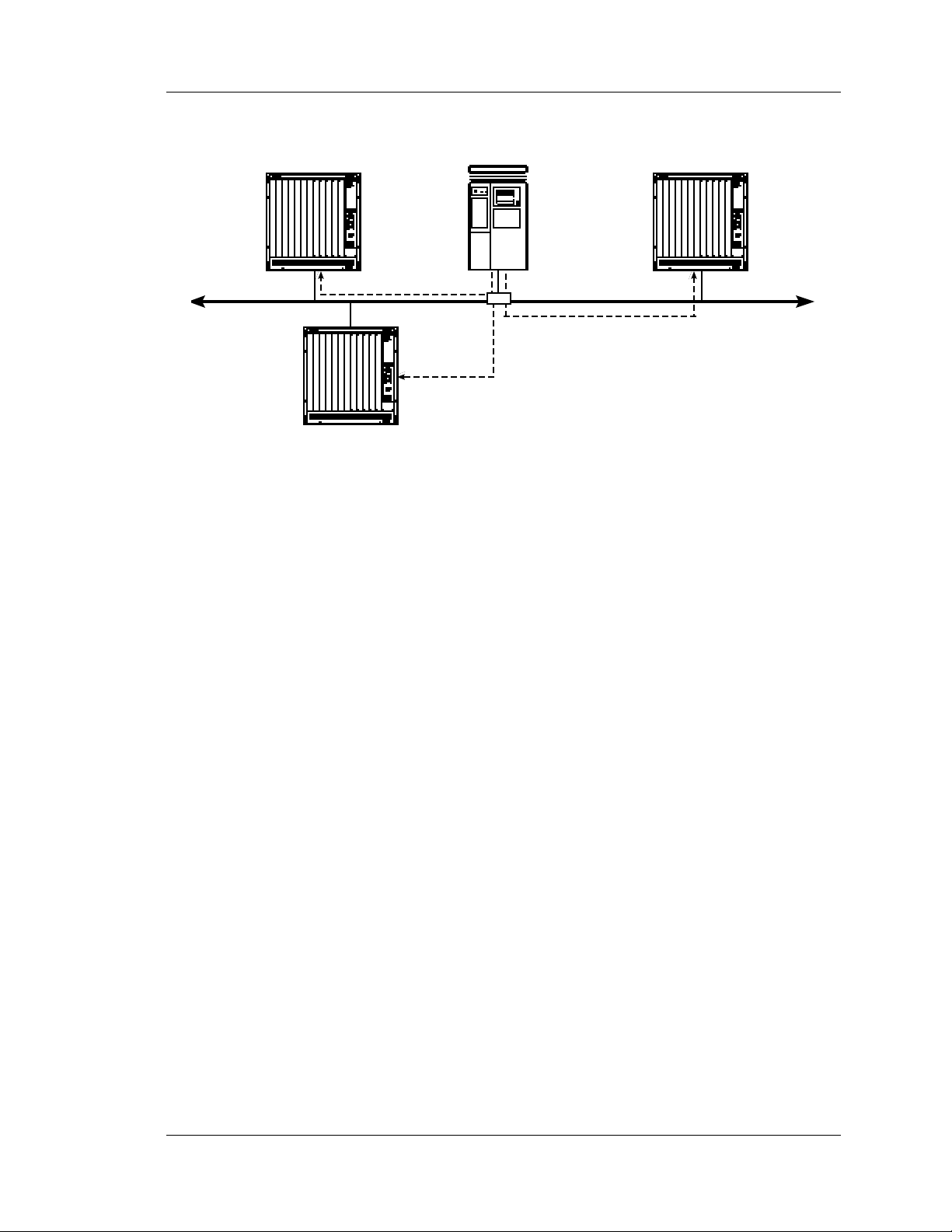
You can create APGEN script files for each type of terminal server on your network. Figure 1-3 represents
a UNIX script server sending APGEN script files to the different types of terminal servers on a LAN.
1 -6 893-769-A
Page 15
Introduction
Model 3000 Hub
with Model 3395
Terminal Server
UNIX Host with
APGEN Script Files
Model 3000 Hub
with Model 3395
Terminal Server
LAN
Model 3000 Hub
with Model 3395
Terminal Server
Figure 1-3. Sending APGEN script files to terminal servers on the network
A user at a terminal server on the network in Figure 1-3 can execute the SCRIPT command to download the
APGEN script from the script server. The user then initializes the communications server for the DEFINE
commands in the script to take effect. You can use UNIX utilities, such as diff and grep, to analyze
different script files on the host through compare and search functions.
The remaining chapters of this book describe how to install and use the APGEN utility. These chapters
provide the following information:
• How to install the apgen utility
• How to create apgen scripts
• How to use UNIX utilities to analyze APGEN scripts
893-769-A 1 -7
Page 16

Chapter 2
Installing the APGEN Utility
The APGEN utility comes with an installation script and a MAN page. You copy the utility from a Model
3395 UNIX media kit into a directory on the UNIX host, then install it using the installation script. You
can install the APGEN utility on any UNIX host running the BSD or the AT&T System V UNIX
operating systems. It has also been tested on hosts running the AIX, MIPS, HP/UX, and ULTRIX
operating systems.
This chapter includes the following information about APGEN:
• General network configuration
• Configuring the terminal server for use with APGEN
• Configuring the UNIX host as a script server
• Running the APGEN installation script
General Network Configuration
To use the APGEN utility, you need to configure a UNIX host as a parameter server and as a script server.
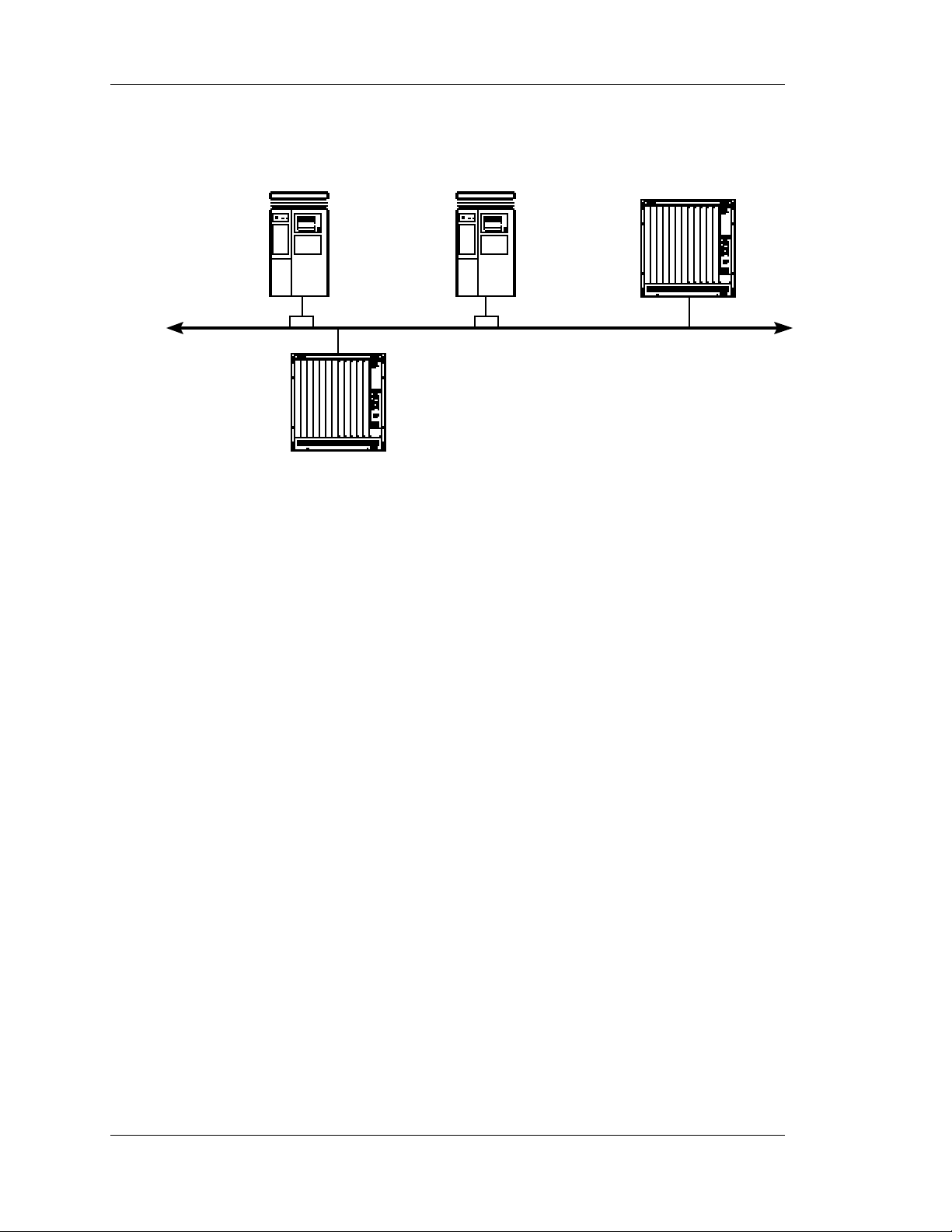
These can be the same host or different hosts on the network. Figure 2-1 represents a network
configuration with a UNIX host running APGEN that also functions as the parameter and the script server.
893-769-A 2-1
Page 17
Installing the APGEN Utility
Model 3000 Hub
with Model 3395
Terminal Server
LAN
VAX/ULTRIX Host
Backup
Parameter
Server
UNIX Host
Running APGEN
Parameter
Server
Script
Server
Model 3000 Hub
with Model 3395
Terminal Server
Figure 2-1. A network configuration that supports the APGEN utility
In Figure 2-1, the UNIX host running the APGEN utility is also a parameter server and a script server for
the terminal servers in the System 3000 hubs. To obtain an APGEN script file, a user on a terminal server
enters the Model 3395 SCRIPT command with the pathname and filename of the script file on the host.
This UNIX host can then download the script file to the terminal server.
Configuring the Terminal Server for Use with APGEN
Your terminal server may already have a UNIX host defined as a parameter server and a script server. If not,
you need to define one or more hosts for this purpose to use the APGEN utility. You can use the same or
different hosts. You must also be sure that Telnet is enabled on the terminal server , and that you have
assigned an Internet address to it.
Defining a UNIX Host as a Parameter Server
The APGEN utility uses a parameter file on a UNIX host to create the script file. You can copy a
parameter file from some other source, such as a VAX/VMS host, onto a UNIX host, or you can assign a
UNIX host as a parameter server. Use the following commands to do this:
DEFINE/SET PARAMETER SERVER
address
node-name
INTERNET ADDRESS
internet-
2-2 893-769-A
Page 18

Installing the APGEN Utility
The following are examples of these commands:
TS3395>> define parameter server xip internet address 140.179.82.6
TS3395>> set parameter server xip internet address 140.179.82.6
TS3395>>
You can use other types of hosts as back-up parameter servers.
Defining the UNIX Script Server
Assign the Internet address of the UNIX script server and the pathname to the script directory with the
following commands:
DEFINE/SET SERVER SCRIPT SERVER
The following are examples of these commands:
TS3395>> define server script server 140.170.82.6 "/tftpboot"
TS3395>> set server script server 140.179.82.6 "/tftpboot"
TS3395>>
The next section describes how to configure the UNIX host as a script server.
domain-name "directory-path
internet-address "directory-path
"
"
Configuring the UNIX Host as a Script Server
Follow these steps to select one or more script servers and create a directory for the APGEN script file on
the script servers.
• Determine which hosts will act as script servers. Script servers must run TFTP. Each terminal server
can have a maximum of four script servers. You can use two or more hosts as back-up script servers.
• Set up a directory to contain the APGEN file on each script server. Consider the TFTP guidelines
described in the next section, “Directory Requirements,” before you do this.
• Create a directory to contain the APGEN script file. On some UNIX systems, you can create a toplevel directory for the APGEN file only, rather than using a directory that already contains many files
such as /usr, /bin, /tftpboot, or /etc. Systems running with the tftp secure option enabled may require
that you place the APGEN file in /tftpboot.
Figure 2-2 illustrates how you can set up a directory to contain the APGEN script files under the directory
/tftpboot. In Figure 2-2, the directory apgen will contain the APGEN script files. The examples which
follow show how to create this directory on a UNIX host.
893-769-A 2-3
Page 19

Installing the APGEN Utility
/tftpboot
/apgen
Figure 2-2. An example of a script server directory structure
The following command creates the apgen directory on a UNIX host:
% cd /tftpboot
% mkdir apgen
%
Directory Requirements
The script server downloads APGEN script files to the terminal server through the Trivial File Transfer
Protocol (TFTP). UNIX systems usually require that you locate all files that TFTP will transfer on the
network in the TFTP “home directory” of the UNIX system. Most UNIX systems allow you to specify the
TFTP home directory or use a default home directory. The default TFTP home directory varies from system
to system. Follow the configuration instructions for the TFTP daemon (tftpd) in system documentation,
such as MAN pages, to determine how to locate the TFTP home directory.
On Sun Workstations, for example, the MAN page for tftpd says that the home directory is specified in the
/etc/inetd.conf file, and that the factory default home directory is /tftpboot. On this system, you can
examine the tftp entry in the /etc/inetd.conf file to see if the host is using the default home directory or a
user-specified home directory. Place the script files in the home directory.
To simplify configuration or to prevent the TFTP home directory from becoming cluttered, you can place
script files in a directory other than the TFTP home directory. To do this, create a link from the TFTP
home directory to the directory containing the script files, so that the TFTP daemon can locate the files.
Give this link appropriate file permissions using commands in this form:
% cd
tftp-home
% ln -s
script-directory-path script-directory-name
-directory
2-4 893-769-A
Page 20

Installing the APGEN Utility
The following example applies to Sun Workstations. The default TFTP home directory is /tftpboot and the
scripts reside in a directory named scripts. The following commands create a link from /tftpboot to scripts:
% cd /tftpboot
% ln -s /usr/synoptics/scripts scripts
#
You may need to enable superuser mode to enter these commands.
The Secure TFTP Option
A UNIX system may be configured for secure TFTP operation. Some implementations, for example, can
limit TFTP to certain directories. If this is the case, you must place all files in a particular home directory,
or in a subdirectory of the home directory. If the files are not located there, TFTP will not find them. For
example, SunOS and some others use a TFTP daemon -s (secure) option that restricts TFTP access to a
particular directory and its subdirectories. Sun Workstations are normally configured with this option
enabled. If you examine the /etc/inetd.conf file, you will see an entry similar to -s /tftpboot in the tftpd
entry. Other vendors may use a different method. The MAN pages on tftp, tftpd, and inetd.conf describe
directory and security requirements on your UNIX system.
Running the APGEN Installation Script
The Model 3395 distribution media includes the APGEN installation script, MAN page, and C source code
in a tar archive named apgen.tar. Use the following procedure to install these items on your UNIX system:
• Log on to the UNIX host. You must log on as root to install the host utilities package in the
apgen.tar archive. Enable Superuser mode with the su command.
• Move to the directory where you want APGEN to reside. For example, if APGEN will reside in
/usr/synoptics, move there:
% cd /usr/synoptics
• Load the distribution tape onto a tape drive, then copy the apgen.tar archive to the UNIX system. You
can copy the archive to any directory using a tar command of this form:
% tar xvf /dev/rst8 apgen.tar
Note: For nine-track tapes, be sure to use the correct tape-drive-device-name to match the format
(QIC11 or QIC24) of the tape.
893-769-A 2-5
Page 21

Installing the APGEN Utility
On Sun workstations, for example, use the following command to extract the apgen.tar archive
from a QIC24 tape:
% tar xvf /dev/rst8 apgen.tar
• Unpack the apgen.tar archive, using a tar command of this form:
% tar xvf apgen.tar
You can delete the apgen.tar archive when the command completes and the files have been extracted
from the archive.
The tar utility automatically copies files and subdirectories from the apgen.tar archive into the
appropriate directories. For example, this utility copies the APGEN C source file (apgen.c) and other
APGEN files into src/apgen, a subdirectory of src/. It copies MAN pages into the man/cat/and
man/src/ directories. You can change the location of these items when you run the installation script.
Figure 2-3 illustrates this directory structure and shows all the APGEN files in src/apgen/.
.release
Install
ReadMe
src/
man/
cat/
apgen.l
src/
apgen.l
Figure 2-3. APGEN files
The text document ReadMe contains some simple installation instructions, warnings, a list of
known problems, information about new host types that can be supported, as well as other up-todate information about the Install script and the APGEN utility.
apgen/
Makefile
apgen.h
param_data.h
print_param.c
apgen.c
uncompress_param.c
utils.c
2-6 893-769-A
Page 22

Installing the APGEN Utility
• Run the APGEN installation script. Unless you use the -d argument with the Install command, the
script prompts you for information while it is executing. This information helps to determine the best
way to install or compile the source file. The prompts vary according to the UNIX implementation,
the particular C compiler and libraries, and the directory structure on the host.
In most situations, you can accept the defaults. To do this, enter the following, hitting the <Return>
key twice:
% Install -d
To run the install script with prompts, enter the following:
% Install
The install script is a Bourne shell script. For supported hosts, the script automatically determines the
host type, looks for libraries, and installs software into default locations.
Each prompt includes the default choice in brackets. To accept the default choice, press the <Return>
key. To enter a different choice, enter the choice and press the <Return> key. For example, the first
prompt that usually appears on the screen is the following:
Where do you want the executables installed (~name ok)?
[/usr/local/bin]
If you want the script to move the APGEN utility into /usr/local/bin, press the <Return> key and the
script will continue. If you want the APGEN utility in a different location, enter the pathname and
press the <Return> key. Some prompts will include the option to use the ~name construct. This
allows you to direct the script to use the default login directory belonging to the user specified in the
~name variable. For example, if you specified ~gsmith, the script will move the executable image
into the log login directory of user gsmith.
If you cannot respond to a prompt from the script, you can use the ! command to escape from the shell
and execute a command or start a subshell. You might want to do this to obtain the names of libraries
or the location of a directory.
While it is executing, the script displays status messages describing the installation process, and the
following prompt:
[Type carriage return to continue]
Press the <Return> key when you are ready to proceed with the script.
893-769-A 2-7
Page 23

Installing the APGEN Utility
• The script displays the message “Install Done” when the APGEN installation is complete. The script
generates a log file called Install.out, which includes a record of the libraries and directories used for the
installation, as well as any errors which prevented the installation.
When the APGEN installation successfully completes, the output is an executable APGEN image.
You can use this to convert parameter files into executable script files. The next chapter, “Using the
APGEN Utility,” describes various ways to use the APGEN utility with terminal server parameter
files.
2-8 893-769-A
Page 24

Chapter 3
Using the APGEN Utility
The APGEN utility creates an ASCII text file from a compressed or an uncompressed binary parameter file.
This script file contains a list of DEFINE commands that specify the characteristics of features and
protocols available on a terminal server. You can use this script file to do the following:
• Maintain a record of features and protocols available on a terminal server, and their status
• Update parameter files of several terminal servers from a central location
• Compare it with other script files to determine the differences between the parameter files of two
terminal servers or the old and new parameter file of the same server
You can also generate scripts that include only those commands that define particular features and protocols.
These limited scripts provide an efficient way of updating portions of a parameter file, and allow you to
determine the status of a feature or protocol quickly and easily.
This chapter includes the following information about how to create an APGEN file, edit it, and execute it
on a terminal server:
• Using the apgen command and options
• Creating the APGEN script file
• Editing the script file to modify command lines
• Executing the APGEN script file
• Updating APGEN script files
This chapter assumes that you have installed the APGEN utility on a UNIX host. Chapter 2 describes the
installation procedure in detail. Chapter 4 describes how to use UNIX utilities to compare and search
through script files.
893-769-A 3-1
Page 25

Using the APGEN Utility
Using the apgen Command and Options
You execute the APGEN utility on a UNIX host with the apgen command. The command supports several
options which determine how much of the parameter file it converts: all of the file, or only a portion that
controls a specific feature or group of features. For example, you can convert only Kerberos characteristics
or only port-specific characteristics.
The syntax for the apgen command is the following:
apgen [-
Where Means
[-option...-option...] Any of the apgen options. If you do not specify an option, the apgen command
parameter-file The pathname of the binary parameter file.
[output-file] The pathname and name of the executable script file. This is optional. If you
option
...-
option
displays the parameter file header only. This is a list of parameter file
information at the beginning of the script and contains no commands.
do not specify an output file, the APGEN utility writes the script to stdout,
which is the terminal screen.
...]
parameter-file
[
output-file
]
3-2 893-769-A
Page 26

Using the APGEN Utility
Option Converts this part of the parameter file:
-all The entire parameter file.
-arap AppleTalk Remote Access Protocol (ARAP) data.
-daemons UNIX daemons data.
-domain All domain data.
-features Terminal server features.
-ip Internet data.
-kerberos Kerberos data.
-lineedit Port line editing data.
-lpd UNIX LPD daemon data.
-manager Manager data.
-menu Menu and nested menu data.
-nvs nonVolatile Storage (NVS) data.
-parameter Parameter server data.
-port[:port-number | all]
Port data for the port you specify in the port-number variable or for all ports. If you do not
specify a port number, APGEN converts all ports. To specify more than one port, but not all,
repeat the -port argument with the port number for the ports you want. This option overrides the arap, -kerberos, -lineedit, -menu, -ppp, -securid, -security, -session, -slip, -telnet, and -xremote
options.
-ppp Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) data.
-rotary Rotary data.
-route[:type] Routing data for the protocol type you specify in the type variable, which converts IP
routing data. This is the default.
-script Script data.
-securid Securid data.
-security Security data.
-server All Server data. This option overrides the -daemons, -features, -ip, -kerberos, -menu, parameter, -ppp, and -snmp options.
-service LAT Service data.
-session Port session data.
-slip Port SLIP data.
-snmp Internet SNMP data.
-telnet Port Telnet data.
-tn3270 TN3270 data.
-verbose List data for each individual port. Use -verbose with one or more of the -all, -kerberos, lineedit, -menu, -port, -ppp, -security, -session, -slip, -telnet, and -xremote options.
-xprinter Xprinter data.
-xremote Xremote data.
893-769-A 3-3
Page 27

Using the APGEN Utility
Creating the APGEN Script File
An APGEN script file has two parts: a header, which includes the line #control_script and information that
describes the parameter file, and the set of DEFINE commands which specify terminal server parameters.
Figure 3-1 shows a parameter file header from an APGEN script file. The header includes information such
as the software version number, the hardware type, and whether or not the parameter file is compressed.
Lines in the header are comments in the script. (The apgen command creates only the header if you enter it
without one or more options.)
#control_script
# APGEN Version 1.1
#
# Parameter File Header
#
# Version : 0x6A
# Date : 25 Oct 1993
# Time : 18:59:02
# Parameter Load Type : 1
# Compressed : Yes
# Software Type : 1
# Stored Format : 7
# Oldest Format : 3
# Hardware Type : 76
# Software Version : V5.2
# Product : Term Server
#
Figure 3-1. A parameter file header from an APGEN script file
The remainder of the parameter file consists of DEFINE commands and comment lines. The script file lists
the commands in functional categories such as server data, IP data, and parameter server information so that
you can read the script more easily. This following sections shows two examples of APGEN script files.
One is a complete parameter file, and one is a portion of a parameter file.
Using the -verbose Option
Unless you use the -verbose option, the APGEN utility combines commands that define features for
individual ports into one command line if the values for these features are the same. For example, if all
ports have DTRWAIT disabled, the script file lists DEFINE PORT ALL DTRWAIT DISABLED. This
saves space in the file, and limits script execution time.
If you use the -verbose option with the apgen command, the script file will list the characteristics for each
individual port. You use -verbose with other options. For example, using -verbose with -all creates a
script which lists all characteristics for all ports. Using -verbose with -session creates a script which lists
session characteristics for all ports. This option can create a very long script file. Appendix B shows a
sample of verbose output.
3-4 893-769-A
Page 28

Using the APGEN Utility
About Comment Lines in the Script
The pound sign # that begins some lines in a script file indicates that the following text is a comment
rather than an executable command. The command processor on the terminal server ignores these lines
when it executes the script file.
The APGEN utility creates comment lines for commands associated with disabled features and protocols
that are configurable or keyed. This reduces script execution time on the terminal server, and provides a
way for you to easily determine which commands enable configurable and keyed features in the script file.
If the TN3270 protocol is disabled, for example, all server and port TN3270 commands are comment lines.
The terminal server ignores them during script execution. See the section “Enabling Configurable and
Keyed Features,” later in this chapter, for more information about these features.
Some comment lines, beginning with #echo, provide status information during script execution. For
example, the line #echo Server Features appears in the script before the commands that manage terminal
server features. The line Server Features appears on the terminal server screen right before the script
executes these commands.
Converting the Entire Parameter File With the -all Option
This example converts an entire binary parameter file to its ASCII equivalent with the
-all option, and stores the script in the file everything.apg. When the conversion is complete, the shell
prompt appears on the screen. This example assumes that the parameter file is in the /tftpboot directory, so
only the filename is required on the command line.
% cd /tftpboot
% apgen -all param-file.prm everything.apg
%
The following example shows portions of the APGEN script file everything.apg. The dots(. . .) indicate
a break in the file. (Appendix A of this manual shows the entire script file.)
#control_script
#
# APGEN Version 1.1
#
# Parameter File Header
#
# Version : 0x6A
# Date : 25 Oct 1993
# Time : 18:59:02
# Parameter Load Type : 1
# Compressed : Yes
# Software Type : 1
# Stored Format : 7
# Oldest Format : 3
# Hardware Type : 76
# Software Version : V5.2
# Product : Term Server
#
#############################################################
.
.
.
893-769-A 3-5
Page 29

Using the APGEN Utility
#
#
#echo Manager Load Data
#
# Products that use version 1 flash or ROM cards:
GLOBAL, NODE
# Products that use version 2 flash or ROM cards:
NODE
# Products that use version 3 flash or ROM cards:
NODE
#
.
.
.
#echo Script Server(s)
#
DEFINE SERVER SCRIPT SERVER 140.179.248.209 "/tftpboot" "/"
#
#echo Menu Prompt Information
#
# DEFINE SERVER MENU PROMPT "Enter number of selection or use
arrow keys: "
# DEFINE SERVER MENU CONTINUE PROMPT "press <RETURN> to
continue... "
#
.
.
.
#echo Server Data
#
DEFINE SERVER ANNOUNCEMENTS ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER BROADCAST ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER CIRCUIT 80
DEFINE SERVER CONSOLE 0
DEFINE SERVER VERBOSE ACCOUNTING ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER VERBOSE PRIORITY 7 LOG FACILITY LOCAL 0
DEFINE SERVER TEXTPOOL 16384
DEFINE SERVER LOCK ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER IDENTIFICATION "Model 3395 Terminal Server"
DEFINE SERVER IDENTIFICATION SIZE 63
DEFINE SERVER DUMP ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER SOFTWARE TS3395.IMG
DEFINE SERVER WELCOME "Welcome to the Model 3395 Terminal
Server."
DEFINE SERVER PACKET COUNT 80
DEFINE SERVER NAME XFF4B15
DEFINE SERVER NUMBER 0
# DEFINE SERVER PRIVILEGED PASSWORD <secret>
# DEFINE SERVER LOGIN PASSWORD <secret>
# DEFINE SERVER MAINTENANCE PASSWORD <secret>
DEFINE SERVER SERVICE GROUPS 0 ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER LAT SOLICITS DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER TIMEZONE 00:00
DEFINE SERVER REPORT ERRORS DISABLED
3-6 893-769-A
Page 30

Using the APGEN Utility
.
.
.
#echo Server Kerberos Information
#
DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS SECURITY NONE
#
#echo Server Menu Information
#
DEFINE SERVER MENU ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER NESTED MENU SIZE 5000
DEFINE SERVER NESTED MENU NAME "mymenu3"
#
#echo Server PPP Information
#
# DEFINE SERVER PPP PAP REMOTE PASSWORD <secret>
#
#echo IP Data
#
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET ADDRESS
140.179.248.218
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET BROADCAST ADDRESS
255.255.255.255
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET PRIMARY DOMAIN ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SECONDARY DOMAIN ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET PRIMARY GATEWAY ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SECONDARY GATEWAY ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SUBNET MASK 255.255.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SUBNET MASK AUTOCONFIGURE ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET NAME NONE
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET DEFAULT DOMAIN SUFFIX NONE
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET TCP CONNECT TIMER 32
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET TTL 64
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET DOMAIN TTL 0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET TCP RESEQUENCING DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET IP REASSEMBLY DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET LOCAL BASE 4000 INCREMENT 100
#
.
.
.
#
#echo Server Features
#
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL TELNET ENABLED LAT ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL MX800 DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL PPP ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL SNMP ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL TN3270 DISABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL XPRINTER ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL XREMOTE DISABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL ARAP DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER RLOGIN ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER IPX PROTOCOL ETHERNET ENABLED
893-769-A 3-7
Page 31

Using the APGEN Utility
DEFINE SERVER IPX PROTOCOL MAC DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS DISABLED
.
.
.
#
#echo *** Port Information ***
#
#
#echo Port Characteristic Information
#
DEFINE PORT 0 MULTISESSIONS DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL MULTISESSIONS DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 AUTHORIZED GROUPS 0 ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL AUTHORIZED GROUPS 0 ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL BREAK LOCAL
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET PREFERRED SERVICE NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 AUTOCONNECT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL AUTOCONNECT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 AUTODEDICATED DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL AUTODEDICATED DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 AUTOPROMPT ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL AUTOPROMPT ENABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 BROADCAST ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL BROADCAST ENABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 CONNECTRESUME DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL CONNECTRESUME DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 INACTIVITY LOGOUT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL INACTIVITY LOGOUT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 INTERRUPTS DISABLED
.
.
.
#
#echo Port Modem and Related Information
#
DEFINE PORT 1-8 ACCESS LOCAL
DEFINE PORT 9-16 ACCESS DYNAMIC
DEFINE PORT ALL SPEED 9600
DEFINE PORT ALL CHARACTER SIZE 8
DEFINE PORT ALL PARITY NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL STOP BITS 4
DEFINE PORT ALL AUTOBAUD ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL FLOW CONTROL XON
DEFINE PORT ALL INPUT FLOW CONTROL ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL OUTPUT FLOW CONTROL ENABLED
DEFINE PORT 1-8 MODEM CONTROL DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 9-16 MODEM CONTROL ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL DIALBACK TIMEOUT 20
DEFINE PORT ALL DCD TIMEOUT 2000
DEFINE PORT ALL DIALBACK DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL DIALUP DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL DSRLOGOUT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL DSRWAIT DISABLED
3-8 893-769-A
Page 32

Using the APGEN Utility
DEFINE PORT ALL DTRWAIT DISABLED
.
.
.
#echo Port ControlledPort Information
#
# DEFINE PORT 0 CONTROLLED PORT LOGIN ""
# DEFINE PORT ALL CONTROLLED PORT LOGIN ""
# DEFINE PORT 0 CONTROLLED PORT LOGOUT ""
# DEFINE PORT ALL CONTROLLED PORT LOGOUT ""
# DEFINE PORT 0 CONTROLLED SESSION INITIALIZE ""
# DEFINE PORT ALL CONTROLLED SESSION INITIALIZE ""
# DEFINE PORT 0 CONTROLLED SESSION TERMINATE ""
# DEFINE PORT ALL CONTROLLED SESSION TERMINATE ""
893-769-A 3-9
Page 33

Using the APGEN Utility
Converting a Portion of a Parameter File
You can create a script file that contains only those commands that define a particular feature or group of
features. These scripts are smaller and more efficient to use if you want to update the status of one
particular feature on a terminal server, rather than the entire parameter file. To create these scripts, use the
appropriate option on the apgen command line. (Chapter 4 also describes how to create scripts from files
created with the UNIX grep utility.)
The following apgen command, with the -session option, creates a script file that includes only the
commands that manage port session characteristics.
%apgen -session xff4b15.prm session.apg
%
The script file session.apg includes the following commands after the parameter file header:
#echo Port Session Information
#
DEFINE PORT 0 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 LOCAL SWITCH ~
DEFINE PORT ALL LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT ALL DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 0 SESSION LIMIT 4
DEFINE PORT ALL SESSION LIMIT 4
3-10 893-769-A
Page 34

Using the APGEN Utility
Editing the Script File to Modify Command Lines
Once you create the script file, you may want to change the values in some of the command lines that
define characteristics, features, protocols, and passwords. To do this, edit the file with any ASCII text
editor. This section describes how to modify a script file in the following ways:
• Changing the values of terminal server characteristics
• Entering terminal server passwords
• Enabling configurable and keyed features
After you edit the script, you will have a parameter file tailored to the requirements of your network. You
can then execute the script on terminal servers throughout your network.
Changing the Values of Terminal Server Characteristics
To modify a command that appears without the # symbol, edit the command line to define the appropriate
value. For example, you might want to change the default Internet subnet mask. To do this, disable the
SUBNET MASK AUTOCONFIGURE characteristic, and specify the new subnet mask. By default, the
commands that control these characteristics appear like this for a class B Internet address:
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SUBNET MASK 255.255.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SUBNET MASK AUTOCONFIGURE ENABLED
Edit these commands to include a nondefault subnet mask and to disable the AUTOCONFIGURE feature:
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SUBNET MASK 255.255.192.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SUBNET MASK AUTOCONFIGURE DISABLED
Entering Terminal Server Passwords
A command which specifies a terminal server password appears in the script file as a comment line by
default. The terminal server privileged password command, for example, appears like this:
# DEFINE SERVER PRIVILEGED PASSWORD <secret>
You can modify this command in two ways. You can replace <secret> with a password, or you can delete
<secret> and require the user to enter a password during script execution. In both cases you delete the
comment line symbol #.
Including the Password in the Script File
To use the script file to define the password, remove the pound sign # and replace <secret> with the
password. The following example changes the privileged password to pswd123:
DEFINE SERVER PRIVILEGED PASSWORD "pswd123"
When you execute the script from the terminal server, the DEFINE command specifies the password
without user intervention. Users with access to the script file can read the password, however, and this may
compromise the security of the terminal server.
893-769-A 3-11
Page 35

Using the APGEN Utility
Prompting the User for the Password
To have the terminal server user interface prompt the user for the password during script execution, remove
the pound sign # and delete <secret>. The following example modifies the command line for the privileged
password in this way:
DEFINE SERVER PRIVILEGED PASSWORD
When you execute the script from the terminal server, the script displays the following prompt:
Password>
Enter the password, which does not appear on the screen. The script then prompts you to enter it again:
Verification>
Enter the password again. If you enter the correct password, the script continues executing. If you enter an
incorrect password, the script displays an error message and continues executing.
Enabling Configurable and Keyed Features
The terminal server allocates memory to certain features and protocols only when you enable them. When
you disable them, the memory is freed for other purposes. These are configurable features. Keyed features
use memory only when enabled, but also require a software password or “key” to enable them. The
Software Management Guide for the Model 3395/3395A Terminal Server and Commands Reference for the
Model 3395/3395A Terminal Server describe keyed features in detail. Contact your SynOptics sales
representative if you need to obtain a software key for a feature.
When a configurable or keyed feature is disabled, the script file includes a comment line indicating this, and
lists some commands associated with the feature as comment lines. Other commands associated with the
feature do not appear at all until you enable it.
Enabling a configurable or keyed feature with an APGEN script is a multistep process. Follow these steps
to enable a configurable or keyed feature with an APGEN script:
• Edit the command in the script file to enable the feature. To do this, remove the # symbol from the
beginning of the command line and change DISABLED to ENABLED.
• Execute the script file on the terminal server. If the feature requires a software ”key,” or password, the
interface prompts you to enter it during the script execution. Enter the password and press the
<Return> key.
When script file execution is complete, wait for about one minute while the terminal server writes out
the new parameters to the parameter server. The Storage State field of the Monitor Parameter Server
screen displays an Idle state when the update is complete.
• Initialize the terminal server after it has updated the parameter server.
• Execute the apgen command on the new parameter file. You can use the option which converts only
those characteristics for the particular feature such as -tn3270 or -kerberos.
• Edit the commands in the script associated with the enabled feature.
• Execute the new APGEN file on the terminal server to change the values of characteristics associated
with the enabled feature.
• Initialize the terminal server again after it has written out the updated parameters to the parameter server
to enable the DEFINE commands.
3-12 893-769-A
Page 36

Using the APGEN Utility
Note: If you need to enable only one or two configurable features on one or two terminal servers,
you may want to do it directly through the Model 3395 command interface.
The following two sections show examples of how to enable Kerberos, which is a configurable feature, and
how to enable TN3270, which is a keyed feature.
Enabling the Kerberos Feature
Kerberos, an Internet network authentication service, is a configurable feature. Follow these steps to enable
Kerberos or any other configurable feature:
• Edit the script file to enable the Kerberos feature.
DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS ENABLED
• Execute the script file on the terminal server.
• Initialize the terminal server after it has updated the parameter server.
• Execute the apgen command on the new parameter file. This example uses the
-kerberos option to create a file with only Kerberos commands:
% apgen -kerberos param-file.prm kerberos.apg
• Edit the script file to modify the Kerberos commands. For example, the Kerberos feature requires that
you specify an Internet host as a Kerberos master. To do this, edit the following command line:
# DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS MASTER NONE
You can specify a Kerberos master with an Internet address as in this example:
DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS MASTER 140.179.224.100
• Execute the new script file, with modified Kerberos commands, on the terminal server.
• Initialize the terminal server again to update the parameter file.
893-769-A 3-13
Page 37

Using the APGEN Utility
Enabling the TN3270 Protocol
TN3270, a protocol which allows users to communicate with an IBM host over the LAN, is a keyed
feature. Follow these steps to enable TN3270 or any other keyed feature:
• Edit the script file to enable the TN3270 protocol.
DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL TN3270 ENABLED
• Execute the script file on the terminal server. The interface will prompt you for the software “key,” or
password, for the feature. Enter the password and press the <New Line> key.
tn3270 password>
The password does not appear on the screen when you enter it.
• Initialize the terminal server after it has updated the parameter server.
• Execute the apgen command on the new parameter file. This example uses the
-tn3270 option to create a file with only TN3270 commands:
% apgen -tn3270 param-file.prm tn3270.apg
• Edit the script file to modify the TN3270 commands. For example, you might need to enable the
TN3270 extended attributes features on some ports. To do this, edit the following command line:
# DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET TN3270 XTDATTRS DISABLED
You can enable extended attributes on specific ports as in this example:
DEFINE PORTS 1-6 TELNET TN3270 XTDATTRS ENABLED
• Execute the new script file, with modified TN3270 commands, on the terminal server.
• Initialize the terminal server again to update the parameter file.
xxxxx
3-14 893-769-A
Page 38

Using the APGEN Utility
Executing the APGEN Script File
To execute the APGEN script file from the terminal server command interface, enter the
SCRIPT command with the pathname and filename of the script. If the script file resides in
the tftp root directory on the script server, usually /tftpboot, you can simply enter the
filename. If the script file resides in some other directory on the script server, include the
pathname and the filename.
The script may prompt you to enter terminal server passwords or software “keys” during execution. Enter
the password and press the <New Line> key. If you enter an incorrect password, the script displays an error
message and continues executing.
In the following example, the script file resides in /tftpboot, so the command includes only the filename.
As the script executes, it can display (echo) text in the script describing each features that it is processing,
although you can edit out these #echo lines. The following example shows the default display for a Model
3395A Terminal Server while executing an APGEN script file containing all parameters and features.
893-769-A 3-15
Page 39

Using the APGEN Utility
TS3395>> script "everything.apg"
Searching for script file. Please wait . . .
Manager Data
Manager Load Data
Script Server(s)
Menu Prompt Information
Kerberos Information
Secure Id Data
XRemote Information
Server Data
Limits
Timers
Server Kerberos Information
Server Menu Information
Server PPP Information
Ip Data
Internet SNMP
Parameter Server Information
Server Features
Features
Daemons
ARAP Server Information
Port Information
Port Characteristic Information
Port Modem and Related Information
Port Internet Information
Port Session Information
Port Security Information
Port Menu Information
Port Nested Menu Information
Port Line Information
Port Kerberos Information
Port Telnet Information
Port Slip Information
Port Xremote Information
Port PPP Information
Port ARAP Information
Port CCL Information
Port Secure ID Information
Port ControlledPort Information
TS3395>>
3-16 893-769-A
Page 40

Using the APGEN Utility
If you are not sure of the location of the script server or the default (root) script server directory path, use
the SHOW SCRIPT SERVER command:
TS3395> show script server
TS/720 V5.2 Rom 470003 HW 00.02.00 Lat Protocol V5.2 Uptime: 118 23:21:23
Address:00-00-81-FF-4B-15 Name:XFF4B15 Ethernet:A Number: 0
Script Servers:
Entry 1: 140.179.305.248 /tftpboot/scripts /
The display shows the domain name or Internet address of the script server and the location of the script file.
Initializing the Terminal Server After Running a Script
After you execute the script file, initialize the terminal server. This updates the permanent database and
causes the DEFINE commands in the script to take effect. If you have the CHANGE feature enabled, some
commands will take effect immediately, because this feature updates the permanent and operational
databases. If you have modified commands in the script file to enable configurable or keyed features, you
will need to modify the script and execute it again. See the section “Enabling Configurable and Keyed
Features,” earlier in this chapter, for more information about this process.
Troubleshooting the Script File
If a command line in the script file contains an error, the command interface displays an error message and
continues executing the script. For example, the following message appears during script execution if the
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SUBNET MASK command specifies an invalid subnet mask:
.
.
.
Server Menu Information
Server PPP Information
Ip Data
Model 3395 -703- Value invalid or out of range "1288"
Internet SNMP
Parameter Server Information
Server Features
.
.
.
893-769-A 3-17
Page 41

Using the APGEN Utility
The position of the error message relative to the comment lines on the screen indicates where the error
occurred: in the section that defines Internet characteristics (Ip Data). To correct the error, open the script
file and find the section on Ip data. Then locate the invalid value.
In this example, the following command has the invalid value:
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SUBNET MASK 1288.3.0.100
Edit the command line to correct the error. You can then execute the script again, or enter the DEFINE
command through the Model 3395 command interface on the terminal server.
Updating APGEN Script Files
When users modify features with DEFINE commands from the terminal server, the server updates the
parameter file on the parameter server. To ensure that the APGEN script file for a terminal server reflects
the most current version of the parameter file, run the utility at regular intervals on the parameter file to
create a current script file. To compare the differences between an old script file and a current script file, use
the UNIX diff utility, described in Chapter 4.
3-18 893-769-A
Page 42

Chapter 4
Using UNIX Utilities with APGEN Script
Files
Several UNIX utilities allow you to search through, edit, and compare APGEN script files. These tools are
particularly useful when you need to manage large scripts with many commands created with the -all or verbose options. This chapter describes some of the basic uses for these tools with APGEN scripts,
including the following information:
• Using the diff utility to compare two APGEN files
• Using the grep utility to search through an APGEN file
For more information about UNIX tools, refer to the UNIX documentation for your system.
Using the diff Utility to Compare Two APGEN Script Files
The diff utility compares two files and lists their differences in the output file you specify. You can
compare the differences between the old and new versions of a parameter file from the same terminal server.
Or, you can compare the differences between the parameter files of two different terminal servers. Some
common uses for these comparisons include the following:
• To determine the reason that performance is better on one terminal server compared to another, or to
learn why the performance on the same terminal server has changed over time
• To determine why a particular feature works on one terminal server but does not work on another
• To create files which log changes in a parameter file over time
See the man pages on your UNIX system for complete information about the diff command.
Creating a File With the diff Utility
The following example compares an old parameter file with a new parameter file. Use the same process to
compare any two APGEN files.
Create an APGEN file from the current parameter file, param.prm:
%apgen -all /tftpboot/param.prm param.now
%
Create an APGEN file from the backup parameter file, param.bck:
%apgen -all /tftpboot/param.bck param.old
%
893-769-A 4-1
Page 43

Using UNIX Tools With APGEN Script Files
Use the diff command to create a file which lists the differences between the two files. This examples sends
the output to a file called result.file. If you do not specify an output file, the utility displays the commands
on the screen. In this example the dots (. . .) indicate a break in the file:
% diff param.now param.old >result.file
%
% more result.file
.
.
.
> #echo Default Security Information
30,32c27,28
< # DEFINE SERVER MANAGER LOAD DISABLED
< # DEFINE SERVER MANAGER LOAD MERIT 9
< # DEFINE SERVER MANAGER SIMULTANEOUS 4
--> DEFINE PORT ALL INTERNET SECURITY DEFAULT INBOUND ALLOW
> DEFINE PORT ALL INTERNET SECURITY DEFAULT OUTBOUND ALLOW
34,188d29
< #
< # DEFINE SERVER MANAGER DUMP DISABLED
< # DEFINE SERVER MANAGER DUMP MERIT 9
< # DEFINE SERVER MANAGER DUMP SIZE SMALL
< # DEFINE SERVER MANAGER LOG FILE 20
< #
.
.
.
> DEFINE SERVER MULTISESSIONS DISABLED
> DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SECURITY ENABLED
450,463d165
< #echo Daemons
< #
< DEFINE SERVER DAEMON LPD DISABLED
< DEFINE SERVER DAEMON FINGERD DISABLED
< DEFINE SERVER DAEMON RWHOD DISABLED
< DEFINE SERVER DAEMON ROUTED DISABLED
< DEFINE SERVER DAEMON SYSLOGD DISABLED
< #
< #echo ARAP Server Information
< #
< # DEFINE SERVER ARAP NODE NAME NONE
< # DEFINE SERVER ARAP DEFAULT ZONE NONE
< # DEFINE SERVER ARAP PASSWORD <SECRET>
< #
469,470c171,176
< DEFINE PORT 0 MULTISESSIONS DISABLED
< DEFINE PORT ALL MULTISESSIONS DISABLED
---
4-2 893-769-A
Page 44

Using UNIX Tool With APGEN Script Files
The result of the diff command shows a list of lines from both scripts. Lines preceded with the < character
appear in the first file, but not the second. Lines preceded with the > character appear in the second file, but
not the first. From this information, you can determine which features are enabled in one file but not the
other, or the value of a particular feature in one file and in the other if they are different.
Using the grep Utility to Search Through an APGEN File
The grep utility, including egrep and fgrep, searches through a file for the text strings you specify. You can
write the output to the screen, or to another file that you can edit and modify. Some common uses of the
grep utility with APGEN script files are the following:
• To extract and display a limited number of command lines from a script file and determine their status
• To extract a limited number of command lines from a script file, write them to another file and create a
script from the new file
See the man pages on your UNIX system for complete information about the grep, egrep, and fgrep
commands.
Displaying Command Lines
The grep utility is useful if you want to extract limited information from a large script file. For example,
you might want to check the value of terminal server time-to-live (TTL) values. Rather than opening the
script file with an editor and searching through it, you can use the TTL string in a grep command. (Most
UNIX systems are case-sensitive, so be sure to enter the string in the correct upper- and lower-case letters.)
% grep -e TTL script.apg
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET TTL 64
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET DOMAIN TTL 0
%
By default, the grep command writes the output to the screen, and you can immediately see the TTL values.
893-769-A 4-3
Page 45

Using UNIX Tools With APGEN Script Files
Creating a Script File
The APGEN utility provides several command options which allow you to create a script with only certain
commands. For example -menu, -ppp, and -slip create script files with only commands that define
characteristics of those features. Chapter 3 describes each option in detail.
You may want to create a script file with a set of commands that do not have a specific APGEN option to
extract them. To do this, you can use the grep utility with a text string that extracts those commands and
writes them into a file.
To create a script file from the output of a grep command, remove the comment symbol and file name (if
applicable) from the command line, and add #control_script to the beginning of the file. The line
#control_script identifies the file as a script to the terminal server. This example shows how you can use
the grep command to extract the Model 3395 commands that specify secret passwords from the script file,
and then to create another script file from the output:
The following command extracts commands with the text string secret, and writes them to the file
pswd.file:
% grep -e secret opt.file > pswd.file
%
The following commands, listed as comment lines, reside in pswd.file:
% more pswd.file
# DEFINE SERVER PRIVILEGED PASSWORD <secret>
# DEFINE SERVER LOGIN PASSWORD <secret>
# DEFINE SERVER MAINTENANCE PASSWORD <secret>
# DEFINE SERVER PPP PAP REMOTE PASSWORD <secret>
To create a script, edit the file to include the line #control_script, and the passwords:
#control_script
DEFINE SERVER PRIVILEGED PASSWORD "egret"
DEFINE SERVER LOGIN PASSWORD "bluejay"
DEFINE SERVER MAINTENANCE PASSWORD "sparrow"
DEFINE SERVER PPP PAP REMOTE PASSWORD "robin"
You can now execute the SCRIPT command with pswd.file from any terminal server on the network.
Note: If you create a script file that includes passwords, consider making it secure with the appropriate
privileges or placing it in a secure directory. Doing so will prevent unauthorized users from
gaining access to the passwords.
4-4 893-769-A
Page 46

Appendix A
A Sample APGEN -all Script
The following is a sample APGEN script created from the parameter file of a Model 3395 Terminal Server
with the -all option.
% apgen -all /tftpboot/xff4b15.prm apg.file
#control_script
#
# APGEN Version 1.1
#
# Parameter File Header
#
# Version : 0x6A
# Date : 25 Oct 1993
# Time : 18:59:02
# Parameter Load Type : 1
# Compressed : Yes
# Software Type : 1
# Stored Format : 7
# Oldest Format : 3
# Hardware Type : 77
# Software Version : V5.2
# Product : Comm Server
#
#############################################################
#
#echo Script Server(s)
#
DEFINE SERVER SCRIPT SERVER 140.179.248.209 "/tftpboot" "/"
#
#echo Menu Prompt Information
#
# DEFINE SERVER MENU PROMPT "Enter number of selection or use arrow keys: "
# DEFINE SERVER MENU CONTINUE PROMPT "press <RETURN> to continue... "
#
#echo Kerberos Information
#
# Kerberos is not enabled, commands are commented out
#
# DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS REALM NONE
# DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS MASTER NONE
# DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS PRIMARY SERVER NONE
# DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS SECONDARY SERVER NONE
# DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS QUERY LIMIT 3
# DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS PORT 750
#
#echo Secure Id Data
#
# DEFINE SERVER SECURID SERVER0 SECURID_0
# DEFINE SERVER SECURID SERVER1 NONE
# DEFINE SERVER SECURID SERVER2 NONE
# DEFINE SERVER SECURID SERVER3 NONE
# DEFINE SERVER SECURID SERVER4 NONE
893-769-A A-1
Page 47

A Sample APGEN -all Script
# DEFINE SERVER SECURID ACMMAXRETRIES 5
# DEFINE SERVER SECURID ACMBASETIMEOUT 3
# DEFINE SERVER SECURID ACM_PORT 755
# DEFINE SERVER SECURID QUERY LIMIT 3
# DEFINE SERVER SECURID ENCRYPTION MODE DES
#
#echo XRemote Information
#
# XRemote is not enabled, commands are commented out
#
# DEFINE SERVER XREMOTE PRIMARY FONT SERVER NONE
# DEFINE SERVER XREMOTE PRIMARY FONT SERVER 0.0.0.0
# DEFINE SERVER XREMOTE SECONDARY FONT SERVER NONE
# DEFINE SERVER XREMOTE SECONDARY FONT SERVER 0.0.0.0
#
#echo Parameter Server Information
#
DEFINE SERVER PARAMETER SERVER 140.179.248.209 INTERNET ADDRESS 140.179.248.209
#
#echo Server Data
#
DEFINE SERVER ANNOUNCEMENTS ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER BROADCAST ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER CIRCUIT 80
DEFINE SERVER CONSOLE 0
DEFINE SERVER VERBOSE ACCOUNTING ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER VERBOSE PRIORITY 7 LOG FACILITY LOCAL 0
DEFINE SERVER TEXTPOOL 16384
DEFINE SERVER LOCK ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER IDENTIFICATION "LattisNet 3395 Terminal Server"
DEFINE SERVER IDENTIFICATION SIZE 63
DEFINE SERVER DUMP ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER SOFTWARE TS3395.IMG
DEFINE SERVER WELCOME "Welcome to the LattisNet 3395 Terminal Server."
DEFINE SERVER PACKET COUNT 80
DEFINE SERVER NAME XFF4B15
DEFINE SERVER NUMBER 0
# DEFINE SERVER PRIVILEGED PASSWORD <secret>
# DEFINE SERVER LOGIN PASSWORD <secret>
# DEFINE SERVER MAINTENANCE PASSWORD <secret>
DEFINE SERVER SERVICE GROUPS 0 ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER LAT SOLICITS DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER TIMEZONE 00:00
DEFINE SERVER REPORT ERRORS DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER PURGE GROUP DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER PURGE NODE ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER CONSOLE LOGOUT DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER CHANGE DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER LOGIN PROMPT "#"
DEFINE SERVER TN3270 PORT KEYMAPS DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER HEARTBEAT DISABLED
#
#echo Limits
#
DEFINE SERVER QUEUE 24
DEFINE SERVER SESSION 64
DEFINE SERVER NODE 100
DEFINE SERVER PASSWORD LIMIT 3
DEFINE SERVER RETRANSMIT 8
DEFINE SERVER ACCOUNTING ENTRIES 50
#
A-2 893-769-A
Page 48

A Sample APGEN -all Script
#echo Timers
#
DEFINE SERVER KEEPALIVE 20
DEFINE SERVER INACTIVITY 30
DEFINE SERVER MULTICAST 30
#
#echo Server Kerberos Information
#
DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS SECURITY NONE
#
#echo Server Menu Information
#
DEFINE SERVER MENU ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER NESTED MENU SIZE 5000
DEFINE SERVER NESTED MENU NAME "mymenu3"
#
#echo Server PPP Information
#
# DEFINE SERVER PPP PAP REMOTE PASSWORD <secret>
#
#echo IP Data
#
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET ADDRESS 140.179.248.218
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET BROADCAST ADDRESS 255.255.255.255
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET PRIMARY DOMAIN ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SECONDARY DOMAIN ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET PRIMARY GATEWAY ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SECONDARY GATEWAY ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SUBNET MASK 255.255.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SUBNET MASK AUTOCONFIGURE ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET NAME NONE
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET DEFAULT DOMAIN SUFFIX NONE
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET TCP CONNECT TIMER 32
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET TTL 64
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET DOMAIN TTL 0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET TCP RESEQUENCING DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET IP REASSEMBLY DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET LOCAL BASE 4000 INCREMENT 100
#
#echo Internet SNMP
#
#
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP SYSTEM CONTACT ""
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP SYSTEM LOCATION ""
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP AUTHENTICATION TRAPS DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP SET COMMUNITY NONE
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP SET CLIENT 1 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP SET CLIENT 2 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP SET CLIENT 3 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP SET CLIENT 4 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP GET COMMUNITY NONE
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP GET CLIENT 1 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP GET CLIENT 2 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP GET CLIENT 3 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP GET CLIENT 4 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP TRAP COMMUNITY "PUBLIC"
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP TRAP CLIENT 1 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP TRAP CLIENT 2 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP TRAP CLIENT 3 0.0.0.0
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SNMP TRAP CLIENT 4 0.0.0.0
#
893-769-A A-3
Page 49

A Sample APGEN -all Script
#echo Parameter Server Information
#
DEFINE SERVER PARAMETER SERVER CHECK ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER PARAMETER SERVER CHECK 30
DEFINE SERVER PARAMETER SERVER RETRANSMIT 3
DEFINE SERVER PARAMETER SERVER RETRANSMIT TIMER 5
DEFINE SERVER PARAMETER SERVER LIMIT 4
DEFINE SERVER PARAMETER SERVER PATH ""
#
#echo Server Features
#
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL TELNET ENABLED LAT ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL MX800 DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL PPP ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL SNMP ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL TN3270 DISABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL XPRINTER ENABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL XREMOTE DISABLED
# DEFINE SERVER PROTOCOL ARAP DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER RLOGIN ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER IPX PROTOCOL ETHERNET ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER IPX PROTOCOL MAC DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER KERBEROS DISABLED
#
#echo Features
#
DEFINE SERVER ULI ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER HELP ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER MULTISESSIONS ENABLED
DEFINE SERVER INTERNET SECURITY DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER SECURID DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER CONTROLLED PORTS DISABLED
#
#echo Daemons
#
DEFINE SERVER DAEMON LPD DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER DAEMON FINGERD DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER DAEMON RWHOD DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER DAEMON ROUTED DISABLED
DEFINE SERVER DAEMON SYSLOGD DISABLED
#
#echo ARAP Server Information
#
# DEFINE SERVER ARAP NODE NAME NONE
# DEFINE SERVER ARAP DEFAULT ZONE NONE
# DEFINE SERVER ARAP PASSWORD <SECRET>
#
#echo *** Port Information ***
#
#
#echo Port Characteristic Information
#
DEFINE PORT 0 MULTISESSIONS DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL MULTISESSIONS DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 AUTHORIZED GROUPS 0 ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL AUTHORIZED GROUPS 0 ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL BREAK LOCAL
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET PREFERRED SERVICE NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 AUTOCONNECT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL AUTOCONNECT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 AUTODEDICATED DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL AUTODEDICATED DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 AUTOPROMPT ENABLED
A-4 893-769-A
Page 50

DEFINE PORT ALL AUTOPROMPT ENABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 BROADCAST ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL BROADCAST ENABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 CONNECTRESUME DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL CONNECTRESUME DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 INACTIVITY LOGOUT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL INACTIVITY LOGOUT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 INTERRUPTS DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL INTERRUPTS DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 LIMITED VIEW DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL LIMITED VIEW DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 LOSS NOTIFICATION ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL LOSS NOTIFICATION ENABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 MESSAGE CODES ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL MESSAGE CODES ENABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 NOLOSS DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL NOLOSS DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 PAUSE DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL PAUSE DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 QUEUING DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL QUEUING DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 RESOLVE SERVICE ANY
DEFINE PORT ALL RESOLVE SERVICE ANY
DEFINE PORT 0 REMOTE MODIFICATION DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL REMOTE MODIFICATION DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 RING DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL RING DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 SCRIPT ECHO DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL SCRIPT ECHO DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 SCRIPT LOGIN DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL SCRIPT LOGIN DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL SIGNAL CHECK DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 VERIFICATION ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL VERIFICATION ENABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 ULI DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL ULI DISABLED
#
#echo Port Modem and Related Information
#
DEFINE PORT ALL ACCESS LOCAL
DEFINE PORT ALL SPEED 9600
DEFINE PORT ALL CHARACTER SIZE 8
DEFINE PORT ALL PARITY NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL STOP BITS 4
DEFINE PORT ALL AUTOBAUD ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL FLOW CONTROL XON
DEFINE PORT ALL INPUT FLOW CONTROL ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL OUTPUT FLOW CONTROL ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL MODEM CONTROL DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL DIALBACK TIMEOUT 20
DEFINE PORT ALL DCD TIMEOUT 2000
DEFINE PORT ALL DIALBACK DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL DIALUP DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL DSRLOGOUT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL DSRWAIT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL DTRWAIT DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL PASSWORD DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 IDLE TIMEOUT 0
DEFINE PORT ALL IDLE TIMEOUT 0
DEFINE PORT 0 TYPEAHEAD SIZE 128
DEFINE PORT ALL TYPEAHEAD SIZE 128
DEFINE PORT 0 USERNAME ""
DEFINE PORT ALL USERNAME ""
DEFINE PORT 0 PROMPT "TS3395"
A Sample APGEN -all Script
893-769-A A-5
Page 51

A Sample APGEN -all Script
DEFINE PORT ALL PROMPT "TS3395"
DEFINE PORT 0-10, 13-16 TYPE SOFTCOPY
DEFINE PORT 11-12 TYPE ANSI
#
#echo Port Internet Information
#
DEFINE PORT 0 INTERNET CONNECTIONS ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL INTERNET CONNECTIONS ENABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 INTERNET TCP KEEPALIVE 0
DEFINE PORT ALL INTERNET TCP KEEPALIVE 0
DEFINE PORT 0 INTERNET TCP WINDOW SIZE 256
DEFINE PORT ALL INTERNET TCP WINDOW SIZE 256
#
#echo Port Session Information
#
DEFINE PORT 0 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 LOCAL SWITCH ~
DEFINE PORT ALL LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT ALL DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 0 SESSION LIMIT 4
DEFINE PORT ALL SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Security Information
#
DEFINE PORT 0 SECURITY DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL SECURITY DISABLED
#
#echo Port Menu Information
#
DEFINE PORT 0 MENU DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL MENU DISABLED
# DEFINE PORT 0 PRIVILEGED MENU DISABLED
# DEFINE PORT ALL PRIVILEGED MENU DISABLED
#
#echo Port Nested Menu Information
#
# DEFINE PORT 0 NESTED MENU DISABLED
# DEFINE PORT ALL NESTED MENU DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0-11, 13-16 NESTED MENU TOP LEVEL 0
DEFINE PORT 12 NESTED MENU TOP LEVEL 1
# DEFINE PORT 0 PRIVILEGED NESTED MENU DISABLED
# DEFINE PORT ALL PRIVILEGED NESTED MENU DISABLED
#
#echo Port Line Information
#
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR ENABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR ENABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR BACKSPACE
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR BACKSPACE
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR FORWARDS
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR FORWARDS
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR END
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR END
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR BEGINNING
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR BEGINNING
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR DELETE LINE
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR DELETE LINE
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR DELETE BEGINNING
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR DELETE BEGINNING
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR PREVIOUS LINE
A-6 893-769-A
Page 52

DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR PREVIOUS LINE
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR NEXT LINE
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR NEXT LINE
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR REDISPLAY
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR REDISPLAY
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR QUOTING CHARACTER
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR QUOTING CHARACTER
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR INSERT TOGGLE
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR INSERT TOGGLE
DEFINE PORT 0 LINE EDITOR CANCEL
DEFINE PORT ALL LINE EDITOR CANCEL
#
#echo Port Kerberos Information
#
DEFINE PORT 0 KERBEROS DISABLED
# DEFINE PORT 0 USER KERBEROS PASSWORD
DEFINE PORT ALL KERBEROS DISABLED
# DEFINE PORT ALL USER KERBEROS PASSWORD
#
#echo Port Telnet Information
#
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET ABORT OUTPUT NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET ABORT OUTPUT NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET ATTENTION NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET ATTENTION NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET BINARY SESSION MODE PASTHRU
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET BINARY SESSION MODE PASTHRU
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET CSI ESCAPE DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET CSI ESCAPE DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET DEFAULT PORT 23
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET DEFAULT PORT 23
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET ECHO MODE REMOTE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET ECHO MODE REMOTE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET ERASE CHARACTER NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET ERASE CHARACTER NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET ERASE LINE NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET ERASE LINE NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET EOR REFLECTION DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET EOR REFLECTION DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET TN3270 ERRORLOCK DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET TN3270 ERRORLOCK DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET INTERRUPT NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET INTERRUPT NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET LOCATION DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET LOCATION DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET NEWLINE NULL
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET NEWLINE NULL
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET NEWLINE FILTERING NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET NEWLINE FILTERING NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET OPTION DISPLAY DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET OPTION DISPLAY DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET QUERY NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET QUERY NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET REMOTE 2000
DEFINE PORT 1 TELNET REMOTE 2100
DEFINE PORT 2 TELNET REMOTE 2200
DEFINE PORT 3 TELNET REMOTE 2300
DEFINE PORT 4 TELNET REMOTE 2400
DEFINE PORT 5 TELNET REMOTE 2500
DEFINE PORT 6 TELNET REMOTE 2600
DEFINE PORT 7 TELNET REMOTE 2700
DEFINE PORT 8 TELNET REMOTE 2800
DEFINE PORT 9 TELNET REMOTE 2900
DEFINE PORT 10 TELNET REMOTE 3000
A Sample APGEN -all Script
893-769-A A-7
Page 53

A Sample APGEN -all Script
DEFINE PORT 11 TELNET REMOTE 3100
DEFINE PORT 12 TELNET REMOTE 3200
DEFINE PORT 13 TELNET REMOTE 3300
DEFINE PORT 14 TELNET REMOTE 3400
DEFINE PORT 15 TELNET REMOTE 3500
DEFINE PORT 16 TELNET REMOTE 3600
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET SYNCHRONIZE NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET SYNCHRONIZE NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET TERMINALTYPE NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET TERMINALTYPE NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET TN3270 DEVICE NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET TN3270 DEVICE NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET TN3270 EOR DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET TN3270 EOR DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET TN3270 PRINTERPORT ANY
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET TN3270 PRINTERPORT ANY
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET TN3270 TRANSLATIONTABLE NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET TN3270 TRANSLATIONTABLE NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET TN3270 XTDATTRS DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET TN3270 XTDATTRS DISABLED
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET TRANSMIT BUFFERED
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET TRANSMIT BUFFERED
DEFINE PORT 0 TELNET URGENT BREAK DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL TELNET URGENT BREAK DISABLED
#
#echo Port Slip Information
#
DEFINE PORT ALL INTERNET SLIP DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL INTERNET SLIP ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE PORT ALL INTERNET SLIP REMOTE 0.0.0.0
DEFINE PORT ALL INTERNET SLIP MASK 0.0.0.0
#
#echo Port XRemote Information
#
# XRemote is not enabled, commands are commented out
#
# DEFINE PORT ALL XREMOTE DISABLED
# DEFINE PORT ALL XDM HOST NONE
# DEFINE PORT ALL XDM QUERY SPECIFIC
#
#echo Port PPP Information
#
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP ACTIVE DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP PAP DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP INTERNET BROADCAST DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP CHARMAP 0
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP RESTART 0
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP CONFIGURE LIMIT 0
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP FAILURE LIMIT 0
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP INTERNET LOCAL ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP INTERNET REMOTE ADDRESS 0.0.0.0
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP INTERNET VJ COMPRESSION DISABLED
DEFINE PORT ALL PPP INTERNET VJ COMPRESSION SLOTS 0
#
#echo Port ARAP Information
#
# DEFINE PORT ALL ARAP DISABLED
# DEFINE PORT ALL ARAP ZONE ACCESS NONE
# DEFINE PORT ALL ARAP MAXIMUM CONNECT TIME 0
# DEFINE PORT ALL ARAP GUEST LOGINS DISABLED
#
A-8 893-769-A
Page 54

#echo Port CCL Information
#
DEFINE PORT ALL CCL NAME NONE
DEFINE PORT ALL CCL MODEM INAUDIBLE
#
#echo Port Secure ID Information
#
# DEFINE PORT 0 SECURID DISABLED
# DEFINE PORT ALL SECURID DISABLED
#
#echo Port ControlledPort Information
#
# DEFINE PORT 0 CONTROLLED PORT LOGIN ""
# DEFINE PORT ALL CONTROLLED PORT LOGIN ""
# DEFINE PORT 0 CONTROLLED PORT LOGOUT ""
# DEFINE PORT ALL CONTROLLED PORT LOGOUT ""
# DEFINE PORT 0 CONTROLLED SESSION INITIALIZE ""
# DEFINE PORT ALL CONTROLLED SESSION INITIALIZE ""
# DEFINE PORT 0 CONTROLLED SESSION TERMINATE ""
# DEFINE PORT ALL CONTROLLED SESSION TERMINATE ""
A Sample APGEN -all Script
893-769-A A-9
Page 55

Appendix B
A Sample APGEN -verbose Script
The following is a sample APGEN script created with the -verbose
and -session options. It includes the port session information for
each port on a 16-port terminal server.
% apgen -verbose -session /tftpboot/xff4b15.prm verb.file
#control_script
#
# APGEN Version 1.1
#
# Parameter File Header
#
# Version : 0x23456959
# Date : 21 Oct 1993
# Time : 13:44:16
# Parameter Load Type : 1
# Compressed : Yes
# Software Type : 1
# Stored Format : 7
# Oldest Format : 3
# Hardware Type : 77
# Software Version : V5.2
# Product : Term Server - One Megabyte
#
#############################################################
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 0
#
DEFINE PORT 0 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 0 LOCAL SWITCH ~
DEFINE PORT 0 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 0 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 1
#
DEFINE PORT 1 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 1 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 1 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 1 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 1 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 2
#
DEFINE PORT 2 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 2 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 2 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 2 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 2 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
893-769-A B-1
Page 56

A Sample APGEN -verbose Script
#echo Port Session Information - Port 3
#
DEFINE PORT 3 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 3 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 3 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 3 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 3 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 4
#
DEFINE PORT 4 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 4 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 4 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 4 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 4 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 5
#
DEFINE PORT 5 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 5 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 5 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 5 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 5 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 6
#
DEFINE PORT 6 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 6 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 6 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 6 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 6 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 7
#
DEFINE PORT 7 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 7 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 7 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 7 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 7 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 8
#
DEFINE PORT 8 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 8 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 8 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 8 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 8 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 9
#
DEFINE PORT 9 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 9 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 9 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 9 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 9 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 10
#
DEFINE PORT 10 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 10 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 10 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 10 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 10 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
B-2 893-769-A
Page 57

A Sample APGEN -verbose Script
#echo Port Session Information - Port 11
#
DEFINE PORT 11 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 11 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 11 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 11 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 11 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 12
#
DEFINE PORT 12 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 12 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 12 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 12 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 12 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 13
#
DEFINE PORT 13 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 13 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 13 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 13 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 13 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 14
#
DEFINE PORT 14 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 14 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 14 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 14 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 14 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 15
#
DEFINE PORT 15 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 15 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 15 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 15 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 15 SESSION LIMIT 4
#
#echo Port Session Information - Port 16
#
DEFINE PORT 16 BACKWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 16 FORWARD SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 16 LOCAL SWITCH NONE
DEFINE PORT 16 DEFAULT SESSION MODE INTERACTIVE
DEFINE PORT 16 SESSION LIMIT 4
893-769-A B-3
Page 58

Index
< and > characters, 4-3
# character, 3-5
A
AIX operating system, 2-1
-all option, 3-5, A-1
apgen command, 1-6, 3-2
options for, 3-3
syntax of, 3-2
using to convert a portion of a parameter
file, 3-9
using with -all option, 3-5
using without options, 3-2, 3-4
APGEN installation script, running, 2-5
APGEN script file, 1-6
comment lines in, 3-5
creating an, 3-4
with the grep utility, 4-4
examples of
with -all option, 3-5, A-1
with -session option, 3-9
with -verbose option, B-1
executing an, 3-14
header, 3-2, 3-4
initializing the communications server after
running, 3-16
troubleshooting, 3-16
updating an, 3-17
apgen.tar archive, 2-5
ASCII Parameter File Generator utility
(APGEN), 1-1, 1-5, see also APGEN script
file
ASCII text editor, editing the script file with,
1-6, 3-10
AT&T System V operating system, 2-1
B
binary parameter file, 1-5, 3-1
Bourne shell, 2-7
BSD operating system, 2-1
C
characteristics, terminal server, changing the
values of, 3-10
command script, 1-5
comment lines in the script, 3-5
communications server,
configuring for use with APGEN, 2-2
defining a UNIX parameter server for, 2-2
defining a UNIX script server for, 2-3
executing a script file from, 3-14
initializing after running a script, 3-16
compressed parameter file, 1-5
configurable features, enabling, 3-17
#control_script, 3-4, 4-4
csportd daemon, 1-4
D
-d option with the Install command, 2-7
default choices in the Install script, 2-7
DEFINE commands
in an APGEN script file, 3-4
updating the parameter file with, 3-16 - 3-17
DEFINE PARAMETER SERVER
command, 2-3
DEFINE SERVER SCRIPT SERVER
command, 2-3
dial-back script, 1-5
diff utility, UNIX, 1-7, 4-1
893-769-A Index-1
Page 59

Index
directory requirements for script servers, 2-4
directory structure, script server, 2-4
E
#echo, in a script file, 3-5
errors in a script file, correcting 3-16
F
features, keyed, enabling, 3-11
file
APGEN script, creating, 3-4
creating with the diff utility, 4-1
creating with the grep utility, 4-4
G
grep utility, UNIX, 1-7, 4-1, 4-3
H
header, in script file, 3-4
HP/UX operating system, 2-1
I
Install command, 2-7
-d option with, 2-7
Install script, APGEN, running the, 2-5
default choices for, 2-7
K
Kerberos feature, enabling, 3-12
keys, software, 3-11, 3-14
keyed features, enabling, 3-11
Model 3395 commands interface, preventing
users from gaining access to, 1-5
Model 3395 host-based management tools, 1-1
Model 3395 loader kit, 1-2
Model 3395 MIB, 1-3
N
~name construct, 2-7
nested menus, 1-5
P
parameter file
compressed, 1-5
converting a portion of, 3-9
converting the entire, 1-5, 3-5
examples of converted, A-1, B-1
uncompressed, 1-5
updating with DEFINE commands, 3-16–
3-17
parameter server
backup, 2-3
defining an UNIX host as a, 2-2–2-4
updating, 3-17
VAX host as a, 1-2, 2-2
passwords in the script file, 3-10
including in the script, 3-10
prompting the user to enter, 3-11
permanent database, updating, 3-16
ports, how they appear in the script, 3-4
pound sign (#) in a script file, 3-5
printer servers, 1-5
protocols, enabling, 3-11
example, using TN3270, 3-13
L
link to the script file, creating from the TFTP
home directory, 2-4
load servers, 1-2
M
MAN page for APGEN file , 2-1, 2-6
MIB, Model 3395, 1-3
MIPS operating system, 2-1
Index-2 893-769-A
Page 60

Index
R
running the APGEN installation script, 2-5
S
SCRIPT command, 1-4, 1-5, 1-7, 2-2
using to execute an APGEN file, 3-14–3-17
script, dialback, 1-5
script file, APGEN, 1-6
comment lines in, 3-5
creating an, 3-4
with the grep utility, 4-4
examples of
with -all option, 3-5f, A-1ff
with -session option, 3-9
with -verbose option, B-1ff
executing an, 3-14ff
header, 3-2, 3-4
initializing the communications server after
running, 3-16
that includes a portion of a parameter file, 3-
9
troubleshooting, 3-16
updating an, 3-17
script server
backup, 2-3
defining a UNIX host as a, 2-3
directory requirements for, 2-4
directory structure, 2-4
<secret>, as the password in a script file,
3-10–3-11
secure TFTP option, 2-3, 2-5
SHOW SCRIPT SERVER command, 3-16
SNMP, 1-3
stdout, as default output, 3-2
SunNet Manager, 1-3
T
tar archive, apgen.tar, 2-5
Telnet, enabling, 2-2
TFTP
home directory, 2-4
requirement for script servers, 2-3
secure option, 2-5
/tftpboot directory
installing the APGEN utility in, 2-5
parameter files in, 3-5
script file in, 3-14
TN3270 protocol, enabling, 3-13
troubleshooting the script file, 3-16
U
ULTRIX operating system, 2-1
uncompressed parameter file, 1-5
UNIX host
as a parameter server, 2-2–2-3
as a script server, 2-3
configured for secure TFTP, 2-5
directory structure, 2-4, 2-6
running the installation script on, 2-5
that support APGEN, 2-1
UNIX
diff utility, 1-7, 4-1
grep utility, 1-7, 4-3
MAN pages, 2-1, 2-6, 4-1, 4-3
V
VAX hosts as parameter servers, 1-2, 2-2
-verbose option, 3-4, B-1
verification, password, 3-11
893-769-A Index-3
 Loading...
Loading...